KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT, ORGANIZATIONAL INTELLIGENCE AND LEARNING, AND COMPLEXITY - Vol. II - Complexity and Sustainable Development - Wei-Bin Zhang
|
|
|
- Jack Morgan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COMPLEXITY AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Wei-Bin Zhang Ritsumeikan Asia Pacific University, Japan Keywords: complexity, sustainable development, population growth, knowledge creation and utilization, environment, government, cultural values Contents 1. Introduction 2. Economic Development and Population Growth 3. Economic Development and Knowledge 4. Economic Development and Environment 5. Economic Development and Government 6. Sustainable Development and Complexity Glossary Bibliography Biographical Sketch Summary This article examines some aspects of socioeconomic development in light of complexity theory. It examines some nonlinear interactions between economic systems, institutions, population growth, knowledge creation and utilization, and cultural values. Multiple possibilities of behavioral patterns resulting from these nonlinear interactions are emphasized. It is argued that when sustainability is referred to some concrete long-term goals in complicated dynamic systems, it is only under limited circumstances that man might be able to achieve them. 1. Introduction Since industrialization has become a global phenomenon, an increasing number of commodities are available to an increasing number of people in the world. Industrialization has brought material affluence to an increasingly large proportion of the world s population. A cursory comparison of the living conditions of many economies in the world from the beginning of this century to the present reveals great material progress. One may ask whether it is possible for industrialized economies to continue living at high levels of material abundance and for underdeveloped economies to enjoy material progresses brought about by industrialization over long periods without disastrous consequences for social, moral, political and environmental systems. In fact, since the publication of the Club of Rome report, there has been an increasing concern over limits to economic growth in a world of finite resources. According to the World Commission on Environment and Development report of 1987 about one million hectares of productive dryland annually turns into worthless desert and more than 11 million hectares of forests are destroyed yearly. The burning of fossil fuels puts into the atmosphere carbon dioxide, which is causing gradual global warming. This greenhouse effect may increase average global
2 temperatures enough to shift agricultural production areas, raise sea levels to flood coastal cities, and disrupt national economies. Other industrial gases threaten to deplete the planet s protective ozone shield to such an extent that the number of human and animal cancers would rise sharply and the oceans food chain would be disrupted. The productive power of the world economy is putting increasing strains on the resource-base and life-support systems of the planet and many of its species. It has been pointed out that if present trends of population growth, environment deterioration and resources usage are continued, the world s people will be poorer in many ways in the near future than in the present (Anthony and Radcliffe, 1996, Donella, 1998). It is obvious that sustainable development cannot be dealt with without a dynamic vision since it involves not only the present but also the future. The purpose of this article is to examine issues related to sustainable development in light of complexity theory. Complexity theory involves the study of complex systems which are characterized by nonlinear interactions between many elements (Haken, 1983, Prigogine, 1997). It reveals how such interactions can bring about qualitatively new structures and how the whole is related to and different from its individual components. The study of complexity has been enhanced with developments in computer technology. A modern computer can explore a far wider class of phenomena than it could have been imagined even a few decades ago. The essential ideas about complexity have found wide applications among a wide range of scientific disciplines, including physics, biology, ecology, psychology, cognitive science, economics and sociology. Many complex systems constructed in those scientific areas have been found to share many common properties. The great variety of applied fields manifests a possibly unifying methodological factor in the sciences. Complexity theory is bringing scientists closer as they explore common structures of different systems. It offers scientists a new tool for exploring and modeling the complexity of nature and society. The new techniques and concepts provide powerful methods for modeling and simulating trajectories of sudden and irreversible change in social and natural systems. Complexity theory has found wide applications in different fields of economics (Rosser, 1991, Zhang, 1991, Lorenz, 1993, Puu, 2000). The range of its applications includes many topics, such as catastrophes, bifurcations, trade cycles, economic chaos, urban pattern formation, sexual division of labor and economic development, economic growth, values and family structure, the role of stochastic noise upon socio-economic structures, fast and slow socio-economic processes, and relationship between microscopic and macroscopic structures. All these topics cannot be effectively examined by traditional analytical methods which are concerned with linearity, stability and static equilibria. This new science has changed economists views about evolution. For instance, the traditional view of the relations between laws and consequences -- between cause and effect -- holds that simple rules imply simple behavior, therefore complicated behavior must arise from complicated rules. This vision had been held by professional economists for a long time. But it has been recently challenged due to the development of complexity theory. Complexity theory shows how complicated behavior may arise from simple rules. A typical example is chaos identified from the simple logistic map. Nonlinear economics attempts to provide a new vision of economic dynamics: a vision toward the multiple, the temporal, the unpredictable, and the complex. There is a tendency to replace simplicity with complexity and specialism with generality in economic research. The concepts such as totality, nonlinearity, selforganization, structural changes, order and chaos have found broad and new meanings by
3 the development of this new science. According to this new science, economic dynamics are considered to resemble a turbulent movement of liquid in which varied and relatively stable forms of current and whirlpools constantly change one another. These changes consist of dynamic processes of self-organization along with the spontaneous formation of increasingly subtle and complicated structures. The accidental nature and the presence of structural changes like catastrophes and bifurcations, which are characteristic of nonlinear systems and whose further trajectory is determined by chance, make dynamics irreversible. This article examines issues related to sustainable development in light of complexity theory. The paper is organized as follows. Section 2 examines interdependence between sustainable development and population growth. Section 3 is concerned with relations between creativity, knowledge utilization and economic development. Section 4 addresses dynamics between environment and economic development. Section 5 examines the role of government in economic systems. Section 6 illustrates sustainable development and cultural values, using Confucianism as an example. Section 7 summarizes the paper, discussing sustainable development and complexity. 2. Economic Development and Population Growth In the early 1800s the world population stood at one billion. As industrialization spread widely, the world population took until 1930 to reach two billion. However, by 1990, the world population had passed five billion. Demographers project that the world s population will double to more than 10 billion by This explosion of the population could not have been sustained without the expansion of the world economy. The growth of population is a major force for change in the contemporary world. It is determined by multiple factors and has consequences for the natural world and for the political order. It is often argued that since production and resources are limited, the world population is over-supplied. But without sufficient population, the division of labor could not be thoroughly carried out and productivity could not be improved. When discussing issues related to interdependence between population growth and sustainable development, one can hardly miss mentioning Malthus Essay on the Principle of Population first published in In this book, Malthus regarded population dynamics as a main cause for both the hope and misery of mankind. The first edition was based on the few materials which were then within Malthus reach. It was one-sided and too pessimistic, as Malthus soon realized himself. After the publication of the first edition, the book generated great interest and received strong criticism. Taking account of various comments, Malthus revised the book several times before his death. Malthus established his theory on the basis of three assumptions. The first is that food is necessary to the existence of man. The second is that the passion between the sexes, and thus the urge to procreate, is necessary and will remain nearly in its present state. The third is that economic production was dominated by decreasing returns to scale. Malthus held that population tends to grow geometrically, whereas food supplies grow only arithmetically. Without any checking, population would double every twenty-five years. It would take only a few generations of geometric increase to outrun the food supply. In the long run, the world would live on the brink of starvation.
4 Adam Smith held that there is a positive connection between the wealth of a nation and living conditions of the lower orders of society. He argued that every increase of wealth tends to increase the demand for labor and to improve the conditions of the lower classes of society. Malthus agreed that the two subjects are closely connected. But he did not hold that Smith gave a sufficiently correct and precise statement about the nature and extent of this connection and the mode in which increasing wealth operates on the condition of the poor. According to Malthus, any policies that attempted to alleviate poverty would be futile due to the operation of this natural law. His population theory implies that paying relief would continue social and economic problems associated with poverty rather than solve them. Since per capita consumption level would always tend toward the subsistence level, any increase in consumption above that level would only cause the poor population to grow until the population achieved its subsistence level again. Moreover, according to Malthus, paying relief may worsen the economy as a whole. Since paying relief tends to increase the population and shifts wealth from more productive to less productive use, this altruistic desire tends to slow down the national economic growth. By emphasizing the interdependence of population growth and food supply, Malthus theory lent support to the subsistence theory of wages which had important influences upon later economists such as Ricardo, Marx and Keynes. By explaining poverty in terms of a simple interdependence between the population and the means of subsistence, the theory still provides important suggestions for economic policy in less developed countries. Malthus economics is one of the first economies functioning with non-constant returns to scale. It is decreasing returns to scale due to population growth that drive the economic system to miserable situations. Malthus saw that the only limit to a geometric population increase was wide diffusion of deadly disease and starvation. Checking forces such as postponed marriages, sexual continence, a greater number of unmarried men and women, and a strict adherence to sexual morality would not be strong enough to prevent disasters. He could not imagine the use of birth control on moral grounds. The record of world history since Malthus time can be used to prove or disprove Malthus conclusions about the relationship between economic development and population growth, depending on when and under what conditions the data were collected. The economies of Western Europe, North America and Japan have experienced simultaneous growth of the population and improvement in the standard of living in terms of the consumption of goods and services. There are many other economies which operate according to Malthus economic dynamics. In those economies every increase in agricultural production is more than offset by a large increase in the population. It should be remarked that it is argued that Western economies are also faced with the Malthusian problems, but in changed forms in the future. The developed economies have seen major shifts in population structure. The numbers in the economically inactive age groups in their sixties or above are rising at a dramatic rate. An aging population is associated with increased longevity and decreasing fertility. The increase in longevity associated with improvements in public health and medical treatment has created a growing burden on social security systems. It is possible that a population with too many old people inflicts too great an economic burden on the shoulders of younger adults. Moreover, when these adults themselves grow old they will need to be supported by a further increase in young adults. This may result in a decline in productivity because of insufficient natural resources. On the other hand, the aging population may have a positive impact on economic growth. The aging population means
5 an extension of the market. If the economic system exhibits increasing returns, the enlarged markets due to aging populations may benefit society due to return-to-scale economies. Changes in age structure may affect overall productivity levels and consumption structures in complicated ways. The distribution of human capital may be changed due to changes in societal age structures. For instance, Sauvy argued that productivity would be associated with aging, but inversely. An aged population may have detrimental effects on the productivity of the young. The tax burden of the unproductive elderly would be a growing cost to the economy yet the society s opinions are much more strongly influenced by the elderly. The young become a minority. He argued that a population without children does not believe in the future and can hardly be expected to have the pioneering spirit. The aging social environment prevents the young from shaking the burden of idleness from their shoulders and from contributing all their vitality. The will to create and build may be weakened in an aged environment. He pointed out that traditional economic analysis had not foreseen a moral and material crisis resulting from demographic stagnation Bibliography TO ACCESS ALL THE 20 PAGES OF THIS CHAPTER, Visit: Aghion, P. and Howitt, P. (1998) Endogenous Growth Theory. Mass., Cambridge: The MIT Press.[A comprehensive book on the neoclassical and new growth theories] Anthony, M.H.C. and Radcliffe, N.J. (1996) Sustainability A System Approach. London: Earthscan Publications Ltd. [A comprehensive introduction to sustainability with a systematical approach] Barro, R.J. and X. Sala-i-Martin (1995) Economic Growth. New York: McGraw-Hill, Inc. [The book provides detailed analyses and empirical studies of economic growth] Donella, M. (1998) Indicators and Information for Sustainable Development. The Sustainability Institute. [An important book for criteria for sustainability and empirically analyzing sustainable development] Grossman, G.M. and Helpman, E. (1991) Innovation and Growth in the Global Economy. Cambridge, Mass.: The MIT Press.[An advanced textbook on theory international trade with monopolistic competition and technological change] Haken, H. (1983) Advanced Synergetics - Instability Hierarchies of Self-Organizing Systems and Devices. Berlin: Springer.[Classic contribution detailing how change occurs via both internal systems dynamics and via external disturbances] Lorenz, H.W. (1993) Nonlinear Dynamical Economics and Chaotic Motion, (second edition) Berlin: Springer-Verlag. [A comprehensive introduction to nonlinear economics] Malthus, T.R. (1820) Principles of Political Economy. London: John Murray.[A classic in Western economics]
6 Prigogine, I. (1997) The End of Certainty - Time, Chaos, and the New Laws of Nature, written in collaboration with I. Stengers. New York: The Free Press. [Very accessible portrait of Prigogine s important insights into evolutionary processes] Puu, T. (2000) Attractors, Bifurcations and Chaos. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.[Many examples of nonlinear economic models; the book is characterized by simulation and beautiful pictures] Rosser, J.B.Jr. (1991) From Catastrophe to Chaos: A General Theory of Economic Discontinuities, Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers.[Interesting presentation of the function of discontinuous events and disruptions in economics systems] Sauvy, A. (1966) General Theory of Population, translated from the French original by C. Campos, London: Weidenfeld and Nicolson. [Good overview of population dynamics] WCED, World Commission on Environment and Development (1987) Our Common Future. Oxford: Oxford University Press.[Stresses the importance of viewing planet earth as the home of all of its inhabitants by showing that all humans have a stake in maintaining a sustainable environment] Zhang, W.B. (1991) Synergetic Economics. Heidelberg: Springer.[Analyzes different dynamic nonlinear economic models and provides a general vision on economic evolution from perspectives of nonlinear theory] Zhang, W.B. (1999) Capital and Knowledge - Dynamics of Exchange Values and Economic Structures. Heidelberg: Springer. [Explores interdependence among physical capital accumulation, knowledge growth, and economic growth] Biographical Sketch Dr. Wei-Bin Zhang, born in 1961, teaches and does research at Ritsumeikan Asia Pacific University in Japan. His main research fields are nonlinear economic dynamics, macroeconomics, regional and international economics, urban economics, East Asian economic development, Chinese philosophy, and ethics. He has published more than 100 academic articles. His books include Economic Dynamics (1990), Synergetic Economics (1991), Knowledge and Value - Economic Structures with Time and Space (1996), Japan versus China in the Industrial Race (1998), Confucianism and Modernization (1999), and Capital and Knowledge (1999), Adam Smith and Confucius - The Theory of Moral Sentiments and The Analects.(2000). A Theory of International Trade Capital, Knowledge and Economic Structures. (2000). He was brought up and received his university education in mainland China. He studied at Kyoto University in Japan for four years. He conducted research in Sweden from 1987 to 1998.
17.181/ SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Theory and Policy
 17.181/17.182 SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Theory and Policy Department of Political Science Fall 2016 Professor N. Choucri 1 ` 17.181/17.182 Week 1 Introduction-Leftover Item 1. INTRODUCTION Background Early
17.181/17.182 SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Theory and Policy Department of Political Science Fall 2016 Professor N. Choucri 1 ` 17.181/17.182 Week 1 Introduction-Leftover Item 1. INTRODUCTION Background Early
Objectives ECONOMIC GROWTH CHAPTER
 9 ECONOMIC GROWTH CHAPTER Objectives After studying this chapter, you will able to Describe the long-term growth trends in the United States and other countries and regions Identify the main sources of
9 ECONOMIC GROWTH CHAPTER Objectives After studying this chapter, you will able to Describe the long-term growth trends in the United States and other countries and regions Identify the main sources of
Learning Outcomes 2. Key Concepts 2. Misconceptions and Teaching Challenges 3. Vocabulary 4. Lesson and Content Overview 5
 UNIT 9 GUIDE Table of Contents Learning Outcomes 2 Key Concepts 2 Misconceptions and Teaching Challenges 3 Vocabulary 4 Lesson and Content Overview 5 BIG HISTORY PROJECT / UNIT 9 GUIDE 1 Unit 9 Acceleration
UNIT 9 GUIDE Table of Contents Learning Outcomes 2 Key Concepts 2 Misconceptions and Teaching Challenges 3 Vocabulary 4 Lesson and Content Overview 5 BIG HISTORY PROJECT / UNIT 9 GUIDE 1 Unit 9 Acceleration
Dublin City Schools Science Graded Course of Study Environmental Science
 I. Content Standard: Earth and Space Sciences Students demonstrate an understanding about how Earth systems and processes interact in the geosphere resulting in the habitability of Earth. This includes
I. Content Standard: Earth and Space Sciences Students demonstrate an understanding about how Earth systems and processes interact in the geosphere resulting in the habitability of Earth. This includes
April Keywords: Imitation; Innovation; R&D-based growth model JEL classification: O32; O40
 Imitation in a non-scale R&D growth model Chris Papageorgiou Department of Economics Louisiana State University email: cpapa@lsu.edu tel: (225) 578-3790 fax: (225) 578-3807 April 2002 Abstract. Motivated
Imitation in a non-scale R&D growth model Chris Papageorgiou Department of Economics Louisiana State University email: cpapa@lsu.edu tel: (225) 578-3790 fax: (225) 578-3807 April 2002 Abstract. Motivated
KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT, ORGANIZATIONAL INTELLIGENCE AND LEARNING, AND COMPLEXITY - Vol. II Complexity and Technology - Loet A.
 COMPLEXITY AND TECHNOLOGY Loet A. Leydesdorff University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands Keywords: technology, innovation, lock-in, economics, knowledge Contents 1. Introduction 2. Prevailing Perspectives
COMPLEXITY AND TECHNOLOGY Loet A. Leydesdorff University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands Keywords: technology, innovation, lock-in, economics, knowledge Contents 1. Introduction 2. Prevailing Perspectives
SYSTEMS SCIENCE AND CYBERNETICS Vol. I - Evolutionary Complex Systems - I. B. Bálsamo
 EVOLUTIONARY COMPLEX SYSTEMS I. B. Bálsamo National Academy of Sciences of Buenos Aires, Argentina Keywords: Evolutionary, Complex Systems, Sustainability, Conceptualization Contents 1. Conceptual Framework
EVOLUTIONARY COMPLEX SYSTEMS I. B. Bálsamo National Academy of Sciences of Buenos Aires, Argentina Keywords: Evolutionary, Complex Systems, Sustainability, Conceptualization Contents 1. Conceptual Framework
Principles of Sociology
 Principles of Sociology DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS ATHENS UNIVERSITY OF ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS [Academic year 2017/18, FALL SEMESTER] Lecturer: Dimitris Lallas Contact information: lallasd@aueb.gr lallasdimitris@gmail.com
Principles of Sociology DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS ATHENS UNIVERSITY OF ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS [Academic year 2017/18, FALL SEMESTER] Lecturer: Dimitris Lallas Contact information: lallasd@aueb.gr lallasdimitris@gmail.com
Geography, Demography, Ecology, and Society
 Geography, Demography, Ecology, and Society Associate Professor Amporn W. Tamronglak, Ph.D. TU 120 Integrated Social Sciences Thammasat University amporn w. tamronglak 1 Read Chapter 5 Hunt and Colander
Geography, Demography, Ecology, and Society Associate Professor Amporn W. Tamronglak, Ph.D. TU 120 Integrated Social Sciences Thammasat University amporn w. tamronglak 1 Read Chapter 5 Hunt and Colander
Unified Growth Theory
 Unified Growth Theory Oded Galor PRINCETON UNIVERSITY PRESS PRINCETON & OXFORD Contents Preface xv CHAPTER 1 Introduction. 1 1.1 Toward a Unified Theory of Economic Growth 3 1.2 Origins of Global Disparity
Unified Growth Theory Oded Galor PRINCETON UNIVERSITY PRESS PRINCETON & OXFORD Contents Preface xv CHAPTER 1 Introduction. 1 1.1 Toward a Unified Theory of Economic Growth 3 1.2 Origins of Global Disparity
UNIT 1 REVIEW SHEET FOUNDATIONS OF COMPLEX SOCIETIES: TECHNOLOGICAL & ENVIRONMENTAL TRANSFORMATIONS, TO 600 BCE
 Name: Due Date: UNIT 1 REVIEW SHEET FOUNDATIONS OF COMPLEX SOCIETIES: TECHNOLOGICAL & ENVIRONMENTAL TRANSFORMATIONS, TO 600 BCE PART 1: Content Review Part 1: Content Review You will define and explain
Name: Due Date: UNIT 1 REVIEW SHEET FOUNDATIONS OF COMPLEX SOCIETIES: TECHNOLOGICAL & ENVIRONMENTAL TRANSFORMATIONS, TO 600 BCE PART 1: Content Review Part 1: Content Review You will define and explain
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University. Subject Description Form
 The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Subject Description Form Please read the notes at the end of the table carefully before completing the form. Subject Code Subject Title HTM1A01 Leisure and Society
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Subject Description Form Please read the notes at the end of the table carefully before completing the form. Subject Code Subject Title HTM1A01 Leisure and Society
Research on the Sustainable Development of Animation Industry Cluster Based on Diamond Model Ke LIU 1,a,*, Xiao-cong DU 2,b
 216 3 rd International Conference on Economics and Management (ICEM 216) ISBN: 978-1-6595-368-7 Research on the Sustainable Development of Animation Industry Cluster Based on Diamond Model Ke LIU 1,a,*,
216 3 rd International Conference on Economics and Management (ICEM 216) ISBN: 978-1-6595-368-7 Research on the Sustainable Development of Animation Industry Cluster Based on Diamond Model Ke LIU 1,a,*,
Programme Curriculum for Master Programme in Economic History
 Programme Curriculum for Master Programme in Economic History 1. Identification Name of programme Scope of programme Level Programme code Master Programme in Economic History 60/120 ECTS Master level Decision
Programme Curriculum for Master Programme in Economic History 1. Identification Name of programme Scope of programme Level Programme code Master Programme in Economic History 60/120 ECTS Master level Decision
Research on Technological Innovation Capability Evaluation of Guangxi Pharmaceutical Industry
 Research on Technological Innovation Capability Evaluation of Guangxi Pharmaceutical Industry Xin Wang, Jun Hong & Peng Liu School of Electrical Engineering, Guangxi University 100 Da Xue Road, Nanning
Research on Technological Innovation Capability Evaluation of Guangxi Pharmaceutical Industry Xin Wang, Jun Hong & Peng Liu School of Electrical Engineering, Guangxi University 100 Da Xue Road, Nanning
Correlation Guide. Wisconsin s Model Academic Standards Level II Text
 Presented by the Center for Civic Education, The National Conference of State Legislatures, and The State Bar of Wisconsin Correlation Guide For Wisconsin s Model Academic Standards Level II Text Jack
Presented by the Center for Civic Education, The National Conference of State Legislatures, and The State Bar of Wisconsin Correlation Guide For Wisconsin s Model Academic Standards Level II Text Jack
Book Review. Complexity: the Emerging Science at the Edge of Order and Chaos. M. Mitchell Waldrop (1992) by Robert Dare
 Book Review Complexity: the Emerging Science at the Edge of Order and Chaos M. Mitchell Waldrop (1992) by Robert Dare Research Seminar in Engineering Systems (ESD.83) Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Book Review Complexity: the Emerging Science at the Edge of Order and Chaos M. Mitchell Waldrop (1992) by Robert Dare Research Seminar in Engineering Systems (ESD.83) Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Unified Growth Theory and Comparative Economic Development. Oded Galor. AEA Continuing Education Program
 Unified Growth Theory and Comparative Economic Development Oded Galor AEA Continuing Education Program Lecture II AEA 2014 Unified Growth Theory and Comparative Economic Development Oded Galor AEA Continuing
Unified Growth Theory and Comparative Economic Development Oded Galor AEA Continuing Education Program Lecture II AEA 2014 Unified Growth Theory and Comparative Economic Development Oded Galor AEA Continuing
Wisconsin Academic Standards Science Grade: 9 - Adopted: 1998
 Main Criteria: Wisconsin Academic Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 9 Correlation Options: Show Correlated Wisconsin Academic Standards Science Grade: 9 - Adopted:
Main Criteria: Wisconsin Academic Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 9 Correlation Options: Show Correlated Wisconsin Academic Standards Science Grade: 9 - Adopted:
REPORT ON THE EUROSTAT 2017 USER SATISFACTION SURVEY
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate A: Cooperation in the European Statistical System; international cooperation; resources Unit A2: Strategy and Planning REPORT ON THE EUROSTAT 2017 USER SATISFACTION
EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate A: Cooperation in the European Statistical System; international cooperation; resources Unit A2: Strategy and Planning REPORT ON THE EUROSTAT 2017 USER SATISFACTION
ACTIVITIES1. Future Vision for a Super Smart Society that Leads to Collaborative Creation Toward an Era that Draws People and Technology Together
 ACTIVITIES1 Future Vision for a Super Smart Society that Leads to Collaborative Creation Toward an Era that Draws People and Technology Together Measures to strengthen various scientific technologies are
ACTIVITIES1 Future Vision for a Super Smart Society that Leads to Collaborative Creation Toward an Era that Draws People and Technology Together Measures to strengthen various scientific technologies are
Module 2: Origin of city in history Lecture 8: The Industrial Revolution and the Rise of the Gesellschaft Part I
 The Lecture Contains: Industrial Revolution Changes at the core of Industrial Revolution Changes within Technology Labour Urbanization Environment Reference file:///d /NPTL%20WORK/Dr.%20Anindita%20Chakrabarti/UrbanSociology/lecture8/8_1.htm
The Lecture Contains: Industrial Revolution Changes at the core of Industrial Revolution Changes within Technology Labour Urbanization Environment Reference file:///d /NPTL%20WORK/Dr.%20Anindita%20Chakrabarti/UrbanSociology/lecture8/8_1.htm
Innovation. Key to Strengthening U.S. Competitiveness. Dr. G. Wayne Clough President, Georgia Institute of Technology
 Innovation Key to Strengthening U.S. Competitiveness Dr. G. Wayne Clough President, Georgia Institute of Technology PDMA Annual Meeting October 23, 2005 Innovation Key to strengthening U.S. competitiveness
Innovation Key to Strengthening U.S. Competitiveness Dr. G. Wayne Clough President, Georgia Institute of Technology PDMA Annual Meeting October 23, 2005 Innovation Key to strengthening U.S. competitiveness
and itseffectsin Rom ania
 86 Current Economic Crisis and itseffectsin Rom ania ~ Prof. Ph. D. (FacultyofEconomicsandBusinessAdministration,West ~ Assist. Prof. Ph. D. (FacultyofEconomicsandBusinessAdministration, Abstract: createdforthesociety.
86 Current Economic Crisis and itseffectsin Rom ania ~ Prof. Ph. D. (FacultyofEconomicsandBusinessAdministration,West ~ Assist. Prof. Ph. D. (FacultyofEconomicsandBusinessAdministration, Abstract: createdforthesociety.
The role of resource management and environmental factors in sustainable development
 DESERT DESERT Online at http://jdesert.ut.ac.ir DESERT 15 (2010) 27-32 The role of resource management and environmental factors in sustainable development Gh.R. Taleghani * Associate Professor, University
DESERT DESERT Online at http://jdesert.ut.ac.ir DESERT 15 (2010) 27-32 The role of resource management and environmental factors in sustainable development Gh.R. Taleghani * Associate Professor, University
Preface PART I. THE MATERIAL 39
 Detailed Contents Preface xi Chapter 1. Environmental Problems and Society 1 Joining the Dialogue 3 The Ecology of Dialogue 4 The Dialogue of Scholarship 6 Sustainability 7 Energy 7 Global Warming 12 The
Detailed Contents Preface xi Chapter 1. Environmental Problems and Society 1 Joining the Dialogue 3 The Ecology of Dialogue 4 The Dialogue of Scholarship 6 Sustainability 7 Energy 7 Global Warming 12 The
General Education Program
 Revised 5/10/2018 General Education Program (For students beginning Fall 2017 or later) General Education provides a common intellectual experience for all university students. It is designed to give students
Revised 5/10/2018 General Education Program (For students beginning Fall 2017 or later) General Education provides a common intellectual experience for all university students. It is designed to give students
ISSN (print) ISSN (online) INTELEKTINĖ EKONOMIKA INTELLECTUAL ECONOMICS 2011, Vol. 5, No. 4(12), p
 ISSN 1822-8011 (print) ISSN 1822-8038 (online) INTELEKTINĖ EKONOMIKA INTELLECTUAL ECONOMICS 2011, Vol. 5, No. 4(12), p. 644 648 The Quality of Life of the Lithuanian Population 1 Review Professor Ona Gražina
ISSN 1822-8011 (print) ISSN 1822-8038 (online) INTELEKTINĖ EKONOMIKA INTELLECTUAL ECONOMICS 2011, Vol. 5, No. 4(12), p. 644 648 The Quality of Life of the Lithuanian Population 1 Review Professor Ona Gražina
World Bank Experts Discuss Korea s Rapid Population Aging
 World Bank Group Korea Office Newsletter NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2015 World Bank Experts Discuss Korea s Rapid Population Aging A roundtable discussion draws implications from the latest World Bank report, Live
World Bank Group Korea Office Newsletter NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2015 World Bank Experts Discuss Korea s Rapid Population Aging A roundtable discussion draws implications from the latest World Bank report, Live
Chapter 2 The Market. The Classical Approach
 Chapter 2 The Market The economic theory of markets has been central to economic growth since the days of Adam Smith. There have been three major phases of this theory: the classical theory, the neoclassical
Chapter 2 The Market The economic theory of markets has been central to economic growth since the days of Adam Smith. There have been three major phases of this theory: the classical theory, the neoclassical
Montclair Public Schools CCSS Social Studies Unit: Marshall A.b Subject Social Studies Grade 6 th Unit # Three Pacing 8-10 Weeks Unit
 Montclair Public Schools CCSS Social Studies Unit: Marshall A.b Subject Social Studies Grade 6 th Unit # Three Pacing 8-10 Weeks Unit The Classical Civilizations of the Mediterranean World: Ancient Greece
Montclair Public Schools CCSS Social Studies Unit: Marshall A.b Subject Social Studies Grade 6 th Unit # Three Pacing 8-10 Weeks Unit The Classical Civilizations of the Mediterranean World: Ancient Greece
THE IMPLICATIONS OF THE KNOWLEDGE-BASED ECONOMY FOR FUTURE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY POLICIES
 General Distribution OCDE/GD(95)136 THE IMPLICATIONS OF THE KNOWLEDGE-BASED ECONOMY FOR FUTURE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY POLICIES 26411 ORGANISATION FOR ECONOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT Paris 1995 Document
General Distribution OCDE/GD(95)136 THE IMPLICATIONS OF THE KNOWLEDGE-BASED ECONOMY FOR FUTURE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY POLICIES 26411 ORGANISATION FOR ECONOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT Paris 1995 Document
design research as critical practice.
 Carleton University : School of Industrial Design : 29th Annual Seminar 2007 : The Circuit of Life design research as critical practice. Anne Galloway Dept. of Sociology & Anthropology Carleton University
Carleton University : School of Industrial Design : 29th Annual Seminar 2007 : The Circuit of Life design research as critical practice. Anne Galloway Dept. of Sociology & Anthropology Carleton University
The Process of Change: Can We Make a Difference? 2015 SAGE Publications, Inc.
 Chapter 14 The Process of Change: Can We Make a Difference? Social change: The Process of Change Variations or alterations over time in the behavior patterns, culture (including norms and values), and
Chapter 14 The Process of Change: Can We Make a Difference? Social change: The Process of Change Variations or alterations over time in the behavior patterns, culture (including norms and values), and
Goals of the AP World History Course Historical Periodization Course Themes Course Schedule (Periods) Historical Thinking Skills
 AP World History 2015-2016 Nacogdoches High School Nacogdoches Independent School District Goals of the AP World History Course Historical Periodization Course Themes Course Schedule (Periods) Historical
AP World History 2015-2016 Nacogdoches High School Nacogdoches Independent School District Goals of the AP World History Course Historical Periodization Course Themes Course Schedule (Periods) Historical
TJHSST Senior Research Project Exploring Artificial Societies Through Sugarscape
 TJHSST Senior Research Project Exploring Artificial Societies Through Sugarscape 2007-2008 Jordan Albright January 22, 2008 Abstract Agent based modeling is a method used to understand complicated systems
TJHSST Senior Research Project Exploring Artificial Societies Through Sugarscape 2007-2008 Jordan Albright January 22, 2008 Abstract Agent based modeling is a method used to understand complicated systems
Modern World History Grade 10 - Learner Objectives BOE approved
 Modern World History Grade 10 - Learner Objectives BOE approved 6-15-2017 Learner Objective: Students will be able to independently use their learning to develop the ability to make informed decisions
Modern World History Grade 10 - Learner Objectives BOE approved 6-15-2017 Learner Objective: Students will be able to independently use their learning to develop the ability to make informed decisions
Japan s Initiative for the Science of Science, Technology and Innovation Policy and Human Resource Development Program
 The University of Tokyo Symposium: Reforming Science, Technology Innovation Policy Making Process and Human Resource Development Session 2: Interdisciplinary Education Program for Science, Technology and
The University of Tokyo Symposium: Reforming Science, Technology Innovation Policy Making Process and Human Resource Development Session 2: Interdisciplinary Education Program for Science, Technology and
How Books Travel. Translation Flows and Practices of Dutch Acquiring Editors and New York Literary Scouts, T.P. Franssen
 How Books Travel. Translation Flows and Practices of Dutch Acquiring Editors and New York Literary Scouts, 1980-2009 T.P. Franssen English Summary In this dissertation I studied the development of translation
How Books Travel. Translation Flows and Practices of Dutch Acquiring Editors and New York Literary Scouts, 1980-2009 T.P. Franssen English Summary In this dissertation I studied the development of translation
THE TRAGEDY OF THE SAPIENT
 1 THE TRAGEDY OF THE SAPIENT As sapient species, we can observe and analyse in some detail where we are heading, but that does not render us capable of changing course. Thanks to genetic and cultural evolution
1 THE TRAGEDY OF THE SAPIENT As sapient species, we can observe and analyse in some detail where we are heading, but that does not render us capable of changing course. Thanks to genetic and cultural evolution
WELCOME TO DBTM THAMMASAT!
 WELCOME TO DBTM THAMMASAT! Faculty of Architecture and Planning, Thammasat University Address: Faculty of Architecture and Planning Thammasat University, Rangsit Campus Klong Luang, Pathumthani, 12120
WELCOME TO DBTM THAMMASAT! Faculty of Architecture and Planning, Thammasat University Address: Faculty of Architecture and Planning Thammasat University, Rangsit Campus Klong Luang, Pathumthani, 12120
When and How Will Growth Cease?
 August 15, 2017 2 4 8 by LIZ Flickr CC BY 2.0 When and How Will Growth Cease? Jason G. Brent Only with knowledge will humanity survive. Our search for knowledge will encounter uncertainties and unknowns,
August 15, 2017 2 4 8 by LIZ Flickr CC BY 2.0 When and How Will Growth Cease? Jason G. Brent Only with knowledge will humanity survive. Our search for knowledge will encounter uncertainties and unknowns,
UNITED NATIONS EDUCATIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND CULTURAL ORGANIZATION. World Summit on Sustainable Development. Address by Mr Koïchiro Matsuura
 DG/2002/82 Original: English UNITED NATIONS EDUCATIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND CULTURAL ORGANIZATION World Summit on Sustainable Development Address by Mr Koïchiro Matsuura Director-General of the United Nations
DG/2002/82 Original: English UNITED NATIONS EDUCATIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND CULTURAL ORGANIZATION World Summit on Sustainable Development Address by Mr Koïchiro Matsuura Director-General of the United Nations
This document has been downloaded from TamPub The Institutional Repository of University of Tampere
 This document has been downloaded from TamPub The Institutional Repository of University of Tampere Publisher's version The permanent address of the publication is http://urn.fi/urn:nbn:fi:uta-201405301524
This document has been downloaded from TamPub The Institutional Repository of University of Tampere Publisher's version The permanent address of the publication is http://urn.fi/urn:nbn:fi:uta-201405301524
Advanced Placement World History Course Description & Philosophy
 Advanced Placement World History Course Description & Philosophy AP World History focuses on developing students' abilities to think conceptually and critically about world history from approximately 600
Advanced Placement World History Course Description & Philosophy AP World History focuses on developing students' abilities to think conceptually and critically about world history from approximately 600
Research Themes of the IALU Research Agenda
 Research Themes of the IALU Research Agenda The IALU shall promote and foster research collaboration among Lasallian researchers in a few, focused research themes. These strategic research themes certainly
Research Themes of the IALU Research Agenda The IALU shall promote and foster research collaboration among Lasallian researchers in a few, focused research themes. These strategic research themes certainly
MS.LS2.A: Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems. MS.LS2.C: Ecosystem Dynamics, Functioning, and Resilience. MS.LS4.D: Biodiversity and Humans
 Disciplinary Core Idea MS.LS2.A: Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems Similarly, predatory interactions may reduce the number of organisms or eliminate whole populations of organisms. Mutually beneficial
Disciplinary Core Idea MS.LS2.A: Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems Similarly, predatory interactions may reduce the number of organisms or eliminate whole populations of organisms. Mutually beneficial
Masters in Environmental History
 History - Environmental History - MLitt & MPhil - 2017/8 - August 2017 Masters in Environmental History Programme Requirements Environmental History - MLitt ((MO5621 (20 credits) and MO5622 (20 credits))
History - Environmental History - MLitt & MPhil - 2017/8 - August 2017 Masters in Environmental History Programme Requirements Environmental History - MLitt ((MO5621 (20 credits) and MO5622 (20 credits))
1. Introduction The Current State of the Korean Electronics Industry and Options for Cooperation with Taiwan
 1. Introduction The fast-changing nature of technological development, which in large part has resulted from the technology shift from analogue to digital systems, has brought about dramatic change in
1. Introduction The fast-changing nature of technological development, which in large part has resulted from the technology shift from analogue to digital systems, has brought about dramatic change in
Summer Assignment. Welcome to AP World History!
 Summer Assignment Welcome to AP World History! You have elected to participate in a college-level world history course that will broaden your understanding of the world, as well as prepare you to take
Summer Assignment Welcome to AP World History! You have elected to participate in a college-level world history course that will broaden your understanding of the world, as well as prepare you to take
Summer Assignment. Due August 29, 2011
 Summer Assignment Welcome to AP World History! You have elected to participate in a college-level world history course that will broaden your understanding of the world, as well as prepare you to take
Summer Assignment Welcome to AP World History! You have elected to participate in a college-level world history course that will broaden your understanding of the world, as well as prepare you to take
New and Emerging Issues Interface to Science Policy
 Ninth Session of the Committee on Sustainable Development and the Africa Regional Forum on Sustainable Development New and Emerging Issues Interface to Science Policy Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 16-18 June
Ninth Session of the Committee on Sustainable Development and the Africa Regional Forum on Sustainable Development New and Emerging Issues Interface to Science Policy Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 16-18 June
SOCIAL AND ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT Vol. VII - Consumption in Affluent Societies of Industrialized Nations - L. Sartori
 CONSUMPTION IN AFFLUENT SOCIETIES OF INDUSTRIALIZED NATIONS L. Sartori Department of Communication, University of Bologna, Italy Keywords: consumption, affluent society, modernity, postmodernity, material
CONSUMPTION IN AFFLUENT SOCIETIES OF INDUSTRIALIZED NATIONS L. Sartori Department of Communication, University of Bologna, Italy Keywords: consumption, affluent society, modernity, postmodernity, material
[PDF] How Culture Shapes The Climate Change Debate
![[PDF] How Culture Shapes The Climate Change Debate [PDF] How Culture Shapes The Climate Change Debate](/thumbs/90/103052787.jpg) [PDF] How Culture Shapes The Climate Change Debate Though the scientific community largely agrees that climate change is underway, debates about this issue remain fiercely polarized. These conversations
[PDF] How Culture Shapes The Climate Change Debate Though the scientific community largely agrees that climate change is underway, debates about this issue remain fiercely polarized. These conversations
Why did the Japanese economy stop growing over time? Why did technological progress in Japan decline?
 Discussion Guide for Why did Japan Stop Growing? a discussion with Professor Takeo Hoshi Organizing Questions Why did the Japanese economy stop growing over time? Why did technological progress in Japan
Discussion Guide for Why did Japan Stop Growing? a discussion with Professor Takeo Hoshi Organizing Questions Why did the Japanese economy stop growing over time? Why did technological progress in Japan
Technologists and economists both think about the future sometimes, but they each have blind spots.
 The Economics of Brain Simulations By Robin Hanson, April 20, 2006. Introduction Technologists and economists both think about the future sometimes, but they each have blind spots. Technologists think
The Economics of Brain Simulations By Robin Hanson, April 20, 2006. Introduction Technologists and economists both think about the future sometimes, but they each have blind spots. Technologists think
Fifth Grade Science Curriculum
 Grade Level: 5 th Grade Book Title and Publisher: Science A Closer Look - MacMillian/McGraw Hill Student Textbook ISBN: 0-02-284138-5 Fifth Grade Science Curriculum Scientific Inquiry (Nature of Science
Grade Level: 5 th Grade Book Title and Publisher: Science A Closer Look - MacMillian/McGraw Hill Student Textbook ISBN: 0-02-284138-5 Fifth Grade Science Curriculum Scientific Inquiry (Nature of Science
Theories of development main ideas
 Theories of development Chapter 4 School of modernization Theories of development main ideas Theories explaining underdevelopment Modernization Dependency The new theories 1 Theories explaining underdevelopment
Theories of development Chapter 4 School of modernization Theories of development main ideas Theories explaining underdevelopment Modernization Dependency The new theories 1 Theories explaining underdevelopment
MEGATRENDS THE TREND TOWARDS
 01: DEMOGRAPHIC CHANGE 02: INDIVIDUALISATION REACHES A NEW STAGE 03: HEALTH THRIVES 04: WOMEN ON THE RISE 05: CULTURAL DIVERSITY 06: NEW PATTERNS OF MOBILITY 07: DIGITAL LIFESTYLE 08: BIOMIMICRY, OR, LEARNING
01: DEMOGRAPHIC CHANGE 02: INDIVIDUALISATION REACHES A NEW STAGE 03: HEALTH THRIVES 04: WOMEN ON THE RISE 05: CULTURAL DIVERSITY 06: NEW PATTERNS OF MOBILITY 07: DIGITAL LIFESTYLE 08: BIOMIMICRY, OR, LEARNING
Advanced Placement World History
 Advanced Placement World History 2018-19 We forget that every good that is worth possessing must be paid for in strokes of daily effort. -William James (1842-1910) I don't wait for moods. You accomplish
Advanced Placement World History 2018-19 We forget that every good that is worth possessing must be paid for in strokes of daily effort. -William James (1842-1910) I don't wait for moods. You accomplish
Policy Evaluation as if sustainable development really mattered: Rethinking evaluation in light of Europe s 2050 Agenda
 Policy Evaluation as if sustainable development really mattered: Rethinking evaluation in light of Europe s 2050 Agenda EEEN Forum, Helsinki, April 28-29, 2014 Dr Hans Bruyninckx Executive Director, European
Policy Evaluation as if sustainable development really mattered: Rethinking evaluation in light of Europe s 2050 Agenda EEEN Forum, Helsinki, April 28-29, 2014 Dr Hans Bruyninckx Executive Director, European
The Environment, Government Policies, and International Trade: A Proceedings Shane, M.D., and H. von Witzke, eds.
 , ' ' y rrna+kan c+aran nx k. a., mc aras.,m xxas y-m s )u a; a.... y; _ 7i "a's 7'. " " F: :if ' e a d66,asva-.~rx:u _... Agriculture and Trade Analysis Division Economic Research Service United States
, ' ' y rrna+kan c+aran nx k. a., mc aras.,m xxas y-m s )u a; a.... y; _ 7i "a's 7'. " " F: :if ' e a d66,asva-.~rx:u _... Agriculture and Trade Analysis Division Economic Research Service United States
Information Sociology
 Information Sociology Educational Objectives: 1. To nurture qualified experts in the information society; 2. To widen a sociological global perspective;. To foster community leaders based on Christianity.
Information Sociology Educational Objectives: 1. To nurture qualified experts in the information society; 2. To widen a sociological global perspective;. To foster community leaders based on Christianity.
Kazakhstan Way of Innovation Clusterization K. Mukhtarova Al-Farabi Kazak National University, Almaty, Kazakhstan
 Journal of Social Sciences (COES&RJ-JSS) ISSN (E): 2305-9249 ISSN (P): 2305-9494 Publisher: Centre of Excellence for Scientific & Research Journalism, COES&RJ LLC Online Publication Date: 1 st January
Journal of Social Sciences (COES&RJ-JSS) ISSN (E): 2305-9249 ISSN (P): 2305-9494 Publisher: Centre of Excellence for Scientific & Research Journalism, COES&RJ LLC Online Publication Date: 1 st January
and R&D Strategies in Creative Service Industries: Online Games in Korea
 RR2007olicyesearcheportInnovation Characteristics and R&D Strategies in Creative Service Industries: Online Games in Korea Choi, Ji-Sun DECEMBER, 2007 Science and Technology Policy Institute P Summary
RR2007olicyesearcheportInnovation Characteristics and R&D Strategies in Creative Service Industries: Online Games in Korea Choi, Ji-Sun DECEMBER, 2007 Science and Technology Policy Institute P Summary
Business Clusters and Innovativeness of the EU Economies
 Business Clusters and Innovativeness of the EU Economies Szczepan Figiel, Professor Institute of Agricultural and Food Economics, National Research Institute, Warsaw, Poland Dominika Kuberska, PhD University
Business Clusters and Innovativeness of the EU Economies Szczepan Figiel, Professor Institute of Agricultural and Food Economics, National Research Institute, Warsaw, Poland Dominika Kuberska, PhD University
Key Concept 6.1 Science and the Environment
 Key Concept 6.1 Science and the Environment Rapid advances in science altered the understanding of the universe and the natural world and led to the development of new technologies. These changes enabled
Key Concept 6.1 Science and the Environment Rapid advances in science altered the understanding of the universe and the natural world and led to the development of new technologies. These changes enabled
MACHINE-HUMAN RELATIONSHIPS
 The 25 years of the Club of Bologna Evolution and prospects of agricultural mechanization in the world 12-13 November 2016 EIMA INTERNATIONAL Bologna, Italy Sinfonia Hall MACHINE-HUMAN RELATIONSHIPS Yoshisuke
The 25 years of the Club of Bologna Evolution and prospects of agricultural mechanization in the world 12-13 November 2016 EIMA INTERNATIONAL Bologna, Italy Sinfonia Hall MACHINE-HUMAN RELATIONSHIPS Yoshisuke
Analysis of Nonlinear Phenomena in Industry University Research Cooperation Innovation System Wei Jiang1, 2
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Information and Computer Science (ICEMC 2017) Analysis of Nonlinear Phenomena in Industry University Research Cooperation Innovation System Wei Jiang1,
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Information and Computer Science (ICEMC 2017) Analysis of Nonlinear Phenomena in Industry University Research Cooperation Innovation System Wei Jiang1,
Terraforming Mars Group Discussion
 Terraforming Mars Group Discussion Group Assignment Meet with the other members of your group. Assign group roles. Print names below. Your name must appear below in order to receive credit. Recorder -
Terraforming Mars Group Discussion Group Assignment Meet with the other members of your group. Assign group roles. Print names below. Your name must appear below in order to receive credit. Recorder -
Research with Impact Aalto Research Day, 26th of September, 2013 Mikko Kosonen, President, Sitra
 Research with Impact Aalto Research Day, 26th of September, 2013 Mikko Kosonen, President, Sitra Megatrends of the interconnected world Superseniors X-Events Data as a source of power and wealth Race for
Research with Impact Aalto Research Day, 26th of September, 2013 Mikko Kosonen, President, Sitra Megatrends of the interconnected world Superseniors X-Events Data as a source of power and wealth Race for
Copyrighted Material. A complete, consistent, unified theory...would be the ultimate triumph of human reason. Stephen W. Hawking
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction A complete, consistent, unified theory would be the ultimate triumph of human reason Stephen W Hawking The transition from an epoch of stagnation to an era of sustained economic
CHAPTER 1 Introduction A complete, consistent, unified theory would be the ultimate triumph of human reason Stephen W Hawking The transition from an epoch of stagnation to an era of sustained economic
The Construction Market in Europe: A Supplier s Point of View
 The Construction Market in Europe: A Supplier s Point of View Dr. Walter Nussbaumer Abstract After the 2009 recession and the 2010 stagnation, recovery took place in 2011 when the World Construction Industry
The Construction Market in Europe: A Supplier s Point of View Dr. Walter Nussbaumer Abstract After the 2009 recession and the 2010 stagnation, recovery took place in 2011 when the World Construction Industry
EC Chapter 1. Burak Alparslan Eroğlu. October 13, Burak Alparslan Eroğlu EC Chapter 1
 EC 101 - Chapter 1 Burak Alparslan Eroğlu October 13, 2016 Outline Introduction to New Course Module Introduction to Unit 1 Hockey Stick Growth Capitalism Inequality Economics and Economy Introduction
EC 101 - Chapter 1 Burak Alparslan Eroğlu October 13, 2016 Outline Introduction to New Course Module Introduction to Unit 1 Hockey Stick Growth Capitalism Inequality Economics and Economy Introduction
Information Societies: Towards a More Useful Concept
 IV.3 Information Societies: Towards a More Useful Concept Knud Erik Skouby Information Society Plans Almost every industrialised and industrialising state has, since the mid-1990s produced one or several
IV.3 Information Societies: Towards a More Useful Concept Knud Erik Skouby Information Society Plans Almost every industrialised and industrialising state has, since the mid-1990s produced one or several
Toward Inclusive and Sustainable Development
 March 15, 2019 Bank of Japan Toward Inclusive and Sustainable Development Remarks at the B20 Tokyo Summit hosted by Nippon Keidanren (Japan Business Federation) Haruhiko Kuroda Governor of the Bank of
March 15, 2019 Bank of Japan Toward Inclusive and Sustainable Development Remarks at the B20 Tokyo Summit hosted by Nippon Keidanren (Japan Business Federation) Haruhiko Kuroda Governor of the Bank of
Two Modeling Cultures. Marco Janssen School of Sustainability Center for Behavior, Institutions and the Environment Arizona State University
 Two Modeling Cultures Marco Janssen School of Sustainability Center for Behavior, Institutions and the Environment Arizona State University Outline Background Brief history of integrated global models
Two Modeling Cultures Marco Janssen School of Sustainability Center for Behavior, Institutions and the Environment Arizona State University Outline Background Brief history of integrated global models
Implications of the current technological trajectories for industrial policy New manufacturing, re-shoring and global value chains.
 Implications of the current technological trajectories for industrial policy New manufacturing, re-shoring and global value chains Mario Cimoli You remember when most economists said that industrialization
Implications of the current technological trajectories for industrial policy New manufacturing, re-shoring and global value chains Mario Cimoli You remember when most economists said that industrialization
202000AAW ASSOCIATE OF ARTS
 Rev. 10/0/18 C E R 1ST YEAR FALL SEMESTER Online Credit Hours Prerequisites 00:111 English Composition I Placement by advisor SPRING SEMESTER C E R 2ND YEAR Quantitative Reasoning Requirement (note a.)
Rev. 10/0/18 C E R 1ST YEAR FALL SEMESTER Online Credit Hours Prerequisites 00:111 English Composition I Placement by advisor SPRING SEMESTER C E R 2ND YEAR Quantitative Reasoning Requirement (note a.)
PART I: Workshop Survey
 PART I: Workshop Survey Researchers of social cyberspaces come from a wide range of disciplinary backgrounds. We are interested in documenting the range of variation in this interdisciplinary area in an
PART I: Workshop Survey Researchers of social cyberspaces come from a wide range of disciplinary backgrounds. We are interested in documenting the range of variation in this interdisciplinary area in an
Richmond, The American International University In London Summer Course Prerequisites
 Richmond, The American International University In London Summer Course Prerequisites SESSION A COURSES FNN 302A: Principles of Investment Prerequisite: FNN 301 FNN 301 Corporate Finance Examines the financial
Richmond, The American International University In London Summer Course Prerequisites SESSION A COURSES FNN 302A: Principles of Investment Prerequisite: FNN 301 FNN 301 Corporate Finance Examines the financial
PART I NEW ACADEMIC PROGRAMS AND PROGRAM CHANGES
 MICHIGAN STATE UNIVERSITY University Committee on Curriculum SUBCOMMITTEE B AGENDA 437 Administration Building 1:30 p.m. PART I ACADEMIC PROGRAMS AND PROGRAM CHANGES COLLEGE OF SOCIAL SCIENCE 1. Request
MICHIGAN STATE UNIVERSITY University Committee on Curriculum SUBCOMMITTEE B AGENDA 437 Administration Building 1:30 p.m. PART I ACADEMIC PROGRAMS AND PROGRAM CHANGES COLLEGE OF SOCIAL SCIENCE 1. Request
Contributions of Scientists and Engineers to Defining Article 15. Margaret Weigers Vitullo, PhD American Sociological Association
 Contributions of Scientists and Engineers to Defining Article 15 Margaret Weigers Vitullo, PhD American Sociological Association Overview of next 25 minutes Methods. Three core questions and concerns.
Contributions of Scientists and Engineers to Defining Article 15 Margaret Weigers Vitullo, PhD American Sociological Association Overview of next 25 minutes Methods. Three core questions and concerns.
Table of Contents. Preface Acknowledgments
 Table of Contents Preface Acknowledgments xii xvi Chapter 1. The Personal Experience of Social Change 1 A Twentieth-Century Life: Iris Summers 2 From Farm to Factory 3 Extending the Reach 6 Generations
Table of Contents Preface Acknowledgments xii xvi Chapter 1. The Personal Experience of Social Change 1 A Twentieth-Century Life: Iris Summers 2 From Farm to Factory 3 Extending the Reach 6 Generations
Econ 911 Midterm Exam. Greg Dow February 27, Please answer all questions (they have equal weight).
 Econ 911 Midterm Exam Greg Dow February 27, 2013 Please answer all questions (they have equal weight). 1. Consider the Upper Paleolithic economy and the modern Canadian economy. What are the main ways
Econ 911 Midterm Exam Greg Dow February 27, 2013 Please answer all questions (they have equal weight). 1. Consider the Upper Paleolithic economy and the modern Canadian economy. What are the main ways
Scenario Development Process
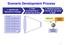 Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
Edgewood College General Education Curriculum Goals
 (Approved by Faculty Association February 5, 008; Amended by Faculty Association on April 7, Sept. 1, Oct. 6, 009) COR In the Dominican tradition, relationship is at the heart of study, reflection, and
(Approved by Faculty Association February 5, 008; Amended by Faculty Association on April 7, Sept. 1, Oct. 6, 009) COR In the Dominican tradition, relationship is at the heart of study, reflection, and
INTRODUCTION TO SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Beyond Brundtland: The Evolution of Sustainable Development in the 1990s - Newman R.L.
 BEYOND BRUNDTLAND: THE EVOLUTION OF SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT IN THE 1990S Newman R.L. York Centre for Applied Sustainability, Toronto, Canada Keywords: ecology, sustainable development, natural capitalism,
BEYOND BRUNDTLAND: THE EVOLUTION OF SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT IN THE 1990S Newman R.L. York Centre for Applied Sustainability, Toronto, Canada Keywords: ecology, sustainable development, natural capitalism,
Many Bible commentators thought the disasters of Biblical prophecy were unrealistic. So they saw:
 Many Bible commentators thought the disasters of Biblical prophecy were unrealistic. So they saw: Jesus descriptions of disaster in Matthew 24 as just the fall of Jerusalem in AD 70; the strange locusts
Many Bible commentators thought the disasters of Biblical prophecy were unrealistic. So they saw: Jesus descriptions of disaster in Matthew 24 as just the fall of Jerusalem in AD 70; the strange locusts
Anchoring: Introducing a Behavioral Economic Topic in Principles of Economics Courses
 Anchoring: Introducing a Behavioral Economic Topic in Principles of Economics Courses J. Douglas Barrett, University of North Alabama Abstract: This case is a teaching application for economics principles
Anchoring: Introducing a Behavioral Economic Topic in Principles of Economics Courses J. Douglas Barrett, University of North Alabama Abstract: This case is a teaching application for economics principles
K.1 Structure and Function: The natural world includes living and non-living things.
 Standards By Design: Kindergarten, First Grade, Second Grade, Third Grade, Fourth Grade, Fifth Grade, Sixth Grade, Seventh Grade, Eighth Grade and High School for Science Science Kindergarten Kindergarten
Standards By Design: Kindergarten, First Grade, Second Grade, Third Grade, Fourth Grade, Fifth Grade, Sixth Grade, Seventh Grade, Eighth Grade and High School for Science Science Kindergarten Kindergarten
Socio-Economic Sciences and Humanities. First Call for proposals. Nikos Kastrinos. Unit L1 Coordination and Horizontal Aspects
 Socio-Economic Sciences and Humanities First Call for proposals Nikos Kastrinos Unit L1 Coordination and Horizontal Aspects Information Day Socio-economic Sciences & the Humanities Thessaloniki 29 March
Socio-Economic Sciences and Humanities First Call for proposals Nikos Kastrinos Unit L1 Coordination and Horizontal Aspects Information Day Socio-economic Sciences & the Humanities Thessaloniki 29 March
Foresight in an Unpredictable World
 The 4th International Seville Conference on Future-Oriented Technology Analysis (FTA) 12 & 13 May 2011 Foresight in an Unpredictable World Ilkka Tuomi MeaningProcessing.com I. Tuomi 13 May 2011 page: 1
The 4th International Seville Conference on Future-Oriented Technology Analysis (FTA) 12 & 13 May 2011 Foresight in an Unpredictable World Ilkka Tuomi MeaningProcessing.com I. Tuomi 13 May 2011 page: 1
AP European History Chapter 22: The Revolution in Energy and Industry
 AP European History Chapter 22: The Revolution in Energy and Industry Name: Period: Complete the graphic organizer as you read Chapter 22. DO NOT simply hunt for the answers; doing so will leave holes
AP European History Chapter 22: The Revolution in Energy and Industry Name: Period: Complete the graphic organizer as you read Chapter 22. DO NOT simply hunt for the answers; doing so will leave holes
I Economic Growth 5. Second Edition. Robert J. Barro Xavier Sala-i-Martin. The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England
 I Economic Growth 5 Second Edition 1 Robert J. Barro Xavier Sala-i-Martin The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England Preface About the Authors xv xvii Introduction 1 1.1 The Importance of Growth
I Economic Growth 5 Second Edition 1 Robert J. Barro Xavier Sala-i-Martin The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England Preface About the Authors xv xvii Introduction 1 1.1 The Importance of Growth
Foresight in an Unpredictable World
 The 4th International Seville Conference on Future-Oriented Technology Analysis (FTA) 12 & 13 May 2011 Foresight in an Unpredictable World Ilkka Tuomi MeaningProcessing.com I. Tuomi 13 May 2011 page: 1
The 4th International Seville Conference on Future-Oriented Technology Analysis (FTA) 12 & 13 May 2011 Foresight in an Unpredictable World Ilkka Tuomi MeaningProcessing.com I. Tuomi 13 May 2011 page: 1
Contents Modeling of Socio-Economic Systems Agent-Based Modeling
 Contents 1 Modeling of Socio-Economic Systems... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Particular Difficulties of Modeling Socio-Economic Systems... 2 1.3 Modeling Approaches... 4 1.3.1 Qualitative Descriptions...
Contents 1 Modeling of Socio-Economic Systems... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Particular Difficulties of Modeling Socio-Economic Systems... 2 1.3 Modeling Approaches... 4 1.3.1 Qualitative Descriptions...
Students are also encouraged to approach all readings, discussions, lectures, and audio-visual materials critically.
 ANTH 100 D Introduction To Anthropology Winter 2006 Bellevue Community College Instructor : Manouchehr Shiva, Ph.D. Office Hours: (by appointment) Division Phone: 425-564-2331, 425-564-2334 E-mail: mshiva@bcc.ctc.edu
ANTH 100 D Introduction To Anthropology Winter 2006 Bellevue Community College Instructor : Manouchehr Shiva, Ph.D. Office Hours: (by appointment) Division Phone: 425-564-2331, 425-564-2334 E-mail: mshiva@bcc.ctc.edu
Endogenous Innovation Creating a Smart Water System Paul Gagliardo Manager Innovation Development
 Endogenous Innovation Creating a Smart Water System Paul Gagliardo Manager Innovation Development Smart Water Infrastructure Summit May 18, 2012 Washington DC What is Innovation? Innovation is the creation
Endogenous Innovation Creating a Smart Water System Paul Gagliardo Manager Innovation Development Smart Water Infrastructure Summit May 18, 2012 Washington DC What is Innovation? Innovation is the creation
