Society 5.0. Keidanren
|
|
|
- Brian Powers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Society Co- c r e a t i n g t h e f u t u r e - (Excerpt 1 ) Keidanren 1 This is an excerpt from the original report (in Japanese). The complete version in Japanese can be accessible from
2 Table of Contents Introduction-Towards a Bright Future... 1 Chapter I: Development of Human Society... 5 Chapter II: Digital Transformation... 7 Chapter III: The Nature of Society Chapter IV: The fruits of Society Chapter V: Blueprint of Society 5.0 for SDGs Cities and Regions Energy Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Healthcare (health, medicine, and nursing) Agriculture and Food Logistics Manufacturing and Services Finance Public Services Summary Conclusion... 26
3 Introduction-Towards a Bright Future Japan is committed to Society 5.0. It is the vision of an emerging form of society characterized as Imagination Society enabled by the digital transformation. Digital transformation, especially with artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics, provides augmented abilities to people enabling them to pursue their dreams, big or small, some of which shall make major contribution for global agenda including sustainability and social inclusions, and other major breakthrough to push human race forward. Society 5.0 is inevitable and an opportunity. First of all, the world is facing an even greater tide of change against a backdrop of rapidly advancing innovation in digital technologies such as AI, the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, and blockchains, as well as biotechnologies. This will go beyond mere technological innovation to trigger revolutionary changes in the forms of industries and societies. Platformers such as Google, Amazon, Facebook, and Apple (GAFA) are not the sole promoters of this innovation. As seen in the German "Industrie 4.0" and Chinese "Made in China 2025" strategies, governments are launching national projects to encourage changes. Secondly, there is a rapid economical and geopolitical shift. The emergence of China as a superpower has radically altered the global landscape from economic and geopolitical perspectives. Besides China, other Asian countries including India and the ASEAN members are expected to achieve rapid growth in the future, which will shift the world economy s center of gravity from the West to Asia. Also, while some countries are facing rapid ageing of the population amid extremely low birthrate, the global population is growing explosively. Such rapid change of population dynamics affects economy and geo-politics with increasing demands to solve sustainability and social inclusion issues among other issues. Third, problems such as global environmental issues and social disparity are worsening, and in 2015 the United Nations adopted Sustainable Development Goals 1
4 (SDGs) 2 aimed at addressing these. In the financial sector, environment, social, and governance (ESG) investment 3 is expanding. These trends demonstrate an emerging change of mindset caused by the shared perception that dealing with external diseconomies is a serious issue affecting political and economic stability and even the survival of humankind. These three major changes, namely technological change, economic and geo-political change, and change in mindset will become more obvious and accelerated in the future. As they exacerbate uncertainty in the world, a sense of insecurity is also rising. However, every change brings opportunities as well. If we accept these changes positively and take advantage of them, we will be able to create a better society. We cannot carve out the future with a pessimistic mindset. The future is not an extension of the past. We must start by moving beyond the experiences and assumptions we have had so far. Imagination is the key to shaping the future. It is important to exercise our imaginations for the future of earth and humankind and recreate the world for the better. Someone may imagine the future deemed crazy by society. However, we should recognize the truth; the people who are crazy enough to think they can change the world, are the ones who do. 4 We will continue to develop the world for the better by unleashing the full range of imagination produced by individuals with diverse backgrounds and sense of values. Diversity is a source of inspirations in times of change. 2 The SDGs are international goals with target dates between 2016 and 2030 that were included in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development adopted by the United Nations in September 2015 following the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) adopted in They are composed of 17 goals and 169 targets to realize a sustainable world. 3 ESG investment places emphasis on selecting firms that consider the environment, society, and governance. Specific emphasis is placed on measures to address climate change in the environmental sphere, attention to human rights in the social domain, and compliance and disclosure in the governance arena. 4 From the "Think Different" advertising campaign, which was launched by Apple Inc. in 1997, right after the return of Steve Jobs. "While some see them as the crazy ones, we see genius. Because the people who are crazy enough to think they can change the world, are the ones who do." This was the start of the dramatic revival of the company, which now has the world s largest market capitalization. 2
5 Japan has the potential to cause the most drastic change in the world. It is facing an unprecedented crisis with a vast array of problems including a declining birthrate and ageing society, a low rate of growth, declining research capabilities, and fiscal deterioration. Conversely, however, it can be said that Japan is blessed with a golden opportunity to make the most of the change occurring in the world. IoT development will connect everything to the Internet. Many Japanese firms have strengths in technologies performing in the physical real world and will be able to take advantage of this trend. Japan also neighbors China, which is a huge and growing market, and has a favorable relationship with rapidly growing India and ASEAN countries. Maintaining close contact with Western nations also gives Japan a geo-political advantage. Moreover, from a cultural perspective, the mindset embodied in the SDGs has long guided Japanese economic activities, as seen in the concepts of "sampo-yoshi"(three parties satisfaction), which emphasizes the importance of business rooted in society and stresses that there must be benefits for the seller, the purchaser, and society, and "mottai-nai" (aversion to waste), which embraces the spirit of symbiosis with nature. Japan s track-record of achieving growth with limited natural resources has been characterized by abundant imagination to create a better society and firm resolution to accomplish this goal. Japan will have a promising future if it can harness various forms of imagination to change society. This host of challenges is also a treasure-chest for problem solving. If it can solve its own problems, it will also be able to help resolve similar challenges that the world is going to face sooner or later. Potential cannot be realized without action. It is essential for Japan to create a vision for the society it wishes to create and reform itself. Humankind is about to enter a new societal phase where development of digital technologies causes tremendous change. Japan has dubbed this "Society 5.0" 5 and is 5 The term "Society 5.0" denotes the fifth stage of society following the Hunting, Agrarian, Industrial, and Information Societies. It was proposed by the private-sector members of the Japanese government s Council for Science, Technology and Innovation as a conceptual model for the society of the future. It was proposed for the first time in the 5th Science and Technology Basic Plan. 3
6 working hard to materialize it. It is hard to say that Japan has presented and proposed concepts encompassing the whole world in the past. From now on, Japan should embrace the role of contributing to sustainable development of society by taking leadership in reforms with a clear concept of the future it wants to create. The main player in these reforms is the business community, and the process will test the ability of business to change itself. Therefore, in this report, Japanese business community sets out concept of and draws a concrete picture of Society 5.0 as a future society that we wish to create with the world, by discussing aims for the society of tomorrow and considers what kind of society to create based on the global changes described above. 4
7 Chapter I: Development of Human Society Chart 1: Development of Human Society Source:Keidanren The rapid spread of the Internet and smartphones since the 1990s has produced abundant data that circulate around the world creating new value all the time. Having inhabited such an Information Society in recent years, humankind is now at an important turning point for civilization. The premises on which society is based are about to change dramatically as people come to terms with the emergence of environmental burden and social disparity caused by traditional economic systems on the one hand and rapid digital transformation on the other. 5
8 Opinions on how to categorize societies vary, but the 5th Science and Technology Basic Plan 6 identified the societies in which humankind lived in the past as the Hunting Society (Society 1.0), Agrarian Society (Society 2.0), Industrial Society (Society 3.0) and Information Society (Society 4.0), and termed a new society to follow them Society 5.0. A series of past revolutions including the agricultural and industrial revolutions have brought about not only technological advances and greater convenience, but also structural changes to society. It is difficult to accurately foresee what kind of society the ongoing Society 5.0 revolution will create. Rather than attempting to predict the future, it is important for us to be key players in the revolution, to indicate direction, and to work with a diverse range of people to create the future. The history of human society has been characterized by liberation from restrictions and acquisition of freedom through enhanced capabilities stemming from new tools and techniques. Moving from the Hunting Society to the Agrarian Society, humans gained and enhanced the ability to produce food, which freed them from hunger. In the Industrial Society they increased production capabilities and mobility by harnessing motive power. In the Information Society digitalization enhanced the capacity of telecommunications and information processing, which drastically increased freedom to access information and communication of all kind, and freely exploring various opportunities for internet-based services. In the following chapters, we will first summarize how the premises on which society is based will be changed by digital transformation. Based on this summary, we will then describe a new society to be created and consider the kinds of capabilities to be acquired and enhanced, restrictions to be eased and freedoms to be gained, and values to pursue in this new society. 6 Government of Japan, The 5th Science and Technology Basic Plan (January 22, 2018) 6
9 Chapter II: Digital Transformation Ongoing digital transformation is triggering the evolution of a new society. Digital transformation means that advances in digital technology and data utilization drastically changes aspects of society including private lives, public administration, industrial structure, and employment. As large-scale collection, transmission, storage, and analysis of data become possible at low cost, various forms of innovation are spurred. Data enables visualization of issues and suggests solutions. Such knowledge and insights can be instantly shared around the world, leading to the resolution of management and social issues. In digital transformation, application of data-based technologies including IoT, AI, robotics and blockchains brings about fundamental changes in society. IoT: IoT means that every "thing" is connected to the Internet. Improved technologies for sensing precise data from physical real world will enable appropriate data to be gathered in real time and deployed in cyberspace. To date, innovative services have been invented utilizing data mainly produced in cyberspace. From now on, it will be possible to convert any kind of activities in both physical real world and cyberspace of our society into digital data. Digital transformation will expand to encompass everything, everyone, and every event. 7
10 AI: The capabilities of AI, which was first proposed in the 1960s and has been the subject of study since then, have been rapidly improved in recent years by invention of deep learning and by a series of technological breakthroughs particularly in a broad field of machine learning, as well as environments enabling computation of large data volumes. Though AI is by no means all-powerful, it has abilities for complex pattern recognition, prediction of behaviors for complex systems, high precision execution of physical system operations, and a certain level of decision-making and can solve highly complex problems if appropriately designed and operated. Many human tasks can be automated by AI. One essential aspect of AI can be viewed as distribution and commoditization of abilities. 7 Driving, for example, has depended upon the individual driving skills of people driving taxis or private vehicles. When AI systems acquire a high level of driving skill far beyond most drivers, users can share the systems and enjoy skilled driving without depending upon individual skill. The Information Society enabled humans to access information from anywhere in the world. With AI innovation, they get access to a high level of abilities from anywhere. This is the distribution and commoditization of abilities" that will transform society by dramatically enhancing individual abilities. Robotics: AI exerts its capabilities not only in cyberspace, but also in physical real world via robots. These are being deployed in manufacturing as well as various service sectors, supported by rapid growth in robotics. In the future, a variety of robots will play important roles everywhere, including homes, offices, and urban areas, and AI and robots will be able to replace or support humans in carrying out routine tasks. For example, a vehicle with autonomous driving functions is considered as a kind of robot. In this way, as AI is incorporated everywhere, everything acquires intelligence and society gets smarter. 7 Kitano, H., The future of blockchains lies in linkage to artificial intelligence, DIAMOND Harvard Business Review, August (in Japanese) 8
11 Distributed Ledger Technology: Distributed ledger technologies such as blockchains do much to improve transaction efficiency and traceability. Such technologies which are currently used as a basic technology for cryptocurrencies, are expected to be applied to a variety of areas as they become able to ensure a high level of transparency and reliability in sharing transaction data via the Internet. This will bring about new forms of credit and trust that could fundamentally overturn the way society operates. In this way, IoT, AI, robotics and blockchains together with data at its core are transforming society, and we call this digital transformation. Most of the abilities that AI obtains by learning a large amount of data will be distributed as trained AI modules. Abilities of individual people, at least in some aspect, can be learned by AI and distributed. "Internet of Abilities" (IoA) 8 will come into being where abilities in both human capability and AI capability can be made transferrable, interconnectable, and work synergistically. In such a society, individual people will be able to create high value business, for example, by exploring their own abilities combined with "abilities of AI". However, not all human abilities will be substituted by AI. Real interactions such as information exchange among people and communication based on empathy that can hardly be distributed will gain even more importance. These unstoppable trends in digital transformation fundamentally change the premises on which society is based. There are countless alternatives for directions in which society will be advanced by technological development. Technologies could have negative effects such as impact on employment and growing disparity and maldistribution of wealth and information. The direction in which we guide future society is up to us. We must consider what kind of society we wish to create rather than trying to foresee the kind of society it will be. It is essential to take the initiative in reform to create an ideal society without being swallowed up by the waves of change. 8 Rekimoto, J., From IoT to IoA, a network to extend humankind, Nikkei Electronics, January (in Japanese) 9
12 Chapter III: The Nature of Society 5.0 While digital transformation heralds a new stage of society, it is important to utilize digital technologies and data to create a society where people can pursue diverse lifestyles and forms of happiness in their own ways. The 5th Science and Technology Basic Plan, which officially presented Society for the first time, termed it a super smart society, 10 but that reflects only one aspect of Society 5.0. As described in the previous section, digital transformation enables anyone to access advanced abilities. With ambition and ideas, people can conduct activities and business that could profoundly change society. As noted in the introduction, people who can fulfill big dreams and fantasies are sometimes deemed crazy, yet they are the ones who can change society. Society 5.0 will require rich imaginations to identify a variety of needs and challenges scattered throughout society and scenarios to solve them, as well as creativity to realize solutions making use of digital technologies and data. The combination of digital 9 Keidanren has also published a number of proposals to realize Society 5.0, including "Toward realization of the new economy and society" (April 19, 2016) and "Revitalizing Japan by Realizing Society Action Plan for Creating the Society of the Future --" (February 14, 2017) 10 In the 5th Science and Technology Basic Plan, the super smart society is characterized as "a society that is capable of providing the necessary goods and services to the people who need them at the required time and in just the right amount; a society that is able to respond precisely to a wide variety of social needs; a society in which all kinds of people can readily obtain high-quality services, overcome differences of age, gender, region, and language, and live vigorous and comfortable lives." 10
13 transformation with the imagination and creativity of diverse people will facilitate not only problem solving but also value creation that will lead to a brighter future. Chart 1: Society 5.0 Source:Keidanren Society 5.0 will be an Imagination Society, where digital transformation combines with the imagination and creativity of diverse people to solve social problems and create value. In Society 5.0, humans will exercise imagination not only for themselves, but also for nature and technology to seek ways of achieving symbiosis with them in order to enable sustainable development. It is a concept that can contribute to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) adopted by the United Nations. 11
14 Chapter IV: The fruits of Society 5.0 As everyone accesses advanced "abilities" in Society 5.0, they will be liberated from various constraints that could not be overcome up to Society 4.0, and will obtain the freedom to pursue diverse lifestyles and contribution to the society. Chart 2: Changes from Society 4.0 to 5.0 Source:Keidanren 12
15 Liberation from focus on efficiency A society where value is created Societies 3.0 and 4.0 pursued scale and efficiency via mass production and consumption in order to guarantee material wealth to growing populations. In such societies, it was considered important to comply with traditional rules and plans and to follow a plan-do-check-act cycle. Goods and services were uniform, and standardized processes were applied to similar things in pursuit of efficiency. In Society 5.0, needs will become more diversified, and the supply side will be ready to meet them with digital technologies. People will be liberated from focus on efficiency and place emphasis on satisfying individual needs, solving problems, and creating value. Liberation from suppression of individuality A society in which anyone can exercise diverse abilities In Society 3.0 and 4.0, people were required to accept uniform goods and services and live uniform lives in conformity with standardized processes. Society 5.0 will require people to have imagination to identify diverse needs and challenges in society and turn them into real business. Diverse people will exercise diverse abilities to pursue diverse values in society. People will be able to live, learn, and work free from suppression of individuality, such as discrimination by gender, race, nationality, etc. and alienation by ways of thinking and sense of values. Liberation from disparity A society in which anyone can get opportunities anytime, anywhere In Society 4.0, concentration of wealth and information in limited hands increased disparity. In Society 5.0, wealth and information will be distributed and decentralized throughout society, and socioeconomic players will share roles horizontally. In spite of growing anxiety about disparity increased by digitalization, we will not leave disparity 13
16 as it is in Society 5.0. We will make sure that wealth and information will not be concentrated so that people will be liberated from disparity, and anyone will be able to get opportunities to play a part anytime, anywhere. Data and benefits derived from them will be shared by diversified players, not concentrated on specific companies. Opportunities to study and work will also be guaranteed to children born in poverty or remote areas. Liberation from anxiety A society in which everyone can live and pursue challenges with peace of mind In Society 4.0, vulnerabilities became apparent such as deterioration of infrastructure developed rapidly and in large quantities, serious damage caused by earthquakes and floods, deterioration of public security associated with increasing disparity, growing social anxiety about terrorism and other crises, and a major surge in damage caused by cyber-attacks. In Society 5.0, new, diversified, and decentralized social infrastructure will enhance resilience 11 and enable sustainable development. People will be liberated from anxiety and live in security. Specifically, resilience against terrorism and disasters in physical spaces and attacks in cyberspace will be enhanced, and safety nets for unemployment and poverty will be strengthened. A high level of medical care will be accessible regardless of location. Liberation from resource and environmental constraints A society where people can live in harmony with nature In Societies 3.0 and 4.0, humans depended on models with high environmental impact and mass consumption of resources. In Society 5.0, as data utilization increases energy efficiency and decentralization, 11 Strength, flexibility, and tenacity. In this report, resilience denotes not only strength, but also ability to recover. 14
17 there is the option of moving off-grid and not depending upon traditional energy networks. At the same time, water supply and waste management will also advance in both technological and systemic terms, enabling people to live sustainable lives in any region. This will create alternatives for living not only in big cities, but also in a diversity of regions in harmony with nature. As the sharing economy develops and interest in traceability grows, food that is better for the environment and health will command a large premium, and food wastage will drop sharply. Value creation, diversity, decentralization, resilience, and sustainability and environmental harmony embody attributes of life and nature. Now is the time for humankind to learn from the strength and brilliance of life and nature and make use of them. We can choose to embrace the wisdom of life and nature, forces which have overcome multiple mass extinctions to create a diverse ecosystem and a beautiful planet, the earth. With state-of-the-art technologies and willingness, our society itself can have the attributes of life and nature. This is the aim of Society 5.0. We will make Society 5.0 a society in which anyone can create value anytime, anywhere, with security and in harmony with nature. 15
18 Chapter V: Blueprint of Society 5.0 for SDGs Society 5.0 will bring major changes to ways of life and industry. In addition to the transformation of existing industries, close partnerships spanning borders and industries in many sectors will enable people to lead diverse lifestyles. The aim of Society 5.0 is to enable all people to pursue their own happiness and lifestyles, and play their parts by unleashing imagination and creativity to achieve sustainable development in harmony with nature through resolution of social issues. This aligns with the SDGs adopted by the United Nations to solve global issues and create sustainable societies. Society 5.0 is a prerequisite for many of the SDGs, but is not enough in itself. While some goals can be achieved directly by developing Society 5.0, others will benefit from diverse solutions devised on the basis of Society 5.0. The concept of Society 5.0 for SDGs 12 will be realized as Society 5.0 brings about creative problem-solving from diverse points of view and supports these solutions with digital transformation. This chapter sets out direction for sector-specific reforms aimed at achieving Society 5.0, including contributions to delivering on SDGs. Specific reforms and roadmaps for each sector will be considered further in the future. 12 Keidanren, "Charter on Corporate Behavior" (Revised on November 8, 2017). Keidanren has revised the Charter focusing on delivering on the SDGs through realization of Society 5.0, and compiled case studies in the policy proposal "Innovation for SDGs - Road to Society 5.0 -". 16
19 Chart 3: The 17 SDG Goals Source: UN Public Relations Center 1. Cities and Regions To facilitate diverse lifestyles and business success, forms of urban (high-density) and provincial (low-density) living will be diversified, and the attractions and quality of life offered by these options will be enhanced. In urban areas, data on energy, transportation, human flows, logistics, waste, etc. will be shared to facilitate smarter solutions. Promotion of autonomous systems such as automated driving and sharing economies will support diverse lifestyles while rapidly reducing environmental impact. Moreover, while maintaining efforts to enhance the competitiveness of large cities, sustainable, decentralized communities will be created in suburbs and rural areas to 17
20 achieve independent, affluent regions where people live in harmony with nature by capitalizing on the features of their respective areas. Access to high standards of medical services and education from anywhere in the world will be guaranteed. Autonomous, decentralized social infrastructure technologies such as off-grid energy will be utilized to establish stable, sustainable social infrastructure while reducing financial burden. In areas lacking public transportation sytems, autonomous vehicles will be available to senior citizens who cannot drive themselves, thus solving problems with daily mobility such as shopping and hospital visits. High-standard, comfortable lives will be achieved even in areas with poor infrastructure. Such developments will increase options for places to live and work, enabling diverse lifestyles and creating a society where diversity is respected. 2. Energy In order to realize sustainable lives anywhere, including smart cities and decentralized communities, the energy mix will change and data will be utilized to establish efficient energy networks. Decentralized micro grids 13 will be developed integrating decentralized renewable energy, power storage systems, and demand-side controls, and these will be aligned with local conditions. Off-grid systems not dependent upon traditional energy networks will become an option for energy use. Affordable, reliable energy will be available to anyone, and similarly decentralized infrastructure will also be applied to sectors other than energy. This will guarantee sustainable and diverse lifestyles anywhere. 13 Autonomous power systems offering both power supply and demand that operate with minimal dependence on power grids. 18
21 3. Disaster Prevention and Mitigation 14 Natural disasters are becoming more intense and widespread around the world, demanding prompt and efficient responses and enhanced resilience. Disaster information collaboration systems will be constructed to facilititate swift responses in the event of disasters by collecting data on damage and rescue supplies from evacuation centers, IoT equipment, and social media and sharing them across regions and organizational boundaries in both the public and private sectors. Moreover, digital technologies will be used for disaster mitigation through day-to-day maintenance and efficient measures to prevent aging of infrastructure. Maintenance and prompt restoration of water and sewerage infrastructure will enable water supply to continue in the event of disasters and accidents. Energy decentralization will be promoted to establish systems that are sustainable in disasters. Medical services will be maintained even in the event of disasters. Society 5.0 will help to improve living standards and resilience, especially in areas with vulnerable infrastructure that are susceptible to disasters. 4. Healthcare (health, medicine, and nursing) 15 Life-long healthcare including health, medicine, and nursing will be transformed. Technological trends such as digitalization of individual physical attributes and 14 Keidanren, "Toward a Stronger Public-Private Partnership for the Response to Large-scale Disasters" (April 19, 2016) 15 Keidanren, "Healthcare in Society 5.0" (March 20, 2018) 19
22 activities and progress in biotechnological investigation of life mechanisms will be harnessed to provide anyone needing care with the necessary attention at the appropriate times. While conventional medicine has provided uniform cures for average patients or symptoms, new approaches will provide care tailored to individual health at the preventive stage to avert onset and aggravation of illness, thus prolonging healthy life expectancy. Individuals will use and manage life-stage data on their own initiative to actively manage health throughout their 100-year lives. Access to high-quality healthcare services will be guaranteed from anywhere by promoting next-generation high-speed communication networks, AI-based medical and wellness support services, 16 and telemedicine, and establishing systems for individuals to actively use and manage their own life-stage data. In this way healthy lives will be ensured for everyone. For example, senior citizens living in remote areas will be able to check their health by telemedicine, and in case of sudden illness they will be transported for treatment in an appropriate hospital identified with the support of AI. These technologies, operational know-how, and systems will contribute to healthcare on a global scale through deployment in remote areas of developing countries. 5. Agriculture and Food 17 Agriculture and the food industry, which support people's diets, will be transformed 16 One element that will dramatically improve global medical access is the emergence of AI-supported telemedicine services. Multilingual translation systems and symptom checks through AI-patient dialogue will combine with symptom description and preliminary screening by background AI-based systems offering preliminary diagnosis. Moreover, based on system results, response approaches and hospitals will be decided through discussion between patients and doctors supported by AI. Such systems will have a tremendous impact. 17 Keidanren, "Agriculture: Its Future as a Leading-Edge Growth Industry -- Policies for the Realization of Society " (September 18, 2018) 20
23 into attractive, independent industries in which anyone can exercise creativity. Full use will be made of cutting-edge technologies such as remote monitoring and control by AI, agricultural robots, and autonomous drones for agricultural work on site. At the same time, working hours will decline sharply, work efficiency will improve dramatically, and productivity will rise exponentially through participation by diverse players including private corporations, youth, and agritech ventures. Ways of increasing biodiversity and minimizing environmental impact will be promoted to preserve rich biodiversity on land and in the water. Data and technologies will also be used to opitimize the food value chain (FVC) covering production, processing, logistics, sales, and export. Data will be collected on diverse consumer needs and promptly reflected in food production and processing. Realtime sharing of stock and sales information will be enabled by integration of data on production, logistics, and export, and food loss will be minimized through coordination of stock, delivery times and volumes, and transportation routes. Consumers will be provided with interactive means of communication and free access to production histories and product information. Moreover, leveraging cooperation with different sectors such as health, medicine, and nursing and enhancing production bases will enable companies to go beyond export of agricultural products to overseas business including technology platforms and services, enhancing profitability across the entire agri-food business. Diversification of players and technological innovation throughout the whole FVC will facilitate the transition to the next generation of agricultural workers and encourage the inflow of young people to rural areas to form the nucleus of sustainable decentralized communities. 6. Logistics Logistics play an essential role in economic growth by facilitating flows of goods, and form a key part of social infrastructure supporting business activities and daily lives. 21
24 Rapid growth of e-commerce and globalization of supply chains will require even more diverse and sophisticated logistics in Society 5.0, and implementation of cutting-edge technologies will transform logistics. For example, cargos and means of transportation will be connected to networks by deploying IoT technologies such as RFID to enable real-time logistical tracking and control. Relevant players will coordinate and optimize entire supply chains by sharing data on procurement, production, transportation, and sales on real-time platforms and by using AI to predict supply and demand. Frameworks will also be built to match shippers' needs with logistics operators' resources on such platforms to coordinate crossindustry efforts to increase efficiency. Moreover, platforms for various trade procedures will also be established to boost efficiency. To free up manpower, most work substitutable by autonomous driving, drones, and robots will be automated. Diverse customer needs will be identified to realize logistics that create new value in areas such as repair, maintenance, assembly, and customization of products, going beyond the existing framework of logistics business. Such developments will enable the handling of huge logistical volumes in urban districts, while providing efficient and prompt services in suburbs, mountainous regions, and remote areas. 7. Manufacturing and Services Distribution of abilities via AI will provide powerful tools for manufacturing and service delivery. Until now a large amount of investment and professional knowledge has been required to analyze data and create useful goods and services. Through digital transformation, these abilities will be distributed and become available as AI modules and services. Combining them will enable speedy creation of higher-quality goods and 22
25 services. 18 Just as the Internet expanded content supply from corporations to individuals, distribution of abilities will enable individuals and small companies to provide high levels of goods and services that satisfy diverse needs, and goods and services offered to consumers will no longer be uniform. Goods relating to food, clothing, housing, hobbies, and leisure, which strongly reflect individual consumers tastes, provide an illustration: systems will be established enabling consumers to easily and affordably make one-of-a-kind items such as clothes of a design, material, color, pattern, and size to suit their own tastes by utilizing 3D printers uncoupled from traditional manufacturing processes. As installation of opensource, modularized digital circuits and sensors becomes common, 19 integration of diverse services and hardware will accelerate. Business models will be based on services, not hardware. 20 In the digitalization era, manufacturing and services will not be an extension of those available in the 20th century. More people will be able to participate in manufacturing and provision of services as part of a digital transformation creating diverse forms of value. 8. Finance Transformation of financial services will be another element that enables individuals and small companies to deliver diverse manufacturing and services. Digital transformation will make available diverse, custom-made financial services including 18 For example, multilingual travel support services will be easily provided by connecting an advanced multilingual translation system, a service listing recommended destinations from results of machine learning based on travelers' wishes and personality traits, a function automatically optimizing itineraries, a service automatically recommending the best-priced airline tickets and hotels, and a chatbot to interact with customers. 19 This scenario envisages hardware such as Raspberry Pi, Arduino, RISC-V and yet-to-be-developed successors. 20 Subscriptions and recurring payments will become mainstream, rather than hardware sales. 23
26 settlement, financing, insurance, and asset formation. Low-cost, convenient, prompt, secure, and diverse methods of settlement will enable people to live anywhere without cash. Apps linking various services and smart contracts will facilitate creation of new services. In an era when people will have 100-year lives, such services will assist stable asset formation suited to individual lifestyles by offering sophisticated asset management and mitigating the risks of illness, injuries, and accidents through optimization and customization of insurance. Necessary funds will be available to new growth industries and other appropriate players, and financial systems will become more stable to allocate funds efficiently and effectively across society. From a global point of view, improved access to financial services will contribute to stable lives, economic independence, higher living standards, and greater income equality in emerging countries through use of digital devices and technologies to provide people with opportunities for financing, asset formation, insurance, settlement, and transfer. Moreover, cryptocurrencies and token economies based on blockchain technologies and other innovations will create new forms of value exchange and enable lifestyles that have been impossible to date. Establishment of secure, smart, and traceable global contract and settlement systems will build a basis for diverse manufacturing and service delivery, enabling diverse individuals to expand a range of manufacturing and services on a global scale. 9. Public Services Public services will also be transformed to support the diverse lives and industries mentioned above. Central and local governments will begin by rebuilding their systems based on digitalization. By digitalizing many of their tasks and quickly sharing data 24
27 among diverse actors, they will provide more creative public services. For example, precise prediction of demand for nurseries, schools, hospitals, and nursing homes through analyisis of demographics and other data will enable public bodies to make timely and appropriate preparations and provide necessary services. Appropriate safety nets established by governments will enable anyone to tackle a variety of challenges with security. 10. Summary Society 5.0 will be a society where anyone can excercise creativity to pursue diverse values free from existing frameworks and constraints. It cannot be accomplished by one company or one country. Japan, as the originator of Society 5.0, wishes to bring the concept to fruition in partnership with players all over the world. We believe it is our mission to contribute to sustainable global development by sharing problem-solving know-how gained in the process. 25
28 Conclusion Society 5.0 is not something to come, but something to co-create. Main player of that society is not technology but human being. It is a society realized by people who pursue diverse values with diverse imagination and creativity. This report demonstrated society 5.0 that we wish to create as "Imagination Society". We hope it will trigger discussion by many people on the kind of future to create in times of drastic change. Keidanren will take an initiative in the reform of Japan's economy and society as a leader of Society 5.0. Following this report, it will discuss and propose more specific measures to take and move forward with its member companies as well as domestic and foreign stakeholders toward realization of Society
Society Co-creating the future - Keidanren. (Excerpt)
 Society 5.0 - Co-creating the future - (Excerpt) Keidanren Great tide of change Technological change The world is facing an even greater tide of change against a backdrop of rapidly advancing innovation
Society 5.0 - Co-creating the future - (Excerpt) Keidanren Great tide of change Technological change The world is facing an even greater tide of change against a backdrop of rapidly advancing innovation
Development and Integration of Artificial Intelligence Technologies for Innovation Acceleration
 Development and Integration of Artificial Intelligence Technologies for Innovation Acceleration Research Supervisor: Minoru Etoh (Professor, Open and Transdisciplinary Research Initiatives, Osaka University)
Development and Integration of Artificial Intelligence Technologies for Innovation Acceleration Research Supervisor: Minoru Etoh (Professor, Open and Transdisciplinary Research Initiatives, Osaka University)
The impact of rapid technological change on sustainable development
 15-17 January 2019, Vienna The impact of rapid technological change on sustainable development Shamika N. Sirimanne Director, Division on Technology and Logistics UNCTAD 2018-2019 CSTD Intersessional Panel
15-17 January 2019, Vienna The impact of rapid technological change on sustainable development Shamika N. Sirimanne Director, Division on Technology and Logistics UNCTAD 2018-2019 CSTD Intersessional Panel
New Industrial Structure Vision
 New Industrial Structure Vision About New Industrial Structure Vision The rapid pace of technological innovation is shaping the course of the future. This Fourth Industrial Revolution spurred by technologies
New Industrial Structure Vision About New Industrial Structure Vision The rapid pace of technological innovation is shaping the course of the future. This Fourth Industrial Revolution spurred by technologies
Toward Inclusive and Sustainable Development
 March 15, 2019 Bank of Japan Toward Inclusive and Sustainable Development Remarks at the B20 Tokyo Summit hosted by Nippon Keidanren (Japan Business Federation) Haruhiko Kuroda Governor of the Bank of
March 15, 2019 Bank of Japan Toward Inclusive and Sustainable Development Remarks at the B20 Tokyo Summit hosted by Nippon Keidanren (Japan Business Federation) Haruhiko Kuroda Governor of the Bank of
Please send your responses by to: This consultation closes on Friday, 8 April 2016.
 CONSULTATION OF STAKEHOLDERS ON POTENTIAL PRIORITIES FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION IN THE 2018-2020 WORK PROGRAMME OF HORIZON 2020 SOCIETAL CHALLENGE 5 'CLIMATE ACTION, ENVIRONMENT, RESOURCE EFFICIENCY AND
CONSULTATION OF STAKEHOLDERS ON POTENTIAL PRIORITIES FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION IN THE 2018-2020 WORK PROGRAMME OF HORIZON 2020 SOCIETAL CHALLENGE 5 'CLIMATE ACTION, ENVIRONMENT, RESOURCE EFFICIENCY AND
Seoul Initiative on the 4 th Industrial Revolution
 ASEM EMM Seoul, Korea, 21-22 Sep. 2017 Seoul Initiative on the 4 th Industrial Revolution Presented by Korea 1. Background The global economy faces unprecedented changes with the advent of disruptive technologies
ASEM EMM Seoul, Korea, 21-22 Sep. 2017 Seoul Initiative on the 4 th Industrial Revolution Presented by Korea 1. Background The global economy faces unprecedented changes with the advent of disruptive technologies
Guidelines to Promote National Integrated Circuit Industry Development : Unofficial Translation
 Guidelines to Promote National Integrated Circuit Industry Development : Unofficial Translation Ministry of Industry and Information Technology National Development and Reform Commission Ministry of Finance
Guidelines to Promote National Integrated Circuit Industry Development : Unofficial Translation Ministry of Industry and Information Technology National Development and Reform Commission Ministry of Finance
Pacts for Europe 2020: Good Practices and Views from EU Cities and Regions
 1 EU Committee of the Regions CoR Territorial Dialogue on "Territorial Pacts to implement Europe 2020" Brussels, 22 February, 2011 Markku Markkula, Member of the Espoo City Council, CoR member, Rapporteur
1 EU Committee of the Regions CoR Territorial Dialogue on "Territorial Pacts to implement Europe 2020" Brussels, 22 February, 2011 Markku Markkula, Member of the Espoo City Council, CoR member, Rapporteur
Partnerships for the 2030 Agenda: Role of Science, Technology, and Innovation
 Partnerships for the 2030 Agenda: Role of Science, Technology, and Innovation United Nations University October 18, 2018 Tokyo, Japan 0 Mahmoud Mohieldin Senior Vice President @wbg2030 worldbank.org/sdgs
Partnerships for the 2030 Agenda: Role of Science, Technology, and Innovation United Nations University October 18, 2018 Tokyo, Japan 0 Mahmoud Mohieldin Senior Vice President @wbg2030 worldbank.org/sdgs
Message from the CEO. Kazuhiro Tsuga. Representative Director President CEO. Panasonic Annual Report 2018
 Message from the CEO Kazuhiro Tsuga Representative Director President CEO 09 Panasonic Annual Report 2018 Growth Strategy Foundation for Growth Results for Fiscal Year Ended March 2018 Pushing Forward
Message from the CEO Kazuhiro Tsuga Representative Director President CEO 09 Panasonic Annual Report 2018 Growth Strategy Foundation for Growth Results for Fiscal Year Ended March 2018 Pushing Forward
Innovation and the Future of Finance
 December 4, 2017 Bank of Japan Innovation and the Future of Finance Remarks at the Paris EUROPLACE Financial Forum in Tokyo Haruhiko Kuroda Governor of the Bank of Japan I. Paris International Expositions
December 4, 2017 Bank of Japan Innovation and the Future of Finance Remarks at the Paris EUROPLACE Financial Forum in Tokyo Haruhiko Kuroda Governor of the Bank of Japan I. Paris International Expositions
High Level Seminar on the Creative Economy and Copyright as Pathways to Sustainable Development. UN-ESCAP/ WIPO, Bangkok December 6, 2017
 High Level Seminar on the Creative Economy and Copyright as Pathways to Sustainable Development UN-ESCAP/ WIPO, Bangkok December 6, 2017 Edna dos Santos-Duisenberg creative.edna@gmail.com Policy Advisor
High Level Seminar on the Creative Economy and Copyright as Pathways to Sustainable Development UN-ESCAP/ WIPO, Bangkok December 6, 2017 Edna dos Santos-Duisenberg creative.edna@gmail.com Policy Advisor
The Fourth Industrial Revolution in Major Countries and Its Implications of Korea: U.S., Germany and Japan Cases
 Vol. 8 No. 20 ISSN -2233-9140 The Fourth Industrial Revolution in Major Countries and Its Implications of Korea: U.S., Germany and Japan Cases KIM Gyu-Pan Director General of Advanced Economies Department
Vol. 8 No. 20 ISSN -2233-9140 The Fourth Industrial Revolution in Major Countries and Its Implications of Korea: U.S., Germany and Japan Cases KIM Gyu-Pan Director General of Advanced Economies Department
The 26 th APEC Economic Leaders Meeting
 The 26 th APEC Economic Leaders Meeting PORT MORESBY, PAPUA NEW GUINEA 18 November 2018 The Chair s Era Kone Statement Harnessing Inclusive Opportunities, Embracing the Digital Future 1. The Statement
The 26 th APEC Economic Leaders Meeting PORT MORESBY, PAPUA NEW GUINEA 18 November 2018 The Chair s Era Kone Statement Harnessing Inclusive Opportunities, Embracing the Digital Future 1. The Statement
Executive Summary Industry s Responsibility in Promoting Responsible Development and Use:
 Executive Summary Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a suite of technologies capable of learning, reasoning, adapting, and performing tasks in ways inspired by the human mind. With access to data and the
Executive Summary Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a suite of technologies capable of learning, reasoning, adapting, and performing tasks in ways inspired by the human mind. With access to data and the
NATIONAL TOURISM CONFERENCE 2018
 NATIONAL TOURISM CONFERENCE 2018 POSITIONING CURAÇAO AS A SMART TOURISM DESTINATION KEYNOTE ADDRESS by Mr. Franklin Sluis CEO Bureau Telecommunication, Post & Utilities Secretariat Taskforce Smart Nation
NATIONAL TOURISM CONFERENCE 2018 POSITIONING CURAÇAO AS A SMART TOURISM DESTINATION KEYNOTE ADDRESS by Mr. Franklin Sluis CEO Bureau Telecommunication, Post & Utilities Secretariat Taskforce Smart Nation
PROGRESS IN BUSINESS MODEL TRANSFORMATION
 PROGRESS IN BUSINESS MODEL TRANSFORMATION PART 1 CREATING VALUE The Fujitsu Group, striving to create new value in the Internet of Things (IoT) era, is working to realign its business structure toward
PROGRESS IN BUSINESS MODEL TRANSFORMATION PART 1 CREATING VALUE The Fujitsu Group, striving to create new value in the Internet of Things (IoT) era, is working to realign its business structure toward
Sultanate of Oman Ministry of Education. Muscat Declaration
 Sultanate of Oman Ministry of Education Muscat Declaration Conference on Education for Sustainable Development in Support of Cultural Diversity and Biodiversity Organized by the Sultanate of Oman in collaboration
Sultanate of Oman Ministry of Education Muscat Declaration Conference on Education for Sustainable Development in Support of Cultural Diversity and Biodiversity Organized by the Sultanate of Oman in collaboration
Collaborative Creation
 Collaborative Creation with Customers 1 NEXPERIENCE Methodology for Collaborative Creation with Customers Hitachi has developed the NEXPERIENCE methodology for collaborative creation with customers based
Collaborative Creation with Customers 1 NEXPERIENCE Methodology for Collaborative Creation with Customers Hitachi has developed the NEXPERIENCE methodology for collaborative creation with customers based
The Emerging Economy 2030:
 The Emerging Economy 2030: Some initial explorations Public Service Foresight Network 22 July 2016 2 THE HORIZONS FORESIGHT METHOD Identify the issue or problem of interest Consider the larger system(s)
The Emerging Economy 2030: Some initial explorations Public Service Foresight Network 22 July 2016 2 THE HORIZONS FORESIGHT METHOD Identify the issue or problem of interest Consider the larger system(s)
APEC Internet and Digital Economy Roadmap
 2017/CSOM/006 Agenda Item: 3 APEC Internet and Digital Economy Roadmap Purpose: Consideration Submitted by: AHSGIE Concluding Senior Officials Meeting Da Nang, Viet Nam 6-7 November 2017 INTRODUCTION APEC
2017/CSOM/006 Agenda Item: 3 APEC Internet and Digital Economy Roadmap Purpose: Consideration Submitted by: AHSGIE Concluding Senior Officials Meeting Da Nang, Viet Nam 6-7 November 2017 INTRODUCTION APEC
(Beijing, China,25 May2017)
 Remarks by the Secretary General of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), Dr. Fang Liu, to the First Session of the 2017 China Civil Aviation Development Forum: New Opportunities for Aviation
Remarks by the Secretary General of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), Dr. Fang Liu, to the First Session of the 2017 China Civil Aviation Development Forum: New Opportunities for Aviation
MOSTI-APCTT Fourth Industrial Revolution Conference 2018
 Background: MOSTI-APCTT Fourth Industrial Revolution Conference 2018 New and Emerging Technologies in Achieving Sustainable Development Goals 3-4 July 2018, Hotel Istana, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Science,
Background: MOSTI-APCTT Fourth Industrial Revolution Conference 2018 New and Emerging Technologies in Achieving Sustainable Development Goals 3-4 July 2018, Hotel Istana, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Science,
Impacts and Risks Caused by AI Networking, and Future Challenges
 Impacts and Risks Caused by AI Networking, and Future Challenges (From Studies on AI Networking in Japan) November 17, 2016 Tatsuya KUROSAKA Project Assistant Professor at Keio University Graduate School
Impacts and Risks Caused by AI Networking, and Future Challenges (From Studies on AI Networking in Japan) November 17, 2016 Tatsuya KUROSAKA Project Assistant Professor at Keio University Graduate School
#Renew2030. Boulevard A Reyers 80 B1030 Brussels Belgium
 #Renew2030 Boulevard A Reyers 80 B1030 Brussels Belgium secretariat@orgalim.eu +32 2 206 68 83 @Orgalim_EU www.orgalim.eu SHAPING A FUTURE THAT S GOOD. Orgalim is registered under the European Union Transparency
#Renew2030 Boulevard A Reyers 80 B1030 Brussels Belgium secretariat@orgalim.eu +32 2 206 68 83 @Orgalim_EU www.orgalim.eu SHAPING A FUTURE THAT S GOOD. Orgalim is registered under the European Union Transparency
DIGITAL FINLAND FRAMEWORK FRAMEWORK FOR TURNING DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION TO SOLUTIONS TO GRAND CHALLENGES
 DIGITAL FINLAND FRAMEWORK FRAMEWORK FOR TURNING DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION TO SOLUTIONS TO GRAND CHALLENGES 1 Digital transformation of industries and society is a key element for growth, entrepreneurship,
DIGITAL FINLAND FRAMEWORK FRAMEWORK FOR TURNING DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION TO SOLUTIONS TO GRAND CHALLENGES 1 Digital transformation of industries and society is a key element for growth, entrepreneurship,
A Message from the President
 A Message from the President Since its establishment in 1928, Minolta has been a pioneer of light-related technology development in a growing number of fields. Currently, society is undergoing great changes
A Message from the President Since its establishment in 1928, Minolta has been a pioneer of light-related technology development in a growing number of fields. Currently, society is undergoing great changes
Framework of STI for SDGs Roadmap case in Japan
 Framework of STI for SDGs Roadmap case in Japan May 8th, 2018 Science, Technology and Innovation Policy Cabinet Office, Japan Current Status of Japan Strength and Weakness Japan is ranked 11th in the SDG
Framework of STI for SDGs Roadmap case in Japan May 8th, 2018 Science, Technology and Innovation Policy Cabinet Office, Japan Current Status of Japan Strength and Weakness Japan is ranked 11th in the SDG
WFEO STANDING COMMITTEE ON ENGINEERING FOR INNOVATIVE TECHNOLOGY (WFEO-CEIT) STRATEGIC PLAN ( )
 WFEO STANDING COMMITTEE ON ENGINEERING FOR INNOVATIVE TECHNOLOGY (WFEO-CEIT) STRATEGIC PLAN (2016-2019) Hosted by The China Association for Science and Technology March, 2016 WFEO-CEIT STRATEGIC PLAN (2016-2019)
WFEO STANDING COMMITTEE ON ENGINEERING FOR INNOVATIVE TECHNOLOGY (WFEO-CEIT) STRATEGIC PLAN (2016-2019) Hosted by The China Association for Science and Technology March, 2016 WFEO-CEIT STRATEGIC PLAN (2016-2019)
7 th Asia Smart City Conference
 7 th Asia Smart City Conference In Yokohama 13-15 Nov. 2018 Program Outline (tentative) Organizers Organizer :City of Yokohama Co-organizer :Tokyo Development Learning Center (World Bank Group) Asian Development
7 th Asia Smart City Conference In Yokohama 13-15 Nov. 2018 Program Outline (tentative) Organizers Organizer :City of Yokohama Co-organizer :Tokyo Development Learning Center (World Bank Group) Asian Development
Framework of STI for SDGs Roadmap case in Japan. May 8th, 2018 Science, Technology and Innovation Policy Cabinet Office, Japan
 Framework of STI for SDGs Roadmap case in Japan May 8th, 2018 Science, Technology and Innovation Policy Cabinet Office, Japan Current Status of Japan Strength and Weakness Japan is ranked 11th in the SDG
Framework of STI for SDGs Roadmap case in Japan May 8th, 2018 Science, Technology and Innovation Policy Cabinet Office, Japan Current Status of Japan Strength and Weakness Japan is ranked 11th in the SDG
Asia Conference Singapore
 Fujitsu World Tour 2017 Asia Conference Singapore Human Centric Innovation: Digital Co-Creation Yoshikuni Takashige Vice President, Marketing Strategy and Vision Fujitsu Limited Fujitsu Technology and
Fujitsu World Tour 2017 Asia Conference Singapore Human Centric Innovation: Digital Co-Creation Yoshikuni Takashige Vice President, Marketing Strategy and Vision Fujitsu Limited Fujitsu Technology and
Keidanren and CBCC s initiatives to deliver on the SDGs. November, 2017 Masaya Futamiya Chairman of CBCC
 Keidanren and CBCC s initiatives to deliver on the SDGs November, 2017 Masaya Futamiya Chairman of CBCC About CBCC and Keidanren Council for Better Corporate Citizenship (http://www.keidanren.or.jp/cbcc
Keidanren and CBCC s initiatives to deliver on the SDGs November, 2017 Masaya Futamiya Chairman of CBCC About CBCC and Keidanren Council for Better Corporate Citizenship (http://www.keidanren.or.jp/cbcc
ASEAN: A Growth Centre in the Global Economy
 Bank Negara Malaysia Governor Dr. Zeti Akhtar Aziz Speech at the ASEAN SME Conference 2015 It is my pleasure to be here this afternoon to speak at this inaugural ASEAN SME Conference. This conference takes
Bank Negara Malaysia Governor Dr. Zeti Akhtar Aziz Speech at the ASEAN SME Conference 2015 It is my pleasure to be here this afternoon to speak at this inaugural ASEAN SME Conference. This conference takes
Comprehensive Strategy on Science, Technology and Innovation 2014
 June 24, 2014 Cabinet Decision Provisional Translation Comprehensive Strategy on Science, Technology and Innovation 2014 Bridge of Innovation toward Creating the Future Executive Summary Bureau of Science,
June 24, 2014 Cabinet Decision Provisional Translation Comprehensive Strategy on Science, Technology and Innovation 2014 Bridge of Innovation toward Creating the Future Executive Summary Bureau of Science,
Technology and Innovation - A Catalyst for Development
 2017/ISOM/SYM/004 Session 1 Technology and Innovation - A Catalyst for Development Submitted by: Papua New Guinea Symposium on APEC 2018 Priorities Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea 5 December 2017 Technology
2017/ISOM/SYM/004 Session 1 Technology and Innovation - A Catalyst for Development Submitted by: Papua New Guinea Symposium on APEC 2018 Priorities Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea 5 December 2017 Technology
Facts Sheet. NEOM project
 Facts Sheet NEOM project NEOM is the world s first independent special zone stretching over three countries. It is set to become a new vibrant destination located in the Northwestern region of Saudi Arabia.
Facts Sheet NEOM project NEOM is the world s first independent special zone stretching over three countries. It is set to become a new vibrant destination located in the Northwestern region of Saudi Arabia.
Colombia s Social Innovation Policy 1 July 15 th -2014
 Colombia s Social Innovation Policy 1 July 15 th -2014 I. Introduction: The background of Social Innovation Policy Traditionally innovation policy has been understood within a framework of defining tools
Colombia s Social Innovation Policy 1 July 15 th -2014 I. Introduction: The background of Social Innovation Policy Traditionally innovation policy has been understood within a framework of defining tools
Public Sector Future Scenarios
 Public Sector Future Scenarios Two main scenarios have been generated as a result of the scenario building exercise that took place in the context of the SONNETS project, as follows: Probable Scenario
Public Sector Future Scenarios Two main scenarios have been generated as a result of the scenario building exercise that took place in the context of the SONNETS project, as follows: Probable Scenario
1. How would you define, or how do you understand, the theme Connecting and Enabling the Next Billion?
 Name Position Organization Website email Shreedeep Rayamajhi Editor Social Activist RayZnews www.rayznews.com shreedeep@rayznews.com weaker41@gmail.com 1. How would you define, or how do you understand,
Name Position Organization Website email Shreedeep Rayamajhi Editor Social Activist RayZnews www.rayznews.com shreedeep@rayznews.com weaker41@gmail.com 1. How would you define, or how do you understand,
FACT SHEET ... RICHNESS IN NATURAL RESOURCES:
 NEOM PROJECT NEOM is the world s first independent special zone stretching over three countries.it is set to become a new vibrant destination located in the north-western region of Saudi Arabia. Expected
NEOM PROJECT NEOM is the world s first independent special zone stretching over three countries.it is set to become a new vibrant destination located in the north-western region of Saudi Arabia. Expected
Climate Change Innovation and Technology Framework 2017
 Climate Change Innovation and Technology Framework 2017 Advancing Alberta s environmental performance and diversification through investments in innovation and technology Table of Contents 2 Message from
Climate Change Innovation and Technology Framework 2017 Advancing Alberta s environmental performance and diversification through investments in innovation and technology Table of Contents 2 Message from
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 11 February 2013 Original: English Economic Commission for Europe Sixty-fifth session Geneva, 9 11 April 2013 Item 3 of the provisional agenda
United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 11 February 2013 Original: English Economic Commission for Europe Sixty-fifth session Geneva, 9 11 April 2013 Item 3 of the provisional agenda
Digital Government and Digital Public Services
 Digital Government and Digital Public Services Dr Sak Segkhoonthod President & CEO Electronic Government Agency (Public Organization) 22 September 2017 1 Thailand Digital Economy and Society Development
Digital Government and Digital Public Services Dr Sak Segkhoonthod President & CEO Electronic Government Agency (Public Organization) 22 September 2017 1 Thailand Digital Economy and Society Development
Fujitsu Technology and Service Vision Executive Summary
 Fujitsu Technology and Service Vision 2016 Executive Summary What is digital transformation? Today, digital technologies can be incorporated into products, services and processes, transforming customer
Fujitsu Technology and Service Vision 2016 Executive Summary What is digital transformation? Today, digital technologies can be incorporated into products, services and processes, transforming customer
TASK FORCE MEETING HILTON HOTEL, KUALA LUMPUR 1 AUGUST
 BRIDGING THE DIGITAL GAP KEYNOTE ADDRESS BY Y. B. DATUK AMAR LEO MOGGIE, MINISTER OF ENERGY, COMMUNICATIONS AND MULTIMEDIA AT THE LUNCHEON TALK IN CONJUNCTION WITH THE 4 th E-ASEAN TASK FORCE MEETING HILTON
BRIDGING THE DIGITAL GAP KEYNOTE ADDRESS BY Y. B. DATUK AMAR LEO MOGGIE, MINISTER OF ENERGY, COMMUNICATIONS AND MULTIMEDIA AT THE LUNCHEON TALK IN CONJUNCTION WITH THE 4 th E-ASEAN TASK FORCE MEETING HILTON
Digital Transformation towards Society /09/07 Shigetoshi SAMESHIMA Research & Development Group, Hitachi, Ltd.
 Digital Transformation towards Society 5.0 2017/09/07 Shigetoshi SAMESHIMA Research & Development Group, Hitachi, Ltd. 1. Changes of Macro-Environment 2. Society 5.0: Society Vision of Japan 3. Autonomous
Digital Transformation towards Society 5.0 2017/09/07 Shigetoshi SAMESHIMA Research & Development Group, Hitachi, Ltd. 1. Changes of Macro-Environment 2. Society 5.0: Society Vision of Japan 3. Autonomous
Enabling ICT for. development
 Enabling ICT for development Interview with Dr M-H Carolyn Nguyen, who explains why governments need to start thinking seriously about how to leverage ICT for their development goals, and why an appropriate
Enabling ICT for development Interview with Dr M-H Carolyn Nguyen, who explains why governments need to start thinking seriously about how to leverage ICT for their development goals, and why an appropriate
Future of Financing. For more information visit ifrc.org/s2030
 Future of Financing The gap between humanitarian and development needs and financing is growing, yet largely we still rely on just a few traditional sources of funding. How do we mobilize alternate sources
Future of Financing The gap between humanitarian and development needs and financing is growing, yet largely we still rely on just a few traditional sources of funding. How do we mobilize alternate sources
ICSB Top 10 Trends for 2019 Micro-, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (MSMEs) continue to be on the move!
 Micro-,Small, and Medium-sized Enterprises (MSMEs) ICSB Top 10 Trends for 2019 Micro-, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (MSMEs) continue to be on the move! Recognized globally for their contributions
Micro-,Small, and Medium-sized Enterprises (MSMEs) ICSB Top 10 Trends for 2019 Micro-, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (MSMEs) continue to be on the move! Recognized globally for their contributions
Our Aspirations Ahead
 Our Aspirations Ahead ~ Pursuing Smart Innovation ~ 1 Introduction For the past decade, under our corporate philosophy Creating a New Communication Culture, and the vision MAGIC, NTT DOCOMO Group has been
Our Aspirations Ahead ~ Pursuing Smart Innovation ~ 1 Introduction For the past decade, under our corporate philosophy Creating a New Communication Culture, and the vision MAGIC, NTT DOCOMO Group has been
Revitalizing Japan by Realizing Society 5.0:
 Revitalizing Japan by Realizing Society 5.0: ~ Action Plan for Creating the Society of the Future ~ Overview February 14, 2017 Japan Business Federation (Keidanren) Table of Contents 1 I. Introduction...
Revitalizing Japan by Realizing Society 5.0: ~ Action Plan for Creating the Society of the Future ~ Overview February 14, 2017 Japan Business Federation (Keidanren) Table of Contents 1 I. Introduction...
Global Printing Summit Forum
 Global Printing Summit Forum November 13 th, 2011 Shanghai, China The Japanese Printing Industry s Challenges - Recovery from the Earthquake Disaster- - Green Practices- -Creation of a New Market- Satoshi
Global Printing Summit Forum November 13 th, 2011 Shanghai, China The Japanese Printing Industry s Challenges - Recovery from the Earthquake Disaster- - Green Practices- -Creation of a New Market- Satoshi
WSIS+10 REVIEW: NON-PAPER 1
 WSIS+10 REVIEW: NON-PAPER 1 Preamble 1. We reaffirm the vision of a people-centred, inclusive and development-oriented Information Society defined by the World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS)
WSIS+10 REVIEW: NON-PAPER 1 Preamble 1. We reaffirm the vision of a people-centred, inclusive and development-oriented Information Society defined by the World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS)
INSIGHT Digital-driven Financial Innovation and Hitachi s Involvement. Takeshi Yoshikawa Nobuhiko Sato Toshiya Cho Atsushi Uchizono
 Digital-driven Financial Innovation and Hitachi s Involvement Takeshi Yoshikawa Nobuhiko Sato Toshiya Cho Atsushi Uchizono ENVIRONMENT SURROUNDING FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS AND THE RISE OF FINTECH SINCE the
Digital-driven Financial Innovation and Hitachi s Involvement Takeshi Yoshikawa Nobuhiko Sato Toshiya Cho Atsushi Uchizono ENVIRONMENT SURROUNDING FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS AND THE RISE OF FINTECH SINCE the
New and Emerging Issues Interface to Science Policy
 Ninth Session of the Committee on Sustainable Development and the Africa Regional Forum on Sustainable Development New and Emerging Issues Interface to Science Policy Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 16-18 June
Ninth Session of the Committee on Sustainable Development and the Africa Regional Forum on Sustainable Development New and Emerging Issues Interface to Science Policy Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 16-18 June
Joint Declaration of Intent. of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications of Japan
 Joint Declaration of Intent of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications of Japan and the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy
Joint Declaration of Intent of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications of Japan and the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy
Our digital future. SEPA online. Facilitating effective engagement. Enabling business excellence. Sharing environmental information
 Our digital future SEPA online Facilitating effective engagement Sharing environmental information Enabling business excellence Foreword Dr David Pirie Executive Director Digital technologies are changing
Our digital future SEPA online Facilitating effective engagement Sharing environmental information Enabling business excellence Foreword Dr David Pirie Executive Director Digital technologies are changing
COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION. Brussels, 9 December 2008 (16.12) (OR. fr) 16767/08 RECH 410 COMPET 550
 COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Brussels, 9 December 2008 (16.12) (OR. fr) 16767/08 RECH 410 COMPET 550 OUTCOME OF PROCEEDINGS of: Competitiveness Council on 1 and 2 December 2008 No. prev. doc. 16012/08
COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Brussels, 9 December 2008 (16.12) (OR. fr) 16767/08 RECH 410 COMPET 550 OUTCOME OF PROCEEDINGS of: Competitiveness Council on 1 and 2 December 2008 No. prev. doc. 16012/08
Encouraging Economic Growth in the Digital Age A POLICY CHECKLIST FOR THE GLOBAL DIGITAL ECONOMY
 Encouraging Economic Growth in the Digital Age A POLICY CHECKLIST FOR THE GLOBAL DIGITAL ECONOMY The Internet is changing the way that individuals launch businesses, established companies function, and
Encouraging Economic Growth in the Digital Age A POLICY CHECKLIST FOR THE GLOBAL DIGITAL ECONOMY The Internet is changing the way that individuals launch businesses, established companies function, and
(Fig.) JPMA Industry Vision 2025
 2. JPMA Industry Vision 2025 Against the background of the changing environment surrounding the pharmaceutical industry and the future predictions *1, we prepared JPMA Industry Vision 2025 Bringing Innovation
2. JPMA Industry Vision 2025 Against the background of the changing environment surrounding the pharmaceutical industry and the future predictions *1, we prepared JPMA Industry Vision 2025 Bringing Innovation
Towards a World in Common Strategy. #WorldInCommon
 Towards a World in Common 2018-2022 Strategy #WorldInCommon Our vision A World in Common AFD Group has a mission to help construct a world in common, a world that preserves and protects five important
Towards a World in Common 2018-2022 Strategy #WorldInCommon Our vision A World in Common AFD Group has a mission to help construct a world in common, a world that preserves and protects five important
7 th Asia Smart City Conference
 (As of 1st Oct.) 7 th Asia Smart City Conference In Yokohama 13-15 Nov. 2018 Program Outline (tentative) 1 Organizers Organizer :City of Yokohama Co-organizer :Tokyo Development Learning Center (World
(As of 1st Oct.) 7 th Asia Smart City Conference In Yokohama 13-15 Nov. 2018 Program Outline (tentative) 1 Organizers Organizer :City of Yokohama Co-organizer :Tokyo Development Learning Center (World
Inclusively Creative
 In Bandung, Indonesia, December 5 th to 7 th 2017, over 100 representatives from the government, civil society, the private sector, think-tanks and academia, international organization as well as a number
In Bandung, Indonesia, December 5 th to 7 th 2017, over 100 representatives from the government, civil society, the private sector, think-tanks and academia, international organization as well as a number
SMART PLACES WHAT. WHY. HOW.
 SMART PLACES WHAT. WHY. HOW. @adambeckurban @smartcitiesanz We envision a world where digital technology, data, and intelligent design have been harnessed to create smart, sustainable cities with highquality
SMART PLACES WHAT. WHY. HOW. @adambeckurban @smartcitiesanz We envision a world where digital technology, data, and intelligent design have been harnessed to create smart, sustainable cities with highquality
Canada-Italy Innovation Award Call for Proposals
 Embassy of Canada to Italy Canada-Italy Innovation Award 2018 Public Affairs and Advocacy www.canada.it Canada-Italy Innovation Award 2018 Call for Proposals Overview The Embassy of Canada to Italy is
Embassy of Canada to Italy Canada-Italy Innovation Award 2018 Public Affairs and Advocacy www.canada.it Canada-Italy Innovation Award 2018 Call for Proposals Overview The Embassy of Canada to Italy is
Copyright: Conference website: Date deposited:
 Coleman M, Ferguson A, Hanson G, Blythe PT. Deriving transport benefits from Big Data and the Internet of Things in Smart Cities. In: 12th Intelligent Transport Systems European Congress 2017. 2017, Strasbourg,
Coleman M, Ferguson A, Hanson G, Blythe PT. Deriving transport benefits from Big Data and the Internet of Things in Smart Cities. In: 12th Intelligent Transport Systems European Congress 2017. 2017, Strasbourg,
Action Policy for Fiscal 2017
 January 18, 2017 Japan Textile Federation Action Policy for Fiscal 2017 Japan Textile Federation (JTF) has been working actively by recognizing identity of the textile industry such as the power to support
January 18, 2017 Japan Textile Federation Action Policy for Fiscal 2017 Japan Textile Federation (JTF) has been working actively by recognizing identity of the textile industry such as the power to support
Denmark as a digital frontrunner
 Denmark as a digital frontrunner Recommendations for the government from the Digital Growth Panel May 2017 Digital Growth Panel Summary Vision: Denmark as a digital frontrunner Denmark and the rest of
Denmark as a digital frontrunner Recommendations for the government from the Digital Growth Panel May 2017 Digital Growth Panel Summary Vision: Denmark as a digital frontrunner Denmark and the rest of
ASEAN Vision A Concert of Southeast Asian Nations
 ASEAN Vision 2020 We, the Heads of State/Government of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, gather today in Kuala Lumpur to reaffirm our commitment to the aims and purposes of the Association as
ASEAN Vision 2020 We, the Heads of State/Government of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, gather today in Kuala Lumpur to reaffirm our commitment to the aims and purposes of the Association as
The Tech Megatrends: 2018
 The Tech Megatrends: 2018 April 17, 2018 Cristina CK Kerley http://allthingsck.comhttp://allthingsck.com TECH MEGATRENDS 2018: Trends & Imperatives 2018 Christina CK Kerley http://allthingsck.com Apr 18,
The Tech Megatrends: 2018 April 17, 2018 Cristina CK Kerley http://allthingsck.comhttp://allthingsck.com TECH MEGATRENDS 2018: Trends & Imperatives 2018 Christina CK Kerley http://allthingsck.com Apr 18,
Universities and Sustainable Development Towards the Global Goals
 Universities and Sustainable Development Towards the Global Goals Universities promote sustainable development The unique contribution of universities Sustainable Development Goals Sustainable development
Universities and Sustainable Development Towards the Global Goals Universities promote sustainable development The unique contribution of universities Sustainable Development Goals Sustainable development
Smart cities: A human-centered approach Engineering and Construction Conference June 20 22, 2018
 Smart cities: A human-centered approach 2018 Engineering and Construction Conference June 20 22, 2018 Agenda Topic Smart City Overview Content Drivers, Framework, Evolution Client Stories Success Factors
Smart cities: A human-centered approach 2018 Engineering and Construction Conference June 20 22, 2018 Agenda Topic Smart City Overview Content Drivers, Framework, Evolution Client Stories Success Factors
Ministry of Industry. Indonesia s 4 th Industrial Revolution. Making Indonesia 4.0. Benchmarking Implementasi Industri 4.0 A.T.
 Ministry of Industry s 4 th Industrial Revolution Making 4.0 Benchmarking Implementasi Industri 4.0 A.T. Kearney Industry 4.0 initiative is the global trend in the manufacturing industry End of 18 th century
Ministry of Industry s 4 th Industrial Revolution Making 4.0 Benchmarking Implementasi Industri 4.0 A.T. Kearney Industry 4.0 initiative is the global trend in the manufacturing industry End of 18 th century
Europe as a Global Actor. International Dimension of Horizon 2020 and Research Opportunities with Third Countries
 Europe as a Global Actor International Dimension of Horizon 2020 and Research Opportunities with Third Countries The way to Horizon 2020 7 PQ CIP EIT Europa 2020 Innovation Union Horizon 2020 2007-2013
Europe as a Global Actor International Dimension of Horizon 2020 and Research Opportunities with Third Countries The way to Horizon 2020 7 PQ CIP EIT Europa 2020 Innovation Union Horizon 2020 2007-2013
Scoping Paper for. Horizon 2020 work programme Societal Challenge 4: Smart, Green and Integrated Transport
 Scoping Paper for Horizon 2020 work programme 2018-2020 Societal Challenge 4: Smart, Green and Integrated Transport Important Notice: Working Document This scoping paper will guide the preparation of the
Scoping Paper for Horizon 2020 work programme 2018-2020 Societal Challenge 4: Smart, Green and Integrated Transport Important Notice: Working Document This scoping paper will guide the preparation of the
INTEL INNOVATION GENERATION
 INTEL INNOVATION GENERATION Overview Intel was founded by inventors, and the company s continued existence depends on innovation. We recognize that the health of local economies including those where our
INTEL INNOVATION GENERATION Overview Intel was founded by inventors, and the company s continued existence depends on innovation. We recognize that the health of local economies including those where our
United Nations Environment Programme 12 February 2019* Guidance note: Leadership Dialogues at fourth session of the UN Environment Assembly
 United Nations Environment Programme 12 February 2019* Guidance note: Leadership Dialogues at fourth session of the UN Environment Assembly A key feature of the high/level segment of the 2019 UN Environment
United Nations Environment Programme 12 February 2019* Guidance note: Leadership Dialogues at fourth session of the UN Environment Assembly A key feature of the high/level segment of the 2019 UN Environment
Looking ahead : Technology trends driving business innovation.
 NTT DATA Technology Foresight 2018 Looking ahead : Technology trends driving business innovation. Technology will drive the future of business. Digitization has placed society at the beginning of the next
NTT DATA Technology Foresight 2018 Looking ahead : Technology trends driving business innovation. Technology will drive the future of business. Digitization has placed society at the beginning of the next
SMU Convocation Address by Victor K. Fung 12 August Preparing for an Era of Great Global Transformations
 SMU Convocation Address by Victor K. Fung 12 August 2016 Preparing for an Era of Great Global Transformations Good evening everyone. Mr. President (De Meyer), Mr. Chancellor (Pillay), Chairman of the Board
SMU Convocation Address by Victor K. Fung 12 August 2016 Preparing for an Era of Great Global Transformations Good evening everyone. Mr. President (De Meyer), Mr. Chancellor (Pillay), Chairman of the Board
Conclusions on the future of information and communication technologies research, innovation and infrastructures
 COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Conclusions on the future of information and communication technologies research, innovation and infrastructures 2982nd COMPETITIVESS (Internal market, Industry and Research)
COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Conclusions on the future of information and communication technologies research, innovation and infrastructures 2982nd COMPETITIVESS (Internal market, Industry and Research)
TRANSFORMATION INTO A KNOWLEDGE-BASED ECONOMY: THE MALAYSIAN EXPERIENCE
 TRANSFORMATION INTO A KNOWLEDGE-BASED ECONOMY: THE MALAYSIAN EXPERIENCE by Honourable Dato Sri Dr. Jamaludin Mohd Jarjis Minister of Science, Technology and Innovation of Malaysia Going Global: The Challenges
TRANSFORMATION INTO A KNOWLEDGE-BASED ECONOMY: THE MALAYSIAN EXPERIENCE by Honourable Dato Sri Dr. Jamaludin Mohd Jarjis Minister of Science, Technology and Innovation of Malaysia Going Global: The Challenges
Scenario Development Process
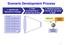 Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
Written Submission for the Pre-Budget Consultations in Advance of the 2019 Budget By: The Danish Life Sciences Forum
 Written Submission for the Pre-Budget Consultations in Advance of the 2019 Budget By: The Danish Life Sciences Forum List of recommendations: Recommendation 1: That the government creates a Life Sciences
Written Submission for the Pre-Budget Consultations in Advance of the 2019 Budget By: The Danish Life Sciences Forum List of recommendations: Recommendation 1: That the government creates a Life Sciences
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. St. Louis Region Emerging Transportation Technology Strategic Plan. June East-West Gateway Council of Governments ICF
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY St. Louis Region Emerging Transportation Technology Strategic Plan June 2017 Prepared for East-West Gateway Council of Governments by ICF Introduction 1 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This document
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY St. Louis Region Emerging Transportation Technology Strategic Plan June 2017 Prepared for East-West Gateway Council of Governments by ICF Introduction 1 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This document
"How to ensure a secure supply of raw materials in the global economy"
 SPEECH/12/304 Antonio TAJANI Vice-President of the European Commission responsible for Industry and Entrepreneurship "How to ensure a secure supply of raw materials in the global economy" Bundestag Berlin,
SPEECH/12/304 Antonio TAJANI Vice-President of the European Commission responsible for Industry and Entrepreneurship "How to ensure a secure supply of raw materials in the global economy" Bundestag Berlin,
Disrupting our way to a Very Human City
 Disrupting our way to a Very Human City Zagreb Forum 2017 Technology Park Zagreb 20 th November 2017 Steve Wells COO, Fast Future Publishing steve@fastfuturepublishing.com Image: http://www.bbc.com Through
Disrupting our way to a Very Human City Zagreb Forum 2017 Technology Park Zagreb 20 th November 2017 Steve Wells COO, Fast Future Publishing steve@fastfuturepublishing.com Image: http://www.bbc.com Through
Industry 4.0: the new challenge for the Italian textile machinery industry
 Industry 4.0: the new challenge for the Italian textile machinery industry Executive Summary June 2017 by Contacts: Economics & Press Office Ph: +39 02 4693611 email: economics-press@acimit.it ACIMIT has
Industry 4.0: the new challenge for the Italian textile machinery industry Executive Summary June 2017 by Contacts: Economics & Press Office Ph: +39 02 4693611 email: economics-press@acimit.it ACIMIT has
Address by Mr Koïchiro Matsuura, Director-General of UNESCO, on the occasion of the Opening ceremony of the UNESCO Future Forum
 Address by Mr Koïchiro Matsuura, Director-General of UNESCO, on the occasion of the Opening ceremony of the UNESCO Future Forum The Future of Knowledge Acquisition and Sharing UNESCO, 11 May 2009 Excellencies,
Address by Mr Koïchiro Matsuura, Director-General of UNESCO, on the occasion of the Opening ceremony of the UNESCO Future Forum The Future of Knowledge Acquisition and Sharing UNESCO, 11 May 2009 Excellencies,
Commission proposal for Horizon Europe. #HorizonEU THE NEXT EU RESEARCH & INNOVATION PROGRAMME ( )
 Commission proposal for Horizon Europe THE NEXT EU RESEARCH & INNOVATION PROGRAMME (2021 2027) #HorizonEU Feilim O'Connor - DG ENER, Unit C.2 ETIP SNET Workshops 19/09/2018 Research and Innovation Commission
Commission proposal for Horizon Europe THE NEXT EU RESEARCH & INNOVATION PROGRAMME (2021 2027) #HorizonEU Feilim O'Connor - DG ENER, Unit C.2 ETIP SNET Workshops 19/09/2018 Research and Innovation Commission
Original: English Rio de Janeiro, Brazil June 2012
 United Nations A/CONF.216/4 Distr.: General 29 May 2012 Original: English Rio de Janeiro, Brazil 20-22 June 2012 Item 9 of the provisional agenda* Reports of the round tables Background note for round
United Nations A/CONF.216/4 Distr.: General 29 May 2012 Original: English Rio de Janeiro, Brazil 20-22 June 2012 Item 9 of the provisional agenda* Reports of the round tables Background note for round
Japan s FinTech Vision
 Japan s FinTech Vision First Comprehensive Industrial Finance Division Economic and Industrial Policy Bureau Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry 1 FinTech: New Finance to Support the Fourth Industrial
Japan s FinTech Vision First Comprehensive Industrial Finance Division Economic and Industrial Policy Bureau Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry 1 FinTech: New Finance to Support the Fourth Industrial
Introduction. digitalsupercluster.ca
 Introduction digitalsupercluster.ca Government of Canada s Innovation Supercluster Initiative Federal government investing $950MM into superclusters to drive growth, prosperity, jobs and global leadership.
Introduction digitalsupercluster.ca Government of Canada s Innovation Supercluster Initiative Federal government investing $950MM into superclusters to drive growth, prosperity, jobs and global leadership.
Our Corporate Strategy Digital
 Our Corporate Strategy Digital Proposed Content for Discussion 9 May 2016 CLASSIFIED IN CONFIDENCE INLAND REVENUE HIGHLY PROTECTED Draft v0.2a 1 Digital: Executive Summary What is our strategic digital
Our Corporate Strategy Digital Proposed Content for Discussion 9 May 2016 CLASSIFIED IN CONFIDENCE INLAND REVENUE HIGHLY PROTECTED Draft v0.2a 1 Digital: Executive Summary What is our strategic digital
INDUSTRY 4.0. Modern massive Data Analysis for Industry 4.0 Industry 4.0 at VŠB-TUO
 INDUSTRY 4.0 Modern massive Data Analysis for Industry 4.0 Industry 4.0 at VŠB-TUO Václav Snášel Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science VŠB-TUO Czech Republic AGENDA 1. Industry 4.0 2.
INDUSTRY 4.0 Modern massive Data Analysis for Industry 4.0 Industry 4.0 at VŠB-TUO Václav Snášel Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science VŠB-TUO Czech Republic AGENDA 1. Industry 4.0 2.
DEPLOYING SPACE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY FOR NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT Prof.R.A. Boroffice, OON TABLE OF CONTENTS
 DEPLOYING SPACE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY FOR NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT Prof.R.A. Boroffice, OON TABLE OF CONTENTS 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Space as a Platform for Development 3.2.1 Vision 2020 and Space Technology
DEPLOYING SPACE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY FOR NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT Prof.R.A. Boroffice, OON TABLE OF CONTENTS 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Space as a Platform for Development 3.2.1 Vision 2020 and Space Technology
Five-year strategy. Harnessing the power of evidence and ideas. Evidence. Ideas. Change. Evidence. Ideas. Change.
 ODI 203 Blackfriars Road London SE1 8NJ +44 (0)20 7922 0300 odi.org Evidence. Ideas. Change. Five-year strategy Harnessing the power of evidence and ideas Evidence. Ideas. Change. Follow us on Twitter
ODI 203 Blackfriars Road London SE1 8NJ +44 (0)20 7922 0300 odi.org Evidence. Ideas. Change. Five-year strategy Harnessing the power of evidence and ideas Evidence. Ideas. Change. Follow us on Twitter
Section 1: Internet Governance Principles
 Internet Governance Principles and Roadmap for the Further Evolution of the Internet Governance Ecosystem Submission to the NetMundial Global Meeting on the Future of Internet Governance Sao Paolo, Brazil,
Internet Governance Principles and Roadmap for the Further Evolution of the Internet Governance Ecosystem Submission to the NetMundial Global Meeting on the Future of Internet Governance Sao Paolo, Brazil,
An Introduction to China s Science and Technology Policy
 An Introduction to China s Science and Technology Policy SHANG Yong, Ph.D. Vice Minister Ministry of Science and Technology, China and Senior Fellow Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs
An Introduction to China s Science and Technology Policy SHANG Yong, Ph.D. Vice Minister Ministry of Science and Technology, China and Senior Fellow Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs
