2. COMBAT EXPERIMENTAL SETTINGS
|
|
|
- Philip Paul
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Coparison of turbulence-induced scintillations for ulti-wavelength laser beacons over tactical (7 k) and long (149 k) atospheric propagation paths M. Vorontsov 1, V. S. Rao Gudietla, G. Carhart 3, T. Weyrauch 1, S. Lachinova 4, E. Polnau 1,. Reierson 1, L. Beresnev 3,. Liu 3, and. F. Riker 5 1. University of Dayton, School of Engineering, 300 College Park College Park Center, LOCI, Dayton, OH, U. S. Air Force Research Laboratory, Directed Energy Directorate, Det. 15, 535 Lipoa Parkway, Kehie, Hi U. S. Ary Research Laboratory, 600 Powder Mill Road, Adelphi. MD, Optonicus LLC, 711 E. Monuent Ave. Suite 101, Dayton, OH U. S. Air Force Research Laboratory, Space Vehicles Directorate, 3550 Aberdeen Ave SE, Kirtland AFB, NM ABSTRACT We report results of the experiental analysis of atospheric effects on laser bea propagation over two distinctive propagation paths: a long-range (149 k) propagation path between Mauna Loa (Island of Hawaii) and Haleakala (Island of Maui) ountains, and a tactical-range (7 k) propagation path between the roof of the Dayton Veterans Adinistration Medical Center (VAMC) and the Intelligent Optics Laboratory (IOL/UD) located on the 5th floor of the University of Dayton College Park Center building. Both testbeds include three laser beacons operating at wavelengths 53 n, 1064 n, and 1550 n and a set of identical optical receiver systes with fast-fraing IR caeras for siultaneous easureents of pupil and focal plane intensity distributions. The results reported here are focused on analysis of intensity scintillations that were siultaneously easured at three wavelengths. Coparison of experiental results shows significant differences in the physics of atospheric turbulence ipact on laser bea propagation over the long- and tactical-range distances. 1. INTRODUCTION In this paper we continue analysis (see ref. [1]) of the experiental data obtained during the Coherent Multi-Bea Atospheric Transceiver (COMBAT) experients perfored in February 010 using a 149 k long nearhorizontal atospheric path between a laser beacon platfor located on Mauna Loa peak and the 3.67 AMOS receiver telescope at the suit of Haleakala in the Hawaii Islands. For coparison of atospheric turbulence ipact on laser bea propagation over considerably different distances, we also included results of ore recent laser bea propagation experients using a 7 k long near-horizontal path. The COMBAT experiental capaign provided a large aount of intensity scintillation data that were obtained by utilizing ulti-wavelength laser beacons. In these experients intensity scintillations were siultaneously easured using three closely (6 c apart) located identical laser beacons that generated truncated (<8% of total energy) Gaussian beas at the following wavelengths: λ 1 = 0.53 μ, λ = 1.06 μ, and λ 3 = 1.55 μ. The COMBAT experiental setting and easureent techniques are described in [1]. After copletion of the longrange experients the COMBAT syste was relocated to the IOL at the University of Dayton and re-assebled using a 7 k propagation path with the beacon platfor located on the roof of the Dayton VA Medical Center (VAMC) and the sensing odules positioned on the 5th floor of the UD College Park Center building. In this paper we copare results of intensity scintillation easureents perfored over the 149 k and the 7 k atospheric propagation paths using identical experiental settings. These two experients are referred to here as long- and tactical-range COMBAT settings or COMBAT/LR and COMBAT/TR.
2 Fig. 1. Elevation profile along the propagation path fro the Mauna Loa NOAA observatory to the AFRL AEOS telescope on Haleakala in the long-range COMBAT experiental setting (left) and snapshot of the 3.67 AEOS receiver telescope (right) taken during the COMBAT/LR experient. The telescope is illuinated by the green (λ 1 = 0.53 μ) laser beacon. The photo provides a rough estiation of the bea footprint of approxiately 10 in diaeter.. COMBAT EXPERIMENTAL SETTINGS The propagation geoetries of both long- and tactical-range COMBAT settings are shown in Figs. 1 and. In the COMBAT/LR setting in Fig. 1 the laser beacon platfor was located on Mauna Loa ountain at elevation h ML = 3397 (11,140 ft), and the receilver telescope at the suit of Haleakala at elevation h H = In the COMBAT/TR setting in Fig. the beacon platfor was located on an optical table inside a shed that was anchored to concrete slabs on the roof of VA edical center building. In both experiental settings, the laser beacon assebly was coprised of three single-ode fiber colliators (each with a clear aperture of 6 ) and the corresponding fiber-coupled laser diodes at wavelengths of λ 1 = 0.53 µ λ = µ and λ 3 = 1.55 µ. For technical reasons only two laser beacons with wavelengths λ 1 = 0.53 µ and λ = µ were used in the COMBAT/TR experients described here. The fiber colliators were ounted together with an aiing telescope in a gibal syste (see Fig. 3) with a sallest angular step size of 1.75 µrad that was used for alignent. After propagation to the receiver site (3.67 AEOS telescope at Haleakala in the COMBAT/LR setting, or 0.35 Schidt-Cassegrain telescope just beyond the IOL window in the COMBAT/TR syste), optical waves fro the Fig.. Graphical representation of the 7 k long atospheric propagation path in the tactical-range COMBAT experiental setting (left) and snapshot of green laser beacon iage taken fro the receiver site at IOL/UD (window on the 5 th floor of the College Park Center building). The beacon platfor was located at elevation 40, while COMBAT/TR optical receiver syste at elevation 15. beacons were received by the telescopes and deagnified by corresponding optical relay systes. The resulting colliated bea of diaeter 10 c (in both COMBAT settings) was subdivided into separate subapertures, each having a usable diaeter of 5, and sent to the receiver odules as shown in Fig. 3 and Fig. 4. Each subaperture corresponds to an area with a diaeter of 91.7 c at the telescope pupil for the long-range and 8.5 c for the tactical-range COMBAT settings. The angular diension of the corresponding receiver subapertures are 6.1 µrad for the COMBAT/LR and 1.1 µrad for the COMBAT/TR settings. Three separate subapertures in the longrange sensing syste and a single sub-aperture in the tactical-range setting were used to record pupil-plane and focal-plane irradiance distributions of the received beas as shown in Fig. 3. Narrow bandpass filters were used to dedicate each receiver odule to a specific wave fro a single beacon. In this paper we discuss only easureents of the pupil-plane intensity distributions, which were recorded using three Sensors Unliited (SU640SDWHvis) 14-
3 Fig. 3. Conceptual scheatics of the long-range (left) and tactical range (right) COMBAT experiental settings. The identical beacon assebly (shown at left upper corner) and the pupil and focal plane sensing odules (shown at right) were used in both COMBAT systes. The adaptive optics and 1550 n sensing odules in the COMBAT/TR syste were not included in the experients described. bit caeras. The caeras were operating in a windowed ode with a 5656 pixel window with pixel size of 55 μ, providing an actual sensor area of and a 100% fill factor. A four-to-one bea reducer was installed in the optical train of each subaperture to atch the bea (pupil) size with the active window size. 3. MEASUREMENTS AND RESULTS 3.1 Short-exposure Intensity Scintillation Patterns. Characteristic snapshots of the received light pupil-plane intensity distributions for beacons with different wavelengths easured in both COMBAT experients are illustrated in Fig. Error! Reference source not found.. The iages show that the spatial scale of intensity scintillations is strongly dependent on the wavelength, i.e., the longer the wavelength the larger the atospheric effects induced intensity speckles. This observation is consistent with the theoretical findings and was also confired by our nuerical siulations. At the sae tie intensity scintillation patterns for the long-range (first Fig. 4. Characteristic exaples of the short-exposure intensity scintillation patterns recorded during the long-range (three photos fro left to right) and tactical-range (two photos at right) COMBAT experients. The bean wavelength is identified by color of sall circles at left upper corner of each photograph: green circle corresponds to λ 1 = 0.53 µ, red to λ = µ and blue to λ 3 = 1.55 µ. three iages at right) and the tactical-range propagation distances are profoundly different despite the fact that in both cases the ratios of the bea footprint (for λ 1 = 0.53 μ) to receiver aperture diaeter were nearly equal in both experiental settings. These ratios are 10.9 for COMBAT/LR and 10.6 for COMBAT/TR. The characteristic speckle size in the intensity iages for λ 1 = 0.53 μ in Fig. 4 are 5-10 for 149 k and 17-0 for 7 k propagation distances. 3. Received Power Fluctuations and Giant Spikes. Consider characteristic exaples of teporal dynaics of the received light power easured inside the 91.7 c aperture for the long-range and 8.5 c aperture for the tactical-range COMBAT settings. The power fluctuations data were siultaneously recorded for three beacons in the long-range and for two (for λ 1 = 0.53 μ and for λ = 1.06 μ) beacons in tactical-range experients. The
4 dependencies of the noralized power Pn ˆ( ) on the consequent short-exposure pupil-plane frae nuber n are shown in Fig. 5 for the long-range and in Fig. 6 for the tactical-range experients. In both cases the received power was noralized by the axiu value corresponding to each experient. As can be seen fro these figures, dynaics of receiver power fluctuations are quite different for 149 k and 7 k propagation paths. The long-range propagation results in appearance of large spikes in the received power that were absent in the experients perfored over the tactical-range distance. These giant spikes, each lasting for only a few illiseconds, result in up to ten-fold increase in received power. Note that in the experients in Fig. 5 the aplitude of spikes appeared to be significantly higher for λ 1 = 0.53 μ. At the sae tie in a different set of experients the largest aplitude of the spikes were observed at different wavelengths. For exaple Fig. 7 shows results of a different set of experients with the largest aplitude spikes observed at λ 3 = 1.55 μ. The giant spikes appeared quite randoly with a characteristic delay tie of the order of a few seconds. This tie scale can be associated with changes occurring in coherent atospheric structures and/or with the dynaics of stable (refractive) and unstable (turbulent) layers aligned with the Earth curvature that the beacon beas propagate through. On the other hand, the extreely Fig. 5. Characteristic teporal dynaics of received optical power fluctuations P ˆ Pn ax n Pn for laser beacons with wavelengths λ 1 = 0.53 μ (top), λ = 1.06 μ (iddle), and λ 3 = 1.55 μ (botto) obtained in the long-range experients. All three sequences of short-exposure fraes with s integration tie and frae rate 00 f/sec were captured siultaneously. short duration (on the order of 5-0 s) of spikes cannot be directly associated with atospheric processes that occur over a significantly longer tie scale. As a possible physical explanation for the foration of these giant spikes, we consider the trapping of the beacon bea inside a relatively narrow stratified layer of air with sharp changes of refractive index at its boundaries. Such a layer can act as a wave-guide siilar to the way an optical fiber acts with respect to an optical bea with wavelength atched to the fiber core size. This waveguiding effect is extreely sensitive to the wavelength of the propagating bea and the coupling angle and can be destroyed with sall variation of the stratified layer geoetry or of the angle of optical wave incidence. These sall variations can indeed occur at a tie scale of the duration of the observed spikes. Fig. 6. Characteristic teporal dynaics of received optical power fluctuations P ˆ Pn ax n Pn for laser beacons with wavelengths λ 1 = 0.53 μ (top) and λ = 1.06 μ (botto) obtained in the tactical-range experients. Sequences of 6000 short-exposure fraes with s integration tie and frae rate 00 fr/sec were captured siultaneously.
5 Fig. 7. Exaple of the received power fluctuation dynaics over 149 k propagation path (siilar to as shown in Fig. 5) with strongest received power spikes at λ 3 = 1.55 μ (left), and the corresponding evolution of the aperture-average scintillation indices ( n) (solid lines) and ( n) for n W = 000 (dashed lines). ns Scintillation Index Dynaics. For analysis of teporal dynaics of the pupil-plane intensity scintillations consider coputation of the noralized variance of intensity fluctuations at each pixel of the photo-array within the receiver aperture area, 1 I ( r ) I ( r ) I ( r ) ( r ), (1) n1 n where r is the transverse coordinate vector defining the th pixel in the plane of the photo-array, { I n ( r ) } (n=1,,n) is the set of N short-exposure pupil-plane intensity distributions that are recorded with frae rate 00 fr/sec, and 1 n n1 WS I ( r ) I ( r ) is an intensity distribution obtained by averaging of subsequent fraes (tieaverage iage). Note that averaging over the set of =N fraes in Eq. (1) is equivalent to tie averaging over nearly 50 seconds. The noralized variance (1) is referred to as the scintillation index. By averaging ( r ) over all pixels inside the receiver aperture area we obtain the aperture-average scintillation index ( r, S ) S where < > S defines averaging over receiver aperture or space averaging. In order to evaluate whether the observed intensity scintillations can be considered as a stationary rando process, consider teporal dynaics of the scintillation index by using either increasing nuber =n of subsequent fraes ns ( n ) or oving (window) averaging of =n sequential fraes WS ( nn, W ), where n W is a nuber of fraes in the selected averaging window. Both ns ( n ) and WS ( n ) dependencies are shown in Fig. 7; the values NS are given inside the corresponding plots.
6 Fig. 8. Characteristic exaples of teporal power spectra for pupil-plane intensity scintillations easured in the long-range COMBAT experients for four different experiental trials. In each plot the spectra correspond to intensity scintillations siultaneously easured at three different wavelengths (λ 1 = 0.53 μ, λ = 1.06 μ, and λ 3 = 1.55 μ). The data were taken on 0/13/10 at 7:30p (top left), and at 10:30p (top right), and on 0/16/10 at 9:51p (botto left), and on 0/17/10 at 9:05p local tie. For convenience of coparison with the teporal power spectru of intensity fluctuations derived fro the Kologorov theory the characteristic -8/3 slope of this spectru as well as -5/3 slope observed in ref [] are shown by the corresponding straight lines. The frequency is noralized by 1.0 Hz. The dependences ns ( n ) and WS ( n ) characterize teporal changes of the aperture-average scintillation index occurring during the tie of easureents trial. The scintillation index plots clearly indicate the statistical nonstationary character of the intensity scintillation process and strong ipact of spikes in the received power. The appearance of the giant spikes results in rapid increases in the scintillation index WS ( nn, W ) that akes the scintillation process highly non-stationary. In Fig. 7 this effect is ore pronounced for the set of data obtained at λ 3 = 1.55 μ. The giant spikes also contribute to non-ergodicity of intensity scintillations. The assuption of ergodicity of the intensity scintillation statistical process can be challenged by coparing values of the scintillation indexes NS and SN that are obtained by changing the order of spatial and teporal averaging in the sae experiental trial. Coparison of the corresponding values NS and SN shows that these values are quite different which akes questionable the applicability of the ergodic hypothesis [3,4]. 3.4 Teporal Spectru of Intensity Scintillations. Consider exaples of a teporal power spectru of the pupil-plane intensity fluctuations which are obtained using coputer processing of the COMBAT experiental data. The aperture-average spectral density of intensity fluctuations S() was defined as M S si (, r ) / si ( 0, ) 1 S( ) r M S 1, () where si (, r ) is a rando realization of a teporal power spectru corresponding to the th pixel of the photoarray, and M S the nuber of pixels used for the power spectru coputations. For each th pixel, teporal spectra si (, r ) were calculated by taking digital Fourier transfors of the set of N=10000 intensity values I n ( r ), where n=1,, N. Note that the photo-array pixel corresponded to a area of the receiver aperture in the longrange and 0.3x0.3 in the tactical-range COMBAT settings. To reduce coputational tie in each of N
7 149 k, λ = 0.53 µ 149 k, λ = 1.06 µ -5/3-5/3-8/3-8/3 λ 7 k = 0.53 λ = 0.53 µ µ -5/3-8/3 Fig. 9. Suary of pupil-plane intensity scintillations teporal power spectra analysis for long-range (top) and tactical-range (botto) experients. The calculated fro the experiental data exponents in the approxiating spectru power-low for different experiental trials and the exaple of the power spectra for 7 k propagation path (botto left) corresponding to the experiental trial indicated by arrow. processed fraes only M S = 1000 intensity values were used. The pixels r, =1,, M S, selected for coputation of si (, r ) were those foring a grid with 10 pixel spacing that was centered on and covers the receiver aperture. Four exaples of the teporal power spectra obtained using COMBAT long-range data are show in Fig. 8. As can be seen fro these exaples the spectral functions S () were changing considerably fro one to another experiental data collection trial. Also note that these experiental spectra are quite different fro the corresponding teporal power spectru functions that are derived fro the Kologorov turbulence theory and Taylor s frozen turbulence hypothesis [3,5]. These theory-based teporal power spectru functions are essentially 1/ 8 / 3 unchanged within the low-frequency band for 0 0.5V /( L) and decay as for higher frequencies [5]. Here V is a transversal coponent of wind velocity. The teporal power spectru curves in Fig. 8 (except the plots at botto right) decay with a nearly constant, and significantly different than -8/3, exponent in the approxiating spectru power-law within the entire frequency band. The exponents in the power-law approxiations of the experiental teporal power spectra obtained for several COMBAT/LR experiental trials are suarized in Fig. 9 for λ 1 = 0.53 μ and λ = 1.06 μ wavelengths. As can be seen fro the data presented 1 in Fig. 9 in ost experiental trials the teporal power spectra can be approxiated as for both wavelengths. These results present significant deviation fro the existing predictive odels. Exaples of intensity fluctuation power spectru obtained for the tactical-range distance and the values of exponent for eight different set of easureents are correspondingly shown in botto left and right plots in Fig. 9. Note that in this case within the low-frequency band ( 0 30 Hz) the power spectru is nearly constant and decays with exponent = -. at higher frequencies as theory predicts. This shape of the power spectru is consistent with the theoretical prediction although the decay exponent is slightly larger than -8/3. In all tactical range experiental trails we observed shapes of spectra siilar to Fig. 9 (botto left) having decay paraeters ranging between -.5 and -1 as shown in Fig. 9 (botto right). This deviation fro theoretical (plane wave) 8 / 3
8 approxiation is ost likely related with violation of Taylor s frozen turbulence hypothesis that assues constant wind velocity along the entire propagation path. 4. SUMMARY To optially design, build, and understand the perforance of the new generation of long-range optical systes requires analysis of optical wave propagation along various atospheric paths that ay cross several extended (deep) regions of atosphere with quite distinctive spatial structures and teporal dynaics, and quite likely, developent of techniques to itigate these effects. This analysis is currently perfored using a fraework of the classical fully developed Kologorov-Obukhov optical turbulence theory [6,7]. In this theory the atosphere is described by three diensional boundless, statistically hoogeneous and isotropic rando fields of refractive index fluctuations (atospheric eddies). In this idealization, the ipact of boundary conditions iposed by terrain, and hydro-therodynaic processes in the atosphere is assued to be forgotten due to a cascade of energy transfer fro larger to saller scale eddies the process that rationalizes the Kologorov s assuption of statistical isotropy of fully developed turbulence. In reality, these ideal hoogeneity and isotropy conditions do not exist at large scales, as they are destroyed by gravity and solar radiation induced buoyancy and friction forces that lead to foration of distinct nearly horizontally aligned atospheric layers [8,9]. These atospheric effects can severely ipact optical wave propagation over long distances. The results of the atospheric characterization experients over long- (149-k) and relatively short (7-k) paths presented allow direct coparison of atospheric effects induced scintillations of laser bea intensity for different wavelengths. They also clearly show difficulties in interpretations of the observed long-range phenoena based solely on the classical Kologorov optical turbulence theory. As a path forward we can point out several future research and developent directions towards better understanding physics of laser bea propagation along longdistances, including: 1. Research focused on erging statistical (Kologorov turbulence based) and deterinistic coputational fluid dynaics approaches, cobined with wave optics odeling of optical wave propagation over atospheric paths.. Developent of atheatical and coputational techniques for predictive odeling of optical wave propagation in highly anisotropic turbulence layers. 3. Developent of theoretical fraework nuerical siulation tools that erge refractive and diffractive optics approaches. 4. Engineering of unconventional optical fields (laser beas) and optical syste architectures which are less sensitive to atospheric distortions over long propagation paths. 5. Developent of unconventional adaptive bea control techniques. We also believe that ore long-range atospheric optical propagation experients are needed to directly associate the observed anoalies in laser bea and iage characteristics with eteorological data and the results of highperforance coputing of atospheric dynaics. 5. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This project was supported through the Cooperative Agreeents between the US Ary Research Laboratory and both the University of Dayton and Optonicus LLC. 6. REFERENCES [1] M. A. Vorontsov, G. W. Carhart, V. S. Rao Gudietla, T. Weyrauch, E. Stevenson, S. L. Lachinova, L. A. Beresnev,. Liu, K. Rehder, and. F. Riker, Characterization of atospheric turbulence effects over 149 k propagation path using ulti-wavelength laser beacons, in Proceedings of the 010 AMOS Conference, S. Ryan, ed., p. E18 (010). [] V.V. Nosov, V.P. Lukin, E.V. Nosov, A.V. Torgaev, V.M. Grigoriev, P.G. Kovadlo, Coherent structures in the turbulent atosphere, Matheatical Models of Non-linear Phenoena, Processes and Systes: Fro Molecular Scale to Planetary Atosphere. By ed. A. Nadykto et al. - N.Y.: Nova Science Publishers, Chapter 0, (010).
9 [3] V. I. Tatarskii, Wave Propagation in a Turbulent Mediu, ser. McGraw-Hill Series in Electrical Engineering. New York: McGraw-Hill, (1961). [4] A. Ishiaru, Wave Propagation and Scattering in Rando Media. New York: Acadeic Press, (1978). [5] L. C. Andrews and R. L. Phillips, Laser Bea Propagation through Rando Media, SPIE, (1998). [6] A. N. Kologorov, The local structure of turbulence in incopressible viscous fluid for very large Reynolds nubers, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, vol. 30, no. 4, pp , 1941, [English translation in Turbulence: Classic Papers on Statistical Theory (ed. S. K. Friedlander and L. Topper), p. 151, Interscience, NY, (1961). [7] A. M. Obukhov, On the distribution of energy in the spectru of turbulent flow, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, vol. 3, no. 1, p., (1941). [8] S. Lovejoy, A. F. Tuck, S.. Hovde, and D. Schertzer, Do stable atospheric layers exist? Geophysical Research Letters, vol. 35, L0180, (008). [9] S. Lovejoy, A. F. Tuck, S.. Hovde, and D. Schertzer, Is isotropic turbulence relevant in the atosphere? Geophysical Research Letters, Vol.. 34, L1580, ( 007).
Characterization of atmospheric turbulence effects over 149 km propagation path using multi-wavelength laser beacons
 Characterization of atospheric turbulence effects over 149 k propagation path using ulti-wavelength laser beacons Mikhail A. Vorontsov School of Engineering, University of Dayton, Dayton, Ohio 45469, USA
Characterization of atospheric turbulence effects over 149 k propagation path using ulti-wavelength laser beacons Mikhail A. Vorontsov School of Engineering, University of Dayton, Dayton, Ohio 45469, USA
Performance Analysis of Atmospheric Field Conjugation Adaptive Arrays
 Perforance Analysis of Atospheric Field Conjugation Adaptive Arrays Aniceto Belonte* a, Joseph M. Kahn b a Technical Univ. of Catalonia, Dept. of Signal Theory and Coun., 08034 Barcelona, Spain; b Stanford
Perforance Analysis of Atospheric Field Conjugation Adaptive Arrays Aniceto Belonte* a, Joseph M. Kahn b a Technical Univ. of Catalonia, Dept. of Signal Theory and Coun., 08034 Barcelona, Spain; b Stanford
Fundamental study for measuring microflow with Michelson interferometer enhanced by external random signal
 Bulletin of the JSME Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systes, and Manufacturing Vol.8, No.4, 2014 Fundaental study for easuring icroflow with Michelson interferoeter enhanced by external rando signal
Bulletin of the JSME Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systes, and Manufacturing Vol.8, No.4, 2014 Fundaental study for easuring icroflow with Michelson interferoeter enhanced by external rando signal
OTC Statistics of High- and Low-Frequency Motions of a Moored Tanker. sensitive to lateral loading such as the SAL5 and
 OTC 61 78 Statistics of High- and Low-Frequency Motions of a Moored Tanker by J.A..Pinkster, Maritie Research Inst. Netherlands Copyright 1989, Offshore Technology Conference This paper was presented at
OTC 61 78 Statistics of High- and Low-Frequency Motions of a Moored Tanker by J.A..Pinkster, Maritie Research Inst. Netherlands Copyright 1989, Offshore Technology Conference This paper was presented at
David Carruthers 1, Xiangyu Sheng 2, Emilie Vanvyve 1
 REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS FOR DISPERSION MODELLING IN TAIWAN INCLUDING THE USE OF ADMS David Carruthers 1, Xiangyu Sheng, Eilie Vanvyve 1 1 CERC, 3 King s Parade, Cabridge CB 1SJ, UK Scott Wilson, Michael
REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS FOR DISPERSION MODELLING IN TAIWAN INCLUDING THE USE OF ADMS David Carruthers 1, Xiangyu Sheng, Eilie Vanvyve 1 1 CERC, 3 King s Parade, Cabridge CB 1SJ, UK Scott Wilson, Michael
Active Imaging and Remote Optical Power Beaming using Fiber Array Laser Transceivers with Adaptive Beam Shaping
 Active Imaging and Remote Optical Power Beaming using Fiber Array Laser Transceivers with Adaptive Beam Shaping Thomas Weyrauch, 1 Mikhail Vorontsov, 1,2 David Bricker 2, Bezhad Bordbar 1, and Yoshihiro
Active Imaging and Remote Optical Power Beaming using Fiber Array Laser Transceivers with Adaptive Beam Shaping Thomas Weyrauch, 1 Mikhail Vorontsov, 1,2 David Bricker 2, Bezhad Bordbar 1, and Yoshihiro
PREDICTING SOUND LEVELS BEHIND BUILDINGS - HOW MANY REFLECTIONS SHOULD I USE? Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK
 PREDICTING SOUND LEVELS BEHIND BUILDINGS - HOW MANY REFLECTIONS SHOULD I USE? W Wei A Cooke J Havie-Clark Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead,
PREDICTING SOUND LEVELS BEHIND BUILDINGS - HOW MANY REFLECTIONS SHOULD I USE? W Wei A Cooke J Havie-Clark Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead,
Turbulence characterization and image processing data sets from a NATO RTO SET 165 trial in Dayton (OH)
 Turbulence characterization and image processing data sets from a NATO RTO SET 165 trial in Dayton (OH) M.-T. Velluet a, Mikhail Vorontsov b, Piet Schwering c, Gabriele Marchi d, Stephane Nicolas e, Jim
Turbulence characterization and image processing data sets from a NATO RTO SET 165 trial in Dayton (OH) M.-T. Velluet a, Mikhail Vorontsov b, Piet Schwering c, Gabriele Marchi d, Stephane Nicolas e, Jim
Sound recording with the application of microphone arrays
 Coputer Applications in Electrical Engineering Sound recording with the application of icrophone arrays Eugeniusz Kornatowski West Poeranian University of Technology 7-26 Szczecin, 26 Kwietnia, e-ail:
Coputer Applications in Electrical Engineering Sound recording with the application of icrophone arrays Eugeniusz Kornatowski West Poeranian University of Technology 7-26 Szczecin, 26 Kwietnia, e-ail:
Modeling Beam forming in Circular Antenna Array with Directional Emitters
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN (Print): 2320-9356 Volue 5 Issue 3 ǁ Mar. 2017 ǁ PP.01-05 Modeling Bea foring in Circular Antenna Array
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN (Print): 2320-9356 Volue 5 Issue 3 ǁ Mar. 2017 ǁ PP.01-05 Modeling Bea foring in Circular Antenna Array
2-Dimensional beamsteering using dispersive deflectors and wavelength tuning
 2-Diensional beasteering using dispersive deflectors and wavelength tuning Trevor Chan, 1,* Evgeny Myslivets, 1 and Joseph E. Ford, 1 1 Departent of Electrical and Coputer Engineering, University of California,
2-Diensional beasteering using dispersive deflectors and wavelength tuning Trevor Chan, 1,* Evgeny Myslivets, 1 and Joseph E. Ford, 1 1 Departent of Electrical and Coputer Engineering, University of California,
Optical fiber beamformer for processing two independent simultaneous RF beams
 Optical fiber beaforer for processing two independent siultaneous RF beas M. Jaeger, S. Granieri *, and A. Siahakoun Departent of Physics and Optical Engineering, Rose-Hulan Institute of Technology Terre
Optical fiber beaforer for processing two independent siultaneous RF beas M. Jaeger, S. Granieri *, and A. Siahakoun Departent of Physics and Optical Engineering, Rose-Hulan Institute of Technology Terre
HIGH FREQUENCY LASER BASED ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY USING A CW GENERATION SOURCE
 HIGH FREQUENCY LASER BASED ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY USING A CW GENERATION SOURCE T.W. Murray, O. Balogun, and N. Pratt Departent of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering, Boston University, Boston MA 0225 Abstract:
HIGH FREQUENCY LASER BASED ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY USING A CW GENERATION SOURCE T.W. Murray, O. Balogun, and N. Pratt Departent of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering, Boston University, Boston MA 0225 Abstract:
Optical Magnetic Response in a Single Metal Nanobrick. Jianwei Tang, Sailing He, et al.
 Optical Magnetic Response in a Single Metal Nanobrick Jianwei Tang, Sailing He, et al. Abstract: Anti-syetric localized surface plasons are deonstrated on a single silver nanostrip sandwiched by SiC layers.
Optical Magnetic Response in a Single Metal Nanobrick Jianwei Tang, Sailing He, et al. Abstract: Anti-syetric localized surface plasons are deonstrated on a single silver nanostrip sandwiched by SiC layers.
Comparison Between PLAXIS Output and Neural Network in the Guard Walls
 Coparison Between PLAXIS Output and Neural Network in the Guard Walls Ali Mahbod 1, Abdolghafar Ghorbani Pour 2, Abdollah Tabaroei 3, Sina Mokhtar 2 1- Departent of Civil Engineering, Shahid Bahonar University,
Coparison Between PLAXIS Output and Neural Network in the Guard Walls Ali Mahbod 1, Abdolghafar Ghorbani Pour 2, Abdollah Tabaroei 3, Sina Mokhtar 2 1- Departent of Civil Engineering, Shahid Bahonar University,
Mitigation of GPS L 2 signal in the H I observation based on NLMS algorithm Zhong Danmei 1, a, Wang zhan 1, a, Cheng zhu 1, a, Huang Da 1, a
 2nd International Conference on Electrical, Coputer Engineering and Electronics (ICECEE 25 Mitigation of GPS L 2 signal in the H I observation based on NLMS algorith Zhong Danei, a, Wang zhan, a, Cheng
2nd International Conference on Electrical, Coputer Engineering and Electronics (ICECEE 25 Mitigation of GPS L 2 signal in the H I observation based on NLMS algorith Zhong Danei, a, Wang zhan, a, Cheng
ROBUST UNDERWATER LOCALISATION OF ULTRA LOW FREQUENCY SOURCES IN OPERATIONAL CONTEXT
 ROBUST UNDERWATER LOCALISATION OF ULTRA LOW FREQUENCY SOURCES IN OPERATIONAL CONTEXT M. Lopatka a, B. Nicolas a, G. Le Touzé a,b, X. Cristol c, B. Chalindar c, J. Mars a, D. Fattaccioli d a GIPSA-Lab /DIS/
ROBUST UNDERWATER LOCALISATION OF ULTRA LOW FREQUENCY SOURCES IN OPERATIONAL CONTEXT M. Lopatka a, B. Nicolas a, G. Le Touzé a,b, X. Cristol c, B. Chalindar c, J. Mars a, D. Fattaccioli d a GIPSA-Lab /DIS/
Fiber Bragg grating based four-bit optical beamformer
 Fiber Bragg grating based four-bit optical beaforer Sean Durrant a, Sergio Granieri a, Azad Siahakoun a, Bruce Black b a Departent of Physics and Optical Engineering b Departent of Electrical and Coputer
Fiber Bragg grating based four-bit optical beaforer Sean Durrant a, Sergio Granieri a, Azad Siahakoun a, Bruce Black b a Departent of Physics and Optical Engineering b Departent of Electrical and Coputer
Characterization and Modeling of Underwater Acoustic Communications Channels for Frequency-Shift-Keying Signals
 Characterization and Modeling of Underwater Acoustic Counications Channels for Frequency-Shift-Keying Signals Wen-Bin Yang and T.C. Yang Naval Research Laboratory Washington, DC 375 USA Abstract In a fading
Characterization and Modeling of Underwater Acoustic Counications Channels for Frequency-Shift-Keying Signals Wen-Bin Yang and T.C. Yang Naval Research Laboratory Washington, DC 375 USA Abstract In a fading
DSI3 Sensor to Master Current Threshold Adaptation for Pattern Recognition
 International Journal of Signal Processing Systes Vol., No. Deceber 03 DSI3 Sensor to Master Current Threshold Adaptation for Pattern Recognition David Levy Infineon Austria AG, Autootive Power Train Systes,
International Journal of Signal Processing Systes Vol., No. Deceber 03 DSI3 Sensor to Master Current Threshold Adaptation for Pattern Recognition David Levy Infineon Austria AG, Autootive Power Train Systes,
EFFECTS OF MASKING ANGLE AND MULTIPATH ON GALILEO PERFORMANCES IN DIFFERENT ENVIRONMENTS
 1 EFFECTS OF MASKING ANGLE AND MULTIPATH ON GALILEO PERFORMANCES IN DIFFERENT ENVIRONMENTS M. Malicorne*, M. Bousquet**, V. Calettes*** SUPAERO, 1 avenue Edouard Belin BP 43, 3155 Toulouse Cedex, France.
1 EFFECTS OF MASKING ANGLE AND MULTIPATH ON GALILEO PERFORMANCES IN DIFFERENT ENVIRONMENTS M. Malicorne*, M. Bousquet**, V. Calettes*** SUPAERO, 1 avenue Edouard Belin BP 43, 3155 Toulouse Cedex, France.
Adaptive Harmonic IIR Notch Filter with Varying Notch Bandwidth and Convergence Factor
 Journal of Counication and Coputer (4 484-49 doi:.765/548-779/4.6. D DAVID PUBLISHING Adaptive Haronic IIR Notch Filter with Varying Notch Bandwidth and Convergence Factor Li Tan, Jean Jiang, and Liango
Journal of Counication and Coputer (4 484-49 doi:.765/548-779/4.6. D DAVID PUBLISHING Adaptive Haronic IIR Notch Filter with Varying Notch Bandwidth and Convergence Factor Li Tan, Jean Jiang, and Liango
Wavelength-Selective Switches for Mode-Division Multiplexing: Scaling and Performance Analysis
 JLT-64-4: K.-P. Ho et al, Wavelength-Selective Switches for Mode-Division Multiplexing Wavelength-Selective Switches for Mode-Division Multiplexing: Scaling and Perforance Analysis Keang-Po Ho, Senior
JLT-64-4: K.-P. Ho et al, Wavelength-Selective Switches for Mode-Division Multiplexing Wavelength-Selective Switches for Mode-Division Multiplexing: Scaling and Perforance Analysis Keang-Po Ho, Senior
Investigating Multiple Alternating Cooperative Broadcasts to Enhance Network Longevity
 Investigating Multiple Alternating Cooperative Broadcasts to Enhance Network Longevity Aravind Kailas School of Electrical and Coputer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia 3033-050,
Investigating Multiple Alternating Cooperative Broadcasts to Enhance Network Longevity Aravind Kailas School of Electrical and Coputer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia 3033-050,
UWB System for Time-Domain Near-Field Antenna Measurement
 UWB Syste for Tie-Doain Near-Field Antenna Measureent B. Levitas #, M. Drozdov #, I. Naidionova #, S. Jefreov #, S. Malyshev *2, A. Chizh *3 www.geozondas.co # Geozondas Ltd., 6, Shevchenko Str., LT-3,
UWB Syste for Tie-Doain Near-Field Antenna Measureent B. Levitas #, M. Drozdov #, I. Naidionova #, S. Jefreov #, S. Malyshev *2, A. Chizh *3 www.geozondas.co # Geozondas Ltd., 6, Shevchenko Str., LT-3,
REPORT ITU-R SA Telecommunication characteristics and requirements for space VLBI systems
 Rep. ITU-R SA.2132 1 REPORT ITU-R SA.2132 Telecounication characteristics and requireents for space VLBI systes (2008) This Report describes the characteristics of the space VLBI systes. These characteristics
Rep. ITU-R SA.2132 1 REPORT ITU-R SA.2132 Telecounication characteristics and requireents for space VLBI systes (2008) This Report describes the characteristics of the space VLBI systes. These characteristics
Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP): Principles of Operation and Setup
 SMARTSkills Workshop for Vessel Users and Researchers, Marine Institute, Galway 29th April 2016 Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP): Principles of Operation and Setup Christian Mohn & Martin White
SMARTSkills Workshop for Vessel Users and Researchers, Marine Institute, Galway 29th April 2016 Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP): Principles of Operation and Setup Christian Mohn & Martin White
ANALYSIS AND OPTIMIZATION OF SYNTHETIC APERTURE ULTRASOUND IMAGING USING THE EFFECTIVE APERTURE APPROACH. Milen Nikolov, Vera Behar
 International Journal "Inforation heories & Applications" Vol. 57 AALYSIS AD OPIMIZAIO OF SYHEIC APEUE ULASOUD IMAGIG USIG HE EFFECIVE APEUE APPOACH Milen ikolov, Vera Behar Abstract: An effective aperture
International Journal "Inforation heories & Applications" Vol. 57 AALYSIS AD OPIMIZAIO OF SYHEIC APEUE ULASOUD IMAGIG USIG HE EFFECIVE APEUE APPOACH Milen ikolov, Vera Behar Abstract: An effective aperture
Mode spectrum of multi-longitudinal mode pumped near-degenerate OPOs with volume Bragg grating output couplers
 Mode spectru of ulti-longitudinal ode puped near-degenerate OPOs with volue Bragg grating output couplers Markus Henriksson 12 * Lars Sjöqvist 1 Valdas Pasiskevicius 2 and Fredrik Laurell 2 1 Laser Systes
Mode spectru of ulti-longitudinal ode puped near-degenerate OPOs with volue Bragg grating output couplers Markus Henriksson 12 * Lars Sjöqvist 1 Valdas Pasiskevicius 2 and Fredrik Laurell 2 1 Laser Systes
Design Optimisation of Compound Parabolic Concentrator (CPC) for Improved Performance R. Abd-Rahman, M. M. Isa, H. H. Goh
 Tokyo Japan May 2-2, 21, 1 () Part XXIII Design Optiisation of Copound Parabolic Concentrator (CPC) for Iproved Perforance R. Abd-Rahan, M. M. Isa, H. H. Goh Abstract A copound parabolic concentrator (CPC)
Tokyo Japan May 2-2, 21, 1 () Part XXIII Design Optiisation of Copound Parabolic Concentrator (CPC) for Iproved Perforance R. Abd-Rahan, M. M. Isa, H. H. Goh Abstract A copound parabolic concentrator (CPC)
Dynamic Model Displacement for Model-mediated Teleoperation
 Dynaic Model Displaceent for Model-ediated Teleoperation Xiao Xu Giulia Paggetti Eckehard Steinbach Institute for Media Technology, Technische Universität München, Munich, Gerany ABSTRACT In this paper,
Dynaic Model Displaceent for Model-ediated Teleoperation Xiao Xu Giulia Paggetti Eckehard Steinbach Institute for Media Technology, Technische Universität München, Munich, Gerany ABSTRACT In this paper,
Torsion System. Encoder #3 ( 3 ) Third encoder/disk for Model 205a only. Figure 1: ECP Torsion Experiment
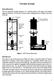 Torsion Syste Introduction This lab experient studies dynaics of a torsional syste with single and ultiple degrees of freedo. The effects of various control configurations are studied in later part of
Torsion Syste Introduction This lab experient studies dynaics of a torsional syste with single and ultiple degrees of freedo. The effects of various control configurations are studied in later part of
WIPL-D Pro: What is New in v12.0?
 WIPL-D Pro: What is New in v12.0? Iproveents/new features introduced in v12.0 are: 1. Extended - Extree Liits a. Extreely LOW contrast aterials b. Extended resolution for radiation pattern c. Extreely
WIPL-D Pro: What is New in v12.0? Iproveents/new features introduced in v12.0 are: 1. Extended - Extree Liits a. Extreely LOW contrast aterials b. Extended resolution for radiation pattern c. Extreely
Notes on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
 Notes on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). Discrete Fourier ransfor As a reinder, the analytic fors of Fourier and inverse Fourier transfors are X f x t t, f dt x t exp j2 ft dt (.) where
Notes on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). Discrete Fourier ransfor As a reinder, the analytic fors of Fourier and inverse Fourier transfors are X f x t t, f dt x t exp j2 ft dt (.) where
Multiconjugate adaptive optics simulator for the Thirty Meter Telescope: design, implementation, and results
 Multiconjugate adaptive optics siulator for the Thirty Meter Telescope: design, ipleentation, and results Etsuko Mieda Jean-Pierre Veran Matthias Rosensteiner Paolo Turri David Andersen Glen Herriot Olivier
Multiconjugate adaptive optics siulator for the Thirty Meter Telescope: design, ipleentation, and results Etsuko Mieda Jean-Pierre Veran Matthias Rosensteiner Paolo Turri David Andersen Glen Herriot Olivier
Ignition and monitoring technique for plasma processing of multicell superconducting radio frequency cavities
 Ignition and onitoring technique for plasa processing of ulticell superconducting radio frequency cavities Marc Doleans Oak Ridge ational Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee 3783, USA E ail: doleans@ornl.gov
Ignition and onitoring technique for plasa processing of ulticell superconducting radio frequency cavities Marc Doleans Oak Ridge ational Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee 3783, USA E ail: doleans@ornl.gov
TESTING OF ADCS BY FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS IN MULTI-TONE MODE
 THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volue 5, Nuber /004, pp.000-000 TESTING OF ADCS BY FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS IN MULTI-TONE MODE Daniel BELEGA
THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volue 5, Nuber /004, pp.000-000 TESTING OF ADCS BY FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS IN MULTI-TONE MODE Daniel BELEGA
A New Simple Model for Land Mobile Satellite Channels
 A New Siple Model for Land Mobile Satellite Channels A. Abdi, W. C. Lau, M.-S. Alouini, and M. Kaveh Dept. of Elec. and Cop. Eng., University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455 Eails: {abdi, wlau, alouini,
A New Siple Model for Land Mobile Satellite Channels A. Abdi, W. C. Lau, M.-S. Alouini, and M. Kaveh Dept. of Elec. and Cop. Eng., University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455 Eails: {abdi, wlau, alouini,
ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
 Adaptive characterization of laser daage fro sparse defects Sa Richan *, Alexander R. Martin, Quentin Turchette and Trey Turner RO, 555 Airport Blvd., Boulder, CO, USA 831 ABSTRACT Standard techniques
Adaptive characterization of laser daage fro sparse defects Sa Richan *, Alexander R. Martin, Quentin Turchette and Trey Turner RO, 555 Airport Blvd., Boulder, CO, USA 831 ABSTRACT Standard techniques
ELEC2202 Communications Engineering Laboratory Frequency Modulation (FM)
 ELEC Counications Engineering Laboratory ---- Frequency Modulation (FM) 1. Objectives On copletion of this laboratory you will be failiar with: Frequency odulators (FM), Modulation index, Bandwidth, FM
ELEC Counications Engineering Laboratory ---- Frequency Modulation (FM) 1. Objectives On copletion of this laboratory you will be failiar with: Frequency odulators (FM), Modulation index, Bandwidth, FM
Travel-Time and Amplitude Sensitivity Kernels
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unliited. Travel-Tie and Aplitude Sensitivity Kernels Eanuel Skarsoulis Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas Institute of
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unliited. Travel-Tie and Aplitude Sensitivity Kernels Eanuel Skarsoulis Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas Institute of
Analysis of Time-Frequency Energy for Environmental Vibration Induced by Metro
 6 th International Conference on Advances in periental Structural ngineering th International Workshop on Advanced Sart Materials and Sart Structures Technology August -, 05, University of Illinois, Urbana-Chapaign,
6 th International Conference on Advances in periental Structural ngineering th International Workshop on Advanced Sart Materials and Sart Structures Technology August -, 05, University of Illinois, Urbana-Chapaign,
Optimal Modulation Index of the Mach-Zehnder Modulator in a Coherent Optical OFDM System Employing Digital Predistortion
 Optial Modulation Index of the Mach-Zehnder Modulator in a Coherent Optical OFDM yste Eploying Digital redistortion David Rörich, Xiaojie Wang, Michael Bernhard, Joachi peidel Universität tuttgart, Institut
Optial Modulation Index of the Mach-Zehnder Modulator in a Coherent Optical OFDM yste Eploying Digital redistortion David Rörich, Xiaojie Wang, Michael Bernhard, Joachi peidel Universität tuttgart, Institut
A New Localization and Tracking Algorithm for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Internet of Things
 Sensors & Transducers 203 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.co A New Localization and Tracking Algorith for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Internet of Things, 2 Zhang Feng, Xue Hui-Feng, 2 Zhang Yong-Heng,
Sensors & Transducers 203 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.co A New Localization and Tracking Algorith for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Internet of Things, 2 Zhang Feng, Xue Hui-Feng, 2 Zhang Yong-Heng,
Multi aperture coherent imaging IMAGE testbed
 Multi aperture coherent imaging IMAGE testbed Nick Miller, Joe Haus, Paul McManamon, and Dave Shemano University of Dayton LOCI Dayton OH 16 th CLRC Long Beach 20 June 2011 Aperture synthesis (part 1 of
Multi aperture coherent imaging IMAGE testbed Nick Miller, Joe Haus, Paul McManamon, and Dave Shemano University of Dayton LOCI Dayton OH 16 th CLRC Long Beach 20 June 2011 Aperture synthesis (part 1 of
POWER QUALITY ASSESSMENT USING TWO STAGE NONLINEAR ESTIMATION NUMERICAL ALGORITHM
 POWER QUALITY ASSESSENT USING TWO STAGE NONLINEAR ESTIATION NUERICAL ALGORITH Vladiir Terzia ABB Gerany vadiir.terzia@de.abb.co Vladiir Stanoevic EPS Yugoslavia vla_sta@hotail.co artin axiini ABB Gerany
POWER QUALITY ASSESSENT USING TWO STAGE NONLINEAR ESTIATION NUERICAL ALGORITH Vladiir Terzia ABB Gerany vadiir.terzia@de.abb.co Vladiir Stanoevic EPS Yugoslavia vla_sta@hotail.co artin axiini ABB Gerany
Model Development for the Wideband Vehicle-to-vehicle 2.4 GHz Channel
 Model Developent for the Wideband Vehicle-to-vehicle.4 GHz Channel Guillero Acosta and Mary Ann Ingra School of ECE, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA 333-5, USA gte437k@ail.gatech.edu, ai@ece.gatech.edu
Model Developent for the Wideband Vehicle-to-vehicle.4 GHz Channel Guillero Acosta and Mary Ann Ingra School of ECE, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA 333-5, USA gte437k@ail.gatech.edu, ai@ece.gatech.edu
A Novel NLOS Mitigation Approach for Wireless Positioning System
 2 3rd International Conference on Coputer and Electrical Engineering (ICCEE 2) IPCSIT vol. 53 (22) (22) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI:.7763/IPCSIT.22.V53.No..54 A Novel NLOS Mitigation Approach for Wireless
2 3rd International Conference on Coputer and Electrical Engineering (ICCEE 2) IPCSIT vol. 53 (22) (22) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI:.7763/IPCSIT.22.V53.No..54 A Novel NLOS Mitigation Approach for Wireless
Exploring the Electron Tunneling Behavior of Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) tip and n-type Semiconductor
 Page 110 Exploring the of Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) tip and n-type Seiconductor M. A. Rahan * and J. U. Ahed Departent of Applied Physics, Electronics & Counication Engineering, University of
Page 110 Exploring the of Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) tip and n-type Seiconductor M. A. Rahan * and J. U. Ahed Departent of Applied Physics, Electronics & Counication Engineering, University of
Calculation and Comparison of Turbulence Attenuation by Different Methods
 16 L. DORDOVÁ, O. WILFERT, CALCULATION AND COMPARISON OF TURBULENCE ATTENUATION BY DIFFERENT METHODS Calculation and Comparison of Turbulence Attenuation by Different Methods Lucie DORDOVÁ 1, Otakar WILFERT
16 L. DORDOVÁ, O. WILFERT, CALCULATION AND COMPARISON OF TURBULENCE ATTENUATION BY DIFFERENT METHODS Calculation and Comparison of Turbulence Attenuation by Different Methods Lucie DORDOVÁ 1, Otakar WILFERT
OUT OF PLANE STRENGTH OF INFILL PANELS
 October 1-17, 008, Beijing, China OUT OF PLANE STRENGTH OF INFILL PANELS M. Mohaadi Ghaziahalleh 1 1 Professor Assistant,Structural Research center, International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and
October 1-17, 008, Beijing, China OUT OF PLANE STRENGTH OF INFILL PANELS M. Mohaadi Ghaziahalleh 1 1 Professor Assistant,Structural Research center, International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and
Intermediate-Node Initiated Reservation (IIR): A New Signaling Scheme for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion
 Interediate-Node Initiated Reservation IIR): A New Signaling Schee for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion Kejie Lu, Jason P. Jue, Tiucin Ozugur, Gaoxi Xiao, and Irich Chlatac The Center
Interediate-Node Initiated Reservation IIR): A New Signaling Schee for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion Kejie Lu, Jason P. Jue, Tiucin Ozugur, Gaoxi Xiao, and Irich Chlatac The Center
Clean Data Training Approach to Active Sonar Classification
 Clean Data Training Approach to Active Sonar Classiication Alexei Kouzoubov (1), Binh Nguyen (1), Shane Wood (1) and Chris Gillard (1) (1) Deence Science and Technology Organisation, Edinburgh, SA, Australia
Clean Data Training Approach to Active Sonar Classiication Alexei Kouzoubov (1), Binh Nguyen (1), Shane Wood (1) and Chris Gillard (1) (1) Deence Science and Technology Organisation, Edinburgh, SA, Australia
NINTH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON SOUND AND VIBRATION, ICSV9 PASSIVE CONTROL OF LAUNCH NOISE IN ROCKET PAYLOAD BAYS
 first nae & faily nae: Rick Morgans Page nuber: 1 NINTH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON SOUND AND VIBRATION, ICSV9 PASSIVE CONTROL OF LAUNCH NOISE IN ROCKET PAYLOAD BAYS Rick Morgans, Ben Cazzolato, Anthony
first nae & faily nae: Rick Morgans Page nuber: 1 NINTH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON SOUND AND VIBRATION, ICSV9 PASSIVE CONTROL OF LAUNCH NOISE IN ROCKET PAYLOAD BAYS Rick Morgans, Ben Cazzolato, Anthony
An orthogonal multi-beam based MIMO scheme. for multi-user wireless systems
 An orthogonal ulti-bea based IO schee for ulti-user wireless systes Dong-chan Oh o and Yong-Hwan Lee School of Electrical Engineering and IC, Seoul ational University Kwana P.O. Box 34, Seoul, 151-600,
An orthogonal ulti-bea based IO schee for ulti-user wireless systes Dong-chan Oh o and Yong-Hwan Lee School of Electrical Engineering and IC, Seoul ational University Kwana P.O. Box 34, Seoul, 151-600,
Design and Experiments of Photon Counting Imaging Test Platform
 Design and Experients of Photon Counting Iaging Test Platfor Liju Yin School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Shandong University of Technology Zibo, China Qian Chen School of Electronic Eng. and
Design and Experients of Photon Counting Iaging Test Platfor Liju Yin School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Shandong University of Technology Zibo, China Qian Chen School of Electronic Eng. and
Impact of the Sternotomy Wires and Aortic Valve Implant on the On-Body UWB Radio Channels
 Ipact of the Sternotoy Wires and Aortic Valve Iplant on the On-Body UWB Radio Channels Mariella Särestöniei, Tio Kupuniei, Matti Hääläinen, Jari Iinatti Centre for Wireless Counications (CWC) University
Ipact of the Sternotoy Wires and Aortic Valve Iplant on the On-Body UWB Radio Channels Mariella Särestöniei, Tio Kupuniei, Matti Hääläinen, Jari Iinatti Centre for Wireless Counications (CWC) University
EXPERIMENTATION FOR ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL
 CHPTER - 6 EXPERIMENTTION FOR CTIVE VIBRTION CONTROL 6. INTRODUCTION The iportant issues in vibration control applications are odeling the sart structure with in-built sensing and actuation capabilities
CHPTER - 6 EXPERIMENTTION FOR CTIVE VIBRTION CONTROL 6. INTRODUCTION The iportant issues in vibration control applications are odeling the sart structure with in-built sensing and actuation capabilities
Additive Synthesis, Amplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation
 Additive Synthesis, Aplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation Pro Eduardo R Miranda Varèse-Gastproessor eduardo.iranda@btinternet.co Electronic Music Studio TU Berlin Institute o Counications Research
Additive Synthesis, Aplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation Pro Eduardo R Miranda Varèse-Gastproessor eduardo.iranda@btinternet.co Electronic Music Studio TU Berlin Institute o Counications Research
Robust Acceleration Control of Electrodynamic Shaker Using µ Synthesis
 Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, and the European Control Conference 5 Seville, Spain, Deceber -5, 5 WeIC8. Robust Acceleration Control of Electrodynaic Shaker Using µ Synthesis
Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, and the European Control Conference 5 Seville, Spain, Deceber -5, 5 WeIC8. Robust Acceleration Control of Electrodynaic Shaker Using µ Synthesis
EXPERIMENTAL VERIFICATION OF SINUSOIDAL APPROXIMATION IN ANALYSIS OF THREE-PHASE TWELVE-PULSE OUTPUT VOLTAGE TYPE RECTIFIERS
 th INTERNATIONAL SYPOSIU on POWER ELECTRONICS - Ee 9 XV eđunarodni sipoziju Energetska elektronika Ee 9 NOVI SAD, REPUBLIC OF SERBIA, October 8 th - th, 9 EXPERIENTAL VERIFICATION OF SINUSOIDAL APPROXIATION
th INTERNATIONAL SYPOSIU on POWER ELECTRONICS - Ee 9 XV eđunarodni sipoziju Energetska elektronika Ee 9 NOVI SAD, REPUBLIC OF SERBIA, October 8 th - th, 9 EXPERIENTAL VERIFICATION OF SINUSOIDAL APPROXIATION
On the field of view of a Galilean telescope
 Transactions of the Optical Society On the field of view of a Galilean telescope To cite this article: H A Hughes and P F Everitt 1920 Trans. Opt. Soc. 22 15 View the article online for updates and enhanceents.
Transactions of the Optical Society On the field of view of a Galilean telescope To cite this article: H A Hughes and P F Everitt 1920 Trans. Opt. Soc. 22 15 View the article online for updates and enhanceents.
Radar Imaging of Non-Uniformly Rotating Targets via a Novel Approach for Multi-Component AM-FM Signal Parameter Estimation
 Sensors 5, 5, 695-693; doi:.339/s53695 Article OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 44-8 www.dpi.co/journal/sensors Radar Iaging of Non-Uniforly Rotating Targets via a Novel Approach for Multi-Coponent AM-FM Signal
Sensors 5, 5, 695-693; doi:.339/s53695 Article OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 44-8 www.dpi.co/journal/sensors Radar Iaging of Non-Uniforly Rotating Targets via a Novel Approach for Multi-Coponent AM-FM Signal
The following tutorial will serve as an outline of the fundamental elements involved in the
 ACOUSTO-OPTICS TUTORIAL G. Ivtsenkov, Ph.D. & V. Pachkov, Ph.D. Light Manageent Group Inc. Research & Developent Burlington, Ontario, Canada INTRODUCTION THE ACOUSTO-OPTIC SWITCH PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS
ACOUSTO-OPTICS TUTORIAL G. Ivtsenkov, Ph.D. & V. Pachkov, Ph.D. Light Manageent Group Inc. Research & Developent Burlington, Ontario, Canada INTRODUCTION THE ACOUSTO-OPTIC SWITCH PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS
Indoor Multiple-Antenna Channel Characterization from 2 to 8 GHz
 Indoor Multiple-Antenna Channel Characterization fro to 8 GHz Ada S Y Poon and Minnie Ho Counications and Interconnect Lab, Intel Corporation Abstract In ultiple-antenna channels, e optiality of a transission
Indoor Multiple-Antenna Channel Characterization fro to 8 GHz Ada S Y Poon and Minnie Ho Counications and Interconnect Lab, Intel Corporation Abstract In ultiple-antenna channels, e optiality of a transission
This file is part of the following reference: Access to this file is available from:
 This file is part of the following reference: Page, Geoff (27) Mass Transport Evaluation using consolidated VHF Radar and Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler data. Masters (Research) thesis, Jaes Cook University.
This file is part of the following reference: Page, Geoff (27) Mass Transport Evaluation using consolidated VHF Radar and Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler data. Masters (Research) thesis, Jaes Cook University.
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, 2
 Subission International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP ) PARAMETRIC AND NON-PARAMETRIC SIGNAL ANALYSIS FOR MAPPING AIR FLOW IN THE EAR-CANALTO TONGUE MOVEMENT: A NEW STRATEGY
Subission International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP ) PARAMETRIC AND NON-PARAMETRIC SIGNAL ANALYSIS FOR MAPPING AIR FLOW IN THE EAR-CANALTO TONGUE MOVEMENT: A NEW STRATEGY
COMBINED FREQUENCY AND SPATIAL DOMAINS POWER DISTRIBUTION FOR MIMO-OFDM TRANSMISSION
 The 8th nnual IEEE International Syposiu on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Counications (PIMRC 07) COMINED FREQUENCY ND SPTIL DOMINS POWER DISTRIUTION FOR MIMO-OFDM TRNSMISSION Wladiir ocquet, Kazunori
The 8th nnual IEEE International Syposiu on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Counications (PIMRC 07) COMINED FREQUENCY ND SPTIL DOMINS POWER DISTRIUTION FOR MIMO-OFDM TRNSMISSION Wladiir ocquet, Kazunori
Track-Before-Detect for an Active Towed Array Sonar
 17-20 Noveber 2013, Victor Harbor, Australia Track-Before-Detect for an Active Towed Array Sonar Han X. Vu (1,2), Sauel J. Davey (1,2), Fiona K. Fletcher (1), Sanjeev Arulapala (1,2), Richard Elle (1)
17-20 Noveber 2013, Victor Harbor, Australia Track-Before-Detect for an Active Towed Array Sonar Han X. Vu (1,2), Sauel J. Davey (1,2), Fiona K. Fletcher (1), Sanjeev Arulapala (1,2), Richard Elle (1)
Performance Evaluation of UWB Sensor Network with Aloha Multiple Access Scheme
 1 Perforance Evaluation of UWB Sensor Network with Aloha Multiple Access Schee Roeo Giuliano 1 and Franco Mazzenga 2 1 RadioLabs Consorzio Università Industria, Via del Politecnico 1, 00133, Roe, Italy,
1 Perforance Evaluation of UWB Sensor Network with Aloha Multiple Access Schee Roeo Giuliano 1 and Franco Mazzenga 2 1 RadioLabs Consorzio Università Industria, Via del Politecnico 1, 00133, Roe, Italy,
Waveform Design and Receive Processing for Nonrecurrent Nonlinear FMCW Radar
 Wavefor Design and Receive Processing for Nonrecurrent Nonlinear FMCW Radar John Jakabosky and Shannon D. Blunt Radar Systes Lab University of Kansas Lawrence, KS Braha Hied Sensors Directorate Air Force
Wavefor Design and Receive Processing for Nonrecurrent Nonlinear FMCW Radar John Jakabosky and Shannon D. Blunt Radar Systes Lab University of Kansas Lawrence, KS Braha Hied Sensors Directorate Air Force
Overlapping Signal Separation in DPX Spectrum Based on EM Algorithm. Chuandang Liu 1, a, Luxi Lu 1, b
 nd International Worshop on Materials Engineering and Coputer Sciences (IWMECS 015) Overlapping Signal Separation in DPX Spectru Based on EM Algorith Chuandang Liu 1, a, Luxi Lu 1, b 1 National Key Laboratory
nd International Worshop on Materials Engineering and Coputer Sciences (IWMECS 015) Overlapping Signal Separation in DPX Spectru Based on EM Algorith Chuandang Liu 1, a, Luxi Lu 1, b 1 National Key Laboratory
Camera 2 Lens 4 Filters 7 Film Image Sensor 9 Flash Units 12 Film v. Digital 17 Equipment Selection Guidelines 21 SAMPLE. Resource List.
 Basic Evidence Photography Contents Table of Contents Equipent Considerations. 2 Caera 2 Lens 4 Filters 7 Fil Iage Sensor 9 Flash Units 12 Fil v. Digital 17 Equipent Selection Guidelines 21 Scene Photography
Basic Evidence Photography Contents Table of Contents Equipent Considerations. 2 Caera 2 Lens 4 Filters 7 Fil Iage Sensor 9 Flash Units 12 Fil v. Digital 17 Equipent Selection Guidelines 21 Scene Photography
Advances in Military Technology Vol. 7, No. 1, June Requirements for Control System of Mobile Free Space Optical Link
 AiMT Advances in Military Technology Vol. 7, No. 1, June 01 Requireents for Control Syste of Mobile Free Space Optical Link J. Čižár * and J. Něeček Departent of Aerospace Electrical Systes, University
AiMT Advances in Military Technology Vol. 7, No. 1, June 01 Requireents for Control Syste of Mobile Free Space Optical Link J. Čižár * and J. Něeček Departent of Aerospace Electrical Systes, University
Alternative Encoding Techniques for Digital Loudspeaker Arrays
 Alternative Encoding Techniques for Digital Loudspeaer Arrays Fotios Kontoichos, Nicolas Alexander Tatlas, and John Mourjopoulos Audio and Acoustic Technology Group, Wire Counications Laboratory, Electrical
Alternative Encoding Techniques for Digital Loudspeaer Arrays Fotios Kontoichos, Nicolas Alexander Tatlas, and John Mourjopoulos Audio and Acoustic Technology Group, Wire Counications Laboratory, Electrical
Binocular and Scope Performance 57. Diffraction Effects
 Binocular and Scope Performance 57 Diffraction Effects The resolving power of a perfect optical system is determined by diffraction that results from the wave nature of light. An infinitely distant point
Binocular and Scope Performance 57 Diffraction Effects The resolving power of a perfect optical system is determined by diffraction that results from the wave nature of light. An infinitely distant point
Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium Claims, Targets, and Standard Alignment for Math
 Sarter Balanced Assessent Consortiu Clais, s, Stard Alignent for Math The Sarter Balanced Assessent Consortiu (SBAC) has created a hierarchy coprised of clais targets that together can be used to ake stateents
Sarter Balanced Assessent Consortiu Clais, s, Stard Alignent for Math The Sarter Balanced Assessent Consortiu (SBAC) has created a hierarchy coprised of clais targets that together can be used to ake stateents
Compensated Single-Phase Rectifier
 Copensated Single-Phase Rectifier Jānis DoniĦš Riga Technical university jdonins@gail.co Abstract- Paper describes ethods of rectified DC pulsation reduction adding a ensation node to a single phase rectifier.
Copensated Single-Phase Rectifier Jānis DoniĦš Riga Technical university jdonins@gail.co Abstract- Paper describes ethods of rectified DC pulsation reduction adding a ensation node to a single phase rectifier.
APPLICATION OF THE FAN-CHIRP TRANSFORM TO HYBRID SINUSOIDAL+NOISE MODELING OF POLYPHONIC AUDIO
 6th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 8), Lausanne, Switzerland, August 5-9, 8, copyright by EURASIP APPLICATION OF THE FAN-CHIRP TRANSFORM TO HYBRID SINUSOIDAL+NOISE MODELING OF POLYPHONIC
6th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 8), Lausanne, Switzerland, August 5-9, 8, copyright by EURASIP APPLICATION OF THE FAN-CHIRP TRANSFORM TO HYBRID SINUSOIDAL+NOISE MODELING OF POLYPHONIC
A Hierarchical Likelihood Classifier With Applications to Remote Sensing
 1th WSEAS International Conference on COMMUICATIOS, Heralion, Greece, July 3-5, 8 A Hierarchical Lielihood Classifier With Applications to Reote Sensing E. A. YFATIS Iage Processing Laboratory School of
1th WSEAS International Conference on COMMUICATIOS, Heralion, Greece, July 3-5, 8 A Hierarchical Lielihood Classifier With Applications to Reote Sensing E. A. YFATIS Iage Processing Laboratory School of
Design of an Arrayed Waveguide Grating with flat spectral response
 Design of an Arrayed Waveguide Grating with flat spectral response Thoas Kaalakis, Thoas Sphicopoulos and Diitris Syvridis (Departent of Inforatics and Telecounications, University of Athens, Panepistiiopolis,
Design of an Arrayed Waveguide Grating with flat spectral response Thoas Kaalakis, Thoas Sphicopoulos and Diitris Syvridis (Departent of Inforatics and Telecounications, University of Athens, Panepistiiopolis,
Statistical Singing Voice Conversion based on Direct Waveform Modification with Global Variance
 INTERSPEECH 15 Statistical Singing Voice Conversion based on Direct Wavefor Modification with Global Variance Kazuhiro Kobayashi, Tooki Toda, Graha Neubig, Sakriani Sakti, Satoshi Nakaura Graduate School
INTERSPEECH 15 Statistical Singing Voice Conversion based on Direct Wavefor Modification with Global Variance Kazuhiro Kobayashi, Tooki Toda, Graha Neubig, Sakriani Sakti, Satoshi Nakaura Graduate School
Secondary-side-only Simultaneous Power and Efficiency Control in Dynamic Wireless Power Transfer System
 069060 Secondary-side-only Siultaneous Power and Efficiency Control in Dynaic Wireless Power Transfer Syste 6 Giorgio ovison ) Daita Kobayashi ) Takehiro Iura ) Yoichi Hori ) ) The University of Tokyo,
069060 Secondary-side-only Siultaneous Power and Efficiency Control in Dynaic Wireless Power Transfer Syste 6 Giorgio ovison ) Daita Kobayashi ) Takehiro Iura ) Yoichi Hori ) ) The University of Tokyo,
This is an author-deposited version published in: Eprints ID: 5737
 Open Archive Toulouse Archive Ouverte (OATAO) OATAO is an open access repository that collects the work of Toulouse researchers and akes it freely available over the web where possible. This is an author-deposited
Open Archive Toulouse Archive Ouverte (OATAO) OATAO is an open access repository that collects the work of Toulouse researchers and akes it freely available over the web where possible. This is an author-deposited
A HIGH POWER FACTOR THREE-PHASE RECTIFIER BASED ON ADAPTIVE CURRENT INJECTION APPLYING BUCK CONVERTER
 9th International onference on Power Electronics Motion ontrol - EPE-PEM Košice A HIGH POWER FATOR THREE-PHASE RETIFIER BASE ON AAPTIVE URRENT INJETION APPYING BUK ONVERTER Žarko Ja, Predrag Pejović EE
9th International onference on Power Electronics Motion ontrol - EPE-PEM Košice A HIGH POWER FATOR THREE-PHASE RETIFIER BASE ON AAPTIVE URRENT INJETION APPYING BUK ONVERTER Žarko Ja, Predrag Pejović EE
Spectrum Sensing in Low SNR: Diversity Combining and Cooperative Communications
 0 6th International Conference on Industrial and Inforation Systes, ICIIS 0, Aug. 6-9, 0, Sri Lanka Spectru Sensing in Low SR: Diversity Cobining and Cooperative Counications Saan Atapattu, Chintha Tellabura,
0 6th International Conference on Industrial and Inforation Systes, ICIIS 0, Aug. 6-9, 0, Sri Lanka Spectru Sensing in Low SR: Diversity Cobining and Cooperative Counications Saan Atapattu, Chintha Tellabura,
POCKET DEFORMABLE MIRROR FOR ADAPTIVE OPTICS APPLICATIONS
 POCKET DEFORMABLE MIRROR FOR ADAPTIVE OPTICS APPLICATIONS Leonid Beresnev1, Mikhail Vorontsov1,2 and Peter Wangsness3 1) US Army Research Laboratory, 2800 Powder Mill Road, Adelphi Maryland 20783, lberesnev@arl.army.mil,
POCKET DEFORMABLE MIRROR FOR ADAPTIVE OPTICS APPLICATIONS Leonid Beresnev1, Mikhail Vorontsov1,2 and Peter Wangsness3 1) US Army Research Laboratory, 2800 Powder Mill Road, Adelphi Maryland 20783, lberesnev@arl.army.mil,
Three Component Time-domain Electromagnetic Surveying: Modeling and Data Analysis
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL., NO., 75 Three Coponent Tie-doain Electroagnetic Surveying: Modeling and Data Analysis Chow-Son Chen 1, Wei-Hsuan Chiu 1, and Ching-Ren Lin 1 Institute of Geophysics, National Central
PIERS ONLINE, VOL., NO., 75 Three Coponent Tie-doain Electroagnetic Surveying: Modeling and Data Analysis Chow-Son Chen 1, Wei-Hsuan Chiu 1, and Ching-Ren Lin 1 Institute of Geophysics, National Central
Comparing structural airframe maintenance strategies based on probabilistic estimates of the remaining useful service life
 22 èe Congrès Français de Mécanique Lyon, 24 au 28 Août 2015 Coparing structural airfrae aintenance strategies based on probabilistic estiates of the reaining useful service life. WAG a, C.GOGU b,.biaud
22 èe Congrès Français de Mécanique Lyon, 24 au 28 Août 2015 Coparing structural airfrae aintenance strategies based on probabilistic estiates of the reaining useful service life. WAG a, C.GOGU b,.biaud
COMPARISON OF TOKEN HOLDING TIME STRATEGIES FOR A STATIC TOKEN PASSING BUS. M.E. Ulug
 COMPARISON OF TOKEN HOLDING TIME STRATEGIES FOR A STATIC TOKEN PASSING BUS M.E. Ulug General Electric Corporate Research and Developent Schenectady, New York 1245 ABSTRACT Waiting ties have been calculated
COMPARISON OF TOKEN HOLDING TIME STRATEGIES FOR A STATIC TOKEN PASSING BUS M.E. Ulug General Electric Corporate Research and Developent Schenectady, New York 1245 ABSTRACT Waiting ties have been calculated
Precise Indoor Localization System For a Mobile Robot Using Auto Calibration Algorithm
 Precise Indoor Localization Syste For a Mobile Robot Using Auto Calibration Algorith Sung-Bu Ki, JangMyung Lee, and I.O. Lee : Pusan National University, http://robotics.ee.pusan.ac.r, : Ninety syste Abstract:
Precise Indoor Localization Syste For a Mobile Robot Using Auto Calibration Algorith Sung-Bu Ki, JangMyung Lee, and I.O. Lee : Pusan National University, http://robotics.ee.pusan.ac.r, : Ninety syste Abstract:
Modeling and Parameter Identification of a DC Motor Using Constraint Optimization Technique
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volue 3, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov. - Dec. 206), PP 46-56 www.iosrjournals.org Modeling and Paraeter Identification
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volue 3, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov. - Dec. 206), PP 46-56 www.iosrjournals.org Modeling and Paraeter Identification
Optical Cavity Designs for Interferometric Gravitational Wave Detectors. Pablo Barriga 17 August 2009
 Optical Cavity Designs for Interferoetric Gravitational Wave Detectors Pablo Barriga 7 August 9 Assignents.- Assuing a cavity of 4k with an ITM of 934 radius of curvature and an ETM of 45 radius of curvature.
Optical Cavity Designs for Interferoetric Gravitational Wave Detectors Pablo Barriga 7 August 9 Assignents.- Assuing a cavity of 4k with an ITM of 934 radius of curvature and an ETM of 45 radius of curvature.
POD-001 PolaDetect. Operation Manual
 POD-001 PolaDetect In-line high speed polarieter Operation Manual August 31, 2005 General Photonics Corp. Ph: (909) 590-5473 5228 Edison Ave. Fax: (909) 902-5536 Chino, CA 91710 USA www.generalphotonics.co
POD-001 PolaDetect In-line high speed polarieter Operation Manual August 31, 2005 General Photonics Corp. Ph: (909) 590-5473 5228 Edison Ave. Fax: (909) 902-5536 Chino, CA 91710 USA www.generalphotonics.co
Relation between C/N Ratio and S/N Ratio
 Relation between C/N Ratio and S/N Ratio In our discussion in the past few lectures, we have coputed the C/N ratio of the received signals at different points of the satellite transission syste. The C/N
Relation between C/N Ratio and S/N Ratio In our discussion in the past few lectures, we have coputed the C/N ratio of the received signals at different points of the satellite transission syste. The C/N
Allocation of Multiple Services in Multi-Access Wireless Systems
 Allocation of Multiple Serices in Multi-Access Wireless Systes Anders Furuskär Wireless@KTH, Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden and Ericsson Research anders.furuskar@era.ericsson.se Abstract This paper
Allocation of Multiple Serices in Multi-Access Wireless Systes Anders Furuskär Wireless@KTH, Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden and Ericsson Research anders.furuskar@era.ericsson.se Abstract This paper
UNIT - II CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS (Line Commutated AC to DC converters) Line Commutated Converter
 UNIT - II CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS (Line Coutated AC to DC converters) INTRODUCTION TO CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS Controlled rectifiers are line coutated ac to power converters which are used to convert a fixed
UNIT - II CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS (Line Coutated AC to DC converters) INTRODUCTION TO CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS Controlled rectifiers are line coutated ac to power converters which are used to convert a fixed
Packet Loss and Delay Combined Optimization for Satellite Channel Bandwidth Allocation Controls
 Packet Loss and Delay obined Optiiation for Satellite hannel Bandwth Allocation ontrols Igor Bisio Meber, IEEE, Mario Marchese Senior Meber, IEEE DIST - Departent of ounication, oputer and Syste Science
Packet Loss and Delay obined Optiiation for Satellite hannel Bandwth Allocation ontrols Igor Bisio Meber, IEEE, Mario Marchese Senior Meber, IEEE DIST - Departent of ounication, oputer and Syste Science
International Journal of Advanced Research in Electronics and Communication Engineering (IJARECE) Volume 3, Issue 9, September 2014
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Electronics and Counication Engineering Volue 3, Issue 9, Septeber 2014 High Speed Error Detection and Data Recovery Architecture for Video Testing Applications
International Journal of Advanced Research in Electronics and Counication Engineering Volue 3, Issue 9, Septeber 2014 High Speed Error Detection and Data Recovery Architecture for Video Testing Applications
NONLINEAR WAVELET PACKET DENOISING OF IMPULSIVE VIBRATION SIGNALS NIKOLAOS G. NIKOLAOU, IOANNIS A. ANTONIADIS
 NONLINEAR WAVELET PACKET DENOISING OF IMPULSIVE VIBRATION SIGNALS NIKOLAOS G. NIKOLAOU, IOANNIS A. ANTONIADIS Departent of Mechanical Engineering, Machine Design and Control Systes Section National Technical
NONLINEAR WAVELET PACKET DENOISING OF IMPULSIVE VIBRATION SIGNALS NIKOLAOS G. NIKOLAOU, IOANNIS A. ANTONIADIS Departent of Mechanical Engineering, Machine Design and Control Systes Section National Technical
