An All-Optical Gain-Controlled Amplifier for Bidirectional Transmission
|
|
|
- Bartholomew Benson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 An All-Optical Gain-Controlled Amplifier for Bidirectional Transmission Bo-Hun Choi, Kyung-Jin Hong, Chang-Bong Kim, and Yong Hyub Won A novel all-optical gain-controlled (AOGC) bidirectional amplifier is proposed and demonstrated in a compact structure. The AOGC function using fiber Bragg grating (FBG) pairs controls both directional signals independently, and combinations of optical interleavers and isolators suppress Rayleigh backscattering (RB) noise. The amplifier achieves high and constant gain with a wide dynamic input signal range and low noise figure. The performance does not depend on the input signal conditions, whether static-state or transient signals, or whether there is symmetric or asymmetric data traffic on bidirectional transmission. Transmission comparison experiments between invariable symmetrical and random variable asymmetric bidirectional data traffic verify that the all-optical gain control and bidirectional amplification functions are successfully combined into this proposed amplifier. Keywords: Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers, gain, optical fiber communication, wavelength-division multiplexing. Manuscript received May 25, 2005; revised Sept. 12, This work was supported in part by the Korea Ministry of Information and Communications, and the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) through the Optical Internet Research Center (OIRC) Project. Bo-Hun Choi (phone: , adamchoi@gwangju.ac.kr) and Kyung-Jin Hong ( tronichkj@gwangju.ac.kr) are with Division of Optical Communications and Electronic Engineering, College of Engineering, Gwangju University, Gwangju, Korea. Chang-Bong Kim ( aggie@kongju.ac.kr) is with Division of Information and Communication Engineering, Kongju National University, Chungnam, Korea. Yong Hyub Won ( yhwon@icu.ac.kr) is with School of Engineering, Information and Communications University, Daejeon, Korea. I. Introduction A bidirectional amplifier has been intensively studied to be applied to wavelength-interleaved bi-directional transmission, which can reduce not only nonlinear effects between adjacent channels, but also implementation cost by sharing one fiber for two transmission directions. One issue with a bidirectional amplifier is how to treat Rayleigh backscattering (RB) caused by the signal reflection [1], [3]. Normally the RB power is low, around -34 db, but it rapidly increases when a bidirectional amplifier is used, so the power difference between an RB light and its parallel propagating signal decreases, as depicted in Fig. 1. Figures 1 and 1 show the RB generation in wavelengthinterleaved bidirectional transmission, and the cross talk (around 14 db) between a signal and RB noise in an optical spectrum, respectively. In order to solve this RB problem, several amplifiers have been proposed using a non-reciprocal optical filter [4], an arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) [5], a Mach- Zehnder wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) coupler [6], [7], a circulator [8], [9], two independent unidirectional amplifiers [10], [11], and an optical band pass filter [12]. The second issue is how to control both direction signal gains independently. It is common that signal inputs launched into both directions are asymmetric in optical bidirectional transmission systems. This asymmetry comes from the difference of channel numbers, the difference of channel powers, and the difference of transmission distances on both signal propagating directions. This is depicted in Fig. 2. An all-optical gain control (AOGC) method has the potential to manage this issue. However, to date it has been applied mainly to unidirectional transmission and has not been used on wavelength-interleaved bi-directional transmission [13]-[18]. Furthermore, these two issues mentioned above have not been studied together. ETRI Journal, Volume 28, Number 1, February 2006 Bo-Hun Choi et al. 1
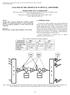
2 Output power (db) Downside signals A propagating signal toward one direction Crosstalk: ~-15 db Upside signals Rayleigh backscattering Wavelength The RB of propagating signals toward another direction Fig. 1. A schematic of RB generation with a bidirectional amplifier and channel crosstalk of interleaved bidirectional WDM signals due to RB noise. λ 2 λ n High power Short distance Small power Fig. 2. Channel number asymmetry and distance asymmetry between both sides of a bidirectional amplifier that can generally happen. Long distance In this paper, a novel structure for an asymmetrically bidirectional amplifier is proposed, which is composed of a twostaged erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) with AOGC function and an optical interleaving module in a compact structure. By combining two functions, RB noise removal and bidirectional AOGC, the structure can accommodate additional modules for functions such as dispersion compensation, channel add/drop, and so on, while asymmetrically treating bi-directional signals without degradation of the amplifier performance. Also, the structure completely blocks lasing signals used for AOGC from propagating beyond the amplifier without needing additional devices. The amplifier has been optimized for high performance criteria such as high gain and low noise figure. The performance is investigated for static and transient input signals. The gain dynamics under asymmetric traffic are examined. Finally, this amplifier is applied to transmission experiments using randomly variable asymmetric bidirectional data traffic. The output spectrum and bit error rate (BER) measurement verify the successful removal of RB light and no gain change due to channel number variation. II. Experiments The experimental setup, as shown in Fig. 3, is composed of an interleaving module and two EDFAs, EDFA-A and EDFA-B, with only one shared 980 nm pump laser diode (LD). Figure 3 explains the simplified schematic, in which EDFA-A and EDFA-B themselves are bidirectional amplifiers, and an interleaving module is located between them. The cascaded amplification structure gives a high gain and wider dynamic gain range together, and the interleaving module has a role to reduce RB noise. Each EDF in the two EDFA modules is 16 m long with an absorption coefficient of 7.6 db/m at 1530 nm, the length being optimized for gain. Odd and even WDM channels come from the A and B sides, respectively. Each direction signal experiences the first EDFA as a preamplifier, and proceeds into a different path consisting of an isolator and an attenuator through an optical interleaver of 100 GHz channel spacing, 2 db insertion loss, and ±15 ps/nm intra-channel dispersion. At the other interleaver, the signal is fed into a shared transmission line again, and is post-amplified by the other EDFA. Each EDFA has a lasing cavity composed of a 9:1 splitter, an attenuator, and a fiber Bragg grating (FBG) pair for an AOGC function. This structure gives the amplifier a low noise figure (NF) for preamplification and high NF for post-amplification, simultaneously [13]. So the overall NF of the amplifier becomes low. It is necessary to block the lasing optical fields from propagating outside the cavities and disturbing other EDFAs. Thus, the lasing wavelengths were chosen differently from input signal wavelengths between even and odd numbers. The reflecting wavelengths of the FBGs in EDFA-A and EDFA-B are nm (even channel) and nm (odd channel), respectively, and their insertion losses are under 0.3 db. Therefore, as shown in Fig. 4, the lasing light toward the other EDFA experiences a different path from the signals through an 2 Bo-Hun Choi et al. ETRI Journal, Volume 28, Number 1, February 2006
3 A EDF Odd channels WDM 9:1 IL MOD-O ISO IL 9:1 EDF WDM B Even channels Even FBG ATT Even FBG MOD-E ISO ATT Odd FBG Odd FBG 3 db 980 nm pump AOGC EDFA-A Interleaving module AOGC EDFA-B Fig. 3. The experimental setup and simplified schematic of the proposed amplifier. FBG: fiber Bragg grating, IL: optical interleaver, ISO: isolator, ATT: optical attenuator, EDF: erbium-doped fiber. Odd channels Even FBG AOGC EDFA module WDM EDF 980 nm pump Even FBG Fig. 4. A lasing optical field has a different path from signal fields through an optical interleaver, and is blocked by an isolator. Used FBGs have 99.9 % reflectivity. 9:1 IL Odd channels Even channels A lasing light path A signal path interleaver and is blocked by an isolator. The lasing light toward an input port of the amplifier was rejected by an FBG with 99.9 % reflectivity. Additionally, in order not to permit even tiny power reflection at optical fiber connectors, connection points were fusion-spliced if possible, and angled physical contact connectors were used if connectors were needed in this setup. III. Results 1. The Amplifier Module Characteristics The measured gains and NFs of the proposed amplifier are shown in Fig. 5 together with those of two EDFAs inside the amplifier. The gain of the EDFAs in Fig. 5 was clamped to 16 db at 1555 nm as a preamplifier by controlling the lasing condition on the inside of the cavities with 70 mw optical pump power. It was kept constant up to 0 dbm input power within a 0.6 db excursion. This dynamic range has a trade-off relation with constant gain level. The pre-amplified signal by one EDFA was attenuated by 10 db and fed to the post-amplifier. This attenuation value was composed of 4.5 db from two interleavers and an isolator, and 5.5 db from MOD-E or MOD-O shown in Fig. 3. Optical attenuators were used to emulate these MOD-E and MOD-O, which correspond to additional modules including an add/drop module or a dispersion compensation fiber (DCF) module to be able to asymmetrically treat bidirectional signals. The net gain of the overall amplifier is 22.5 db, identically for both directions, and the input signal dynamic range with 1 db gain excursion is up to -6 dbm as shown in Fig. 3. The worst NF is 6.8 db within the dynamic range. These values were measured at a 1555 nm signal wavelength with a single tone. It is believed that this NF is close to the optimized value, considering the influence of AOGC and bidirectional amplification to NF [9], [13], and [14]. This low NF results from the use of the selected lasing structure and the interleavers to suppress amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) between the two EDFAs. These results indicate that this bi-directional amplifier has high and constant gain with a wide dynamic rage of input signal and low noise figure in the simplified structure compared to the previous results [13], [14], and [17]. Moreover, add/drop or DCF modules, etc, can be merged into this amplifier without the present performance degradation. ETRI Journal, Volume 28, Number 1, February 2006 Bo-Hun Choi et al. 3
4 Gain & NF (db) Gain & NF (db) Dynamic range at 1 db gain excursion Gain NF Gain Dynamic range at 1 db gain excursion N B-to-A direction A-to-B direction Input power (dbm) EDFA-A EDFA-B Input power (dbm) Fig. 5. The measured gain and NF of EDFA-A and EDFA-B and the overall amplifier at input power between -30 and 0 dbm. Case I : Symmetry Case II : Asymmetry-1 λ 2 λ n/2 λ 2 λ n... λ n/2+1 λ n/2+2 λ n The gain variation according to three different signal inputs was investigated to consider asymmetric data traffic, as shown in Fig. 6. The table in Fig. 6 presents the input signal conditions, in which λ is a measured signal and the number n means the total used signal number. In the experiment, the single channel power was -25 dbm, and the powers of two saturation tones (ST) to replace a number of WDM signals were varied according to a required total channel number between 2 and 64. For symmetric data traffic (Case I), the sum power of a measured signal ( nm) and ST (ST-1, nm) on one side was identical to another ST (ST-2, nm) on the other side. For extremely asymmetric traffic, all channels have the same direction (Case II), or all channels have the opposite direction (Case III) except for one measured channel. The resultant gain deviations are around 0.3 db for three different cases at -7 dbm input power of 64 channels, and are not affected by the asymmetry of the input signals. If these amplifiers are cascaded for long distance transmission, this gain deviation value will be one of the important system specifications because the worst accumulated gain deviation at the final destination is proportional to the value and the number of the amplifiers to be passed [15]. The transient response of the result in Fig. 6 was measured, and is shown in Fig. 7. For the worst case scenario, 63 of 64 WDM channels were added and dropped at 1 khz frequency by using direct modulation, as shown in the downside of Fig. 7. The maximum gain variation is 0.4 db to include an overshoot and undershoot of less than 0.1 db. It is not different from the steady-state gain variation experiments in Figs. 5 and 6. The relaxation oscillation frequencies are 58 and 75 khz on signal addition and drop, respectively [16], [18]. The consistent result explains that the gain in steady-state and transient response is satisfactorily controlled by AOGC. Thus, this amplifier is able to be used on bidirectional transmission not only to have asymmetric transmission distances, but also to use asymmetric Gain deviation (db) Case III : Asymmetry-2 λ 2 λ 3. λ n Symmetry Asymmetry-1 Asymmetry-2 Output power variation (db) db 64 Input channel number The number of input channels Fig. 6. The gain deviation according to three different signal inputs in symmetric or asymmetric (asymmetry-1 and asymmetry-2) data traffic Time (ms) Fig. 7. The transient response of the output power of the surviving channel when 63 of 64 WDM channels were added and dropped with 1 khz frequency. 4 Bo-Hun Choi et al. ETRI Journal, Volume 28, Number 1, February 2006
5 signal powers, as explained in Fig The Amplifier Application on Bidirectional Transmission This amplifier was applied to bidirectional transmission experiments for the output spectrum and BER measurement. The experimental setup was presented in Fig. 8. Six odd channels between and nm, and six even channels between and nm with 100 GHz channel spacing were launched from both sides into this amplifier placed in the middle of two 26.4 km single mode fiber (SMF) spools. 10 Gb/s NRZ data was generated at each channel using a Mach-Zehnder modulator and pseudo random bit sequence (PRBS). After they were transmitted through another 26.4 km SMF followed by DCF, the signals were measured. The transmission length was long enough for the RB light to be induced nm nm nm nm nm nm nm nm nm nm nm nm MOD 10 Gb/s The proposed amplifier 10 Gb/s MOD EDFA EDFA 26.4 km SMF 26.4 km SMF 26.4 km SMF DCF Fig. 8. The transmission experiment setup. MOD: modulator, PM: power meter, SMF: single mode fiber, DCF: dispersion compensation fiber. The optical spectra were measured after the transmission, and the results are given in Fig. 9. Figures 9 and 9 show the signal output spectra for odd and even channels, respectively, at both sides. In each direction, two different cases were measured and compared between a case where all twelve channels were turned on (the dashed blue line) and a case where all channels except for one were turned off (the solid red line). The results showed a constant gain whether the channel number is twelve or one, and this WMD signal experiment was Rx consistent with the results of Fig. 5 and 6 using saturation tones. The small signals seen between high power signals are the RB of the optical signal propagating in the opposite direction. The RB level was well suppressed down to the ASE level of the EDFA, and the results on both directions were identical. The crosstalk between adjacent bidirectional channels is around -30 db. This means that our design using optical interleavers and isolators rejects RB lights effectively. Figures 9(c) and 9(d) show measured spectra at around the lasing light wavelength for both sides. A tiny mark is shown at the wavelength used as a lasing light. These spectra indicate that lasing lights used for an AOGC function were successfully isolated inside each EDFA. The BER measurement is shown in Fig. 10. Three channels were measured among six channels for each direction on symmetric bidirectional transmission. There are no error floors among the channels. The power penalty is below 0.5 db at 10-9 error probability. The power penalty is considered to be within measurement error range, when taking into account that a back-to-back BER was measured directly from the source to the receiver without transmission line. Optical power (db) Optical power (db) Odd channels 12 channel input 1 channel survival out of 12 Fig. 9. The measured optical spectra for odd and even signal channels after transmission. The dashed line is for the case where all twelve channels were turned on, and the solid line is for the case where all channels were turned off except one channel. (c) and (d) show the optical spectra of even channel and odd channel output ports, respectively, at around lasing light wavelengths Even channels RB lights from even channels Wavelength (nm) Wavelength (nm) Removed lasing light -20 Removed lasing light Wavelength (nm) Wavelength (nm) (c) (d) 3. Amplifier Application on Asymmetric Bidirectional Transmission with Random Variable Data Traffic If burst mode signal traffic is considered on the transmission, the amplifier is required to be applied not only to fixed asymmetric traffic, but also to randomly variable asymmetric data traffic. The setup and experimental conditions in Fig. 8 ETRI Journal, Volume 28, Number 1, February 2006 Bo-Hun Choi et al. 5
6 were used for this purpose. Additionally, five channels among all six channels were independently turned on and off at a low frequency modulation speed, as shown in Fig. 11, while all channels were modulated at 10 Gb/s. To make the random variable bidirectional data traffic, one traffic form among various forms of traffic was arbitrarily chosen as a general traffic pattern, as shown in Fig. 11. This traffic pattern is a random mixture of six different power levels according to the surviving channel number between one and six. The highest power means all six channels are turned on at both directions and the lowest power means only one channel is turned on. The BERs of a channel of no low-frequency modulation were measured while the traffic pattern from the other channels was periodically repeated with frequencies (f c ) between 200 Hz, 500 Hz, 1 khz, and 75 khz. Thus, the input power into the amplifier was changed to between -18 and -10 dbm. log (bit error rate) Odd back-to-back nm nm nm Even back-to-back nm nm nm Received power (dbm) Fig. 10. Bit error measurement for three odd and three even channels on 80 km SMF symmetric bidirectional transmission nm nm nm 10 Gb/s MOD Total input power Low frequency modulation Bidirectional amplifier 1/f c 2/f c Time 10 Gb/s MOD nm nm nm Fig. 11. A schematic of BER measurement experiments for random variable asymmetric bidirectional data traffic. Five channels among all six channels were independently turned on and off at a low frequency modulation speed, and a random mixture pattern of six different power levels was made. The result is given in Fig. 12. The back-to-back BER was measured by the surviving channel after the transmission without the other signals. There were no signal degradations except for a 1 db power penalty at 10-9 error probability, even at the relaxation frequency of this bi-directional amplifier, 75 khz, which was measured in Fig. 7. This penalty came from the remaining gain fluctuation after the usage of AOGC. The results show that the amplifier keeps its performance unchanged in a dynamic data traffic change of bi-directional transmission. log (error probability) BTB. f c = 200 Hz 500 Hz. 1 khz 75 khz Received power (dbm) Fig. 12. The BERs of a surviving channel were measured while the random data traffic composed of six 10 Gb/s WDM channels was repeated with the frequency (f c ) between 200 Hz, 500 Hz, 1 khz, and 75 khz. BTB: back-toback BER. IV. Conclusion A bidirectional amplifier with both an AOGC function and RB suppression was proposed and demonstrated in a simplified structure. It was composed of two EDFAs, which have lasing cavities using FBG pairs for AOGC, and a combination of optical interleavers and isolators to reduce RB noise. The amplifier achieved a high and constant gain of 22 db with a 0.3 db gain excursion up to -6 dbm input power. The worst NF was 6.8 db even though AOGC and a two-stage amplification configuration were used together. The gain value was stably maintained under serious asymmetric bidirectional input signal variations from one to 64 channels, and there was no difference between the static and transient responses of the gain. The amplifier structure satisfactorily removed RB light to -30 db and simultaneously confined lasing lights of AOGC in each EDFA. Transmission experiments for invariable symmetrical traffic and randomly variable asymmetric data traffic showed no signal degradation except at best 0.5 db and 1 db power penalties, respectively, at 10-9 error probability. 6 Bo-Hun Choi et al. ETRI Journal, Volume 28, Number 1, February 2006
7 Acknowledgement I wish to thank the Photonics Research Laboratory, in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Australia, for their help. References [1] R.K. Staubli and P. Gysel, Crosstalk Penalties Due to Coherent Rayleigh Noise in Bidirectional Optical Communication Systems, IEEE J. Lightwave Technology, vol. 9, no. 3, 1991, pp [2] Bo-Hun Choi, Moo-Jung Chu, Hyo-Hoon Park, and Jong-Hyun Lee, Performances of Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier Using 1530nm-Band Pump for Long Wavelength Multichannel Amplification, ETRI J., vol. 23, no. 1, 2001, pp [3] W.J. Chung, H.S. Seo, B.J. Park, J.T. Ahn, and Y.G. Choi, Selenide Glass Optical Fiber Doped with Pr 35 for U-Band Optical Amplifier, ETRI J., vol. 27, no. 4, Aug. 2005, pp [4] T.-W. Oh, J.-H. Shin, H.D. Kim, C.-H. Lee, M.S. Lee, and B.Y. Kim, Bidirectional Erbium-Doped Fibre Amplifier with Nonreciprocal Optical Filter, Electron. Lett., vol. 37, no. 5, 2001, pp [5] J.-W. Park and C.-H. Lee, Wavelength Interleaved Bidirectional Add/Drop Amplifier Module, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., vol. 12, no. 2, 2000, pp [6] M. Sumida, H. Maeda, and Y. Tada, Asymmetric Bi-directional WDM Transmission of 8 (total) 10 Gbit/s Channels Using Bidirectional Amplifier Comprising Single Unidirectional Optical Amplifier and Four-port Mach-Zehnder WDM Coupler, Electron. Lett., vol. 36, no. 20, 2000, pp [7] M. Sumida, H. Maeda, and T. Imai, Ten-repeatered Bi-directional WDM Transmission of Eight Channels at 10 Gbit/s Using Singlewavelength Band-operating Bi-directional Amplifiers, Electron. Lett., vol. 37, no. 13, 2001, pp [8] C.W. Barnard, J. Chrostowski, and M. Kavehrad, Bidirectional Fiber Amplifiers, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., vol. 4, no. 8, 1992, pp [9] H.D. Kim, J. H. Shin, S. T. Hwang, Y.J. Oh, and C. H. Lee, Bidirectional Amplifier Employing the Bidirectional Dispersion Compensation Technique, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., vol. 13, 2001, pp [10] K.-I. Suzuki, H. Masuda, S. Kawai, K. Aida, and K. Nakagawa, Bidirectional IO-channel 2.5 Gbit/s WDM Transmission over 250 km Using 76 nm ( nm) Gain-band Bidirectional Erbium-doped Fibre Amplifiers, Electron. Lett., vol. 33, no. 23, 1997, pp [11] J. Kani, M. Jinno, T. Sakamoto, K. Hattori, and K. Oguchi, Bidirectional Transmission to Suppress Interwavelength-Band Nonlinear Interactions in Ultrawide-Band WDM Transmission Systems, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., vol. 11, no. 3, 1999, pp [12] F. Khaleghi, J. Li, M. Kavehrad, and H. Kim, Increasing Repeater Span in High-speed Bidirectional WDM Transmission Systems Using a New Bidirectional EDFA Configuration, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., vol. 8, no. 9, 1996, pp [13] J. Chung, S.Y. Kim, and C.J. Chae, All-Optical Gain-Clamped EDFAs with Different Feedback Wavelengths for Use in Multiwavelength Optical Networks, Electron. Lett., vol. 32, no. 23, 1996, pp [14] J. Massicott, C. Lebre, R. Wyatt, R. Kashyap, D. Williams, and A. Yu, Low Noise, All-Optical Gain Controlled Er3+ Doped Fibre Amplifier Using Asymmetric Control Laser Cavity Design, Electron. Lett., vol. 32, no. 9, 1996, pp [15] D.H. Richards, J.L. Jackel, and M.A. Ali, A Theoretical Investigation of Dynamic All-Optical Automatic Gain Control in Multichannel EDFA s and EDFA Cascades, IEEE J., Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, vol. 3, no. 4, 1997, pp [16] B. Landousies, T. Georges, E. Delevaque, R. Lebref, and M. Monerie, Low Power Transient in Multichannel Equalized and Stabilized Gain Amplifier Using Passive Gain Control, Electron. Lett., vol. 32, no. 20, 1996, pp [17] C.H. Kim, S.B. Yoon, S.B. Lee, C. H. Lee, and Y.C. Chung, All- Optical Gain-Controlled Bidirectional Add-Drop Amplifier Using Fiber Bragg Gratings, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., vol. 12, 2000, pp [18] G. Luo, J.L. Zyskind, J.A. Nagel, and Mohamed A. Ali, Experimental and Theoretical Analysis of Relaxation- Oscillations and Spectral Hole Burning Effects in All-Optical Gain-Clamped EDFA s for WDM Networks, IEEE J. Lightwave Technology, vol. 16, no. 4, 1998, pp Bo-Hun Choi is a Lecturer in the Division of Optical Communications and Electronic Engineering, Gwangju University. He was born in Busan, Korea, on Nov. 5, He received the BS and MS degrees in physics from Pusan National University, Busan, Korea, in 1992 and He worked as an Engineer in the Photonics Device Lab, Hyundai Electronics from 1994 to He worked as an Assistant Manager in the Optical Communications R&D Group, Samsung Electronics from 1996 to He received the PhD degree in engineering from Information and Communications University (ICU) in He has worked as a Research Fellow in the Photonics Research Lab (PRL), Dept. of Electrical & Electronic Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. In PRL, he was involved in developing optical communication systems, bidirectional amplifiers, and modulation formats for ultra high speed transmission. His current research interests are in optical fiber amplifiers, WDM optical transmission systems, and optical Internet. ETRI Journal, Volume 28, Number 1, February 2006 Bo-Hun Choi et al. 7
8 Kyung-Jin Hong is a Lecturer in the Division of Optical Communications and Electronic Engineering, Gwangju University. He received the PhD degree in engineering from Chonnam National University in He has worked as a Research Fellow in the Inorganic Material Institute (IMI), Tsukuba, Japan. In IMI, he was involved in developing electrical devices. His current research interests are in fractal theory, thin film processing, and surface analysis. Chang-Bong Kim received the BS degree in electronics from Korea University, Seoul, Korea, in 1983, the MS degree in electrical engineering from Florida Institute of Technology, Melbourne, FL, USA, in 1988, and the PhD degree in electrical engineering from Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, in He joined Samsung Consumer Electronics, Suwon, Korea, in From 1992 to 1993, he was the Senior Researcher of the Audio Electronic Division, developing an optical pick-up for domestic products. His research interests are in optical fiber sensors, bidirectional optical amplifiers, and optical transmission systems. Currently he is a Professor in the Division of Information and Communication Engineering at Kongju National University. He is a Senior Member of IEEE. Yong Hyub Won is a Professor in ICU, Korea. He received the BS degree from University of Ulsan in 1978, the MS degree from Seoul National University in 1981, and the PhD degree from Cornell University, USA, in He worked as a Technical Staff Member and a Research Team Leader in Electronics and Telecommunication Research Institute (ETRI) from 1981 to In ETRI, he was involved in developing optical communication systems, optical logical devices, polymeric optical waveguide devices, and optical switching. His recent work in ICU has focused on optical CDMA, and optical packet/burst switching systems and devices. He has authored more than 150 journal or conference papers, holds 80 pending or registered patents, and has written 2 book chapters. His current research interests include optical packet/burst switching systems and networks, photonic sensors, and sensor networks. He has served as a member of Technical Program Committee in various international conferences including ECOC, OECC, COIN, Optics East and APOC. 8 Bo-Hun Choi et al. ETRI Journal, Volume 28, Number 1, February 2006
An Amplified WDM-PON Using Broadband Light Source Seeded Optical Sources and a Novel Bidirectional Reach Extender
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 15, No. 3, September 2011, pp. 222-226 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2011.15.3.222 An Amplified WDM-PON Using Broadband Light Source Seeded Optical Sources
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 15, No. 3, September 2011, pp. 222-226 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2011.15.3.222 An Amplified WDM-PON Using Broadband Light Source Seeded Optical Sources
S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique
 S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique Chien-Hung Yeh 1, *, Ming-Ching Lin 3, Ting-Tsan Huang 2, Kuei-Chu Hsu 2 Cheng-Hao Ko 2, and Sien Chi
S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique Chien-Hung Yeh 1, *, Ming-Ching Lin 3, Ting-Tsan Huang 2, Kuei-Chu Hsu 2 Cheng-Hao Ko 2, and Sien Chi
Gain-clamping techniques in two-stage double-pass L-band EDFA
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 66, No. 3 journal of March 2006 physics pp. 539 545 Gain-clamping techniques in two-stage double-pass L-band EDFA S W HARUN 1, N Md SAMSURI 2 and H AHMAD 2 1 Faculty
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 66, No. 3 journal of March 2006 physics pp. 539 545 Gain-clamping techniques in two-stage double-pass L-band EDFA S W HARUN 1, N Md SAMSURI 2 and H AHMAD 2 1 Faculty
Optical Fiber Technology
 Optical Fiber Technology 18 (2012) 29 33 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Optical Fiber Technology www.elsevier.com/locate/yofte A novel WDM passive optical network architecture supporting
Optical Fiber Technology 18 (2012) 29 33 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Optical Fiber Technology www.elsevier.com/locate/yofte A novel WDM passive optical network architecture supporting
Colorless Amplified WDM-PON Employing Broadband Light Source Seeded Optical Sources and Channel-by-Channel Dispersion Compensators for >100 km Reach
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 18, No. 5, October 014, pp. 46-441 ISSN: 16-4776(Print) / ISSN: 09-6885(Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.807/josk.014.18.5.46 Colorless Amplified WDM-PON Employing
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 18, No. 5, October 014, pp. 46-441 ISSN: 16-4776(Print) / ISSN: 09-6885(Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.807/josk.014.18.5.46 Colorless Amplified WDM-PON Employing
Downstream Transmission in a WDM-PON System Using a Multiwavelength SOA-Based Fiber Ring Laser Source
 JOURNAL OF L A TEX CLASS FILES, VOL. X, NO. XX, XXXX XXX 1 Downstream Transmission in a WDM-PON System Using a Multiwavelength SOA-Based Fiber Ring Laser Source Jérôme Vasseur, Jianjun Yu Senior Member,
JOURNAL OF L A TEX CLASS FILES, VOL. X, NO. XX, XXXX XXX 1 Downstream Transmission in a WDM-PON System Using a Multiwavelength SOA-Based Fiber Ring Laser Source Jérôme Vasseur, Jianjun Yu Senior Member,
Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion
 Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion M. A. Khayer Azad and M. S. Islam Institute of Information and Communication
Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion M. A. Khayer Azad and M. S. Islam Institute of Information and Communication
Optical fiber-fault surveillance for passive optical networks in S-band operation window
 Optical fiber-fault surveillance for passive optical networks in S-band operation window Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2,3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer and Communications Research Laboratories,
Optical fiber-fault surveillance for passive optical networks in S-band operation window Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2,3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer and Communications Research Laboratories,
Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor
 Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor P. S. Chan, C. Y. Chow, and H. K. Tsang Department of Electronic Engineering, The
Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor P. S. Chan, C. Y. Chow, and H. K. Tsang Department of Electronic Engineering, The
Gigabit Transmission in 60-GHz-Band Using Optical Frequency Up-Conversion by Semiconductor Optical Amplifier and Photodiode Configuration
 22 Gigabit Transmission in 60-GHz-Band Using Optical Frequency Up-Conversion by Semiconductor Optical Amplifier and Photodiode Configuration Jun-Hyuk Seo, and Woo-Young Choi Department of Electrical and
22 Gigabit Transmission in 60-GHz-Band Using Optical Frequency Up-Conversion by Semiconductor Optical Amplifier and Photodiode Configuration Jun-Hyuk Seo, and Woo-Young Choi Department of Electrical and
EDFA TRANSIENT REDUCTION USING POWER SHAPING
 Proceedings of the Eighth IASTED International Conference WIRELESS AND OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS (WOC 2008) May 26-28, 2008 Quebec City, Quebec, Canada EDFA TRANSIENT REDUCTION USING POWER SHAPING Trent Jackson
Proceedings of the Eighth IASTED International Conference WIRELESS AND OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS (WOC 2008) May 26-28, 2008 Quebec City, Quebec, Canada EDFA TRANSIENT REDUCTION USING POWER SHAPING Trent Jackson
Linear cavity erbium-doped fiber laser with over 100 nm tuning range
 Linear cavity erbium-doped fiber laser with over 100 nm tuning range Xinyong Dong, Nam Quoc Ngo *, and Ping Shum Network Technology Research Center, School of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Nanyang
Linear cavity erbium-doped fiber laser with over 100 nm tuning range Xinyong Dong, Nam Quoc Ngo *, and Ping Shum Network Technology Research Center, School of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Nanyang
from ocean to cloud SEAMLESS OADM FUNCTIONALITY FOR SUBMARINE BU
 SEAMLESS OADM FUNCTIONALITY FOR SUBMARINE BU Shigui Zhang, Yan Wang, Hongbo Sun, Wendou Zhang and Liping Ma sigurd.zhang@huaweimarine.com Huawei Marine Networks, Hai-Dian District, Beijing, P.R. China,
SEAMLESS OADM FUNCTIONALITY FOR SUBMARINE BU Shigui Zhang, Yan Wang, Hongbo Sun, Wendou Zhang and Liping Ma sigurd.zhang@huaweimarine.com Huawei Marine Networks, Hai-Dian District, Beijing, P.R. China,
Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber
 Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber H. Ahmad 1, S. Shahi 1 and S. W. Harun 1,2* 1 Photonics Research Center, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2 Department
Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber H. Ahmad 1, S. Shahi 1 and S. W. Harun 1,2* 1 Photonics Research Center, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2 Department
Optimisation of DSF and SOA based Phase Conjugators. by Incorporating Noise-Suppressing Fibre Gratings
 Optimisation of DSF and SOA based Phase Conjugators by Incorporating Noise-Suppressing Fibre Gratings Paper no: 1471 S. Y. Set, H. Geiger, R. I. Laming, M. J. Cole and L. Reekie Optoelectronics Research
Optimisation of DSF and SOA based Phase Conjugators by Incorporating Noise-Suppressing Fibre Gratings Paper no: 1471 S. Y. Set, H. Geiger, R. I. Laming, M. J. Cole and L. Reekie Optoelectronics Research
RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 25 33, 2009 RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, C.-H. Lee,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 25 33, 2009 RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, C.-H. Lee,
Optical phase-locked loop for coherent transmission over 500 km using heterodyne detection with fiber lasers
 Optical phase-locked loop for coherent transmission over 500 km using heterodyne detection with fiber lasers Keisuke Kasai a), Jumpei Hongo, Masato Yoshida, and Masataka Nakazawa Research Institute of
Optical phase-locked loop for coherent transmission over 500 km using heterodyne detection with fiber lasers Keisuke Kasai a), Jumpei Hongo, Masato Yoshida, and Masataka Nakazawa Research Institute of
Photonics (OPTI 510R 2017) - Final exam. (May 8, 10:30am-12:30pm, R307)
 Photonics (OPTI 510R 2017) - Final exam (May 8, 10:30am-12:30pm, R307) Problem 1: (30pts) You are tasked with building a high speed fiber communication link between San Francisco and Tokyo (Japan) which
Photonics (OPTI 510R 2017) - Final exam (May 8, 10:30am-12:30pm, R307) Problem 1: (30pts) You are tasked with building a high speed fiber communication link between San Francisco and Tokyo (Japan) which
Study of Multiwavelength Fiber Laser in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber
 Study of Multiwavelength Fiber Laser in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber I. H. M. Nadzar 1 and N. A.Awang 1* 1 Faculty of Science, Technology and Human Development, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Johor,
Study of Multiwavelength Fiber Laser in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber I. H. M. Nadzar 1 and N. A.Awang 1* 1 Faculty of Science, Technology and Human Development, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Johor,
Optical Fibre Amplifiers Continued
 1 Optical Fibre Amplifiers Continued Stavros Iezekiel Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Cyprus ECE 445 Lecture 09 Fall Semester 2016 2 ERBIUM-DOPED FIBRE AMPLIFIERS BASIC
1 Optical Fibre Amplifiers Continued Stavros Iezekiel Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Cyprus ECE 445 Lecture 09 Fall Semester 2016 2 ERBIUM-DOPED FIBRE AMPLIFIERS BASIC
Performance of optical automatic gain control EDFA with dual-oscillating control lasers
 Optics Communications 224 (2003) 281 287 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Performance of optical automatic gain control EDFA with dual-oscillating control lasers Chun-Liu Zhao a,b,c, *, Bai-Ou Guan a,b,
Optics Communications 224 (2003) 281 287 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Performance of optical automatic gain control EDFA with dual-oscillating control lasers Chun-Liu Zhao a,b,c, *, Bai-Ou Guan a,b,
Transient Control in Dynamically Reconfigured Networks with Cascaded Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers
 Transient Control in Dynamically Reconfigured Networks with Cascaded Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers Lei Zong, Ting Wang lanezong@nec-labs.com NEC Laboratories America, Princeton, New Jersey, USA WOCC 2007
Transient Control in Dynamically Reconfigured Networks with Cascaded Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers Lei Zong, Ting Wang lanezong@nec-labs.com NEC Laboratories America, Princeton, New Jersey, USA WOCC 2007
Wideband Rare-earth-doped Fiber Amplification Technologies Gain Bandwidth Expansion in the C and L bands
 Wideband Rare-earth-doped Fiber Amplification Technologies Gain Bandwidth Expansion in the C and L bands Tadashi Sakamoto, Atsushi Mori, Hiroji Masuda, and Hirotaka Ono Abstract We are expanding the gain
Wideband Rare-earth-doped Fiber Amplification Technologies Gain Bandwidth Expansion in the C and L bands Tadashi Sakamoto, Atsushi Mori, Hiroji Masuda, and Hirotaka Ono Abstract We are expanding the gain
CONTROLLABLE WAVELENGTH CHANNELS FOR MULTIWAVELENGTH BRILLOUIN BISMUTH/ERBIUM BAS-ED FIBER LASER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 9 18, 29 CONTROLLABLE WAVELENGTH CHANNELS FOR MULTIWAVELENGTH BRILLOUIN BISMUTH/ERBIUM BAS-ED FIBER LASER H. Ahmad, M. Z. Zulkifli, S. F. Norizan,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 9 18, 29 CONTROLLABLE WAVELENGTH CHANNELS FOR MULTIWAVELENGTH BRILLOUIN BISMUTH/ERBIUM BAS-ED FIBER LASER H. Ahmad, M. Z. Zulkifli, S. F. Norizan,
A WDM passive optical network enabling multicasting with color-free ONUs
 A WDM passive optical network enabling multicasting with color-free ONUs Yue Tian, Qingjiang Chang, and Yikai Su * State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department
A WDM passive optical network enabling multicasting with color-free ONUs Yue Tian, Qingjiang Chang, and Yikai Su * State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department
Dr. Monir Hossen ECE, KUET
 Dr. Monir Hossen ECE, KUET 1 Outlines of the Class Principles of WDM DWDM, CWDM, Bidirectional WDM Components of WDM AWG, filter Problems with WDM Four-wave mixing Stimulated Brillouin scattering WDM Network
Dr. Monir Hossen ECE, KUET 1 Outlines of the Class Principles of WDM DWDM, CWDM, Bidirectional WDM Components of WDM AWG, filter Problems with WDM Four-wave mixing Stimulated Brillouin scattering WDM Network
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4, 116, 12M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4, 116, 12M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors
Implementation of Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing FBG
 AUSTRALIAN JOURNAL OF BASIC AND APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN:1991-8178 EISSN: 2309-8414 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Implementation of Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Network with FBG 1 J. Sharmila
AUSTRALIAN JOURNAL OF BASIC AND APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN:1991-8178 EISSN: 2309-8414 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Implementation of Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Network with FBG 1 J. Sharmila
Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer Based on Fiber Bragg Gratings for Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Networks
 Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer Based on Fiber Bragg Gratings for Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Networks P. S. André 1, 2, A. Nolasco Pinto 1, 3, J. L. Pinto 1, 2, T. Almeida 1, 4 and M. Pousa 1,4
Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer Based on Fiber Bragg Gratings for Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Networks P. S. André 1, 2, A. Nolasco Pinto 1, 3, J. L. Pinto 1, 2, T. Almeida 1, 4 and M. Pousa 1,4
Evolution from TDM-PONs to Next-Generation PONs
 Evolution from TDM-PONs to Next-Generation PONs Ki-Man Choi, Jong-Hoon Lee, and Chang-Hee Lee Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology,
Evolution from TDM-PONs to Next-Generation PONs Ki-Man Choi, Jong-Hoon Lee, and Chang-Hee Lee Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology,
SEMICONDUCTOR lasers and amplifiers are important
 240 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 28, NO. 3, FEBRUARY 1, 2010 Temperature-Dependent Saturation Characteristics of Injection Seeded Fabry Pérot Laser Diodes/Reflective Optical Amplifiers Hongyun
240 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 28, NO. 3, FEBRUARY 1, 2010 Temperature-Dependent Saturation Characteristics of Injection Seeded Fabry Pérot Laser Diodes/Reflective Optical Amplifiers Hongyun
Power Transients in Hybrid Optical Amplifier (EDFA + DFRA) Cascades
 Power Transients in Hybrid Optical Amplifier (EDFA + DFRA) Cascades Bárbara Dumas and Ricardo Olivares Electronic Engineering Department Universidad Técnica Federico Santa María Valparaíso, Chile bpilar.dumas@gmail.com,
Power Transients in Hybrid Optical Amplifier (EDFA + DFRA) Cascades Bárbara Dumas and Ricardo Olivares Electronic Engineering Department Universidad Técnica Federico Santa María Valparaíso, Chile bpilar.dumas@gmail.com,
Bit error rate and cross talk performance in optical cross connect with wavelength converter
 Vol. 6, No. 3 / March 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 295 Bit error rate and cross talk performance in optical cross connect with wavelength converter M. S. Islam and S. P. Majumder Department of
Vol. 6, No. 3 / March 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 295 Bit error rate and cross talk performance in optical cross connect with wavelength converter M. S. Islam and S. P. Majumder Department of
Optical Amplifiers Photonics and Integrated Optics (ELEC-E3240) Zhipei Sun Photonics Group Department of Micro- and Nanosciences Aalto University
 Photonics Group Department of Micro- and Nanosciences Aalto University Optical Amplifiers Photonics and Integrated Optics (ELEC-E3240) Zhipei Sun Last Lecture Topics Course introduction Ray optics & optical
Photonics Group Department of Micro- and Nanosciences Aalto University Optical Amplifiers Photonics and Integrated Optics (ELEC-E3240) Zhipei Sun Last Lecture Topics Course introduction Ray optics & optical
BROAD-BAND rare-earth-doped fiber sources have been
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 15, NO. 8, AUGUST 1997 1587 Feedback Effects in Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier/Source for Open-Loop Fiber-Optic Gyroscope Hee Gap Park, Kyoung Ah Lim, Young-Jun Chin,
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 15, NO. 8, AUGUST 1997 1587 Feedback Effects in Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier/Source for Open-Loop Fiber-Optic Gyroscope Hee Gap Park, Kyoung Ah Lim, Young-Jun Chin,
Performance Evaluation of 32 Channel DWDM System Using Dispersion Compensation Unit at Different Bit Rates
 Performance Evaluation of 32 Channel DWDM System Using Dispersion Compensation Unit at Different Bit Rates Simarpreet Kaur Gill 1, Gurinder Kaur 2 1Mtech Student, ECE Department, Rayat- Bahra University,
Performance Evaluation of 32 Channel DWDM System Using Dispersion Compensation Unit at Different Bit Rates Simarpreet Kaur Gill 1, Gurinder Kaur 2 1Mtech Student, ECE Department, Rayat- Bahra University,
Long-distance fiber grating sensor system using a fiber ring laser with EDWA and SOA
 Optics Communications 252 (2005) 127 131 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Long-distance fiber grating sensor system using a fiber ring laser with EDWA and SOA Peng-Chun Peng a, *, Kai-Ming Feng b, Wei-Ren
Optics Communications 252 (2005) 127 131 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Long-distance fiber grating sensor system using a fiber ring laser with EDWA and SOA Peng-Chun Peng a, *, Kai-Ming Feng b, Wei-Ren
A Comparative Study of Techniques to Control Power Transients in Optical WDM Networks
 A Comparative Study of Techniques to Control Power Transients in Optical WDM Networks R. Olivares 1 and J. R. Souza 2 1 Departamento de Electrónica, Universidad Técnica Federico Santa María Casilla Postal
A Comparative Study of Techniques to Control Power Transients in Optical WDM Networks R. Olivares 1 and J. R. Souza 2 1 Departamento de Electrónica, Universidad Técnica Federico Santa María Casilla Postal
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF HIGH PERFORMANCE C AND L BAND ERBIUM DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIERS (C,L-EDFAs)
 DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF HIGH PERFORMANCE C AND L BAND ERBIUM DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIERS (C,L-EDFAs) Ahmet Altuncu Arif Başgümüş Burçin Uzunca Ekim Haznedaroğlu e-mail: altuncu@dumlupinar.edu.tr e-mail:
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF HIGH PERFORMANCE C AND L BAND ERBIUM DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIERS (C,L-EDFAs) Ahmet Altuncu Arif Başgümüş Burçin Uzunca Ekim Haznedaroğlu e-mail: altuncu@dumlupinar.edu.tr e-mail:
EDFA WDM Optical Network using GFF
 EDFA WDM Optical Network using GFF Shweta Bharti M. Tech, Digital Communication, (Govt. Women Engg. College, Ajmer), Rajasthan, India ABSTRACT This paper describes the model and simulation of EDFA WDM
EDFA WDM Optical Network using GFF Shweta Bharti M. Tech, Digital Communication, (Govt. Women Engg. College, Ajmer), Rajasthan, India ABSTRACT This paper describes the model and simulation of EDFA WDM
Setup of the four-wavelength Doppler lidar system with feedback controlled pulse shaping
 Setup of the four-wavelength Doppler lidar system with feedback controlled pulse shaping Albert Töws and Alfred Kurtz Cologne University of Applied Sciences Steinmüllerallee 1, 51643 Gummersbach, Germany
Setup of the four-wavelength Doppler lidar system with feedback controlled pulse shaping Albert Töws and Alfred Kurtz Cologne University of Applied Sciences Steinmüllerallee 1, 51643 Gummersbach, Germany
Stable dual-wavelength oscillation of an erbium-doped fiber ring laser at room temperature
 Stable dual-wavelength oscillation of an erbium-doped fiber ring laser at room temperature Donghui Zhao.a, Xuewen Shu b, Wei Zhang b, Yicheng Lai a, Lin Zhang a, Ian Bennion a a Photonics Research Group,
Stable dual-wavelength oscillation of an erbium-doped fiber ring laser at room temperature Donghui Zhao.a, Xuewen Shu b, Wei Zhang b, Yicheng Lai a, Lin Zhang a, Ian Bennion a a Photonics Research Group,
A novel 3-stage structure for a low-noise, high-gain and gain-flattened L-band erbium doped fiber amplifier *
 Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE ISSN 9-9 http://www.zju.edu.cn/jzus E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.cn A novel -stage structure for a low-noise, high-gain and gain-flattened L-band erbium doped fiber amplifier
Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE ISSN 9-9 http://www.zju.edu.cn/jzus E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.cn A novel -stage structure for a low-noise, high-gain and gain-flattened L-band erbium doped fiber amplifier
Active mode-locking of miniature fiber Fabry-Perot laser (FFPL) in a ring cavity
 Active mode-locking of miniature fiber Fabry-Perot laser (FFPL) in a ring cavity Shinji Yamashita (1)(2) and Kevin Hsu (3) (1) Dept. of Frontier Informatics, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences The University
Active mode-locking of miniature fiber Fabry-Perot laser (FFPL) in a ring cavity Shinji Yamashita (1)(2) and Kevin Hsu (3) (1) Dept. of Frontier Informatics, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences The University
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF 4 CHANNEL WDM_EDFA SYSTEM WITH GAIN EQUALISATION
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF 4 CHANNEL WDM_EDFA SYSTEM WITH GAIN EQUALISATION S.Hemalatha 1, M.Methini 2 M.E.Student, Department Of ECE, Sri Sairam Engineering College,Chennai,India1 Assistant professsor,department
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF 4 CHANNEL WDM_EDFA SYSTEM WITH GAIN EQUALISATION S.Hemalatha 1, M.Methini 2 M.E.Student, Department Of ECE, Sri Sairam Engineering College,Chennai,India1 Assistant professsor,department
Microwave and Optical Technology Letters. Minhui Yan, Qing-Yang Xu 1, Chih-Hung Chen, Wei-Ping Huang, and Xiaobin Hong
 Page of 0 0 0 0 0 0 Schemes of Optical Power Splitter Nodes for Direct ONU-ONU Intercommunication Minhui Yan, Qing-Yang Xu, Chih-Hung Chen, Wei-Ping Huang, and Xiaobin Hong Department of Electrical and
Page of 0 0 0 0 0 0 Schemes of Optical Power Splitter Nodes for Direct ONU-ONU Intercommunication Minhui Yan, Qing-Yang Xu, Chih-Hung Chen, Wei-Ping Huang, and Xiaobin Hong Department of Electrical and
Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers
 Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers 1.0 Modulation depth 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Laser 3 Laser 2 Laser 4 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Absorbed pump power (W) Laser 1 W. Guan and J. R.
Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers 1.0 Modulation depth 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Laser 3 Laser 2 Laser 4 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Absorbed pump power (W) Laser 1 W. Guan and J. R.
AN EFFICIENT L-BAND ERBIUM-DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIER WITH ZIRCONIA-YTTRIA-ALUMINUM CO-DOPED SILICA FIBER
 Journal of Non - Oxide Glasses Vol. 10, No. 3, July - September 2018, p. 65-70 AN EFFICIENT L-BAND ERBIUM-DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIER WITH ZIRCONIA-YTTRIA-ALUMINUM CO-DOPED SILICA FIBER A. A. ALMUKHTAR a, A.
Journal of Non - Oxide Glasses Vol. 10, No. 3, July - September 2018, p. 65-70 AN EFFICIENT L-BAND ERBIUM-DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIER WITH ZIRCONIA-YTTRIA-ALUMINUM CO-DOPED SILICA FIBER A. A. ALMUKHTAR a, A.
To investigate effects of extinction ratio on SOA based wavelength Converters for all Optical Networks
 289 To investigate effects of extinction ratio on SOA based wavelength Converters for all Optical Networks Areet Aulakh 1, Kulwinder Singh Malhi 2 1 Student, M.Tech, ECE department, Punjabi University,
289 To investigate effects of extinction ratio on SOA based wavelength Converters for all Optical Networks Areet Aulakh 1, Kulwinder Singh Malhi 2 1 Student, M.Tech, ECE department, Punjabi University,
OBSERVATION AND MITIGATION OF POWER TRANSIENTS IN 160Gbps OPTICAL BACKHAUL NETWORKS
 OBSERVATION AND MITIGATION OF POWER TRANSIENTS IN 160Gbps OPTICAL BACKHAUL NETWORKS Vikrant Sharma Anurag Sharma Electronics and Communication Engineering, CT Group of Institutions, Jalandhar Dalveer Kaur
OBSERVATION AND MITIGATION OF POWER TRANSIENTS IN 160Gbps OPTICAL BACKHAUL NETWORKS Vikrant Sharma Anurag Sharma Electronics and Communication Engineering, CT Group of Institutions, Jalandhar Dalveer Kaur
Multiwavelength and Switchable Erbium-Doped Fiber Lasers
 Multiwavelength and Switchable Erbium-Doped Fiber Lasers Rosa Ana PEREZ-HERRERA (1), Montserrat Fernandez-Vallejo (1), Silvia Diaz (1), M. Angeles Quintela (2), Manuel Lopez-Amo (1), and José Miguel López-Higuera
Multiwavelength and Switchable Erbium-Doped Fiber Lasers Rosa Ana PEREZ-HERRERA (1), Montserrat Fernandez-Vallejo (1), Silvia Diaz (1), M. Angeles Quintela (2), Manuel Lopez-Amo (1), and José Miguel López-Higuera
Optical Communications and Networking 朱祖勍. Oct. 9, 2017
 Optical Communications and Networking Oct. 9, 2017 1 Optical Amplifiers In optical communication systems, the optical signal from the transmitter are attenuated by the fiber and other passive components
Optical Communications and Networking Oct. 9, 2017 1 Optical Amplifiers In optical communication systems, the optical signal from the transmitter are attenuated by the fiber and other passive components
EDFA-WDM Optical Network Analysis
 EDFA-WDM Optical Network Analysis Narruvala Lokesh, kranthi Kumar Katam,Prof. Jabeena A Vellore Institute of Technology VIT University, Vellore, India Abstract : Optical network that apply wavelength division
EDFA-WDM Optical Network Analysis Narruvala Lokesh, kranthi Kumar Katam,Prof. Jabeena A Vellore Institute of Technology VIT University, Vellore, India Abstract : Optical network that apply wavelength division
WDM-PON Delivering 5-Gbps Downstream/2.5-Gbps Upstream Data
 WDM-PON Delivering 5-Gbps Downstream/2.5-Gbps Upstream Data Balaji Raobawale P. G. Department M.B.E.S. College of Engineering, Ambajogai, India S. K. Sudhansu P. G. Department M.B.E.S. College of Engineering,
WDM-PON Delivering 5-Gbps Downstream/2.5-Gbps Upstream Data Balaji Raobawale P. G. Department M.B.E.S. College of Engineering, Ambajogai, India S. K. Sudhansu P. G. Department M.B.E.S. College of Engineering,
Performance Analysis of Gb/s DWDM Metropolitan Area Network using SMF-28 and MetroCor Optical Fibres
 Research Cell: An International Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN: 2229-6913 Issue Sept 2011, Vol. 4 11 Performance Analysis of 32 2.5 Gb/s DWDM Metropolitan Area Network using SMF-28 and MetroCor Optical
Research Cell: An International Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN: 2229-6913 Issue Sept 2011, Vol. 4 11 Performance Analysis of 32 2.5 Gb/s DWDM Metropolitan Area Network using SMF-28 and MetroCor Optical
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF GB/S BIDIRECTIONAL DWDM PASSIVE OPTICAL NETWORK BASED ON CYCLIC AWG
 http:// PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF 1.25 16 GB/S BIDIRECTIONAL DWDM PASSIVE OPTICAL NETWORK BASED ON CYCLIC AWG Arashdeep Kaur 1, Ramandeep Kaur 2 1 Student, M.Tech, Department of Electronics and Communication
http:// PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF 1.25 16 GB/S BIDIRECTIONAL DWDM PASSIVE OPTICAL NETWORK BASED ON CYCLIC AWG Arashdeep Kaur 1, Ramandeep Kaur 2 1 Student, M.Tech, Department of Electronics and Communication
Multiwavelength Single-Longitudinal-Mode Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Laser. Citation IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., 2013, v. 25, p.
 Title Multiwavelength Single-Longitudinal-Mode Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Laser Author(s) ZHOU, Y; Chui, PC; Wong, KKY Citation IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., 2013, v. 25, p. 385-388 Issued Date 2013 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/189009
Title Multiwavelength Single-Longitudinal-Mode Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Laser Author(s) ZHOU, Y; Chui, PC; Wong, KKY Citation IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., 2013, v. 25, p. 385-388 Issued Date 2013 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/189009
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Computer Science 93 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 93 (016 ) 647 654 6th International Conference On Advances In Computing & Communications, ICACC 016, 6-8 September 016,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 93 (016 ) 647 654 6th International Conference On Advances In Computing & Communications, ICACC 016, 6-8 September 016,
Loop Mirror Multi-wavelength Brillouin Fiber Laser Utilizing Semiconductor Optical Amplifier and Fiber Bragg Grating
 Loop Mirror Multi-wavelength Brillouin Fiber Laser Utilizing Semiconductor Optical Amplifier and Fiber Bragg Grating N. A. Idris 1,2,*, N. A. M. Ahmad Hambali 1,2, M.H.A. Wahid 1,2, N. A. Ariffin 1,2,
Loop Mirror Multi-wavelength Brillouin Fiber Laser Utilizing Semiconductor Optical Amplifier and Fiber Bragg Grating N. A. Idris 1,2,*, N. A. M. Ahmad Hambali 1,2, M.H.A. Wahid 1,2, N. A. Ariffin 1,2,
Optimized Flattened Gain Spectrum in C Band WDM using Automatic Gain Control in Bi-Directionally Pumped EDFA
 Optimized Flattened Gain Spectrum in C Band WDM using Automatic Gain Control in Bi-Directionally Pumped EDFA 1 V. S. Lavanya*, 2 V. K. Vaidyan 1,2 Department of Physics, Mar Ivanios College, Thiruvananthapuram,
Optimized Flattened Gain Spectrum in C Band WDM using Automatic Gain Control in Bi-Directionally Pumped EDFA 1 V. S. Lavanya*, 2 V. K. Vaidyan 1,2 Department of Physics, Mar Ivanios College, Thiruvananthapuram,
32-Channel DWDM System Design and Simulation by Using EDFA with DCF and Raman Amplifiers
 2012 International Conference on Information and Computer Networks (ICICN 2012) IPCSIT vol. 27 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore 32-Channel DWDM System Design and Simulation by Using EDFA with DCF
2012 International Conference on Information and Computer Networks (ICICN 2012) IPCSIT vol. 27 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore 32-Channel DWDM System Design and Simulation by Using EDFA with DCF
Design and Performance Evaluation of 20 GB/s Bidirectional DWDM Passive Optical Network Based on Array Waveguide Gratings
 ISSN: 2278 909X International Journal of Advanced Research in Electronics and Communication Engineering (IJARECE) Volume 2, Issue 9, September 2013 Design and Performance Evaluation of 20 GB/s Bidirectional
ISSN: 2278 909X International Journal of Advanced Research in Electronics and Communication Engineering (IJARECE) Volume 2, Issue 9, September 2013 Design and Performance Evaluation of 20 GB/s Bidirectional
Cost-effective wavelength-tunable fiber laser using self-seeding Fabry-Perot laser diode
 Cost-effective wavelength-tunable fiber laser using self-seeding Fabry-Perot laser diode Chien Hung Yeh, 1* Fu Yuan Shih, 2 Chia Hsuan Wang, 3 Chi Wai Chow, 3 and Sien Chi 2, 3 1 Information and Communications
Cost-effective wavelength-tunable fiber laser using self-seeding Fabry-Perot laser diode Chien Hung Yeh, 1* Fu Yuan Shih, 2 Chia Hsuan Wang, 3 Chi Wai Chow, 3 and Sien Chi 2, 3 1 Information and Communications
Study of All-Optical Wavelength Conversion and Regeneration Subsystems for use in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Telecommunication Networks.
 Study of All-Optical Wavelength Conversion and Regeneration Subsystems for use in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Telecommunication Networks. Hercules Simos * National and Kapodistrian University
Study of All-Optical Wavelength Conversion and Regeneration Subsystems for use in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Telecommunication Networks. Hercules Simos * National and Kapodistrian University
Performance Comparison of Pre-, Post-, and Symmetrical Dispersion Compensation for 96 x 40 Gb/s DWDM System using DCF
 Performance Comparison of Pre-, Post-, and Symmetrical Dispersion Compensation for 96 x 40 Gb/s DWDM System using Sabina #1, Manpreet Kaur *2 # M.Tech(Scholar) & Department of Electronics & Communication
Performance Comparison of Pre-, Post-, and Symmetrical Dispersion Compensation for 96 x 40 Gb/s DWDM System using Sabina #1, Manpreet Kaur *2 # M.Tech(Scholar) & Department of Electronics & Communication
Transient gain dynamics in long-haul transmission systems with electronic EDFA gain control
 Vol. 6, No. 9 / September 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 1129 Transient gain dynamics in long-haul transmission systems with electronic EDFA gain control Stephan Pachnicke, 1, * Peter M. Krummrich,
Vol. 6, No. 9 / September 2007 / JOURNAL OF OPTICAL NETWORKING 1129 Transient gain dynamics in long-haul transmission systems with electronic EDFA gain control Stephan Pachnicke, 1, * Peter M. Krummrich,
International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering
 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: Performance Analysis of WDM/SCM System Using EDFA Mukesh Kumar
ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: Performance Analysis of WDM/SCM System Using EDFA Mukesh Kumar
Utilizing Self-Seeding RSOA with Faraday Rotator Mirror for Colorless Access Network
 Utilizing Self-Seeding RSOA with Faraday Rotator Mirror for Colorless Access Network Yu-Fu Wu a, Jinu-Yu Sung a, and Chi-Wai Chow a, and Chien-Hung Yeh* b,c a Department of Photonics and Institute of Electro-Optical
Utilizing Self-Seeding RSOA with Faraday Rotator Mirror for Colorless Access Network Yu-Fu Wu a, Jinu-Yu Sung a, and Chi-Wai Chow a, and Chien-Hung Yeh* b,c a Department of Photonics and Institute of Electro-Optical
Recon gurable WDM add/drop multiplexer based on optical switches and bre Bragg gratings
 Optical and Quantum Electronics 31 (1999) 77±83 Recon gurable WDM add/drop multiplexer based on optical switches and bre Bragg gratings SHIEN-KUEI LIAW Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National
Optical and Quantum Electronics 31 (1999) 77±83 Recon gurable WDM add/drop multiplexer based on optical switches and bre Bragg gratings SHIEN-KUEI LIAW Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National
Comparative Analysis Of Different Dispersion Compensation Techniques On 40 Gbps Dwdm System
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF TECHNOLOGY ENHANCEMENTS AND EMERGING ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOL 3, ISSUE 06 34 Comparative Analysis Of Different Dispersion Compensation Techniques On 40 Gbps Dwdm System Meenakshi,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF TECHNOLOGY ENHANCEMENTS AND EMERGING ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOL 3, ISSUE 06 34 Comparative Analysis Of Different Dispersion Compensation Techniques On 40 Gbps Dwdm System Meenakshi,
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements HW #5 is assigned (due April 9) April 9 th class will be in
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements HW #5 is assigned (due April 9) April 9 th class will be in
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 28, NO. 16, AUGUST 15, /$ IEEE
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 28, NO. 16, AUGUST 15, 2010 2213 Full Colorless WDM-Radio Over Fiber Access Network Supporting Simultaneous Transmission of Millimeter-Wave Band and Baseband Gigabit
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 28, NO. 16, AUGUST 15, 2010 2213 Full Colorless WDM-Radio Over Fiber Access Network Supporting Simultaneous Transmission of Millimeter-Wave Band and Baseband Gigabit
OBSERVATION AND EVALUATION OF POWER TRANSIENTS IN 45 CHANNEL SSDWDM OPTICAL NETWORK
 OBSERVATION AND EVALUATION OF POWER TRANSIENTS IN 45 CHANNEL SSDWDM OPTICAL NETWORK Vikrant Sharma, Dalveer Kaur 1,2 Department of ECE,IKG PTU, Jalandhar, India Abstract: Erbium doped fiber amplifiers
OBSERVATION AND EVALUATION OF POWER TRANSIENTS IN 45 CHANNEL SSDWDM OPTICAL NETWORK Vikrant Sharma, Dalveer Kaur 1,2 Department of ECE,IKG PTU, Jalandhar, India Abstract: Erbium doped fiber amplifiers
Visible to infrared high-speed WDM transmission over PCF
 Visible to infrared high-speed WDM transmission over PCF Koji Ieda a), Kenji Kurokawa, Katsusuke Tajima, and Kazuhide Nakajima NTT Access Network Service Systems Laboratories, NTT Corporation, 1 7 1 Hanabatake,
Visible to infrared high-speed WDM transmission over PCF Koji Ieda a), Kenji Kurokawa, Katsusuke Tajima, and Kazuhide Nakajima NTT Access Network Service Systems Laboratories, NTT Corporation, 1 7 1 Hanabatake,
1170 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 23, NO. 3, MARCH 2005
 1170 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 23, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 Design and Experimental Characterization of EDFA-Based WDM Ring Networks With Free ASE Light Recirculation and Link Control for Network
1170 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 23, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 Design and Experimental Characterization of EDFA-Based WDM Ring Networks With Free ASE Light Recirculation and Link Control for Network
Performance Evaluation of Hybrid (Raman+EDFA) Optical Amplifiers in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed Optical Transmission System
 Performance Evaluation of Hybrid (Raman+EDFA) Optical Amplifiers in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed Optical Transmission System Gagandeep Singh Walia 1, Kulwinder Singh 2, Manjit Singh Bhamrah 3
Performance Evaluation of Hybrid (Raman+EDFA) Optical Amplifiers in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed Optical Transmission System Gagandeep Singh Walia 1, Kulwinder Singh 2, Manjit Singh Bhamrah 3
S Optical Networks Course Lecture 4: Transmission System Engineering
 S-72.3340 Optical Networks Course Lecture 4: Transmission System Engineering Edward Mutafungwa Communications Laboratory, Helsinki University of Technology, P. O. Box 2300, FIN-02015 TKK, Finland Tel:
S-72.3340 Optical Networks Course Lecture 4: Transmission System Engineering Edward Mutafungwa Communications Laboratory, Helsinki University of Technology, P. O. Box 2300, FIN-02015 TKK, Finland Tel:
1.25 Gb/s Broadcast Signal Transmission in WDM-PON Based on Mutually Injected Fabry-Perot Laser Diodes
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 16, No. 2, June 2012, pp. 101-106 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2012.16.2.101 1.25 Gb/s Broadcast Signal Transmission in WDM-PON Based on Mutually Injected
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 16, No. 2, June 2012, pp. 101-106 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2012.16.2.101 1.25 Gb/s Broadcast Signal Transmission in WDM-PON Based on Mutually Injected
Simulation of All-Optical XOR, AND, OR gate in Single Format by Using Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers
 Simulation of All-Optical XOR, AND, OR gate in Single Format by Using Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers Chang Wan Son* a,b, Sang Hun Kim a, Young Min Jhon a, Young Tae Byun a, Seok Lee a, Deok Ha Woo a,
Simulation of All-Optical XOR, AND, OR gate in Single Format by Using Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers Chang Wan Son* a,b, Sang Hun Kim a, Young Min Jhon a, Young Tae Byun a, Seok Lee a, Deok Ha Woo a,
LW Technology. Passive Components. LW Technology (Passive Components).PPT - 1 Copyright 1999, Agilent Technologies
 LW Technology Passive Components LW Technology (Passive Components).PPT - 1 Patchcords Jumper cables to connect devices and instruments Adapter cables to connect interfaces using different connector styles
LW Technology Passive Components LW Technology (Passive Components).PPT - 1 Patchcords Jumper cables to connect devices and instruments Adapter cables to connect interfaces using different connector styles
Compensation of Dispersion in 10 Gbps WDM System by Using Fiber Bragg Grating
 International Journal of Computational Engineering & Management, Vol. 15 Issue 5, September 2012 www..org 16 Compensation of Dispersion in 10 Gbps WDM System by Using Fiber Bragg Grating P. K. Raghav 1,
International Journal of Computational Engineering & Management, Vol. 15 Issue 5, September 2012 www..org 16 Compensation of Dispersion in 10 Gbps WDM System by Using Fiber Bragg Grating P. K. Raghav 1,
Development of Etalon-Type Gain-Flattening Filter
 Development of Etalon-Type Gain-Flattening Filter by Kazuyou Mizuno *, Yasuhiro Nishi *, You Mimura *, Yoshitaka Iida *, Hiroshi Matsuura *, Daeyoul Yoon *, Osamu Aso *, Toshiro Yamamoto *2, Tomoaki Toratani
Development of Etalon-Type Gain-Flattening Filter by Kazuyou Mizuno *, Yasuhiro Nishi *, You Mimura *, Yoshitaka Iida *, Hiroshi Matsuura *, Daeyoul Yoon *, Osamu Aso *, Toshiro Yamamoto *2, Tomoaki Toratani
ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS
 MANDEEP SINGH AND S K RAGHUWANSHI: ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS DOI: 10.1917/ijct.013.0106 ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS Mandeep Singh 1 and S. K. Raghuwanshi 1 Department
MANDEEP SINGH AND S K RAGHUWANSHI: ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS DOI: 10.1917/ijct.013.0106 ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS Mandeep Singh 1 and S. K. Raghuwanshi 1 Department
Channel wavelength selectable singleõdualwavelength erbium-doped fiber ring laser
 Channel wavelength selectable singleõdualwavelength erbium-doped fiber ring laser Tong Liu Yeng Chai Soh Qijie Wang Nanyang Technological University School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang
Channel wavelength selectable singleõdualwavelength erbium-doped fiber ring laser Tong Liu Yeng Chai Soh Qijie Wang Nanyang Technological University School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang
The Report of Gain Performance Characteristics of the Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA)
 The Report of Gain Performance Characteristics of the Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA) Masruri Masruri (186520) 22/05/2008 1 Laboratory Setup The laboratory setup using in this laboratory experiment
The Report of Gain Performance Characteristics of the Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA) Masruri Masruri (186520) 22/05/2008 1 Laboratory Setup The laboratory setup using in this laboratory experiment
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI) phase stabilization. (a) DC output of the MZI with and without phase stabilization. (b) Performance of MZI stabilization
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI) phase stabilization. (a) DC output of the MZI with and without phase stabilization. (b) Performance of MZI stabilization
PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF TWO-CHANNEL DISPERSION SUPPORTED TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS USING SINGLE AND DOUBLE-CAVITY FABRY-PEROT FILTERS AS DEMULTIPLEXERS
 PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF TWO-CHANNEL DISPERSION SUPPORTED TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS USING SINGLE AND DOUBLE-CAVITY FABRY-PEROT FILTERS AS DEMULTIPLEXERS Mário M. Freire Department of Mathematics and Information
PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF TWO-CHANNEL DISPERSION SUPPORTED TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS USING SINGLE AND DOUBLE-CAVITY FABRY-PEROT FILTERS AS DEMULTIPLEXERS Mário M. Freire Department of Mathematics and Information
EDFA-WDM Optical Network Design System
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 53 ( 2013 ) 294 302 Malaysian Technical Universities Conference on Engineering & Technology 2012, MUCET 2012 Part -1 Electronic and Electrical
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 53 ( 2013 ) 294 302 Malaysian Technical Universities Conference on Engineering & Technology 2012, MUCET 2012 Part -1 Electronic and Electrical
Spectrum Sliced WDM-PON System as Energy Efficient Solution for Optical Access Systems
 Spectrum Sliced WDM-PON System as Energy Efficient Solution for Optical Access Systems Vjaceslavs Bobrovs, Sandis Spolitis, Ilja Trifonovs, Girts Ivanovs Institute of Telecommunications Riga Technical
Spectrum Sliced WDM-PON System as Energy Efficient Solution for Optical Access Systems Vjaceslavs Bobrovs, Sandis Spolitis, Ilja Trifonovs, Girts Ivanovs Institute of Telecommunications Riga Technical
CSO/CTB PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT BY USING FABRY-PEROT ETALON AT THE RECEIVING SITE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 107 113, 2009 CSO/CTB PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT BY USING FABRY-PEROT ETALON AT THE RECEIVING SITE S.-J. Tzeng, H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, K.-H. Chang,and C.-H.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 107 113, 2009 CSO/CTB PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT BY USING FABRY-PEROT ETALON AT THE RECEIVING SITE S.-J. Tzeng, H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, K.-H. Chang,and C.-H.
Performance Analysis of Designing a Hybrid Optical Amplifier (HOA) for 32 DWDM Channels in L-band by using EDFA and Raman Amplifier
 Performance Analysis of Designing a Hybrid Optical Amplifier (HOA) for 32 DWDM Channels in L-band by using EDFA and Raman Amplifier Aied K. Mohammed, PhD Department of Electrical Engineering, University
Performance Analysis of Designing a Hybrid Optical Amplifier (HOA) for 32 DWDM Channels in L-band by using EDFA and Raman Amplifier Aied K. Mohammed, PhD Department of Electrical Engineering, University
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF OPTICAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM USING FBG AND BESSEL FILTERS
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF OPTICAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM USING FBG AND BESSEL FILTERS Antony J. S., Jacob Stephen and Aarthi G. ECE Department, School of Electronics Engineering, VIT University, Vellore, Tamil
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF OPTICAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM USING FBG AND BESSEL FILTERS Antony J. S., Jacob Stephen and Aarthi G. ECE Department, School of Electronics Engineering, VIT University, Vellore, Tamil
Spectral Response of FWM in EDFA for Long-haul Optical Communication
 Spectral Response of FWM in EDFA for Long-haul Optical Communication Lekshmi.S.R 1, Sindhu.N 2 1 P.G.Scholar, Govt. Engineering College, Wayanad, Kerala, India 2 Assistant Professor, Govt. Engineering
Spectral Response of FWM in EDFA for Long-haul Optical Communication Lekshmi.S.R 1, Sindhu.N 2 1 P.G.Scholar, Govt. Engineering College, Wayanad, Kerala, India 2 Assistant Professor, Govt. Engineering
Chapter 12: Optical Amplifiers: Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs)
 Chapter 12: Optical Amplifiers: Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs) Prof. Dr. Yaocheng SHI ( 时尧成 ) yaocheng@zju.edu.cn http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/yaocheng 1 Traditional Optical Communication System Loss
Chapter 12: Optical Amplifiers: Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs) Prof. Dr. Yaocheng SHI ( 时尧成 ) yaocheng@zju.edu.cn http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/yaocheng 1 Traditional Optical Communication System Loss
OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S
 OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S-108.3110 1 Course program 1. Introduction and Optical Fibers 2. Nonlinear Effects in Optical Fibers 3. Fiber-Optic Components 4. Transmitters and Receivers 5. Fiber-Optic Measurements
OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S-108.3110 1 Course program 1. Introduction and Optical Fibers 2. Nonlinear Effects in Optical Fibers 3. Fiber-Optic Components 4. Transmitters and Receivers 5. Fiber-Optic Measurements
Temporal phase mask encrypted optical steganography carried by amplified spontaneous emission noise
 Temporal phase mask encrypted optical steganography carried by amplified spontaneous emission noise Ben Wu, * Zhenxing Wang, Bhavin J. Shastri, Matthew P. Chang, Nicholas A. Frost, and Paul R. Prucnal
Temporal phase mask encrypted optical steganography carried by amplified spontaneous emission noise Ben Wu, * Zhenxing Wang, Bhavin J. Shastri, Matthew P. Chang, Nicholas A. Frost, and Paul R. Prucnal
Introduction Fundamental of optical amplifiers Types of optical amplifiers
 ECE 6323 Introduction Fundamental of optical amplifiers Types of optical amplifiers Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers Semiconductor optical amplifier Others: stimulated Raman, optical parametric Advanced application:
ECE 6323 Introduction Fundamental of optical amplifiers Types of optical amplifiers Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers Semiconductor optical amplifier Others: stimulated Raman, optical parametric Advanced application:
Implementation and analysis of 2 Tbps MDRZ DWDM system at ultra narrow channel spacing
 Implementation and analysis of 2 Tbps MDRZ DWDM system at ultra narrow channel spacing 1 Ragini Sharma, 2 Kamaldeep Kaur 1 Student, 2 Assistant Professor Department of Electrical Engineering BBSBEC, Fatehgarh
Implementation and analysis of 2 Tbps MDRZ DWDM system at ultra narrow channel spacing 1 Ragini Sharma, 2 Kamaldeep Kaur 1 Student, 2 Assistant Professor Department of Electrical Engineering BBSBEC, Fatehgarh
To generate a broadband light source by using mutually injection-locked Fabry-Perot laser diodes
 To generate a broadband light source by using mutually injection-locked Fabry-Perot laser diodes Cheng-Ling Ying 1, Yu-Chieh Chi 2, Chia-Chin Tsai 3, Chien-Pen Chuang 3, and Hai-Han Lu 2a) 1 Department
To generate a broadband light source by using mutually injection-locked Fabry-Perot laser diodes Cheng-Ling Ying 1, Yu-Chieh Chi 2, Chia-Chin Tsai 3, Chien-Pen Chuang 3, and Hai-Han Lu 2a) 1 Department
SIMULATION OF FIBER LOOP BUFFER MEMORY OF ALL-OPTICAL PACKET SWITCH. Mandar Naik, Yatindra Nath Singh
 SIMULATION OF FIBER LOOP BUFFER MEMORY ABSTRACT OF ALL-OPTICAL PACKET SWITCH Mandar Naik, Yatindra Nath Singh Center for Laser Technology Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur - 28 16 India {mandy,ynsingh}@iitk.ac.in
SIMULATION OF FIBER LOOP BUFFER MEMORY ABSTRACT OF ALL-OPTICAL PACKET SWITCH Mandar Naik, Yatindra Nath Singh Center for Laser Technology Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur - 28 16 India {mandy,ynsingh}@iitk.ac.in
