4096-OFDM Implementation on the HFC plant with Fiber Deep and Distributed Access Architecture. Maxwell Huang
|
|
|
- Jonah Ball
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4096-OFDM Implementation on the HFC plant with Fiber Deep and Distributed Access Architecture Maxwell Huang
2 Study on 4096-OFDM Implementation on R-PHY + FD Architecture Remote PHY + Fiber Deep Architecture 4096-QAM =12 bit / symbol =58.4Mbps / 6MHz 42dB MER required Lower to 36dB by OFDM w/ LDPC 4096-OFDM implementation over entire HFC plant becomes feasible because CNR is improved significantly by R-PHY. Distortion and noise are significantly improved by FD. MER distribution becomes consistent over the entire plant by R-PHY+FD. Device MER (db) Room Temp. Over Temp. R-PHY Power Amplifier CPE EOL MER EOL MER Estimate
3 Study on PAPR Increase CCDF Comparison Probability All SC- QAM 6*4096-OFDM 10% % % % % % Peak PAPR and Compression OFDM suffers the more degradation in MER than QAM when power amplifier operates close to its maximum output power. Assume 2dB degradation in the MER caused by compression due to PAPR Device MER (db) Room Temp. Over Temp. R-PHY Power Compression CPE EOL MER (db) EOL MER Estimate May not support 4096-OFDM
4 Partial Band CFR _ A Solution Under Investigation Adaptive Baseband Proposed solution to PAPR reduction: Applying the Crest Factor Reduction (CFR) technique such as Adaptive Baseband on the partial band. e.g. ONLY for highest OFDM (channel A). Reasoning: Partial band CFR still effectively reduces PAPR but mitigating the trade-offs in performance and computational complexity. Apply the Adaptive Baseband on OFDM channel A
5 Study on Power Increase R-PHY + FD architecture could bring an unprecedented thermal challenges for the node because Roughly 25 watt of DC power increase results from enabling the super high output capability needed for fiber deep deployment. Roughly 20Watt DC power increase results from introducing R-PHY module in the node.
6 A proposed power saving solution The Dynamic Power Saving feature makes the bias current adjustable in field, so that node can smartly set the bias current according to the actual cable losses and the change in spectrum loading. APSIS Compliant Power saving associated with cable loss distribution Power saving associated with Spectrum Loading
7 Thank You!
8 The Capacity of Analog Optics in DOCSIS 3.1 HFC Networks Michael He John Skrobko, Wen Zhang, Qi Zhang
9 Measured Upstream NPR for Multiple Loads 12 db DR 12 db DR 24 db DR Note: 1. The US Rx optical input power is -13 dbm. The EIN of US analog Rx is 1.3pA/ Hz. 2. Typically the US optical link required min. NPR dynamic range (DR) is 12 db.
10 Thermal Noise Contributes more to CNR at Low OIP 9.5dB Constellation (QAM) Required CNR (db) US OFDMA US Min OIP (dbm) 5-85 MHz MHz (measured) dbm Note: 1. OMI (5%/6.4MHz) for this example is chosen for MHz loading. The EIN is 1.3pA/ Hz. 2. The US Min OIP results (in table) are in meeting the Required CNR with 12 db of dynamic range, and are extrapolated base on the measured NPR DR at -13 dbm
11 WDM Demux Link budget (db) Link Budget vs. Fiber Deep Requirements Probable Fiber Deep Optical Link Tx 1 Tx 2 Tx n WDM Mux Fiber link (40km) Rx 1 Rx 2 Rx n Downstream (up to 1218 MHz) Upstream (5-204 MHz) Loss (db) Total: 15 Analog (moderate order) Analog (high order) 10G Digital Note: 1. Assuming output power of analog Tx DS(US) is 10 dbm (3 dbm) for link budget calculation. 2. Assuming 10GE optical transmission link budgets is with the EML Tx minimum output of 0 dbm, and APD Rx receiving sensitivity of -21 dbm (w/ 2dB fiber dispersion penalty). 2K-qam 4K-qam R-phy 512-qam 1K-qam R-phy/EDR
12 Summary CNR of analog optical links is dominated by EIN of the optical Rx at low optical input power. Analog optical link is still workable for 4K-qam OFDM DS (up to 1218 MHz) at -2dBm OIP, while for 1K-qam OFDMA US (5-204MHz) at -13dBm OIP. Digital optics can support 4K/1K OFDM/OFDMA with 9 db and 5 db more link power budget than DS/US analog optics, respectively.
13 Thank You Michael He Cisco Systems
14 DOCSIS 3.1 Profile Management Application and Algorithms Greg White, Karthik Sundaresan (CableLabs)
15 D3.1 Profiles & Creation Problem N-Dimensional Vectors Modulation Profile: Vector of modulation orders CM MER: Vector of reported signal quality How to choose best profiles? CMTS supports up to 16 profiles per channel Profile A : lowest common denominator Dimensionality Problem N = 3800 or 7600 subcarriers possible profiles (8 bit - 14 bit Modulations) choose-15 = ~ possible 16-profile sets Simplifying assumptions don t help
16 D3.1 Profiles : Objective Function What function are we trying to maximize? GGGGGGGG JJ = channel capacity using set of profiles P channel capacity using only profile A JJ PP,AA = KK AA 1 Φxx xx PPKKxx Φ x = N x /N (fraction of users assigned to profile x) K x = sum of bit-loading values (all subcarriers) for profile X
17 Optimization Methods (1): PCA Profile Coalescation Algorithm
18 Optimization Methods (2): K-Means Clustering using K-Means
19 Optimization Methods (3): KCA K- Means PCA KCA Start with K-Means to quickly get initial clusters Use PCA to reduce to optimal set of profiles
20 Algorithm Comparison KCA : best choice for fast runtime Use PCA to reduce to profiles using K-Means
21 DOCSIS 3.1 Multicast Profile Management Mechanism Evan Sun Ph.D. Standard Engineer
22 Multicast Profile Management Multicast Profile (MP) Optimization Prerequisite CM joins or Leaves multicast group Internal Profile Management CM joins or leaves procedures External Profile Application Interfaces between the PMA and CMTS
23 MP Optimization Trigger Conditions CMTS Multicast Group One Multicast Group Two CM A CM B CM C CM D Client 1 Client 2 CM is working on DOCSIS 3.1 mode with OFDM downstream channel; First Client connected with CM wants to join the multicast group; Last Client connected with CM leaves the multicast group.
24 Internal Profile Management CM Joins Multicast Group CM Leaves Multicast Group PM Module CM supports the multicast profile Yes End Find a higher profile for the remaining group members can support PM Module Choose a lower common profile, and then test it using the OPT messages All CMs support the new profile Yes End All CMs support the new profile Yes Using the new profile Force to replicate the multicast on multiple profiles Using the current profile
25 External Profile Management PMA CMTS CM 1 CM 2 Multicast Profile Optimization Trigger Message Profile Optimization Testing Completed Multicast Profile Test REQ OFDM DS Profile Test RSP (CM1) OFDM DS Profile Test RSP (CM2) Multicast Profile Switchover Message OPT-REQ OPT-RSP OPT-ACK DBC-REQ DBC-RSP OPT-REQ OPT-RSP OPT-ACK DBC-REQ DBC-RSP DBC-ACK DBC-ACK Interfaces between CMTS and PMA 1. CM Joins/Leaves Descriptor 2. OFDM DS Multicast Profile Test Request Message 3. OFDM DS Multicast Profile Test Response Message 4. Multicast Group Information Request Message 5. Multicast Group Information Descriptor
26 HUAWEI To enrich life through communication
27 The World Is Flat Capacity Optimization in a Coaxial Network, Constrained by Total RF Power Karl Moerder PhD, Futurewei Technologies Inc. Fred Harris PhD, San Diego State University
28 The world is flat Capacity Optimization What do we think? What do we know? What can we prove? What does it mean?
29 What do we think? Modulation Constellation Density 256 QAM 256 QAM 256 QAM 256 QAM 256 QAM Input PSD f Frequenc y 800 MHz Output PSD 6dB 12dB 18dB 24dB 30dB f Frequenc y 800 MHz
30 What do we know? Modulation Constellation Density QAM 4096 QAM 1024 QAM 256 QAM 64 QAM 6dB Input PSD f Frequenc y MHz Output PSD 6dB f Frequenc y 800 MHz
31 What can we prove? 4000 Power vs Frequency Power (Arbitrary Scale) Frequency (MHz) 64-QAM 16-QAM 4-QAM
32 What does it mean? It means the closer we come to a flat power spectral density out of the amplifier and into the coax, the more efficiently we use our limited RF power. For the same total RF power, a nearly flat spectrum at the amplifier output significantly reduces the distortion from the amplifier. The above points become increasingly important as the total bandwidth gets wider. Pre-emphasis can be approximated with smaller constellations at higher frequency and boosting the gain for the smaller constellations.
33 Thank You Karl Moerder, Fred Harris,
34 Hi Ho, Hi Ho to a Gigabit We Go Positioning the HFC Network for the New Gigabit Era Phil Miguelez Comcast
35 What s driving the need for a new network architecture? Competition HSD growth D3.1 / R-Phy Future FDX Source
36 Architecture Migration Goals Continue to extend the life of the HFC network Provide expanded capacity needed to meet subscriber usage demands and fend off competitive challenges with D3.1 Reduce node serving area size to increase data capacity per HHP Improve OpEx and network reliability by eliminating RF actives Enable a passive coax access link to the home Provide a future migration path to an all IP / all fiber network Fiber Deep Distributed Access Architecture FTTH
37 Network Migration Options Description / Benefits Cost Pros Cons Drop-In BW Expansion Fiber Deep FTTH Maintain existing station locations and HHP Upgrade Amps and Node electronics to 85/1GHz or 1.2 GHz Enables 1 Gb DS / Mb US peak rates. Lower avg rates High HP per node limits HSD tier rate penetration Lower, $XX/HHP for avg system Large cost variations due to density and plant condition Rapid scalability Operationally familiar No long term network benefit Requires continued node splits Higher cost solution over time Eliminate all RF Amps and reduce serving area size to 128 HP per node max Upgrade Node to 85/1218 MHz Enables true 1 Gb DS / 200 Mb US delivered data rates Lower HP per node permits increased HSD tier rate penetration Modest, $XXX/HHP based on assumed 60/40 aerial / UG split Modular transition to R-PHY Migration path to FTTH Workforce training and scale Slower to ramp Replace HFC network with RFoG / PON overlay Enables 1 Gb DS and US symmetric data rates High, $XXXX/HHP Incremental $XXX to connect each subscriber Low OpEx cost Allows 2Gb to 10Gb HSD Cost prohibitive Slowest to scale Requires all new CPE
38 Fiber Deep N+0 Architecture Concept
39 Fiber Deep N+0 Design Challenges High output node level and tilt to allow maximum HP reach 64 dbmv analog ref output, Linear tilt extension from 1 GHz to 1.2 GHz N+0 node expansion ratio is typically 12:1 (Average: 70 HP, Max: 128 HP) Express cable used to reach additional taps 85 MHz Mid Split migration Legacy STB OOB agility issues means changing out older STB s Maintain existing plant power design Node power consumption design closely watched PS location and size remain unchanged to avoid permit issues Added coax power lines, Access Cable bridging Network design training, Construction training
40 Conclusions / Lessons Learned Gigabit over builders are an expanding threat to every MSO D3.1 plus Fiber Deep N+0 provides the data capacity to meet competitive challenges and deliver Gb per subscriber rates US BW change creates the largest challenge due to the wide array of deployed legacy STB s and requires the most planning Commercial customers determine the node cut in schedule Continual communication with the municipality and customer is key to a successful, pain free network migration plan
41
2016 Spring Technical Forum Proceedings
 The Capacity of Analog Optics in DOCSIS 3.1 HFC Networks Zian He, John Skrobko, Qi Zhang, Wen Zhang Cisco Systems Abstract The DOCSIS 3.1 (D3.1) HFC network, supporting OFDM, requires potentially higher
The Capacity of Analog Optics in DOCSIS 3.1 HFC Networks Zian He, John Skrobko, Qi Zhang, Wen Zhang Cisco Systems Abstract The DOCSIS 3.1 (D3.1) HFC network, supporting OFDM, requires potentially higher
HFC Cable Architecture
 HFC Cable Architecture Wade Holmes wade.holmes@gmail.com 3/22/2018 [all images from CableLabs, Cisco, Arris or otherwise noted] Agenda Overview of Cable as a technology: what the future holds Architecture
HFC Cable Architecture Wade Holmes wade.holmes@gmail.com 3/22/2018 [all images from CableLabs, Cisco, Arris or otherwise noted] Agenda Overview of Cable as a technology: what the future holds Architecture
2015 Spring Technical Forum Proceedings
 HFC IMPROVEMENT FOR DOCSIS 3.1 EVOLUTION Maxwell Huang Cisco Systems Abstract The DOCSIS 3.1 PHY and MAC standards have specified the QAM modulation order as high as to 16384QAM, however, we could not
HFC IMPROVEMENT FOR DOCSIS 3.1 EVOLUTION Maxwell Huang Cisco Systems Abstract The DOCSIS 3.1 PHY and MAC standards have specified the QAM modulation order as high as to 16384QAM, however, we could not
2016 Spring Technical Forum Proceedings
 Full Duplex DOCSIS Technology over HFC Networks Belal Hamzeh CableLabs, Inc. Abstract DOCSIS 3.1 technology provides a significant increase in network capacity supporting 10 Gbps downstream capacity and
Full Duplex DOCSIS Technology over HFC Networks Belal Hamzeh CableLabs, Inc. Abstract DOCSIS 3.1 technology provides a significant increase in network capacity supporting 10 Gbps downstream capacity and
Putting the D back into DWDM Full-band Multi-wavelength Systems Mani Ramachandran CEO / CTO InnoTrans Communications
 April 14 2015 Putting the D back into DWDM Full-band Multi-wavelength Systems Mani Ramachandran CEO / CTO InnoTrans Communications Perception vs. Reality of full-band multiwavelength systems 40 wavelength
April 14 2015 Putting the D back into DWDM Full-band Multi-wavelength Systems Mani Ramachandran CEO / CTO InnoTrans Communications Perception vs. Reality of full-band multiwavelength systems 40 wavelength
Are You Ready for DOCSIS 3.1. Presenter: Pete Zarrelli VeEX Field Applications Engineer
 Are You Ready for DOCSIS 3.1 Presenter: Pete Zarrelli VeEX Field Applications Engineer Today s Speaker Pete Zarrelli Senior Field Engineer VeEX Inc. (215) 514-1083 pete@veexinc.com 14 Years PBX/Business
Are You Ready for DOCSIS 3.1 Presenter: Pete Zarrelli VeEX Field Applications Engineer Today s Speaker Pete Zarrelli Senior Field Engineer VeEX Inc. (215) 514-1083 pete@veexinc.com 14 Years PBX/Business
IEEE p802.3bn EPoC. Channel Model Ad Hoc committee Baseline Channel Model
 IEEE p802.3bn EPoC Channel Model Ad Hoc committee Baseline Channel Model N-Way 2-Way Headend Baseline Topology Opt TRx HFC TAP TAP TAP TAP CLT CLT EPON OLT CLT CLT RG-6 (+) 150 Ft. (50M) max RG-6 < 6 Ft.
IEEE p802.3bn EPoC Channel Model Ad Hoc committee Baseline Channel Model N-Way 2-Way Headend Baseline Topology Opt TRx HFC TAP TAP TAP TAP CLT CLT EPON OLT CLT CLT RG-6 (+) 150 Ft. (50M) max RG-6 < 6 Ft.
Return Plant Issues SCTE Cascade Range Chapter. Micah Martin January 13, 2008
 Return Plant Issues SCTE Cascade Range Chapter Micah Martin January 13, 2008 1 1 Agenda Experience with DOCSIS upgrade Digital review & digital modulation Carrier to Noise issues Coaxial Plant Optical
Return Plant Issues SCTE Cascade Range Chapter Micah Martin January 13, 2008 1 1 Agenda Experience with DOCSIS upgrade Digital review & digital modulation Carrier to Noise issues Coaxial Plant Optical
SCTE. San Diego Chapter March 19, 2014
 SCTE San Diego Chapter March 19, 2014 RFOG WHAT IS RFOG? WHY AND WHERE IS THIS TECHNOLOGY A CONSIDERATION? RFoG could be considered the deepest fiber version of HFC RFoG pushes fiber to the side of the
SCTE San Diego Chapter March 19, 2014 RFOG WHAT IS RFOG? WHY AND WHERE IS THIS TECHNOLOGY A CONSIDERATION? RFoG could be considered the deepest fiber version of HFC RFoG pushes fiber to the side of the
VIRTUAL SEGMENTATION. Executive summary. Online. Website: technetix.com
 VIRTUAL SEGMENTATION Executive summary Online Email: info-usa@technetix.com Website: technetix.com Nov/2017 Introduction The steady evolution of the DOCSIS system and Hybrid Fiber Coaxial (HFC) plants
VIRTUAL SEGMENTATION Executive summary Online Email: info-usa@technetix.com Website: technetix.com Nov/2017 Introduction The steady evolution of the DOCSIS system and Hybrid Fiber Coaxial (HFC) plants
Opti Max Optical Node Series
 arris.com Opti Max Optical Node Series OM6000 1.2 GHz 4x4 HFC Segmentable Node FEATURES Supports 1.2 GHz Downstream and 204 MHz Upstream bandpass for DOCSIS 3.1 migration Integrated segmentation switches
arris.com Opti Max Optical Node Series OM6000 1.2 GHz 4x4 HFC Segmentable Node FEATURES Supports 1.2 GHz Downstream and 204 MHz Upstream bandpass for DOCSIS 3.1 migration Integrated segmentation switches
Testing Upstream and Downstream DOCSIS 3.1 Devices
 Testing Upstream and Downstream DOCSIS 3.1 Devices April 2015 Steve Hall DOCSIS 3.1 Business Development Manager Agenda 1. Decoding and demodulating a real downstream DOCSIS 3.1 signal and reporting key
Testing Upstream and Downstream DOCSIS 3.1 Devices April 2015 Steve Hall DOCSIS 3.1 Business Development Manager Agenda 1. Decoding and demodulating a real downstream DOCSIS 3.1 signal and reporting key
2016 Spring Technical Forum Proceedings
 DOCSIS 3.1 Profile Management Application and Algorithms Greg White and Karthik Sundaresan Cable Television Laboratories, Inc. (CableLabs) Abstract DOCSIS 3.1 OFDM Profiles provide a wide range of modulation
DOCSIS 3.1 Profile Management Application and Algorithms Greg White and Karthik Sundaresan Cable Television Laboratories, Inc. (CableLabs) Abstract DOCSIS 3.1 OFDM Profiles provide a wide range of modulation
OPTIMIZING DOCSIS 3.1 NETWORKS: The Benefits of Protocol Analysis
 WHITE PAPER OPTIMIZING DOCSIS 3.1 NETWORKS: The Benefits of Protocol Analysis By Craig Chamberlain, Gabriel Naud, and Alex Pelland About the Authors Based in Denver, Colorado, Craig Chamberlain is a broadband
WHITE PAPER OPTIMIZING DOCSIS 3.1 NETWORKS: The Benefits of Protocol Analysis By Craig Chamberlain, Gabriel Naud, and Alex Pelland About the Authors Based in Denver, Colorado, Craig Chamberlain is a broadband
MODEL BLN GHz FIBER DEEP NODE STARLINE SERIES
 MODEL BLN100 1 1 GHz FIBER DEEP NODE STARLINE SERIES The BLN100 optical node is an essential building block in evolving Hybrid Fiber Coaxial (HFC) network architectures enabling amplifier to node conversions.
MODEL BLN100 1 1 GHz FIBER DEEP NODE STARLINE SERIES The BLN100 optical node is an essential building block in evolving Hybrid Fiber Coaxial (HFC) network architectures enabling amplifier to node conversions.
Digital Return System
 arris.com Digital Return System SG4 DRT 2X 85 and MBN DRT 2X 85 Transmitters GX2 DRR 2X 85 and CHP D2RRX 85 Receivers FEATURES Allows return bandwidth expansion up to 85 MHz Easy node segmentation with
arris.com Digital Return System SG4 DRT 2X 85 and MBN DRT 2X 85 Transmitters GX2 DRR 2X 85 and CHP D2RRX 85 Receivers FEATURES Allows return bandwidth expansion up to 85 MHz Easy node segmentation with
Digital Return System
 SG4 DRT 2X 85 and MBN DRT 2X 85 Transmitters GX2 DRR 2X 85 and CHP D2RRX 85 Receivers FEATURES Allows return bandwidth expansion up to 85 MHz Easy node segmentation with 2X RF TDM Simplified logistics
SG4 DRT 2X 85 and MBN DRT 2X 85 Transmitters GX2 DRR 2X 85 and CHP D2RRX 85 Receivers FEATURES Allows return bandwidth expansion up to 85 MHz Easy node segmentation with 2X RF TDM Simplified logistics
Model 6944 and 6940 Node bdr Digital Reverse 4:1 Multiplexing System designed for Prisma II Platform
 Optoelectronics Model 6944 and 6940 Node bdr Digital Reverse 4:1 Multiplexing System designed for Prisma II Platform Description The bdr Digital Reverse 4:1 Multiplexing System expands the functionality
Optoelectronics Model 6944 and 6940 Node bdr Digital Reverse 4:1 Multiplexing System designed for Prisma II Platform Description The bdr Digital Reverse 4:1 Multiplexing System expands the functionality
Wavelength-Enhanced Passive Optical Networks with Extended Reach
 Wavelength-Enhanced Passive Optical Networks with Extended Reach Ken Reichmann and Pat Iannone Optical Systems Research AT&T Labs, Middletown NJ Thanks to Han Hyub Lee, Xiang Zhou, and Pete Magill Wavelength-Enhanced
Wavelength-Enhanced Passive Optical Networks with Extended Reach Ken Reichmann and Pat Iannone Optical Systems Research AT&T Labs, Middletown NJ Thanks to Han Hyub Lee, Xiang Zhou, and Pete Magill Wavelength-Enhanced
Prisma II 1 GHz SuperQAM Full Spectrum Transmitter
 Prisma II 1 GHz SuperQAM Full Spectrum Transmitter The Prisma II optical networks allow for best in class architectures with increased reliability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. The Prisma II 1
Prisma II 1 GHz SuperQAM Full Spectrum Transmitter The Prisma II optical networks allow for best in class architectures with increased reliability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. The Prisma II 1
Data-Over-Cable Service Interface Specifications Technical Reports. Midsplit Migration Implications on the HFC Network Technical Report
 Data-Over-Cable Service Interface Specifications Midsplit Migration Implications on the HFC Network Technical Report Released Notice This DOCSIS technical report is the result of a cooperative effort undertaken
Data-Over-Cable Service Interface Specifications Midsplit Migration Implications on the HFC Network Technical Report Released Notice This DOCSIS technical report is the result of a cooperative effort undertaken
End of Life. Headend Optics Platform (HLP) SPL7210S/A. HL2 Series SUPRALink High Density DWDM Transmitter FEATURES PRODUCT OVERVIEW. arris.
 arris.com Headend Optics Platform (HLP) SPL7210S/A HL2 Series SUPRALink High Density DWDM Transmitter FEATURES Compact size enables 20 DFB modules to fit in a 3RU platform DWDM technology optimizes HFC
arris.com Headend Optics Platform (HLP) SPL7210S/A HL2 Series SUPRALink High Density DWDM Transmitter FEATURES Compact size enables 20 DFB modules to fit in a 3RU platform DWDM technology optimizes HFC
System Impairments Mitigation for NGPON2 via OFDM
 System Impairments Mitigation for NGPON2 via OFDM Yingkan Chen (1) Christian Ruprecht (2) Prof. Dr. Ing. Norbert Hanik (1) (1). Institute for Communications Engineering, TU Munich, Germany (2). Chair for
System Impairments Mitigation for NGPON2 via OFDM Yingkan Chen (1) Christian Ruprecht (2) Prof. Dr. Ing. Norbert Hanik (1) (1). Institute for Communications Engineering, TU Munich, Germany (2). Chair for
Prisma II 1 GHz SuperQAM Transmitter
 Prisma II 1 GHz SuperQAM Transmitter The Prisma II optical networks allow for best in class architectures with increased reliability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. The Prisma II 1 GHz SuperQAM Transmitter
Prisma II 1 GHz SuperQAM Transmitter The Prisma II optical networks allow for best in class architectures with increased reliability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. The Prisma II 1 GHz SuperQAM Transmitter
MODEL BTN GHz OPTICAL NODE STARLINE SERIES
 MODEL BTN100 1 1 GHz OPTICAL NODE STARLINE SERIES The BTN100 optical node complements evolving fiber-deep networks by providing operators with a low cost amplifier to node drop in conversion with flexibility
MODEL BTN100 1 1 GHz OPTICAL NODE STARLINE SERIES The BTN100 optical node complements evolving fiber-deep networks by providing operators with a low cost amplifier to node drop in conversion with flexibility
7820R Optical Receiver MHz RFoG Return Path
 The 7820R RFoG return path optical receiver is a single-mode fiber pigtailed module featuring a low-noise, impedance-matched broadband photodiode and RF amplification. The device receives optical analog
The 7820R RFoG return path optical receiver is a single-mode fiber pigtailed module featuring a low-noise, impedance-matched broadband photodiode and RF amplification. The device receives optical analog
CX380X Advanced Spectrum and Burst QAM Analyzer
 Advanced Spectrum and Burst QAM Analyzer Preventative Network Monitoring With VeEX s VeSion system, the advanced Spectrum Analyzer and Bursty Demodulator captures rogue cable modems and provides proactive
Advanced Spectrum and Burst QAM Analyzer Preventative Network Monitoring With VeEX s VeSion system, the advanced Spectrum Analyzer and Bursty Demodulator captures rogue cable modems and provides proactive
GS7000 and GainMaker Reverse Segmentable Node bdr Digital Reverse 2:1 Multiplexing System
 GS7000 and GainMaker Reverse Segmentable Node bdr Digital Reverse 2:1 Multiplexing System The bdr Digital Reverse 2:1 Multiplexing System expands the functionality of the GS7000 and GainMaker Reverse Segmentable
GS7000 and GainMaker Reverse Segmentable Node bdr Digital Reverse 2:1 Multiplexing System The bdr Digital Reverse 2:1 Multiplexing System expands the functionality of the GS7000 and GainMaker Reverse Segmentable
DOCSIS 3.1 Downstream Early Lessons Learned
 DOCSIS 3.1 Downstream Early Lessons Learned A Technical Paper prepared for SCTE/ISBE by John J. Downey CMTS Technical Leader Cisco Systems Inc. RTP, NC 919-392-9150 jdowney@cisco.com 2017 SCTE-ISBE and
DOCSIS 3.1 Downstream Early Lessons Learned A Technical Paper prepared for SCTE/ISBE by John J. Downey CMTS Technical Leader Cisco Systems Inc. RTP, NC 919-392-9150 jdowney@cisco.com 2017 SCTE-ISBE and
Cisco Prisma II 1.2 GHz High Density Long Reach Multiwave Transmitter
 Data Sheet Cisco Prisma II 1.2 GHz High Density Long Reach Multiwave Transmitter The Cisco Prisma II 1.2 GHz High Density Long Reach Multiwave (HD-LRMW) Transmitter (Figure 1) is the CATV industry s first
Data Sheet Cisco Prisma II 1.2 GHz High Density Long Reach Multiwave Transmitter The Cisco Prisma II 1.2 GHz High Density Long Reach Multiwave (HD-LRMW) Transmitter (Figure 1) is the CATV industry s first
Cisco dan Hotel Crowne Plaza Beograd, Srbija.
 Cisco dan 31. 3. 2016. Hotel Crowne Plaza Beograd, Srbija www.ciscoday.com Novosti iz DOCSIS sveta Bojan Nedelcev Product Sales Specialist, SP Video & Cable Access, South East Europe March, 2016 DOCSIS
Cisco dan 31. 3. 2016. Hotel Crowne Plaza Beograd, Srbija www.ciscoday.com Novosti iz DOCSIS sveta Bojan Nedelcev Product Sales Specialist, SP Video & Cable Access, South East Europe March, 2016 DOCSIS
Cisco Enhanced Digital Return (EDR) 85 System Compact Segmentable Nodes
 Cisco Enhanced Digital Return (EDR) 85 System Compact Segmentable Nodes The Cisco Enhanced Digital Return (EDR) 85 System expands the functionality of Compact Segmentable Nodes by increasing the performance,
Cisco Enhanced Digital Return (EDR) 85 System Compact Segmentable Nodes The Cisco Enhanced Digital Return (EDR) 85 System expands the functionality of Compact Segmentable Nodes by increasing the performance,
PARTNERSHIP FOR EXTENDED CAPACITY: DOCSIS 3.1 WITH RFOG
 PARTNERSHIP FOR EXTENDED CAPACITY: DOCSIS 3.1 WITH RFOG VENK MUTALIK, VP TECHNOLOGY AND STRATEGY MARCEL SCHEMMANN, PRINCIPAL ENGINEER AYHAM AL- BANNA, DISTINGUISHED SYSTEMS ENGINEER ZORAN MARICEVIC, ENGINEERING
PARTNERSHIP FOR EXTENDED CAPACITY: DOCSIS 3.1 WITH RFOG VENK MUTALIK, VP TECHNOLOGY AND STRATEGY MARCEL SCHEMMANN, PRINCIPAL ENGINEER AYHAM AL- BANNA, DISTINGUISHED SYSTEMS ENGINEER ZORAN MARICEVIC, ENGINEERING
GS7000 & GainMaker Reverse Segmentable Node bdr Digital Reverse 2:1 Multiplexing System
 Optoelectronics GS7000 & GainMaker Reverse Segmentable Node bdr Digital Reverse 2:1 Multiplexing System Description The bdr Digital Reverse 2:1 Multiplexing System expands the functionality of the Scientific-Atlanta
Optoelectronics GS7000 & GainMaker Reverse Segmentable Node bdr Digital Reverse 2:1 Multiplexing System Description The bdr Digital Reverse 2:1 Multiplexing System expands the functionality of the Scientific-Atlanta
Frequency Reuse How Do I Maximize the Value of My Spectrum?
 Frequency Reuse How Do I Maximize the Value of My Spectrum? Eric Wilson VP Systems Management, Vyyo Broadband Wireless Forum, February 20, 2001 Spectrum Reuse Outline Definition / concept Alternatives
Frequency Reuse How Do I Maximize the Value of My Spectrum? Eric Wilson VP Systems Management, Vyyo Broadband Wireless Forum, February 20, 2001 Spectrum Reuse Outline Definition / concept Alternatives
Cisco EDR 85 System: Modules for Cisco GainMaker and GS7000
 Data Sheet Cisco EDR 85 System: Modules for Cisco GainMaker and GS7000 The Cisco Enhanced Digital Return (EDR) 85 System expands the functionality of Cisco GS7000 and Cisco GainMaker Nodes by increasing
Data Sheet Cisco EDR 85 System: Modules for Cisco GainMaker and GS7000 The Cisco Enhanced Digital Return (EDR) 85 System expands the functionality of Cisco GS7000 and Cisco GainMaker Nodes by increasing
Broadband System - J
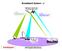 Broadband System - J Satellites are spaced every 2nd degrees above earth "C" Band Toward satellite 6.0 GHz Toward earth 4.0 GHz "L" Band Toward satellite 14.0 GHz Toward earth 12.0 GHz TV TRANSMITTER Headend
Broadband System - J Satellites are spaced every 2nd degrees above earth "C" Band Toward satellite 6.0 GHz Toward earth 4.0 GHz "L" Band Toward satellite 14.0 GHz Toward earth 12.0 GHz TV TRANSMITTER Headend
SignalOn Series WHITE PAPER. Impact of CCAP on RF Management Isolation. Pat. #s U.S. 6,842,348; 7,043,236; Cdn. 2,404,840; 2,404,844
 SignalOn Series Pat. #s U.S. 6,84,48; 7,04,6; Cdn.,404,840;,404,844 D. / CCAP Compliant Impact of CCAP on RF Management Isolation Although every effort has been taken to ensure the accuracy of this document
SignalOn Series Pat. #s U.S. 6,84,48; 7,04,6; Cdn.,404,840;,404,844 D. / CCAP Compliant Impact of CCAP on RF Management Isolation Although every effort has been taken to ensure the accuracy of this document
Homeworx Lessons? What can we learn from the first deployment of OFDMA on HFC? Hal Roberts, Calix
 Homeworx Lessons? What can we learn from the first deployment of OFDMA on HFC? Hal Roberts, Calix The information contained in this presentation is not a commitment, promise, or legal obligation to deliver
Homeworx Lessons? What can we learn from the first deployment of OFDMA on HFC? Hal Roberts, Calix The information contained in this presentation is not a commitment, promise, or legal obligation to deliver
TELESTE AC NODE SPECIFIC MODULES
 TELESTE AC NODE SPECIFIC MODULES AC 6310 Power supply module for Teleste AC8000 and AC8800 optical nodes. Can work alone or it can be operated parallel to split the work load and create the redundancy
TELESTE AC NODE SPECIFIC MODULES AC 6310 Power supply module for Teleste AC8000 and AC8800 optical nodes. Can work alone or it can be operated parallel to split the work load and create the redundancy
Evolution from TDM-PONs to Next-Generation PONs
 Evolution from TDM-PONs to Next-Generation PONs Ki-Man Choi, Jong-Hoon Lee, and Chang-Hee Lee Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology,
Evolution from TDM-PONs to Next-Generation PONs Ki-Man Choi, Jong-Hoon Lee, and Chang-Hee Lee Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology,
Cisco Prisma II Quad Optical Input Enhanced Digital Return (EDR) Receiver for Compact Segmentable Nodes
 Data Sheet Cisco Prisma II Quad Optical Input Enhanced Digital Return (EDR) Receiver for Compact Segmentable Nodes The Cisco Quad Optical Input Enhanced Digital Return (Q-EDR) 85 Receiver expands the Cisco
Data Sheet Cisco Prisma II Quad Optical Input Enhanced Digital Return (EDR) Receiver for Compact Segmentable Nodes The Cisco Quad Optical Input Enhanced Digital Return (Q-EDR) 85 Receiver expands the Cisco
CPD POINTER PNM ENABLED CPD DETECTION FOR THE HFC NETWORK WHITE PAPER ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY
 ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY CPD POINTER PNM ENABLED CPD DETECTION FOR THE HFC NETWORK WHITE PAPER 185 AINSLEY DRIVE SYRACUSE, NY 13210 800.448.1655 I WWW.ARCOMDIGITAL.COM The continued evolution of Proactive Network
ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY CPD POINTER PNM ENABLED CPD DETECTION FOR THE HFC NETWORK WHITE PAPER 185 AINSLEY DRIVE SYRACUSE, NY 13210 800.448.1655 I WWW.ARCOMDIGITAL.COM The continued evolution of Proactive Network
CHP Max CORWave Full Spectrum Multi-Wavelength Forward Transmitters
 CHP Max CORWave Full Spectrum Multi-Wavelength Forward Transmitters Bandwidth Usage is Expanding 100G 10G 1G 100M 10M Max Permitted Bandwidth for Modems (bps) The past 25-years show a constant increase
CHP Max CORWave Full Spectrum Multi-Wavelength Forward Transmitters Bandwidth Usage is Expanding 100G 10G 1G 100M 10M Max Permitted Bandwidth for Modems (bps) The past 25-years show a constant increase
Editor: this header only appears here to set number 100 and is not to be included.
 100 LEVEL 1 Editor: this header only appears here to set number 100 and is not to be included. 100.2 Level two Editor: this header only appears here to set number 2 and is not to be included. Change Subclause
100 LEVEL 1 Editor: this header only appears here to set number 100 and is not to be included. 100.2 Level two Editor: this header only appears here to set number 2 and is not to be included. Change Subclause
Subminiature, Low power DACs Address High Channel Density Transmitter Systems
 Subminiature, Low power DACs Address High Channel Density Transmitter Systems By: Analog Devices, Inc. (ADI) Daniel E. Fague, Applications Engineering Manager, High Speed Digital to Analog Converters Group
Subminiature, Low power DACs Address High Channel Density Transmitter Systems By: Analog Devices, Inc. (ADI) Daniel E. Fague, Applications Engineering Manager, High Speed Digital to Analog Converters Group
4x100GE through 2 and 10km SMF Using DMT and 1.3mm LAN-WDM EMLs. Winston Way, Trevor Chan, NeoPhotonics, USA
 4x100GE through 2 and 10km SMF Using and 1.3mm LAN-WDM EMLs Winston Way, Trevor Chan, NeoPhotonics, USA IEEE802.3 400GbE Study Group, November 2013 Objectives Study the technical feasibility of using to
4x100GE through 2 and 10km SMF Using and 1.3mm LAN-WDM EMLs Winston Way, Trevor Chan, NeoPhotonics, USA IEEE802.3 400GbE Study Group, November 2013 Objectives Study the technical feasibility of using to
7820C CATV Optical Receiver 200 MHz HFC Return Path
 The 7820C optical receiver is a single-mode fiber pigtailed module featuring a low-noise, impedance-matched broadband photodiode and RF amplification. The device receives optical analog and/or digital
The 7820C optical receiver is a single-mode fiber pigtailed module featuring a low-noise, impedance-matched broadband photodiode and RF amplification. The device receives optical analog and/or digital
Baseline Proposal for EPoC PHY Layer IEEE 802.3bn EPoC September 2012 AVI KLIGER, BROADCOM LEO MONTREUIL, BROADCOM ED BOYD, BROADCOM
 Baseline Proposal for EPoC PHY Layer IEEE 802.3bn EPoC September 2012 AVI KLIGER, BROADCOM LEO MONTREUIL, BROADCOM ED BOYD, BROADCOM NOTE This presentation includes results based on an inhouse Channel
Baseline Proposal for EPoC PHY Layer IEEE 802.3bn EPoC September 2012 AVI KLIGER, BROADCOM LEO MONTREUIL, BROADCOM ED BOYD, BROADCOM NOTE This presentation includes results based on an inhouse Channel
IEEE P802.3bn Tutorial E P o C
 IEEE P802.3bn Tutorial Part 2 (Teil 2) EPON Protocol Over Coax EPoC Monday, 9 March 2015 Mark Laubach, Chair, Broadcom Duane Remein, Chief Editor, Huawei Agenda Review of Part 1 from November 2014 Introduction
IEEE P802.3bn Tutorial Part 2 (Teil 2) EPON Protocol Over Coax EPoC Monday, 9 March 2015 Mark Laubach, Chair, Broadcom Duane Remein, Chief Editor, Huawei Agenda Review of Part 1 from November 2014 Introduction
Baseline Proposal for EPoC PHY Layer
 Baseline Proposal for EPoC PHY Layer AVI KLIGER, BROADCOM LEO MONTREUIL, BROADCOM ED BOYD, BROADCOM NOTE This presentation includes results based on an in house Channel Models When an approved Task Force
Baseline Proposal for EPoC PHY Layer AVI KLIGER, BROADCOM LEO MONTREUIL, BROADCOM ED BOYD, BROADCOM NOTE This presentation includes results based on an in house Channel Models When an approved Task Force
Deploying the Promise of NLOS WiMAX. Les Sparrey Director of NA Sales
 Deploying the Promise of NLOS WiMAX Les Sparrey Director of NA Sales WiMAX Coverage, Capacity & Affordability Superior Range More Throughput Much Lower Cost 2 Product Introduction About develops high performance,
Deploying the Promise of NLOS WiMAX Les Sparrey Director of NA Sales WiMAX Coverage, Capacity & Affordability Superior Range More Throughput Much Lower Cost 2 Product Introduction About develops high performance,
GainStar 1 GHz Node with 42/54 MHz Split
 GainStar 1 GHz Node with 42/54 MHz Split The 1 GHz GainStar Node (GSN) is specifically designed to serve in HFC networks. With its modular design of Optics and RF amplifier electronics, the GSN can provide
GainStar 1 GHz Node with 42/54 MHz Split The 1 GHz GainStar Node (GSN) is specifically designed to serve in HFC networks. With its modular design of Optics and RF amplifier electronics, the GSN can provide
Optimize Cell-Site Deployments
 Optimize Cell-Site Deployments CellAdvisor BBU Emulation Mobile operators continue to face an insatiable demand for capacity, driven by multimedia applications and the ever-increasing number of devices
Optimize Cell-Site Deployments CellAdvisor BBU Emulation Mobile operators continue to face an insatiable demand for capacity, driven by multimedia applications and the ever-increasing number of devices
CWDM Cisco CWDM wavelengths (nm)
 Cisco Enhanced Wavelength Division Multiplexing Product Line The Cisco enhanced wavelength-division multiplexing (EWDM) product line allows users to scale the speed and capacity of the services offered
Cisco Enhanced Wavelength Division Multiplexing Product Line The Cisco enhanced wavelength-division multiplexing (EWDM) product line allows users to scale the speed and capacity of the services offered
The BT87 also offers high gain. This allows the operator to hold existing amplifier locations during system upgrades thereby reducing system costs.
 BT87 870 MHz Amplifier STARLINE Series Motorola s STARLINE series amplifier, model BT87*/*, leads the industry in features and performance and is designed to meet the needs of today's expanding broadband
BT87 870 MHz Amplifier STARLINE Series Motorola s STARLINE series amplifier, model BT87*/*, leads the industry in features and performance and is designed to meet the needs of today's expanding broadband
Maintaining an All Digital Plant
 Maintaining an All Digital Plant Presenter: Tony Holmes SCTE Iowa Heartland Chapter Technical Session Overview Physical Layer (PHY) metrics used by operators to measure digital health QAM performance metrics
Maintaining an All Digital Plant Presenter: Tony Holmes SCTE Iowa Heartland Chapter Technical Session Overview Physical Layer (PHY) metrics used by operators to measure digital health QAM performance metrics
ODN4P. Optical Distribution Node, Four Ports. About the Product
 About the Product The Light Link Series 2, deep-fibre Optical Distribution Node ODN4P is a prime building block for highperformance networks, designed for adaptability, scalability and optional return-path
About the Product The Light Link Series 2, deep-fibre Optical Distribution Node ODN4P is a prime building block for highperformance networks, designed for adaptability, scalability and optional return-path
SmartScan. Application Note. Intelligent Frequency Response and Limits in Plant Distribution. VIAVI Solutions
 Application Note SmartScan Intelligent Frequency Response and Limits in Plant Distribution VIAVI Solutions As signals travel through the coaxial cable network they are attenuated more at higher frequencies.
Application Note SmartScan Intelligent Frequency Response and Limits in Plant Distribution VIAVI Solutions As signals travel through the coaxial cable network they are attenuated more at higher frequencies.
The Physical Layer Outline
 The Physical Layer Outline Theoretical Basis for Data Communications Digital Modulation and Multiplexing Guided Transmission Media (copper and fiber) Public Switched Telephone Network and DSLbased Broadband
The Physical Layer Outline Theoretical Basis for Data Communications Digital Modulation and Multiplexing Guided Transmission Media (copper and fiber) Public Switched Telephone Network and DSLbased Broadband
Super-PON. Scale Fully Passive Optical Access Networks to Longer Reaches and to a Significantly Higher Number of Subscribers
 Super-PON Scale Fully Passive Optical Access Networks to Longer Reaches and to a Significantly Higher Number of Subscribers Claudio DeSanti Liang Du Cedric Lam Joy Jiang Agenda Super-PON Idea Why Super-PON?
Super-PON Scale Fully Passive Optical Access Networks to Longer Reaches and to a Significantly Higher Number of Subscribers Claudio DeSanti Liang Du Cedric Lam Joy Jiang Agenda Super-PON Idea Why Super-PON?
25G TDM PON overview. Ed Harstead, member Fixed Networks CTO Dora van Veen, Vincent Houtsma, and Peter Vetter, Bell Labs
 25G TDM PON overview Ed Harstead, member Fixed Networks CTO Dora van Veen, Vincent Houtsma, and Peter Vetter, Bell Labs September 2015 1 Downstream capacity (Mb/s) Background: Evolution of TDM PON bit
25G TDM PON overview Ed Harstead, member Fixed Networks CTO Dora van Veen, Vincent Houtsma, and Peter Vetter, Bell Labs September 2015 1 Downstream capacity (Mb/s) Background: Evolution of TDM PON bit
WPS GHz Linear Power Amplifier Data Sheet
 Features 15.0 db Gain 36 dbm P1dB 48 dbm IP3 EVM < 2.5% at 29 dbm Pout Applications 802.16 WiMax 802.11 WLAN Wireless Communications Telecomm Infrastructure Prematch for Easy Cascade Pb Free Surface Mount
Features 15.0 db Gain 36 dbm P1dB 48 dbm IP3 EVM < 2.5% at 29 dbm Pout Applications 802.16 WiMax 802.11 WLAN Wireless Communications Telecomm Infrastructure Prematch for Easy Cascade Pb Free Surface Mount
WPS GHz Linear Power Amplifier Data Sheet
 Features 15.0 db Gain 36 dbm P1dB 48 dbm IP3 EVM < 2.5% at 29 dbm Pout Prematch for Easy Cascade Pb Free Surface Mount Pkg MTTF > 100 yrs @ T C 150 C Applications 802.16 WiMax 802.11 WLAN Wireless Communications
Features 15.0 db Gain 36 dbm P1dB 48 dbm IP3 EVM < 2.5% at 29 dbm Pout Prematch for Easy Cascade Pb Free Surface Mount Pkg MTTF > 100 yrs @ T C 150 C Applications 802.16 WiMax 802.11 WLAN Wireless Communications
Polarization Mode Dispersion and Its Mitigation Techniques in High Speed Fiber Optical Communication Systems
 Polarization Mode Dispersion and Its Mitigation Techniques in High Speed Fiber Optical Communication Systems Chongjin Xie Bell Labs, Lucent Technologies 791 Holmdel-Keyport Road, Holmdel, NJ 07733 WOCC
Polarization Mode Dispersion and Its Mitigation Techniques in High Speed Fiber Optical Communication Systems Chongjin Xie Bell Labs, Lucent Technologies 791 Holmdel-Keyport Road, Holmdel, NJ 07733 WOCC
Understanding Low Phase Noise Signals. Presented by: Riadh Said Agilent Technologies, Inc.
 Understanding Low Phase Noise Signals Presented by: Riadh Said Agilent Technologies, Inc. Introduction Instabilities in the frequency or phase of a signal are caused by a number of different effects. Each
Understanding Low Phase Noise Signals Presented by: Riadh Said Agilent Technologies, Inc. Introduction Instabilities in the frequency or phase of a signal are caused by a number of different effects. Each
Error! No text of specified style in document. Table Error! No text of specified style in document.-1 - CNU transmitter output signal characteristics
 1.1.1 CNU Transmitter Output Requirements The CNU shall output an RF Modulated signal with characteristics delineated in Table Error! No text of specified style in document.-1. Table -1 - CNU transmitter
1.1.1 CNU Transmitter Output Requirements The CNU shall output an RF Modulated signal with characteristics delineated in Table Error! No text of specified style in document.-1. Table -1 - CNU transmitter
EPoC Upstream Modulation Profiles Eugene Dai, PhD, Cox Communications Hal Roberts, Calix Networks
 EPoC Upstream Modulation Profiles Eugene Dai, PhD, Cox Communications Hal oberts, Calix Networks IEEE 8023 Plenary Meeting 8023bn EPON Protocol over Coax Task Force July 14th 19th, Geneva Switzerland Outline
EPoC Upstream Modulation Profiles Eugene Dai, PhD, Cox Communications Hal oberts, Calix Networks IEEE 8023 Plenary Meeting 8023bn EPON Protocol over Coax Task Force July 14th 19th, Geneva Switzerland Outline
Monitoring Cable Technologies
 27 CHAPTER Cable broadband communication operates in compliance with the Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS) standard which prescribes multivendor interoperability and promotes a retail
27 CHAPTER Cable broadband communication operates in compliance with the Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS) standard which prescribes multivendor interoperability and promotes a retail
Agilent 83440B/C/D High-Speed Lightwave Converters
 Agilent 8344B/C/D High-Speed Lightwave Converters DC-6/2/3 GHz, to 6 nm Technical Specifications Fast optical detector for characterizing lightwave signals Fast 5, 22, or 73 ps full-width half-max (FWHM)
Agilent 8344B/C/D High-Speed Lightwave Converters DC-6/2/3 GHz, to 6 nm Technical Specifications Fast optical detector for characterizing lightwave signals Fast 5, 22, or 73 ps full-width half-max (FWHM)
Application Note. Measuring distortion and Un-equalized MER
 Application Note Measuring distortion and Un-equalized MER The Verification Experts Background Modern Cable Modems, Set-top-boxes and Cable Modem Termination Systems (CMTS) use advanced Adaptive Equalizer
Application Note Measuring distortion and Un-equalized MER The Verification Experts Background Modern Cable Modems, Set-top-boxes and Cable Modem Termination Systems (CMTS) use advanced Adaptive Equalizer
Cisco s CLEC Networkers Power Session
 Course Number Presentation_ID 1 Cisco s CLEC Networkers Power Session Session 2 The Business Case for ONS 15800 3 What s Driving the Demand? Data Voice 4 What s Driving the Demand? Internet 36,700,000
Course Number Presentation_ID 1 Cisco s CLEC Networkers Power Session Session 2 The Business Case for ONS 15800 3 What s Driving the Demand? Data Voice 4 What s Driving the Demand? Internet 36,700,000
Active Antennas: The Next Step in Radio and Antenna Evolution
 Active Antennas: The Next Step in Radio and Antenna Evolution Kevin Linehan VP, Chief Technology Officer, Antenna Systems Dr. Rajiv Chandrasekaran Director of Technology Development, RF Power Amplifiers
Active Antennas: The Next Step in Radio and Antenna Evolution Kevin Linehan VP, Chief Technology Officer, Antenna Systems Dr. Rajiv Chandrasekaran Director of Technology Development, RF Power Amplifiers
Upstream Challenges With DOCSIS 3.1
 Upstream Challenges With DOCSIS 3.1 White Paper A Technical Paper prepared for SCTE/ISBE by Jan Ariesen Chief Technology Officer Technetix Inc 2017 SCTE-ISBE and NCTA. All rights reserved. Title Table
Upstream Challenges With DOCSIS 3.1 White Paper A Technical Paper prepared for SCTE/ISBE by Jan Ariesen Chief Technology Officer Technetix Inc 2017 SCTE-ISBE and NCTA. All rights reserved. Title Table
Screening Attenuation When enough is enough
 Screening Attenuation When enough is enough Anders Møller-Larsen, Ph.D. M.Sc. E.E. Product Manager, Coax Network Introduction This white paper describes the requirements to screening attenuation of cables
Screening Attenuation When enough is enough Anders Møller-Larsen, Ph.D. M.Sc. E.E. Product Manager, Coax Network Introduction This white paper describes the requirements to screening attenuation of cables
GainMaker Optoelectronic Node 1 GHz with 40/52 MHz Split and RF Redundancy
 Optoelectronics GainMaker Optoelectronic Node 1 GHz with 40/52 MHz Split and RF Redundancy Description The GainMaker Node is designed to serve as the cornerstone of today s emerging fiber deeper network
Optoelectronics GainMaker Optoelectronic Node 1 GHz with 40/52 MHz Split and RF Redundancy Description The GainMaker Node is designed to serve as the cornerstone of today s emerging fiber deeper network
product overview optical nodes
 product overview optical nodes As a specialist for HFC- and RFoG-networks, DELTA Electronics offers a wide range of optical nodes. They are optimized for the individual applications at different locations.
product overview optical nodes As a specialist for HFC- and RFoG-networks, DELTA Electronics offers a wide range of optical nodes. They are optimized for the individual applications at different locations.
Spectrum Management and Advanced Spectrum Management
 Spectrum Management and Advanced Spectrum Management This chapter describes the spectrum management features supported for the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) routers. Spectrum management support
Spectrum Management and Advanced Spectrum Management This chapter describes the spectrum management features supported for the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) routers. Spectrum management support
SmartAX MA5633 D-CCAP Head End Device
 SmartAX MA5633 D-CCAP Head End Device Product Overview Huawei SmartAX MA5633 distributed converged cable access platform (D-CCAP) head end device (MA5633 for short) is a full-service, digital cable network
SmartAX MA5633 D-CCAP Head End Device Product Overview Huawei SmartAX MA5633 distributed converged cable access platform (D-CCAP) head end device (MA5633 for short) is a full-service, digital cable network
1 GHz SASMAX II series
 1 GHz SASMAX II series SASMAX II Line Extender (Legacy LEII style) Description: The 1 GHz SASMAX II series broadband line extender is essentially a drop-in-upgrade module that allows the customer to perform
1 GHz SASMAX II series SASMAX II Line Extender (Legacy LEII style) Description: The 1 GHz SASMAX II series broadband line extender is essentially a drop-in-upgrade module that allows the customer to perform
IEEE July 2001 Plenary Meeting Portland, OR Robert S. Carlisle Sr. Market Development Engineer
 Ethernet PON Fiber Considerations IEEE July 2001 Plenary Meeting Portland, OR Robert S. Carlisle Sr. Market Development Engineer Special Thanks to Contributors Kendall Musgrove - Sr. Market Development
Ethernet PON Fiber Considerations IEEE July 2001 Plenary Meeting Portland, OR Robert S. Carlisle Sr. Market Development Engineer Special Thanks to Contributors Kendall Musgrove - Sr. Market Development
Using 1 GHz GainMaker Amplifiers in an 870 MHz System Application Note
 Using 1 GHz GainMaker Amplifiers in an 870 MHz System Application Note Overview Introduction The move to a 1 GHz cable telecommunications system infrastructure is being driven by the increasing need for
Using 1 GHz GainMaker Amplifiers in an 870 MHz System Application Note Overview Introduction The move to a 1 GHz cable telecommunications system infrastructure is being driven by the increasing need for
CXE880 FIBRE OPTIC NODE
 Kari Mäki 21.4.2011 1(6) CXE880 FIBRE OPTIC NODE The CXE880 is a fibre deep optical node. It is designed for cases where high performance and cost effectiveness are a demand. Requirements of future networks,
Kari Mäki 21.4.2011 1(6) CXE880 FIBRE OPTIC NODE The CXE880 is a fibre deep optical node. It is designed for cases where high performance and cost effectiveness are a demand. Requirements of future networks,
Agilent Highly Accurate Amplifier ACLR and ACPR Testing with the Agilent N5182A MXG Vector Signal Generator. Application Note
 Agilent Highly Accurate Amplifier ACLR and ACPR Testing with the Agilent N5182A MXG Vector Signal Generator Application Note Introduction 1 0 0 1 Symbol encoder I Q Baseband filters I Q IQ modulator Other
Agilent Highly Accurate Amplifier ACLR and ACPR Testing with the Agilent N5182A MXG Vector Signal Generator Application Note Introduction 1 0 0 1 Symbol encoder I Q Baseband filters I Q IQ modulator Other
Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers (SOAs) as Power Boosters. Applications Note No. 0001
 Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers (s) as Power Boosters Applications Note No. 0001 Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers (s) as Power Boosters There is a growing need to manage the increase in loss budgets associated
Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers (s) as Power Boosters Applications Note No. 0001 Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers (s) as Power Boosters There is a growing need to manage the increase in loss budgets associated
Datasheet. Shielded airmax ac Radio with Isolation Antenna. Model: IS-5AC. Interchangeable Isolation Antenna Horn. All-Metal, Shielded Radio Base
 Shielded airmax ac Radio with Isolation Antenna Model: IS-5AC Interchangeable Isolation Antenna Horn All-Metal, Shielded Radio Base airmax ac Processor for Superior Performance Overview Ubiquiti Networks
Shielded airmax ac Radio with Isolation Antenna Model: IS-5AC Interchangeable Isolation Antenna Horn All-Metal, Shielded Radio Base airmax ac Processor for Superior Performance Overview Ubiquiti Networks
Project: IEEE P Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks N
 Project: IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks N (WPANs) Title: [The Scalability of UWB PHY Proposals] Date Submitted: [July 13, 2004] Source: [Matthew Welborn] Company [Freescale
Project: IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks N (WPANs) Title: [The Scalability of UWB PHY Proposals] Date Submitted: [July 13, 2004] Source: [Matthew Welborn] Company [Freescale
Radio over Fiber technology for 5G Cloud Radio Access Network Fronthaul
 Radio over Fiber technology for 5G Cloud Radio Access Network Fronthaul Using a highly linear fiber optic transceiver with IIP3 > 35 dbm, operating at noise level of -160dB/Hz, we demonstrate 71 km RF
Radio over Fiber technology for 5G Cloud Radio Access Network Fronthaul Using a highly linear fiber optic transceiver with IIP3 > 35 dbm, operating at noise level of -160dB/Hz, we demonstrate 71 km RF
2012 LitePoint Corp LitePoint, A Teradyne Company. All rights reserved.
 LTE TDD What to Test and Why 2012 LitePoint Corp. 2012 LitePoint, A Teradyne Company. All rights reserved. Agenda LTE Overview LTE Measurements Testing LTE TDD Where to Begin? Building a LTE TDD Verification
LTE TDD What to Test and Why 2012 LitePoint Corp. 2012 LitePoint, A Teradyne Company. All rights reserved. Agenda LTE Overview LTE Measurements Testing LTE TDD Where to Begin? Building a LTE TDD Verification
SOA pre-amplified upstream signal power in 100G EPON
 SOA pre-amplified upstream signal power in 100G EPON Hanhyub Lee, and Hwan Seok Chung IEEE P802.3ca 100G-EPON Task Force May 22-26, 2017 New Orleans, Louisiana, USA 100G EPON OLT must use a pre-amplifer
SOA pre-amplified upstream signal power in 100G EPON Hanhyub Lee, and Hwan Seok Chung IEEE P802.3ca 100G-EPON Task Force May 22-26, 2017 New Orleans, Louisiana, USA 100G EPON OLT must use a pre-amplifer
CXE880 FIBRE OPTIC NODE
 Kari Mäki 4.3.2008 1(6) CXE880 FIBRE OPTIC NODE The CXE880 is a fibre deep optical node. It is designed for cases where high performance and cost effectiveness are a demand. Requirements of future networks,
Kari Mäki 4.3.2008 1(6) CXE880 FIBRE OPTIC NODE The CXE880 is a fibre deep optical node. It is designed for cases where high performance and cost effectiveness are a demand. Requirements of future networks,
Adtran, Inc All rights reserved. Total Access 5000 Gigabit Passive Optical Network GPON Overview
 1 Total Access 5000 Gigabit Passive Optical Network GPON Overview 2 What is a PON? Passive no electronics in OSP Less maintenance, higher reliability Splitters to allow sharing of network unpowered, unmanaged
1 Total Access 5000 Gigabit Passive Optical Network GPON Overview 2 What is a PON? Passive no electronics in OSP Less maintenance, higher reliability Splitters to allow sharing of network unpowered, unmanaged
UPSTREAM CHALLENGES WITH DOCSIS 3.1
 UPSTREAM CHALLENGES WITH DOCSIS 3.1 White Paper By Jan Ariesen Chief Technology Officer 24th August 2017 Aug/2017 Contents 1.0 Introduction... 1 2. Passive intermodulation (PIM) in in-home splitters...
UPSTREAM CHALLENGES WITH DOCSIS 3.1 White Paper By Jan Ariesen Chief Technology Officer 24th August 2017 Aug/2017 Contents 1.0 Introduction... 1 2. Passive intermodulation (PIM) in in-home splitters...
Optical Digital Transmission Systems. Xavier Fernando ADROIT Lab Ryerson University
 Optical Digital Transmission Systems Xavier Fernando ADROIT Lab Ryerson University Overview In this section we cover point-to-point digital transmission link design issues (Ch8): Link power budget calculations
Optical Digital Transmission Systems Xavier Fernando ADROIT Lab Ryerson University Overview In this section we cover point-to-point digital transmission link design issues (Ch8): Link power budget calculations
RF Over Fiber Design Guide Overview. Provided by OPTICAL ZONU CORPORATION
 RF Over Fiber Design Guide Overview Provided by OPTICAL ZONU CORPORATION Why use fiber? Transmission of RF and Microwave Signals via waveguides or coaxial cable suffers high insertion loss and susceptibility
RF Over Fiber Design Guide Overview Provided by OPTICAL ZONU CORPORATION Why use fiber? Transmission of RF and Microwave Signals via waveguides or coaxial cable suffers high insertion loss and susceptibility
OFDMA PHY for EPoC: a Baseline Proposal. Andrea Garavaglia and Christian Pietsch Qualcomm PAGE 1
 OFDMA PHY for EPoC: a Baseline Proposal Andrea Garavaglia and Christian Pietsch Qualcomm PAGE 1 Supported by Jorge Salinger (Comcast) Rick Li (Cortina) Lup Ng (Cortina) PAGE 2 Outline OFDM: motivation
OFDMA PHY for EPoC: a Baseline Proposal Andrea Garavaglia and Christian Pietsch Qualcomm PAGE 1 Supported by Jorge Salinger (Comcast) Rick Li (Cortina) Lup Ng (Cortina) PAGE 2 Outline OFDM: motivation
Model 6942 Four Port Optoelectronic Node 870 MHz with 42/54 MHz Split
 Optoelectronics Model 6942 Four ort Optoelectronic Node 870 MHz with 42/54 MHz Split Description The Model 6942 Node is a high performance, four output optoelectronic node. The Model 6942 Node can be configured
Optoelectronics Model 6942 Four ort Optoelectronic Node 870 MHz with 42/54 MHz Split Description The Model 6942 Node is a high performance, four output optoelectronic node. The Model 6942 Node can be configured
Increasing the Performance and Capacity of Digital Reverse Systems. A study of system performance using 4:1 bdr technology
 Increasing the Performance and Capacity of Digital Reverse Systems A study of system performance using 4:1 bdr technology Notices Trademark Acknowledgments Cisco, the Cisco logo, Cisco Systems, the Cisco
Increasing the Performance and Capacity of Digital Reverse Systems A study of system performance using 4:1 bdr technology Notices Trademark Acknowledgments Cisco, the Cisco logo, Cisco Systems, the Cisco
MRI & NMR spectrometer
 AMOS MRI & NMR spectrometer The AMOS Spectrometer is a highly modular and flexible unit that provides the ability to customize synchronized configurations for preclinical and clinical MR applications.
AMOS MRI & NMR spectrometer The AMOS Spectrometer is a highly modular and flexible unit that provides the ability to customize synchronized configurations for preclinical and clinical MR applications.
Achieving 1 Gbps Symmetrical Service
 Achieving 1 Gbps Symmetrical Service Werner Coomans, Bell Labs May 20 th, 2015 1 G.fast timeline 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 G.fast proof of concept Early operator lab tests G.fast prototype More lab tests
Achieving 1 Gbps Symmetrical Service Werner Coomans, Bell Labs May 20 th, 2015 1 G.fast timeline 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 G.fast proof of concept Early operator lab tests G.fast prototype More lab tests
