University of Pittsburgh
|
|
|
- Lesley Nelson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Pittsburgh Experiment #6 Lab Report Active Filters and Oscillators Submission Date: 7/9/28 Instructors: Dr. Ahmed Dallal Shangqian Gao Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex Williams Station #2 ECE 22: Electronic Circuit Design Laboratory
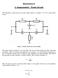
2 Introduction The purpose of this experiment will be to design, build, and test three active filters: two low pass filters and a band pass filter. The purpose of an active filter is to not only filter out a given range of frequencies, like a passive filter, but also to amplify the signal being filtered. In the case of Experiment #6, amplification was accomplished using the 74 operational amplifier (op-amp). Based on the observations made in Experiment #, known frequency response characteristics of op-amps were considered in the design of the filters in Experiment #6. In addition to the active filters, a Wien-bridge oscillator was also designed, built, and tested. The Wien-bridge oscillator works by utilizing an op-amp (in this case, the 74), and several passive circuit elements to generate a sinusoidal output. It should be noted that, unlike the other circuits designed thus far in the course, the Wien-bridge oscillator requires no input signal to produce the output, relying only on the op-amp supply voltage for power. Procedure Part I: Low-Pass Filters In Part I, the low-pass filter in Fig. was designed given two sets of design constraints. For both cases, resistors R and R 2 were to be equal, and the filter was to be designed to operate at a corner frequency of 38 Hz. Figure : Active Low-Pass Filter Designed in Part I For the first filter, capacitors C and C 2 were required to be equal, and the Q-factor was specified to be.77. Eq. gives an approximation of the Q value to ensure amplifier stability. Using this approximation with the known gain of the non-inverting amplifier, the ratio of R B/R A for Filter was calculated to be K 3 Q = + R B R A () Next, Eq. 2 was used and time constant RC was calculated given that R = R 2 and C = C 2 for Filter. From this, RC was calculated to be 4.88 x -4. Based on readily available capacitor values, a value of C = C 2 =. µf was chosen, leading to R = R 2 = 48.8 Ω for Filter. f o = (2) 2π R R 2 C C 2 For Filter 2, the amplifier was required to behave as a voltage follower, meaning resistor R B was theoretically zero, while R A was theoretically infinite. Also, the Q factor was specified to be. Given that the only other design criteria for Filter 2 was the corner frequency of 38 Hz, as with Filter, values of R, R 2, C, and C 2 for Filter 2 were chosen to be the same values used in Filter. Design constraints and chosen parameter values for both filters are summarized in Table.
3 Filter (Calculated) Filter (Actual) Filter 2 (Calculated) Filter 2 (Actual) Corner Frequency (f o) 38 Hz 38 Hz 38 Hz 38 Hz Q-Factor (Q) Resistor R A. kω. kω Ω Open Resistor R B Ω 59 Ω Ω Short Resistor R 48.8 Ω 47 Ω 48.8 Ω 47 Ω Resistor R Ω 47 Ω 48.8 Ω 47 Ω Capacitor C. µf. µf. µf. µf Capacitor C 2. µf. µf. µf. µf Table : Calculated and Actual Active Low-Pass Filter Design Parameters for Part I Using the values in Table, the first low-pass filter was constructed and tested. For both Filter and Filter 2, a supply voltage of V CC = ±2 V and a sinusoidal input signal with V pp =. V were used. A frequency response of Filter, shown in Fig. 2, was generated using the function generator, multimeter, and LabView software. Next, the value of resistor R B was altered by ±5% to the values shown in Table 2. R B 59 Ω R B + 5% 69 Ω R B 5% 5 Ω Table 2: Resistor RB with Variation of Approximately ±5% Using the value in Table 2 for R B, two more frequency responses were generated, shown in Fig. 3 and Fig. 4. Next, Filter 2 was constructed with the op-amp functioning as a voltage follower. Again, a supply voltage of V CC = ±2 V and a sinusoidal input signal with V pp =. V were used. The frequency response of Filter 2 is shown in Fig. 5. Part II: Band-Pass Filter In Part II, the band-pass filter in Fig. 6 was designed. The filter was to have a Q-factor of 7, and be designed to operate at a corner frequency of 62 Hz. Using Eq. 3, the ratio of R 2/R was calculated to be 44. Figure 6: Active Band-Pass Filter Designed in Part II Q = 3 + R 2 R (3) Based on readily-available capacitor values, C was decided to be 22 nf. Using this value and the ratio determined in Eq. 3, R was calculated using Eq. 4, allowing R 2 to be calculated based on the ratio established in Eq. 3. f o = 2π C 2 (R R 2 + R 2 ) (4)
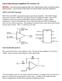
4 A summary of the device parameters chosen for the band pass filter is shown in Table 3. Filter 3 (Calculated) Filter 3 (Actual) Resistor R Ω 56 Ω Resistor R kω kω Capacitor C 22 nf 22 nf Table 3: Calculated and Actual Active Band-Pass Filter Design Parameters for Part II Using the parameters in Table 3, the band-pass filter was constructed using a supply voltage of V CC = ±2 V and a sinusoidal input signal of V pp =. V. The input signal voltage was decreased because, unlike the low-pass filter, the active band-pass filter produced a considerably higher gain. If output voltage were to exceed ±2 V, clipping would occur as the op-amp saturated, so the input signal voltage was reduced to prevent this. As in Part I, a frequency response was generated, shown in Fig. 7. As with the first low-pass filter, the value of resistor R 2 was altered by ±% to the values shown in Table 4, and corresponding frequency responses were generated, shown in Fig. 8 and Fig. 9. Part III: Oscillators R kω R 2 + % 27 kω R 2 % 22 kω Table 4: Resistor R2 with Variation of Approximately ±% In Part III, the Wien-Bridge oscillator in Fig. was designed, constructed, and tested. The purpose of an oscillator is to generate an oscillating (AC) signal from a DC source, in this case, the op-amp supply voltage. Figure : Wien-Bridge Oscillator Designed in Part III The frequency of the Wien-Bridge oscillator is determined by the values of R and C in Fig., while the amplification of the signal is determined by R 2 and R, which function as a non-inverting amplifier. For Experiment 6, values of R = 2 kω and C =. µf were provided. Based on these values, the frequency of oscillation was determined by applying the Barkhausen criterion. Applying the Barkhausen criterion, which requires that the absolute value of L(jω) =, to Eq. 5 shows that the oscillator is unstable under these conditions. V o = A L(jω) (5) Using the provided values of R and C, the frequency of oscillation was determined to be Hz using Eq. 6. ω = 2πf = RC (6) Next, the impedance of the parallel (Z p) and series (Z s) combinations of R and C were determined and applied to the Barkhausen criterion considering the frequency determined using Eq. 6. This led to the conclusion that the ratio of R 2/R must be no less than 2 for the Barkhausen criterion to apply for the desired frequency.
5 Voltage Gain (V/V) Given the required R 2/R ratio, the oscillator was constructed using the provide values of R and C, and a kω resistor, which measured to be Ω, for R. A decade potentiometer was connected to function as R 2 and adjusted until oscillations were observed on the output using an oscilloscope. Oscillations were observed, as shown in Fig., at R 2 = 2. kω. Oscillations were observed at a frequency of Hz, less than Hz from the predicted value of Hz. The value of R 2 was increased until near-square waves were observed, which occurred at R 2 = 2. kω. The near-square waves were observed at a frequency of 64.3 Hz. Next, resistor R was replaced with a lamp, whose resistance varies proportionally with applied voltage. This property can be useful in preventing clipping of the oscillator output. Given a limited op-amp supply voltage, the output waveform can be clipped as its voltage amplitude reaches that of the supply voltage. Considering the ideal gain of the non-inverting amplifier created with R and R 2, increasing R will reduce the voltage gain. This allows the lamp to stabilize the oscillator by varying the resistance of R with output voltage. As output voltage increases, the voltage across the lamp increases, which in turn increases the lamp s resistance. This increase reduces the voltage gain of the amplifier, reducing the output voltage. With the stabilization circuit constructed, decade potentiometer R 2 was again varied until oscillations were observed at the output, which occurred at R 2 = 57 Ω, as shown in Fig. 2. Results Part I Fig. 2, 3, and 4 show the magnitude frequency response of low-pass Filter. Considering the initial value of R B, maximum voltage gain was approximately.6 V/V. Given the values of R A and R B calculated in the prelab, a theoretical voltage gain of.586 V/V was expected, approximately the experimental values observed. A corner frequency of 38 Hz was also predicted, again similar to the experimental corner frequency Figure 2: Frequency Response of Filter with RB As can be seen in Fig. 3 and 4, increased voltage gain will result in higher Q-factors. In terms of magnitude frequency response, increased voltage gain will result in steeper frequency response curves and decreased bandwidth.
6 Voltage Gain (V/V) Voltage Gain (V/V) Figure 3: Frequency Response of Filter with RB + 5% Figure 4: Frequency Response of Filter with RB - 5% Fig. 5 shows the magnitude frequency response of low-pass Filter 2. Maximum voltage gain was approximately V/V, again nearly equal to the experimental voltage gains observed. In the case of Filter 2, the voltage follower configuration limits the voltage gain to approximately V/V. Applying the general voltage gain constraint to ensure filter stability, the equation below can be derived assuming an ideal voltage gain of V/V. ω Q = 4 (7) RC From Eq. 7, to increase Q-factor for a given frequency, the values of R and C would need to be increased due to the inherent fixed voltage gain of the voltage follower.
7 Voltage Gain (V/V) Voltage Gain (V/V) Figure 5: Frequency Response of Filter 2 Part II Fig. 7, 8, and 9 show the magnitude frequency response of band-pass Filter 3. In the pre-lab, the maximum gain of the filter was expected to be approximately 5 V/V. The maximum gain of the filter in Fig. 7 was 64.4 V/V. Fig. 7 shows the frequency response for Filter 3 with the initial value of R 2. Fig. 8 shows the response with a smaller resistor, resulting in a lower center frequency as expected. Fig. 9 shows the frequency response using a larger resistance for R 2, and thus shows a higher center frequency Figure 7: Frequency Response of Filter 3 with R2
8 Voltage Gain (V/V) Voltage Gain (V/V) Figure 8: Frequency Response of Filter 3 with R2 + % Figure 9: Frequency Response of Filter 3 with R2 % Part III Outputs of the Wien-Bridge oscillator constructed in Part III are shown in Fig. and 2. Fig. shows the oscillator output without the stabilizing lamp connected, showing the lowest value of R 2 that generates oscillations. Fig. 2 is the oscillator output with the lamp added for stabilization, and the R 2 value is the highest value before the circuit experiences clipping of its sinusoidal output. Figure : Oscillator Output for Non-Stabilized Circuit with R2 = 2. kω
9 Figure 2: Oscillator Output for Stabilized Circuit with R2 = 57 Ω Discussion In this experiment, we were able to successfully design, build, and test each part, and get results within the expected range. In Part I, we tested the frequency response of several low pass filters. Here we were met with success as the cutoff frequency was near predicted. The building and testing of the circuit went smoothly, which is mostly what we were expecting. After completing multiple experiments, we have found op-amps to perform near calculated theoretical values, as opposed to MOSFETs and BJTs which usually have more performance issues when implemented. In Part II, we examined band pass filters and implemented several similar circuits. Our circuit performance and results were as expected. We hypothesized that the amplification range would vary from Eq. 4, which did occur. As predicted, a lower R 2 value would both decrease gain and increase corner frequency. In building this circuit we did have some difficulty, with the largest issue being improper capacitor selection due to mislabeling. We identified the issue by manually measuring capacitor values and were able to correct the problem and implement the circuit correctly. Part III proceeded smoothly according to the calculations performed. For the non-stabilized circuit we calculated a resistor ratio of R 2/R = 2 to achieve oscillation, and with a kω resistor and decade potentiometer set to 2.kΩ, oscillations were observed. A possible experiment to follow up this part would be to analyze the performance of the oscillator when loaded and see how well it is able to perform and maintain its oscillation. Conclusion In Part I, the results followed near what was expected, the corner frequency in Fig. 2 was 38 Hz with a maximum gain of.6 V/V, near our expected gain of about.58 V/V. The increase in voltage gain results in an increase in Q-factor, and, as predicted, increased values of R 2 resulted in a steeper drop off in the frequency response curve. The frequency response of our circuit in Part II was very near predicted values, in Fig. 7 the maximum point occurs very near to the predicted 68 Hz. Our maximum gain however, was limited to 64.4 V/V. This might be because of the variance in the capacitor values from the calculations we performed. For our theoretical 22 µf capacitor, 2 µf capacitors, measured to be about 9.5 µf each, were placed in parallel. Part III resulted in oscillation at when R 2 was 2. kω, very near the predicted value of 2 kω. We were surprised at how susceptible to change in resistor values this circuit was, as when the decade box for R 2 was set to 2.9 kω, there was no oscillation or output at all, but a Ω increase resulted in perfect sinusoidal output with a maximum V pp of V. References Dr. Ahmed Dallal s ECE 22 Lecture Notes Texas Instruments ua74 General-Purpose Operational Amplifier Data Sheet
University of Pittsburgh
 University of Pittsburgh Experiment #1 Lab Report Frequency Response of Operational Amplifiers Submission Date: 05/29/2018 Instructors: Dr. Ahmed Dallal Shangqian Gao Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex Williams
University of Pittsburgh Experiment #1 Lab Report Frequency Response of Operational Amplifiers Submission Date: 05/29/2018 Instructors: Dr. Ahmed Dallal Shangqian Gao Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex Williams
University of Pittsburgh
 University of Pittsburgh Experiment #4 Lab Report MOSFET Amplifiers and Current Mirrors Submission Date: 07/03/2018 Instructors: Dr. Ahmed Dallal Shangqian Gao Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex Williams
University of Pittsburgh Experiment #4 Lab Report MOSFET Amplifiers and Current Mirrors Submission Date: 07/03/2018 Instructors: Dr. Ahmed Dallal Shangqian Gao Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex Williams
University of Pittsburgh
 University of Pittsburgh Experiment #7 Lab Report Analog-Digital Applications Submission Date: 08/01/2018 Instructors: Dr. Ahmed Dallal Shangqian Gao Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex Williams Station #2
University of Pittsburgh Experiment #7 Lab Report Analog-Digital Applications Submission Date: 08/01/2018 Instructors: Dr. Ahmed Dallal Shangqian Gao Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex Williams Station #2
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS
 UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS ANALOG ELECTRONICS II EMT 212 2009/2010 EXPERIMENT # 3 OP-AMP (OSCILLATORS) 1 1. OBJECTIVE: 1.1 To demonstrate the Wien bridge oscillator 1.2 To demonstrate the RC phase-shift
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS ANALOG ELECTRONICS II EMT 212 2009/2010 EXPERIMENT # 3 OP-AMP (OSCILLATORS) 1 1. OBJECTIVE: 1.1 To demonstrate the Wien bridge oscillator 1.2 To demonstrate the RC phase-shift
Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits
 Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits This laboratory session involves circuits which contain a double-t (or TT), a passive RC circuit: Figure 1. Double T passive RC circuit module The upper
Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits This laboratory session involves circuits which contain a double-t (or TT), a passive RC circuit: Figure 1. Double T passive RC circuit module The upper
BENE 2163 ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS
 UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRONIK DAN KEJURUTERAAN KOMPUTER BENE 263 ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS LAB SESSION 3 WEIN BRIDGE OSCILLATOR Revised: February 20 Lab 3 Wien Bridge Oscillator
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRONIK DAN KEJURUTERAAN KOMPUTER BENE 263 ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS LAB SESSION 3 WEIN BRIDGE OSCILLATOR Revised: February 20 Lab 3 Wien Bridge Oscillator
Figure 1: Closed Loop System
 SIGNAL GENERATORS 3. Introduction Signal sources have a variety of applications including checking stage gain, frequency response, and alignment in receivers and in a wide range of other electronics equipment.
SIGNAL GENERATORS 3. Introduction Signal sources have a variety of applications including checking stage gain, frequency response, and alignment in receivers and in a wide range of other electronics equipment.
Operational Amplifiers: Part II
 1. Introduction Operational Amplifiers: Part II The name "operational amplifier" comes from this amplifier's ability to perform mathematical operations. Three good examples of this are the summing amplifier,
1. Introduction Operational Amplifiers: Part II The name "operational amplifier" comes from this amplifier's ability to perform mathematical operations. Three good examples of this are the summing amplifier,
Mechatronics. Analog and Digital Electronics: Studio Exercises 1 & 2
 Mechatronics Analog and Digital Electronics: Studio Exercises 1 & 2 There is an electronics revolution taking place in the industrialized world. Electronics pervades all activities. Perhaps the most important
Mechatronics Analog and Digital Electronics: Studio Exercises 1 & 2 There is an electronics revolution taking place in the industrialized world. Electronics pervades all activities. Perhaps the most important
BME 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters
 BME 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Laboratory Equipment: Agilent Oscilloscope Model 546A Agilent Function Generator
BME 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Laboratory Equipment: Agilent Oscilloscope Model 546A Agilent Function Generator
EE 368 Electronics Lab. Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2)
 EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING
 ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING Objectives: To familiarize the student with the concepts of signal conditioning. At the end of the lab, the student should be able to: Understand the
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING Objectives: To familiarize the student with the concepts of signal conditioning. At the end of the lab, the student should be able to: Understand the
BME/ISE 3512 Bioelectronics. Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers
 BME/ISE 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers Learning Objectives: Be familiar with the operation of a basic op-amp circuit. Be familiar with the characteristics of both ideal and
BME/ISE 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers Learning Objectives: Be familiar with the operation of a basic op-amp circuit. Be familiar with the characteristics of both ideal and
LAB 4: OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS
 LAB 4: OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS ELEC 225 Introduction Operational amplifiers (OAs) are highly stable, high gain, difference amplifiers that can handle signals from zero frequency (dc signals) up
LAB 4: OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS ELEC 225 Introduction Operational amplifiers (OAs) are highly stable, high gain, difference amplifiers that can handle signals from zero frequency (dc signals) up
Assist Lecturer: Marwa Maki. Active Filters
 Active Filters In past lecture we noticed that the main disadvantage of Passive Filters is that the amplitude of the output signals is less than that of the input signals, i.e., the gain is never greater
Active Filters In past lecture we noticed that the main disadvantage of Passive Filters is that the amplitude of the output signals is less than that of the input signals, i.e., the gain is never greater
BME 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers
 BME 351 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers Learning Objectives: Be familiar with the operation of a basic op-amp circuit. Be familiar with the characteristics of both ideal and real
BME 351 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers Learning Objectives: Be familiar with the operation of a basic op-amp circuit. Be familiar with the characteristics of both ideal and real
Friday, 1/27/17 Constraints on A(jω)
 Friday, 1/27/17 Constraints on A(jω) The simplest electronic oscillators are op amp based, and A(jω) is typically a simple op amp fixed gain amplifier, such as the negative gain and positive gain amplifiers
Friday, 1/27/17 Constraints on A(jω) The simplest electronic oscillators are op amp based, and A(jω) is typically a simple op amp fixed gain amplifier, such as the negative gain and positive gain amplifiers
University of Pittsburgh
 University of Pittsburgh Experiment #11 Lab Report Inductance/Transformers Submission Date: 12/04/2017 Instructors: Dr. Minhee Yun John Erickson Yanhao Du Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex Williams Station
University of Pittsburgh Experiment #11 Lab Report Inductance/Transformers Submission Date: 12/04/2017 Instructors: Dr. Minhee Yun John Erickson Yanhao Du Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex Williams Station
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET REV. NO. : REV.
 Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET LABORATORY MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO. ISSUE NO. : ISSUE DATE: July 200 REV. NO. : REV.
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET LABORATORY MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO. ISSUE NO. : ISSUE DATE: July 200 REV. NO. : REV.
WAVEFORM GENERATOR CIRCUITS USING OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 15EEE287 Electronic Circuits & Simulation Lab - II Lab #8 WAVEFORM GENERATOR CIRCUITS USING OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to design and construct circuits to generate
15EEE287 Electronic Circuits & Simulation Lab - II Lab #8 WAVEFORM GENERATOR CIRCUITS USING OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to design and construct circuits to generate
UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA EE 206
 UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA EE 206 TRANSISTOR BIASING CIRCUITS Introduction: One of the most critical considerations in the design of transistor amplifier stages is the ability of the circuit to maintain
UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA EE 206 TRANSISTOR BIASING CIRCUITS Introduction: One of the most critical considerations in the design of transistor amplifier stages is the ability of the circuit to maintain
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 5 GAIN-BANDWIDTH PRODUCT AND SLEW RATE OBJECTIVES In this experiment the student will explore two
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 5 GAIN-BANDWIDTH PRODUCT AND SLEW RATE OBJECTIVES In this experiment the student will explore two
2. SINGLE STAGE BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR (BJT) AMPLIFIERS
 2. SINGLE STAGE BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR (BJT) AMPLIFIERS I. Objectives and Contents The goal of this experiment is to become familiar with BJT as an amplifier and to evaluate the basic configurations
2. SINGLE STAGE BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR (BJT) AMPLIFIERS I. Objectives and Contents The goal of this experiment is to become familiar with BJT as an amplifier and to evaluate the basic configurations
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5)
 Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
BME 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Six - Active Filters
 BME 5 Bioelectronics Laboratory Six - Active Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of active filters. Describe the differences between active and passive filters. Laboratory Equipment:
BME 5 Bioelectronics Laboratory Six - Active Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of active filters. Describe the differences between active and passive filters. Laboratory Equipment:
11. Chapter: Amplitude stabilization of the harmonic oscillator
 Punčochář, Mohylová: TELO, Chapter 10 1 11. Chapter: Amplitude stabilization of the harmonic oscillator Time of study: 3 hours Goals: the student should be able to define basic principles of oscillator
Punčochář, Mohylová: TELO, Chapter 10 1 11. Chapter: Amplitude stabilization of the harmonic oscillator Time of study: 3 hours Goals: the student should be able to define basic principles of oscillator
University of Pittsburgh
 University of Pittsburgh Experiment #5 Lab Report Diode Applications and PSPICE Introduction Submission Date: 10/10/2017 Instructors: Dr. Minhee Yun John Erickson Yanhao Du Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex
University of Pittsburgh Experiment #5 Lab Report Diode Applications and PSPICE Introduction Submission Date: 10/10/2017 Instructors: Dr. Minhee Yun John Erickson Yanhao Du Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex
Experiment No. 3 Pre-Lab Phase Locked Loops and Frequency Modulation
 Experiment No. 3 Pre-Lab Phase Locked Loops and Frequency Modulation The Pre-Labs are informational and although they follow the procedures in the experiment, they are to be completed outside of the laboratory.
Experiment No. 3 Pre-Lab Phase Locked Loops and Frequency Modulation The Pre-Labs are informational and although they follow the procedures in the experiment, they are to be completed outside of the laboratory.
EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS. Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi
 EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi 2.1 INTRODUCTION An electronic circuit which is designed to generate a periodic waveform continuously at
EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi 2.1 INTRODUCTION An electronic circuit which is designed to generate a periodic waveform continuously at
Operational Amplifiers
 Operational Amplifiers Continuing the discussion of Op Amps, the next step is filters. There are many different types of filters, including low pass, high pass and band pass. We will discuss each of the
Operational Amplifiers Continuing the discussion of Op Amps, the next step is filters. There are many different types of filters, including low pass, high pass and band pass. We will discuss each of the
Common-Source Amplifiers
 Lab 2: Common-Source Amplifiers Introduction The common-source stage is the most basic amplifier stage encountered in CMOS analog circuits. Because of its very high input impedance, moderate-to-high gain,
Lab 2: Common-Source Amplifiers Introduction The common-source stage is the most basic amplifier stage encountered in CMOS analog circuits. Because of its very high input impedance, moderate-to-high gain,
EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers
 EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers Fall 2017 Contents Objective:... 2 Discussion:... 2 Components Needed:... 2 Part 1 Voltage Controlled Amplifier... 2 Part 2 Common Source Amplifier...
EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers Fall 2017 Contents Objective:... 2 Discussion:... 2 Components Needed:... 2 Part 1 Voltage Controlled Amplifier... 2 Part 2 Common Source Amplifier...
CHARACTERISTICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS - I
 CHARACTERISTICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS - I OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to examine non-ideal characteristics of an operational amplifier. The characteristics that are investigated include
CHARACTERISTICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS - I OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to examine non-ideal characteristics of an operational amplifier. The characteristics that are investigated include
Oscillators. An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier.
 Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
Laboratory Exercises for Analog Circuits and Electronics as Hardware Homework with Student Laptop Computer Instrumentation
 Laboratory Exercises for Analog Circuits and Electronics as Hardware Homework with Student Laptop Computer Instrumentation Marion O. Hagler Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Mississippi
Laboratory Exercises for Analog Circuits and Electronics as Hardware Homework with Student Laptop Computer Instrumentation Marion O. Hagler Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Mississippi
Lab 10: Single Supply Amplifier
 Overview This lab assignment implements an inverting voltage amplifier circuit with a single power supply. The amplifier output contains a bias point which is removed by AC coupling the output signal.
Overview This lab assignment implements an inverting voltage amplifier circuit with a single power supply. The amplifier output contains a bias point which is removed by AC coupling the output signal.
ECEN Network Analysis Section 3. Laboratory Manual
 ECEN 3714----Network Analysis Section 3 Laboratory Manual LAB 07: Active Low Pass Filter Oklahoma State University School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Section 3 Laboratory manual - 1 - Spring
ECEN 3714----Network Analysis Section 3 Laboratory Manual LAB 07: Active Low Pass Filter Oklahoma State University School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Section 3 Laboratory manual - 1 - Spring
PHYS 3322 Modern Laboratory Methods I AC R, RC, and RL Circuits
 Purpose PHYS 3322 Modern Laboratory Methods I AC, C, and L Circuits For a given frequency, doubling of the applied voltage to resistors, capacitors, and inductors doubles the current. Hence, each of these
Purpose PHYS 3322 Modern Laboratory Methods I AC, C, and L Circuits For a given frequency, doubling of the applied voltage to resistors, capacitors, and inductors doubles the current. Hence, each of these
Project Report Designing Wein-Bridge Oscillator
 Abu Dhabi University EEN 360 - Electronic Devices and Circuits II Project Report Designing Wein-Bridge Oscillator Author: Muhammad Obaidullah 03033 Bilal Arshad 0929 Supervisor: Dr. Riad Kanan Section
Abu Dhabi University EEN 360 - Electronic Devices and Circuits II Project Report Designing Wein-Bridge Oscillator Author: Muhammad Obaidullah 03033 Bilal Arshad 0929 Supervisor: Dr. Riad Kanan Section
Chapter 3, Sections Electrical Filters
 Chapter 3, Sections 3.2.4-3.2.5 Electrical Filters Signals DC and AC Components - Many signals can be constructed as sums of AC and DC components: 2.5 2 1.5 2 1.5 1.5 1 2 3 4 1.5 -.5-1 1 2 3 4 = + 2.5
Chapter 3, Sections 3.2.4-3.2.5 Electrical Filters Signals DC and AC Components - Many signals can be constructed as sums of AC and DC components: 2.5 2 1.5 2 1.5 1.5 1 2 3 4 1.5 -.5-1 1 2 3 4 = + 2.5
EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers
 EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers Fall 2018 Contents Objective:...2 Discussion:...2 Components Needed:...2 Part 1 Voltage Controlled Amplifier...2 Part 2 A Nonlinear Application...3
EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers Fall 2018 Contents Objective:...2 Discussion:...2 Components Needed:...2 Part 1 Voltage Controlled Amplifier...2 Part 2 A Nonlinear Application...3
ANALYSIS OF AN NPN COMMON-EMITTER AMPLIFIER
 ANALYSIS OF AN NPN COMMON-EMITTER AMPLIFIER Experiment Performed by: Michael Gonzalez Filip Rege Alexis Rodriguez-Carlson Report Written by: Filip Rege Alexis Rodriguez-Carlson November 28, 2007 Objectives:
ANALYSIS OF AN NPN COMMON-EMITTER AMPLIFIER Experiment Performed by: Michael Gonzalez Filip Rege Alexis Rodriguez-Carlson Report Written by: Filip Rege Alexis Rodriguez-Carlson November 28, 2007 Objectives:
ECE 2201 PRELAB 6 BJT COMMON EMITTER (CE) AMPLIFIER
 ECE 2201 PRELAB 6 BJT COMMON EMITTER (CE) AMPLIFIER Hand Analysis P1. Determine the DC bias for the BJT Common Emitter Amplifier circuit of Figure 61 (in this lab) including the voltages V B, V C and V
ECE 2201 PRELAB 6 BJT COMMON EMITTER (CE) AMPLIFIER Hand Analysis P1. Determine the DC bias for the BJT Common Emitter Amplifier circuit of Figure 61 (in this lab) including the voltages V B, V C and V
Laboratory 9. Required Components: Objectives. Optional Components: Operational Amplifier Circuits (modified from lab text by Alciatore)
 Laboratory 9 Operational Amplifier Circuits (modified from lab text by Alciatore) Required Components: 1x 741 op-amp 2x 1k resistors 4x 10k resistors 1x l00k resistor 1x 0.1F capacitor Optional Components:
Laboratory 9 Operational Amplifier Circuits (modified from lab text by Alciatore) Required Components: 1x 741 op-amp 2x 1k resistors 4x 10k resistors 1x l00k resistor 1x 0.1F capacitor Optional Components:
EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope
 EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope For students to become more familiar with oscilloscopes and function generators. Pre laboratory Work Read the TDS 210 Oscilloscope
EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope For students to become more familiar with oscilloscopes and function generators. Pre laboratory Work Read the TDS 210 Oscilloscope
ECE 3155 Experiment I AC Circuits and Bode Plots Rev. lpt jan 2013
 Signature Name (print, please) Lab section # Lab partner s name (if any) Date(s) lab was performed ECE 3155 Experiment I AC Circuits and Bode Plots Rev. lpt jan 2013 In this lab we will demonstrate basic
Signature Name (print, please) Lab section # Lab partner s name (if any) Date(s) lab was performed ECE 3155 Experiment I AC Circuits and Bode Plots Rev. lpt jan 2013 In this lab we will demonstrate basic
ECE ECE285. Electric Circuit Analysis I. Spring Nathalia Peixoto. Rev.2.0: Rev Electric Circuits I
 ECE285 Electric Circuit Analysis I Spring 2014 Nathalia Peixoto Rev.2.0: 140124. Rev 2.1. 140813 1 Lab reports Background: these 9 experiments are designed as simple building blocks (like Legos) and students
ECE285 Electric Circuit Analysis I Spring 2014 Nathalia Peixoto Rev.2.0: 140124. Rev 2.1. 140813 1 Lab reports Background: these 9 experiments are designed as simple building blocks (like Legos) and students
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance
 Objective Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance To understand how the reactance of inductors and capacitors change with frequency, and how the two can cancel each other to leave
Objective Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance To understand how the reactance of inductors and capacitors change with frequency, and how the two can cancel each other to leave
Project 6: Oscillator Circuits
 : Oscillator Circuits Ariel Moss The purpose of this experiment was to design two oscillator circuits: a Wien-Bridge oscillator at 3 khz oscillation and a Hartley Oscillator using a BJT at 5 khz oscillation.
: Oscillator Circuits Ariel Moss The purpose of this experiment was to design two oscillator circuits: a Wien-Bridge oscillator at 3 khz oscillation and a Hartley Oscillator using a BJT at 5 khz oscillation.
ECE Lab #4 OpAmp Circuits with Negative Feedback and Positive Feedback
 ECE 214 Lab #4 OpAmp Circuits with Negative Feedback and Positive Feedback 20 February 2018 Introduction: The TL082 Operational Amplifier (OpAmp) and the Texas Instruments Analog System Lab Kit Pro evaluation
ECE 214 Lab #4 OpAmp Circuits with Negative Feedback and Positive Feedback 20 February 2018 Introduction: The TL082 Operational Amplifier (OpAmp) and the Texas Instruments Analog System Lab Kit Pro evaluation
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II
 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II LAB 5 INTRO: INTRODUCTION TO INVERTING AMPLIFIERS AND OTHER OP-AMP CIRCUITS GOALS In this lab, you will characterize the gain and frequency dependence of inverting op-amp
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II LAB 5 INTRO: INTRODUCTION TO INVERTING AMPLIFIERS AND OTHER OP-AMP CIRCUITS GOALS In this lab, you will characterize the gain and frequency dependence of inverting op-amp
Thursday, 1/23/19 Automatic Gain Control As previously shown, 1 0 is a nonlinear system that produces a limit cycle with a distorted sinusoid for
 Thursday, 1/23/19 Automatic Gain Control As previously shown, 1 0 is a nonlinear system that produces a limit cycle with a distorted sinusoid for x(t), which is not a very good sinusoidal oscillator. A
Thursday, 1/23/19 Automatic Gain Control As previously shown, 1 0 is a nonlinear system that produces a limit cycle with a distorted sinusoid for x(t), which is not a very good sinusoidal oscillator. A
Experiment #8: Designing and Measuring a Common-Collector Amplifier
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #8: Designing and Measuring a Common-Collector Amplifier
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #8: Designing and Measuring a Common-Collector Amplifier
Lecture 8: More on Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps)
 Lecture 8: More on Operational mplifiers (Op mps) Input Impedance of Op mps and Op mps Using Negative Feedback: Consider a general feedback circuit as shown. ssume that the amplifier has input impedance
Lecture 8: More on Operational mplifiers (Op mps) Input Impedance of Op mps and Op mps Using Negative Feedback: Consider a general feedback circuit as shown. ssume that the amplifier has input impedance
Positive Feedback and Oscillators
 Physics 3330 Experiment #5 Fall 2011 Positive Feedback and Oscillators Purpose In this experiment we will study how spontaneous oscillations may be caused by positive feedback. You will construct an active
Physics 3330 Experiment #5 Fall 2011 Positive Feedback and Oscillators Purpose In this experiment we will study how spontaneous oscillations may be caused by positive feedback. You will construct an active
ECE 363 FINAL (F16) 6 problems for 100 pts Problem #1: Fuel Pump Controller (18 pts)
 ECE 363 FINAL (F16) NAME: 6 problems for 100 pts Problem #1: Fuel Pump Controller (18 pts) You are asked to design a high-side switch for a remotely operated fuel pump. You decide to use the IRF9520 power
ECE 363 FINAL (F16) NAME: 6 problems for 100 pts Problem #1: Fuel Pump Controller (18 pts) You are asked to design a high-side switch for a remotely operated fuel pump. You decide to use the IRF9520 power
BME/ISE 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters
 BME/ISE 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Supplies and Components: Breadboard 4.7 K Resistor 0.047 F Capacitor
BME/ISE 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Supplies and Components: Breadboard 4.7 K Resistor 0.047 F Capacitor
EMT212 Analog Electronic II. Chapter 4. Oscillator
 EMT Analog Electronic II Chapter 4 Oscillator Objectives Describe the basic concept of an oscillator Discuss the basic principles of operation of an oscillator Analyze the operation of RC, LC and crystal
EMT Analog Electronic II Chapter 4 Oscillator Objectives Describe the basic concept of an oscillator Discuss the basic principles of operation of an oscillator Analyze the operation of RC, LC and crystal
EE 462G Laboratory #1 Measuring Capacitance
 EE 462G Laboratory #1 Measuring Capacitance Drs. A.V. Radun and K.D. Donohue (1/24/07) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 Updated 8/31/2007 by
EE 462G Laboratory #1 Measuring Capacitance Drs. A.V. Radun and K.D. Donohue (1/24/07) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 Updated 8/31/2007 by
ECE4902 C Lab 7
 ECE902 C2012 - Lab MOSFET Differential Amplifier Resistive Load Active Load PURPOSE: The primary purpose of this lab is to measure the performance of the differential amplifier. This is an important topology
ECE902 C2012 - Lab MOSFET Differential Amplifier Resistive Load Active Load PURPOSE: The primary purpose of this lab is to measure the performance of the differential amplifier. This is an important topology
THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG. Department of Electrical and Electrical Engineering
 THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Department of Electrical and Electrical Engineering Experiment EC1 The Common-Emitter Amplifier Location: Part I Laboratory CYC 102 Objective: To study the basic operation and
THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Department of Electrical and Electrical Engineering Experiment EC1 The Common-Emitter Amplifier Location: Part I Laboratory CYC 102 Objective: To study the basic operation and
ECE 3274 Common-Emitter Amplifier Project
 ECE 3274 Common-Emitter Amplifier Project 1. Objective The objective of this lab is to design and build three variations of the common- emitter amplifier. 2. Components Qty Device 1 2N2222 BJT Transistor
ECE 3274 Common-Emitter Amplifier Project 1. Objective The objective of this lab is to design and build three variations of the common- emitter amplifier. 2. Components Qty Device 1 2N2222 BJT Transistor
Comparison of Signal Attenuation of Multiple Frequencies Between Passive and Active High-Pass Filters
 Comparison of Signal Attenuation of Multiple Frequencies Between Passive and Active High-Pass Filters Aaron Batker Pritzker Harvey Mudd College 23 November 203 Abstract Differences in behavior at different
Comparison of Signal Attenuation of Multiple Frequencies Between Passive and Active High-Pass Filters Aaron Batker Pritzker Harvey Mudd College 23 November 203 Abstract Differences in behavior at different
Phy 335, Unit 4 Transistors and transistor circuits (part one)
 Mini-lecture topics (multiple lectures): Phy 335, Unit 4 Transistors and transistor circuits (part one) p-n junctions re-visited How does a bipolar transistor works; analogy with a valve Basic circuit
Mini-lecture topics (multiple lectures): Phy 335, Unit 4 Transistors and transistor circuits (part one) p-n junctions re-visited How does a bipolar transistor works; analogy with a valve Basic circuit
Experiment No. 9 DESIGN AND CHARACTERISTICS OF COMMON BASE AND COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIERS
 Experiment No. 9 DESIGN AND CHARACTERISTICS OF COMMON BASE AND COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIERS 1. Objective: The objective of this experiment is to explore the basic applications of the bipolar junction transistor
Experiment No. 9 DESIGN AND CHARACTERISTICS OF COMMON BASE AND COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIERS 1. Objective: The objective of this experiment is to explore the basic applications of the bipolar junction transistor
Application Note AN45
 Application Note Wien Bridge Oscillators using E 2 POTs by Applications Staff, October 1994 Wien Bridge Oscillators In 1939, William R. Hewlett (later of Hewlett-Packard fame) first combined the network
Application Note Wien Bridge Oscillators using E 2 POTs by Applications Staff, October 1994 Wien Bridge Oscillators In 1939, William R. Hewlett (later of Hewlett-Packard fame) first combined the network
AC Magnitude and Phase
 AC Magnitude and Phase Objectives: oday's experiment provides practical experience with the meaning of magnitude and phase in a linear circuits and the use of phasor algebra to predict the response of
AC Magnitude and Phase Objectives: oday's experiment provides practical experience with the meaning of magnitude and phase in a linear circuits and the use of phasor algebra to predict the response of
ECE 310L : LAB 9. Fall 2012 (Hay)
 ECE 310L : LAB 9 PRELAB ASSIGNMENT: Read the lab assignment in its entirety. 1. For the circuit shown in Figure 3, compute a value for R1 that will result in a 1N5230B zener diode current of approximately
ECE 310L : LAB 9 PRELAB ASSIGNMENT: Read the lab assignment in its entirety. 1. For the circuit shown in Figure 3, compute a value for R1 that will result in a 1N5230B zener diode current of approximately
Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits
 Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits Will Chemelewski Partner: Brian Enders TA: Nielsen See laboratory book #1 pages 5-7, data taken September 1, 2009 September 7, 2009 Abstract Transient
Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits Will Chemelewski Partner: Brian Enders TA: Nielsen See laboratory book #1 pages 5-7, data taken September 1, 2009 September 7, 2009 Abstract Transient
Lecture 28 RC Phase Shift Oscillator using Op-amp
 Integrated Circuits, MOSFETs, OP-Amps and their Applications Prof. Hardik J Pandya Department of Electronic Systems Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture 28 RC Phase Shift Oscillator
Integrated Circuits, MOSFETs, OP-Amps and their Applications Prof. Hardik J Pandya Department of Electronic Systems Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture 28 RC Phase Shift Oscillator
Chapter.8: Oscillators
 Chapter.8: Oscillators Objectives: To understand The basic operation of an Oscillator the working of low frequency oscillators RC phase shift oscillator Wien bridge Oscillator the working of tuned oscillator
Chapter.8: Oscillators Objectives: To understand The basic operation of an Oscillator the working of low frequency oscillators RC phase shift oscillator Wien bridge Oscillator the working of tuned oscillator
Laboratory 4 Operational Amplifier Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of California, San Diego MAE170
 Laboratory 4 Operational Amplifier Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of California, San Diego MAE170 Megan Ong Diana Wu Wong B01 Tuesday 11am April 28 st, 2015 Abstract: The
Laboratory 4 Operational Amplifier Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of California, San Diego MAE170 Megan Ong Diana Wu Wong B01 Tuesday 11am April 28 st, 2015 Abstract: The
Lab 4 : Transistor Oscillators
 Objective: Lab 4 : Transistor Oscillators In this lab, you will learn how to design and implement a colpitts oscillator. In part II you will implement a RC phase shift oscillator Hardware Required : Pre
Objective: Lab 4 : Transistor Oscillators In this lab, you will learn how to design and implement a colpitts oscillator. In part II you will implement a RC phase shift oscillator Hardware Required : Pre
Experiment 6: Biasing Circuitry
 1 Objective UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE105 Lab Experiments Experiment 6: Biasing Circuitry Setting up a biasing
1 Objective UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE105 Lab Experiments Experiment 6: Biasing Circuitry Setting up a biasing
ECE 3274 Common-Emitter Amplifier Project
 ECE 3274 Common-Emitter Amplifier Project 1. Objective The objective of this lab is to design and build the common-emitter amplifier with partial bypass of the emitter resistor to control the AC voltage
ECE 3274 Common-Emitter Amplifier Project 1. Objective The objective of this lab is to design and build the common-emitter amplifier with partial bypass of the emitter resistor to control the AC voltage
Assume availability of the following components to DESIGN and DRAW the circuits of the op. amp. applications listed below:
 ========================================================================================== UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN MAINE Dept. of Electrical Engineering TEST #3 Prof. M.G.Guvench ELE343/02 ==========================================================================================
========================================================================================== UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN MAINE Dept. of Electrical Engineering TEST #3 Prof. M.G.Guvench ELE343/02 ==========================================================================================
Operational Amplifier BME 360 Lecture Notes Ying Sun
 Operational Amplifier BME 360 Lecture Notes Ying Sun Characteristics of Op-Amp An operational amplifier (op-amp) is an analog integrated circuit that consists of several stages of transistor amplification
Operational Amplifier BME 360 Lecture Notes Ying Sun Characteristics of Op-Amp An operational amplifier (op-amp) is an analog integrated circuit that consists of several stages of transistor amplification
Experiment #7: Designing and Measuring a Common-Emitter Amplifier
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #7: Designing and Measuring a Common-Emitter Amplifier
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #7: Designing and Measuring a Common-Emitter Amplifier
E84 Lab 3: Transistor
 E84 Lab 3: Transistor Cherie Ho and Siyi Hu April 18, 2016 Transistor Testing 1. Take screenshots of both the input and output characteristic plots observed on the semiconductor curve tracer with the following
E84 Lab 3: Transistor Cherie Ho and Siyi Hu April 18, 2016 Transistor Testing 1. Take screenshots of both the input and output characteristic plots observed on the semiconductor curve tracer with the following
RLC Frequency Response
 1. Introduction RLC Frequency Response The student will analyze the frequency response of an RLC circuit excited by a sinusoid. Amplitude and phase shift of circuit components will be analyzed at different
1. Introduction RLC Frequency Response The student will analyze the frequency response of an RLC circuit excited by a sinusoid. Amplitude and phase shift of circuit components will be analyzed at different
Homework Assignment 03
 Homework Assignment 03 Question 1 (Short Takes), 2 points each unless otherwise noted. 1. Two 0.68 μf capacitors are connected in series across a 10 khz sine wave signal source. The total capacitive reactance
Homework Assignment 03 Question 1 (Short Takes), 2 points each unless otherwise noted. 1. Two 0.68 μf capacitors are connected in series across a 10 khz sine wave signal source. The total capacitive reactance
Low Pass Filter Introduction
 Low Pass Filter Introduction Basically, an electrical filter is a circuit that can be designed to modify, reshape or reject all unwanted frequencies of an electrical signal and accept or pass only those
Low Pass Filter Introduction Basically, an electrical filter is a circuit that can be designed to modify, reshape or reject all unwanted frequencies of an electrical signal and accept or pass only those
LABORATORY EXPERIMENT. Infrared Transmitter/Receiver
 LABORATORY EXPERIMENT Infrared Transmitter/Receiver (Note to Teaching Assistant: The week before this experiment is performed, place students into groups of two and assign each group a specific frequency
LABORATORY EXPERIMENT Infrared Transmitter/Receiver (Note to Teaching Assistant: The week before this experiment is performed, place students into groups of two and assign each group a specific frequency
Transistor Digital Circuits
 Recapitulation Transistor Digital Circuits The transistor Operating principle and regions Utilization of the transistor Transfer characteristics, symbols Controlled switch model BJT digital circuits MOSFET
Recapitulation Transistor Digital Circuits The transistor Operating principle and regions Utilization of the transistor Transfer characteristics, symbols Controlled switch model BJT digital circuits MOSFET
STATION NUMBER: LAB SECTION: RC Oscillators. LAB 5: RC Oscillators ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 43/100. University Of California, Berkeley
 YOUR NAME: YOUR SID: Lab 5: RC Oscillators EE43/100 Spring 2013 Kris Pister YOUR PARTNER S NAME: YOUR PARTNER S SID: STATION NUMBER: LAB SECTION: Pre- Lab GSI Sign- Off: Pre- Lab Score: /40 In- Lab Score:
YOUR NAME: YOUR SID: Lab 5: RC Oscillators EE43/100 Spring 2013 Kris Pister YOUR PARTNER S NAME: YOUR PARTNER S SID: STATION NUMBER: LAB SECTION: Pre- Lab GSI Sign- Off: Pre- Lab Score: /40 In- Lab Score:
EE431 Lab 1 Operational Amplifiers
 Feb. 10, 2015 Report all measured data and show all calculations Introduction The purpose of this laboratory exercise is for the student to gain experience with measuring and observing the effects of common
Feb. 10, 2015 Report all measured data and show all calculations Introduction The purpose of this laboratory exercise is for the student to gain experience with measuring and observing the effects of common
5.25Chapter V Problem Set
 5.25Chapter V Problem Set P5.1 Analyze the circuits in Fig. P5.1 and determine the base, collector, and emitter currents of the BJTs as well as the voltages at the base, collector, and emitter terminals.
5.25Chapter V Problem Set P5.1 Analyze the circuits in Fig. P5.1 and determine the base, collector, and emitter currents of the BJTs as well as the voltages at the base, collector, and emitter terminals.
Performance-based assessments for analog integrated circuit competencies
 Performance-based assessments for analog integrated circuit competencies This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of
Performance-based assessments for analog integrated circuit competencies This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET REV. NO. : REV.
 Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET LABORATORY MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO. 1 ISSUE NO. : ISSUE DATE: July 2010 REV. NO. : REV.
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET LABORATORY MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO. 1 ISSUE NO. : ISSUE DATE: July 2010 REV. NO. : REV.
ASTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR
 555 TIMER ASTABLE MULTIIBRATOR MONOSTABLE MULTIIBRATOR 555 TIMER PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) 555 TIMER Introduction The 555 timer is an integrated circuit (chip) implementing a variety of
555 TIMER ASTABLE MULTIIBRATOR MONOSTABLE MULTIIBRATOR 555 TIMER PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) 555 TIMER Introduction The 555 timer is an integrated circuit (chip) implementing a variety of
LABORATORY MODULE. Analog Electronics. Semester 2 (2005/2006)
 LABORATORY MODULE ENT 162 Analog Electronics Semester 2 (2005/2006) EXPERIMENT 5 : The Class A Common-Emitter Power Amplifier Name Matrix No. : : PUSAT PENGAJIAN KEJURUTERAAN MEKATRONIK KOLEJ UNIVERSITI
LABORATORY MODULE ENT 162 Analog Electronics Semester 2 (2005/2006) EXPERIMENT 5 : The Class A Common-Emitter Power Amplifier Name Matrix No. : : PUSAT PENGAJIAN KEJURUTERAAN MEKATRONIK KOLEJ UNIVERSITI
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS LAB
 1 of 6 BEFORE YOU BEGIN PREREQUISITE LABS OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS LAB Introduction to Matlab Introduction to Arbitrary/Function Generator Resistive Circuits EXPECTED KNOWLEDGE Students should be familiar
1 of 6 BEFORE YOU BEGIN PREREQUISITE LABS OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS LAB Introduction to Matlab Introduction to Arbitrary/Function Generator Resistive Circuits EXPECTED KNOWLEDGE Students should be familiar
Experiment #6: Biasing an NPN BJT Introduction to CE, CC, and CB Amplifiers
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #6: Biasing an NPN BJT Introduction to CE, CC, and CB
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #6: Biasing an NPN BJT Introduction to CE, CC, and CB
Experiment 6: Biasing Circuitry
 1 Objective UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE105 Lab Experiments Experiment 6: Biasing Circuitry Setting up a biasing
1 Objective UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE105 Lab Experiments Experiment 6: Biasing Circuitry Setting up a biasing
EET 223 RF COMMUNICATIONS LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS
 EET 223 RF COMMUNICATIONS LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS Experimental Goals A good technician needs to make accurate measurements, keep good records and know the proper usage and limitations of the instruments
EET 223 RF COMMUNICATIONS LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS Experimental Goals A good technician needs to make accurate measurements, keep good records and know the proper usage and limitations of the instruments
Homework Assignment 01
 Homework Assignment 01 In this homework set students review some basic circuit analysis techniques, as well as review how to analyze ideal op-amp circuits. Numerical answers must be supplied using engineering
Homework Assignment 01 In this homework set students review some basic circuit analysis techniques, as well as review how to analyze ideal op-amp circuits. Numerical answers must be supplied using engineering
LAB 4 : FET AMPLIFIERS
 LEARNING OUTCOME: LAB 4 : FET AMPLIFIERS In this lab, students design and implement single-stage FET amplifiers and explore the frequency response of the real amplifiers. Breadboard and the Analog Discovery
LEARNING OUTCOME: LAB 4 : FET AMPLIFIERS In this lab, students design and implement single-stage FET amplifiers and explore the frequency response of the real amplifiers. Breadboard and the Analog Discovery
PHASORS AND PHASE SHIFT CIRCUITS
 PHASORS AND PHASE SHIFT CIRCUITS YOUR NAME GTA S SIGNATURE LAB MEETING TIME PHASOR CIRCUIT 4. Assemble the series RC circuit with the following circuit element values: C = 0.027 μf R = 10 kω v s (t) =
PHASORS AND PHASE SHIFT CIRCUITS YOUR NAME GTA S SIGNATURE LAB MEETING TIME PHASOR CIRCUIT 4. Assemble the series RC circuit with the following circuit element values: C = 0.027 μf R = 10 kω v s (t) =
