THE MM 100 OPTICAL COMPARATOR*,t
|
|
|
- Della Austin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
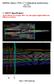
1 S6 PHOTOGRAMMETRIC ENGINEERING cation of a pictorial art. Codification is also hampered by the lack of scientific terms necessary to designate the new fields of interest. It would be more appropriate for instance to substitute "chronogrammetry" for "high-speed photography" when used for metrical purposes. A paper will be presented by Mr. Jean St. Thomas at the Society of Photographic Engineers Annual Conference at West Point next Spring, proposing a logical structure of scientific nomenclature to serve as a unifying back-bone for the organizational detail suggested by Shaftan. It is suggested that work for organizing metrical photography be actively undertaken by committees appointed by the American Society of Photogrammetry, The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers, and the Society of Photographic Engineers. Such a joint committee would be the logical body for the preparation of an outline for a metrical photography handbook which might be published jointly. It is not suggested that these Societies merge, since each is essentially concerned with branches of technical photographic knowledge of extensive, specialized and non-overlapping nature. It is further suggested that appropriate inter-society efforts be concentrated on the recognition of the field of metrical photography and photographic instrumentation, and that such recognition be sought at a level commensurate with the mathematical and engineering knowledge necessary to engage in this new professional direction. REFERENCES 1. Shaftan, Kenneth, "Photographic Instrumentation in 1950," Journal of the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers. November Shaftan, Kenneth, "Photographic Instrumentation and a Proposed System of Organization." Photographic Engineering Volume 3, No Lacmann, Otto, "Photogrammetry in Its Application to Non-Topographic Fields," S. Hirzel Verlag, Leipzig, Germany HaBert, B. "A Symposium-Non-Topographic Photogrammetry." PHOTOGRAMMETRIC EN GINEERING. September and December McNeil, G. T., "Photogrammetry Takes the Position of the Third Man." Paper presented at the 1952 International Photogrammetry Congress, Washington, D. C. THE MM 100 OPTICAL COMPARATOR*,t Everett L. Merritt, Technical Director, Photogrammetry, Inc., Silver Spring, Maryland I. INTRODUCTION T HE comparator, sometimes referred to as a measuring machine, is one of the most basic instruments in the realm of research, experimentation, fabrication, production, and manufacture. The measurement of data is a fundamental activity shared by the physicist, chemist, engineer, and instrument maker. The comparator, therefore, is the instrument familiar to, and employed by, men in the fields of science, engineering and industry. Photogrammetry is the science of measurement with photographs. The primary purpose of photogrammetry is to serve the field of science, engineering, and industry in that capacity. While the idea of a comparator precedes the maturation of the science of photogram- * A preliminary report published by Photographic Engineering is in part included in this paper with the permission of its editors. t Presented at Semi Annual Meeting of the Society, Philadelphia, Pa., Sept. 16, 1954.
2 SYMPOSIUM-NON-TOPOGRAPHIC PHOTOGRAMMETRIC INSTRUMENTS 57 metry, and while the photogrammetrist employs numerous other measuring devices, the comparator is the instrument fundamental to his field. A comparator is a device for transporting a system of points, lying in a plane, through measured distances in x and/or y directions. For purposes of photogrammetry, a system of images recorded on film define such a plane. To this end, the film is mounted on a suitable stage that is translated on precise ways by turning screws. A viewing microscope is provided to point on images, and x and y micrometer microscopes and scales to read the amount of translation in the x and y directions between two images, or between an image and a reference point or line. II. DESIGN OBJECTIVES There are numerous reasonably precise coordinate comparators. These comparators have translations that range from approximately 50 to 400 millimeters. Some move in x and y, while others move only in x and achieve y measurements by a rotation through 90 degrees. Translation to the right or left is considered x while translation toward or away from the operator is considered y. Most coordinate comparators have either a drum or vernier type of micrometer. The simplicity of the drum type is offset by errors of the screw. The functionalism of the vernier type is offset by the insufficient refinement in the x and y verniers and the awkwardness of two widely separated x and y reading microscopes. The MM 100 mm. comparator currently under design consideration is shown in Figure 1. The design is proposed FIG. l.-dptical 100 mm. comparator. to accommodate 35 mm., 70 mm., and 100 mm. film. The MM 100 has x and y translations of 100 mm., an azimuth rotation through 360 degrees, and a film feed and take-up spool to pass the film between two planar glass plates. The latter feature is not shown in Figure 1. The instrument is intended to combine the best principles of micrometer accuracy, image illumination, convenient operation, and simplicity in a single measuring instrument. The optical system is shown in Figure 2. Ill. MICROMETER Interpolation.accuracy is achieved through the weak prism translation principle. A weak prism attached to a drum or scale and movable by rack and pinion is employed to interpolate a point falling between the least graduations of the coarse scale. The principle is based on the deviation 0 of a weak wedge with prism angle A. This principle is illustratyd in Figure 3. For weak wedges o = (n - It may be seen that Li is proportional to x only. 0 is constant; therefore Li = ox. A large change in x produces a small change in Li which permits a large fixed scale to be graduated into microns. This arrangement gives an optical leverage l)a.
3 58 PHOTOGRAMMETRIC ENGINEERING Viwinq.tiq!lt Source,. )LO FIG. 3.--optical micrometer. FIG. 2.-0ptical diagram. I, " 1 :" \ ,, L. \ " o I 2 J " 5, 7 d 1IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIi[IIII1II1IIII1I1II1III1II1III1II1I1IJ I 'i 1- that is free from mechanical errors and for this reason is regarded as the most precise of micrometers. The prism is transported with a rack and pinion which does not affect the accuracy of the reading inasmuch as the movement is recorded on a fixed scale. Suppose in the illustration that the index appears in the focal plane of the microscope between 0.1 and 0.2, By turning the coincidence knob, the prism is translated until the index coincides with the coarse graduation corresponding to 0.1. The amount of translation is read on the micron scale which in this case is.062. The reading then is millimeters. Convenient operation of the MM 100 is achieved with a micrometer eyepiece parallel to, and to the left of, the viewing microscope eyepiece.. IV. OPTICAL SYSTEM Both the x and y coarse scales and the common micrometer scale are read in the same eyepiece. The viewing microscope is equipped with a rack and pinion for vertical motion, to bring the emulsion surface into sharp focus. To read the coordinates of a system of points, the film is clamped and the zero x line oriented parallel to the x ways by turning the azimuth motion. The selected image is bi-
4 SYMPOSIUM-NON-TOPOGRAPHIC PJ-IOTOGRAMMETRIC INSTRUMENTS 59 FIG. 4.-Y Platform. sected with the cross-hairs of the viewing microscope. The coincidence knob is turned until a coarse graduation coincides with the index mark. The x and y coarse graduations are made to coincide with the index mark in two separate turns of the coincidence knob. The coarse graduation and common micron scale are read and recorded for each corresponding coincidence. This operation is repeated on each image in the direct and reverse positions. The reverse position is an azimuth rotation of 180 degrees. The x and y coarse scales are glass with a least graduation of one-tenth of a millimeter (0.1 mm.). The micrometer scale is graduated into one hundred parts, each division representing one micron. The micrometer scale is attached to the coincidence wedge so that when a coarse graduation is separated one division, movement of the wedge, which intercepts the light path from the coarse scales, causes the micron index to read ± 100 microns, depending on whether coincidence is executed positively or negatively. The x and y scales are illuminated with a common light source located on the x platform. The optical relation and common magnification of two scales having mutually orthogonal translation are achieved by superimposition of an image of the y coarse graduations on the surface of the x scale just above the x graduations. The y scale is attached to the y platform. The y platform is shown in Figure 4. The surface of the y scale moves in the focal plane of a lens fixed to the x scale. The collimated bundle of light including the y coarse graduation is made, LIGHT I& f) SOURCE o )( SCREW FIG. 5.-X Platform.
5 60 PHOTOGRAMMETRIC ENGINEERING through use of prisms attached to the ~ platform, to be collinear with the axis of a second lens attached to the base. The x scale attached to the x platform moves in the focal plane of the second lens, and therefore the image of the y scale is superimposed on the x scale above the x coarse graduations. The x platform is shown in Figure S. The y scale lens on the x platform and the x scale lens on the base have the same focal length so that the images of the y graduations have a one to one ratio to the x graduations. The light rays between the two lenses are collimated and therefore are independent of the variable distance due to x translation. Thus the two scales are optically linked FIG. 6.-Base and optical micrometer. at a common magnification despite orthogonal translation. The x scale lies in the focal plane of the reading microscope objective attached to the base. The base platform is shown in Figure 6. The images of the two scales, formed by the microscope objective after passage through the optical wedge, and the image of the micron ladder lie in a common focal plane where they are viewed through the reading microscope eyepiece. The micron ladder is illuminated from the side, and the viewing stage from the bottom. This concludes a brief description of the design considerations of the MM 100 mm. comparator. I DISCUSSION OF MR. FISCHER'S PAPER: PHOTO GEOLOGIC INSTRUMENTATION IN THE U. S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY Bertil Hallert N HIS paper, Mr. Fischer mentioned the use of the mirror stereoscope and the parallax bar for the determination of elevation differences on the ground, from approximately vertical aerial photographs. Because, up to now, only the x-parallaxes seem to be used for such determinations, I will briefly mention how the quality of the results can be considerably increased if the y-parallaxes are also taken into account. Some other related questions will be discussed. In my teaching work at Ohio State University it was necessary that I use the mirror stereoscope and parallax bar as the main stereoscopic instrument because none of the ordinary high precision stereoscopic instruments were available. The German phrase"in der Not frisst der Taufel FlOhen" is a good expression in such situations. This simple instrument-the mirror stereoscope and parallax bar-has also OTE: Following Mr. Fischer's reading of his paper at the Semi-Annual Meeting, a discussion was invited. At that time Dr. Hallert made some remarks. Due to the interest in his statements then and later indicated, Dr. Hallert, after his return to Columbus, embodied the statements in this paper arid also included other material-editor.
Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere. Lecture 24 Measurement of Screw Thread Element
 Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere Lecture 24 Measurement of Screw Thread Element I welcome you all for the module 6 lecture 2, in this lecture
Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere Lecture 24 Measurement of Screw Thread Element I welcome you all for the module 6 lecture 2, in this lecture
14th Congress of the International Society of Photogrammetry Hamburg Commission II. Presented Paper STEREOMARKING INSTRUMENTS DSI-T AND NT
 14th Congress of the International Society of Photogrammetry Hamburg 1980 Commission II Presented Paper STEREOMARKING INSTRUMENTS DSI-T AND NT Iljin L.B. TsNIIGAiK, Moscow, USSR ABSTRACT: Efficient use
14th Congress of the International Society of Photogrammetry Hamburg 1980 Commission II Presented Paper STEREOMARKING INSTRUMENTS DSI-T AND NT Iljin L.B. TsNIIGAiK, Moscow, USSR ABSTRACT: Efficient use
I-I. S/Scientific Report No. I. Duane C. Brown. C-!3 P.O0. Box 1226 Melbourne, Florida
 S AFCRL.-63-481 LOCATION AND DETERMINATION OF THE LOCATION OF THE ENTRANCE PUPIL -0 (CENTER OF PROJECTION) I- ~OF PC-1000 CAMERA IN OBJECT SPACE S Ronald G. Davis Duane C. Brown - L INSTRUMENT CORPORATION
S AFCRL.-63-481 LOCATION AND DETERMINATION OF THE LOCATION OF THE ENTRANCE PUPIL -0 (CENTER OF PROJECTION) I- ~OF PC-1000 CAMERA IN OBJECT SPACE S Ronald G. Davis Duane C. Brown - L INSTRUMENT CORPORATION
BASED on the comments of several members of the American Society of
 SYMPOSIUM ON PHOTOGRAMMETRIC TECHNIQUES-COMMERCIAL OPERATIONS 349 The time of development is controlled by altering the speed of the motor and, under ordinary circumstances, we are able to process three
SYMPOSIUM ON PHOTOGRAMMETRIC TECHNIQUES-COMMERCIAL OPERATIONS 349 The time of development is controlled by altering the speed of the motor and, under ordinary circumstances, we are able to process three
Name:.. KSU ID:. Date:././201..
 Name:.. KSU ID:. Date:././201.. Objective (1): Verification of law of reflection and determination of refractive index of Acrylic glass Required Equipment: (i) Optical bench, (ii) Glass lens, mounted,
Name:.. KSU ID:. Date:././201.. Objective (1): Verification of law of reflection and determination of refractive index of Acrylic glass Required Equipment: (i) Optical bench, (ii) Glass lens, mounted,
Metrology Prof.Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere
 Metrology Prof.Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere Lecture 33 Electrical and Electronic Comparators, Optical comparators (Refer Slide Time: 00:17) I welcome
Metrology Prof.Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere Lecture 33 Electrical and Electronic Comparators, Optical comparators (Refer Slide Time: 00:17) I welcome
Experiment 2 Simple Lenses. Introduction. Focal Lengths of Simple Lenses
 Experiment 2 Simple Lenses Introduction In this experiment you will measure the focal lengths of (1) a simple positive lens and (2) a simple negative lens. In each case, you will be given a specific method
Experiment 2 Simple Lenses Introduction In this experiment you will measure the focal lengths of (1) a simple positive lens and (2) a simple negative lens. In each case, you will be given a specific method
Chapter Ray and Wave Optics
 109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
Principles of Photogrammetry
 Winter 2014 1 Instructor: Contact Information. Office: Room # ENE 229C. Tel: (403) 220-7105. E-mail: ahabib@ucalgary.ca Lectures (SB 148): Monday, Wednesday& Friday (10:00 a.m. 10:50 a.m.). Office Hours:
Winter 2014 1 Instructor: Contact Information. Office: Room # ENE 229C. Tel: (403) 220-7105. E-mail: ahabib@ucalgary.ca Lectures (SB 148): Monday, Wednesday& Friday (10:00 a.m. 10:50 a.m.). Office Hours:
PHOTOGRAMMETRY STEREOSCOPY FLIGHT PLANNING PHOTOGRAMMETRIC DEFINITIONS GROUND CONTROL INTRODUCTION
 PHOTOGRAMMETRY STEREOSCOPY FLIGHT PLANNING PHOTOGRAMMETRIC DEFINITIONS GROUND CONTROL INTRODUCTION Before aerial photography and photogrammetry became a reliable mapping tool, planimetric and topographic
PHOTOGRAMMETRY STEREOSCOPY FLIGHT PLANNING PHOTOGRAMMETRIC DEFINITIONS GROUND CONTROL INTRODUCTION Before aerial photography and photogrammetry became a reliable mapping tool, planimetric and topographic
Physics 1411 Telescopes Lab
 Name: Section: Partners: Physics 1411 Telescopes Lab Refracting and Reflecting telescopes are the two most common types of telescopes you will find. Each of these can be mounted on either an equatorial
Name: Section: Partners: Physics 1411 Telescopes Lab Refracting and Reflecting telescopes are the two most common types of telescopes you will find. Each of these can be mounted on either an equatorial
EXPERIMENT 4 INVESTIGATIONS WITH MIRRORS AND LENSES 4.2 AIM 4.1 INTRODUCTION
 EXPERIMENT 4 INVESTIGATIONS WITH MIRRORS AND LENSES Structure 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Aim 4.3 What is Parallax? 4.4 Locating Images 4.5 Investigations with Real Images Focal Length of a Concave Mirror Focal
EXPERIMENT 4 INVESTIGATIONS WITH MIRRORS AND LENSES Structure 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Aim 4.3 What is Parallax? 4.4 Locating Images 4.5 Investigations with Real Images Focal Length of a Concave Mirror Focal
P202/219 Laboratory IUPUI Physics Department THIN LENSES
 THIN LENSES OBJECTIVE To verify the thin lens equation, m = h i /h o = d i /d o. d o d i f, and the magnification equations THEORY In the above equations, d o is the distance between the object and the
THIN LENSES OBJECTIVE To verify the thin lens equation, m = h i /h o = d i /d o. d o d i f, and the magnification equations THEORY In the above equations, d o is the distance between the object and the
STEINDORFF NYMC Polarizing Microscope
 NYMC38000 Polarizing Microscope In order to exert performance of this microscope and to ensure the safety, please read the operating instruction carefully before use. 1 I. APPLICATION: NYMC38000 series
NYMC38000 Polarizing Microscope In order to exert performance of this microscope and to ensure the safety, please read the operating instruction carefully before use. 1 I. APPLICATION: NYMC38000 series
Volume 1 - Module 6 Geometry of Aerial Photography. I. Classification of Photographs. Vertical
 RSCC Volume 1 Introduction to Photo Interpretation and Photogrammetry Table of Contents Module 1 Module 2 Module 3.1 Module 3.2 Module 4 Module 5 Module 6 Module 7 Module 8 Labs Volume 1 - Module 6 Geometry
RSCC Volume 1 Introduction to Photo Interpretation and Photogrammetry Table of Contents Module 1 Module 2 Module 3.1 Module 3.2 Module 4 Module 5 Module 6 Module 7 Module 8 Labs Volume 1 - Module 6 Geometry
CHAPTER 3LENSES. 1.1 Basics. Convex Lens. Concave Lens. 1 Introduction to convex and concave lenses. Shape: Shape: Symbol: Symbol:
 CHAPTER 3LENSES 1 Introduction to convex and concave lenses 1.1 Basics Convex Lens Shape: Concave Lens Shape: Symbol: Symbol: Effect to parallel rays: Effect to parallel rays: Explanation: Explanation:
CHAPTER 3LENSES 1 Introduction to convex and concave lenses 1.1 Basics Convex Lens Shape: Concave Lens Shape: Symbol: Symbol: Effect to parallel rays: Effect to parallel rays: Explanation: Explanation:
not to be republished NCERT Introduction To Aerial Photographs Chapter 6
 Chapter 6 Introduction To Aerial Photographs Figure 6.1 Terrestrial photograph of Mussorrie town of similar features, then we have to place ourselves somewhere in the air. When we do so and look down,
Chapter 6 Introduction To Aerial Photographs Figure 6.1 Terrestrial photograph of Mussorrie town of similar features, then we have to place ourselves somewhere in the air. When we do so and look down,
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING DESIGN AND PRODUCTION ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT. Credit Hour System Metrology Lab 1 MDP 240. Protractors. Metrology laboratory
 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING DESIGN AND PRODUCTION ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Report On: Credit Hour System Metrology Lab 1 MDP 240 (12) Protractors Metrology laboratory Class No: B.N. Student Name Remark Signature
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING DESIGN AND PRODUCTION ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Report On: Credit Hour System Metrology Lab 1 MDP 240 (12) Protractors Metrology laboratory Class No: B.N. Student Name Remark Signature
MICROSCOPE LAB. Resolving Power How well specimen detail is preserved during the magnifying process.
 AP BIOLOGY Cells ACTIVITY #2 MICROSCOPE LAB OBJECTIVES 1. Demonstrate proper care and use of a compound microscope. 2. Identify the parts of the microscope and describe the function of each part. 3. Compare
AP BIOLOGY Cells ACTIVITY #2 MICROSCOPE LAB OBJECTIVES 1. Demonstrate proper care and use of a compound microscope. 2. Identify the parts of the microscope and describe the function of each part. 3. Compare
SWIFT SERIES M2252DGL MICROSCOPE
 SWIFT SERIES M2252DGL MICROSCOPE The M2252DGL Series is ideal for elementary to high school classrooms. Built to withstand student use, this series has locked-on eyepieces, objectives, illuminator housing
SWIFT SERIES M2252DGL MICROSCOPE The M2252DGL Series is ideal for elementary to high school classrooms. Built to withstand student use, this series has locked-on eyepieces, objectives, illuminator housing
Week IV: FIRST EXPERIMENTS WITH THE ADVANCED OPTICS SET
 Week IV: FIRST EXPERIMENTS WITH THE ADVANCED OPTICS SET The Advanced Optics set consists of (A) Incandescent Lamp (B) Laser (C) Optical Bench (with magnetic surface and metric scale) (D) Component Carriers
Week IV: FIRST EXPERIMENTS WITH THE ADVANCED OPTICS SET The Advanced Optics set consists of (A) Incandescent Lamp (B) Laser (C) Optical Bench (with magnetic surface and metric scale) (D) Component Carriers
Systems Biology. Optical Train, Köhler Illumination
 McGill University Life Sciences Complex Imaging Facility Systems Biology Microscopy Workshop Tuesday December 7 th, 2010 Simple Lenses, Transmitted Light Optical Train, Köhler Illumination What Does a
McGill University Life Sciences Complex Imaging Facility Systems Biology Microscopy Workshop Tuesday December 7 th, 2010 Simple Lenses, Transmitted Light Optical Train, Köhler Illumination What Does a
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam. Name:
 EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB
 ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 3: Imaging 2 the Microscope Original Version: Professor McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the use of one or more lenses to create highly
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 3: Imaging 2 the Microscope Original Version: Professor McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the use of one or more lenses to create highly
ML7520 ML7530 DIOPTER ADJUSTMENT RING BINOCULAR BODY, INCLINED 30. (a) Field Iris Control Lever. (c) Filter Slots EYEPIECES, KHW10X
 JAPAN DIOPTER ADJUSTMENT RING BINOCULAR BODY, INCLINED 30 (a) Field Iris Control Lever (c) Filter Slots EYEPIECES, KHW10X ANALYZER CONTROL LEVER (b) Aperture Iris Control Lever LIGHT SOURCE HOUSING VERTICAL
JAPAN DIOPTER ADJUSTMENT RING BINOCULAR BODY, INCLINED 30 (a) Field Iris Control Lever (c) Filter Slots EYEPIECES, KHW10X ANALYZER CONTROL LEVER (b) Aperture Iris Control Lever LIGHT SOURCE HOUSING VERTICAL
OMM300. Inverted Metallurgical Microscope
 OMM300 Inverted Metallurgical Microscope Instruction Manual Please read the instructions carefully before operating CONTENTS Safety 2 Parts List 2 Features 3 Assembly 5 Operation 7 Maintenance 9 Specifications
OMM300 Inverted Metallurgical Microscope Instruction Manual Please read the instructions carefully before operating CONTENTS Safety 2 Parts List 2 Features 3 Assembly 5 Operation 7 Maintenance 9 Specifications
Section 8. Objectives
 8-1 Section 8 Objectives Objectives Simple and Petval Objectives are lens element combinations used to image (usually) distant objects. To classify the objective, separated groups of lens elements are
8-1 Section 8 Objectives Objectives Simple and Petval Objectives are lens element combinations used to image (usually) distant objects. To classify the objective, separated groups of lens elements are
LEOK-3 Optics Experiment kit
 LEOK-3 Optics Experiment kit Physical optics, geometrical optics and fourier optics Covering 26 experiments Comprehensive documents Include experiment setups, principles and procedures Cost effective solution
LEOK-3 Optics Experiment kit Physical optics, geometrical optics and fourier optics Covering 26 experiments Comprehensive documents Include experiment setups, principles and procedures Cost effective solution
Components of the Microscope
 Swift M3 Microscope The Swift M3 is a versatile microscope designed for both microscopic (high magnification, small field of view) and macroscopic (low magnification, large field of view) applications.
Swift M3 Microscope The Swift M3 is a versatile microscope designed for both microscopic (high magnification, small field of view) and macroscopic (low magnification, large field of view) applications.
Parity and Plane Mirrors. Invert Image flip about a horizontal line. Revert Image flip about a vertical line.
 Optical Systems 37 Parity and Plane Mirrors In addition to bending or folding the light path, reflection from a plane mirror introduces a parity change in the image. Invert Image flip about a horizontal
Optical Systems 37 Parity and Plane Mirrors In addition to bending or folding the light path, reflection from a plane mirror introduces a parity change in the image. Invert Image flip about a horizontal
Person s Optics Test KEY SSSS
 Person s Optics Test KEY SSSS 2017-18 Competitors Names: School Name: All questions are worth one point unless otherwise stated. Show ALL WORK or you may not receive credit. Include correct units whenever
Person s Optics Test KEY SSSS 2017-18 Competitors Names: School Name: All questions are worth one point unless otherwise stated. Show ALL WORK or you may not receive credit. Include correct units whenever
Laser Telemetric System (Metrology)
 Laser Telemetric System (Metrology) Laser telemetric system is a non-contact gauge that measures with a collimated laser beam (Refer Fig. 10.26). It measure at the rate of 150 scans per second. It basically
Laser Telemetric System (Metrology) Laser telemetric system is a non-contact gauge that measures with a collimated laser beam (Refer Fig. 10.26). It measure at the rate of 150 scans per second. It basically
Marine Invertebrate Zoology Microscope Introduction
 Marine Invertebrate Zoology Microscope Introduction Introduction A laboratory tool that has become almost synonymous with biology is the microscope. As an extension of your eyes, the microscope is one
Marine Invertebrate Zoology Microscope Introduction Introduction A laboratory tool that has become almost synonymous with biology is the microscope. As an extension of your eyes, the microscope is one
Chapters 1 & 2. Definitions and applications Conceptual basis of photogrammetric processing
 Chapters 1 & 2 Chapter 1: Photogrammetry Definitions and applications Conceptual basis of photogrammetric processing Transition from two-dimensional imagery to three-dimensional information Automation
Chapters 1 & 2 Chapter 1: Photogrammetry Definitions and applications Conceptual basis of photogrammetric processing Transition from two-dimensional imagery to three-dimensional information Automation
Laboratory 7: Properties of Lenses and Mirrors
 Laboratory 7: Properties of Lenses and Mirrors Converging and Diverging Lens Focal Lengths: A converging lens is thicker at the center than at the periphery and light from an object at infinity passes
Laboratory 7: Properties of Lenses and Mirrors Converging and Diverging Lens Focal Lengths: A converging lens is thicker at the center than at the periphery and light from an object at infinity passes
7. Michelson Interferometer
 7. Michelson Interferometer In this lab we are going to observe the interference patterns produced by two spherical waves as well as by two plane waves. We will study the operation of a Michelson interferometer,
7. Michelson Interferometer In this lab we are going to observe the interference patterns produced by two spherical waves as well as by two plane waves. We will study the operation of a Michelson interferometer,
Century focus and test chart instructions
 Century focus and test chart instructions INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK Page 2 Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Page 4 System Contents Page 4 Resolution: A note from Schneider Optics Page 6
Century focus and test chart instructions INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK Page 2 Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Page 4 System Contents Page 4 Resolution: A note from Schneider Optics Page 6
Chapter 3 Mirrors. The most common and familiar optical device
 Chapter 3 Mirrors The most common and familiar optical device Outline Plane mirrors Spherical mirrors Graphical image construction Two mirrors; The Cassegrain Telescope Plane mirrors Common household mirrors:
Chapter 3 Mirrors The most common and familiar optical device Outline Plane mirrors Spherical mirrors Graphical image construction Two mirrors; The Cassegrain Telescope Plane mirrors Common household mirrors:
ON THE CREATION OF PANORAMIC IMAGES FROM IMAGE SEQUENCES
 ON THE CREATION OF PANORAMIC IMAGES FROM IMAGE SEQUENCES Petteri PÖNTINEN Helsinki University of Technology, Institute of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Finland petteri.pontinen@hut.fi KEY WORDS: Cocentricity,
ON THE CREATION OF PANORAMIC IMAGES FROM IMAGE SEQUENCES Petteri PÖNTINEN Helsinki University of Technology, Institute of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Finland petteri.pontinen@hut.fi KEY WORDS: Cocentricity,
Chapter 18 Optical Elements
 Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Physics 2020 Lab 8 Lenses
 Physics 2020 Lab 8 Lenses Name Section Introduction. In this lab, you will study converging lenses. There are a number of different types of converging lenses, but all of them are thicker in the middle
Physics 2020 Lab 8 Lenses Name Section Introduction. In this lab, you will study converging lenses. There are a number of different types of converging lenses, but all of them are thicker in the middle
Reading: Lenses and Mirrors; Applications Key concepts: Focal points and lengths; real images; virtual images; magnification; angular magnification.
 Reading: Lenses and Mirrors; Applications Key concepts: Focal points and lengths; real images; virtual images; magnification; angular magnification. 1.! Questions about objects and images. Can a virtual
Reading: Lenses and Mirrors; Applications Key concepts: Focal points and lengths; real images; virtual images; magnification; angular magnification. 1.! Questions about objects and images. Can a virtual
LEA_IT_COD High precision Optical Collimator. Instruments and Systems for Geotechnical and Structural Monitoring
 LEA_IT_COD1101100 High precision Optical Collimator LEA_IT_COD1101100 High precision Optical Collimator Description _ The optical alignment collimator is an instrument produced by Pizzi Instruments and
LEA_IT_COD1101100 High precision Optical Collimator LEA_IT_COD1101100 High precision Optical Collimator Description _ The optical alignment collimator is an instrument produced by Pizzi Instruments and
Lab 8 Microscope. Name. I. Introduction/Theory
 Lab 8 Microscope Name I. Introduction/Theory The purpose of this experiment is to construct a microscope and determine the magnification. A microscope magnifies an object that is close to the microscope.
Lab 8 Microscope Name I. Introduction/Theory The purpose of this experiment is to construct a microscope and determine the magnification. A microscope magnifies an object that is close to the microscope.
The Stereomicroscope CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 The Stereomicroscope The stereomicroscope is used in most preliminary forensic examinations. This low magnification microscope provides viewing of samples in a manner that is similar to the view
CHAPTER 1 The Stereomicroscope The stereomicroscope is used in most preliminary forensic examinations. This low magnification microscope provides viewing of samples in a manner that is similar to the view
SUBJECT: PHYSICS. Use and Succeed.
 SUBJECT: PHYSICS I hope this collection of questions will help to test your preparation level and useful to recall the concepts in different areas of all the chapters. Use and Succeed. Navaneethakrishnan.V
SUBJECT: PHYSICS I hope this collection of questions will help to test your preparation level and useful to recall the concepts in different areas of all the chapters. Use and Succeed. Navaneethakrishnan.V
Lab 10: Lenses & Telescopes
 Physics 2020, Fall 2010 Lab 8 page 1 of 6 Circle your lab day and time. Your name: Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri TA name: 8-10 10-12 12-2 2-4 4-6 INTRODUCTION Lab 10: Lenses & Telescopes In this experiment, you
Physics 2020, Fall 2010 Lab 8 page 1 of 6 Circle your lab day and time. Your name: Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri TA name: 8-10 10-12 12-2 2-4 4-6 INTRODUCTION Lab 10: Lenses & Telescopes In this experiment, you
Media Cybernetics White Paper Spherical Aberration
 Media Cybernetics White Paper Spherical Aberration Brian Matsumoto, University of California, Santa Barbara Introduction Digital photomicrographers assume that lens aberrations are corrected by the microscope
Media Cybernetics White Paper Spherical Aberration Brian Matsumoto, University of California, Santa Barbara Introduction Digital photomicrographers assume that lens aberrations are corrected by the microscope
1.When an object is sharply focused and the slide is moved towards you, in which direction does the
 image upright or inverted? Name: Date: _ BIOLOGY EXPERIMENT:Class: Using a Compound Light Microscope II: Depth Perception, resolution, field of view MATERIALS: Compound light microscopecolor magazine clipping
image upright or inverted? Name: Date: _ BIOLOGY EXPERIMENT:Class: Using a Compound Light Microscope II: Depth Perception, resolution, field of view MATERIALS: Compound light microscopecolor magazine clipping
13. Optical Instruments*
 13. Optical Instruments* Objective: Here what you have been learning about thin lenses is applied to make a telescope. In the process you encounter general optical instrument design concepts. The learning
13. Optical Instruments* Objective: Here what you have been learning about thin lenses is applied to make a telescope. In the process you encounter general optical instrument design concepts. The learning
Following are the geometrical elements of the aerial photographs:
 Geometrical elements/characteristics of aerial photograph: An aerial photograph is a central or perspective projection, where the bundles of perspective rays meet at a point of origin called perspective
Geometrical elements/characteristics of aerial photograph: An aerial photograph is a central or perspective projection, where the bundles of perspective rays meet at a point of origin called perspective
CXI 1 micron Precision Instrument Stand
 Engineering specification Document (ESD) Doc. No. SP-391-001-44 R0 LUSI SUB-SYSTEM CXI Instrument Prepared by: Jean-Charles Castagna Design Engineer Signature Date Co-authored by: Paul Montanez CXI Lead
Engineering specification Document (ESD) Doc. No. SP-391-001-44 R0 LUSI SUB-SYSTEM CXI Instrument Prepared by: Jean-Charles Castagna Design Engineer Signature Date Co-authored by: Paul Montanez CXI Lead
Photographic Interpretation Handbook, United States Forces: Section 09 Height and Depth Finding from Parallax
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln DOD Military Intelligence U.S. Department of Defense 4-1944 Photographic Interpretation Handbook, United States Forces:
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln DOD Military Intelligence U.S. Department of Defense 4-1944 Photographic Interpretation Handbook, United States Forces:
REFLECTION THROUGH LENS
 REFLECTION THROUGH LENS A lens is a piece of transparent optical material with one or two curved surfaces to refract light rays. It may converge or diverge light rays to form an image. Lenses are mostly
REFLECTION THROUGH LENS A lens is a piece of transparent optical material with one or two curved surfaces to refract light rays. It may converge or diverge light rays to form an image. Lenses are mostly
PHYS 160 Astronomy. When analyzing light s behavior in a mirror or lens, it is helpful to use a technique called ray tracing.
 Optics Introduction In this lab, we will be exploring several properties of light including diffraction, reflection, geometric optics, and interference. There are two sections to this lab and they may
Optics Introduction In this lab, we will be exploring several properties of light including diffraction, reflection, geometric optics, and interference. There are two sections to this lab and they may
MINNESOTA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION OFFICE OF LAND MANAGEMENT SURVEYING AND MAPPING SECTION PHOTOGRAMMETRY UNIT
 SEP. 2011 MINNESOTA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION OFFICE OF LAND MANAGEMENT SURVEYING AND MAPPING SECTION PHOTOGRAMMETRY UNIT SPECIAL PROVISIONS FOR: GROUP 1: AERIAL PHOTOGRAPHY/PHOTOGRAMMETRIC LAB SERVICES
SEP. 2011 MINNESOTA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION OFFICE OF LAND MANAGEMENT SURVEYING AND MAPPING SECTION PHOTOGRAMMETRY UNIT SPECIAL PROVISIONS FOR: GROUP 1: AERIAL PHOTOGRAPHY/PHOTOGRAMMETRIC LAB SERVICES
11/25/2009 CHAPTER THREE INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION (CONT D) THE AERIAL CAMERA: LENS PHOTOGRAPHIC SENSORS
 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER THREE IC SENSORS Photography means to write with light Today s meaning is often expanded to include radiation just outside the visible spectrum, i. e. ultraviolet and near infrared
INTRODUCTION CHAPTER THREE IC SENSORS Photography means to write with light Today s meaning is often expanded to include radiation just outside the visible spectrum, i. e. ultraviolet and near infrared
Sample Copy. Not For Distribution.
 Photogrammetry, GIS & Remote Sensing Quick Reference Book i EDUCREATION PUBLISHING Shubham Vihar, Mangla, Bilaspur, Chhattisgarh - 495001 Website: www.educreation.in Copyright, 2017, S.S. Manugula, V.
Photogrammetry, GIS & Remote Sensing Quick Reference Book i EDUCREATION PUBLISHING Shubham Vihar, Mangla, Bilaspur, Chhattisgarh - 495001 Website: www.educreation.in Copyright, 2017, S.S. Manugula, V.
Chapter 8. The Telescope. 8.1 Purpose. 8.2 Introduction A Brief History of the Early Telescope
 Chapter 8 The Telescope 8.1 Purpose In this lab, you will measure the focal lengths of two lenses and use them to construct a simple telescope which inverts the image like the one developed by Johannes
Chapter 8 The Telescope 8.1 Purpose In this lab, you will measure the focal lengths of two lenses and use them to construct a simple telescope which inverts the image like the one developed by Johannes
Dr. Achim Z i c k 1 e r JENOPTIK JENA GmbH, GDR 69 Jena, Carl-Zeiss-Platz 1
 14th International Congress of ISP Commission 1 Hamburg 1980 Werking Group - Frasented Paper Dr. Achim Z i c k 1 e r JENOPTIK JENA GmbH, GDR 69 Jena, Carl-Zeiss-Platz 1 MKF-6 Multispectral Camera from
14th International Congress of ISP Commission 1 Hamburg 1980 Werking Group - Frasented Paper Dr. Achim Z i c k 1 e r JENOPTIK JENA GmbH, GDR 69 Jena, Carl-Zeiss-Platz 1 MKF-6 Multispectral Camera from
The following article is a translation of parts of the original publication of Karl-Ludwig Bath in the german astronomical magazine:
 The following article is a translation of parts of the original publication of Karl-Ludwig Bath in the german astronomical magazine: Sterne und Weltraum 1973/6, p.177-180. The publication of this translation
The following article is a translation of parts of the original publication of Karl-Ludwig Bath in the german astronomical magazine: Sterne und Weltraum 1973/6, p.177-180. The publication of this translation
Optical Components - Scanning Lenses
 Optical Components Scanning Lenses Scanning Lenses (Ftheta) Product Information Figure 1: Scanning Lenses A scanning (Ftheta) lens supplies an image in accordance with the socalled Ftheta condition (y
Optical Components Scanning Lenses Scanning Lenses (Ftheta) Product Information Figure 1: Scanning Lenses A scanning (Ftheta) lens supplies an image in accordance with the socalled Ftheta condition (y
A simple and effective first optical image processing experiment
 A simple and effective first optical image processing experiment Dale W. Olson Physics Department, University of Northern Iowa, Cedar Falls, IA 50614-0150 Abstract: Optical image processing experiments
A simple and effective first optical image processing experiment Dale W. Olson Physics Department, University of Northern Iowa, Cedar Falls, IA 50614-0150 Abstract: Optical image processing experiments
Microscope Tutorial. How to use a compound microscope
 Microscope Tutorial How to use a compound microscope Read this first Microscopes are extremely delicate and extremely expensive! You MUST be extremely careful when using the microscope. Always hold the
Microscope Tutorial How to use a compound microscope Read this first Microscopes are extremely delicate and extremely expensive! You MUST be extremely careful when using the microscope. Always hold the
Module-2 Lecture-2 Combination set, Vernier calipers. (Refer Slide Time: 00:16)
 Metrology Prof. Dr. Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Department of Industrial and Production Engineering Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology-Davangere Module-2 Lecture-2 Combination set, Vernier calipers
Metrology Prof. Dr. Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Department of Industrial and Production Engineering Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology-Davangere Module-2 Lecture-2 Combination set, Vernier calipers
A SYSTEM FOR THE NORMAL CASE OF CLOSE-RANGE PHOTOGRAPHY WITH TERRESTRIAL CAMERA
 A SYSTEM FOR THE NORMAL CASE OF CLOSE-RANGE PHOTOGRAPHY WITH TERRESTRIAL CAMERA Oguz MÜFTÜOGLU - Cankut ÖRMEC! Surveying Department of Civil Engineering Faculty!stanbul Technical University,!stanbul -
A SYSTEM FOR THE NORMAL CASE OF CLOSE-RANGE PHOTOGRAPHY WITH TERRESTRIAL CAMERA Oguz MÜFTÜOGLU - Cankut ÖRMEC! Surveying Department of Civil Engineering Faculty!stanbul Technical University,!stanbul -
Final Reg Optics Review SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Final Reg Optics Review 1) How far are you from your image when you stand 0.75 m in front of a vertical plane mirror? 1) 2) A object is 12 cm in front of a concave mirror, and the image is 3.0 cm in front
Final Reg Optics Review 1) How far are you from your image when you stand 0.75 m in front of a vertical plane mirror? 1) 2) A object is 12 cm in front of a concave mirror, and the image is 3.0 cm in front
PHYSICS 289 Experiment 8 Fall Geometric Optics II Thin Lenses
 PHYSICS 289 Experiment 8 Fall 2005 Geometric Optics II Thin Lenses Please look at the chapter on lenses in your text before this lab experiment. Please submit a short lab report which includes answers
PHYSICS 289 Experiment 8 Fall 2005 Geometric Optics II Thin Lenses Please look at the chapter on lenses in your text before this lab experiment. Please submit a short lab report which includes answers
28 Thin Lenses: Ray Tracing
 28 Thin Lenses: Ray Tracing A lens is a piece of transparent material whose surfaces have been shaped so that, when the lens is in another transparent material (call it medium 0), light traveling in medium
28 Thin Lenses: Ray Tracing A lens is a piece of transparent material whose surfaces have been shaped so that, when the lens is in another transparent material (call it medium 0), light traveling in medium
Fine Recording in Time Direction for Seismological Observation
 Fine Recording in Time Direction for Seismological Observation 550. 341 by S. Suyehiro Meteorological Research Institute, Tokyo (Received June 4, 1959) Abstract In the routine seismological observation,
Fine Recording in Time Direction for Seismological Observation 550. 341 by S. Suyehiro Meteorological Research Institute, Tokyo (Received June 4, 1959) Abstract In the routine seismological observation,
General Physics Experiment 5 Optical Instruments: Simple Magnifier, Microscope, and Newtonian Telescope
 General Physics Experiment 5 Optical Instruments: Simple Magnifier, Microscope, and Newtonian Telescope Objective: < To observe the magnifying properties of the simple magnifier, the microscope and the
General Physics Experiment 5 Optical Instruments: Simple Magnifier, Microscope, and Newtonian Telescope Objective: < To observe the magnifying properties of the simple magnifier, the microscope and the
Hubble Optics CDK 17 Collimation Instructions 03/27/2012 Hubble Optics
 Hubble Optics CDK 17 Collimation Instructions 03/27/2012 Hubble Optics 1: CDK17 Specification: System Effective Focal Length: 2894.7 mm, (this might be slightly different for different set of optics) Figure
Hubble Optics CDK 17 Collimation Instructions 03/27/2012 Hubble Optics 1: CDK17 Specification: System Effective Focal Length: 2894.7 mm, (this might be slightly different for different set of optics) Figure
1.0 MEASUREMENT OF PARAXIAL PROPERTIES OF OPTICAL SYSTEMS
 .0 MEASUREMENT OF PARAXIAL PROPERTIES OF OPTICAL SYSTEMS James C. Wyant Optical Sciences Center University of Arizona Tucson, AZ 8572 jcwyant@u.arizona.eu If we wish to completely characterize the paraxial
.0 MEASUREMENT OF PARAXIAL PROPERTIES OF OPTICAL SYSTEMS James C. Wyant Optical Sciences Center University of Arizona Tucson, AZ 8572 jcwyant@u.arizona.eu If we wish to completely characterize the paraxial
Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging
 Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging Hernan G. Garcia August 1, 2005 1 Light Microscopy Basics In this section we will briefly describe the basic principles of operation and
Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging Hernan G. Garcia August 1, 2005 1 Light Microscopy Basics In this section we will briefly describe the basic principles of operation and
Snell s Law, Lenses, and Optical Instruments
 Physics 4 Laboratory Snell s Law, Lenses, and Optical Instruments Prelab Exercise Please read the Procedure section and try to understand the physics involved and how the experimental procedure works.
Physics 4 Laboratory Snell s Law, Lenses, and Optical Instruments Prelab Exercise Please read the Procedure section and try to understand the physics involved and how the experimental procedure works.
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET
 LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
A tutorial for designing. fundamental imaging systems
 A tutorial for designing fundamental imaging systems OPTI 521 College of Optical Science University of Arizona November 2009 Abstract This tutorial shows what to do when we design opto-mechanical system
A tutorial for designing fundamental imaging systems OPTI 521 College of Optical Science University of Arizona November 2009 Abstract This tutorial shows what to do when we design opto-mechanical system
AN INTRODUCTION TO CHROMATIC ABERRATION IN REFRACTORS
 AN INTRODUCTION TO CHROMATIC ABERRATION IN REFRACTORS The popularity of high-quality refractors draws attention to color correction in such instruments. There are several point of confusion and misconceptions.
AN INTRODUCTION TO CHROMATIC ABERRATION IN REFRACTORS The popularity of high-quality refractors draws attention to color correction in such instruments. There are several point of confusion and misconceptions.
Corundum C Axis Device for Sample Preparation Timothy Thomas, M.E., M.S.E.E. GIA Laboratory June 4, 2009
 Abstract Corundum C Axis Device for Sample Preparation Timothy Thomas, M.E., M.S.E.E. GIA Laboratory June 4, 2009 As a part of GIA s on going project to establish a comprehensive corundum database a need
Abstract Corundum C Axis Device for Sample Preparation Timothy Thomas, M.E., M.S.E.E. GIA Laboratory June 4, 2009 As a part of GIA s on going project to establish a comprehensive corundum database a need
Manual for BMS E1 eplan series, compound microscope
 Manual for BMS E1 eplan series, compound microscope The compound microscope allows it to study, at cell level, structures of textures of botanical and zoological nature. (e.g. slides of roots, leaves and
Manual for BMS E1 eplan series, compound microscope The compound microscope allows it to study, at cell level, structures of textures of botanical and zoological nature. (e.g. slides of roots, leaves and
Kit for building your own THz Time-Domain Spectrometer
 Kit for building your own THz Time-Domain Spectrometer 16/06/2016 1 Table of contents 0. Parts for the THz Kit... 3 1. Delay line... 4 2. Pulse generator and lock-in detector... 5 3. THz antennas... 6
Kit for building your own THz Time-Domain Spectrometer 16/06/2016 1 Table of contents 0. Parts for the THz Kit... 3 1. Delay line... 4 2. Pulse generator and lock-in detector... 5 3. THz antennas... 6
A new model of Refractometer.
 354 A new model of Refractometer. By G. F. tt~a~ert S~IT~, M.A., D.Se., F.G.S. Assistant in the Mineral Department of the British Museum. [Read January 29, 1907.] HE instrument described in this paper
354 A new model of Refractometer. By G. F. tt~a~ert S~IT~, M.A., D.Se., F.G.S. Assistant in the Mineral Department of the British Museum. [Read January 29, 1907.] HE instrument described in this paper
DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSMs) on Axio Imager Stands
 DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSMs) on Axio Imager Stands Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) imaging is a technique used to increase contrast in brightfield images. In confocal systems,
DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSMs) on Axio Imager Stands Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) imaging is a technique used to increase contrast in brightfield images. In confocal systems,
Basics of Light Microscopy and Metallography
 ENGR45: Introduction to Materials Spring 2012 Laboratory 8 Basics of Light Microscopy and Metallography In this exercise you will: gain familiarity with the proper use of a research-grade light microscope
ENGR45: Introduction to Materials Spring 2012 Laboratory 8 Basics of Light Microscopy and Metallography In this exercise you will: gain familiarity with the proper use of a research-grade light microscope
Week IX: INTERFEROMETER EXPERIMENTS
 Week IX: INTERFEROMETER EXPERIMENTS Notes on Adjusting the Michelson Interference Caution: Do not touch the mirrors or beam splitters they are front surface and difficult to clean without damaging them.
Week IX: INTERFEROMETER EXPERIMENTS Notes on Adjusting the Michelson Interference Caution: Do not touch the mirrors or beam splitters they are front surface and difficult to clean without damaging them.
Tangents. The f-stops here. Shedding some light on the f-number. by Marcus R. Hatch and David E. Stoltzmann
 Tangents Shedding some light on the f-number The f-stops here by Marcus R. Hatch and David E. Stoltzmann The f-number has peen around for nearly a century now, and it is certainly one of the fundamental
Tangents Shedding some light on the f-number The f-stops here by Marcus R. Hatch and David E. Stoltzmann The f-number has peen around for nearly a century now, and it is certainly one of the fundamental
Date of Application, 16th Jan., 1904 Complete Specification Left, 20th Feb., Accepted, 12th May, 1904
 N o 1196 A.D. 1904 Date of Application, 16th Jan., 1904 Complete Specification Left, 20th Feb., 1904 - Accepted, 12th May, 1904 PROVISIONAL SPECIFICATION. Improved Method and Apparatus for the Systematic
N o 1196 A.D. 1904 Date of Application, 16th Jan., 1904 Complete Specification Left, 20th Feb., 1904 - Accepted, 12th May, 1904 PROVISIONAL SPECIFICATION. Improved Method and Apparatus for the Systematic
Activity 6.1 Image Formation from Spherical Mirrors
 PHY385H1F Introductory Optics Practicals Day 6 Telescopes and Microscopes October 31, 2011 Group Number (number on Intro Optics Kit):. Facilitator Name:. Record-Keeper Name: Time-keeper:. Computer/Wiki-master:..
PHY385H1F Introductory Optics Practicals Day 6 Telescopes and Microscopes October 31, 2011 Group Number (number on Intro Optics Kit):. Facilitator Name:. Record-Keeper Name: Time-keeper:. Computer/Wiki-master:..
An Arduino based automated procedure for measuring refractive indices of optical materials for educational purposes using Michelson s interferometer
 An Arduino based automated procedure for measuring refractive indices of optical materials for educational purposes using Michelson s interferometer Abstract George Mitsou 1 and Ioannis Sianoudis 2 1.
An Arduino based automated procedure for measuring refractive indices of optical materials for educational purposes using Michelson s interferometer Abstract George Mitsou 1 and Ioannis Sianoudis 2 1.
This experiment is under development and thus we appreciate any and all comments as we design an interesting and achievable set of goals.
 Experiment 7 Geometrical Optics You will be introduced to ray optics and image formation in this experiment. We will use the optical rail, lenses, and the camera body to quantify image formation and magnification;
Experiment 7 Geometrical Optics You will be introduced to ray optics and image formation in this experiment. We will use the optical rail, lenses, and the camera body to quantify image formation and magnification;
Image Formation. Light from distant things. Geometrical optics. Pinhole camera. Chapter 36
 Light from distant things Chapter 36 We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can process. This chapter concerns
Light from distant things Chapter 36 We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can process. This chapter concerns
Chapter 7. Optical Measurement and Interferometry
 Chapter 7 Optical Measurement and Interferometry 1 Introduction Optical measurement provides a simple, easy, accurate and reliable means for carrying out inspection and measurements in the industry the
Chapter 7 Optical Measurement and Interferometry 1 Introduction Optical measurement provides a simple, easy, accurate and reliable means for carrying out inspection and measurements in the industry the
ENHANCEMENT OF THE RADIOMETRIC IMAGE QUALITY OF PHOTOGRAMMETRIC SCANNERS.
 ENHANCEMENT OF THE RADIOMETRIC IMAGE QUALITY OF PHOTOGRAMMETRIC SCANNERS Klaus NEUMANN *, Emmanuel BALTSAVIAS ** * Z/I Imaging GmbH, Oberkochen, Germany neumann@ziimaging.de ** Institute of Geodesy and
ENHANCEMENT OF THE RADIOMETRIC IMAGE QUALITY OF PHOTOGRAMMETRIC SCANNERS Klaus NEUMANN *, Emmanuel BALTSAVIAS ** * Z/I Imaging GmbH, Oberkochen, Germany neumann@ziimaging.de ** Institute of Geodesy and
OPTICAL BENCH - simple type
 GENERAL DESCRIPTION: OPTICAL BENCH - simple type Cat: HL2240-001 Complete with Hodson Light Box. Cat: HL2241-001 Not including Hodson Light Box The IEC Optical Bench system is designed to be used with
GENERAL DESCRIPTION: OPTICAL BENCH - simple type Cat: HL2240-001 Complete with Hodson Light Box. Cat: HL2241-001 Not including Hodson Light Box The IEC Optical Bench system is designed to be used with
Performance Comparison of Spectrometers Featuring On-Axis and Off-Axis Grating Rotation
 Performance Comparison of Spectrometers Featuring On-Axis and Off-Axis Rotation By: Michael Case and Roy Grayzel, Acton Research Corporation Introduction The majority of modern spectrographs and scanning
Performance Comparison of Spectrometers Featuring On-Axis and Off-Axis Rotation By: Michael Case and Roy Grayzel, Acton Research Corporation Introduction The majority of modern spectrographs and scanning
Complete the diagram to show what happens to the rays. ... (1) What word can be used to describe this type of lens? ... (1)
 Q1. (a) The diagram shows two parallel rays of light, a lens and its axis. Complete the diagram to show what happens to the rays. (2) Name the point where the rays come together. (iii) What word can be
Q1. (a) The diagram shows two parallel rays of light, a lens and its axis. Complete the diagram to show what happens to the rays. (2) Name the point where the rays come together. (iii) What word can be
PH 481/581 Physical Optics Winter 2014
 PH 481/581 Physical Optics Winter 2014 Laboratory #1 Week of January 13 Read: Handout (Introduction & Projects #2 & 3 from Newport Project in Optics Workbook), pp.150-170 of Optics by Hecht Do: 1. Experiment
PH 481/581 Physical Optics Winter 2014 Laboratory #1 Week of January 13 Read: Handout (Introduction & Projects #2 & 3 from Newport Project in Optics Workbook), pp.150-170 of Optics by Hecht Do: 1. Experiment
DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSM) on Inverted Stands
 DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSM) on Inverted Stands Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) imaging is a technique used to increase contrast in brightfield images. In confocal systems,
DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSM) on Inverted Stands Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) imaging is a technique used to increase contrast in brightfield images. In confocal systems,
INSIDE LAB 6: The Properties of Lenses and Telescopes
 INSIDE LAB 6: The Properties of Lenses and Telescopes OBJECTIVE: To construct a simple refracting telescope and to measure some of its properties. DISCUSSION: In tonight s lab we will build a simple telescope
INSIDE LAB 6: The Properties of Lenses and Telescopes OBJECTIVE: To construct a simple refracting telescope and to measure some of its properties. DISCUSSION: In tonight s lab we will build a simple telescope
Converging Lenses. Parallel rays are brought to a focus by a converging lens (one that is thicker in the center than it is at the edge).
 Chapter 30: Lenses Types of Lenses Piece of glass or transparent material that bends parallel rays of light so they cross and form an image Two types: Converging Diverging Converging Lenses Parallel rays
Chapter 30: Lenses Types of Lenses Piece of glass or transparent material that bends parallel rays of light so they cross and form an image Two types: Converging Diverging Converging Lenses Parallel rays
