|
|
|
- Tiffany Little
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COMS W4172 Travel 2 Steven Feiner Department of Computer Science Columbia University New York, NY April 3, Physical Locomotion Walking Simulators CirculaFloor (H. Iwata et al., U. Tsukuba, 2004) Four tracked moving tiles automatically reconfigure to meet feet of (slow) tracked user Different configurations correspond to tracked user direction 1:29 Later version includes lifting actuators 2
2 Physical Locomotion Walking Simulators VirtuSphere ( User walks inside large (8.5 ft. diam.) modular plastic sphere Base platform uses rollers to support and track rotation (and prevent translation) Display and trackers worn by user must be selfcontained or wireless 3 Motion Platforms MPI CyberMotion simulator Industrial robot arm controls passenger pod with projection screen MPI CableRobot simulator Eight cables attached to motorized winches drive platform 0:16 0:40 4
3 Steering User specifies relative or absolute direction of motion Flying by finger pointing W. Robinett, 1986 (see W. Robinett and R. Holloway, Implementation of Flying, Scaling, and Grabbing in Virtual Worlds, Proc. Symp. on Interactive 3D Graphics, 1992, ) 6 Steering Gaze-Directed Move along direction of gaze [see note] Immersive Use head tracker or eye tracker Desktop Move along vector from eye to center of window (center line of frustum) Can also support motion perp. to gaze Easy to understand Hard to move precisely // to ground But can constrain to lie on ground Uncomfortable to look straight up/down Can only look ahead when traveling! g s' s, where s and s' are old g and new position, is scale factor, g is gaze direction Dries Buytaert Note: Eye tracking is needed for true gaze-directed steering. Head tracking alone determines only headorientation directed steering 7
4 Steering Pointing-Directed Move along direction of pointing Immersive Use hand / finger tracker Can sense direction proprioceptively Desktop Use cursor keys if mouse already used for eye control Use keyboard modifier to determine what mouse controls pd s' s, where s and s' are old pd and new position, is scale factor, p is (dominant) hand pointing direction d STEM controller (sixense.com) 8 Steering Two-Handed Pointing-Directed Use vector between two hands Direction direction Magnitude velocity hd hnd s' s, where s and s' are old h h d and new position, is scale factor, is scale factor determined by distance between hands, h and h are dominant and nondominant d hand positions nd nd M. Mine, F. Brooks, C. Sequin, SIGGRAPH 97 9
5 Steering Torso-Directed Use belt-worn orientation tracker direction Decouples gaze/travel directions, so user can look anywhere while traveling Hands-free Hard to steer up/down with torso b s' s, where s and s' are old b and new position, is scale factor, b is body (torso) direction 10 Steering Camera in Hand (aka Eyeball in Hand) User holds 6DOF tracker in hand Tracker position/orientation camera position/orientation Takes advantage of proprioception Can position hand-held camera (controller) in scaled physical model c Tt, where c is camera position, t is tracker position, and T is transformation (typically scale) Wanda ( 11
6 Steering Physical Props Use controls for vehicle of choice Car, ship, plane, rocket, Can feel real (or not) Performance of system may not match expectations Steering Semi-automated User is provided only partial control River Analogy (T. Galyean, 1995) Boat is carried down the river by the current, but the user can influence its movement with the rudder Anchor (boat) follows path (river) User attached to anchor by spring View direction exerts force on user (pulling user toward items of interest) Variables Anchor speed Rate to reach new speed from old View thrust amount Spring constant Damping constant User controls only their view direction 13
7 Steering Semi-automated User may determine speed of travel only or rough deviations from system-determined path Disney Aladdin s Magic Carpet Ride User can explicitly modify constraints on path Interactive navigation of colon (L. Hong et al., SIGGRAPH 1997) Pausch et al., D voxel rep of colon Distance to target Distance to wall L. Hong et al., SIGGRAPH Route Planning User specifies a path Can review/edit path System moves user along path User exerts control prior to travel Can attend to other tasks while traveling 15
8 Route Planning Drawing T. Igarashi, 1998 User draws stroke on view of 3D world System projects stroke onto walking surface to create path Note: Constrained height User s orientation is upright and tangent to stroke User can draw new stroke to modify path Long stroke full path Short stroke at goal goal position and orientation Short stroke at user s foot Change orientation Takes into account scene structure Obstacle avoidance, slope climbing 17 Target Selection User specifies target destination Move avatar or place target object in WIM, map, or environment Select in WIM, map, or environment Choose from menu, enter coords as number, enter destination name as text System moves user to target Interpolation avoids confusion of discontinuous teleportation 18
9 Target Selection Move Avatar in WIM Pausch et al User places avatar in WIM at desired target position/orientation System flies user into WIM, which becomes world Originally tried approach of interpolating user in world Users found it disorienting Hypothesis: User is cognitively vested in avatar, so avoid shifting focus to world by making user become avatar 19 Target Selection Select Target in World Hachet et al., 2008 Navidget (M. Hachet, F. Decle, S. Knödel, and P. Guitton, 3DUI 2008) User circles, and then uses a 3D widget Widget appears after click and wait Half-Sphere Faces viewpoint Border Ring Selects viewpoint perpendicular to current viewing direction Size Actuators Allows widget to change size Virtual Camera Preview Window 0:00 3:35 Three alternatives for translating the camera when the user circles CENTER = depth at center of circled area (naïve) MAX = most frequent depth value in circled area NEARER = nearest depth value in circled area (conservative) 22
10 Target Selection Head Butt Zoom Mine, Brooks, & Sequin, 1997 User image-plane selects object of interest System leaves frame in air User butts head into frame to move forward, pulls head out to return to original position User can quickly switch between two viewpoints hands-free User can step forward to move to new view for an extended time, back to return Mine, Brooks, & Sequin, Manual Manipulation User manipulates viewpoint as if manipulating an object 24
11 Manual Manipulation Grabbing the Air If user selection action (grabbing) doesn t select a movable object, then select the entire world Translate world origin (but ignore rotation to avoid confusion) w' w n' d nd, where w and w' are old and new world positions, and nd and n' d are old and new dominant hand positions Use two hands as if pulling a rope (Mapes & Moshell, 1995) Can be tiring J. Pierce, 2001 Variation: Image-plane select with hands outside of yellow outline during trigger grabs air for travel. (Based on observation that users positioned hands away from center of image plane when grabbing air. J. Pierce, Manual Manipulation Fixed-Object Manipulation User selects object, acts as if manipulating it, but viewpoint is changed instead (e.g., differentiate based on button pressed) Image-plane select object, move hand(s) closer to eye to move to object (Pierce et al. 1997) Scaled-world grab object, move self relative to object (Mine, Brooks, Sequin 1997) 26
12 Travel by Scaling Scale down world (Scale up user) Move Scale up world (Scale down user) E.g., S. Bryson & C. Levit, IEEE Visualization 91; J. Butterworth et al., 92 Use virtual body to help user understand scale Scaling affects precision May cause cybersickness in egocentric environment 27 Controlling Viewing Orientation Head tracking Natural Improves spatial understanding Orbital viewing (J. Chung, I3D 92) Select position p and distance r Head rotations are mapped to move viewpoint about surface of sphere with center p and radius r, looking at p Look left, right, up, down to see object s right, left, bottom, top, respectively Good for inspection of one object at p, but Can be confusing with more objects in environment Can cause cybersickness 28
13 Controlling Viewing Orientation Nonisomorphic rotation Modify treatment of user orientation while walking Redirected Walking (S. Razzaque) Provide user with experience of walking in a much larger environment m real rotation ~ ½ m virtual rotation Inject most of distortion while changing physical orientation, add the rest while walking Redirected Walking in Place (S. Razzaque) Avoid having user look at missing CAVE rear wall to maintain presence Gradually adjust world orientation while user walks in place csw4172/resources/rdwip_sg2002_hifi.mov Path in virtual room Path in real room 2:33 3:18 S. Razzaque, Z. Kohn, and M. Whitton, Eurographics Controlling Viewing Orientation Redirected walking with distractors Distract user attention while distorting the mapping of real orientation to virtual orientation E.g., virtual butterfly flutters in front of the user while walking in a virtual outdoor environment Path in virtual room Path in real room T. Peck, M. Whitton, and H. Fuchs, IEEE VR
CSE 165: 3D User Interaction. Lecture #11: Travel
 CSE 165: 3D User Interaction Lecture #11: Travel 2 Announcements Homework 3 is on-line, due next Friday Media Teaching Lab has Merge VR viewers to borrow for cell phone based VR http://acms.ucsd.edu/students/medialab/equipment
CSE 165: 3D User Interaction Lecture #11: Travel 2 Announcements Homework 3 is on-line, due next Friday Media Teaching Lab has Merge VR viewers to borrow for cell phone based VR http://acms.ucsd.edu/students/medialab/equipment
Interacting within Virtual Worlds (based on talks by Greg Welch and Mark Mine)
 Interacting within Virtual Worlds (based on talks by Greg Welch and Mark Mine) Presentation Working in a virtual world Interaction principles Interaction examples Why VR in the First Place? Direct perception
Interacting within Virtual Worlds (based on talks by Greg Welch and Mark Mine) Presentation Working in a virtual world Interaction principles Interaction examples Why VR in the First Place? Direct perception
CSC 2524, Fall 2017 AR/VR Interaction Interface
 CSC 2524, Fall 2017 AR/VR Interaction Interface Karan Singh Adapted from and with thanks to Mark Billinghurst Typical Virtual Reality System HMD User Interface Input Tracking How can we Interact in VR?
CSC 2524, Fall 2017 AR/VR Interaction Interface Karan Singh Adapted from and with thanks to Mark Billinghurst Typical Virtual Reality System HMD User Interface Input Tracking How can we Interact in VR?
Virtuelle Realität. Overview. Part 13: Interaction in VR: Navigation. Navigation Wayfinding Travel. Virtuelle Realität. Prof.
 Part 13: Interaction in VR: Navigation Virtuelle Realität Wintersemester 2006/07 Prof. Bernhard Jung Overview Navigation Wayfinding Travel Further information: D. A. Bowman, E. Kruijff, J. J. LaViola,
Part 13: Interaction in VR: Navigation Virtuelle Realität Wintersemester 2006/07 Prof. Bernhard Jung Overview Navigation Wayfinding Travel Further information: D. A. Bowman, E. Kruijff, J. J. LaViola,
3D Interaction Techniques
 3D Interaction Techniques Hannes Interactive Media Systems Group (IMS) Institute of Software Technology and Interactive Systems Based on material by Chris Shaw, derived from Doug Bowman s work Why 3D Interaction?
3D Interaction Techniques Hannes Interactive Media Systems Group (IMS) Institute of Software Technology and Interactive Systems Based on material by Chris Shaw, derived from Doug Bowman s work Why 3D Interaction?
Guidelines for choosing VR Devices from Interaction Techniques
 Guidelines for choosing VR Devices from Interaction Techniques Jaime Ramírez Computer Science School Technical University of Madrid Campus de Montegancedo. Boadilla del Monte. Madrid Spain http://decoroso.ls.fi.upm.es
Guidelines for choosing VR Devices from Interaction Techniques Jaime Ramírez Computer Science School Technical University of Madrid Campus de Montegancedo. Boadilla del Monte. Madrid Spain http://decoroso.ls.fi.upm.es
Réalité Virtuelle et Interactions. Interaction 3D. Année / 5 Info à Polytech Paris-Sud. Cédric Fleury
 Réalité Virtuelle et Interactions Interaction 3D Année 2016-2017 / 5 Info à Polytech Paris-Sud Cédric Fleury (cedric.fleury@lri.fr) Virtual Reality Virtual environment (VE) 3D virtual world Simulated by
Réalité Virtuelle et Interactions Interaction 3D Année 2016-2017 / 5 Info à Polytech Paris-Sud Cédric Fleury (cedric.fleury@lri.fr) Virtual Reality Virtual environment (VE) 3D virtual world Simulated by
Virtual Environments: Tracking and Interaction
 Virtual Environments: Tracking and Interaction Simon Julier Department of Computer Science University College London http://www.cs.ucl.ac.uk/teaching/ve Outline Problem Statement: Models of Interaction
Virtual Environments: Tracking and Interaction Simon Julier Department of Computer Science University College London http://www.cs.ucl.ac.uk/teaching/ve Outline Problem Statement: Models of Interaction
Welcome. My name is Jason Jerald, Co-Founder & Principal Consultant at Next Gen Interactions I m here today to talk about the human side of VR
 Welcome. My name is Jason Jerald, Co-Founder & Principal Consultant at Next Gen Interactions I m here today to talk about the human side of VR Interactions. For the technology is only part of the equationwith
Welcome. My name is Jason Jerald, Co-Founder & Principal Consultant at Next Gen Interactions I m here today to talk about the human side of VR Interactions. For the technology is only part of the equationwith
Cosc VR Interaction. Interaction in Virtual Environments
 Cosc 4471 Interaction in Virtual Environments VR Interaction In traditional interfaces we need to use interaction metaphors Windows, Mouse, Pointer (WIMP) Limited input degrees of freedom imply modality
Cosc 4471 Interaction in Virtual Environments VR Interaction In traditional interfaces we need to use interaction metaphors Windows, Mouse, Pointer (WIMP) Limited input degrees of freedom imply modality
CSE 165: 3D User Interaction. Lecture #14: 3D UI Design
 CSE 165: 3D User Interaction Lecture #14: 3D UI Design 2 Announcements Homework 3 due tomorrow 2pm Monday: midterm discussion Next Thursday: midterm exam 3D UI Design Strategies 3 4 Thus far 3DUI hardware
CSE 165: 3D User Interaction Lecture #14: 3D UI Design 2 Announcements Homework 3 due tomorrow 2pm Monday: midterm discussion Next Thursday: midterm exam 3D UI Design Strategies 3 4 Thus far 3DUI hardware
ThumbsUp: Integrated Command and Pointer Interactions for Mobile Outdoor Augmented Reality Systems
 ThumbsUp: Integrated Command and Pointer Interactions for Mobile Outdoor Augmented Reality Systems Wayne Piekarski and Bruce H. Thomas Wearable Computer Laboratory School of Computer and Information Science
ThumbsUp: Integrated Command and Pointer Interactions for Mobile Outdoor Augmented Reality Systems Wayne Piekarski and Bruce H. Thomas Wearable Computer Laboratory School of Computer and Information Science
Virtual Environment Interaction Techniques
 Virtual Environment Interaction Techniques Mark R. Mine Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, NC 27599-3175 mine@cs.unc.edu 1. Introduction Virtual environments have
Virtual Environment Interaction Techniques Mark R. Mine Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, NC 27599-3175 mine@cs.unc.edu 1. Introduction Virtual environments have
Are Existing Metaphors in Virtual Environments Suitable for Haptic Interaction
 Are Existing Metaphors in Virtual Environments Suitable for Haptic Interaction Joan De Boeck Chris Raymaekers Karin Coninx Limburgs Universitair Centrum Expertise centre for Digital Media (EDM) Universitaire
Are Existing Metaphors in Virtual Environments Suitable for Haptic Interaction Joan De Boeck Chris Raymaekers Karin Coninx Limburgs Universitair Centrum Expertise centre for Digital Media (EDM) Universitaire
AUTOMATIC SPEED CONTROL FOR NAVIGATION IN 3D VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENT
 AUTOMATIC SPEED CONTROL FOR NAVIGATION IN 3D VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENT DOMOKOS M. PAPOI A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER
AUTOMATIC SPEED CONTROL FOR NAVIGATION IN 3D VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENT DOMOKOS M. PAPOI A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER
COMS W4172 Design Principles
 COMS W4172 Design Principles Steven Feiner Department of Computer Science Columbia University New York, NY 10027 www.cs.columbia.edu/graphics/courses/csw4172 January 25, 2018 1 2D & 3D UIs: What s the
COMS W4172 Design Principles Steven Feiner Department of Computer Science Columbia University New York, NY 10027 www.cs.columbia.edu/graphics/courses/csw4172 January 25, 2018 1 2D & 3D UIs: What s the
Virtual Environment Interaction Based on Gesture Recognition and Hand Cursor
 Virtual Environment Interaction Based on Gesture Recognition and Hand Cursor Chan-Su Lee Kwang-Man Oh Chan-Jong Park VR Center, ETRI 161 Kajong-Dong, Yusong-Gu Taejon, 305-350, KOREA +82-42-860-{5319,
Virtual Environment Interaction Based on Gesture Recognition and Hand Cursor Chan-Su Lee Kwang-Man Oh Chan-Jong Park VR Center, ETRI 161 Kajong-Dong, Yusong-Gu Taejon, 305-350, KOREA +82-42-860-{5319,
Unreal Studio Project Template
 Unreal Studio Project Template Product Viewer What is the Product Viewer project template? This is a project template which grants the ability to use Unreal as a design review tool, allowing you to see
Unreal Studio Project Template Product Viewer What is the Product Viewer project template? This is a project template which grants the ability to use Unreal as a design review tool, allowing you to see
User s handbook Last updated in December 2017
 User s handbook Last updated in December 2017 Contents Contents... 2 System info and options... 3 Mindesk VR-CAD interface basics... 4 Controller map... 5 Global functions... 6 Tool palette... 7 VR Design
User s handbook Last updated in December 2017 Contents Contents... 2 System info and options... 3 Mindesk VR-CAD interface basics... 4 Controller map... 5 Global functions... 6 Tool palette... 7 VR Design
Fly Over, a 3D Interaction Technique for Navigation in Virtual Environments Independent from Tracking Devices
 Author manuscript, published in "10th International Conference on Virtual Reality (VRIC 2008), Laval : France (2008)" Fly Over, a 3D Interaction Technique for Navigation in Virtual Environments Independent
Author manuscript, published in "10th International Conference on Virtual Reality (VRIC 2008), Laval : France (2008)" Fly Over, a 3D Interaction Technique for Navigation in Virtual Environments Independent
Learning Guide. ASR Automated Systems Research Inc. # Douglas Crescent, Langley, BC. V3A 4B6. Fax:
 Learning Guide ASR Automated Systems Research Inc. #1 20461 Douglas Crescent, Langley, BC. V3A 4B6 Toll free: 1-800-818-2051 e-mail: support@asrsoft.com Fax: 604-539-1334 www.asrsoft.com Copyright 1991-2013
Learning Guide ASR Automated Systems Research Inc. #1 20461 Douglas Crescent, Langley, BC. V3A 4B6 Toll free: 1-800-818-2051 e-mail: support@asrsoft.com Fax: 604-539-1334 www.asrsoft.com Copyright 1991-2013
X11 in Virtual Environments ARL
 COMS W4172 Case Study: 3D Windows/Desktops 2 Steven Feiner Department of Computer Science Columbia University New York, NY 10027 www.cs.columbia.edu/graphics/courses/csw4172 February 8, 2018 1 X11 in Virtual
COMS W4172 Case Study: 3D Windows/Desktops 2 Steven Feiner Department of Computer Science Columbia University New York, NY 10027 www.cs.columbia.edu/graphics/courses/csw4172 February 8, 2018 1 X11 in Virtual
Using Pinch Gloves for both Natural and Abstract Interaction Techniques in Virtual Environments
 Using Pinch Gloves for both Natural and Abstract Interaction Techniques in Virtual Environments Doug A. Bowman, Chadwick A. Wingrave, Joshua M. Campbell, and Vinh Q. Ly Department of Computer Science (0106)
Using Pinch Gloves for both Natural and Abstract Interaction Techniques in Virtual Environments Doug A. Bowman, Chadwick A. Wingrave, Joshua M. Campbell, and Vinh Q. Ly Department of Computer Science (0106)
A Multimodal Locomotion User Interface for Immersive Geospatial Information Systems
 F. Steinicke, G. Bruder, H. Frenz 289 A Multimodal Locomotion User Interface for Immersive Geospatial Information Systems Frank Steinicke 1, Gerd Bruder 1, Harald Frenz 2 1 Institute of Computer Science,
F. Steinicke, G. Bruder, H. Frenz 289 A Multimodal Locomotion User Interface for Immersive Geospatial Information Systems Frank Steinicke 1, Gerd Bruder 1, Harald Frenz 2 1 Institute of Computer Science,
A Novel Human Computer Interaction Paradigm for Volume Visualization in Projection-Based. Environments
 Virtual Environments 1 A Novel Human Computer Interaction Paradigm for Volume Visualization in Projection-Based Virtual Environments Changming He, Andrew Lewis, and Jun Jo Griffith University, School of
Virtual Environments 1 A Novel Human Computer Interaction Paradigm for Volume Visualization in Projection-Based Virtual Environments Changming He, Andrew Lewis, and Jun Jo Griffith University, School of
Interaction in VR: Manipulation
 Part 8: Interaction in VR: Manipulation Virtuelle Realität Wintersemester 2007/08 Prof. Bernhard Jung Overview Control Methods Selection Techniques Manipulation Techniques Taxonomy Further reading: D.
Part 8: Interaction in VR: Manipulation Virtuelle Realität Wintersemester 2007/08 Prof. Bernhard Jung Overview Control Methods Selection Techniques Manipulation Techniques Taxonomy Further reading: D.
Pop Through Button Devices for VE Navigation and Interaction
 Pop Through Button Devices for VE Navigation and Interaction Robert C. Zeleznik Joseph J. LaViola Jr. Daniel Acevedo Feliz Daniel F. Keefe Brown University Technology Center for Advanced Scientific Computing
Pop Through Button Devices for VE Navigation and Interaction Robert C. Zeleznik Joseph J. LaViola Jr. Daniel Acevedo Feliz Daniel F. Keefe Brown University Technology Center for Advanced Scientific Computing
Chapter 1 - Introduction
 1 "We all agree that your theory is crazy, but is it crazy enough?" Niels Bohr (1885-1962) Chapter 1 - Introduction Augmented reality (AR) is the registration of projected computer-generated images over
1 "We all agree that your theory is crazy, but is it crazy enough?" Niels Bohr (1885-1962) Chapter 1 - Introduction Augmented reality (AR) is the registration of projected computer-generated images over
Hands-Free Multi-Scale Navigation in Virtual Environments
 Hands-Free Multi-Scale Navigation in Virtual Environments Abstract This paper presents a set of interaction techniques for hands-free multi-scale navigation through virtual environments. We believe that
Hands-Free Multi-Scale Navigation in Virtual Environments Abstract This paper presents a set of interaction techniques for hands-free multi-scale navigation through virtual environments. We believe that
ARCHICAD Introduction Tutorial
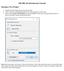 Starting a New Project ARCHICAD Introduction Tutorial 1. Double-click the Archicad Icon from the desktop 2. Click on the Grey Warning/Information box when it appears on the screen. 3. Click on the Create
Starting a New Project ARCHICAD Introduction Tutorial 1. Double-click the Archicad Icon from the desktop 2. Click on the Grey Warning/Information box when it appears on the screen. 3. Click on the Create
Designing A Successful HMD-Based Experience
 Designing A Successful HMD-Based Experience Jeffrey S. Pierce, Randy Pausch, Christopher B. Sturgill, Kevin D. Christiansen Carnegie Mellon University {jpierce, pausch}@cs.cmu.edu Contact info: Jeff Pierce
Designing A Successful HMD-Based Experience Jeffrey S. Pierce, Randy Pausch, Christopher B. Sturgill, Kevin D. Christiansen Carnegie Mellon University {jpierce, pausch}@cs.cmu.edu Contact info: Jeff Pierce
 VEWL: A Framework for Building a Windowing Interface in a Virtual Environment Daniel Larimer and Doug A. Bowman Dept. of Computer Science, Virginia Tech, 660 McBryde, Blacksburg, VA dlarimer@vt.edu, bowman@vt.edu
VEWL: A Framework for Building a Windowing Interface in a Virtual Environment Daniel Larimer and Doug A. Bowman Dept. of Computer Science, Virginia Tech, 660 McBryde, Blacksburg, VA dlarimer@vt.edu, bowman@vt.edu
Panel: Lessons from IEEE Virtual Reality
 Panel: Lessons from IEEE Virtual Reality Doug Bowman, PhD Professor. Virginia Tech, USA Anthony Steed, PhD Professor. University College London, UK Evan Suma, PhD Research Assistant Professor. University
Panel: Lessons from IEEE Virtual Reality Doug Bowman, PhD Professor. Virginia Tech, USA Anthony Steed, PhD Professor. University College London, UK Evan Suma, PhD Research Assistant Professor. University
Tracking. Alireza Bahmanpour, Emma Byrne, Jozef Doboš, Victor Mendoza and Pan Ye
 Tracking Alireza Bahmanpour, Emma Byrne, Jozef Doboš, Victor Mendoza and Pan Ye Outline of this talk Introduction: what makes a good tracking system? Example hardware and their tradeoffs Taxonomy of tasks:
Tracking Alireza Bahmanpour, Emma Byrne, Jozef Doboš, Victor Mendoza and Pan Ye Outline of this talk Introduction: what makes a good tracking system? Example hardware and their tradeoffs Taxonomy of tasks:
Touching and Walking: Issues in Haptic Interface
 Touching and Walking: Issues in Haptic Interface Hiroo Iwata 1 1 Institute of Engineering Mechanics and Systems, University of Tsukuba, 80, Tsukuba, 305-8573 Japan iwata@kz.tsukuba.ac.jp Abstract. This
Touching and Walking: Issues in Haptic Interface Hiroo Iwata 1 1 Institute of Engineering Mechanics and Systems, University of Tsukuba, 80, Tsukuba, 305-8573 Japan iwata@kz.tsukuba.ac.jp Abstract. This
ROBOTICS ENG YOUSEF A. SHATNAWI INTRODUCTION
 ROBOTICS INTRODUCTION THIS COURSE IS TWO PARTS Mobile Robotics. Locomotion (analogous to manipulation) (Legged and wheeled robots). Navigation and obstacle avoidance algorithms. Robot Vision Sensors and
ROBOTICS INTRODUCTION THIS COURSE IS TWO PARTS Mobile Robotics. Locomotion (analogous to manipulation) (Legged and wheeled robots). Navigation and obstacle avoidance algorithms. Robot Vision Sensors and
Working in a Virtual World: Interaction Techniques Used in the Chapel Hill Immersive Modeling Program
 Working in a Virtual World: Interaction Techniques Used in the Chapel Hill Immersive Modeling Program Mark R. Mine Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, NC 27599-3175
Working in a Virtual World: Interaction Techniques Used in the Chapel Hill Immersive Modeling Program Mark R. Mine Department of Computer Science University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, NC 27599-3175
MAKING THE FAN HOUSING
 Our goal is to make the following part: 39-245 RAPID PROTOTYPE DESIGN CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY SPRING 2007 MAKING THE FAN HOUSING This part is made up of two plates joined by a cylinder with holes in
Our goal is to make the following part: 39-245 RAPID PROTOTYPE DESIGN CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY SPRING 2007 MAKING THE FAN HOUSING This part is made up of two plates joined by a cylinder with holes in
SolidWize. Online SolidWorks Training. Simple Sweep: Head Scratcher
 SolidWize Online SolidWorks Training Simple Sweep: Head Scratcher Step 1: Creating the Handle: Sketch Using Inches as the unit create a sketch on the Front plane. Start with the sketch shown below: Create
SolidWize Online SolidWorks Training Simple Sweep: Head Scratcher Step 1: Creating the Handle: Sketch Using Inches as the unit create a sketch on the Front plane. Start with the sketch shown below: Create
Mid-term report - Virtual reality and spatial mobility
 Mid-term report - Virtual reality and spatial mobility Jarl Erik Cedergren & Stian Kongsvik October 10, 2017 The group members: - Jarl Erik Cedergren (jarlec@uio.no) - Stian Kongsvik (stiako@uio.no) 1
Mid-term report - Virtual reality and spatial mobility Jarl Erik Cedergren & Stian Kongsvik October 10, 2017 The group members: - Jarl Erik Cedergren (jarlec@uio.no) - Stian Kongsvik (stiako@uio.no) 1
3D UIs 101 Doug Bowman
 3D UIs 101 Doug Bowman Welcome, Introduction, & Roadmap 3D UIs 101 3D UIs 201 User Studies and 3D UIs Guidelines for Developing 3D UIs Video Games: 3D UIs for the Masses The Wii Remote and You 3D UI and
3D UIs 101 Doug Bowman Welcome, Introduction, & Roadmap 3D UIs 101 3D UIs 201 User Studies and 3D UIs Guidelines for Developing 3D UIs Video Games: 3D UIs for the Masses The Wii Remote and You 3D UI and
3D User Interaction CS-525U: Robert W. Lindeman. Intro to 3D UI. Department of Computer Science. Worcester Polytechnic Institute.
 CS-525U: 3D User Interaction Intro to 3D UI Robert W. Lindeman Worcester Polytechnic Institute Department of Computer Science gogo@wpi.edu Why Study 3D UI? Relevant to real-world tasks Can use familiarity
CS-525U: 3D User Interaction Intro to 3D UI Robert W. Lindeman Worcester Polytechnic Institute Department of Computer Science gogo@wpi.edu Why Study 3D UI? Relevant to real-world tasks Can use familiarity
user guide for windows creative learning tools
 user guide for windows creative learning tools Page 2 Contents Welcome to MissionMaker! Please note: This user guide is suitable for use with MissionMaker 07 build 1.5 and MissionMaker 2.0 This guide will
user guide for windows creative learning tools Page 2 Contents Welcome to MissionMaker! Please note: This user guide is suitable for use with MissionMaker 07 build 1.5 and MissionMaker 2.0 This guide will
Chapter 15 Principles for the Design of Performance-oriented Interaction Techniques
 Chapter 15 Principles for the Design of Performance-oriented Interaction Techniques Abstract Doug A. Bowman Department of Computer Science Virginia Polytechnic Institute & State University Applications
Chapter 15 Principles for the Design of Performance-oriented Interaction Techniques Abstract Doug A. Bowman Department of Computer Science Virginia Polytechnic Institute & State University Applications
Application and Taxonomy of Through-The-Lens Techniques
 Application and Taxonomy of Through-The-Lens Techniques Stanislav L. Stoev Egisys AG stanislav.stoev@egisys.de Dieter Schmalstieg Vienna University of Technology dieter@cg.tuwien.ac.at ASTRACT In this
Application and Taxonomy of Through-The-Lens Techniques Stanislav L. Stoev Egisys AG stanislav.stoev@egisys.de Dieter Schmalstieg Vienna University of Technology dieter@cg.tuwien.ac.at ASTRACT In this
Unit. Drawing Accurately OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION 8-1
 8-1 Unit 8 Drawing Accurately OVERVIEW When you attempt to pick points on the screen, you may have difficulty locating an exact position without some type of help. Typing the point coordinates is one method.
8-1 Unit 8 Drawing Accurately OVERVIEW When you attempt to pick points on the screen, you may have difficulty locating an exact position without some type of help. Typing the point coordinates is one method.
Using Google SketchUp
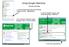 Using Google SketchUp Opening sketchup 1. From the program menu click on the SketchUp 8 folder and select 3. From the Template Selection select Architectural Design Millimeters. 2. The Welcome to SketchUp
Using Google SketchUp Opening sketchup 1. From the program menu click on the SketchUp 8 folder and select 3. From the Template Selection select Architectural Design Millimeters. 2. The Welcome to SketchUp
The Effect of 3D Widget Representation and Simulated Surface Constraints on Interaction in Virtual Environments
 The Effect of 3D Widget Representation and Simulated Surface Constraints on Interaction in Virtual Environments Robert W. Lindeman 1 John L. Sibert 1 James N. Templeman 2 1 Department of Computer Science
The Effect of 3D Widget Representation and Simulated Surface Constraints on Interaction in Virtual Environments Robert W. Lindeman 1 John L. Sibert 1 James N. Templeman 2 1 Department of Computer Science
Introduction to CATIA V5
 Introduction to CATIA V5 Release 17 (A Hands-On Tutorial Approach) Kirstie Plantenberg University of Detroit Mercy SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks. Lower
Introduction to CATIA V5 Release 17 (A Hands-On Tutorial Approach) Kirstie Plantenberg University of Detroit Mercy SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks. Lower
Immersive Visualization and Collaboration with LS-PrePost-VR and LS-PrePost-Remote
 8 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Visualization Immersive Visualization and Collaboration with LS-PrePost-VR and LS-PrePost-Remote Todd J. Furlong Principal Engineer - Graphics and Visualization
8 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Visualization Immersive Visualization and Collaboration with LS-PrePost-VR and LS-PrePost-Remote Todd J. Furlong Principal Engineer - Graphics and Visualization
Development of a Finger Mounted Type Haptic Device Using a Plane Approximated to Tangent Plane
 Journal of Communication and Computer 13 (2016) 329-337 doi:10.17265/1548-7709/2016.07.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING Development of a Finger Mounted Type Haptic Device Using a Plane Approximated to Tangent Plane
Journal of Communication and Computer 13 (2016) 329-337 doi:10.17265/1548-7709/2016.07.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING Development of a Finger Mounted Type Haptic Device Using a Plane Approximated to Tangent Plane
Eliminating Design and Execute Modes from Virtual Environment Authoring Systems
 Eliminating Design and Execute Modes from Virtual Environment Authoring Systems Gary Marsden & Shih-min Yang Department of Computer Science, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa Email: gaz@cs.uct.ac.za,
Eliminating Design and Execute Modes from Virtual Environment Authoring Systems Gary Marsden & Shih-min Yang Department of Computer Science, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa Email: gaz@cs.uct.ac.za,
Table of Contents. Lesson 1 Getting Started
 NX Lesson 1 Getting Started Pre-reqs/Technical Skills Basic computer use Expectations Read lesson material Implement steps in software while reading through lesson material Complete quiz on Blackboard
NX Lesson 1 Getting Started Pre-reqs/Technical Skills Basic computer use Expectations Read lesson material Implement steps in software while reading through lesson material Complete quiz on Blackboard
Generating 3D interaction techniques by identifying and breaking assumptions
 Generating 3D interaction techniques by identifying and breaking assumptions Jeffrey S. Pierce 1, Randy Pausch 2 (1)IBM Almaden Research Center, San Jose, CA, USA- Email: jspierce@us.ibm.com Abstract (2)Carnegie
Generating 3D interaction techniques by identifying and breaking assumptions Jeffrey S. Pierce 1, Randy Pausch 2 (1)IBM Almaden Research Center, San Jose, CA, USA- Email: jspierce@us.ibm.com Abstract (2)Carnegie
Chapter 1 Virtual World Fundamentals
 Chapter 1 Virtual World Fundamentals 1.0 What Is A Virtual World? {Definition} Virtual: to exist in effect, though not in actual fact. You are probably familiar with arcade games such as pinball and target
Chapter 1 Virtual World Fundamentals 1.0 What Is A Virtual World? {Definition} Virtual: to exist in effect, though not in actual fact. You are probably familiar with arcade games such as pinball and target
Kinect Interface for UC-win/Road: Application to Tele-operation of Small Robots
 Kinect Interface for UC-win/Road: Application to Tele-operation of Small Robots Hafid NINISS Forum8 - Robot Development Team Abstract: The purpose of this work is to develop a man-machine interface for
Kinect Interface for UC-win/Road: Application to Tele-operation of Small Robots Hafid NINISS Forum8 - Robot Development Team Abstract: The purpose of this work is to develop a man-machine interface for
MEM380 Applied Autonomous Robots I Winter Feedback Control USARSim
 MEM380 Applied Autonomous Robots I Winter 2011 Feedback Control USARSim Transforming Accelerations into Position Estimates In a perfect world It s not a perfect world. We have noise and bias in our acceleration
MEM380 Applied Autonomous Robots I Winter 2011 Feedback Control USARSim Transforming Accelerations into Position Estimates In a perfect world It s not a perfect world. We have noise and bias in our acceleration
Evaluating Visual/Motor Co-location in Fish-Tank Virtual Reality
 Evaluating Visual/Motor Co-location in Fish-Tank Virtual Reality Robert J. Teather, Robert S. Allison, Wolfgang Stuerzlinger Department of Computer Science & Engineering York University Toronto, Canada
Evaluating Visual/Motor Co-location in Fish-Tank Virtual Reality Robert J. Teather, Robert S. Allison, Wolfgang Stuerzlinger Department of Computer Science & Engineering York University Toronto, Canada
The Revolve Feature and Assembly Modeling
 The Revolve Feature and Assembly Modeling PTC Clock Page 52 PTC Contents Introduction... 54 The Revolve Feature... 55 Creating a revolved feature...57 Creating face details... 58 Using Text... 61 Assembling
The Revolve Feature and Assembly Modeling PTC Clock Page 52 PTC Contents Introduction... 54 The Revolve Feature... 55 Creating a revolved feature...57 Creating face details... 58 Using Text... 61 Assembling
A Virtual Environments Editor for Driving Scenes
 A Virtual Environments Editor for Driving Scenes Ronald R. Mourant and Sophia-Katerina Marangos Virtual Environments Laboratory, 334 Snell Engineering Center Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115 USA
A Virtual Environments Editor for Driving Scenes Ronald R. Mourant and Sophia-Katerina Marangos Virtual Environments Laboratory, 334 Snell Engineering Center Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115 USA
VR System Input & Tracking
 Human-Computer Interface VR System Input & Tracking 071011-1 2017 년가을학기 9/13/2017 박경신 System Software User Interface Software Input Devices Output Devices User Human-Virtual Reality Interface User Monitoring
Human-Computer Interface VR System Input & Tracking 071011-1 2017 년가을학기 9/13/2017 박경신 System Software User Interface Software Input Devices Output Devices User Human-Virtual Reality Interface User Monitoring
Narrative Guidance. Tinsley A. Galyean. MIT Media Lab Cambridge, MA
 Narrative Guidance Tinsley A. Galyean MIT Media Lab Cambridge, MA. 02139 tag@media.mit.edu INTRODUCTION To date most interactive narratives have put the emphasis on the word "interactive." In other words,
Narrative Guidance Tinsley A. Galyean MIT Media Lab Cambridge, MA. 02139 tag@media.mit.edu INTRODUCTION To date most interactive narratives have put the emphasis on the word "interactive." In other words,
MOVING COWS IN SPACE: EXPLOITING PROPRIOCEPTION AS A FRAMEWORK FOR VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENT INTERACTION
 1 MOVING COWS IN SPACE: EXPLOITING PROPRIOCEPTION AS A FRAMEWORK FOR VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENT INTERACTION Category: Research Format: Traditional Print Paper ABSTRACT Manipulation in immersive virtual environments
1 MOVING COWS IN SPACE: EXPLOITING PROPRIOCEPTION AS A FRAMEWORK FOR VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENT INTERACTION Category: Research Format: Traditional Print Paper ABSTRACT Manipulation in immersive virtual environments
In the end, the code and tips in this document could be used to create any type of camera.
 Overview The Adventure Camera & Rig is a multi-behavior camera built specifically for quality 3 rd Person Action/Adventure games. Use it as a basis for your custom camera system or out-of-the-box to kick
Overview The Adventure Camera & Rig is a multi-behavior camera built specifically for quality 3 rd Person Action/Adventure games. Use it as a basis for your custom camera system or out-of-the-box to kick
2809 CAD TRAINING: Part 1 Sketching and Making 3D Parts. Contents
 Contents Getting Started... 2 Lesson 1:... 3 Lesson 2:... 13 Lesson 3:... 19 Lesson 4:... 23 Lesson 5:... 25 Final Project:... 28 Getting Started Get Autodesk Inventor Go to http://students.autodesk.com/
Contents Getting Started... 2 Lesson 1:... 3 Lesson 2:... 13 Lesson 3:... 19 Lesson 4:... 23 Lesson 5:... 25 Final Project:... 28 Getting Started Get Autodesk Inventor Go to http://students.autodesk.com/
FLEXLINK DESIGN TOOL VR GUIDE. documentation
 FLEXLINK DESIGN TOOL VR GUIDE User documentation Contents CONTENTS... 1 REQUIREMENTS... 3 SETUP... 4 SUPPORTED FILE TYPES... 5 CONTROLS... 6 EXPERIENCE 3D VIEW... 9 EXPERIENCE VIRTUAL REALITY... 10 Requirements
FLEXLINK DESIGN TOOL VR GUIDE User documentation Contents CONTENTS... 1 REQUIREMENTS... 3 SETUP... 4 SUPPORTED FILE TYPES... 5 CONTROLS... 6 EXPERIENCE 3D VIEW... 9 EXPERIENCE VIRTUAL REALITY... 10 Requirements
A FRAMEWORK FOR TELEPRESENT GAME-PLAY IN LARGE VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENTS
 A FRAMEWORK FOR TELEPRESENT GAME-PLAY IN LARGE VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENTS Patrick Rößler, Frederik Beutler, and Uwe D. Hanebeck Intelligent Sensor-Actuator-Systems Laboratory Institute of Computer Science and
A FRAMEWORK FOR TELEPRESENT GAME-PLAY IN LARGE VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENTS Patrick Rößler, Frederik Beutler, and Uwe D. Hanebeck Intelligent Sensor-Actuator-Systems Laboratory Institute of Computer Science and
Introduction to Autodesk Inventor for F1 in Schools (Australian Version)
 Introduction to Autodesk Inventor for F1 in Schools (Australian Version) F1 in Schools race car In this course you will be introduced to Autodesk Inventor, which is the centerpiece of Autodesk s Digital
Introduction to Autodesk Inventor for F1 in Schools (Australian Version) F1 in Schools race car In this course you will be introduced to Autodesk Inventor, which is the centerpiece of Autodesk s Digital
Video Games and Interfaces: Past, Present and Future Class #2: Intro to Video Game User Interfaces
 Video Games and Interfaces: Past, Present and Future Class #2: Intro to Video Game User Interfaces Content based on Dr.LaViola s class: 3D User Interfaces for Games and VR What is a User Interface? Where
Video Games and Interfaces: Past, Present and Future Class #2: Intro to Video Game User Interfaces Content based on Dr.LaViola s class: 3D User Interfaces for Games and VR What is a User Interface? Where
TRAVEL IN SMILE : A STUDY OF TWO IMMERSIVE MOTION CONTROL TECHNIQUES
 IADIS International Conference Computer Graphics and Visualization 27 TRAVEL IN SMILE : A STUDY OF TWO IMMERSIVE MOTION CONTROL TECHNIQUES Nicoletta Adamo-Villani Purdue University, Department of Computer
IADIS International Conference Computer Graphics and Visualization 27 TRAVEL IN SMILE : A STUDY OF TWO IMMERSIVE MOTION CONTROL TECHNIQUES Nicoletta Adamo-Villani Purdue University, Department of Computer
3D interaction strategies and metaphors
 3D interaction strategies and metaphors Ivan Poupyrev Interaction Lab, Sony CSL Ivan Poupyrev, Ph.D. Interaction Lab, Sony CSL E-mail: poup@csl.sony.co.jp WWW: http://www.csl.sony.co.jp/~poup/ Address:
3D interaction strategies and metaphors Ivan Poupyrev Interaction Lab, Sony CSL Ivan Poupyrev, Ph.D. Interaction Lab, Sony CSL E-mail: poup@csl.sony.co.jp WWW: http://www.csl.sony.co.jp/~poup/ Address:
Generating 3D interaction techniques by identifying and breaking assumptions
 Virtual Reality (2007) 11: 15 21 DOI 10.1007/s10055-006-0034-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Jeffrey S. Pierce Æ Randy Pausch Generating 3D interaction techniques by identifying and breaking assumptions Received: 22
Virtual Reality (2007) 11: 15 21 DOI 10.1007/s10055-006-0034-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Jeffrey S. Pierce Æ Randy Pausch Generating 3D interaction techniques by identifying and breaking assumptions Received: 22
Development of A Finger Mounted Type Haptic Device Using A Plane Approximated to Tangent Plane
 Development of A Finger Mounted Type Haptic Device Using A Plane Approximated to Tangent Plane Makoto Yoda Department of Information System Science Graduate School of Engineering Soka University, Soka
Development of A Finger Mounted Type Haptic Device Using A Plane Approximated to Tangent Plane Makoto Yoda Department of Information System Science Graduate School of Engineering Soka University, Soka
Physical Hand Interaction for Controlling Multiple Virtual Objects in Virtual Reality
 Physical Hand Interaction for Controlling Multiple Virtual Objects in Virtual Reality ABSTRACT Mohamed Suhail Texas A&M University United States mohamedsuhail@tamu.edu Dustin T. Han Texas A&M University
Physical Hand Interaction for Controlling Multiple Virtual Objects in Virtual Reality ABSTRACT Mohamed Suhail Texas A&M University United States mohamedsuhail@tamu.edu Dustin T. Han Texas A&M University
INTELLIGENT GUIDANCE IN A VIRTUAL UNIVERSITY
 INTELLIGENT GUIDANCE IN A VIRTUAL UNIVERSITY T. Panayiotopoulos,, N. Zacharis, S. Vosinakis Department of Computer Science, University of Piraeus, 80 Karaoli & Dimitriou str. 18534 Piraeus, Greece themisp@unipi.gr,
INTELLIGENT GUIDANCE IN A VIRTUAL UNIVERSITY T. Panayiotopoulos,, N. Zacharis, S. Vosinakis Department of Computer Science, University of Piraeus, 80 Karaoli & Dimitriou str. 18534 Piraeus, Greece themisp@unipi.gr,
Accepted Manuscript (to appear) IEEE 10th Symp. on 3D User Interfaces, March 2015
 ,,. Cite as: Jialei Li, Isaac Cho, Zachary Wartell. Evaluation of 3D Virtual Cursor Offset Techniques for Navigation Tasks in a Multi-Display Virtual Environment. In IEEE 10th Symp. on 3D User Interfaces,
,,. Cite as: Jialei Li, Isaac Cho, Zachary Wartell. Evaluation of 3D Virtual Cursor Offset Techniques for Navigation Tasks in a Multi-Display Virtual Environment. In IEEE 10th Symp. on 3D User Interfaces,
Rusty s JL Winch Mount RR-WM55-JL INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
 Rusty s JL 2018+ Winch Mount RR-WM55-JL INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS Introduction: Rusty s recommends that this installation be performed by a certified automotive technician or a person with professional
Rusty s JL 2018+ Winch Mount RR-WM55-JL INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS Introduction: Rusty s recommends that this installation be performed by a certified automotive technician or a person with professional
Geo-Located Content in Virtual and Augmented Reality
 Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series October 02, 2017 Geo-Located Content in Virtual and Augmented Reality Thomas Anglaret Follow this and additional works at: http://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series October 02, 2017 Geo-Located Content in Virtual and Augmented Reality Thomas Anglaret Follow this and additional works at: http://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
The original image. Let s get started! The final result.
 Miniature Effect With Tilt-Shift In Photoshop CS6 In this tutorial, we ll learn how to create a miniature effect in Photoshop CS6 using its brand new Tilt-Shift blur filter. Tilt-shift camera lenses are
Miniature Effect With Tilt-Shift In Photoshop CS6 In this tutorial, we ll learn how to create a miniature effect in Photoshop CS6 using its brand new Tilt-Shift blur filter. Tilt-shift camera lenses are
Guided Head Rotation and Amplified Head Rotation: Evaluating Semi-natural Travel and Viewing Techniques in Virtual Reality
 Guided Head Rotation and Amplified Head Rotation: Evaluating Semi-natural Travel and Viewing Techniques in Virtual Reality Shyam Prathish Sargunam * Kasra Rahimi Moghadam Mohamed Suhail Eric D. Ragan Texas
Guided Head Rotation and Amplified Head Rotation: Evaluating Semi-natural Travel and Viewing Techniques in Virtual Reality Shyam Prathish Sargunam * Kasra Rahimi Moghadam Mohamed Suhail Eric D. Ragan Texas
CREO.1 MODELING A BELT WHEEL
 CREO.1 MODELING A BELT WHEEL Figure 1: A belt wheel modeled in this exercise. Learning Targets In this exercise you will learn: Using symmetry when sketching Using pattern to copy features Using RMB when
CREO.1 MODELING A BELT WHEEL Figure 1: A belt wheel modeled in this exercise. Learning Targets In this exercise you will learn: Using symmetry when sketching Using pattern to copy features Using RMB when
Simple Machines & Energy
 Simple Machines & Energy SPS8. Students will determine relationships among force, mass, and motion. e. Calculate amounts of work and mechanical advantage using simple machines. Our use of machines Machines
Simple Machines & Energy SPS8. Students will determine relationships among force, mass, and motion. e. Calculate amounts of work and mechanical advantage using simple machines. Our use of machines Machines
A Study of Navigation and Selection Techniques in Virtual Environments Using Microsoft Kinect
 A Study of Navigation and Selection Techniques in Virtual Environments Using Microsoft Kinect Peter Dam 1, Priscilla Braz 2, and Alberto Raposo 1,2 1 Tecgraf/PUC-Rio, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil peter@tecgraf.puc-rio.br
A Study of Navigation and Selection Techniques in Virtual Environments Using Microsoft Kinect Peter Dam 1, Priscilla Braz 2, and Alberto Raposo 1,2 1 Tecgraf/PUC-Rio, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil peter@tecgraf.puc-rio.br
Overcoming World in Miniature Limitations by a Scaled and Scrolling WIM
 Please see supplementary material on conference DVD. Overcoming World in Miniature Limitations by a Scaled and Scrolling WIM Chadwick A. Wingrave, Yonca Haciahmetoglu, Doug A. Bowman Department of Computer
Please see supplementary material on conference DVD. Overcoming World in Miniature Limitations by a Scaled and Scrolling WIM Chadwick A. Wingrave, Yonca Haciahmetoglu, Doug A. Bowman Department of Computer
Towards Usable VR: An Empirical Study of User Interfaces for Immersive Virtual Environments
 Towards Usable VR: An Empirical Study of User Interfaces for Immersive Virtual Environments Robert W. Lindeman John L. Sibert James K. Hahn Institute for Computer Graphics The George Washington University
Towards Usable VR: An Empirical Study of User Interfaces for Immersive Virtual Environments Robert W. Lindeman John L. Sibert James K. Hahn Institute for Computer Graphics The George Washington University
Classifying 3D Input Devices
 IMGD 5100: Immersive HCI Classifying 3D Input Devices Robert W. Lindeman Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Worcester Polytechnic Institute gogo@wpi.edu But First Who are you? Name Interests
IMGD 5100: Immersive HCI Classifying 3D Input Devices Robert W. Lindeman Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Worcester Polytechnic Institute gogo@wpi.edu But First Who are you? Name Interests
The architectural walkthrough one of the earliest
 Editors: Michael R. Macedonia and Lawrence J. Rosenblum Designing Animal Habitats within an Immersive VE The architectural walkthrough one of the earliest virtual environment (VE) applications is still
Editors: Michael R. Macedonia and Lawrence J. Rosenblum Designing Animal Habitats within an Immersive VE The architectural walkthrough one of the earliest virtual environment (VE) applications is still
CS Problem Solving and Structured Programming Lab 1 - Introduction to Programming in Alice designed by Barb Lerner Due: February 9/10
 CS 101 - Problem Solving and Structured Programming Lab 1 - Introduction to Programming in lice designed by Barb Lerner Due: February 9/10 Getting Started with lice lice is installed on the computers in
CS 101 - Problem Solving and Structured Programming Lab 1 - Introduction to Programming in lice designed by Barb Lerner Due: February 9/10 Getting Started with lice lice is installed on the computers in
Preparing Photos for Laser Engraving
 Preparing Photos for Laser Engraving Epilog Laser 16371 Table Mountain Parkway Golden, CO 80403 303-277-1188 -voice 303-277-9669 - fax www.epiloglaser.com Tips for Laser Engraving Photographs There is
Preparing Photos for Laser Engraving Epilog Laser 16371 Table Mountain Parkway Golden, CO 80403 303-277-1188 -voice 303-277-9669 - fax www.epiloglaser.com Tips for Laser Engraving Photographs There is
Capability for Collision Avoidance of Different User Avatars in Virtual Reality
 Capability for Collision Avoidance of Different User Avatars in Virtual Reality Adrian H. Hoppe, Roland Reeb, Florian van de Camp, and Rainer Stiefelhagen Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) {adrian.hoppe,rainer.stiefelhagen}@kit.edu,
Capability for Collision Avoidance of Different User Avatars in Virtual Reality Adrian H. Hoppe, Roland Reeb, Florian van de Camp, and Rainer Stiefelhagen Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) {adrian.hoppe,rainer.stiefelhagen}@kit.edu,
MRT: Mixed-Reality Tabletop
 MRT: Mixed-Reality Tabletop Students: Dan Bekins, Jonathan Deutsch, Matthew Garrett, Scott Yost PIs: Daniel Aliaga, Dongyan Xu August 2004 Goals Create a common locus for virtual interaction without having
MRT: Mixed-Reality Tabletop Students: Dan Bekins, Jonathan Deutsch, Matthew Garrett, Scott Yost PIs: Daniel Aliaga, Dongyan Xu August 2004 Goals Create a common locus for virtual interaction without having
-6- lllllllllllllllll. (12) United States Patent Foxlin. (io) Patent No.: US 6,757,068 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29,2004 US B2
 (12) United States Patent Foxlin lllllllllllllllll US006757068B2 (io) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29,2004 (54) SELF-REFERENCED TRACKING (75) Inventor: Eric Foxlin, Arlington, MA (US) (73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent Foxlin lllllllllllllllll US006757068B2 (io) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29,2004 (54) SELF-REFERENCED TRACKING (75) Inventor: Eric Foxlin, Arlington, MA (US) (73) Assignee:
Autonomous Stair Climbing Algorithm for a Small Four-Tracked Robot
 Autonomous Stair Climbing Algorithm for a Small Four-Tracked Robot Quy-Hung Vu, Byeong-Sang Kim, Jae-Bok Song Korea University 1 Anam-dong, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul, Korea vuquyhungbk@yahoo.com, lovidia@korea.ac.kr,
Autonomous Stair Climbing Algorithm for a Small Four-Tracked Robot Quy-Hung Vu, Byeong-Sang Kim, Jae-Bok Song Korea University 1 Anam-dong, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul, Korea vuquyhungbk@yahoo.com, lovidia@korea.ac.kr,
Multiscale traveling: crossing the boundary between space and scale
 Virtual Reality (2009) 13:101 115 DOI 10.1007/s10055-009-0114-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Multiscale traveling: crossing the boundary between space and scale Xiaolong (Luke) Zhang Received: 21 December 2006 / Accepted:
Virtual Reality (2009) 13:101 115 DOI 10.1007/s10055-009-0114-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Multiscale traveling: crossing the boundary between space and scale Xiaolong (Luke) Zhang Received: 21 December 2006 / Accepted:
ITS '14, Nov , Dresden, Germany
 3D Tabletop User Interface Using Virtual Elastic Objects Figure 1: 3D Interaction with a virtual elastic object Hiroaki Tateyama Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Saitama University 255 Shimo-Okubo,
3D Tabletop User Interface Using Virtual Elastic Objects Figure 1: 3D Interaction with a virtual elastic object Hiroaki Tateyama Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Saitama University 255 Shimo-Okubo,
BEST PRACTICES COURSE WEEK 14 PART 2 Advanced Mouse Constraints and the Control Box
 BEST PRACTICES COURSE WEEK 14 PART 2 Advanced Mouse Constraints and the Control Box Copyright 2012 by Eric Bobrow, all rights reserved For more information about the Best Practices Course, visit http://www.acbestpractices.com
BEST PRACTICES COURSE WEEK 14 PART 2 Advanced Mouse Constraints and the Control Box Copyright 2012 by Eric Bobrow, all rights reserved For more information about the Best Practices Course, visit http://www.acbestpractices.com
Classifying 3D Input Devices
 IMGD 5100: Immersive HCI Classifying 3D Input Devices Robert W. Lindeman Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Worcester Polytechnic Institute gogo@wpi.edu Motivation The mouse and keyboard
IMGD 5100: Immersive HCI Classifying 3D Input Devices Robert W. Lindeman Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Worcester Polytechnic Institute gogo@wpi.edu Motivation The mouse and keyboard
Page 1 part 1 PART 2
 Page 1 part 1 PART 2 Page 2 Part 1 Part 2 Page 3 part 1 Part 2 Page 4 Page 5 Part 1 10. Which point on the curve y x 2 1 is closest to the point 4,1 11. The point P lies in the first quadrant on the graph
Page 1 part 1 PART 2 Page 2 Part 1 Part 2 Page 3 part 1 Part 2 Page 4 Page 5 Part 1 10. Which point on the curve y x 2 1 is closest to the point 4,1 11. The point P lies in the first quadrant on the graph
Practical Data Visualization and Virtual Reality. Virtual Reality VR Display Systems. Karljohan Lundin Palmerius
 Practical Data Visualization and Virtual Reality Virtual Reality VR Display Systems Karljohan Lundin Palmerius Synopsis Virtual Reality basics Common display systems Visual modality Sound modality Interaction
Practical Data Visualization and Virtual Reality Virtual Reality VR Display Systems Karljohan Lundin Palmerius Synopsis Virtual Reality basics Common display systems Visual modality Sound modality Interaction
