1-What type of graph is used to show trends? 2-What type of graph is used to compare information?
|
|
|
- Melina Howard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AGENDA ABSENT BLOCK 9/3 & 9/4 week-4 TOPIC: the NATURE of SCIENCE OBJ : 9, 10, 11 DO NOW: 1-What type of graph is used to show trends? 2-What type of graph is used to compare information? Science of Life EXT: 1.3 Skittles Graph DUE DATE: Friday 9/5 DW: Skittles Activity UNIT EXAM- FRIDAY 9/ Scenarios -Concept Map -WORKTIME: Skittles Graph HANDOUTS to PICK-UP: -Scientific Method Concept Map -Skittles Graph -Skittles Graph Rubric -Graphing Tips TURN IN to ABS box: SEMINAR 2: BEFORE/AFTER SCHOOL: DW-NONE EXIT: Fill in Level of Understanding/17 word Summary
2 UNIT OBJECTIVES 9- -IDENTIFY/SEQUENCE the flow of scientific method 10- -IDENTIFY & DIFFERENTIATE: - independent variable / dependent variable - experimental group / control group - prediction / hypothesis - conclusion / theory - qualitative data / quantitative data / constants 11- -DETERMINE / CONSTRUCT an appropriate graph for a given set of data Add on to each QUESTION every night as REVIEW!
3 BLOCK Write this in RED PEN LEVEL OF UNDERSTANDING NONE RED X in BOX DW GRADE: 2 1 0
4 Scenarios 1-Which people are in the control group? 2-What is the IV? 3-What is the DV? 4-What should Mr. Krab s conclusion be? 5-Why do you think 8 people in group B reported feeling better?
5 Scenarios 1-What is the initial observation? 2-What is the IV? 3-What is the DV? 4-What should Sponge Bob s conclusion be?
6 SCIENTIFIC METHOD is an organized plan OBSERVATIONS -information gathered thru senses QUESTIONS/PROBLEM -what you want to know HYPOTHESIS -proposed answer to problem/question EXPERIMENT -collect data / test hypothesis CONCLUSION -analyze data -decision / opinion formed following investigation THEORY -supported explanation -based on many observs /experimental results / over period of time
7 DATAinfo gained from observations Quantitative -numerical measurements (# s) -EX: -time -temp -length -mass -area -volume -density -MEAN /MEDIAN /MODE Qualitative -descriptions (WORDS) -interpreted differently -senses detect -EX: -see -hear -touch -taste
8 VARIABLESfactors in an experiment that CHANGE INDEPENDENT -the ONE FACTOR changed in a controlled experiment. -factor TESTED and affects the outcome of the experiment. DEPENDENT -factor BEING MEASURED in a controlled experiment. -value CHANGES because of changes to IV.
9 CONTROLLED EXPERIMENTinvestigation in a CONTROLLED setting CONTROL GROUP -used for comparison -not exposed to factor being tested EXPERIMENTAL GROUP -test group (what are you testing?) -exposed to factors being tested CONSTANTS -factors remain same for entire exp
10 1.3 DATA COLLECTION / GRAPHING PRACTICE GRAPHING is an important procedure used by scientist to DISPLAY the DATA that is COLLECTED during a CONTROLLED EXPERIMENT. 5 MAJOR PARTS -title -independent variable -dependent variable -scales for each variable -a key/ legend
11 #1 DETERMINE- type of graph
12 line graphs -show trends -change over time title Y-axis (DV) X-axis (IV) X-axis
13 Bar graphs -used to compare data from 2 or more items title Y-axis Let s Practice! X-axis
14 circle graph shows how the parts make up the whole use color/% title
15 #1 DETERMINE- type of graph X X X X X X X X
16 #2 LABELING axes
17 variables -something that changes INDEPENDENT variable -controlled by experimenter (I CONTROL) -EX: time (dates, min), depth (meter), temp (celsius) -X AXIS -horizontal DEPENDENT variable -directly affected by the IV -THE RESULTS -Y AXIS -vertical
18 #2 LABELING axes Bounce Height (cm) Distanced dropped (m) Candle burn time (s) Jar volume (ml)
19 #2 LABELING axes Bounce Height (cm) Distanced dropped (m) Candle burn time (s) Jar volume (ml)
20 #3 SCALING axes 75% graph
21 SCALES Where to plot points representing data? 1-Determine the variable range. - Subtract the lowest data value from the highest data value. - Do each variable separately. 2-Determine the scale of the graph -Determine a scale,(the numerical value for each square), that best fits the range of each variable. -Spread the graph to use MOST of the available space (75%)
22 #3 SCALING STEP
23 #3 SCALING STEP = 5.9 = 1.15 =.5
24 #3 SCALING STEP =24/7=3.42= =2.2/12=.18=
25 #4 CREATING titles
26 title -Your title should clearly tell what the graph is about -By reading title get an idea about the graph CONCISE STATEMENT placed above graph
27 #4 CREATING titles Distance vs. Ball height Ball height when dropped several distances above floor Jar Volume vs. Burn Time Burn time of candle with different jar volumes
28
29 KEY/LEGEND LEGEND -short descriptive narrative concerning data -placed under graph KEY If more than one line/bar is drawn on a single graph, a "key" is provided near the title to identify the lines.
30 1.3 SKITTLES GRAPH DIRECTIONS: 1-Using your bag of Skittles and directions from your teacher, complete steps 2-5. COLLECT DATA: 2-SORT your bag of skittles by color and RECORD the data table showing the # of each color in your bag. 3-COLLECT data from your table partner s bag of skittles: RECORD in data table.
31 1.3 SKITTLES GRAPH GRAPHS: 4- Use the information from the data table ABOVE and construct a graph. [check the rubric for all needed areas] 5-Using the data provided BELOW, construct a graph to show the blood sugar levels of Mr. Smith over a period of an hour after eating a bag of Skittles. [check the rubric for all needed areas] blood samples were taken every 10 minutes for 1 hour milligrams per deciliter of blood (mg/dl) time in minutes
32 EXIT FILL-IN: level of understanding of today s objective 9- -IDENTIFY/SEQUENCE the flow of scientific method 10- -IDENTIFY & DIFFERENTIATE: - independent variable / dependent variable - experimental group / control group - prediction / hypothesis - conclusion / theory - qualitative data / quantitative data / constants 11- -DETERMINE / CONSTRUCT an appropriate graph for a given set of data
Scientific Investigation Use and Interpret Graphs Promotion Benchmark 3 Lesson Review Student Copy
 Scientific Investigation Use and Interpret Graphs Promotion Benchmark 3 Lesson Review Student Copy Vocabulary Data Table A place to write down and keep track of data collected during an experiment. Line
Scientific Investigation Use and Interpret Graphs Promotion Benchmark 3 Lesson Review Student Copy Vocabulary Data Table A place to write down and keep track of data collected during an experiment. Line
Graphing Guidelines. Controlled variables refers to all the things that remain the same during the entire experiment.
 Graphing Graphing Guidelines Graphs must be neatly drawn using a straight edge and pencil. Use the x-axis for the manipulated variable and the y-axis for the responding variable. Manipulated Variable AKA
Graphing Graphing Guidelines Graphs must be neatly drawn using a straight edge and pencil. Use the x-axis for the manipulated variable and the y-axis for the responding variable. Manipulated Variable AKA
Released Science Inquiry Task Mass and Matter Grade 8 Student Answer Booklet
 Date: Your Name: Released Science Inquiry Task Mass and Matter 2010 Grade 8 Student Answer Booklet Organizing and Presenting Your Data Directions: You will work on your own to organize your data, use your
Date: Your Name: Released Science Inquiry Task Mass and Matter 2010 Grade 8 Student Answer Booklet Organizing and Presenting Your Data Directions: You will work on your own to organize your data, use your
WELCOME TO LIFE SCIENCES
 WELCOME TO LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 10 (your new favourite subject) Scientific method Life science is the scientific study of living things from molecular level to their environment. Certain methods are generally
WELCOME TO LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 10 (your new favourite subject) Scientific method Life science is the scientific study of living things from molecular level to their environment. Certain methods are generally
Mathematics Success Grade 8
 T936 Mathematics Success Grade 8 [OBJECTIVE] The student will find the line of best fit for a scatter plot, interpret the equation and y-intercept of the linear representation, and make predictions based
T936 Mathematics Success Grade 8 [OBJECTIVE] The student will find the line of best fit for a scatter plot, interpret the equation and y-intercept of the linear representation, and make predictions based
Science Binder and Science Notebook. Discussions
 Lane Tech H. Physics (Joseph/Machaj 2016-2017) A. Science Binder Science Binder and Science Notebook Name: Period: Unit 1: Scientific Methods - Reference Materials The binder is the storage device for
Lane Tech H. Physics (Joseph/Machaj 2016-2017) A. Science Binder Science Binder and Science Notebook Name: Period: Unit 1: Scientific Methods - Reference Materials The binder is the storage device for
Collecting and Organizing Data. The Scientific Method (part 3) Rules for making data tables: Collecting and Organizing Data
 Collecting and Organizing Data The Scientific Method (part 3) As you work on your experiment, you are making observations that will become your experimental data. Data can be collected in a variety of
Collecting and Organizing Data The Scientific Method (part 3) As you work on your experiment, you are making observations that will become your experimental data. Data can be collected in a variety of
Graphing Techniques. Figure 1. c 2011 Advanced Instructional Systems, Inc. and the University of North Carolina 1
 Graphing Techniques The construction of graphs is a very important technique in experimental physics. Graphs provide a compact and efficient way of displaying the functional relationship between two experimental
Graphing Techniques The construction of graphs is a very important technique in experimental physics. Graphs provide a compact and efficient way of displaying the functional relationship between two experimental
Information for teachers
 Topic Drawing line graphs Level Key Stage 3/GCSE (or any course for students aged - 6) Outcomes. Students identify what is wrong with a line graph 2. Students use a mark scheme to peer assess a line graph
Topic Drawing line graphs Level Key Stage 3/GCSE (or any course for students aged - 6) Outcomes. Students identify what is wrong with a line graph 2. Students use a mark scheme to peer assess a line graph
Using Graphing Skills
 Name Class Date Laboratory Skills 8 Using Graphing Skills Introduction Recorded data can be plotted on a graph. A graph is a pictorial representation of information recorded in a data table. It is used
Name Class Date Laboratory Skills 8 Using Graphing Skills Introduction Recorded data can be plotted on a graph. A graph is a pictorial representation of information recorded in a data table. It is used
Chapter 2 Frequency Distributions and Graphs
 Chapter 2 Frequency Distributions and Graphs Outline 2-1 Organizing Data 2-2 Histograms, Frequency Polygons, and Ogives 2-3 Other Types of Graphs Objectives Organize data using a frequency distribution.
Chapter 2 Frequency Distributions and Graphs Outline 2-1 Organizing Data 2-2 Histograms, Frequency Polygons, and Ogives 2-3 Other Types of Graphs Objectives Organize data using a frequency distribution.
Chapter 10. Definition: Categorical Variables. Graphs, Good and Bad. Distribution
 Chapter 10 Graphs, Good and Bad Chapter 10 3 Distribution Definition: Tells what values a variable takes and how often it takes these values Can be a table, graph, or function Categorical Variables Places
Chapter 10 Graphs, Good and Bad Chapter 10 3 Distribution Definition: Tells what values a variable takes and how often it takes these values Can be a table, graph, or function Categorical Variables Places
Engage Examine the picture on the left. 1. What s happening? What is this picture about?
 AP Physics Lesson 1.a Kinematics Graphical Analysis Outcomes Interpret graphical evidence of motion (uniform speed & uniform acceleration). Apply an understanding of position time graphs to novel examples.
AP Physics Lesson 1.a Kinematics Graphical Analysis Outcomes Interpret graphical evidence of motion (uniform speed & uniform acceleration). Apply an understanding of position time graphs to novel examples.
Notes 5C: Statistical Tables and Graphs
 Notes 5C: Statistical Tables and Graphs Frequency Tables A frequency table is an easy way to display raw data. A frequency table typically has between two to four columns: The first column lists all the
Notes 5C: Statistical Tables and Graphs Frequency Tables A frequency table is an easy way to display raw data. A frequency table typically has between two to four columns: The first column lists all the
Unit 5: Graphs. Input. Output. Cartesian Coordinate System. Ordered Pair
 Section 5.1: The Cartesian plane Section 5.2: Working with Scale in the Cartesian Plane Section 5.3: Characteristics of Graphs Section 5.4: Interpreting Graphs Section 5.5: Constructing good graphs from
Section 5.1: The Cartesian plane Section 5.2: Working with Scale in the Cartesian Plane Section 5.3: Characteristics of Graphs Section 5.4: Interpreting Graphs Section 5.5: Constructing good graphs from
Electric Circuits. Introduction. In this lab you will examine how voltage changes in series and parallel circuits. Item Picture Symbol.
 Electric Circuits Introduction In this lab you will examine how voltage changes in series and parallel circuits. Item Picture Symbol Wires (6) Voltmeter (1) Bulbs (3) (Resistors) Batteries (3) 61 Procedure
Electric Circuits Introduction In this lab you will examine how voltage changes in series and parallel circuits. Item Picture Symbol Wires (6) Voltmeter (1) Bulbs (3) (Resistors) Batteries (3) 61 Procedure
PLC Papers Created For:
 PLC Papers Created For: Year 11 Topic Practice Paper: Histograms Histograms with unequal class widths 1 Grade 6 Objective: Construct and interpret a histogram with unequal class widths (for grouped discrete
PLC Papers Created For: Year 11 Topic Practice Paper: Histograms Histograms with unequal class widths 1 Grade 6 Objective: Construct and interpret a histogram with unequal class widths (for grouped discrete
Mathematics Success Grade 6
 T428 Mathematics Success Grade 6 [OBJECTIVE] The students will plot ordered pairs containing rational values to identify vertical and horizontal lengths between two points in order to solve real-world
T428 Mathematics Success Grade 6 [OBJECTIVE] The students will plot ordered pairs containing rational values to identify vertical and horizontal lengths between two points in order to solve real-world
2. Look up the definition of a chemical change in your text and as a group write a paraphrase of the definition here:
 RUN TIME: 50 MIN LAB REPORT REQUIRED PL04 Page 1 of 5 POGIL LAB EXERCISE 04 Practicing the Skills of Observation and Experimentation on a Burning Candle Each member should assume his or her role at this
RUN TIME: 50 MIN LAB REPORT REQUIRED PL04 Page 1 of 5 POGIL LAB EXERCISE 04 Practicing the Skills of Observation and Experimentation on a Burning Candle Each member should assume his or her role at this
Using Graphing Skills
 Name Class Date Laboratory Skills 8 Using Graphing Skills Introduction Recorded data can be plotted on a graph. A graph is a pictorial representation of information recorded in a data table. It is used
Name Class Date Laboratory Skills 8 Using Graphing Skills Introduction Recorded data can be plotted on a graph. A graph is a pictorial representation of information recorded in a data table. It is used
Honors Chemistry Summer Assignment
 Honors Chemistry Summer Assignment Page 1 Honors Chemistry Summer Assignment 2014-2015 Materials needed for class: Scientific or Graphing Calculator Mrs. Dorman ldorman@ringgold.org Notebook with folder
Honors Chemistry Summer Assignment Page 1 Honors Chemistry Summer Assignment 2014-2015 Materials needed for class: Scientific or Graphing Calculator Mrs. Dorman ldorman@ringgold.org Notebook with folder
Sect Linear Equations in Two Variables
 99 Concept # Sect. - Linear Equations in Two Variables Solutions to Linear Equations in Two Variables In this chapter, we will examine linear equations involving two variables. Such equations have an infinite
99 Concept # Sect. - Linear Equations in Two Variables Solutions to Linear Equations in Two Variables In this chapter, we will examine linear equations involving two variables. Such equations have an infinite
Lab 4 Projectile Motion
 b Lab 4 Projectile Motion What You Need To Know: x x v v v o ox ox v v ox at 1 t at a x FIGURE 1 Linear Motion Equations The Physics So far in lab you ve dealt with an object moving horizontally or an
b Lab 4 Projectile Motion What You Need To Know: x x v v v o ox ox v v ox at 1 t at a x FIGURE 1 Linear Motion Equations The Physics So far in lab you ve dealt with an object moving horizontally or an
Page 21 GRAPHING OBJECTIVES:
 Page 21 GRAPHING OBJECTIVES: 1. To learn how to present data in graphical form manually (paper-and-pencil) and using computer software. 2. To learn how to interpret graphical data by, a. determining the
Page 21 GRAPHING OBJECTIVES: 1. To learn how to present data in graphical form manually (paper-and-pencil) and using computer software. 2. To learn how to interpret graphical data by, a. determining the
Using Graphing Skills
 Name Class Date Laboratory Skills 8 Using Graphing Skills Time required: 30 minutes Introduction Recorded data can be plotted on a graph. A graph is a pictorial representation of information recorded in
Name Class Date Laboratory Skills 8 Using Graphing Skills Time required: 30 minutes Introduction Recorded data can be plotted on a graph. A graph is a pictorial representation of information recorded in
PHY 1405 Conceptual Physics I Making a Spring Scale. Leader: Recorder: Skeptic: Encourager:
 PHY 1405 Conceptual Physics I Making a Spring Scale Leader: Recorder: Skeptic: Encourager: Materials Helical Spring Newton mass set Slotted gram mass set Mass hanger Laptop Balloon Ring stand with meter
PHY 1405 Conceptual Physics I Making a Spring Scale Leader: Recorder: Skeptic: Encourager: Materials Helical Spring Newton mass set Slotted gram mass set Mass hanger Laptop Balloon Ring stand with meter
A A B B C C D D. NC Math 2: Transformations Investigation
 NC Math 2: Transformations Investigation Name # For this investigation, you will work with a partner. You and your partner should take turns practicing the rotations with the stencil. You and your partner
NC Math 2: Transformations Investigation Name # For this investigation, you will work with a partner. You and your partner should take turns practicing the rotations with the stencil. You and your partner
Appendix C: Graphing. How do I plot data and uncertainties? Another technique that makes data analysis easier is to record all your data in a table.
 Appendix C: Graphing One of the most powerful tools used for data presentation and analysis is the graph. Used properly, graphs are an important guide to understanding the results of an experiment. They
Appendix C: Graphing One of the most powerful tools used for data presentation and analysis is the graph. Used properly, graphs are an important guide to understanding the results of an experiment. They
Experiment G: Introduction to Graphical Representation of Data & the Use of Excel
 Experiment G: Introduction to Graphical Representation of Data & the Use of Excel Scientists answer posed questions by performing experiments which provide information about a given problem. After collecting
Experiment G: Introduction to Graphical Representation of Data & the Use of Excel Scientists answer posed questions by performing experiments which provide information about a given problem. After collecting
Data Analysis and Probability
 Data Analysis and Probability Vocabulary List Mean- the sum of a group of numbers divided by the number of addends Median- the middle value in a group of numbers arranged in order Mode- the number or item
Data Analysis and Probability Vocabulary List Mean- the sum of a group of numbers divided by the number of addends Median- the middle value in a group of numbers arranged in order Mode- the number or item
Sidcot intranet - Firefly. Useful links: Instant classroom. MyMaths. Objectives
 Useful links: Sidcot intranet - Firefly Instant classroom MyMaths Objectives Objectives To revise scatter graphs To use them to make estimations Scatter Graphs Revision powerpoint Now make some revision
Useful links: Sidcot intranet - Firefly Instant classroom MyMaths Objectives Objectives To revise scatter graphs To use them to make estimations Scatter Graphs Revision powerpoint Now make some revision
Describing Data: Frequency Tables, Frequency Distributions, and Graphic Presentation. Chapter 2
 Describing Data: Frequency Tables, Frequency Distributions, and Graphic Presentation Chapter 2 Learning Objectives Organize qualitative data into a frequency table. Present a frequency table as a bar chart
Describing Data: Frequency Tables, Frequency Distributions, and Graphic Presentation Chapter 2 Learning Objectives Organize qualitative data into a frequency table. Present a frequency table as a bar chart
General tips for all graphs Choosing the right kind of graph scatter graph bar graph
 Excerpted and adapted from: McDonald, J.H. 2014. Handbook of Biological Statistics (3rd ed.). Sparky House Publishing, Baltimore, MD. (http://www.biostathandbook.com/graph.html) Guide to fairly good graphs
Excerpted and adapted from: McDonald, J.H. 2014. Handbook of Biological Statistics (3rd ed.). Sparky House Publishing, Baltimore, MD. (http://www.biostathandbook.com/graph.html) Guide to fairly good graphs
Video Speed is not Important, https://youcubed.org/weeks/week-3-grade-3-5/
 Grades 3-5 Introduction This activity is a fun way to develop an understanding of quantity and ways to make a total of 25. In this activity students will have an opportunity to count, add, keep track of
Grades 3-5 Introduction This activity is a fun way to develop an understanding of quantity and ways to make a total of 25. In this activity students will have an opportunity to count, add, keep track of
Lab 10. Images with Thin Lenses
 Lab 10. Images with Thin Lenses Goals To learn experimental techniques for determining the focal lengths of positive (converging) and negative (diverging) lenses in conjunction with the thin-lens equation.
Lab 10. Images with Thin Lenses Goals To learn experimental techniques for determining the focal lengths of positive (converging) and negative (diverging) lenses in conjunction with the thin-lens equation.
Sample Lesson Plan for Standard 5.MD.B.2: Creating Line Plots. An Introduction to Line Plots Using Whole Numbers
 Sample Lesson Plan for Standard 5.MD.B.2: Creating Line Plots An Introduction to Line Plots Using Whole Numbers Grade Level Expectations For this standard, fifth grade students are expected to create line
Sample Lesson Plan for Standard 5.MD.B.2: Creating Line Plots An Introduction to Line Plots Using Whole Numbers Grade Level Expectations For this standard, fifth grade students are expected to create line
Year 10 Practical Assessment Skills Lesson 1 Results tables and Graph Skills
 Year 10 Practical Assessment Skills Lesson 1 Results tables and Graph Skills Aim: to be able to present results and draw appropriate types of graphs Must: identify mistakes in data recording Should: be
Year 10 Practical Assessment Skills Lesson 1 Results tables and Graph Skills Aim: to be able to present results and draw appropriate types of graphs Must: identify mistakes in data recording Should: be
Can you predict the speed of the car as it moves down the track? Example Distance Time Speed
 1.2 Speed Can you predict the speed of the car as it moves down the track? What happens to the speed of a car as it rolls down a ramp? Does the speed stay constant or does it change? In this investigation,
1.2 Speed Can you predict the speed of the car as it moves down the track? What happens to the speed of a car as it rolls down a ramp? Does the speed stay constant or does it change? In this investigation,
Sensors and Scatterplots Activity Excel Worksheet
 Name: Date: Sensors and Scatterplots Activity Excel Worksheet Directions Using our class datasheets, we will analyze additional scatterplots, using Microsoft Excel to make those plots. To get started,
Name: Date: Sensors and Scatterplots Activity Excel Worksheet Directions Using our class datasheets, we will analyze additional scatterplots, using Microsoft Excel to make those plots. To get started,
Physics 131 Lab 1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL MOTION
 1 Name Date Partner(s) Physics 131 Lab 1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES To familiarize yourself with motion detector hardware. To explore how simple motions are represented on a displacement-time graph.
1 Name Date Partner(s) Physics 131 Lab 1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES To familiarize yourself with motion detector hardware. To explore how simple motions are represented on a displacement-time graph.
Sect 4.5 Inequalities Involving Quadratic Function
 71 Sect 4. Inequalities Involving Quadratic Function Objective #0: Solving Inequalities using a graph Use the graph to the right to find the following: Ex. 1 a) Find the intervals where f(x) > 0. b) Find
71 Sect 4. Inequalities Involving Quadratic Function Objective #0: Solving Inequalities using a graph Use the graph to the right to find the following: Ex. 1 a) Find the intervals where f(x) > 0. b) Find
A Visual Display. A graph is a visual display of information or data. This is a graph that shows a girl walking her dog. Communicating with Graphs
 A Visual Display A graph is a visual display of information or data. This is a graph that shows a girl walking her dog. A Visual Display The horizontal axis, or the x-axis, measures time. Time is the independent
A Visual Display A graph is a visual display of information or data. This is a graph that shows a girl walking her dog. A Visual Display The horizontal axis, or the x-axis, measures time. Time is the independent
Name. Scientific Numbers Significant Figures Graphing
 Name Honors Chemistry Summer Assignment 2017 Welcome to Honors Chemistry. Included are several sections that assess your math and science skills. Each section contains an informational portion that explains
Name Honors Chemistry Summer Assignment 2017 Welcome to Honors Chemistry. Included are several sections that assess your math and science skills. Each section contains an informational portion that explains
Chapter 3. Graphical Methods for Describing Data. Copyright 2005 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
 Chapter 3 Graphical Methods for Describing Data 1 Frequency Distribution Example The data in the column labeled vision for the student data set introduced in the slides for chapter 1 is the answer to the
Chapter 3 Graphical Methods for Describing Data 1 Frequency Distribution Example The data in the column labeled vision for the student data set introduced in the slides for chapter 1 is the answer to the
Lesson 1: Chance Experiments
 Student Outcomes Students understand that a probability is a number between and that represents the likelihood that an event will occur. Students interpret a probability as the proportion of the time that
Student Outcomes Students understand that a probability is a number between and that represents the likelihood that an event will occur. Students interpret a probability as the proportion of the time that
Video Mistakes are Powerful, https://youcubed.org/weeks/week-3-grade-1-2/ Agenda for the activity Activity Time Description Materials Mindset Message
 Grades 1-2 Introduction This activity is a fun way to develop an understanding of quantity and ways to make a total of 10. In this activity students will have an opportunity to count, add, keep track of
Grades 1-2 Introduction This activity is a fun way to develop an understanding of quantity and ways to make a total of 10. In this activity students will have an opportunity to count, add, keep track of
Resistance and Resistivity
 Resistance and Resistivity Lab Section (circle): Day: Monday Tuesday Time: 8:00 9:30 1:10 2:40 Name: Partners: Pre-Lab You are required to finish this section before coming to the lab it will be checked
Resistance and Resistivity Lab Section (circle): Day: Monday Tuesday Time: 8:00 9:30 1:10 2:40 Name: Partners: Pre-Lab You are required to finish this section before coming to the lab it will be checked
Math Labs. Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates. Procedure
 Math Labs Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates Problem Statement Use the Cartesian coordinate system to draw rectangle ABCD. Use an x-y-z coordinate system to draw a rectangular
Math Labs Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates Problem Statement Use the Cartesian coordinate system to draw rectangle ABCD. Use an x-y-z coordinate system to draw a rectangular
Bioacoustics Lab- Spring 2011 BRING LAPTOP & HEADPHONES
 Bioacoustics Lab- Spring 2011 BRING LAPTOP & HEADPHONES Lab Preparation: Bring your Laptop to the class. If don t have one you can use one of the COH s laptops for the duration of the Lab. Before coming
Bioacoustics Lab- Spring 2011 BRING LAPTOP & HEADPHONES Lab Preparation: Bring your Laptop to the class. If don t have one you can use one of the COH s laptops for the duration of the Lab. Before coming
E. Slope-Intercept Form and Direct Variation (pp )
 and Direct Variation (pp. 32 35) For any two points, there is one and only one line that contains both points. This fact can help you graph a linear equation. Many times, it will be convenient to use the
and Direct Variation (pp. 32 35) For any two points, there is one and only one line that contains both points. This fact can help you graph a linear equation. Many times, it will be convenient to use the
Mathematics Geometry Grade 6AB
 Mathematics Geometry Grade 6AB It s the Right Thing Subject: Mathematics: Geometry: Ratio and Proportion Level: Grade 7 Abstract: Students will learn the six types of triangles and the characteristics
Mathematics Geometry Grade 6AB It s the Right Thing Subject: Mathematics: Geometry: Ratio and Proportion Level: Grade 7 Abstract: Students will learn the six types of triangles and the characteristics
Spreadsheets 3: Charts and Graphs
 Spreadsheets 3: Charts and Graphs Name: Main: When you have finished this handout, you should have the following skills: Setting up data correctly Labeling axes, legend, scale, title Editing symbols, colors,
Spreadsheets 3: Charts and Graphs Name: Main: When you have finished this handout, you should have the following skills: Setting up data correctly Labeling axes, legend, scale, title Editing symbols, colors,
Algebra Mathematics S. J. Cooper
 THOMAS WHITHAM SIXTH FORM Algebra Mathematics S. J. Cooper Year 7 B U R N L E Y C@M P U S, B U R N L E Y, L A N C A S H I R E, B B 1 0 1 J D. T EL. 6 8 2 2 7 2 Algebra (1) Simplif each of the following
THOMAS WHITHAM SIXTH FORM Algebra Mathematics S. J. Cooper Year 7 B U R N L E Y C@M P U S, B U R N L E Y, L A N C A S H I R E, B B 1 0 1 J D. T EL. 6 8 2 2 7 2 Algebra (1) Simplif each of the following
CHEMISTRY BOOT CAMP: GRAPHING SKILLS
 Name: Date: Hour: CHEMISTRY BOOT CAMP: GRAPHING SKILLS Rules for Good Graph Making (adapted from misterguch.brinkster.net) 1. Always give your graph a title in the following form: The dependence of [the
Name: Date: Hour: CHEMISTRY BOOT CAMP: GRAPHING SKILLS Rules for Good Graph Making (adapted from misterguch.brinkster.net) 1. Always give your graph a title in the following form: The dependence of [the
Step 1: Set up the variables AB Design. Use the top cells to label the variables that will be displayed on the X and Y axes of the graph
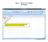 Step 1: Set up the variables AB Design Use the top cells to label the variables that will be displayed on the X and Y axes of the graph Step 1: Set up the variables X axis for AB Design Enter X axis label
Step 1: Set up the variables AB Design Use the top cells to label the variables that will be displayed on the X and Y axes of the graph Step 1: Set up the variables X axis for AB Design Enter X axis label
Resting pulse After exercise Resting pulse After exercise. Trial Trial Trial Trial. Subject Subject
 EXERCISE 2.3 Data Presentation Objectives After completing this exercise, you should be able to 1. Explain the difference between discrete and continuous variables and give examples. 2. Use one given data
EXERCISE 2.3 Data Presentation Objectives After completing this exercise, you should be able to 1. Explain the difference between discrete and continuous variables and give examples. 2. Use one given data
12 Projectile Motion 12 - Page 1 of 9. Projectile Motion
 12 Projectile Motion 12 - Page 1 of 9 Equipment Projectile Motion 1 Mini Launcher ME-6825A 2 Photogate ME-9498A 1 Photogate Bracket ME-6821A 1 Time of Flight ME-6810 1 Table Clamp ME-9472 1 Rod Base ME-8735
12 Projectile Motion 12 - Page 1 of 9 Equipment Projectile Motion 1 Mini Launcher ME-6825A 2 Photogate ME-9498A 1 Photogate Bracket ME-6821A 1 Time of Flight ME-6810 1 Table Clamp ME-9472 1 Rod Base ME-8735
Mathematics Success Grade 8
 Mathematics Success Grade 8 T429 [OBJECTIVE] The student will solve systems of equations by graphing. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] solving equations [MATERIALS] Student pages S207 S220 Rulers [ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS]
Mathematics Success Grade 8 T429 [OBJECTIVE] The student will solve systems of equations by graphing. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] solving equations [MATERIALS] Student pages S207 S220 Rulers [ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS]
Geometric Optics. This is a double-convex glass lens mounted in a wooden frame. We will use this as the eyepiece for our microscope.
 I. Before you come to lab Read through this handout in its entirety. II. Learning Objectives As a result of performing this lab, you will be able to: 1. Use the thin lens equation to determine the focal
I. Before you come to lab Read through this handout in its entirety. II. Learning Objectives As a result of performing this lab, you will be able to: 1. Use the thin lens equation to determine the focal
CBL Lab WHY ARE THERE MORE REDS IN MY BAG? MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM GRADE SIX. Florida Sunshine State Mathematics Standards
 MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM GRADE SIX CBL Lab Florida Sunshine State Mathematics Standards WHY ARE THERE MORE REDS IN MY BAG? John Klimek, Math Coordinator Curt Witthoff, Math/Science Specialist Dr. Benjamin
MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM GRADE SIX CBL Lab Florida Sunshine State Mathematics Standards WHY ARE THERE MORE REDS IN MY BAG? John Klimek, Math Coordinator Curt Witthoff, Math/Science Specialist Dr. Benjamin
ESSENTIAL MATHEMATICS 1 WEEK 17 NOTES AND EXERCISES. Types of Graphs. Bar Graphs
 ESSENTIAL MATHEMATICS 1 WEEK 17 NOTES AND EXERCISES Types of Graphs Bar Graphs Bar graphs are used to present and compare data. There are two main types of bar graphs: horizontal and vertical. They are
ESSENTIAL MATHEMATICS 1 WEEK 17 NOTES AND EXERCISES Types of Graphs Bar Graphs Bar graphs are used to present and compare data. There are two main types of bar graphs: horizontal and vertical. They are
THE ENGLISH SCHOOL ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes
 THE ENGLISH SCHOOL ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS 2014 MATHEMATICS FIRST FORM Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Answer ALL questions. Show all necessary working on the question paper in the spaces provided and
THE ENGLISH SCHOOL ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS 2014 MATHEMATICS FIRST FORM Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Answer ALL questions. Show all necessary working on the question paper in the spaces provided and
Graphs. This tutorial will cover the curves of graphs that you are likely to encounter in physics and chemistry.
 Graphs Graphs are made by graphing one variable which is allowed to change value and a second variable that changes in response to the first. The variable that is allowed to change is called the independent
Graphs Graphs are made by graphing one variable which is allowed to change value and a second variable that changes in response to the first. The variable that is allowed to change is called the independent
Appendix III Graphs in the Introductory Physics Laboratory
 Appendix III Graphs in the Introductory Physics Laboratory 1. Introduction One of the purposes of the introductory physics laboratory is to train the student in the presentation and analysis of experimental
Appendix III Graphs in the Introductory Physics Laboratory 1. Introduction One of the purposes of the introductory physics laboratory is to train the student in the presentation and analysis of experimental
Laboratory 2: Graphing
 Purpose It is often said that a picture is worth 1,000 words, or for scientists we might rephrase it to say that a graph is worth 1,000 words. Graphs are most often used to express data in a clear, concise
Purpose It is often said that a picture is worth 1,000 words, or for scientists we might rephrase it to say that a graph is worth 1,000 words. Graphs are most often used to express data in a clear, concise
MiSP Permeability and Porosity Worksheet #1 L3
 MiSP Permeability and Porosity Worksheet #1 L3 Name Date Water Movement Through the Ground Introduction You have learned about permeability and porosity. Porosity is a measure of the empty space that is
MiSP Permeability and Porosity Worksheet #1 L3 Name Date Water Movement Through the Ground Introduction You have learned about permeability and porosity. Porosity is a measure of the empty space that is
Chapter Displaying Graphical Data. Frequency Distribution Example. Graphical Methods for Describing Data. Vision Correction Frequency Relative
 Chapter 3 Graphical Methods for Describing 3.1 Displaying Graphical Distribution Example The data in the column labeled vision for the student data set introduced in the slides for chapter 1 is the answer
Chapter 3 Graphical Methods for Describing 3.1 Displaying Graphical Distribution Example The data in the column labeled vision for the student data set introduced in the slides for chapter 1 is the answer
Problem Solving with Length, Money, and Data
 Grade 2 Module 7 Problem Solving with Length, Money, and Data OVERVIEW Module 7 presents an opportunity for students to practice addition and subtraction strategies within 100 and problem-solving skills
Grade 2 Module 7 Problem Solving with Length, Money, and Data OVERVIEW Module 7 presents an opportunity for students to practice addition and subtraction strategies within 100 and problem-solving skills
MARBLE RACING. Practice Calculating Speed
 MARBLE RACING Practice Calculating Speed Problem How does the angle of the ramp affect the marble s speed? Materials Ruler Meter stick Masking Tape 5 Books Marble Timer Protractor Procedure 1. Mark a finish
MARBLE RACING Practice Calculating Speed Problem How does the angle of the ramp affect the marble s speed? Materials Ruler Meter stick Masking Tape 5 Books Marble Timer Protractor Procedure 1. Mark a finish
PROPER USE OF LAB EQUIPMENT and DATA ANALYSIS SKILLS
 Make sure that each section has its heading on a separate line - underlined. Write title PROPER USE OF LAB EQUIPMENT and DATA ANALYSIS SKILLS Paraphrase Introduction Include title Introduction: A good
Make sure that each section has its heading on a separate line - underlined. Write title PROPER USE OF LAB EQUIPMENT and DATA ANALYSIS SKILLS Paraphrase Introduction Include title Introduction: A good
You re the Teacher. Writing Equations with Specific Characteristics. Word Problem Worksheet
 Name # Accelerated Algebra: Marking Period 2 Choice Board Per. 150 points Directions: Create a TIC-TAC-TOE (up and down, left and right, or diagonal) to complete THREE total tasks. Each task is worth 50
Name # Accelerated Algebra: Marking Period 2 Choice Board Per. 150 points Directions: Create a TIC-TAC-TOE (up and down, left and right, or diagonal) to complete THREE total tasks. Each task is worth 50
Geometry Activity. Then enter the following numbers in L 1 and L 2 respectively. L 1 L
 Geometry Activity Introduction: In geometry we can reflect, rotate, translate, and dilate a figure. In this activity lists and statistical plots on the TI-83 Plus Silver Edition will be used to illustrate
Geometry Activity Introduction: In geometry we can reflect, rotate, translate, and dilate a figure. In this activity lists and statistical plots on the TI-83 Plus Silver Edition will be used to illustrate
Scatter Plots, Correlation, and Lines of Best Fit
 Lesson 7.3 Objectives Interpret a scatter plot. Identify the correlation of data from a scatter plot. Find the line of best fit for a set of data. Scatter Plots, Correlation, and Lines of Best Fit A video
Lesson 7.3 Objectives Interpret a scatter plot. Identify the correlation of data from a scatter plot. Find the line of best fit for a set of data. Scatter Plots, Correlation, and Lines of Best Fit A video
Fungus Farmers LEAF CUTTING ANTS A C T I V I T Y. Activity Overview. How much leaf do leaf cutter ants chew?
 How much leaf do leaf cutter ants chew? Activity Overview Leaf cutting ants carry away leaf pieces that are up to 30 times their weight. They sometimes carry these pieces 100-200 meters (about 2 football
How much leaf do leaf cutter ants chew? Activity Overview Leaf cutting ants carry away leaf pieces that are up to 30 times their weight. They sometimes carry these pieces 100-200 meters (about 2 football
Properties of Magnetism
 Science Objectives Students will describe the magnetic field around an electromagnet. Students will relate the strength of a solenoid-type electromagnet to the number of turns of a wire on the electromagnet.
Science Objectives Students will describe the magnetic field around an electromagnet. Students will relate the strength of a solenoid-type electromagnet to the number of turns of a wire on the electromagnet.
TJP TOP TIPS FOR IGCSE STATS & PROBABILITY
 TJP TOP TIPS FOR IGCSE STATS & PROBABILITY Dr T J Price, 2011 First, some important words; know what they mean (get someone to test you): Mean the sum of the data values divided by the number of items.
TJP TOP TIPS FOR IGCSE STATS & PROBABILITY Dr T J Price, 2011 First, some important words; know what they mean (get someone to test you): Mean the sum of the data values divided by the number of items.
Lab 4 Projectile Motion
 b Lab 4 Projectile Motion Physics 211 Lab What You Need To Know: 1 x = x o + voxt + at o ox 2 at v = vox + at at 2 2 v 2 = vox 2 + 2aΔx ox FIGURE 1 Linear FIGURE Motion Linear Equations Motion Equations
b Lab 4 Projectile Motion Physics 211 Lab What You Need To Know: 1 x = x o + voxt + at o ox 2 at v = vox + at at 2 2 v 2 = vox 2 + 2aΔx ox FIGURE 1 Linear FIGURE Motion Linear Equations Motion Equations
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level BIOLOGY 5090/3 Paper 3 Practical Test MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 40 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level BIOLOGY 5090/3 Paper 3 Practical Test MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 40 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and
Objective: Investigate patterns in vertical and horizontal lines, and interpret points on the plane as distances from the axes.
 Lesson 5 Objective: Investigate patterns in vertical and horizontal lines, and interpret Suggested Lesson Structure Application Problem Fluency Practice Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (7
Lesson 5 Objective: Investigate patterns in vertical and horizontal lines, and interpret Suggested Lesson Structure Application Problem Fluency Practice Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (7
A B C. 142 D. 96
 Data Displays and Analysis 1. stem leaf 900 3 3 4 5 7 9 901 1 1 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 8 8 9 9 902 1 3 3 3 4 6 8 9 9 903 1 2 2 3 3 3 4 7 8 9 904 1 1 2 4 5 6 8 8 What is the range of the data shown in the stem-and-leaf
Data Displays and Analysis 1. stem leaf 900 3 3 4 5 7 9 901 1 1 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 8 8 9 9 902 1 3 3 3 4 6 8 9 9 903 1 2 2 3 3 3 4 7 8 9 904 1 1 2 4 5 6 8 8 What is the range of the data shown in the stem-and-leaf
AWM 11 UNIT 1 WORKING WITH GRAPHS
 AWM 11 UNIT 1 WORKING WITH GRAPHS Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Introduction to Statistics Read the introduction no written assignment 2 Bar Graphs Bar Graphs 3 Double Bar Graphs Double
AWM 11 UNIT 1 WORKING WITH GRAPHS Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Introduction to Statistics Read the introduction no written assignment 2 Bar Graphs Bar Graphs 3 Double Bar Graphs Double
Plotting Points & The Cartesian Plane. Scatter Plots WS 4.2. Line of Best Fit WS 4.3. Curve of Best Fit WS 4.4. Graphing Linear Relations WS 4.
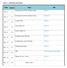 UNIT 4 - GRAPHING RELATIONS Date Lesson Topic HW Nov. 3 4.1 Plotting Points & The Cartesian Plane WS 4.1 Nov. 6 4.1 Plotting Points & The Cartesian Plane WS 4.1-II Nov. 7 4.2 Scatter Plots WS 4.2 Nov.
UNIT 4 - GRAPHING RELATIONS Date Lesson Topic HW Nov. 3 4.1 Plotting Points & The Cartesian Plane WS 4.1 Nov. 6 4.1 Plotting Points & The Cartesian Plane WS 4.1-II Nov. 7 4.2 Scatter Plots WS 4.2 Nov.
Line Graphs. Name: The independent variable is plotted on the x-axis. This axis will be labeled Time (days), and
 Name: Graphing Review Graphs and charts are great because they communicate information visually. For this reason graphs are often used in newspapers, magazines, and businesses around the world. Sometimes,
Name: Graphing Review Graphs and charts are great because they communicate information visually. For this reason graphs are often used in newspapers, magazines, and businesses around the world. Sometimes,
P202/219 Laboratory IUPUI Physics Department THIN LENSES
 THIN LENSES OBJECTIVE To verify the thin lens equation, m = h i /h o = d i /d o. d o d i f, and the magnification equations THEORY In the above equations, d o is the distance between the object and the
THIN LENSES OBJECTIVE To verify the thin lens equation, m = h i /h o = d i /d o. d o d i f, and the magnification equations THEORY In the above equations, d o is the distance between the object and the
TEKSING TOWARD STAAR MATHEMATICS GRADE 6. Student Book
 TEKSING TOWARD STAAR MATHEMATICS GRADE 6 Student Book TEKSING TOWARD STAAR 2014 Six Weeks 1 Lesson 1 STAAR Category 1 Grade 6 Mathematics TEKS 6.2A/6.2B Problem-Solving Model Step Description of Step 1
TEKSING TOWARD STAAR MATHEMATICS GRADE 6 Student Book TEKSING TOWARD STAAR 2014 Six Weeks 1 Lesson 1 STAAR Category 1 Grade 6 Mathematics TEKS 6.2A/6.2B Problem-Solving Model Step Description of Step 1
Graphs and Probability
 Name: Chapter Date: Practice 1 Making and Interpreting Double Bar Graphs Complete. Use the data in the graph. The double bar graph shows the number of boys and girls in two classes, 5A and 5B. Students
Name: Chapter Date: Practice 1 Making and Interpreting Double Bar Graphs Complete. Use the data in the graph. The double bar graph shows the number of boys and girls in two classes, 5A and 5B. Students
Chapter 5 Pictorial sketching
 Chapter 5 Pictorial sketching Contents Freehand sketching techniques Pictorial projections - Axonometric - Oblique Isometric projection vs isometric sketch Isometric sketch from an orthographic views Isometric
Chapter 5 Pictorial sketching Contents Freehand sketching techniques Pictorial projections - Axonometric - Oblique Isometric projection vs isometric sketch Isometric sketch from an orthographic views Isometric
MiSP Permeability and Porosity Worksheet 1 L3
 MiSP Permeability and Porosity Worksheet 1 L3 Name Date Water Movement Through the Ground Introduction: You have learned about permeability and porosity. Porosity is a measure of the empty space that is
MiSP Permeability and Porosity Worksheet 1 L3 Name Date Water Movement Through the Ground Introduction: You have learned about permeability and porosity. Porosity is a measure of the empty space that is
Review. In an experiment, there is one variable that is of primary interest. There are several other factors, which may affect the measured result.
 Review Observational study vs experiment Experimental designs In an experiment, there is one variable that is of primary interest. There are several other factors, which may affect the measured result.
Review Observational study vs experiment Experimental designs In an experiment, there is one variable that is of primary interest. There are several other factors, which may affect the measured result.
How to make a line graph
 How to make a line graph Line graphs are powerful in science because of the relationship they show between two variables (showing how one variable changes as the other changes). Step One You need the topic
How to make a line graph Line graphs are powerful in science because of the relationship they show between two variables (showing how one variable changes as the other changes). Step One You need the topic
Biggar High School Mathematics Department. S1 Block 1. Revision Booklet GOLD
 Biggar High School Mathematics Department S1 Block 1 Revision Booklet GOLD Contents MNU 3-01a MNU 3-03a MNU 3-03b Page Whole Number Calculations & Decimals 3 MTH 3-05b MTH 3-06a MTH 4-06a Multiples, Factors,
Biggar High School Mathematics Department S1 Block 1 Revision Booklet GOLD Contents MNU 3-01a MNU 3-03a MNU 3-03b Page Whole Number Calculations & Decimals 3 MTH 3-05b MTH 3-06a MTH 4-06a Multiples, Factors,
Grade 6 Math Circles Winter 2013 Mean, Median, Mode
 1 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Grade 6 Math Circles Winter 2013 Mean, Median, Mode Mean, Median and Mode The word average is a broad term. There are in fact three kinds of averages: mean,
1 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Grade 6 Math Circles Winter 2013 Mean, Median, Mode Mean, Median and Mode The word average is a broad term. There are in fact three kinds of averages: mean,
Name: Date: Period: Histogram Worksheet
 Name: Date: Period: Histogram Worksheet 1 5. For the following five histograms, list at least 3 characteristics that describe each histogram (consider symmetric, skewed to left, skewed to right, unimodal,
Name: Date: Period: Histogram Worksheet 1 5. For the following five histograms, list at least 3 characteristics that describe each histogram (consider symmetric, skewed to left, skewed to right, unimodal,
Sections Descriptive Statistics for Numerical Variables
 Math 243 Sections 2.1.2-2.2.5 Descriptive Statistics for Numerical Variables A framework to describe quantitative data: Describe the Shape, Center and Spread, and Unusual Features Shape How is the data
Math 243 Sections 2.1.2-2.2.5 Descriptive Statistics for Numerical Variables A framework to describe quantitative data: Describe the Shape, Center and Spread, and Unusual Features Shape How is the data
Motion Graphs. Plotting distance against time can tell you a lot about motion. Let's look at the axes:
 Motion Graphs 1 Name Motion Graphs Describing the motion of an object is occasionally hard to do with words. Sometimes graphs help make motion easier to picture, and therefore understand. Remember: Motion
Motion Graphs 1 Name Motion Graphs Describing the motion of an object is occasionally hard to do with words. Sometimes graphs help make motion easier to picture, and therefore understand. Remember: Motion
Appendix 3 - Using A Spreadsheet for Data Analysis
 105 Linear Regression - an Overview Appendix 3 - Using A Spreadsheet for Data Analysis Scientists often choose to seek linear relationships, because they are easiest to understand and to analyze. But,
105 Linear Regression - an Overview Appendix 3 - Using A Spreadsheet for Data Analysis Scientists often choose to seek linear relationships, because they are easiest to understand and to analyze. But,
Period 12 Activity Sheet Solutions: Electric Circuits
 Period 2 Activity Sheet Solutions: Electric Circuits Activity 2.: How are Voltage, Current, and Resistance Related? a) Data Collection Connect the DC power supply to the thin 30 cm length of nichrome wire.
Period 2 Activity Sheet Solutions: Electric Circuits Activity 2.: How are Voltage, Current, and Resistance Related? a) Data Collection Connect the DC power supply to the thin 30 cm length of nichrome wire.
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8. satspapers.org
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 6 8 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 6 8 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
MiSP Permeability and Porosity Worksheet #1 L1
 MiSP Permeability and Porosity Worksheet #1 L1 Name Date Water Movement Through the Ground Introduction You have learned about permeability and porosity. Porosity is a measure of the empty space that is
MiSP Permeability and Porosity Worksheet #1 L1 Name Date Water Movement Through the Ground Introduction You have learned about permeability and porosity. Porosity is a measure of the empty space that is
3.4 and 4.3 Explain Graphing and Writing Linear Equations in Standard Form - Notes
 3.4 and 4.3 Explain Graphing and Writing Linear Equations in Standard Form - Notes Essential Question: How can you describe the graph of the equation Ax + By = C? How can you write the equation of a line
3.4 and 4.3 Explain Graphing and Writing Linear Equations in Standard Form - Notes Essential Question: How can you describe the graph of the equation Ax + By = C? How can you write the equation of a line
