MATHEMATICS FOR A NEW GENERATION OF STUDENTS. Henderson Avenue P.S.
|
|
|
- Brian Melton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MATHEMATICS FOR A NEW GENERATION OF STUDENTS Henderson Avenue P.S. February 03, 2017
2 Positive Norms to Encourage in Math Class By Jo Boaler Everyone Can Learn Math to the Highest Levels 1. Encourage students to believe in themselves. There is no such thing as a math person. Everyone can reach the highest levels they want to, with hard work. 2. Mistakes are Valuable Mistakes grow your brain! It is good to struggle and make mistakes. 3. Questions are Really Important Always ask questions, always answer questions. Ask yourself: why does that make sense? 4. Math is about Creativity and Making Sense Math is a very creative subject that is, at its core, about visualizing patterns and creating solution paths that others can see, discuss and critique. 5. Math is about Connections and Communicating Math is a connected subject, and a form of communication. Represent math in different forms e.g. words, a picture, a graph, an equation, and link them. Color code! 6. Depth is much more important than Speed Top mathematicians, such as Laurent Schwartz, think slowly and deeply. 7. Math Class is about Learning not Performing Math is a growth subject, it takes time to learn and it is all about effort 1
3 Getting Started: Thinking Mathematically Grades 1 and 2 Today John and Paul added their ages and got 12. What number will they get in four years? Grades 3 and 4 A group of 31 students went camping taking nine tents. Each tent shelters either three or five students. If all students were covered by a tent, at least how many of the tents housed five students? Grades 5 and 6 Four points A, B, C, and D are given on a line, in some order, so that AB=1, BC = 2, CD = 3 and DA = 4. Which two points are the farthest from each other? 2
4 3
5 Problem of the Week [Grades 3 and 4] Sam s Fish Tank Sam has a large fish tank. He can fit up to 23 fish in his tank. If he groups them in groups of 3, he has 1 fish left. If he groups them in groups of 4, he has 2 fish left. What is the maximum number of fish that Sam could have in his tank? 4
6 Problem of the Week [Number Sense and Numeration] There are 26 students in Ms. Scott s class. They were discussing pets they have at home. When asked, How many of you have dogs at home?, 17 students put up their hands. When asked How many of you have cats at home?, 15 students put up their hands. When asked, How many of you have both a cat and a dog at home?, 9 students put up their hands. How many students have neither cats nor dogs at home? Use a Venn diagram to help you solve this problem. Dogs Cats 5
7 Painted Cube Imagine a large cube made up from 27 small red cubes. Imagine dipping the large cube into a pot of yellow paint so the whole outer surface is covered, and then breaking the cube up into its small cubes. How many of the small cubes will have yellow paint on their faces? Will they all look the same? Now imagine doing the same with other cubes made up from small red cubes. What can you say about the number of small cubes with yellow paint on? 6
8 Amy's Dominoes [Number Sense and Numeration] Amy has a box containing ordinary domino pieces but she does not think it is a complete set. She has 24 dominoes in her box and there are 125 spots on them altogether. Which of her domino pieces are missing? 7
9 Spatial Sense and Geometry Need: Interlocking cubes and isometric paper to record answers. Building Number 1 Clue # 1 Clue #2 There are six cubes in all. One of the cubes is yellow. The green cube shares one face with each of the other cubes. Clue #3 Clue #4 The two red cubes do not touch each other. The two blue cubes do not touch each other. One of the cubes is yellow. Building Number 2 Clue #1 Clue #2 There are six cubes in all, in a tower six The red cube is above the green cube cubes high. Clue #3 Clue #4 One of yellows is above the green cube, the other is below it. Each of the blue cubes shares a face with the green cube. Building Number 3 Clue #1 Clue #2 There is a red cube directly below a yellow cube. There is a green cube on the bottom level. There is a red cube on top of a yellow cube. The highest cube is on the third level Clue # 3 Clue #4 There are six cubes in all. An orange cube shares a face with a green cube and two others A blue cube shares a face with a yellow cube. There is a red cube on the bottom level. 8
10 Probability A magician pulls out pigeons from his hat. Which of the following statements are true, maybe true, or false, if we know that there are 3 gray, 1 white and 2 colorful pigeons in the hat: a) if he pull out 4 pigeons, there will be at least one gray among them. b) if he pull out 3 pigeons, there will be at least one of each kind of pigeon. c) if he pull out 4 pigeons, there will be at least two pigeons of the same color. d) if he pull out 6 pigeons, there will be at least two pigeons of each color. e) if he pull out 5 pigeons, there will be more colorful than gray. f) if he pull out 5 pigeons, there will be more gray than colorful. 9
11 Probability Tony is playing with colored glass balls. There are 12 red and 8 blue balls in the box. He takes balls out of the box randomly. a) How many balls does he have to take out to have two consecutive red balls taken out? b) How many balls does he have to take out to have two consecutive blue balls taken out? 10
12 Mathematics: The Science of Patterns This is a basic form of the ancient game of Nim. You will need seven objects, such as counters or blocks. It is a game for two players. Place the 7 counters in a pile and decide who will go first. (In the next game, the other player will have the first turn.) Each player takes turns to take away either one or two counters. The player who takes the last counter wins. Keep playing until you work out a winning strategy. Does it matter who has the first turn? What happens when you start the game with more counters? 11
13 Counting Polyominoes Polyominoes are shapes that are made by gluing identical squares along their edges. A domino is a shape made from two squares glued along an edge: A triomino is a shape made from three squares. There are only two different trominoes: A tetromino is a shape made from gluing four squares together.these two blue tetrominoes are actually the same because one can be rotated and flipped on its back to make the other. These two tetrominoes are different. How many different tetrominoes can you find? A pentomino is a shape made from gluing five squares. The picture on The right shows two different pentominoes. How many different pentominoes are there? 12
14 Problem of the Week {Gauss Math Contest: University of Waterloo} Measurement Strand Need: Interlocking Cubes Tabia has 18 blocks. Show the number of different solid, rectangular prisms she can build, using all 18 cubes. Note: A rectangular prism is a 3-D figure with six rectangular faces. 13
15 Noah {Number Sense and Numeration} Noah watched the animals going into the ark. He was counting the legs of the animals and by noon he got to 12. How many creatures did he see? See if you can find other answers. Try to tell someone how you found out these answers. 14
16 There are three baskets, a brown one, a red one and a pink one, holding a total of ten eggs. The Brown basket has one more egg in it than the Red basket. The Red basket has three fewer eggs than the Pink basket. How many eggs are in each basket? 15
17 The Prisoners [Data Management and Probability] How would you place 6 counters in the cells, so that you can remove them before your partner? No. of Players: Two Need: Two Number cubes {Dice} Rules: a) Each player can place his/her counters into any cells on his/her own game board. b) You can place one in each cell, or two in some cells and none in others, or all six in one cell. c) Take turns to roll the number cubes. Calculate the difference between the two numbers. You can remove one counter (only one) from the cell with that number. d) The winner is the first to remove all his/her counters from the board. 16
18 Tangrams {Spatial Sense and Geometry} a) If the area of the small triangle is one square unit, what is the area of the other pieces? b) If the value of the square is twenty cents, what is the value of the other pieces? Making Polygons with Tangram Pieces Triangle Square Rectangle Parallelogram Rhombus Pentagon 2 pieces 3 pieces 4 pieces 5 pieces 6 pieces 7 pieces Comments 17
19 Geoboards {Geometry and Spatial Sense} Need: Geoboards Part A Try to make each of the following quadrilaterals {four-sided figures} on your geoboard. How many of each can you make? a) 4 equal sides b) 3 equal sides c) 2 equal sides d) one pair of perpendicular sides e) two pairs of perpendicular sides f) a right isosceles triangle g) a right scalene triangle Part B a) How many different (?) triangles can you make on a geoboard? b) How many different {?} quadrilaterals can you make on a geoboard? c) How many different sizes of squares can you make on a 5 by 5 geoboard? d) How many non-congruent figures can you make with an area of 2 square units? 18
20 How Much Can We Spend? {Number Sense and Numeration} A country has decided to have just two different coins. It has been suggested that these should be 3z and 5z coins. The shops think this is a good idea since most totals can be made. 2 3z+1 5z=11z 7 3z+2 5z=31z Unfortunately some totals can't be made, for example 4z. Which totals can be made? Is there a largest total that cannot be made? How do you know? They have decided that they will definitely have 3z coins but can't make up their minds about the other coin. 19
21 Experiment with other pairings containing 3z, and explore which totals can be made. Can you find a relationship between 3z, the second coin, and the totals that can and can't be made? In other countries they have also decided to have just two coins, but instead of the 3z coins they have chosen a different prime number. Can you find a relationship between pairs of coin values and the totals that can and can't be made with them? 20
22 Medal Muddle {Spatial Sense} Thirteen nations competed in a sports tournament. Unfortunately, we do not have the final medal table, but we have the following pieces of information: 1. Turkey and Mexico both finished above Italy and New Zealand. 2. Portugal finished above Venezuela, Mexico, Spain and Romania. 3. Romania finished below Algeria, Greece, Spain and Serbia. 4. Serbia finished above Turkey and Portugal, both of whom finished below Algeria and Russia. 5. Russia finished above France and Algeria. 6. Algeria finished below France but above Serbia and Spain. 7. Italy finished below Greece and Venezuela, but above New Zealand. 8. Venezuela finished above New Zealand but below Greece. 9. Greece finished below Turkey, who came below France. 10. Portugal finished below Greece and France. 11. France finished above Serbia, who came above Mexico. 12. Venezuela finished below Mexico, and New Zealand came above Spain. Can you recreate the medal table from this information? Can you describe an efficient strategy for solving problems like this? 21
23 What's it worth? {Patterning and Algebra} Each symbol has a numerical value. The total for the symbols is written at the end of each row and column. Can you find the missing total that should go where the question mark has been put? 22
24 Cuboid Challenge {Measurement} From a square sheet of paper 20cm by 20cm, we can make a box without a lid by cutting a square from each corner and folding up the flaps. Find the different volumes of box it is possible to make by varying the size of the cut-out squares. What is the maximum possible volume? What is the size of the square cut-out that produces it? 23
25 Shape Times Shape {Patterning and Algebra} The shaded shapes stand for eleven of the numbers from 0 to 12. Each shape is a different number. Can you work out what they are from the multiplications below? 24
26 Spatial; Sense Task for Young Mathematicians Read the clues and put the letters in the grids. Task 1 A is on the bottom. B is on the right. C is under D. D you know where it is! Task 2 A is not on the left. B is not under C. C is on the bottom, on the right. D is on top. Task 3 A is under C. B is on the bottom. C I forgot D is on the left. Task 4 A is on the right. B is on the left. C is o top. D is under A. 25
27 Task 5 A is in a corner. B is between D and F. C is touching F. D is touching A. E is on top, on the left. F is on the left. Task 6 A is under E. B is in a corner on top. C is not touching E. D is on the bottom, but not on the left. E is on the right. F is on top. Task 7 A is touching E. B is not in the middle. C is between A and F. D is on the right. E is next to D. F is on the bottom. Can you figure out two different solutions? 26
28 Task 8 A is in a corner on the bottom. B is to the left of G. C is next to H. D is in the centre. E is touching D. F is under E. G is under D. H is on top. I is between A and C. Task 9 A is touching C and D. B is under H. C is on the left. D is on the bottom, on the right. E is next to H. F is not touching D. G is in the centre. H is on the left. I is touching D. 27
29 Biscuit Decorations {Number Sense and Numeration} Andrew decorated 20 biscuits to take to a party. He lined them up and put icing on every second biscuit. Then he put a cherry on every third biscuit. Then he put a chocolate button on every fourth biscuit. So there was nothing on the first biscuit. How many other biscuits had no decoration? Did any biscuits get all three decorations? 28
30 2-digit 1-digit Multiplication Arrays {Base Ten Materials} Begin with 2-digit 1-digit problems. Gauge your students' understanding in this activity to determine the pacing for the 2-digit 2-digit activity. Work through the example problem 14 6 to introduce the solution method. Before you begin showing students arrays, have them estimate the answer. This helps develop mental math skills and gives a benchmark to judge accuracy when they complete the problem. Since 14 is closer to 10 than 20, approximate the answer to be about 10 6 = 60. Since we rounded down, the actual answer will be a bit bigger than 60. Model the partial product arrays for students using the 14 6 example. Model the following steps, using the illustration as a guide: Decompose the first factor into tens and ones to give (10 + 4) 6. The problem can now be solved using the distributive property. Draw an array that is Break the 14-unit horizontal line into a tens piece and ones piece. In this case, the pieces will be 10 and 4. Draw a vertical line through the rectangle at this point, creating two rectangles. Label the length and width of both rectangles. Label the 10 6 rectangle as 60, and the 4 6 rectangle as 24, as shown. The rectangles represent 2 partial products. Ask the students what to do with the 60 and 24. It is important that students know that partial means each array represents just part of the problem. They should also understand that to get the total product you need to add. The solution is = 84. As you model, have students participate by coming up to help build the model. Next, demonstrate solving another problem while students create their own base 10 block or paper grid models. Have less capable students work with a partner. To transition to more individualized work, have individuals and pairs compare their work with that of others and describe their partial arrays aloud. Do as many problems as needed to support your variety of learners. Keep in mind that large 2-digit numbers get unwieldy to work with; numbers between 10 and 30 work the best for modeling. 29
31 2-digit 2-digit Multiplication Arrays Model the problem Once students understand the process, they can work problems at your direction for continual practice. Important points for 2-digit by 2-digit multiplication include: The problem must be decomposed. It becomes (10 + 3) (10 + 6). Draw an array that is 13 by 16. Decompose the factors by breaking the array into smaller pieces. Break the 13-unit horizontal line into 10- and 3-unit long pieces. Then, break the 16-unit vertical line into 10- and 6-unit long pieces. Draw lines to separate the tens from the ones (10 from 3 and 10 from 6). This creates 4 rectangles. Label the outside dimensions. Students should be able to see the 4 partial products of this problem: (10 10), (3 10), (6 10), and (3 6). Label the inside areas of the 4 partial products. Finally, add the partial products together: =
32 Low Stress Long Division {Very Easy!} Context: How many packages of 8 cookies if there are 348 cookies to package? Using just the 10 x, 5 x, 2 x and 1 x tables {8 x 10} {8 x 20} {8 x {2 x 8} {1 x 8} r 4 {Answer} 31
33 Ten Frames 32
34 Arranging Colour Tiles Task #1 The yellow tile is not at the bottom. The blue tile is not between the green tile and the red tile. The green tile is between the yellow tile and the blue tile. The red tile is above the yellow tile. Task #2 The red tile is somewhere below the yellow tile. The blue tile is somewhere above the yellow tile. The top tile is not blue. The tile below the green tile is red. Task #3 No tiles of the same colour are next to each other. The yellow tile is not at the bottom. The blue tile is not between the green tile and the red tile. The green tile is between the yellow tile and the blue tile. The red tile is above the yellow tile. 33
35 Always, Sometimes or Never? {Assessment Tasks} Are the following statements always true, sometimes true or never true? 34
36 35
37 A Brief History of Magic Squares Magic squares have a rich history dating to around 2200 B.C. A Chinese myth claimed that while the Chinese Emperor Yu was walking along the Yellow River, he noticed a tortoise with a unique diagram on its shell (see the picture to the right). The Emperor decided to call the unusual numerical pattern lo shu. The earliest magic square on record, however, appeared in the first-century book Da-Dai Liji. Use the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 to form a Magic Square. The horizontal, vertical, and diagonal sums are the same. The original Magic Square 36
38 A Dicey Situation [Data Management and Probability] Jamie made up a new dice game. Two players each roll an ordinary six-sided die. Of the two numbers showing, the smaller is subtracted from the larger. Scoring: If the difference is 0, 1, or 2, player A gets 1 point. If the difference is 3, 4, or 5, player B gets 1 point. The game ends after 12 rounds. The player with the most points wins the game. If you were given the choice of being Player A or Player B, which would you pick, assuming you want to win? Remember to explain all the steps you use in making your decision. Extra: Describe another way of scoring that is fair for this game of differences. Explain how you know it is fair. [A mathematician considers a game to be fair if all players have an equal chance of winning.] 37
LEARNING ABOUT MATH FOR K TO 5. Dorset Public School. April 6, :30 pm 8:00 pm. presented by Kathy Kubota-Zarivnij
 LEARNING ABOUT MATH FOR K TO 5 Dorset Public School April 6, 2016 6:30 pm 8:00 pm presented by Kathy Kubota-Zarivnij kathkubo@rogers.com TODAY S MATH TOOLS FOR colour square tiles Hexalink cubes KKZ, 2016
LEARNING ABOUT MATH FOR K TO 5 Dorset Public School April 6, 2016 6:30 pm 8:00 pm presented by Kathy Kubota-Zarivnij kathkubo@rogers.com TODAY S MATH TOOLS FOR colour square tiles Hexalink cubes KKZ, 2016
Meet #5 March Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts
 Meet #5 March 2008 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet #5 March 2008 Category 1 Mystery 1. In the diagram to the right, each nonoverlapping section of the large rectangle is
Meet #5 March 2008 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet #5 March 2008 Category 1 Mystery 1. In the diagram to the right, each nonoverlapping section of the large rectangle is
Exploring Concepts with Cubes. A resource book
 Exploring Concepts with Cubes A resource book ACTIVITY 1 Gauss s method Gauss s method is a fast and efficient way of determining the sum of an arithmetic series. Let s illustrate the method using the
Exploring Concepts with Cubes A resource book ACTIVITY 1 Gauss s method Gauss s method is a fast and efficient way of determining the sum of an arithmetic series. Let s illustrate the method using the
Essentials. Week by. Week. Calculate!
 Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade WEEK 7 Calculate! Find two numbers whose product would be between 0 and 50. Can you find more solutions? Find two numbers whose product would be between,500 and,600.
Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade WEEK 7 Calculate! Find two numbers whose product would be between 0 and 50. Can you find more solutions? Find two numbers whose product would be between,500 and,600.
Use repeated addition to find the total number of fingers. Find the total of each group by using repeated addition. Multiplication and Division
 Introducing multiplication groups of 5 Use repeated addition to find the total number of fingers. 5 + 5 + 5 = 5 groups of 5 is equal to 5. Find the total of each group by using repeated addition. a How
Introducing multiplication groups of 5 Use repeated addition to find the total number of fingers. 5 + 5 + 5 = 5 groups of 5 is equal to 5. Find the total of each group by using repeated addition. a How
MATHEMATICS. Name: Primary School: Boy or Girl: Date of Birth: Today s Date: Test taken at:
 MATHEMATICS Name: Primary School: Boy or Girl: Date of Birth: Today s Date: Test taken at: READ THE FOLLOWING CAREFULLY 1. Do not open this booklet until you are told to do so. 2. You may work the questions
MATHEMATICS Name: Primary School: Boy or Girl: Date of Birth: Today s Date: Test taken at: READ THE FOLLOWING CAREFULLY 1. Do not open this booklet until you are told to do so. 2. You may work the questions
LEARNING ABOUT MATH FOR GR 1 TO 2. Conestoga Public School OCTOBER 13, presented by Kathy Kubota-Zarivnij
 LEARNING ABOUT MATH FOR GR 1 TO 2 Conestoga Public School OCTOBER 13, 2016 6:30 pm 8:00 pm presented by Kathy Kubota-Zarivnij kathkubo@gmail.com TODAY S MATH TOOLS FOR counters playing cards dice interlocking
LEARNING ABOUT MATH FOR GR 1 TO 2 Conestoga Public School OCTOBER 13, 2016 6:30 pm 8:00 pm presented by Kathy Kubota-Zarivnij kathkubo@gmail.com TODAY S MATH TOOLS FOR counters playing cards dice interlocking
Multiplication and Division
 D Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic 1 Introducing multiplication (pp. 1 7) groups of 5 5 times table 10 times table multiplying any number by 10 multiplying numbers by 0 and 1 Date completed Topic
D Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic 1 Introducing multiplication (pp. 1 7) groups of 5 5 times table 10 times table multiplying any number by 10 multiplying numbers by 0 and 1 Date completed Topic
Year 1. Mastery Overview Autumn
 Mastery Overview Autumn SOL Overview As well as providing term by term overviews for the new as a Maths Hub we are aiming to support primary schools by providing more detailed Schemes of Learning, which
Mastery Overview Autumn SOL Overview As well as providing term by term overviews for the new as a Maths Hub we are aiming to support primary schools by providing more detailed Schemes of Learning, which
Geometry. Learning Goals U N I T
 U N I T Geometry Building Castles Learning Goals describe, name, and sort prisms construct prisms from their nets construct models of prisms identify, create, and sort symmetrical and non-symmetrical shapes
U N I T Geometry Building Castles Learning Goals describe, name, and sort prisms construct prisms from their nets construct models of prisms identify, create, and sort symmetrical and non-symmetrical shapes
Multiplication and Division
 E Student Book 6 7 = 4 Name Series E Contents Topic Multiplication facts (pp. 7) 5 and 0 times tables and 4 times tables 8 times table and 6 times tables Date completed Topic Using known facts (pp. 8 )
E Student Book 6 7 = 4 Name Series E Contents Topic Multiplication facts (pp. 7) 5 and 0 times tables and 4 times tables 8 times table and 6 times tables Date completed Topic Using known facts (pp. 8 )
Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities
 Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities For more information about the materials you find in this packet, contact: Sharon Rendon (605) 431-0216 sharonrendon@cpm.org 1 2-51. SPECIAL
Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities For more information about the materials you find in this packet, contact: Sharon Rendon (605) 431-0216 sharonrendon@cpm.org 1 2-51. SPECIAL
Lines and angles parallel and perpendicular lines. Look at each group of lines. Tick the parallel lines.
 Lines and angles parallel and perpendicular lines Parallel lines are always the same distance away from each other at any point and can never meet. They can be any length and go in any direction. Look
Lines and angles parallel and perpendicular lines Parallel lines are always the same distance away from each other at any point and can never meet. They can be any length and go in any direction. Look
Job Cards and Other Activities. Write a Story for...
 Job Cards and Other Activities Introduction. This Appendix gives some examples of the types of Job Cards and games that we used at the Saturday Clubs. We usually set out one type of card per table, along
Job Cards and Other Activities Introduction. This Appendix gives some examples of the types of Job Cards and games that we used at the Saturday Clubs. We usually set out one type of card per table, along
Contents. The Counting Stick 2. Squashy Boxes 5. Piles of Dominoes 6. Nelly Elephants 7. Sneaky Snakes 9. Data in Games 11. Day and Night Game 12
 Contents Title Page The Counting Stick 2 Squashy Boxes 5 Piles of Dominoes 6 Nelly Elephants 7 Sneaky Snakes 9 Data in Games 11 Day and Night Game 12 Favourite Instrument 14 2 The Counting Stick A counting
Contents Title Page The Counting Stick 2 Squashy Boxes 5 Piles of Dominoes 6 Nelly Elephants 7 Sneaky Snakes 9 Data in Games 11 Day and Night Game 12 Favourite Instrument 14 2 The Counting Stick A counting
CPM Educational Program
 CC COURSE 2 ETOOLS Table of Contents General etools... 5 Algebra Tiles (CPM)... 6 Pattern Tile & Dot Tool (CPM)... 9 Area and Perimeter (CPM)...11 Base Ten Blocks (CPM)...14 +/- Tiles & Number Lines (CPM)...16
CC COURSE 2 ETOOLS Table of Contents General etools... 5 Algebra Tiles (CPM)... 6 Pattern Tile & Dot Tool (CPM)... 9 Area and Perimeter (CPM)...11 Base Ten Blocks (CPM)...14 +/- Tiles & Number Lines (CPM)...16
CHARACTERISTICS AND CLASSIFICATION OF SHAPES and 1.3.2
 CHARACTERISTICS AND CLASSIFICATION OF SHAPES 1.3.1 and 1.3.2 Geometric shapes occur in many places. After studying them using transformations, students start to see certain characteristics of different
CHARACTERISTICS AND CLASSIFICATION OF SHAPES 1.3.1 and 1.3.2 Geometric shapes occur in many places. After studying them using transformations, students start to see certain characteristics of different
Angles and. Learning Goals U N I T
 U N I T Angles and Learning Goals name, describe, and classify angles estimate and determine angle measures draw and label angles provide examples of angles in the environment investigate the sum of angles
U N I T Angles and Learning Goals name, describe, and classify angles estimate and determine angle measures draw and label angles provide examples of angles in the environment investigate the sum of angles
Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary. Correlations
 Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary Correlations Saxon Math Program Page Math K 2 Math 1 8 Math 2 14 California Math K 21 California Math 1 27 California Math 2 33 1 Saxon Math Manipulatives in
Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary Correlations Saxon Math Program Page Math K 2 Math 1 8 Math 2 14 California Math K 21 California Math 1 27 California Math 2 33 1 Saxon Math Manipulatives in
= 20 + = = 2 30 = 2 15 = = + 10 = = = 40 2 = = + 20 = = = 8 2 =
 Answers will vary. This is one example. Name MENTAL MATHS Addition & Subtraction Multiplication + = + = = = = + = + = = = = + = + = = = = + = + = = = = + = + = = = = Number & place value Write each number
Answers will vary. This is one example. Name MENTAL MATHS Addition & Subtraction Multiplication + = + = = = = + = + = = = = + = + = = = = + = + = = = = + = + = = = = Number & place value Write each number
The learner will recognize and use geometric properties and relationships.
 The learner will recognize and use geometric properties and relationships. Notes 3and textbook 3.01 Use the coordinate system to describe the location and relative position of points and draw figures in
The learner will recognize and use geometric properties and relationships. Notes 3and textbook 3.01 Use the coordinate system to describe the location and relative position of points and draw figures in
Geometry 2001 part 1
 Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
Year 4. Term by Term Objectives. Year 4 Overview. Autumn. Spring Number: Fractions. Summer. Number: Addition and Subtraction.
 Summer Overview Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Autumn Number: Place Value Number: Addition and Subtraction Number: Multiplication and Division Measurement:
Summer Overview Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Autumn Number: Place Value Number: Addition and Subtraction Number: Multiplication and Division Measurement:
Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Wednesday, February 22, 2006
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Wednesday, February 22, 2006 C.M.C.
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Wednesday, February 22, 2006 C.M.C.
Addition and Subtraction
 D Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic 1 Addition mental strategies (pp. 114) look for a ten look for patterns doubles and near doubles bridge to ten jump strategy split strategy version 1 split strategy
D Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic 1 Addition mental strategies (pp. 114) look for a ten look for patterns doubles and near doubles bridge to ten jump strategy split strategy version 1 split strategy
Grade 6 Math Circles February 15, 2012 Math Puzzles
 1 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles February 15, 2012 Math Puzzles Problem Solving Tips 1) Read and re-read the question.
1 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles February 15, 2012 Math Puzzles Problem Solving Tips 1) Read and re-read the question.
Milton Public Schools Elementary Summer Math
 Milton Public Schools Elementary Summer Math Did you know that the average American child loses between 1 and 3 months of learning in reading and math each summer? You can continue to love and enjoy your
Milton Public Schools Elementary Summer Math Did you know that the average American child loses between 1 and 3 months of learning in reading and math each summer? You can continue to love and enjoy your
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
QUESTION 4(1) 4(F) 5(1) 5(F) 6(1) 6(F) 7(1) 7(F) VRAAG
 MEMORANDUM 20 QUESTION () (F) 5() 5(F) 6() 6(F) 7() 7(F) VRAAG D E C A B B B A 2 B B B B A B C D 2 A B C A E C B B E C C B E E A C 5 C C C E E D A B 5 6 E B D B D C D D 6 7 D C B B D A A B 7 8 B B E A
MEMORANDUM 20 QUESTION () (F) 5() 5(F) 6() 6(F) 7() 7(F) VRAAG D E C A B B B A 2 B B B B A B C D 2 A B C A E C B B E C C B E E A C 5 C C C E E D A B 5 6 E B D B D C D D 6 7 D C B B D A A B 7 8 B B E A
Shuli s Math Problem Solving Column
 Shuli s Math Problem Solving Column Volume 1, Issue 19 May 1, 2009 Edited and Authored by Shuli Song Colorado Springs, Colorado shuli_song@yahoocom Contents 1 Math Trick: Mental Calculation: 199a 199b
Shuli s Math Problem Solving Column Volume 1, Issue 19 May 1, 2009 Edited and Authored by Shuli Song Colorado Springs, Colorado shuli_song@yahoocom Contents 1 Math Trick: Mental Calculation: 199a 199b
Essentials. Week by. Week. Calculate! What is the largest product you can compute on your calculator? largest quotient?
 Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade WEEK 5 Calculate! What is the largest product you can compute on your calculator? largest quotient? Is the answer the same for all the calculators in your class?
Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade WEEK 5 Calculate! What is the largest product you can compute on your calculator? largest quotient? Is the answer the same for all the calculators in your class?
Cross Out Singles. 3. Players then find the sums of the rows, columns, and diagonal, and record them in the respective circles.
 Materials: Cross Out Singles recording sheet, and 1 die. Cross Out Singles How To Play: 1. The die is rolled. Both players put this number in whichever one of the squares on their Round 1 chart they choose.
Materials: Cross Out Singles recording sheet, and 1 die. Cross Out Singles How To Play: 1. The die is rolled. Both players put this number in whichever one of the squares on their Round 1 chart they choose.
Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD. We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential
 Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential Grade 2 Module 8 Parent Handbook The materials contained within this packet have been taken
Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential Grade 2 Module 8 Parent Handbook The materials contained within this packet have been taken
Instruction Cards Sample
 Instruction Cards Sample mheducation.com/prek-12 Instruction Cards Table of Contents Level A: Tunnel to 100... 1 Level B: Race to the Rescue...15 Level C: Fruit Collector...35 Level D: Riddles in the Labyrinth...41
Instruction Cards Sample mheducation.com/prek-12 Instruction Cards Table of Contents Level A: Tunnel to 100... 1 Level B: Race to the Rescue...15 Level C: Fruit Collector...35 Level D: Riddles in the Labyrinth...41
2nd Grade Facts Presentation
 Slide 1 / 246 Slide 2 / 246 2nd Grade Facts Presentation 1 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 246 Presentation 1 Table of Contents Facts Click on a topic to go to that section. Recall from Memory Addition
Slide 1 / 246 Slide 2 / 246 2nd Grade Facts Presentation 1 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 246 Presentation 1 Table of Contents Facts Click on a topic to go to that section. Recall from Memory Addition
Second Grade Mathematics Goals
 Second Grade Mathematics Goals Operations & Algebraic Thinking 2.OA.1 within 100 to solve one- and twostep word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart,
Second Grade Mathematics Goals Operations & Algebraic Thinking 2.OA.1 within 100 to solve one- and twostep word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart,
Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities
 Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities For more information about the materials you find in this packet, contact: Chris Mikles 916-719-3077 chrismikles@cpm.org 1 2 2-51. SPECIAL
Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities For more information about the materials you find in this packet, contact: Chris Mikles 916-719-3077 chrismikles@cpm.org 1 2 2-51. SPECIAL
5 th /6 th Grade Test February 4, 2017
 DO NOT OPEN UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO Don Bosco Technical Institute proudly presents the 45 th Annual Mathematics Contest Directions: This test contains 30 questions. 5 th /6 th Grade Test February 4,
DO NOT OPEN UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO Don Bosco Technical Institute proudly presents the 45 th Annual Mathematics Contest Directions: This test contains 30 questions. 5 th /6 th Grade Test February 4,
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM MATHEMATICS
 THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 2 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 8 January 2016 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 2 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 8 January 2016 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
UK JUNIOR MATHEMATICAL CHALLENGE. April 25th 2013 EXTENDED SOLUTIONS
 UK JUNIOR MATHEMATICAL CHALLENGE April 5th 013 EXTENDED SOLUTIONS These solutions augment the printed solutions that we send to schools. For convenience, the solutions sent to schools are confined to two
UK JUNIOR MATHEMATICAL CHALLENGE April 5th 013 EXTENDED SOLUTIONS These solutions augment the printed solutions that we send to schools. For convenience, the solutions sent to schools are confined to two
Year 9 mathematics: holiday revision. 2 How many nines are there in fifty-four?
 DAY 1 ANSWERS Mental questions 1 Multiply seven by seven. 49 2 How many nines are there in fifty-four? 54 9 = 6 6 3 What number should you add to negative three to get the answer five? -3 0 5 8 4 Add two
DAY 1 ANSWERS Mental questions 1 Multiply seven by seven. 49 2 How many nines are there in fifty-four? 54 9 = 6 6 3 What number should you add to negative three to get the answer five? -3 0 5 8 4 Add two
International Contest-Game MATH KANGAROO Canada, 2007
 International Contest-Game MATH KANGAROO Canada, 007 Grade 9 and 10 Part A: Each correct answer is worth 3 points. 1. Anh, Ben and Chen have 30 balls altogether. If Ben gives 5 balls to Chen, Chen gives
International Contest-Game MATH KANGAROO Canada, 007 Grade 9 and 10 Part A: Each correct answer is worth 3 points. 1. Anh, Ben and Chen have 30 balls altogether. If Ben gives 5 balls to Chen, Chen gives
LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII. Mathematics Laboratory
 LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII Mathematics Laboratory The concept of Mathematics Laboratory has been introduced by the Board in its affiliated schools with the objective
LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII Mathematics Laboratory The concept of Mathematics Laboratory has been introduced by the Board in its affiliated schools with the objective
Chapter 4: Patterns and Relationships
 Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
Building Successful Problem Solvers
 Building Successful Problem Solvers Genna Stotts Region 16 ESC How do math games support problem solving for children? 1. 2. 3. 4. Diffy Boxes (Draw a large rectangle below) 1 PIG (Addition & Probability)
Building Successful Problem Solvers Genna Stotts Region 16 ESC How do math games support problem solving for children? 1. 2. 3. 4. Diffy Boxes (Draw a large rectangle below) 1 PIG (Addition & Probability)
A = 5; B = 4; C = 3; B = 2; E = 1; F = 26; G = 25; H = 24;.; Y = 7; Z = 6 D
 1. message is coded from letters to numbers using this code: = 5; B = 4; = 3; B = 2; E = 1; F = 26; G = 25; H = 24;.; Y = 7; Z = 6 When the word MISSISSIPPI is coded, what is the sum of all eleven numbers?.
1. message is coded from letters to numbers using this code: = 5; B = 4; = 3; B = 2; E = 1; F = 26; G = 25; H = 24;.; Y = 7; Z = 6 When the word MISSISSIPPI is coded, what is the sum of all eleven numbers?.
Counting in 4s, 8s, 50s and 100s Page 8
 Counting in 4s, 8s, 50s and 100s Page 8 1 Add 2 2 Add 10 3 Add 3 4 10, 30, 35 5 52, 62, 102 6 31, 51, 61 1 12, 16, 20 2 24, 32, 48 3 300, 400, 600 4 75 5 350 6 14 1 Horizontal row: 12 / Vertical column:
Counting in 4s, 8s, 50s and 100s Page 8 1 Add 2 2 Add 10 3 Add 3 4 10, 30, 35 5 52, 62, 102 6 31, 51, 61 1 12, 16, 20 2 24, 32, 48 3 300, 400, 600 4 75 5 350 6 14 1 Horizontal row: 12 / Vertical column:
Grade 3 NAPLAN preparation pack:
 Grade 3 NAPLAN preparation pack: Below is a guide with example questions to use with students preparing for NAPLAN for three weeks prior to the test. By this stage students are expected to have spent a
Grade 3 NAPLAN preparation pack: Below is a guide with example questions to use with students preparing for NAPLAN for three weeks prior to the test. By this stage students are expected to have spent a
Let s Make. Math Fun. Volume 19 January/February Dice Challenges. Telling the Time. Printable Games. Mastering Multiplication.
 Let s Make Volume 19 January/February 2013 Math Fun Dice Challenges Printable Games Telling the Time Mastering Multiplication Bingo Math Fun Help Them to Fall in Love with Math THE LET S MAKE MATH FUN
Let s Make Volume 19 January/February 2013 Math Fun Dice Challenges Printable Games Telling the Time Mastering Multiplication Bingo Math Fun Help Them to Fall in Love with Math THE LET S MAKE MATH FUN
2.NBT.1 20) , 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, NBT.2
 Saxon Math 2 Class Description: Saxon mathematics is based on the principle of developing math skills incrementally and reviewing past skills daily. It also incorporates regular and cumulative assessments.
Saxon Math 2 Class Description: Saxon mathematics is based on the principle of developing math skills incrementally and reviewing past skills daily. It also incorporates regular and cumulative assessments.
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES -
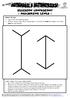 ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
Notes ~ 1. Frank Tapson 2004 [trolxp:2]
![Notes ~ 1. Frank Tapson 2004 [trolxp:2] Notes ~ 1. Frank Tapson 2004 [trolxp:2]](/thumbs/82/86361598.jpg) Pentominoes Notes ~ 1 Background This unit is concerned with providing plenty of spatial work within a particular context. It could justifiably be titled Puzzling with Pentominoes. Pentominoes are just
Pentominoes Notes ~ 1 Background This unit is concerned with providing plenty of spatial work within a particular context. It could justifiably be titled Puzzling with Pentominoes. Pentominoes are just
Shapes. Practice. Family Note. Unit. show 3-sided, 4-sided, 5-sided, and 6-sided shapes. Ask an adult for permission first. Add.
 Home Link 8-1 Shapes In this lesson children examined different shapes, such as triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and hexagons. They also discussed these shapes attributes or characteristics such as
Home Link 8-1 Shapes In this lesson children examined different shapes, such as triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and hexagons. They also discussed these shapes attributes or characteristics such as
UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet 24.1 The Pythagorean Theorem Explore the Pythagorean theorem numerically, algebraically, and geometrically. Understand a proof
Name Period Date UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet 24.1 The Pythagorean Theorem Explore the Pythagorean theorem numerically, algebraically, and geometrically. Understand a proof
Grade 6 Middle School Mathematics Contest A parking lot holds 64 cars. The parking lot is 7/8 filled. How many spaces remain in the lot?
 Grade 6 Middle School Mathematics Contest 2004 1 1. A parking lot holds 64 cars. The parking lot is 7/8 filled. How many spaces remain in the lot? a. 6 b. 8 c. 16 d. 48 e. 56 2. How many different prime
Grade 6 Middle School Mathematics Contest 2004 1 1. A parking lot holds 64 cars. The parking lot is 7/8 filled. How many spaces remain in the lot? a. 6 b. 8 c. 16 d. 48 e. 56 2. How many different prime
Situations Involving Multiplication and Division with Products to 50
 Mathematical Ideas Composing, decomposing, addition, and subtraction of numbers are foundations of multiplication and division. The following are examples of situations that involve multiplication and/or
Mathematical Ideas Composing, decomposing, addition, and subtraction of numbers are foundations of multiplication and division. The following are examples of situations that involve multiplication and/or
Correlation of Nelson Mathematics 2 to The Ontario Curriculum Grades 1-8 Mathematics Revised 2005
 Correlation of Nelson Mathematics 2 to The Ontario Curriculum Grades 1-8 Mathematics Revised 2005 Number Sense and Numeration: Grade 2 Section: Overall Expectations Nelson Mathematics 2 read, represent,
Correlation of Nelson Mathematics 2 to The Ontario Curriculum Grades 1-8 Mathematics Revised 2005 Number Sense and Numeration: Grade 2 Section: Overall Expectations Nelson Mathematics 2 read, represent,
Notes ~ 1. CIMT; University of Exeter 2001 [trolxp:2]
![Notes ~ 1. CIMT; University of Exeter 2001 [trolxp:2] Notes ~ 1. CIMT; University of Exeter 2001 [trolxp:2]](/thumbs/71/66218984.jpg) Pentominoes 0012345 0012345 0012345 0012345 0012345 0012345 0012345 0012345 789012345 789012345 789012345 789012345 789012345 789012345 789012345 789012345 0012345 0012345 0012345 0012345 0012345 0012345
Pentominoes 0012345 0012345 0012345 0012345 0012345 0012345 0012345 0012345 789012345 789012345 789012345 789012345 789012345 789012345 789012345 789012345 0012345 0012345 0012345 0012345 0012345 0012345
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet
 GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. a) Study: 6 units 6 tens 6 hundreds 6 thousands 6 ten-thousands 6 hundredthousands HTh T Th Th H T U 6 6 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. a) Study: 6 units 6 tens 6 hundreds 6 thousands 6 ten-thousands 6 hundredthousands HTh T Th Th H T U 6 6 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0
Foundation Stage. Using and applying mathematics. Framework review. Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems
 Foundation Stage Using and applying mathematics Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems Look at the apples. Are there more green apples or more red apples? How can you
Foundation Stage Using and applying mathematics Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems Look at the apples. Are there more green apples or more red apples? How can you
MANIPULATIVE MATHEMATICS FOR STUDENTS
 MANIPULATIVE MATHEMATICS FOR STUDENTS Manipulative Mathematics Using Manipulatives to Promote Understanding of Elementary Algebra Concepts Lynn Marecek MaryAnne Anthony-Smith This file is copyright 07,
MANIPULATIVE MATHEMATICS FOR STUDENTS Manipulative Mathematics Using Manipulatives to Promote Understanding of Elementary Algebra Concepts Lynn Marecek MaryAnne Anthony-Smith This file is copyright 07,
Hundreds Grid. MathShop: Hundreds Grid
 Hundreds Grid MathShop: Hundreds Grid Kindergarten Suggested Activities: Kindergarten Representing Children create representations of mathematical ideas (e.g., use concrete materials; physical actions,
Hundreds Grid MathShop: Hundreds Grid Kindergarten Suggested Activities: Kindergarten Representing Children create representations of mathematical ideas (e.g., use concrete materials; physical actions,
Chapter 4 Number Theory
 Chapter 4 Number Theory Throughout the study of numbers, students Á should identify classes of numbers and examine their properties. For example, integers that are divisible by 2 are called even numbers
Chapter 4 Number Theory Throughout the study of numbers, students Á should identify classes of numbers and examine their properties. For example, integers that are divisible by 2 are called even numbers
SPIRE MATHS Stimulating, Practical, Interesting, Relevant, Enjoyable Maths For All
 Imaginings in shape and space TYPE: Main OBJECTIVE(S): DESCRIPTION: OVERVIEW: EQUIPMENT: Begin to identify and use angle, side and symmetry properties of triangles and quadrilaterals; solve geometrical
Imaginings in shape and space TYPE: Main OBJECTIVE(S): DESCRIPTION: OVERVIEW: EQUIPMENT: Begin to identify and use angle, side and symmetry properties of triangles and quadrilaterals; solve geometrical
Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers
 Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Student Book Series D Mathletics Instant Workbooks Copyright Contents Series D Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Looking at whole numbers reading and
Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Student Book Series D Mathletics Instant Workbooks Copyright Contents Series D Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Looking at whole numbers reading and
SECOND EDITION HOME CONNECTIONS GRADE
 SECOND EDITION HOME CONNECTIONS GRADE 1 Bridges in Mathematics Second Edition Grade 1 Home Connections Volumes 1 & 2 The Bridges in Mathematics Grade 1 package consists of: Bridges in Mathematics Grade
SECOND EDITION HOME CONNECTIONS GRADE 1 Bridges in Mathematics Second Edition Grade 1 Home Connections Volumes 1 & 2 The Bridges in Mathematics Grade 1 package consists of: Bridges in Mathematics Grade
A Focus on Proportional Reasoning, Grades 4-8
 A Focus on Proportional Reasoning, Grades 4-8 February, 2015 Marian Small Agenda What does/can proportional reasoning look like in Grades 4 8? Agenda What have we seen Ontario students do when confronted
A Focus on Proportional Reasoning, Grades 4-8 February, 2015 Marian Small Agenda What does/can proportional reasoning look like in Grades 4 8? Agenda What have we seen Ontario students do when confronted
Winter Quarter Competition
 Winter Quarter Competition LA Math Circle (Advanced) March 13, 2016 Problem 1 Jeff rotates spinners P, Q, and R and adds the resulting numbers. What is the probability that his sum is an odd number? Problem
Winter Quarter Competition LA Math Circle (Advanced) March 13, 2016 Problem 1 Jeff rotates spinners P, Q, and R and adds the resulting numbers. What is the probability that his sum is an odd number? Problem
Ready Made Mathematical Task Cards
 Mathematical Resource Package For Number Sense and Numeration, Grades 4 to 6 Ready Made Mathematical Task Cards Made For Teachers By Teachers Developed By: J. Barretto-Mendoca, K. Bender, A. Conidi, T.
Mathematical Resource Package For Number Sense and Numeration, Grades 4 to 6 Ready Made Mathematical Task Cards Made For Teachers By Teachers Developed By: J. Barretto-Mendoca, K. Bender, A. Conidi, T.
Essentials. Week by. Week. Investigations. Let s Write Write a note to explain to your teacher how you and your partner played Race to a Dollar.
 Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade 2 WEEK 17 Let s Write Write a note to explain to your teacher how you and your partner played Race to a Dollar. Seeing Math What Do You Think? The students wanted
Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade 2 WEEK 17 Let s Write Write a note to explain to your teacher how you and your partner played Race to a Dollar. Seeing Math What Do You Think? The students wanted
The Grade 6 Common Core State Standards for Geometry specify that students should
 The focus for students in geometry at this level is reasoning about area, surface area, and volume. Students also learn to work with visual tools for representing shapes, such as graphs in the coordinate
The focus for students in geometry at this level is reasoning about area, surface area, and volume. Students also learn to work with visual tools for representing shapes, such as graphs in the coordinate
Grade 1 Calendar Grid Answer Key
 Grade 1 Calendar Grid Answer Key September Date Model Tens Ones Equation 1 Tally Mark 0 1 0 + 1 = 1 2 Bundles & Sticks 0 2 0 + 2 = 2 3 Ten-Frame 0 3 0 + 3 = 3 4 Tally Mark 0 4 0 + 4 = 4 5 Bundles & Sticks
Grade 1 Calendar Grid Answer Key September Date Model Tens Ones Equation 1 Tally Mark 0 1 0 + 1 = 1 2 Bundles & Sticks 0 2 0 + 2 = 2 3 Ten-Frame 0 3 0 + 3 = 3 4 Tally Mark 0 4 0 + 4 = 4 5 Bundles & Sticks
Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT
 Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT The Coalition Government took office on 11 May 2010. This publication was published prior to that date and may not reflect current government policy. You may choose
Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT The Coalition Government took office on 11 May 2010. This publication was published prior to that date and may not reflect current government policy. You may choose
SERIES Addition and Subtraction
 D Teacher Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic Section Addition Answers mental (pp. 48) strategies (pp. 4) look addition for a mental ten strategies_ look subtraction for patterns_ mental strategies
D Teacher Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic Section Addition Answers mental (pp. 48) strategies (pp. 4) look addition for a mental ten strategies_ look subtraction for patterns_ mental strategies
Canadian Math Kangaroo Contest
 Canadian Math Kangaroo Contest Part A: Each correct answer is worth 3 points 1. Amy, Bert, Carl, Doris and Ernst each rolled two dice and added the number of dots. Who rolled the largest total? Amy Bert
Canadian Math Kangaroo Contest Part A: Each correct answer is worth 3 points 1. Amy, Bert, Carl, Doris and Ernst each rolled two dice and added the number of dots. Who rolled the largest total? Amy Bert
Counting Problems
 Counting Problems Counting problems are generally encountered somewhere in any mathematics course. Such problems are usually easy to state and even to get started, but how far they can be taken will vary
Counting Problems Counting problems are generally encountered somewhere in any mathematics course. Such problems are usually easy to state and even to get started, but how far they can be taken will vary
Games for Drill and Practice
 Frequent practice is necessary to attain strong mental arithmetic skills and reflexes. Although drill focused narrowly on rote practice with operations has its place, Everyday Mathematics also encourages
Frequent practice is necessary to attain strong mental arithmetic skills and reflexes. Although drill focused narrowly on rote practice with operations has its place, Everyday Mathematics also encourages
The problems in this booklet are organized into strands. A problem often appears in multiple strands. The problems are suitable for most students in
 The problems in this booklet are organized into strands. A problem often appears in multiple strands. The problems are suitable for most students in Grade 7 or higher. Problem C Totally Unusual The dice
The problems in this booklet are organized into strands. A problem often appears in multiple strands. The problems are suitable for most students in Grade 7 or higher. Problem C Totally Unusual The dice
OPERATIONS AND ALGEBRAIC THINKING NUMBER AND OPERATIONS IN BASE TEN MEASUREMENT AND DATA GEOMETRY USER LICENSE 535
 OPERATIONS AND ALGEBRAIC THINKING 003-164 REPRESENT AND SOLVE PROBLEMS INVOLVING ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION ADD AND SUBTRACT WITHIN 20 WORK WITH EQUAL GROUPS OF OBJECTS TO GAIN FOUNDATIONS FOR MULTIPLICATION
OPERATIONS AND ALGEBRAIC THINKING 003-164 REPRESENT AND SOLVE PROBLEMS INVOLVING ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION ADD AND SUBTRACT WITHIN 20 WORK WITH EQUAL GROUPS OF OBJECTS TO GAIN FOUNDATIONS FOR MULTIPLICATION
MEP : Feeder Primary Project / Reception Year. R: Counting up to nine C: Decomposing nine E: Observational and manual skills.
 1 5 min 2 15 min 3 20 min : Counting up to nine C: Decomposing nine E: Observational and manual skills. Short term memory Nine shells T: Share nine shells with your partner. Explain your sharing A and
1 5 min 2 15 min 3 20 min : Counting up to nine C: Decomposing nine E: Observational and manual skills. Short term memory Nine shells T: Share nine shells with your partner. Explain your sharing A and
Operations and Algebraic Thinking: Fluency within 5
 Unit 13 Operations and Algebraic Thinking: Fluency within 5 Introduction In this unit, students will develop fluency in addition and subtraction within 5. By this point, they have learned several methods
Unit 13 Operations and Algebraic Thinking: Fluency within 5 Introduction In this unit, students will develop fluency in addition and subtraction within 5. By this point, they have learned several methods
4 th Grade Mathematics Instructional Week 30 Geometry Concepts Paced Standards: 4.G.1: Identify, describe, and draw parallelograms, rhombuses, and
 4 th Grade Mathematics Instructional Week 30 Geometry Concepts Paced Standards: 4.G.1: Identify, describe, and draw parallelograms, rhombuses, and trapezoids using appropriate tools (e.g., ruler, straightedge
4 th Grade Mathematics Instructional Week 30 Geometry Concepts Paced Standards: 4.G.1: Identify, describe, and draw parallelograms, rhombuses, and trapezoids using appropriate tools (e.g., ruler, straightedge
Correlation of USA Daily Math Grade 2 to Common Core State Standards for Mathematics
 2.OA 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems with unknowns in all positions. 2.OA.2 Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies. 2.OA.3 Determine
2.OA 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems with unknowns in all positions. 2.OA.2 Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies. 2.OA.3 Determine
Answers Solving mathematical problems
 Solving mathematical problems 1 in the middle (p.8) Many answers are possible, for example: 10, 11, 1, 13, 14 (on in steps of 1) 14, 13, 1, 11, 10 (back in steps of 1) 8, 10, 1, 14, 16 (on in steps of
Solving mathematical problems 1 in the middle (p.8) Many answers are possible, for example: 10, 11, 1, 13, 14 (on in steps of 1) 14, 13, 1, 11, 10 (back in steps of 1) 8, 10, 1, 14, 16 (on in steps of
Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Grade 04
 Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Problem Solving Mathematical Process Expectations 4m1 develop, select, and apply problem-solving strategies as they pose and solve problems and conduct investigations, to
Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Problem Solving Mathematical Process Expectations 4m1 develop, select, and apply problem-solving strategies as they pose and solve problems and conduct investigations, to
Counters in a Cup In and Out. The student sets up the cup, drops the counters on it, and records how many landed in and out of the cup.
 Counters in a Cup In and Out Cup Counters Recording Paper The student sets up the cup, drops the counters on it, and records how many landed in and out of the cup. 3 + 4 =7 2 + 5 =7 For subtraction, take
Counters in a Cup In and Out Cup Counters Recording Paper The student sets up the cup, drops the counters on it, and records how many landed in and out of the cup. 3 + 4 =7 2 + 5 =7 For subtraction, take
Essentials. Week by. Week. Investigations. Let s Write Write a story about what you can do in one minute. Seeing Math
 . Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade 2 WEEK 9 Let s Write Write a story about what you can do in one minute. 4 1 2 Investigations Given this number, what number would you add to get the sum of 15?
. Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade 2 WEEK 9 Let s Write Write a story about what you can do in one minute. 4 1 2 Investigations Given this number, what number would you add to get the sum of 15?
Methods in Mathematics (Linked Pair Pilot)
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Methods in Mathematics (Linked Pair Pilot) Unit 2 Geometry and Algebra Monday 11 November 2013
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Methods in Mathematics (Linked Pair Pilot) Unit 2 Geometry and Algebra Monday 11 November 2013
1. Take out a piece of notebook paper and make a hot dog fold over from the right side over to the pink line. Foldable
 Four sided polygon 1. Take out a piece of notebook paper and make a hot dog fold over from the right side over to the pink line. Foldable Foldable The fold crease 2. Now, divide the right hand section
Four sided polygon 1. Take out a piece of notebook paper and make a hot dog fold over from the right side over to the pink line. Foldable Foldable The fold crease 2. Now, divide the right hand section
2016 Summer Break Packet for Students Entering Geometry Common Core
 2016 Summer Break Packet for Students Entering Geometry Common Core Name: Note to the Student: In middle school, you worked with a variety of geometric measures, such as: length, area, volume, angle, surface
2016 Summer Break Packet for Students Entering Geometry Common Core Name: Note to the Student: In middle school, you worked with a variety of geometric measures, such as: length, area, volume, angle, surface
Math Kangaroo 2002 Level of grades 7-8
 1 of 5 www.mathkangaroo.com Math Kangaroo 2002 Level of grades 7-8 Problems 3 points each: 1. This year the International Competition in Mathematics Kangaroo takes places on March 21 st. How many prime
1 of 5 www.mathkangaroo.com Math Kangaroo 2002 Level of grades 7-8 Problems 3 points each: 1. This year the International Competition in Mathematics Kangaroo takes places on March 21 st. How many prime
Addition and Subtraction
 Series Student Addition and Subtraction My name D Copyright 2009 3P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 2009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from 3P Learning
Series Student Addition and Subtraction My name D Copyright 2009 3P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 2009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from 3P Learning
Performance Assessment Task Quilt Making Grade 4. Common Core State Standards Math - Content Standards
 Performance Assessment Task Quilt Making Grade 4 The task challenges a student to demonstrate understanding of concepts of 2-dimensional shapes and ir properties. A student must be able to use characteristics,
Performance Assessment Task Quilt Making Grade 4 The task challenges a student to demonstrate understanding of concepts of 2-dimensional shapes and ir properties. A student must be able to use characteristics,
Essentials. Week by. Week. Investigations. Let s Write Write a story about. Seeing Math $ $ $ $ What Do You Think? Patterns, Patterns, Patterns
 Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade 2 WEEK 21 Let s Write Write a story about 1 2 Seeing Math What Do You Think? Suppose you hit the target with three darts. How could you score 15? Is there more
Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade 2 WEEK 21 Let s Write Write a story about 1 2 Seeing Math What Do You Think? Suppose you hit the target with three darts. How could you score 15? Is there more
Sample Pages. out of 17. out of 15. a $1.15 b $0.85. a 4280 b 2893 c 724. a Which of these are odd? b Which of these are even?
 1:1 out of 15 1:2 out of 17 7 + 8 13 4 12 9 3 3 4 2 9 plus 5. 8 + 6 4 groups of 5. 1 8 + 1 1 1 5 4 12 + 7 9 2 16 + 4 7 4 10 7 17 subtract 7. 11 6 20 minus 12. 6 7 + 2 2 7 9 4 3 Write these numbers on the
1:1 out of 15 1:2 out of 17 7 + 8 13 4 12 9 3 3 4 2 9 plus 5. 8 + 6 4 groups of 5. 1 8 + 1 1 1 5 4 12 + 7 9 2 16 + 4 7 4 10 7 17 subtract 7. 11 6 20 minus 12. 6 7 + 2 2 7 9 4 3 Write these numbers on the
Pair counting. Maths focus: Counting on in ones, tens or hundreds from any number. What you need: Instructions
 Cambridge University Press 978-1-107-69401-9 Cambridge Primary Mathematics Stage 3 Cherri Moseley and Janet Rees Excerpt More information Place value games Largest and smallest Maths focus: To understand
Cambridge University Press 978-1-107-69401-9 Cambridge Primary Mathematics Stage 3 Cherri Moseley and Janet Rees Excerpt More information Place value games Largest and smallest Maths focus: To understand
Travelling Integers. Materials
 Travelling Integers Number of players 2 (or more) Adding and subtracting integers Deck of cards with face cards removed Number line (from -25 to 25) Chips/pennies to mark players places on the number line
Travelling Integers Number of players 2 (or more) Adding and subtracting integers Deck of cards with face cards removed Number line (from -25 to 25) Chips/pennies to mark players places on the number line
Mathematics, Grade 8
 Session 1, Multiple-Choice Questions 44084 C 1 13608 C 2 (0.5)(0.5)(0.5) is equal to which of the following? A. 0.000125 B. 0.00125 C. 0.125 D. 1.25 Reporting Category for Item 1: Number Sense and Operations
Session 1, Multiple-Choice Questions 44084 C 1 13608 C 2 (0.5)(0.5)(0.5) is equal to which of the following? A. 0.000125 B. 0.00125 C. 0.125 D. 1.25 Reporting Category for Item 1: Number Sense and Operations
St Thomas of Canterbury Catholic Primary School Where every child is special
 Helping your child with Maths games and FUN! Helping with Maths at home can often be an issue we ve all been there, tears and frustration and your children aren t happy either! The key is to try to make
Helping your child with Maths games and FUN! Helping with Maths at home can often be an issue we ve all been there, tears and frustration and your children aren t happy either! The key is to try to make
