Unit 5 Shape and space
|
|
|
- Gwendoline Brooks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 5 Shape and space Five daily lessons Year 4 Summer term Unit Objectives Year 4 Sketch the reflection of a simple shape in a mirror line parallel to Page 106 one side (all sides parallel or perpendicular to the mirror line). Recognise positions and directions: for example, describe and Page 108 find the position of a point on a grid of squares where the lines are numbered. Recognise simple examples of horizontal and vertical lines. Page 108 (Key objectives in bold) Year 3 Link Objectives Year 5 Identify and sketch lines of symmetry in simple shapes, and recognise shapes with no lines of symmetry. Sketch the reflection of a simple shape in a mirror line along one edge. Read and begin to write the vocabulary related to position, direction and movement: for example, describe and find the position of a square on a grid of squares with the rows and columns labelled. Recognise reflective symmetry in regular polygons. Complete symmetrical patterns with two lines of symmetry at right angles. Recognise where a shape will be after reflection in a mirror line parallel to one side (sides not all parallel or perpendicular to the mirror line). Recognise where a shape will be after a translation. Recognise positions and directions: read and plot co-ordinates in the first quadrant. This Unit Plan is designed to guide your teaching. You will need to adapt it to meet the needs of your class. Resources needed to teach this unit: Resource sheet 5.1 Activity sheet 5.1 Activity sheet 5.2/OHT 5.6 OHT 5.1 OHT 5.2 OHT 5.3 OHT 5.4 OHT 5.5 OHT cm 2 grid Arrow cards Digit cards Whiteboards Large mirror Small mirrors Large symmetrical shape cut from paper Scissors A4 paper Overhead projector Squared paper Small shapes Display of repeating patterns, e.g. Islamic patterns, tiling patterns, brick patterns, wallpaper, etc.
2 Planning Day One Unit 5 Shape and space Term: Summer Year Group: 4 sheet Oral and Mental Main Teaching Derive doubles of multiples of: whole numbers to 50; multiples of 10 to 500; multiples of 100 to 5000 and the corresponding halves. Write 4 on the board. Q What is 4 10? 40 10? ? Record responses in columns and remind the children that digits move one place to the left when multiplying by 10. Q What is double 4? 40? 400? Record alongside the previous list: Q What do you notice about the list of doubles? Establish that the original digit is unchanged and that double 4 is used to derive the other double facts. Use the list to establish that half of 8 is the fact used for all the other halves. Identify lines of symmetry in 2-D shapes. Understand and use the associated vocabulary. Remind the class that they learned about symmetrical shapes in year 3. Hold up a large symmetrical shape cut from paper such as: Q Where would I fold this shape so that one side would fit exactly over the other? Try out suggestions and establish the correct fold line. Draw a picture similar to the shape on the board and ask a child to indicate where the fold line could be drawn. Draw in the line and remind the class that this line is called a line of symmetry, the line which divides the shape so that one half is a reflection of the other. Illustrate by holding a large mirror along the line. Invite children in groups to come out and observe the reflection, whilst the remaining children make a list of symmetrical shapes they can see in the classroom. Discuss the observed reflection with each group and establish that the mirror image shows the covered half of the shape. Q How is the reflected half of the shape different from the other half? Establish that it is reversed. Illustrate by making a cross on one edge of the shape on the board. Ask the children to suggest where the cross should be placed on the reflected side of the shape. Draw it in the correct position. Draw a shape in which more than one line of symmetry can be identified on the board. Plenary /Focus Questions Discuss the activity and clarify any misconceptions. Q Which shapes had only one line of symmetry? Q Which had more than one? Q Which shapes are not symmetrical? Record the letters of the appropriate shapes under headings, e.g. one line of symmetry, on the board. Discuss, and if necessary model, the number of lines of symmetry on a square and a star. Ask the children to give examples of shapes in the classroom which are symmetrical. Add these to the lists. Ask the children to explain or indicate where lines of symmetry could be drawn on them. double half Arrow cards Repeat, starting with 32 and reinforce the patterns. Q What is double 26? So what is double 260? Double 2600? Q What is half of 46? 460? 4600? Ask a variety of doubling and halving questions for children to show answers using arrow cards, e.g. double 350, half 8400, double 2700, half 72, etc. line of symmetry mirror line symmetrical reflect reflection Large symmetrical shape cut from paper Large mirror Small mirrors, one per group. Activity sheet 5.1 Q Where can a mirror line be drawn on this shape? Q Can you see any more lines of symmetry? Draw the lines then repeat with another shape. Establish that some shapes have more than one line of symmetry. Draw a shape with no lines of symmetry, ask the children whether they can identify a mirror line and establish that some shapes are not symmetrical. Give out Activity sheet 5.1. Ask the children to visualise then draw all the lines of symmetry they can find in each shape in question 1, then check by placing a mirror vertically on the line. Ask them to complete the shapes in question 2 by drawing their reflections through the mirror lines. By the end of the lesson the children should be able to: Use the vocabulary associated with symmetry; Identify and sketch two or more lines of symmetry; Recognise shapes with no lines of symmetry. (Refer to supplement of examples, section 6, page 106.)
3 Planning Day Two Unit 5 Shape and space Term: Summer Year Group: 4 sheet Oral and Mental Main Teaching Read and write whole numbers to in figures and words and know what each digit represents. Round any positive integer less then 1000 to the nearest 10 or 100. Write a four-digit number on the board and ask the class to read it aloud together on your signal. Point to individual digits and ask them to say what they represent, e.g. in 7428, the 2 is 20, etc. Repeat with four or five further four-digit numbers, including some containing a zero. Ask the children in pairs to order the numbers, smallest to largest. Take feedback and record in a vertical list on the board, emphasising how the digits are compared from the left of the numbers, since these have the greatest place value. Remind the class about the rules for rounding numbers. Indicate the first number in the ordered numbers on the board. Q What is this number when rounded to the nearest 10? The nearest 100? Record each alongside the first number on the board. Ask the children to round the other numbers to the nearest 10 and then the nearest 100. Take feedback and model on the board. Classify 2-D shapes according to their lines of symmetry. line of symmetry symmetrical mirror line reflection horizontal vertical diagonal quadrilateral pentagon Remind the class that in the previous lesson they identified lines of symmetry in shapes. Draw a square on the board and ask a child to come out and draw one line of symmetry. Q Why is this a line of symmetry? Establish that a line of symmetry divides a shape in half so that one half is a mirror image, or reflection, of the other. Repeat with three further squares on the board, asking the children to draw a line of symmetry in a different position. Emphasise the different positions of the lines; horizontal, vertical and diagonal. Ask the children to draw a triangle, quadrilateral and pentagon. Explain that the shape need not be regular and draw examples of irregular shapes on the board to illustrate. Ask them to cut out their shapes very carefully along the edges. Give out a set of symmetrical paper shapes to each group, e.g. cut out from Resource sheet 5.1. Ask the group to use these and the shapes they made themselves and to sort them into three sets according to their symmetry; none, one or more than one line of symmetry. Explain that they can check by drawing lines of symmetry, by using a mirror or by folding the shapes. Discuss the checking methods with groups as they work and reinforce the teaching points made earlier and the associated vocabulary. Extend the activity by asking the groups to subdivide the set with more than one line of symmetry according to their own criteria. Plenary /Focus Questions Ask the children to explain the criteria they used for sorting the shapes with more than one line of symmetry and to hold up a shape that each set contained. Q Do all squares have four lines of symmetry? Q What about rectangles? Circles? Through questioning and discussion, establish that all rectangles have two lines of symmetry, that squares have four and circles have an infinite number. Use OHT 5.1. Ask a child to choose one shape and place it in the appropriate section of the diagram. Continue, using other shapes. By the end of the lesson the children should be able to: Identify two or more lines of symmetry in 2-D shapes; Sort shapes according to their lines of symmetry. (Refer to supplement of examples, section 6, page 106.) place value round A4 paper Rulers Scissors Mirrors Overhead projector Resource sheet 5.1 OHT 5.1
4 Planning Day Three Unit 5 Shape and space Term: Summer Year Group: 4 sheet Oral and Mental Main Teaching Recall multiplication facts in 2, 3, 4, 5, 10 tables and of multiples of 10. Multiply TU by U mentally. Ask quick questions to revise multiplication facts, using associated vocabulary, e.g. What are 8 threes? What is the product of 7 and 5? What is 5 times 30? Write 14 3 on the board. Q How can we use the multiplication facts we know to work this out? Establish the use of 10 3 and 4 3. Repeat with 16 5 and Ask a variety of TU U questions using known facts. The children work in pairs with digit cards or whiteboards, one showing the multiple of the 10s, the other showing the multiple of the units. Ask the children to give the complete answer orally. Ask further questions for the children to work individually giving the complete answer. Sketch the reflection of a simple shape or pattern where the sides of the shape do not touch the mirror line (lines all parallel or perpendicular to the mirror line). Know that equivalent points are the same distance from the line of symmetry. Revise the use of co-ordinates. Display shape 1 on OHT 5.2. Explain that the dotted line represents a mirror. Point out that the shape does not touch the mirror. Ask a child to come up and indicate where the reflection of the shape should be placed. Draw the reflection and emphasise that it is the same distance away from the mirror line as the original shape on the other side of the line. Remind the children that a reflected shape is the same size as the original but flipped over, or reversed. Repeat with shapes 2 and 3 on the OHT. Mark a cross in one of the squares to the right of the first mirror line. The cross should not touch the line. Q How many squares to the left of the line will the reflection of the cross be? Establish that the reflection will be the same number of squares from the line as the original cross. Ask a child to draw its reflection. Repeat with other marks for the children to reflect in the different mirror lines. Show OHT 5.3 and repeat. Then show OHT 5.4. When the children have difficulty in positioning the reflection in 2, rotate the OHT so that the mirror line is horizontal or vertical to help them, then return it to its original position to view the completed reflection. Hand out squared paper with mirror lines drawn on them, suitably spaced for the activity described below. Ask the children to work in pairs. They each draw a shape or pattern on one side of each mirror line. The shapes/patterns must not touch the line. The children swap with a partner, then draw the reflections of their partner s shapes or patterns. Plenary /Focus Questions Discuss the paired activity and clarify any misconceptions. Display OHT 5.5. Remind the class how to use co-ordinates to describe position. Ask the children to record the co-ordinates of the reflection of the shape. Take feedback and draw the reflection according to the agreed co-ordinates. HOMEWORK Make a pattern on squared paper on one side of a mirror line by colouring squares, then draw its reflection. By the end of the lesson the children should be able to: Sketch the reflection of simple shapes or patterns in mirror lines; Use co-ordinates to describe position. (Refer to supplement of examples, section 6, page 106.) times multiplied by multiple product Digit cards or whiteboards mirror Line line of symmetry reflection co-ordinates OHT 5.2 OHT 5.3 OHT 5.4 OHT 5.5 Squared paper with spaced mirror lines
5 Planning Day Four Unit 5 Shape and space Term: Summer Year Group: 4 sheet Oral and Mental Main Teaching Derive quickly pairs of numbers that total 100. Add/subtract a pair of two-digit numbers. total digit Digit cards or whiteboards Ask the children to show the number which makes a total of 100 when added to 82, using whiteboards or digit cards. Write = 100 on the board and remind the class that when numbers total 100, the units total 10 and the 10s total 90. Ask the children to work with a partner. They each hold up a two-digit number which together total 100. Give any pair of two-digit numbers and ask the children to show the total. Record the equation and ask the children to explain the strategies they used to find the answer. Give a target number. Ask the children and partners to show a pair of numbers which have the target number as their total. Discuss and record some of the pairs. Repeat with other target numbers. Make patterns by repeatedly translating or reflecting shapes. Know that rows on a grid are described as horizontal, columns as vertical. movement repeating pattern reflection translation horizontal vertical OHP OHT cm 2 grid Small shapes, e.g. circles, letter shapes, triangles, etc. Squared paper Examples of repeating patterns on display, e.g. Islamic patterns, brick patterns, tiling patterns, wallpaper, etc. Place a shape on a grid on the OHP. Slide it to the right in a straight line. Q How has this shape been moved? Encourage different descriptions and establish that the shape has moved in a horizontal straight line to the right. Repeat, sliding the shape in straight lines to the left horizontally, and up and down vertically. Explain to the class that when a shape is moved in a straight line, the movement is called a translation. Ask the children to come up and move the shape according to your instructions, e.g. translate the shape upwards vertically. Q Can you think of another way to move a shape which is not a translation? Discuss suggestions and establish that reflection is a different type of movement. (If rotation is suggested, agree and discuss, but don t dwell on it in this unit). Demonstrate reflecting the shape in different ways on the OHP. Make a pattern of shapes on the OHP which involves translation, e.g. a row of identical triangles, or a row of triangles, circles, triangles, etc. Ask the children to describe it using translated. Repeat with a pattern in which a shape is repeatedly reflected. Q What happens when a shape is translated? Reflected? Emphasise that translation and reflection only change the position of the shapes, their size and shape remain the same. The same shape appears in reverse when reflected. Look at one of the repeating patterns on display. Ask the children to describe the basic pattern and how it repeats. Prompt them to use appropriate vocabulary. Ask the children to make their own patterns which involve repeated translation and/or reflection. Provide squared paper and explain that their patterns will be displayed in the plenary. At an appropriate time use a computer program to create and reflect patterns and tiles. Plenary /Focus Questions Ask a volunteer to come out and hold up their pattern. Ask other children to describe how the pattern is repeated. Repeat with other children. If possible, display all the children s patterns in the classroom after the lesson. By the end of the lesson the children should be able to: Understand and use the terms horizontal, vertical, translation and reflections; Make and describe repeating patterns which involve translation or reflection. (Refer to supplement of examples, section 6, pages 106 and 108.)
6 Planning Day Five Unit 5 Shape and space Term: Summer Year Group: 4 sheet Oral and Mental Main Teaching Use knowledge of multiplication and division. Write 24 on the board. Ask the children to suggest all the different multiplication and division facts they can which have 24 as the answer. Write the facts in a list or around 24 as a web. Q What other facts about 24 can we write from those on the board? Encourage the use of doubling and halving, e.g. from 6 4 derive 12 2, from 48 2 derive 96 4, etc. Record all correct suggestions. Give another target, e.g. 36, and ask the children to record all the facts they can for the target, using multiplication and division, doubling and halving. Use co-ordinates to describe position. Translate and reflect shapes. Review the homework set on day 3. Ask volunteers to display their work and to indicate squares at random for other children to identify in the reflection. Show OHT 5.6. Use the triangle on the lower part of the OHT cut from thin card. Place the triangle so that its corners exactly match intersections on the grid. Ask the children to identify the co-ordinates of the vertices. Record them on board, e.g. (2,3) (4,7) (4,3). Q If I translate the triangle 2 squares to the right what will the new co-ordinates be? Discuss, record agreed co-ordinates on the board, then move the shape to demonstrate that they are correct. Repeat with one or two other translations. Q If I flip the shape over its vertical side, what will the new co-ordinates be? Discuss, record co-ordinates and reflect the shape to check. Q How else do we describe a flipping movement? Establish that it is a reflection. Reflect the shape through different sides and repeat the identification and recording of co-ordinates. Ask the children to work in pairs. Pupils need two copies of Activity sheet 5.2. Each child draws a shape on a numbered grid, then translates it and reflects it and draws the shape in the new positions. They take turns to describe the original position of the shape using co-ordinates. Their partner records the co-ordinates, plots them on another numbered grid and joins the points to make the shape. Each child describes to their partner how they translated and then reflected their shape. The partner draws the translation and reflection on their grid. Finally, they compare drawings. Plenary /Focus Questions Ask questions to review the main teaching points and vocabulary covered in the unit, e.g. Q What do we call the movement of a shape in a straight line? Q What does a letter P look like when it is reflected in a horizontal mirror line? Q What are the co-ordinates of a point which is 2 squares to the right of (6,3)? 3 squares vertically below (7,2)? Q How many lines of symmetry can be drawn on a rectangle? An equilateral triangle? Write examples of symmetrical capital letters, etc. Children could record their answers if required for assessment. multiplication division doubling halving co-ordinates translate reflect horizontal vertical OHT 5.6 Activity sheet 5.2 By the end of the lesson the children should be able to: Translate and reflect shapes; Describe position on a grid using co ordinates. (Refer to supplement of examples, section 6, pages 106 and 108.)
7 Unit 5 Year 4 (Summer Term) Activity sheet 5.1 Lines of Symmetry 1. Use a ruler to draw all the lines of symmetry you can on each shape, then check with a mirror. A B C D E F G H 2. Draw the reflection of each shape on the other side of the dotted mirror line.
8 Unit 5 Year 4 (Summer Term) OHT 5.6/Activity sheet 5.2 Numbered Grid
9 Unit 5 Year 4 (Summer Term) Resource sheet 5.1 Symmetrical Shapes To be copied and cut out for children to sort, one set of shapes per group
10 Unit 5 Year 4 (Summer Term) OHT 5.1 Sorting Diagram Shapes with no lines of symmetry Shapes with at least one line of symmetry
11 Unit 5 Year 4 (Summer Term) OHT 5.2 Reflections in a Mirror line 1 2 3
12 Unit 5 Year 4 (Summer Term) OHT Reflections X O X O X O X O X O X O X O OHT 5.4 2
13 Unit 5 Year 4 (Summer Term) OHT 5.5 Using Co-ordinates
Shape, space and measures 4
 Shape, space and measures 4 contents There are three lessons in this unit, Shape, space and measures 4. S4.1 Rotation and rotation symmetry 3 S4.2 Reflection and line symmetry 6 S4.3 Problem solving 9
Shape, space and measures 4 contents There are three lessons in this unit, Shape, space and measures 4. S4.1 Rotation and rotation symmetry 3 S4.2 Reflection and line symmetry 6 S4.3 Problem solving 9
Basic Mathematics Review 5232
 Basic Mathematics Review 5232 Symmetry A geometric figure has a line of symmetry if you can draw a line so that if you fold your paper along the line the two sides of the figure coincide. In other words,
Basic Mathematics Review 5232 Symmetry A geometric figure has a line of symmetry if you can draw a line so that if you fold your paper along the line the two sides of the figure coincide. In other words,
LESSON PLAN: Symmetry
 LESSON PLAN: Symmetry Subject Mathematics Content Area Space and Shape Topic Symmetry Concept Recognise and draw line of symmetry in 2-D geometrical and non geometrical shapes Determine line of symmetry
LESSON PLAN: Symmetry Subject Mathematics Content Area Space and Shape Topic Symmetry Concept Recognise and draw line of symmetry in 2-D geometrical and non geometrical shapes Determine line of symmetry
Geometry. Learning Goals U N I T
 U N I T Geometry Building Castles Learning Goals describe, name, and sort prisms construct prisms from their nets construct models of prisms identify, create, and sort symmetrical and non-symmetrical shapes
U N I T Geometry Building Castles Learning Goals describe, name, and sort prisms construct prisms from their nets construct models of prisms identify, create, and sort symmetrical and non-symmetrical shapes
Downloaded from
 Symmetry 1.Can you draw a figure whose mirror image is identical to the figure itself? 2.Find out if the figure is symmetrical or not? 3.Count the number of lines of symmetry in the figure. 4.A line
Symmetry 1.Can you draw a figure whose mirror image is identical to the figure itself? 2.Find out if the figure is symmetrical or not? 3.Count the number of lines of symmetry in the figure. 4.A line
Downloaded from
 Symmetry 1 1.A line segment is Symmetrical about its ---------- bisector (A) Perpendicular (B) Parallel (C) Line (D) Axis 2.How many lines of symmetry does a reactangle have? (A) Four (B) Three (C)
Symmetry 1 1.A line segment is Symmetrical about its ---------- bisector (A) Perpendicular (B) Parallel (C) Line (D) Axis 2.How many lines of symmetry does a reactangle have? (A) Four (B) Three (C)
Downloaded from
 Symmetry 1 1.Find the next figure None of these 2.Find the next figure 3.Regular pentagon has line of symmetry. 4.Equlilateral triangle has.. lines of symmetry. 5.Regular hexagon has.. lines of symmetry.
Symmetry 1 1.Find the next figure None of these 2.Find the next figure 3.Regular pentagon has line of symmetry. 4.Equlilateral triangle has.. lines of symmetry. 5.Regular hexagon has.. lines of symmetry.
SPIRE MATHS Stimulating, Practical, Interesting, Relevant, Enjoyable Maths For All
 Imaginings in shape and space TYPE: Main OBJECTIVE(S): DESCRIPTION: OVERVIEW: EQUIPMENT: Begin to identify and use angle, side and symmetry properties of triangles and quadrilaterals; solve geometrical
Imaginings in shape and space TYPE: Main OBJECTIVE(S): DESCRIPTION: OVERVIEW: EQUIPMENT: Begin to identify and use angle, side and symmetry properties of triangles and quadrilaterals; solve geometrical
SHAPE level 2 questions. 1. Match each shape to its name. One is done for you. 1 mark. International School of Madrid 1
 SHAPE level 2 questions 1. Match each shape to its name. One is done for you. International School of Madrid 1 2. Write each word in the correct box. faces edges vertices 3. Here is half of a symmetrical
SHAPE level 2 questions 1. Match each shape to its name. One is done for you. International School of Madrid 1 2. Write each word in the correct box. faces edges vertices 3. Here is half of a symmetrical
autumn 2 a) Ring each number that has four tens. b) Tick (!) each number that has eight units
 Name... 1 Write the seasons in order. Use these words. summer spring winter autumn 2 a) Ring each number that has four tens. b) Tick (!) each number that has eight units. 28 84 47 54 14 40 78 3 Match each
Name... 1 Write the seasons in order. Use these words. summer spring winter autumn 2 a) Ring each number that has four tens. b) Tick (!) each number that has eight units. 28 84 47 54 14 40 78 3 Match each
Planning Guide. Shape and Space (Transformations) Specific Outcomes 5, 6
 Mathematics Planning Guide Grade 4 Transformations Shape and Space (Transformations) Specific Outcomes 5, 6 This Planning Guide can be accessed online at: http://www.learnalberta.ca/content/mepg4/html/pg4_transformations/index.html
Mathematics Planning Guide Grade 4 Transformations Shape and Space (Transformations) Specific Outcomes 5, 6 This Planning Guide can be accessed online at: http://www.learnalberta.ca/content/mepg4/html/pg4_transformations/index.html
18 Two-Dimensional Shapes
 18 Two-Dimensional Shapes CHAPTER Worksheet 1 Identify the shape. Classifying Polygons 1. I have 3 sides and 3 corners. 2. I have 6 sides and 6 corners. Each figure is made from two shapes. Name the shapes.
18 Two-Dimensional Shapes CHAPTER Worksheet 1 Identify the shape. Classifying Polygons 1. I have 3 sides and 3 corners. 2. I have 6 sides and 6 corners. Each figure is made from two shapes. Name the shapes.
Year 5 Problems and Investigations Spring
 Year 5 Problems and Investigations Spring Week 1 Title: Alternating chains Children create chains of alternating positive and negative numbers and look at the patterns in their totals. Skill practised:
Year 5 Problems and Investigations Spring Week 1 Title: Alternating chains Children create chains of alternating positive and negative numbers and look at the patterns in their totals. Skill practised:
Angles and. Learning Goals U N I T
 U N I T Angles and Learning Goals name, describe, and classify angles estimate and determine angle measures draw and label angles provide examples of angles in the environment investigate the sum of angles
U N I T Angles and Learning Goals name, describe, and classify angles estimate and determine angle measures draw and label angles provide examples of angles in the environment investigate the sum of angles
Contents. Congruent Triangles. Additional Practice Answers to Check Your Work. Section
 Contents Section Congruent Triangles Flip, Turn, Resize, and Slide 1 Transformed Triangles 2 Constructing Parallel Lines 5 Transformations 6 Reflections 7 Rotations 10 Summary 13 Check Your Work 14 Additional
Contents Section Congruent Triangles Flip, Turn, Resize, and Slide 1 Transformed Triangles 2 Constructing Parallel Lines 5 Transformations 6 Reflections 7 Rotations 10 Summary 13 Check Your Work 14 Additional
NCERT Solution Class 7 Mathematics Symmetry Chapter: 14. Copy the figures with punched holes and find the axes of symmetry for the following:
 Downloaded from Q.1) Exercise 14.1 NCERT Solution Class 7 Mathematics Symmetry Chapter: 14 Copy the figures with punched holes and find the axes of symmetry for the following: Sol.1) S.No. Punched holed
Downloaded from Q.1) Exercise 14.1 NCERT Solution Class 7 Mathematics Symmetry Chapter: 14 Copy the figures with punched holes and find the axes of symmetry for the following: Sol.1) S.No. Punched holed
Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD. We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential
 Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential Grade 2 Module 8 Parent Handbook The materials contained within this packet have been taken
Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential Grade 2 Module 8 Parent Handbook The materials contained within this packet have been taken
Angle Measure and Plane Figures
 Grade 4 Module 4 Angle Measure and Plane Figures OVERVIEW This module introduces points, lines, line segments, rays, and angles, as well as the relationships between them. Students construct, recognize,
Grade 4 Module 4 Angle Measure and Plane Figures OVERVIEW This module introduces points, lines, line segments, rays, and angles, as well as the relationships between them. Students construct, recognize,
Yr 4: Unit 4E Modelling effects on screen
 ICT SCHEME OF WORK Modelling on screen in LOGO PoS: KS 2 1c 2a 2c Yr 4: Unit 4E Modelling effects on screen Class: Date: Theme: Children learn to enter instructions to control a screen turtle and will
ICT SCHEME OF WORK Modelling on screen in LOGO PoS: KS 2 1c 2a 2c Yr 4: Unit 4E Modelling effects on screen Class: Date: Theme: Children learn to enter instructions to control a screen turtle and will
Year 4 Homework Activities
 Year 4 Homework Activities Teacher Guidance The Inspire Maths Home Activities provide opportunities for children to explore maths further outside the classroom. The engaging Home Activities help you to
Year 4 Homework Activities Teacher Guidance The Inspire Maths Home Activities provide opportunities for children to explore maths further outside the classroom. The engaging Home Activities help you to
Class VI Mathematics (Ex. 13.1) Questions
 Class VI Mathematics (Ex. 13.1) Questions 1. List any four symmetrical from your home or school. 2. For the given figure, which one is the mirror line, l 1 or l 2? 3. Identify the shapes given below. Check
Class VI Mathematics (Ex. 13.1) Questions 1. List any four symmetrical from your home or school. 2. For the given figure, which one is the mirror line, l 1 or l 2? 3. Identify the shapes given below. Check
Objective: Draw trapezoids to clarify their attributes, and define trapezoids based on those attributes.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 16 5 5 Lesson 16 Objective: Draw trapezoids to clarify their attributes, and define trapezoids based Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 16 5 5 Lesson 16 Objective: Draw trapezoids to clarify their attributes, and define trapezoids based Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important
 Many artists use geometric concepts in their work. Think about what you have learned in geometry. How do these examples of First Nations art and architecture show geometry ideas? What You ll Learn Identify
Many artists use geometric concepts in their work. Think about what you have learned in geometry. How do these examples of First Nations art and architecture show geometry ideas? What You ll Learn Identify
6. True or false? Shapes that have no right angles also have no perpendicular segments. Draw some figures to help explain your thinking.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 3 Homework 4 4 5. Use your right angle template as a guide and mark each right angle in the following figure with a small square. (Note that a right angle
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 3 Homework 4 4 5. Use your right angle template as a guide and mark each right angle in the following figure with a small square. (Note that a right angle
Lines and angles parallel and perpendicular lines. Look at each group of lines. Tick the parallel lines.
 Lines and angles parallel and perpendicular lines Parallel lines are always the same distance away from each other at any point and can never meet. They can be any length and go in any direction. Look
Lines and angles parallel and perpendicular lines Parallel lines are always the same distance away from each other at any point and can never meet. They can be any length and go in any direction. Look
MFL and Numeracy. Teachers of MFL in KS2 and KS3 reinforce:
 MFL and Numeracy "When evaluating the achievement of pupils, inspectors consider...how well pupils develop a range of skills, including reading, writing, communication and mathematical skills, and how
MFL and Numeracy "When evaluating the achievement of pupils, inspectors consider...how well pupils develop a range of skills, including reading, writing, communication and mathematical skills, and how
1 TG Grade 4 Unit 9 Lesson 11 Answer Key. Answer Key Lesson 11: Workshop: Shapes and Properties. Workshop: Shapes and Properties
 Answer Key esson 11: Student Guide Self-Check: Questions 1 3 Cut out the pieces of the puzzle on the Mosaic Puzzle page in the Student Activity ook. Use the puzzle pieces to answer Self-Check: Questions
Answer Key esson 11: Student Guide Self-Check: Questions 1 3 Cut out the pieces of the puzzle on the Mosaic Puzzle page in the Student Activity ook. Use the puzzle pieces to answer Self-Check: Questions
Maths Makes Sense. 3 Medium-term plan
 Maths Makes Sense 3 Medium-term plan 2 Maths Makes Sense 3 Block 1 End-of-block objectives Arithmetic 1 Respond to I will act the Real Story, you write the Maths Story (including the answer), for addition
Maths Makes Sense 3 Medium-term plan 2 Maths Makes Sense 3 Block 1 End-of-block objectives Arithmetic 1 Respond to I will act the Real Story, you write the Maths Story (including the answer), for addition
Objective: Draw rectangles and rhombuses to clarify their attributes, and define rectangles and rhombuses based on those attributes.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 18 5 5 Lesson 18 Objective: Draw rectangles and rhombuses to clarify their attributes, and define Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 18 5 5 Lesson 18 Objective: Draw rectangles and rhombuses to clarify their attributes, and define Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem
Performance Assessment Task Quilt Making Grade 4. Common Core State Standards Math - Content Standards
 Performance Assessment Task Quilt Making Grade 4 The task challenges a student to demonstrate understanding of concepts of 2-dimensional shapes and ir properties. A student must be able to use characteristics,
Performance Assessment Task Quilt Making Grade 4 The task challenges a student to demonstrate understanding of concepts of 2-dimensional shapes and ir properties. A student must be able to use characteristics,
Algebra/Geometry Institute Summer 2004
 Algebra/Geometry Institute Summer 2004 Lesson Plan 1 Faculty Name: Janice Walker School: Greenville-Weston, Greenville, MS Grade Level: Geometry 9 10 Reflections 1 Teaching objective(s): Students will
Algebra/Geometry Institute Summer 2004 Lesson Plan 1 Faculty Name: Janice Walker School: Greenville-Weston, Greenville, MS Grade Level: Geometry 9 10 Reflections 1 Teaching objective(s): Students will
MODULE FRAMEWORK AND ASSESSMENT SHEET
 MODULE FRAMEWORK AND ASSESSMENT SHEET LEARNING OUTCOMES (LOS) ASSESSMENT STANDARDS (ASS) FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT ASs Pages and (mark out of 4) LOs (ave. out of 4) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT Tasks or tests Ave for
MODULE FRAMEWORK AND ASSESSMENT SHEET LEARNING OUTCOMES (LOS) ASSESSMENT STANDARDS (ASS) FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT ASs Pages and (mark out of 4) LOs (ave. out of 4) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT Tasks or tests Ave for
1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: and. b. Use a straightedge to draw.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 Problem Set 4 Name Date 1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: and. b. Use a straightedge to draw.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 Problem Set 4 Name Date 1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: and. b. Use a straightedge to draw.
1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: and. b. Use a straightedge to draw.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 Homework 4 Name Date 1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: and. b. Use a straightedge to draw. c.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 Homework 4 Name Date 1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: and. b. Use a straightedge to draw. c.
Same Area, Different Perimeter; Same Perimeter, Different Area
 S E S S I O N 2. 5 A Same Area, Different Perimeter; Same Perimeter, Different Area Math Focus Points Using tiles to find the area and perimeter of a rectangle Understanding that rectangles can have the
S E S S I O N 2. 5 A Same Area, Different Perimeter; Same Perimeter, Different Area Math Focus Points Using tiles to find the area and perimeter of a rectangle Understanding that rectangles can have the
Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT
 Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT The Coalition Government took office on 11 May 2010. This publication was published prior to that date and may not reflect current government policy. You may choose
Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT The Coalition Government took office on 11 May 2010. This publication was published prior to that date and may not reflect current government policy. You may choose
Middle School Geometry. Session 2
 Middle School Geometry Session 2 Topic Activity Name Page Number Related SOL Spatial Square It 52 6.10, 6.13, Relationships 7.7, 8.11 Tangrams Soma Cubes Activity Sheets Square It Pick Up the Toothpicks
Middle School Geometry Session 2 Topic Activity Name Page Number Related SOL Spatial Square It 52 6.10, 6.13, Relationships 7.7, 8.11 Tangrams Soma Cubes Activity Sheets Square It Pick Up the Toothpicks
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet
 GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. a) Study: 6 units 6 tens 6 hundreds 6 thousands 6 ten-thousands 6 hundredthousands HTh T Th Th H T U 6 6 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. a) Study: 6 units 6 tens 6 hundreds 6 thousands 6 ten-thousands 6 hundredthousands HTh T Th Th H T U 6 6 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0
Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers
 LESSON 61 page 328 Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers Name Teacher Notes: Introduce Hint #21 Multiplication/ Division Fact Families. Review Multiplication Table on page 5 and Quadrilaterals on
LESSON 61 page 328 Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers Name Teacher Notes: Introduce Hint #21 Multiplication/ Division Fact Families. Review Multiplication Table on page 5 and Quadrilaterals on
Exploring Concepts with Cubes. A resource book
 Exploring Concepts with Cubes A resource book ACTIVITY 1 Gauss s method Gauss s method is a fast and efficient way of determining the sum of an arithmetic series. Let s illustrate the method using the
Exploring Concepts with Cubes A resource book ACTIVITY 1 Gauss s method Gauss s method is a fast and efficient way of determining the sum of an arithmetic series. Let s illustrate the method using the
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES -
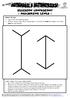 ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
learning about tangram shapes
 Introduction A Tangram is an ancient puzzle, invented in China and consisting of a square divided into seven geometric shapes: Two large right triangles One medium right triangle Tangram Two small right
Introduction A Tangram is an ancient puzzle, invented in China and consisting of a square divided into seven geometric shapes: Two large right triangles One medium right triangle Tangram Two small right
Name Date Class Practice A. 5. Look around your classroom. Describe a geometric pattern you see.
 Practice A Geometric Patterns Identify a possible pattern. Use the pattern to draw the next figure. 5. Look around your classroom. Describe a geometric pattern you see. 6. Use squares to create a geometric
Practice A Geometric Patterns Identify a possible pattern. Use the pattern to draw the next figure. 5. Look around your classroom. Describe a geometric pattern you see. 6. Use squares to create a geometric
Prism or Pyramid? Which nets make pyramids? Find out. RBKC SMILE 2001
 Prism or Pyramid? Which nets make pyramids? Find out. A B D C RBKC SMILE 2001 50 110 104 37 48 32 100 140 60 70 120 119 45 76 Carefully cut out the following shapes. Angle Fit 20 d a c 39 101 b 105 64
Prism or Pyramid? Which nets make pyramids? Find out. A B D C RBKC SMILE 2001 50 110 104 37 48 32 100 140 60 70 120 119 45 76 Carefully cut out the following shapes. Angle Fit 20 d a c 39 101 b 105 64
PENNSYLVANIA. List properties, classify, draw, and identify geometric figures in two dimensions.
 Know: Understand: Do: CC.2.3.4.A.1 -- Draw lines and angles and identify these in two-dimensional figures. CC.2.3.4.A.2 -- Classify twodimensional figures by properties of their lines and angles. CC.2.3.4.A.3
Know: Understand: Do: CC.2.3.4.A.1 -- Draw lines and angles and identify these in two-dimensional figures. CC.2.3.4.A.2 -- Classify twodimensional figures by properties of their lines and angles. CC.2.3.4.A.3
Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary. Correlations
 Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary Correlations Saxon Math Program Page Math K 2 Math 1 8 Math 2 14 California Math K 21 California Math 1 27 California Math 2 33 1 Saxon Math Manipulatives in
Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary Correlations Saxon Math Program Page Math K 2 Math 1 8 Math 2 14 California Math K 21 California Math 1 27 California Math 2 33 1 Saxon Math Manipulatives in
Year 4. Term by Term Objectives. Year 4 Overview. Autumn. Spring Number: Fractions. Summer. Number: Addition and Subtraction.
 Summer Overview Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Autumn Number: Place Value Number: Addition and Subtraction Number: Multiplication and Division Measurement:
Summer Overview Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Autumn Number: Place Value Number: Addition and Subtraction Number: Multiplication and Division Measurement:
Angles, UNIT 11 Bearings Lesson Plan 1 and Maps
 1A 1B 1C UNIT 11 Bearings Lesson Plan 1 Revising classification of angles T: We're going to review what we've learned about angles so far. Can you list the different types of angles from 0 to 360? (Acute,
1A 1B 1C UNIT 11 Bearings Lesson Plan 1 Revising classification of angles T: We're going to review what we've learned about angles so far. Can you list the different types of angles from 0 to 360? (Acute,
Grade 4 + DIGITAL. EL Strategies. DOK 1-4 RTI Tiers 1-3. Flexible Supplemental K-8 ELA & Math Online & Print
 Standards PLUS Flexible Supplemental K-8 ELA & Math Online & Print Grade 4 SAMPLER Mathematics EL Strategies DOK 1-4 RTI Tiers 1-3 15-20 Minute Lessons Assessments Consistent with CA Testing Technology
Standards PLUS Flexible Supplemental K-8 ELA & Math Online & Print Grade 4 SAMPLER Mathematics EL Strategies DOK 1-4 RTI Tiers 1-3 15-20 Minute Lessons Assessments Consistent with CA Testing Technology
Objective: Classify shapes based on defining attributes using examples, variants, and non-examples. (10 minutes) (5 minutes)
 Lesson 1 1 Lesson 1 Objective: Classify shapes based on defining attributes using examples, variants, Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief
Lesson 1 1 Lesson 1 Objective: Classify shapes based on defining attributes using examples, variants, Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief
Objective: Draw polygons with specified attributes to solve problems. (3 minutes) (5 minutes) (60 minutes)
 Lesson 6 3 7 Lesson 6 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (8 minutes) (30 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Lesson 6 3 7 Lesson 6 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (8 minutes) (30 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Inductive Reasoning Practice Test. Solution Booklet. 1
 Inductive Reasoning Practice Test Solution Booklet 1 www.assessmentday.co.uk Question 1 Solution: B In this question, there are two rules to follow. The first rule is that the curved and straight-edged
Inductive Reasoning Practice Test Solution Booklet 1 www.assessmentday.co.uk Question 1 Solution: B In this question, there are two rules to follow. The first rule is that the curved and straight-edged
A A B B C C D D. NC Math 2: Transformations Investigation
 NC Math 2: Transformations Investigation Name # For this investigation, you will work with a partner. You and your partner should take turns practicing the rotations with the stencil. You and your partner
NC Math 2: Transformations Investigation Name # For this investigation, you will work with a partner. You and your partner should take turns practicing the rotations with the stencil. You and your partner
Representing Square Numbers. Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array.
 1.1 Student book page 4 Representing Square Numbers You will need counters a calculator Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array. 5 5 25 number
1.1 Student book page 4 Representing Square Numbers You will need counters a calculator Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array. 5 5 25 number
Transformation Games
 Transformation Games These are a set of activities/games to help visualize geometric transformations (or rigid motions) movements of an object that do not change the size or shape of the object. The 3
Transformation Games These are a set of activities/games to help visualize geometric transformations (or rigid motions) movements of an object that do not change the size or shape of the object. The 3
Standards of Learning Guided Practice Suggestions. For use with the Mathematics Tools Practice in TestNav TM 8
 Standards of Learning Guided Practice Suggestions For use with the Mathematics Tools Practice in TestNav TM 8 Table of Contents Change Log... 2 Introduction to TestNav TM 8: MC/TEI Document... 3 Guided
Standards of Learning Guided Practice Suggestions For use with the Mathematics Tools Practice in TestNav TM 8 Table of Contents Change Log... 2 Introduction to TestNav TM 8: MC/TEI Document... 3 Guided
Vocabulary slope, parallel, perpendicular, reciprocal, negative reciprocal, horizontal, vertical, rise, run (earlier grades)
 Slope Reporting Category Reasoning, Lines, and Transformations Topic Exploring slope, including slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines Primary SOL G.3 The student will use pictorial representations,
Slope Reporting Category Reasoning, Lines, and Transformations Topic Exploring slope, including slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines Primary SOL G.3 The student will use pictorial representations,
Refer to Blackboard for Activities and/or Resources
 Lafayette Parish School System Curriculum Map Mathematics: Grade 5 Unit 4: Properties in Geometry (LCC Unit 5) Time frame: 16 Instructional Days Assess2know Testing Date: March 23, 2012 Refer to Blackboard
Lafayette Parish School System Curriculum Map Mathematics: Grade 5 Unit 4: Properties in Geometry (LCC Unit 5) Time frame: 16 Instructional Days Assess2know Testing Date: March 23, 2012 Refer to Blackboard
Numeracy Warm Up. Introduction
 Numeracy Warm Up Introduction Numeracy Warm Up is a set of numeracy exercises that can be used for starters, main lessons and plenaries. It is aimed at Numeracy lessons covering National Curriculum Levels
Numeracy Warm Up Introduction Numeracy Warm Up is a set of numeracy exercises that can be used for starters, main lessons and plenaries. It is aimed at Numeracy lessons covering National Curriculum Levels
Learn to use translations, reflections, and rotations to transform geometric shapes.
 Learn to use translations, reflections, and rotations to transform geometric shapes. Insert Lesson Title Here Vocabulary transformation translation rotation reflection line of reflection A rigid transformation
Learn to use translations, reflections, and rotations to transform geometric shapes. Insert Lesson Title Here Vocabulary transformation translation rotation reflection line of reflection A rigid transformation
Mathematics Success Level F
 T598 [OBJECTIVE] The student will find the perimeter and area of rectangles and triangles. [MATERIALS] Student pages S204 S212 Transparencies T612, T614, T616, T618, T620, T622 Ruler Scissors Gridded index
T598 [OBJECTIVE] The student will find the perimeter and area of rectangles and triangles. [MATERIALS] Student pages S204 S212 Transparencies T612, T614, T616, T618, T620, T622 Ruler Scissors Gridded index
. line segment. 1. Draw a line segment to connect the word to its picture. ray. line. point. angle. 2. How is a line different from a line segment?
 COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 Exit Ticket 4 1. Draw a line segment to connect the word to its picture. ray line. line segment point angle 2. How is a line different from a line segment? Lesson
COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 Exit Ticket 4 1. Draw a line segment to connect the word to its picture. ray line. line segment point angle 2. How is a line different from a line segment? Lesson
Introduction. It gives you some handy activities that you can do with your child to consolidate key ideas.
 (Upper School) Introduction This booklet aims to show you how we teach the 4 main operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) at St. Helen s College. It gives you some handy activities
(Upper School) Introduction This booklet aims to show you how we teach the 4 main operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) at St. Helen s College. It gives you some handy activities
Copying a Line Segment
 Copying a Line Segment Steps 1 4 below show you how to copy a line segment. Step 1 You are given line segment AB to copy. A B Step 2 Draw a line segment that is longer than line segment AB. Label one of
Copying a Line Segment Steps 1 4 below show you how to copy a line segment. Step 1 You are given line segment AB to copy. A B Step 2 Draw a line segment that is longer than line segment AB. Label one of
Weekly Planning Sheet: Maths Teacher: Miss Morris and Mrs Coates Year: 1 Date:
 Tu and W I can add two numbers together Adding Up with a Partner With a partner, and using a whiteboard, find out how many letters they have in their names altogether. Write the number sentence. WALT recognise
Tu and W I can add two numbers together Adding Up with a Partner With a partner, and using a whiteboard, find out how many letters they have in their names altogether. Write the number sentence. WALT recognise
4 th Grade Mathematics Instructional Week 30 Geometry Concepts Paced Standards: 4.G.1: Identify, describe, and draw parallelograms, rhombuses, and
 4 th Grade Mathematics Instructional Week 30 Geometry Concepts Paced Standards: 4.G.1: Identify, describe, and draw parallelograms, rhombuses, and trapezoids using appropriate tools (e.g., ruler, straightedge
4 th Grade Mathematics Instructional Week 30 Geometry Concepts Paced Standards: 4.G.1: Identify, describe, and draw parallelograms, rhombuses, and trapezoids using appropriate tools (e.g., ruler, straightedge
The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy
 The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy The Willows Primary Mental Maths Policy Teaching methodology and organisation Teaching time All pupils will receive between 10 and 15 minutes of mental
The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy The Willows Primary Mental Maths Policy Teaching methodology and organisation Teaching time All pupils will receive between 10 and 15 minutes of mental
Shapes. Practice. Family Note. Unit. show 3-sided, 4-sided, 5-sided, and 6-sided shapes. Ask an adult for permission first. Add.
 Home Link 8-1 Shapes In this lesson children examined different shapes, such as triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and hexagons. They also discussed these shapes attributes or characteristics such as
Home Link 8-1 Shapes In this lesson children examined different shapes, such as triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and hexagons. They also discussed these shapes attributes or characteristics such as
Page 3 of 26 Copyright 2014 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 1. This picture shows the side of Allen's desk. What type of angle is made by the top of Allen's desk and one of the legs? A acute B obtuse C right D straight 2. Look at these two shapes on the grid. Draw
1. This picture shows the side of Allen's desk. What type of angle is made by the top of Allen's desk and one of the legs? A acute B obtuse C right D straight 2. Look at these two shapes on the grid. Draw
Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem
 UNIT 1 Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem Just for Fun What Do You Notice? Follow the steps. An example is given. Example 1. Pick a 4-digit number with different digits. 3078 2. Find the greatest
UNIT 1 Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem Just for Fun What Do You Notice? Follow the steps. An example is given. Example 1. Pick a 4-digit number with different digits. 3078 2. Find the greatest
Teacher Lesson Pack Lines and Angles. Suitable for Gr. 6-9
 Teacher Lesson Pack Lines and Angles Suitable for Gr. 6-9 1 2 Sir Cumference and the Great Knight of Angleland By: Cindy Neuschwander, Charlsebridge Publishing, ISBN: 1570911525 Read the book to the students.
Teacher Lesson Pack Lines and Angles Suitable for Gr. 6-9 1 2 Sir Cumference and the Great Knight of Angleland By: Cindy Neuschwander, Charlsebridge Publishing, ISBN: 1570911525 Read the book to the students.
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 3 Booklet
 GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 3 Booklet Learner s name: School name: _ Day 1 1. Read carefully: a) The place or position of a digit in a number gives the value of that digit. b) In the number 273, 2,
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 3 Booklet Learner s name: School name: _ Day 1 1. Read carefully: a) The place or position of a digit in a number gives the value of that digit. b) In the number 273, 2,
G 1 3 G13 BREAKING A STICK #1. Capsule Lesson Summary
 G13 BREAKING A STICK #1 G 1 3 Capsule Lesson Summary Given two line segments, construct as many essentially different triangles as possible with each side the same length as one of the line segments. Discover
G13 BREAKING A STICK #1 G 1 3 Capsule Lesson Summary Given two line segments, construct as many essentially different triangles as possible with each side the same length as one of the line segments. Discover
Grade 4 Mathematics Item Specification C1 TL
 Task Model 1a Hot Spot DOK Level 1 4.G.A.1 Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute, obtuse), and perpendicular and parallel lines. Identify these in two-dimensional figures. Prompt
Task Model 1a Hot Spot DOK Level 1 4.G.A.1 Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute, obtuse), and perpendicular and parallel lines. Identify these in two-dimensional figures. Prompt
Activity 5.2 Making Sketches in CAD
 Activity 5.2 Making Sketches in CAD Introduction It would be great if computer systems were advanced enough to take a mental image of an object, such as the thought of a sports car, and instantly generate
Activity 5.2 Making Sketches in CAD Introduction It would be great if computer systems were advanced enough to take a mental image of an object, such as the thought of a sports car, and instantly generate
CREATIVE CONNECTIONS ART AND MATHS PROJECT WORKBOOK THIS BOOK BELONGS TO: ... CLASS / YEAR GROUP: ...
 CREATIVE CONNECTIONS ART AND MATHS PROJECT WORKBOOK THIS BOOK BELONGS TO:... CLASS / YEAR GROUP:... INTRODUCTION This workbook has been created in order to identify the clear and fascinating connections
CREATIVE CONNECTIONS ART AND MATHS PROJECT WORKBOOK THIS BOOK BELONGS TO:... CLASS / YEAR GROUP:... INTRODUCTION This workbook has been created in order to identify the clear and fascinating connections
FSA Math Review. **Rounding / Estimating** **Addition and Subtraction** Rounding a number: Key vocabulary: round, estimate, about
 FSA Math Review **Rounding / Estimating** Rounding a number: Key vocabulary: round, estimate, about 5 or more add one more-----round UP 0-4 just ignore-----stay SAME Find the number in the place value
FSA Math Review **Rounding / Estimating** Rounding a number: Key vocabulary: round, estimate, about 5 or more add one more-----round UP 0-4 just ignore-----stay SAME Find the number in the place value
Solving Problems. PS1 Use and apply mathematics to solve problems, communicate and reason Year 1. Activities. PS1.1 Number stories 1.
 PS1 Use and apply mathematics to solve problems, communicate and reason Year 1 PS1.1 Number stories 1 PS1.2 Difference arithmagons PS1.3 Changing orders PS1.4 Making shapes PS1.5 Odd or even? PS1.6 Odd
PS1 Use and apply mathematics to solve problems, communicate and reason Year 1 PS1.1 Number stories 1 PS1.2 Difference arithmagons PS1.3 Changing orders PS1.4 Making shapes PS1.5 Odd or even? PS1.6 Odd
Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities
 Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities For more information about the materials you find in this packet, contact: Sharon Rendon (605) 431-0216 sharonrendon@cpm.org 1 2-51. SPECIAL
Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities For more information about the materials you find in this packet, contact: Sharon Rendon (605) 431-0216 sharonrendon@cpm.org 1 2-51. SPECIAL
Measuring and Drawing Angles and Triangles
 NME DTE Measuring and Drawing ngles and Triangles Measuring an angle 30 arm origin base line 0 180 0 If the arms are too short to reach the protractor scale, lengthen them. Step 1: lace the origin of the
NME DTE Measuring and Drawing ngles and Triangles Measuring an angle 30 arm origin base line 0 180 0 If the arms are too short to reach the protractor scale, lengthen them. Step 1: lace the origin of the
Summer Solutions Common Core Mathematics 4. Common Core. Mathematics. Help Pages
 4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
Released January Years 3/4. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area
 Released January 208 Years 3/4 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area Year 3/4 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 3 Year 4 Measure length Equivalent lengths
Released January 208 Years 3/4 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area Year 3/4 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 3 Year 4 Measure length Equivalent lengths
California 1 st Grade Standards / Excel Math Correlation by Lesson Number
 California 1 st Grade Standards / Excel Math Correlation by Lesson Lesson () L1 Using the numerals 0 to 9 Sense: L2 Selecting the correct numeral for a Sense: 2 given set of pictures Grouping and counting
California 1 st Grade Standards / Excel Math Correlation by Lesson Lesson () L1 Using the numerals 0 to 9 Sense: L2 Selecting the correct numeral for a Sense: 2 given set of pictures Grouping and counting
Counting Problems
 Counting Problems Counting problems are generally encountered somewhere in any mathematics course. Such problems are usually easy to state and even to get started, but how far they can be taken will vary
Counting Problems Counting problems are generally encountered somewhere in any mathematics course. Such problems are usually easy to state and even to get started, but how far they can be taken will vary
2. Here are some triangles. (a) Write down the letter of the triangle that is. right-angled, ... (ii) isosceles. ... (2)
 Topic 8 Shapes 2. Here are some triangles. A B C D F E G (a) Write down the letter of the triangle that is (i) right-angled,... (ii) isosceles.... (2) Two of the triangles are congruent. (b) Write down
Topic 8 Shapes 2. Here are some triangles. A B C D F E G (a) Write down the letter of the triangle that is (i) right-angled,... (ii) isosceles.... (2) Two of the triangles are congruent. (b) Write down
MCAS/DCCAS Mathematics Correlation Chart Grade 4
 MCAS/DCCAS Mathematics Correlation Chart Grade 4 MCAS Finish Line Mathematics Grade 4 MCAS Standard DCCAS Standard DCCAS Standard Description Unit 1: Number Sense Lesson 1: Whole Number Place Value Lesson
MCAS/DCCAS Mathematics Correlation Chart Grade 4 MCAS Finish Line Mathematics Grade 4 MCAS Standard DCCAS Standard DCCAS Standard Description Unit 1: Number Sense Lesson 1: Whole Number Place Value Lesson
Year 5. Mathematics A booklet for parents
 Year 5 Mathematics A booklet for parents About the statements These statements show some of the things most children should be able to do by the end of Year 5. A statement might be harder than it seems,
Year 5 Mathematics A booklet for parents About the statements These statements show some of the things most children should be able to do by the end of Year 5. A statement might be harder than it seems,
Symmetrical Figures. Geometry. Objective. Common Core State Standards Talk About It. Solve It. More Ideas. Formative Assessment
 5 Objective Symmetrical Figures In this lesson, students solve problems involving symmetry. Because relationships across a line of symmetry correspond exactly in terms of size, form, and arrangement, students
5 Objective Symmetrical Figures In this lesson, students solve problems involving symmetry. Because relationships across a line of symmetry correspond exactly in terms of size, form, and arrangement, students
Grow your. Yellow 2 The wee Maths Book. Growth. of Big Brain
 Grow your Yellow 2 The wee Maths Book of Big Brain Growth Measure, Symmetry, coordinates and Angles. Guaranteed to make your brain grow, just add some effort and hard work Don t be afraid if you don t
Grow your Yellow 2 The wee Maths Book of Big Brain Growth Measure, Symmetry, coordinates and Angles. Guaranteed to make your brain grow, just add some effort and hard work Don t be afraid if you don t
Mathematics Paper 2. Stage minutes. Page Mark. Name.. Additional materials: Ruler Calculator Protractor READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST
 1 55 minutes Mathematics Paper 2 Stage 7 Name.. Additional materials: Ruler Calculator Protractor READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST Answer all questions in the spaces provided on the question paper. You should
1 55 minutes Mathematics Paper 2 Stage 7 Name.. Additional materials: Ruler Calculator Protractor READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST Answer all questions in the spaces provided on the question paper. You should
Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry
 Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry This Guide Belongs to: Date: Table of Contents Using Sketchpad - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry This Guide Belongs to: Date: Table of Contents Using Sketchpad - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
lines of weakness building for the future All of these walls have a b c d Where are these lines?
 All of these walls have lines of weakness a b c d Where are these lines? A standard British brick is twice as wide as it is tall. Using British bricks, make a rectangle that does not have any lines of
All of these walls have lines of weakness a b c d Where are these lines? A standard British brick is twice as wide as it is tall. Using British bricks, make a rectangle that does not have any lines of
LEARNING ABOUT MATH FOR K TO 5. Dorset Public School. April 6, :30 pm 8:00 pm. presented by Kathy Kubota-Zarivnij
 LEARNING ABOUT MATH FOR K TO 5 Dorset Public School April 6, 2016 6:30 pm 8:00 pm presented by Kathy Kubota-Zarivnij kathkubo@rogers.com TODAY S MATH TOOLS FOR colour square tiles Hexalink cubes KKZ, 2016
LEARNING ABOUT MATH FOR K TO 5 Dorset Public School April 6, 2016 6:30 pm 8:00 pm presented by Kathy Kubota-Zarivnij kathkubo@rogers.com TODAY S MATH TOOLS FOR colour square tiles Hexalink cubes KKZ, 2016
Name Date Class Period. What happens to ordered pairs when a rule is applied to the coordinates?
 Name Date Class Period Activity B Extension 4.1 Modeling Transformations MATERIALS small white boards or paper markers masking tape yarn QUESTION What happens to ordered pairs when a rule is applied to
Name Date Class Period Activity B Extension 4.1 Modeling Transformations MATERIALS small white boards or paper markers masking tape yarn QUESTION What happens to ordered pairs when a rule is applied to
The Parkland Federation. February 2016
 The Parkland Federation February 206 EYFS/KS Calculations: Recording Addition (page of ). Aggregation/combining 2. Augmentation/counting on 3. Counting Contexts: + + + + Pupils physically combining groups
The Parkland Federation February 206 EYFS/KS Calculations: Recording Addition (page of ). Aggregation/combining 2. Augmentation/counting on 3. Counting Contexts: + + + + Pupils physically combining groups
Lesson 69 Putting shapes together
 Lesson 69 Putting Learning objectives Children will: fit 2D over larger 2D. compose 2D to make larger. copy a model composed of 3D objects. Australian Curriculum Content Descriptions Measurement and Geometry
Lesson 69 Putting Learning objectives Children will: fit 2D over larger 2D. compose 2D to make larger. copy a model composed of 3D objects. Australian Curriculum Content Descriptions Measurement and Geometry
Clarification of Standards for Parents Grade 3 Mathematics Unit 4
 Clarification of Standards for Parents Grade 3 Mathematics Unit 4 Dear Parents, We want to make sure that you have an understanding of the mathematics your child will be learning this year. Below you will
Clarification of Standards for Parents Grade 3 Mathematics Unit 4 Dear Parents, We want to make sure that you have an understanding of the mathematics your child will be learning this year. Below you will
UK JUNIOR MATHEMATICAL CHALLENGE. April 25th 2013 EXTENDED SOLUTIONS
 UK JUNIOR MATHEMATICAL CHALLENGE April 5th 013 EXTENDED SOLUTIONS These solutions augment the printed solutions that we send to schools. For convenience, the solutions sent to schools are confined to two
UK JUNIOR MATHEMATICAL CHALLENGE April 5th 013 EXTENDED SOLUTIONS These solutions augment the printed solutions that we send to schools. For convenience, the solutions sent to schools are confined to two
Standard 4.G.1 4.G.2 5.G.3 5.G.4 4.MD.5
 Draw and identify lines and angles, as well as classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles (Standards 4.G.1 3). Standard 4.G.1 Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute,
Draw and identify lines and angles, as well as classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles (Standards 4.G.1 3). Standard 4.G.1 Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute,
DOWNSEND SCHOOL YEAR 5 EASTER REVISION BOOKLET
 DOWNSEND SCHOOL YEAR 5 EASTER REVISION BOOKLET This booklet is an optional revision aid for the Summer Exam Name: Maths Teacher: Revision List for Summer Exam Topic Junior Maths Bk 3 Place Value Chapter
DOWNSEND SCHOOL YEAR 5 EASTER REVISION BOOKLET This booklet is an optional revision aid for the Summer Exam Name: Maths Teacher: Revision List for Summer Exam Topic Junior Maths Bk 3 Place Value Chapter
