Nets of pyramids. Smile You will need compasses, ruler, card, a sharp pencil and sellotape or glue.
|
|
|
- Anna Rogers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nets of pyramids Smile 0720 You will need compasses, ruler, card, a sharp pencil and sellotape or glue. 1. Draw this net of a pyramid using a ruler, pencil and compasses only. First draw the square. Then use compasses to draw the triangles accurately. Add flaps to every other side. Cut the net out and fold it to make a square based pyramid. You should find that for this pyramid, the top is directly above the centre of the square base. It is called a right pyramid. The pyramids below all have square bases but they are not right pyramids. They are not drawn to scale. 4cm Draw sketches of their nets. Mark the measurements on the sketches. When you are convinced that the sketches are correct, draw the nets accurately. Add flaps. Check by cutting, folding and sticking. Turn over.
2 5. Draw these nets accurately. Cut and fold. What happens? Why? 6cm 6cm 6cm 6cm RBKC SMILE 1994.
3 Smile 0721 Squares Tangram You will need cm squared paper, scissors, coloured pencils and glue. 1. Draw this pattern carefully on cm squared paper. 2. Colour the 3 shaded pieces. 3. Cut out the 10 pieces This is an 8cm square. This is a 6cm square. Fit the 3 shaded pieces together to cover this square. Stick the square you have made into your book. Fit the other 7 pieces together to cover this square. (You may turn pieces over). 0 Stick the square you have made into your book. 6. What was the area of the square you started with? 7. What are the areas of the other 2 squares? 8. Copy and complete: 100 = RBKC SMILE 1994.
4 Smile 0722 PROVE Think of a whou number. Square, it. Divide, by Try several numbers. What do you notice? Of course, it does. Weli, an even number mutt kwlct Some o-ther Lt c*n. An odd number is one Less khan an ei I'U call the oddjiik cali If you you ivou and W/itttistheruleand fiow was it proved?
5 Race Track Smile Worksheet 0725 This is a game for 2 to 4 players that simulates cars racing around a track. Each player moves in turn and the moves must be written as vectors. ssl Rules _. Each player starts off from rest, i.e. with the vector. To move, each component of the previous move maybe changed by 1 or left alone..' " '.;' ::. ;i'h : ':-!'.. '.:: V'^'U>'':--:''^' /_ JV--./.H './'' "' :':',"';/;'' ''' '? ^'^ ^ ' ; "'. ' ' \' ',' i "">\ f " " > ;.,; ''.,''-' VV:/''J For example after a move of [^ ^ j any of the following moves are possible; ; > ; :; /--2\ /-1 \ "./ 0 \ l-4\ Pi \ / 0 \ fe 1 RBKC SMILE 2001
6 Smile 0727 always tells the truth but Phil and Will sometimes lie. 1. Which one is Bill? 2. Where are Will and Phil? Explain all your answers. RBKC SMILE 2001
7 Smile Worksheet 0730 Rotations Rotate the shapes as instructed below. Tracing paper might help. Shape A has been done for you. IJsHi^ei ;;plnti^ ^fl ^alro t Mftirfi^: ] i^0iion l A B C D E F G H I J K L (-5, 3) (-7, 7) (3,9) (1,1). (-12,3) (5,4) (-7, -2) (-3, -4) (2, -3) (11,6) (7, -4) (11,1) clockwise clockwise anti-clockwise anti-clockwise anti-clockwise clockwise anti-clockwise anti-clockwise clockwise anti-clockwise J - (-5 3) =6- k 1) M (10, -7) 1 2 RBKC SMILE 2001
8 Smile 0731 n = number of sides V = angle at each vertex A = angle at centre \e> there a connection between V and A? 1. Measure angles V and A for the different regular polygons on the inside pages. 2. Record your results in a table. June 9th Smile 0751 Regular Polygons Polygon Triangle Square 4 60' 90' 120 C 3. On a graph plot V against A. V 69 ^o.jjm A 4. Why should you not join the points on this graph? 5. What do your table and graph suggest about a connection between V and A? Now turn to the back page.
9 Equilateral triangle Regular Quadrilateral (Square) V Regular Pentagon Regular Hexagon
10 Regular Heptagon Regular Octagon Regular Nonagon Regular Decagon
11 Q Consider any regular polygon with its centre O and one side PQ. 6. What type of triangle is OPQ? 7. What can you say about the line OP and the angle V? 8. RPQ = V; what is /^OPQ? 9. What is ZPQO? 10. Use the sum of the angles of a triangle to write an equation connecting V and A. 11. Your answer to question 5 should have suggested the connection between V and A. Your answer to question 10 should have proved the connection between V and A. What do you think is the difference between these two approaches? RBKC SMILE 1995.
12 Smile 0732 These drawings are not to scale. Can you draw this triangle accurately using only: a ruler a sharp pencil and a compass? 4cm 6cm Here's how! 7cm Mark off 7cm on a line. 7cm Draw an arc centre P, radius 4cm. Draw another arc; centre Q, radius 6cm. Draw the triangle PQR. Check the measurements.
13 Draw these triangles accurately, using only a ruler, a sharp pencil and a compass. 1) 6cm 8cm 6cm 2) 3cm 7cm 8cm 3) 4cm 5cm 7cm Try to draw these triangles accurately, some are impossible. 4) 5cm, 5cm, 9cm. 5) 15cm, 8cm, 7cm. 6) 8cm, 8cm, 8cm. 7) 4cm, 7cm, 11cm 8) Which triangles are impossible to draw? - Explain why. 9) Look at the triangles you have drawn. Which ones are isosceles? Which one is equilateral? RBKC SMILE 1996.
14 Start with a Smile 0734 Start with a2, a square of side length a... ; k a i f < >. -^ ^.^ J- a2 increase the length by b. a ; > b i I f k f a2 I II I I I I I J 1. How much bigger is the (a + b) square than the (a) square? This diagram will help. The increase in size = (a x b) + (b x a) + b2 = 2ab + b2 2. Copy and complete: (a + b)2 = a2 + + a v A Substitute the values a = 5 and b = 3, to check that your identity works. Use your identity to calculate (102) 2. If b = a, verify that (2a) 2 = 4a2. What is the difference between (a + b) 2 and a2 + b2. Substitute the value b = - 4 to calculate (96)2. Put b = - c and rewrite your identity (a - c)2 =
15 Start with a2, a square of side length a.. reduce the length by b. a a.j 9. How much smaller is the (a - b) square than the (a) square? <* - * < This diagram will help. The decrease in size = b(a - b) + b(a - b) + b2 ba-b2+b2 = 2ab-b2 Copy and complete: (a-b)2 = a2 -(2ab-b2) = a2 - + On the opposite page there are two other methods of finding the area. Check the result with your answer to questions 8 and 9.
16 Here are two ways of working out (a - b)a Start with a2 Remove right-hand rectangle Start with a2 Remove ab from the right " a-b Left-hand rectangle = a2 - ab Remainder a2 -ab Remove bottom rectangle Remove ab from the bottom a-b Bottom rectangle = b(a-b) = ba-b2 Remainder (a2 - ab) - ab a2-2ab Therefore the unshaded square (a-b)2 = (a2 - ab) - (ba - b2) = a2 - ab - ba + b2 = a2-2ab + b2 This has taken away the bottom right-hand square twice, so add it back once: (a-b)2 = a2-2ab+ b2 10. Substitute the values a = 7 and b = 4 to check the identity (a - b) 2 = a2-2ab + b2 11. Use the identity to calculate 99*. 12. What is the difference between (a- b)2 and a2 - b2? 13. What is the difference between (a + b)2 and (a - b)2?
17 Start wjth a2, a square of side length a... remove b2, a square of side length b... cut along the dotted line. \ \\ \ \\. Turn one piece over and re-fit to create this rectangle. 14. What are the length and width of the rectangle? 15. Copy and complete: (a + b)(a - b) = - H 16. Substitute the values a = 10 and b = 1 to check that your identity works. 17. Use your identity to calculate 103 x Ifx = (a + b) and y = (a - b) use the identities you have found to simplify a) x2 + 2xy + y2 b) (x + y)2 isr* ctin c
18 Knots Smile Worksheet 0735 knots II 0 Li 1 H T 5. BI I 8. knots B B y o Knots II B U 11 II S I H B D ii 1 i3 i inn knots knots T i D B u y 13 u RBKC SMILE 2001
19 > SMILE 0736 Solving equations 7(3* + 5) -91 Can you solve this equation and find the value of ;c? RBKC SMILE 1999
20 7(3* + 5) -91 Undo the operations, one at a time, by turning over the pages.
21 CM X CM 00
22
23 LO
24 O C\)
25 Now solve these = (4d-3) = ^ = 24 8.
26 \ / Smile 0737 You will need : 2 dice and squared paper. 1. If you throw two dice and find the difference between the two numbers a) What is the largest difference you can get? b) What is the smallest difference you can get? 2. Draw a graph like this: Throw two dice on the table and record the difference between the two numbers by shading a square in the correct column. For example: if you threw 10 9 I 8 f you would shade the first square in the 2 column. Carry on until one of the columns reaches the top Difference a) What column won? b) Can you think of a reason why? c) How many times did you throw the two dice? turn over
27 3. Now copy and complete this table to show all the possible differences. Second Dice a) Write down anything you notice about your completed table. b) How many different ways of getting a difference are there altogether? 4. a) Shade all the O's in your table. How many are there? The probability of scoring 0 is_6_. Why? 36 b) Shade all the 1 's. How many are there? The probability of scoring 1 is U). 36 c) Copy and complete this table to show all the probabilities. Difference Probability d) Add up all the probability fractions - what do you notice? 5. Problem If you win 1 p each time you throw a difference of L 2, 3 or 4 and you lose 4p each time you throw a difference of 0 or 5, are you likely to have more or less money after 36 throws? Try to explain your answer. RBKC SMILE 2001
28 Smile 0738 The Family of Quadrilaterals J fg&. >-;.*B.?^?v^ V:->-B;:;:.: You will need Smile Worksheet 0738a. You may like to use Smile 2163 Geometry Facts. 1. What is the definition of a kite? 2. What is the definition of a rhombus? 3. Is it possible to draw: a) a kite that does not fit the description of a rhombus b) a rhombus that does not fit the description of a kite? 4. Complete these sentences and the labels on the Venn diagram with the words 'rhombuses'and 'kites'. Quadrilaterals are are special cases of There are other quadrilaterals that are special cases of each other. Compare the following pairs of quadrilaterals, use their definitions to decide if one is a 'special case 1 of the other. You make like to draw Venn diagrams. a) Rhombuses and squares b) Squares and rectangles c) Rhombuses and parallelograms d) Rectangles and parallelograms e) Kites and parallelograms f) Trapeziums and parallelograms g) Trapeziums and kites h) Rhombuses and rectangles i) Kites and quadrilaterals j) Trapeziums and quadrilaterals On Quadrilaterals Worksheet 0738a fill in the arrows on the 'is a special case of diagram. On the back of the worksheet is the outline of a Venn diagram that can be used to display all the 'special cases of relationships between quadrilaterals. Label each section of the diagram. RBKC SMILE 1996.
29 Smile Worksheet 0738a The Family of Quadrilaterals Show the relationship 'is a special case of by adding arrows in the diagram below. B means *A is a special case of B". turn over
30 RBKC SMILE 2001
31 If 2x + 3 = 26 then x =? m
32 Use intelligent guess work to solve these. The information opposite may help you. 1. 2x + 3 = x + 3 = x + 3 = x + 3 = (p - 4) = x + 3 = 6 7. _y - 10 = (t + 4) = (a + 4) - 7 = 5.6
33 2x + 3 Multiply by 2 and then add 3 6(p - 4) 0 P - 4 Subtract 4 then multiply by 6 x Add 3 then divide by 2 Divide by 2 then subtract 10 4) Add 4 then multiply by 5 then divide by 6 3(a + 4) -7->-( a Add 4 then multiply by 3 then subtract 7
34 Some of these may have negative answers (p + 5) = A + 21 = (3x + 25) = = (/3 + 9) = (ft - 2) + 15 = 30 3 is Beta Q is Omega e is Theta 4> is Phi These are letters from the Ancient Greek alphabet. They are often used as symbols in mathematical problems.
35 The Smile 0741 Triangle Number T2 =3 and so on., Make a table of n and Tn for n= 1,2, 3,... 6 Draw a suitable grid and plot! against n. Why would It not be sensible to join the points on this graph?
36 2. X X X T2 = 2 X XX XXX and so on... Generalise this pattern for 3. X X + 2 = T XXX 3 = T and so on... Generalise this pattern for,
37 Both your generalisations use and T Re - arrange the first so that it becomes 'n-l Re - arrange the second so that it too becomes 'n-l You now have two expressions for T 'n- 1 SO Re - arrange this to write a formula for Tn in terms of n. Test your result. % x X X Does this number pattern confirm your formula for Tn? X XX XXX Turn over
38 How does the formula for Tn explain the shape of your graph? Find a) T 100 b) The thirty eighth triangle number. RBKC SMILE 1995.
39 Smile 0743 Solving by graphs You will need graph paper. i. uictw ct iiictp jimy diagram of vj JC ^ ^ *»».. - J^ ^P8*^ cjt <: > ^. vviue niu iiictppiiil -7 5 P as co-ordinates: " ( -2, -7) (C), ) (^ I, 5 ) 1 6 (^ 3. Draw the graph by plotting the co-ordinates and joining with a straiglit line.?r-3 4. Read off the solution: ^r~ / / l X / % 5. Check the solution. ^***** w"***, 1 x 2 }.#***''**'**"%, I \ \~^f 1 1 x 2jc 1-J 2jc-3 \ J \, J ) ^" aiamtir ^SwaMa***^ X.^.^x \ ~^ " i J >, / i ;4 i / c >) / / / ^ ^ f^~\ x 2 \ ^f>smm«^ 3 \ ^s****^ 1 -i -i \ 14 j i i i -4 -f 2- p A 2 /I - / y /, / i / j y 2,/ / 4 6 r solution V. f/ 1 J-^ > r / Y > -7 / / - \«^ R- ) /» / -R- turn over
40 6. Use your graph to read off the solutions for: a) 2*-3 = 3 b) 2*-3 = -5 c) 2r-3 = 7 d) 2r-3 = 0 Remember to check your solutions! 7. Draw the graph of the mapping jc ^ 3(x + 4) Use it to solve: a) 3(* + 4) = 15 b) 3(jc + 4) = -7.5 c) 3(* + 4) = 10 Check your solutions. 8. Draw one graph to solve all these: a) x + 5 = 2 2 i_\ i- /-» b) *^5 = 6 c) x + 5 = d) RBKC SMILE 2001
41 Smile 0744 Equations and graphs Can you solve this equation inn 9/ X + 7 = 2(X + 4) 2 1. Try to guess a value of x which would make the equation true. Turn over for a method.
42 Mapping diagrams will help: x + 7 = 2(jc + 4) 2 2 x < " * 4 1 / / , 2. Can you find a value of x which gives the same result for both mappings?
43 3. Draw the graphs of both mappings: 4. Which point lies on both lines?
44 5. So which number maps to the same result in both and x- 6. Check your solutions by substituting into the equation: + 7 = 2 ( + 4) 7. Use graphs to solve these: a) 6 - x = x b) X2 = X + 6 (2 solutions) and check your solutions.
45 Inverses Smile 0745 These mapping diagrams show that 'add 6' and 'subtract 6' are inverses of each other / ^. * > / V ^ * > x- 6 K 3 1 / "I Draw mapping diagrams to show that the mappings x > 2x and x * x are inverses of each other. 2 Draw mapping diagrams to find the inverses of a) x» x + 7 b) x c) x d) x x-2 What is special about the mapping x Xf Draw mapping diagrams to find the inverses of a) x > 3-x b) x- c) x MO-* d) x- Explain why these mappings are called 'self-inverse mappings'. 10 x Find some other self-inverse mappings. RBKC SMILE 1994.
46 Smile 0746 Pascal's Triangle An activity for a small group. Contents: 0746A Sorting Yard 0746B Flipping Coins 0746C Coin Game 0746D Probability Maze 0746E A boat for three Share out the work between you. f When you have finished answer these questions. 1. What similarities are there between the five pieces of work? 2. How do they compare with Pascal's Triangle?
47 Sorting Yard Smile 0746A Lorries are sorted according to their contents. This sorting yard has 3 levels. L Vegetables lorry Fruit lorry Tinned lorry Frozen food lorry Coal lorry Timber lorry R Furniture lorry R Mail lorry A Coal lorry would have to be sent right, left and left again at each level to get to the correct bay. This can be coded RLL. 1. What is the code for sorting a Frozen food lorry? 2. How many different codes are there? 3. The code LRL and LLR both have two Us and one R. Are there any more with two L's and one R? Copy and complete this table: Combinations Three L's Two L's and one R Two R's and one L Three R's LLL Path LLR, LRL, RLL Total number of paths Investigate what happens if you have a sorting yard with four sorting levels. RBKC SMILE 1997
48 Flipping Coins Smile 0746B You will need 3 coins. Flip a coin 3 times and trace your path through the tree diagram. First throw Second throw Third throw H 1. How many different paths are there? 2. These 3 coins were flipped at the same time: H How many different ways could this result have occured? Record them all. 3. Copy and complete the table below: Combinations Path Total number of paths Probability 3 Heads HHH 1 j_ 8 2 Heads and 1 Tail HHT,HTH,THH 3 J3_ 8 2 Tails and 1 Head 3 Tails Total of probabilities
49 4. Investigate the probabilities if you flip 2 coins only. Jo, try this game. We both flip a coin, if either coin shows a head, you score 1 point, if no head shows I score 2 points. I don't know John. I Is that a fair game?/ Is it a fair game? Explain your answer. If you flip 4 coins you can get five different combinations of heads and tails. They are : 4 Heads 3 Heads and 1 Tail 2 Heads and 2 Tails 1 Head and 3 Tails 4 Tails Draw a tree diagram and use it to work out the probabilities for each of the five combinations. RBKC SMILE 1997
50 Coin Game You will need: 16 counters each and 1 coin. Smile 0746C Heads Tails Player 1 Start counter here Home A Square A game for 2 people. Home B Square Home c Square Home D Square Rules: Each player places one counter on the starting square. Take it in turns to flip a coin and follow the rules below. Home E Square Home F Square Player 2 Start counter here Heads Tails Player 1 Player 2 If Heads move counter one square to the right If Heads move counter one square to the left If Tails move counter one square down If Tails move counter one square up As each counter reaches a Home Square, start another counter off. When all counters are on Home Squares, the winner is the one with the most counters on Home Squares A and F. Is there any pattern to the results?
51 1. Player 2 needs 5 Heads in a row to get to Home Square A. Why? 2. To get to Home Square B, Player 2 needs 4 Heads and 1 Tail. There are 5 possible paths. List them all. 3. Copy and complete this table of possible routes for Player 2. (Use a whole page) Home Square Path Total number of paths HHHHH B HHHHT HHHTH HHTHH HTHHH THHHH 4. How would Player's 1 table be different? 5. If you played the same game on a 5 x 5 board, how many possible paths would there be for Player 2 to get to Home Squares A, B, C, D ande? D E B What are the possibilities with a 4 x 4 board? 3x3 board? Is there a pattern to your results? Can you use the pattern to find the number of paths to each Home Square on a 6 x 6 board? What about an 8 x 8 board? RBKC SMILE 1997
52 Probability Maze Smile 0746D You will need: a probability maze or MicroSMILE program Pinball If you roll a ball through the maze several times, how often will it fall in each column? You can answer by: a) Guessing b) Doing an experiment using the probability maze or MicroSMILE program Pinball c) Working it out. See the hints on the back of this card. Compare your answers to b) and c). Explain any differences.
53 Hints for working out the probabilities.. Each time the ball drops onto a peg, it has an even chance of falling to the left or to the right. What would happen if a ball falls through the maze 16 times? Copy and complete the grids below to find the number of balls you could expect to land in each column. a) Q A 88 D /< D X D 4411 D na x D D / D v D v D v D * D b) D 16 D D " D 1"6 D 1~6 D " D D D S D S D S D S D D S D D D S D ' D D What would happen if the maze had another row of pegs? Investigate. RBKC SMILE 1997
54 Smile 0746E A boat for three Davey, Hilary, Simon and Tim decided to hire out a boat. 1. How many ways could they choose one person to go to hire the boat? Write all these ways dqwn. c< 2. They decided to send two people to go off to buy some food for the boat trip. How many different ways could they choose two people to go? Write them all down. 3. The boat only held three people. How many different ways could they choose three people to go in the boat? Write them all down. BOATS FOR HIKE. ( The next day Ronnie came with them, so there were five people altogether. 4. How many ways could they choose one person to hire the boat? 5. Write down all the ways they could choose two people to buy the food. 6. Write down all the ways they could picmhree people to^jo out in the boat. 7. Four people were needed to carry all the equipment back to the boat house. How many ways could they choose four people to carry the equipment back?
55 Smile 0748 The TIMES Crossword Copy and complete this crossword. How to solve the clues All the answers are familiar three letter words The three letters are represented by factors of the number in the clue. Use the code to translate factors to letters. - Clues 789 Example Clue 11 Downis910. Three factors of 910 are needed. Across Down S oon c oon M 12 E N = 2 x 5 x 91 or._ 2 x 7 x 65 or Hint: 2 x 13 x 35 or Start with prime 5 x 7 x 26 or factors. 5 x 13 x 14 or 7 x 10 x = 2x 5x 7x13 The highest number that can be used is 26. These are all the possible answers x7x 26 translates to EGZ 5x13x14 translates to n 7x10x13 translates to G J M Code A B C D E F G I 111! llifl llli Illll ; j f W$3 H I J K L M Rearrange the letters. is the only possible word. N O P Q R S T I Sill IllS Sfili ill! U V W X Y Z Try 13 /\croe>e> next. You already have 'NT so '14' must be one of the factors. RBKC SMILE 1996.
56 Three Numbers Smile 0749 Choose any three numbers next to each other to make sentences with different answers. 9 * (5-2) x = 5 X (2 + 7) 1) Make sentences for these answers: ) Challenge a friend! Take turns to set an answer and see who can find it first. RBKC SMILE 2001
57 SMILE THREE NUMBERS Choose any 3 numbers next to each other to make sentences with different answers. 9 = (5-2) x 3 = 5 x (2 + 7) (1) Make sentences for these answers: (2) Challenge a friend! Take turns to set an, answer and see who can find it first.
58 Monopoly Smile 0750 You are eeven squares away from Mayfair which Is owned by your rival and has a hotel on It, which means that if you land there It will cost you It Is your turn. Is It wise to spend money developing your own property before you throw the dice, or should you save It In case you have to pay? Give reasons for your decision. Turn over
59 There is only 1 way of scoring two : There are 2 ways of scoring three : There are 3 ways of scoring four : or or or (2) Copy and complete this table for all the scores. (Remember that 6 is the highest number on a dice.) Score Ways of getting the score Total \ / \ <^ (3) How many ways are there of scoring six? > \ (4) How many ways are there of scoring ten? (5) Are you more likely to score six or ten? Why? (6) Are you more likely to score five or nine? Why? (7) How many different ways are there of scoring altogether 1 (8) Why is seven away from Mayfair dangerous?
60 Another way to list all the possible scores with two dice is to make a table. (9) Copy and complete this table. You should have 36 entries in table. (10) Now shade all the sevens. You should shade 6 sevens This means that there are 6 ways out of 36 to score seven so the probability of scoring seven is 6 36 (11) Use the entries In your table to copy and complete the table below, which shows the probabilities for each score. Score Probability
61 (12) A problem: At a school f te two boys run a stall. Competitors pay 1p per go and throw two dice. Competitors win 3p if they throw a double 2p if they throw a total of eeven Are the boys likely to make a profit? (13) Now make your final decision about question (1) and explain It. RBKC SMILE 1997.
Prism or Pyramid? Which nets make pyramids? Find out. RBKC SMILE 2001
 Prism or Pyramid? Which nets make pyramids? Find out. A B D C RBKC SMILE 2001 50 110 104 37 48 32 100 140 60 70 120 119 45 76 Carefully cut out the following shapes. Angle Fit 20 d a c 39 101 b 105 64
Prism or Pyramid? Which nets make pyramids? Find out. A B D C RBKC SMILE 2001 50 110 104 37 48 32 100 140 60 70 120 119 45 76 Carefully cut out the following shapes. Angle Fit 20 d a c 39 101 b 105 64
DOWNSEND SCHOOL YEAR 5 EASTER REVISION BOOKLET
 DOWNSEND SCHOOL YEAR 5 EASTER REVISION BOOKLET This booklet is an optional revision aid for the Summer Exam Name: Maths Teacher: Revision List for Summer Exam Topic Junior Maths Bk 3 Place Value Chapter
DOWNSEND SCHOOL YEAR 5 EASTER REVISION BOOKLET This booklet is an optional revision aid for the Summer Exam Name: Maths Teacher: Revision List for Summer Exam Topic Junior Maths Bk 3 Place Value Chapter
LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII. Mathematics Laboratory
 LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII Mathematics Laboratory The concept of Mathematics Laboratory has been introduced by the Board in its affiliated schools with the objective
LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII Mathematics Laboratory The concept of Mathematics Laboratory has been introduced by the Board in its affiliated schools with the objective
Mathematics Paper 2. Stage minutes. Page Mark. Name.. Additional materials: Ruler Calculator Protractor READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST
 1 55 minutes Mathematics Paper 2 Stage 7 Name.. Additional materials: Ruler Calculator Protractor READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST Answer all questions in the spaces provided on the question paper. You should
1 55 minutes Mathematics Paper 2 Stage 7 Name.. Additional materials: Ruler Calculator Protractor READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST Answer all questions in the spaces provided on the question paper. You should
Key Stage 3 Mathematics. Common entrance revision
 Key Stage 3 Mathematics Key Facts Common entrance revision Number and Algebra Solve the equation x³ + x = 20 Using trial and improvement and give your answer to the nearest tenth Guess Check Too Big/Too
Key Stage 3 Mathematics Key Facts Common entrance revision Number and Algebra Solve the equation x³ + x = 20 Using trial and improvement and give your answer to the nearest tenth Guess Check Too Big/Too
SHAPE level 2 questions. 1. Match each shape to its name. One is done for you. 1 mark. International School of Madrid 1
 SHAPE level 2 questions 1. Match each shape to its name. One is done for you. International School of Madrid 1 2. Write each word in the correct box. faces edges vertices 3. Here is half of a symmetrical
SHAPE level 2 questions 1. Match each shape to its name. One is done for you. International School of Madrid 1 2. Write each word in the correct box. faces edges vertices 3. Here is half of a symmetrical
Developing geometric thinking. A developmental series of classroom activities for Gr. 1-9
 Developing geometric thinking A developmental series of classroom activities for Gr. 1-9 Developing geometric thinking ii Contents Van Hiele: Developing Geometric Thinking... 1 Sorting objects using Geostacks...
Developing geometric thinking A developmental series of classroom activities for Gr. 1-9 Developing geometric thinking ii Contents Van Hiele: Developing Geometric Thinking... 1 Sorting objects using Geostacks...
Lines and angles parallel and perpendicular lines. Look at each group of lines. Tick the parallel lines.
 Lines and angles parallel and perpendicular lines Parallel lines are always the same distance away from each other at any point and can never meet. They can be any length and go in any direction. Look
Lines and angles parallel and perpendicular lines Parallel lines are always the same distance away from each other at any point and can never meet. They can be any length and go in any direction. Look
Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 Practice Paper Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Foundation Tier Paper Reference 5MM1F/01
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 Practice Paper Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Foundation Tier Paper Reference 5MM1F/01
Paper 1. Mathematics test. Calculator not allowed. satspapers.org. First name. Last name. School KEY STAGE TIER
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 4 6 2003 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 4 6 2003 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Second Practice Test 1 Level 5-7
 Mathematics Second Practice Test 1 Level 5-7 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your school
Mathematics Second Practice Test 1 Level 5-7 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your school
MATHEMATICS UNIT 2: CALCULATOR-ALLOWED FOUNDATION TIER
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE NEW 3300U20-1 S17-3300U20-1 MATHEMATICS UNIT 2: CALCULATOR-ALLOWED FOUNDATION TIER TUESDAY, 20 JUNE 2017 AFTERNOON 1 hour 30 minutes For s use
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE NEW 3300U20-1 S17-3300U20-1 MATHEMATICS UNIT 2: CALCULATOR-ALLOWED FOUNDATION TIER TUESDAY, 20 JUNE 2017 AFTERNOON 1 hour 30 minutes For s use
Paper 1. Mathematics test. Calculator not allowed KEY STAGE TIERS. First name. Last name. School
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIERS 4 6 2006 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIERS 4 6 2006 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of
Methods in Mathematics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Foundation Tier Monday 17 June 2013 Morning
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Foundation Tier Monday 17 June 2013 Morning
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet
 GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. a) Study: 6 units 6 tens 6 hundreds 6 thousands 6 ten-thousands 6 hundredthousands HTh T Th Th H T U 6 6 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. a) Study: 6 units 6 tens 6 hundreds 6 thousands 6 ten-thousands 6 hundredthousands HTh T Th Th H T U 6 6 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM MATHEMATICS
 THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 2 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 11 January 2013 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 2 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 11 January 2013 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
Minute Simplify: 12( ) = 3. Circle all of the following equal to : % Cross out the three-dimensional shape.
 Minute 1 1. Simplify: 1( + 7 + 1) =. 7 = 10 10. Circle all of the following equal to : 0. 0% 5 100. 10 = 5 5. Cross out the three-dimensional shape. 6. Each side of the regular pentagon is 5 centimeters.
Minute 1 1. Simplify: 1( + 7 + 1) =. 7 = 10 10. Circle all of the following equal to : 0. 0% 5 100. 10 = 5 5. Cross out the three-dimensional shape. 6. Each side of the regular pentagon is 5 centimeters.
x \ \ \ 1 Tangram 1 You will need centimetre squared paper and scissors. Smile 0005 Draw this on centimetre squared paper. Cut out the pieces.
 Tangram 1 You will need centimetre squared paper and scissors. Draw this on centimetre squared paper. Cut out the pieces. I k 4c m i i A r r i m «/ 4 x cm xr- ^ tt;m x x x \ \ \ Smile 000 i / R i ^m r
Tangram 1 You will need centimetre squared paper and scissors. Draw this on centimetre squared paper. Cut out the pieces. I k 4c m i i A r r i m «/ 4 x cm xr- ^ tt;m x x x \ \ \ Smile 000 i / R i ^m r
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES -
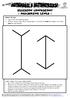 ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
Copying a Line Segment
 Copying a Line Segment Steps 1 4 below show you how to copy a line segment. Step 1 You are given line segment AB to copy. A B Step 2 Draw a line segment that is longer than line segment AB. Label one of
Copying a Line Segment Steps 1 4 below show you how to copy a line segment. Step 1 You are given line segment AB to copy. A B Step 2 Draw a line segment that is longer than line segment AB. Label one of
Maths Makes Sense. 3 Medium-term plan
 Maths Makes Sense 3 Medium-term plan 2 Maths Makes Sense 3 Block 1 End-of-block objectives Arithmetic 1 Respond to I will act the Real Story, you write the Maths Story (including the answer), for addition
Maths Makes Sense 3 Medium-term plan 2 Maths Makes Sense 3 Block 1 End-of-block objectives Arithmetic 1 Respond to I will act the Real Story, you write the Maths Story (including the answer), for addition
Mathematics 43601F. Geometry. In the style of General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier. Past Paper Questions by Topic TOTAL
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials In the style of General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier Pages 2 3 4 5 Mark
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials In the style of General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier Pages 2 3 4 5 Mark
Instructions. Information. Advice
 Instructions Use black 3N ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all questions. Answer the questions in the spaces provided
Instructions Use black 3N ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all questions. Answer the questions in the spaces provided
Workshops: The heart of the MagiKats Programme
 Workshops: The heart of the MagiKats Programme Every student is assigned to a Stage, based on their academic year and assessed study level. Stage 2 students are approximately 8 to 10 years old. The sheets
Workshops: The heart of the MagiKats Programme Every student is assigned to a Stage, based on their academic year and assessed study level. Stage 2 students are approximately 8 to 10 years old. The sheets
The Grade 6 Common Core State Standards for Geometry specify that students should
 The focus for students in geometry at this level is reasoning about area, surface area, and volume. Students also learn to work with visual tools for representing shapes, such as graphs in the coordinate
The focus for students in geometry at this level is reasoning about area, surface area, and volume. Students also learn to work with visual tools for representing shapes, such as graphs in the coordinate
Investigation. Triangle, Triangle, Triangle. Work with a partner.
 Investigation Triangle, Triangle, Triangle Work with a partner. Materials: centimetre ruler 1-cm grid paper scissors Part 1 On grid paper, draw a large right triangle. Make sure its base is along a grid
Investigation Triangle, Triangle, Triangle Work with a partner. Materials: centimetre ruler 1-cm grid paper scissors Part 1 On grid paper, draw a large right triangle. Make sure its base is along a grid
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8. satspapers.org
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 6 8 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 6 8 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Exploring Concepts with Cubes. A resource book
 Exploring Concepts with Cubes A resource book ACTIVITY 1 Gauss s method Gauss s method is a fast and efficient way of determining the sum of an arithmetic series. Let s illustrate the method using the
Exploring Concepts with Cubes A resource book ACTIVITY 1 Gauss s method Gauss s method is a fast and efficient way of determining the sum of an arithmetic series. Let s illustrate the method using the
Hexagon Puzzle. four. ten three. eighteen. twenty-one. six. fourteen. twenty. one hundred. seventeen. sixteen. one quarter. two.
 Cut out the equilateral triangles along the dotted lines. Match the words to the numbers. Fit the triangles together to make one large hexagon. The shaded sections mark the edges of the hexagon. Stick
Cut out the equilateral triangles along the dotted lines. Match the words to the numbers. Fit the triangles together to make one large hexagon. The shaded sections mark the edges of the hexagon. Stick
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 4 Booklet
 GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 4 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. Read carefully: a) The place or position of a digit in a number gives the value of that digit. b) In the number 4237, 4,
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 4 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. Read carefully: a) The place or position of a digit in a number gives the value of that digit. b) In the number 4237, 4,
GCSE Foundation! Set B! Non - Calculator Paper
 Name: GCSE Foundation! Set B! Non - Calculator Paper Equipment 1. A blue or black ink ball-point pen. 2. A pencil. 3. An eraser. 4. A ruler. 5. A pair of compasses. 6. A protractor. Guidance 1. Read each
Name: GCSE Foundation! Set B! Non - Calculator Paper Equipment 1. A blue or black ink ball-point pen. 2. A pencil. 3. An eraser. 4. A ruler. 5. A pair of compasses. 6. A protractor. Guidance 1. Read each
Year 4. Term by Term Objectives. Year 4 Overview. Autumn. Spring Number: Fractions. Summer. Number: Addition and Subtraction.
 Summer Overview Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Autumn Number: Place Value Number: Addition and Subtraction Number: Multiplication and Division Measurement:
Summer Overview Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Autumn Number: Place Value Number: Addition and Subtraction Number: Multiplication and Division Measurement:
Paper 1. Mathematics test. Calculator not allowed. First name. Last name. School KEY STAGE TIER
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 3 5 2003 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 3 5 2003 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
UKMT UKMT UKMT. Junior Kangaroo Mathematical Challenge. Tuesday 13th June 2017
 UKMT UKMT UKMT Junior Kangaroo Mathematical Challenge Tuesday 3th June 207 Organised by the United Kingdom Mathematics Trust The Junior Kangaroo allows students in the UK to test themselves on questions
UKMT UKMT UKMT Junior Kangaroo Mathematical Challenge Tuesday 3th June 207 Organised by the United Kingdom Mathematics Trust The Junior Kangaroo allows students in the UK to test themselves on questions
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM MATHEMATICS
 THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 2 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 6 January 2017 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
THE NORTH LONDON INDEPENDENT GIRLS SCHOOLS CONSORTIUM Group 2 YEAR 7 ENTRANCE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Friday 6 January 2017 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes First Name:... Surname:... Instructions: Please
Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers
 Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Student Book Series D Mathletics Instant Workbooks Copyright Contents Series D Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Looking at whole numbers reading and
Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Student Book Series D Mathletics Instant Workbooks Copyright Contents Series D Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Looking at whole numbers reading and
Mathematics Paper 2. Stage minutes. Name.. Additional materials: Ruler Calculator Tracing paper Geometrical instruments
 1 55 minutes Mathematics Paper 2 Stage 8 Name.. Additional materials: Ruler Calculator Tracing paper Geometrical instruments READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST Answer all questions in the spaces provided on
1 55 minutes Mathematics Paper 2 Stage 8 Name.. Additional materials: Ruler Calculator Tracing paper Geometrical instruments READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST Answer all questions in the spaces provided on
Middle School Geometry. Session 2
 Middle School Geometry Session 2 Topic Activity Name Page Number Related SOL Spatial Square It 52 6.10, 6.13, Relationships 7.7, 8.11 Tangrams Soma Cubes Activity Sheets Square It Pick Up the Toothpicks
Middle School Geometry Session 2 Topic Activity Name Page Number Related SOL Spatial Square It 52 6.10, 6.13, Relationships 7.7, 8.11 Tangrams Soma Cubes Activity Sheets Square It Pick Up the Toothpicks
TUESDAY, 8 NOVEMBER 2016 MORNING 1 hour 45 minutes
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE NEW 3300U30- A6-3300U30- MATHEMATICS UNIT : NON-CALCULATOR INTERMEDIATE TIER TUESDAY, 8 NOVEMBER 206 MORNING hour 45 minutes For s use ADDITIONAL
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE NEW 3300U30- A6-3300U30- MATHEMATICS UNIT : NON-CALCULATOR INTERMEDIATE TIER TUESDAY, 8 NOVEMBER 206 MORNING hour 45 minutes For s use ADDITIONAL
Mathematical Investigations
 Mathematical Investigations We are learning to investigate problems We are learning to look for patterns and generalise We are developing multiplicative thinking Exercise 1: Crossroads Equipment needed:
Mathematical Investigations We are learning to investigate problems We are learning to look for patterns and generalise We are developing multiplicative thinking Exercise 1: Crossroads Equipment needed:
Paper 1. Mathematics test. Calculator not allowed KEY STAGE TIERS. First name. Last name. School
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIERS 5 7 2006 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIERS 5 7 2006 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of
8 LEVELS 4 6 PAPER. Paper 2. Year 8 mathematics test. Calculator allowed. First name. Last name. Class. Date YEAR
 Ma YEAR 8 LEVELS 4 6 PAPER 2 Year 8 mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your details in the spaces
Ma YEAR 8 LEVELS 4 6 PAPER 2 Year 8 mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your details in the spaces
Job Cards and Other Activities. Write a Story for...
 Job Cards and Other Activities Introduction. This Appendix gives some examples of the types of Job Cards and games that we used at the Saturday Clubs. We usually set out one type of card per table, along
Job Cards and Other Activities Introduction. This Appendix gives some examples of the types of Job Cards and games that we used at the Saturday Clubs. We usually set out one type of card per table, along
Addition and Subtraction
 D Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic 1 Addition mental strategies (pp. 114) look for a ten look for patterns doubles and near doubles bridge to ten jump strategy split strategy version 1 split strategy
D Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic 1 Addition mental strategies (pp. 114) look for a ten look for patterns doubles and near doubles bridge to ten jump strategy split strategy version 1 split strategy
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important
 Many artists use geometric concepts in their work. Think about what you have learned in geometry. How do these examples of First Nations art and architecture show geometry ideas? What You ll Learn Identify
Many artists use geometric concepts in their work. Think about what you have learned in geometry. How do these examples of First Nations art and architecture show geometry ideas? What You ll Learn Identify
FRIDAY, 10 NOVEMBER 2017 MORNING 1 hour 30 minutes
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 3300U10-1 A17-3300U10-1 MATHEMATICS UNIT 1: NON-CALCULATOR FOUNDATION TIER FRIDAY, 10 NOVEMBER 2017 MORNING 1 hour 30 minutes For s use ADDITIONAL
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 3300U10-1 A17-3300U10-1 MATHEMATICS UNIT 1: NON-CALCULATOR FOUNDATION TIER FRIDAY, 10 NOVEMBER 2017 MORNING 1 hour 30 minutes For s use ADDITIONAL
Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2 (Calculator)
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics B Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2 (Calculator) Tuesday 14 June 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 30
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics B Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2 (Calculator) Tuesday 14 June 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 30
Introduction. It gives you some handy activities that you can do with your child to consolidate key ideas.
 (Upper School) Introduction This booklet aims to show you how we teach the 4 main operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) at St. Helen s College. It gives you some handy activities
(Upper School) Introduction This booklet aims to show you how we teach the 4 main operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) at St. Helen s College. It gives you some handy activities
Summer Solutions Problem Solving Level 4. Level 4. Problem Solving. Help Pages
 Level Problem Solving 6 General Terms acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 addend a number being added angle formed by two rays that share a common endpoint area the size of a surface; always expressed
Level Problem Solving 6 General Terms acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 addend a number being added angle formed by two rays that share a common endpoint area the size of a surface; always expressed
Length and area Block 1 Student Activity Sheet
 Block 1 Student Activity Sheet 1. Write the area and perimeter formulas for each shape. 2. What does each of the variables in these formulas represent? 3. How is the area of a square related to the area
Block 1 Student Activity Sheet 1. Write the area and perimeter formulas for each shape. 2. What does each of the variables in these formulas represent? 3. How is the area of a square related to the area
Methods in Mathematics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Foundation Tier Monday 10 November
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Foundation Tier Monday 10 November
ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes
 ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS 2017 MATHEMATICS FIRST FORM Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Answer ALL questions. Show all necessary working on the question paper in the spaces provided and write your answers
ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS 2017 MATHEMATICS FIRST FORM Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Answer ALL questions. Show all necessary working on the question paper in the spaces provided and write your answers
Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities
 Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities For more information about the materials you find in this packet, contact: Sharon Rendon (605) 431-0216 sharonrendon@cpm.org 1 2-51. SPECIAL
Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities For more information about the materials you find in this packet, contact: Sharon Rendon (605) 431-0216 sharonrendon@cpm.org 1 2-51. SPECIAL
Numeracy Practice Tests
 ROUND 3 KEY STAGE 2 LEVELS 3 5 TEST B Numeracy Practice Tests CALCULATOR ALLOWED Mitch Bec Dan First name Last name School Test Instructions You may use a calculator to answer any questions in this test.
ROUND 3 KEY STAGE 2 LEVELS 3 5 TEST B Numeracy Practice Tests CALCULATOR ALLOWED Mitch Bec Dan First name Last name School Test Instructions You may use a calculator to answer any questions in this test.
Topic. Easter Intervention. If you have any questions, feel free to
 Easter Intervention Foundation Questions Topic Angles Transformations Multiples, Factors, Primes Indices Algebra Area and Perimeter Factions, Decimals and Percentages Ratio Equations Probability Averages
Easter Intervention Foundation Questions Topic Angles Transformations Multiples, Factors, Primes Indices Algebra Area and Perimeter Factions, Decimals and Percentages Ratio Equations Probability Averages
Reigate Grammar School. 11+ Entrance Examination January 2012 MATHEMATICS
 Reigate Grammar School + Entrance Examination January 0 MATHEMATICS Time allowed: 45 minutes NAME Work through the paper carefully You do not have to finish everything Do not spend too much time on any
Reigate Grammar School + Entrance Examination January 0 MATHEMATICS Time allowed: 45 minutes NAME Work through the paper carefully You do not have to finish everything Do not spend too much time on any
Maths Makes Sense. 1 Medium-term plan
 Maths Makes Sense 1 Medium-term plan 2 Maths Makes Sense 1 Block 1 End-of-block objectives Arithmetic 1 Copy addition and subtraction Maths Stories with 1-digit, zero, a half and a quarter, e.g. 2 + 1
Maths Makes Sense 1 Medium-term plan 2 Maths Makes Sense 1 Block 1 End-of-block objectives Arithmetic 1 Copy addition and subtraction Maths Stories with 1-digit, zero, a half and a quarter, e.g. 2 + 1
Maths SATs practice paper 2: reasoning
 Maths SATs paper 2: reasoning First name... Middle name... Last name... Date of birth Day... Month... Year... School name... www.teachitprimary.co.uk 208 320 Page of 8 Instructions You must not use a calculator
Maths SATs paper 2: reasoning First name... Middle name... Last name... Date of birth Day... Month... Year... School name... www.teachitprimary.co.uk 208 320 Page of 8 Instructions You must not use a calculator
Test B. Calculator allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School KEY STAGE 2 LEVELS 3 5
 Ma KEY STAGE 2 LEVELS 3 5 Mathematics test Test B Calculator allowed First name Last name School 2007 For marker s use only Page 5 7 Marks 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 TOTAL Borderline check Jamie Kate Hassan
Ma KEY STAGE 2 LEVELS 3 5 Mathematics test Test B Calculator allowed First name Last name School 2007 For marker s use only Page 5 7 Marks 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 TOTAL Borderline check Jamie Kate Hassan
MATHEMATICS. Name: Primary School: Boy or Girl: Date of Birth: Today s Date: Test taken at:
 MATHEMATICS Name: Primary School: Boy or Girl: Date of Birth: Today s Date: Test taken at: READ THE FOLLOWING CAREFULLY 1. Do not open this booklet until you are told to do so. 2. You may work the questions
MATHEMATICS Name: Primary School: Boy or Girl: Date of Birth: Today s Date: Test taken at: READ THE FOLLOWING CAREFULLY 1. Do not open this booklet until you are told to do so. 2. You may work the questions
GCSE LINKED PAIR PILOT 4363/01 METHODS IN MATHEMATICS UNIT 1: Methods (Non-Calculator) FOUNDATION TIER
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE LINKED PAIR PILOT 4363/01 METHODS IN MATHEMATICS UNIT 1: Methods (Non-Calculator) FOUNDATION TIER A.M. TUESDAY, 11 June 2013 1 1 hours 2 CALCULATORS
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE LINKED PAIR PILOT 4363/01 METHODS IN MATHEMATICS UNIT 1: Methods (Non-Calculator) FOUNDATION TIER A.M. TUESDAY, 11 June 2013 1 1 hours 2 CALCULATORS
Choose a circle to show how much each sentence is like you. Very Unlike Me. Unlike Me. Like Me. 01. I like maths at school. 02. I am good at maths.
 Choose a circle to show how much each sentence is like you Very Unlike Me Unlike Me Like Me Very Like Me 1 2 3 4 01. I like maths at school. 02. I am good at maths. 03. My teacher thinks I am good at maths.
Choose a circle to show how much each sentence is like you Very Unlike Me Unlike Me Like Me Very Like Me 1 2 3 4 01. I like maths at school. 02. I am good at maths. 03. My teacher thinks I am good at maths.
Mathematics Second Practice Test 1 Levels 3-5 Calculator not allowed
 Mathematics Second Practice Test 1 Levels 3-5 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your school
Mathematics Second Practice Test 1 Levels 3-5 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your school
Stage 2 PROMPT sheet. 2/3 Estimate numbers. 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables. 2/4 Order numbers. Count in 10s.
 Stage 2 PROMPT sheet 2/3 Estimate numbers Eyeball estimate Here are 3 sweets 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables 0 x 2 = 0 1 x 2 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 3 x 2 = 6 4 x 2 = 8 5 x 2 = 10 6 x 2 = 12 7 x 2 = 14 8 x
Stage 2 PROMPT sheet 2/3 Estimate numbers Eyeball estimate Here are 3 sweets 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables 0 x 2 = 0 1 x 2 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 3 x 2 = 6 4 x 2 = 8 5 x 2 = 10 6 x 2 = 12 7 x 2 = 14 8 x
Stage 2 PROMPT sheet. 2/3 Estimate numbers. 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables. 2/4 Order numbers. 2/2 Place value
 tens units tens units Stage 2 PROMPT sheet 2/3 Estimate numbers Eyeball estimate Here are 3 sweets 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables 0 x 2 = 0 1 x 2 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 3 x 2 = 6 4 x 2 = 8 5 x 2 = 10 6 x
tens units tens units Stage 2 PROMPT sheet 2/3 Estimate numbers Eyeball estimate Here are 3 sweets 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables 0 x 2 = 0 1 x 2 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 3 x 2 = 6 4 x 2 = 8 5 x 2 = 10 6 x
GCSE Mathematics Specification (8300/2F)
 NEW SPECIMEN PAPERS PUBLISHED JUNE 2015 GCSE Mathematics Specification (8300/2F) Paper 2 Foundation tier F Date Morning 1 hour 30 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a calculator mathematical
NEW SPECIMEN PAPERS PUBLISHED JUNE 2015 GCSE Mathematics Specification (8300/2F) Paper 2 Foundation tier F Date Morning 1 hour 30 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a calculator mathematical
Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers
 LESSON 61 page 328 Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers Name Teacher Notes: Introduce Hint #21 Multiplication/ Division Fact Families. Review Multiplication Table on page 5 and Quadrilaterals on
LESSON 61 page 328 Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers Name Teacher Notes: Introduce Hint #21 Multiplication/ Division Fact Families. Review Multiplication Table on page 5 and Quadrilaterals on
Geometry Mrs. Crocker Spring 2014 Final Exam Review
 Name: Mod: Geometry Mrs. Crocker Spring 2014 Final Exam Review Use this exam review to complete your flip book and to study for your upcoming exam. You must bring with you to the exam: 1. Pencil, eraser,
Name: Mod: Geometry Mrs. Crocker Spring 2014 Final Exam Review Use this exam review to complete your flip book and to study for your upcoming exam. You must bring with you to the exam: 1. Pencil, eraser,
19! = 1, st July. On the grid is one side of a quadrilateral with 3 acute angles. Complete the quadrilateral
 1st July 19! = 1,000 750 822 On the grid is one side of a quadrilateral with 3 acute angles. Complete the quadrilateral Georgia and Emma share 40 sweets in the ratio 3:5. How many sweets does Emma get?
1st July 19! = 1,000 750 822 On the grid is one side of a quadrilateral with 3 acute angles. Complete the quadrilateral Georgia and Emma share 40 sweets in the ratio 3:5. How many sweets does Emma get?
Unit 2: Number, Algebra, Geometry 1 (Non-Calculator) Foundation Tier
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics B Unit 2: Number, Algebra, Geometry 1 (Non-Calculator) Foundation Tier Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics B Unit 2: Number, Algebra, Geometry 1 (Non-Calculator) Foundation Tier Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning
Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities
 Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities For more information about the materials you find in this packet, contact: Chris Mikles 916-719-3077 chrismikles@cpm.org 1 2 2-51. SPECIAL
Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities For more information about the materials you find in this packet, contact: Chris Mikles 916-719-3077 chrismikles@cpm.org 1 2 2-51. SPECIAL
SPECIMEN PAPER GROUP E MATHEMATICS
 SPECIMEN PAPER GROUP E MATHEMATICS Time Allowed: 45 minutes Name: INSTRUCTIONS You will need a pencil and a ruler. No Calculator allowed. Write your answers in the spaces provided on this paper. Use any
SPECIMEN PAPER GROUP E MATHEMATICS Time Allowed: 45 minutes Name: INSTRUCTIONS You will need a pencil and a ruler. No Calculator allowed. Write your answers in the spaces provided on this paper. Use any
Mathematics (Linear) 4365/1F
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Pages Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier November 2014 Mathematics
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Pages Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier November 2014 Mathematics
First Name: Last Name: Select the one best answer for each question. DO NOT use a calculator in completing this packet.
 5 Entering 5 th Grade Summer Math Packet First Name: Last Name: 5 th Grade Teacher: I have checked the work completed: Parent Signature Select the one best answer for each question. DO NOT use a calculator
5 Entering 5 th Grade Summer Math Packet First Name: Last Name: 5 th Grade Teacher: I have checked the work completed: Parent Signature Select the one best answer for each question. DO NOT use a calculator
Section 1: Whole Numbers
 Grade 6 Play! Mathematics Answer Book 67 Section : Whole Numbers Question Value and Place Value of 7-digit Numbers TERM 2. Study: a) million 000 000 A million has 6 zeros. b) million 00 00 therefore million
Grade 6 Play! Mathematics Answer Book 67 Section : Whole Numbers Question Value and Place Value of 7-digit Numbers TERM 2. Study: a) million 000 000 A million has 6 zeros. b) million 00 00 therefore million
Sample test questions All questions
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 LEVELS 3 8 Sample test questions All questions 2003 Contents Question Level Attainment target Page Completing calculations 3 Number and algebra 3 Odd one out 3 Number and algebra 4 Hexagon
Ma KEY STAGE 3 LEVELS 3 8 Sample test questions All questions 2003 Contents Question Level Attainment target Page Completing calculations 3 Number and algebra 3 Odd one out 3 Number and algebra 4 Hexagon
Geometry 2001 part 1
 Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
Excel / Education. GCSE Mathematics. Paper 4B (Calculator) Foundation Tier. Time: 1 hour 30 minutes. Turn over
 Excel / Education GCSE Mathematics Paper 4B (Calculator) Foundation Tier Time: 1 hour 30 minutes 4B Materials required for examination Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses,
Excel / Education GCSE Mathematics Paper 4B (Calculator) Foundation Tier Time: 1 hour 30 minutes 4B Materials required for examination Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses,
Mrs. Ambre s Math Notebook
 Mrs. Ambre s Math Notebook Almost everything you need to know for 7 th grade math Plus a little about 6 th grade math And a little about 8 th grade math 1 Table of Contents by Outcome Outcome Topic Page
Mrs. Ambre s Math Notebook Almost everything you need to know for 7 th grade math Plus a little about 6 th grade math And a little about 8 th grade math 1 Table of Contents by Outcome Outcome Topic Page
Class : VI - Mathematics
 O. P. JINDAL SCHOOL, RAIGARH (CG) 496 001 Phone : 07762-227042, 227293, (Extn. 227001-49801, 02, 04, 06); Fax : 07762-262613; e-mail: opjsraigarh@jspl.com; website : www.opjsrgh.in Class : VI - Mathematics
O. P. JINDAL SCHOOL, RAIGARH (CG) 496 001 Phone : 07762-227042, 227293, (Extn. 227001-49801, 02, 04, 06); Fax : 07762-262613; e-mail: opjsraigarh@jspl.com; website : www.opjsrgh.in Class : VI - Mathematics
Year 9 mathematics: holiday revision. 2 How many nines are there in fifty-four?
 DAY 1 ANSWERS Mental questions 1 Multiply seven by seven. 49 2 How many nines are there in fifty-four? 54 9 = 6 6 3 What number should you add to negative three to get the answer five? -3 0 5 8 4 Add two
DAY 1 ANSWERS Mental questions 1 Multiply seven by seven. 49 2 How many nines are there in fifty-four? 54 9 = 6 6 3 What number should you add to negative three to get the answer five? -3 0 5 8 4 Add two
Angles and. Learning Goals U N I T
 U N I T Angles and Learning Goals name, describe, and classify angles estimate and determine angle measures draw and label angles provide examples of angles in the environment investigate the sum of angles
U N I T Angles and Learning Goals name, describe, and classify angles estimate and determine angle measures draw and label angles provide examples of angles in the environment investigate the sum of angles
S1/2 Checklist S1/2 Checklist. Whole Numbers. No. Skill Done CfE Code(s) 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting
 Whole Numbers 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting MNU 0-0a number such as 0, 1,, 3, 4, Count past 10 MNU 0-03a 3 Know why place value is important MNU 1-0a 4 Know that approximating means to
Whole Numbers 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting MNU 0-0a number such as 0, 1,, 3, 4, Count past 10 MNU 0-03a 3 Know why place value is important MNU 1-0a 4 Know that approximating means to
SERIES Addition and Subtraction
 D Teacher Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic Section Addition Answers mental (pp. 48) strategies (pp. 4) look addition for a mental ten strategies_ look subtraction for patterns_ mental strategies
D Teacher Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic Section Addition Answers mental (pp. 48) strategies (pp. 4) look addition for a mental ten strategies_ look subtraction for patterns_ mental strategies
Methods in Mathematics (Linked Pair Pilot)
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Methods in Mathematics (Linked Pair Pilot) Unit 2 Geometry and Algebra Monday 11 November 2013
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Methods in Mathematics (Linked Pair Pilot) Unit 2 Geometry and Algebra Monday 11 November 2013
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, pen, HB pencil, eraser. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International Primary Curriculum Centre Number Mathematics Year 6 Achievement Test Candidate Number Thursday 4 June 2015 Morning Time: 1 hour Paper
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International Primary Curriculum Centre Number Mathematics Year 6 Achievement Test Candidate Number Thursday 4 June 2015 Morning Time: 1 hour Paper
About Add-ons. Using Add-ons ADD-ONS. How to use these resources NOTES. 1 Number: place value. 2 Number: money problems
 ADD-ONS How to use these resources About NOTES are part of the T5 ( ) pack. There are twelve, each covering one of the major areas of mathematics drawn from the level 4 6 Key Stage 3 National Curriculum
ADD-ONS How to use these resources About NOTES are part of the T5 ( ) pack. There are twelve, each covering one of the major areas of mathematics drawn from the level 4 6 Key Stage 3 National Curriculum
RightStart Mathematics
 Most recent update: April 18, 2018 RightStart Mathematics Corrections and Updates for Level E/Grade 4 Lessons and Worksheets, second edition LESSON / WORKSHEET CHANGE DATE Lesson 8 04/18/2018 Lesson 36
Most recent update: April 18, 2018 RightStart Mathematics Corrections and Updates for Level E/Grade 4 Lessons and Worksheets, second edition LESSON / WORKSHEET CHANGE DATE Lesson 8 04/18/2018 Lesson 36
CHARACTERISTICS AND CLASSIFICATION OF SHAPES and 1.3.2
 CHARACTERISTICS AND CLASSIFICATION OF SHAPES 1.3.1 and 1.3.2 Geometric shapes occur in many places. After studying them using transformations, students start to see certain characteristics of different
CHARACTERISTICS AND CLASSIFICATION OF SHAPES 1.3.1 and 1.3.2 Geometric shapes occur in many places. After studying them using transformations, students start to see certain characteristics of different
Addition and Subtraction
 Series Student Addition and Subtraction My name D Copyright 2009 3P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 2009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from 3P Learning
Series Student Addition and Subtraction My name D Copyright 2009 3P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 2009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from 3P Learning
3301/1F. MATHEMATICS (SPECIFICATION A) 3301/1F Foundation Tier Paper 1 Non-Calculator. General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2004
 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2004 MATHEMATICS (SPECIFICATION A) 3301/1F Foundation Tier Paper 1 Non-Calculator
Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2004 MATHEMATICS (SPECIFICATION A) 3301/1F Foundation Tier Paper 1 Non-Calculator
Year 5. Mathematics A booklet for parents
 Year 5 Mathematics A booklet for parents About the statements These statements show some of the things most children should be able to do by the end of Year 5. A statement might be harder than it seems,
Year 5 Mathematics A booklet for parents About the statements These statements show some of the things most children should be able to do by the end of Year 5. A statement might be harder than it seems,
Paper Reference. Mathematics A Paper 3 (Non Calculator) Intermediate Tier Tuesday 8 June 2004 Afternoon Time: 2 hours
 Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 5503 03 Signature Paper Reference(s) 5503/03 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A 1387 Paper 3 (Non Calculator) Intermediate Tier Tuesday 8 June 2004 Afternoon
Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 5503 03 Signature Paper Reference(s) 5503/03 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A 1387 Paper 3 (Non Calculator) Intermediate Tier Tuesday 8 June 2004 Afternoon
Whole Numbers. Predecessor and successor Given any natural number, you can add 1 to that number and get the next number i.e. you
 Whole Numbers Chapter.1 Introduction As we know, we use 1,, 3, 4,... when we begin to count. They come naturally when we start counting. Hence, mathematicians call the counting numbers as Natural numbers.
Whole Numbers Chapter.1 Introduction As we know, we use 1,, 3, 4,... when we begin to count. They come naturally when we start counting. Hence, mathematicians call the counting numbers as Natural numbers.
Paper 2. Mathematics test. Calculator allowed. First name. Last name. School KEY STAGE TIER
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8 2004 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8 2004 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
TUESDAY, 8 NOVEMBER 2016 MORNING 1 hour 30 minutes
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE NEW 3300U10-1 A16-3300U10-1 MATHEMATICS UNIT 1: NON-CALCULATOR FOUNDATION TIER TUESDAY, 8 NOVEMBER 2016 MORNING 1 hour 30 minutes For s use ADDITIONAL
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE NEW 3300U10-1 A16-3300U10-1 MATHEMATICS UNIT 1: NON-CALCULATOR FOUNDATION TIER TUESDAY, 8 NOVEMBER 2016 MORNING 1 hour 30 minutes For s use ADDITIONAL
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 5 7. satspapers.org
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 5 7 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 5 7 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Mathematics, Grade 8
 Session 1, Multiple-Choice Questions 44084 C 1 13608 C 2 (0.5)(0.5)(0.5) is equal to which of the following? A. 0.000125 B. 0.00125 C. 0.125 D. 1.25 Reporting Category for Item 1: Number Sense and Operations
Session 1, Multiple-Choice Questions 44084 C 1 13608 C 2 (0.5)(0.5)(0.5) is equal to which of the following? A. 0.000125 B. 0.00125 C. 0.125 D. 1.25 Reporting Category for Item 1: Number Sense and Operations
25 C3. Rachel gave half of her money to Howard. Then Howard gave a third of all his money to Rachel. They each ended up with the same amount of money.
 24 s to the Olympiad Cayley Paper C1. The two-digit integer 19 is equal to the product of its digits (1 9) plus the sum of its digits (1 + 9). Find all two-digit integers with this property. If such a
24 s to the Olympiad Cayley Paper C1. The two-digit integer 19 is equal to the product of its digits (1 9) plus the sum of its digits (1 + 9). Find all two-digit integers with this property. If such a
GCSE Mathematics Practice Tests: Set 5
 GCSE Mathematics Practice Tests: Set 5 Paper 1H (Non-calculator) Time: 1 hour 30 minutes You should have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, pair of compasses, pen, HB pencil,
GCSE Mathematics Practice Tests: Set 5 Paper 1H (Non-calculator) Time: 1 hour 30 minutes You should have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, pair of compasses, pen, HB pencil,
