Introduction to Control Systems
|
|
|
- Britney Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Control Systems MEM 355 Performance Enhancement of Dynamical Systems Harry G. Kwatny Department of Mechanical Engineering & Mechanics Drexel University
2 Outline Course practical information Control: open loop and closed loop Short history of control Contemporary applications Technology drivers Summary What is the course content? What is control? Why should an ME care? Why all the math?
3 Practical Information Lectures: Tues & Thurs 3:30-4:50 pm URL: Text Book: Kwatny & Chang, Introduction to Control Systems Engineering, Cognella. Software: The MathWorks, Inc. The Student Edition of MATLAB, Version +Control Toolbox. (UG lab, CAD lab). Grading: Homework (4): 20% Exam 1 (in class): 25% Exam 2 (in class): 25% Project (take home): 30%
4 What you should know going in Basics of Laplace transform Concepts of state space and transfer function models of a linear system. The meaning of poles & zeros The frequency transfer function and Bode Plots Block diagram manipulation Eigenvalues & eigenvectors, modal analysis and similarity transformations. Stability and Routh table. Basic ability to use MATLAB.
5 What you should know going out Understand why automatic control is useful for a mechanical engineer Recognize the value of integrated control and process design Understand the key concepts of control system design Be able to solve simple control problems Recognize difficult control problems Know relevant mathematical theory Have competence in using computational tools
6 Specific Goals Define the control system design problem and develop a preliminary appreciation of the tradeoffs involved and requirements for robust stability and performance. Develop concepts and tools for ultimate state error analysis. Develop the relationship between time domain and frequency domain performance specifications, e.g, rise time, overshoot, settling time, sensitivity function and bandwidth. Develop frequency domain design methods, including: the root locus method, Nyquist & Bode methods, and stability margins. Provide an introduction to state space design: controllability and observability, pole placement, design via the separation principle (time permitting). Emphasize computational methods using MATLAB.
7 What is Control? Control refers to the manipulation of the inputs to a physical system in order to cause desirable behavior. Cause output variables to track desired values Impose desirable dynamical behavior, e.g., stabilize an unstable system Open loop (feedforward) control Exploit knowledge of system behavior to compute necessary inputs Requires accurate model of system Closed loop (feedback, active) control Process information from sensors to derive appropriate inputs Allows compensation for model uncertainty, disturbances, noise Alters system dynamics
8 Familiar Examples Household Temperature Control Cruise Control + Traction Control Electronic Stabilization Airplane Autopilot
9 What do Control Engineers Do? System Design/System Integration Participate in defining system/subsystem requirements and specifications Develop subsystem/component specifications including cyberstructure Participate in component selection/design Develop math models and simulations of components/subsystems/system Design/implement control systems Participate in testing/validation/verification
10 Open & Closed Loop Control Control computer Feedforward does not alter plant dynamics. Feedback does.
11 The Magic of Feedback The adjustment of system inputs based on the observation of its outputs Feedback is a universal strategy to cope with uncertainty In engineering we use feedback to: Cause a system to behave as desired Keep variables constant Stabilize unstable system Reduce effects of disturbances Minimize the effect of component variations Another alternative for designers
12 Origins of Control Engineering Clocks (escapement) Windmills 1787 Steam Engines (Watt) 1788 Maxwell ~ Governors 1868 Water Turbines 1893 Wright brothers ~ Airplane 1903 Sperry ~ Autopilot (Gyro) 1914 Minorsky ~ Ship steering 1922 Black ~ Feedback amplifier 1928 Ivanoff ~ Temperature regulation 1934 First real control system anaysis. First journal article. Invention of new control paradigm.
13 Wilber Wright 1901 We know how to construct airplanes. Men also know how to build engines. The inability to balance and steer still confronts students of the flying problem. When this one feature has been worked out, the age of flying will have arrived, for all other difficulties are of minor importance.
14 Contemporary Applications Widespread use of automatic control in many fields Power generation Power transmission Process control Discrete manufacturing Robotics Communications Automotive Buildings Aerospace Medicine Marine Engineering Computers Instrumentation Mechatronics Materials Physics Biology Economics There is a unified framework of theory, design methods and computer tools that cut across fields of application.
15 Examples Flight control systems Commercial & military fly-by-wire Autopilot, auto-landing UAV Robotics Precision positioning in manufacturing Remote space/sea environments Minimally-invasive surgery RPV s for surveillance, search and rescue Automotive Mercedes Benz SLR Engine Transmission Cruise, climate control ABS, Traction control, ESP Active suspension Self driving Power plants Various temps/pressures Power output Emissions control Heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC)
16 Examples Materials processing Rapid thermal processing Vapor deposition Noise and vibration control Active mounts Speaker systems Intelligent vehicle highway systems platooning for high speed, high density travel Automatic merge Obstacle avoidance Lane Following Long haul fuel optimization Smart engines Compression systems stall, surge, flutter control Combustion systems lean air/fuel ratio for low emissions, improved efficiency GE 7000
17 Evolution of the Control Discipline Classical control 1940 Frequency-domain based tools for linear systems Mainly useful for single-input single-output (SISO) systems WWII years saw 1 st application of optimal control Still the main tools used in practice Modern control 1960 State space approach for linear systems Useful for SISO and multi-input multi-output (MIMO) systems Relies on linear algebra computations rather than Laplace transform Performance and robustness measures not always explicit Just in time for space exploration Optimal control 1970 Find the input that optimizes some objective function (e.g., min fuel, min time) Used for both open loop and closed loop design Robust control 1980 Generalizes classical control to MIMO case Enabled by modern control development Nonlinear, adaptive, hybrid 1990 Geometric theory of affine systems, variable structure Self-tuning and adaptive control Discrete Event & Hybrid Systems Mixed Logic-Dynamical Systems
18 Key Technology Trends Computation/microprocessors Cheap and powerful microprocessors opened the door to widespread control applications from 1970 s onward Sensors and actuators Sensors continue to get smaller, cheaper, faster Macro/micro scale actuation evolving (power electronics, piezo-electric, EM-rheological fluids) Communications and networking Networks replacing point-to-point communication in large systems (e.g., electric power systems) and small (e.g. automotive)
19 Active Control in Automobiles A typical automobile has feedback controllers. Here are a few examples in a contemporary Mercedes. Cruise Control ABC-active body control ABS-anti-lock braking system ASR acceleration skid control ESP electronic stabilization program SBC sensotronic brake control BAS brake assist system Proximity controlled cruising
20 The Mercedes A-class Automatic control gives extra freedom to the designer Unstable behavior improved by Electronic Stabilization Program (ESP) Now standard on virtually all new vehicles
21 Mercedes Benz Electronic Stabilization Package
22 Active Body Control ABC continuously matches the stiffness and damping characteristics to current driving conditions. It is possible, for example, to compensate for the rolling motion of the body when taking a bend in the road. Hydraulic cylinders in series with the coil springs, generate forces that counteract wheel load. This is performed with sensors that measure yaw rate, longitudinal and transverse acceleration, vertical acceleration.
23 Biology/Biomechanics Feedback governs how we grow, respond to stress and challenge. Feedback regulates factors such as body temperature, blood pressure, and cholesterol level. Feedback makes it possible for us to stand upright. Feedback enables locomotion. Feedback operates at every level, from the interaction of proteins in cells to the interaction of organisms in complex ecologies. Feedback control is used to design drug treatment strategies for diseases like HIV/Aids, Cancer Biologically inspired control
24 Research Applications in MEM Automotive Aircraft/Flight Safety Power Plants Robotics Autonomous Vehicles Mechatronics Biology/Biomechanics Electric Power Systems (terrestrial, automotive, ship)
25 State Space & Transfer Function Models State Space x Ax Bu y Cx Du State space models are also referred to as time-domain models Y s G s U s Y s L y t 1 G s C si A B D U s L u t Transfer Function Transfer function models are also Referred to as frequency domain models.
26 Summary Course content. What is a control system? Open loop/closed loop (feedforward/feedback) Why is control relevant to ME? Applications! Applications! Applications! Why so much math? Abstraction to accommodate many applications in a common framework Explicit design approaches to meet (optimize) specific performance goals.
Control Engineering. Hidden Technology. K. J. Åström Lund Institute of Technology Lund University. the Hidden Technology
 Control Engineering the K. J. Åström Lund Institute of Technology Lund University The Widely used Very successful Seldom talked about Except when disaster strikes Why? Easier to talk about devices than
Control Engineering the K. J. Åström Lund Institute of Technology Lund University The Widely used Very successful Seldom talked about Except when disaster strikes Why? Easier to talk about devices than
Chapter 1: Introduction to Control Systems Objectives
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Control Systems Objectives In this chapter we describe a general process for designing a control system. A control system consisting of interconnected components is designed
Chapter 1: Introduction to Control Systems Objectives In this chapter we describe a general process for designing a control system. A control system consisting of interconnected components is designed
Biomedical Control Systems. Lecture#01
 1 Biomedical Control Systems Lecture#01 2 Text Books Modern Control Engineering, 5 th Edition; Ogata. Feedback & Control Systems, 2 nd edition; Schaum s outline, Joseph J, Allen R. Control Systems Engineering,
1 Biomedical Control Systems Lecture#01 2 Text Books Modern Control Engineering, 5 th Edition; Ogata. Feedback & Control Systems, 2 nd edition; Schaum s outline, Joseph J, Allen R. Control Systems Engineering,
Welcome to SENG 480B / CSC 485A / CSC 586A Self-Adaptive and Self-Managing Systems
 Welcome to SENG 480B / CSC 485A / CSC 586A Self-Adaptive and Self-Managing Systems Dr. Hausi A. Müller Department of Computer Science University of Victoria http://courses.seng.uvic.ca/courses/2015/summer/seng/480a
Welcome to SENG 480B / CSC 485A / CSC 586A Self-Adaptive and Self-Managing Systems Dr. Hausi A. Müller Department of Computer Science University of Victoria http://courses.seng.uvic.ca/courses/2015/summer/seng/480a
Glossary of terms. Short explanation
 Glossary Concept Module. Video Short explanation Abstraction 2.4 Capturing the essence of the behavior of interest (getting a model or representation) Action in the control Derivative 4.2 The control signal
Glossary Concept Module. Video Short explanation Abstraction 2.4 Capturing the essence of the behavior of interest (getting a model or representation) Action in the control Derivative 4.2 The control signal
MEM380 Applied Autonomous Robots I Winter Feedback Control USARSim
 MEM380 Applied Autonomous Robots I Winter 2011 Feedback Control USARSim Transforming Accelerations into Position Estimates In a perfect world It s not a perfect world. We have noise and bias in our acceleration
MEM380 Applied Autonomous Robots I Winter 2011 Feedback Control USARSim Transforming Accelerations into Position Estimates In a perfect world It s not a perfect world. We have noise and bias in our acceleration
EECE 460 : Control System Design
 EECE 460 : Control System Design January 2012 Guy A. Dumont UBC EECE Introduction Guy A. Dumont (UBC EECE) EECE 460 : Control System Design Introduction 1 / 24 Contents Contents Practical information Your
EECE 460 : Control System Design January 2012 Guy A. Dumont UBC EECE Introduction Guy A. Dumont (UBC EECE) EECE 460 : Control System Design Introduction 1 / 24 Contents Contents Practical information Your
Intro to Automation and Controls by: P. Ribeiro Calvin College
 Intro to Automation and Controls by: P. Ribeiro Calvin College Link: https://www.calvin.edu/~pribeiro/courses/engr315/lecturesnotes/ Chapter 1: Introduction to Control Systems Objectives In this chapter
Intro to Automation and Controls by: P. Ribeiro Calvin College Link: https://www.calvin.edu/~pribeiro/courses/engr315/lecturesnotes/ Chapter 1: Introduction to Control Systems Objectives In this chapter
ECE317 : Feedback and Control
 ECE317 : Feedback and Control Lecture : Frequency domain specifications Frequency response shaping (Loop shaping) Dr. Richard Tymerski Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Portland State University
ECE317 : Feedback and Control Lecture : Frequency domain specifications Frequency response shaping (Loop shaping) Dr. Richard Tymerski Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Portland State University
AUTOMOTIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS
 AUTOMOTIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS This engineering textbook is designed to introduce advanced control systems for vehicles, including advanced automotive concepts and the next generation of vehicles for Intelligent
AUTOMOTIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS This engineering textbook is designed to introduce advanced control systems for vehicles, including advanced automotive concepts and the next generation of vehicles for Intelligent
Executive Summary. Chapter 1. Overview of Control
 Chapter 1 Executive Summary Rapid advances in computing, communications, and sensing technology offer unprecedented opportunities for the field of control to expand its contributions to the economic and
Chapter 1 Executive Summary Rapid advances in computing, communications, and sensing technology offer unprecedented opportunities for the field of control to expand its contributions to the economic and
Networked and Distributed Control Systems Lecture 1. Tamas Keviczky and Nathan van de Wouw
 Networked and Distributed Control Systems Lecture 1 Tamas Keviczky and Nathan van de Wouw Lecturers / contact information Dr. T. Keviczky (Tamas) Office: 34-C-3-310 E-mail: t.keviczky@tudelft.nl Prof.dr.ir.
Networked and Distributed Control Systems Lecture 1 Tamas Keviczky and Nathan van de Wouw Lecturers / contact information Dr. T. Keviczky (Tamas) Office: 34-C-3-310 E-mail: t.keviczky@tudelft.nl Prof.dr.ir.
CHAPTER 1 Introduction of Control System
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction of Control System DR. SHAFISHUHAZA SAHLAN DR. SHAHDAN SUDIN DR. HERMAN WAHID DR. FATIMAH SHAM ISMAIL Department of Control and Mechatronics Engineering Faculty of Electrical Engineering
CHAPTER 1 Introduction of Control System DR. SHAFISHUHAZA SAHLAN DR. SHAHDAN SUDIN DR. HERMAN WAHID DR. FATIMAH SHAM ISMAIL Department of Control and Mechatronics Engineering Faculty of Electrical Engineering
DEGREE: Biomedical Engineering YEAR: TERM: 1
 COURSE: Control Engineering DEGREE: Biomedical Engineering YEAR: TERM: 1 La asignatura tiene 14 sesiones que se distribuyen a lo largo de 7 semanas. Los dos laboratorios puede situarse en cualquiera de
COURSE: Control Engineering DEGREE: Biomedical Engineering YEAR: TERM: 1 La asignatura tiene 14 sesiones que se distribuyen a lo largo de 7 semanas. Los dos laboratorios puede situarse en cualquiera de
SMJE 3153 Control System. Department of ESE, MJIIT, UTM 2014/2015
 SMJE 3153 Control System Department of ESE, MJIIT, UTM 2014/2015 1 Course Outline Course Instructors Prof Nozomu Hamada (hamada@utm.my)and Dr. Mohd Azizi Abdul Rahman Course Web site UTM e-learning site
SMJE 3153 Control System Department of ESE, MJIIT, UTM 2014/2015 1 Course Outline Course Instructors Prof Nozomu Hamada (hamada@utm.my)and Dr. Mohd Azizi Abdul Rahman Course Web site UTM e-learning site
Flight Dynamics AE426
 KING FAHD UNIVERSITY Department of Aerospace Engineering AE426: Flight Dynamics Instructor Dr. Ayman Hamdy Kassem What is flight dynamics? Is the study of aircraft motion and its characteristics. Is it
KING FAHD UNIVERSITY Department of Aerospace Engineering AE426: Flight Dynamics Instructor Dr. Ayman Hamdy Kassem What is flight dynamics? Is the study of aircraft motion and its characteristics. Is it
Classical Control Design Guidelines & Tools (L10.2) Transfer Functions
 Classical Control Design Guidelines & Tools (L10.2) Douglas G. MacMartin Summarize frequency domain control design guidelines and approach Dec 4, 2013 D. G. MacMartin CDS 110a, 2013 1 Transfer Functions
Classical Control Design Guidelines & Tools (L10.2) Douglas G. MacMartin Summarize frequency domain control design guidelines and approach Dec 4, 2013 D. G. MacMartin CDS 110a, 2013 1 Transfer Functions
Chapter 2 Mechatronics Disrupted
 Chapter 2 Mechatronics Disrupted Maarten Steinbuch 2.1 How It Started The field of mechatronics started in the 1970s when mechanical systems needed more accurate controlled motions. This forced both industry
Chapter 2 Mechatronics Disrupted Maarten Steinbuch 2.1 How It Started The field of mechatronics started in the 1970s when mechanical systems needed more accurate controlled motions. This forced both industry
Design of Missile Two-Loop Auto-Pilot Pitch Using Root Locus
 International Journal Of Advances in Engineering and Management (IJAEM) Page 141 Volume 1, Issue 5, November - 214. Design of Missile Two-Loop Auto-Pilot Pitch Using Root Locus 1 Rami Ali Abdalla, 2 Muawia
International Journal Of Advances in Engineering and Management (IJAEM) Page 141 Volume 1, Issue 5, November - 214. Design of Missile Two-Loop Auto-Pilot Pitch Using Root Locus 1 Rami Ali Abdalla, 2 Muawia
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MCE 527 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MCE 527 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the
CDS 101: Lecture 1 Introduction to Feedback and Control. Richard M. Murray 30 September 2002
 1 CDS 101: Lecture 1 Introduction to Feedback and Control Richard M. Murray 30 September 2002 Goals: Define what a control system is and learn how to recognize its main features Describe what control systems
1 CDS 101: Lecture 1 Introduction to Feedback and Control Richard M. Murray 30 September 2002 Goals: Define what a control system is and learn how to recognize its main features Describe what control systems
Automatic Control Systems
 Automatic Control Systems Lecture-1 Basic Concepts of Classical control Emam Fathy Department of Electrical and Control Engineering email: emfmz@yahoo.com 1 What is Control System? A system Controlling
Automatic Control Systems Lecture-1 Basic Concepts of Classical control Emam Fathy Department of Electrical and Control Engineering email: emfmz@yahoo.com 1 What is Control System? A system Controlling
Design of Compensator for Dynamical System
 Design of Compensator for Dynamical System Ms.Saroja S. Chavan PimpriChinchwad College of Engineering, Pune Prof. A. B. Patil PimpriChinchwad College of Engineering, Pune ABSTRACT New applications of dynamical
Design of Compensator for Dynamical System Ms.Saroja S. Chavan PimpriChinchwad College of Engineering, Pune Prof. A. B. Patil PimpriChinchwad College of Engineering, Pune ABSTRACT New applications of dynamical
CDS 101/110a: Lecture 8-1 Frequency Domain Design
 CDS 11/11a: Lecture 8-1 Frequency Domain Design Richard M. Murray 17 November 28 Goals: Describe canonical control design problem and standard performance measures Show how to use loop shaping to achieve
CDS 11/11a: Lecture 8-1 Frequency Domain Design Richard M. Murray 17 November 28 Goals: Describe canonical control design problem and standard performance measures Show how to use loop shaping to achieve
Figure 1.1: Quanser Driving Simulator
 1 INTRODUCTION The Quanser HIL Driving Simulator (QDS) is a modular and expandable LabVIEW model of a car driving on a closed track. The model is intended as a platform for the development, implementation
1 INTRODUCTION The Quanser HIL Driving Simulator (QDS) is a modular and expandable LabVIEW model of a car driving on a closed track. The model is intended as a platform for the development, implementation
COURSE MODULES LEVEL 3.1 & 3.2
 COURSE MODULES LEVEL 3.1 & 3.2 6-Month Internship The six-month internship provides students with the opportunity to apply the knowledge acquired in the classroom to work situations, and demonstrate problem
COURSE MODULES LEVEL 3.1 & 3.2 6-Month Internship The six-month internship provides students with the opportunity to apply the knowledge acquired in the classroom to work situations, and demonstrate problem
Control Design for Servomechanisms July 2005, Glasgow Detailed Training Course Agenda
 Control Design for Servomechanisms 12 14 July 2005, Glasgow Detailed Training Course Agenda DAY 1 INTRODUCTION TO SYSTEMS AND MODELLING 9.00 Introduction The Need For Control - What Is Control? - Feedback
Control Design for Servomechanisms 12 14 July 2005, Glasgow Detailed Training Course Agenda DAY 1 INTRODUCTION TO SYSTEMS AND MODELLING 9.00 Introduction The Need For Control - What Is Control? - Feedback
AUTOMATION & MECHATRONIC SYSTEMS COURSE MODULES
 AUTOMATION & MECHATRONIC SYSTEMS COURSE MODULES A bionic arm, a self-driving car and an autopilot train system - these are some icons of the amazing world of automation technology that are brought about
AUTOMATION & MECHATRONIC SYSTEMS COURSE MODULES A bionic arm, a self-driving car and an autopilot train system - these are some icons of the amazing world of automation technology that are brought about
Dr. Ashish Dutta. Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, INDIA
 Introduction: History of Robotics - past, present and future Dr. Ashish Dutta Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, INDIA Origin of Automation: replacing human
Introduction: History of Robotics - past, present and future Dr. Ashish Dutta Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, INDIA Origin of Automation: replacing human
Modern Control System Theory and Design. Dr. Huang, Min Chemical Engineering Program Tongji University
 Modern Control System Theory and Design Dr. Huang, Min Chemical Engineering Program Tongji University Syllabus Instructor: Dr. Huang, Min Time and Place to meet Office Hours: Text Book and References Modern
Modern Control System Theory and Design Dr. Huang, Min Chemical Engineering Program Tongji University Syllabus Instructor: Dr. Huang, Min Time and Place to meet Office Hours: Text Book and References Modern
ROBOTICS ENG YOUSEF A. SHATNAWI INTRODUCTION
 ROBOTICS INTRODUCTION THIS COURSE IS TWO PARTS Mobile Robotics. Locomotion (analogous to manipulation) (Legged and wheeled robots). Navigation and obstacle avoidance algorithms. Robot Vision Sensors and
ROBOTICS INTRODUCTION THIS COURSE IS TWO PARTS Mobile Robotics. Locomotion (analogous to manipulation) (Legged and wheeled robots). Navigation and obstacle avoidance algorithms. Robot Vision Sensors and
Autonomous Mobile Robot Design. Dr. Kostas Alexis (CSE)
 Autonomous Mobile Robot Design Dr. Kostas Alexis (CSE) Course Goals To introduce students into the holistic design of autonomous robots - from the mechatronic design to sensors and intelligence. Develop
Autonomous Mobile Robot Design Dr. Kostas Alexis (CSE) Course Goals To introduce students into the holistic design of autonomous robots - from the mechatronic design to sensors and intelligence. Develop
ME451: Control Systems. Course roadmap
 ME451: Control Systems Lecture 20 Root locus: Lead compensator design Dr. Jongeun Choi Department of Mechanical Engineering Michigan State University Fall 2008 1 Modeling Course roadmap Analysis Design
ME451: Control Systems Lecture 20 Root locus: Lead compensator design Dr. Jongeun Choi Department of Mechanical Engineering Michigan State University Fall 2008 1 Modeling Course roadmap Analysis Design
Designing neuro-fuzzy controller for electromagnetic anti-lock braking system (ABS) on electric vehicle
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Designing neuro-fuzzy controller for electromagnetic anti-lock braking system (ABS) on electric vehicle To cite this article: Josaphat Pramudijanto
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Designing neuro-fuzzy controller for electromagnetic anti-lock braking system (ABS) on electric vehicle To cite this article: Josaphat Pramudijanto
Design of a Flight Stabilizer System and Automatic Control Using HIL Test Platform
 Design of a Flight Stabilizer System and Automatic Control Using HIL Test Platform Şeyma Akyürek, Gizem Sezin Özden, Emre Atlas, and Coşku Kasnakoğlu Electrical & Electronics Engineering, TOBB University
Design of a Flight Stabilizer System and Automatic Control Using HIL Test Platform Şeyma Akyürek, Gizem Sezin Özden, Emre Atlas, and Coşku Kasnakoğlu Electrical & Electronics Engineering, TOBB University
Lecture#1 Handout. Plant has one or more inputs and one or more outputs, which can be represented by a block, as shown below.
 Lecture#1 Handout Introduction A system or a process or a plant is a segment of environment that is under consideration (working definition). Control is a term that describes the process of forcing a system
Lecture#1 Handout Introduction A system or a process or a plant is a segment of environment that is under consideration (working definition). Control is a term that describes the process of forcing a system
INTRODUCTION TO KALMAN FILTERS
 ECE5550: Applied Kalman Filtering 1 1 INTRODUCTION TO KALMAN FILTERS 1.1: What does a Kalman filter do? AKalmanfilterisatool analgorithmusuallyimplementedasa computer program that uses sensor measurements
ECE5550: Applied Kalman Filtering 1 1 INTRODUCTION TO KALMAN FILTERS 1.1: What does a Kalman filter do? AKalmanfilterisatool analgorithmusuallyimplementedasa computer program that uses sensor measurements
Loop Design. Chapter Introduction
 Chapter 8 Loop Design 8.1 Introduction This is the first Chapter that deals with design and we will therefore start by some general aspects on design of engineering systems. Design is complicated because
Chapter 8 Loop Design 8.1 Introduction This is the first Chapter that deals with design and we will therefore start by some general aspects on design of engineering systems. Design is complicated because
Automation and Mechatronics Engineering Program. Your Path Towards Success
 Automation and Mechatronics Engineering Program Your Path Towards Success What is Mechatronics? Mechatronics combines the principles of mechanical, computer, electronic, and control engineering into a
Automation and Mechatronics Engineering Program Your Path Towards Success What is Mechatronics? Mechatronics combines the principles of mechanical, computer, electronic, and control engineering into a
Lecture 1. Introduction - Course mechanics History Control engineering at present. EE392m - Spring 2005 Gorinevsky. Control Engineering 1-1
 Lecture 1 Introduction - Course mechanics History Control engineering at present Control Engineering 1-1 Introduction - Course Mechanics What this course is about? Prerequisites & course place in the curriculum
Lecture 1 Introduction - Course mechanics History Control engineering at present Control Engineering 1-1 Introduction - Course Mechanics What this course is about? Prerequisites & course place in the curriculum
Analysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits Lecture 1. Overview of Course, NGspice Demo, Review of Thevenin/Norton Modeling
 Analysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits Lecture 1 Overview of Course, NGspice Demo, Review of Thevenin/Norton Modeling Michael H. Perrott January 22, 2012 Copyright 2012 by Michael H. Perrott
Analysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits Lecture 1 Overview of Course, NGspice Demo, Review of Thevenin/Norton Modeling Michael H. Perrott January 22, 2012 Copyright 2012 by Michael H. Perrott
Time Triggered Protocol (TTP/C): A Safety-Critical System Protocol
 Time Triggered Protocol (TTP/C): A Safety-Critical System Protocol Literature Review EE382c Fall 1999 Howard Curtis Global Technology Services MCC Robert France Global Software Division Motorola, Inc.
Time Triggered Protocol (TTP/C): A Safety-Critical System Protocol Literature Review EE382c Fall 1999 Howard Curtis Global Technology Services MCC Robert France Global Software Division Motorola, Inc.
CHASSIS DYNAMOMETER TORQUE CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN BY DIRECT INVERSE COMPENSATION. C.Matthews, P.Dickinson, A.T.Shenton
 CHASSIS DYNAMOMETER TORQUE CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN BY DIRECT INVERSE COMPENSATION C.Matthews, P.Dickinson, A.T.Shenton Department of Engineering, The University of Liverpool, Liverpool L69 3GH, UK Abstract:
CHASSIS DYNAMOMETER TORQUE CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN BY DIRECT INVERSE COMPENSATION C.Matthews, P.Dickinson, A.T.Shenton Department of Engineering, The University of Liverpool, Liverpool L69 3GH, UK Abstract:
CDS 101/110a: Lecture 8-1 Frequency Domain Design. Frequency Domain Performance Specifications
 CDS /a: Lecture 8- Frequency Domain Design Richard M. Murray 7 November 28 Goals:! Describe canonical control design problem and standard performance measures! Show how to use loop shaping to achieve a
CDS /a: Lecture 8- Frequency Domain Design Richard M. Murray 7 November 28 Goals:! Describe canonical control design problem and standard performance measures! Show how to use loop shaping to achieve a
Automotive Technology
 Automotive Technology Dr. Mohamad Zoghi, Acting Chair Automotive Technology Department Mohamad.Zoghi@farmingdale.edu 631-794-6292 School of Engineering Technology Associate in Applied Science Degree The
Automotive Technology Dr. Mohamad Zoghi, Acting Chair Automotive Technology Department Mohamad.Zoghi@farmingdale.edu 631-794-6292 School of Engineering Technology Associate in Applied Science Degree The
CONTROLLER DESIGN ON ARX MODEL OF ELECTRO-HYDRAULIC ACTUATOR
 Journal of Fundamental and Applied Sciences ISSN 1112-9867 Research Article Special Issue Available online at http://www.jfas.info MODELING AND CONTROLLER DESIGN ON ARX MODEL OF ELECTRO-HYDRAULIC ACTUATOR
Journal of Fundamental and Applied Sciences ISSN 1112-9867 Research Article Special Issue Available online at http://www.jfas.info MODELING AND CONTROLLER DESIGN ON ARX MODEL OF ELECTRO-HYDRAULIC ACTUATOR
Laboratory Tutorial#1
 Laboratory Tutorial#1 1.1. Objective: To become familiar with the modules and how they operate. 1.2. Equipment Required: Following equipment is required to perform above task. Quantity Apparatus 1 OU150A
Laboratory Tutorial#1 1.1. Objective: To become familiar with the modules and how they operate. 1.2. Equipment Required: Following equipment is required to perform above task. Quantity Apparatus 1 OU150A
Laboratory Tutorial#1
 Laboratory Tutorial#1 1.1. Objective: To become familiar with the modules and how they operate. 1.2. Equipment Required: Following equipment is required to perform above task. Quantity Apparatus 1 OU150A
Laboratory Tutorial#1 1.1. Objective: To become familiar with the modules and how they operate. 1.2. Equipment Required: Following equipment is required to perform above task. Quantity Apparatus 1 OU150A
CDS 101/110: Lecture 8.2 PID Control
 CDS 11/11: Lecture 8.2 PID Control November 16, 216 Goals: Nyquist Example Introduce and review PID control. Show how to use loop shaping using PID to achieve a performance specification Discuss the use
CDS 11/11: Lecture 8.2 PID Control November 16, 216 Goals: Nyquist Example Introduce and review PID control. Show how to use loop shaping using PID to achieve a performance specification Discuss the use
GE420 Laboratory Assignment 8 Positioning Control of a Motor Using PD, PID, and Hybrid Control
 GE420 Laboratory Assignment 8 Positioning Control of a Motor Using PD, PID, and Hybrid Control Goals for this Lab Assignment: 1. Design a PD discrete control algorithm to allow the closed-loop combination
GE420 Laboratory Assignment 8 Positioning Control of a Motor Using PD, PID, and Hybrid Control Goals for this Lab Assignment: 1. Design a PD discrete control algorithm to allow the closed-loop combination
Control Systems Overview REV II
 Control Systems Overview REV II D R. T A R E K A. T U T U N J I M E C H A C T R O N I C S Y S T E M D E S I G N P H I L A D E L P H I A U N I V E R S I T Y 2 0 1 4 Control Systems The control system is
Control Systems Overview REV II D R. T A R E K A. T U T U N J I M E C H A C T R O N I C S Y S T E M D E S I G N P H I L A D E L P H I A U N I V E R S I T Y 2 0 1 4 Control Systems The control system is
Experiment 9. PID Controller
 Experiment 9 PID Controller Objective: - To be familiar with PID controller. - Noting how changing PID controller parameter effect on system response. Theory: The basic function of a controller is to execute
Experiment 9 PID Controller Objective: - To be familiar with PID controller. - Noting how changing PID controller parameter effect on system response. Theory: The basic function of a controller is to execute
EE 482 : CONTROL SYSTEMS Lab Manual
 University of Bahrain College of Engineering Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 482 : CONTROL SYSTEMS Lab Manual Dr. Ebrahim Al-Gallaf Assistance Professor of Intelligent Control and Robotics
University of Bahrain College of Engineering Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 482 : CONTROL SYSTEMS Lab Manual Dr. Ebrahim Al-Gallaf Assistance Professor of Intelligent Control and Robotics
CDS 101/110: Lecture 9.1 Frequency DomainLoop Shaping
 CDS /: Lecture 9. Frequency DomainLoop Shaping November 3, 6 Goals: Review Basic Loop Shaping Concepts Work through example(s) Reading: Åström and Murray, Feedback Systems -e, Section.,.-.4,.6 I.e., we
CDS /: Lecture 9. Frequency DomainLoop Shaping November 3, 6 Goals: Review Basic Loop Shaping Concepts Work through example(s) Reading: Åström and Murray, Feedback Systems -e, Section.,.-.4,.6 I.e., we
Design and simulation of MEMS piezoelectric gyroscope
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research, 2014, 3 (2):8-12 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 2278 0041 Design
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Applied Engineering and Scientific Research, 2014, 3 (2):8-12 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 2278 0041 Design
Modeling a Hybrid Electric Vehicle and Controller to Optimize System Performance
 Root Locus Bode Plot Ref. Voltage + - + Ref. - Speed Controller Controller Real Axis Frequency Modeling a Hybrid Electric Vehicle and Controller to Optimize System Performance 2005 The MathWorks, Inc.
Root Locus Bode Plot Ref. Voltage + - + Ref. - Speed Controller Controller Real Axis Frequency Modeling a Hybrid Electric Vehicle and Controller to Optimize System Performance 2005 The MathWorks, Inc.
TRACK-FOLLOWING CONTROLLER FOR HARD DISK DRIVE ACTUATOR USING QUANTITATIVE FEEDBACK THEORY
 Proceedings of the IASTED International Conference Modelling, Identification and Control (AsiaMIC 2013) April 10-12, 2013 Phuket, Thailand TRACK-FOLLOWING CONTROLLER FOR HARD DISK DRIVE ACTUATOR USING
Proceedings of the IASTED International Conference Modelling, Identification and Control (AsiaMIC 2013) April 10-12, 2013 Phuket, Thailand TRACK-FOLLOWING CONTROLLER FOR HARD DISK DRIVE ACTUATOR USING
Readings: FC: p : lead compensation. 9/9/2011 Classical Control 1
 MM0 Frequency Response Design Readings: FC: p389-407: lead compensation 9/9/20 Classical Control What Have We Talked about in MM9? Control design based on Bode plot Stability margins (Gain margin and phase
MM0 Frequency Response Design Readings: FC: p389-407: lead compensation 9/9/20 Classical Control What Have We Talked about in MM9? Control design based on Bode plot Stability margins (Gain margin and phase
ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL OF HARD-DISK DRIVES USING PZT ACTUATED SUSPENSION SYSTEMS. Meng-Shiun Tsai, Wei-Hsiung Yuan and Jia-Ming Chang
 ICSV14 Cairns Australia 9-12 July, 27 ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL OF HARD-DISK DRIVES USING PZT ACTUATED SUSPENSION SYSTEMS Abstract Meng-Shiun Tsai, Wei-Hsiung Yuan and Jia-Ming Chang Department of Mechanical
ICSV14 Cairns Australia 9-12 July, 27 ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL OF HARD-DISK DRIVES USING PZT ACTUATED SUSPENSION SYSTEMS Abstract Meng-Shiun Tsai, Wei-Hsiung Yuan and Jia-Ming Chang Department of Mechanical
JUNE 2014 Solved Question Paper
 JUNE 2014 Solved Question Paper 1 a: Explain with examples open loop and closed loop control systems. List merits and demerits of both. Jun. 2014, 10 Marks Open & Closed Loop System - Advantages & Disadvantages
JUNE 2014 Solved Question Paper 1 a: Explain with examples open loop and closed loop control systems. List merits and demerits of both. Jun. 2014, 10 Marks Open & Closed Loop System - Advantages & Disadvantages
ENGG4420 END OF CHAPTER 1 QUESTIONS AND PROBLEMS
 CHAPTER 1 By Radu Muresan University of Guelph Page 1 ENGG4420 END OF CHAPTER 1 QUESTIONS AND PROBLEMS September 25 12 12:45 PM QUESTIONS SET 1 1. Give 3 advantages of feedback in control. 2. Give 2 disadvantages
CHAPTER 1 By Radu Muresan University of Guelph Page 1 ENGG4420 END OF CHAPTER 1 QUESTIONS AND PROBLEMS September 25 12 12:45 PM QUESTIONS SET 1 1. Give 3 advantages of feedback in control. 2. Give 2 disadvantages
BSNL TTA Question Paper Control Systems Specialization 2007
 BSNL TTA Question Paper Control Systems Specialization 2007 1. An open loop control system has its (a) control action independent of the output or desired quantity (b) controlling action, depending upon
BSNL TTA Question Paper Control Systems Specialization 2007 1. An open loop control system has its (a) control action independent of the output or desired quantity (b) controlling action, depending upon
Estimation of State Variables of Active Suspension System using Kalman Filter
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347 5161 217 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Estimation
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347 5161 217 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Estimation
Step vs. Servo Selecting the Best
 Step vs. Servo Selecting the Best Dan Jones Over the many years, there have been many technical papers and articles about which motor is the best. The short and sweet answer is let s talk about the application.
Step vs. Servo Selecting the Best Dan Jones Over the many years, there have been many technical papers and articles about which motor is the best. The short and sweet answer is let s talk about the application.
Classical Control Based Autopilot Design Using PC/104
 Classical Control Based Autopilot Design Using PC/104 Mohammed A. Elsadig, Alneelain University, Dr. Mohammed A. Hussien, Alneelain University. Abstract Many recent papers have been written in unmanned
Classical Control Based Autopilot Design Using PC/104 Mohammed A. Elsadig, Alneelain University, Dr. Mohammed A. Hussien, Alneelain University. Abstract Many recent papers have been written in unmanned
STUDY OF FIXED WING AIRCRAFT DYNAMICS USING SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION APPROACH
 STUDY OF FIXED WING AIRCRAFT DYNAMICS USING SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION APPROACH A.Kaviyarasu 1, Dr.A.Saravan Kumar 2 1,2 Department of Aerospace Engineering, Madras Institute of Technology, Anna University,
STUDY OF FIXED WING AIRCRAFT DYNAMICS USING SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION APPROACH A.Kaviyarasu 1, Dr.A.Saravan Kumar 2 1,2 Department of Aerospace Engineering, Madras Institute of Technology, Anna University,
Dr Ian R. Manchester
 Week Content Notes 1 Introduction 2 Frequency Domain Modelling 3 Transient Performance and the s-plane 4 Block Diagrams 5 Feedback System Characteristics Assign 1 Due 6 Root Locus 7 Root Locus 2 Assign
Week Content Notes 1 Introduction 2 Frequency Domain Modelling 3 Transient Performance and the s-plane 4 Block Diagrams 5 Feedback System Characteristics Assign 1 Due 6 Root Locus 7 Root Locus 2 Assign
Intelligent Active Force Controller for an Anti-lock Brake System Application
 Intelligent Active Force Controller for an Anti-lock Brake System Application MOHAMMED H. AL-MOLA, M. MAILAH, A.H. MUHAIMIN AND M.Y. ABDULLAH Department of System Dynamics and Control Faculty of Mechanical
Intelligent Active Force Controller for an Anti-lock Brake System Application MOHAMMED H. AL-MOLA, M. MAILAH, A.H. MUHAIMIN AND M.Y. ABDULLAH Department of System Dynamics and Control Faculty of Mechanical
MTE 360 Automatic Control Systems University of Waterloo, Department of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering
 MTE 36 Automatic Control Systems University of Waterloo, Department of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering Laboratory #1: Introduction to Control Engineering In this laboratory, you will become familiar
MTE 36 Automatic Control Systems University of Waterloo, Department of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering Laboratory #1: Introduction to Control Engineering In this laboratory, you will become familiar
Available theses (October 2011) MERLIN Group
 Available theses (October 2011) MERLIN Group Politecnico di Milano - Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione MERLIN Group 2 Luca Bascetta bascetta@elet.polimi.it Gianni Ferretti ferretti@elet.polimi.it
Available theses (October 2011) MERLIN Group Politecnico di Milano - Dipartimento di Elettronica e Informazione MERLIN Group 2 Luca Bascetta bascetta@elet.polimi.it Gianni Ferretti ferretti@elet.polimi.it
Frequency Response Analysis and Design Tutorial
 1 of 13 1/11/2011 5:43 PM Frequency Response Analysis and Design Tutorial I. Bode plots [ Gain and phase margin Bandwidth frequency Closed loop response ] II. The Nyquist diagram [ Closed loop stability
1 of 13 1/11/2011 5:43 PM Frequency Response Analysis and Design Tutorial I. Bode plots [ Gain and phase margin Bandwidth frequency Closed loop response ] II. The Nyquist diagram [ Closed loop stability
Development of Hybrid Flight Simulator with Multi Degree-of-Freedom Robot
 Development of Hybrid Flight Simulator with Multi Degree-of-Freedom Robot Kakizaki Kohei, Nakajima Ryota, Tsukabe Naoki Department of Aerospace Engineering Department of Mechanical System Design Engineering
Development of Hybrid Flight Simulator with Multi Degree-of-Freedom Robot Kakizaki Kohei, Nakajima Ryota, Tsukabe Naoki Department of Aerospace Engineering Department of Mechanical System Design Engineering
ME 487 Mechatronics. Office: JH 515, Tel.: (505)
 ME 487 Mechatronics Instructor: Assistant: Dr. Ou Ma Office: JH 515, Email: oma@nmsu.edu Tel.: (505)646-6534 Xiumin Diao (Ph.D. student) Office: JH 608, Email: xiumin@nmsu.edu Tel.: (505)646-6544 Dept.
ME 487 Mechatronics Instructor: Assistant: Dr. Ou Ma Office: JH 515, Email: oma@nmsu.edu Tel.: (505)646-6534 Xiumin Diao (Ph.D. student) Office: JH 608, Email: xiumin@nmsu.edu Tel.: (505)646-6544 Dept.
Automatic Control Motion control Advanced control techniques
 Automatic Control Motion control Advanced control techniques (luca.bascetta@polimi.it) Politecnico di Milano Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Motivations (I) 2 Besides the classical
Automatic Control Motion control Advanced control techniques (luca.bascetta@polimi.it) Politecnico di Milano Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Motivations (I) 2 Besides the classical
ME 375 System Modeling and Analysis
 ME 375 System Modeling and Analysis G(s) H(s) Section 9 Block Diagrams and Feedback Control Spring 2009 School of Mechanical Engineering Douglas E. Adams Associate Professor 9.1 Key Points to Remember
ME 375 System Modeling and Analysis G(s) H(s) Section 9 Block Diagrams and Feedback Control Spring 2009 School of Mechanical Engineering Douglas E. Adams Associate Professor 9.1 Key Points to Remember
Digital Control of MS-150 Modular Position Servo System
 IEEE NECEC Nov. 8, 2007 St. John's NL 1 Digital Control of MS-150 Modular Position Servo System Farid Arvani, Syeda N. Ferdaus, M. Tariq Iqbal Faculty of Engineering, Memorial University of Newfoundland
IEEE NECEC Nov. 8, 2007 St. John's NL 1 Digital Control of MS-150 Modular Position Servo System Farid Arvani, Syeda N. Ferdaus, M. Tariq Iqbal Faculty of Engineering, Memorial University of Newfoundland
High Performance Computing
 High Performance Computing and the Smart Grid Roger L. King Mississippi State University rking@cavs.msstate.edu 11 th i PCGRID 26 28 March 2014 The Need for High Performance Computing High performance
High Performance Computing and the Smart Grid Roger L. King Mississippi State University rking@cavs.msstate.edu 11 th i PCGRID 26 28 March 2014 The Need for High Performance Computing High performance
4F3 - Predictive Control
 4F3 Predictive Control - Lecture 1 p. 1/13 4F3 - Predictive Control Lecture 1 - Introduction to Predictive Control Jan Maciejowski jmm@eng.cam.ac.uk http://www-control.eng.cam.ac.uk/homepage/officialweb.php?id=1
4F3 Predictive Control - Lecture 1 p. 1/13 4F3 - Predictive Control Lecture 1 - Introduction to Predictive Control Jan Maciejowski jmm@eng.cam.ac.uk http://www-control.eng.cam.ac.uk/homepage/officialweb.php?id=1
Engineering, & Mathematics
 8O260 Applied Mathematics for Technical Professionals (R) 1 credit Gr: 10-12 Prerequisite: Recommended prerequisites: Algebra I and Geometry Description: (SGHS only) Applied Mathematics for Technical Professionals
8O260 Applied Mathematics for Technical Professionals (R) 1 credit Gr: 10-12 Prerequisite: Recommended prerequisites: Algebra I and Geometry Description: (SGHS only) Applied Mathematics for Technical Professionals
Robust Control Design for Rotary Inverted Pendulum Balance
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(28), DOI: 1.17485/ijst/216/v9i28/9387, July 216 ISSN (Print) : 974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 974-5645 Robust Control Design for Rotary Inverted Pendulum Balance
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(28), DOI: 1.17485/ijst/216/v9i28/9387, July 216 ISSN (Print) : 974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 974-5645 Robust Control Design for Rotary Inverted Pendulum Balance
VOLTAGE MODE CONTROL OF SOFT SWITCHED BOOST CONVERTER BY TYPE II & TYPE III COMPENSATOR
 1002 VOLTAGE MODE CONTROL OF SOFT SWITCHED BOOST CONVERTER BY TYPE II & TYPE III COMPENSATOR NIKITA SINGH 1 ELECTRONICS DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY, M.TECH NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF ELECTRONICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
1002 VOLTAGE MODE CONTROL OF SOFT SWITCHED BOOST CONVERTER BY TYPE II & TYPE III COMPENSATOR NIKITA SINGH 1 ELECTRONICS DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY, M.TECH NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF ELECTRONICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Position Control of DC Motor by Compensating Strategies
 Position Control of DC Motor by Compensating Strategies S Prem Kumar 1 J V Pavan Chand 1 B Pangedaiah 1 1. Assistant professor of Laki Reddy Balireddy College Of Engineering, Mylavaram Abstract - As the
Position Control of DC Motor by Compensating Strategies S Prem Kumar 1 J V Pavan Chand 1 B Pangedaiah 1 1. Assistant professor of Laki Reddy Balireddy College Of Engineering, Mylavaram Abstract - As the
Ball Balancing on a Beam
 1 Ball Balancing on a Beam Muhammad Hasan Jafry, Haseeb Tariq, Abubakr Muhammad Department of Electrical Engineering, LUMS School of Science and Engineering, Pakistan Email: {14100105,14100040}@lums.edu.pk,
1 Ball Balancing on a Beam Muhammad Hasan Jafry, Haseeb Tariq, Abubakr Muhammad Department of Electrical Engineering, LUMS School of Science and Engineering, Pakistan Email: {14100105,14100040}@lums.edu.pk,
Embracing Complexity. Gavin Walker Development Manager
 Embracing Complexity Gavin Walker Development Manager 1 MATLAB and Simulink Proven Ability to Make the Complex Simpler 1970 Stanford Ph.D. thesis, with thousands of lines of Fortran code 2 MATLAB and Simulink
Embracing Complexity Gavin Walker Development Manager 1 MATLAB and Simulink Proven Ability to Make the Complex Simpler 1970 Stanford Ph.D. thesis, with thousands of lines of Fortran code 2 MATLAB and Simulink
Andrea Zanchettin Automatic Control 1 AUTOMATIC CONTROL. Andrea M. Zanchettin, PhD Spring Semester, Linear control systems design
 Andrea Zanchettin Automatic Control 1 AUTOMATIC CONTROL Andrea M. Zanchettin, PhD Spring Semester, 2018 Linear control systems design Andrea Zanchettin Automatic Control 2 The control problem Let s introduce
Andrea Zanchettin Automatic Control 1 AUTOMATIC CONTROL Andrea M. Zanchettin, PhD Spring Semester, 2018 Linear control systems design Andrea Zanchettin Automatic Control 2 The control problem Let s introduce
and using the step routine on the closed loop system shows the step response to be less than the maximum allowed 20%.
 Phase (deg); Magnitude (db) 385 Bode Diagrams 8 Gm = Inf, Pm=59.479 deg. (at 62.445 rad/sec) 6 4 2-2 -4-6 -8-1 -12-14 -16-18 1-1 1 1 1 1 2 1 3 and using the step routine on the closed loop system shows
Phase (deg); Magnitude (db) 385 Bode Diagrams 8 Gm = Inf, Pm=59.479 deg. (at 62.445 rad/sec) 6 4 2-2 -4-6 -8-1 -12-14 -16-18 1-1 1 1 1 1 2 1 3 and using the step routine on the closed loop system shows
Optimizing Performance Using Slotless Motors. Mark Holcomb, Celera Motion
 Optimizing Performance Using Slotless Motors Mark Holcomb, Celera Motion Agenda 1. How PWM drives interact with motor resistance and inductance 2. Ways to reduce motor heating 3. Locked rotor test vs.
Optimizing Performance Using Slotless Motors Mark Holcomb, Celera Motion Agenda 1. How PWM drives interact with motor resistance and inductance 2. Ways to reduce motor heating 3. Locked rotor test vs.
Structure Specified Robust H Loop Shaping Control of a MIMO Electro-hydraulic Servo System using Particle Swarm Optimization
 Structure Specified Robust H Loop Shaping Control of a MIMO Electrohydraulic Servo System using Particle Swarm Optimization Piyapong Olranthichachat and Somyot aitwanidvilai Abstract A fixedstructure controller
Structure Specified Robust H Loop Shaping Control of a MIMO Electrohydraulic Servo System using Particle Swarm Optimization Piyapong Olranthichachat and Somyot aitwanidvilai Abstract A fixedstructure controller
Humanoid robot. Honda's ASIMO, an example of a humanoid robot
 Humanoid robot Honda's ASIMO, an example of a humanoid robot A humanoid robot is a robot with its overall appearance based on that of the human body, allowing interaction with made-for-human tools or environments.
Humanoid robot Honda's ASIMO, an example of a humanoid robot A humanoid robot is a robot with its overall appearance based on that of the human body, allowing interaction with made-for-human tools or environments.
Nandha Engineering College (Autonomous) Erode Examination -Sep 2018 Department Wise Time Table
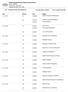 B.E - Computer Science and Engineering F.N: 09.30 AM to 12.30 PM A.N: 01.30 AM to 04.30 PM Date Session Code Subject 14-11-2018 FN 13CSX08 Network Analysis and Management AN 13CSX15 Software Testing Methodologies
B.E - Computer Science and Engineering F.N: 09.30 AM to 12.30 PM A.N: 01.30 AM to 04.30 PM Date Session Code Subject 14-11-2018 FN 13CSX08 Network Analysis and Management AN 13CSX15 Software Testing Methodologies
CONTROLLER DESIGN FOR POWER CONVERSION SYSTEMS
 CONTROLLER DESIGN FOR POWER CONVERSION SYSTEMS Introduction A typical feedback system found in power converters Switched-mode power converters generally use PI, pz, or pz feedback compensators to regulate
CONTROLLER DESIGN FOR POWER CONVERSION SYSTEMS Introduction A typical feedback system found in power converters Switched-mode power converters generally use PI, pz, or pz feedback compensators to regulate
Getting the Best Performance from Challenging Control Loops
 Getting the Best Performance from Challenging Control Loops Jacques F. Smuts - OptiControls Inc, League City, Texas; jsmuts@opticontrols.com KEYWORDS PID Controls, Oscillations, Disturbances, Tuning, Stiction,
Getting the Best Performance from Challenging Control Loops Jacques F. Smuts - OptiControls Inc, League City, Texas; jsmuts@opticontrols.com KEYWORDS PID Controls, Oscillations, Disturbances, Tuning, Stiction,
Robot Motion Planning
 Robot Motion Planning Dinesh Manocha dm@cs.unc.edu The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL Robots are used everywhere HRP4C humanoid Swarm robots da vinci Big dog MEMS bugs Snake robot 2 The UNIVERSITY
Robot Motion Planning Dinesh Manocha dm@cs.unc.edu The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL Robots are used everywhere HRP4C humanoid Swarm robots da vinci Big dog MEMS bugs Snake robot 2 The UNIVERSITY
AC : A STUDENT-ORIENTED CONTROL LABORATORY US- ING PROGRAM CC
 AC 2011-490: A STUDENT-ORIENTED CONTROL LABORATORY US- ING PROGRAM CC Ziqian Liu, SUNY Maritime College Ziqian Liu received the Ph.D. degree from the Southern Illinois University Carbondale in 2005. He
AC 2011-490: A STUDENT-ORIENTED CONTROL LABORATORY US- ING PROGRAM CC Ziqian Liu, SUNY Maritime College Ziqian Liu received the Ph.D. degree from the Southern Illinois University Carbondale in 2005. He
Andrea Zanchettin Automatic Control 1 AUTOMATIC CONTROL. Andrea M. Zanchettin, PhD Winter Semester, Linear control systems design Part 1
 Andrea Zanchettin Automatic Control 1 AUTOMATIC CONTROL Andrea M. Zanchettin, PhD Winter Semester, 2018 Linear control systems design Part 1 Andrea Zanchettin Automatic Control 2 Step responses Assume
Andrea Zanchettin Automatic Control 1 AUTOMATIC CONTROL Andrea M. Zanchettin, PhD Winter Semester, 2018 Linear control systems design Part 1 Andrea Zanchettin Automatic Control 2 Step responses Assume
Introduction to MS150
 Introduction to MS150 Objective: To become familiar with the modules and how they operate. Equipment Required: Following equipment is required to perform above task. Quantity Apparatus 1 OU150A Operation
Introduction to MS150 Objective: To become familiar with the modules and how they operate. Equipment Required: Following equipment is required to perform above task. Quantity Apparatus 1 OU150A Operation
Open Access Design of Diesel Engine Adaptive Active Disturbance Rejection Speed Controller
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 05, 7, 49-433 49 Open Access Design of Diesel Engine Adaptive Active Disturbance Rejection Speed
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 05, 7, 49-433 49 Open Access Design of Diesel Engine Adaptive Active Disturbance Rejection Speed
MOBY-DIC. Grant Agreement Number Model-based synthesis of digital electronic circuits for embedded control. Publishable summary
 MOBY-DIC Grant Agreement Number 248858 Model-based synthesis of digital electronic circuits for embedded control Report version: 1 Due date: M24 (second periodic report) Period covered: December 1, 2010
MOBY-DIC Grant Agreement Number 248858 Model-based synthesis of digital electronic circuits for embedded control Report version: 1 Due date: M24 (second periodic report) Period covered: December 1, 2010
Control Design Made Easy By Ryan Gordon
 Control Design Made Easy By Ryan Gordon 2014 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Key Themes You can automatically tune PID controllers in MATLAB from acquired data You can automatically tune PID controllers from dynamic
Control Design Made Easy By Ryan Gordon 2014 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Key Themes You can automatically tune PID controllers in MATLAB from acquired data You can automatically tune PID controllers from dynamic
