Electronic Instrumentation
|
|
|
- Franklin Day
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 December- 0 Third Semeser B.E. Degree Examinaion Elecronic Insrumenaion Time: 3 hrs. Max. Marks: 00 Noe:. Answer any FIE full quesions, selecing a leas TWO quesions from each par. PART - A. (a) Explain he following in brief: (08 Marks) (i) Gross errors : (ii) Relaive errors : (iii) Accuracy ; (iv) Resoluion. (i) Gross errors : Gross errors are hose ha are generaed by human facor involved in measuremens. These include incorrec adjusmens, improper applicaions and misreading of insrumens. These Gross errors can be conrolled by aking proper care while reading, calculaing and recording a quaniy under measuremen. Repeaed readings of he same quaniy (a leas 3-4 imes) should be aken o minimize he error. (ii) Relaive errors : Relaive error is de ned as he raio of he absolue error produced in a given measuremen o he measured value. For example; When a resisor having a known % of error i is called relaive error for example R = 00 ± 0%. (iii) Accuracy : Accuracy refers o he degree of closeness wih which any insrumen reading approaches he rue value of he variable or quaniy being measured. For example, consider he rue value is vols and he measured value is 0.5 vols. This indicaes he exacness of he meer. (iv) Resoluion : Resoluion is de ned as he smalles change in he measured value o which he insrumen responds. Consider a volmeer ha can read volages from 0 o ol. If he meer has his range divided ino 0 equal pars, hen each par will represen 0. ( = 0) ol. Then we say ha he revoluion of he meer is 0.. I can be noed ha his meer can no be used o measure a volage ha is less han 0.. (b) Explain he working of a rue RMS volmeer wih he help of a Block diagram. (0 Marks) Figure () Any complex waveforms can be accuraely measured using rue rms - volmeer. These insrumens sense 4 Elecronic Insru. December 00 December 0.indd 4 8//03 :55:5
2 Elecronic Insrumenaion December 0 Dec - waveforms heaing power and produces meer indicaion proporional o square or rms value of volage. This heaing power is ampli ed & fed o hermo couple and hen he measured oupu volage is proporional o square of rms - value. To measure rue rms volage, wo hermocouples conneced forming a bridge nework is used as shown in gure. The inpu volage o be measured is applied o he heaer elemen of he measuring hermocouple. The heaing effec of heaer is measured by hermocouple and generaes corresponding volage called. The inpu volage is ampli ed and hen given o he heaer elemen of measuring hermocouple o produce enough heaing so ha =. These wo hermocouples balancing and measuring form a bridge n/w and when = he bridge is balanced, oupu volage A( ) = K irms, 0 = sine A is gain of dc ampli er () =. 0 irms = K, = = K. = irms 0 = rms value of he inpu = 0 irms (c) De ne sensiiviy. Deermine he value of he muliplier resisance on he 50 range of a dc volmeer ha uses a 50 A meer movemen wih an inernal resisance of 00. (0 Marks) Sensiiviy of a volmeer is de ned as he resisance of he meer for an applied volage of. In mahemaical erm, full scale de ecion I fsd. and a large resisance of order of k is presen in he mere circui hen for differen volages applied o he mere, he mere wih I fsd produces a volage wih sensiiviy S = I fsd Given daa : 50 Range dc volmeer I fsd = 50 A = 00 R m S = 50 μ A = 4 k /v R = S range = R m R = 40 k /v 500 v 00 = = R = 99.9kΩ. (a) Explain he ramp ype digial volmeer wih he help of a block diagram. (0 Marks) December 0.indd 5 8//03 :55:56
3 Dec - December 0 Elecronic Insrumenaion Figure (a) Ramp ype DM Fig b. Ramp echnique The ramp ype of DM basically consiss of inpu aenuaor and inpu comparaor, ground comparaor and a gae, couner arranged as shown in gure. (a). The basic principle of measuremen is based on he measuremen of he ime aken by a linear ramp o raise from 0 vol o he level of inpu volage i. The ime is measured wih a couner and displayed in numeric form. The linear ramp consiss of ramp generaor generaing ve going ramp ranging from. To sar he measuremen he ramp volage is iniiaed wih inpu volage i and compared coninuously wih i, when hese wo volages are no same he inpu comparaor oupu generaes a sar pulse, where oscillaions are allowed o ener ino he couner. These are illusraed in Fib b. The ramp is coninuously driven o zero vol when he ground comparaor inpus become equal and gae generaes a sop - pulse. The magniude of he coun is proporional o ime inerval beween sar and sop pulse. December 0.indd 6 8//03 :55:56
4 Elecronic Insrumenaion December 0 Dec - The magniude of he coun indicaes he magniude of O which is displayed by he display uni. (b) Wih block diagram, explain he principle and operaion of digial frequency meer. (0 Marks) Digial frequency meer Figure 3(a) Block diagram of digial frequency meer Frequency of an unknown signal is deermined by convering he signal o rigger pulses and applied o an AND gae, a pulse of sec is applied o he oher inpu of he AND gae. The number of pulses couned during sec indicaes he unknown frequency. The signal whose frequency is o be measured is convered ino a rain of pulses, pulse for each cycle of inpu signal. Depending upon he number of pulses occurring in a de nie ime inerval is hen couned by a couner, he number of couns is direcly proporional o frequency of unknown signal. The block - diagram of he digial frequency meer is as shown in he gure.3(a) which consiss of ampli er and Schmi - rigger. The ampli er is used o amplify he inpu signal and Schmi rigger is used o conver inpu sine wave o square wave. As a resul, he oupu from he schmi rigger is a rain of pulses, one pulse for each cycle of inpu signal. The oupu pulse from schmi Trigger is fed o he gae and when gae is enabled he pulses reach couner, which couns he number of pulses. The number of coun is direcly proporional o frequency.. 3. (a) Explain he CRT feaures brie y. (05 Marks) The CRT used in a cahode ray oscilloscope is elecrosaic ype and hey are available in various size and bandwidh o sui individual requiremens. The main feaures of his kind of cahode ray ube are explained here.. Size: I refers o he screen diameer like he T speci caion. CRTs are available from o 7 inches in various sizes, however 3 inch CRT is commonly used in porable insrumens. Recangular ype CRTs are mosly used nowadays raher han he round ype.. Phosphor: This refers o he uorescen maerial used o coa he screen, which decides he color and persisence of he race. These are indicaed by he phosphor. The race colors available for elecrosaic CRTs are blue, green and blue green. Persisence is expressed as shor, medium and long, which refers o he lengh of ime he race remains on he screen afer he signal is removed. The phosphor of CRT is speci ed like P (green medium), P( blue green medium), P (Blue shor) ec. Some ime he speci caions are combined in he ube ype number. For example 5GP indicaes ha i is a 5 inch ube wih medium persisence green race. 3. Operaing olage: Typical operaing volages a differen poins of CRT are lised below, which may vary depend on he model of CRT. a) The heaer volage of he CRT is 6.3 ac/dc, 600 ma. b) Negaive grid conrol volage is 4 o 00. c) Focusing anode volage is 00 o 00. d) Acceleraing anode volage is 600 o 6k 4. De ecion olages: De ecion of beam is achieved hrough eiher ac or dc volage. The de ecion sensiiviy of he ube is usually speci ed as he dc volage required for each cm of de ecion of he spo on he screen. 5. iewing Screen: The viewing screen is he glass face plae of which he inside wall is coaed wih phosphor. I is recangular in shape wih graicule marked on i in cenimeer scale for he purpose of aking measuremens; each cenimeer corresponds o one division. The sandard size of he screen is 8 cm 0 cm. December 0.indd 7 8//03 :55:57
5 Dec - December 0 Elecronic Insrumenaion (b) Draw he basic block diagram of an oscilloscope. Explain he funcions of each block (0 Marks) The block diagram of a basic CRO is shown in gure. The funcion of he various blocks are as follows. Cahode Ray ube (CRT): The funcion of cahode ray ube is o emi elecrons ha srikes he phosphorous screen o provide a visual display of he signals.. erical Ampli er: The inpu signals o be measured are applied o verical ampli er sage o amplify and pass faihfully he enire band of frequencies, and herefore he ampli er used is wide band. 3. Delay line: Delay line basically consiss of RC/LC circui o delay he signal for someime in he verical secion, if delay line is no used hen a par of he oupu signal is los. 4. Time Base generaor: The ime base generaor is used o generae a sawooh volage, which is required o de ec he elecion beam in he horizonal direcion. 5. Horizonal ampli er: The saw ooh volage generaed by he ime base generaor may no be of suf cien srengh o drive he horizonal de ecion plaes, i is ampli ed using a high volage gain ampli er. 6. Trigger circui: The horizonal de ecion of elecion beam should sar a he same poin of he inpu verical signal, and o synchronize horizonal de ecion wih verical de ecion a rigger circui is used. The rigger circui convers he inpu signal ino rigger pules so ha he inpu signal and sweep frequency can be synchronized. 7. Power supply: There are wo power supplies namely, high volage (around -.5k) supply and low volage (around 400) supply wo volages are generaed and passed hrough a bleeder resisor a a few ma. These inermediae volages of bleeder resisor are used for inensiy, focus, horizonal ampli er, verical ampli er. (c) Describe he following modes of operaion available in a dual race oscilloscope: (i) ALTERNATE mode ; (ii) CHOP mode, (05 Marks) In a dual race oscilloscope, a mode conrol swich is used o enable he elecronic swich o display wo signals simulaneously. There are wo modes of operaion ALTERNATE and CHOPE depend on he range of inpu signal frequency (high or low). (i) ALTERNATE MODE: When he swich is in alernae posiion, he elecronic swich alernaely connecs he main verical ampli er o he wo channels, say A and B, and adds differen dc componen o each signal. This dc signal direcs he beam o he upper or lower half of he screen alernaely. The swiching happens a December 0.indd 8 8//03 :55:57
6 Elecronic Insrumenaion December 0 Dec - he sar of each new sweep of he sweep generaor. The swiching rae is synchronized wih he sweep signal so ha he channel A is ge raced on he screen in one sweep and channel B on he succeeding sweep and he cycle coninues as shown in he waveform of Fig. 3(b). Channel A Channel B Channel A Inensiy OFF Fig. 3 (b)time relaion in ALTERNATE MODE (ii) CHOP MODE: In chop mode of CRT, he elecronic swich is free running a rae of KHz, independen of sweep generaor. The swich successively connecs small segmens of A and B channels waveforms o he main verical ampli er a a fas chopping rae of 500KHz as shown in Fig. 3(c). If he chopping rae is slow, he coninuiy of display is los and i is beer o change o ALTERNATE mode. Waveform for chop mode Channel A Channel B Inensiy Off Chop Transiens Blanking Inensiy Brigh Fig. 3 (b)time relaion in CHOP MODE 4. (a) Explain why ime delay is necessary in oscilloscopes. (04 Marks) In a regular CRO, one wihou a ime-delay circui incorporaed ino is sweep circui, he sweep volage will be in synchronism wih he applied inpu volage; hen only we can observe a seady waveform on he screen. The number of he full cycles of he waveform observed on he screen can be seen o be an inegral muliple of he ime-base frequency. However, we can no observe various porions of he applied waveform wih his simple sweep. To observe each and every par of a given waveform in minue deails, we have o use he delayed ime-base. Tha is, o analyze a given waveform, we mus apply he ime base a he appropriae poin on he waveform o be observed. A delayed-ime-base oscilloscope is one in which a variable ime delay is used in he horizonal sweep of a convenional CRO. This allows he sweep o be applied a he end of he delay ime. Figure 4. shows he block diagram of a ypical delayed-ime-base circui. In his case, here are wo ime-base circuis. Time base and a reference volage R are applied o a Schmi-rigger circui. Depending on he value of R, he Schmi rigger oupus a square wave ha drives ime-base circui, as shown. The oupu of ime- December 0.indd 9 8//03 :55:57
7 Dec - December 0 Elecronic Insrumenaion base circui is used o drive he X-X de ecion plaes of he CRO. Figure 4. shows he acion of a ime-delay sweep. Figure 4.(a) shows a sandard sweep and Fig. 4.(b) shows he resuling waveform displayed on he CRT screen. Trigger Time base Schmi Time base rigger CRT R v Fig. 4. Delayed ime-base circui (a) Sandard sweep (b) Resuling wave Time delay (c) Delayed sweep (d) resuling wave Fig. 4. Waveforms associaed wih sandard and delayed sweeps Figure 4.(c) shows a delayed sweep and Fig. 4.(d) shows he resuling delayed waveform. I can be seen ha he delayed sweep sars a he peak of he applied waveform and hence we observe he saring of he display from he peak poin of he applied wave, as shown in Fig. 4.(d). (b) Explain he principle and operaion of sampling oscilloscope wih relevan block diagrams. (08 Marks) Ans: In an ordinary CRO, when we ry o measure high frequency, he image brilliance reduces. I is because, December 0.indd 0 8//03 :55:57
8 Elecronic Insrumenaion December 0 Dec - when he frequency of he verical deflecion signal increases, he wriing speed of elecron beam increases. In order o obain sufficien image brilliance and o mainain normal image brighness he elecron beam mus be acceleraed o a higher velociy so ha more kineic energy is available for ransfer of elecron o he screen. The higher elecron beem velociy can be easily achieved by raising he acceleraing anode volage. A high velociy beam also requires a greaer deflecion poenial o mainain he deflecion sensiiviy. All hese leads o higher demands on he verical amplifier. To make he maer simple, a sampling oscilloscope uses a differen approach alogeher o improve he high frequency performance. In he sampling scope, he inpu waveform is reconsruced from many samples aken during recurren cycles of he inpu wave form and hus over come he frequency limiaions of convenional CRT. This sampling echnique is illusraed in Fig 4(a). From he figure, i can be seen ha he high frequency inpu being sampled by a rain of sampling pulses. The principle involves in aking one sample each from each recurren full cycle of he applied wave a a slighly laer delayed posiion. As illusraed in he figure, sample is aken form he firs cycle, sample from cycle, sample 3 from cycle 3 and so on bu from a slighly advanced posiion or from differen poins on he applied wave, when regrouped hese poins will form a single wave, which is he replica of he applied wave form as shown in he figure 4(a). Reconsruced oupu wave Higher frequency inpu wave Triggering pulse Sampling poins Sampling pulses Sampling pulses Fig: 4(a) Sampling of high frequency signal ino a low frequency signal A simplified block diagram of he sampling circuiry used in he sampling scope is shown in Fig. 4(b). The inpu wave form o be observed is applied o he sampling gae. Sampling pulses momenarily bias he diodes of he balanced sampling gae in he forward direcions briefly connecing he gae inpu capaciance o he es poin. These capaciances are slighly charged owards he volage level of he inpu circui. December 0.indd 8//03 :55:58
9 Dec - December 0 Elecronic Insrumenaion Inpu signal Sampling gae erical Amplifier To verical deflecion plae Trigger Inpu Blocking oscillaor Ramp Generaor olage Comparaor Saircase Generaor To horizonal deflecion plae Aenuaor Fig. 4(b) black diagram of he sampling circuiry in a sampling scope The capacior volage is amplified by he verical amplifier and applied o he verical deflecion plaes. Since he sampling mus be synchronized wih he inpu signal frequency, he signal is delayed in verical amplifier, allowing he sweep riggering o be done by he inpu signal. When he rigger pulse is received, he avalanche blocking oscillaor sars an exacly linear ramp volage, which is applied o volage comparaor. The volage comparaor compares he ramp volage o he oupu volage of a saircase generaor. When he wo volages are equal in ampliude, he saircase generaor is allowed o advance one sep and simulaneously a sampling pulse is applied o he sampling gae. A his movemen, a sample of he inpu volage is aken, amplified and applied he verical deflecion plae. (c) Explain he operaion of digial sorage oscilloscope wih he help of a block diagram. Menion he advanages. (08 Marks) Digial sorage oscilloscope: Inpu signal Inpu erical amplifier S/H circui A/D converer Memory D/A converer Trigger circui Conrol logic D/A converer erical deflecion amplifier Horizonal deflecion amplifier CRT deflecion plans In a digial sorage Oscilloscope, he waveform o be displayed and sored is convered ino binary digis (s December 0.indd 8//03 :55:58
10 Elecronic Insrumenaion December 0 Dec - and 0s), sored in a random access memory, and rerieved for display on screen. The sored wave form may be coninuously displayed by repeaedly scanning he sored waveform and, herefore, a convenional oscilloscope ube can be used for he display. The sored daa can be displayed inde niely as long as power is applied o he memory. The digiized waveform can be analyzed by eiher he oscilloscope iself or by using a digial compuer conneced o i. Figure 4.3 shows he block diagram of a digial sorage oscilloscope. The inpu is ampli ed and aenuaed wih inpu ampli ers as in any oscilloscope. The digial sorage oscilloscope uses he same ypes of inpu circuiry as a convenional oscilloscope and can operae in a convenional mode, bypassing he digiizing and soring feaures. As shown in he gure, he inpu signal ampli ed by he verical ampli er-aenuaor combinaion is applied o an analog-o-digial converer, which hen drives a random-access memory (RAM). This emporarily sores he digiized inpu daa. A conrol logic circui is used o conrol he operaions of he ADC and he memory. The oupu of he memory is applied o a digial-o-analog (DA) converer, which in urn is used o drive he verical de ecion ampli er and verical de ecion plaes. The conrol logic also drives he horizonal-sweep DAC and he horizonal de ecion ampli er. The combined acion of he de ecion plaes, as in he convenional oscilloscope produces display on he screen. Advanages of digial sorage oscilloscope. They can be used o observe fas and slow phenomena alike. Can be used o analyze minue deails in any ype of waveform.. Daa can be sored permanenly for viewing a convenience. 3. Real-ime analysis is also possible. 4. Can be direcly conneced o digial compuers for analysis of waveforms. 5. Waveforms appearing only once (like a ransien) can be observed and analyzed easily. 6. Wih large memory capaciy, a lo of daa can be sored in a DSO. 7. Several channels are possible in modern DSO s which help in analyzing waveform a differen pars of a sysem simulaneously. 8. Can be used o pre-rigger view. 9. Compaible wih modern a-panel displays using TFT s 0. Analyses can be displayed on he screen iself by compuaional abiliy of he scope.. Brigher and bigger display.. Differen colors employed o disinguish muliple races. 3. Much higher resoluions possible. 4. Deecion of peak signal possible. 5. Waveform zooming in and zooming ou is possible for ner examinaions. 6. Allows auomaion. 7. Three dimensional imaging easy. PART - B 5. (a) Wih block diagram, explain convenional sandard signal generaor. Menion he applicaions. (0Marks) December 0.indd 3 8//03 :55:58
11 Dec - December 0 Elecronic Insrumenaion The above gure shown is a +ve feed back sysem. I basically consiss of ampli er wih gain (A) and feedback nework whose feedback fracion is. When he produc of he loop gain A = and oal phase shif around he loop is 360 susained oscillaions are generaed called barkhausen crieria. Figure 5a shows he block diagram of a sandard signal generaor, which some imes is called he sandard AM/FM signal generaor. I consiss of an RF generaor, an AF generaor an ampliude modulaor, a frequency modulaor, an ampli er and an aenuaor. The radio-frequency (RF) oscillaor is used o produce sine waves in he range of I MHz o 00 MHz. Usually, an RF oscillaor of he Harley or Colpi s ype is used o produce he desired radio-frequency sine waves. The oupu frequency of he oscillaor can be varied by varying he ank-circui inducance using ferrie uning. The audio-frequency (AF) oscillaor is of he Wien-bridge ype and is used o produce sine waves in he range of 0 Hz o 00 khz. The ampliude- and frequency- modulaor circuis are, respecively, used o ampliude and frequency modulae he RF waves wih AF waves. These modulaions are aken ou hrough a band swich S o an ampli er-aenuaor combinaion circui. The ampli er-aenuaor combinaion circui is used o conrol he ampliude of he oupu signal. Some imes, a es-signal erminal of -vol, 000-Hz sine wave is also incorporaed on he equipmen s panel board. Sandard AM/FM signal generaor is used o es and measure he performances of radio circuis. They are used as laboraory sandards for esing and repairing RF ransmission sysems. They also help in uning radio receivers for opimum performance in facories and repair shops. In miliary and police signaling schemes, sandard AM/FM signal generaor is one of he highly essenial es equipmens. AM Modulaor AF oscillaor RF oscillaor AM S FM Amplifier Aenuaor Oupu FM Modulaor Fig. 5. a Sandard (AM/FM) signal generaor (b) Explain he operaion of a funcion generaor wih he help of a block diagram. (0 Marks) Consan-curren source Schmi rigger Square Frequency conrol circui I I Inegraor Triangle Consan-curren source Wave-shaper Sine Fig. 5. (a) Block diagram of a ypical funcion generaor December 0.indd 4 8//03 :55:58
12 Elecronic Insrumenaion December 0 Dec - A funcion generaor is an insrumen more versaile han he sine- and square-wave generaor. A funcion generaor, in general, is used o generae sine waves, square waves, riangular waves, and sweep waves. These wave forms are useful for a variey of applicaions in a lab. Figure 5. (a) shows he block schemaics of a funcion generaor. In his circui, wo consan-curren sources driving an inegraor. To produce he required oscillaions he op consan-curren source is used o charge he inegraor capacior a a uniform rae, and his produces a posiive-going ramp. The capacior, afer reaching a finie value, will discharge hrough he second consan-curren source, and a negaive-going ramp resuls in. b + c + d Original Shaped sine wave wave Fig. 5. (b,c,d) Triangular, square, and shaped sine waves The wo acions (i.e., charging and discharging of he capacior) will produce a riangular wave. The riangular wave is applied o schmi rigger circui o produce square wave, as shown in fig. 5. b. The riangular wave is applied Schmi rigger circui o produce square wave, as shown in fig. 5. c. To ge he sinewae oupu, we use a wave-shaping circui using diodes or bipolar juncion ransisors. The wave-shaping circui will curve he edges of he riangular wave o form ino a sine wave, as shown in Fig. 5. d. Similarly, when riangular wave is fed o shaping circui, i produces sinusoidal funcions. The frequency is conrolled by varying he magniude of curren hrough he inegraor. When funcion generaor is urned ON he upper source supplies consan curren o he inegraor whose oupu is given by ou = i.d C 6. (a) Explain he Wheasone bridge and derive he balance equaion for Wheasone bridge. Menion he limiaions. (08 Marks) The circui diagram of WheasoneÊs bridge is shown in Fig 6(a). I consiss of four arms made up of resisive elemens R, R, R 3 and R 4 respecively as shown in figure. A dc volage source, conneced across he nodes A and C of he bridge, energizes he circui. A galvanomeer G is conneced across B and D of he circui indicaes he balancing condiion of he bridge. The arm consising of resisors R and R are called he raio arms of he bridge while he arm consising of he R 3 is called he sandard arm since i uses a sandard resisance for comparison and measuremen. The resisor R 4 conneced o he fourh arm of he bridge is usually having he unknown value. i is his resisance o be measured using he bridge. I can be seen ha, if he hree resisors have known values, hen he value of he fourh resisor can be accuraely found. December 0.indd 5 8//03 :55:58
13 Dec - December 0 Elecronic Insrumenaion A R R B I I 3 G D R 3 I G C R 4 Fig: 6(a) WheasoneÊs bride To analyse he balancing condiion of he bridge refer fig.6(a). Le curren I flow hrough resisors R and R and le curren I flow hrough resisors R 3 and R 4, as shown in he figure. These condiions assume ha here will be no curren hrough he galvanomeer (i.e., I G = 0). The condiion ha I G = 0 is known as he balancing condiion of he bridge. From he figure, we find ha curren I = R + R and curren I = R + R 3 4 The volage drop across R can now be obained as R BC = IR = R + R and ha across R 4 can be obained as DC 4 R 4 = I R = R + R 3 4 The ne volage across he nodes B and D is given by R R 4 BD = BC DC = R + R R + R 3 4 The bridge is said be balanced when volage BD = 0, so ha he curren flowing hrough he galvanomeer is zero. Tha is R R 4 BD = BC DC = = 0 R + R R + R Simplifying he above equaion, yields 3 4 R R4 = R + R R + R 3 4 Rearranging, simplifying, and canceling similar erms on eiher side of he above equaion yields he necessary condiion for balancing he bridge as Which may also be wrien as R R 3 = R R 4 R R R = R 3 4 December 0.indd 6 8//03 :55:58
14 Elecronic Insrumenaion December 0 Dec - This is he required balance equaion for he WheasoneÊs bridge The limiaions of Wheasone s bridge are :. The resisance of he leads and conacs becomes signi can in he low resisance measuremen ha inroduces error.. In he measuremen of high resisive values, he resisance presened by he Wheasoone s bridge becomes so large ha he galvanomeer will be insensiive due o imbalance. 3. The heaing effec of he curren ha rise he emperaure which in urn causes a change in he value of resisance in bridge arms. Excessive curren cause a permanen change in he value of resisance ha affecs he measuremen. (b) Find he equivalen parallel resisance and capaciance ha causes a wein bridge o null wih he following componen values : (06 Marks) R = 3. k, C = 5. F, R = 5k, f =.5 khz and R 4 = 00 k. Wein bridge R = 3 k, C = 5. f, R = 5k f =.5 khz, R4 = 00k C = ω RCR 3 3 R R C = + R R C R R = + R R C R R 4 3 ω 3 5kΩ 3.k = + π ( ) ( ) ( ) 00k R R 3 5k Ω 3.k = C = 00k R 3 ω RCR R k 00k 5k C 3 = ( ) ( ) R 3 =.4kΩ C3 = π = 0.8pF (c) Wrie a noe on Wagner s earh connecion. (06 Marks) December 0.indd 7 8//03 :55:58
15 B R R R 3 A S C s Headphone deecor C s C R R 4 Sray capaciances C C C 4 D Fig. 6. a Wanger earh connecion Figure 6 (a) shows he Wagner earh connecion. This circui is employed o eliminae he effecs of sray capaciances exising beween he deecor erminals and he ground C s and C S in Fig. of a bridge circui. An AC supply volage is applied o excie he nework. The bridge is made up of Resisors R, R, R 3 and R 4 as well as capaciors C, and C 4. An addiional R - C nework is conneced across, as shown. The deecor is conneced o he bridge hrough a band swich when i is in posiion. This swich, in is posiion, is conneced o he ground and his connecion is known as he Wagner ground connecion. Working Principles: Iniially, he headphone deecor is conneced o posiion of S and resisor R is adjused o for a null or minimum sound in i. Then S is moved o posiion (Wagner ground) and resisor R is adjused o for a null or minimum sound in he headphone. Now, we move S o posiion again. This acion may possibly inroduce some unbalance in he circui. R and R 3 are now adjused for a minimum sound from he deecor. S is hen moved o posiion and R is adjused furher for minimum sound. This procedure is repeaed several imes unil he headphone produces minimum sound in boh he posiions of S. This means ha swich posiions and are a he same ground poenial, which indicaes ha sray capaciances C S and C S are effecively shored ou, and hence heir effec on he balancing of he bridge is eliminaed. In a similar way, ha sray capaciances from poins B and D are can also be seen o be eliminaed hrough his mehod. 7. (a) Wha are he facors o be considered for he selecion of beer ransducer? Explain (08 Marks) The following poins are o be observed for selecing a ransducer suiable for a given applicaion:. Sensiiviy: The ransducer seleced mus produce a suf cienly large oupu even for a very small inpu.. Range: I mus cover faihfully and accuraely he enire range of operaion of he quaniy o be convered by i. 3. Errors: Transducers mus be free from errors as far as possible. This means ha he conversion mus be as faihful as possible and should be proeced from error-generaing surroundings. 4. Thermal sabiliy: The ransducer seleced for a given applicaion mus have good hermal sabiliy. 5. Ruggedness: I mus wihsand shock and vibraion. 6. Frequency response: Should be capable of producing uniform oupu hroughou he range of frequencies in which i has o operae. 7. Elecrical characerisics: The ransducer (used in elecrical conversion) mus be seleced based on is elecrical characerisics such as he value of is oupu impedance, response ime, rise ime, elecrical power-supply December 0.indd 8 8//03 :55:58
16 requiremens, ampli caion/aenuaion produced, ransfer characerisics, phase-shif produced, and so on. 8. Physical size: In he modern world of miniaurizaion, a ransducer seleced mus be as small as possible; a he same ime, i should no affec he value of he oupu produced by i. 9. Simple consrucion: The ransducer consrucional feaures mus be as simple as possible. 0. Weigh: I mus be noed ha he weigh of a good ransducer mus be as small as possible for easy handling.. Simple heory of operaion: The principle of operaion mus also be as simple as possible.. Cos: Any designer will always be cos-conscious. Thus any ransducer seleced for a given applicaion should be as inexpensive as possible. 3. Easy availabiliy: Any ransducer chosen mus be easily and speedily available from he open marke. (b) Explain he consrucion, principle and operaion of LDT. ( Marks) LDT: Figure shows he consrucion of he linear variable differenial ransformer (LDT). The differenial ransformer consiss of single primary winding and wo secondary windings wound on a hallow cylindrical former. The wo secondary windings have equal number of urns and are placed on boh sides of he primary winding. The primary winding is excied by an ac source. A movable sof iron core slides in and ou he hallow former effecing he magneic coupling beween primary and wo secondary windings. When he core is a he normal posiion (exacly a he middle of he former) he secondary volages induced are equal and hence he oupu volage is he difference of hese wo volages, o = E E = 0. 0 = 0. When he core is moved o he boom more ux links S han S he oupu volage is E, he oupu volage 0 = E E. when he moved o boom mos, he oupu volage is very negligible (almos zero). E = 0 so0 E Similarly, when he core is moved in he opposie posiion o = E =E. A he exreme end, E = 0 0 = E Thus, we find ha, as he posiion of he core changes wihin he former, he volages induced in he individual December 0.indd 9 8//03 :55:58
17 secondary coils differ; his produces an oupu volage ha is linearly proporional o he posiion of he core; hence he name linear variable differenial ransformer. The ransfer curve of he LDT is shown in Fig. 7 (c). The ransfer characerisic shows a fairly linear operaion of he LDT. 0 = 0 0 Posiion of he core ( X) X max +X max Posiion of he core (+X) 0 = 0 0 Fig. 7. c Transfer characerisic of LDT 8. (a) Explain piezo elecric ransducer, wih circui diagram. (8 Marks) Ans: Piezo means press. Then piezo elecriciy means press and generae elecriciy. I is found ha when cerain crysaline maerials such as quarz, Rochelle sal and Barium ianae placed under sress, hey generaed elecriciy. This propery is used in he consrucion of piezoelecric ransducer, where a crysal is placed beween a solid base and he force summing member as shown in Fig 8 (a). Force - summing C R oupu L C p Base Crysal (Barium Tianae Rochelle Sal Quarz) Equivalen Circui of Crysal Fig. 8.a Peizo Elecrical Transducer An exernally applied force enering he ransducer hrough is pressure par applies pressure o he op of he crysal, which produces an emf across he crysal proporional o he magniude of he exernal pressure. Equivalen elecrical circui of he crysal is also shown in Fig. 8 (a). The basic expression for he generaed emf is given by E = Q C P where E = generaed elecriciy Q = generaed charge C P = Shun capaciance For a pizeo elecric elemen under pressure, par of energy is convered o an elecrical poenial ha appears on December 0.indd 30 8//03 :55:59
18 opposie faces of he elemen, analogous o a charge on he plaes of a capacior. The res of he applied energy is convered o mechanical energy, analogues o compressions of a spring. The piezo elecric elemen reurns o is original shape and losses is charge, when he exernal pressure is removed. From hese relaionship, i is derived ha Mechanical energy convered ino elecric energy K = Applied mechanical energy or Elecrical energy convered ino Mechanical energy K = Applied elecric energy The piezo elecric effec is reversible. Tha means, hese crysals exhibi he propery of elecrosricion when an elecric field is applied across he crysal, mechanical sress is produced. An alernaing volage is applied o he crysal causes i o vibrae a is naural frequency. This propery is used in high frequency acceleromeers. (b) Compare LED and LCD ypes of displays. (06 Marks) Comparison LED LCD. Small and compac. Medium and compac. Small size. Small size 3. Brigh displayed 3. Good conras 4. Low power 4. Low- power 5. high speed 5. Medium speed (c) Wrie a shor noe on signal condiioning sysem. (6 Marks) Signal - condiioner: Signal condiioning equipmen is required o perform basic linear processes such as aenuaion, ampli caion and mahemaical operaions like inegraion and differeniaion. They can also be used o perform non-linear process such as lering, muliplicaion, sampling and modulaion/demodulaion. These funcions require proper selecion of componens and faihful reproducion of he required nal oupu. The signal condiioning / daa acquisiion sysem is an exciaion sysem/ampli caion sysem for passive ransducers, or i can be an ampli caion sysem for acive ransducer. Ampli er Fig. DC signal condiioning sysem For a passive ransducer exciaion is essenially required. The passive ransducer like srain gauge hermomeers, capaciive ransducers and poeniomeers o be excied from an exernal dc source. The acive ransducers like hermocouples, phoo diode piezoelecric ransducers does no require any exernal dc source for exciaion. Bu hese ransducers are conneced o ampli ers o amplify he low level inpu signal. A simple dc signal condiioning sysem is as shown in gure. The dc bridge is excied by a dc source and sain gauge is conneced o one arm of he wheasone s - bridge. The bridge can be basically balanced using a poeniomeer and oupu of calibraion is applied o dc ampli er he essenial requiremens of dc-ampli er are as follows. December 0.indd 3 8//03 :55:59
EXPERIMENT #9 FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS LINK
 EXPERIMENT #9 FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS LINK INTRODUCTION: Much of daa communicaions is concerned wih sending digial informaion hrough sysems ha normally only pass analog signals. A elephone line is such
EXPERIMENT #9 FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS LINK INTRODUCTION: Much of daa communicaions is concerned wih sending digial informaion hrough sysems ha normally only pass analog signals. A elephone line is such
THE OSCILLOSCOPE AND NOISE. Objectives:
 -26- Preparaory Quesions. Go o he Web page hp://www.ek.com/measuremen/app_noes/xyzs/ and read a leas he firs four subsecions of he secion on Trigger Conrols (which iself is a subsecion of he secion The
-26- Preparaory Quesions. Go o he Web page hp://www.ek.com/measuremen/app_noes/xyzs/ and read a leas he firs four subsecions of he secion on Trigger Conrols (which iself is a subsecion of he secion The
Communication Systems. Department of Electronics and Electrical Engineering
 COMM 704: Communicaion Lecure : Analog Mulipliers Dr Mohamed Abd El Ghany Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Mohamed.abdel-ghany@guc.edu.eg nroducion Nonlinear operaions on coninuous-valued analog signals are ofen
COMM 704: Communicaion Lecure : Analog Mulipliers Dr Mohamed Abd El Ghany Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Mohamed.abdel-ghany@guc.edu.eg nroducion Nonlinear operaions on coninuous-valued analog signals are ofen
EXPERIMENT #4 AM MODULATOR AND POWER AMPLIFIER
 EXPERIMENT #4 AM MODULATOR AND POWER AMPLIFIER INTRODUCTION: Being able o ransmi a radio frequency carrier across space is of no use unless we can place informaion or inelligence upon i. This las ransmier
EXPERIMENT #4 AM MODULATOR AND POWER AMPLIFIER INTRODUCTION: Being able o ransmi a radio frequency carrier across space is of no use unless we can place informaion or inelligence upon i. This las ransmier
EE201 Circuit Theory I Fall
 EE1 Circui Theory I 17 Fall 1. Basic Conceps Chaper 1 of Nilsson - 3 Hrs. Inroducion, Curren and Volage, Power and Energy. Basic Laws Chaper &3 of Nilsson - 6 Hrs. Volage and Curren Sources, Ohm s Law,
EE1 Circui Theory I 17 Fall 1. Basic Conceps Chaper 1 of Nilsson - 3 Hrs. Inroducion, Curren and Volage, Power and Energy. Basic Laws Chaper &3 of Nilsson - 6 Hrs. Volage and Curren Sources, Ohm s Law,
Memorandum on Impulse Winding Tester
 Memorandum on Impulse Winding Teser. Esimaion of Inducance by Impulse Response When he volage response is observed afer connecing an elecric charge sored up in he capaciy C o he coil L (including he inside
Memorandum on Impulse Winding Teser. Esimaion of Inducance by Impulse Response When he volage response is observed afer connecing an elecric charge sored up in he capaciy C o he coil L (including he inside
Diodes. Diodes, Page 1
 Diodes, Page 1 Diodes V-I Characerisics signal diode Measure he volage-curren characerisic of a sandard signal diode, he 1N914, using he circui shown below. The purpose of he back-o-back power supplies
Diodes, Page 1 Diodes V-I Characerisics signal diode Measure he volage-curren characerisic of a sandard signal diode, he 1N914, using he circui shown below. The purpose of he back-o-back power supplies
Explanation of Maximum Ratings and Characteristics for Thyristors
 8 Explanaion of Maximum Raings and Characerisics for Thyrisors Inroducion Daa shees for s and riacs give vial informaion regarding maximum raings and characerisics of hyrisors. If he maximum raings of
8 Explanaion of Maximum Raings and Characerisics for Thyrisors Inroducion Daa shees for s and riacs give vial informaion regarding maximum raings and characerisics of hyrisors. If he maximum raings of
Experiment 6: Transmission Line Pulse Response
 Eperimen 6: Transmission Line Pulse Response Lossless Disribued Neworks When he ime required for a pulse signal o raverse a circui is on he order of he rise or fall ime of he pulse, i is no longer possible
Eperimen 6: Transmission Line Pulse Response Lossless Disribued Neworks When he ime required for a pulse signal o raverse a circui is on he order of he rise or fall ime of he pulse, i is no longer possible
EE 330 Lecture 24. Amplification with Transistor Circuits Small Signal Modelling
 EE 330 Lecure 24 Amplificaion wih Transisor Circuis Small Signal Modelling Review from las ime Area Comparison beween BJT and MOSFET BJT Area = 3600 l 2 n-channel MOSFET Area = 168 l 2 Area Raio = 21:1
EE 330 Lecure 24 Amplificaion wih Transisor Circuis Small Signal Modelling Review from las ime Area Comparison beween BJT and MOSFET BJT Area = 3600 l 2 n-channel MOSFET Area = 168 l 2 Area Raio = 21:1
4 20mA Interface-IC AM462 for industrial µ-processor applications
 Because of he grea number of indusrial buses now available he majoriy of indusrial measuremen echnology applicaions sill calls for he sandard analog curren nework. The reason for his lies in he fac ha
Because of he grea number of indusrial buses now available he majoriy of indusrial measuremen echnology applicaions sill calls for he sandard analog curren nework. The reason for his lies in he fac ha
Table of Contents. 3.0 SMPS Topologies. For Further Research. 3.1 Basic Components. 3.2 Buck (Step Down) 3.3 Boost (Step Up) 3.4 Inverter (Buck/Boost)
 Table of Conens 3.0 SMPS Topologies 3.1 Basic Componens 3.2 Buck (Sep Down) 3.3 Boos (Sep Up) 3.4 nverer (Buck/Boos) 3.5 Flyback Converer 3.6 Curren Boosed Boos 3.7 Curren Boosed Buck 3.8 Forward Converer
Table of Conens 3.0 SMPS Topologies 3.1 Basic Componens 3.2 Buck (Sep Down) 3.3 Boos (Sep Up) 3.4 nverer (Buck/Boos) 3.5 Flyback Converer 3.6 Curren Boosed Boos 3.7 Curren Boosed Buck 3.8 Forward Converer
Chapter 2 Introduction: From Phase-Locked Loop to Costas Loop
 Chaper 2 Inroducion: From Phase-Locked Loop o Cosas Loop The Cosas loop can be considered an exended version of he phase-locked loop (PLL). The PLL has been invened in 932 by French engineer Henri de Belleszice
Chaper 2 Inroducion: From Phase-Locked Loop o Cosas Loop The Cosas loop can be considered an exended version of he phase-locked loop (PLL). The PLL has been invened in 932 by French engineer Henri de Belleszice
Multiple Load-Source Integration in a Multilevel Modular Capacitor Clamped DC-DC Converter Featuring Fault Tolerant Capability
 Muliple Load-Source Inegraion in a Mulilevel Modular Capacior Clamped DC-DC Converer Feauring Faul Toleran Capabiliy Faisal H. Khan, Leon M. Tolber The Universiy of Tennessee Elecrical and Compuer Engineering
Muliple Load-Source Inegraion in a Mulilevel Modular Capacior Clamped DC-DC Converer Feauring Faul Toleran Capabiliy Faisal H. Khan, Leon M. Tolber The Universiy of Tennessee Elecrical and Compuer Engineering
MEASUREMENTS OF VARYING VOLTAGES
 MEASUREMENTS OF ARYING OLTAGES Measuremens of varying volages are commonly done wih an oscilloscope. The oscilloscope displays a plo (graph) of volage versus imes. This is done by deflecing a sream of
MEASUREMENTS OF ARYING OLTAGES Measuremens of varying volages are commonly done wih an oscilloscope. The oscilloscope displays a plo (graph) of volage versus imes. This is done by deflecing a sream of
A1 K. 12V rms. 230V rms. 2 Full Wave Rectifier. Fig. 2.1: FWR with Transformer. Fig. 2.2: Transformer. Aim: To Design and setup a full wave rectifier.
 2 Full Wave Recifier Aim: To Design and seup a full wave recifier. Componens Required: Diode(1N4001)(4),Resisor 10k,Capacior 56uF,Breadboard,Power Supplies and CRO and ransformer 230V-12V RMS. + A1 K B1
2 Full Wave Recifier Aim: To Design and seup a full wave recifier. Componens Required: Diode(1N4001)(4),Resisor 10k,Capacior 56uF,Breadboard,Power Supplies and CRO and ransformer 230V-12V RMS. + A1 K B1
Synchronization of single-channel stepper motor drivers reduces noise and interference
 hronizaion of single-channel sepper moor drivers reduces noise and inerference n mos applicaions, a non-synchronized operaion causes no problems. However, in some cases he swiching of he wo channels inerfere,
hronizaion of single-channel sepper moor drivers reduces noise and inerference n mos applicaions, a non-synchronized operaion causes no problems. However, in some cases he swiching of he wo channels inerfere,
4.5 Biasing in BJT Amplifier Circuits
 4/5/011 secion 4_5 Biasing in MOS Amplifier Circuis 1/ 4.5 Biasing in BJT Amplifier Circuis eading Assignmen: 8086 Now le s examine how we C bias MOSFETs amplifiers! f we don bias properly, disorion can
4/5/011 secion 4_5 Biasing in MOS Amplifier Circuis 1/ 4.5 Biasing in BJT Amplifier Circuis eading Assignmen: 8086 Now le s examine how we C bias MOSFETs amplifiers! f we don bias properly, disorion can
Pulse Train Controlled PCCM Buck-Boost Converter Ming Qina, Fangfang Lib
 5h Inernaional Conference on Environmen, Maerials, Chemisry and Power Elecronics (EMCPE 016 Pulse Train Conrolled PCCM Buck-Boos Converer Ming Qina, Fangfang ib School of Elecrical Engineering, Zhengzhou
5h Inernaional Conference on Environmen, Maerials, Chemisry and Power Elecronics (EMCPE 016 Pulse Train Conrolled PCCM Buck-Boos Converer Ming Qina, Fangfang ib School of Elecrical Engineering, Zhengzhou
RITEC, Inc. 60 Alhambra Rd., Suite 5 Warwick, RI (401) FAX (401) Powerful Ultrasonic Research Tool. A Modular Approach
 RITEC RAM-5 Versaile Compuer Conrolled Ulrasonic Sysem: Modular Approach allows Cusomizaion o Specific Experimenal Requiremens. High Power RF Burs Oupus as high as 5 kilowas for frequencies o 7 MHz. Three
RITEC RAM-5 Versaile Compuer Conrolled Ulrasonic Sysem: Modular Approach allows Cusomizaion o Specific Experimenal Requiremens. High Power RF Burs Oupus as high as 5 kilowas for frequencies o 7 MHz. Three
Development of Temporary Ground Wire Detection Device
 Inernaional Journal of Smar Grid and Clean Energy Developmen of Temporary Ground Wire Deecion Device Jing Jiang* and Tao Yu a Elecric Power College, Souh China Universiy of Technology, Guangzhou 5164,
Inernaional Journal of Smar Grid and Clean Energy Developmen of Temporary Ground Wire Deecion Device Jing Jiang* and Tao Yu a Elecric Power College, Souh China Universiy of Technology, Guangzhou 5164,
AN303 APPLICATION NOTE
 AN303 APPLICATION NOTE LATCHING CURRENT INTRODUCTION An imporan problem concerning he uilizaion of componens such as hyrisors or riacs is he holding of he componen in he conducing sae afer he rigger curren
AN303 APPLICATION NOTE LATCHING CURRENT INTRODUCTION An imporan problem concerning he uilizaion of componens such as hyrisors or riacs is he holding of he componen in he conducing sae afer he rigger curren
Electric amplifiers. Table of contents. Features. RE 30095/04.11 Replaces: Types VT 5005 to VT Component series 1X 1/8
 Elecric amplifiers RE 30095/04. Replaces: 05.0 /8 Types VT 5005 o VT 5008 Componen series X 558_d Table of conens Conens Page eaures Ordering code uncional descripion Block diagram / pinou: VT 5005 and
Elecric amplifiers RE 30095/04. Replaces: 05.0 /8 Types VT 5005 o VT 5008 Componen series X 558_d Table of conens Conens Page eaures Ordering code uncional descripion Block diagram / pinou: VT 5005 and
Active Filters - 1. Active Filters - 2
 PHY35 - Elecronics Laboraory, all Term (K rong) Acie ilers - By combining op-amps wih energy-sorage elemens, circuis can be designed o gie frequency-dependen op-amp responses Acie filers are hose ha use
PHY35 - Elecronics Laboraory, all Term (K rong) Acie ilers - By combining op-amps wih energy-sorage elemens, circuis can be designed o gie frequency-dependen op-amp responses Acie filers are hose ha use
Control circuit for a Self-Oscillating Power Supply (SOPS) TDA8385
 FEATURES Bandgap reference generaor Slow-sar circuiry Low-loss peak curren sensing Over-volage proecion Hyseresis conrolled sand-by funcion Error amplifier wih gain seing Programmable ransfer characer
FEATURES Bandgap reference generaor Slow-sar circuiry Low-loss peak curren sensing Over-volage proecion Hyseresis conrolled sand-by funcion Error amplifier wih gain seing Programmable ransfer characer
Dimensions. Model Number. Electrical connection emitter. Features. Electrical connection receiver. Product information. Indicators/operating means
 OBE-R-SE Dimensions.8.8 ø..75 7.5 6. 5 6.7 4.9 4. 5.9 ø.6 Model Number OBE-R-SE Elecrical connecion emier Thru-beam sensor wih m fixed cable Feaures 45 cable oule for maximum mouning freedom under exremely
OBE-R-SE Dimensions.8.8 ø..75 7.5 6. 5 6.7 4.9 4. 5.9 ø.6 Model Number OBE-R-SE Elecrical connecion emier Thru-beam sensor wih m fixed cable Feaures 45 cable oule for maximum mouning freedom under exremely
ECMA st Edition / June Near Field Communication Wired Interface (NFC-WI)
 ECMA-373 1 s Ediion / June 2006 Near Field Communicaion Wired Inerface (NFC-WI) Sandard ECMA-373 1 s Ediion / June 2006 Near Field Communicaion Wired Inerface (NFC-WI) Ecma Inernaional Rue du Rhône 114
ECMA-373 1 s Ediion / June 2006 Near Field Communicaion Wired Inerface (NFC-WI) Sandard ECMA-373 1 s Ediion / June 2006 Near Field Communicaion Wired Inerface (NFC-WI) Ecma Inernaional Rue du Rhône 114
Sensing, Computing, Actuating
 Sensing, Compuing, Acuaing Sander Suik (s.suik@ue.nl) Deparmen of Elecrical Engineering Elecronic Sysems INDUCTIE SENSOS (Chaper.5,.6,.0, 5.4) 3 Inducive sensors damping conrol wheel speed sensor (ABS)
Sensing, Compuing, Acuaing Sander Suik (s.suik@ue.nl) Deparmen of Elecrical Engineering Elecronic Sysems INDUCTIE SENSOS (Chaper.5,.6,.0, 5.4) 3 Inducive sensors damping conrol wheel speed sensor (ABS)
10. The Series Resistor and Inductor Circuit
 Elecronicsab.nb 1. he Series esisor and Inducor Circui Inroducion he las laboraory involved a resisor, and capacior, C in series wih a baery swich on or off. I was simpler, as a pracical maer, o replace
Elecronicsab.nb 1. he Series esisor and Inducor Circui Inroducion he las laboraory involved a resisor, and capacior, C in series wih a baery swich on or off. I was simpler, as a pracical maer, o replace
ECE3204 Microelectronics II Bitar / McNeill. ECE 3204 / Term D-2017 Problem Set 7
 EE3204 Microelecronics II Biar / McNeill Due: Monday, May 1, 2017 EE 3204 / Term D-2017 Problem Se 7 All ex problems from Sedra and Smih, Microelecronic ircuis, 7h ediion. NOTES: Be sure your NAME and
EE3204 Microelecronics II Biar / McNeill Due: Monday, May 1, 2017 EE 3204 / Term D-2017 Problem Se 7 All ex problems from Sedra and Smih, Microelecronic ircuis, 7h ediion. NOTES: Be sure your NAME and
Lecture 5: DC-DC Conversion
 1 / 31 Lecure 5: DC-DC Conversion ELEC-E845 Elecric Drives (5 ECTS) Mikko Rouimo (lecurer), Marko Hinkkanen (slides) Auumn 217 2 / 31 Learning Oucomes Afer his lecure and exercises you will be able o:
1 / 31 Lecure 5: DC-DC Conversion ELEC-E845 Elecric Drives (5 ECTS) Mikko Rouimo (lecurer), Marko Hinkkanen (slides) Auumn 217 2 / 31 Learning Oucomes Afer his lecure and exercises you will be able o:
M2 3 Introduction to Switching Regulators. 1. What is a switching power supply? 2. What types of switchers are available?
 M2 3 Inroducion o Swiching Regulaors Objecive is o answerhe following quesions: 1. Wha is a swiching power supply? 2. Wha ypes of swichers are available? 3. Why is a swicher needed? 4. How does a swicher
M2 3 Inroducion o Swiching Regulaors Objecive is o answerhe following quesions: 1. Wha is a swiching power supply? 2. Wha ypes of swichers are available? 3. Why is a swicher needed? 4. How does a swicher
Analog Circuits EC / EE / IN. For
 Analog Circuis For EC / EE / IN By www.hegaeacademy.com Syllabus Syllabus for Analog Circuis Small Signal Equivalen Circuis of Diodes, BJTs, MOSFETs and Analog CMOS. Simple Diode Circuis, Clipping, Clamping,
Analog Circuis For EC / EE / IN By www.hegaeacademy.com Syllabus Syllabus for Analog Circuis Small Signal Equivalen Circuis of Diodes, BJTs, MOSFETs and Analog CMOS. Simple Diode Circuis, Clipping, Clamping,
Dimensions. Transmitter Receiver ø2.6. Electrical connection. Transmitter +UB 0 V. Emitter selection. = Light on = Dark on
 OBE-R-SE Dimensions Transmier.. 7.5 9..5.8 4.9 4 5 M 8.9 7.5 9..5.8 4 5 M 8.9 ø.6 ø.6 Model Number OBE-R-SE Thru-beam sensor wih m fixed cable Elecrical connecion Transmier Feaures BN +UB WH IN Ulra-small
OBE-R-SE Dimensions Transmier.. 7.5 9..5.8 4.9 4 5 M 8.9 7.5 9..5.8 4 5 M 8.9 ø.6 ø.6 Model Number OBE-R-SE Thru-beam sensor wih m fixed cable Elecrical connecion Transmier Feaures BN +UB WH IN Ulra-small
Primary Side Control SMPS with Integrated MOSFET
 General Descripion GG64 is a primary side conrol SMPS wih an inegraed MOSFET. I feaures programmable cable drop compensaion and a peak curren compensaion funcion, PFM echnology, and a CV/CC conrol loop
General Descripion GG64 is a primary side conrol SMPS wih an inegraed MOSFET. I feaures programmable cable drop compensaion and a peak curren compensaion funcion, PFM echnology, and a CV/CC conrol loop
Dimensions. Transmitter Receiver ø2.6. Electrical connection. Transmitter +UB 0 V. Emitter selection. = Light on = Dark on
 OBE-R-SE Dimensions Transmier.. 7.5 9..5.8 4.9 4 5 M 8.9 7.5 9..5.8 4 5 M 8.9 ø.6 ø.6 Model Number OBE-R-SE Thru-beam sensor wih m fixed cable Elecrical connecion Transmier Feaures BN +UB WH IN Ulra-small
OBE-R-SE Dimensions Transmier.. 7.5 9..5.8 4.9 4 5 M 8.9 7.5 9..5.8 4 5 M 8.9 ø.6 ø.6 Model Number OBE-R-SE Thru-beam sensor wih m fixed cable Elecrical connecion Transmier Feaures BN +UB WH IN Ulra-small
Universal microprocessor-based ON/OFF and P programmable controller MS8122A MS8122B
 COMPETENCE IN MEASUREMENT Universal microprocessor-based ON/OFF and P programmable conroller MS8122A MS8122B TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION AND INSTRUCTION FOR USE PLOVDIV 2003 1 I. TECHNICAL DATA Analog inpus
COMPETENCE IN MEASUREMENT Universal microprocessor-based ON/OFF and P programmable conroller MS8122A MS8122B TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION AND INSTRUCTION FOR USE PLOVDIV 2003 1 I. TECHNICAL DATA Analog inpus
GG6005. General Description. Features. Applications DIP-8A Primary Side Control SMPS with Integrated MOSFET
 General Descripion GG65 is a primary side conrol PSR SMPS wih an inegraed MOSFET. I feaures a programmable cable drop compensaion funcion, PFM echnology, and a CV/CC conrol loop wih high reliabiliy and
General Descripion GG65 is a primary side conrol PSR SMPS wih an inegraed MOSFET. I feaures a programmable cable drop compensaion funcion, PFM echnology, and a CV/CC conrol loop wih high reliabiliy and
EE 40 Final Project Basic Circuit
 EE 0 Spring 2006 Final Projec EE 0 Final Projec Basic Circui Par I: General insrucion 1. The final projec will coun 0% of he lab grading, since i s going o ake lab sessions. All oher individual labs will
EE 0 Spring 2006 Final Projec EE 0 Final Projec Basic Circui Par I: General insrucion 1. The final projec will coun 0% of he lab grading, since i s going o ake lab sessions. All oher individual labs will
16.5 ADDITIONAL EXAMPLES
 16.5 ADDITIONAL EXAMPLES For reiew purposes, more examples of boh piecewise linear and incremenal analysis are gien in he following subsecions. No new maerial is presened, so readers who do no need addiional
16.5 ADDITIONAL EXAMPLES For reiew purposes, more examples of boh piecewise linear and incremenal analysis are gien in he following subsecions. No new maerial is presened, so readers who do no need addiional
Industrial, High Repetition Rate Picosecond Laser
 RAPID Indusrial, High Repeiion Rae Picosecond Laser High Power: RAPID is a very cos efficien, compac, diode pumped Nd:YVO4 picosecond laser wih 2 W average power a 1064 nm. Is 10 ps-pulses have high pulse
RAPID Indusrial, High Repeiion Rae Picosecond Laser High Power: RAPID is a very cos efficien, compac, diode pumped Nd:YVO4 picosecond laser wih 2 W average power a 1064 nm. Is 10 ps-pulses have high pulse
P. Bruschi: Project guidelines PSM Project guidelines.
 Projec guidelines. 1. Rules for he execuion of he projecs Projecs are opional. Their aim is o improve he sudens knowledge of he basic full-cusom design flow. The final score of he exam is no affeced by
Projec guidelines. 1. Rules for he execuion of he projecs Projecs are opional. Their aim is o improve he sudens knowledge of he basic full-cusom design flow. The final score of he exam is no affeced by
The ramp is normally enabled but can be selectively disabled by suitable wiring to an external switch.
 Vickers Amplifier Cards Power Amplifiers for Proporional Valves EEA-PAM-56*-A-14 Design EEA-PAM-561-A-14 for use wih valve ypes: KDG5V-5, * and KDG5V-7, 1* series EEA-PAM-568-A-14 for use wih valve ypes:
Vickers Amplifier Cards Power Amplifiers for Proporional Valves EEA-PAM-56*-A-14 Design EEA-PAM-561-A-14 for use wih valve ypes: KDG5V-5, * and KDG5V-7, 1* series EEA-PAM-568-A-14 for use wih valve ypes:
Automatic Power Factor Control Using Pic Microcontroller
 IDL - Inernaional Digial Library Of Available a:www.dbpublicaions.org 8 h Naional Conference on Advanced Techniques in Elecrical and Elecronics Engineering Inernaional e-journal For Technology And Research-2017
IDL - Inernaional Digial Library Of Available a:www.dbpublicaions.org 8 h Naional Conference on Advanced Techniques in Elecrical and Elecronics Engineering Inernaional e-journal For Technology And Research-2017
MODEL: M6NXF1. POWER INPUT DC Power R: 24 V DC
 Screw Terminal Ulra-Slim Signal Condiioners M6N Series FUNCTION MODULE (PC programmable) Funcions & Feaures Single inpu filer and funcion module 12 ypes of funcions are PC programmable 7.5-mm wide ulra-slim
Screw Terminal Ulra-Slim Signal Condiioners M6N Series FUNCTION MODULE (PC programmable) Funcions & Feaures Single inpu filer and funcion module 12 ypes of funcions are PC programmable 7.5-mm wide ulra-slim
Signal Characteristics
 Signal Characerisics Analog Signals Analog signals are always coninuous (here are no ime gaps). The signal is of infinie resoluion. Discree Time Signals SignalCharacerisics.docx 8/28/08 10:41 AM Page 1
Signal Characerisics Analog Signals Analog signals are always coninuous (here are no ime gaps). The signal is of infinie resoluion. Discree Time Signals SignalCharacerisics.docx 8/28/08 10:41 AM Page 1
Connection. Input II EEx ia IIC without SC red. Composition
 Sandsill conroller Oupu: relay Connecion Inpu I EEx ia IIC Inpu II EEx ia IIC 1-channel Conrol circui EEx ia IIC Addiional inpu or roaion direcion deecion or sar-up override 2 relay oupus Inpu requency
Sandsill conroller Oupu: relay Connecion Inpu I EEx ia IIC Inpu II EEx ia IIC 1-channel Conrol circui EEx ia IIC Addiional inpu or roaion direcion deecion or sar-up override 2 relay oupus Inpu requency
Investigation and Simulation Model Results of High Density Wireless Power Harvesting and Transfer Method
 Invesigaion and Simulaion Model Resuls of High Densiy Wireless Power Harvesing and Transfer Mehod Jaber A. Abu Qahouq, Senior Member, IEEE, and Zhigang Dang The Universiy of Alabama Deparmen of Elecrical
Invesigaion and Simulaion Model Resuls of High Densiy Wireless Power Harvesing and Transfer Mehod Jaber A. Abu Qahouq, Senior Member, IEEE, and Zhigang Dang The Universiy of Alabama Deparmen of Elecrical
PRM and VTM Parallel Array Operation
 APPLICATION NOTE AN:002 M and V Parallel Array Operaion Joe Aguilar VI Chip Applicaions Engineering Conens Page Inroducion 1 High-Level Guidelines 1 Sizing he Resisor 4 Arrays of Six or More Ms 5 Sysem
APPLICATION NOTE AN:002 M and V Parallel Array Operaion Joe Aguilar VI Chip Applicaions Engineering Conens Page Inroducion 1 High-Level Guidelines 1 Sizing he Resisor 4 Arrays of Six or More Ms 5 Sysem
Proceedings of International Conference on Mechanical, Electrical and Medical Intelligent System 2017
 on Mechanical, Elecrical and Medical Inelligen Sysem 7 Consan On-ime Conrolled Four-phase Buck Converer via Saw-oohwave Circui and is Elemen Sensiiviy Yi Xiong a, Koyo Asaishi b, Nasuko Miki c, Yifei Sun
on Mechanical, Elecrical and Medical Inelligen Sysem 7 Consan On-ime Conrolled Four-phase Buck Converer via Saw-oohwave Circui and is Elemen Sensiiviy Yi Xiong a, Koyo Asaishi b, Nasuko Miki c, Yifei Sun
Technology Trends & Issues in High-Speed Digital Systems
 Deailed comparison of dynamic range beween a vecor nework analyzer and sampling oscilloscope based ime domain reflecomeer by normalizing measuremen ime Sho Okuyama Technology Trends & Issues in High-Speed
Deailed comparison of dynamic range beween a vecor nework analyzer and sampling oscilloscope based ime domain reflecomeer by normalizing measuremen ime Sho Okuyama Technology Trends & Issues in High-Speed
MODEL: M6SXF1. POWER INPUT DC Power R: 24 V DC
 Tension-Clamp Ulra-Slim Signal Condiioners M6S Series FUNCTION MODULE (PC programmable) Funcions & Feaures Mainenance-free ension clamp connecion Single inpu filer and funcion module 12 ypes of funcions
Tension-Clamp Ulra-Slim Signal Condiioners M6S Series FUNCTION MODULE (PC programmable) Funcions & Feaures Mainenance-free ension clamp connecion Single inpu filer and funcion module 12 ypes of funcions
Solid State Modulators for PIII Applications
 Solid Sae Modulaors for P Applicaions Dr. Marcel P.J. Gaudreau, P.E., Dr. Jeffrey A. Casey, Timohy J. Hawkey, Michael A. Kempkes, J. Michael Mulvaney; Diversified Technologies, nc. Absrac One of he key
Solid Sae Modulaors for P Applicaions Dr. Marcel P.J. Gaudreau, P.E., Dr. Jeffrey A. Casey, Timohy J. Hawkey, Michael A. Kempkes, J. Michael Mulvaney; Diversified Technologies, nc. Absrac One of he key
DISCONTINUED MODEL Replaced with Model JPS3
 Plug-in Signal Condiioners M-UNIT PUSE ADDER (field-programmable) MODE MODE & SUFFIX CODE SEECTI MODE A : Dry conac B :Volage pulse (Specify sensiiviy) C : V pulse (sensiiviy V) D : V/V pulse (sensiiviy
Plug-in Signal Condiioners M-UNIT PUSE ADDER (field-programmable) MODE MODE & SUFFIX CODE SEECTI MODE A : Dry conac B :Volage pulse (Specify sensiiviy) C : V pulse (sensiiviy V) D : V/V pulse (sensiiviy
ORDER INFORMATION TO pin 320 ~ 340mV AMC7150DLF
 www.addmek.com DESCRIPTI is a PWM power ED driver IC. The driving curren from few milliamps up o 1.5A. I allows high brighness power ED operaing a high efficiency from 4Vdc o 40Vdc. Up o 200KHz exernal
www.addmek.com DESCRIPTI is a PWM power ED driver IC. The driving curren from few milliamps up o 1.5A. I allows high brighness power ED operaing a high efficiency from 4Vdc o 40Vdc. Up o 200KHz exernal
F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [CO/IF/CM/CW] Basic Electronics
![F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [CO/IF/CM/CW] Basic Electronics F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [CO/IF/CM/CW] Basic Electronics](/thumbs/90/104331640.jpg) F.Y. Diploma : Sem. [CO/F/CM/CW] asic lecronics Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Quesion Paper Soluion [Marks : 70 Q.1 Aemp any FV of he following : [10] Q.1(a) Classify elecronic componens. [2] Ans. Classificaion
F.Y. Diploma : Sem. [CO/F/CM/CW] asic lecronics Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Quesion Paper Soluion [Marks : 70 Q.1 Aemp any FV of he following : [10] Q.1(a) Classify elecronic componens. [2] Ans. Classificaion
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Second ediion ober W. Erickson Dragan Maksimovic Universiy of Colorado, Boulder.. Inroducion o power processing.. Some applicaions of power elecronics.3. Elemens of power elecronics Summary of he course.
Second ediion ober W. Erickson Dragan Maksimovic Universiy of Colorado, Boulder.. Inroducion o power processing.. Some applicaions of power elecronics.3. Elemens of power elecronics Summary of he course.
Programmable DC Electronic Load 8600 Series
 Daa Shee Programmable DC Elecronic Load The programmable DC elecronic loads provide he performance of modular sysem DC elecronic loads in a compac benchop form facor. Wih fas ransien operaion speeds and
Daa Shee Programmable DC Elecronic Load The programmable DC elecronic loads provide he performance of modular sysem DC elecronic loads in a compac benchop form facor. Wih fas ransien operaion speeds and
Electrical amplifiers
 Elecrical amplifiers RE 30/0.0 Replaces: 09.05 / Type VT-VSPA- and VT-VSPAK- Componen series X H589_d Table of conens Conens Page Feaures Ordering code Funcional descripion and 3 Block circui diagram /
Elecrical amplifiers RE 30/0.0 Replaces: 09.05 / Type VT-VSPA- and VT-VSPAK- Componen series X H589_d Table of conens Conens Page Feaures Ordering code Funcional descripion and 3 Block circui diagram /
Time Control Technique
 Time Conrol Technique muliimer Mulifuncion Relay MK 785N/2 23928 Your Advanages Up o 1 funcions in one uni Simplified sorage Increased flexibiliy Quick seing of long ime values Opions wih Pluggable Terminal
Time Conrol Technique muliimer Mulifuncion Relay MK 785N/2 23928 Your Advanages Up o 1 funcions in one uni Simplified sorage Increased flexibiliy Quick seing of long ime values Opions wih Pluggable Terminal
BOUNCER CIRCUIT FOR A 120 MW/370 KV SOLID STATE MODULATOR
 BOUNCER CIRCUIT FOR A 120 MW/370 KV SOLID STATE MODULATOR D. Gerber, J. Biela Laboraory for High Power Elecronic Sysems ETH Zurich, Physiksrasse 3, CH-8092 Zurich, Swizerland Email: gerberdo@ehz.ch This
BOUNCER CIRCUIT FOR A 120 MW/370 KV SOLID STATE MODULATOR D. Gerber, J. Biela Laboraory for High Power Elecronic Sysems ETH Zurich, Physiksrasse 3, CH-8092 Zurich, Swizerland Email: gerberdo@ehz.ch This
Solid-state Multi-functional Timer
 Solid-sae Muli-funcional Timer Eigh operaing modes (H3DE-M) and four operaing modes (H3DE-S) cover a wide range of applicaions. Programmable conac enables he building of a self-holding relay circui (-
Solid-sae Muli-funcional Timer Eigh operaing modes (H3DE-M) and four operaing modes (H3DE-S) cover a wide range of applicaions. Programmable conac enables he building of a self-holding relay circui (-
A New Voltage Sag and Swell Compensator Switched by Hysteresis Voltage Control Method
 Proceedings of he 8h WSEAS Inernaional Conference on ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEMS, HIGH VOLTAGES, ELECTRIC MACHINES (POWER '8) A New Volage Sag and Swell Compensaor Swiched by Hyseresis Volage Conrol Mehod AMIR
Proceedings of he 8h WSEAS Inernaional Conference on ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEMS, HIGH VOLTAGES, ELECTRIC MACHINES (POWER '8) A New Volage Sag and Swell Compensaor Swiched by Hyseresis Volage Conrol Mehod AMIR
Application Note 5324
 Desauraion Faul Deecion Opocoupler Gae Drive Producs wih Feaure: PLJ, PL0J, PLJ, PL1J and HCPLJ Applicaion Noe 1. Inroducion A desauraion faul deecion circui provides proecion for power semiconducor swiches
Desauraion Faul Deecion Opocoupler Gae Drive Producs wih Feaure: PLJ, PL0J, PLJ, PL1J and HCPLJ Applicaion Noe 1. Inroducion A desauraion faul deecion circui provides proecion for power semiconducor swiches
Programmable DC Electronic Loads 8600 Series
 Daa Shee Programmable DC Elecronic Loads The programmable DC elecronic loads provide he performance of modular sysem DC elecronic loads in a compac benchop form facor. Wih fas ransien operaion speeds and
Daa Shee Programmable DC Elecronic Loads The programmable DC elecronic loads provide he performance of modular sysem DC elecronic loads in a compac benchop form facor. Wih fas ransien operaion speeds and
LECTURE 1 CMOS PHASE LOCKED LOOPS
 Lecure 01 (8/9/18) Page 1-1 Objecive LECTURE 1 CMOS PHASE LOCKED LOOPS OVERVIEW Undersand he principles and applicaions of phase locked loops using inegraed circui echnology wih emphasis on CMOS echnology.
Lecure 01 (8/9/18) Page 1-1 Objecive LECTURE 1 CMOS PHASE LOCKED LOOPS OVERVIEW Undersand he principles and applicaions of phase locked loops using inegraed circui echnology wih emphasis on CMOS echnology.
Design of Power Factor Correction Circuit Using AP1662
 Applicaion Noe 075 Design of Power Facor Correcion Circui Using AP66 Prepared by Wang Zhao Kun ysem Engineering Deparmen. nroducion. Produc Feaures The AP66 is an acive power facor conrol C which is designed
Applicaion Noe 075 Design of Power Facor Correcion Circui Using AP66 Prepared by Wang Zhao Kun ysem Engineering Deparmen. nroducion. Produc Feaures The AP66 is an acive power facor conrol C which is designed
Notes on the Fourier Transform
 Noes on he Fourier Transform The Fourier ransform is a mahemaical mehod for describing a coninuous funcion as a series of sine and cosine funcions. The Fourier Transform is produced by applying a series
Noes on he Fourier Transform The Fourier ransform is a mahemaical mehod for describing a coninuous funcion as a series of sine and cosine funcions. The Fourier Transform is produced by applying a series
Electronic timer CT-MVS.12 Multifunctional with 1 c/o contact Data sheet
 Feaures Raed conrol supply volage 24-48 V DC, 24-240 V AC Mulifuncion imer wih 10 iming funcions: ON-delay, OFF-delay wih auxiliary volage, Impulse-ON, Impulse-OFF wih auxiliary volage, Symmerical ON-
Feaures Raed conrol supply volage 24-48 V DC, 24-240 V AC Mulifuncion imer wih 10 iming funcions: ON-delay, OFF-delay wih auxiliary volage, Impulse-ON, Impulse-OFF wih auxiliary volage, Symmerical ON-
Power Efficient Battery Charger by Using Constant Current/Constant Voltage Controller
 Circuis and Sysems, 01, 3, 180-186 hp://dx.doi.org/10.436/cs.01.304 Published Online April 01 (hp://www.scirp.org/journal/cs) Power Efficien Baery Charger by Using Consan Curren/Consan olage Conroller
Circuis and Sysems, 01, 3, 180-186 hp://dx.doi.org/10.436/cs.01.304 Published Online April 01 (hp://www.scirp.org/journal/cs) Power Efficien Baery Charger by Using Consan Curren/Consan olage Conroller
Time Control Technique
 Time Conrol Technique MULTITIMER Mulifuncion Relay MK 785N/2 23928 Your Advanages Up o 1 funcions in one uni Simplified sorage Increased flexibiliy Quick seing of long ime values Circui Diagrams B1 22
Time Conrol Technique MULTITIMER Mulifuncion Relay MK 785N/2 23928 Your Advanages Up o 1 funcions in one uni Simplified sorage Increased flexibiliy Quick seing of long ime values Circui Diagrams B1 22
Photo-electric detectors
 Phoo-elecric deecors Osiris specific applicaion deecors, mechanical handling series d.c. supply. Solid sae oupu pages /8 o / References, characerisics Compac design Sysem hru-beam Reflex Diffuse Diffuse
Phoo-elecric deecors Osiris specific applicaion deecors, mechanical handling series d.c. supply. Solid sae oupu pages /8 o / References, characerisics Compac design Sysem hru-beam Reflex Diffuse Diffuse
Valve amplifiers for proportional pressure valves
 Valve amplifiers for proporional pressure valves Type VT-VSPA-, VT-VSPAK- RE 30 Ediion: 03- Replaces: 0.0 Componen series X Suiable for he conrol of all direc and pilo operaed proporional pressure valves
Valve amplifiers for proporional pressure valves Type VT-VSPA-, VT-VSPAK- RE 30 Ediion: 03- Replaces: 0.0 Componen series X Suiable for he conrol of all direc and pilo operaed proporional pressure valves
CURRENT MODE PWM+PFM CONTROLLER WITH BUILT-IN HIGH VOLTAGE MOSFET
 CURRENT MODE PWM+PFM CONTROLLER WITH BUILT-IN HIGH VOLTAGE MOSFET DESCRIPTION SD6835 is curren mode PWM+PFM conroller used for SMPS wih buil-in high-volage MOSFET and exernal sense resisor. I feaures low
CURRENT MODE PWM+PFM CONTROLLER WITH BUILT-IN HIGH VOLTAGE MOSFET DESCRIPTION SD6835 is curren mode PWM+PFM conroller used for SMPS wih buil-in high-volage MOSFET and exernal sense resisor. I feaures low
Lab 3 Acceleration. What You Need To Know: Physics 211 Lab
 b Lab 3 Acceleraion Wha You Need To Know: The Physics In he previous lab you learned ha he velociy of an objec can be deermined by finding he slope of he objec s posiion vs. ime graph. x v ave. = v ave.
b Lab 3 Acceleraion Wha You Need To Know: The Physics In he previous lab you learned ha he velociy of an objec can be deermined by finding he slope of he objec s posiion vs. ime graph. x v ave. = v ave.
Electronic drivers type E-MI-AC analog, DIN plug-in format, for proportional valves without transducer
 www.aos.com Table G010-15/E Elecronic drivers ype E-MI-AC analog, DIN 43650 plug-in forma, for proporional valves wihou ransducer USER FUNCTIONS AND CONTROL OPTIONS DEAD BAND ADJUSTMENT RAMP GENERATOR
www.aos.com Table G010-15/E Elecronic drivers ype E-MI-AC analog, DIN 43650 plug-in forma, for proporional valves wihou ransducer USER FUNCTIONS AND CONTROL OPTIONS DEAD BAND ADJUSTMENT RAMP GENERATOR
Design And Implementation Of Multiple Output Switch Mode Power Supply
 Inernaional Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) Volume Issue 0-Oc 0 Design And Implemenaion Of Muliple Oupu Swich Mode Power Supply Ami, Dr. Manoj Kumar Suden of final year B.Tech. E.C.E.,
Inernaional Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) Volume Issue 0-Oc 0 Design And Implemenaion Of Muliple Oupu Swich Mode Power Supply Ami, Dr. Manoj Kumar Suden of final year B.Tech. E.C.E.,
Obsolete Product(s) - Obsolete Product(s)
 DUAL SWITCH-MODE SOLENOID DRIER HIGH CURRENT CAPABILITY (up o.5a per channel) HIGH OLTAGE OPERATI (up o 46 for power sage) HIGH EFFICIENCY SWITCHMODE OPERATI REGULATED OUTPUT CURRENT (adjusable) FEW EXTERNAL
DUAL SWITCH-MODE SOLENOID DRIER HIGH CURRENT CAPABILITY (up o.5a per channel) HIGH OLTAGE OPERATI (up o 46 for power sage) HIGH EFFICIENCY SWITCHMODE OPERATI REGULATED OUTPUT CURRENT (adjusable) FEW EXTERNAL
Programmable DC Electronic Loads 8600 Series
 Daa Shee Programmable DC Elecronic Loads 99 Washingon Sree Melrose, MA 02176 Phone 781-665-1400 Toll Free 1-800-517-8431 Visi us a www.tesequipmendepo.com 2U half-rack 3U 6U USB RS232 GPIB The programmable
Daa Shee Programmable DC Elecronic Loads 99 Washingon Sree Melrose, MA 02176 Phone 781-665-1400 Toll Free 1-800-517-8431 Visi us a www.tesequipmendepo.com 2U half-rack 3U 6U USB RS232 GPIB The programmable
A Bidirectional Three-Phase Push-Pull Converter With Dual Asymmetrical PWM Method
 A Bidirecional Three-Phase Push-Pull Converer Wih Dual Asymmeral PWM Mehod Minho Kwon, Junsung Par, Sewan Choi, IEEE Senior Member Deparmen of Elecral and Informaion Engineering Seoul Naional Universiy
A Bidirecional Three-Phase Push-Pull Converer Wih Dual Asymmeral PWM Mehod Minho Kwon, Junsung Par, Sewan Choi, IEEE Senior Member Deparmen of Elecral and Informaion Engineering Seoul Naional Universiy
Accurate Tunable-Gain 1/x Circuit Using Capacitor Charging Scheme
 Accurae Tunable-Gain 1/x Circui Using Capacior Charging Scheme Byung-Do Yang and Seo Weon Heo This paper proposes an accurae unable-gain 1/x circui. The oupu volage of he 1/x circui is generaed by using
Accurae Tunable-Gain 1/x Circui Using Capacior Charging Scheme Byung-Do Yang and Seo Weon Heo This paper proposes an accurae unable-gain 1/x circui. The oupu volage of he 1/x circui is generaed by using
MX629. DELTA MODULATION CODEC meets Mil-Std DATA BULLETIN. Military Communications Multiplexers, Switches, & Phones
 DATA BULLETIN MX629 DELTA MODULATION CODEC mees Mil-Sd-188-113 Feaures Mees Mil-Sd-188-113 Single Chip Full Duplex CVSD CODEC On-chip Inpu and Oupu Filers Programmable Sampling Clocks 3- or 4-bi Companding
DATA BULLETIN MX629 DELTA MODULATION CODEC mees Mil-Sd-188-113 Feaures Mees Mil-Sd-188-113 Single Chip Full Duplex CVSD CODEC On-chip Inpu and Oupu Filers Programmable Sampling Clocks 3- or 4-bi Companding
Installation and Operating Instructions for ROBA -brake-checker Typ
 (B.018102.EN) Guidelines on he Declaraion of Conformiy A conformiy evaluaion has been carried ou for he produc in erms of he EC Low Volage Direcive 2006/95/ EC and EMC Direcive 2004/108/EC. The Declaraion
(B.018102.EN) Guidelines on he Declaraion of Conformiy A conformiy evaluaion has been carried ou for he produc in erms of he EC Low Volage Direcive 2006/95/ EC and EMC Direcive 2004/108/EC. The Declaraion
f t 2cos 2 Modulator Figure 21: DSB-SC modulation.
 4.5 Ampliude modulaion: AM 4.55. DSB-SC ampliude modulaion (which is summarized in Figure 21) is easy o undersand and analyze in boh ime and frequency domains. However, analyical simpliciy is no always
4.5 Ampliude modulaion: AM 4.55. DSB-SC ampliude modulaion (which is summarized in Figure 21) is easy o undersand and analyze in boh ime and frequency domains. However, analyical simpliciy is no always
Chapter 2 Summary: Continuous-Wave Modulation. Belkacem Derras
 ECEN 44 Communicaion Theory Chaper Summary: Coninuous-Wave Modulaion.1 Modulaion Modulaion is a process in which a parameer of a carrier waveform is varied in accordance wih a given message (baseband)
ECEN 44 Communicaion Theory Chaper Summary: Coninuous-Wave Modulaion.1 Modulaion Modulaion is a process in which a parameer of a carrier waveform is varied in accordance wih a given message (baseband)
Control and Protection Strategies for Matrix Converters. Control and Protection Strategies for Matrix Converters
 Conrol and Proecion Sraegies for Marix Converers Dr. Olaf Simon, Siemens AG, A&D SD E 6, Erlangen Manfred Bruckmann, Siemens AG, A&D SD E 6, Erlangen Conrol and Proecion Sraegies for Marix Converers To
Conrol and Proecion Sraegies for Marix Converers Dr. Olaf Simon, Siemens AG, A&D SD E 6, Erlangen Manfred Bruckmann, Siemens AG, A&D SD E 6, Erlangen Conrol and Proecion Sraegies for Marix Converers To
Power Amplifier EEA-PAM-5**-A-32 for Proportional Control Valves Contents The following power amplifier models are covered in this catalog
 Vickers Accessories Power Amplifier EEA-PAM-5**-A-32 for Proporional Conrol Valves Conens The following power amplifier models are covered in his caalog Power Amplifier EEA-PAM-513-A-32 EEA-PAM-523-A-32
Vickers Accessories Power Amplifier EEA-PAM-5**-A-32 for Proporional Conrol Valves Conens The following power amplifier models are covered in his caalog Power Amplifier EEA-PAM-513-A-32 EEA-PAM-523-A-32
General data 8/91. Overview
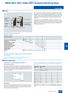 SIRIUS 3RS0, 3RS, 3RS0, 3RS Temperaure Monioring Relays General daa Overview Temperaure seing LED "Device on volage" LED "Relay swiched" Hyseresis swich NSB0_04a LED for display "Up and Down" keys Roary
SIRIUS 3RS0, 3RS, 3RS0, 3RS Temperaure Monioring Relays General daa Overview Temperaure seing LED "Device on volage" LED "Relay swiched" Hyseresis swich NSB0_04a LED for display "Up and Down" keys Roary
49.8. Control Relays and Timers. Contents. Product Selection Guide. Timing Relays
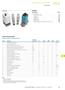 Conrol Relays and Timers.8 Produc Selecion Guide Noes Applies o TRN model only. Applies o TRF model only. The E5-248 is baery powered and has hree programmable rigger funcions. This produc may perform
Conrol Relays and Timers.8 Produc Selecion Guide Noes Applies o TRN model only. Applies o TRF model only. The E5-248 is baery powered and has hree programmable rigger funcions. This produc may perform
Transformer of tgδ on MSP430F1331 single chip microcomputer WANG Han 1 CAI Xinjing 1,XiaoJieping 2,Liu weiqing 2
 2nd Inernaional Workshop on Maerials Engineering and ompuer Sciences (IWMES 205 Transformer of gδ on MSP430F33 single chip microcompuer WANG Han AI Xinjing,XiaoJieping 2,Liu weiqing 2 School of elecrical
2nd Inernaional Workshop on Maerials Engineering and ompuer Sciences (IWMES 205 Transformer of gδ on MSP430F33 single chip microcompuer WANG Han AI Xinjing,XiaoJieping 2,Liu weiqing 2 School of elecrical
COMBITRON Program Schedule
 OMBITRO Program Schedule OMBITRO are supply and acuaor modules for he elecromagne cluches and brakes. As power supply for D- or A-side swiching differen single-wave and bridge recifiers as well as rapid
OMBITRO Program Schedule OMBITRO are supply and acuaor modules for he elecromagne cluches and brakes. As power supply for D- or A-side swiching differen single-wave and bridge recifiers as well as rapid
Solid-state Timer H3CT
 Solid-sae Timer H3CT DIN 48 x 48-mm Sandard Size Analog Timer Wide ime range (for 4 series of models); 0.1 s o 30 hrs. Wih H3CT-8H models, he oupu ype can be swiched beween ime limi DPDT and ime limi SPDT
Solid-sae Timer H3CT DIN 48 x 48-mm Sandard Size Analog Timer Wide ime range (for 4 series of models); 0.1 s o 30 hrs. Wih H3CT-8H models, he oupu ype can be swiched beween ime limi DPDT and ime limi SPDT
ECMA-373. Near Field Communication Wired Interface (NFC-WI) 2 nd Edition / June Reference number ECMA-123:2009
 ECMA-373 2 nd Ediion / June 2012 Near Field Communicaion Wired Inerface (NFC-WI) Reference number ECMA-123:2009 Ecma Inernaional 2009 COPYRIGHT PROTECTED DOCUMENT Ecma Inernaional 2012 Conens Page 1 Scope...
ECMA-373 2 nd Ediion / June 2012 Near Field Communicaion Wired Inerface (NFC-WI) Reference number ECMA-123:2009 Ecma Inernaional 2009 COPYRIGHT PROTECTED DOCUMENT Ecma Inernaional 2012 Conens Page 1 Scope...
Phase-Shifting Control of Double Pulse in Harmonic Elimination Wei Peng1, a*, Junhong Zhang1, Jianxin gao1, b, Guangyi Li1, c
 Inernaional Symposium on Mechanical Engineering and Maerial Science (ISMEMS 016 Phase-Shifing Conrol of Double Pulse in Harmonic Eliminaion Wei Peng1, a*, Junhong Zhang1, Jianxin gao1, b, Guangyi i1, c
Inernaional Symposium on Mechanical Engineering and Maerial Science (ISMEMS 016 Phase-Shifing Conrol of Double Pulse in Harmonic Eliminaion Wei Peng1, a*, Junhong Zhang1, Jianxin gao1, b, Guangyi i1, c
Impacts of the dv/dt Rate on MOSFETs Outline:
 Ouline: A high dv/d beween he drain and source of he MOSFET may cause problems. This documen describes he cause of his phenomenon and is counermeasures. Table of Conens Ouline:... 1 Table of Conens...
Ouline: A high dv/d beween he drain and source of he MOSFET may cause problems. This documen describes he cause of his phenomenon and is counermeasures. Table of Conens Ouline:... 1 Table of Conens...
Microwave Transistor Oscillator Design
 Tuorial on Modern Ulra Low Noise Microwave Transisor Oscillaor Design olumbia Universiy Sepember, 9 Ulrich L. Rohde, Ph.D.* hairman Synergy Microwave orp. *Prof. of RF ircui and Microwave ircui Design
Tuorial on Modern Ulra Low Noise Microwave Transisor Oscillaor Design olumbia Universiy Sepember, 9 Ulrich L. Rohde, Ph.D.* hairman Synergy Microwave orp. *Prof. of RF ircui and Microwave ircui Design
The student will create simulations of vertical components of circular and harmonic motion on GX.
 Learning Objecives Circular and Harmonic Moion (Verical Transformaions: Sine curve) Algebra ; Pre-Calculus Time required: 10 150 min. The sudens will apply combined verical ranslaions and dilaions in he
Learning Objecives Circular and Harmonic Moion (Verical Transformaions: Sine curve) Algebra ; Pre-Calculus Time required: 10 150 min. The sudens will apply combined verical ranslaions and dilaions in he
PERFORMANCE SPECIFICATION SHEET ELECTRON TUBE, RECEIVING TYPE 8233
 INCH-POUND MIL-PRF-1/1593E 15 Augus 2012 SUPERSEDING MIL-PRF-1/1593D 17 Augus 2004 DESCRIPTION: Penode, sharp cuoff. Ouline: See figure 1. PERFORMANCE SPECIFICATION SHEET ELECTRON TUBE, RECEIVING TYPE
INCH-POUND MIL-PRF-1/1593E 15 Augus 2012 SUPERSEDING MIL-PRF-1/1593D 17 Augus 2004 DESCRIPTION: Penode, sharp cuoff. Ouline: See figure 1. PERFORMANCE SPECIFICATION SHEET ELECTRON TUBE, RECEIVING TYPE
Generating Polar Modulation with R&S SMU200A
 Rohde & Schwarz producs: SMU00 Generaing Polar Modulaion wih R&S SMU00 Polar modulaion is a mehod where digial modulaion is realized as a combinaion of phase and ampliude modulaion, raher han using an
Rohde & Schwarz producs: SMU00 Generaing Polar Modulaion wih R&S SMU00 Polar modulaion is a mehod where digial modulaion is realized as a combinaion of phase and ampliude modulaion, raher han using an
Development of Pulse Width Modulation LED drive
 ISSN 23069392, Inernaional Journal of Technology People Developing, Vol. 2, No. 3, DEC. 2012 Developmen of Pulse Widh Modulaion LED drive YuanPiao. Lee 1 ShihKuen. Changchien 2 ChainKuo Technology Universiy,
ISSN 23069392, Inernaional Journal of Technology People Developing, Vol. 2, No. 3, DEC. 2012 Developmen of Pulse Widh Modulaion LED drive YuanPiao. Lee 1 ShihKuen. Changchien 2 ChainKuo Technology Universiy,
