Commission H (Waves in Plasmas) Activity Report. December 7th, T. Okada, Y. Omura, and H. Matsumoto
|
|
|
- Delilah Adams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Commission H (Waves in Plasmas) Activity Report December 7th, 2006 T. Okada, Y. Omura, and H. Matsumoto Research Topics AKEBONO and GEOTAIL has been making observations since 1989, and 1992, respectively. Detailed status of these satellites are shown in the previous Commission H (Waves in Plasmas) Activity Report on August 3 rd <Magnetospheric Plasma Waves and related Phenomena> The investigation of the earth's plasmasphere should be advanced not only for scientific interests but also for engineering applications since the plasmaspheric plasma cannot be ignored for high-precision navigation and positioning from artificial satellites. As direct observations from the ground cannot be performed caused by the disturbance of the ionosphere, the electron density in the plasmasphere is generally observed from spacecraft. Goto et al. (2006) proposed an estimation method of the plasmaspheric electron density profile using the information from natural VLF waves observed on the scientific satellites in the plasmasphere. They demonstrated that the electron density profile in the plasmasphere can be successfully reconstructed based on the wave normal angles and spectrum of the whistler mode waves observed in the plasmasphere. The validity of the estimation method was verified in many simulations. The upper left figure shows a scatter plot of the delay times of whistler waves as a function of frequency at an observation point in the plasmasphere, and the left figure shows the electron density profile of the plasmasphere. Narita extensively studies low-frequency waves both in the upstream and down stream regions of the Earth s bow shock with the four-point measurements by the Cluster spacecraft. The right-hand polarized magnetosonic/whistler mode and the ion beam resonant mode and the ion beam resonant mode exit in the upstream region. These waves show a transition to the mirror mode in the downstream region. The upstream waves propagate nearly parallel to the background magnetic field, while the waves propagate nearly perpendicular in the downstream region. Hence, the propagation pattern is outward divergent and aligned with the shock normal direction in the upstream region, away from the solar wind direction toward the flank region and aligned with the plasma flow direction in the magnetosheath, and inward convergent toward the magnetopause. Near the foreshock region, wave spectra have the Kolmogorov s slope of -5/3, and show energy injection, inertial, and
2 dissipation. These results have added significantly to our present knowledge of low-frequency waves in the bow sock region. Figure shows a simplified sketch of the propagation pattern. Arrows represent wave phase velocities. The outer and inner solid curved lines represent the bow shock and the magnetopause, respectively. Using high-sensitive all-sky imager, Sakaguchi et al. (2006) reported isolated proton arcs observed in the subauroral region at Athabasca, Canada (54.7N, 246.7E, MLAT=62.0N). Their appearance clearly coincides with intense Pc 1 geomagnetic pulsations observed by an induction magnetometer. Using simultaneous polar-orbiting satellite data, Sakaguchi et al. concluded that the observed isolated arc were driven by the EMIC waves, which were generated near the plasmapause and scattered the ring current protons resonantly into the loss cone. Figure shows the Keograms of 557.7nm, 630.0nm, H-beta (from top to bottom) obtained at Athabasca, Canada, magnetic field variations obtained at Meanook near Athabasca, and dynamic spectrum of H component geomagnetic field variations at Athabasca on September 5, Abe et al. [2006] identified the plume from the ground for the first time by using ULF waves measured by ground magnetometers. They confirmed the identification by comparisons with the data from the EUV imager on board the IMAGE satellite. Kawano et al. presented an invited talk at the "Mesosphere-Themosphere-Ionosphere Workshop" about the progress on theestimation of plasmaspheric O+ ratio by comparing the mass density estimated using the ground-observed ULF waves with the He+ intensity measured by IMAGE/EUV. The following figure is from Abe et al. [2006]:(a) The IMAGE/EUV He+ column abundance [He+/cm2] corresponding to the point (called "mapped TIK-CHD midpoint" below) where the field line running through the midpoint between the two ground magnetometers, placed at stations named TIK and CHD, intersects the equatorial plane. The horizontal axis shows time (UT). The column abundance increases (decreases) as the "mapped TIK-CHD midpoint" enters (exits) the plume. (b) H-component power ratio dynamic spectra on the ground (TIK/CHD). The vertical axis shows frequency [mhz], and the horizontal
3 axis shows time (UT). There exists a red band with decreasing frequency with time, and a blue band with increasing frequency with time, as marked by a white loop and arrows. (c) Same as (b), but pixels with coherence < 0.83 are set blank. Just below the red (blue) band marked by the white loop of Figure 5b, one can identify a blue (red) band. These are the features of the field-line resonance (FLR). The FLR frequency is inversely proportional to the plasma density at the "mapped TIK-CHD midpoint"; thus, the decrease-then-increase of the frequency (Panel b) is consistent with the simultaneous increase-then-decrease of the He+ column abundance (Panel a). <Solar Radio Bursts and related Phenomena> Morioka et al. (2006) studied detailed features of micro-type-iii radio bursts, which are elements of the so-called type III storm, by using long-term observations made by the Geotail and Akebono satellites. Micro-type-III radio bursts are characterized by short-lived, continuous, and weak emissions. The occurrence distribution of these bursts with respect to the emitted power flux is different from that of ordinary type III bursts, indicating that they are not just the weaker components of the ordinary bursts. It was found that both micro and ordinary type-iii bursts emanated from the same active region without interference, indicating the coexistence of independent electron acceleration processes. Figure: High time-resolution dynamic spectrogram of micro-type III bursts observed by the Akebono satellite on May 23, 2001.
4 Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) waves which are thought to play an important role in acceleration of the solar wind are detected in the decametric type III solar radio bursts obtained at Tohoku University Iitate observatory (Nakagawa and Iizima,2006). The power spectrum (Figure) shows several peaks in the frequency range from 16 to 40 MHz, indicating that the energy conversion from the plasma wave into the radio wave is enhanced locally at several altitudes of about 0.3 to 1.0 solar radius from the Sun. At these altitudes the waveforms of the MHD waves are supposed to become steepened (Suzuki and Inutsuka, 2005), and the steep gradients of the plasma density enhance the conversion rate to the radio waves. Figure: An example of a type III solar burst (the right-hand polarized component of the radio wave) observed at Iitate observatory of Tohoku University, Japan, on September 15, <Antenna Analysis> Nagai et al. [2006] have tried to evaluate the impedance of wire antennas onboard Geotail spacecraft, by using the waveforms of chorus emissions observed in the magnetosphere. Since the propagation characteristics of chorus emissions are well-known, it is possible to calculate the theoretical values of the wave electric fields, only from the wave magnetic fields measured by search coil magnetometers. By comparing the theoretical electric fields with those actually observed by the wire antennas, the antenna impedances can be inversely estimated. Treating the antenna sheath to be the parallel circuit of R (resistance) and C (capacitance), they have found that the antenna impedance varies with the spin of the spacecraft, indicating the variation of the antenna sheath with respect to the angle between the antenna and the ambient geomagnetic field line. Figure: An example of the antenna sheath capacitance estimated from the Geotail observations of chorus emissions. The capacitance varies with almost the half of the spin period of Geotail (3 sec).
5 Yamashita et al. [2006] have investigated the characteristics of wire antennas at low frequencies by theoretical calculations and numerical simulations. With the previous experimental measurements called Rheometry, which measures the output voltages of a scale-model antenna immersed in the quasi-static electric field generated in a water tank, they had found an interesting frequency dependence of antenna sensitivity (here evaluated as the antenna effective lengths ). For a wire dipole antenna covered by the thin insulators except for its tips, the effective length is almost equal to its tip-to-tip length at very low frequencies (less than hundreds of Hz), while it becomes half of it at higher frequencies. Such a frequency dependence of the effective length has been explained by theoretical calculations based on an equivalent electric circuit model. They have also confirmed the frequency dependence by using numerical electromagnetic simulations, which have revealed the detailed spatial distributions of ambient electric fields and potentials deformed under the influence of the antenna wires. Figure: Electric field and potential distributions around a wire dipole antenna. <Single Probe Application onboard Satellite> Ishisaka et al. [2006] have investigated the relationship between the Geotail spacecraft potential, the electron density and the electron temperature in the near tail regions during the period from November 1994 to March 1997, and obtained the empirical formula shown the relationship between the spacecraft potential and electron density considering the electron temperature. The amount of scatter of the measured value from the empirical formula was about +/-20%. Therefore the electron density in the solar wind and the magnetosphere could be estimated by the spacecraft potential and the empirical formula. The electron density obtained from the spacecraft potential was determined by the electrons in wider energy range includes cold components that are not measured by the particle detectors. Using the spacecraft potential and the plasma particle density obtained by the low energy particle instrument (LEP) onboard Geotail, we investigated the distribution of low energy plasma in the magnetosphere. They have obtained the map shown the spatial distribution of low energy plasma and have clearly seen a large amount of low energy plasma existed near the magnetopause in the magnetosphere.
6 <Polar Region Experiments> Ozaki et al. [2006] have been observing natural ELF/VLF waves (chorus and hiss) in Antarctica from December 2005 to December 2006, by using three low-power magnetometer systems placed at three sites near Showa Station: West Ongul, Skallen, and H100. Each system has a crossed loop antenna to pick up the north-south and east-west components of ELF/VLF magnetic fields, whose intensities and polarizations are measured at 4 spaced frequency bands (500, 1 k, 2 k and 6 khz), with less than 1 minute resolution. With the preliminary analysis they have confirmed that the intensities and polarizations of the observed waves could be used to calculate their ionospheric exit points, during substorms as well as in quiet times. Such ground-based ELF/VLF observations will be compared with riometer observations at Syowa Station, as well as with Akebono satellite observations of the ELF/VLF waves above Antarctica, for the study of the stereoscopic structure of the ELF/VLF propagation over the polar ionosphere and magnetosphere. Figure: An example of ELF/VLF wave intensities measured at three unmanned stations near Syowa Station on March 19, The difference in intensities observed at 2 khz gives the information on their ionospheric exit points. <Lightning Location> Yagitani et al. [2006] have developed a lightning detection system to determine the lightning locations by observing the sferic waveforms at a single station. By receiving two horizontal magnetic components and one vertical electric component at VLF frequencies, this system measures a series of sequential pulses on each of the observed sferics, which are used to compute both the direction and distance to the corresponding lightning stroke. Compared with the lightning locations identified by a conventional lightning location system (LLS) with multiple stations, it has been confirmed that the developed system could locate the lightnings within the distance of several hundred km with the location errors of about 10%, for the VLF sferics measured with distinguishable pulse trains.
7 Geomag. North (51.2 o ) 49.1 o Estimation km LLS (236.8 km) Kanazawa Figure: An example of the lightning location estimated by the developed system (solid line), compared with that identified by a conventional lightning location system (LLS) (dotted line). <SELENE> Refer to the previous Commission H (Waves in Plasmas) Activity Report on August 3 rd <BepiColombo> Refer to the previous Commission H (Waves in Plasmas) Activity Report on August 3 rd <Ionospheric Sounding by Plasama Wave Observation> Refer to the previous Commission H (Waves in Plasmas) Activity Report on August 3 rd <New Technology> Development of the analogue chip for plasma wave receivers The development of analogue chips for plasma wave receivers has been started in Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere of Kyoto University. The development is based upon the ASIC technology (ASIC: Application-Specific Integrated Circuit). This development leads to realizing lightweight plasma wave receivers, which can be used in multiple spacecraft missions or deep space missions. They designed the analogue circuits and their layouts to be realized inside a chip. At the first step, they incorporated the first stage differential amplifier and low pass filter with the cutoff frequency of 100kHz into chips. The first prototype they developed is shown in the figure. The performance tests for the developed chips have been conducted in Kyoto University.
8 The picture shows the first prototype of the analogue chip designed in Kyoto University. The chip contains the differential amplifiers, filters and main amplifiers which are essential to plasma wave receivers. <Space Plasma Wave Simulation> The electric field structure around the moon is studied by using a 2-dimensional, electromagnetic full particle simulation (Kimura and Nakagawa, 2006). A plasma wake is formed behind the moon in the solar wind flow, and more intense electric field is produced at the terminator region of the moon due to the absorption of the plasma particles at the surface of the moon. Figure shows the magnitude of the electric field around the moon in the solar wind flowing from the left. Katoh and Iizima (2006) studied the mode conversion process from slow X-mode waves to fast X-mode waves by the tunneling effect by means of the computer simulation. On the basis of the new approach by the simulation, they have confirmed that the mode conversion to the fast X-mode waves is especially effective in a case where the width of the evanescent layer which exists between the local UHR frequency and the local fast X-mode cut off frequency is of the order of the wave length of the incident slow X-mode waves. Katoh et al. (2006) studied generation of ion cyclotron waves through the ion pickup process surrounding Io by hybrid simulation. They simulated the excitation of ion cyclotron waves and discuss the modification of the velocity distribution of picked-up ions due to the wave-particle interaction. By using full electromagnetic particle simulation, Hikishima et al. [2006] have been investigating the
9 generation and propagation mechanisms of chorus emissions and VLF emissions, through the cyclotron resonant interaction between whistler mode waves and anisotropic electrons. With a one-dimensional simulation model along a nonuniform magnetic field line in the dayside outer magnetosphere, they have found that a whistler mode wave generated around the magnetic equator exhibits the rising-tone-like frequency-time structure when observed at a fixed location away from the equator. Detailed analyses of wave-particle interactions involved are under way. In the science session of space plasma theories and simulations, SGEPSS (Society of Geomagnetism and Earth, Planetary and Space Sciences) Fall meeting, Sagamihara, 4-7 November 2006, 24 oral and 9 poster papers were presented: MHD and fluid-type simulations associated with Kelvin-Helmholtz instability and the resulting plasma mixing process are presented by Matsumoto and Seki (2006), Nakamura and Fujimoto (2006), and Takagi et al. (2006). Particle simulations associated with tearing instability occurring in the magnetic reconnection at the current sheet were conducted in order to analyze the electron acceleration and heating by Haijima et al. (2006), Shinohara et al.(2006), Fujimoto et al.(2006), and Hayakawa (2006). Advanced techniques of MHD, Vlasov and interlocked PIC-MHD simulations are also presented by Yagi et al.(2006), Miyoshi and Kusano (2006), Umeda (2006), Sugiyama and Kusano (2006), and Ouki and Shinohara (2006). A simulation project for spacecraft environment was introduced by Usui et al. (2006). From a view point of space engineering, PIC simulations on interaction of intense electromagnetic waves such as SPS microwave beam with the ionospheric electrons were conducted by Nakamoto et al. (2006). Antenna characteristics in the photoelectron environment were also investigated with 3D PIC-EM simulations by Miyake et al. (2006). Other research results were presented such as Whistler-electron nonlinear interactions by Katoh and Omura (2006), Furuya et al. (2006) and Hikishima et al. (2006), moon-plasma interactions by Kimura and Nakagawa (2006), Alfven wave nonlinear interactions by Nariyuki and Hada (2006) and Tanaka et al. (2006), and Show waves by Amano and Hoshino (2006) and Matsukiyo (2006). Reconnection process has effects on large scales and quite often our interest is in this aspect. However, electron dynamics at the X-line needs to be treated appropriately at the same time. It is a clever idea to include kinetic effects only in the close proximity of the X-line but coarse-grain the physics to MHD approximation or at remote locations. Sugiyama et al [SGEPSS, 2006] is developing a code (multi-scale code) in this direction. One-dimensional Alfven wave propagation has been successfully tested. As a similar but different approach, one may think of including high resolution treatment only in the X-line proximity. Fujimoto et al [SGEPSS, 2006] has introduced the AMR scheme together with particle splitting scheme into a full particle code, whereby higher resolution is attained whenever and wherever it is needed. This enables the authors to run long time simulations and observe the elongation of the X-line and the associated decline in the reconnection rate.
10 Conferences and Meetings ( July 2006 ~ December 2006) 1) The 30th Symposium on Space and Upper Atmospheric Sciences in the Polar Regions, Aug. 3-4, 2006, NIPR, Tokyo 2) Advanced School in Space Environment-2006: Solar-Terrestrial Physics, Italia L aquila, Sept , 2006, 1) International Symposium on Recent Observations and Simulations of the Sun-Earth System (ISROSES), Varna, Bulgaria, Sept , 2006, 2) The XXIInd International Symposium on Discharges and Electrical Insulation in Vacuum (ISDEIV2006), Sept , 2006, 3) BepiColombo SWT #3 Sept , Padova, Italy 4) The XXIInd International Symposium on Discharges and Electrical Insulation in Vacuum (ISDEIV2006) Sept , Matsue. 5) Scientific Data and Knowledge within the Information Society, Beijing, China, Oct , 2006, 6) Future perspectives of space plasma and particle instrumentation and international collaborations, Nov., 1-3,2006, Rikkyo Univ., Tokyo, Japan 7) SGEPSS Fall meeting, Sagamihara, Nov. 4-7, 2006, 8) CAWSES Workshop on Space Weather Modeling (CSWM), Nov , 2006 Future Conferences and Meetings 1) AGU fall meeting, San Fransisco, Dec , 2006, 2) Chapman Conference on Midlatitude Ionospheric Dynamics and Disturbances, Yosemite National Park, California, Jan. 3-6, 2007, 3) 8th International School/Symposium for Space Simulations (ISSS-8) 25 February - 3 March 2007, Kauai, Hawaii
11 Reference Abe, S., H. Kawano, J. Goldstein, S. Ohtani, S. I. Solovyev, D. G. Baishev, and K. Yumoto (2006), Simultaneous identification of a plasmaspheric plume by a ground magnetometer pair and IMAGE Extreme Ultraviolet Imager, J. Geophys. Res., 111, No. A11, A11202, doi: /2006ja Amano T., Masahiro Hoshino, Effect of Shock Angle on the Electron Acceleration Efficiency in Quasi-Perpendicular Shocks, B008-23, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Fujimoto, A., S. Watanabe, M. Shinohara, K. Yumoto, and MAGDAS/CPMN Group, Wave Characteristics of Long-period Pulsations at Ground and Satellite during Huge Magnetic Storms, SGEPSS 2006 Fall Meeting, Sagamihara. Fujimoto, K., et al., Presentation at the Fall SGEPSS Meeting, Fujimoto K., Hironori Shimazu, Takahiro Obara, Magnetic reconnection in large and fully kinetic system: Time evolution of electron diffusion region and reconnection rate, B008-09, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Furuya N., Yoshiharu Omura, Danny Summers, Necessary conditions for relativistic resohaijima, K., K.G. Tanaka, I. Shinohara, and M. Fujimoto, Electron temperature anisotropy effects on tearing mode in thick current sheets, submitted to Adv. Space Res., Haijima K., Kentaro Tanaka, Masaki Fujimoto, Iku Shinohara, Effect of temperature anisotropy on two-dimensional tearing instability, B008-06, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Hayakawa, T., et al., Presentation at the Fall SGEPSS Meeting, Hayakawa T., Numerical Research on Coalescence of Magnetic Islands to Study Effects of Impotant Parameters on Structural Changes around O-point, B008-P004, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Hikishima M., S. Yagitani, I.Nagano, Y. Omura, H. Matsumoto, Particle simulation with the triggered waves for chorus in a nonuniform magnetic field, B008-P001, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Iizima M., MHD waves responsible for solar wind heating detected in the type III solar radio bursts The Sixth International Workshop on Nonlinear Waves and Turbulence in Space Plasmas, Oct. 9-13, 2006, Fkuoka, Japan. Ishisaka, K. Y. Kasaba, T. Okada, H. Hayakawa, H. Kojima, H. Matsumoto, Y. Saito, T. Mukai Investigation of low energy plasma distribution in the magnetosphere using spacecraft potential AOGS 2006, Singapore, July Iyemori, T., M. Matsumura, Y. Tanaka, A. Saito, M. Nose, N. Oshiman, and Y. Odagi, Observation of atmospheric pressure oscillation and its comparison with geomagnetic pulsations, SGEPSS 2006 Fall Meeting, Sagamihara. Katoh, Y., and M. Iizima, Mode conversion from slow X-mode to fast X- mode by the tunneling effect, Earth Planets Space, 58, 11, e53--e56, Katoh, Y., F. Tsuchiya, H. Misawa, A. Morioka, S. Okano, and T. Sugiyama, Hybrid simulation of ion pickup process at Io, SGEPSS Fall meeting, Sagamihara, Kanagawa, Japan, November 4-7, Katoh Y., Y. Omura, Simulation study on the generation mechanism of whistler-mode chorus emissions, B008-02, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Kawano, H., T. Teshima, J. Goldstein, S. Ohtani, K. Yumoto, and the CPMN group, Estimation of the O+ ratio by comparing the IMAGE EUV data and the CPMN ground magnetometer data, Mesosphere-Themosphere-Ionosphere Workshop, Toyokawa, September Kawano, H., T. Teshima, J. Goldstein, S. Ohtani, and K. Yumoto, Comparison of CPMN-based and IMAGE EUV-based estimates of the plasmaspheric density at L~1.65, The 30th Symposium on Space and Upper Atmospheric Sciences in the Polar Regions, Tokyo, August 2006.
12 Kawano, H., S. Ohtani, T. Uozumi, S. Abe, K. Kitamura, Y. Tanaka, K. Yumoto, and MAGDAS/CPMN group, Cluster-CPMN/MAGDAS conjunction study of Pi2 waves in the inner magnetosphere, SGEPSS 2006 Fall Meeting, Sagamihara. Kimura, T., H. Kawano, S. Abe, Y. Obana, and K. Yumoto, Latitudinal dependence of the magnetospheric plasma density observed at the MAGDAS stations, SGEPSS 2006 Fall Meeting, Sagamihara. Kimura, S., T. Nakagawa, A 2-dimensional electromagnetic full particle simulation of electric structures around the moon, 2006 SGEPSS Fall Meeting, Nov. 4-7, 2006, Sagamihara, Japan.Nakagawa, T., and Kimura S., Tomoko Nakagawa, A 2-Dimensional electromagnetic full particle simulation of electric structures around the moon, B008-16, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Kitamura, K., S. Watari, M. Kunitake, and T. Obara, Comparison between the high-energy electron flux at the geosynchronous orbit and the geomagnetic Pc5 pulsations, SGEPSS 2006 Fall Meeting, Sagamihara. Matsukiyo S., Electron heating in the foot of high Mach number quasi-perpendicular shocks, B008-24, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Matsumoto Y., Kanako Seki, Turbulent evolution of the KH instability: Comparison between 2-D and 3-D secondary instabilities, B008-04, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Miyoshi T., Kanya Kusano, A proper projection methomorioka, A., Y. Miyoshi, S. Masuda, F. Tsuchiya, H. Misawa, H. Matsumoto, K. Hashimoto, and H. Oya, Micro-Type III bursts, Astrophysical Journal, in press, Morioka, A., Y. Miyoshi, S. Masuda, F. Tsuchiya, H. Misawa, H. Matsumoto, K. Hashimoto, and H. Oya, Micro-Type III bursts, Astrophysical Journal, in press, Nagai, O., T. Imachi, S. Yagitani, M. Hikishima, R. Higashi, I. Nagano, and H. Matsumoto, Analysis of low-frequency electric field antenna impedance aboard scientific spacecraft, 120th SGEPSS Fall Meeting, Sagamihara, Japan, November Nakamoto N., H. Usui, Y. Omura, Computer experiments on space plasmas perturbation caused by a spatial gradient of intense EM beam intensity, B008-21, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Nakamura T., M. Fujimoto, The coalescence of MHD-scale Kelvin-Helmholtz vortices; Two-dimensional two-fluid simulations including finite electron inertia,b008-05, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Narita, Y., K.-H. Glassmeier, S. Schäfer, U. Motschmann, M. Fränz, I. Dandouras, K.-H. Fornaçon, E. Georgescu, A. Korth, H. Rème, I. Richter Alfvén waves in the foreshock propagating upstream in the plasma rest frame: statistics from Cluster observation, Ann. Geophysicae, 22, , Narita, Y., and K.-H. Glassmeier, Dispersion analysis of low-frequency waves through the terrestrial bow shock, J. Geophys. Res., 110, A12215, doi: /2005ja011256, Narita, Y., K.-H. Glassmeier, and R. A. Treumann, Wave-number spectra and intermittency in the terrestrial foreshock region, Phys. Rev. Lett., 97, , Narita, Y., K.-H. Glassmeier, K.-H. Fornacon, I. Richter, S. Schafer, U. Motschmann, I. Dandouras, H. Reme, and E. Georgescu, Low-frequency wave characteristics in the upstream and downstream regime of the terrestrial bow shock, J. Geophys. Res., 111, A1203, doi: /2005ja011231, Narita, Y., K.-H. Glassmeier, S. Schafer, U. Motschmann, K. Sauer, I. Dandouras, K.-H. Fornacon, E. Georgescu, and H. Reme, Dispersion analysis of ULF waves in the foreshock using cluster data and the wave telescope technique, Geophys. Rev. Lett., 30, 1710, doi: /2003gl017432, Nariyuki Y., T. Hada, Kinetically modified parametric instabilities of circularly-polarizedalfven waves: Ion kinetic effects, B008-22, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Ohki M., I. Shinohara, Development and evaluation of a new plasma simulation based on the Discrete Event Simulation method 2, B008-P005, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Ozaki, M., Y. Hata, I. Nagano, S. Yagitani, H. Yamagishi, N. Sato, and A. Kadokura, Estimation of the
13 ionospheric exit point of natural VLF emissions by tri-unmanned ground stations in Antarctica, 120th SGEPSS Fall Meeting, Sagamihara, Japan, November Retinò A., et al., Structure of the separatrix region close to a magnetic reconnection X-line: Cluster observations, Geophys. Res. Lett., 33, L06101, doi: /2005gl024650, Sakaguchi, K., K. Shiokawa, A. Ieda, Y. Miyoshi, Y. Otsuka, T. Ogawa, M. Connors, E. F. Donovan, and F. J. Rich, Simultaneous ground and satellite observations of an isolated proton arc at subauroral latitudes, J. Geophys. Res., in press., Sakurai, T., and Y. Tonegawa, How is the excitation of Pc 5 oscillations in the magnetosphere?, The 30th Symposium on Space and Upper Atmospheric Sciences in the Polar Regions, Tokyo, August Shinohara, M., K. Nozaki, A. Yoshikawa, K. Yumoto, and MAGDAS/CPMN Group, Electric field perturbations of Pc4 pulsations observed by the FM-CW HF radar at low latitudes, SGEPSS 2006 Fall Meeting, Sagamihara. Shinohara I., Kentaro Tanaka, Masaki Fujimoto, Efficiency of electron acceleration associated with tearing island coalescence, B008-08, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Sugiyama T., Kanya Kusano, PIC - MHD Interlocked Simulation in Space Plasma, B008-11, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Suzuki, T. K. and S. Inutsuka, Making the corona and the fast solar wind: a self-consistent simulation for the low-frequency Alfv'en waves from the photosphere to 0.3 AU, Astrophys. J. Lett., 632, L49-L52, Takagi K., H. Hasegawa, M. Fujimoto, The Effects of Spatial Evolution on the Kelvin-Helmholtz Vortices with Three-Dimensional Simulation, B008-P003, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Takasaki, S., N. Sato, A. Kadokura, Y. Tanaka, Y. Ebihara, and H. Yamagishi, Remote sensing of magnetospheric plasma density by using the unattended antarctic magnetometer network and the conjugate Iceland magnetometer, The 30th Symposium on Space and Upper Atmospheric Sciences in the Polar Regions, Tokyo, August Tanaka S., Takayuki Umeda, Tatsuki Ogino, Simulation study of large-amplitude Alfven waves in the solar wind, B008-P007, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara, Tanaka, K.G., I. Shinohara, and M. Fujimoto, Parameter dependence of quick magnetic reconnection triggering: A survey study using two-dimensional simulations, J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 111, No. A11, A11S18, /2006JA011968, Tanaka K., I. Shinohara, M. Fujimoto, Dependence of electron dynamics on reconnection layer structure with density asymmetric current sheet, B008-07, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Tanaka S., T. Umeda, T. Ogino, Simulation study of large-amplitude Alfven waves in the solar wind, B008-P007, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara, Teramoto, M., M. Nose, and H. Kamei, On Pi2 magnetic pulsations observed by the low-altitude satellite DE-1 and mid- to low-latitude ground magnetometer stations, The 30th Symposium on Space and Upper Atmospheric Sciences in the Polar Regions, Tokyo, August Takasaki, S., N. Sato, A. Kadokura, H. Yamagishi, Y. Ebihara, and Y. Tanaka, High-spatial resolution remote sensing of the magnetospheric mass density: Observations at ground-based conjugate pairs at L~6, SGEPSS 2006 Fall Meeting, Sagamihara. Teramoto, M., M. Nose, and T. Kamei, Statistical analysis of Pi2 pulsation by polar orbiting DE-1 satellite and three mid- and low-latitudes ground stations, SGEPSS 2006 Fall Meeting, Sagamihara. Tokunaga, T., H. Kohta, A. Yoshikawa, T. Uozumi, H. Kawano, and K. Yumoto, Wave characteristics of high-latitude Pi 2's extracted by using the Independent Component Analysis, The 30th Symposium on Space and Upper Atmospheric Sciences in the Polar Regions, Tokyo, August Tokunaga, T., A. Morioka, H. Kohta, A. Yoshikawa, T. Uozumi, K. Yumoto, and MAGDAS/CPMN Group, Comparison between High-Latitude Pi 2 Pulsations Extracted by ICA (Independent Component
14 Analysis) and AKR, SGEPSS 2006 Fall Meeting, Sagamihara. Umeda T., Numerical interpolation schemes for Vlasov simulations, B008-13, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Uozumi, T., K. Yumoto, and MAGDAS/CPMN Group, Long-term variation of Pi 2 magnetic pulsations derived from CPMN database, SGEPSS 2006 Fall Meeting, Sagamihara. Usui H., Iku Shinohara, Hiroko, O Ueda, Masaki Okada, Development of spacecraft environment plasma simulator, B008-12, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Yagi M., Kanako Seki, Yosuke Matsumoto, Development of the 3-D MHD code with the vector potential formulation to guarantee the divb=0 property using R-CIP algorithm, B008-14, SGEPSS Fall Meeting, November, Sagamihara,2006. Yagitani, S., I. Nagano, and M. Ozaki, Lightning detection system with sferics observation at a single station, 28th International Conference on Lightning Protection (ICLP 2006), Vol.1, II-11, , Kanazawa, Japan, September, Yamashita, K., S. Yagitani, T. Imachi, and I. Nagano, Characteristics of electric wire antenna onboard scientific spacecraft, 120th SGEPSS Fall Meeting, Sagamihara, Japan, November ( End )
Commission H (Waves in Plasmas) Activity Report. July 15th, T. Okada, Y. Omura, and H. Matsumoto
 Commission H (Waves in Plasmas) Activity Report July 15th, 2005 T. Okada, Y. Omura, and H. Matsumoto Research Topics Kumamoto et al. [2004] investigated Long-term variations of ambient electron
Commission H (Waves in Plasmas) Activity Report July 15th, 2005 T. Okada, Y. Omura, and H. Matsumoto Research Topics Kumamoto et al. [2004] investigated Long-term variations of ambient electron
NON-TYPICAL SERIES OF QUASI-PERIODIC VLF EMISSIONS
 NON-TYPICAL SERIES OF QUASI-PERIODIC VLF EMISSIONS J. Manninen 1, N. Kleimenova 2, O. Kozyreva 2 1 Sodankylä Geophysical Observatory, Finland, e-mail: jyrki.manninen@sgo.fi; 2 Institute of Physics of the
NON-TYPICAL SERIES OF QUASI-PERIODIC VLF EMISSIONS J. Manninen 1, N. Kleimenova 2, O. Kozyreva 2 1 Sodankylä Geophysical Observatory, Finland, e-mail: jyrki.manninen@sgo.fi; 2 Institute of Physics of the
The Ionosphere and Thermosphere: a Geospace Perspective
 The Ionosphere and Thermosphere: a Geospace Perspective John Foster, MIT Haystack Observatory CEDAR Student Workshop June 24, 2018 North America Introduction My Geospace Background (Who is the Lecturer?
The Ionosphere and Thermosphere: a Geospace Perspective John Foster, MIT Haystack Observatory CEDAR Student Workshop June 24, 2018 North America Introduction My Geospace Background (Who is the Lecturer?
Particle simulations of whistler-mode rising-tone emissions triggered by waves with different amplitudes
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011ja017428, 2012 Particle simulations of whistler-mode rising-tone emissions triggered by waves with different amplitudes Mitsuru Hikishima 1,2
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011ja017428, 2012 Particle simulations of whistler-mode rising-tone emissions triggered by waves with different amplitudes Mitsuru Hikishima 1,2
Commission H (Waves in Plasmas) Activity Report. March 10th, T. Okada and Y. Omura
 資料 0-H Commission H (Waves in Plasmas) Activity Report (Ver.3) March 0th, 2009 T. Okada and Y. Omura Rese arch Topics GEOTAIL spacecraft has been operated since 992. The Plasma
資料 0-H Commission H (Waves in Plasmas) Activity Report (Ver.3) March 0th, 2009 T. Okada and Y. Omura Rese arch Topics GEOTAIL spacecraft has been operated since 992. The Plasma
Recent results of EMIC/ELF/VLF wave measurements at Athabasca (L=4.2), Canada. Kazuo Shiokawa (ISEE, Nagoya Univ.) Martin Connors (Athabasca Univ.
 Recent results of EMIC/ELF/VLF wave measurements at Athabasca (L=4.2), Canada Kazuo Shiokawa (ISEE, Nagoya Univ.) Martin Connors (Athabasca Univ.) Athabasca (September 3, 2005-) all-sky imager meridian-scanning
Recent results of EMIC/ELF/VLF wave measurements at Athabasca (L=4.2), Canada Kazuo Shiokawa (ISEE, Nagoya Univ.) Martin Connors (Athabasca Univ.) Athabasca (September 3, 2005-) all-sky imager meridian-scanning
The Cassini Radio and Plasma Wave Science Instrument
 The Cassini Radio and Plasma Wave Science Instrument Roger Karlsson Space Research Institute of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, Graz Graz in Space, September 7, 2006 The Cassini Radio and Plasma Wave
The Cassini Radio and Plasma Wave Science Instrument Roger Karlsson Space Research Institute of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, Graz Graz in Space, September 7, 2006 The Cassini Radio and Plasma Wave
Ground-based network observations for investigation of the inner magnetosphere
 Ground-based network observations for investigation of the inner magnetosphere Shiokawa, K. 1, Y. Miyoshi 1, K. Keika 2, M. Connors 3, A. Kadokura 4, T. Nagatsuma 5, N. Nishitani 1, H. Ohya 6, F. Tsuchiya
Ground-based network observations for investigation of the inner magnetosphere Shiokawa, K. 1, Y. Miyoshi 1, K. Keika 2, M. Connors 3, A. Kadokura 4, T. Nagatsuma 5, N. Nishitani 1, H. Ohya 6, F. Tsuchiya
HAARP Generated ELF/VLF Waves for Magnetospheric Probing. Mark Gołkowski
 HAARP Generated ELF/VLF Waves for Magnetospheric Probing Mark Gołkowski University of Colorado Denver M.B. Cohen, U. S. Inan, D. Piddyachiy Stanford University RF Ionospheric Workshop 20 April 2010 Outline
HAARP Generated ELF/VLF Waves for Magnetospheric Probing Mark Gołkowski University of Colorado Denver M.B. Cohen, U. S. Inan, D. Piddyachiy Stanford University RF Ionospheric Workshop 20 April 2010 Outline
A generic description of planetary aurora
 A generic description of planetary aurora J. De Keyser, R. Maggiolo, and L. Maes Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy, Brussels, Belgium Johan.DeKeyser@aeronomie.be Context We consider a rotating planetary
A generic description of planetary aurora J. De Keyser, R. Maggiolo, and L. Maes Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy, Brussels, Belgium Johan.DeKeyser@aeronomie.be Context We consider a rotating planetary
SHEDDING NEW LIGHT ON SOLITARY WAVES OBSERVED IN SPACE
 University of Iowa SHEDDING NEW LIGHT ON SOLITARY WAVES OBSERVED IN SPACE J. S. Pickett, L.-J. Chen, D. A. Gurnett, J. M. Swanner, O. SantolRk P. M. E. Décréau, C. BJghin, D. Sundkvist, B. Lefebvre, M.
University of Iowa SHEDDING NEW LIGHT ON SOLITARY WAVES OBSERVED IN SPACE J. S. Pickett, L.-J. Chen, D. A. Gurnett, J. M. Swanner, O. SantolRk P. M. E. Décréau, C. BJghin, D. Sundkvist, B. Lefebvre, M.
RESONANCE Project for Studies of Wave-Particle Interactions in the Inner Magnetosphere. Anatoly Petrukovich and Resonance team
 RESONANCE Project for Studies of Wave-Particle Interactions in the Inner Magnetosphere Ω Anatoly Petrukovich and Resonance team РЕЗОНАНС RESONANCE Resonance Inner magnetospheric mission Space weather Ring
RESONANCE Project for Studies of Wave-Particle Interactions in the Inner Magnetosphere Ω Anatoly Petrukovich and Resonance team РЕЗОНАНС RESONANCE Resonance Inner magnetospheric mission Space weather Ring
Scientific Objectives of ERG/PWE Relativistic electron acceleration by plasma waves Verification of quasi-linear theory & Development of non-linear mo
 P2-102 ERG/PWE: Plasma Wave Experiment ~ from Mercury (BepiColombo/MMO-PWI) to Earth s Radiation Belt ~ Y. Kasaba (Tohoku Univ.) H. Kojima (Kyoto Univ.) S. Yagitani, Y. Kasahara, T. Imachi, M. Ozaki (Kanazawa
P2-102 ERG/PWE: Plasma Wave Experiment ~ from Mercury (BepiColombo/MMO-PWI) to Earth s Radiation Belt ~ Y. Kasaba (Tohoku Univ.) H. Kojima (Kyoto Univ.) S. Yagitani, Y. Kasahara, T. Imachi, M. Ozaki (Kanazawa
IONOSPHERIC SIGNATURES OF SEISMIC EVENTS AS OBSERVED BY THE DEMETER SATELLITE
 IONOSPHERIC SIGNATURES OF SEISMIC EVENTS AS OBSERVED BY THE DEMETER SATELLITE M. Parrot and F. Lefeuvre LPC2E/CNRS, 3 A Av Recherche Scientifique 45071 Orleans cedex 2 France lefeuvre@cnrs-orleans.fr URSI
IONOSPHERIC SIGNATURES OF SEISMIC EVENTS AS OBSERVED BY THE DEMETER SATELLITE M. Parrot and F. Lefeuvre LPC2E/CNRS, 3 A Av Recherche Scientifique 45071 Orleans cedex 2 France lefeuvre@cnrs-orleans.fr URSI
Ionospheric Absorption
 Ionospheric Absorption Prepared by Forrest Foust Stanford University, Stanford, CA IHY Workshop on Advancing VLF through the Global AWESOME Network VLF Injection Into the Magnetosphere Earth-based VLF
Ionospheric Absorption Prepared by Forrest Foust Stanford University, Stanford, CA IHY Workshop on Advancing VLF through the Global AWESOME Network VLF Injection Into the Magnetosphere Earth-based VLF
Study of Very Low Frequency (VLF) Phenomena at Maitri, Antarctica
 Nineteenth Indian Expedition to Antarctica, Scientific Report, 2004 Department of Ocean Development, Technical Publication No. 17, pp 107-114 Study of Very Low Frequency (VLF) Phenomena at Maitri, Antarctica
Nineteenth Indian Expedition to Antarctica, Scientific Report, 2004 Department of Ocean Development, Technical Publication No. 17, pp 107-114 Study of Very Low Frequency (VLF) Phenomena at Maitri, Antarctica
ESS 7 Lectures 15 and 16 November 3 and 5, The Atmosphere and Ionosphere
 ESS 7 Lectures 15 and 16 November 3 and 5, 2008 The Atmosphere and Ionosphere The Earth s Atmosphere The Earth s upper atmosphere is important for groundbased and satellite radio communication and navigation.
ESS 7 Lectures 15 and 16 November 3 and 5, 2008 The Atmosphere and Ionosphere The Earth s Atmosphere The Earth s upper atmosphere is important for groundbased and satellite radio communication and navigation.
Workshop on Physical Processes in Non-Uniform Finite Magnetospheric Systems
 Workshop on Physical Processes in Non-Uniform Finite Magnetospheric Systems 50 Years of Tamao's Resonant Mode Coupling Theory Program Sept. 12, 2011 Session Chair: D.-H. Lee 13:00-13:10 S. Fujita opening
Workshop on Physical Processes in Non-Uniform Finite Magnetospheric Systems 50 Years of Tamao's Resonant Mode Coupling Theory Program Sept. 12, 2011 Session Chair: D.-H. Lee 13:00-13:10 S. Fujita opening
The Earth s Atmosphere
 ESS 7 Lectures 15 and 16 May 5 and 7, 2010 The Atmosphere and Ionosphere The Earth s Atmosphere The Earth s upper atmosphere is important for groundbased and satellite radio communication and navigation.
ESS 7 Lectures 15 and 16 May 5 and 7, 2010 The Atmosphere and Ionosphere The Earth s Atmosphere The Earth s upper atmosphere is important for groundbased and satellite radio communication and navigation.
COMMISSION H: WAVES IN PLASMAS
 COMMISSION H: WAVES IN PLASMAS Edited by Yoshiharu Omura and Toshimi Okada Based on papers published from November of 1998 to October of 2001, we compiled major achievements in the field of plasma waves
COMMISSION H: WAVES IN PLASMAS Edited by Yoshiharu Omura and Toshimi Okada Based on papers published from November of 1998 to October of 2001, we compiled major achievements in the field of plasma waves
Scientific Studies of the High-Latitude Ionosphere with the Ionosphere Dynamics and ElectroDynamics - Data Assimilation (IDED-DA) Model
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Scientific Studies of the High-Latitude Ionosphere with the Ionosphere Dynamics and ElectroDynamics - Data Assimilation
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Scientific Studies of the High-Latitude Ionosphere with the Ionosphere Dynamics and ElectroDynamics - Data Assimilation
Multi-band Whistler-mode Chorus Emissions Observed by the Cluster Spacecraft
 WDS'11 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part II, 91 96, 211. ISBN 978-8-7378-185-9 MATFYZPRESS Multi-band Whistler-mode Chorus Emissions Observed by the Cluster Spacecraft E. Macúšová and O. Santolík
WDS'11 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part II, 91 96, 211. ISBN 978-8-7378-185-9 MATFYZPRESS Multi-band Whistler-mode Chorus Emissions Observed by the Cluster Spacecraft E. Macúšová and O. Santolík
Plasma wave receivers for scientific satellites
 An Introduction to Space Instrumentation, Edited by K. Oyama and C. Z. Cheng, 7 37. Plasma wave receivers for scientific satellites H. Kojima Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University,
An Introduction to Space Instrumentation, Edited by K. Oyama and C. Z. Cheng, 7 37. Plasma wave receivers for scientific satellites H. Kojima Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University,
The Role of Ground-Based Observations in M-I I Coupling Research. John Foster MIT Haystack Observatory
 The Role of Ground-Based Observations in M-I I Coupling Research John Foster MIT Haystack Observatory CEDAR/GEM Student Workshop Outline Some Definitions: Magnetosphere, etc. Space Weather Ionospheric
The Role of Ground-Based Observations in M-I I Coupling Research John Foster MIT Haystack Observatory CEDAR/GEM Student Workshop Outline Some Definitions: Magnetosphere, etc. Space Weather Ionospheric
SNIPE mission for Space Weather Research. CubeSat Developers Workshop 2017 Jaejin Lee (KASI)
 SNIPE mission for Space Weather Research CubeSat Developers Workshop 2017 Jaejin Lee (KASI) New Challenge with Nanosatellites In observing small-scale plasma structures, single satellite inherently suffers
SNIPE mission for Space Weather Research CubeSat Developers Workshop 2017 Jaejin Lee (KASI) New Challenge with Nanosatellites In observing small-scale plasma structures, single satellite inherently suffers
A significant mass density increase during a large magnetic storm in October 2003 obtained by ground-based ULF observations at L 1.
 Earth Planets Space, 58, 617 622, 26 A significant mass density increase during a large magnetic storm in October 23 obtained by ground-based ULF observations at L 1.4 Satoko Takasaki 1,2, Hideaki Kawano
Earth Planets Space, 58, 617 622, 26 A significant mass density increase during a large magnetic storm in October 23 obtained by ground-based ULF observations at L 1.4 Satoko Takasaki 1,2, Hideaki Kawano
A generation mechanism of chorus emissions using BWO theory
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series A generation mechanism of chorus emissions using BWO theory To cite this article: Ashutosh K Singh et al 2010 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 208 012067 View the article online
Journal of Physics: Conference Series A generation mechanism of chorus emissions using BWO theory To cite this article: Ashutosh K Singh et al 2010 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 208 012067 View the article online
Excitation and Propagation of Low Frequency Waves in a FRC plasma
 1 Excitation and Propagation of Low Frequency Waves in a FRC plasma S. Okada, K. Yamanaka, S. Yamamoto, T. Masumoto, K. Kitano, T. Asai, F. Kodera, M. Inomoto, S. Yoshimura, M. Okubo, S. Sugimoto, S. Ohi
1 Excitation and Propagation of Low Frequency Waves in a FRC plasma S. Okada, K. Yamanaka, S. Yamamoto, T. Masumoto, K. Kitano, T. Asai, F. Kodera, M. Inomoto, S. Yoshimura, M. Okubo, S. Sugimoto, S. Ohi
The observation of ULF emissions at Nakatsugawa in possible association with the 2004 Mid Niigata Prefecture earthquake
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 57, 1103 1108, 2005 The observation of ULF emissions at Nakatsugawa in possible association with the 2004 Mid Niigata Prefecture earthquake Kenji Ohta 1, Nobuo Watanabe 1, and
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 57, 1103 1108, 2005 The observation of ULF emissions at Nakatsugawa in possible association with the 2004 Mid Niigata Prefecture earthquake Kenji Ohta 1, Nobuo Watanabe 1, and
Aurora - acceleration processes
 Aurora - acceleration processes S. L. G. Hess LATMOS IPSL/CNRS, Université Versailles St Quentin, France M. Kivelson's talk : Plasma moves in the magnetosphere. M. Galand's talk : This generates currents
Aurora - acceleration processes S. L. G. Hess LATMOS IPSL/CNRS, Université Versailles St Quentin, France M. Kivelson's talk : Plasma moves in the magnetosphere. M. Galand's talk : This generates currents
Penetration of VLF Radio Waves through the Ionosphere
 Penetration of VLF Radio Waves through the Ionosphere By Ken-ichi MAEDA and Hiroshi OYA Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan (Read May 24; Received November 25, 1962) Abstract The rate of energy penetration
Penetration of VLF Radio Waves through the Ionosphere By Ken-ichi MAEDA and Hiroshi OYA Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan (Read May 24; Received November 25, 1962) Abstract The rate of energy penetration
Investigation of electron density profile in the lower ionosphere by SRP-4 rocket experiment
 Earth Planets Space, 57, 879 884, 25 Investigation of electron density profile in the lower ionosphere by SRP-4 rocket experiment K. Ishisaka 1, T. Okada 1, J. Hawkins 2, S. Murakami 1, T. Miyake 1, Y.
Earth Planets Space, 57, 879 884, 25 Investigation of electron density profile in the lower ionosphere by SRP-4 rocket experiment K. Ishisaka 1, T. Okada 1, J. Hawkins 2, S. Murakami 1, T. Miyake 1, Y.
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION The dependence of society to technology increased in recent years as the technology has enhanced. increased. Moreover, in addition to technology, the dependence of society to nature
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION The dependence of society to technology increased in recent years as the technology has enhanced. increased. Moreover, in addition to technology, the dependence of society to nature
The Effects of Pulsed Ionospheric Flows on EMIC Wave Behaviour
 The Effects of Pulsed Ionospheric Flows on EMIC Wave Behaviour S. C. Gane (1), D. M. Wright (1), T. Raita (2), ((1), (2) Sodankylä Geophysical Observatory) Continuous ULF Pulsations (Pc) Frequency band
The Effects of Pulsed Ionospheric Flows on EMIC Wave Behaviour S. C. Gane (1), D. M. Wright (1), T. Raita (2), ((1), (2) Sodankylä Geophysical Observatory) Continuous ULF Pulsations (Pc) Frequency band
Ground based measurements of ionospheric turbulence manifestations induced by the VLF transmitter ABSTRACT
 Ground based measurements of ionospheric turbulence manifestations induced by the VLF transmitter Dmitry S. Kotik, 1 Fedor I. Vybornov, 1 Alexander V. Ryabov, 1 Alexander V. Pershin 1 and Vladimir A. Yashnov
Ground based measurements of ionospheric turbulence manifestations induced by the VLF transmitter Dmitry S. Kotik, 1 Fedor I. Vybornov, 1 Alexander V. Ryabov, 1 Alexander V. Pershin 1 and Vladimir A. Yashnov
Radio Science. Estimate of a D region ionospheric electron density profile from MF radio wave observations by the S rocket
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Observed the MF radio wave propagation characteristics in the ionospheric D region The polarized mode waves propagation characteristics obtained by analyzing the observed waveform
RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Observed the MF radio wave propagation characteristics in the ionospheric D region The polarized mode waves propagation characteristics obtained by analyzing the observed waveform
Precipitation of Energetic Protons from the Radiation Belts. using Lower Hybrid Waves
 Precipitation of Energetic Protons from the Radiation Belts using Lower Hybrid Waves Lower hybrid waves are quasi-electrostatic whistler mode waves whose wave normal direction is very close to the whistler
Precipitation of Energetic Protons from the Radiation Belts using Lower Hybrid Waves Lower hybrid waves are quasi-electrostatic whistler mode waves whose wave normal direction is very close to the whistler
Resonance project and active experiments
 Resonance project and active experiments A. G. Demekhov Institute of Applied Physics, Nizhny Novgorod, Russia M. M. Mogilevsky, L. M. Zelenyi Space Research Institute, Moscow, Russia RBSP SWG Meeting,
Resonance project and active experiments A. G. Demekhov Institute of Applied Physics, Nizhny Novgorod, Russia M. M. Mogilevsky, L. M. Zelenyi Space Research Institute, Moscow, Russia RBSP SWG Meeting,
Title waves at Syowa Station in Antarctic. Author(s) Yusuke; Sato, Natsuo; Nagano, Isamu.
 Title Observed correlation between pulsat waves at Syowa Station in Antarctic Ozaki, Mitsunori; Yagitani, Satoshi Author(s) Shiokawa, Kazuo; Miyoshi, Yoshizumi Yamagishi, Hisao; Kataoka, Ryuho; I Yusuke;
Title Observed correlation between pulsat waves at Syowa Station in Antarctic Ozaki, Mitsunori; Yagitani, Satoshi Author(s) Shiokawa, Kazuo; Miyoshi, Yoshizumi Yamagishi, Hisao; Kataoka, Ryuho; I Yusuke;
Study of Ion Cyclotron Emissions due to DD Fusion Product Ions on JT-60U
 1 Study of Ion Cyclotron Emissions due to DD Fusion Product Ions on JT-6U M. Ichimura 1), M. Katano 1), Y. Yamaguchi 1), S. Sato 1), Y. Motegi 1), H. Muro 1), T. Ouchi 1), S. Moriyama 2), M. Ishikawa 2),
1 Study of Ion Cyclotron Emissions due to DD Fusion Product Ions on JT-6U M. Ichimura 1), M. Katano 1), Y. Yamaguchi 1), S. Sato 1), Y. Motegi 1), H. Muro 1), T. Ouchi 1), S. Moriyama 2), M. Ishikawa 2),
C. A. Kletzing Department of Physics and Asttronomy The University of Iowa THE UNIVERSITY OF IOWA REPW 2007
 1 Waves in the Earth s Radiation Belt: The Electric and Magnetic Field Instrument Suite with Integrated Science (EMFISIS) on the Radiation Belt Storm Probes C. A. Kletzing Department of Physics and Asttronomy
1 Waves in the Earth s Radiation Belt: The Electric and Magnetic Field Instrument Suite with Integrated Science (EMFISIS) on the Radiation Belt Storm Probes C. A. Kletzing Department of Physics and Asttronomy
The frequency variation of Pc5 ULF waves during a magnetic storm
 Earth Planets Space, 57, 619 625, 2005 The frequency variation of Pc5 ULF waves during a magnetic storm A. Du 1,2,W.Sun 2,W.Xu 1, and X. Gao 3 1 Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of
Earth Planets Space, 57, 619 625, 2005 The frequency variation of Pc5 ULF waves during a magnetic storm A. Du 1,2,W.Sun 2,W.Xu 1, and X. Gao 3 1 Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of
First Results from the 2014 Coordinated Measurements Campaign with HAARP and CASSIOPE/ePOP
 First Results from the 2014 Coordinated Measurements Campaign with HAARP and CASSIOPE/ePOP Carl L. Siefring, Paul A. Bernhardt, Stanley J. Briczinski, and Michael McCarrick Naval Research Laboratory Matthew
First Results from the 2014 Coordinated Measurements Campaign with HAARP and CASSIOPE/ePOP Carl L. Siefring, Paul A. Bernhardt, Stanley J. Briczinski, and Michael McCarrick Naval Research Laboratory Matthew
Study of small scale plasma irregularities. Đorđe Stevanović
 Study of small scale plasma irregularities in the ionosphere Đorđe Stevanović Overview 1. Global Navigation Satellite Systems 2. Space weather 3. Ionosphere and its effects 4. Case study a. Instruments
Study of small scale plasma irregularities in the ionosphere Đorđe Stevanović Overview 1. Global Navigation Satellite Systems 2. Space weather 3. Ionosphere and its effects 4. Case study a. Instruments
Developme nt of Active Phased Array with Phase-controlled Magnetrons
 Developme nt of Active Phased Array with Phase-controlled Magnetrons Naoki SHINOHARA, Junsuke FUJIWARA, and Hiroshi MATSUMOTO Radio Atmospheric Science Center, Kyoto University Gokasho, Uji, Kyoto, 611-0011,
Developme nt of Active Phased Array with Phase-controlled Magnetrons Naoki SHINOHARA, Junsuke FUJIWARA, and Hiroshi MATSUMOTO Radio Atmospheric Science Center, Kyoto University Gokasho, Uji, Kyoto, 611-0011,
Modeling and Subionospheric VLF perturbations caused by direct and indirect effects of lightning
 Modeling and Subionospheric VLF perturbations caused by direct and indirect effects of lightning Prepared by Benjamin Cotts Stanford University, Stanford, CA IHY Workshop on Advancing VLF through the Global
Modeling and Subionospheric VLF perturbations caused by direct and indirect effects of lightning Prepared by Benjamin Cotts Stanford University, Stanford, CA IHY Workshop on Advancing VLF through the Global
Impedance of a Short Dipole Antenna in a Cold Plasma
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 49, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2001 1377 Impedance of a Short Dipole Antenna in a Cold Plasma Pavel Nikitin and Charles Swenson Abstract This paper presents the
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 49, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2001 1377 Impedance of a Short Dipole Antenna in a Cold Plasma Pavel Nikitin and Charles Swenson Abstract This paper presents the
Three-dimensional ray tracing of VLF waves in a magnetospheric environment containing a plasmaspheric plume
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L22101, doi:10.1029/2009gl040451, 2009 Three-dimensional ray tracing of VLF waves in a magnetospheric environment containing a plasmaspheric
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L22101, doi:10.1029/2009gl040451, 2009 Three-dimensional ray tracing of VLF waves in a magnetospheric environment containing a plasmaspheric
An error analysis on nature and radar system noises in deriving the phase and group velocities of vertical propagation waves
 Earth Planets Space, 65, 911 916, 2013 An error analysis on nature and radar system noises in deriving the phase and group velocities of vertical propagation waves C. C. Hsiao 1,J.Y.Liu 1,2,3, and Y. H.
Earth Planets Space, 65, 911 916, 2013 An error analysis on nature and radar system noises in deriving the phase and group velocities of vertical propagation waves C. C. Hsiao 1,J.Y.Liu 1,2,3, and Y. H.
Verification of the backward wave oscillator model of VLF chorus generation using data from MAGION 5 satellite
 Annales Geophysicae (2003) 21: 1073 1081 c European Geosciences Union 2003 Annales Geophysicae Verification of the backward wave oscillator model of VLF chorus generation using data from MAGION 5 satellite
Annales Geophysicae (2003) 21: 1073 1081 c European Geosciences Union 2003 Annales Geophysicae Verification of the backward wave oscillator model of VLF chorus generation using data from MAGION 5 satellite
and Atmosphere Model:
 1st VarSITI General Symposium, Albena, Bulgaria, 2016 Canadian Ionosphere and Atmosphere Model: model status and applications Victor I. Fomichev 1, O. V. Martynenko 1, G. G. Shepherd 1, W. E. Ward 2, K.
1st VarSITI General Symposium, Albena, Bulgaria, 2016 Canadian Ionosphere and Atmosphere Model: model status and applications Victor I. Fomichev 1, O. V. Martynenko 1, G. G. Shepherd 1, W. E. Ward 2, K.
Convection Development in the Inner Magnetosphere-Ionosphere Coupling System
 Convection Development in the Inner Magnetosphere-Ionosphere Coupling System Hashimoto,K.K. Alfven layer Tanaka Department of Environmental Risk Management, School of Policy Management, Kibi International
Convection Development in the Inner Magnetosphere-Ionosphere Coupling System Hashimoto,K.K. Alfven layer Tanaka Department of Environmental Risk Management, School of Policy Management, Kibi International
Case studies on the wave propagation and polarization of ELF emissions observed by Freja around the local proton gyrofrequency
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 104, NO. A2, PAGES 2459 2475, FEBRUARY 1, 1999 Case studies on the wave propagation and polarization of ELF emissions observed by Freja around the local proton gyrofrequency
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 104, NO. A2, PAGES 2459 2475, FEBRUARY 1, 1999 Case studies on the wave propagation and polarization of ELF emissions observed by Freja around the local proton gyrofrequency
Whistler Wave Generation by Continuous HF Heating of the F-region Ionosphere
 Whistler Wave Generation by Continuous HF Heating of the F-region Ionosphere Aram Vartanyan 1 G. M. Milikh 1, B. Eliasson 1,2, A. C. Najmi 1, M. Parrot 3, K. Papadopoulos 1 1 Departments of Physics and
Whistler Wave Generation by Continuous HF Heating of the F-region Ionosphere Aram Vartanyan 1 G. M. Milikh 1, B. Eliasson 1,2, A. C. Najmi 1, M. Parrot 3, K. Papadopoulos 1 1 Departments of Physics and
EISCAT Experiments. Anders Tjulin EISCAT Scientific Association 2nd March 2017
 EISCAT Experiments Anders Tjulin EISCAT Scientific Association 2nd March 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Overview 3 2.1 The radar systems.......................... 3 2.2 Antenna scan patterns........................
EISCAT Experiments Anders Tjulin EISCAT Scientific Association 2nd March 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Overview 3 2.1 The radar systems.......................... 3 2.2 Antenna scan patterns........................
Estimation of Lightning Location from Single Station Observations of Sferics
 Electronics and Communications in Japan, Part 1, Vol. 90, No. 1, 2007 Translated from Denshi Joho Tsushin Gakkai Ronbunshi, Vol. J89-B, No. 1, January 2006, pp. 22 29 Estimation of Lightning Location from
Electronics and Communications in Japan, Part 1, Vol. 90, No. 1, 2007 Translated from Denshi Joho Tsushin Gakkai Ronbunshi, Vol. J89-B, No. 1, January 2006, pp. 22 29 Estimation of Lightning Location from
Near Earth space monitoring with LOFAR PL610 station in Borówiec
 Near Earth space monitoring with LOFAR PL610 station in Borówiec Hanna Rothkaehl 1, Mariusz Pożoga 1, Marek Morawski 1, Barbara Matyjasiak 1, Dorota Przepiórka 1, Marcin Grzesiak 1 and Roman Wronowski
Near Earth space monitoring with LOFAR PL610 station in Borówiec Hanna Rothkaehl 1, Mariusz Pożoga 1, Marek Morawski 1, Barbara Matyjasiak 1, Dorota Przepiórka 1, Marcin Grzesiak 1 and Roman Wronowski
Chapter 6 Propagation
 Chapter 6 Propagation Al Penney VO1NO Objectives To become familiar with: Classification of waves wrt propagation; Factors that affect radio wave propagation; and Propagation characteristics of Amateur
Chapter 6 Propagation Al Penney VO1NO Objectives To become familiar with: Classification of waves wrt propagation; Factors that affect radio wave propagation; and Propagation characteristics of Amateur
EFFECT OF IONOSPHERIC INDUCED DEPOLARIZA- TION ON SATELLITE SOLAR POWER STATION
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 39 47, 29 EFFECT OF IONOSPHERIC INDUCED DEPOLARIZA- TION ON SATELLITE SOLAR POWER STATION K. Chaudhary and B. R. Vishvakarma Electronics Engineering
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 39 47, 29 EFFECT OF IONOSPHERIC INDUCED DEPOLARIZA- TION ON SATELLITE SOLAR POWER STATION K. Chaudhary and B. R. Vishvakarma Electronics Engineering
A study of the ionospheric effect on GBAS (Ground-Based Augmentation System) using the nation-wide GPS network data in Japan
 A study of the ionospheric effect on GBAS (Ground-Based Augmentation System) using the nation-wide GPS network data in Japan Takayuki Yoshihara, Electronic Navigation Research Institute (ENRI) Naoki Fujii,
A study of the ionospheric effect on GBAS (Ground-Based Augmentation System) using the nation-wide GPS network data in Japan Takayuki Yoshihara, Electronic Navigation Research Institute (ENRI) Naoki Fujii,
Magnetospheric electron densities inferred from upper-hybrid band emissions
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L20803, doi:10.1029/2004gl020847, 2004 Magnetospheric electron densities inferred from upper-hybrid band emissions R. F. Benson, 1 P. A. Webb, 2 J. L. Green, 1 L.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L20803, doi:10.1029/2004gl020847, 2004 Magnetospheric electron densities inferred from upper-hybrid band emissions R. F. Benson, 1 P. A. Webb, 2 J. L. Green, 1 L.
ionospheric satellite cluster scientific premises and proposed configuration
 ionospheric satellite cluster scientific premises and proposed configuration O. Fedorov, Institute of Space Research, Kyiv, Ukraine V. Korepanov, Lviv Centre of Institute of Space Research, Lviv, Ukraine
ionospheric satellite cluster scientific premises and proposed configuration O. Fedorov, Institute of Space Research, Kyiv, Ukraine V. Korepanov, Lviv Centre of Institute of Space Research, Lviv, Ukraine
[titlelscientific Studies of the High-Latitude Ionosphere with the Ionosphere Dynamics and Electrodynamics-Data Assimilation (IDED-DA) Model
 [titlelscientific Studies of the High-Latitude Ionosphere with the Ionosphere Dynamics and Electrodynamics-Data Assimilation (IDED-DA) Model [awardnumberl]n00014-13-l-0267 [awardnumber2] [awardnumbermore]
[titlelscientific Studies of the High-Latitude Ionosphere with the Ionosphere Dynamics and Electrodynamics-Data Assimilation (IDED-DA) Model [awardnumberl]n00014-13-l-0267 [awardnumber2] [awardnumbermore]
New applications of the portable heater. Gennady Milikh, UMD-SPP group
 New applications of the portable heater Gennady Milikh, UMD-SPP group 1 Stabilization of equatorial spread F (ESF) by ion injection 2 ESF characterizes spreading in the height of F-region backscatter return
New applications of the portable heater Gennady Milikh, UMD-SPP group 1 Stabilization of equatorial spread F (ESF) by ion injection 2 ESF characterizes spreading in the height of F-region backscatter return
Using the Radio Spectrum to Understand Space Weather
 Using the Radio Spectrum to Understand Space Weather Ray Greenwald Virginia Tech Topics to be Covered What is Space Weather? Origins and impacts Analogies with terrestrial weather Monitoring Space Weather
Using the Radio Spectrum to Understand Space Weather Ray Greenwald Virginia Tech Topics to be Covered What is Space Weather? Origins and impacts Analogies with terrestrial weather Monitoring Space Weather
[EN-107] Impact of the low latitude ionosphere disturbances on GNSS studied with a three-dimensional ionosphere model
![[EN-107] Impact of the low latitude ionosphere disturbances on GNSS studied with a three-dimensional ionosphere model [EN-107] Impact of the low latitude ionosphere disturbances on GNSS studied with a three-dimensional ionosphere model](/thumbs/86/93972301.jpg) ENRI Int. Workshop on ATM/CNS. Tokyo, Japan (EIWAC21) [EN-17] Impact of the low latitude ionosphere disturbances on GNSS studied with a three-dimensional ionosphere model + S. Saito N. FUjii Communication
ENRI Int. Workshop on ATM/CNS. Tokyo, Japan (EIWAC21) [EN-17] Impact of the low latitude ionosphere disturbances on GNSS studied with a three-dimensional ionosphere model + S. Saito N. FUjii Communication
Non-inductive Production of Extremely Overdense Spherical Tokamak Plasma by Electron Bernstein Wave Excited via O-X-B Method in LATE
 1 EXW/P4-4 Non-inductive Production of Extremely Overdense Spherical Tokamak Plasma by Electron Bernstein Wave Excited via O-X-B Method in LATE H. Tanaka, M. Uchida, T. Maekawa, K. Kuroda, Y. Nozawa, A.
1 EXW/P4-4 Non-inductive Production of Extremely Overdense Spherical Tokamak Plasma by Electron Bernstein Wave Excited via O-X-B Method in LATE H. Tanaka, M. Uchida, T. Maekawa, K. Kuroda, Y. Nozawa, A.
POLAR AERONOMY AND RADIO SCIENCE (PARS) ULF/ELF/VLF PROJECT
 Page 1 of 28 POLAR AERONOMY AND RADIO SCIENCE (PARS) ULF/ELF/VLF PROJECT U. S. Inan and T. F. Bell STAR Laboratory, Stanford University Page 2 of 28 Outline 1. INTRODUCTION 2. SCIENTIFIC BACKGROUND 2.1.
Page 1 of 28 POLAR AERONOMY AND RADIO SCIENCE (PARS) ULF/ELF/VLF PROJECT U. S. Inan and T. F. Bell STAR Laboratory, Stanford University Page 2 of 28 Outline 1. INTRODUCTION 2. SCIENTIFIC BACKGROUND 2.1.
Hermanus Magnetic Observatory (HMO)
 Hermanus Magnetic Observatory (HMO) As a Space Physics facility in Africa Presented by Danie Gouws & Elda Saunderson The HMO in a nutshell... The Hermanus Magnetic Observatory (HMO) is a national facility
Hermanus Magnetic Observatory (HMO) As a Space Physics facility in Africa Presented by Danie Gouws & Elda Saunderson The HMO in a nutshell... The Hermanus Magnetic Observatory (HMO) is a national facility
SPACE WEATHER SIGNATURES ON VLF RADIO WAVES RECORDED IN BELGRADE
 Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 80 (2006), 191-195 Contributed paper SPACE WEATHER SIGNATURES ON VLF RADIO WAVES RECORDED IN BELGRADE DESANKA ŠULIĆ1, VLADIMIR ČADEŽ2, DAVORKA GRUBOR 3 and VIDA ŽIGMAN4
Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 80 (2006), 191-195 Contributed paper SPACE WEATHER SIGNATURES ON VLF RADIO WAVES RECORDED IN BELGRADE DESANKA ŠULIĆ1, VLADIMIR ČADEŽ2, DAVORKA GRUBOR 3 and VIDA ŽIGMAN4
Special Thanks: M. Magoun, M. Moldwin, E. Zesta, C. Valladares, and AMBER, SCINDA, & C/NOFS teams
 Longitudinal Variability of Equatorial Electrodynamics E. Yizengaw 1, J. Retterer 1, B. Carter 1, K. Groves 1, and R. Caton 2 1 Institute for Scientific Research, Boston College 2 AFRL, Kirtland AFB, NM,
Longitudinal Variability of Equatorial Electrodynamics E. Yizengaw 1, J. Retterer 1, B. Carter 1, K. Groves 1, and R. Caton 2 1 Institute for Scientific Research, Boston College 2 AFRL, Kirtland AFB, NM,
MHD wave characteristics inferred from correlations between X-rays, VLF, and ULFs at Syowa Station, Antarctica and Tjörnes, Iceland (L 6)
 Earth Planets Space, 51, 33 41, 1999 MHD wave characteristics inferred from correlations between X-rays, VLF, and ULFs at Syowa Station, Antarctica and Tjörnes, Iceland (L 6) Yo Hirasima 1, Hisashi Shimobayashi
Earth Planets Space, 51, 33 41, 1999 MHD wave characteristics inferred from correlations between X-rays, VLF, and ULFs at Syowa Station, Antarctica and Tjörnes, Iceland (L 6) Yo Hirasima 1, Hisashi Shimobayashi
V-shaped VLF streaks recorded on DEMETER above powerful thunderstorms
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013336, 2008 V-shaped VLF streaks recorded on DEMETER above powerful thunderstorms M. Parrot, 1,2 U. S. Inan, 3
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013336, 2008 V-shaped VLF streaks recorded on DEMETER above powerful thunderstorms M. Parrot, 1,2 U. S. Inan, 3
Modulation of whistler mode chorus waves: 2. Role of density variations
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2010ja016313, 2011 Modulation of whistler mode chorus waves: 2. Role of density variations W. Li, 1 J. Bortnik, 1 R. M. Thorne, 1 Y. Nishimura, 1,2
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2010ja016313, 2011 Modulation of whistler mode chorus waves: 2. Role of density variations W. Li, 1 J. Bortnik, 1 R. M. Thorne, 1 Y. Nishimura, 1,2
ON THE FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF THE BA ANTENNA FOR MEASURING ELF RADIO SIG. Author(s) OGAWA, Toshio; TANAKA, Yoshikazu; M
 Title ON THE FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF THE BA ANTENNA FOR MEASURING ELF RADIO SIG Author(s) OGAWA, Toshio; TANAKA, Yoshikazu; M Citation Special Contributions of the Geophy University (1966), 6: 9-12 Issue
Title ON THE FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF THE BA ANTENNA FOR MEASURING ELF RADIO SIG Author(s) OGAWA, Toshio; TANAKA, Yoshikazu; M Citation Special Contributions of the Geophy University (1966), 6: 9-12 Issue
Variability in the response time of the high-latitude ionosphere to IMF and solar-wind variations
 Variability in the response time of the high-latitude ionosphere to IMF and solar-wind variations Murray L. Parkinson 1, Mike Pinnock 2, and Peter L. Dyson 1 (1) Department of Physics, La Trobe University,
Variability in the response time of the high-latitude ionosphere to IMF and solar-wind variations Murray L. Parkinson 1, Mike Pinnock 2, and Peter L. Dyson 1 (1) Department of Physics, La Trobe University,
Large Amplitude Pc 1 Events at College
 JOURNAL OF GEOMAGNETISM AND GEOELECTRICITY VOL. 20, No. 3, 1968 Large Amplitude Pc 1 Events at College R.R. HEACOCK Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, College, Alaska 99701 (Received April 2,
JOURNAL OF GEOMAGNETISM AND GEOELECTRICITY VOL. 20, No. 3, 1968 Large Amplitude Pc 1 Events at College R.R. HEACOCK Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, College, Alaska 99701 (Received April 2,
Observation of discrete VLF emissions at low latitudes and their generation mechanism
 Earth Planets Space, 56, 1067 1074, 2004 Observation of discrete VLF emissions at low latitudes and their generation mechanism Abhay Kumar Singh 1 and R. P. Singh 2 1 Department of Physics, Maharaja College,
Earth Planets Space, 56, 1067 1074, 2004 Observation of discrete VLF emissions at low latitudes and their generation mechanism Abhay Kumar Singh 1 and R. P. Singh 2 1 Department of Physics, Maharaja College,
DETECTION OF TERRESTRIAL IONOSPHERIC PERTURBATIONS CAUSED BY DIFFERENT ASTROPHYSICAL PHENOMENA
 Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 96 (2017), 365-370 PhD Thesis DETECTION OF TERRESTRIAL IONOSPHERIC PERTURBATIONS CAUSED BY DIFFERENT ASTROPHYSICAL PHENOMENA A. NINA 1,V.M.ČADEŽ2,L.Č. POPOVIĆ2,V.A.SREĆKOVIĆ1
Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 96 (2017), 365-370 PhD Thesis DETECTION OF TERRESTRIAL IONOSPHERIC PERTURBATIONS CAUSED BY DIFFERENT ASTROPHYSICAL PHENOMENA A. NINA 1,V.M.ČADEŽ2,L.Č. POPOVIĆ2,V.A.SREĆKOVIĆ1
VLF & ULF Signals, Receivers & Antennas - Listening to the sounds of the atmosphere
 VLF & ULF Signals, Receivers & Antennas - Listening to the sounds of the atmosphere A presentation to Manly-Warringah Radio Society from Geoff Osborne VK2TGO VLF & ULF Signals, Receivers and Antennas 1.
VLF & ULF Signals, Receivers & Antennas - Listening to the sounds of the atmosphere A presentation to Manly-Warringah Radio Society from Geoff Osborne VK2TGO VLF & ULF Signals, Receivers and Antennas 1.
 Page 1 of 8 Search Contact NRL Personnel Locator Human Resources Public Affairs Office Visitor Info Planning a Visit Directions Maps Weather & Traffic Field Sites Stennis Monterey VXS-1 Chesapeake Bay
Page 1 of 8 Search Contact NRL Personnel Locator Human Resources Public Affairs Office Visitor Info Planning a Visit Directions Maps Weather & Traffic Field Sites Stennis Monterey VXS-1 Chesapeake Bay
Space-born system for on-line precursors monitoring of eathquakes,, natural and man-made made catastrophes
 Space-born system for on-line precursors monitoring of eathquakes,, natural and man-made made catastrophes The main goal of the Project In my brief report, I would like to inform about the work on developing
Space-born system for on-line precursors monitoring of eathquakes,, natural and man-made made catastrophes The main goal of the Project In my brief report, I would like to inform about the work on developing
Simulation Studies of Field-Reversed Configurations with Rotating Magnetic Field Current Drive
 Simulation Studies of Field-Reversed Configurations with Rotating Magnetic Field Current Drive E. V. Belova 1), R. C. Davidson 1), 1) Princeton University Plasma Physics Laboratory, Princeton NJ, USA E-mail:ebelova@pppl.gov
Simulation Studies of Field-Reversed Configurations with Rotating Magnetic Field Current Drive E. V. Belova 1), R. C. Davidson 1), 1) Princeton University Plasma Physics Laboratory, Princeton NJ, USA E-mail:ebelova@pppl.gov
Daily and seasonal variations of TID parameters over the Antarctic Peninsula
 Daily and seasonal variations of TID parameters over the Antarctic Peninsula A. Zalizovski 1, Y. Yampolski 1, V. Paznukhov 2, E. Mishin 3, A. Sopin 1 1. Institute of Radio Astronomy, National Academy of
Daily and seasonal variations of TID parameters over the Antarctic Peninsula A. Zalizovski 1, Y. Yampolski 1, V. Paznukhov 2, E. Mishin 3, A. Sopin 1 1. Institute of Radio Astronomy, National Academy of
J. Geomag. Geoelectr., 41, , 1989
 J. Geomag. Geoelectr., 41, 1025-1042, 1989 1026 T. OBARA and H. OYA However, detailed study on the spread F phenomena in the polar cap ionosphere has been deferred until very recently because of the lack
J. Geomag. Geoelectr., 41, 1025-1042, 1989 1026 T. OBARA and H. OYA However, detailed study on the spread F phenomena in the polar cap ionosphere has been deferred until very recently because of the lack
Low Frequency Radio Astronomy from the Lunar Surface
 Low Frequency Radio Astronomy from the Lunar Surface R. J. MacDowall (1), T. J. Lazio (2), J. Burns (3) (1) NASA/GSFC, Greenbelt, MD, USA (2) JPL/Caltech, Pasadena, CA, USA (3) U. Colorado, Boulder, CO,
Low Frequency Radio Astronomy from the Lunar Surface R. J. MacDowall (1), T. J. Lazio (2), J. Burns (3) (1) NASA/GSFC, Greenbelt, MD, USA (2) JPL/Caltech, Pasadena, CA, USA (3) U. Colorado, Boulder, CO,
Sferic signals for lightning sourced electromagnetic surveys
 Sferic signals for lightning sourced electromagnetic surveys Lachlan Hennessy* RMIT University hennessylachlan@gmail.com James Macnae RMIT University *presenting author SUMMARY Lightning strikes generate
Sferic signals for lightning sourced electromagnetic surveys Lachlan Hennessy* RMIT University hennessylachlan@gmail.com James Macnae RMIT University *presenting author SUMMARY Lightning strikes generate
Discovery of very large amplitude whistler-mode waves in Earth s radiation belts
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L01105, doi:10.1029/2007gl032009, 2008 Discovery of very large amplitude whistler-mode waves in Earth s radiation belts C. Cattell, 1 J. R. Wygant, 1 K. Goetz, 1
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L01105, doi:10.1029/2007gl032009, 2008 Discovery of very large amplitude whistler-mode waves in Earth s radiation belts C. Cattell, 1 J. R. Wygant, 1 K. Goetz, 1
MWA Ionospheric Science Opportunities Space Weather Storms & Irregularities (location location location) John Foster MIT Haystack Observatory
 MWA Ionospheric Science Opportunities Space Weather Storms & Irregularities (location location location) John Foster MIT Haystack Observatory Storm Enhanced Density: Longitude-specific Ionospheric Redistribution
MWA Ionospheric Science Opportunities Space Weather Storms & Irregularities (location location location) John Foster MIT Haystack Observatory Storm Enhanced Density: Longitude-specific Ionospheric Redistribution
The Basics Of Seismo-Ionospheric Coupling
 The Basics Of Seismo-Ionospheric Coupling Sergey Pulinets Institute of Geophysics, National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM) Mexico 106 It is now well acknowledged that atmospheric electricity plays
The Basics Of Seismo-Ionospheric Coupling Sergey Pulinets Institute of Geophysics, National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM) Mexico 106 It is now well acknowledged that atmospheric electricity plays
Study of Ionospheric Perturbations during Strong Seismic Activity by Correlation Technique using NmF2 Data
 Research Journal of Recent Sciences Res.J.Recent Sci. Study of Ionospheric Perturbations during Strong Seismic Activity by Correlation Technique using NmF2 Data Abstract Gwal A.K., Jain Santosh, Panda
Research Journal of Recent Sciences Res.J.Recent Sci. Study of Ionospheric Perturbations during Strong Seismic Activity by Correlation Technique using NmF2 Data Abstract Gwal A.K., Jain Santosh, Panda
Models of ionospheric VLF absorption of powerful ground based transmitters
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl054437, 2012 Models of ionospheric VLF absorption of powerful ground based transmitters M. B. Cohen, 1 N. G. Lehtinen, 1 and U. S. Inan 1,2 Received
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl054437, 2012 Models of ionospheric VLF absorption of powerful ground based transmitters M. B. Cohen, 1 N. G. Lehtinen, 1 and U. S. Inan 1,2 Received
AN electromagnetic launcher system can accelerate a projectile
 4434 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS, VOL. 33, NO. 6, NOVEMBER 1997 Hyper Velocity Acceleration by a Pulsed Coilgun Using Traveling Magnetic Field Katsumi Masugata, Member, IEEE Abstract A method is proposed
4434 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS, VOL. 33, NO. 6, NOVEMBER 1997 Hyper Velocity Acceleration by a Pulsed Coilgun Using Traveling Magnetic Field Katsumi Masugata, Member, IEEE Abstract A method is proposed
1 Introduction. 2 Scientific Objectives and Mission Contents. SHEN Xuhui
 0254-6124/2014/34(5)-558 05 Chin. J. Space Sci. Ξ ΛΠΠ Shen Xuhui. The experimental satellite on electromagnetism monitoring. Chin. J. Space Sci., 2014, 34(5): 558-562, doi:10.11728/ cjss2014.05.558 The
0254-6124/2014/34(5)-558 05 Chin. J. Space Sci. Ξ ΛΠΠ Shen Xuhui. The experimental satellite on electromagnetism monitoring. Chin. J. Space Sci., 2014, 34(5): 558-562, doi:10.11728/ cjss2014.05.558 The
Plasma Confinement by Pressure of Rotating Magnetic Field in Toroidal Device
 1 ICC/P5-41 Plasma Confinement by Pressure of Rotating Magnetic Field in Toroidal Device V. Svidzinski 1 1 FAR-TECH, Inc., San Diego, USA Corresponding Author: svidzinski@far-tech.com Abstract: Plasma
1 ICC/P5-41 Plasma Confinement by Pressure of Rotating Magnetic Field in Toroidal Device V. Svidzinski 1 1 FAR-TECH, Inc., San Diego, USA Corresponding Author: svidzinski@far-tech.com Abstract: Plasma
(CSES) Introduction for China Seismo- Electromagnetic Satellite
 Introduction for China Seismo- Electromagnetic Satellite (CSES) Wang Lanwei Working Group of China Earthquake-related related Satellites Mission China Earthquake Administration Outline Project Objectives
Introduction for China Seismo- Electromagnetic Satellite (CSES) Wang Lanwei Working Group of China Earthquake-related related Satellites Mission China Earthquake Administration Outline Project Objectives
CONSIDERATION OF THE JOVIAN S-BURSTS AND NB-EMISSION BASED ON THE PARAMETRIC MODEL
 CONSIDERATION OF THE JOVIAN S-BURSTS AND NB-EMISSION BASED ON THE PARAMETRIC MODEL V. E. Shaposhnikov *, A. V. Kostrov,H.O.Rucker, S. V. Korobkov, M. E. Gushchin,andG.V.Litvinenko Abstract The new mechanism
CONSIDERATION OF THE JOVIAN S-BURSTS AND NB-EMISSION BASED ON THE PARAMETRIC MODEL V. E. Shaposhnikov *, A. V. Kostrov,H.O.Rucker, S. V. Korobkov, M. E. Gushchin,andG.V.Litvinenko Abstract The new mechanism
First Observation of Stimulated Coherent Transition Radiation
 SLAC 95 6913 June 1995 First Observation of Stimulated Coherent Transition Radiation Hung-chi Lihn, Pamela Kung, Chitrlada Settakorn, and Helmut Wiedemann Applied Physics Department and Stanford Linear
SLAC 95 6913 June 1995 First Observation of Stimulated Coherent Transition Radiation Hung-chi Lihn, Pamela Kung, Chitrlada Settakorn, and Helmut Wiedemann Applied Physics Department and Stanford Linear
4/29/2012. General Class Element 3 Course Presentation. Radio Wave Propagation. Radio Wave Propagation. Radio Wave Propagation.
 General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G3 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures G3 G4 Amateur Radio
General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G3 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures G3 G4 Amateur Radio
New Synergistic Opportunities for Magnetosphere-Ionosphere-Thermosphere Coupling Investigations Using Swarm and CASSIOPE e-pop
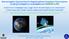 New Synergistic Opportunities for Magnetosphere-Ionosphere-Thermosphere Coupling Investigations Using Swarm and CASSIOPE e-pop Andrew W. Yau 1, R. Floberghagen 2, Leroy L. Cogger 1, Eelco N. Doornbos 3,
New Synergistic Opportunities for Magnetosphere-Ionosphere-Thermosphere Coupling Investigations Using Swarm and CASSIOPE e-pop Andrew W. Yau 1, R. Floberghagen 2, Leroy L. Cogger 1, Eelco N. Doornbos 3,
