ARTICLE IN PRESS. Journal of Electrostatics xxx (2009) 1 7. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Journal of Electrostatics
|
|
|
- Todd Taylor
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ARTICLE IN PRESS ELSTAT2356_proof Š 14 February 2009 Š 1/7 Journal of Electrostatics xxx (2009) 1 7 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Electrostatics journal homepage: Honeycomb discharge for diesel exhaust cleaning Satoshi Sato a, Karol Hensel b, Hideaki Hayashi a, Kazunori Takashima a, Akira Mizuno a, * a Department of Ecological Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology, Tempaku-cho, Toyohashi, Aichi, , Japan b Department of Astronomy, Earth Physics and Meteorology, Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Informatics, Comenius University, Bratislava, Slovakia article info Article history: Received 15 September 2008 Received in revised form 22 January 2009 Accepted 1 February 2009 Available online xxx Keywords: Electrical discharge Non-thermal plasma Honeycomb catalyst Diesel exhaust DeNO x 1. Introduction abstract Various types of atmospheric pressure discharges have been developed for electrostatic processes and for plasma chemical processes, such as removing particles, cleaning exhaust gas and volatile organic compounds(vocs), etc. [1 4]. In order to improve the selectivity and energy efficiency of plasma chemical processes, a combination of plasma and catalyst is effective. For example, catalyst pellets can be used in the packed bed discharge to improve removal efficiency of nitrogen oxides and VOCs [5,6]. Honeycomb is a commonly used geometry of catalysts. It has been difficult to generate electrical discharge evenly inside a honeycomb [3]. If discharge is generated inside a honeycomb, a larger surface area can be obtained with a lower pressure drop for improved chemical reactions. Several important works have been reported recently. One is the superposition of surface discharge and AC discharge to obtain a large discharge volume [5]. Surface discharge is generated on the inner wall of a cylinder, and AC voltage is applied between the centered electrode and the electrode placed on the inner wall for the surface discharge. The other is a sliding discharge that has been used to cover the large surface area of the wings of airplanes to stabilize airflow [7]. Surface discharge is generated using a pair of electrodes placed between a sheet of insulator film. The other electrode is set * Corresponding author. address: mizuno@eco.tut.ac.jp (A. Mizuno) /$ see front matter Ó 2009 Published by Elsevier B.V. doi: / Selectivity and energy efficiency of plasma chemical processes can be significantly improved if plasma is combined with a catalyst. The generation of stable discharge plasma inside the narrow capillaries of an automobile catalytic honeycomb is, however, quite difficult. This paper presents a novel method which utilizes the combination of packed-bed or barrier discharge connected in series with the honeycomb capillaries. By the application of DC voltage across the capillaries, streamers are extended from the packed-bed discharge into the capillaries. With this method, ionization can be made inside fine channels of honeycomb catalyst made of insulating materials. This discharge is designated as honeycomb discharge. Electrical and optical characteristics of the honeycomb discharge are measured. Ó 2009 Published by Elsevier B.V. apart from the electrode for surface discharge on the film and energized with negative DC. From the surface discharge, streamers are extended by the DC electric field and cover the large surface area. In order to ionize honeycombs consisting of fine channels, a packed-bed discharge is used in front and a DC electric field is applied across the honeycomb. This electrode configuration enables the ionization of the fine channels (1 mm 2 ) of a honeycomb made of cordierite. In this study, conditions for establishing plasma inside a bundle of transparent glass capillary tubes (inner diameter 1 or 2 mm) that simulate the channels of honeycomb catalysts has been studied. This is because the glow associated with the discharge can be visualized in this setup. The characteristics of a honeycomb discharge in a bundle of glass capillaries are reported. 2. Instrumentation 2.1. Plasma reactor Fig. 1 illustrates the plasma reactor used in this study. A packed-bed discharge was used to form the preceding discharge. The g-al 2 O 3 pellets (3 mm) were set in a quartz glass tube (inner diameter 26 mm) with a stainless steel rod (diameter 6 mm) at the center as a discharge electrode. The outer surface of the quartz glass tube was covered with an aluminum sheet of 15 mm length as a ground electrode. In this experiment, bundled thin quartz glass capillary tubes were used to simulate a honeycomb catalyst and to observe the
2 ARTICLE IN PRESS ELSTAT2356_proof Š 14 February 2009 Š 2/7 2 S. Sato et al. / Journal of Electrostatics xxx (2009) Quartz Glass tube ( 26mm) Quartz Glass Capillary Gas Flow 4.5L/min light emission. The inner diameter of the quartz glass capillary was 1 or 2 mm and the length was 20 mm. The diameter of the bundle was 26 mm and the bundle was inserted into the outer quartz glass tube. A stainless steel mesh (16 mesh) was placed on the upper end of the capillaries. This stainless steel mesh was connected to a DC power supply to form the honeycomb discharge in the capillary. In the packed bed, discharges are generated at contacting points of the g-al 2 O 3 pellets (3 mm). The packed-bed discharge is used as the preceding discharge. When DC high voltage is applied between the bundle of quartz glass capillaries, the inside of the capillaries can be ionized, as if the AC discharge (packed bed discharge) is sliding into the capillaries by the DC electric field Experimental setup 20mm 15mm AC High Voltage DC High Voltage Aluminum Sheet Al 2 O 3 Stainless Mesh (16mesh) Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the reactor with bundle of capillary. Fig. 2 illustrates the experimental setup used in this study. The experimental measurements were carried out at room temperature Fig. 2. Experimental setup. under normal pressures. An air pump placed downstream of this system was used to generate gas flow. The gas flow rate was 5 L/min for room air, or 3 L/min for N 2 gas. A DC high voltage power supply (Pulse Electronic Engineering Co., Ltd. HDV-50K3SUD) and an AC high voltage power supply (TREK Model20/20C High Voltage Amplifier) equipped with a function generator (Agilent Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generator 33220A) were used. The waveform of the applied voltage was measured using a digital oscilloscope (Tektronix TDS 2014) equipped with a high voltage probe (Tektronix P644A). The starting voltage of the honeycomb discharge in the capillary is defined as the voltage when the light emission of the discharge is observed inside the capillary. The maximum voltage is defined as the voltage when sparking takes place and the DC high voltage cannot be applied any more. Fig. 3. Photographs of the honeycomb discharge in the bundle of capillary (exposure time of the camera was 6 s). Quartz capillary: 1 mm inner diameter, 20 mm in length, AC 25 kv p-p, 1 khz, DC 11 kv
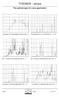
3 ARTICLE IN PRESS ELSTAT2356_proof Š 14 February 2009 Š 3/7 S. Sato et al. / Journal of Electrostatics xxx (2009) Fig. 4. Relationship between DC and AC high voltage for generation of the uniform discharge plasma. Capillary length, 20 mm; Q-1, 1.0 mm; Q-2, 2.0 mm inner diameter; Vs, the maximum voltage (the flashover voltage); Vc, the starting voltage; Vs, the maximum voltage (the flashover voltage). Fig. 5. Waveform of AC high voltage and total current for generation only packed bed discharge (negative DC high voltage 0 kv, 2.0 mm inner diameter, AC high voltage 20 kv p-p, 20 mm capillary). Fig. 6. Waveform of AC high voltage and total current for generation of the uniform slide discharge (negative DC high voltage 12.5 kv, AC high voltage 20 kv p-p, 2.0 mm inner diameter, 20 mm capillary). Fig. 7. Waveform of AC high voltage and total current for generation of the uniform slide discharge (negative DC high voltage 10 kv, AC high voltage 25 kv p-p, 2.0 mm inner diameter, 20 mm capillary). Fig. 8. Waveform of AC high voltage and total current for generation of the uniform slide discharge (negative DC high voltage 8 kv, AC high voltage 30 kv p-p, 2.0 mm inner diameter, 20 mm capillary)
4 ARTICLE IN PRESS ELSTAT2356_proof Š 14 February 2009 Š 4/7 4 S. Sato et al. / Journal of Electrostatics xxx (2009) Fig. 9. DC high voltages vs. emission (AC 50 Hz, 2.0 mm inner diameter, 20 mm capillary) Measurement of wave form The waveform of AC high voltage was measured using a digital oscilloscope. The waveform of the total discharge current was measured with a non-inductive shunt resistor. A 1-kU resistor was inserted in the circuit between the grounded electrode and the ground. 3. Results and discussion 3.1. Basic characteristics of the honeycomb discharge in the bundle of capillaries Fig. 3 shows photographs of the discharge in the bundle of quartz glass capillaries of 1 mm inner diameter. Each photo in Fig. 3 is as follows: (a) without applied voltage, (b) AC alone, (c) DC alone, (d) both AC and DC to form a honeycomb discharge in the bundle. The applied AC high voltage was 25 kv p-p, 1 khz, and the DC high voltage was 11 kv. In Fig. 3(b) when the AC voltage was applied, the packed bed discharge was observed. In Fig. 3(c) with the DC alone, light emission was observed only in the upper part of the quartz glass tube. In Fig. 3(d) with the AC and DC, the honeycomb discharge in the bundle of capillaries was taking place, and uniform light emission along the capillary tube was observed. The intensity of the light emission increased with the increasing DC voltage until sparking occurred The relationship between DC and AC high voltage The relationship between DC and AC high voltages to generate uniform honeycomb discharges in quartz glass capillary was measured. Fig. 4 indicates the starting voltage Vc of the honeycomb discharge in the quartz glass capillary and the maximum voltage Vs (flashover voltage) of the DC voltages when the AC voltage is changed. The DC voltage is negative in Fig. 4(a), and positive in Fig. 4(b). DC voltage was increased slowly from zero until sparking took place. When it was measured, the AC high voltage and the frequency were fixed. The influence of the inner diameter size of the quartz glass capillary was also measured. In Fig. 4, Vc decreased with the increasing AC voltage. With negative DC voltage, (Vs Vc) was larger than that with positive DC. With negative DC, both Vs and Vc values were lower than those with positive DC. It is well known that positive streamers tend to extend further compared to negative streamers. In this honeycomb discharge in the capillary, ionized gases in the packed-bed discharge act as an electrode, which supply electrons, ions, and photons more easily than metal electrodes. Therefore, more effective streamer generation and propagation could be achieved. Fig. 10. Photographs of honeycomb discharge (DC high voltage 16 kv, Camera exposure time: 0.5 s)
5 ARTICLE IN PRESS ELSTAT2356_proof Š 14 February 2009 Š 5/7 S. Sato et al. / Journal of Electrostatics xxx (2009) Fig. 11. DC current vs. emission (AC 50 Hz, 2.0 mm inner diameter, 20 mm capillary). In the experimental conditions, the honeycomb discharge took place roughly with an average DC electric field in the capillary of kv/cm and depended on the AC voltage value. In the meantime, stronger light emission was observed from the quartz glass tube when negative high voltage was applied Waveform measurement The waveform of AC high voltage and total current was measured. Fig. 5 shows the waveform of AC high voltage and total current when no DC high voltage was applied. Positive and negative current were observed when the AC voltage was increasing or decreasing with time. The current pulses disappeared when the applied AC voltage reached the maximum and minimum. Because only packed-bed discharge was generated in this case, the current shown in Fig. 5 was typical of barrier discharges. Fig. 6 shows the waveform of the AC high voltage and the total current when the honeycomb discharge was generated by the DC application to the bundle of capillaries. When the AC voltage reached the maximum in the positive half cycle, a negative current pulse was observed. This result suggests that the negative pulse current can be attributed to the honeycomb discharge. In Fig. 6, the current pulse at the peak of the AC voltage (at dv/ dt ¼ 0) was observed only in the positive half cycle of the applied Fig. 12. Photographs of honeycomb discharge (AC 25 kv p-p 1 khz, DC 15 kv 2 ma, N 2 gas 3 L/min, 2.0 mm inner diameter, 20 mm capillary, camera exposure time 4 s). voltage. This is because the capillary tubes were negatively biased and the positive voltage to the packed bed enhances the electric field along the capillary tubes. Figs. 7 and 8 show the waveforms of the AC high voltage and the total current with higher AC voltage and lower DC voltage. The maximum potential differences were nearly the same in all the experiments ( kv). The AC and DC voltages were 25 kv p-p and 10 kv in Fig. 7 and 30 kv p-p and 8kVinFig. 8. Figs. 6, 7 and 8 show that amplitude of the current pulse associated with the honeycomb discharge is nearly the same in these figures. The current pulses associated with the honeycomb discharge started at a different value of AC voltages but at nearly the same AC þ DC voltages (20 kv). These results suggest that honeycomb discharge is initiated when the electric field exceeds a certain value. The threshold value was about 10 kv/cm in these experimental conditions Emission spectra of the honeycomb discharge in the bundle of capillaries Fig. 9 indicates the DC high voltage vs. emission of the honeycomb discharge. The emission of honeycomb discharge was measured using a spectrometer (Ocean Optics SD2000 and USB4000). These results were measured 30 s after starting the discharge. The peak value of the measured emission of nm (N 2 C-B, 0-0) is plotted. The inner diameter was 2 mm and the length was 20 mm of the bundle of quartz glass capillaries. AC frequency was set to 50 Hz. The applied AC high voltage was set 20 kv p-p,25kv p-p,30kv p-p, 50 Hz, and the DC high voltage was varied when measuring the emission of honeycomb discharge. With the same AC voltage, the emission was stronger with increasing DC voltages. At the same DC voltage, the emission was stronger with increasing AC voltages. Fig. 10 shows photographs of the honeycomb discharge when the light emission was measured. The DC voltage was 16 kv. The AC voltage of each photograph is as follows: (a) 20 kv p-p, (b) 25 kv p- p, (c) 30 kv p-p, to form a honeycomb discharge in the bundle. Using the transparent quartz glass tube, generation of the ionization inside these tubes was confirmed. In the case of each AC high voltage, the quartz glass capillaries confirmed that an electric discharge with the emission of light occurs uniformly. In addition, light emission was confirmed that was stronger along AC high voltage values. Fig. 13. Wavelength vs. intensity (AC 25 kv p-p 1 khz, DC 15 kv 2 ma, N 2 gas 3 L/min, 2.0 mm inner diameter, 20 mm capillary)
6 ARTICLE IN PRESS ELSTAT2356_proof Š 14 February 2009 Š 6/7 6 S. Sato et al. / Journal of Electrostatics xxx (2009) Table 1 Temperature of the N 2 gas in the honeycomb reactor. T r (K) dt r (K) T v (K) dt v (K) Packed middle Honeycomb underside Honeycomb middle Honeycomb upside Fig. 11 shows the light emission intensity vs. DC current. The AC high voltage was set to 20 kv p-p,25kv p-p,30kv p-p, 50 Hz, and the DC high voltage was changed when measuring the emission. The light emission seems proportional to the DC current. Unlike the relations between DC high voltage and emission, the DC high voltage current rose with the value of DC high voltage regardless of a value of the AC high voltage. This suggested that the emission spectrum of the honeycomb discharge depended on the current of the DC high voltage. Fig. 12 shows photographs of the honeycomb discharge when the light emission was measured. The AC high voltage was set to 25 kv p-p, 1 khz and the DC high voltage was set to 15 kv. The gas flow was set to 3 L/min N 2 gas. The emission intensity was measured at the upper, middle and under side, as indicated in Figs. 12 and 13, which show the wavelength vs. light emission intensity at those parts. The AC high voltage was set to 25 kv p-p, 1 khz and the DC high voltage was set to 15 kv. The gas flow was set to 3 L/min N 2 gas. The emission intensity of the under-side was the strongest. Next was the middle (89% of the under-side) and the lowest was from the upper-side (81%). This result showed the attenuation of the light emission was 10% at 1 cm. These results suggested that the emission spectrum and intensity of the honeycomb discharge depended on the length of the honeycomb. Table 1 shows the N 2 gas temperature in the honeycomb reactor. These temperatures were calculated from the emission intensity. Based on the spectral band we also determined rotational (T R ) and vibrational (T V ) temperatures by using Specair software. The typical measured temperatures were T R ¼ K, T V ¼ K. The plasma generated by the sliding discharge was relatively cold with a high level of non-equilibrium Generation of honeycomb discharge using AC high voltage and negative pulse It is well known that pulse discharge has greater efficiency with chemical reactions than DC high voltage. The DC high voltage was changed to the negative pulse high voltage. The packed-bed discharge was used as generated by AC high voltage. When pulsed high voltage is applied inside the capillaries they can be ionized, as if the AC discharge is sliding into the capillaries. Fig. 14 shows photographs of the discharge using pulsed high voltage. Each photograph in Fig. 14 is as follows: (a) applied negative pulse high voltage at the positive peak of AC high voltage, (b) applied negative pulse high voltage before 100 ms at the positive peak of AC high voltage, (c) applied negative pulse high voltage after 100 ms at the positive peak of AC high voltage. The applied AC high voltage was 30 kv p-p, 1 khz and the pulse high voltage was 10 kv, 1 khz. In Fig. 14(a) the most shiny honeycomb discharge was observed. The honeycomb discharge in the bundle of capillaries was taking place and uniform light emission along the capillary tube was observed. In Fig. 14(b) before 100 ms, honeycomb discharge was partly observed. In Fig. 14(c) after 100 ms at the peak of AC high voltage, honeycomb discharge was normally observed. The emission intensity was measured at the middle side (as indicated in Fig. 12). Fig. 15 shows the wavelength vs. light emission intensity. The AC high voltage was set to 30 kv p-p, 1 khz and the pulse high voltage was set to 10 kv, 1 khz. The gas flow was set to 3 L/min air. The emission intensity of the pulse applied at the peak of AC high voltage was the strongest. The next was after 100 ms and the Fig. 14. Photographs of the honeycomb discharge using the pulse high voltage. Quartz capillary: 2 mm outer diameter; 20 mm in length; AC 30 kv p-p ; 1 khz; pulse 10 kv, 1 khz; camera exposure time 1.6 s
7 ARTICLE IN PRESS ELSTAT2356_proof Š 14 February 2009 Š 7/7 S. Sato et al. / Journal of Electrostatics xxx (2009) Fig. 15. Wavelength vs. emission intensity (AC 30 kv p-p 1 khz, pulse 10 kv, 1 khz, air 3 L/min, 2.0 mm inner diameter, 20 mm capillary). lowest was before 100 ms. This result showed the intensity of the light emission was related to the peak of the preceding AC discharge. At 100 ms before the AC high voltage peak, the preceding AC discharge is just generating. As a result, the pulse high voltage cannot expand into the discharge area. These results suggest that the emission spectrum and intensity of the honeycomb discharge depend on the timing of the pulse and the preceding AC discharge. 4. Conclusion Using both AC and DC high voltage, generation of plasma inside a honeycomb has become possible. Using a bundle of transparent capillaries simulating honeycomb catalyst, the characteristics of honeycomb discharge have been studied. AC voltage was applied to the packed bed, and DC voltage was applied to the bundle. To generate a stable honeycomb discharge, the condition of the AC and DC voltages are clarified as the onset and the flashover voltages. The average electric field strength for the onset of the honeycomb discharge was about 10 kv/cm in these experimental conditions. The honeycomb discharge is pulsating, detected as the current pulses at an instant of the maximum of the AC voltage. The light emission intensity from the honeycomb discharge is roughly in proportion to the DC current. The emission intensity of the under-side was the strongest. Next was the middle (89% of the under-side) and the lowest was from the upper-side (81%). The plasma generated by the sliding discharge is relatively cold with a high level of non-equilibrium. The emission intensity of the pulse applied at the peak of the AC high voltage was the strongest. The next was after 100 ms and the lowest was before 100 ms. This result showed the intensity of the light emission was related to the peak of the preceding AC discharge. Acknowledgments The authors are grateful to Prof. G. Touchard and Prof. E. Moreau of University of Poitiers for the discussions and suggestions given to this work. References [1] E.P. Weijers, A.Y. Khlystov, G.P.A. Kos, J.W. Erisman, Variability of particulate matter concentrations along roads and motorways determined by a moving measurement unit, Atmospheric Environment 38 (2004) [2] Y. Daisho, A prospect on automobiles for the 21st century resolving problems associated with environment and energy, JSAE Technical Paper, , Vol. 56, No. 1, 2002, pp (in Japanese). [3] T. Yamamoto, M. Okubo, T. Kuroki, Y. Miyairi, Nonthermal plasma regeneration of diesel particulate filter, SAE Technical paper, SP-1759, No [4] H.J. White, Industrial Electrostatic Precipitation, Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., [5] K. Urashima, J.-S. Chang, J.-Y. Park, D.-C. Lee, A. Chakrabarti, T. Ito, Reduction of NO x from natural gas combustion flue gases by corona discharge radical injection techniques, IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 34 (5) (1998) [6] T. Oda, T. Kato, T. Takahashi, K. Shimizu, Nitric oxide decomposition in air by using nonthermal plasma processing with additives and catalyst, IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 34 (2) (1998) [7] C. Louste, G. Artana, E. Moreau, G. Touchard, Sliding discharge in air at atmospheric pressure: electrical properties, Journal of Electrostatics 63 (2005)
Study of DBD electrostatic precipitator under different high voltage waveforms
 Study of DBD electrostatic precipitator under different high voltage waveforms R. Gouri Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Béchar, 8, Béchar, Algeria r.gouri@gmail.com N. Zouzou, E. Moreau,
Study of DBD electrostatic precipitator under different high voltage waveforms R. Gouri Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Béchar, 8, Béchar, Algeria r.gouri@gmail.com N. Zouzou, E. Moreau,
NOx Removal Using a Non-thermal Surface Plasma Discharge Powered by a Modulated Voltage
 74 International Journal of Plasma Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 6, No. 1, MARCH 2012 NOx Removal Using a Non-thermal Surface Plasma Discharge Powered by a Modulated Voltage J. Jolibois 1, K.
74 International Journal of Plasma Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 6, No. 1, MARCH 2012 NOx Removal Using a Non-thermal Surface Plasma Discharge Powered by a Modulated Voltage J. Jolibois 1, K.
Generation of Extended Surface Barrier Discharge on Dielectric Surface -Electrical Properties-
 Takashima et al. 14 Generation of Extended Surface Barrier Discharge on Dielectric Surface -Electrical Properties- K. Takashima 1,2, N. Zouzou 2, E. Moreau 2, A. Mizuno 1, and G. Touchard 2 1 Department
Takashima et al. 14 Generation of Extended Surface Barrier Discharge on Dielectric Surface -Electrical Properties- K. Takashima 1,2, N. Zouzou 2, E. Moreau 2, A. Mizuno 1, and G. Touchard 2 1 Department
Enhancement of Non-Equilibrium Atmospheric Pressure He Plasma Discharges by Using Silicon Diode for Alternating Current
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Enhancement of Non-Equilibrium Atmospheric Pressure He Plasma Discharges by Using Silicon Diode for Alternating Current To cite this article: Yujiro Sumiishi
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Enhancement of Non-Equilibrium Atmospheric Pressure He Plasma Discharges by Using Silicon Diode for Alternating Current To cite this article: Yujiro Sumiishi
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE DIELECTRIC BARRIER DISCHARGE IN AIR
 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE DIELECTRIC BARRIER DISCHARGE IN AIR P. Shrestha 1*, D P. Subedi, U.M Joshi 1 Central Department of Physics, Tribhuvan University, Kirtipur, Nepal Department
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE DIELECTRIC BARRIER DISCHARGE IN AIR P. Shrestha 1*, D P. Subedi, U.M Joshi 1 Central Department of Physics, Tribhuvan University, Kirtipur, Nepal Department
ANALYSIS OF A PULSED CORONA CIRCUIT
 ANALYSIS OF A PULSED CORONA CIRCUIT R. Korzekwa (MS-H851) and L. Rosocha (MS-E526) Los Alamos National Laboratory P.O. Box 1663, Los Alamos, NM 87545 M. Grothaus Southwest Research Institute 6220 Culebra
ANALYSIS OF A PULSED CORONA CIRCUIT R. Korzekwa (MS-H851) and L. Rosocha (MS-E526) Los Alamos National Laboratory P.O. Box 1663, Los Alamos, NM 87545 M. Grothaus Southwest Research Institute 6220 Culebra
Design and construction of double-blumlein HV pulse power supply
 Sādhan ā, Vol. 26, Part 5, October 2001, pp. 475 484. Printed in India Design and construction of double-blumlein HV pulse power supply DEEPAK K GUPTA and P I JOHN Institute for Plasma Research, Bhat,
Sādhan ā, Vol. 26, Part 5, October 2001, pp. 475 484. Printed in India Design and construction of double-blumlein HV pulse power supply DEEPAK K GUPTA and P I JOHN Institute for Plasma Research, Bhat,
Behavior of Pulsed Streamer Discharge in a Wire-Plate Electrode with Varied Gap Distances
 98 International Journal of Plasma Environmental Science & Technology, Vol.11, No.1, APRIL 17 Behavior of Pulsed Streamer Discharge in a Wire-Plate Electrode with Varied Gap Distances K. Nakamura 1, D.
98 International Journal of Plasma Environmental Science & Technology, Vol.11, No.1, APRIL 17 Behavior of Pulsed Streamer Discharge in a Wire-Plate Electrode with Varied Gap Distances K. Nakamura 1, D.
Control of Induction Thermal Plasmas by Coil Current Modulation in Arbitrary-waveform
 J. Plasma Fusion Res. SERIES, Vol. 8 (29) Control of Induction Thermal Plasmas by Coil Current Modulation in Arbitrary-waveform Yuki TSUBOKAWA, Farees EZWAN, Yasunori TANAKA and Yoshihiko UESUGI Division
J. Plasma Fusion Res. SERIES, Vol. 8 (29) Control of Induction Thermal Plasmas by Coil Current Modulation in Arbitrary-waveform Yuki TSUBOKAWA, Farees EZWAN, Yasunori TANAKA and Yoshihiko UESUGI Division
Enable Highly-Stable Plasma Operations at High Pressures with the Right RPS Solution
 Enable Highly-Stable Plasma Operations at High Pressures with the Right RPS Solution Created by Advanced Energy Industries, Inc., Fort Collins, CO Abstract Conventional applications for remote plasma sources
Enable Highly-Stable Plasma Operations at High Pressures with the Right RPS Solution Created by Advanced Energy Industries, Inc., Fort Collins, CO Abstract Conventional applications for remote plasma sources
Visualization of the Ionization Phenomenon in Porous Materials under Lightning Impulse
 Visualization of the Ionization Phenomenon in Porous Materials under Lightning Impulse A. Elzowawi, A. Haddad, H. Griffiths Abstract the electric discharge and soil ionization phenomena have a great effect
Visualization of the Ionization Phenomenon in Porous Materials under Lightning Impulse A. Elzowawi, A. Haddad, H. Griffiths Abstract the electric discharge and soil ionization phenomena have a great effect
Heavy-Duty High-Repetition-Rate Generators
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PLASMA SCIENCE, VOL. 30, NO. 5, OCTOBER 2002 1627 Heavy-Duty High-Repetition-Rate Generators E. J. M. van Heesch, K. Yan, and A. J. M. Pemen, Member, IEEE Abstract We present our recent
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PLASMA SCIENCE, VOL. 30, NO. 5, OCTOBER 2002 1627 Heavy-Duty High-Repetition-Rate Generators E. J. M. van Heesch, K. Yan, and A. J. M. Pemen, Member, IEEE Abstract We present our recent
Plasma Generators
 Plasma Generators Lamp Power Supplies Plasma Generators DC Power Supplies Optical Interface Others Plasma Generators Introduction Applications Plasma is generated from a gas by introducing energy, usually
Plasma Generators Lamp Power Supplies Plasma Generators DC Power Supplies Optical Interface Others Plasma Generators Introduction Applications Plasma is generated from a gas by introducing energy, usually
Corona Current-Voltage Characteristics in Wire-Duct Electrostatic Precipitators Theory versus Experiment
 Ziedan et al. 154 Corona Current-Voltage Characteristics in Wire-Duct Electrostatic Precipitators Theory versus Experiment H. Ziedan 1, J. Tlustý 2, A. Mizuno 3, A. Sayed 1, and A. Ahmed 1 1 Department
Ziedan et al. 154 Corona Current-Voltage Characteristics in Wire-Duct Electrostatic Precipitators Theory versus Experiment H. Ziedan 1, J. Tlustý 2, A. Mizuno 3, A. Sayed 1, and A. Ahmed 1 1 Department
OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS OF THE GEIGER COUNTER
 OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS OF THE GEIGER COUNTER OBJECTIVE The objective of this laboratory is to determine the operating voltage for a Geiger tube and to calculate the effect of the dead time and recovery
OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS OF THE GEIGER COUNTER OBJECTIVE The objective of this laboratory is to determine the operating voltage for a Geiger tube and to calculate the effect of the dead time and recovery
Analysis on Acoustic Attenuation by Periodic Array Structure EH KWEE DOE 1, WIN PA PA MYO 2
 www.semargroup.org, www.ijsetr.com ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.03,Issue.24 September-2014, Pages:4885-4889 Analysis on Acoustic Attenuation by Periodic Array Structure EH KWEE DOE 1, WIN PA PA MYO 2 1 Dept of Mechanical
www.semargroup.org, www.ijsetr.com ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.03,Issue.24 September-2014, Pages:4885-4889 Analysis on Acoustic Attenuation by Periodic Array Structure EH KWEE DOE 1, WIN PA PA MYO 2 1 Dept of Mechanical
DEVELOPMENT OF MEASUREMENT SYSTEM USING OPTICAL FIBER AE SENSORS FOR ACTUAL PIPING
 DEVELOPMENT OF MEASUREMENT SYSTEM USING OPTICAL FIBER AE SENSORS FOR ACTUAL PIPING SATOSHI NISHINOIRI, PORNTHEP CHIVAVIBUL, HIROYUKI FUKUTOMI and TAKASHI OGATA Materials Science Research Laboratory, Central
DEVELOPMENT OF MEASUREMENT SYSTEM USING OPTICAL FIBER AE SENSORS FOR ACTUAL PIPING SATOSHI NISHINOIRI, PORNTHEP CHIVAVIBUL, HIROYUKI FUKUTOMI and TAKASHI OGATA Materials Science Research Laboratory, Central
EFA Loudspeakers. Proc. ESA Annual Meeting on Electrostatics 2008, Paper A2 1
 Proc. ESA Annual Meeting on Electrostatics 2008, Paper A2 1 EFA Loudspeakers Igor A. Krichtafovitch, Sergey V. Karpov, Nels E. Jewell-Larsen, Jacob L. Oharah, Vladislav A. Korolev Kronos Air Technologies
Proc. ESA Annual Meeting on Electrostatics 2008, Paper A2 1 EFA Loudspeakers Igor A. Krichtafovitch, Sergey V. Karpov, Nels E. Jewell-Larsen, Jacob L. Oharah, Vladislav A. Korolev Kronos Air Technologies
Analysis of the Corona Currents in an Electrostatic Discharge System in Normal Atmospheric Pressure and Temperature
 Analysis of the Corona Currents in an Electrostatic Discharge System in Normal Atmospheric Pressure and Temperature GABRIEL NICOLAE POPA SORIN IOAN DEACONU IOSIF POPA Department of Electrical Engineering
Analysis of the Corona Currents in an Electrostatic Discharge System in Normal Atmospheric Pressure and Temperature GABRIEL NICOLAE POPA SORIN IOAN DEACONU IOSIF POPA Department of Electrical Engineering
CUSTOMIZED RIGID DISCHARGE ELECTRODES SHOW SUPERIOR PERFORMANCE IN PULP & PAPER APPLICATIONS
 CUSTOMIZED RIGID DISCHARGE ELECTRODES SHOW SUPERIOR PERFORMANCE IN PULP & PAPER APPLICATIONS Mick Chambers Proposal Manager Southern Environmental, Inc. Pensacola, Florida Gary J. Grieco Consultant Air
CUSTOMIZED RIGID DISCHARGE ELECTRODES SHOW SUPERIOR PERFORMANCE IN PULP & PAPER APPLICATIONS Mick Chambers Proposal Manager Southern Environmental, Inc. Pensacola, Florida Gary J. Grieco Consultant Air
UV GAS LASERS PREPARED BY: STUDENT NO: COURSE NO: EEE 6503 COURSE TITLE: LASER THEORY
 UV GAS LASERS PREPARED BY: ISMAIL HOSSAIN FARHAD STUDENT NO: 0411062241 COURSE NO: EEE 6503 COURSE TITLE: LASER THEORY Introduction The most important ultraviolet lasers are the nitrogen laser and the
UV GAS LASERS PREPARED BY: ISMAIL HOSSAIN FARHAD STUDENT NO: 0411062241 COURSE NO: EEE 6503 COURSE TITLE: LASER THEORY Introduction The most important ultraviolet lasers are the nitrogen laser and the
Report on BLP Spectroscopy Experiments Conducted on October 6, 2017: M. Nansteel
 Report on BLP Spectroscopy Experiments Conducted on October 6, 2017: M. Nansteel Summary Several spectroscopic measurements were conducted on October 6, 2017 at BLP to characterize the radiant power of
Report on BLP Spectroscopy Experiments Conducted on October 6, 2017: M. Nansteel Summary Several spectroscopic measurements were conducted on October 6, 2017 at BLP to characterize the radiant power of
Development of Measuring and Computer Interface System for an Industrial Electrostatic Precipitator
 Helwan University From the SelectedWorks of Omar H. Abdalla April, 2007 Development of Measuring and Computer Interface System for an Industrial Electrostatic Precipitator Omar H. Abdalla Soliman M. Sharaf
Helwan University From the SelectedWorks of Omar H. Abdalla April, 2007 Development of Measuring and Computer Interface System for an Industrial Electrostatic Precipitator Omar H. Abdalla Soliman M. Sharaf
6 - Stage Marx Generator
 6 - Stage Marx Generator Specifications - 6-stage Marx generator has two capacitors per stage for the total of twelve capacitors - Each capacitor has 90 nf with the rating of 75 kv - Charging voltage used
6 - Stage Marx Generator Specifications - 6-stage Marx generator has two capacitors per stage for the total of twelve capacitors - Each capacitor has 90 nf with the rating of 75 kv - Charging voltage used
Removal of diesel soot particules using an esp supplied by a hybrid voltage
 Eur.Phys.J.Appl.Phys.43, 3 9 (28) DOI:.51/epjap:28125 Removal of diesel soot particules using an esp supplied by a hybrid voltage A. Silvestre de Ferron, T. Reess, L. Pécastaing, A. Gibert, P. Domens and
Eur.Phys.J.Appl.Phys.43, 3 9 (28) DOI:.51/epjap:28125 Removal of diesel soot particules using an esp supplied by a hybrid voltage A. Silvestre de Ferron, T. Reess, L. Pécastaing, A. Gibert, P. Domens and
Generation of Sub-nanosecond Pulses
 Chapter - 6 Generation of Sub-nanosecond Pulses 6.1 Introduction principle of peaking circuit In certain applications like high power microwaves (HPM), pulsed laser drivers, etc., very fast rise times
Chapter - 6 Generation of Sub-nanosecond Pulses 6.1 Introduction principle of peaking circuit In certain applications like high power microwaves (HPM), pulsed laser drivers, etc., very fast rise times
High Voltage Engineering
 High Voltage Engineering Course Code: EE 2316 Prof. Dr. Magdi M. El-Saadawi www.saadawi1.net E-mail : saadawi1@gmail.com www.facebook.com/magdi.saadawi 1 Contents Chapter 1 Introduction to High Voltage
High Voltage Engineering Course Code: EE 2316 Prof. Dr. Magdi M. El-Saadawi www.saadawi1.net E-mail : saadawi1@gmail.com www.facebook.com/magdi.saadawi 1 Contents Chapter 1 Introduction to High Voltage
Study on Glow Discharge Plasma Used in Polyester. surface modification
 Study on Glow Discharge Plasma Used in Polyester Surface Modification LIU Wenzheng ( ), LEI Xiao ( ), ZHAO Qiang ( ) School of Electrical Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
Study on Glow Discharge Plasma Used in Polyester Surface Modification LIU Wenzheng ( ), LEI Xiao ( ), ZHAO Qiang ( ) School of Electrical Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
ON THE IGNITION VOLTAGE AND STRUCTURE OF COPLANAR BARRIER DISCHARGES
 ON THE IGNITION VOLTAGE AND STRUCTURE OF COPLANAR BARRIER DISCHARGES L. Hulka and G. J. Pietsch Electrical Engineering and Gas Discharge Technology, RWTH Aachen, Schinkelstr. 2, 52056 Aachen, GERMANY Abstract.
ON THE IGNITION VOLTAGE AND STRUCTURE OF COPLANAR BARRIER DISCHARGES L. Hulka and G. J. Pietsch Electrical Engineering and Gas Discharge Technology, RWTH Aachen, Schinkelstr. 2, 52056 Aachen, GERMANY Abstract.
EIS Measurement of a Very Low Impedance Lithium Ion Battery
 EIS Measurement of a Very Low Impedance Lithium Ion Battery Introduction Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy, EIS, is a very powerful way to gain information about electrochemical systems. It is often
EIS Measurement of a Very Low Impedance Lithium Ion Battery Introduction Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy, EIS, is a very powerful way to gain information about electrochemical systems. It is often
Ultra-short pulse ECM using electrostatic induction feeding method
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia CIRP 6 (213 ) 39 394 The Seventeenth CIRP Conference on Electro Physical and Chemical Machining (ISEM) Ultra-short pulse ECM using electrostatic induction
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia CIRP 6 (213 ) 39 394 The Seventeenth CIRP Conference on Electro Physical and Chemical Machining (ISEM) Ultra-short pulse ECM using electrostatic induction
Liquid sensor probe using reflecting SH-SAW delay line
 Sensors and Actuators B 91 (2003) 298 302 Liquid sensor probe using reflecting SH-SAW delay line T. Nomura *, A. Saitoh, T. Miyazaki Faculty of Engineering, Shibaura Institute of Technology, 3-9-14 Shibaura,
Sensors and Actuators B 91 (2003) 298 302 Liquid sensor probe using reflecting SH-SAW delay line T. Nomura *, A. Saitoh, T. Miyazaki Faculty of Engineering, Shibaura Institute of Technology, 3-9-14 Shibaura,
A1. Experimental Setup
 Scaling Laws for Pulsed Electrohydrodynamic Drop Formation: Supplemental Information C.-H. Chen, D. A. Saville, and I. A. Aksay Department of Chemical Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey
Scaling Laws for Pulsed Electrohydrodynamic Drop Formation: Supplemental Information C.-H. Chen, D. A. Saville, and I. A. Aksay Department of Chemical Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey
Thermo Scientific icap 7000 Plus Series ICP-OES: Innovative ICP-OES optical design
 TECHNICAL NOTE 43333 Thermo Scientific icap 7000 Plus Series ICP-OES: Innovative ICP-OES optical design Keywords Optical design, Polychromator, Spectrometer Key Benefits The Thermo Scientific icap 7000
TECHNICAL NOTE 43333 Thermo Scientific icap 7000 Plus Series ICP-OES: Innovative ICP-OES optical design Keywords Optical design, Polychromator, Spectrometer Key Benefits The Thermo Scientific icap 7000
Non-Contact AC Voltage Probe SP3000, AC Voltage Probe SP9001
 1 Non-Contact AC Voltage Probe SP3000, AC Voltage Probe SP9001 Abstract The Non-Contact AC Voltage Probe SP3000 is a compact probe that can be used with the AC Voltage Probe SP9001 to detect voltage signals
1 Non-Contact AC Voltage Probe SP3000, AC Voltage Probe SP9001 Abstract The Non-Contact AC Voltage Probe SP3000 is a compact probe that can be used with the AC Voltage Probe SP9001 to detect voltage signals
Advanced post-acceleration methodology for pseudospark-sourced electron beam
 Advanced post-acceleration methodology for pseudospark-sourced electron beam J. Zhao 1,2,3,a), H. Yin 3, L. Zhang 3, G. Shu 3, W. He 3, Q. Zhang 1,2, A. D. R. Phelps 3 and A. W. Cross 3 1 State Key Laboratory
Advanced post-acceleration methodology for pseudospark-sourced electron beam J. Zhao 1,2,3,a), H. Yin 3, L. Zhang 3, G. Shu 3, W. He 3, Q. Zhang 1,2, A. D. R. Phelps 3 and A. W. Cross 3 1 State Key Laboratory
1409. Comparison study between acoustic and optical sensors for acoustic wave
 1409. Comparison study between acoustic and optical sensors for acoustic wave Malik Abdulrazzaq Alsaedi Department of Electrical, Faculty of Engineering, University of Misan, Amarah, Iraq E-mail: maliksaady@yahoo.com
1409. Comparison study between acoustic and optical sensors for acoustic wave Malik Abdulrazzaq Alsaedi Department of Electrical, Faculty of Engineering, University of Misan, Amarah, Iraq E-mail: maliksaady@yahoo.com
Characteristics of a Normal Glow Discharge Excited by DC Voltage in Atmospheric Pressure Air
 Plasma Science and Technology, Vol.15, No.11, Nov. 2013 Characteristics of a Normal Glow Discharge Excited by DC Voltage in Atmospheric Pressure Air LI Xuechen ( ) 1,2, ZHAO Huanhuan ( ) 1,2, JIA Pengying
Plasma Science and Technology, Vol.15, No.11, Nov. 2013 Characteristics of a Normal Glow Discharge Excited by DC Voltage in Atmospheric Pressure Air LI Xuechen ( ) 1,2, ZHAO Huanhuan ( ) 1,2, JIA Pengying
LYRA 501 USER S MANUAL
 LYRA 501 USER S MANUAL D O R A D O e n e r g y Belgrade, February 2005 1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 1.1. IMPORTANT NOTICE 2 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS CONTENTS 2.1. INPUT (MAINS) 2.2. OUTPUT 2.3. ENVIROMENTAL CONDITIONS
LYRA 501 USER S MANUAL D O R A D O e n e r g y Belgrade, February 2005 1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 1.1. IMPORTANT NOTICE 2 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS CONTENTS 2.1. INPUT (MAINS) 2.2. OUTPUT 2.3. ENVIROMENTAL CONDITIONS
Design and Construction of 2.45 GHz Microwave Plasma Source at Atmospheric Pressure
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 8 (2011) 94 100 2 nd International Science, Social-Science, Engineering and Energy Conference 2010: Engineering Science and Management Design
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 8 (2011) 94 100 2 nd International Science, Social-Science, Engineering and Energy Conference 2010: Engineering Science and Management Design
An aging study ofa MICROMEGAS with GEM preamplification
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 515 (2003) 261 265 An aging study ofa MICROMEGAS with GEM preamplification S. Kane, J. May, J. Miyamoto*, I. Shipsey Deptartment of Physics, Purdue
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 515 (2003) 261 265 An aging study ofa MICROMEGAS with GEM preamplification S. Kane, J. May, J. Miyamoto*, I. Shipsey Deptartment of Physics, Purdue
Lecture 36 Measurements of High Voltages (cont) (Refer Slide Time: 00:14)
 Advances in UHV Transmission and Distribution Prof. B Subba Reddy Department of High Voltage Engg (Electrical Engineering) Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture 36 Measurements of High Voltages
Advances in UHV Transmission and Distribution Prof. B Subba Reddy Department of High Voltage Engg (Electrical Engineering) Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture 36 Measurements of High Voltages
arxiv:hep-ex/ v1 19 Apr 2002
 STUDY OF THE AVALANCHE TO STREAMER TRANSITION IN GLASS RPC EXCITED BY UV LIGHT. arxiv:hep-ex/0204026v1 19 Apr 2002 Ammosov V., Gapienko V.,Kulemzin A., Semak A.,Sviridov Yu.,Zaets V. Institute for High
STUDY OF THE AVALANCHE TO STREAMER TRANSITION IN GLASS RPC EXCITED BY UV LIGHT. arxiv:hep-ex/0204026v1 19 Apr 2002 Ammosov V., Gapienko V.,Kulemzin A., Semak A.,Sviridov Yu.,Zaets V. Institute for High
The effect of phase difference between powered electrodes on RF plasmas
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 14 (2005) 407 411 PLASMA SOURCES SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY doi:10.1088/0963-0252/14/3/001 The effect of phase difference between powered electrodes
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 14 (2005) 407 411 PLASMA SOURCES SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY doi:10.1088/0963-0252/14/3/001 The effect of phase difference between powered electrodes
Figure 4.1 Vector representation of magnetic field.
 Chapter 4 Design of Vector Magnetic Field Sensor System 4.1 3-Dimensional Vector Field Representation The vector magnetic field is represented as a combination of three components along the Cartesian coordinate
Chapter 4 Design of Vector Magnetic Field Sensor System 4.1 3-Dimensional Vector Field Representation The vector magnetic field is represented as a combination of three components along the Cartesian coordinate
Leakage Flux Recovery Coil for Energy Harvesting Using Magnetoplated Wire
 APSAEM14 Jorunal of the Japan Society of Applied Electromagnetics and Mechanics Vol.3, No.3 (15) Regular Paper Leakage Flux Recovery Coil for Energy Harvesting Using Magnetoplated Wire Tatsuya YAMAMOTO
APSAEM14 Jorunal of the Japan Society of Applied Electromagnetics and Mechanics Vol.3, No.3 (15) Regular Paper Leakage Flux Recovery Coil for Energy Harvesting Using Magnetoplated Wire Tatsuya YAMAMOTO
A large area VHF plasma source for atmospheric air plasma treatment of coated surfaces
 A large area VHF plasma source for atmospheric air plasma treatment of coated surfaces Brandon Byrns, Daniel Wooten, and Steve Shannon North Carolina State University Department of Nuclear Engineering
A large area VHF plasma source for atmospheric air plasma treatment of coated surfaces Brandon Byrns, Daniel Wooten, and Steve Shannon North Carolina State University Department of Nuclear Engineering
Generation of a Homogeneous Glow Discharge: A Comparative Study between the Use of Fine Wire Mesh and Perforated Aluminium Electrodes
 www.ccsenet.org/apr Applied Physics Research Vol. 3, No. 1; May 11 Generation of a Homogeneous Glow Discharge: A Comparative Study between the Use of Fine Wire Mesh and Perforated Aluminium Electrodes
www.ccsenet.org/apr Applied Physics Research Vol. 3, No. 1; May 11 Generation of a Homogeneous Glow Discharge: A Comparative Study between the Use of Fine Wire Mesh and Perforated Aluminium Electrodes
AC BARRIER PIN-PLANE CORONA: SIMILARITIES AND DISTINCTIONS TO DC POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE CORONAS AND DIELECTRIC BARRIER DISCHARGE
 AC BARRIER PIN-PLANE CORONA: SIMILARITIES AND DISTINCTIONS TO DC POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE CORONAS AND DIELECTRIC BARRIER DISCHARGE Yu. S. Akishev, A.V. Demyanov, V. B Karal nik, A. E. Monich, N. I. Trushkin
AC BARRIER PIN-PLANE CORONA: SIMILARITIES AND DISTINCTIONS TO DC POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE CORONAS AND DIELECTRIC BARRIER DISCHARGE Yu. S. Akishev, A.V. Demyanov, V. B Karal nik, A. E. Monich, N. I. Trushkin
A Narrow-Band Tunable Diode Laser System with Grating Feedback
 A Narrow-Band Tunable Diode Laser System with Grating Feedback S.P. Spirydovich Draft Abstract The description of diode laser was presented. The tuning laser system was built and aligned. The free run
A Narrow-Band Tunable Diode Laser System with Grating Feedback S.P. Spirydovich Draft Abstract The description of diode laser was presented. The tuning laser system was built and aligned. The free run
Excilamps as efficient UV VUV light sources*
 Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 74, No. 3, pp. 465 469, 2002. 2002 IUPAC Excilamps as efficient UV VUV light sources* Victor F. Tarasenko High Current Electronics Institute, 4, Akademichesky Ave., Tomsk, 634055,
Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 74, No. 3, pp. 465 469, 2002. 2002 IUPAC Excilamps as efficient UV VUV light sources* Victor F. Tarasenko High Current Electronics Institute, 4, Akademichesky Ave., Tomsk, 634055,
Thermal Johnson Noise Generated by a Resistor
 Thermal Johnson Noise Generated by a Resistor Complete Pre- Lab before starting this experiment HISTORY In 196, experimental physicist John Johnson working in the physics division at Bell Labs was researching
Thermal Johnson Noise Generated by a Resistor Complete Pre- Lab before starting this experiment HISTORY In 196, experimental physicist John Johnson working in the physics division at Bell Labs was researching
PHY 123/253 Shot Noise
 PHY 123/253 Shot Noise HISTORY Complete Pre- Lab before starting this experiment In 1918, experimental physicist Walter Scottky working in the research lab at Siemens was investigating the origins of noise
PHY 123/253 Shot Noise HISTORY Complete Pre- Lab before starting this experiment In 1918, experimental physicist Walter Scottky working in the research lab at Siemens was investigating the origins of noise
Partial Replication of Storms/Scanlan Glow Discharge Radiation
 Partial Replication of Storms/Scanlan Glow Discharge Radiation Rick Cantwell and Matt McConnell Coolescence, LLC March 2008 Introduction The Storms/Scanlan paper 1 presented at the 8 th international workshop
Partial Replication of Storms/Scanlan Glow Discharge Radiation Rick Cantwell and Matt McConnell Coolescence, LLC March 2008 Introduction The Storms/Scanlan paper 1 presented at the 8 th international workshop
Breakdown in short rod-plane air gaps under positive lightning impulse stress
 Breakdown in short rod-plane air gaps under positive lightning impulse stress Hans Kristian Hygen Meyer, Frank Mauseth, Martine Husøy Norwegian University of Science and Technology Jonas Ekeberg ABB Switzerland
Breakdown in short rod-plane air gaps under positive lightning impulse stress Hans Kristian Hygen Meyer, Frank Mauseth, Martine Husøy Norwegian University of Science and Technology Jonas Ekeberg ABB Switzerland
Citation X-Ray Spectrometry (2011), 40(4): 2. Right final form at
 TitleSi PIN X-ray photon counter Author(s) Nakaye, Yasukazu; Kawai, Jun Citation X-Ray Spectrometry (2011), 40(4): 2 Issue Date 2011-03-24 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/197743 This is the peer reviewed
TitleSi PIN X-ray photon counter Author(s) Nakaye, Yasukazu; Kawai, Jun Citation X-Ray Spectrometry (2011), 40(4): 2 Issue Date 2011-03-24 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/197743 This is the peer reviewed
THEIMER - lamps. The optimal type for every application. Ga - Fe doped: Multi spectrum type TH...2 Ga - Pb doped: Dual spectrum type THS...
 The optimal type for every application 12 12 1 1 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 3 35 4 45 5 55 6 65 7 Xenon puls: For reprographic camera type KX... 3 32 34 36 38 4 42 44 46 48 5 52 54 56 58 6 Hg undoped: For UV curing
The optimal type for every application 12 12 1 1 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 3 35 4 45 5 55 6 65 7 Xenon puls: For reprographic camera type KX... 3 32 34 36 38 4 42 44 46 48 5 52 54 56 58 6 Hg undoped: For UV curing
PULSED BREAKDOWN CHARACTERISTICS OF HELIUM IN PARTIAL VACUUM IN KHZ RANGE
 PULSED BREAKDOWN CHARACTERISTICS OF HELIUM IN PARTIAL VACUUM IN KHZ RANGE K. Koppisetty ξ, H. Kirkici Auburn University, Auburn, Auburn, AL, USA D. L. Schweickart Air Force Research Laboratory, Wright
PULSED BREAKDOWN CHARACTERISTICS OF HELIUM IN PARTIAL VACUUM IN KHZ RANGE K. Koppisetty ξ, H. Kirkici Auburn University, Auburn, Auburn, AL, USA D. L. Schweickart Air Force Research Laboratory, Wright
Coaxial-type water load for measuring high voltage, high current and short pulse of a compact Marx system for a high power microwave source
 PHYSICAL REVIEW SPECIAL TOPICS - ACCELERATORS AND BEAMS 12, 113501 (2009) Coaxial-type water load for measuring high voltage, high current and short pulse of a compact Marx system for a high power microwave
PHYSICAL REVIEW SPECIAL TOPICS - ACCELERATORS AND BEAMS 12, 113501 (2009) Coaxial-type water load for measuring high voltage, high current and short pulse of a compact Marx system for a high power microwave
CHAPTER 2. v-t CHARACTERISTICS FOR STANDARD IMPULSE VOLTAGES
 23 CHAPTER 2 v-t CHARACTERISTICS FOR STANDARD IMPULSE VOLTAGES 2.1 INTRODUCTION For reliable design of power system, proper insulation coordination among the power system equipment is necessary. Insulation
23 CHAPTER 2 v-t CHARACTERISTICS FOR STANDARD IMPULSE VOLTAGES 2.1 INTRODUCTION For reliable design of power system, proper insulation coordination among the power system equipment is necessary. Insulation
Modelling of Pulsed Eddy Current Testing of wall thinning of carbon steel pipes through insulation and cladding
 Modelling of Pulsed Eddy Current Testing of wall thinning of carbon steel pipes through insulation and cladding S Majidnia a,b, J Rudlin a, R. Nilavalan b a TWI Ltd, Granta Park Cambridge, b Brunel University
Modelling of Pulsed Eddy Current Testing of wall thinning of carbon steel pipes through insulation and cladding S Majidnia a,b, J Rudlin a, R. Nilavalan b a TWI Ltd, Granta Park Cambridge, b Brunel University
Transparent Electrode
 Transparent Electrode KPP-100-250 Transparent Conductors for Electrography (Kirlian Photography) Features and Specifications Large transparent, electrically conductive surface Conductive layer < 7 ohms/m
Transparent Electrode KPP-100-250 Transparent Conductors for Electrography (Kirlian Photography) Features and Specifications Large transparent, electrically conductive surface Conductive layer < 7 ohms/m
A. ABSORPTION OF X = 4880 A LASER BEAM BY ARGON IONS
 V. GEOPHYSICS Prof. F. Bitter Prof. G. Fiocco Dr. T. Fohl Dr. W. D. Halverson Dr. J. F. Waymouth R. J. Breeding J. C. Chapman A. J. Cohen B. DeWolf W. Grams C. Koons Urbanek A. ABSORPTION OF X = 4880 A
V. GEOPHYSICS Prof. F. Bitter Prof. G. Fiocco Dr. T. Fohl Dr. W. D. Halverson Dr. J. F. Waymouth R. J. Breeding J. C. Chapman A. J. Cohen B. DeWolf W. Grams C. Koons Urbanek A. ABSORPTION OF X = 4880 A
Strathprints Institutional Repository
 Strathprints Institutional Repository Given, M and Mason, Ronald and Judd, Martin and Mcglone, Phillip and Timoshkin, Igor and Wilson, Mark () Comparison between RF and electrical signals from the partial
Strathprints Institutional Repository Given, M and Mason, Ronald and Judd, Martin and Mcglone, Phillip and Timoshkin, Igor and Wilson, Mark () Comparison between RF and electrical signals from the partial
Partial Discharge Patterns in High Voltage Insulation
 22 IEEE International Conference on Power and Energy (PECon), 2-5 December 22, Kota Kinabalu Sabah, Malaysia Partial Discharge Patterns in High Voltage Insulation Hazlee Illias, Teo Soon Yuan, Ab Halim
22 IEEE International Conference on Power and Energy (PECon), 2-5 December 22, Kota Kinabalu Sabah, Malaysia Partial Discharge Patterns in High Voltage Insulation Hazlee Illias, Teo Soon Yuan, Ab Halim
Application of Ultrasonic Guided Waves for Characterization of Defects in Pipeline of Nuclear Power Plants. Younho Cho
 Application of Ultrasonic Guided Waves for Characterization of Defects in Pipeline of Nuclear Power Plants Younho Cho School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University, Korea ABSTRACT State-of-art
Application of Ultrasonic Guided Waves for Characterization of Defects in Pipeline of Nuclear Power Plants Younho Cho School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University, Korea ABSTRACT State-of-art
A Novel Multipass Optical System Oleg Matveev University of Florida, Department of Chemistry, Gainesville, Fl
 A Novel Multipass Optical System Oleg Matveev University of Florida, Department of Chemistry, Gainesville, Fl BACKGROUND Multipass optical systems (MOS) are broadly used in absorption, Raman, fluorescence,
A Novel Multipass Optical System Oleg Matveev University of Florida, Department of Chemistry, Gainesville, Fl BACKGROUND Multipass optical systems (MOS) are broadly used in absorption, Raman, fluorescence,
Conductance switching in Ag 2 S devices fabricated by sulphurization
 3 Conductance switching in Ag S devices fabricated by sulphurization The electrical characterization and switching properties of the α-ag S thin films fabricated by sulfurization are presented in this
3 Conductance switching in Ag S devices fabricated by sulphurization The electrical characterization and switching properties of the α-ag S thin films fabricated by sulfurization are presented in this
Measuring the Ion Current to the Substrate During Deposition of Thin Films by Hollow Cathode Plasma Jet
 WDS'07 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part II, 212 217, 2007. ISBN 978-80-7378-024-1 MATFYZPRESS Measuring the Ion Current to the Substrate During Deposition of Thin Films by Hollow Cathode Plasma
WDS'07 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part II, 212 217, 2007. ISBN 978-80-7378-024-1 MATFYZPRESS Measuring the Ion Current to the Substrate During Deposition of Thin Films by Hollow Cathode Plasma
is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic
 is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. The
is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. The
Development of a 300-kV Marx generator and its application to drive a relativistic electron beam
 Sādhanā Vol. 30, Part 6, December 2005, pp. 757 764. Printed in India Development of a 300-kV Marx generator and its application to drive a relativistic electron beam Y CHOYAL, LALIT GUPTA, PREETI VYAS,
Sādhanā Vol. 30, Part 6, December 2005, pp. 757 764. Printed in India Development of a 300-kV Marx generator and its application to drive a relativistic electron beam Y CHOYAL, LALIT GUPTA, PREETI VYAS,
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 27 EDFA In the last lecture, we talked about wavelength
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 27 EDFA In the last lecture, we talked about wavelength
CHAPTER 9 CURRENT VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS
 CHAPTER 9 CURRENT VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS 9.1 INTRODUCTION The phthalocyanines are a class of organic materials which are generally thermally stable and may be deposited as thin films by vacuum evaporation
CHAPTER 9 CURRENT VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS 9.1 INTRODUCTION The phthalocyanines are a class of organic materials which are generally thermally stable and may be deposited as thin films by vacuum evaporation
Design and Implementation of 8 - Stage Marx Generator Used for Gas Lasers
 Design and Implementation of 8 - Stage Marx Generator Used for Gas Lasers Dr. Naseer Mahdi Hadi Ministry of Science & Technology, Laser & Electro-Optics Research Center, Baghdad, Iraq. Dr. Kadhim Abid
Design and Implementation of 8 - Stage Marx Generator Used for Gas Lasers Dr. Naseer Mahdi Hadi Ministry of Science & Technology, Laser & Electro-Optics Research Center, Baghdad, Iraq. Dr. Kadhim Abid
INVESTIGATION OF PULSED MICRO-DISCHARGES AND OZONE PRODUCTION BY DIELECTRIC BARRIER DISCHARGES
 Huang, G. M. and Zhou, Y. J. and Wilson, M. P. and Wang, T. and Timoshkin, I. V. and MacGregor, S. J. and Given, M. J. (2015) Investigation of pulsed micro-discharges and ozone production by dielectric
Huang, G. M. and Zhou, Y. J. and Wilson, M. P. and Wang, T. and Timoshkin, I. V. and MacGregor, S. J. and Given, M. J. (2015) Investigation of pulsed micro-discharges and ozone production by dielectric
RF discharge at medium and high pressure & its possibilities for material surface modification
 RF discharge at medium and high pressure & its possibilities for material surface modification Approved tor Public ReleaseA.F.Aiexandrov, G.E. Bugrov, E.A. Kralkina, V.B. Pavlov, V. Plaksin, Distribution
RF discharge at medium and high pressure & its possibilities for material surface modification Approved tor Public ReleaseA.F.Aiexandrov, G.E. Bugrov, E.A. Kralkina, V.B. Pavlov, V. Plaksin, Distribution
Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II
 Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II 3.1 Applications of the Quantum Model of Radiant Energy 1) Photon Absorption and Emission 12/29/04 The diagrams below illustrate an atomic nucleus
Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II 3.1 Applications of the Quantum Model of Radiant Energy 1) Photon Absorption and Emission 12/29/04 The diagrams below illustrate an atomic nucleus
Experiment 6: Franck Hertz Experiment v1.3
 Experiment 6: Franck Hertz Experiment v1.3 Background This series of experiments demonstrates the energy quantization of atoms. The concept was first implemented by James Franck and Gustaf Ludwig Hertz
Experiment 6: Franck Hertz Experiment v1.3 Background This series of experiments demonstrates the energy quantization of atoms. The concept was first implemented by James Franck and Gustaf Ludwig Hertz
Partial Discharge Inception and Propagation Characteristics of Magnet Wire for Inverter-fed Motor under Surge Voltage Application
 IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation Vol. 14, No. 1; February 27 39 Partial Discharge Inception and Propagation Characteristics of Magnet Wire for Inverter-fed Motor under Surge Voltage
IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation Vol. 14, No. 1; February 27 39 Partial Discharge Inception and Propagation Characteristics of Magnet Wire for Inverter-fed Motor under Surge Voltage
ASSESSMENT OF WALL-THINNING IN CARBON STEEL PIPE BY USING LASER-GENERATED GUIDED WAVE
 ASSESSMENT OF WALL-THINNING IN CARBON STEEL PIPE BY USING LASER-GENERATED GUIDED WAVE DOYOUN KIM, YOUNHO CHO * and JOONHYUN LEE Graduate School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University Jangjeon-dong,
ASSESSMENT OF WALL-THINNING IN CARBON STEEL PIPE BY USING LASER-GENERATED GUIDED WAVE DOYOUN KIM, YOUNHO CHO * and JOONHYUN LEE Graduate School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University Jangjeon-dong,
5.4 Production of the R.F. Magnetic Field 5.11
 Chapter 5 - Experimental Apparatus 5.1 Introduction 5.1 5.2 Large System 5.1 5.3 The Solenoid 5.'7 5.4 Production of the R.F. Magnetic Field 5.11 5.5 Small System 5. 5.1 5.1 Introduction Details of the
Chapter 5 - Experimental Apparatus 5.1 Introduction 5.1 5.2 Large System 5.1 5.3 The Solenoid 5.'7 5.4 Production of the R.F. Magnetic Field 5.11 5.5 Small System 5. 5.1 5.1 Introduction Details of the
Development of DEEL (Deep Electrochemical Etching with Laser assistance) technology for low heat affected zone and high aspect ratio processing
 IWMF2014, 9 th INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON MICROFACTORIES OCTOBER 5-8, 2014, HONOLULU, U.S.A. / 1 Development of DEEL (Deep Electrochemical Etching with Laser assistance) technology for low heat affected
IWMF2014, 9 th INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON MICROFACTORIES OCTOBER 5-8, 2014, HONOLULU, U.S.A. / 1 Development of DEEL (Deep Electrochemical Etching with Laser assistance) technology for low heat affected
AD A PARAMETRIC.CHAACER S ICS OF ANEE TICALLY NIATED HE LAERU) FOREIGN TECHNOLOG YDIV WRIOH -PAT ERSON AFB
 AD A 44 324 PARAMETRIC.CHAACER S ICS OF ANEE TICALLY NIATED HE LAERU) FOREIGN TECHNOLOG YDIV WRIOH -PAT ERSON AFB OH d AU ET AL. 19 JUL 84 TD- ID(RS)T-0TI3-84 UNCLASSIFIED F/G 20/5 NL 136 1112. 136 OW_
AD A 44 324 PARAMETRIC.CHAACER S ICS OF ANEE TICALLY NIATED HE LAERU) FOREIGN TECHNOLOG YDIV WRIOH -PAT ERSON AFB OH d AU ET AL. 19 JUL 84 TD- ID(RS)T-0TI3-84 UNCLASSIFIED F/G 20/5 NL 136 1112. 136 OW_
Individually ventilated cages microclimate monitoring using photoacoustic spectroscopy
 Individually ventilated cages microclimate monitoring using photoacoustic spectroscopy Jean-Philippe Besson*, Marcel Gyger**, Stéphane Schilt *, Luc Thévenaz *, * Nanophotonics and Metrology Laboratory
Individually ventilated cages microclimate monitoring using photoacoustic spectroscopy Jean-Philippe Besson*, Marcel Gyger**, Stéphane Schilt *, Luc Thévenaz *, * Nanophotonics and Metrology Laboratory
Advancements in solar simulators for Terrestrial solar cells at high concentration (500 to 5000 Suns) levels
 Advancements in solar simulators for Terrestrial solar cells at high concentration (5 to 5 Suns) levels Doug Jungwirth, Lynne C. Eigler and Steve Espiritu Spectrolab, Inc., 5 Gladstone Avenue, Sylmar,
Advancements in solar simulators for Terrestrial solar cells at high concentration (5 to 5 Suns) levels Doug Jungwirth, Lynne C. Eigler and Steve Espiritu Spectrolab, Inc., 5 Gladstone Avenue, Sylmar,
Objectives Demonstrate new sensing techniques to improve performance of CA refrigeration systems.
 FINAL REPORT Project Title: PI: Organization: Co-PI(s): and Affiliation(s) Sensors for CA Refrigeration Systems Jeff Griffin Battelle Northwest Doubl Kold, Stemilt Growers Objectives Demonstrate new sensing
FINAL REPORT Project Title: PI: Organization: Co-PI(s): and Affiliation(s) Sensors for CA Refrigeration Systems Jeff Griffin Battelle Northwest Doubl Kold, Stemilt Growers Objectives Demonstrate new sensing
Resonance Tube Lab 9
 HB 03-30-01 Resonance Tube Lab 9 1 Resonance Tube Lab 9 Equipment SWS, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads
HB 03-30-01 Resonance Tube Lab 9 1 Resonance Tube Lab 9 Equipment SWS, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads
Spectrophotometer. An instrument used to make absorbance, transmittance or emission measurements is known as a spectrophotometer :
 Spectrophotometer An instrument used to make absorbance, transmittance or emission measurements is known as a spectrophotometer : Spectrophotometer components Excitation sources Deuterium Lamp Tungsten
Spectrophotometer An instrument used to make absorbance, transmittance or emission measurements is known as a spectrophotometer : Spectrophotometer components Excitation sources Deuterium Lamp Tungsten
LASER GENERATION AND DETECTION OF SURFACE ACOUSTIC WAVES
 LASER GENERATION AND DETECTION OF SURFACE ACOUSTIC WAVES USING GAS-COUPLED LASER ACOUSTIC DETECTION INTRODUCTION Yuqiao Yang, James N. Caron, and James B. Mehl Department of Physics and Astronomy University
LASER GENERATION AND DETECTION OF SURFACE ACOUSTIC WAVES USING GAS-COUPLED LASER ACOUSTIC DETECTION INTRODUCTION Yuqiao Yang, James N. Caron, and James B. Mehl Department of Physics and Astronomy University
Measurement 42 (2009) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Measurement. journal homepage:
 Measurement 42 (2009) 71 77 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Measurement journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/measurement A new instrument for the measurement of peak value of non-sinusoidal
Measurement 42 (2009) 71 77 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Measurement journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/measurement A new instrument for the measurement of peak value of non-sinusoidal
Characterisation of SiPM Index :
 Characterisation of SiPM --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Index : 1. Basics of SiPM* 2. SiPM module 3. Working principle 4. Experimental setup
Characterisation of SiPM --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Index : 1. Basics of SiPM* 2. SiPM module 3. Working principle 4. Experimental setup
The Coaxial Multipactor Experiment (CMX): A facility for investigating multipactor discharges
 PSFC/JA-05-28 The Coaxial Multipactor Experiment (CMX): A facility for investigating multipactor discharges T. P. Graves, B. LaBombard, S. J. Wukitch, and I.H. Hutchinson 31 October 2005 Plasma Science
PSFC/JA-05-28 The Coaxial Multipactor Experiment (CMX): A facility for investigating multipactor discharges T. P. Graves, B. LaBombard, S. J. Wukitch, and I.H. Hutchinson 31 October 2005 Plasma Science
Comparison of Pressures Driven by Repetitive Nanosecond Pulses to AC Result
 AIAA SciTech 13-17 January 214, National Harbor, Maryland 2nd Aerospace Sciences Meeting AIAA 214-94 Comparison of Pressures Driven by Repetitive Nanosecond Pulses to AC Result Qi Chen 1, Xuanshi Meng
AIAA SciTech 13-17 January 214, National Harbor, Maryland 2nd Aerospace Sciences Meeting AIAA 214-94 Comparison of Pressures Driven by Repetitive Nanosecond Pulses to AC Result Qi Chen 1, Xuanshi Meng
SIPP 2011 / UKM Ouargla / February/Février 2011
 INFRARED RADIATION IN CO 2 :N 2 :He ACOUSTOPLASMA oa7 Aleksan. S. ABRAHAMYAN, Suren. A. CHILINGARYAN, Ruben. Yu. CHILINGARYAN, Karen. V. HAKOBYAN, Aghasi. S. MIKAYELYAN and Kristine. G. SAHAKYAN Institute
INFRARED RADIATION IN CO 2 :N 2 :He ACOUSTOPLASMA oa7 Aleksan. S. ABRAHAMYAN, Suren. A. CHILINGARYAN, Ruben. Yu. CHILINGARYAN, Karen. V. HAKOBYAN, Aghasi. S. MIKAYELYAN and Kristine. G. SAHAKYAN Institute
SF 6 Capacitive Voltage Divider
 SF 6 Capacitive oltage Divider Cattareeya Suwanasri and Thanapong Suwanasri Abstract This paper aims to develop a 100 k capacitive voltage divider. The divider was separated into high voltage and low voltage
SF 6 Capacitive oltage Divider Cattareeya Suwanasri and Thanapong Suwanasri Abstract This paper aims to develop a 100 k capacitive voltage divider. The divider was separated into high voltage and low voltage
PMT tests at UMD. Vlasios Vasileiou Version st May 2006
 PMT tests at UMD Vlasios Vasileiou Version 1.0 1st May 2006 Abstract This memo describes the tests performed on three Milagro PMTs in UMD. Initially, pulse-height distributions of the PMT signals were
PMT tests at UMD Vlasios Vasileiou Version 1.0 1st May 2006 Abstract This memo describes the tests performed on three Milagro PMTs in UMD. Initially, pulse-height distributions of the PMT signals were
AC CREEPAGE DISCHARGES IN SF 6, CO 2, N 2 AND SF 6 -CO 2 AND SF 6 - N 2 MIXTURES
 AC CREEPAGE DISCHARGES IN SF 6, CO 2, N 2 AND SF 6 -CO 2 AND SF 6 - N 2 MIXTURES F. Sadaoui and A. Beroual* Ecole Centrale de Lyon, AMPERE CNRS UMR 5005, 36, Avenue Guy de Collongue, 69134 Ecully, France
AC CREEPAGE DISCHARGES IN SF 6, CO 2, N 2 AND SF 6 -CO 2 AND SF 6 - N 2 MIXTURES F. Sadaoui and A. Beroual* Ecole Centrale de Lyon, AMPERE CNRS UMR 5005, 36, Avenue Guy de Collongue, 69134 Ecully, France
A Low Impedance Marx Generator as a Test bed for Vacuum Diodes
 A Low Impedance Marx Generator as a Test bed for Vacuum Diodes Biswajit Adhikary, P Deb, R.Verma, R. Shukla, S.K.Sharma P.Banerjee, R Das, T Prabaharan, BK Das and Anurag Shyam Energetics and Electromagnetics
A Low Impedance Marx Generator as a Test bed for Vacuum Diodes Biswajit Adhikary, P Deb, R.Verma, R. Shukla, S.K.Sharma P.Banerjee, R Das, T Prabaharan, BK Das and Anurag Shyam Energetics and Electromagnetics
Experimental Study on W-Band ( GHz) Oversized Surface Wave Oscillator Driven by Weakly Relativistic Electron Beams )
 Experimental Study on W-Band (75-110 GHz) Oversized Surface Wave Oscillator Driven by Weakly Relativistic Electron Beams ) Min Thu SAN, Kazuo OGURA, Kiyoyuki YAMBE, Yuta ANNAKA, Shaoyan GONG, Jun KAWAMURA,
Experimental Study on W-Band (75-110 GHz) Oversized Surface Wave Oscillator Driven by Weakly Relativistic Electron Beams ) Min Thu SAN, Kazuo OGURA, Kiyoyuki YAMBE, Yuta ANNAKA, Shaoyan GONG, Jun KAWAMURA,
photolithographic techniques (1). Molybdenum electrodes (50 nm thick) are deposited by
 Supporting online material Materials and Methods Single-walled carbon nanotube (SWNT) devices are fabricated using standard photolithographic techniques (1). Molybdenum electrodes (50 nm thick) are deposited
Supporting online material Materials and Methods Single-walled carbon nanotube (SWNT) devices are fabricated using standard photolithographic techniques (1). Molybdenum electrodes (50 nm thick) are deposited
