USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,534,804 Woo (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 1996
|
|
|
- Juliet Carr
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
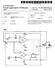
1 III USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Woo (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 1996 (54) CMOS POWER-ON RESET CIRCUIT USING 4,983,857 1/1991 Steele /143 HYSTERESS 5,136,181 8/1992 Yukawa /143 5,334,883 8/1994 Rosenthal ,6 75) Inventor: Ann K. Woo, Cupertino, Calif. 5,349,244 9/1994 Confalonieri /143 5,440,5 8/1995 Fournel /143 73) Assignee: Alyn yist Devices, Inc., Primary Examiner-Edward P. Westin unnyvale, p Assistant Examiner-Benjamin D. Driscoll Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Davis Chin 21 Appl. No.: 387, Filed: Feb. 13, 1995 (57) ABSTRACT 6 ACMOS power-on reset circuit for generating a reset signal 51) int. Cl.... HO3K 19/0948 in response to the activation of a power supply includes a (52) U.S. Cl /143; 327/5; 326/27 voltage clamping stage (14) and a hysteresis switching stage 58) Field of Search /142, 143, (16). The voltage clamping stage (14) is formed of an 56) References Cited 327/5, 6; 326/24, 27, 98, 121 N-channel resistor (M1), a first resistor (R1), and a second U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,409,501 10/1983 Eickerman et al /143 4,506,168 3/1985 Uya /6 4,539,489 9/1985 Vaughn /2O6 4,970,408 11/1990 Hanke et al /143 resistor (R2). The hysteresis switching stage (16) includes a P-channel pull-up transistor (M2), a first N-channel pull down transistor (M3), a current-source transistor (M4), a second N-channel pull-down transistor (M5), and an inverter (G1). 10 Claims, 1 Drawing Sheet V. R R Year the won timb ss - LOGIC/ Gl. RESET E. CKTRY the on qual w is name sum - CMOS POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT
2 U.S. Patent Jul. 9, 1996 LGIC/ RESET MEMORY CKTRY CMOS POWER-ON-RESET CIRCUIT *3V----- FIG 1 TERMINAL 18 - (c) NODE A-1 1 (d) NODE B-1 N M TERMINAL 12 (e) RESET OV tit2 t t4 t5 FIG
3 1. CMOS POWER-ON RESET CIRCUIT USENG HYSTERESIS BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION This invention relates generally to power-up reset circuits and more particularly, it relates to an improved CMOS power-on reset circuit which includes hysteresis switching means for turning off a reset signal when a first predeter mined trip level has been reached and forturning on the reset signal when a second predetermined trip level has been reached and which is lower than the first predetermined trip level. In a variety of CMOS or bipolar digital integrated circuit devices, such as flip-flops, latches, counters, memory state registers and the like, the outputs thereof can have two or more stable states. It is often desirable to initialize or reset these types of logic and/or memory circuits to a particular known logic state prior to their normal operation every time when power is first applied (i.e., "power-up"). As is gener ally well-known, this initialization process is commonly achieved by a reset signal generated by a power-on reset circuit which is applied for a brief period of time when the power supply voltage is ramping up so as to reset or initialize the outputs of the digital integrated circuit devices. Accordingly, this proper initialization ensures the operating state of the various logic and/or memory circuits in the digital integrated circuit devices as well as simplifies test procedures to be performed on them. This reset signal is then switched off after the power supply voltage exceeds a predetermined level, which is below the normal power supply voltage. However, in the event of a transient noise occurring after the power supply voltage has exceeded the predetermined level but while it is still ramping up, this will cause the disadvantage of generating an unwanted reset signal which tends to interfere with the normal operation of the digital integrated circuit devices. It is generally desirable to prevent the generation of the reset signal due to this transient noise in order that the digital integrated circuit devices are maintained in the functional state and to permit the generation of the reset signal only in the event of an actual power-down. Accordingly, it would be desirable to provide an improved power-on reset circuit which avoids the generation of a reset signal due to transient noise after the power supply voltage has exceeded the predetermined level. Further, in order to reduce the amount of space required, it would be expedient to have the power on reset circuit formed as a part of the same monolithic semiconductor integrated circuit chip containing the digital logic devices. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION Accordingly, it is a general object of the present invention to provide an improved CMOS power-on reset circuit which is relatively simple and economical to manufacture and assemble, but yet overcomes the problems encountered in the prior art reset circuits. It is an object of the present invention to provide an improved CMOS power-on reset circuit which includes hysteresis switching means for turning off a reset signal when a first predetermined trip level has been reached and for turning on the reset signal when a second predetermined trip level has been reached and which is lower than the first preset trip level It is another object of the present invention to provide an improved CMOS power-on reset circuit which includes voltage clamping means responsive to a power supply voltage for generating a first control voltage and hysteresis switching means responsive to the power supply voltage and the first control voltage for generating a second control voltage which is used to turn off the reset signal when a first predetermined trip level has been reached and for turning on the reset signal when a second predetermined trip level has been reached and which is lower than the first predetermined trip level. It is still another object of the present invention to provide an improved CMOS power-on reset circuit which is formed as a part of the same monolithic semiconductor integrated circuit chip containing logic and/or memory devices. In accordance with these aims and objectives, the present invention is concerned with the provision of a CMOS power-on reset circuit for generating a reset signal in response to the activation of a power supply voltage. The power-on reset circuit includes a voltage clamping circuit and a hysteresis switching circuit. A power supply terminal is provided to receive a power supply voltage. The voltage clamping circuit is responsive to the power supply voltage for generating a first control voltage. The hysteresis switching circuit is responsive to the power supply voltage and the first control voltage for generating a second control voltage which is used to turn off the reset signal at an output node when a first predetermined trip level has been exceeded and for turning on the reset signal when a second predetermined trip level has been reached and which is lower than the first predetermined trip level. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS These and other objects and advantages of the present invention will become more fully apparent from the follow ing detailed description when read in conjunction with the accompanying drawings with like reference numerals indi cating corresponding parts throughout, wherein: FIG. 1 is a schematic circuit diagram of a CMOS power on reset circuit, constructed in accordance with the prin ciples of the present invention; and FIGS. 2(a) through 2Ce) are waveforms at various points in the circuit of FIG. 1, which are useful in understanding the operation thereof. DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT Referring now in detail the drawings, there is shown in FIG. 1 a schematic circuit diagram of an improved CMOS power-on reset circuit 10 which is constructed in accordance with the principles of the present invention. The reset circuit 10 provides a reset signal RESET on its output terminal 12 which is connectable to various digital logic and/or memory devices 13. These digital logic and/or memory devices 13 are formed as a part of the same monolithic semiconductor integrated circuit chip. This reset signal RESET is a logic signal and initiates a reset to the digital logic and/or memory circuits 13 when it is at a high logic level (active state). On the other hand, the reset is inactive or turned off from the devices when the reset signal RESET is at a low logic level. The reset circuit 10 includes a voltage clamping stage 14 and a hysteresis switching stage 16. The voltage clamping stage 14 is comprised of a first resistor R1, a second resistor R2, and a first N-channel MOS transistor M1. The first
4 3 resistor R1 has its one end connected to a first power supply terminal 18 for receiving a power supply voltage or potential VDD. The other end of the resistor R1 is connected to one end of the resistor R2 and to a first internal node A. The other end of the resistor R2 is connected to a second internal node B. The gate and drain electrodes of the N-channel transistor M1 are connected together and to the node B. The source electrode of the transistor M1 is connected to a second power supply terminal for receiving a second power supply voltage or potential VSS (which is typically at a ground potential or zero volts). Initially, the power supply voltage VDD is turned off and both of the internal nodes A and B in the voltage clamping stage 14 are at the ground potential. When the reset circuit 10 is powered up from an inactive or off state, the power supply potential VDD does not immediately obtain its nominal level (i.e., +3 volts), but it will rather ramp up to this steady-state level. It should be noted that the ramp time for typical power supplies vary and is somewhere in the range of approximately one-tenth of a microsecond (0.1 S) and one hundred milliseconds (100 ms). The hysteresis switching stage 16 is comprised of a P-channel MOS pull-up transistor M2, a first N-channel pull-down MOS transistor M3, a current-source N-channel MOS transistor M4, a second pull-down N-channel MOS transistor MS, and an inverter G1. The P-channel transistor M2 has its source electrode connected to the first power supply terminal 18, its gate electrode connected to the first internal node A, and its drain electrode connected to the third internal node C. The first pull-down transistor M3 has its drain electrode connected to the drain electrode of the pull-up transistor M2, to the third internal node C, and to the drain electrode of the second pull-down transistor M5. The gate electrode of the pull-down transistor M3 is connected to the gate electrodes of the transistors M2, M5 and to the first internal node A. The source electrode of the pull-down transistor M3 is connected to the drain electrode of the current-source transistor M4. The source electrode of the current-source transistor M4 is connected to the second power supply terminal and to the source electrode of the second pull-down transistor M5. The drain electrode of the second pull-down transistor M5 is also connected to the input of inverter G1. The output of the inverter G1 provides the reset signal RESET to the logic/ memory circuitry 13 via the output terminal 12. The output of the inverter G1 is also connected to the gate of the current-source transistor M4. In order to provide an understanding of the operation of the CMOS power-on reset circuit 10 of the present inven tion, reference is now made to FIGS. 2(a) through e) of the drawings which illustrate waveforms appearing at various points in the reset circuit of FIG. 1. Initially, it is assumed that prior to time t1 the power supply voltage VDD applied to the power supply terminal 18 is in the turned-off condition or inactive state. As a consequence, all of the transistors M1 through M5 are non-conducting and the reset signal RESET will below (i.e., zero volts) at the time t1. The power supply voltage VDD is shown in FIG. 2(a), and the reset signal RESET is shown in FIG. 2(e). Further, the nodes A, B and C are at a low or logic "zero level (VSS), as depicted in respect to FIGS. 2(c), 2Cd) and b). When the power supply voltage VDD is powered up or turned on at the time t1, the voltage level at the first power Supply terminal 18 will begin ramping up towards its normal level, in this case +3.0 volts. The node A will also begin to rise and follows the power supply voltage VDD since the O threshold of the transistor M1 has not been exceeded and thus there is no conduction through the resistors R1 and R2. The transistor M1 will remain turned off until the time t2 when the voltage level at the node B begins to exceed the threshold voltage of the transistor MI. At the time t2, the transistor M1 will be rendered conductive so that the node B as shown in FIG. 2(d) will be clamped. Further, the node A as illustrated in FIG. 2(c) will thereafter increase at a slower rate relative to the power supply potential VDD, as this slower rate of rise is controlled by the voltage divider formed by the resistors R1 and R2. It will be noted that the power supply voltage after the time t2 will continue to rise up towards the normal level. At this same time t2, the second pull-down transistor M5 will also be turned on so as to maintain a low impedance at the node C. As can be seen in FIG. 2(b), the voltage at the node C is approximately zero volts. Thus, the output of the inverter G1 will be at a high level or state, which corre sponds to the reset signal RESET, The reset signal will now begin to follow the power supply voltage VDD. As the power supply voltage VDD continues to ramp up after the time t2, the transistor M2 will be rendered more and more conductive due to the increasing gate-to-source voltage V so as to cause more current to fiów into the transistors M5 and M3. As a result, the drain-to-source voltage V across the transistors M5 and M3 will be increased. This will, in turn, cause the node C to follow the power supply voltage VDD to rise until it reaches the switching threshold voltage at point 22 of the inverter G1 at time t3. As should be apparent to those skilled in the art, the threshold voltage of the inverter G1 is approximately equal to VDD/2. At this time t3, the output of the inverter G1 will go low so as to switch off the reset signal RESET, which will cause the transistor M4 to turn off. As the transistor M4 is turned off this causes the node C to rise to the power supply potential VDD since it will now have a high impedance. Therefore, the current flowing into the transistor M3 will now be added to the transistor MS. Moreover, it will be noted that at the time t3 the power supply voltage will have reached a certain voltage defining a first predetermined trip level V. Thereafter, the voltage at the node C will follow the power supply voltage VDD. This condition will remain unchanged in the normal operating range when the power supply voltage VDD is at +3.0 volts. In the event of a power-down mode, when the power supply voltage VDD begins to decrease, such as at time ta, the reset signal RESET will not return back to the high level again until the voltage at the node C decreases below the switching threshold voltage at point 24 of the inverter G1. As can be seen, at time t5 the reset signal RESET will be returned to the high logic level, which in turn renders the transistor M4 conductive. As a result, the impedance at the node C will become low and thus will be at the ground potential. Again, it will be noted that at the time t5the power supply voltage VDD has decreased to a certain voltage defining a second predetermined trip point V. This second predetermined trip level V is substantially lower than the first predetermined trip level V. The differ ence in the voltage levels between the first trip voltage and the second trip voltage is referred to as VDD hysteresis voltage. This built-in hysteresis serves to provide a certain noise margin for the power supply voltage VDD so as to prevent the generation of an unwanted reset signal which interferes with the normal operation of the logic devices. In other words, this hysteresis voltage serves to prevent acti vating a reset signal when the power supply voltage VDD decreases due to transient noise rather than an actual power down mode of operation.
5 S It should be appreciated that the voltage clamping stage 14 of the present CMOS reset circuit 10 is utilized to establish a first control voltage at the internal node A in response to the power supply voltage VDD by connecting the N-channel transistor M1 in series with the voltage divider formed by the resistors R1 and R2. While the transistor M1 functions to maintain the advantage of track ing with the other transistors, the voltage divider is used to establish a fraction of the threshold voltage of the N-channel transistor M1 at the internal node A so as to provide a low power supply voltage VDD operation. Further, it should be clearly understood that the hysteresis switching stage 16 is responsive to the power supply voltage VDD and the first control voltage so as to generate the second control voltage at the internal node C. It is this second control voltage which causes the switching of the inverter G1. It should be appar ent to those skilled in the art that the second predetermined trip level is determined by the relative sizes of the transistors M2 through M5. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the ratio of the values of the resistors R1 to R2 is chosen to be 2:1 and the pull-down transistor was operated in the sub-threshold region. As a result, it was found that the highest value for the first predetermined trip level V to be approximately +2.7 V and that the VDDhysteresis voltage was 0.4V nominal. This was found to be quite suitable for the desired power supply voltage operation of +3.0 volts. It should also be understood that the CMOS reset circuit 10 may be formed as a part of the same semiconductor integrated circuit chip contain ing the logic devices 13, thereby reducing the amount of chip area required. From the foregoing detailed description, it can thus be seen that the present invention provides an improved CMOS power-on reset circuit which includes a hysteresis switching circuit for turning off the reset signal after a first predeter mined trip level has been reached and forturning on the reset signal after a second predetermined trip level has been reached and which is lower than the first predetermined trip level. Further, the reset circuit may beformed as a part of the same semiconductor integrated circuit chip containing logic gate devices. While there has been illustrated and described what is at present considered to be a preferred embodiment of the present invention, it will be understood by those skilled in the art that various changes and modifications may be made, and equivalents may be substituted for elements thereof without departing from the true scope of the invention. In addition, many modifications may be made to adapt a particular situation or material to the teachings of the invention without departing from the central scope thereof. Therefore, it is intended that this invention not be limited to the particular embodiment disclosed as the best mode con templated for carrying out the invention, but that the inven tion will include all embodiments falling within the scope of the appended claims. What is claimed is: 1. A CMOS power-on reset circuit for generating a reset signal in response to the activation of a power supply voltage, said reset circuit comprising: a power supply terminal (18) for receiving a power supply voltage (VDD); voltage clamping means (14) responsive to said power supply voltage (VDD) for generating a first control voltage; said voltage clamping means including an N-channel transistor (M1), a first resistor (R1), and a second resistor (R2); said first resistor having its one end connected to the power supply terminal and its other end connected to one end of said second resistor at a first internal node (A) to provide the first control voltage, said N-channel transistor (M1) having its drain and gate electrodes connected together and to the other end of said second resistor, said N-channel transistor (M1) having its source electrode connected to a ground potential (VSS); and hysteresis switching means responsive to said power supply voltage (VDD) and said first control voltage for generating a second control voltage which is used to turn off a reset signal at an output node when a first predetermined trip level has been exceeded and for turning on said reset signal when a second predeter mined trip level has been reached which is lower than said first predetermined trip level. 2. A reset circuit as claimed in claim 1, wherein said hysteresis switching means includes a P-channel pull-up transistor (M2), a first N-channel pull-down transistor (M3), a current-source transistor (M4), a second N-channel pull down transistor (M5), and an inverter (G1). 3. A reset circuit as claimed in claim 2, wherein said P-channel transistor (M2) has its source electrode connected to the power supply terminal (18), its gate electrode con nected to the first internal node (A), and its drain electrode connected to a second internal node (C) to provide the second control signal, said first N-channel pull-down tran sistor (M3) having its drain electrode connected to the second internal node (C) and its gate electrode connected to the first internal node (A), said current-source transistor (M4) having its drain electrode connected to the source of said first N-channel pull-down transistor (M3), its gate electrode connected to the output of said inverter (G1), and its source electrode connected to the ground potential (VSS), said second N-channel pull-down transistor (MS) having its drain connected to the second internal node (C), its gate electrode connected to the first internal node (A), and its source electrode connected to the ground potential, said inverter (G1) having its input connected also to the second internal node (C) and its output connected to the output terminal (12) to provide the reset signal. 4. A reset circuit as claimed in claim3, further comprising at least one of logic and memory devices (13) being formed on a single monolithic semiconductor integrated circuit chip () and being responsive to said reset signal. 5. A reset circuit as claimed in claim 4, wherein said reset circuit (10) is formed as a part of the same integrated circuit chip () containing the at least one of logic and memory devices (13). 6. A reset circuit as claimed in claim 1, further comprising at least one of logic and memory devices (13) being formed on a single monolithic semiconductor integrated circuit chip () and being responsive to said reset signal. 7. A reset circuit as claimed in claim 6, wherein said reset circuit (10) is formed as a part of the same integrated circuit chip () containing the at least one of logic and memory devices (13). 8. A CMOS power-on reset circuit for generating a reset signal in response to the activation of a power supply voltage, said reset circuit comprising: a power supply terminal (18) for receiving a power supply voltage (VDD); voltage clamping means (14) responsive to said power supply voltage (VDD) for generating a first control voltage; said voltage clamping means including an N-channel transistor (M1), a first resistor (R1), and a second resistor (R2);
6 7 said first resistor having its one end connected to the power supply terminal and its other end connected to one end of said second resistor at a first internal node (A) to provide the first control voltage, said N-channel transistor (M) having its drain and gate electrodes connected together and to the other end of said second resistor, said N-channel transistor (M1) having its source electrode connected to a ground potential (VSS); hysteresis switching means responsive to said power supply voltage (VDD) and said first control voltage for generating a second control voltage which is used to turn off a reset signal at an output node when a first predetermined trip level has been exceeded and for turning on said reset signal when a second predeter mined trip level has been reached which is lower than said first predetermined trip level; said hysteresis switching means including a P-channel pull-up transistor (M2), a first N-channel pull-down transistor (M3), a current-source transistor (M4), a second N-channel pull-down transistor (M5), and an inverter (G1); said P-channel transistor (M2) having its source electrode connected to the power supply terminal (18), its gate electrode connected to the first internal node (A), and its drain electrode connected to a second internal node (C) to provide the second control signal, said first N-channel pull-down transistor (M3) having its drain 0. 8 electrode connected to the second internal node (C) and its gate electrode connected to the first internal node (A), said current-source transistor (M4) having its drain electrode connected to the source of said first N-chan nel pull-down transistor (M3), its gate electrode con nected to the output of said inverter (G1), and its source electrode connected to the ground potential (VSS), said second N-channel pull-down transistor (M5) having its drain connected to the second internal node (C), its gate electrode connected to the first internal node (A), and its source electrode connected to the ground potential, said inverter (G1) having its input connected also to the second internal node (C) and its output connected to the output terminal (12) to provide the reset signal; and logic and/or memory devices (13) operatively connected to the power supply voltage and said reset signal and being responsive thereto. 9. A reset circuit as claimed in claim 8, further comprising at least one of logic and memory devices (13) being formed on a single monolithic semiconductor integrated circuit chip (). 10. A reset circuit as claimed in claim 9, wherein said reset circuit (10) is formed as a part of the same integrated circuit chip () containing the at least one of logic and memory devices (13).
III. I. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,121,014. Huang
 United States Patent (19) Huang (54) CMOS DELAY CIRCUIT WITH LABLE DELAY 75 Inventor: Eddy C. Huang, San Jose, Calif. 73) Assignee: VLSI Technology, Inc., San Jose, Calif. (21) Appl. o.: 6,377 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Huang (54) CMOS DELAY CIRCUIT WITH LABLE DELAY 75 Inventor: Eddy C. Huang, San Jose, Calif. 73) Assignee: VLSI Technology, Inc., San Jose, Calif. (21) Appl. o.: 6,377 22 Filed:
in-s-he Gua (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,388,499 B1 (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 Vddint : SFF LSOUT Tien et al.
 (12) United States Patent Tien et al. USOO6388499B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) LEVEL-SHIFTING SIGNAL BUFFERS THAT SUPPORT HIGHER VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLIES USING LOWER VOLTAGE
(12) United States Patent Tien et al. USOO6388499B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) LEVEL-SHIFTING SIGNAL BUFFERS THAT SUPPORT HIGHER VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLIES USING LOWER VOLTAGE
United States Patent (19) Wrathal
 United States Patent (19) Wrathal (54) VOLTAGE REFERENCE CIRCUIT (75) Inventor: Robert S. Wrathall, Tempe, Ariz. 73) Assignee: Motorola, Inc., Schaumburg, Ill. (21) Appl. No.: 219,797 (22 Filed: Dec. 24,
United States Patent (19) Wrathal (54) VOLTAGE REFERENCE CIRCUIT (75) Inventor: Robert S. Wrathall, Tempe, Ariz. 73) Assignee: Motorola, Inc., Schaumburg, Ill. (21) Appl. No.: 219,797 (22 Filed: Dec. 24,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kang et al. USOO6906581B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2005 (54) FAST START-UP LOW-VOLTAGE BANDGAP VOLTAGE REFERENCE CIRCUIT (75) Inventors: Tzung-Hung Kang,
(12) United States Patent Kang et al. USOO6906581B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2005 (54) FAST START-UP LOW-VOLTAGE BANDGAP VOLTAGE REFERENCE CIRCUIT (75) Inventors: Tzung-Hung Kang,
United States Patent (19) Morris
 United States Patent (19) Morris 54 CMOS INPUT BUFFER WITH HIGH SPEED AND LOW POWER 75) Inventor: Bernard L. Morris, Allentown, Pa. 73) Assignee: AT&T Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, N.J. 21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Morris 54 CMOS INPUT BUFFER WITH HIGH SPEED AND LOW POWER 75) Inventor: Bernard L. Morris, Allentown, Pa. 73) Assignee: AT&T Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, N.J. 21 Appl. No.:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1
 USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Black, Jr. USOO6759836B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 2004 (54) LOW DROP-OUT REGULATOR (75) Inventor: Robert G. Black, Jr., Oro Valley, AZ (US) (73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent Black, Jr. USOO6759836B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 2004 (54) LOW DROP-OUT REGULATOR (75) Inventor: Robert G. Black, Jr., Oro Valley, AZ (US) (73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent
 US009 159725B2 (12) United States Patent Forghani-Zadeh et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) CONTROLLED ON AND OFF TIME SCHEME FORMONOLTHC
US009 159725B2 (12) United States Patent Forghani-Zadeh et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) CONTROLLED ON AND OFF TIME SCHEME FORMONOLTHC
us/ (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1 (19) United States / 112 / 108 Frederick et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb.
 (19) United States US 20080030263A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0030263 A1 Frederick et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2008 (54) CONTROLLER FOR ORING FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR
(19) United States US 20080030263A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0030263 A1 Frederick et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2008 (54) CONTROLLER FOR ORING FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,512,361 B1
 USOO6512361B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,512,361 B1 Becker (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 28, 2003 (54) 14/42-VOLTAUTOMOTIVE CIRCUIT 5,420.503 5/1995 Beha TESTER 5,517,183 A 5/1996 Bozeman,
USOO6512361B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,512,361 B1 Becker (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 28, 2003 (54) 14/42-VOLTAUTOMOTIVE CIRCUIT 5,420.503 5/1995 Beha TESTER 5,517,183 A 5/1996 Bozeman,
United States Patent (19) Schnetzka et al.
 United States Patent (19) Schnetzka et al. 54 (75) GATE DRIVE CIRCUIT FOR AN SCR Inventors: Harold R. Schnetzka; Dean K. Norbeck; Donald L. Tollinger, all of York, Pa. Assignee: York International Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Schnetzka et al. 54 (75) GATE DRIVE CIRCUIT FOR AN SCR Inventors: Harold R. Schnetzka; Dean K. Norbeck; Donald L. Tollinger, all of York, Pa. Assignee: York International Corporation,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007576582B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,576,582 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) LOW-POWER CLOCK GATING CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Dae Woo
(12) United States Patent US007576582B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,576,582 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) LOW-POWER CLOCK GATING CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Dae Woo
United States Patent (19) Nilssen
 United States Patent (19) Nilssen (4) HIGH-EFFICIENCY SINGLE-ENDED INVERTER CRCUIT 76) Inventor: Ole K. Nilssen, Caesar Dr. Rte. 4, Barrington, Ill. 60010 21 Appl. No.: 33,33 (22) Filed: Apr. 2, 1979 (1)
United States Patent (19) Nilssen (4) HIGH-EFFICIENCY SINGLE-ENDED INVERTER CRCUIT 76) Inventor: Ole K. Nilssen, Caesar Dr. Rte. 4, Barrington, Ill. 60010 21 Appl. No.: 33,33 (22) Filed: Apr. 2, 1979 (1)
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
HHHHHH. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,079,455. McCafferty et al. tor to provide a negative feedback path for charging the
 United States Patent (19) McCafferty et al. (54. SURGE CURRENT-LIMITING CIRCUIT FOR A LARGE-CAPACITANCE LOAD 75 Inventors: Lory N. McCafferty; Raymond K. Orr, both of Kanata, Canada 73) Assignee: Northern
United States Patent (19) McCafferty et al. (54. SURGE CURRENT-LIMITING CIRCUIT FOR A LARGE-CAPACITANCE LOAD 75 Inventors: Lory N. McCafferty; Raymond K. Orr, both of Kanata, Canada 73) Assignee: Northern
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
(19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0163811A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0163811 A1 MARINAS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2011 (54) FAST CLASS AB OUTPUT STAGE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2011 0163811A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0163811 A1 MARINAS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2011 (54) FAST CLASS AB OUTPUT STAGE Publication Classification
III IIIIHIIII. United States Patent 19 Mo. Timing & WIN. Control Circuit. 11 Patent Number: 5,512, Date of Patent: Apr.
 United States Patent 19 Mo 54) SWITCHED HIGH-SLEW RATE BUFFER (75) Inventor: Zhong H. Mo, Daly City, Calif. 73) Assignee: TelCom Semiconductor, Inc., Mountain View, Calif. 21 Appl. No.: 316,161 22 Filed:
United States Patent 19 Mo 54) SWITCHED HIGH-SLEW RATE BUFFER (75) Inventor: Zhong H. Mo, Daly City, Calif. 73) Assignee: TelCom Semiconductor, Inc., Mountain View, Calif. 21 Appl. No.: 316,161 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19 11 Patent Number: 5,592,073 Redlich 45) Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 1997
 IIII US005592073A United States Patent (19 11 Patent Number: 5,592,073 Redlich 45) Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 1997 54) TRIAC CONTROL CIRCUIT Ramshaw, R. S., "Power Electronics Semiconductor 75) Inventor:
IIII US005592073A United States Patent (19 11 Patent Number: 5,592,073 Redlich 45) Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 1997 54) TRIAC CONTROL CIRCUIT Ramshaw, R. S., "Power Electronics Semiconductor 75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7068OB2 (12) United States Patent Moraveji et al. (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) CURRENT LIMITING CIRCUITRY Inventors: Farhood Moraveji,
USOO7068OB2 (12) United States Patent Moraveji et al. (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) CURRENT LIMITING CIRCUITRY Inventors: Farhood Moraveji,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0188326 A1 Lee et al. US 2011 0188326A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) DUAL RAIL STATIC RANDOMACCESS MEMORY (75) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0188326 A1 Lee et al. US 2011 0188326A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) DUAL RAIL STATIC RANDOMACCESS MEMORY (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007 184283B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,184,283 B2 Yang et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 27, 2007 (54) SWITCHING FREQUENCYJITTER HAVING (56) References Cited OUTPUT RIPPLE CANCEL
(12) United States Patent US007 184283B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,184,283 B2 Yang et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 27, 2007 (54) SWITCHING FREQUENCYJITTER HAVING (56) References Cited OUTPUT RIPPLE CANCEL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,561 B1. Le et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001
 USOO6208561B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,561 B1 Le et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 9 (54) METHOD TO REDUCE CAPACITIVE 5,787,037 7/1998 Amanai... 365/185.23 LOADING IN
USOO6208561B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,561 B1 Le et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 9 (54) METHOD TO REDUCE CAPACITIVE 5,787,037 7/1998 Amanai... 365/185.23 LOADING IN
III. United States Patent (19) Ashe. 5,495,245 Feb. 27, OTHER PUBLICATIONS Grebene, Bipolar and MOS Analog Integrated Circuit
 United States Patent (19) Ashe 54) DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER WITH SEGMENTED RESISTOR STRING 75 Inventor: James J. Ashe, Saratoga, Calif. 73 Assignee: Analog Devices, Inc., Norwood, Mass. 21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Ashe 54) DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER WITH SEGMENTED RESISTOR STRING 75 Inventor: James J. Ashe, Saratoga, Calif. 73 Assignee: Analog Devices, Inc., Norwood, Mass. 21 Appl. No.:
:2: E. 33% ment decreases. Consequently, the first stage switching
 O USOO5386153A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Voss et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 31, 1995 54 BUFFER WITH PSEUDO-GROUND Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Blakely, Sokoloff, Taylor & HYSTERESS Zafiman
O USOO5386153A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Voss et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 31, 1995 54 BUFFER WITH PSEUDO-GROUND Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Blakely, Sokoloff, Taylor & HYSTERESS Zafiman
4,695,748 Sep. 22, 1987
 United States Patent [19] Kumamoto [11] Patent Number: [45] Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 1987 [54] COMPARING DEVICE [75] Inventor: Toshio Kumamoto, Itami, Japan [73] Assignee: Mitsubishi Denki Kabushiki Kaisha,
United States Patent [19] Kumamoto [11] Patent Number: [45] Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 1987 [54] COMPARING DEVICE [75] Inventor: Toshio Kumamoto, Itami, Japan [73] Assignee: Mitsubishi Denki Kabushiki Kaisha,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
(19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
United States Patent (19) Harnden
 United States Patent (19) Harnden 54) 75 (73) LMITING SHOOT THROUGH CURRENT INA POWER MOSFET HALF-BRIDGE DURING INTRINSIC DODE RECOVERY Inventor: Assignee: James A. Harnden, San Jose, Calif. Siliconix
United States Patent (19) Harnden 54) 75 (73) LMITING SHOOT THROUGH CURRENT INA POWER MOSFET HALF-BRIDGE DURING INTRINSIC DODE RECOVERY Inventor: Assignee: James A. Harnden, San Jose, Calif. Siliconix
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 200600498.68A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0049868A1 Yeh (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE DRIVING CIRCUIT WITH A COMPENSATING CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 200600498.68A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0049868A1 Yeh (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE DRIVING CIRCUIT WITH A COMPENSATING CIRCUIT
United States Patent 19 Hsieh
 United States Patent 19 Hsieh US00566878OA 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 1997 54 BABY CRY RECOGNIZER 75 Inventor: Chau-Kai Hsieh, Chiung Lin, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Industrial Technology Research
United States Patent 19 Hsieh US00566878OA 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 1997 54 BABY CRY RECOGNIZER 75 Inventor: Chau-Kai Hsieh, Chiung Lin, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Industrial Technology Research
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015 0028681A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0028681 A1 L (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 29, 2015 (54) MULTI-LEVEL OUTPUT CASCODE POWER (57) ABSTRACT STAGE (71)
(19) United States US 2015 0028681A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0028681 A1 L (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 29, 2015 (54) MULTI-LEVEL OUTPUT CASCODE POWER (57) ABSTRACT STAGE (71)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,970,124 B1. Patterson (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 29, 2005
 USOO697O124B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Patterson (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 29, 2005 (54) INHERENT-OFFSET COMPARATOR AND 6,798.293 B2 9/2004 Casper et al.... 330/258 CONVERTER SYSTEMS
USOO697O124B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Patterson (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 29, 2005 (54) INHERENT-OFFSET COMPARATOR AND 6,798.293 B2 9/2004 Casper et al.... 330/258 CONVERTER SYSTEMS
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,512,817. Nagaraj (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 30, 1996
 IIIHIIII USOO5512817A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Nagaraj (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 30, 1996 54 BANDGAP VOLTAGE REFERENCE 5,309,083 5/1994 Pierret et al.... 323/313 GENERATOR 5,39980 2/1995
IIIHIIII USOO5512817A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Nagaraj (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 30, 1996 54 BANDGAP VOLTAGE REFERENCE 5,309,083 5/1994 Pierret et al.... 323/313 GENERATOR 5,39980 2/1995
United States Patent (19) Mazin et al.
 United States Patent (19) Mazin et al. (54) HIGH SPEED FULL ADDER 75 Inventors: Moshe Mazin, Andover; Dennis A. Henlin, Dracut; Edward T. Lewis, Sudbury, all of Mass. 73 Assignee: Raytheon Company, Lexington,
United States Patent (19) Mazin et al. (54) HIGH SPEED FULL ADDER 75 Inventors: Moshe Mazin, Andover; Dennis A. Henlin, Dracut; Edward T. Lewis, Sudbury, all of Mass. 73 Assignee: Raytheon Company, Lexington,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,815,941 B2. Butler (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 9, 2004
 USOO6815941B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,815,941 B2 Butler (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 9, 2004 (54) BANDGAP REFERENCE CIRCUIT 6,052,020 * 4/2000 Doyle... 327/539 6,084,388 A 7/2000 Toosky
USOO6815941B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,815,941 B2 Butler (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 9, 2004 (54) BANDGAP REFERENCE CIRCUIT 6,052,020 * 4/2000 Doyle... 327/539 6,084,388 A 7/2000 Toosky
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,080,983 B2
 US008080983B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: LOurens et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 20, 2011 (54) LOW DROP OUT (LDO) BYPASS VOLTAGE 6,465,994 B1 * 10/2002 Xi... 323,274 REGULATOR 7,548,051
US008080983B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: LOurens et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 20, 2011 (54) LOW DROP OUT (LDO) BYPASS VOLTAGE 6,465,994 B1 * 10/2002 Xi... 323,274 REGULATOR 7,548,051
U.S.C. 154(b) by 21 days. (21) Appl. No.: 09/784,724 (22) Filed: Feb. 15, 2001 (51) Int. Cl... HO3F 3/45 330/300 'YG) T -- L.
 (12) United States Patent Ivanov et al. USOO64376B1 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) SLEW RATE BOOST CIRCUITRY AND METHOD (75) Inventors: Vadim V. Ivanov; David R. Baum, both of Tucson,
(12) United States Patent Ivanov et al. USOO64376B1 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) SLEW RATE BOOST CIRCUITRY AND METHOD (75) Inventors: Vadim V. Ivanov; David R. Baum, both of Tucson,
USOO A. United States Patent (19) (11 Patent Number: 5,422,590 Coffman et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 1995
 b III USOO5422590A United States Patent (19) (11 Patent Number: 5,422,590 Coffman et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 1995 54 HIGH VOLTAGE NEGATIVE CHARGE 4,970,409 11/1990 Wada et al.... 307/264 PUMP WITH
b III USOO5422590A United States Patent (19) (11 Patent Number: 5,422,590 Coffman et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 1995 54 HIGH VOLTAGE NEGATIVE CHARGE 4,970,409 11/1990 Wada et al.... 307/264 PUMP WITH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 2012014.6687A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/014.6687 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: (54) IMPEDANCE CALIBRATION CIRCUIT AND Publication Classification MPEDANCE
US 2012014.6687A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/014.6687 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: (54) IMPEDANCE CALIBRATION CIRCUIT AND Publication Classification MPEDANCE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Muza (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 6, 2012 HIGH IMPEDANCE BASING NETWORK (57) ABSTRACT
 US 20120223 770A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0223770 A1 Muza (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 6, 2012 (54) RESETTABLE HIGH-VOLTAGE CAPABLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 327/581
US 20120223 770A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0223770 A1 Muza (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 6, 2012 (54) RESETTABLE HIGH-VOLTAGE CAPABLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 327/581
M3 d. (12) United States Patent US 7,317,435 B2. Jan. 8, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (75) Inventor: Wei-Chieh Hsueh, Tainan (TW) T GND
 US7317435B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 8, 2008 (54) PIXEL DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHD FR USE IN ACTIVE MATRIX LED WITH THRESHLD VLTAGE CMPENSATIN (75) Inventor:
US7317435B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 8, 2008 (54) PIXEL DRIVING CIRCUIT AND METHD FR USE IN ACTIVE MATRIX LED WITH THRESHLD VLTAGE CMPENSATIN (75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) Price, Jr.
 United States Patent (19) Price, Jr. 11 4) Patent Number: Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 1986 4) (7) (73) 21) 22 1) 2 8) NPN BAND GAP VOLTAGE REFERENCE Inventor: John J. Price, Jr., Mesa, Ariz. Assignee: Motorola,
United States Patent (19) Price, Jr. 11 4) Patent Number: Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 1986 4) (7) (73) 21) 22 1) 2 8) NPN BAND GAP VOLTAGE REFERENCE Inventor: John J. Price, Jr., Mesa, Ariz. Assignee: Motorola,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,940,338 B2. Kizaki et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005
 USOO694.0338B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kizaki et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT 6,570,436 B1 * 5/2003 Kronmueller et al.... 327/538 (75)
USOO694.0338B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kizaki et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT 6,570,436 B1 * 5/2003 Kronmueller et al.... 327/538 (75)
United States Patent (19) Onuki et al.
 United States Patent (19) Onuki et al. 54). IGNITION APPARATUS FOR AN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE 75 Inventors: Hiroshi Onuki; Takashi Ito, both of Hitachinaka, Katsuaki Fukatsu, Naka-gun; Ryoichi Kobayashi,
United States Patent (19) Onuki et al. 54). IGNITION APPARATUS FOR AN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE 75 Inventors: Hiroshi Onuki; Takashi Ito, both of Hitachinaka, Katsuaki Fukatsu, Naka-gun; Ryoichi Kobayashi,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008019 1794A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0191794 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 14, 2008 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FORTUNING AN Publication Classification
US 2008019 1794A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0191794 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 14, 2008 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FORTUNING AN Publication Classification
(51) Int. Cl... HoH 316 trolling a state of conduction of AC current between the
 USOO58599A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,8,599 ROSenbaum () Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54 GROUND FAULT CIRCUIT INTERRUPTER 57 ABSTRACT SYSTEM WITH UNCOMMITTED CONTACTS A ground fault
USOO58599A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,8,599 ROSenbaum () Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54 GROUND FAULT CIRCUIT INTERRUPTER 57 ABSTRACT SYSTEM WITH UNCOMMITTED CONTACTS A ground fault
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Tang USOO647.6671B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 5, 2002 (54) PING-PONG AMPLIFIER WITH AUTO ZERONG AND CHOPPING (75) Inventor: Andrew T. K. Tang, San Jose, CA (US)
(12) United States Patent Tang USOO647.6671B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 5, 2002 (54) PING-PONG AMPLIFIER WITH AUTO ZERONG AND CHOPPING (75) Inventor: Andrew T. K. Tang, San Jose, CA (US)
(12) (10) Patent N0.: US 6,538,473 B2 Baker (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 25, 2003
 United States Patent US006538473B2 (12) (10) Patent N0.: Baker (45) Date of Patent: Mar., 2003 (54) HIGH SPEED DIGITAL SIGNAL BUFFER 5,323,071 A 6/1994 Hirayama..... 307/475 AND METHOD 5,453,704 A * 9/1995
United States Patent US006538473B2 (12) (10) Patent N0.: Baker (45) Date of Patent: Mar., 2003 (54) HIGH SPEED DIGITAL SIGNAL BUFFER 5,323,071 A 6/1994 Hirayama..... 307/475 AND METHOD 5,453,704 A * 9/1995
IIHIII III. Azé V-y (Y. United States Patent (19) Remillard et al. Aa a C (> 2,4122.2% Z4622 C. A. 422 s (2/7aa/Z eazazazzasa saaaaaze
 United States Patent (19) Remillard et al. (54) LOCK-IN AMPLIFIER 75 Inventors: Paul A. Remillard, Littleton, Mass.; Michael C. Amorelli, Danville, N.H. 73) Assignees: Louis R. Fantozzi, N.H.; Lawrence
United States Patent (19) Remillard et al. (54) LOCK-IN AMPLIFIER 75 Inventors: Paul A. Remillard, Littleton, Mass.; Michael C. Amorelli, Danville, N.H. 73) Assignees: Louis R. Fantozzi, N.H.; Lawrence
United States Patent (19) Ohta
 United States Patent (19) Ohta (54) NON-SATURATING COMPLEMENTARY TYPE UNITY GAIN AMPLIFER 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Genichiro Ohta, Ebina, Japan Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan
United States Patent (19) Ohta (54) NON-SATURATING COMPLEMENTARY TYPE UNITY GAIN AMPLIFER 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Genichiro Ohta, Ebina, Japan Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan
United States Patent (19) Minowa
 United States Patent (19) Minowa 54 ANALOG DISPLAY ELECTRONIC STOPWATCH (75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Yoshiki Minowa, Suwa, Japan Kubushiki Kaisha Suwa Seikosha, Tokyo, Japan 21) Appl. No.: 30,963 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Minowa 54 ANALOG DISPLAY ELECTRONIC STOPWATCH (75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Yoshiki Minowa, Suwa, Japan Kubushiki Kaisha Suwa Seikosha, Tokyo, Japan 21) Appl. No.: 30,963 22 Filed:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,765,374 B1
 USOO6765374B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2004 (54) LOW DROP-OUT REGULATOR AND AN 6,373.233 B2 * 4/2002 Bakker et al.... 323/282 POLE-ZERO CANCELLATION
USOO6765374B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2004 (54) LOW DROP-OUT REGULATOR AND AN 6,373.233 B2 * 4/2002 Bakker et al.... 323/282 POLE-ZERO CANCELLATION
II I III. United States Patent (19) Johnson, Jr. 73 Assignee: Exide Electronics Corporation,
 United States Patent (19) Johnson, Jr. (54) ISOLATED GATE DRIVE (75) Inventor: Robert W. Johnson, Jr., Raleigh, N.C. 73 Assignee: Exide Electronics Corporation, Raleigh, N.C. (21) Appl. No.: 39,932 22
United States Patent (19) Johnson, Jr. (54) ISOLATED GATE DRIVE (75) Inventor: Robert W. Johnson, Jr., Raleigh, N.C. 73 Assignee: Exide Electronics Corporation, Raleigh, N.C. (21) Appl. No.: 39,932 22
6,064,277 A * 5/2000 Gilbert 331/117 R 6,867,658 Bl * 3/2005 Sibrai et al 331/185 6,927,643 B2 * 8/2005 Lazarescu et al. 331/186. * cited by examiner
 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US007274264B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent o.: US 7,274,264 B2 Gabara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep.25,2007 (54) LOW-POWER-DISSIPATIO
111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US007274264B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent o.: US 7,274,264 B2 Gabara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep.25,2007 (54) LOW-POWER-DISSIPATIO
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O286333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0286333 A1 Gupta et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) HIGH-VOLTAGE TOLERANT INPUT BUFFER CIRCUIT (76)
(19) United States US 2005O286333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0286333 A1 Gupta et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) HIGH-VOLTAGE TOLERANT INPUT BUFFER CIRCUIT (76)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,353,344 B1
 USOO635,334.4B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lafort (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 5, 2002 (54) HIGH IMPEDANCE BIAS CIRCUIT WO WO 96/10291 4/1996... HO3F/3/185 (75) Inventor: Adrianus M. Lafort,
USOO635,334.4B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lafort (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 5, 2002 (54) HIGH IMPEDANCE BIAS CIRCUIT WO WO 96/10291 4/1996... HO3F/3/185 (75) Inventor: Adrianus M. Lafort,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,577,002 B2. Yang (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 18, 2009
 US007577002B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,577,002 B2 Yang (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 18, 2009 (54) FREQUENCY HOPPING CONTROL CIRCUIT 5,892,352 A * 4/1999 Kolar et al.... 323,213 FOR
US007577002B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,577,002 B2 Yang (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 18, 2009 (54) FREQUENCY HOPPING CONTROL CIRCUIT 5,892,352 A * 4/1999 Kolar et al.... 323,213 FOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,433,976 B1. Phillips (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 13, 2002
 USOO6433976B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,433,976 B1 Phillips (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 13, 2002 (54) INSTANTANEOUS ARC FAULT LIGHT 4,791,518 A 12/1988 Fischer... 361/42 DETECTOR WITH
USOO6433976B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,433,976 B1 Phillips (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 13, 2002 (54) INSTANTANEOUS ARC FAULT LIGHT 4,791,518 A 12/1988 Fischer... 361/42 DETECTOR WITH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O108129A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0108129 A1 Voglewede et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL FOR (21) Appl. No.: 10/012,530 DIGITAL
US 2003O108129A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0108129 A1 Voglewede et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL FOR (21) Appl. No.: 10/012,530 DIGITAL
VG1P I MlP EN 20 MZPHFVGZP. mm mm m nuunnyyo I]! [(1816 [[Lllllllllllllllllll. VG1N MIN \gp L2 M2N [ vg2n V1.. V2. 5,508,639 Apr.
![VG1P I MlP EN 20 MZPHFVGZP. mm mm m nuunnyyo I]! [(1816 [[Lllllllllllllllllll. VG1N MIN \gp L2 M2N [ vg2n V1.. V2. 5,508,639 Apr. VG1P I MlP EN 20 MZPHFVGZP. mm mm m nuunnyyo I]! [(1816 [[Lllllllllllllllllll. VG1N MIN \gp L2 M2N [ vg2n V1.. V2. 5,508,639 Apr.](/thumbs/72/66774825.jpg) United States Patent [191 Fattaruso mm mm m nuunnyyo I]! [(1816 [[Lllllllllllllllllll [11] Patent Number: [45] Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 1996 [54] CMOS CLOCK DRIVERS WITH INDUCTIVE COUPLING [75] Inventor:
United States Patent [191 Fattaruso mm mm m nuunnyyo I]! [(1816 [[Lllllllllllllllllll [11] Patent Number: [45] Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 1996 [54] CMOS CLOCK DRIVERS WITH INDUCTIVE COUPLING [75] Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O187416A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0187416A1 Bakker (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) SMART DRIVER FOR FLYBACK Publication Classification CONVERTERS
US 2011 O187416A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0187416A1 Bakker (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) SMART DRIVER FOR FLYBACK Publication Classification CONVERTERS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150366008A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0366008 A1 Barnetson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 17, 2015 (54) LED RETROFIT LAMP WITH ASTRIKE (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 20150366008A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0366008 A1 Barnetson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 17, 2015 (54) LED RETROFIT LAMP WITH ASTRIKE (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,766,692 B1
 US008766692B1 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Durbha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 1, 2014 (54) SUPPLY VOLTAGE INDEPENDENT SCHMITT (56) References Cited TRIGGER INVERTER U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
US008766692B1 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Durbha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 1, 2014 (54) SUPPLY VOLTAGE INDEPENDENT SCHMITT (56) References Cited TRIGGER INVERTER U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Bohan, Jr. (54) 75 RELAXATION OSCILLATOR TYPE SPARK GENERATOR Inventor: John E. Bohan, Jr., Minneapolis, Minn. (73) Assignee: Honeywell Inc., Minneapolis, Minn. (21) Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Bohan, Jr. (54) 75 RELAXATION OSCILLATOR TYPE SPARK GENERATOR Inventor: John E. Bohan, Jr., Minneapolis, Minn. (73) Assignee: Honeywell Inc., Minneapolis, Minn. (21) Appl. No.:
Norwalk, Conn. (21) Appl. No.: 344, Filed: Jan. 29, ) Int. Cl... G05B 19/40
 United States Patent (19) Overfield 54 CONTROL CIRCUIT FOR STEPPER MOTOR (75) Inventor: Dennis O. Overfield, Fairfield, Conn. 73 Assignee: The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, Norwalk, Conn. (21) Appl. No.: 344,247
United States Patent (19) Overfield 54 CONTROL CIRCUIT FOR STEPPER MOTOR (75) Inventor: Dennis O. Overfield, Fairfield, Conn. 73 Assignee: The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, Norwalk, Conn. (21) Appl. No.: 344,247
Si,"Sir, sculptor. Sinitialising:
 (19) United States US 20090097281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0097281 A1 LIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2009 (54) LEAKAGE-INDUCTANCE ENERGY Publication Classification RECYCLING
(19) United States US 20090097281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0097281 A1 LIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2009 (54) LEAKAGE-INDUCTANCE ENERGY Publication Classification RECYCLING
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2. Drottar (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 5, 2007
 United States Patent US0072274.14B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,227.414 B2 Drottar (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 5, 2007 (54) APPARATUS FOR RECEIVER 5,939,942 A * 8/1999 Greason et al.... 330,253 EQUALIZATION
United States Patent US0072274.14B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,227.414 B2 Drottar (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 5, 2007 (54) APPARATUS FOR RECEIVER 5,939,942 A * 8/1999 Greason et al.... 330,253 EQUALIZATION
VDD. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. (19) United States. I Data. (76) Inventors: Wen-Cheng Yen, Taichung (TW);
 (19) United States US 2004O150593A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150593 A1 Yen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) ACTIVE MATRIX LED DISPLAY DRIVING CIRCUIT (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2004O150593A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150593 A1 Yen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) ACTIVE MATRIX LED DISPLAY DRIVING CIRCUIT (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,597,159 B2
 USOO65971.59B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yang (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 22, 2003 (54) PULSE WIDTH MODULATION 5,790,391 A 8/1998 Stich et al. CONTROLLER HAVING FREQUENCY 5,903,138 A 5/1999
USOO65971.59B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yang (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 22, 2003 (54) PULSE WIDTH MODULATION 5,790,391 A 8/1998 Stich et al. CONTROLLER HAVING FREQUENCY 5,903,138 A 5/1999
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,889,643 Elms (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 30, 1999
 USOO5889643A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,889,643 Elms (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 30, 1999 54). APPARATUS FOR DETECTING ARCING Primary Examiner Jeffrey Gaffin FAULTS AND GROUND FAULTS IN
USOO5889643A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,889,643 Elms (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 30, 1999 54). APPARATUS FOR DETECTING ARCING Primary Examiner Jeffrey Gaffin FAULTS AND GROUND FAULTS IN
United States Patent (19) Archibald
 United States Patent (19) Archibald 54 ELECTROSURGICAL UNIT 75 Inventor: G. Kent Archibald, White Bear Lake, Minn. 73 Assignee: Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing Company, Saint Paul, Minn. (21) Appl.
United States Patent (19) Archibald 54 ELECTROSURGICAL UNIT 75 Inventor: G. Kent Archibald, White Bear Lake, Minn. 73 Assignee: Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing Company, Saint Paul, Minn. (21) Appl.
(*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this E. E. E. " "...O.E.
 USOO6957055B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,957,055 B2 Gamliel (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 18, 2005 (54) DOUBLE BALANCED FET MIXER WITH 5,361,409 A 11/1994 Vice... 455/326 HIGH IP3 AND
USOO6957055B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,957,055 B2 Gamliel (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 18, 2005 (54) DOUBLE BALANCED FET MIXER WITH 5,361,409 A 11/1994 Vice... 455/326 HIGH IP3 AND
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7123644B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 2006 (54) PEAK CANCELLATION APPARATUS OF BASE STATION TRANSMISSION UNIT (75) Inventors: Won-Hyoung Park,
USOO7123644B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 2006 (54) PEAK CANCELLATION APPARATUS OF BASE STATION TRANSMISSION UNIT (75) Inventors: Won-Hyoung Park,
73 Assignee: Dialight Corporation, Manasquan, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 09/144, Filed: Aug. 31, 1998 (51) Int. Cl... G05F /158; 315/307
 United States Patent (19) Grossman et al. 54) LED DRIVING CIRCUITRY WITH VARIABLE LOAD TO CONTROL OUTPUT LIGHT INTENSITY OF AN LED 75 Inventors: Hyman Grossman, Lambertville; John Adinolfi, Milltown, both
United States Patent (19) Grossman et al. 54) LED DRIVING CIRCUITRY WITH VARIABLE LOAD TO CONTROL OUTPUT LIGHT INTENSITY OF AN LED 75 Inventors: Hyman Grossman, Lambertville; John Adinolfi, Milltown, both
rectifying smoothing circuit
 USOO648671.4B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ushida et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) HALF-BRIDGE INVERTER CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Atsuya Ushida, Oizumi-machi
USOO648671.4B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ushida et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) HALF-BRIDGE INVERTER CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Atsuya Ushida, Oizumi-machi
3.1 vs. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1. (19) United States FB2 D ME VSS VOLIAGE REFER
 (19) United States US 20020089860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0089860 A1 Kashima et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT (76) Inventors: Masato Kashima,
(19) United States US 20020089860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0089860 A1 Kashima et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT (76) Inventors: Masato Kashima,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030042949A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0042949 A1 Si (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2003 (54) CURRENT-STEERING CHARGE PUMP Related U.S. Application Data
US 20030042949A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0042949 A1 Si (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2003 (54) CURRENT-STEERING CHARGE PUMP Related U.S. Application Data
United States Patent (19) 11) 4,163,947
 United States Patent (19) 11) Weedon (45) Aug. 7, 1979 (54) CURRENT AND VOLTAGE AUTOZEROING Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Weingarten, Maxham & INTEGRATOR Schurgin 75 Inventor: Hans J. Weedon, Salem, Mass. (57)
United States Patent (19) 11) Weedon (45) Aug. 7, 1979 (54) CURRENT AND VOLTAGE AUTOZEROING Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Weingarten, Maxham & INTEGRATOR Schurgin 75 Inventor: Hans J. Weedon, Salem, Mass. (57)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,549,050 B1
 USOO6549050B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Meyers et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr., 2003 (54) PROGRAMMABLE LATCH THAT AVOIDS A 6,429,712 B1 8/2002 Gaiser et al.... 327/217 NON-DESIRED OUTPUT
USOO6549050B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Meyers et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr., 2003 (54) PROGRAMMABLE LATCH THAT AVOIDS A 6,429,712 B1 8/2002 Gaiser et al.... 327/217 NON-DESIRED OUTPUT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0162354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0162354 A1 Zhu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 27, 2013 (54) CASCODE AMPLIFIER (52) U.S. Cl. USPC... 330/278
(19) United States US 2013 0162354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0162354 A1 Zhu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 27, 2013 (54) CASCODE AMPLIFIER (52) U.S. Cl. USPC... 330/278
USOO A. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,272,450 Wisherd (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 1993
 O HIHHHHHHHHHHHHIII USOO5272450A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,272,450 Wisherd (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 1993 (54) DCFEED NETWORK FOR WIDEBANDRF POWER AMPLIFIER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS
O HIHHHHHHHHHHHHIII USOO5272450A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,272,450 Wisherd (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 1993 (54) DCFEED NETWORK FOR WIDEBANDRF POWER AMPLIFIER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,387,795 B1
 USOO6387795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shao (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) WAFER-LEVEL PACKAGING 5,045,918 A * 9/1991 Cagan et al.... 357/72 (75) Inventor: Tung-Liang Shao, Taoyuan
USOO6387795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shao (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) WAFER-LEVEL PACKAGING 5,045,918 A * 9/1991 Cagan et al.... 357/72 (75) Inventor: Tung-Liang Shao, Taoyuan
United States Patent (19) Sun
 United States Patent (19) Sun 54 INFORMATION READINGAPPARATUS HAVING A CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Chung-Yueh Sun, Tainan, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Mustek Systems, Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan 21 Appl. No. 916,941
United States Patent (19) Sun 54 INFORMATION READINGAPPARATUS HAVING A CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Chung-Yueh Sun, Tainan, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Mustek Systems, Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan 21 Appl. No. 916,941
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013
 (19) United States US 20130279282A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0279282 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013 (54) E-FUSE ARRAY CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... GI IC 17/16 (2013.01);
(19) United States US 20130279282A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0279282 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013 (54) E-FUSE ARRAY CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... GI IC 17/16 (2013.01);
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,705,355 B1
 USOO670.5355B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,705,355 B1 Wiesenfeld (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 16, 2004 (54) WIRE STRAIGHTENING AND CUT-OFF (56) References Cited MACHINE AND PROCESS NEAN
USOO670.5355B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,705,355 B1 Wiesenfeld (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 16, 2004 (54) WIRE STRAIGHTENING AND CUT-OFF (56) References Cited MACHINE AND PROCESS NEAN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
(19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,009,450 B2
 USOO700945OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,009,450 B2 Parkhurst et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 7, 2006 (54) LOW DISTORTION AND HIGH SLEW RATE OUTPUT STAGE FOR WOLTAGE FEEDBACK (56)
USOO700945OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,009,450 B2 Parkhurst et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 7, 2006 (54) LOW DISTORTION AND HIGH SLEW RATE OUTPUT STAGE FOR WOLTAGE FEEDBACK (56)
324/334, 232, ; 340/551 producing multiple detection fields. In one embodiment,
 USOO5969528A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,969,528 Weaver (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 1999 54) DUAL FIELD METAL DETECTOR 4,605,898 8/1986 Aittoniemi et al.... 324/232 4,686,471 8/1987
USOO5969528A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,969,528 Weaver (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 1999 54) DUAL FIELD METAL DETECTOR 4,605,898 8/1986 Aittoniemi et al.... 324/232 4,686,471 8/1987
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0194836A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0194836A1 Morris et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ISOLATED FLYBACK CONVERTER WITH (52) U.S. Cl. EFFICIENT LIGHT
(19) United States US 2013 0194836A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0194836A1 Morris et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ISOLATED FLYBACK CONVERTER WITH (52) U.S. Cl. EFFICIENT LIGHT
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,116,081 B2. Wilson (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 2006
 United States Patent USOO7116081 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Wilson (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 2006 (54) THERMAL PROTECTION SCHEME FOR 5,497,071 A * 3/1996 Iwatani et al.... 322/28 HIGH OUTPUT VEHICLE ALTERNATOR
United States Patent USOO7116081 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Wilson (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 2006 (54) THERMAL PROTECTION SCHEME FOR 5,497,071 A * 3/1996 Iwatani et al.... 322/28 HIGH OUTPUT VEHICLE ALTERNATOR
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7312649B2 (10) Patent No.: Origasa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 25, 2007 (54) VOLTAGE BOOSTER POWER SUPPLY 6,195.305 B1* 2/2001 Fujisawa et al.... 365,226 CIRCUIT 6,285,622
(12) United States Patent USOO7312649B2 (10) Patent No.: Origasa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 25, 2007 (54) VOLTAGE BOOSTER POWER SUPPLY 6,195.305 B1* 2/2001 Fujisawa et al.... 365,226 CIRCUIT 6,285,622
(12) United States Patent
 US008133074B1 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 13, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) GUIDED MISSILE/LAUNCHER TEST SET REPROGRAMMING INTERFACE ASSEMBLY
US008133074B1 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 13, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) GUIDED MISSILE/LAUNCHER TEST SET REPROGRAMMING INTERFACE ASSEMBLY
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Nagano 54 FULL WAVE RECTIFIER 75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Katsumi Nagano, Hiratsukashi, Japan Tokyo Shibaura Denki Kabushiki Kaisha, Kawasaki, Japan 21 Appl. No.: 188,662 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Nagano 54 FULL WAVE RECTIFIER 75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Katsumi Nagano, Hiratsukashi, Japan Tokyo Shibaura Denki Kabushiki Kaisha, Kawasaki, Japan 21 Appl. No.: 188,662 22 Filed:
part data signal (12) United States Patent control 33 er m - sm is US 7,119,773 B2
 US007 119773B2 (12) United States Patent Kim (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 10, 2006 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING GRAY LEVEL FOR DISPLAY PANEL (75) Inventor: Hak Su Kim, Seoul
US007 119773B2 (12) United States Patent Kim (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 10, 2006 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING GRAY LEVEL FOR DISPLAY PANEL (75) Inventor: Hak Su Kim, Seoul
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
11 Patent Number: 5,874,830 Baker (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 23, ADAPTIVELY BAISED VOLTAGE OTHER PUBLICATIONS
 USOO5874-83OA 11 Patent Number: Baker (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 23, 1999 United States Patent (19) 54 ADAPTIVELY BAISED VOLTAGE OTHER PUBLICATIONS REGULATOR AND OPERATING METHOD Micropower Techniques,
USOO5874-83OA 11 Patent Number: Baker (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 23, 1999 United States Patent (19) 54 ADAPTIVELY BAISED VOLTAGE OTHER PUBLICATIONS REGULATOR AND OPERATING METHOD Micropower Techniques,
USOO513828OA. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,138,280. Gingrich et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 11, 1992
 O USOO513828OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,138,280 Gingrich et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 11, 1992 54 MULTICHANNEL AMPLIFIER WITH GAIN MATCHING OTHER PUBLICATIONS (75) Inventors: Randal
O USOO513828OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,138,280 Gingrich et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 11, 1992 54 MULTICHANNEL AMPLIFIER WITH GAIN MATCHING OTHER PUBLICATIONS (75) Inventors: Randal
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,104 B1
 USOO6275104B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Holter (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 14, 2001 (54) MULTISTAGE AMPLIFIER WITH LOCAL 4,816,711 3/1989 Roza... 330/149 ERROR CORRECTION 5,030.925 7/1991
USOO6275104B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Holter (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 14, 2001 (54) MULTISTAGE AMPLIFIER WITH LOCAL 4,816,711 3/1989 Roza... 330/149 ERROR CORRECTION 5,030.925 7/1991
United States Patent (19) Rousseau et al.
 United States Patent (19) Rousseau et al. USOO593.683OA 11 Patent Number: 5,936,830 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 1999 54). IGNITION EXCITER FOR A GASTURBINE 58 Field of Search... 361/253, 256, ENGINE
United States Patent (19) Rousseau et al. USOO593.683OA 11 Patent Number: 5,936,830 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 1999 54). IGNITION EXCITER FOR A GASTURBINE 58 Field of Search... 361/253, 256, ENGINE
