MATLAB/SIMULINK Based Model of Single- Machine Infinite-Bus with TCSC for Stability Studies and Tuning Employing GA
|
|
|
- Doreen Reynolds
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vol:, No:3, 7 MATLAB/SIMULINK Based Model of Single- Machine Infinite-Bus with TCSC for Stability Studies and Tuning Employing GA Sidhartha Panda and Narayana Prasad Padhy International Science Index, Energy and Power Engineering Vol:, No:3, 7 waset.org/publication/56 Abstract With constraints on data availability and for study of power system stability it is adequate to model the synchronous generator with field circuit and one equivalent damper on q-axis known as the model.. This paper presents a systematic procedure for modelling and simulation of a single-machine infinite-bus power system installed with a thyristor controlled series compensator (TCSC) where the synchronous generator is represented by model., so that impact of TCSC on power system stability can be more reasonably evaluated. The model of the example power system is developed using MATLAB/SIMULINK which can be can be used for teaching the power system stability phenomena, and also for research works especially to develop generator controllers using advanced technologies. Further, the parameters of the TCSC controller are optimized using genetic algorithm. The non-linear simulation results are presented to validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach. Keywords Genetic algorithm, MATLAB/SIMULINK, modelling and simulation, power system stability, single-machine infinite-bus power system, thyristor controlled series compensator. δ NOMELATURE Rotor angle of synchronous generator in radians ω B Rotor speed deviation in rad/sec S m Generator slip in p.u. S mo Initial operating slip in p.u. H D Inertia constant Damping coefficient T m Mechanical power input in p.u. T e Electrical power output in p.u. E fd Excitation system voltage in p.u. T do Open circuit d-axis time constant in sec Sidhartha Panda is a research scholar in the Department of Electrical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, Uttaranchal, 47667, India. ( speeddee@iitr.ernet.in, panda_sidhartha@rediffmail.com). Narayana Prasad Padhy is Associate professor in the Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT, Roorkee India.( , nppeefee@iitr.ernet.in) T qo Open circuit q-axis time constant in sec x d d-axis synchronous reactance in p.u. x d d-axis transient reactance in p.u. x q q-axis synchronous reactance in p.u. x q q-axis transient reactance in p.u. X C Nominal reactance of the fixed capacitor C X P Inductive reactance of inductor L connected in σ α parallel with C. Conduction angle of TCSC Firing angle of TCSC k Compensation ratio, k = X C / X P T I. INTRODUCTION RADITIONALLY, for the small signal stability studies of a single-machine infinite-bus (SMIB) power system, the linear model of Phillips-Heffron has been used for years, providing reliable results []-[]. It has also been successfully used for designing and tuning the classical power system stabilizers (PSS). Although the model is a linear model, it is quite accurate for studying low frequency oscillations and stability of power systems. With the advent of Flexible AC Transmission System (FACTS) devices [3], such as thyristor controlled series compensator (TCSC), static synchronous compensator (STATCOM) and unified power flow controller (UPFC), the unified model of SMIB power system installed with a TCSC, STATCOM and a UPFC have been developed [4]-[6]. These models are the popular tools amongst power engineers for studying the dynamic behaviour of synchronous generators, with a view to design control equipment. However, the model only takes into account the generator main field winding and hence these models may not always yield a realistic dynamic assessment of the SMIB power system with FACTS because the generator damping winding in q-axis is not accounted for. Further, liner methods cannot properly capture complex dynamics of the system, especially during International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation (3) 7 56 scholar.waset.org/37-689/56
2 Vol:, No:3, 7 International Science Index, Energy and Power Engineering Vol:, No:3, 7 waset.org/publication/56 major disturbances. This presents difficulties for designing the FACTS controllers in that, the controllers designed to provide desired performance at small signal condition do not guarantee acceptable performance in the event of major disturbances. It is well known that the reactance adjusting of TCSC is a complex dynamic process. Effective design and accurate evaluation of the TCSC control strategy depend on the accuracy of modelling of this process. In [7], a systematic procedure for modeling, simulation and optimal tuning of TCSC controller in a SMIB power system was presented where the MATLAB/SIMULINK based model was developed and Genetic Algorithm (GA) was employed to design the TCSC controller. However, the model only takes into account the generator main field winding and the synchronous machine was represented by model (.). This paper presents a higher-order synchronous machine model, which includes one damper winding along the q-axis, for a power system installed with a TCSC. Despite significant strides in the development of advanced control schemes over the past two decades, the conventional lead-lag (LL) structure controller as well as the classical proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller and its variants, remain the controllers of choice in many industrial applications. These controller structures remain an engineer s preferred choice because of their structural simplicity, reliability, and the favorable ratio between performance and cost. Beyond these benefits, these controllers also offer simplified dynamic modeling, lower user-skill requirements, and minimal development effort, which are issues of substantial importance to engineering practice [8]-[9]. In [], a comparative study about the TCSC based controller design was presented, where it has been shown that that LL structured TCSC controller with the controller parameters optimized using Integral of Time multiplied Absolute value of the Error (ITAE) as objective function, gives the best system response compared to all other alternatives. In view of the above, a LL controller structure is used for the TCSC controller. The problem of TCSC controller parameter tuning is a complex exercise. A number of conventional techniques have been reported in the literature pertaining to design problems of conventional power system stabilizers namely: the eigenvalue assignment, mathematical programming, gradient procedure for optimization and also the modern control theory. Unfortunately, the conventional techniques are time consuming as they are iterative and require heavy computation burden and slow convergence. In addition, the search process is susceptible to be trapped in local minima and the solution obtained may not be optimal []. Genetic Algorithm (GA) is becoming popular for solving the optimisation problems in different fields of application, mainly because of their robustness in finding an optimal solution and ability to provide a near-optimal solution close to a global minimum. Unlike strict mathematical methods, the GA does not require the condition that the variables in the optimisation problem be continuous and different; it only requires that the problem to be solved can be computed. GA employs search procedures based on the mechanics of natural selection and survival of the fittest. The GAs, which use a multiple-point instead of a single-point search and work with the coded structure of variables instead of the actual variables, require only the objective function, thereby making searching for a global optimum simpler []. Therefore, in the present work GA is employed to optimize the parameters of TCSC controller. This paper is organized as follows. In Section II, the modeling of power system under study, which is a SMIB power system with a TCSC, is presented. The proposed controller structures and problem formulation are described in Section III. A short overview of GA is presented in Section IV. Simulation results are provided and discussed in Section V and conclusions are given in Section VI II. POWER SYSTEM UNDER STUDY The SMIB power system with TCSC shown in Fig. is considered in this study. The synchronous generator is delivering power to the infinite-bus through a double circuit transmission line and a TCSC. In Fig., V t and Eb are the generator terminal and infinite bus voltage respectively; X T, X L and XTH represent the reactance of the transformer, transmission line per circuit and the Thevenin s impedance of the receiving end system respectively. Generator V t θ jxt jx L jx L TCSC E b jx TH Infinite-bus Fig. Single-machine infinite-bus power system with TCSC A. Modelling the Synchronous Generator Infinite-bus Power System The synchronous generator is represented by model., i.e. with field circuit and one equivalent damper winding on q- axis. The machine equations are [3]: dδ = ωb dt ( S S ) m mo dsm = [ D ( Sm Smo ) + Tm Te ] () dt H [ E ( q + xd x d ) id + E fd ] de q = (3) dt T do [ ( E d + xq x q ) iq ] de d = (4) dt T qo () International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation (3) 7 56 scholar.waset.org/37-689/56
3 Vol:, No:3, 7 International Science Index, Energy and Power Engineering Vol:, No:3, 7 waset.org/publication/56 The electrical torque E d, E q, i d and i q as: Te is expressed in terms of variables ( x d x q ) id iq Te = E d id + E q iq + (5) For a lossless network, the stator algebraic equations and the network equations are expressed as: E q + x d id = vq (6) E d x q iq = vd (7) vq = xe id + Eb cosδ (8) vd = xe iq Eb sinδ (9) Solving the above equations, the variables i d be obtained as: E b cosδ E q id = x e + x d E b sinδ + E q iq = x e + x q and i q can () () The above notation for the variables and parameters described are standard and defined in the nomenclature. For more details, the readers are suggested to refer [3]-[4]. B. Modelling the Thyristor Controlled Series Compensator (TCSC) TCSC is one of the most important and best known series FACTS controllers. It has been in use for many years to increase line power transfer as well as to enhance system stability. The basic module of a TCSC is shown in Fig.. It consists of three components: capacitor banks C, bypass inductor L and bidirectional thyristors T and T. The firing angles of the thyristors are controlled to adjust the TCSC reactance in accordance with a system control algorithm, normally in response to some system parameter variations. i S i L i C L V C T T Fig. Basic module of a TCSC i S According to the variation of the thyristor firing angle (α ) or conduction angle (σ ), this process can be modelled as a fast switch between corresponding reactance offered to the power system. Assuming that the total current passing through the TCSC is sinusoidal; the equivalent reactance at the fundamental frequency can be represented as a variable reactance X TCSC. There exists a steady-state relationship between α and the reactance X TCSC. This relationship can be described by the following equation [5]: X ( σ sinσ ) X ( α ) X C + TCSC = C ( XC X P ) π 4X cos C ( σ / ) [ k tan( kσ / ) tan( σ / ) + ( X X ) ( k C P ) π () Since the relationship between α and the equivalent fundamental frequency reactance offered by TCSC, X TCSC ( α ) is a unique-valued function, the TCSC is modeled here as a variable capacitive reactance within the operating region defined by the limits imposed by α. Thus X TCSCmin X TCSC X TCSCmax, with X TCSCmax = X TCSC (α min ) and X TCSCmin = X TCSC (8 ) = X C. In this paper, the controller is assumed to operate only in the capacitive region, i.e., α min > α r where α r corresponds to the resonant point, as the inductive region associated with 9 < α < α r induces high harmonics that cannot be properly modeled in stability studies. III. PROBLEM FORMULATION A. Structure of the TCSC Controller The structure of TCSC-based damping controller, to modulate the reactance offered by the TCSC, X TCSC ( α ) is shown in Fig. 3. The input signal of the proposed controllers is the speed deviation ( ω), and the output signal is the reactance offered by the TCSC, X TCSC ( α ). The structure consists of a gain block with gain K T, a signal washout block and two-stage phase compensation blocks. The signal washout block serves as a high-pass filter, with the time constant T WT, high enough to allow signals associated with oscillations in input signal to pass unchanged. σ + + Δσ σ + Δσ + st3t + st4t Max. + st TCSC Min. + stt + stt Two stage lead-lag Block stwt + stwt Washout Block X TCSC ( α ) Output Fig. 3 Structure of TCSC-based controller K T Gain Block Δω Input International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation (3) 7 56 scholar.waset.org/37-689/56
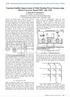
4 Vol:, No:3, 7 International Science Index, Energy and Power Engineering Vol:, No:3, 7 waset.org/publication/56 From the viewpoint of the washout function, the value of T WT is not critical and may be in the range of to seconds [4]. The phase compensation block (time constants T T, T T and T 3T, T 4T ) provides the appropriate phase-lead characteristics to compensate for the phase lag between input and the output signals. In the Fig. 3, σ represents the initial conduction angle as desired by the power flow control loop. The steady state power flow loop acts quite slowly in practice and hence, in the present study, σ is assumed to be constant during large disturbance transient period. B. Problem Formulation In the present study, a washout time constant of T WT =s is used. The controller gain K T and the time constants T T, T T, T 3T and T 4T are to be determined. During steady state conditions Δ σ and σ are constant. During dynamic conditions, conduction angle ( σ ) and hence X TCSC ( α ) is modulated to improve power system stability. The desired value of compensation is obtained through the change in the conduction angle ( Δ σ ), according to the variation in Δ ω. The effective conduction angle σ during dynamic conditions is given by: σ = σ + Δσ (3) C. Objective Function In this paper, an Integral of Time multiplied Absolute value of the Error (ITAE) is taken as the objective function []. The objective function is defined as follows: tsim J = t Δ ω ()dt t (4) where, Δ ω() t is the speed deviation following a disturbance and tsim is the time range of simulation. IV. OVERVIEW OF GENETIC ALGORITHM (GA) GA has been used for optimizing the parameters of the control system that are complex and difficult to solve by conventional optimisation methods. GA maintains a set of candidate solutions called population and repeatedly modifies them. At each step, the GA selects individuals from the current population to be parents and uses them to produce the children for the next generation. Candidate solutions are usually represented as strings of fixed length, called chromosomes. A fitness or objective function is used to reflect the goodness of each member of the population. Given a random initial population, GA operates in cycles called generations, as follows: Each member of the population is evaluated using a fitness function. The population undergoes reproduction in a number of iterations. One or more parents are chosen stochastically, but strings with higher fitness values have higher probability of contributing an offspring. Genetic operators, such as crossover and mutation, are applied to parents to produce offspring. The offspring are inserted into the population and the process is repeated. The computational flow chart of the GA optimization approach followed in the present paper is shown in Fig. 5. Gen.=Gen.+ Start Specify the parameters for GA Generate initial population Gen.= Time-domain simulation Find the fittness of each individual in the current population Gen. > Max. Gen.? Yes No Apply GA operators: selection,crossover and mutation Fig. 4 Flowchart of the genetic algorithm Stop Tuning a controller parameter can be viewed as an optimization problem in multi-modal space as many settings of the controller could be yielding good performance. Traditional method of tuning doesn t guarantee optimal parameters and in most cases the tuned parameters needs improvement through trial and error. In GA based method, the tuning process is associated with an optimality concept through the defined objective function and the time domain simulation. The designer has the freedom to explicitly specify the required performance objectives in terms of time domain bounds on the closed loop responses. Hence the GA methods yield optimal parameters and the method is free from the curse of local optimality. In view of the above, the proposed approach employs GA to solve this optimization problem and search for optimal set of TCSC-based damping controller parameters. V. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS A. Application of GA Optimization Technique In order to optimally tune the parameters of the TCSCbased controller, as well as to assess its performance and robustness under wide range of operating conditions with various fault disturbances and fault clearing sequences, the MATLAB/SIMULINK model of the example power system shown in Fig. is developed using equations () (9). The developed MATLAB/SIMULINK model of synchronous generator with TCSC is shown in Fig. 5. International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation (3) scholar.waset.org/37-689/56
5 Vol:, No:3, 7 D Electrical power after fault clearence [pe] Mechanical power input Peo Damping -K- -K- /H Smo s *pi*f Speed sig s sigo Power angle [delta] International Science Index, Energy and Power Engineering Vol:, No:3, 7 waset.org/publication/56 Clock Pe Electrical power before & during fault Efd [efd] xd-xdd xd-xd [id] xd-xd xq-xqd [iq] [edd] [eqd] [id] [iq] Reactance Xe, before, during & after fault clearence Clock (xd-xd)id (xd-xxq)id Mux [Xe] Time Time Switch Kp Switch. Tw.s Tw.s+ T.s+ T.s+ Saturation. Clock. Xtcsco Xe Reactance before & after fault Fig. 5 SIMULINK model of SMIB with TCSC controller /Tdo -K- -K- /Tqo f(u) s s Eq [edd] Ed Electrical power after fault clearence [pe] [eqd] Pe = Eq iq + Ed id +(xd - xq) id iq [delta] Eb [Xe] [id] [delta] [efd] Efd [iq] [Xe] Mux Mux Saturation` T3.s+ T4.s+ xtcsc sig sigma to xtcsc f(u) dsig sig+dsig [id] id=(ebcos(delta) - Eq)/(Xe+xd) iq=(ebsin(delta) + Ed)/(Xe+xq) f(u) [iq] Vt = Sqrt (vq ^ +vd^) f(u) Vt = sqrt [(( -Xe id + Ebcos(delta))^) +((Xe iq -Eb sin(delta))^)] 4.5s+ Excitation Vref xdd-xqd. Fig. 6 SIMULINK model for calculation of i d, i q, E d, E q and P e International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation (3) scholar.waset.org/37-689/56
6 Vol:, No:3, 7 International Science Index, Energy and Power Engineering Vol:, No:3, 7 waset.org/publication/56 The SIMULINK model for calculation of i d, i q, E d, E q and P e is shown in Fig.6. The relevant parameters are given in appendix. The objective function is evaluated for each individual by simulating the system dynamic model considering a threephase fault at the generator terminal busbar at t =. sec. For the purpose of optimisation of equation (4), routines from GA toolbox were used. The fitness function comes from timedomain simulation of power system model shown in Fig. 5. Using each set of controllers parameters, the time-domain simulation is performed and the fitness value is determined. Good solutions are selected, and by means of the GA operators, new and better solutions are achieved. This procedure continues until a desired termination criterion is achieved. Although the chances of GA giving a local optimal solution are very few, sometimes getting a suboptimal solution is also possible. While applying GA, a number of parameters are required to be specified. An appropriate choice of these parameters affects the speed of convergence of the algorithm. For different problems, it is possible that the same parameters for GA do not give the best solution, and so these can be changed according to the situation. TABLE I PARAMETERS USED IN GENETIC ALGORITHM Parameter Value/Type Maximum generations Population size 5 Type of selection Normal geometric [.8] Type of crossover Arithmetic [] Type of mutation Nonuniform [ 3] Termination method Maximum generation TABLE II OPTIMIZED TCSC CONTROLLER PARAMETERS USING GENETIC ALGORITHM Gain Time constants K T T T T T T 3T T 4T In Table I the parameters for GA optimization routines are given. The description of these operators and their properties can be found in reference [6]. One more important point that affects the optimal solution more or less is the range for unknowns. For the very first execution of the programme, a wider solution space can be given and after getting the solution one can shorten the solution space nearer to the values obtained in the previous iteration. Optimization is terminated by the prespecified number of generations. The best individual of the final generation is the solution. The optimized parameters are shown in Table II. Fig. 7 shows the convergence rate objective function J with the number of generations. Convergence of J Generations Fig. 7 Convergence rate of objective function J. B. Simulation Results In order to show the advantages of modelling the synchronous generator with TCSC controller and tuning its parameters in the way presented in this paper, simulation studies are carried out for the example power system subjected to various severe disturbances as well as small disturbance. The following cases are considered: Case-: Three-phase Fault Disturbance A three phase fault is applied at the generator terminal busbar at t = sec and cleared after 5 cycles. The original system is restored upon the fault clearance. To study the performance of TCSC controller, two cases are considered; with and without genetically tuned TCSC controller. The response without the controller (no control) is shown with dotted line with legend ; and the responses with TCSC controller optimized using GA is shown with solid line with legend GATCSC. δ (deg) Fig. 8 Variation of power angle δ, without and with TCSC controller for a 5-cycle three-phase fault disturbance (Case-) The system power angle response for the above contingency is shown in Fig. 8. It is clear from the Fig. 8 that, without controller even though the system is stable, power system oscillations are poorly damped. It is also clear that, proposed TCSC controller significantly suppresses the oscillations in the power angle and provides good damping characteristics to low frequency oscillations by stabilizing the International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation (3) scholar.waset.org/37-689/56
7 Vol:, No:3, Δ ω -.5 E fd.5 -. Fig. 9 Variation of speed deviation Δ ω : Case-.5 Fig. 3 Variation of voltage E fd : Case- International Science Index, Energy and Power Engineering Vol:, No:3, 7 waset.org/publication/56 P e E d E q Fig. Variation of electrical power P e : Case- Fig. Variation of voltage E d : Case-.9 Fig. Variation of voltage E q : Case- I d I q V t Fig. 4 Variation of terminal voltage V t : Case Fig. 5 Variation of current I d : Case Fig. 6 Variation of current q International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation (3) scholar.waset.org/37-689/56
8 Vol:, No:3, X TCSC.55.5 P e.7.6 International Science Index, Energy and Power Engineering Vol:, No:3, 7 waset.org/publication/ Fig. 7 Variation of X TCSC : Case- system much faster. Figs. 9-7 shows the variation of speed deviation Δ ω,electrical power P e, voltages E d, E q, E fd, V t, currents i d, i q and reactance offered by TCSC: X TCSC, respectively all with respect to time for the above mentioned contingency (Case-). It is clear from these figures that, the genetically tuned TCSC controller improves the stability performance of the example power system and power system oscillations are well damped out. Case-: Line-outage Disturbance In this case another severe disturbance is considered. One of the transmission line is permanently tripped out at t = sec. The system response for the above contingency is shown in Figs δ (deg) Δ ω Fig. 8 Variation of power angleδ : Case- 6 x Fig. 9 Variation of speed deviation Δ ω : Case- Eq E d E fd.5.4 Fig. Variation of electrical power P : Case e Fig. Variation of voltage E d : Case- Fig. Variation of voltage E q : Case- Fig. 3 Variation of voltage : Case- E fd International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation (3) scholar.waset.org/37-689/56
9 Vol:, No:3, 7.5 International Science Index, Energy and Power Engineering Vol:, No:3, 7 waset.org/publication/56 X L I V t Fig. 4 Variation of terminal voltage V t : Case- Fig. 5 Variation of line current I: Case-. Fig. 6 Variation of transfer reactance X L : Case- The simulation results show the effectiveness of the proposed modelling and tuning approach. It is also clear form the Figs. that he proposed GA optimized TCSC-based controller has good damping characteristics to low frequency oscillations and quickly stabilizes the system under this severe disturbance. Case-3: Small Disturbance In order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed TCSC controller optimized using GA, under small disturbance, the mechanical power input to the generator is decreased by pu at t = sec and the disturbance is removed at t = 6 sec. The system response under this small disturbance contingency is shown in Figs δ (deg) Δ ω P e V t x -3 Fig. 7 Variation of power angle δ : Case Fig. 8 Variation of speed deviation Δ ω : Case Fig. 9 Variation of electrical power P e : Case Fig. 3 Variation of terminal voltage V : Case-3 t International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation (3) scholar.waset.org/37-689/56
10 Vol:, No:3, 7 International Science Index, Energy and Power Engineering Vol:, No:3, 7 waset.org/publication/56 X TCSC Fig. 3 Variation of X TCSC : Case-3 It is clear form the Figs. 7-3 that, the proposed GA optimized TCSC-based controller has good damping characteristics to low frequency oscillations and quickly stabilizes the system under this small disturbance VI. COLUSION The MATLAB/SIMULINK model of a single-machine infinite-bus power system with a TCSC controller presented in the paper provides a means for carrying out power system stability analysis and for explaining the generator dynamic behaviour as effected by a TCSC. This model is far more realistic compared to the model available in open literature, since the synchronous generator with field circuit and one equivalent damper on q-axis is considered. Further, for the TCSC controller design problem, a parameter-constrained, time-domain based, objective function, is developed to improve the performance of power system subjected to a disturbance. Then, GA is employed to search for the optimal TCSC controller parameters. The controller is tested on example power system subjected to various large and small disturbances. The simulation results show that, the genetically tuned TCSC controller improves the stability performance of the power system and power system oscillations are effectively damped out. Hence, it is concluded that the proposed model is suitable for carrying out power system stability studies in cases where the dynamic interactions of a synchronous generator and a TCSC are the main concern. APPENDIX System data: All data are in pu unless specified otherwise. Generator: H = 3.54, D =, X d =.757, X q =.5845, X d =.445, X q =.4, T do = 6.66, T qo =.44, Ra=, P e =.6, Q e =.4, δ = Exciter: K A =4, T A =.5 s Transmission line: R=, X L =.85, X T =.364, X TH =.3636, G=, B=; TCSC Controller: T TCSC = 5 ms, α = 4, X TCSC =.669, k=, T W = s, X MAX =.8 X L, X MIN =. REFEREES [] W.G. Heffron and R.A. Phillips, Effect of modem amplidyne voltage regulator characteristics, IEEE Transactions, PAS-7, pp , 95. [] F.P. Demello and C. Concordla, Concepts of synchronous machine stability as affected by excitation control, IEEE Transactions, PAS-88,(4 ), pp. 89-, 969. [3] N. G. Hingorani and L. Gyugyi, Understanding FACTS: Concepts and Technology of Flexible AC Transmission System. IEEE Press.. [4] H.F.Wang and F.J.Swift, A unified model for the analysis of FACTS devices in damping power system oscillations part I: single-machine infinite-bus power systems, IEEE Trans. Power Delivery, Vol., No., pp , 997. [5] H.F.Wang Phillips-Heffron model of power systems installed with STATCOM and applications IEE Proc-Gener. Transm. Distrib., Vol. 46, No. 5, pp. 5-57, 999. [6] H.F.Wang A Unified Model for the Analysis of FACTS Devices in Damping Power System Oscillations Part III: Unified Power Flow Controller, IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, Vol. 5, No. 3, pp ,. [7] S. Panda, N.P.Padhy and R.N.Patel, Modelling, simulation and optimal tuning of TCSC controller, International Journal of Simulation Modelling, Vol. 6, No., pp , 7. [8] Available: [9] Y.L. Abdel-Magid and M.A. Abido, Coordinated design of a PSS and a SVC-based controller to enhance power system stability, Electrical Power & Energy Syst, Vol. 5, pp , 3. [] S. Panda, N.P.Padhy Thyristor Controlled Series Compensator-based Controller Design Employing Genetic Algorithm: A Comparative Study, International Journal of Electronics Circuits and Systems, Vol., No., pp , 7. [] Y.L. Abdel-Magid and M.A.Abido, Robust coordinated design of excitation and TCSC-based stabilizers using genetic algorithms, International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, Vol. 69, No. -3, pp. 9-4, 4. [] D. E. Goldberg, Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization and Machine Learning. Addison-Wesley, 989. [3] K. R. Padiyar, Power System Dynamics Stability and Control, BS Publications, nd Edition, Hyderabad, India,. [4] P. Kundur, Power System Stability and Control. New York: McGraw- Hill, 994. [5] R. M Mathur and R. K. Verma, Thyristor-based FACTS Controllers for Electrical Transmission Systems, IEEE press, Piscataway,. [6] C. Houck, J. Joines and M. Kay, A genetic algorithm for function optimization: A MTLAM implementation. SU-IE, TR Available: Sidhartha Panda received the M.E. degree in Power Systems Engineering from University College of Engineering, Burla, Sambalpur University, India in. Currently, he is a Research Scholar in Electrical Engineering Department of Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, India. He was an Associate Professor in the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, VITAM College of Engineering, Andhra Pradesh, India and Lecturer in the Department of Electrical Engineering, SMIT, Orissa, India. His areas of research include power system transient stability, power system dynamic stability, FACTS, optimization techniques, distributed generation and wind energy. Narayana Prasad Padhy was born in India and received his Degree (Electrical Engineering), Masters Degree (Power Systems Engineering) with Distinction and Ph.D., Degree (Power Systems Engineering) in the year 99, 993 and 997 respectively in India. Then he has joined the Department of Electrical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) India, as a Lecturer, Assistant Professor and Associate Professor during 998, and 6 respectively. Presently he is working as a Associate Professor in the Department of Electrical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) India. He has visited the Department of Electronics and Electrical Engineering, University of Bath, UK under Boyscast Fellowship during 5-6. His area of research interest is mainly Power System Privatization, Restructuring and Deregulation, Transmission and Distribution network charging, Artificial Intelligence Applications to Power System and FACTS. International Scholarly and Scientific Research & Innovation (3) scholar.waset.org/37-689/56
Power System with PSS and FACTS Controller: Modelling, Simulation and Simultaneous Tuning Employing Genetic Algorithm
 International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering : 7 Power System with PSS and FACTS Controller: Modelling, Simulation and Simultaneous Tuning Employing Genetic Algorithm Sidhartha Panda
International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering : 7 Power System with PSS and FACTS Controller: Modelling, Simulation and Simultaneous Tuning Employing Genetic Algorithm Sidhartha Panda
Improvement of Dynamic Stability of a Single Machine Infinite-Bus Power System using Fuzzy Logic based Power System Stabilizer
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 4, Issue 5 (October 2012), PP. 60-70 Improvement of Dynamic Stability of a Single
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 4, Issue 5 (October 2012), PP. 60-70 Improvement of Dynamic Stability of a Single
IMPROVING POWER SYSTEM STABILITY USING REAL-CODED GENETIC ALGORITHM BASED PI CONTROLLER FOR STATCOM
 IMPROVING POWER SYSTEM STABILITY USING REAL-CODED GENETIC ALGORITHM BASED PI CONTROLLER FOR STATCOM SANGRAM KESHORI MOHAPATRA 1 & KUMARESH ROUT 2 1 Dept. of Electrical Engineering, C V Raman College of
IMPROVING POWER SYSTEM STABILITY USING REAL-CODED GENETIC ALGORITHM BASED PI CONTROLLER FOR STATCOM SANGRAM KESHORI MOHAPATRA 1 & KUMARESH ROUT 2 1 Dept. of Electrical Engineering, C V Raman College of
Optimal Location and Design of TCSC controller For Improvement of Stability
 Optimal Location and Design of TCSC controller For Improvement of Stability Swathi Kommamuri & P. Sureshbabu Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, NEC Narasaraopet,India E-mail : swathikommamuri@gmail.com,
Optimal Location and Design of TCSC controller For Improvement of Stability Swathi Kommamuri & P. Sureshbabu Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, NEC Narasaraopet,India E-mail : swathikommamuri@gmail.com,
Comparison of FACTS Devices for Power System Stability Enhancement
 Comparison of FACTS Devices for Power System Stability Enhancement D. Murali Research Scholar in EEE Dept., Government College of Engineering, Bargur-635 104, Tamilnadu, India. Dr. M. Rajaram Professor
Comparison of FACTS Devices for Power System Stability Enhancement D. Murali Research Scholar in EEE Dept., Government College of Engineering, Bargur-635 104, Tamilnadu, India. Dr. M. Rajaram Professor
A Novel PSS Design for Single Machine Infinite Bus System Based on Artificial Bee Colony
 A Novel PSS Design for Single Machine Infinite Bus System Based on Artificial Bee Colony Prof. MS Jhamad*, Surbhi Shrivastava** *Department of EEE, Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekananda Technical University,
A Novel PSS Design for Single Machine Infinite Bus System Based on Artificial Bee Colony Prof. MS Jhamad*, Surbhi Shrivastava** *Department of EEE, Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekananda Technical University,
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 4, April -2017 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 Damping
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 4, April -2017 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 Damping
Increasing Dynamic Stability of the Network Using Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC)
 Increasing Dynamic Stability of the Network Using Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) K. Manoz Kumar Reddy (Associate professor, Electrical and Electronics Department, Sriaditya Engineering College, India)
Increasing Dynamic Stability of the Network Using Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) K. Manoz Kumar Reddy (Associate professor, Electrical and Electronics Department, Sriaditya Engineering College, India)
Arvind Pahade and Nitin Saxena Department of Electrical Engineering, Jabalpur Engineering College, Jabalpur, (MP), India
 e t International Journal on Emerging Technologies 4(1): 10-16(2013) ISSN No. (Print) : 0975-8364 ISSN No. (Online) : 2249-3255 Control of Synchronous Generator Excitation and Rotor Angle Stability by
e t International Journal on Emerging Technologies 4(1): 10-16(2013) ISSN No. (Print) : 0975-8364 ISSN No. (Online) : 2249-3255 Control of Synchronous Generator Excitation and Rotor Angle Stability by
Damping Power system Oscillation using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC)
 Damping Power system Oscillation using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC) Girish Kumar Prasad 1, Dr. Malaya S Dash 2 1M-Tech Scholar, Dept. of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Technocrats
Damping Power system Oscillation using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC) Girish Kumar Prasad 1, Dr. Malaya S Dash 2 1M-Tech Scholar, Dept. of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Technocrats
PERFORMANCE COMPARISON OF POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER WITH AND WITHOUT FACTS DEVICE
 PERFORMANCE COMPARISON OF POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER WITH AND WITHOUT FACTS DEVICE Amit Kumar Vidyarthi 1, Subrahmanyam Tanala 2, Ashish Dhar Diwan 1 1 M.Tech Scholar, 2 Asst. Prof. Dept. of Electrical Engg.,
PERFORMANCE COMPARISON OF POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER WITH AND WITHOUT FACTS DEVICE Amit Kumar Vidyarthi 1, Subrahmanyam Tanala 2, Ashish Dhar Diwan 1 1 M.Tech Scholar, 2 Asst. Prof. Dept. of Electrical Engg.,
Modelling of Fuzzy Generic Power System Stabilizer for SMIB System
 Modelling of Fuzzy Generic Power System Stabilizer for SMIB System D.Jasmitha 1, Dr.R.Vijayasanthi 2 PG Student, Dept. of EEE, Andhra University (A), Visakhapatnam, India 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of
Modelling of Fuzzy Generic Power System Stabilizer for SMIB System D.Jasmitha 1, Dr.R.Vijayasanthi 2 PG Student, Dept. of EEE, Andhra University (A), Visakhapatnam, India 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of
Transient stability improvement by using shunt FACT device (STATCOM) with Reference Voltage Compensation (RVC) control scheme
 I J E E E C International Journal of Electrical, Electronics ISSN No. (Online) : 2277-2626 and Computer Engineering 2(1): 7-12(2013) Transient stability improvement by using shunt FACT device (STATCOM)
I J E E E C International Journal of Electrical, Electronics ISSN No. (Online) : 2277-2626 and Computer Engineering 2(1): 7-12(2013) Transient stability improvement by using shunt FACT device (STATCOM)
International Journal of Scientific Research Engineering & Technology (IJSRET), ISSN Volume 3, Issue 7, October 2014
 1044 OPTIMIZATION AND SIMULATION OF SIMULTANEOUS TUNING OF STATIC VAR COMPENSATOR AND POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER TO IMPROVE POWER SYSTEM STABILITY USING PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUE Abishek Paliwal
1044 OPTIMIZATION AND SIMULATION OF SIMULTANEOUS TUNING OF STATIC VAR COMPENSATOR AND POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER TO IMPROVE POWER SYSTEM STABILITY USING PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUE Abishek Paliwal
SIMULATION OF D-Q CONTROL SYSTEM FOR A UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER
 SIMULATION OF D-Q CONTROL SYSTEM FOR A UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER S. Tara Kalyani 1 and G. Tulasiram Das 1 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, Hyderabad,
SIMULATION OF D-Q CONTROL SYSTEM FOR A UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER S. Tara Kalyani 1 and G. Tulasiram Das 1 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, Hyderabad,
A.V.Sudhakara Reddy 1, M. Ramasekhara Reddy 2, Dr. M. Vijaya Kumar 3
 Stability Improvement During Damping of Low Frequency Oscillations with Fuzzy Logic Controller A.V.Sudhakara Reddy 1, M. Ramasekhara Reddy 2, Dr. M. Vijaya Kumar 3 1 (M. Tech, Department of Electrical
Stability Improvement During Damping of Low Frequency Oscillations with Fuzzy Logic Controller A.V.Sudhakara Reddy 1, M. Ramasekhara Reddy 2, Dr. M. Vijaya Kumar 3 1 (M. Tech, Department of Electrical
LOW FREQUENCY OSCILLATION DAMPING BY DISTRIBUTED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER WITH A ROBUST FUZZY SUPPLEMENTARY CONTROLLER
 LOW FREQUENCY OSCILLATION DAMPING BY DISTRIBUTED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER WITH A ROBUST FUZZY SUPPLEMENTARY CONTROLLER C. Narendra Raju 1, V.Naveen 2 1PG Scholar, Department of EEE, JNTU Anantapur, Andhra
LOW FREQUENCY OSCILLATION DAMPING BY DISTRIBUTED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER WITH A ROBUST FUZZY SUPPLEMENTARY CONTROLLER C. Narendra Raju 1, V.Naveen 2 1PG Scholar, Department of EEE, JNTU Anantapur, Andhra
Real-Coded Genetic Algorithm for Robust Design of UPFC Supplementary Damping Controller
 Real-Coded Genetic Algorithm for Robust Design of UPFC Supplementary Damping Controller S. C. Swain, S. Mohapatra, S. Panda & S. R. Nayak Abstract - In this paper is used in Designing UPFC based supplementary
Real-Coded Genetic Algorithm for Robust Design of UPFC Supplementary Damping Controller S. C. Swain, S. Mohapatra, S. Panda & S. R. Nayak Abstract - In this paper is used in Designing UPFC based supplementary
Improving the Transient and Dynamic stability of the Network by Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC)
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 5, May 2012 1 Improving the Transient and Dynamic stability of the Network by Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) K. Manoz
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 5, May 2012 1 Improving the Transient and Dynamic stability of the Network by Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) K. Manoz
Chapter 10: Compensation of Power Transmission Systems
 Chapter 10: Compensation of Power Transmission Systems Introduction The two major problems that the modern power systems are facing are voltage and angle stabilities. There are various approaches to overcome
Chapter 10: Compensation of Power Transmission Systems Introduction The two major problems that the modern power systems are facing are voltage and angle stabilities. There are various approaches to overcome
I. INTRODUCTION. Keywords:- FACTS, TCSC, TCPAR,UPFC,ORPD
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 11, Issue 11 (November 2015), PP.13-18 Modelling Of Various Facts Devices for Optimal
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 11, Issue 11 (November 2015), PP.13-18 Modelling Of Various Facts Devices for Optimal
Application of SSSC-Damping Controller for Power System Stability Enhancement
 Kalpa Publications in Engineering Volume 1, 2017, Pages 123 133 ICRISET2017. International Conference on Research and Innovations in Science, Engineering &Technology. Selected Papers in Engineering Application
Kalpa Publications in Engineering Volume 1, 2017, Pages 123 133 ICRISET2017. International Conference on Research and Innovations in Science, Engineering &Technology. Selected Papers in Engineering Application
Interline Power Flow Controller For Damping Low Frequency Oscillations By Comparing PID Controller Andcontroller Using Genetic Algorithm
 Interline Power Flow Controller For Damping Low Frequency Oscillations By Comparing PID Controller Andcontroller Using Genetic Algorithm Anubha Prajapati M Tech (LNCT Bhopal-MP) Kanchan Chaturvedi Assistant
Interline Power Flow Controller For Damping Low Frequency Oscillations By Comparing PID Controller Andcontroller Using Genetic Algorithm Anubha Prajapati M Tech (LNCT Bhopal-MP) Kanchan Chaturvedi Assistant
Design of Fractional Order PID Controller for SMIB Power System with UPFC Tuned by Multi-Objectives Genetic Algorithm. Abstract:
 16 th International Conference on AEROSPACE SCIENCES & AVIATION TECHNOLOGY, ASAT - 16 May 26-28, 215, E-Mail: asat@mtc.edu.eg Military Technical College, Kobry Elkobbah, Cairo, Egypt Tel : +(22) 2425292
16 th International Conference on AEROSPACE SCIENCES & AVIATION TECHNOLOGY, ASAT - 16 May 26-28, 215, E-Mail: asat@mtc.edu.eg Military Technical College, Kobry Elkobbah, Cairo, Egypt Tel : +(22) 2425292
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJARET)
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJARET) International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 ISSN 0976-6480 (Print) ISSN
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJARET) International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 ISSN 0976-6480 (Print) ISSN
ECE 422/522 Power System Operations & Planning/Power Systems Analysis II 5 - Reactive Power and Voltage Control
 ECE 422/522 Power System Operations & Planning/Power Systems Analysis II 5 - Reactive Power and Voltage Control Spring 2014 Instructor: Kai Sun 1 References Saadat s Chapters 12.6 ~12.7 Kundur s Sections
ECE 422/522 Power System Operations & Planning/Power Systems Analysis II 5 - Reactive Power and Voltage Control Spring 2014 Instructor: Kai Sun 1 References Saadat s Chapters 12.6 ~12.7 Kundur s Sections
Keywords: Stability, Power transfer, Flexible a.c. transmission system (FACTS), Unified power flow controller (UPFC). IJSER
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume, Issue, March-4 74 ISSN 9-8 IMPACT OF UPFC ON SWING, VOLTAGE STABILITY AND POWER TRANSFER CAPABILITY IN TRANSMISSION SYSTEM Mr. Rishi
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume, Issue, March-4 74 ISSN 9-8 IMPACT OF UPFC ON SWING, VOLTAGE STABILITY AND POWER TRANSFER CAPABILITY IN TRANSMISSION SYSTEM Mr. Rishi
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET)
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET) ISSN 0976 6545(Print) ISSN 0976 6553(Online) Volume 3, Issue 1, January- June (2012), pp. 226-234 IAEME: www.iaeme.com/ijeet.html Journal
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET) ISSN 0976 6545(Print) ISSN 0976 6553(Online) Volume 3, Issue 1, January- June (2012), pp. 226-234 IAEME: www.iaeme.com/ijeet.html Journal
Designing Of Distributed Power-Flow Controller
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) ISSN: 2278-1676 Volume 2, Issue 5 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 01-09 Designing Of Distributed Power-Flow Controller 1 R. Lokeswar Reddy (M.Tech),
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) ISSN: 2278-1676 Volume 2, Issue 5 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 01-09 Designing Of Distributed Power-Flow Controller 1 R. Lokeswar Reddy (M.Tech),
Application Of Power System Stabilizer At Serir Power Plant
 Vol. 3 Issue 4, April - 27 Application Of Power System Stabilizer At Serir Power Plant *T. Hussein, **A. Shameh Electrical and Electronics Dept University of Benghazi Benghazi- Libya *Tawfiq.elmenfy@uob.edu.ly
Vol. 3 Issue 4, April - 27 Application Of Power System Stabilizer At Serir Power Plant *T. Hussein, **A. Shameh Electrical and Electronics Dept University of Benghazi Benghazi- Libya *Tawfiq.elmenfy@uob.edu.ly
ELEMENTS OF FACTS CONTROLLERS
 1 ELEMENTS OF FACTS CONTROLLERS Rajiv K. Varma Associate Professor Hydro One Chair in Power Systems Engineering University of Western Ontario London, ON, CANADA rkvarma@uwo.ca POWER SYSTEMS - Where are
1 ELEMENTS OF FACTS CONTROLLERS Rajiv K. Varma Associate Professor Hydro One Chair in Power Systems Engineering University of Western Ontario London, ON, CANADA rkvarma@uwo.ca POWER SYSTEMS - Where are
Development of Real time controller of a Single Machine Infinite Bus system with PSS
 Development of Real time controller of a Single Machine Infinite Bus system with PSS Mrs.Ami T.Patel 1, Mr.Hardik A.Shah 2 Prof.S. K.Shah 3 1 Research Scholar, Electrical Engineering Department: FTE,M.S.University
Development of Real time controller of a Single Machine Infinite Bus system with PSS Mrs.Ami T.Patel 1, Mr.Hardik A.Shah 2 Prof.S. K.Shah 3 1 Research Scholar, Electrical Engineering Department: FTE,M.S.University
STATCOM Tuned Based on Tabu Search for Voltage Support in Power Systems
 J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., 1(10)1334-1341, 2011 2011, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-424X Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com STATCOM Tuned Based on Tabu Search for Voltage
J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., 1(10)1334-1341, 2011 2011, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-424X Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com STATCOM Tuned Based on Tabu Search for Voltage
A Real-Time Platform for Teaching Power System Control Design
 A Real-Time Platform for Teaching Power System Control Design G. Jackson, U.D. Annakkage, A. M. Gole, D. Lowe, and M.P. McShane Abstract This paper describes the development of a real-time digital simulation
A Real-Time Platform for Teaching Power System Control Design G. Jackson, U.D. Annakkage, A. M. Gole, D. Lowe, and M.P. McShane Abstract This paper describes the development of a real-time digital simulation
ISSUES OF SYSTEM AND CONTROL INTERACTIONS IN ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEMS
 ISSUES OF SYSTEM AND CONTROL INTERACTIONS IN ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEMS INDO-US Workshop October 2009, I.I.T. Kanpur INTRODUCTION Electric Power Systems are very large, spread over a wide geographical area
ISSUES OF SYSTEM AND CONTROL INTERACTIONS IN ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEMS INDO-US Workshop October 2009, I.I.T. Kanpur INTRODUCTION Electric Power Systems are very large, spread over a wide geographical area
Transient Stability Improvement Of IEEE 9 Bus System With Shunt FACTS Device STATCOM
 Transient Stability Improvement Of IEEE 9 Bus System With Shunt FACTS Device STATCOM P.P. Panchbhai 1, P.S.Vaidya 2 1Pratiksha P Panchbhai, Dept. of Electrical Engineering, G H Raisoni College of Engineering
Transient Stability Improvement Of IEEE 9 Bus System With Shunt FACTS Device STATCOM P.P. Panchbhai 1, P.S.Vaidya 2 1Pratiksha P Panchbhai, Dept. of Electrical Engineering, G H Raisoni College of Engineering
Address for Correspondence
 Research Paper COMPENSATION BY TCSC IN OPEN LOOP CONTROL SYSTEM 1* Sunita Tiwari, S.P. Shukla Address for Correspondence 1* Sr. Lecturer, Polytechnic,Durg Professor, Bhilai Institute of Technology, Durg
Research Paper COMPENSATION BY TCSC IN OPEN LOOP CONTROL SYSTEM 1* Sunita Tiwari, S.P. Shukla Address for Correspondence 1* Sr. Lecturer, Polytechnic,Durg Professor, Bhilai Institute of Technology, Durg
Controller Design of STATCOM for Power System Stability Improvement Using Honey Bee Mating Optimization
 Controller Design of STATCOM for Power System Stability Improvement Using Honey Bee Mating Optimization A. Safari *1, A. Ahmadian 2, M. A. A. Golkar 3 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Ahar Branch,
Controller Design of STATCOM for Power System Stability Improvement Using Honey Bee Mating Optimization A. Safari *1, A. Ahmadian 2, M. A. A. Golkar 3 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Ahar Branch,
Stability Enhancement for Transmission Lines using Static Synchronous Series Compensator
 Stability Enhancement for Transmission Lines using Static Synchronous Series Compensator Ishwar Lal Yadav Department of Electrical Engineering Rungta College of Engineering and Technology Bhilai, India
Stability Enhancement for Transmission Lines using Static Synchronous Series Compensator Ishwar Lal Yadav Department of Electrical Engineering Rungta College of Engineering and Technology Bhilai, India
The Eect of an Interline Power Flow Controller (IPFC) on Damping Inter-area Oscillations in Interconnected Power Systems
 Scientia Iranica, Vol. 15, No., pp 11{1 c Sharif University of Technology, April 8 Research Note The Eect of an Interline Power Flow Controller (IPFC) on Damping Inter-area Oscillations in Interconnected
Scientia Iranica, Vol. 15, No., pp 11{1 c Sharif University of Technology, April 8 Research Note The Eect of an Interline Power Flow Controller (IPFC) on Damping Inter-area Oscillations in Interconnected
IJSER. Fig-1: Interconnection diagram in the vicinity of the RajWest power plant
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 7, July-2014 696 AN INVESTIGATION ON USE OF POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER ON DYNAMIC STABILITY OF POWER SYSTEM Mr. Bhuwan Pratap Singh
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 7, July-2014 696 AN INVESTIGATION ON USE OF POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER ON DYNAMIC STABILITY OF POWER SYSTEM Mr. Bhuwan Pratap Singh
Static Synchronous Compensator (STATCOM) for the improvement of the Electrical System performance with Non Linear load 1
 Static Synchronous Compensator (STATCOM) for the improvement of the Electrical System performance with Non Linear load MADHYAMA V. WANKHEDE Department Of Electrical Engineering G. H. Raisoni College of
Static Synchronous Compensator (STATCOM) for the improvement of the Electrical System performance with Non Linear load MADHYAMA V. WANKHEDE Department Of Electrical Engineering G. H. Raisoni College of
Dynamic Simulation of the Generalized Unified Power Flow Controller in Multi-Machine Power Systems
 International Journal of Electrical & Computer Sciences IJECS-IJENS Vol: No: 3 75 Dynamic Simulation of the Generalized Unified Power Flow Controller in Multi-Machine Power Systems Rakhmad Syafutra Lubis,
International Journal of Electrical & Computer Sciences IJECS-IJENS Vol: No: 3 75 Dynamic Simulation of the Generalized Unified Power Flow Controller in Multi-Machine Power Systems Rakhmad Syafutra Lubis,
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,9 6, 2M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,9 6, 2M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are
Optimal tuning of power system stabilizer using genetic algorithm to improve power system stability
 Optimal tuning of power system stabilizer using genetic algorithm to improve power system stability Salma KESKES, Nouha BOUCHIBA 2, Souhir SALLEM 3, Larbi CHRIFI-ALAOUI 4, M.B.A KAMMOUN 5 Research unit
Optimal tuning of power system stabilizer using genetic algorithm to improve power system stability Salma KESKES, Nouha BOUCHIBA 2, Souhir SALLEM 3, Larbi CHRIFI-ALAOUI 4, M.B.A KAMMOUN 5 Research unit
6545(Print), ISSN (Online) Volume 4, Issue 1, January- February (2013), IAEME & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET)
 INTERNATIONAL International Journal of JOURNAL Electrical Engineering OF ELECTRICAL and Technology (IJEET), ENGINEERING ISSN 0976 & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET) ISSN 0976 6545(Print) ISSN 0976 6553(Online) Volume
INTERNATIONAL International Journal of JOURNAL Electrical Engineering OF ELECTRICAL and Technology (IJEET), ENGINEERING ISSN 0976 & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET) ISSN 0976 6545(Print) ISSN 0976 6553(Online) Volume
I. INTRODUCTION IJSRST Volume 3 Issue 2 Print ISSN: Online ISSN: X
 2017 IJSRST Volume 3 Issue 2 Print ISSN: 2395-6011 Online ISSN: 2395-602X National Conference on Advances in Engineering and Applied Science (NCAEAS) 16 th February 2017 In association with International
2017 IJSRST Volume 3 Issue 2 Print ISSN: 2395-6011 Online ISSN: 2395-602X National Conference on Advances in Engineering and Applied Science (NCAEAS) 16 th February 2017 In association with International
Damping of Sub-synchronous Resonance and Power Swing using TCSC and Series capacitor
 Damping of Sub-synchronous Resonance and Power Swing using TCSC and Series capacitor Durga Prasad Ananthu Assistant Professor, EEE dept. Guru Nanak Dev Engg College, Bidar adp.ananthu@gmail.com Rami Reddy
Damping of Sub-synchronous Resonance and Power Swing using TCSC and Series capacitor Durga Prasad Ananthu Assistant Professor, EEE dept. Guru Nanak Dev Engg College, Bidar adp.ananthu@gmail.com Rami Reddy
VSC Based HVDC Active Power Controller to Damp out Resonance Oscillation in Turbine Generator System
 VSC Based HVDC Active Power Controller to Damp out Resonance Oscillation in Turbine Generator System Rajkumar Pal 1, Rajesh Kumar 2, Abhay Katyayan 3 1, 2, 3 Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical
VSC Based HVDC Active Power Controller to Damp out Resonance Oscillation in Turbine Generator System Rajkumar Pal 1, Rajesh Kumar 2, Abhay Katyayan 3 1, 2, 3 Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical
P Shrikant Rao and Indraneel Sen
 A QFT Based Robust SVC Controller For Improving The Dynamic Stability Of Power Systems.. P Shrikant Rao and Indraneel Sen ' Abstract A novel design technique for an SVC based Power System Damping Controller
A QFT Based Robust SVC Controller For Improving The Dynamic Stability Of Power Systems.. P Shrikant Rao and Indraneel Sen ' Abstract A novel design technique for an SVC based Power System Damping Controller
Design and Simulation of Fuzzy Logic controller for DSTATCOM In Power System
 Design and Simulation of Fuzzy Logic controller for DSTATCOM In Power System Anju Gupta Department of Electrical and Electronics Engg. YMCA University of Science and Technology anjugupta112@gmail.com P.
Design and Simulation of Fuzzy Logic controller for DSTATCOM In Power System Anju Gupta Department of Electrical and Electronics Engg. YMCA University of Science and Technology anjugupta112@gmail.com P.
Analysis and Enhancement of Voltage Stability using Shunt Controlled FACTs Controller
 Volume 1, Issue 2, October-December, 2013, pp. 25-33, IASTER 2013 www.iaster.com, Online: 2347-5439, Print: 2348-0025 Analysis and Enhancement of Voltage Stability using Shunt Controlled FACTs Controller
Volume 1, Issue 2, October-December, 2013, pp. 25-33, IASTER 2013 www.iaster.com, Online: 2347-5439, Print: 2348-0025 Analysis and Enhancement of Voltage Stability using Shunt Controlled FACTs Controller
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE ROLE OF STABILIZERS IN THE ENHANCEMENT OF AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE REGULATORS PERFORMANCE
 Engineering Journal of Qatar University, Vol. 4, 1991, p. 91-102. EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE ROLE OF STABILIZERS IN THE ENHANCEMENT OF AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE REGULATORS PERFORMANCE K. I. Saleh* and M.
Engineering Journal of Qatar University, Vol. 4, 1991, p. 91-102. EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE ROLE OF STABILIZERS IN THE ENHANCEMENT OF AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE REGULATORS PERFORMANCE K. I. Saleh* and M.
Optimal Placement of Unified Power Flow Controller for Minimization of Power Transmission Line Losses
 Optimal Placement of Unified Power Flow Controller for inimization of Power Transmission Line Losses Sreerama umar R., Ibrahim. Jomoah, and Abdullah Omar Bafail Abstract This paper proposes the application
Optimal Placement of Unified Power Flow Controller for inimization of Power Transmission Line Losses Sreerama umar R., Ibrahim. Jomoah, and Abdullah Omar Bafail Abstract This paper proposes the application
Available ONLINE
 Available ONLINE www.ijart.org IJART, Vol. 2 Issue 3, 2012,94-98 ISSN NO: 6602 3127 R E S E A R C H A R T II C L E Enhancement Of Voltage Stability And Power Oscillation Damping Using Static Synchronous
Available ONLINE www.ijart.org IJART, Vol. 2 Issue 3, 2012,94-98 ISSN NO: 6602 3127 R E S E A R C H A R T II C L E Enhancement Of Voltage Stability And Power Oscillation Damping Using Static Synchronous
Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter Based UPFC with ANN
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 04, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 04, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter
INTELLIGENT PID POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER FOR A SYNCHRONOUS MACHINE IN SIMULINK ENVIRONMENT
 International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Research (IJEEER) ISSN 2250-155X Vol. 3, Issue 4, Oct 2013, 139-148 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. INTELLIGENT PID POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER FOR A SYNCHRONOUS
International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Research (IJEEER) ISSN 2250-155X Vol. 3, Issue 4, Oct 2013, 139-148 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. INTELLIGENT PID POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER FOR A SYNCHRONOUS
ECEN 667 Power System Stability Lecture 12: Exciter Models
 ECEN 667 Power System Stability Lecture 12: Exciter Models Prof. Tom Overbye Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University, overbye@tamu.edu 1 Announcements Read Chapter 4 Homework
ECEN 667 Power System Stability Lecture 12: Exciter Models Prof. Tom Overbye Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University, overbye@tamu.edu 1 Announcements Read Chapter 4 Homework
INSTANTANEOUS POWER CONTROL OF D-STATCOM FOR ENHANCEMENT OF THE STEADY-STATE PERFORMANCE
 INSTANTANEOUS POWER CONTROL OF D-STATCOM FOR ENHANCEMENT OF THE STEADY-STATE PERFORMANCE Ms. K. Kamaladevi 1, N. Mohan Murali Krishna 2 1 Asst. Professor, Department of EEE, 2 PG Scholar, Department of
INSTANTANEOUS POWER CONTROL OF D-STATCOM FOR ENHANCEMENT OF THE STEADY-STATE PERFORMANCE Ms. K. Kamaladevi 1, N. Mohan Murali Krishna 2 1 Asst. Professor, Department of EEE, 2 PG Scholar, Department of
Optimal Placement and Tuning of TCSC for Damping Oscillations
 Optimal Placement and Tuning of TCSC for Damping Oscillations Maryam Mohiti, Mahtab Khalilifar, Ahmad Salehi, Rahim Zeinali Power System Research center Monenco Iran Consultant Engineers Tehran, Iran maryammohiti@gmail.com,khalilifar.mahtab@monenco.com,salehi.ahmad@monenco.com,zeinali.rahim@monenco.com
Optimal Placement and Tuning of TCSC for Damping Oscillations Maryam Mohiti, Mahtab Khalilifar, Ahmad Salehi, Rahim Zeinali Power System Research center Monenco Iran Consultant Engineers Tehran, Iran maryammohiti@gmail.com,khalilifar.mahtab@monenco.com,salehi.ahmad@monenco.com,zeinali.rahim@monenco.com
Real and Reactive Power Control by using 48-pulse Series Connected Three-level NPC Converter for UPFC
 Real and Reactive Power Control by using 48-pulse Series Connected Three-level NPC Converter for UPFC A.Naveena, M.Venkateswara Rao 2 Department of EEE, GMRIT, Rajam Email id: allumalla.naveena@ gmail.com,
Real and Reactive Power Control by using 48-pulse Series Connected Three-level NPC Converter for UPFC A.Naveena, M.Venkateswara Rao 2 Department of EEE, GMRIT, Rajam Email id: allumalla.naveena@ gmail.com,
TCPST (thyristor control phase shifting transformer) impact on power quality
 Sousse, Tunisie - 213 TCPST (thyristor control phase shifting transformer) impact on power quality A.KHELFI #1,T.MESBAH #2,A.DJELLAD #3 # Electrical Engineering Department Badji Mokhtar-Annaba University,
Sousse, Tunisie - 213 TCPST (thyristor control phase shifting transformer) impact on power quality A.KHELFI #1,T.MESBAH #2,A.DJELLAD #3 # Electrical Engineering Department Badji Mokhtar-Annaba University,
ROBUST POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER TUNING BASED ON MULTIOBJECTIVE DESIGN USING HIERARCHICAL AND PARALLEL MICRO GENETIC ALGORITHM
 ROBUST POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER TUNING BASED ON MULTIOBJECTIVE DESIGN USING HIERARCHICAL AND PARALLEL MICRO GENETIC ALGORITHM Komsan Hongesombut, Sanchai Dechanupaprittha, Yasunori Mitani, and Issarachai
ROBUST POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER TUNING BASED ON MULTIOBJECTIVE DESIGN USING HIERARCHICAL AND PARALLEL MICRO GENETIC ALGORITHM Komsan Hongesombut, Sanchai Dechanupaprittha, Yasunori Mitani, and Issarachai
Energy-Based Damping Evaluation for Exciter Control in Power Systems
 Energy-Based Damping Evaluation for Exciter Control in Power Systems Luoyang Fang 1, Dongliang Duan 2, Liuqing Yang 1 1 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Colorado State University, Fort Collins,
Energy-Based Damping Evaluation for Exciter Control in Power Systems Luoyang Fang 1, Dongliang Duan 2, Liuqing Yang 1 1 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Colorado State University, Fort Collins,
Improving The Quality Of Energy Using Phase Shifting Transformer PST
 WSEAS TRANSACTIONS on POWER SYSTEMS Improving The Quality Of Energy Using Phase Shifting Transformer PST KHELFI ABDERREZAK Electrical Engineering Department Badji Mokhtar-Annaba University P.O. Box 12,
WSEAS TRANSACTIONS on POWER SYSTEMS Improving The Quality Of Energy Using Phase Shifting Transformer PST KHELFI ABDERREZAK Electrical Engineering Department Badji Mokhtar-Annaba University P.O. Box 12,
Development of Dynamic Test Cases in OPAL-RT Real-time Power System Simulator
 Development of Dynamic Test Cases in OPAL-RT Real-time Power System Simulator Shiv Kumar Singh, Bibhu P. Padhy, Student Member, IEEE, S. Chakrabarti, Senior Member, IEEE, S.N. Singh, Senior Member, IEEE,
Development of Dynamic Test Cases in OPAL-RT Real-time Power System Simulator Shiv Kumar Singh, Bibhu P. Padhy, Student Member, IEEE, S. Chakrabarti, Senior Member, IEEE, S.N. Singh, Senior Member, IEEE,
Power System Oscillations Damping and Transient Stability Enhancement with Application of SSSC FACTS Devices
 Available online www.ejaet.com European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 2015, 2(11): 73-79 Research Article ISSN: 2394-658X Power System Oscillations Damping and Transient Stability
Available online www.ejaet.com European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 2015, 2(11): 73-79 Research Article ISSN: 2394-658X Power System Oscillations Damping and Transient Stability
Comparison of Simulation Results of D-Facts & UPFC Used for Power Quality Improvement
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 9, September 2013 1 Comparison of Simulation Results of D-Facts & UPFC Used for Power Quality Improvement Dr.K.Ravichandrudu
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 9, September 2013 1 Comparison of Simulation Results of D-Facts & UPFC Used for Power Quality Improvement Dr.K.Ravichandrudu
Optimal Placement of Shunt Connected Facts Device in a Series Compensated Long Transmission Line
 Journal of Agriculture and Life Sciences Vol. 1, No. 1; June 2014 Optimal Placement of Shunt Connected Facts Device in a Series Compensated Long Transmission Line Sudhakar. Muthyala EEE Dept. University
Journal of Agriculture and Life Sciences Vol. 1, No. 1; June 2014 Optimal Placement of Shunt Connected Facts Device in a Series Compensated Long Transmission Line Sudhakar. Muthyala EEE Dept. University
EVALUATION OF A NEW MODEL FOR UPFC OPERATING AS IMPEDANCE COMPENSATION APPLIED TO MULTI- MACHINE SYSTEMS WITH NONLINEAR LOAD
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology ol. 9, No. 6 (04) 678-689 School of Engineering, Taylor s University EALUATION OF A NEW MODEL FOR UPFC OPERATING AS IMPEDANCE COMPENSATION APPLIED TO MULTI-
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology ol. 9, No. 6 (04) 678-689 School of Engineering, Taylor s University EALUATION OF A NEW MODEL FOR UPFC OPERATING AS IMPEDANCE COMPENSATION APPLIED TO MULTI-
ANALYTICAL AND SIMULATION RESULTS
 6 ANALYTICAL AND SIMULATION RESULTS 6.1 Small-Signal Response Without Supplementary Control As discussed in Section 5.6, the complete A-matrix equations containing all of the singlegenerator terms and
6 ANALYTICAL AND SIMULATION RESULTS 6.1 Small-Signal Response Without Supplementary Control As discussed in Section 5.6, the complete A-matrix equations containing all of the singlegenerator terms and
Robust controller design for LFO damping
 International society of academic and industrial research www.isair.org IJARAS International Journal of Academic Research in Applied Science 1(4): 1-8, 2012 ijaras.isair.org Robust controller design for
International society of academic and industrial research www.isair.org IJARAS International Journal of Academic Research in Applied Science 1(4): 1-8, 2012 ijaras.isair.org Robust controller design for
Position Control of DC Motor by Compensating Strategies
 Position Control of DC Motor by Compensating Strategies S Prem Kumar 1 J V Pavan Chand 1 B Pangedaiah 1 1. Assistant professor of Laki Reddy Balireddy College Of Engineering, Mylavaram Abstract - As the
Position Control of DC Motor by Compensating Strategies S Prem Kumar 1 J V Pavan Chand 1 B Pangedaiah 1 1. Assistant professor of Laki Reddy Balireddy College Of Engineering, Mylavaram Abstract - As the
Optimum Coordination of Overcurrent Relays: GA Approach
 Optimum Coordination of Overcurrent Relays: GA Approach 1 Aesha K. Joshi, 2 Mr. Vishal Thakkar 1 M.Tech Student, 2 Asst.Proff. Electrical Department,Kalol Institute of Technology and Research Institute,
Optimum Coordination of Overcurrent Relays: GA Approach 1 Aesha K. Joshi, 2 Mr. Vishal Thakkar 1 M.Tech Student, 2 Asst.Proff. Electrical Department,Kalol Institute of Technology and Research Institute,
Design and Control of Small Scale Laboratory Model of a Thyristor Controlled Series Capacitor (TCSC) to Improve System Stability
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 5, May-2012 1 Design and Control of Small Scale Laboratory Model of a Thyristor Controlled Series Capacitor (TCSC) to Improve
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 5, May-2012 1 Design and Control of Small Scale Laboratory Model of a Thyristor Controlled Series Capacitor (TCSC) to Improve
SIMULATION OF D-STATCOM AND DVR IN POWER SYSTEMS
 SIMUATION OF D-STATCOM AND DVR IN POWER SYSTEMS S.V Ravi Kumar 1 and S. Siva Nagaraju 1 1 J.N.T.U. College of Engineering, KAKINADA, A.P, India E-mail: ravijntu@gmail.com ABSTRACT A Power quality problem
SIMUATION OF D-STATCOM AND DVR IN POWER SYSTEMS S.V Ravi Kumar 1 and S. Siva Nagaraju 1 1 J.N.T.U. College of Engineering, KAKINADA, A.P, India E-mail: ravijntu@gmail.com ABSTRACT A Power quality problem
Optimal Power flow with FACTS devices using Genetic Algorithm
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume, Issue 8, August 2013 Optimal Power flow with FACTS devices using Genetic Algorithm Serene C Kurian, Jo Joy Abstract Increasing demands
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume, Issue 8, August 2013 Optimal Power flow with FACTS devices using Genetic Algorithm Serene C Kurian, Jo Joy Abstract Increasing demands
Interline Power Flow Controller: Review Paper
 Vol. (0) No. 3, pp. 550-554 ISSN 078-365 Interline Power Flow Controller: Review Paper Akhilesh A. Nimje, Chinmoy Kumar Panigrahi, Ajaya Kumar Mohanty Abstract The Interline Power Flow Controller (IPFC)
Vol. (0) No. 3, pp. 550-554 ISSN 078-365 Interline Power Flow Controller: Review Paper Akhilesh A. Nimje, Chinmoy Kumar Panigrahi, Ajaya Kumar Mohanty Abstract The Interline Power Flow Controller (IPFC)
Genetic Algorithm Based Performance Analysis of Self Excited Induction Generator
 Engineering, 2011, 3, 859-864 doi:10.4236/eng.2011.38105 Published Online August 2011 (http://www.cip.org/journal/eng) Genetic Algorithm Based Performance Analysis of elf Excited Induction Generator Abstract
Engineering, 2011, 3, 859-864 doi:10.4236/eng.2011.38105 Published Online August 2011 (http://www.cip.org/journal/eng) Genetic Algorithm Based Performance Analysis of elf Excited Induction Generator Abstract
HARMONIC distortion complicates the computation of. The Optimal Passive Filters to Minimize Voltage Harmonic Distortion at a Load Bus
 1592 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 20, NO. 2, APRIL 2005 The Optimal Passive Filters to Minimize Voltage Harmonic Distortion at a Load Bus Ahmed Faheem Zobaa, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract A
1592 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 20, NO. 2, APRIL 2005 The Optimal Passive Filters to Minimize Voltage Harmonic Distortion at a Load Bus Ahmed Faheem Zobaa, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract A
Comparison and Performance Analysis of FACTs Controller in System Stability
 Circuits and Systems, 2016, 7, 2948-2958 Published Online August 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/cs http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/cs.2016.710253 Comparison and Performance Analysis of FACTs Controller
Circuits and Systems, 2016, 7, 2948-2958 Published Online August 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/cs http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/cs.2016.710253 Comparison and Performance Analysis of FACTs Controller
Transfer Capability Enhancement of Transmission Line using Static Synchronous Compensator (STATCOM)
 International Journal of Advanced Computer Research (ISSN (print): 49777 ISSN (online): 77797) Volume Number4 Issue7 December Transfer Capability Enhancement of Transmission Line using Static Synchronous
International Journal of Advanced Computer Research (ISSN (print): 49777 ISSN (online): 77797) Volume Number4 Issue7 December Transfer Capability Enhancement of Transmission Line using Static Synchronous
DESIGNING POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER FOR MULTIMACHINE POWER SYSTEM USING NEURO-FUZZY ALGORITHM
 DESIGNING POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER FOR MULTIMACHINE POWER SYSTEM 55 Jurnal Teknologi, 35(D) Dis. 2001: 55 64 Universiti Teknologi Malaysia DESIGNING POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER FOR MULTIMACHINE POWER SYSTEM
DESIGNING POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER FOR MULTIMACHINE POWER SYSTEM 55 Jurnal Teknologi, 35(D) Dis. 2001: 55 64 Universiti Teknologi Malaysia DESIGNING POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER FOR MULTIMACHINE POWER SYSTEM
1. Governor with dynamics: Gg(s)= 1 2. Turbine with dynamics: Gt(s) = 1 3. Load and machine with dynamics: Gp(s) = 1
 Load Frequency Control of Two Area Power System Using PID and Fuzzy Logic 1 Rajendra Murmu, 2 Sohan Lal Hembram and 3 A.K. Singh 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Reseach Scholar, Associate Professor 1,2,3 Electrical
Load Frequency Control of Two Area Power System Using PID and Fuzzy Logic 1 Rajendra Murmu, 2 Sohan Lal Hembram and 3 A.K. Singh 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Reseach Scholar, Associate Professor 1,2,3 Electrical
Voltage Control and Power System Stability Enhancement using UPFC
 International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ 14) Cordoba (Spain), 8 th to 10 th April, 2014 Renewable Energy and Power Quality Journal (RE&PQJ) ISSN 2172-038 X, No.12, April
International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ 14) Cordoba (Spain), 8 th to 10 th April, 2014 Renewable Energy and Power Quality Journal (RE&PQJ) ISSN 2172-038 X, No.12, April
COMPARATIVE PERFORMANCE OF SMART WIRES SMARTVALVE WITH EHV SERIES CAPACITOR: IMPLICATIONS FOR SUB-SYNCHRONOUS RESONANCE (SSR)
 7 February 2018 RM Zavadil COMPARATIVE PERFORMANCE OF SMART WIRES SMARTVALVE WITH EHV SERIES CAPACITOR: IMPLICATIONS FOR SUB-SYNCHRONOUS RESONANCE (SSR) Brief Overview of Sub-Synchronous Resonance Series
7 February 2018 RM Zavadil COMPARATIVE PERFORMANCE OF SMART WIRES SMARTVALVE WITH EHV SERIES CAPACITOR: IMPLICATIONS FOR SUB-SYNCHRONOUS RESONANCE (SSR) Brief Overview of Sub-Synchronous Resonance Series
G.N.L.Sravani *, Dr.M.Sridhar ** *(Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, GIER, JNTU University, Kakinada)
 Damping Of Low Frequency Power Oscillations and Transient Stability Enhancement by Using Auxiliary Fuzzy Logic Based Static Synchronous Series Compensator G.N.L.Sravani *, Dr.M.Sridhar ** *(Department
Damping Of Low Frequency Power Oscillations and Transient Stability Enhancement by Using Auxiliary Fuzzy Logic Based Static Synchronous Series Compensator G.N.L.Sravani *, Dr.M.Sridhar ** *(Department
TRANSIENT STABILITY ENHANCEMENT OF POWER SYSTEM USING INTELLIGENT TECHNIQUE
 TRANSIENT STABILITY ENHANCEMENT OF POWER SYSTEM USING INTELLIGENT TECHNIQUE K.Satyanarayana 1, Saheb Hussain MD 2, B.K.V.Prasad 3 1 Ph.D Scholar, EEE Department, Vignan University (A.P), India, ksatya.eee@gmail.com
TRANSIENT STABILITY ENHANCEMENT OF POWER SYSTEM USING INTELLIGENT TECHNIQUE K.Satyanarayana 1, Saheb Hussain MD 2, B.K.V.Prasad 3 1 Ph.D Scholar, EEE Department, Vignan University (A.P), India, ksatya.eee@gmail.com
Analysis of Effect on Transient Stability of Interconnected Power System by Introduction of HVDC Link.
 Analysis of Effect on Transient Stability of Interconnected Power System by Introduction of HVDC Link. Mr.S.B.Dandawate*, Mrs.S.L.Shaikh** *,**(Department of Electrical Engineering, Walchand College of
Analysis of Effect on Transient Stability of Interconnected Power System by Introduction of HVDC Link. Mr.S.B.Dandawate*, Mrs.S.L.Shaikh** *,**(Department of Electrical Engineering, Walchand College of
Brief Study on TSCS, SSSC, SVC Facts Device
 Brief Study on TSCS, SSSC, SVC Facts Device Ramesh Kumari, Parveen M.Tech. Student, Department of EEE, Mata Rajkaur Institute of Engineering & technology, Rewari, Haryana, India Asst. Professor, Department
Brief Study on TSCS, SSSC, SVC Facts Device Ramesh Kumari, Parveen M.Tech. Student, Department of EEE, Mata Rajkaur Institute of Engineering & technology, Rewari, Haryana, India Asst. Professor, Department
Enhancement of Power Quality in Distribution System Using D-Statcom for Different Faults
 Enhancement of Power Quality in Distribution System Using D-Statcom for Different s Dr. B. Sure Kumar 1, B. Shravanya 2 1 Assistant Professor, CBIT, HYD 2 M.E (P.S & P.E), CBIT, HYD Abstract: The main
Enhancement of Power Quality in Distribution System Using D-Statcom for Different s Dr. B. Sure Kumar 1, B. Shravanya 2 1 Assistant Professor, CBIT, HYD 2 M.E (P.S & P.E), CBIT, HYD Abstract: The main
Design And Analysis Of Control Circuit For TCSC FACTS Controller
 Design And Analysis Of Control Circuit For TCSC FACTS Controller Chiranjit Sain Dr. Soumitra Kumar Mandal Sanjukta Dey Siliguri Institute of Technology, Electrical Engineering Department National Institute
Design And Analysis Of Control Circuit For TCSC FACTS Controller Chiranjit Sain Dr. Soumitra Kumar Mandal Sanjukta Dey Siliguri Institute of Technology, Electrical Engineering Department National Institute
Improvement of Transient stability in Power Systems with Neuro- Fuzzy UPFC
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-11, pp-48-60 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Improvement of Transient stability in Power Systems
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-11, pp-48-60 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Improvement of Transient stability in Power Systems
DESIGN OF A MODE DECOUPLING FOR VOLTAGE CONTROL OF WIND-DRIVEN IG SYSTEM
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 8, Issue 5 (Nov. - Dec. 2013), PP 41-45 DESIGN OF A MODE DECOUPLING FOR VOLTAGE CONTROL OF
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 8, Issue 5 (Nov. - Dec. 2013), PP 41-45 DESIGN OF A MODE DECOUPLING FOR VOLTAGE CONTROL OF
Application of DE & PSO Algorithm For The Placement of FACTS Devices For Economic Operation of a Power System
 Application DE & PSO Algorithm For The Placement Devices For Economic Operation a Power System B. BHATTACHARYYA, VIKASH KUMAR GUPTA 2 Department Electrical Engineering, Indian School Mines, Dhanbad, Jharkhanbd
Application DE & PSO Algorithm For The Placement Devices For Economic Operation a Power System B. BHATTACHARYYA, VIKASH KUMAR GUPTA 2 Department Electrical Engineering, Indian School Mines, Dhanbad, Jharkhanbd
STUDY AND SIMULATION OF THE UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER (UPFC) IN POWER SYSTEM
 IETJOURAL ofegieerig &TECHOLOGY Winter 2011 STUDY AD SIMULATIO OF THE UIFIED POWER FLOW COTROLLER (UPFC) I POWER SYSTEM Ragini Malviya' co co L{) I (J) Z (j) (j) The main objectives Abstract of Flexible
IETJOURAL ofegieerig &TECHOLOGY Winter 2011 STUDY AD SIMULATIO OF THE UIFIED POWER FLOW COTROLLER (UPFC) I POWER SYSTEM Ragini Malviya' co co L{) I (J) Z (j) (j) The main objectives Abstract of Flexible
Power Flow Control/Limiting Short Circuit Current Using TCSC
 Power Flow Control/Limiting Short Circuit Current Using TCSC Gannavarapu Akhilesh 1 * D.Raju 2 1. ACTS, JNTU-H, PO box 500035, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India 2. M.Tech (NIT Nagpur), Hyderabad, Andhra
Power Flow Control/Limiting Short Circuit Current Using TCSC Gannavarapu Akhilesh 1 * D.Raju 2 1. ACTS, JNTU-H, PO box 500035, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India 2. M.Tech (NIT Nagpur), Hyderabad, Andhra
Fuzzy PID Controller Enhancement of Power System using TCSC
 Fuzzy PID Controller Enhancement of Power System using TCSC O.Srivani 1, B.Bhargava reddy 2 1 M.Tech STUDENT, DEPT. OF EEE BITS 2 ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, HOD, DEPT. OF EEE BITS Abstract This project presents
Fuzzy PID Controller Enhancement of Power System using TCSC O.Srivani 1, B.Bhargava reddy 2 1 M.Tech STUDENT, DEPT. OF EEE BITS 2 ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, HOD, DEPT. OF EEE BITS Abstract This project presents
factors that can be affecting the performance of a electrical power transmission system. Main problems which cause instability to a power system is vo
 2011 International Conference on Signal, Image Processing and Applications With workshop of ICEEA 2011 IPCSIT vol.21 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Location of FACTS devices for Real and Reactive
2011 International Conference on Signal, Image Processing and Applications With workshop of ICEEA 2011 IPCSIT vol.21 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Location of FACTS devices for Real and Reactive
Governor with dynamics: Gg(s)= 1 Turbine with dynamics: Gt(s) = 1 Load and machine with dynamics: Gp(s) = 1
 Load Frequency Control of Two Area Power System Using Conventional Controller 1 Rajendra Murmu, 2 Sohan Lal Hembram and 3 Ajay Oraon, 1 Assistant Professor, Electrical Engineering Department, BIT Sindri,
Load Frequency Control of Two Area Power System Using Conventional Controller 1 Rajendra Murmu, 2 Sohan Lal Hembram and 3 Ajay Oraon, 1 Assistant Professor, Electrical Engineering Department, BIT Sindri,
