Measurements on tones generated in a corrugated flow pipe with special attention to the influence of a low frequency oscillation.
|
|
|
- Ilene Curtis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Measurements on tones generated in a corrugated flow pipe with special attention to the influence of a low frequency oscillation. arxiv: v2 [physics.class-ph] 6 Jun 2011 Ulf R. Kristiansen 1, Pierre-Olivier Mattei 2, Cedric Pinhde 2, Muriel Amielh 3 1 Acoustics Research Center, NTNU, O.S. Bragstads plass 2b, 7491 Trondheim, Norway 2 Laboratoire de Mécanique et d Acoustique, CNRS, 31 Chemin Joseph Aiguier, Marseille, France 3 Institut de Recherche sur les Phénomènes Hors Équilibre, 49 rue F. Joliot Curie, Marseille, France In proceedings of the 34th Scandinavian Symposium on Physical Acoustics, Geilo, Norway, 30 January - 2 February ISBN , Summary It is well known that an air flow in a corrugated pipe might excite the longitudinal acoustic modes of the pipe. In this letter is reported experiments where a low frequency, oscillating flow with velocity magnitudes of the same order as the air flow has been added. Depending on the oscillation strength, it might silence the pipe or move the resonances to higher harmonics. It is also shown that a low frequency oscillation by itself might excite a higher frequency acoustic resonance of the pipe. PACS no Ks,43.28.Ra 1 Introduction Sound production in corrugated pipes has been a topic for scientific investigation for almost a century. Short pipes has been used in physics demonstrations and served as musical toys, but also been a topic for scientific research. The flow acoustic interaction is complicated as it involves a close interaction between the flow and the acoustics. A review of the literature on the topic up to about 2006 is given by Kristiansen and Wiik [4]. The studies up to that time were largely experimental. Simplified models of sound sources interacting with the pipe flow has later been presented by Goyder [3], Debut et al.[2], and Tonon et al. [7]. In a more direct numerical approach, Popescu and Johansen recently showed, by solving the compressible Navier Stokes equation numerically for a short corrugated pipe, that strong cavity vortices would interact with the boundary layer in parts of the pipe[5]. No full explanation of the sound generation by the flow and its feedback effect has, to the knowledge of the authors, been published. The topic has received renewed interest as the so called singing riser problem has become apparent in the natural gas industry. The long flexible pipes used for conveying gas are corrugated on the inside and are known to exhibit strong sound levels at pure tones on some off shore installations. Some recent publications directly treating the singing riser problem are published by Reinen [6], Belfroid et al. [1]. In the study by Reinen, a 20m long plastic tube, embedded in concrete, was used. Resonances were established between an open entry end, and a downstream side branch resonator. With air flowing through the pipe, it would sound at the side branch resonances. In a special test it was found that injecting sound from an attached loudspeaker, at a frequency one order of magnitude lower, and at a level of the same order as the flow induced resonance, would silence the pipe. 1
2 Figure 1: A sketch of the experimental set up. In the present communication we report the influence of low frequency sound on corrugated pipe resonances in a simple experimental arrangement. A hard walled box has been constructed with two openings, one connected to a small diameter corrugated pipe, and the other to a vacuum cleaner able to draw air through the system and thereby excite the corrugated pipe s longitudinal acoustic resonances. A loudspeaker is attached to one side of the box. For a low frequency pure tone sound from the loudspeaker, the arrangement effectively makes up an excited Helmholtz resonator with the air in the corrugated pipe oscillating as a single fluid body. For frequencies close to the Helmholtz resonance, high sound pressure levels and particle velocities (pipe fluid volume oscillations) are expected in the pipe. The Helmholtz resonance made up by the box and the corrugated pipe is in the present arrangement around 8.8Hz. The vacuum cleaner connecting pipe and different ways of attaching the vacuum cleaner in order to get the right velocity, would slightly change this value. At 10Hz the loudspeaker would give an adequate signal to observe the phenomenon and was therefore chosen as the test frequency. For a Helmholtz resonator of this type the oscillation velocity is expected nearly constant over the length of the pipe, while the pressure will decrease from the box towards the open end. 2 Experimental set up Asketchoftheexperimentalsetupisshowninfigure1. Theinnerboxvolumemeasures0.29x0.29x0.55 m 3. The corrugated pipe has an inner diameter of 25.4mm, and is 0.64m long. One end is mounted flush with the box s inner surface. The cavity pitch is 5.5 mm. The pipe geometry is similar to the one discussed reference 4. A 35mm inner diameter pipe connects the box to a vacuum cleaner. A 240 mm diameter loudspeaker is positioned at one of the box walls. The loudspeaker was fed 10Hz signals between 0 and 12V. To minimize static pressure differences on both side of the loudspeaker in a flow situation, it is backed by a 0.07 m 3 volume communicating with the box through small holes. The velocity is measured with a Pitot tube at the box side opening of the pipe. The Pitot tube is connected to an electronic manometer of type Alnor AXD. In a special test, a standard hot wire anemometer probe (type 55P11 operated with a DANTEC Streamline CTA system) was used to measure the fluctuating velocity at the pipe s entry section. The sound levels were recorded with a 160mm long probe microphone (type G.R.A.S. 40SC), positioned so that it measured the sound levels 30mm into the pipe. A second probe microphone was used as a control microphone in the middle of the tube. The signals were transferred to a computer and analyzed by the dbfa suite 4.9 (01dB Metravib). The microphone was calibrated using standard calibration equipment. The probe corrections are supplied by the manufacturer and were accounted for. 2
3 Figure 2: Sound pressure levels of dominant frequencies measured at 30mm position as function of flow velocity. 3 Results 3.1 Flow generated resonances In figure 2 are shown the resonances generated by letting the vacuum cleaner draw air through the pipe. The sound pressure level of the dominant peak (measured 30mm into the pipe from the air entry end) is plotted against the velocity measured at the box end of the pipe by the Pitot tube, U pt. The fundamental longitudinal resonance could not be excited. By increasing the velocity, harmonics were found at 506 (square), 751(circle), 1012(star), 1256(diamond), and 1517(plus) Hz. 3.2 Resonances generated by 10Hz oscillation alone It was also observed that with no air flow drawn through the system, the 10Hz oscillation could by itself excite resonances in the corrugated tube. Figure 3 shows the different dominant peaks as function of L 10 (30), the 10Hz sound pressure level measured 30mm from the flow entry opening. Figure 4 shows the spectrum at a L 10 (30) level of 107.6dB. We see that the peak is rather broad and modulated by the 10Hz tone. In what follows, we chose to represent the oscillating field by a sound pressure level value at a given position, namely the L 10 (30) value. Figure 3: Resonances generated by 10Hz tone alone. 3
4 3.3 Hot wire measurements Figure 4: Spectrum measured for L 10 (30) = 107.6dB. Some hot wire velocity measurements were done at the pipe s inflow end to record oscillation velocities directly. As no simultaneous velocity and pressure measurements were done, we have not tried to relate velocity values to pressure values at specific positions. The purpose of the velocity measurements were to record order of magnitude values. The measurements were done in the entry plane of the pipe on the axis position. Figure 5 shows an example of a fluctuating flow driven by the 10Hz tone alone. The difference in heights was interpreted as caused by the difference in exit and entry flows at this position. The exit flow would be more jet like than the entry flow, where air is sucked from all directions. In figure 6 is plotted the velocity when air is drawn through the system by the vacuum cleaner. The flow is here always entering the pipe which makes the signal more symmetric. The velocity measured with no loudspeaker signal is also plotted. As this signal also contains the flow excited resonance, we can observe the orders of magnitude difference in 10Hz oscillation velocities and the high frequency particle velocities. The difference in the mean level measured by the hot wire and the Pitot value is attributed to the difference in exit and entry flows discussed above. Figure 5: Hot wire measurement at center of the pipe s entry section. U pt = 0m/s; Vacuum cleaner end closed. Loudspeaker voltage 7.5V, L 10 (30)=101.1dB. 3.4 Influence of 10Hz tone on flow generated resonances In figure 7 are plotted spectra showing the influence of the 10Hz oscillation on the 2nd. longitudinal pipe resonance. With no 10Hz tone present, this resonance was easily excited with an air flow measured at 6.5m/s with the Pitot tube. Comparing the upper spectra with the one below, it is seen that the resonant peak is reduced at this position by about 40dB with an added L 10 (30) value of 89.4dB. Increasing the tone s level even more, higher order resonances become apparent. It is also seen that these are much broader. A zoom of the lower panel of figure 7 around the 5 th resonance peakshowsittobestronglyinfluenced bythe10hzsignal, seefigure8. Thesoundlevels aremeasured 4
5 Figure 6: Hot wire measurement at center of entry section, U pt = 10.9m/s. Loudspeaker voltage 9.0V. L 10 (30) = 110.5dB at a position 30mm into the tube from the air entry end. The sound levels will be higher at the different resonances pressure peak positions inside the pipe. In figures 9, 10, and 11 the 2nd, 3rd and 4th longitudinal resonances were generated by flow velocities U pt = 6.3,9.9and12.0m/s respectively. It is seen also here that by adding and increasing the 10Hz signal, the resonance levels are first lowered before the dominant peaks are shifted to the higher harmonics. 4 Summary The experimental results showed that a constant air flow above about 5m/s would excite the longitudinal acoustic resonances in a 0.64m long, 25mm inner diameter corrugated pipe, and that a superposed oscillating flow, with velocity amplitudes of the same order, would alter the acoustic field in a systematic manner. The oscillating (10Hz) flow would also by itself excite the acoustic resonances. The oscillating flow was for all measurements represented by the 10Hz sound pressure level measured at a position 30mm from the end of the pipe. For a given steady flow velocity exciting one of the acoustic resonances, the addition of a low frequency flow oscillation of a certain velocity amplitude would reduce the resonant pressure considerably. A further increase in the oscillation velocity would then shift the dominant acoustic peak to the higher resonant frequencies. Some hot wire measurements are presented to show that in the present experiment, the oscillation velocities were of the same order as the constant flow velocities. No detailed measurements have however yet been done on the details of the boundary layer in order to better understand the sound generating mechanism, or features like for instance the presence of acoustic streaming. We hope to give further information on this in future communications. References [1] S.P.C Belfroid and R.J Swindel and N. Kitney. Flow induced pulsations due to flexible risers. Offshore technology conference held in Houston Texas, paper OCT 19904,Houston Texas [2] V. Debut and J. Antunes and M. Moreira. Flow-acoustic interaction in corrugated pipes: time domain simulation of experimental phenomena. Ninth international conference on flow-induced vibration. Prague, Czech republic: [3] H. Goyder. On the modelling of noise generation in corrugated pipes. Journal of pressure vessel technology. 132:
6 Figure 7: Influence of 10Hz tone on the second longitudinal pipe resonance. Upper figure: resonance generated with flow velocity U pt = 6.5m/s (no 10Hz tone). Lower panels show the effect of an added 10Hz tone at increasing levels: (L 10 (30) = 0, 89.4, 96.6, and 109.4dB) [4] U. R. Kristiansen and G. A. Wiik. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. Experiments on sound generation in corrugated pipes with flow. 121: [5] M. Popescu and S. T. Johansen. Modelling of aero-acoustic wave propagation in low Mach number corrugated pipe flow. Prog. Comp. Fluid Dyn. 9: , [6] T. A. Reinen, Singing risers experimental work. Summary of results and conclusions. SINTEF Technical Report F [7] D. Tonon and B.J.T. Landry and S.P.C. Belfroid and J.F.H. Willems and G.J.C. Hofmans and A. Hirschberg. Whistling of a Pipe System With Multiple Side Branches: Comparison With Corrugated Pipes. Journal of Sound and Vibration. 329, ,
7 Figure 8: Close up of the resonance peak around 1250 Hz (5th longitudinal resonance) in the lower panel of figure 7. Figure 9: Effect of increasing 10Hz tone level on dominant spectrum peak. Start point is 2nd. harmonic excited with U pt = 6.3m/s. Figure 10: Effect of increasing 10Hz tone level on dominant spectrum peak. Start point is 3rd. harmonic excited with U pt = 9.9m/s. Figure 11: Effect of increasing 10Hz tone level on dominant spectrum peak. Start point is 4th harmonic excited with U pt = 12.0m/s. 7
Scaled Laboratory Experiments of Shallow Water Acoustic Propagation
 Scaled Laboratory Experiments of Shallow Water Acoustic Propagation Panagiotis Papadakis, Michael Taroudakis FORTH/IACM, P.O.Box 1527, 711 10 Heraklion, Crete, Greece e-mail: taroud@iacm.forth.gr Patrick
Scaled Laboratory Experiments of Shallow Water Acoustic Propagation Panagiotis Papadakis, Michael Taroudakis FORTH/IACM, P.O.Box 1527, 711 10 Heraklion, Crete, Greece e-mail: taroud@iacm.forth.gr Patrick
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Sound 16-1 Characteristics of Sound Sound can travel through h any kind of matter, but not through a vacuum. The speed of sound is different in different materials; in general, it is slowest
Chapter 16 Sound 16-1 Characteristics of Sound Sound can travel through h any kind of matter, but not through a vacuum. The speed of sound is different in different materials; in general, it is slowest
Examination of Organ Flue Pipe Resonator Eigenfrequencies by Means of the Boundary Element Method
 Examination of Organ Flue Pipe Resonator Eigenfrequencies by Means of the Boundary Element Method Gábor Szoliva Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department of Telecommunications, H-1117
Examination of Organ Flue Pipe Resonator Eigenfrequencies by Means of the Boundary Element Method Gábor Szoliva Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department of Telecommunications, H-1117
Reed chamber resonances and attack transients in free reed instruments
 PROCEEDINGS of the 22 nd International Congress on Acoustics Wind Instruments: Paper ICA2016-748 Reed chamber resonances and attack transients in free reed instruments James Cottingham (a) (a) Coe College,
PROCEEDINGS of the 22 nd International Congress on Acoustics Wind Instruments: Paper ICA2016-748 Reed chamber resonances and attack transients in free reed instruments James Cottingham (a) (a) Coe College,
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics
 Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 2013 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Physical Acoustics Session 4aPA: Nonlinear Acoustics I 4aPA8. Radiation
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 2013 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Physical Acoustics Session 4aPA: Nonlinear Acoustics I 4aPA8. Radiation
Noise from Pulsating Supercavities Prepared by:
 Noise from Pulsating Supercavities Prepared by: Timothy A. Brungart Samuel E. Hansford Jules W. Lindau Michael J. Moeny Grant M. Skidmore Applied Research Laboratory The Pennsylvania State University Flow
Noise from Pulsating Supercavities Prepared by: Timothy A. Brungart Samuel E. Hansford Jules W. Lindau Michael J. Moeny Grant M. Skidmore Applied Research Laboratory The Pennsylvania State University Flow
THE INFLUENCE OF MODULATED SLOTTED SYNTHETIC JET ON THE BYPASS OF HUMP
 Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 20, 2013, No. 3/4, p. 271 280 271 THE INFLUENCE OF MODULATED SLOTTED SYNTHETIC JET ON THE BYPASS OF HUMP Petr Pick*, Miroslav Andrle*, Vladislav Skála*, Milan Matějka* The articles
Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 20, 2013, No. 3/4, p. 271 280 271 THE INFLUENCE OF MODULATED SLOTTED SYNTHETIC JET ON THE BYPASS OF HUMP Petr Pick*, Miroslav Andrle*, Vladislav Skála*, Milan Matějka* The articles
Waves & Interference
 Waves & Interference I. Definitions and Types II. Parameters and Equations III. Sound IV. Graphs of Waves V. Interference - superposition - standing waves The student will be able to: HW: 1 Define, apply,
Waves & Interference I. Definitions and Types II. Parameters and Equations III. Sound IV. Graphs of Waves V. Interference - superposition - standing waves The student will be able to: HW: 1 Define, apply,
PIV STUDY OF STANDING WAVES IN A RESONANT AIR COLUMN
 PIV STUDY OF STANDING WAVES IN A RESONANT AIR COLUMN Pacs: 43.58.Fm, 43.20.Ye, 43.20.Ks Tonddast-Navaei, Ali; Sharp, David Open University Department of Environmental and Mechanical Engineering, Open University,
PIV STUDY OF STANDING WAVES IN A RESONANT AIR COLUMN Pacs: 43.58.Fm, 43.20.Ye, 43.20.Ks Tonddast-Navaei, Ali; Sharp, David Open University Department of Environmental and Mechanical Engineering, Open University,
describe sound as the transmission of energy via longitudinal pressure waves;
 1 Sound-Detailed Study Study Design 2009 2012 Unit 4 Detailed Study: Sound describe sound as the transmission of energy via longitudinal pressure waves; analyse sound using wavelength, frequency and speed
1 Sound-Detailed Study Study Design 2009 2012 Unit 4 Detailed Study: Sound describe sound as the transmission of energy via longitudinal pressure waves; analyse sound using wavelength, frequency and speed
Chapter 7. Waves and Sound
 Chapter 7 Waves and Sound What is wave? A wave is a disturbance that propagates from one place to another. Or simply, it carries energy from place to place. The easiest type of wave to visualize is a transverse
Chapter 7 Waves and Sound What is wave? A wave is a disturbance that propagates from one place to another. Or simply, it carries energy from place to place. The easiest type of wave to visualize is a transverse
Chapter 12. Preview. Objectives The Production of Sound Waves Frequency of Sound Waves The Doppler Effect. Section 1 Sound Waves
 Section 1 Sound Waves Preview Objectives The Production of Sound Waves Frequency of Sound Waves The Doppler Effect Section 1 Sound Waves Objectives Explain how sound waves are produced. Relate frequency
Section 1 Sound Waves Preview Objectives The Production of Sound Waves Frequency of Sound Waves The Doppler Effect Section 1 Sound Waves Objectives Explain how sound waves are produced. Relate frequency
No Brain Too Small PHYSICS
 WAVES: STANDING WAVES QUESTIONS No Brain Too Small PHYSICS PAN FLUTES (2016;1) Assume the speed of sound in air is 343 m s -1. A pan flute is a musical instrument made of a set of pipes that are closed
WAVES: STANDING WAVES QUESTIONS No Brain Too Small PHYSICS PAN FLUTES (2016;1) Assume the speed of sound in air is 343 m s -1. A pan flute is a musical instrument made of a set of pipes that are closed
About Doppler-Fizeau effect on radiated noise from a rotating source in cavitation tunnel
 PROCEEDINGS of the 22 nd International Congress on Acoustics Signal Processing in Acoustics (others): Paper ICA2016-111 About Doppler-Fizeau effect on radiated noise from a rotating source in cavitation
PROCEEDINGS of the 22 nd International Congress on Acoustics Signal Processing in Acoustics (others): Paper ICA2016-111 About Doppler-Fizeau effect on radiated noise from a rotating source in cavitation
Ph 2306 Experiment 2: A Look at Sound
 Name ID number Date Lab CRN Lab partner Lab instructor Ph 2306 Experiment 2: A Look at Sound Objective Because sound is something that we can only hear, it is difficult to analyze. You have probably seen
Name ID number Date Lab CRN Lab partner Lab instructor Ph 2306 Experiment 2: A Look at Sound Objective Because sound is something that we can only hear, it is difficult to analyze. You have probably seen
WAVES. Chapter Fifteen MCQ I
 Chapter Fifteen WAVES MCQ I 15.1 Water waves produced by a motor boat sailing in water are (a) neither longitudinal nor transverse. (b) both longitudinal and transverse. (c) only longitudinal. (d) only
Chapter Fifteen WAVES MCQ I 15.1 Water waves produced by a motor boat sailing in water are (a) neither longitudinal nor transverse. (b) both longitudinal and transverse. (c) only longitudinal. (d) only
Interaction Between Main Line Standing Waves and Side Branch Resonance Frequencies
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange University of Tennessee Honors Thesis Projects University of Tennessee Honors Program 5-2007 Interaction Between Main
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange University of Tennessee Honors Thesis Projects University of Tennessee Honors Program 5-2007 Interaction Between Main
A mechanical wave is a disturbance which propagates through a medium with little or no net displacement of the particles of the medium.
 Waves and Sound Mechanical Wave A mechanical wave is a disturbance which propagates through a medium with little or no net displacement of the particles of the medium. Water Waves Wave Pulse People Wave
Waves and Sound Mechanical Wave A mechanical wave is a disturbance which propagates through a medium with little or no net displacement of the particles of the medium. Water Waves Wave Pulse People Wave
Analysis on Acoustic Attenuation by Periodic Array Structure EH KWEE DOE 1, WIN PA PA MYO 2
 www.semargroup.org, www.ijsetr.com ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.03,Issue.24 September-2014, Pages:4885-4889 Analysis on Acoustic Attenuation by Periodic Array Structure EH KWEE DOE 1, WIN PA PA MYO 2 1 Dept of Mechanical
www.semargroup.org, www.ijsetr.com ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.03,Issue.24 September-2014, Pages:4885-4889 Analysis on Acoustic Attenuation by Periodic Array Structure EH KWEE DOE 1, WIN PA PA MYO 2 1 Dept of Mechanical
Structure of Speech. Physical acoustics Time-domain representation Frequency domain representation Sound shaping
 Structure of Speech Physical acoustics Time-domain representation Frequency domain representation Sound shaping Speech acoustics Source-Filter Theory Speech Source characteristics Speech Filter characteristics
Structure of Speech Physical acoustics Time-domain representation Frequency domain representation Sound shaping Speech acoustics Source-Filter Theory Speech Source characteristics Speech Filter characteristics
Experimental Investigation on the Flame Wrinkle Fluctuation under External Acoustic Excitation
 26 th ICDERS July 30 th August 4 th, 2017 Boston, MA, USA Experimental Investigation on the Flame Wrinkle Fluctuation under External Acoustic Excitation Lukai Zheng*, Shuaida Ji, and Yang Zhang Department
26 th ICDERS July 30 th August 4 th, 2017 Boston, MA, USA Experimental Investigation on the Flame Wrinkle Fluctuation under External Acoustic Excitation Lukai Zheng*, Shuaida Ji, and Yang Zhang Department
Waves Q1. MockTime.com. (c) speed of propagation = 5 (d) period π/15 Ans: (c)
 Waves Q1. (a) v = 5 cm (b) λ = 18 cm (c) a = 0.04 cm (d) f = 50 Hz Q2. The velocity of sound in any gas depends upon [1988] (a) wavelength of sound only (b) density and elasticity of gas (c) intensity
Waves Q1. (a) v = 5 cm (b) λ = 18 cm (c) a = 0.04 cm (d) f = 50 Hz Q2. The velocity of sound in any gas depends upon [1988] (a) wavelength of sound only (b) density and elasticity of gas (c) intensity
INFLUENCE OF VORTEX STRUCTURES ON PRESSURE AND ULTRASOUND IN VORTEX FLOW-METERS
 INFLUENCE OF VORTEX STRUCTURES ON PRESSURE AND ULTRASOUND IN VORTEX FLOW-METERS V. Hans*, H. Windorfer*, S. Perpeet** *Institute of Measurement and Control **Institute of Turbomachinery University of Essen,
INFLUENCE OF VORTEX STRUCTURES ON PRESSURE AND ULTRASOUND IN VORTEX FLOW-METERS V. Hans*, H. Windorfer*, S. Perpeet** *Institute of Measurement and Control **Institute of Turbomachinery University of Essen,
Airflow visualization in a model of human glottis near the self-oscillating vocal folds model
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 5 (2011) 21 28 Airflow visualization in a model of human glottis near the self-oscillating vocal folds model J. Horáček a,, V. Uruba a,v.radolf a, J. Veselý a,v.bula
Applied and Computational Mechanics 5 (2011) 21 28 Airflow visualization in a model of human glottis near the self-oscillating vocal folds model J. Horáček a,, V. Uruba a,v.radolf a, J. Veselý a,v.bula
Identification of Delamination Damages in Concrete Structures Using Impact Response of Delaminated Concrete Section
 Identification of Delamination Damages in Concrete Structures Using Impact Response of Delaminated Concrete Section Sung Woo Shin 1), *, Taekeun Oh 2), and John S. Popovics 3) 1) Department of Safety Engineering,
Identification of Delamination Damages in Concrete Structures Using Impact Response of Delaminated Concrete Section Sung Woo Shin 1), *, Taekeun Oh 2), and John S. Popovics 3) 1) Department of Safety Engineering,
The EarSpring Model for the Loudness Response in Unimpaired Human Hearing
 The EarSpring Model for the Loudness Response in Unimpaired Human Hearing David McClain, Refined Audiometrics Laboratory, LLC December 2006 Abstract We describe a simple nonlinear differential equation
The EarSpring Model for the Loudness Response in Unimpaired Human Hearing David McClain, Refined Audiometrics Laboratory, LLC December 2006 Abstract We describe a simple nonlinear differential equation
Flow tones in a pipeline-cavity system:effect of pipe asymmetry
 Journal of Fluids and Structures 17 (2003) 511 523 www.elsevier.nl/locate/jnlabr/yjfls Flow tones in a pipeline-cavity system:effect of pipe asymmetry D. Erdem a, D. Rockwell a, *, P. Oshkai a, M. Pollack
Journal of Fluids and Structures 17 (2003) 511 523 www.elsevier.nl/locate/jnlabr/yjfls Flow tones in a pipeline-cavity system:effect of pipe asymmetry D. Erdem a, D. Rockwell a, *, P. Oshkai a, M. Pollack
Psychology of Language
 PSYCH 150 / LIN 155 UCI COGNITIVE SCIENCES syn lab Psychology of Language Prof. Jon Sprouse 01.10.13: The Mental Representation of Speech Sounds 1 A logical organization For clarity s sake, we ll organize
PSYCH 150 / LIN 155 UCI COGNITIVE SCIENCES syn lab Psychology of Language Prof. Jon Sprouse 01.10.13: The Mental Representation of Speech Sounds 1 A logical organization For clarity s sake, we ll organize
Pre Test 1. Name. a Hz b Hz c Hz d Hz e Hz. 1. d
 Name Pre Test 1 1. The wavelength of light visible to the human eye is on the order of 5 10 7 m. If the speed of light in air is 3 10 8 m/s, find the frequency of the light wave. 1. d a. 3 10 7 Hz b. 4
Name Pre Test 1 1. The wavelength of light visible to the human eye is on the order of 5 10 7 m. If the speed of light in air is 3 10 8 m/s, find the frequency of the light wave. 1. d a. 3 10 7 Hz b. 4
Section 1 Sound Waves. Chapter 12. Sound Waves. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Section 1 Sound Waves Sound Waves Section 1 Sound Waves The Production of Sound Waves, continued Sound waves are longitudinal. Section 1 Sound Waves Frequency and Pitch The frequency for sound is known
Section 1 Sound Waves Sound Waves Section 1 Sound Waves The Production of Sound Waves, continued Sound waves are longitudinal. Section 1 Sound Waves Frequency and Pitch The frequency for sound is known
Frequency f determined by the source of vibration; related to pitch of sound. Period T time taken for one complete vibrational cycle
 Unit 1: Waves Lesson: Sound Sound is a mechanical wave, a longitudinal wave, a pressure wave Periodic sound waves have: Frequency f determined by the source of vibration; related to pitch of sound Period
Unit 1: Waves Lesson: Sound Sound is a mechanical wave, a longitudinal wave, a pressure wave Periodic sound waves have: Frequency f determined by the source of vibration; related to pitch of sound Period
Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure
 Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure Andy St-Onge* 1a, David W. Eaton 1b, and Adam Pidlisecky 1c 1 Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW Calgary,
Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure Andy St-Onge* 1a, David W. Eaton 1b, and Adam Pidlisecky 1c 1 Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW Calgary,
Flow around a NACA0018 airfoil with a cavity and its dynamical response to acoustic forcing
 Exp Fluids (2) 5:493 59 DOI.7/s348--65-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Flow around a NACA8 airfoil with a cavity and its dynamical response to acoustic forcing W. F. J. Olsman J. F. H. Willems A. Hirschberg T. Colonius
Exp Fluids (2) 5:493 59 DOI.7/s348--65-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Flow around a NACA8 airfoil with a cavity and its dynamical response to acoustic forcing W. F. J. Olsman J. F. H. Willems A. Hirschberg T. Colonius
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 14-7 Superposition and Interference Waves of small amplitude traveling through the same medium combine, or superpose, by simple addition. 14-7 Superposition and Interference If two pulses combine to give
14-7 Superposition and Interference Waves of small amplitude traveling through the same medium combine, or superpose, by simple addition. 14-7 Superposition and Interference If two pulses combine to give
PC1141 Physics I. Speed of Sound. Traveling waves of speed v, frequency f and wavelength λ are described by
 PC1141 Physics I Speed of Sound 1 Objectives Determination of several frequencies of the signal generator at which resonance occur in the closed and open resonance tube respectively. Determination of the
PC1141 Physics I Speed of Sound 1 Objectives Determination of several frequencies of the signal generator at which resonance occur in the closed and open resonance tube respectively. Determination of the
EVOLUTION OF SOUND SPECTRA OF FLUE INSTRUMENTS WITH THE CONTROL PARAMETERS AND THE ROLE OF AEROACOUSTICAL SOURCES.
 EVOLUTION OF SOUND SPECTRA OF FLUE INSTRUMENTS WITH THE CONTROL PARAMETERS AND THE ROLE OF AEROACOUSTICAL SOURCES. A. Almeida, B. Fabre, N. Montgermont, F. Blanc May 25, 27 Abstract In flue instruments,
EVOLUTION OF SOUND SPECTRA OF FLUE INSTRUMENTS WITH THE CONTROL PARAMETERS AND THE ROLE OF AEROACOUSTICAL SOURCES. A. Almeida, B. Fabre, N. Montgermont, F. Blanc May 25, 27 Abstract In flue instruments,
TOWARDS PRECISE PREDICTION OF FLOW PATTERS OF RESONATORS UNDER GRAZING FLOWS BY USING CARTESIAN- MESH CFD
 6th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM 6) 7th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD 7) 11 15 June 2018, Glasgow, UK TOWARDS PRECISE PREDICTION OF FLOW PATTERS OF RESONATORS
6th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM 6) 7th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD 7) 11 15 June 2018, Glasgow, UK TOWARDS PRECISE PREDICTION OF FLOW PATTERS OF RESONATORS
Pressure Response of a Pneumatic System
 Pressure Response of a Pneumatic System by Richard A., PhD rick.beier@okstate.edu Mechanical Engineering Technology Department Oklahoma State University, Stillwater Abstract This paper describes an instructive
Pressure Response of a Pneumatic System by Richard A., PhD rick.beier@okstate.edu Mechanical Engineering Technology Department Oklahoma State University, Stillwater Abstract This paper describes an instructive
PRODUCT DATA. Sound Intensity Calibrator Type 4297
 PRODUCT DATA Sound Intensity Calibrator Type 4297 Sound Intensity Calibrator Type 4297 is used for on-site sound-pressure calibration and pressure-residual intensity-index verification. Its most important
PRODUCT DATA Sound Intensity Calibrator Type 4297 Sound Intensity Calibrator Type 4297 is used for on-site sound-pressure calibration and pressure-residual intensity-index verification. Its most important
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF DIFFERENT MICROPHONE INSTALLATIONS FOR ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL IN DUCTS
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF DIFFERENT MICROPHONE INSTALLATIONS FOR ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL IN DUCTS M. Larsson, S. Johansson, L. Håkansson and I. Claesson Department of Signal Processing Blekinge Institute
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF DIFFERENT MICROPHONE INSTALLATIONS FOR ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL IN DUCTS M. Larsson, S. Johansson, L. Håkansson and I. Claesson Department of Signal Processing Blekinge Institute
Sound Waves Practice Problems PSI AP Physics 1. (D) It cannot be determined with the given information.
 Sound Waves Practice Problems PSI AP Physics 1 Name Multiple Choice 1. Two sound sources S 1 and S 2 produce waves with frequencies 500 Hz and 250 Hz. When we compare the speed of wave 1 to the speed of
Sound Waves Practice Problems PSI AP Physics 1 Name Multiple Choice 1. Two sound sources S 1 and S 2 produce waves with frequencies 500 Hz and 250 Hz. When we compare the speed of wave 1 to the speed of
CHAPTER 12 SOUND ass/sound/soundtoc. html. Characteristics of Sound
 CHAPTER 12 SOUND http://www.physicsclassroom.com/cl ass/sound/soundtoc. html Characteristics of Sound Intensity of Sound: Decibels The Ear and Its Response; Loudness Sources of Sound: Vibrating Strings
CHAPTER 12 SOUND http://www.physicsclassroom.com/cl ass/sound/soundtoc. html Characteristics of Sound Intensity of Sound: Decibels The Ear and Its Response; Loudness Sources of Sound: Vibrating Strings
Preview. Sound Section 1. Section 1 Sound Waves. Section 2 Sound Intensity and Resonance. Section 3 Harmonics
 Sound Section 1 Preview Section 1 Sound Waves Section 2 Sound Intensity and Resonance Section 3 Harmonics Sound Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and
Sound Section 1 Preview Section 1 Sound Waves Section 2 Sound Intensity and Resonance Section 3 Harmonics Sound Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and
of bamboo. notes. in the D4. learning to. amplitudes and. pipe. The the.5% to. each. individual. 2% range.
 Analysis of Bambooo as an Acousticall Medium Isaac Carrasquillo Physics 406 Final Report 2014-5-16 Abstract This semester I constructed and took measurements on a set of bamboo pan flute pipes. Construction
Analysis of Bambooo as an Acousticall Medium Isaac Carrasquillo Physics 406 Final Report 2014-5-16 Abstract This semester I constructed and took measurements on a set of bamboo pan flute pipes. Construction
CHAPTER 3 DEFECT IDENTIFICATION OF BEARINGS USING VIBRATION SIGNATURES
 33 CHAPTER 3 DEFECT IDENTIFICATION OF BEARINGS USING VIBRATION SIGNATURES 3.1 TYPES OF ROLLING ELEMENT BEARING DEFECTS Bearings are normally classified into two major categories, viz., rotating inner race
33 CHAPTER 3 DEFECT IDENTIFICATION OF BEARINGS USING VIBRATION SIGNATURES 3.1 TYPES OF ROLLING ELEMENT BEARING DEFECTS Bearings are normally classified into two major categories, viz., rotating inner race
Effect of Flow Impingement on the Acoustic Resonance Excitation in A Shallow Rectangular Cavity
 Effect of Flow Impingement on the Acoustic Resonance Excitation in A Shallow Rectangular Cavity Ahmed Omer 1), Atef Mohany 2) * and Marwan Hassan 3) 1),2) University of Ontario Institute of Technology,
Effect of Flow Impingement on the Acoustic Resonance Excitation in A Shallow Rectangular Cavity Ahmed Omer 1), Atef Mohany 2) * and Marwan Hassan 3) 1),2) University of Ontario Institute of Technology,
Resonance Tube. 1 Purpose. 2 Theory. 2.1 Air As A Spring. 2.2 Traveling Sound Waves in Air
 Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Numerical Study of a High Head Francis Turbine with Measurements from the Francis-99 Project
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Numerical Study of a High Head Francis Turbine with Measurements from the Francis-99 Project To cite this article: H Wallimann and R Neubauer 2015 J. Phys.:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Numerical Study of a High Head Francis Turbine with Measurements from the Francis-99 Project To cite this article: H Wallimann and R Neubauer 2015 J. Phys.:
Quarterly Progress and Status Report. A note on the vocal tract wall impedance
 Dept. for Speech, Music and Hearing Quarterly Progress and Status Report A note on the vocal tract wall impedance Fant, G. and Nord, L. and Branderud, P. journal: STL-QPSR volume: 17 number: 4 year: 1976
Dept. for Speech, Music and Hearing Quarterly Progress and Status Report A note on the vocal tract wall impedance Fant, G. and Nord, L. and Branderud, P. journal: STL-QPSR volume: 17 number: 4 year: 1976
Aeroacoustics in a Flow Pipe with a small, variable-length Cavity
 Aeroacoustics in a Flow Pipe with a small, variable-length Cavity Anders Bakke Krogvig Master of Science in Electronics Submission date: June 2012 Supervisor: Ulf R Kristiansen, IET Norwegian University
Aeroacoustics in a Flow Pipe with a small, variable-length Cavity Anders Bakke Krogvig Master of Science in Electronics Submission date: June 2012 Supervisor: Ulf R Kristiansen, IET Norwegian University
Waves are generated by an oscillator which has to be powered.
 Traveling wave is a moving disturbance. Can transfer energy and momentum from one place to another. Oscillations occur simultaneously in space and time. Waves are characterized by 1. their velocity 2.
Traveling wave is a moving disturbance. Can transfer energy and momentum from one place to another. Oscillations occur simultaneously in space and time. Waves are characterized by 1. their velocity 2.
APPENDIX T: Off Site Ambient Tests
 Appendix T1 APPENDIX T: Off Site Ambient Tests End of Blowholes road Substation access Surf Club East end of Blowholes Road Appendix T2 West end of Blowholes Road Appendix T3 West end of Blowholes Rd west
Appendix T1 APPENDIX T: Off Site Ambient Tests End of Blowholes road Substation access Surf Club East end of Blowholes Road Appendix T2 West end of Blowholes Road Appendix T3 West end of Blowholes Rd west
Chapter 16. Waves and Sound
 Chapter 16 Waves and Sound 16.1 The Nature of Waves 1. A wave is a traveling disturbance. 2. A wave carries energy from place to place. 1 16.1 The Nature of Waves Transverse Wave 16.1 The Nature of Waves
Chapter 16 Waves and Sound 16.1 The Nature of Waves 1. A wave is a traveling disturbance. 2. A wave carries energy from place to place. 1 16.1 The Nature of Waves Transverse Wave 16.1 The Nature of Waves
Resonance Tube Lab 9
 HB 03-30-01 Resonance Tube Lab 9 1 Resonance Tube Lab 9 Equipment SWS, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads
HB 03-30-01 Resonance Tube Lab 9 1 Resonance Tube Lab 9 Equipment SWS, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads
Guided Wave in Engineering Structures Using Non-Contact Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducers A Numerical Approach for the Technique Optimisation.
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Guided Wave in Engineering Structures Using Non-Contact Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducers A Numerical Approach for the Technique Optimisation.
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Guided Wave in Engineering Structures Using Non-Contact Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducers A Numerical Approach for the Technique Optimisation.
Characterization and Validation of Acoustic Cavities of Automotive Vehicles
 Characterization and Validation of Acoustic Cavities of Automotive Vehicles John G. Cherng and Gang Yin R. B. Bonhard Mark French Mechanical Engineering Department Ford Motor Company Robert Bosch Corporation
Characterization and Validation of Acoustic Cavities of Automotive Vehicles John G. Cherng and Gang Yin R. B. Bonhard Mark French Mechanical Engineering Department Ford Motor Company Robert Bosch Corporation
PHY-2464 Physical Basis of Music
 Physical Basis of Music Presentation 19 Characteristic Sound (Timbre) of Wind Instruments Adapted from Sam Matteson s Unit 3 Session 30 and Unit 1 Session 10 Sam Trickey Mar. 15, 2005 REMINDERS: Brass
Physical Basis of Music Presentation 19 Characteristic Sound (Timbre) of Wind Instruments Adapted from Sam Matteson s Unit 3 Session 30 and Unit 1 Session 10 Sam Trickey Mar. 15, 2005 REMINDERS: Brass
Inquiring activities on the acoustic phenomena at the classroom using sound card in personal computer
 Inquiring activities on the acoustic phenomena at the classroom using sound card in personal computer Y.H. Kim Korea Science Academy, 111 Backyangkwanmoonro, Busanjin-ku, 614-822 Busan, Republic of Korea
Inquiring activities on the acoustic phenomena at the classroom using sound card in personal computer Y.H. Kim Korea Science Academy, 111 Backyangkwanmoonro, Busanjin-ku, 614-822 Busan, Republic of Korea
An FEA-Based Acoustic Fatigue Analysis Methodology
 An FEA-Based Acoustic Fatigue Analysis Methodology Timothy C. Allison, Ph.D. Lawrence J. Goland, P.E. Southwest Research Institute San Antonio, TX ANSYS Regional Conference: Engineering the System August
An FEA-Based Acoustic Fatigue Analysis Methodology Timothy C. Allison, Ph.D. Lawrence J. Goland, P.E. Southwest Research Institute San Antonio, TX ANSYS Regional Conference: Engineering the System August
R. J. Jones Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017
 R. J. Jones Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Semiconductor Lasers (2 weeks) Semiconductor (diode) lasers are by far the most widely used lasers today. Their small size and properties of the light output
R. J. Jones Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Semiconductor Lasers (2 weeks) Semiconductor (diode) lasers are by far the most widely used lasers today. Their small size and properties of the light output
Resonant Tubes A N A N
 1 Resonant Tubes Introduction: Resonance is a phenomenon which is peculiar to oscillating systems. One example of resonance is the famous crystal champagne glass and opera singer. If you tap a champagne
1 Resonant Tubes Introduction: Resonance is a phenomenon which is peculiar to oscillating systems. One example of resonance is the famous crystal champagne glass and opera singer. If you tap a champagne
Compound quantitative ultrasonic tomography of long bones using wavelets analysis
 Compound quantitative ultrasonic tomography of long bones using wavelets analysis Philippe Lasaygues To cite this version: Philippe Lasaygues. Compound quantitative ultrasonic tomography of long bones
Compound quantitative ultrasonic tomography of long bones using wavelets analysis Philippe Lasaygues To cite this version: Philippe Lasaygues. Compound quantitative ultrasonic tomography of long bones
Date Period Name. Write the term that corresponds to the description. Use each term once. beat
 Date Period Name CHAPTER 15 Study Guide Sound Vocabulary Review Write the term that corresponds to the description. Use each term once. beat Doppler effect closed-pipe resonator fundamental consonance
Date Period Name CHAPTER 15 Study Guide Sound Vocabulary Review Write the term that corresponds to the description. Use each term once. beat Doppler effect closed-pipe resonator fundamental consonance
 15-8 1/31/2014 PRELAB PROBLEMS 1. Why is the boundary condition of the cavity such that the component of the air displacement χ perpendicular to a wall must vanish at the wall? 2. Show that equation (5)
15-8 1/31/2014 PRELAB PROBLEMS 1. Why is the boundary condition of the cavity such that the component of the air displacement χ perpendicular to a wall must vanish at the wall? 2. Show that equation (5)
Shallow cavity flow tone experiments: onset of locked-on states
 Journal of Fluids and Structures 17 (2003) 381 414 www.elsevier.nl/locate/jnlabr/yjfls Shallow cavity flow tone experiments: onset of locked-on states D. Rockwell a, *, J.-C. Lin a, P. Oshkai a, M. Reiss
Journal of Fluids and Structures 17 (2003) 381 414 www.elsevier.nl/locate/jnlabr/yjfls Shallow cavity flow tone experiments: onset of locked-on states D. Rockwell a, *, J.-C. Lin a, P. Oshkai a, M. Reiss
Whole geometry Finite-Difference modeling of the violin
 Whole geometry Finite-Difference modeling of the violin Institute of Musicology, Neue Rabenstr. 13, 20354 Hamburg, Germany e-mail: R_Bader@t-online.de, A Finite-Difference Modelling of the complete violin
Whole geometry Finite-Difference modeling of the violin Institute of Musicology, Neue Rabenstr. 13, 20354 Hamburg, Germany e-mail: R_Bader@t-online.de, A Finite-Difference Modelling of the complete violin
Speed of Sound. Introduction. Ryerson University - PCS 130
 Introduction Speed of Sound In many experiments, the speed of an object such as a ball dropping or a toy car down a track can be measured (albeit with some help from devices). In these instances, these
Introduction Speed of Sound In many experiments, the speed of an object such as a ball dropping or a toy car down a track can be measured (albeit with some help from devices). In these instances, these
Review of Standing Waves on a String
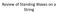 Review of Standing Waves on a String Below is a picture of a standing wave on a 30 meter long string. What is the wavelength of the running waves that the standing wave is made from? 30 m A.
Review of Standing Waves on a String Below is a picture of a standing wave on a 30 meter long string. What is the wavelength of the running waves that the standing wave is made from? 30 m A.
INFLUENCE OF MEMBRANE AMPLITUDE AND FORCING FREQUENCY ON SYNTHETIC JET VELOCITY
 TASKQUARTERLYvol.19,No2,2015,pp.111 120 INFLUENCE OF MEMBRANE AMPLITUDE AND FORCING FREQUENCY ON SYNTHETIC JET VELOCITY MARCIN KUROWSKI AND PIOTR DOERFFER Institute of Fluid-Flow Machinery, Polish Academy
TASKQUARTERLYvol.19,No2,2015,pp.111 120 INFLUENCE OF MEMBRANE AMPLITUDE AND FORCING FREQUENCY ON SYNTHETIC JET VELOCITY MARCIN KUROWSKI AND PIOTR DOERFFER Institute of Fluid-Flow Machinery, Polish Academy
Sound Waves and Beats
 Physics Topics Sound Waves and Beats If necessary, review the following topics and relevant textbook sections from Serway / Jewett Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 9th Ed. Traveling Waves (Serway
Physics Topics Sound Waves and Beats If necessary, review the following topics and relevant textbook sections from Serway / Jewett Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 9th Ed. Traveling Waves (Serway
L 5 Review of Standing Waves on a String
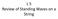 L 5 Review of Standing Waves on a String Below is a picture of a standing wave on a 30 meter long string. What is the wavelength of the running waves that the standing wave is made from? 30
L 5 Review of Standing Waves on a String Below is a picture of a standing wave on a 30 meter long string. What is the wavelength of the running waves that the standing wave is made from? 30
Development of a Reactive Silencer for Turbo Compressors
 Development of a Reactive Silencer for Turbo Compressors Jan Smeulers Nestor Gonzalez TNO Fluid Dynamics TNO Fluid Dynamics Stieltjesweg 1 Stieltjesweg 1 2628CK Delft 2628CK Delft jan.smeulers@tno.nl nestor.gonzalezdiez@tno.nl
Development of a Reactive Silencer for Turbo Compressors Jan Smeulers Nestor Gonzalez TNO Fluid Dynamics TNO Fluid Dynamics Stieltjesweg 1 Stieltjesweg 1 2628CK Delft 2628CK Delft jan.smeulers@tno.nl nestor.gonzalezdiez@tno.nl
Noise Suppression Spoiler for the Air Ring of a Large Polyethylene Film-Blowing Equipment
 Noise Suppression Spoiler for the Air Ring of a Large Polyethylene Film-Blowing Equipment K. K. Botros, E. Clavelle, J. Geerligs, J. Marler, R. Raynard, D. Cust and B. Rehlau NOVA Research & Technology
Noise Suppression Spoiler for the Air Ring of a Large Polyethylene Film-Blowing Equipment K. K. Botros, E. Clavelle, J. Geerligs, J. Marler, R. Raynard, D. Cust and B. Rehlau NOVA Research & Technology
Chapter 16 Sound. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Sound 16-6 Interference of Sound Waves; Beats Sound waves interfere in the same way that other waves do in space. 16-6 Interference of Sound Waves; Beats Example 16-12: Loudspeakers interference.
Chapter 16 Sound 16-6 Interference of Sound Waves; Beats Sound waves interfere in the same way that other waves do in space. 16-6 Interference of Sound Waves; Beats Example 16-12: Loudspeakers interference.
Resonant characteristics of flow pulsation in pipes due to swept sine constraint
 TRANSACTIONS OF THE INSTITUTE OF FLUID-FLOW MACHINERY No. 133, 2016, 131 144 Tomasz Pałczyński Resonant characteristics of flow pulsation in pipes due to swept sine constraint Institute of Turbomachinery,
TRANSACTIONS OF THE INSTITUTE OF FLUID-FLOW MACHINERY No. 133, 2016, 131 144 Tomasz Pałczyński Resonant characteristics of flow pulsation in pipes due to swept sine constraint Institute of Turbomachinery,
An experimental investigation of cavity noise control using mistuned Helmholtz resonators
 An experimental investigation of cavity noise control using mistuned Helmholtz resonators ABSTRACT V Surya Narayana Reddi CHINTAPALLI; Chandramouli PADMANABHAN 1 Machine Design Section, Department of Mechanical
An experimental investigation of cavity noise control using mistuned Helmholtz resonators ABSTRACT V Surya Narayana Reddi CHINTAPALLI; Chandramouli PADMANABHAN 1 Machine Design Section, Department of Mechanical
Acoustic Yagi Uda Antenna Using Resonance Tubes
 Acoustic Yagi Uda Antenna Using Resonance Tubes Yuki TAMURA 1 ; Kohei YATABE 2 ; Yasuhiro OUCHI 3 ; Yasuhiro OIKAWA 4 ; Yoshio YAMASAKI 5 1 5 Waseda University, Japan ABSTRACT A Yagi Uda antenna gets high
Acoustic Yagi Uda Antenna Using Resonance Tubes Yuki TAMURA 1 ; Kohei YATABE 2 ; Yasuhiro OUCHI 3 ; Yasuhiro OIKAWA 4 ; Yoshio YAMASAKI 5 1 5 Waseda University, Japan ABSTRACT A Yagi Uda antenna gets high
Multi-spectral acoustical imaging
 Multi-spectral acoustical imaging Kentaro NAKAMURA 1 ; Xinhua GUO 2 1 Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan 2 University of Technology, China ABSTRACT Visualization of object through acoustic waves is generally
Multi-spectral acoustical imaging Kentaro NAKAMURA 1 ; Xinhua GUO 2 1 Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan 2 University of Technology, China ABSTRACT Visualization of object through acoustic waves is generally
Optimization of an Acoustic Waveguide for Professional Audio Applications
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Optimization of an Acoustic Waveguide for Professional Audio Applications Mattia Cobianchi* 1, Roberto Magalotti 1 1 B&C Speakers S.p.A.
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Optimization of an Acoustic Waveguide for Professional Audio Applications Mattia Cobianchi* 1, Roberto Magalotti 1 1 B&C Speakers S.p.A.
Acoustics and Fourier Transform Physics Advanced Physics Lab - Summer 2018 Don Heiman, Northeastern University, 1/12/2018
 1 Acoustics and Fourier Transform Physics 3600 - Advanced Physics Lab - Summer 2018 Don Heiman, Northeastern University, 1/12/2018 I. INTRODUCTION Time is fundamental in our everyday life in the 4-dimensional
1 Acoustics and Fourier Transform Physics 3600 - Advanced Physics Lab - Summer 2018 Don Heiman, Northeastern University, 1/12/2018 I. INTRODUCTION Time is fundamental in our everyday life in the 4-dimensional
An overview of recent research on AM and OAM of wind turbine noise
 An overview of recent research on AM and OAM of wind turbine noise Helge Aagaard Madsen Franck Bertagnolio Andreas Fischer DTU Wind Energy Technical University of Denmark P.O. 49, DK-4000 Roskilde, Denmark
An overview of recent research on AM and OAM of wind turbine noise Helge Aagaard Madsen Franck Bertagnolio Andreas Fischer DTU Wind Energy Technical University of Denmark P.O. 49, DK-4000 Roskilde, Denmark
AERODYNAMIC NOISE RADIATED BY THE INTERCOACH SPACING AND THE BOGIE OF A HIGH-SPEED TRAIN
 Journal of Sound and
Journal of Sound and
High intensity and low frequency tube sound transmission loss measurements for automotive intake components
 High intensity and low frequency tube sound transmission loss measurements for automotive intake components Edward R. Green a) Sound Answers, Inc., 6855 Commerce Boulevard, Canton, Michigan, 48187 USA
High intensity and low frequency tube sound transmission loss measurements for automotive intake components Edward R. Green a) Sound Answers, Inc., 6855 Commerce Boulevard, Canton, Michigan, 48187 USA
Sound. Production of Sound
 Sound Production o Sound Sound is produced by a vibrating object. A loudspeaker has a membrane or diaphragm that is made to vibrate by electrical currents. Musical instruments such as gongs or cymbals
Sound Production o Sound Sound is produced by a vibrating object. A loudspeaker has a membrane or diaphragm that is made to vibrate by electrical currents. Musical instruments such as gongs or cymbals
Module 3: Velocity Measurement Lecture 13: Two wire hotwire measurement. The Lecture Contains: Hotwire Anemometry. Electromagnetic Actuator
 The Lecture Contains: Hotwire Anemometry Hotwire Probes CTA Bridge and Accessories Data Acquisition System Electromagnetic Actuator Auxiliary Instruments Digital Micromanometer Digital Multimeter Spectrum
The Lecture Contains: Hotwire Anemometry Hotwire Probes CTA Bridge and Accessories Data Acquisition System Electromagnetic Actuator Auxiliary Instruments Digital Micromanometer Digital Multimeter Spectrum
Demonstrate understanding of wave systems. Demonstrate understanding of wave systems. Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence
 Demonstrate understanding of wave systems Subject Reference Physics 3.3 Title Demonstrate understanding of wave systems Level 3 Credits 4 Assessment External This achievement standard involves demonstrating
Demonstrate understanding of wave systems Subject Reference Physics 3.3 Title Demonstrate understanding of wave systems Level 3 Credits 4 Assessment External This achievement standard involves demonstrating
Development of a reactive silencer for turbocompressors
 Development of a reactive silencer for turbocompressors N. González Díez, J.P.M. Smeulers, D. Meulendijks 1 S. König TNO Heat Transfer & Fluid Dynamics Siemens AG Energy Sector The Netherlands Duisburg/Germany
Development of a reactive silencer for turbocompressors N. González Díez, J.P.M. Smeulers, D. Meulendijks 1 S. König TNO Heat Transfer & Fluid Dynamics Siemens AG Energy Sector The Netherlands Duisburg/Germany
StandingWaves_P2 [41 marks]
![StandingWaves_P2 [41 marks] StandingWaves_P2 [41 marks]](/thumbs/87/95906524.jpg) StandingWaves_P2 [41 marks] A loudspeaker emits sound towards the open end of a pipe. The other end is closed. A standing wave is formed in the pipe. The diagram represents the displacement of molecules
StandingWaves_P2 [41 marks] A loudspeaker emits sound towards the open end of a pipe. The other end is closed. A standing wave is formed in the pipe. The diagram represents the displacement of molecules
Cold-Head Vibrations of a Coaxial Pulse Tube Refrigerator
 Cold-Head Vibrations of a Coaxial Pulse Tube Refrigerator T. Koettig 1, F. Richter 2, C. Schwartz 2, R. Nawrodt 2, M. Thürk 2 and P. Seidel 2 1 CERN, AT-CRG-CL, CH-1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland 2 Friedrich-Schiller-Universität
Cold-Head Vibrations of a Coaxial Pulse Tube Refrigerator T. Koettig 1, F. Richter 2, C. Schwartz 2, R. Nawrodt 2, M. Thürk 2 and P. Seidel 2 1 CERN, AT-CRG-CL, CH-1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland 2 Friedrich-Schiller-Universität
Physics I Notes: Chapter 13 Sound
 Physics I Notes: Chapter 13 Sound I. Properties of Sound A. Sound is the only thing that one can hear! Where do sounds come from?? Sounds are produced by VIBRATING or OSCILLATING OBJECTS! Sound is a longitudinal
Physics I Notes: Chapter 13 Sound I. Properties of Sound A. Sound is the only thing that one can hear! Where do sounds come from?? Sounds are produced by VIBRATING or OSCILLATING OBJECTS! Sound is a longitudinal
Dynamic Modeling of Air Cushion Vehicles
 Proceedings of IMECE 27 27 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress Seattle, Washington, November -5, 27 IMECE 27-4 Dynamic Modeling of Air Cushion Vehicles M Pollack / Applied Physical Sciences
Proceedings of IMECE 27 27 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress Seattle, Washington, November -5, 27 IMECE 27-4 Dynamic Modeling of Air Cushion Vehicles M Pollack / Applied Physical Sciences
Determination of an unknown frequency (beats)
 Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Determination of an unknown frequency (beats) (Item No.: P6011900) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: Age 16-19 Topic: Acoustics Subtopic: Wave
Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Determination of an unknown frequency (beats) (Item No.: P6011900) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: Age 16-19 Topic: Acoustics Subtopic: Wave
PanPhonics Panels in Active Control of Sound
 PanPhonics White Paper PanPhonics Panels in Active Control of Sound Seppo Uosukainen VTT Building and Transport Contents Introduction... 1 Active control of sound... 1 Interference... 2 Control system...
PanPhonics White Paper PanPhonics Panels in Active Control of Sound Seppo Uosukainen VTT Building and Transport Contents Introduction... 1 Active control of sound... 1 Interference... 2 Control system...
Acoustic Resonance Lab
 Acoustic Resonance Lab 1 Introduction This activity introduces several concepts that are fundamental to understanding how sound is produced in musical instruments. We ll be measuring audio produced from
Acoustic Resonance Lab 1 Introduction This activity introduces several concepts that are fundamental to understanding how sound is produced in musical instruments. We ll be measuring audio produced from
Resonance Tube. 1 Purpose. 2 Theory. 2.1 Air As A Spring. 2.2 Traveling Sound Waves in Air
 Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adapters, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adapters, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Sound, acoustics Slides based on: Rossing, The science of sound, 1990.
 Sound, acoustics Slides based on: Rossing, The science of sound, 1990. Acoustics 1 1 Introduction Acoustics 2! The word acoustics refers to the science of sound and is a subcategory of physics! Room acoustics
Sound, acoustics Slides based on: Rossing, The science of sound, 1990. Acoustics 1 1 Introduction Acoustics 2! The word acoustics refers to the science of sound and is a subcategory of physics! Room acoustics
Sound absorption of Helmholtz resonator included a winding built-in neck extension
 Sound absorption of Helmholtz resonator included a winding built-in neck extension Shinsuke NAKANISHI 1 1 Hiroshima International University, Japan ABSTRACT Acoustic resonant absorber like a perforated
Sound absorption of Helmholtz resonator included a winding built-in neck extension Shinsuke NAKANISHI 1 1 Hiroshima International University, Japan ABSTRACT Acoustic resonant absorber like a perforated
SUMMARY. ) f s Shock wave Sonic boom UNIT. Waves transmit energy. Sound is a longitudinal mechanical wave. KEY CONCEPTS CHAPTER SUMMARY
 UNIT D SUMMARY KEY CONCEPTS CHAPTER SUMMARY 9 Waves transmit energy. Crest, trough, amplitude, wavelength Longitudinal and transverse waves Cycle Period, frequency f 1_ T Universal wave equation v fλ Wave
UNIT D SUMMARY KEY CONCEPTS CHAPTER SUMMARY 9 Waves transmit energy. Crest, trough, amplitude, wavelength Longitudinal and transverse waves Cycle Period, frequency f 1_ T Universal wave equation v fλ Wave
Noise source characterization by highfrequency surface pressure measurements
 Noise source characterization by highfrequency surface pressure measurements Helge Aagaard Madsen Andreas Fischer Franck Bertagnolio Christian Bak Section Aeroelastic Design Department of Wind Energy hama@dtu.dk
Noise source characterization by highfrequency surface pressure measurements Helge Aagaard Madsen Andreas Fischer Franck Bertagnolio Christian Bak Section Aeroelastic Design Department of Wind Energy hama@dtu.dk
3D Distortion Measurement (DIS)
 3D Distortion Measurement (DIS) Module of the R&D SYSTEM S4 FEATURES Voltage and frequency sweep Steady-state measurement Single-tone or two-tone excitation signal DC-component, magnitude and phase of
3D Distortion Measurement (DIS) Module of the R&D SYSTEM S4 FEATURES Voltage and frequency sweep Steady-state measurement Single-tone or two-tone excitation signal DC-component, magnitude and phase of
