GLOSSARY OF TERMS. A device used to read a bar code symbol.
|
|
|
- Corey Gibbs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2-D Matrix Symbology A two dimensional arrangement of contrasting marks encoding information in accordance to specific rules. The resolution of the symbol's markings is substantially equal in two orthogonal axes. 2-D Stacked Symbology A symbology consisting of 2 or more adjacen and associated rows of varying-width parallel bars and spaces. All of the rows in a symbol are the same length. 2-Dimensional Bar Code Accuracy AIM Alignment ANSI Aperture ASCII Aspect Ratio Autodiscrimination Average Background Reflectance Background Bar Bar Code Bar Code Character Bar Code Density Bar Code Label Bar Code Reader Bar Code Symbol Bar Height Bar Length Bar Width Bar Width Reduction Blemish Percent CCD Character Character Alignment Two dimensional symbology composed of rows of data arranged in a rectangular or square pattern. The rows of data are stacked onto each other to encode an array of data. The determination of whether any element width or intercharacter gap width (if applicable) differs from its nominal width by more than the printing tolerance. Automatic Identification Manufacturers organization supported by manufacturers and suppliers of automatic identification products and services. In an automatic identification system, the relative position and orientation of a scanner to the symbol. The American National Standards Institute, a nongovernmental organization responsible for the development of voluntary standards. The opening in an optical system that establishes he field of view. The character set and code described in American national Standard Code for Information Interchange, ANSI X Each ANCII character is encoded with 7 bits. The ASCII character set is used for information interchange between data In a bar code symbol, the ratio of bar height to symbol length. Capability of reading and decoding more than one bar code symbology in a single piece of equipment. Expressed as a percent; the simple arithmetic average of the background reflectance from at least five different points on the sheet. The spaces, quiet zones and area surrounding a printed symbol. The darker element of a printed bar code symbol. An automatic identification technology that encodes information into an array of adjacent varying width parallel rectangular bars and spaces. A single group of bars and spaces that represents a specific number (often one) of numbers, letters, punctuation marks or other symbols. This is the smallest subset of a bar code symbol that contains data. The number of data characters that can be represented in a linear unit of measure. Bar code density is often expressed in characters per inch. A label that carries a bar code symbol and is suitable to be affixed to an article. A device used to read a bar code symbol. See Symbol. See Bar Length. The bar dimension perpendicular to the bar width. Also called height. Scanning is performed in an axis perpendicular to the bar length. The thickness of a bar measured from the edge closest to the symbol start character to the trailing edge of the same bar. Reduction of the nominal bar width dimension on field masters or printing plates to compensate for systematic errors in some printing processes. Bar width reduction can have positive or negative values. The Blemish Percent is an indication of what percent of the total measured bar height has spots or voids or is damaged with ink or toner blobs. A Charge Coupled Device is a bar code scanner which senses the light and dark areas of a symbol. 1. A single group of bars and spaces that represents a specific number (usually one) of numbers, letters, punctuation marks, or other symbols. 2. A graphic shape representing a letter, numeral, or symbol. 3. A letter, digit, or other symbol that is used as part of the organization, control or representation of data. The vertical or horizontal position of characters with respect to a given set of reference lines.
2 Character Density Character Set Check Character Check Digit Clear Area Cloaking Codabar Code 128 Code 16K Code 39 Coercivity Concatenation Continuous Code CPS CRT Data Matrix Decode Decoder Defects Density Depth of Field Diffuse Reflection For a conventional single-row bar code symbol, the number of characters represented in the symbol divided by the total width of the symbol, expressed as characters per unit width (as in characters per inch, cpi). For a multi-row bar code symbol, the number of characters represented by the symbol, expressed as characters per unit area. Those characters available for encodation in a particular automatic identification technology. Those characters included within a string of data whose value is used for the purpose of performing a mathematical check to ensure the accuracy of the data. A check digit serves the same purpose as a check character, but it may assume numeric values only. See Quiet Zone. A term used to describe placing an electronical mask over a bar code label. It is used when there is more than one bar code image in the field of view at the same time. A numeric only bar code consisting of seven black and white bars. Two bars are wide (Code 27). A alphanumeric bar code capable of encoding all 128 ASCII characters. Multi-row (stacked) code in which each symbol can have between two and sixteen rows or stacks. Each row is separated by a one module separator bar, and consists of 18 bars and 17 spaces. The code is analogous to sentences in a paragraph. A full alphanumeric bar code consisting of nine black and white bars. Three bars are wide (Code 3 of 9). Code 39 is the most frequently used symbology in industrial bar code systems today. Value of the opposing magnetic intensity that must be applied to a material to remove the residual magnetism when it has been magnetized to saturation. The ability of a reading system to join together the data from multiple symbols and interpret it as a single message. A bar code symbology where all spaces within the symbol are parts of characters, e.g., Interleaved 2 of 5. There is no intercharacter gap in a continuous code. Characters Per Second. Cathode Ray Tube. Also called a terminal or monitor. Variable size two dimensional matrix symbology that is inherently omnidirectional. Data Matrix has a high degree error correction capability and is used primarily for part marking and tracking. Each bar code symbology has a specific decode algorithm. If a symbol is decoded correctly, it will receive an "A" grade. If not, it will receive an "F" grade. The ANSI grade of Decode checks for: -Valid Characters -Correct start and stop characters (patterns) -Correct check digits (when applicable) -Legal quiet zones (i.e. blank space before and after a bar code) -Correct number and format of characters As part of a bar code reading system, the electronic package that receives the signals from the scanner, performs the algorithm to interpret the signals into meaningful data, and provides the interface to other devices. Defects are voids found in the bars or spots found in the spaces and quiet zones of a bar code symbol. Defects are measured by the ratio between the maximum element reflectance nonuniformity and symbol contrast. Element reflectance nonuniformity is the difference in reflectance between the highest peak and lowest value within an element (bar or space) of the bar code symbol. When an element consists of a single peak or valley, its reflectance nonuniformity is zero. Defects = ERNmax/SC. The grade for Defects is determined by: A(4.0)<=.15 B(3.0)<=.20 C(2.0)<=.25 D(1.0)<=.30 F(0)>.30. See Character Density. The distance between the maximum and minimum plane in which a code reader is capable of reading symbols of a specified X dimension. The component of reflected light that emanates in all directions from the reflecting surface.
3 Direct Thermal Discrete Code DPI EAN Edge Contrast Minimum (Ecmin) Edge Determination Element FCC FFO Film Master First Read Rate Font Font-Independent OCR Global Threshold GT Guard Bars A process in which a set of pins on a printhead are selectively heated onto heatsensitive paper (or label stock). In turn, the paper turns dark and a bar code is formed. Over time, a Direct Thermal image will eventually fade. Also known as Thermal Printing. A bar code symbology where the spaces between characters (interchanger gap) are not part of the code, e.g., Code 39. Dots Per Inch. European Article Numbering system, the international standard bar code for retail food packages. The Edge Contrast Minimum is the minimum difference in the reflectance value between any particular space (including quiet zones) and its adjoining bar within a bar code symbol. The smallest difference that is found across a bar code symbol must be at least 15%. In order to calculate the grade of Edge Determination, the Global Threshold (GT) of the bar code must first be determine: GT = Rmin + (SC/2). Once the Global Threshold is established, the elements of a bar code are defined as: BAR: Any point on the SRP at or below the Global Threshold. SPACE: Any point on the SRP above the Global Threshold. If the number of elements for a bar code symbology are invalid, the symbol will receive an "F"grade for Edge Determination. In a bar code symbol, a single bar or space. Federal Communication Commission. Fixed Focus Optics technology uses a small aperture and non-moving lenses to digitize an image over a wider range of distance than the traditional CCD reader. A photographic film representation of a specific bar code or OCR symbol from which a printing plate is produces. The ratio of the number of successful reads on the first scanning attempt to the number of attempts. Commonly expressed as a percentage. Abbreviated as FRR. A specific size and style of printer's type. Optical character recognition by generalized algorithms allowing wide ranges of character fonts. In the most general case, this extends to bar code patterns as well. See definition of GT. Abbreviation for Global Threshold. The global threshold is a position located half way between the highest recorded reflectance and the lowest recorded reflectance on a scan reflectance profile. The bars that are at both ends and center of a UPC and EAN symbol. They provide reference points for scanning, serving a function similar to start/stop codes. GUI Graphical User Interface. The visual design of a software application. Height This number indicates how many horizontal scan lines of the video camera detected bar code data. It is figured out by determining the difference between the lowest scan line number ever decoded and the highest scan line ever decoded. A standard UPC label will have a height of 140. This figure can be found on the SETUP SCREEN. Helium Neon Laser A type of laser commonly used in bar code scanners. It emits coherent red light in a wavelength of 633 nanometers. Horizontal Bar Code A bar code or symbol presented in such a manner that its overall length dimension is parallel to the horizon. The bars are presented in an array which look like a picket fence. I - 25 See Interleaved 2 of 5. IAN Industrial Article Numbering. See EAN. Ideal It is a number which indicates the ideal IRIS setting in a camera based reader. In Spec A term used to describe a bar code symbol that has been printed in complete compliance with the symbology specification's requirements for element widths and tolerances, element reflectivity and uniformity, spots, voids, and edge roughness.
4 Infrared Laser Diode Input Device Intercharacter Gap Interleaved 2 of 5 Interleaved Bar Code Iris Iso Label Repeat Ladder Barcode Laser Scanner LCD LED Light Pen LPM MaxiCode MICR Mil Minimum Reflectance (Rmin) Misread Modulation Module Modulo Check Digit or Character Moving Beam Bar Code Reader MRD MSI Plessey N Nanometer Narrow bar An invisible light beam used in some bar code readers to scan a bar code that is invisible to the human eye. This technology is used specifically to prohibit people from visually reading the bar code. Analogous to night vision goggles. That portion of a bar code reading system that employs electro-optical techniques to determine the localized reflectivity of a symbol. The space between two adjacent bar code characters in a discrete code. For example, the space between two characters in Code 39. A numeric only bar code consisting of five bars. Two bars are wide, three are narrow. Used generally in industrial and master carton labeling. A bar code in which characters are paired together using bars to represent the first character and spaces to represent the second, i.e., Interleaved 2 of 5 (See Continuous Code). [Vmax - Vmin = Iris] This number is an indication of how much light is being allowed on to the surface of the CCD element of the video camera. It is always equal to Vmax minus Vmin. It can be found on the SETUP SCREEN. The international standards organization,k and international nongovernmental organization responsible for the development of voluntary standards. The distance between the top of a bar code image to the top of the next bar code image. See Vertical Bar Code. An optical bar code reading device using a low energy laser light beam as is source of illumination. Liquid Crystal Display. Light emitting diode. A semiconductor that produces light at a wavelength determined by its chemical composition. The light source often used in light pens. In a bar code system, a hand-held scanning wand that is used as a contact bar code reader held in the hand. (See Wand Scanner.) Lines per minute. Fixed size two dimensional symbology having elements arranged around a unique circular finder pattern. MaxiCode is omnidirectional and is primarily used for freight sortation and tracking. Magnetic Ink Character Recognition style printing on the bottom of personal and bank checks. One one-thousandth of an inch (0.001"). Bar code densities are commonly referred to as number of mils (i.e. 10 mils). The reflectance value of the darkest bar within a bar code symbol must be less than or equal to half the reflectance of the lightest space. A condition that occurs when the data output of a reader does not agree with the data encoded in the bar code symbol. Modulation relates to how a scanner "sees" wide elements in relationship to narrow elements, as represented by reflectance values in the Scan Reflectance Profile. Scanners typically "see" narrow spaces as being less reflective than wide spaces. The closer the grades of Edge Contrast Minimum and Symbol Contrast, the higher the Modulation grade. MOD = ECmin/SC. The grade for Modulation is determined by: A(4.0)>=.70 B(3.0)>=.60 C(2.0)>=.50 D(1.0)>=.40 F(0)<.40 The narrowest nominal width unit of measure in a bar code. See Check Character. A scanning device where scanning motion is achieved by mechanically or electronically moving the optical geometry. Minimum Reflectance Differential. A method that is used to determine if there is an adequate difference between absorbed and reflected light. Modified Plessey Code is a pulse width modulated bar code used primarily for making retail shelving. The ratio between the widths of wide elements and narrow elements in a 2-width symbology. A unit of measure used to define the wavelength of light. Equal to 10-9 meters. 1. An indication of the bar width in nanoseconds. 2. This generally refers to the narrowest bar in a bar code.
5 Nominal Non-Read Numeric OCR OCR - A OCR - B Omnidirectional Omnidirectional Label Opacity Optical throw Orientation Overhead Oversquare PCS PDF417 PDT Picket Fence Code Pitch PostNet Print Contrast Print Quality Printhead Quiet Zone Raster Ratio The exact (or ideal) intended value for a specified parameter. Tolerances are specified as positive and negative deviations from this value. In a bar code system, the absence of data at the scanner output after an attempted scan due to no code, defective code, scanner failure or operator error. A character set that includes only the numbers. Optical Character Recognition is a technology designed specifically to read certain stylized fonts (such as OCR-A and OCR-B) containing the full alphanumeric character set. The term OCR is also used when translating and inputting other stylized fonts (such as Courier) or text found in magazines and newspapers into a computer. This technology is also referred to as Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR). An abbreviation commonly applied to the character set contained in ANSI Standard X An abbreviation commonly applied to the character set contained in ANSI Standard X A scanner that can read in both horizontal and vertical label positions, or any position between horizonal and vertical. Two oversquare bar codes, placed perpendicular to each other. A common application is the airline baggage label. The optical property of a substrate material that quantifies the show-through from the back side or the next sheet. The ratio of the reflectance with a black backing to the reflectance with a white backing. Ink opacity is the property of an ink that prevents the substrate from showing through. The region between the scanner and the readable depth of field. The alignment of a bar code symbol with respect to horizontal. Two possible orientations are horizontal with vertical bars and spaces (picket fence) and vertical with horizontal bars and spaces (ladder). Overhead - In a bar code system, the fixed number of characters required for start, stop and checking in a given symbol. For example, a symbol requiring a start/stop and 2 check characters contains 4 characters of overhead. Thus to encode 3 characters, 7 characters are required to be printed. A label in which the height is greater than the length. Print Contrast Signal. A measurement of the ratio of the reflectivities between the bars and spaces of a symbol, commonly expressed in percent. PCS is calculated as: R L -R D /R L x 100%, where RL = reflectivity of the light elements and RD = reflectivity of the dark elements. Two-dimensional bar code providing error correction, detection and security used primarily in parcel tracking applications and hazardous material control. Portable Data Terminal. Handheld terminal capable of storing and recording data that is captured remotely and later transmitted into a computer. See Horizontal Bar Code. Rotation of a bar code symbol about an axis parallel to the direction of the bars. Postal Numeric Encoding Technique used to encode ZIP code information on letter mail. PostNet uses redundant information within a compact bar code format to provide error detection capability and a significant degree of error correction capability. See PCS. The measure of compliance of a bar code symbol to the requirements of dimensional tolerance, edge roughness, spots, voids, reflectance, PCS, quiet zone, and encodation. The device on a direct thermal or thermal transfer printer containing the heating element that causes that image to be transferred to the facestock. A clear space, containing no dark marks, that precedes the start character of a bar code symbol and follows the stop characters. Sometimes called the "clear area". More than one scan line in two or more horizontal dimensions to allow reading of bar codes in different positions. The ratio between wide elements and narrow elements. It is used to measure decodability properly. This applies to symbologies such as Code 39 Codabar and, 2 of 5.
6 Read window Reader Reduced Scale Symbology Reflectance Resolution RF Ribbon RSS-14 RS-232 RS-422 RSS RSS Expanded RSS Limited RSS Stacked Scan line Scan rate Scan Reflectance Profile (SRP) Scanner Self-Checking Serial Communication Skew Skew Space Space Width Spectral Response Specular Reflection Specular reflection zone The region within which the scanner is capable of reading bar code. The read window is defined by the scanner's scan width, focal point, and depth of field. See Bar Code Reader. See RSS. The ratio of the amount of light of a specified wavelength or series of wavelengths reflected from a test surface to the amount of light reflected from a Barium Oxide or Magnesium Oxide standard under similar illumination conditions. In a bar code system, the narrowest element dimension that can be distinguished by a particular reading device or printed with a particular device or method. Radio Frequency. Wireless communication technology using electromagnetic waves to transmit and receive data. RF provides real-time access to a host computer. Material used with thermal transfer printers producing visible marks on a label (or substrate). A printhead is heated and the ribbon is burned on the label stock producing the bar code. Encodes the full 14 digit EAN.UCC item identification in a linear symbol. The most common communication interface (e.g. serial (COM) port) standard using a DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) and DCE (Data Communications Equipment) interface. Also known as serial communication. The second most common communication interface standard which extends beyond the 100 feet limitation of RS-232 data communication supporting a maximum distance of 4000 feet. A bar code symbology that contains three linear symbologies to be used with the EAN.UCC system. The use of the symbologies are restricted and subject to compliance with the EAN International (EAN) and Uniform Code Council Inc (UCC) rules and registration procedure. Encodes EAN.UCC item identification plus supplementary AI element strings such as weight and "best before" date in a linear symbology. RSS expanded can also be pinted in multiple rows as a stacked symbol. Encodes the 14-digit EAN.UCC item identification with indicator digits of zero or one in a linear symbol for use on small items. A version of the RSS-14 symbology that is stacked in two rows and is used when the normal symbol would be too wide for the application. It comes in two versions, a truncated version used for small item marking applications and a taller omnidirectional version which is designed to be read by omnidirectional scanners. RSS expanded can also be pinted in multiple rows as a stacked symbol. The beam of light that reads across the bar code for information. Scanner speed, in scans per second. A map (or plot) of the localized symbol reflectivity as a measuring aperture is scanned across the symbol along a specific path. The "peaks" of the SRP indicate the largest value of reflectance (the spaces in the bar code) and the "valleys" of the SRP indicate the smallest value of reflectance (the bars in the bar code). An electronic device that electro-optically converts optical information into electrical signals. A symbology is termed self-checking if a single printing defect will not cause a character to be transposed into another valid character in the same symbology. See RS-232. Rotation of a bar code symbol about an axis parallel to the symbols length. The rotation of a bar code symbol about an axis parallel to the bars. The lighter element of a bar code usually formed by the background between bars. The thickness of a space measured from the edge closest to the symbol start character to the trailing edge of the same space. The variation in sensitivity of a reading device or the variation in reflectivity of a test surface to light of different wavelengths. The mirror-like reflection of light from a surface. A narrow zone in front of the scanner in which direct, non-diffused light blinds the scanner.
7 Spot SRP Stack Code Standard Start/Stop Character or Pattern Substitution Error Rate (SER) Substrate Symbol Symbol Contrast: (SC) Symbol Density Symbol Length Target Thermal Thermal Transfer Tilt Traditional OCR Trigger UCC UCS Uniform Code Council (UCC) UPC UPC-A UPC-E USS Verifier Vertical Bar Code Visible Laser Diode 1. The undesirable presence of ink or dirt in a space. 2. The area on a bar code symbol that is being examined by an input device at any given point of time. See scan reflectance profile. Two-dimensional bar code where linear bar codes are stacked one upon another and are printed in a rectangular shape to achieve the most efficient use of label area. A set of rules, specifications, instructions, or directions for printing, labeling, scanning, etc. bar coded information. A special bar code character that provides the scanner with start and stop reading instructions as well as scanning direction indicator. The start character is normally at the left-hand end of a horizontally oriented symbol. The stop character is normally at the right-hand end of a horizontally oriented symbol. The rate of occurrence of incorrect characters from an automatic identification system. The surface on which a bar code symbol is printed. A combination of bar code characters including start/stop characters, quiet zones, data characters, and check characters required by a particular symbology, that forms a complete, scannable entity. The difference between the largest (including quiet zones) and smallest reflectance values within a Scan Reflectance Profile. SC = R,ax - Rmin. The grade for Symbol Contrast is determined by: A (4.0)>=70% B (3.0)>=55% C(2.0)>=40% D(1.0)>=20% F(0)<20% See Bar Code Density. The distance between the outside edges of the quiet zones on the two ends of a bar code symbol. This number correlates vision based bar code data to wand bar code data. A target value will increase or decrease due to differences in X dimensions, bar heights, or electronic noise. A full size UPC label will have a target of 190. See Direct Thermal. A process in which a set of pins on a printhead are selectively heated onto a ribbon and the ink from the ribbon is burned (transferred) onto the label stock. Thermal transfer leaves a permanent image on the label. Rotation of a bar code symbol about an axis perpendicular to the substrate. The first form of 2-dimensional OCR developed, using the stylized OCR-A and OCR- B fonts. A method for informing the scanner/decoder of when to look for bar codes. This can be an external sensor device or a host-generated signal. Uniform Code Council is an organization which administers the UPC and other retail standards. Uniform Container Symbol. Previously the Uniform Product Code Council, the organization that administers the UPC and other retail standards. Universal Product Code, the standard bar code symbol for retail food packages in the United States. A UPC symbol encoding a number system character, 10 digits of data, and a check digit. A UPC symbol encoding 6 digits of data in an arrangement that occupies less area than a UPC-A symbol. Also called a "zero-suppressed" symbol because a 10 digit UPC-A code can be compressed to a 6 digit UPC-E format by suppressing redundant zeros. Uniform Symbol Specification. The current series of symbology specifications published by AIM; currently include USS-Interleaved 2 of 5, USS-39, USS-93, USS- Codabar, and USS-128. A device which measures the characteristics of a bar code including the contrast, reflectance, modulation, and compliance with the parameters of the bar code symbology to ANSI/ISO standards. A code pattern presented in such orientation that the axis of the symbol from start to stop is perpendicular to the horizon. The individual bars are in an array appearing as rungs of a ladder. Used in most handheld scanners to project a visible red light for scanning human readable bar codes.
8 Vmax Vmin Void Wand Wand Scanner Wedge WYSIWYG X Dimension X Dimension Z Dimension This number indicates a value for the highest point of reflectivity in the image of a bar code as used in camera based systems. This number indicates a value for the lowest point of reflectivity in the image of a bar code label as used in camera based systems. The undesirable absence of ink in a printed bar. See Wand Scanner. A handheld scanning device used as a contact bar code or OCR reader. A hardware device or software program (Software Wedge) which uses a scanner for input and sends data directly into an application by emulating a keyboard stroke. A wedge (hardware wedge) is an external device and plugs between the keyboard and terminal. "What You See Is What You Get" is a term used to describe the presentation of the printable output viewed as is on the terminal. The nominal width dimension of the narrow bars and spaces in a bar code symbol. The narrowest element of a barcode image. The dimension of the narrowest bar in a bar code. The achieved width of the narrow elements, calculated as the average of the average narrow bar width and the average narrow space width.
Bar code Verifier Conformance Specifications. Using the INTEGRA-9000
 Bar code Verifier Conformance Specifications Using the INTEGRA-9000 From: Label Vision Systems, Inc. (LVS) Document Created: 4-1998 Edit / Print Date: 2-2003 C:\My Documents\INTEGRA -9000 VERIFIER CONFORMANCE
Bar code Verifier Conformance Specifications Using the INTEGRA-9000 From: Label Vision Systems, Inc. (LVS) Document Created: 4-1998 Edit / Print Date: 2-2003 C:\My Documents\INTEGRA -9000 VERIFIER CONFORMANCE
Barcode Slot Reader (B) For use with bar coded badge ID Cards Available in MiniTerm 905, 906, 907 & 910 models
 17741 Mitchell North Irvine, CA 92614 USA Phone: (949) 833-3355 Fax: (949) 833-0322 Sales: (800) 822-4333 www.genovation.com sales@genovation.com Barcode Slot Reader (B) For use with bar coded badge ID
17741 Mitchell North Irvine, CA 92614 USA Phone: (949) 833-3355 Fax: (949) 833-0322 Sales: (800) 822-4333 www.genovation.com sales@genovation.com Barcode Slot Reader (B) For use with bar coded badge ID
Bar Code Labels. Introduction
 Introduction to Bar Code Reading Technology Introduction Most people are familiar with bar codes. These are the bands of stripe lines which can be found on many grocery items and are used by scanning devices
Introduction to Bar Code Reading Technology Introduction Most people are familiar with bar codes. These are the bands of stripe lines which can be found on many grocery items and are used by scanning devices
Improving bar code quality
 Improving bar code quality The guidance documented here is intended to help packaging designers and printers achieve good quality printed bar codes on their packaging and products. This advice is particularly
Improving bar code quality The guidance documented here is intended to help packaging designers and printers achieve good quality printed bar codes on their packaging and products. This advice is particularly
dlsoft Barcode Analyser By dlsoft
 dlsoft Barcode Analyser By dlsoft This manual was produced using ComponentOne Doc-To-Help. Contents BarAnalyser 1 Introduction... 1 Barcode symbologies... 5 How to use BarAnalyser... 5 Walk through...
dlsoft Barcode Analyser By dlsoft This manual was produced using ComponentOne Doc-To-Help. Contents BarAnalyser 1 Introduction... 1 Barcode symbologies... 5 How to use BarAnalyser... 5 Walk through...
ISO Verification Fact Sheet
 Introduction To maintain scanning efficiency, barcodes need to be printed correctly and be of a high quality. Verification equipment can assist in providing an indication of the print quality of barcodes.
Introduction To maintain scanning efficiency, barcodes need to be printed correctly and be of a high quality. Verification equipment can assist in providing an indication of the print quality of barcodes.
Getting it Right. 1D Bar Code Quality Step By Step. Connecting the Dots from the Verification Report to Solving Your Linear Barcode Problems
 Getting it Right 1D Bar Code Quality Step By Step Connecting the Dots from the Verification Report to Solving Your Linear Barcode Problems www.barcode-test.com 630-235-6077 Second Edition June 2013 1 2013
Getting it Right 1D Bar Code Quality Step By Step Connecting the Dots from the Verification Report to Solving Your Linear Barcode Problems www.barcode-test.com 630-235-6077 Second Edition June 2013 1 2013
Regions Retail Lockbox
 Regions Retail Lockbox Envelope & Document Guide It s time to expect more. Regions Bank Member FDIC Revised 03/2018 ENVELOPE SPECIFICATIONS Courtesy Envelopes: Regions requires the Retail Lockbox client
Regions Retail Lockbox Envelope & Document Guide It s time to expect more. Regions Bank Member FDIC Revised 03/2018 ENVELOPE SPECIFICATIONS Courtesy Envelopes: Regions requires the Retail Lockbox client
DIRECT PART MARKING THE NEXT GENERATION OF DIRECT PART MARKING (DPM)
 DIRECT PART MARKING THE NEXT GENERATION OF DIRECT PART MARKING (DPM) Direct Part Marking (DPM) is a process by which bar codes are permanently marked onto a variety of materials. The DPM process allows
DIRECT PART MARKING THE NEXT GENERATION OF DIRECT PART MARKING (DPM) Direct Part Marking (DPM) is a process by which bar codes are permanently marked onto a variety of materials. The DPM process allows
Getting it Right. Bar Code Quality Step By Step. Connecting the Dots from the Verification Report to Solving Your Barcode Problems
 Getting it Right Bar Code Quality Step By Step Connecting the Dots from the Verification Report to Solving Your Barcode Problems First Edition August 2012 1 2012 Barcode-Test LLC Table of Contents Introduction
Getting it Right Bar Code Quality Step By Step Connecting the Dots from the Verification Report to Solving Your Barcode Problems First Edition August 2012 1 2012 Barcode-Test LLC Table of Contents Introduction
Laser Beam Analysis Using Image Processing
 Journal of Computer Science 2 (): 09-3, 2006 ISSN 549-3636 Science Publications, 2006 Laser Beam Analysis Using Image Processing Yas A. Alsultanny Computer Science Department, Amman Arab University for
Journal of Computer Science 2 (): 09-3, 2006 ISSN 549-3636 Science Publications, 2006 Laser Beam Analysis Using Image Processing Yas A. Alsultanny Computer Science Department, Amman Arab University for
Instructions for the Experiment
 Instructions for the Experiment Excitonic States in Atomically Thin Semiconductors 1. Introduction Alongside with electrical measurements, optical measurements are an indispensable tool for the study of
Instructions for the Experiment Excitonic States in Atomically Thin Semiconductors 1. Introduction Alongside with electrical measurements, optical measurements are an indispensable tool for the study of
Laser Telemetric System (Metrology)
 Laser Telemetric System (Metrology) Laser telemetric system is a non-contact gauge that measures with a collimated laser beam (Refer Fig. 10.26). It measure at the rate of 150 scans per second. It basically
Laser Telemetric System (Metrology) Laser telemetric system is a non-contact gauge that measures with a collimated laser beam (Refer Fig. 10.26). It measure at the rate of 150 scans per second. It basically
Elements of a Bar Code System. Application Note 1013
 Elements of a Bar Code System Application Note 1013 Introduction Bar code technology provides an accurate, easy, and inexpensive method of data storage and data entry for computerized information management
Elements of a Bar Code System Application Note 1013 Introduction Bar code technology provides an accurate, easy, and inexpensive method of data storage and data entry for computerized information management
DECISION NUMBER FOURTEEN TO THE TREATY ON OPEN SKIES
 DECISION NUMBER FOURTEEN TO THE TREATY ON OPEN SKIES OSCC.DEC 14 12 October 1994 METHODOLOGY FOR CALCULATING THE MINIMUM HEIGHT ABOVE GROUND LEVEL AT WHICH EACH VIDEO CAMERA WITH REAL TIME DISPLAY INSTALLED
DECISION NUMBER FOURTEEN TO THE TREATY ON OPEN SKIES OSCC.DEC 14 12 October 1994 METHODOLOGY FOR CALCULATING THE MINIMUM HEIGHT ABOVE GROUND LEVEL AT WHICH EACH VIDEO CAMERA WITH REAL TIME DISPLAY INSTALLED
Technical Explanation for Displacement Sensors and Measurement Sensors
 Technical Explanation for Sensors and Measurement Sensors CSM_e_LineWidth_TG_E_2_1 Introduction What Is a Sensor? A Sensor is a device that measures the distance between the sensor and an object by detecting
Technical Explanation for Sensors and Measurement Sensors CSM_e_LineWidth_TG_E_2_1 Introduction What Is a Sensor? A Sensor is a device that measures the distance between the sensor and an object by detecting
MVP Plus Printers Section [01596] [ ] Page 1
![MVP Plus Printers Section [01596] [ ] Page 1 MVP Plus Printers Section [01596] [ ] Page 1](/thumbs/93/111130855.jpg) 2005-05-16 Page 1 This section includes a manufacturer's guide specification for a thermal tape/label printer - with sophisticated features and a range of accessories for project site usage. This section
2005-05-16 Page 1 This section includes a manufacturer's guide specification for a thermal tape/label printer - with sophisticated features and a range of accessories for project site usage. This section
The Xiris Glossary of Machine Vision Terminology
 X The Xiris Glossary of Machine Vision Terminology 2 Introduction Automated welding, camera technology, and digital image processing are all complex subjects. When you combine them in a system featuring
X The Xiris Glossary of Machine Vision Terminology 2 Introduction Automated welding, camera technology, and digital image processing are all complex subjects. When you combine them in a system featuring
Considerations: Evaluating Three Identification Technologies
 Considerations: Evaluating Three Identification Technologies A variety of automatic identification and data collection (AIDC) trends have emerged in recent years. While manufacturers have relied upon one-dimensional
Considerations: Evaluating Three Identification Technologies A variety of automatic identification and data collection (AIDC) trends have emerged in recent years. While manufacturers have relied upon one-dimensional
Delete Current Exhibit VI and replace with this Exhibit VI Keep same Title
 Delete Current Exhibit VI and replace with this Exhibit VI Keep same Title PURPOSE -Provide measurable criteria for image exchange -Alert receiving bank personnel -Allow for automated detection and flagging
Delete Current Exhibit VI and replace with this Exhibit VI Keep same Title PURPOSE -Provide measurable criteria for image exchange -Alert receiving bank personnel -Allow for automated detection and flagging
ALLEN-BRADLEY Bulletin 2755 Industrial Medium and High-Spped Bar Code Scanners
 ALLEN-BRADLEY Bulletin 2755 Industrial Medium and High-Spped Bar Code Scanners (Catalog Numbers 2755-L7SA, -L7RA, -L7SB, -L7RB, -L7SC, -L7SD, -L7RD, -L9SA, -L9RA, -L9SB, -L9RB, -L9SD, -L9RD) User Manual
ALLEN-BRADLEY Bulletin 2755 Industrial Medium and High-Spped Bar Code Scanners (Catalog Numbers 2755-L7SA, -L7RA, -L7SB, -L7RB, -L7SC, -L7SD, -L7RD, -L9SA, -L9RA, -L9SB, -L9RB, -L9SD, -L9RD) User Manual
ECEN. Spectroscopy. Lab 8. copy. constituents HOMEWORK PR. Figure. 1. Layout of. of the
 ECEN 4606 Lab 8 Spectroscopy SUMMARY: ROBLEM 1: Pedrotti 3 12-10. In this lab, you will design, build and test an optical spectrum analyzer and use it for both absorption and emission spectroscopy. The
ECEN 4606 Lab 8 Spectroscopy SUMMARY: ROBLEM 1: Pedrotti 3 12-10. In this lab, you will design, build and test an optical spectrum analyzer and use it for both absorption and emission spectroscopy. The
CD: (compact disc) A 4 3/4" disc used to store audio or visual images in digital form. This format is usually associated with audio information.
 Computer Art Vocabulary Bitmap: An image made up of individual pixels or tiles Blur: Softening an image, making it appear out of focus Brightness: The overall tonal value, light, or darkness of an image.
Computer Art Vocabulary Bitmap: An image made up of individual pixels or tiles Blur: Softening an image, making it appear out of focus Brightness: The overall tonal value, light, or darkness of an image.
APPLICATIONS FOR TELECENTRIC LIGHTING
 APPLICATIONS FOR TELECENTRIC LIGHTING Telecentric lenses used in combination with telecentric lighting provide the most accurate results for measurement of object shapes and geometries. They make attributes
APPLICATIONS FOR TELECENTRIC LIGHTING Telecentric lenses used in combination with telecentric lighting provide the most accurate results for measurement of object shapes and geometries. They make attributes
S303D. Programming Guide. 2D Imaging Barcode Scanner. Advanced Handheld High-Speed Laser Scanner
 S303D 2D Imaging Barcode Scanner Programming Guide 1 Advanced Handheld High-Speed Laser Scanner Important Notice No warranty of any kind is made in regard to this material, including, but not limited
S303D 2D Imaging Barcode Scanner Programming Guide 1 Advanced Handheld High-Speed Laser Scanner Important Notice No warranty of any kind is made in regard to this material, including, but not limited
inemi Reel Labeling Workshop 2/27/2005 Glenn Aspenns
 inemi Reel Labeling Workshop 2/27/2005 Glenn Aspenns inemi Reel Labeling Workshop Presentation topics Elements for printing robustness Reading robustness Optimal label formatting Elements for Printing
inemi Reel Labeling Workshop 2/27/2005 Glenn Aspenns inemi Reel Labeling Workshop Presentation topics Elements for printing robustness Reading robustness Optimal label formatting Elements for Printing
Be aware that there is no universal notation for the various quantities.
 Fourier Optics v2.4 Ray tracing is limited in its ability to describe optics because it ignores the wave properties of light. Diffraction is needed to explain image spatial resolution and contrast and
Fourier Optics v2.4 Ray tracing is limited in its ability to describe optics because it ignores the wave properties of light. Diffraction is needed to explain image spatial resolution and contrast and
I-150. Programming Guide. Linear Imaging Barcode Scanner. Advanced Handheld High-Speed Laser Scanner
 I-150 Linear Imaging Barcode Scanner Programming Guide 1 Advanced Handheld High-Speed Laser Scanner Important Notice No warranty of any kind is made in regard to this material, including, but not limited
I-150 Linear Imaging Barcode Scanner Programming Guide 1 Advanced Handheld High-Speed Laser Scanner Important Notice No warranty of any kind is made in regard to this material, including, but not limited
Easy, Accurate, Trusted. User Manual. Phone: 877.WEBSCAN or Fax:
 Easy, Accurate, Trusted. User Manual Address: 1341 Sherman Drive Unit D, Longmont CO 80501 USA Phone: 877.WEBSCAN or 303.485.6811 Fax: 303.485.6353 Email: support@webscaninc.com Web: www.webscaninc.com
Easy, Accurate, Trusted. User Manual Address: 1341 Sherman Drive Unit D, Longmont CO 80501 USA Phone: 877.WEBSCAN or 303.485.6811 Fax: 303.485.6353 Email: support@webscaninc.com Web: www.webscaninc.com
Topic 3: Output Devices
 Topic 3: Output Devices 3.1 Introduction Output devices are used to translate computer signals into human readable forms. These devices enable the computer to communicate with the user: - Output: Information
Topic 3: Output Devices 3.1 Introduction Output devices are used to translate computer signals into human readable forms. These devices enable the computer to communicate with the user: - Output: Information
DATAVS2 series.
 VISION SENSORS DATAVS2 series The DATAVS2 vision sensor series presents all the characteristics able to solve artificial machine vision applications in a flexible and intuitive way. DATAVS2 is a completely
VISION SENSORS DATAVS2 series The DATAVS2 vision sensor series presents all the characteristics able to solve artificial machine vision applications in a flexible and intuitive way. DATAVS2 is a completely
Direct Part Mark Bar Code according to InData Systems
 Direct Part Mark Bar Code according to InData Systems Overview: Direct Part marking with a bar code symbol has had increasing drive in recent times as the need for traceability of parts history (manufacturer,
Direct Part Mark Bar Code according to InData Systems Overview: Direct Part marking with a bar code symbol has had increasing drive in recent times as the need for traceability of parts history (manufacturer,
Chapter 8. Representing Multimedia Digitally
 Chapter 8 Representing Multimedia Digitally Learning Objectives Explain how RGB color is represented in bytes Explain the difference between bits and binary numbers Change an RGB color by binary addition
Chapter 8 Representing Multimedia Digitally Learning Objectives Explain how RGB color is represented in bytes Explain the difference between bits and binary numbers Change an RGB color by binary addition
Capturing and Editing Digital Images *
 Digital Media The material in this handout is excerpted from Digital Media Curriculum Primer a work written by Dr. Yue-Ling Wong (ylwong@wfu.edu), Department of Computer Science and Department of Art,
Digital Media The material in this handout is excerpted from Digital Media Curriculum Primer a work written by Dr. Yue-Ling Wong (ylwong@wfu.edu), Department of Computer Science and Department of Art,
Optimizing throughput with Machine Vision Lighting. Whitepaper
 Optimizing throughput with Machine Vision Lighting Whitepaper Optimizing throughput with Machine Vision Lighting Within machine vision systems, inappropriate or poor quality lighting can often result in
Optimizing throughput with Machine Vision Lighting Whitepaper Optimizing throughput with Machine Vision Lighting Within machine vision systems, inappropriate or poor quality lighting can often result in
Vixar High Power Array Technology
 Vixar High Power Array Technology I. Introduction VCSELs arrays emitting power ranging from 50mW to 10W have emerged as an important technology for applications within the consumer, industrial, automotive
Vixar High Power Array Technology I. Introduction VCSELs arrays emitting power ranging from 50mW to 10W have emerged as an important technology for applications within the consumer, industrial, automotive
Machine Vision for the Life Sciences
 Machine Vision for the Life Sciences Presented by: Niels Wartenberg June 12, 2012 Track, Trace & Control Solutions Niels Wartenberg Microscan Sr. Applications Engineer, Clinical Senior Applications Engineer
Machine Vision for the Life Sciences Presented by: Niels Wartenberg June 12, 2012 Track, Trace & Control Solutions Niels Wartenberg Microscan Sr. Applications Engineer, Clinical Senior Applications Engineer
VISION. DataVS2 DATAVS2
 DATAVS2 The DataVS2 vision sensor series presents all the characteristics to solve artificial machine vision applications in a flexible and intuitive way. DataVS2 is a completely embedded device: the optic,
DATAVS2 The DataVS2 vision sensor series presents all the characteristics to solve artificial machine vision applications in a flexible and intuitive way. DataVS2 is a completely embedded device: the optic,
SURFACE ANALYSIS STUDY OF LASER MARKING OF ALUMINUM
 SURFACE ANALYSIS STUDY OF LASER MARKING OF ALUMINUM Julie Maltais 1, Vincent Brochu 1, Clément Frayssinous 2, Réal Vallée 3, Xavier Godmaire 4 and Alex Fraser 5 1. Summer intern 4. President 5. Chief technology
SURFACE ANALYSIS STUDY OF LASER MARKING OF ALUMINUM Julie Maltais 1, Vincent Brochu 1, Clément Frayssinous 2, Réal Vallée 3, Xavier Godmaire 4 and Alex Fraser 5 1. Summer intern 4. President 5. Chief technology
Coherent Laser Measurement and Control Beam Diagnostics
 Coherent Laser Measurement and Control M 2 Propagation Analyzer Measurement and display of CW laser divergence, M 2 (or k) and astigmatism sizes 0.2 mm to 25 mm Wavelengths from 220 nm to 15 µm Determination
Coherent Laser Measurement and Control M 2 Propagation Analyzer Measurement and display of CW laser divergence, M 2 (or k) and astigmatism sizes 0.2 mm to 25 mm Wavelengths from 220 nm to 15 µm Determination
STUDENT REVIEW QUESTION SET K CR/DR CONTENT AREA
 STUDENT REVIEW QUESTION SET K CR/DR CONTENT AREA RADT 2913 COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW 1 The CR cassette is backed by aluminum that: A. reflects x-rays B. absorbs x-rays C. captures the image D. transmits x-rays
STUDENT REVIEW QUESTION SET K CR/DR CONTENT AREA RADT 2913 COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW 1 The CR cassette is backed by aluminum that: A. reflects x-rays B. absorbs x-rays C. captures the image D. transmits x-rays
MS-520 Scan Head User's Manual. P/N Rev E
 MS-520 Scan Head User's Manual P/N 83-000500 Rev E Information and specifications in this manual are subject to change without notice. Copyright 2007 by Microscan Systems, Inc., 1201 S.W. 7th Street, Renton,
MS-520 Scan Head User's Manual P/N 83-000500 Rev E Information and specifications in this manual are subject to change without notice. Copyright 2007 by Microscan Systems, Inc., 1201 S.W. 7th Street, Renton,
FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION
 FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION Revised November 15, 2017 INTRODUCTION The simplest and most commonly described examples of diffraction and interference from two-dimensional apertures
FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION Revised November 15, 2017 INTRODUCTION The simplest and most commonly described examples of diffraction and interference from two-dimensional apertures
I-500. Programming Guide. 2D Imaging Barcode Scanner. Advanced Handheld High-Speed Laser Scanner
 I-500 2D Imaging Barcode Scanner Programming Guide 1 Advanced Handheld High-Speed Laser Scanner Important Notice No warranty of any kind is made in regard to this material, including, but not limited
I-500 2D Imaging Barcode Scanner Programming Guide 1 Advanced Handheld High-Speed Laser Scanner Important Notice No warranty of any kind is made in regard to this material, including, but not limited
NDFG Non-collinear difference frequency generator
 NDFG Non-collinear difference frequency generator Last Rev. 2011.09.21 PREFACE This manual contains user information for the non-collinear deference frequency generator (NDFG). Please, read this part of
NDFG Non-collinear difference frequency generator Last Rev. 2011.09.21 PREFACE This manual contains user information for the non-collinear deference frequency generator (NDFG). Please, read this part of
COLOR CONTRAST AND LUMINESCENCE SENSORS
 WHITE PAPER COLOR CONTRAST AND LUMINESCENCE SENSORS THE KEY TO SUCCESSFUL AUTOMATION CONTROL Bill Letterle Senior Engineer EMX Industries, Inc. PHOTOELECTRICS: THE KEY TO SUCCESSFUL AUTOMATION CONTROL
WHITE PAPER COLOR CONTRAST AND LUMINESCENCE SENSORS THE KEY TO SUCCESSFUL AUTOMATION CONTROL Bill Letterle Senior Engineer EMX Industries, Inc. PHOTOELECTRICS: THE KEY TO SUCCESSFUL AUTOMATION CONTROL
ISO/IEC INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Information technology Automatic identification and data capture techniques Bar code master test specifications
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/IEC 15421 Second edition 2010-06-01 Information technology Automatic identification and data capture techniques Bar code master test specifications Technologies de l'information
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/IEC 15421 Second edition 2010-06-01 Information technology Automatic identification and data capture techniques Bar code master test specifications Technologies de l'information
Chapter 11. Preparing a Document for Prepress and Printing Delmar, Cengage Learning
 Chapter 11 Preparing a Document for Prepress and Printing 2011 Delmar, Cengage Learning Objectives Explore color theory and resolution issues Work in CMYK mode Specify spot colors Create crop marks Create
Chapter 11 Preparing a Document for Prepress and Printing 2011 Delmar, Cengage Learning Objectives Explore color theory and resolution issues Work in CMYK mode Specify spot colors Create crop marks Create
Radial Polarization Converter With LC Driver USER MANUAL
 ARCoptix Radial Polarization Converter With LC Driver USER MANUAL Arcoptix S.A Ch. Trois-portes 18 2000 Neuchâtel Switzerland Mail: info@arcoptix.com Tel: ++41 32 731 04 66 Principle of the radial polarization
ARCoptix Radial Polarization Converter With LC Driver USER MANUAL Arcoptix S.A Ch. Trois-portes 18 2000 Neuchâtel Switzerland Mail: info@arcoptix.com Tel: ++41 32 731 04 66 Principle of the radial polarization
CPSC 4040/6040 Computer Graphics Images. Joshua Levine
 CPSC 4040/6040 Computer Graphics Images Joshua Levine levinej@clemson.edu Lecture 04 Displays and Optics Sept. 1, 2015 Slide Credits: Kenny A. Hunt Don House Torsten Möller Hanspeter Pfister Agenda Open
CPSC 4040/6040 Computer Graphics Images Joshua Levine levinej@clemson.edu Lecture 04 Displays and Optics Sept. 1, 2015 Slide Credits: Kenny A. Hunt Don House Torsten Möller Hanspeter Pfister Agenda Open
SECTION I - CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL IMAGING PROCESSING CONCEPTS
 RADT 3463 - COMPUTERIZED IMAGING Section I: Chapter 2 RADT 3463 Computerized Imaging 1 SECTION I - CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL IMAGING PROCESSING CONCEPTS RADT 3463 COMPUTERIZED IMAGING Section I: Chapter 2 RADT
RADT 3463 - COMPUTERIZED IMAGING Section I: Chapter 2 RADT 3463 Computerized Imaging 1 SECTION I - CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL IMAGING PROCESSING CONCEPTS RADT 3463 COMPUTERIZED IMAGING Section I: Chapter 2 RADT
ROBOT VISION. Dr.M.Madhavi, MED, MVSREC
 ROBOT VISION Dr.M.Madhavi, MED, MVSREC Robotic vision may be defined as the process of acquiring and extracting information from images of 3-D world. Robotic vision is primarily targeted at manipulation
ROBOT VISION Dr.M.Madhavi, MED, MVSREC Robotic vision may be defined as the process of acquiring and extracting information from images of 3-D world. Robotic vision is primarily targeted at manipulation
Unit 1.1: Information representation
 Unit 1.1: Information representation 1.1.1 Different number system A number system is a writing system for expressing numbers, that is, a mathematical notation for representing numbers of a given set,
Unit 1.1: Information representation 1.1.1 Different number system A number system is a writing system for expressing numbers, that is, a mathematical notation for representing numbers of a given set,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Technical overview drawing of the Roadrunner goniometer. The goniometer consists of three main components: an inline sample-viewing microscope, a high-precision scanning unit for
Supplementary Figure 1 Technical overview drawing of the Roadrunner goniometer. The goniometer consists of three main components: an inline sample-viewing microscope, a high-precision scanning unit for
Spatially Resolved Backscatter Ceilometer
 Spatially Resolved Backscatter Ceilometer Design Team Hiba Fareed, Nicholas Paradiso, Evan Perillo, Michael Tahan Design Advisor Prof. Gregory Kowalski Sponsor, Spectral Sciences Inc. Steve Richstmeier,
Spatially Resolved Backscatter Ceilometer Design Team Hiba Fareed, Nicholas Paradiso, Evan Perillo, Michael Tahan Design Advisor Prof. Gregory Kowalski Sponsor, Spectral Sciences Inc. Steve Richstmeier,
Module 5: Experimental Modal Analysis for SHM Lecture 36: Laser doppler vibrometry. The Lecture Contains: Laser Doppler Vibrometry
 The Lecture Contains: Laser Doppler Vibrometry Basics of Laser Doppler Vibrometry Components of the LDV system Working with the LDV system file:///d /neha%20backup%20courses%2019-09-2011/structural_health/lecture36/36_1.html
The Lecture Contains: Laser Doppler Vibrometry Basics of Laser Doppler Vibrometry Components of the LDV system Working with the LDV system file:///d /neha%20backup%20courses%2019-09-2011/structural_health/lecture36/36_1.html
Evaluating Barcode Reading Technologies
 Evaluating Barcode Reading Technologies Is a Laser Scanner or an Imager the Best Choice for Your Application? Product Line Card Evaluating Barcode Reading Technologies: Laser vs. Imager Microscan Systems,
Evaluating Barcode Reading Technologies Is a Laser Scanner or an Imager the Best Choice for Your Application? Product Line Card Evaluating Barcode Reading Technologies: Laser vs. Imager Microscan Systems,
A Handheld Image Analysis System for Portable and Objective Print Quality Analysis
 A Handheld Image Analysis System for Portable and Objective Print Quality Analysis Ming-Kai Tse Quality Engineering Associates (QEA), Inc. Contact information as of 2010: 755 Middlesex Turnpike, Unit 3
A Handheld Image Analysis System for Portable and Objective Print Quality Analysis Ming-Kai Tse Quality Engineering Associates (QEA), Inc. Contact information as of 2010: 755 Middlesex Turnpike, Unit 3
PICO MASTER 200. UV direct laser writer for maskless lithography
 PICO MASTER 200 UV direct laser writer for maskless lithography 4PICO B.V. Jan Tinbergenstraat 4b 5491 DC Sint-Oedenrode The Netherlands Tel: +31 413 490708 WWW.4PICO.NL 1. Introduction The PicoMaster
PICO MASTER 200 UV direct laser writer for maskless lithography 4PICO B.V. Jan Tinbergenstraat 4b 5491 DC Sint-Oedenrode The Netherlands Tel: +31 413 490708 WWW.4PICO.NL 1. Introduction The PicoMaster
Code Reader 2500 and Code Reader 3500 User Manual Appendix Appendix C - CR2500 and CR3500 Programming Code Matrix
 Code Reader 2500 and Code Reader 3500 User Manual Appendix Appendix C - CR2500 and CR3500 Programming Code Matrix C004675_AB_CR2500_CR3500_User Guide_Appendix _C 1 Table of Contents Batch Settings Batch
Code Reader 2500 and Code Reader 3500 User Manual Appendix Appendix C - CR2500 and CR3500 Programming Code Matrix C004675_AB_CR2500_CR3500_User Guide_Appendix _C 1 Table of Contents Batch Settings Batch
One Week to Better Photography
 One Week to Better Photography Glossary Adobe Bridge Useful application packaged with Adobe Photoshop that previews, organizes and renames digital image files and creates digital contact sheets Adobe Photoshop
One Week to Better Photography Glossary Adobe Bridge Useful application packaged with Adobe Photoshop that previews, organizes and renames digital image files and creates digital contact sheets Adobe Photoshop
This document is a preview generated by EVS
 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION SPÉCIFICATION TECHNIQUE TECHNISCHE SPEZIFIKATION CEN/TS 14826 August 2004 ICS 03.240; 35.040 English version Postal services - Automatic identification of items - Two dimensional
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION SPÉCIFICATION TECHNIQUE TECHNISCHE SPEZIFIKATION CEN/TS 14826 August 2004 ICS 03.240; 35.040 English version Postal services - Automatic identification of items - Two dimensional
Criteria for Optical Systems: Optical Path Difference How do we determine the quality of a lens system? Several criteria used in optical design
 Criteria for Optical Systems: Optical Path Difference How do we determine the quality of a lens system? Several criteria used in optical design Computer Aided Design Several CAD tools use Ray Tracing (see
Criteria for Optical Systems: Optical Path Difference How do we determine the quality of a lens system? Several criteria used in optical design Computer Aided Design Several CAD tools use Ray Tracing (see
LENSES. INEL 6088 Computer Vision
 LENSES INEL 6088 Computer Vision Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor array Each cell in the array is a Charge Coupled Device light-sensitive diode that converts photons to electrons
LENSES INEL 6088 Computer Vision Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor array Each cell in the array is a Charge Coupled Device light-sensitive diode that converts photons to electrons
CD-3600/3601 (U/R) 2D Image Scanner Quick Setup Guide
 CD-3600/3601 (U/R) 2D Image Scanner Quick Setup Guide Package Contents CD-3600U/3601U 2D image scanner USB cable Quick setup guide CD-3600-SK/CD-3601-SK 2D image scanner USB cable for SK-300 Quick setup
CD-3600/3601 (U/R) 2D Image Scanner Quick Setup Guide Package Contents CD-3600U/3601U 2D image scanner USB cable Quick setup guide CD-3600-SK/CD-3601-SK 2D image scanner USB cable for SK-300 Quick setup
Exercise questions for Machine vision
 Exercise questions for Machine vision This is a collection of exercise questions. These questions are all examination alike which means that similar questions may appear at the written exam. I ve divided
Exercise questions for Machine vision This is a collection of exercise questions. These questions are all examination alike which means that similar questions may appear at the written exam. I ve divided
Background. Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing. Improved Bartlane transmitted image. Example Bartlane transmitted image
 Background Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing Introduction to Digital Image Processing Interest comes from two primary backgrounds Improvement of pictorial information for human perception How
Background Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing Introduction to Digital Image Processing Interest comes from two primary backgrounds Improvement of pictorial information for human perception How
SMART LASER SENSORS SIMPLIFY TIRE AND RUBBER INSPECTION
 PRESENTED AT ITEC 2004 SMART LASER SENSORS SIMPLIFY TIRE AND RUBBER INSPECTION Dr. Walt Pastorius LMI Technologies 2835 Kew Dr. Windsor, ON N8T 3B7 Tel (519) 945 6373 x 110 Cell (519) 981 0238 Fax (519)
PRESENTED AT ITEC 2004 SMART LASER SENSORS SIMPLIFY TIRE AND RUBBER INSPECTION Dr. Walt Pastorius LMI Technologies 2835 Kew Dr. Windsor, ON N8T 3B7 Tel (519) 945 6373 x 110 Cell (519) 981 0238 Fax (519)
Xenon Area-Imaging Scanner. Features
 Xenon 1900 Area-Imaging Scanner Xenon 1900, Honeywell s sixth-generation of area-imaging technology, is redefining the standard for hand-held scanners. Featuring a custom sensor that is optimized for bar
Xenon 1900 Area-Imaging Scanner Xenon 1900, Honeywell s sixth-generation of area-imaging technology, is redefining the standard for hand-held scanners. Featuring a custom sensor that is optimized for bar
SPECTRAL SCANNER. Recycling
 SPECTRAL SCANNER The Spectral Scanner, produced on an original project of DV s.r.l., is an instrument to acquire with extreme simplicity the spectral distribution of the different wavelengths (spectral
SPECTRAL SCANNER The Spectral Scanner, produced on an original project of DV s.r.l., is an instrument to acquire with extreme simplicity the spectral distribution of the different wavelengths (spectral
User Manual. P6 Barcode Scanner. English
 User Manual P6 Barcode Scanner English Contents IMPORTANT NOTICE 4 Safety Precaution 4 Maintenance Precaution 4 Overview of Inateck P6 barcode Scanner 4 Appearance 4 Features of the Scanner 5 Introduction
User Manual P6 Barcode Scanner English Contents IMPORTANT NOTICE 4 Safety Precaution 4 Maintenance Precaution 4 Overview of Inateck P6 barcode Scanner 4 Appearance 4 Features of the Scanner 5 Introduction
PROGRAMMING GUIDE S302D. 2D Imaging Barcode Scanner. Programming Guide. Advanced imaging barcode scanner
 S302D 2D Imaging Barcode Scanner Programming Guide Advanced imaging barcode scanner i Important Notice No warranty of any kind is made in regard to this material, including, but not limited to, implied
S302D 2D Imaging Barcode Scanner Programming Guide Advanced imaging barcode scanner i Important Notice No warranty of any kind is made in regard to this material, including, but not limited to, implied
Design Description Document
 UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER Design Description Document Flat Output Backlit Strobe Dare Bodington, Changchen Chen, Nick Cirucci Customer: Engineers: Advisor committee: Sydor Instruments Dare Bodington, Changchen
UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER Design Description Document Flat Output Backlit Strobe Dare Bodington, Changchen Chen, Nick Cirucci Customer: Engineers: Advisor committee: Sydor Instruments Dare Bodington, Changchen
K600. Single colour wide array ink jet printing system. data sheet
 K600 Single colour wide array ink jet printing system data sheet K600 Single Colour Ink Jet Module For printers requiring variable data printing, the K600 is the only configurable wide array solution combining
K600 Single colour wide array ink jet printing system data sheet K600 Single Colour Ink Jet Module For printers requiring variable data printing, the K600 is the only configurable wide array solution combining
Images and Displays. Lecture Steve Marschner 1
 Images and Displays Lecture 2 2008 Steve Marschner 1 Introduction Computer graphics: The study of creating, manipulating, and using visual images in the computer. What is an image? A photographic print?
Images and Displays Lecture 2 2008 Steve Marschner 1 Introduction Computer graphics: The study of creating, manipulating, and using visual images in the computer. What is an image? A photographic print?
UNIVERSAL POSTAL UNION. POC SB PEG Doc 6. Postal Operations Council. Standards Board PHYSICAL ENCODING GROUP. Berne, 11 December 2002
 UNIVERSAL POSTAL UNION POC SB PEG 2002.4 Doc 6 Postal Operations Council Standards Board PHYSICAL ENCODING GROUP Berne, 11 December 2002 Colour and durability attributes of franking marks Please find attached
UNIVERSAL POSTAL UNION POC SB PEG 2002.4 Doc 6 Postal Operations Council Standards Board PHYSICAL ENCODING GROUP Berne, 11 December 2002 Colour and durability attributes of franking marks Please find attached
Online data sheet. CLV601-0D200 CLV60x BAR CODE SCANNERS
 Online data sheet CLV601-0D200 CLV60x A B C D E F H I J K L M N O P Q R S T Detailed technical data Features Connection type Reading field Scanner design Focus Sensor Sensor resolution Light source Ordering
Online data sheet CLV601-0D200 CLV60x A B C D E F H I J K L M N O P Q R S T Detailed technical data Features Connection type Reading field Scanner design Focus Sensor Sensor resolution Light source Ordering
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall, 2008. Digital Image Processing
Digital Image Processing Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall, 2008. Digital Image Processing
Table of Contents. For Pre-Sales Support or Questions call
 Printer Media Guide Table of Contents I. OVERVIEW: Printing with Barcodes PRINTER TYPES: Desktop vs. industrial PRINT METHOD: Direct thermal vs. thermal transfer PRINT MATERIAL: Choosing the right labels
Printer Media Guide Table of Contents I. OVERVIEW: Printing with Barcodes PRINTER TYPES: Desktop vs. industrial PRINT METHOD: Direct thermal vs. thermal transfer PRINT MATERIAL: Choosing the right labels
SICK AG WHITEPAPER HDDM + INNOVATIVE TECHNOLOGY FOR DISTANCE MEASUREMENT FROM SICK
 SICK AG WHITEPAPER HDDM + INNOVATIVE TECHNOLOGY FOR DISTANCE MEASUREMENT FROM SICK 2017-11 AUTHOR Dr. Thorsten Theilig Head of Product Unit Long Range Distance Sensors at SICK AG in Waldkirch / Germany
SICK AG WHITEPAPER HDDM + INNOVATIVE TECHNOLOGY FOR DISTANCE MEASUREMENT FROM SICK 2017-11 AUTHOR Dr. Thorsten Theilig Head of Product Unit Long Range Distance Sensors at SICK AG in Waldkirch / Germany
Installation Custom Sensors Series RS12100 CCD Scan Engine
 Installation Custom Sensors Series RS12100 CCD Scan Engine Introduction The RS12100 Series CCD Scan Engines are designed to be incorporated into equipment designs. Two interfaces are provided. The RS-232
Installation Custom Sensors Series RS12100 CCD Scan Engine Introduction The RS12100 Series CCD Scan Engines are designed to be incorporated into equipment designs. Two interfaces are provided. The RS-232
Digital Image Fundamentals. Digital Image Processing. Human Visual System. Contents. Structure Of The Human Eye (cont.) Structure Of The Human Eye
 Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Those who wish to succeed must ask the right preliminary questions Aristotle Images
Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Those who wish to succeed must ask the right preliminary questions Aristotle Images
Digital Image Fundamentals. Digital Image Processing. Human Visual System. Contents. Structure Of The Human Eye (cont.) Structure Of The Human Eye
 Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall,
Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall,
Eric B. Burgh University of Wisconsin. 1. Scope
 Southern African Large Telescope Prime Focus Imaging Spectrograph Optical Integration and Testing Plan Document Number: SALT-3160BP0001 Revision 5.0 2007 July 3 Eric B. Burgh University of Wisconsin 1.
Southern African Large Telescope Prime Focus Imaging Spectrograph Optical Integration and Testing Plan Document Number: SALT-3160BP0001 Revision 5.0 2007 July 3 Eric B. Burgh University of Wisconsin 1.
Bias errors in PIV: the pixel locking effect revisited.
 Bias errors in PIV: the pixel locking effect revisited. E.F.J. Overmars 1, N.G.W. Warncke, C. Poelma and J. Westerweel 1: Laboratory for Aero & Hydrodynamics, University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands,
Bias errors in PIV: the pixel locking effect revisited. E.F.J. Overmars 1, N.G.W. Warncke, C. Poelma and J. Westerweel 1: Laboratory for Aero & Hydrodynamics, University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands,
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall, 2008. Digital Image Processing
Digital Image Processing Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall, 2008. Digital Image Processing
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHOTOELECTRIC SENSING. Beam Make. Beam Break SECTION 1. Light State. Dark State. Dark State. Light. State 1-1
 Introduction Today s photoelectric sensor is one of the most versatile non-contact sensing devices known to man. The reliability of photoelectric eyes or sensors took a giant leap forward in the early
Introduction Today s photoelectric sensor is one of the most versatile non-contact sensing devices known to man. The reliability of photoelectric eyes or sensors took a giant leap forward in the early
Perfect Print Specification
 Perfect Print Specification 1 of 6 System Description This specification describes a system that will allow the CD printer in the Rimage Producer transporters to print in alignment with an art-screened
Perfect Print Specification 1 of 6 System Description This specification describes a system that will allow the CD printer in the Rimage Producer transporters to print in alignment with an art-screened
LVS 9580/9585 Operating Instructions
 LVS 9580/9585 Operating Instructions English LVS-9580 LVS-9585 P/N 84-9310011-02 Rev B Copyright 2017 Microscan Systems, Inc. Tel: +1.425.226.5700 / 800.762.1149 Fax: +1.425.226.8250 All rights reserved.
LVS 9580/9585 Operating Instructions English LVS-9580 LVS-9585 P/N 84-9310011-02 Rev B Copyright 2017 Microscan Systems, Inc. Tel: +1.425.226.5700 / 800.762.1149 Fax: +1.425.226.8250 All rights reserved.
White Paper: Modifying Laser Beams No Way Around It, So Here s How
 White Paper: Modifying Laser Beams No Way Around It, So Here s How By John McCauley, Product Specialist, Ophir Photonics There are many applications for lasers in the world today with even more on the
White Paper: Modifying Laser Beams No Way Around It, So Here s How By John McCauley, Product Specialist, Ophir Photonics There are many applications for lasers in the world today with even more on the
IMAGE FORMATION. Light source properties. Sensor characteristics Surface. Surface reflectance properties. Optics
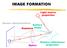 IMAGE FORMATION Light source properties Sensor characteristics Surface Exposure shape Optics Surface reflectance properties ANALOG IMAGES An image can be understood as a 2D light intensity function f(x,y)
IMAGE FORMATION Light source properties Sensor characteristics Surface Exposure shape Optics Surface reflectance properties ANALOG IMAGES An image can be understood as a 2D light intensity function f(x,y)
Digital Imaging Rochester Institute of Technology
 Digital Imaging 1999 Rochester Institute of Technology So Far... camera AgX film processing image AgX photographic film captures image formed by the optical elements (lens). Unfortunately, the processing
Digital Imaging 1999 Rochester Institute of Technology So Far... camera AgX film processing image AgX photographic film captures image formed by the optical elements (lens). Unfortunately, the processing
Scanning Setup Guide for TWAIN Datasource
 Scanning Setup Guide for TWAIN Datasource Starting the Scan Validation Tool... 2 The Scan Validation Tool dialog box... 3 Using the TWAIN Datasource... 4 How do I begin?... 5 Selecting Image settings...
Scanning Setup Guide for TWAIN Datasource Starting the Scan Validation Tool... 2 The Scan Validation Tool dialog box... 3 Using the TWAIN Datasource... 4 How do I begin?... 5 Selecting Image settings...
Quick Printing Guide (for BarTender )
 Quick Printing Guide (for BarTender ) M00087100 Rev.A Trademarks EPSON is a registered trademark of Seiko Epson Corporation. Exceed Your Vision is registered trademark or trademark of Seiko Epson Corporation.
Quick Printing Guide (for BarTender ) M00087100 Rev.A Trademarks EPSON is a registered trademark of Seiko Epson Corporation. Exceed Your Vision is registered trademark or trademark of Seiko Epson Corporation.
WE BRING QUALITY TO LIGHT DTS 500. Positioner Systems AUTOMATED DISPLAY AND LIGHT MEASUREMENT
 WE BRING QUALITY TO LIGHT DTS 500 Positioner Systems AUTOMATED DISPLAY AND LIGHT MEASUREMENT Standalone XYZ positioners (260 to 560 mm max. travel range) Standalone 2-axis goniometers (up to 70 cm diagonal
WE BRING QUALITY TO LIGHT DTS 500 Positioner Systems AUTOMATED DISPLAY AND LIGHT MEASUREMENT Standalone XYZ positioners (260 to 560 mm max. travel range) Standalone 2-axis goniometers (up to 70 cm diagonal
1D Scan Engine Integration Guide
 1D Scan Engine Integration Guide Content Chapter 1Getting Started... 3 Introduction...3 Feature...4 Application Field...5 Optics Reference...8 Appearance...10 Structure and dimension...11 Data Interface...13
1D Scan Engine Integration Guide Content Chapter 1Getting Started... 3 Introduction...3 Feature...4 Application Field...5 Optics Reference...8 Appearance...10 Structure and dimension...11 Data Interface...13
The Performance Improvement of a Linear CCD Sensor Using an Automatic Threshold Control Algorithm for Displacement Measurement
 The Performance Improvement of a Linear CCD Sensor Using an Automatic Threshold Control Algorithm for Displacement Measurement Myung-Kwan Shin*, Kyo-Soon Choi*, and Kyi-Hwan Park** Department of Mechatronics,
The Performance Improvement of a Linear CCD Sensor Using an Automatic Threshold Control Algorithm for Displacement Measurement Myung-Kwan Shin*, Kyo-Soon Choi*, and Kyi-Hwan Park** Department of Mechatronics,
Reading Barcodes from Digital Imagery
 Reading Barcodes from Digital Imagery Timothy R. Tuinstra Cedarville University Email: tuinstra@cedarville.edu Abstract This document was prepared for Dr. John Loomis as part of the written PhD. candidacy
Reading Barcodes from Digital Imagery Timothy R. Tuinstra Cedarville University Email: tuinstra@cedarville.edu Abstract This document was prepared for Dr. John Loomis as part of the written PhD. candidacy
SONAR THEORY AND APPLICATIONS
 SONAR THEORY AND APPLICATIONS EXCERPT FROM IMAGENEX MODEL 855 COLOR IMAGING SONAR USER'S MANUAL IMAGENEX TECHNOLOGY CORP. #209-1875 BROADWAY ST. PORT COQUITLAM, B.C. V3C 4Z1 CANADA TEL: (604) 944-8248
SONAR THEORY AND APPLICATIONS EXCERPT FROM IMAGENEX MODEL 855 COLOR IMAGING SONAR USER'S MANUAL IMAGENEX TECHNOLOGY CORP. #209-1875 BROADWAY ST. PORT COQUITLAM, B.C. V3C 4Z1 CANADA TEL: (604) 944-8248
Use of Photogrammetry for Sensor Location and Orientation
 Use of Photogrammetry for Sensor Location and Orientation Michael J. Dillon and Richard W. Bono, The Modal Shop, Inc., Cincinnati, Ohio David L. Brown, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, Ohio In this
Use of Photogrammetry for Sensor Location and Orientation Michael J. Dillon and Richard W. Bono, The Modal Shop, Inc., Cincinnati, Ohio David L. Brown, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, Ohio In this
