USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,831,842 Ogasawara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 3, 1998
|
|
|
- Melanie Day
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
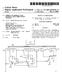
1 USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,831,842 Ogasawara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 3, ACTIVE COMMON MODE CANCELER 4.937,720 6/1990 Kirchberg /41 5, /1994 Akagi et al /34 75 Inventors: Satoshi Ogasawara; Hirofumi Akagi, 5,483,140 1/1996 Hess et al /34 both of Okayama; Hideki Ayano, 5,568,371 10/1996 Pitel et al /39 Okayama-ken, all of Japan 5,661,390 8/1997 Lipo et al /37 Primary Examiner Peter S. Wong 73 Assignee: President of Okayama University, Assistant Examiner Rajnikant B. Patel Okayama, Japan Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Oblon, Spivak, McClelland, Maier & Neustadt, P.C. 21 Appl. No.: 906, ABSTRACT 22 Filed: Aug. 5, 1997 An active common mode canceler includes a Voltage detec 30 Foreign Application Priority Data tion circuit including a plurality of capacitors connected to Sep. 18, 1996 JP Japan... s24002 the output terminals of a power converter for performing power conversion by Switching a power Semiconductor 51 Int. Cl.... H02M 1/12; H02M 5/45; device and Serving to detect a common mode Voltage HO2J 3/00 generated when the power Semiconductor device is 52 U.S. Cl /40; 363/37; 363/41; Switched, a push-pull type emitter follower circuit which is 363/34 controlled by the common mode voltage detected by the 58 Field of Search /40, 41, 39, Voltage detection voltage to output a Voltage equal in 363/37, 34, 132; 323/222 magnitude and opposite in polarity to the common mode Voltage, and a common mode transformer having multiple 56) References Cited windings and Serving to cancel out the common mode Voltage by Superimposing the Voltage output from the emit U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,679,130 7/1987 Moscovici /17 4,876,637 10/1989 Mose et al /37 18 Claims, 4 Drawing Sheets ter follower circuit on the output from the power converter. 39As DODE 200 V RECTFER 60 HZ IGBT INVERTER COMMON MODE CANCELER
2 U.S. Patent Nov. 3, 1998 Sheet 1 of 4 5,831,842 39As DODE IGBT 2OOV RECTFER INVERTER L2 6 COMMON MODE CANCELER F G. COMMON MODE CANCELER - - 2
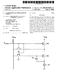
3 U.S. Patent Nov. 3, 1998 Sheet 2 of 4 5,831,842 COMMON MODE CURRENT 0.2A T OA COMMON MODE CURRENT Oov /N- F G. 3 2S COMMON MODE CURRENT O.2 A CURRENT IOOv
4 U.S. Patent Nov. 3, 1998 Sheet 3 of 4 5,831,842 3 g5 DODE IGBT 200V RECTFER INVERTER L2 6OHZ \ &AF ki it t \ irr, 2 =10kHz le?s H i(t) t CEV 10 MPFER H \, F G. 5-3 f DODE IGBT 200v RECTIFIER INVERTER 60 HZ 3.
5 U.S. Patent Nov. 3, 1998 Sheet 4 of 4 5, DODE IGBT 36v RECTFER 60 HZ 3 INVERTER COMMON MODE CANCELER F G. 7 3 gas DODE 200 V RECTFER NVERTER 4 L2 60Hz - - CONTROL CIRCUIT COMMON MODE CANCELE F G. 8
6 1 ACTIVE COMMON MODE CANCELER BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION The present invention relates to an active common mode canceler for canceling out a common mode Voltage (Zero phase-sequence voltage) generated when power conversion is performed by Switching a power Semiconductor device represented by a power converter, e.g., an inverter. In recent years, the range of applications of power con verters such as voltage-source PWM inverters for control ling the operations of motors as loads has widened, and the characteristics of power Semiconductor device have improved. With this trend, there have been increasing ten dencies to increase the carrier frequencies of the Voltage Source PWM inverters. With Such an increase in the frequency of a Voltage-Source PWM inverter, the following problems have become seri OUIS (1) a high-frequency leakage current flowing in the ground line through the Stray capacitance of the load; (2) electromagnetic interference (EMI) associated with conductivity and radioactive characteristics, (3) deterioration of motor winding insulation; and (4) disturbances caused by a motor shaft voltage, a bearing current, and the like. "Deterioration of motor winding insulation' is a phenomenon which occurs when the Sharply increasing components of the Step wise Voltage generated in the inverter concentrate at the input terminal of the motor winding. The term motor shaft Voltage means the Voltage generated between the frame and Shaft of the motor. This Voltage is applied on the thin oil film between each ball and the inner and outer races of the bearing. If the oil film is torn, a so-called bearing current flows. The bearing current causes a undesirable chemical reaction at the contact between the bearing and the motor shaft, inevitably shortening the lifetime of the bearing. These disturbances are caused by an abrupt change in Voltage or a current generated at the time of Switching of the voltage-source PWM inverter. AS to EMI, in particular, it is expected that Some council for Standards having international binding force, Such as CISPR (International Special Committee on Radio Interference) or IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), will discuss EMI standards for power elec tronics devices Such as inverters. Conventionally, to SuppreSS these disturbances, a com mon mode choke or an EMI filter is provided for the input circuit or output circuit of a Voltage-Source inverter. However, these elements are constituted by combinations of only passive elements, Such as reactors and capacitors. Even if, therefore, abrupt changes in current and Voltage may be Suppressed by Such an arrangement, the causes of distur bances themselves cannot be completely eliminated. BRIEF SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION It is an object of the present invention to provide an active common mode canceler which can completely eliminate disturbances caused by Stepwise changes in common mode Voltage generated at the time of Switching of the power Semiconductor device of a power converter. In order to achieve the above object, an active common mode canceler is constituted by the following means. According to the first aspect of the present invention, there is provided an active common mode canceler com 5,831, prising Voltage detection means for detecting a common mode Voltage generated when a power Semiconductor device of a power converter for performing power conver Sion by Switching the power Semiconductor device is Switched, a control Voltage Source which is controlled by the common mode Voltage detected by the Voltage detection means to generate a Voltage equal in magnitude and opposite in polarity to the common mode Voltage, and Voltage Super imposition means for canceling out the common mode Voltage by Superimposing the Voltage generated by the control Voltage Source on an output from the power con Verter. According to the Second aspect of the present invention, there is provided an active common mode canceler com prising a control Voltage Source for outputting a common mode Voltage to cancel out a common mode Voltage gen erated when a power Semiconductor device of a power converter for performing power conversion by Switching the power Semiconductor device is Switched, Voltage Superim position means for Superimposing the common mode Volt age output from the control Voltage Source on the common mode Voltage generated by the power converter, and Voltage detection means for detecting the common mode Voltages from the power converter and the control Voltage Source which are Superimposed by the Voltage Superimposition means, and feeding back the detected Voltage to the control Voltage Source, wherein the control Voltage Source controls to Set the Voltage detected by the Voltage detection means to ZCO. According to the third aspect of the present invention, there is provided an active common mode canceler com prising a control Voltage Source for outputting a common mode Voltage to cancel out a common mode Voltage gen erated when a power Semiconductor device of a power converter for performing power converter by Switching the power Semiconductor device is Switched, Voltage Superim position means for Superimposing the common mode Volt age output from the control Voltage Source on the common mode Voltage generated by the power converter, and current detection means for detecting a common mode current which flows when the common mode voltages from the power converter and the control Voltage Source are Super imposed by the Voltage Superimposition means, and feeding back the detected current to the control Voltage Source, wherein the control Voltage Source controls to Set the current detected by the current detection means to Zero. According to the fourth aspect of the present invention, there is provided an active common mode canceler com prising computation means for computing a common mode Voltage, which is generated when a power Semiconductor device of a power converter for performing power conver Sion by Switching the power Semiconductor device is Switched, on the basis of a reference value used to ON/OFF control the power Semiconductor device, a control Voltage Source which is controlled by the common mode Voltage obtained by the computation means to generate a Voltage equal in magnitude and opposite in polarity to the common mode Voltage, and Voltage Superimposition means for can celing out the common mode Voltage by Superimposing the Voltage generated by the Voltage control Source on an output from the power converter. In the active common mode cancelers according to the first to fourth aspects of the present invention, a common mode Voltage equal in magnitude and opposite in polarity to the common mode Voltage generated when the power Semi conductor device of the power converter is Switched is generated, and the common mode Voltage applied to the load
7 3 can be canceled out by Superimposing this common mode Voltage on an output from the power converter. Therefore, the harmful common mode Voltage generated by the power converter can be completely eliminated. Additional objects and advantages of the invention will be set forth in the description which follows, and in part will be obvious from the description, or may be learned by practice of the invention. The objects and advantages of the invention may be realized and obtained by means of the instrumen talities and combinations particularly pointed out in the appended claims. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE SEVERAL VIEWS OF THE DRAWING The accompanying drawings, which are incorporated in and constitute a part of the Specification, illustrate presently preferred embodiments of the invention, and together with the general description given above and the detailed descrip tion of the preferred embodiments given below, servo to explain the principles of the invention. FIG. 1 is a circuit diagram showing the first embodiment of the present invention in which an active common mode canceler of the present invention is applied to the main circuit of a System for performing vector control on an induction motor by using a voltage-source PWM inverter; FIG. 2 is an equivalent circuit diagram of the active common mode canceler of the first embodiment; FIG. 3 is a graph showing the waveform of a common mode current flowing from an inverter to an induction motor when no active common mode canceler is used; FIG. 4 is a graph showing the waveform of a common mode current flowing from an inverter to an induction motor when an active common mode canceler is used; FIG. 5 is a circuit diagram showing the Second embodi ment of the present invention; FIG. 6 is a circuit diagram showing the third embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 7 is a circuit diagram showing the fourth embodi ment of the present invention; and FIG. 8 is a circuit diagram showing the fifth embodiment of the present invention. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION The embodiments of the present invention will be described below. FIG. 1 is a circuit diagram showing the first embodiment of the present invention in which an active common mode canceler of the present invention is applied to the main circuit of a System for performing vector control on an induction motor by using a voltage-source PWM inverter. Referring to FIG. 1, reference numeral 1 denotes a three-phase AC power Supply; 2, a rectifier for converting an AC output from the three-phase AC power Supply 1 into a DC output, 3, a Smoothing capacitor for Smoothing the DC output from the rectifier 2; and 4, a voltage-source PWM inverter (to be simply referred to as an inverter hereinafter) for receiving the DC voltage Smoothed by the Smoothing capacitor 3 and converting the DC voltage into a three-phase AC voltage by Switching a power Semiconductor device (IGPT). The three-phase AC output terminals of the inverter 4 are connected to an induction motor 6 through cables 5. The Stator frame (to be simply referred to as a frame hereinafter) 5,831, of the induction motor 6 is connected to the ground terminal through the ground line. A common mode canceler 7 is connected to the output terminals of the inverter 4 of this main circuit arrangement. The common mode canceler 7 includes a Voltage detection circuit 8 having capacitors 8a (Co) star-connected to the three-phase AC output terminals of the inverter 4 and Serving to detect a common mode Voltage, a push-pull type emitter follower circuit 9 using complementary transistors Tr and Tr for amplifying the common mode Voltage obtained from the neutral point of the Voltage detection circuit 8, and a common mode transformer 11 in which a primary coil L1 receives an output from the emitter follower circuit 9 through capacitors 10 (C), and Secondary coils L2 are connected to the cable 5. In addition, driving power is obtained from the input side of the inverter 4. A control Voltage Source used for the common mode canceler is required to have fast-response characteristics that allow the common mode Voltage of the inverter, which changes Stepwise for every Switching operation, to be output with high fidelity, and low-output-impedance characteris tics. The emitter follower circuit 9 realizes a control voltage Source that meets this requirement. AS the common mode Voltage of the Voltage-Source inverter, the potential at the neutral points of the capacitors star-connected to the output terminals of the inverter. When the capacitance of the Voltage detection circuit 8 is large, an excessive large Spike-like impulse current flows in the power Semiconductor device at the time of Switching, and may damage the device. However, this system uses the capacitors (180 pfx3) having almost the Same capacitance as the output capaci tance of the power semiconductor device of the inverter. For this reason, almost no problem is posed in terms of the influences of this impulse current on the power Semicon ductor device. Since the input impedance of the emitter follower circuit 9 is sufficiently high, the common mode voltage of the inverter 4 can be detected with sufficient precision even by using Such a Small-capacitance capacity. In addition, Since the output impedance of the emitter follower circuit 9 is Sufficiently low, an exciting current i, for the common mode transformer 11 is supplied from only the emitter follower circuit 9. Furthermore, Since a high power Supply Voltage is obtained as driving power for the common mode canceler from the input Side of the inverter 4, a transformer having a turn ratio (between the primary and Secondary windings) of 1:1 is used as the common mode transformer 11. The function of the common mode canceler having the above arrangement will be described next with reference to FIG. 2. FIG. 2 is an equivalent circuit diagram of a common mode circuit using a common mode canceler. Referring to FIG. 2, reference Symbol C denotes the Stray capacitance between the winding of the motor and the frame; and 1 and r, the inductance and resistance of the Overall interconnection. When one phase of the inverter is Switched, a common mode Voltage V output from the inverter changes Stepwise in units of E/3. When the common mode Voltage V is input to the emitter follower circuit 9, the circuit can be expressed by a control Voltage Source for outputting a voltage V equal in magnitude to the common mode Voltage. The common mode transformer 11 connected to the output terminal of the emitter follower circuit 9 is expressed by only an exciting inductance L, with the leakage inductance being neglected.
8 S Every time the inverter 4 is Switched, the Zero phase Sequence Voltage output from the inverter 4, i.e., the com mon mode, changes Stepwise. As a result, a common mode current i(t) flows to the ground line through the Stray capacitance between the winding of the motor 6 and the frame. At this time, if the voltage detection circuit 8 constituted by the Star-connected capacitors 8a detects the common mode Voltage of the inverter 4, and outputs the Voltage V. equal in magnitude and opposite in polarity to the common mode Voltage V to the common mode transformer 11 connected in Series with the circuit 8, the common mode Voltage can be completely canceled out. As a result, no common mode current i(t) flows. In this manner, the common mode canceler 7 can elimi nate both the common mode Voltage and the common Current at Once. FIG. 3 shows the waveform of a common mode current obtained when no common mode canceler is used. A common mode current flows through the Stray capaci tance between the inductance of the interconnection, the winding of the motor, and the frame every time the inverter is Switched. This current has a waveform Similar to an attenuating oscillation waveform obtained when a step Volt age is applied to an LCR Series resonance circuit. For this reason, the equivalent circuit diagram of a common mode circuit can be regarded as an LCR Series resonance circuit in which the two ends of the exciting inductance L, in FIG. 2 are short-circuited. As shown in FIG. 3, every time the inverter is Switched, a common mode current having a peak value of 0.44A and an oscillation frequency of 290 Hz flows. This common mode current is relatively large as compared with the rated current in the System, and hence may cause an operation error in an earth leakage breaker or EMI. FIG. 4 shows the waveform of a common mode current obtained when the common mode canceler is used. AS is apparent from FIG. 4, when the common mode canceler is used, the common mode current can be Suppressed almost perfectly. It is apparent that the common mode current can be reduced very effectively by using the common mode canceler. Another embodiment of the present invention will be described next with reference to FIGS. 5 to 8. The same reference numerals in FIGS. 5 to 8 denote the same parts as in FIG. 1, and a description thereof will be omitted; only different points will be described below. FIG. 5 is a circuit diagram showing the Second embodi ment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 1, the capacitors are Star-connected to the cables of the respective phases on the output Side of the inverter, and a common mode Voltage is extracted from the neutral point to be input to the emitter follower circuit 9. In the second embodiment, however, a common Voltage obtained from the neutral point of a Voltage detection circuit 8 constituted by capacitors 8a Star-connected to cables of the respective phases on the Secondary winding output Side of a common mode trans former 11 is detected, the detected Voltage is amplified by an amplifier 12, and the amplified Voltage is input to an emitter follower circuit 9. With the use of the common mode canceler having the above arrangement, therefore, the common mode Voltage obtained by adding the common mode Voltage of the control Voltage Source to the common mode Voltage generated by the inverter is detected, and the detected Voltage is properly amplified by the amplifier 12 to be fed back to the control 5,831, Voltage Source. With this operation, the common mode Voltage applied to the load can be completely canceled out. FIG. 6 is a circuit diagram showing the third embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 5, the capacitors are Star-connected to the cables of the respective phase on the Secondary winding output Side of the common mode transformer 11, and the common mode Voltage obtained from the neutral point is detected. In the third embodiment, however, a current flowing in the cables on the Secondary winding output Side of a common mode transformer 11 is detected by a current transformer 13, and the detected current is amplified by an amplifier 14 to be input to an emitter follower circuit 9. With the use of the common mode canceler having the above arrangement, therefore, the common mode Voltage of the control Voltage Source is Superimposed on the common mode Voltage generated by an inverter 4, and the common mode current detected by the current transformer 13 is amplified by the amplifier 14 to be input to the emitter follower circuit 9. With this operation, the control voltage Source performs feedback control to Set the common mode Current to Zero. FIG. 7 is a circuit diagram showing the fourth embodi ment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 1, the driving power for the common mode canceler is obtained from the input side of the inverter 4. In the fourth embodiment, however, another DC power supply 15 with a low power Supply Voltage is used as the driving power Supply for the common mode canceler. In this case, the common mode Voltage obtained from the neutral point of a Voltage detection circuit 8 constituted by Star-connected capacitors 8a is input to an emitter follower circuit 9 through an attenuator 17. When a power supply voltage is to be obtained from the input side of the inverter, as shown in FIG. 1, since the Voltage is high, the turn ratio of the primary and Secondary windings of the common mode transfer is set to 1:1. When another power Supply 15 with a low power Supply Voltage is used as in the fourth embodiment, the same effects as those of the first embodiment can be obtained by changing the turn ratio of the primary and Secondary windings of the common mode transfer. In this case, as transistors Tr1 and Tr2 of the emitter follower circuit 9, transistors with low breakdown Voltages can be used. FIG. 8 is a circuit diagram showing the fifth embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 1, as the common mode Voltage generated by the inverter, the common mode Voltage obtained from the neutral point of the Star-connected capacitors is detected. In the fifth embodiment, however, a control circuit 16 for an inverter 4 has the computation function of computing the common mode Voltage generated by the inverter 4 on the basis of a reference value for ON/OFF-controlling the power semiconductor device, and the common mode Voltage obtained by this computation function is input to an emitter follower circuit 9 of the common mode canceler. With the use of the common mode canceler having the above arrangement, therefore, no capacitor need be arranged on the output Side of the Voltage-fed inverter, and hence no Spike-like current flows in the Switching element. In each embodiment described above, the active common mode canceler 7 of the present invention is applied to the System for operating the induction motor by using the voltage-source PWM inverter. However, this canceler can be applied to other power converter, such as a DC-DC converter, in which a common mode Voltage is generated when the power Semiconductor device is Switched.
9 7 Apparently, the present invention is not limited to the above embodiment described with the accompanying drawings, and various changes and modifications of the embodiments can be made without departing from the Spirit and Scope of the invention. Additional advantages and modifications will readily occur to those skilled in the art. Therefore, the invention in its broader aspects is not limited to the Specific details and representative embodiments shown and described herein. Accordingly, various modifications may be made without departing from the Spirit or Scope of the general inventive concept as defined by the appended claims and their equiva lents. We claim: 1. An active common mode canceler comprising: Voltage detection means for detecting a common mode Voltage generated when a power Semiconductor device of a power converter for performing power conversion by Switching Said power Semiconductor device is Switched; a control Voltage Source which is controlled by the common mode Voltage detected by Said Voltage detec tion means to generate a Voltage equal in magnitude and opposite in polarity to the common mode Voltage; and Voltage Superimposition means for canceling out the common mode Voltage by Superimposing the Voltage generated by Said control Voltage Source, on a common mode Voltage output from Said power converter. 2. A canceler according to claim 1, wherein Said Voltage detection means uses a capacitor having a capacitance Smaller than an output capacitance of Said power Semicon ductor device of Said power converter. 3. A canceler according to claim 1, wherein Said Voltage Superimposition means comprises a common mode trans former having multiple windings. 4. A canceler according to claim 1, wherein Said control Voltage Source comprises a push-pull type emitter follower circuit using a transistor for amplifying a common mode Voltage. 5. A canceler according to claim 1, wherein Said control Voltage Source obtains driving power from an input Side of Said power converter. 6. A canceler according to claim 1, wherein Said control Voltage Source uses a DC power Supply as a driving power Supply. 7. An active common mode canceler comprising: a Voltage detection circuit including a plurality of capaci tors connected to output terminals of a power converter for performing power conversion by Switching a power Semiconductor device and adapted to detect a common mode Voltage generated when Said power Semiconduc tor device is Switched; a push-pull type emitter follower circuit which is controlled by the common mode volt age detected by Said Voltage detection Voltage to output a Voltage equal in magnitude and opposite in polarity to the common mode Voltage, and a common mode trans former having multiple windings and adapted to cancel out the common mode Voltage by Superimposing a Voltage output from Said emitter follower circuit on an output from Said power converter. 8. An active common mode canceler comprising: a control Voltage Source for outputting a common mode Voltage to cancel out a common mode Voltage gener ated when a power Semiconductor device of a power converter for performing power conversion by Switch 5,831, ing Said power Semiconductor device is Switched; Volt age Superimposition means for Superimposing the com mon mode Voltage output from Said control Voltage Source on the common mode Voltage generated by Said power converter, and Voltage detection means for detecting the common mode Voltages from Said power converter and Said control Voltage Source which are Superimposed by Said Voltage Superimposition means, and feeding back the detected Voltage to Said control Voltage Source, wherein Said control Voltage Source controls to Set the Voltage detected by Said Voltage detection means to Zero. 9. A canceler according to claim 8, wherein Said Voltage detection means uses a capacitor having a capacitance Smaller than an output capacitance of Said power Semicon ductor device of Said power converter. 10. A canceler according to claim 8, wherein Said Voltage Superimposition means comprises a common mode trans former having multiple windings. 11. A canceler according to claim 8, wherein Said control Voltage Source comprises a push-pull type emitter follower circuit using a transistor for amplifying a common mode Voltage. 12. An active common mode canceler comprising: a push-pull type emitter follower circuit using a transistor and adapted to output a common mode Voltage to cancel out a common mode Voltage generated when a power Semiconductor device of a power converter for performing power conversion by Switching Said power Semiconductor device is Switched; a common mode which has multiple windings and is arranged on an output Side of Said power converter to cancel out the common mode Voltage by Superimposing the common mode Voltage output from Said emitter follower circuit on the common mode Voltage generated by Said power converter, and a Voltage detection circuit having a plurality of capacitors and adapted to detect the com mon mode Voltages from Said power converter and Said emitter follower circuit which are Superimposed by Said common mode transformer, and to control to Set the detected Voltage to Zero by feeding back the detected Voltage to Said emitter follower circuit. 13. An active common mode canceler comprising: a control Voltage Source for outputting a common mode Voltage to cancel out a common mode Voltage gener ated when a power Semiconductor device of a power converter for performing power conversion by Switch ing Said power Semiconductor device is Switched; Volt age Superimposition means for Superimposing the com mon mode Voltage output from Said control Voltage Source on the common mode Voltage generated by Said power converter; and current detection means for detecting a common mode current which flows when the common mode Voltages from Said power converter and Said control Voltage Source are Superimposed by Said Voltage Super imposition means, and feeding back the detected cur rent to Said control voltage Source, wherein Said control Voltage Source controls to Set the current detected by Said current detection means to Zero. 14. A canceler according to claim 13, wherein Said Voltage Superimposition means comprises a common mode trans former having multiple windings. 15. A canceler according to claim 13, wherein Said control Voltage Source comprises a push-pull type emitter follower circuit using a transistor for amplifying a common mode Voltage.
10 16. An active common mode canceler comprising: computation means for computing a common mode Voltage, which is generated when a power Semicon ductor device of a power converter for performing power conversion by Switching Said power Semicon ductor device is Switched, on the basis of a reference value used to ON/OFF-control said power semiconduc tor device; a control Voltage Source which is controlled by the common mode Voltage obtained by Said com putation means to generate a Voltage equal in magni tude and opposite in polarity to the common mode Voltage; and Voltage Superimposition means for can celing out the common mode Voltage by Superimposing 5,831, the Voltage generated by Said Voltage control Source, on a common mode Voltage output from Said power con Verter. 17. A canceler according to claim 16, wherein Said Voltage Superimposition means comprises a common mode trans former having multiple windings. 18. A canceler according to claim 16, wherein Said control Voltage Source comprises a push-pull type emitter follower circuit using a transistor for amplifying a common mode Voltage.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007035123B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,035,123 B2 Schreiber et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2006 (54) FREQUENCY CONVERTER AND ITS (56) References Cited CONTROL METHOD FOREIGN
(12) United States Patent US007035123B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,035,123 B2 Schreiber et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2006 (54) FREQUENCY CONVERTER AND ITS (56) References Cited CONTROL METHOD FOREIGN
United States Patent (19) Ohta
 United States Patent (19) Ohta (54) NON-SATURATING COMPLEMENTARY TYPE UNITY GAIN AMPLIFER 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Genichiro Ohta, Ebina, Japan Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan
United States Patent (19) Ohta (54) NON-SATURATING COMPLEMENTARY TYPE UNITY GAIN AMPLIFER 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Genichiro Ohta, Ebina, Japan Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003.01225O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0122502 A1 Clauberg et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 3, 2003 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE DRIVER (52) U.S. Cl....
US 2003.01225O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0122502 A1 Clauberg et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 3, 2003 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE DRIVER (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9304615B2 (12) United States Patent Katsurahira (54) CAPACITIVE STYLUS PEN HAVING A TRANSFORMER FOR BOOSTING ASIGNAL (71) Applicant: Wacom Co., Ltd., Saitama (JP) (72) Inventor: Yuji Katsurahira, Saitama
USOO9304615B2 (12) United States Patent Katsurahira (54) CAPACITIVE STYLUS PEN HAVING A TRANSFORMER FOR BOOSTING ASIGNAL (71) Applicant: Wacom Co., Ltd., Saitama (JP) (72) Inventor: Yuji Katsurahira, Saitama
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1
 USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
United States Patent (19) Nilssen
 United States Patent (19) Nilssen (4) HIGH-EFFICIENCY SINGLE-ENDED INVERTER CRCUIT 76) Inventor: Ole K. Nilssen, Caesar Dr. Rte. 4, Barrington, Ill. 60010 21 Appl. No.: 33,33 (22) Filed: Apr. 2, 1979 (1)
United States Patent (19) Nilssen (4) HIGH-EFFICIENCY SINGLE-ENDED INVERTER CRCUIT 76) Inventor: Ole K. Nilssen, Caesar Dr. Rte. 4, Barrington, Ill. 60010 21 Appl. No.: 33,33 (22) Filed: Apr. 2, 1979 (1)
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Pfeffer et al. 11 (45 Oct. 5, 1976 54) (75) 73) 22) 21 (52) 51) 58) ALTERNATOR-RECTFER UNIT WITH PHASE WINDING AND RECTIFIER SETS SUBJECT TO SERIES-PARALLEL SWITCHING Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Pfeffer et al. 11 (45 Oct. 5, 1976 54) (75) 73) 22) 21 (52) 51) 58) ALTERNATOR-RECTFER UNIT WITH PHASE WINDING AND RECTIFIER SETS SUBJECT TO SERIES-PARALLEL SWITCHING Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Rousseau et al.
 United States Patent (19) Rousseau et al. USOO593.683OA 11 Patent Number: 5,936,830 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 1999 54). IGNITION EXCITER FOR A GASTURBINE 58 Field of Search... 361/253, 256, ENGINE
United States Patent (19) Rousseau et al. USOO593.683OA 11 Patent Number: 5,936,830 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 1999 54). IGNITION EXCITER FOR A GASTURBINE 58 Field of Search... 361/253, 256, ENGINE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US B2. Chokkalingam et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 1, 2009
 USOO7626469B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.626.469 B2 Chokkalingam et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 1, 2009 (54) ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search... 33 1/8, 331/16-18,
USOO7626469B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.626.469 B2 Chokkalingam et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 1, 2009 (54) ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT (58) Field of Classification Search... 33 1/8, 331/16-18,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,228,693 B2
 USOO8228693B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,228,693 B2 Petersson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 24, 2012 (54) DC FILTER AND VOLTAGE SOURCE (56) References Cited CONVERTER STATION COMPRISING
USOO8228693B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,228,693 B2 Petersson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 24, 2012 (54) DC FILTER AND VOLTAGE SOURCE (56) References Cited CONVERTER STATION COMPRISING
Kiuchi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2011
 (12) United States Patent US007902952B2 (10) Patent No.: Kiuchi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2011 (54) SHARED REACTOR TRANSFORMER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Hiroshi Kiuchi, Chiyoda-ku
(12) United States Patent US007902952B2 (10) Patent No.: Kiuchi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2011 (54) SHARED REACTOR TRANSFORMER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Hiroshi Kiuchi, Chiyoda-ku
Measurement and reduction of EMI radiated by a PWM inverter-fed AC motor drive system
 Engineering Electrical Engineering fields Okayama University Year 1997 Measurement and reduction of EMI radiated by a PWM inverter-fed AC motor drive system Satoshi Ogasawara Okayama University Hirofumi
Engineering Electrical Engineering fields Okayama University Year 1997 Measurement and reduction of EMI radiated by a PWM inverter-fed AC motor drive system Satoshi Ogasawara Okayama University Hirofumi
United States Patent (19) Onuki et al.
 United States Patent (19) Onuki et al. 54). IGNITION APPARATUS FOR AN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE 75 Inventors: Hiroshi Onuki; Takashi Ito, both of Hitachinaka, Katsuaki Fukatsu, Naka-gun; Ryoichi Kobayashi,
United States Patent (19) Onuki et al. 54). IGNITION APPARATUS FOR AN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE 75 Inventors: Hiroshi Onuki; Takashi Ito, both of Hitachinaka, Katsuaki Fukatsu, Naka-gun; Ryoichi Kobayashi,
( 19 ) United States ( 12 ) Patent Application Publication ( 10 ) Pub. No. : US 2017 / A1 ( 52 ) U. S. CI. CPC... HO2P 9 / 48 ( 2013.
 THE MAIN TEA ETA AITOA MA EI TA HA US 20170317630A1 ( 19 ) United States ( 12 ) Patent Application Publication ( 10 ) Pub No : US 2017 / 0317630 A1 Said et al ( 43 ) Pub Date : Nov 2, 2017 ( 54 ) PMG BASED
THE MAIN TEA ETA AITOA MA EI TA HA US 20170317630A1 ( 19 ) United States ( 12 ) Patent Application Publication ( 10 ) Pub No : US 2017 / 0317630 A1 Said et al ( 43 ) Pub Date : Nov 2, 2017 ( 54 ) PMG BASED
4,695,748 Sep. 22, 1987
 United States Patent [19] Kumamoto [11] Patent Number: [45] Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 1987 [54] COMPARING DEVICE [75] Inventor: Toshio Kumamoto, Itami, Japan [73] Assignee: Mitsubishi Denki Kabushiki Kaisha,
United States Patent [19] Kumamoto [11] Patent Number: [45] Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 1987 [54] COMPARING DEVICE [75] Inventor: Toshio Kumamoto, Itami, Japan [73] Assignee: Mitsubishi Denki Kabushiki Kaisha,
HHHHHH. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,079,455. McCafferty et al. tor to provide a negative feedback path for charging the
 United States Patent (19) McCafferty et al. (54. SURGE CURRENT-LIMITING CIRCUIT FOR A LARGE-CAPACITANCE LOAD 75 Inventors: Lory N. McCafferty; Raymond K. Orr, both of Kanata, Canada 73) Assignee: Northern
United States Patent (19) McCafferty et al. (54. SURGE CURRENT-LIMITING CIRCUIT FOR A LARGE-CAPACITANCE LOAD 75 Inventors: Lory N. McCafferty; Raymond K. Orr, both of Kanata, Canada 73) Assignee: Northern
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
(19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7123644B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 2006 (54) PEAK CANCELLATION APPARATUS OF BASE STATION TRANSMISSION UNIT (75) Inventors: Won-Hyoung Park,
USOO7123644B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 2006 (54) PEAK CANCELLATION APPARATUS OF BASE STATION TRANSMISSION UNIT (75) Inventors: Won-Hyoung Park,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1
 USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007 184283B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,184,283 B2 Yang et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 27, 2007 (54) SWITCHING FREQUENCYJITTER HAVING (56) References Cited OUTPUT RIPPLE CANCEL
(12) United States Patent US007 184283B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,184,283 B2 Yang et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 27, 2007 (54) SWITCHING FREQUENCYJITTER HAVING (56) References Cited OUTPUT RIPPLE CANCEL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060280289A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0280289 A1 Hanington et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 14, 2006 (54) X-RAY TUBE DRIVER USING AM AND FM (57) ABSTRACT
US 20060280289A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0280289 A1 Hanington et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 14, 2006 (54) X-RAY TUBE DRIVER USING AM AND FM (57) ABSTRACT
Si,"Sir, sculptor. Sinitialising:
 (19) United States US 20090097281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0097281 A1 LIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2009 (54) LEAKAGE-INDUCTANCE ENERGY Publication Classification RECYCLING
(19) United States US 20090097281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0097281 A1 LIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2009 (54) LEAKAGE-INDUCTANCE ENERGY Publication Classification RECYCLING
(12) United States Patent
 US009 159725B2 (12) United States Patent Forghani-Zadeh et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) CONTROLLED ON AND OFF TIME SCHEME FORMONOLTHC
US009 159725B2 (12) United States Patent Forghani-Zadeh et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) CONTROLLED ON AND OFF TIME SCHEME FORMONOLTHC
United States Patent Patent Number: 5,683,539 Qian et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 1997
 USOO5683539A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: Qian et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 1997 54 NDUCTIVELY COUPLED RF PLASMA 5,458,732 10/1995 Butler et al.... 216/61 REACTORWTH FLOATING COL 5,525,159
USOO5683539A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: Qian et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 1997 54 NDUCTIVELY COUPLED RF PLASMA 5,458,732 10/1995 Butler et al.... 216/61 REACTORWTH FLOATING COL 5,525,159
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
United States Patent (19) 11) 4,163,947
 United States Patent (19) 11) Weedon (45) Aug. 7, 1979 (54) CURRENT AND VOLTAGE AUTOZEROING Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Weingarten, Maxham & INTEGRATOR Schurgin 75 Inventor: Hans J. Weedon, Salem, Mass. (57)
United States Patent (19) 11) Weedon (45) Aug. 7, 1979 (54) CURRENT AND VOLTAGE AUTOZEROING Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Weingarten, Maxham & INTEGRATOR Schurgin 75 Inventor: Hans J. Weedon, Salem, Mass. (57)
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007576582B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,576,582 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) LOW-POWER CLOCK GATING CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Dae Woo
(12) United States Patent US007576582B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,576,582 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) LOW-POWER CLOCK GATING CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Dae Woo
United States Patent (19) Curcio
 United States Patent (19) Curcio (54) (75) (73) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) (56) ELECTRONICFLTER WITH ACTIVE ELEMENTS Inventor: Assignee: Joseph John Curcio, Boalsburg, Pa. Paoli High Fidelity Consultants Inc.,
United States Patent (19) Curcio (54) (75) (73) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) (56) ELECTRONICFLTER WITH ACTIVE ELEMENTS Inventor: Assignee: Joseph John Curcio, Boalsburg, Pa. Paoli High Fidelity Consultants Inc.,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
(19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Nagano 54 FULL WAVE RECTIFIER 75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Katsumi Nagano, Hiratsukashi, Japan Tokyo Shibaura Denki Kabushiki Kaisha, Kawasaki, Japan 21 Appl. No.: 188,662 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Nagano 54 FULL WAVE RECTIFIER 75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Katsumi Nagano, Hiratsukashi, Japan Tokyo Shibaura Denki Kabushiki Kaisha, Kawasaki, Japan 21 Appl. No.: 188,662 22 Filed:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO881 1048B2 (12) United States Patent Zhang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 19, 2014 (54) MEDIUM VOLTAGE VARIABLE FREQUENCY DRIVING SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Yi Zhang, Shanghai (CN);
USOO881 1048B2 (12) United States Patent Zhang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 19, 2014 (54) MEDIUM VOLTAGE VARIABLE FREQUENCY DRIVING SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Yi Zhang, Shanghai (CN);
rectifying smoothing circuit
 USOO648671.4B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ushida et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) HALF-BRIDGE INVERTER CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Atsuya Ushida, Oizumi-machi
USOO648671.4B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ushida et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) HALF-BRIDGE INVERTER CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Atsuya Ushida, Oizumi-machi
United States Patent (19) Lee
 United States Patent (19) Lee (54) POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT FOR DRIVING MAGNETRON 75 Inventor: Kyong-Keun Lee, Suwon, Rep. of Korea 73) Assignee: Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Suweon City, Rep. of Korea (21)
United States Patent (19) Lee (54) POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT FOR DRIVING MAGNETRON 75 Inventor: Kyong-Keun Lee, Suwon, Rep. of Korea 73) Assignee: Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Suweon City, Rep. of Korea (21)
United States Patent (19) Schnetzka et al.
 United States Patent (19) Schnetzka et al. 54 (75) GATE DRIVE CIRCUIT FOR AN SCR Inventors: Harold R. Schnetzka; Dean K. Norbeck; Donald L. Tollinger, all of York, Pa. Assignee: York International Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Schnetzka et al. 54 (75) GATE DRIVE CIRCUIT FOR AN SCR Inventors: Harold R. Schnetzka; Dean K. Norbeck; Donald L. Tollinger, all of York, Pa. Assignee: York International Corporation,
USOO A. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,272,450 Wisherd (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 1993
 O HIHHHHHHHHHHHHIII USOO5272450A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,272,450 Wisherd (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 1993 (54) DCFEED NETWORK FOR WIDEBANDRF POWER AMPLIFIER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS
O HIHHHHHHHHHHHHIII USOO5272450A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,272,450 Wisherd (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 1993 (54) DCFEED NETWORK FOR WIDEBANDRF POWER AMPLIFIER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS
part data signal (12) United States Patent control 33 er m - sm is US 7,119,773 B2
 US007 119773B2 (12) United States Patent Kim (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 10, 2006 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING GRAY LEVEL FOR DISPLAY PANEL (75) Inventor: Hak Su Kim, Seoul
US007 119773B2 (12) United States Patent Kim (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 10, 2006 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING GRAY LEVEL FOR DISPLAY PANEL (75) Inventor: Hak Su Kim, Seoul
United States Patent (19) Price, Jr.
 United States Patent (19) Price, Jr. 11 4) Patent Number: Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 1986 4) (7) (73) 21) 22 1) 2 8) NPN BAND GAP VOLTAGE REFERENCE Inventor: John J. Price, Jr., Mesa, Ariz. Assignee: Motorola,
United States Patent (19) Price, Jr. 11 4) Patent Number: Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 1986 4) (7) (73) 21) 22 1) 2 8) NPN BAND GAP VOLTAGE REFERENCE Inventor: John J. Price, Jr., Mesa, Ariz. Assignee: Motorola,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,770,955 B1
 USOO6770955B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Coccioli et al. () Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 2004 (54) SHIELDED ANTENNA INA 6,265,774 B1 * 7/2001 Sholley et al.... 7/728 SEMCONDUCTOR PACKAGE 6,282,095
USOO6770955B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Coccioli et al. () Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 2004 (54) SHIELDED ANTENNA INA 6,265,774 B1 * 7/2001 Sholley et al.... 7/728 SEMCONDUCTOR PACKAGE 6,282,095
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160090275A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0090275 A1 Piech et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2016 (54) WIRELESS POWER SUPPLY FOR SELF-PROPELLED ELEVATOR
(19) United States US 20160090275A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0090275 A1 Piech et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2016 (54) WIRELESS POWER SUPPLY FOR SELF-PROPELLED ELEVATOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,449,544 B2
 USOO9449544B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Duan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 20, 2016 (54) AMOLED PIXEL CIRCUIT AND DRIVING (58) Field of Classification Search METHOD CPC... A01B 12/006;
USOO9449544B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Duan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 20, 2016 (54) AMOLED PIXEL CIRCUIT AND DRIVING (58) Field of Classification Search METHOD CPC... A01B 12/006;
58) Field of Seash, which is located on the first core leg. The fifth winding,
 US006043569A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Ferguson (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 2000 54) ZERO PHASE SEQUENCE CURRENT Primary Examiner Richard T. Elms FILTER APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR Attorney,
US006043569A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Ferguson (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 2000 54) ZERO PHASE SEQUENCE CURRENT Primary Examiner Richard T. Elms FILTER APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR Attorney,
United States Patent (19) Harnden
 United States Patent (19) Harnden 54) 75 (73) LMITING SHOOT THROUGH CURRENT INA POWER MOSFET HALF-BRIDGE DURING INTRINSIC DODE RECOVERY Inventor: Assignee: James A. Harnden, San Jose, Calif. Siliconix
United States Patent (19) Harnden 54) 75 (73) LMITING SHOOT THROUGH CURRENT INA POWER MOSFET HALF-BRIDGE DURING INTRINSIC DODE RECOVERY Inventor: Assignee: James A. Harnden, San Jose, Calif. Siliconix
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O2.13871 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0213871 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 26, 2010 54) BACKLIGHT DRIVING SYSTEM 3O Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2010O2.13871 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0213871 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 26, 2010 54) BACKLIGHT DRIVING SYSTEM 3O Foreign Application
3.1 vs. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1. (19) United States FB2 D ME VSS VOLIAGE REFER
 (19) United States US 20020089860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0089860 A1 Kashima et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT (76) Inventors: Masato Kashima,
(19) United States US 20020089860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0089860 A1 Kashima et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT (76) Inventors: Masato Kashima,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United S tates US 20020003503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0003503 A1 Justice (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 10, 2002 (54) TWIN COILA NTENNA (76) Inventor: Christopher M. Justice,
(19) United S tates US 20020003503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0003503 A1 Justice (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 10, 2002 (54) TWIN COILA NTENNA (76) Inventor: Christopher M. Justice,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent JakobSSOn USOO6608999B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 19, 2003 (54) COMMUNICATION SIGNAL RECEIVER AND AN OPERATING METHOD THEREFOR (75) Inventor: Peter Jakobsson,
(12) United States Patent JakobSSOn USOO6608999B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 19, 2003 (54) COMMUNICATION SIGNAL RECEIVER AND AN OPERATING METHOD THEREFOR (75) Inventor: Peter Jakobsson,
F1 OSCILLATOR. United States Patent (19) Masaki 4,834,701 OSCILLATOR. May 30, Patent Number:, (45) Date of Patent:
 United States Patent (19) Masaki 11 Patent Number:, (45) Date of Patent: 4,834,701 May 30, 1989 (54) APPARATUS FOR INDUCING FREQUENCY REDUCTION IN BRAIN WAVE 75 Inventor: Kazumi Masaki, Osaka, Japan 73)
United States Patent (19) Masaki 11 Patent Number:, (45) Date of Patent: 4,834,701 May 30, 1989 (54) APPARATUS FOR INDUCING FREQUENCY REDUCTION IN BRAIN WAVE 75 Inventor: Kazumi Masaki, Osaka, Japan 73)
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,555,242 Saitou 45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 1996
 IIII USOO5555242A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Saitou 45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 1996 54 SUBSTATION APPARATUS FOR SATELLITE 5,216,427 6/1993 Yan et al.... 370/85.2 COMMUNICATIONS 5,257,257
IIII USOO5555242A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Saitou 45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 1996 54 SUBSTATION APPARATUS FOR SATELLITE 5,216,427 6/1993 Yan et al.... 370/85.2 COMMUNICATIONS 5,257,257
in-s-he Gua (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,388,499 B1 (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 Vddint : SFF LSOUT Tien et al.
 (12) United States Patent Tien et al. USOO6388499B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) LEVEL-SHIFTING SIGNAL BUFFERS THAT SUPPORT HIGHER VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLIES USING LOWER VOLTAGE
(12) United States Patent Tien et al. USOO6388499B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) LEVEL-SHIFTING SIGNAL BUFFERS THAT SUPPORT HIGHER VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLIES USING LOWER VOLTAGE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,512,361 B1
 USOO6512361B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,512,361 B1 Becker (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 28, 2003 (54) 14/42-VOLTAUTOMOTIVE CIRCUIT 5,420.503 5/1995 Beha TESTER 5,517,183 A 5/1996 Bozeman,
USOO6512361B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,512,361 B1 Becker (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 28, 2003 (54) 14/42-VOLTAUTOMOTIVE CIRCUIT 5,420.503 5/1995 Beha TESTER 5,517,183 A 5/1996 Bozeman,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Crawford 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 1990 54 (76) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) 56 LASERRANGEFINDER RECEIVER. PREAMPLETER Inventor: Ian D. Crawford, 1805 Meadowbend
United States Patent (19) Crawford 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 1990 54 (76) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) 56 LASERRANGEFINDER RECEIVER. PREAMPLETER Inventor: Ian D. Crawford, 1805 Meadowbend
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9463468B2 () Patent No.: Hiley (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2016 (54) COMPACT HIGH VOLTAGE RF BO3B 5/08 (2006.01) GENERATOR USING A SELF-RESONANT GOIN 27/62 (2006.01) INDUCTOR
(12) United States Patent USOO9463468B2 () Patent No.: Hiley (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2016 (54) COMPACT HIGH VOLTAGE RF BO3B 5/08 (2006.01) GENERATOR USING A SELF-RESONANT GOIN 27/62 (2006.01) INDUCTOR
(12) United States Patent
 US007098655B2 (12) United States Patent Yamada et al. (54) EDDY-CURRENT SENSOR WITH PLANAR MEANDER EXCITING COIL AND SPIN VALVE MAGNETORESISTIVE ELEMENT FOR NONDESTRUCTIVE TESTING (75) Inventors: Sotoshi
US007098655B2 (12) United States Patent Yamada et al. (54) EDDY-CURRENT SENSOR WITH PLANAR MEANDER EXCITING COIL AND SPIN VALVE MAGNETORESISTIVE ELEMENT FOR NONDESTRUCTIVE TESTING (75) Inventors: Sotoshi
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O134516A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Du (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) DUAL BAND SLEEVE ANTENNA (52) U.S. Cl.... 3437790 (75) Inventor: Xin Du, Schaumburg,
(19) United States US 2005O134516A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Du (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) DUAL BAND SLEEVE ANTENNA (52) U.S. Cl.... 3437790 (75) Inventor: Xin Du, Schaumburg,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9641 137B2 (12) United States Patent Duenser et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,641,137 B2 May 2, 2017 (54) ELECTRIC AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT FOR AMPLIFYING AN OUTPUT SIGNAL OF A MCROPHONE
USOO9641 137B2 (12) United States Patent Duenser et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,641,137 B2 May 2, 2017 (54) ELECTRIC AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT FOR AMPLIFYING AN OUTPUT SIGNAL OF A MCROPHONE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0103860 A1 Kominami et al. US 201401.03860A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 17, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) POWER CONVERTER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0103860 A1 Kominami et al. US 201401.03860A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 17, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) POWER CONVERTER
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,889,643 Elms (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 30, 1999
 USOO5889643A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,889,643 Elms (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 30, 1999 54). APPARATUS FOR DETECTING ARCING Primary Examiner Jeffrey Gaffin FAULTS AND GROUND FAULTS IN
USOO5889643A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,889,643 Elms (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 30, 1999 54). APPARATUS FOR DETECTING ARCING Primary Examiner Jeffrey Gaffin FAULTS AND GROUND FAULTS IN
United States Patent (19) Archibald
 United States Patent (19) Archibald 54 ELECTROSURGICAL UNIT 75 Inventor: G. Kent Archibald, White Bear Lake, Minn. 73 Assignee: Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing Company, Saint Paul, Minn. (21) Appl.
United States Patent (19) Archibald 54 ELECTROSURGICAL UNIT 75 Inventor: G. Kent Archibald, White Bear Lake, Minn. 73 Assignee: Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing Company, Saint Paul, Minn. (21) Appl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
(19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
MODELLING AND SIMULATION OF DIODE CLAMP MULTILEVEL INVERTER FED THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR FOR CMV ANALYSIS USING FILTER
 MODELLING AND SIMULATION OF DIODE CLAMP MULTILEVEL INVERTER FED THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR FOR CMV ANALYSIS USING FILTER Akash A. Chandekar 1, R.K.Dhatrak 2 Dr.Z.J..Khan 3 M.Tech Student, Department of
MODELLING AND SIMULATION OF DIODE CLAMP MULTILEVEL INVERTER FED THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR FOR CMV ANALYSIS USING FILTER Akash A. Chandekar 1, R.K.Dhatrak 2 Dr.Z.J..Khan 3 M.Tech Student, Department of
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,577,002 B2. Yang (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 18, 2009
 US007577002B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,577,002 B2 Yang (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 18, 2009 (54) FREQUENCY HOPPING CONTROL CIRCUIT 5,892,352 A * 4/1999 Kolar et al.... 323,213 FOR
US007577002B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,577,002 B2 Yang (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 18, 2009 (54) FREQUENCY HOPPING CONTROL CIRCUIT 5,892,352 A * 4/1999 Kolar et al.... 323,213 FOR
Mar. 29, 1999 (SE) (51) Int. Cl... H02M 7/5387. (52) U.S. Cl /132; 363/137 (58) Field of Search /132, w. to 2.
 (12) United States Patent Asplund et al. USOO65,191.69B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,519,169 B1 Feb. 11, 2003 (54) MULTIPHASE INVERTER WITH SERIES OF CONNECTED PHASE LEGS (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent Asplund et al. USOO65,191.69B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,519,169 B1 Feb. 11, 2003 (54) MULTIPHASE INVERTER WITH SERIES OF CONNECTED PHASE LEGS (75) Inventors:
- I 12 \ C LC2 N28. United States Patent (19) Swanson et al. EMITTERS (22) 11 Patent Number: 5,008,594 (45) Date of Patent: Apr.
 United States Patent (19) Swanson et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 1991 54 (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) SELF-BALANCNG CIRCUT FOR CONVECTION AIR ONZERS Inventors: Assignee: Appl.
United States Patent (19) Swanson et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 1991 54 (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) SELF-BALANCNG CIRCUT FOR CONVECTION AIR ONZERS Inventors: Assignee: Appl.
73 Assignee: Dialight Corporation, Manasquan, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 09/144, Filed: Aug. 31, 1998 (51) Int. Cl... G05F /158; 315/307
 United States Patent (19) Grossman et al. 54) LED DRIVING CIRCUITRY WITH VARIABLE LOAD TO CONTROL OUTPUT LIGHT INTENSITY OF AN LED 75 Inventors: Hyman Grossman, Lambertville; John Adinolfi, Milltown, both
United States Patent (19) Grossman et al. 54) LED DRIVING CIRCUITRY WITH VARIABLE LOAD TO CONTROL OUTPUT LIGHT INTENSITY OF AN LED 75 Inventors: Hyman Grossman, Lambertville; John Adinolfi, Milltown, both
A///X 2. N N-14. NetNNNNNNN N. / Et EY / E \ \ (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
United States Patent (19) Hakala et al.
 United States Patent (19) Hakala et al. 54 PROCEDURE AND APPARATUS FOR BRAKING ASYNCHRONOUS MOTOR 75 Inventors: Harri Hakala, Hyvinkää, Esko Aulanko, Kerava; Jorma Mustalahti, Hyvinkää, all of Finland
United States Patent (19) Hakala et al. 54 PROCEDURE AND APPARATUS FOR BRAKING ASYNCHRONOUS MOTOR 75 Inventors: Harri Hakala, Hyvinkää, Esko Aulanko, Kerava; Jorma Mustalahti, Hyvinkää, all of Finland
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,765,631 B2. Ishikawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2004
 USOO6765631 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,765,631 B2 Ishikawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2004 (54) VEHICLE WINDSHIELD RAIN SENSOR (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Junichi
USOO6765631 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,765,631 B2 Ishikawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2004 (54) VEHICLE WINDSHIELD RAIN SENSOR (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Junichi
United States Patent (19) Morris
 United States Patent (19) Morris 54 CMOS INPUT BUFFER WITH HIGH SPEED AND LOW POWER 75) Inventor: Bernard L. Morris, Allentown, Pa. 73) Assignee: AT&T Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, N.J. 21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Morris 54 CMOS INPUT BUFFER WITH HIGH SPEED AND LOW POWER 75) Inventor: Bernard L. Morris, Allentown, Pa. 73) Assignee: AT&T Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, N.J. 21 Appl. No.:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Su US 2005O127853A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) MULTI-LEVEL DC BUS INVERTER FOR PROVIDING SNUSODAL AND PWM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Su US 2005O127853A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) MULTI-LEVEL DC BUS INVERTER FOR PROVIDING SNUSODAL AND PWM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 2007.0109826A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0109826A1 Lu (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2007 (54) LUS SEMICONDUCTOR AND SYNCHRONOUS RECTFER CIRCUITS (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2007.0109826A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0109826A1 Lu (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2007 (54) LUS SEMICONDUCTOR AND SYNCHRONOUS RECTFER CIRCUITS (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070046374A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/00463.74 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) LINEARITY-IMPROVED DIFFERENTIAL Publication Classification AMPLIFICATION
US 20070046374A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/00463.74 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) LINEARITY-IMPROVED DIFFERENTIAL Publication Classification AMPLIFICATION
United States Patent (19 11 Patent Number: 5,592,073 Redlich 45) Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 1997
 IIII US005592073A United States Patent (19 11 Patent Number: 5,592,073 Redlich 45) Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 1997 54) TRIAC CONTROL CIRCUIT Ramshaw, R. S., "Power Electronics Semiconductor 75) Inventor:
IIII US005592073A United States Patent (19 11 Patent Number: 5,592,073 Redlich 45) Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 1997 54) TRIAC CONTROL CIRCUIT Ramshaw, R. S., "Power Electronics Semiconductor 75) Inventor:
Vmod (12) United States Patent US 7.411,469 B2. *Aug. 12, Perry et al. (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.:
 USOO741 1469B2 (12) United States Patent Perry et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.411,469 B2 *Aug. 12, 2008 (54) CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENT (75) Inventors: Colin Leslie Perry, Swindon (GB); Stephen
USOO741 1469B2 (12) United States Patent Perry et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.411,469 B2 *Aug. 12, 2008 (54) CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENT (75) Inventors: Colin Leslie Perry, Swindon (GB); Stephen
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,804,379 B2
 US007804379B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kris et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) PULSE WIDTH MODULATION DEAD TIME 5,764,024 A 6, 1998 Wilson COMPENSATION METHOD AND 6,940,249
US007804379B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kris et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2010 (54) PULSE WIDTH MODULATION DEAD TIME 5,764,024 A 6, 1998 Wilson COMPENSATION METHOD AND 6,940,249
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
VDD. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. (19) United States. I Data. (76) Inventors: Wen-Cheng Yen, Taichung (TW);
 (19) United States US 2004O150593A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150593 A1 Yen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) ACTIVE MATRIX LED DISPLAY DRIVING CIRCUIT (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2004O150593A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150593 A1 Yen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) ACTIVE MATRIX LED DISPLAY DRIVING CIRCUIT (76) Inventors:
% 2 22 % United States Patent (19) Cain et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,036,323 (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 30, 1991
 United States Patent (19) Cain et al. 54 ACTIVE RADAR STEALTH DEVICE (75) Inventors R. Neal Cain, Fredericksburg; Albert J. Corda, Dahlgren, both of Va. 73) Assignee The United States of America as represented
United States Patent (19) Cain et al. 54 ACTIVE RADAR STEALTH DEVICE (75) Inventors R. Neal Cain, Fredericksburg; Albert J. Corda, Dahlgren, both of Va. 73) Assignee The United States of America as represented
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0043209A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0043209 A1 Zhu (43) Pub. Date: (54) COIL DECOUPLING FORAN RF COIL (52) U.S. Cl.... 324/322 ARRAY (57) ABSTRACT
(19) United States US 2011 0043209A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0043209 A1 Zhu (43) Pub. Date: (54) COIL DECOUPLING FORAN RF COIL (52) U.S. Cl.... 324/322 ARRAY (57) ABSTRACT
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Schwab et al. US006335619B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR COMPRISING ARESONANT OSCILLATORY CIRCUIT RESPONDING TO CHANGES IN
(12) United States Patent Schwab et al. US006335619B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR COMPRISING ARESONANT OSCILLATORY CIRCUIT RESPONDING TO CHANGES IN
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,433,976 B1. Phillips (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 13, 2002
 USOO6433976B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,433,976 B1 Phillips (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 13, 2002 (54) INSTANTANEOUS ARC FAULT LIGHT 4,791,518 A 12/1988 Fischer... 361/42 DETECTOR WITH
USOO6433976B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,433,976 B1 Phillips (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 13, 2002 (54) INSTANTANEOUS ARC FAULT LIGHT 4,791,518 A 12/1988 Fischer... 361/42 DETECTOR WITH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 20110241597A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0241597 A1 Zhu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2011 (54) H-BRIDGE DRIVE CIRCUIT FOR STEP Publication Classification
US 20110241597A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0241597 A1 Zhu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2011 (54) H-BRIDGE DRIVE CIRCUIT FOR STEP Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kang et al. USOO6906581B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2005 (54) FAST START-UP LOW-VOLTAGE BANDGAP VOLTAGE REFERENCE CIRCUIT (75) Inventors: Tzung-Hung Kang,
(12) United States Patent Kang et al. USOO6906581B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2005 (54) FAST START-UP LOW-VOLTAGE BANDGAP VOLTAGE REFERENCE CIRCUIT (75) Inventors: Tzung-Hung Kang,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,815,941 B2. Butler (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 9, 2004
 USOO6815941B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,815,941 B2 Butler (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 9, 2004 (54) BANDGAP REFERENCE CIRCUIT 6,052,020 * 4/2000 Doyle... 327/539 6,084,388 A 7/2000 Toosky
USOO6815941B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,815,941 B2 Butler (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 9, 2004 (54) BANDGAP REFERENCE CIRCUIT 6,052,020 * 4/2000 Doyle... 327/539 6,084,388 A 7/2000 Toosky
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,104 B1
 USOO6275104B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Holter (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 14, 2001 (54) MULTISTAGE AMPLIFIER WITH LOCAL 4,816,711 3/1989 Roza... 330/149 ERROR CORRECTION 5,030.925 7/1991
USOO6275104B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Holter (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 14, 2001 (54) MULTISTAGE AMPLIFIER WITH LOCAL 4,816,711 3/1989 Roza... 330/149 ERROR CORRECTION 5,030.925 7/1991
TEPZZ 48A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02M 3/335 ( ) H02M 1/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 48A T (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 3/33 (2006.01) H02M 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1178647.2 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 48A T (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 3/33 (2006.01) H02M 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1178647.2 (22)
III. Main N101 ( Y-104. (10) Patent No.: US 7,142,997 B1. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 28, Supply. Capacitors B
 US007 142997 B1 (12) United States Patent Widner (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) AUTOMATIC POWER FACTOR CORRECTOR Inventor: Edward D. Widner, Austin, CO (US) Assignee: Tripac Systems,
US007 142997 B1 (12) United States Patent Widner (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) AUTOMATIC POWER FACTOR CORRECTOR Inventor: Edward D. Widner, Austin, CO (US) Assignee: Tripac Systems,
United States Patent (19) Davis
 United States Patent (19) Davis 54 ACTIVE TERMINATION FOR A TRANSMISSION LINE 75 Inventor: 73 Assignee: Thomas T. Davis, Bartlesville, Okla. Phillips Petroleum Company, Bartlesville, Okla. 21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Davis 54 ACTIVE TERMINATION FOR A TRANSMISSION LINE 75 Inventor: 73 Assignee: Thomas T. Davis, Bartlesville, Okla. Phillips Petroleum Company, Bartlesville, Okla. 21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 LLP 57)
 III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
United States Patent (19) Rottmerhusen
 United States Patent (19) Rottmerhusen USOO5856731A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 5, 1999 54 ELECTRICSCREWDRIVER 75 Inventor: Hermann Rottmerhusen, Tellingstedt, Germany 73 Assignee: Metabowerke
United States Patent (19) Rottmerhusen USOO5856731A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 5, 1999 54 ELECTRICSCREWDRIVER 75 Inventor: Hermann Rottmerhusen, Tellingstedt, Germany 73 Assignee: Metabowerke
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7768461 B2 (12) United States Patent Cheng et al. (54) ANTENNA DEVICE WITH INSERT-MOLDED ANTENNA PATTERN (75) Inventors: Yu-Chiang Cheng, Taipei (TW); Ping-Cheng Chang, Chaozhou Town (TW); Cheng-Zing
USOO7768461 B2 (12) United States Patent Cheng et al. (54) ANTENNA DEVICE WITH INSERT-MOLDED ANTENNA PATTERN (75) Inventors: Yu-Chiang Cheng, Taipei (TW); Ping-Cheng Chang, Chaozhou Town (TW); Cheng-Zing
EA CE. R.I.O.C. 6 so that the drive signal is not influenced by an output
 USOO64.62965B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ues0no (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) SWITCHING POWER SUPPLY FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS T-75336 3/1995 (75) Inventor: Nobutaka Uesono, Nagaoka
USOO64.62965B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ues0no (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) SWITCHING POWER SUPPLY FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS T-75336 3/1995 (75) Inventor: Nobutaka Uesono, Nagaoka
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004
 (19) United States US 2004.0058664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0058664 A1 Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004 (54) SAW FILTER (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2004.0058664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0058664 A1 Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004 (54) SAW FILTER (30) Foreign Application Priority
II I III. United States Patent (19) Johnson, Jr. 73 Assignee: Exide Electronics Corporation,
 United States Patent (19) Johnson, Jr. (54) ISOLATED GATE DRIVE (75) Inventor: Robert W. Johnson, Jr., Raleigh, N.C. 73 Assignee: Exide Electronics Corporation, Raleigh, N.C. (21) Appl. No.: 39,932 22
United States Patent (19) Johnson, Jr. (54) ISOLATED GATE DRIVE (75) Inventor: Robert W. Johnson, Jr., Raleigh, N.C. 73 Assignee: Exide Electronics Corporation, Raleigh, N.C. (21) Appl. No.: 39,932 22
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,164,500 B2
 USOO8164500B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ahmed et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 24, 2012 (54) JITTER CANCELLATION METHOD FOR OTHER PUBLICATIONS CONTINUOUS-TIME SIGMA-DELTA Cherry et al.,
USOO8164500B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ahmed et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 24, 2012 (54) JITTER CANCELLATION METHOD FOR OTHER PUBLICATIONS CONTINUOUS-TIME SIGMA-DELTA Cherry et al.,
Eff *: (12) United States Patent PROCESSOR T PROCESSOR US 8,860,335 B2 ( ) Oct. 14, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: Gries et al.
 USOO8860335B2 (12) United States Patent Gries et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 14, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) SYSTEM FORMANAGING DC LINK SWITCHINGHARMONICS Inventors:
USOO8860335B2 (12) United States Patent Gries et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 14, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) SYSTEM FORMANAGING DC LINK SWITCHINGHARMONICS Inventors:
Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl. No.: 952, Filed: Sep. 29, 1992 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 1, 1991 JP Japan
 United States Patent (19) Miki et al. 54 ANALOGVOLTAGE SUBTRACTING CIRCUIT AND AN A/D CONVERTER HAVING THE SUBTRACTING CIRCUIT 75) Inventors: Takahiro Miki; Toshio Kumamoto, both of Hyogo, Japan 73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Miki et al. 54 ANALOGVOLTAGE SUBTRACTING CIRCUIT AND AN A/D CONVERTER HAVING THE SUBTRACTING CIRCUIT 75) Inventors: Takahiro Miki; Toshio Kumamoto, both of Hyogo, Japan 73) Assignee:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 200600498.68A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0049868A1 Yeh (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE DRIVING CIRCUIT WITH A COMPENSATING CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 200600498.68A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0049868A1 Yeh (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) REFERENCE VOLTAGE DRIVING CIRCUIT WITH A COMPENSATING CIRCUIT
