Floating Output DC-DC Converter Using Single Winding Reactor and Its Applications
|
|
|
- Sabrina Jefferson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 / 5 SANYO DENKI Technical Report No.6 Nov General Theses Floating Output DC-DC Converter Using Single Winding Reactor and Its Applications Hirohisa Yamazaki 1. Introduction Networking based on a PC server is becoming increasingly popular and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) need to be made more compact, lightweight and cheaper. The typical UPS now functions not only as a backup power supply during a power failure, but also improves the power factor and cleans the commercial power supply by absorbing the harmonics that are generated by equipment acting as loads. To achieve such targets, various rectifier circuits have been developed for UPSs. Although Sanyo Denki has been marketing step-up chopper type and high frequency insulation type products, various problems as discussed in Chapter 2 of this paper make it difficult to use the products with 200 V input. We report here on recent developments and a new product using a DC-DC converter (1) that can generate an output that is floating (separated) from the input. The new product is the 3 kva UPS using the technology in the rectifier circuit. The operating system of this DC-DC converter and UPS, and its characteristics are described. 2. Requirements for Rectifier Circuit of Compact UPS The typical load of a compact UPS is a personal computer. This means that the compact UPS supplies AC power to the switching regulator of the power supply circuit of the personal computer. Therefore, the output of the UPS includes various harmonics having a high current crest value. At the same time, arresters and ceramic varistors are used to protect the system from surges, and a high frequency filter is inserted in the input circuit of the switching regulator to protect the system from noise. The earth line of the system and the neutral line of the input/output AC power line should have minimum potential difference so that the circuit components do not operate on an abnormal potential with regard to the earth potential. For that purpose, the input circuit and output circuit of a UPS should not be separated, but the neutral lines of the input and output circuits should preferably be connected directly. The circuit in which full wave rectification and a full bridge inverter are combined in the general purpose inverter is shown in Fig. 1. In this circuit, the DC voltage that exists in the middle of the output of the inverter is super-imposed on the output voltage. This makes it difficult to connect the input and output because of the potential difference between the neutral line of the input circuit and output circuit. Therefore, the circuit operation becomes unstable with regard to the earth potential and this can cause troubles such as burning of the varistor of the load circuit or troubles due to noise. In order to connect the neutral lines of the input and output circuits, the input
2 2 / 5 could be isolated from the output. The circuit configuration using an insulation transformer in the output circuit is shown in Fig. 2. The circuit configuration of connecting an insulation transformer in the input circuit, or inserting a DC-DC converter between the input and output, has the same result, but insulation transformers are large, heavy and expensive. Use of the DC-DC converter makes the circuit configuration complicated, and manufacturing an insulation transformer for a large capacity inverter is difficult and limits application of this circuit configuration to small capacity inverters. A circuit configuration using a voltage-doubler rectifier + half-bridge inverter is shown in Fig. 3. The rectifier circuit that is used in Fig. 3, is a high power factor converter circuit. The DC voltage in the middle of this circuit becomes as follows when taking fluctuation of the input voltage into consideration: 100V = 325V When this circuit is used for 200 V, double the voltage of the above figure becomes necessary. This means that the semiconductors used in the latter stage of the inverter must have a high withstand voltage, which reduces the efficiency. Furthermore, it requires a larger air clearance and a longer creepage distance, which hinder the design of a compact unit. In addition, the mid-point voltage of capacity fluctuates in the half-bridge inverter when an unbalanced load such as a half-wave rectifier load is connected. Fluctuation of the mid-point voltage of capacity can create deviations of magnetism and insufficient withstand voltage of the capacitor. Each circuit system has its own merits and demerits as we have examined. We have developed a floating output DC-DC converter (FCON) in order to solve these problems for a UPS that operates on 200 V input and delivers output voltages of 3 kva or more. 3. FCON Circuit 3.1 Operation of FCON The FCON circuit that provides a floating output with respect to the input is shown in Fig. 4 (A). The input energy is stored in the reactor L through the two semiconductor switches Q1 and Q2. The stored energy is discharged through the two diodes D1 and D2. This circuit operation is the same as that of a flyback converter or of a polarity-inverting chopper circuit except that an insulating transformer is not necessary. The spike voltage that is created normally in the polarity-inverting chopper circuit due to its leakage inductance, is absorbed by Cdc and is suppressed. The principle of obtaining a floating output using FCON is described below. Fig. 4 (B) shows the energy storage mode in the reactor L. When Q1 and Q2 are turned on, current flows into reactor L from the DC power supply, and stores electromagnetic energy in L. The capacity of the reactor that is required here is about 4% of the input impedance, and is fairly small compared with the transformer. During storage mode, the diodes D1 and D2 are reverse-biased by the reactor L and the capacitor Cdc voltages, so that any current does not flow into the output side that is separated from the input side. When Q1 and Q2 are turned off, the system enters energy discharge mode as shown in Fig. 4 (C). Energy that was stored in L during the storage mode is now discharged into capacitor Cdc and the load side circuit through D1 and D2. Because Q1 and Q2 are turned off during the discharge mode, the output side is separated from the input side. This separation of the output from the input is obtained by repeating the two modes of (B) and (C).
3 3 / 5 The current patterns of the respective semiconductor devices constituting the circuit are shown in Fig. 4 (D). Current Iq of Q1 and Q2, and current Id of D1 and D2 increase and decrease with the following slopes. (1) (2) The relationship between the switching duty ratio D of Q1 and Q2, and the output voltage can be expressed by the following equations assuming that voltage drop due to semiconductor devices is 0 and assuming that the resistive component is 0. (3) (4) The relationship between the input/output and duty ratio is shown in Fig. 4 (E). The input voltage can be stepped up or down by changing the duty as shown in Fig. 4 (E). However, non-linearity increases and controllability deteriorates when the duty ratio exceeds Limitations of FCON The single winding reactor that is used in FCON can be easily manufactured because it does not have the leakage inductance problem, and so should be useful for large-capacity systems. However, the conversion to the floating output of FCON has a limitation compared with the transformer that is a passive component. The floating output of FCON is obtained by switching the semiconductor switch and diode in a time-shared manner. Among the switching elements, the diode turns on depending on external conditions because it is a passive element even during the period in which it must be turned off. In other words, it can create a mode in which the input and output are directly connected, thus losing the separation of input from output that is required for floating output. The conditions that are inhibited during use of FCON are shown in Fig. 5. When external voltage Ex is applied as shown in Fig. 5, diode D1 conducts when IGBT or FET or transistor is used for switch Q1 because it cannot prevent the circuit from reverse voltage. In the same manner, when voltage Ey is applied, diode D2 conducts so that the input and output circuits are directly connected and floating output cannot be obtained. When a snubber circuit or equivalent is connected in parallel with Q1 and Q2, or D1 and D2, the input and output circuits are connected through it. The structure of the snubber must be considered carefully. 4. Application of FCON to UPS 4.1 Structure of Rectifier Circuit FCON is equipped with a floating output that is necessary for the UPS rectifier as described in Chapters 2 and 3. No rush current suppression circuit is necessary because the rush current to capacitor Cdc during start-up can be suppressed by implementing soft-start of the semiconductor switches Q1 and Q2 that are used to
4 4 / 5 separate the input side. At the same time, because the fundamental operation of this circuit is that of a flyback converter, this circuit can be operated as a high power factor converter by comparing the current flowing through the reactor L with the input voltage as reference voltage, and by controlling the current flowing through L into a sine wave current. The circuit structure as a high power factor converter is shown in Fig. 6 The characteristics as a high power factor converter are, from the above circuit, Input power factor: 99.3% when input and output powers are rated power, and Conversion efficiency: 88.4% when input and output powers are rated power. Fig. 7 Waveforms at key circuits when FCON is used as a high power factor converter 4.2 UPS using FCON The structure of the UPS using FCON is shown in Fig. 8. The output voltage of the rectifier circuit as described in section 4.1, is sent to the inverter consisting of a full bridge structure, and the inverter outputs a sine wave AC voltage of constant frequency and constant voltage. This output is floating from the input of the UPS by FCON. LO and CO that are connected to the AC input circuit constitute a filter that suppresses ripples caused by switching of semiconductor switches Q1 and Q2, and absorbs high frequency noise. The AC filter forms a circuit that connects the DC bus and the AC output terminal with a capacitor. This assures the reverse bias voltage of the diode D1 and D2 which prevents leakage of noise into this circuit. The neutral line of the AC input power supply and one of the output lines are connected in common. This connection solves the problems related to earth as described in Chapter 2. The next section considers whether the common connection line as described above causes any problems for the FCON operation. An unnecessary forward bias must not be applied to the diode for the correct functioning of FCON as described before. The bias status of the diode is explained by the bias modes of the FCON diodes in Fig. 9. Figs. 9 (A) and (B) illustrate the bias status of diode D1. In the mode shown in Fig. 9 (A), the voltage across AC filter capacitor C1 is applied to D1 as a reverse bias via the input/output connection line. This connection cannot work as a forward bias. In the mode shown in Fig. 9 (B), the sum of voltages across AC filter capacitor C0 and C2 is applied to D1 as a reverse bias. The modes shown in Figs. 9 (C) and (D) are the bias mode for diode D2. In the mode shown in Fig. 9 (C), the sum of the voltages across C0 and C2 are applied as a reverse bias. In the mode shown in Fig. 9 (D), the C2 voltage is applied as a reverse bias. As explained above, diodes D1 and D2 cannot be forward-biased while the main power is on. This allows the FCON UPS to deliver its full performance. The newly developed 3 kva UPS and the conventional 3 kva UPS are compared below. Contents New UPS Conventional UPS Volume 51 liters 101 liters Mass 75 kg 125 kg Input power factor 99.3 % 99 % Input voltage range 170 V to 265 V 176 V to 224 V Overall efficiency 84.3 % 78.9 % Noise specification VCCI approved Conforms to VCCI
5 5 / 5 Note: The conventional UPS is the ASH30 input/output 200 V type. 5. Conclusion We have verified the floating output DC-DC converter (FCON) using a single winding reactor with a UPS. The floating output DC-DC converter is a high power factor converter and is used as the rectifier circuit of a UPS of single-phase, 200 V, 2 kva output. The floating output DC-DC converter with single winding reactor has the following features: (1) Because FCON uses a single winding reactor to obtain the floating output, the DC-DC converter is easy to manufacture, and an inverter having a large power conversion capacity can be manufactured. (2) Because FCON can be stepped up and down, an inverter having a wide range of input voltage deviations is realized. (3) Because the conventional inverter uses a transformer, equipment is large and heavy. The new inverter is compact and light. (4) Transformers running at commercial frequency are expensive. Since the transformer is no longer needed, the cost of the new inverter is lower. We intend to apply this new technology to three-phase circuits, increase the efficiency, and so on in future. Further development of this technology will be based on its unique characteristics. References (1) Sekino, Yamazaki: "Floating Output DC-DC Converter Using Single Winding Reactor". The Institute of Electronics, Information and Communication Engineers Technical Report, EE98-1 (1998-6) Hirohisa Yamazaki Joined company in 1974 Power Systems Division, 2nd Design Dept. Worked on design and development of small capacity UPS
6 Fig. 1 Full wave rectification + full bridge inverter 1 / 1
7 Fig. 2 Connecting an insulation transformer 1 / 1
8 Fig. 3 Voltage-doubler rectifier + half-bridge inverter 1 / 1
9 1 / 1 (A) Circuit configuration (B) Storage mode (C) Discharge mode (D) Current patterns of the respective semiconductor devices Fig.4 F4 FCON circuit and its operating principle (E) Duty ratio curve
10 Fig. 5 Conditions that are inhibited during use of FCON 1 / 1
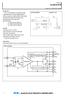
11 1 / 1 (A) Main circuit structure (B) Structure of control circuit (C) Description of operation Fig. 6 Circuit structure as a high power factor converter
12 Fig.7 Waveforms at key circuits when FCON is used as a high power factor converter 1 / 1
13 Fig. 8 Structure of UPS using FCON 1 / 1
14 Fig. 9 Bias modes of the FCON diodes 1 / 1
COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION
 CPC H H02 COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION ELECTRICITY (NOTE omitted) GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER H02M APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN
CPC H H02 COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION ELECTRICITY (NOTE omitted) GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER H02M APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN
Calhoon MEBA Engineering School. Study Guide for Proficiency Testing Industrial Electronics
 Calhoon MEBA Engineering School Study Guide for Proficiency Testing Industrial Electronics January 0. Which factors affect the end-to-end resistance of a metallic conductor?. A waveform shows three complete
Calhoon MEBA Engineering School Study Guide for Proficiency Testing Industrial Electronics January 0. Which factors affect the end-to-end resistance of a metallic conductor?. A waveform shows three complete
Voltage and current regulation circuits operating according to the non-switched (linear) principle are classified in subclass G05F
 CPC - H02M - 2017.08 H02M APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER
CPC - H02M - 2017.08 H02M APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER
LeMeniz Infotech. 36, 100 Feet Road, Natesan Nagar, Near Indira Gandhi Statue, Pondicherry Call: , ,
 Analysis of the Interleaved Isolated Boost Converter with Coupled Inductors Abstract Introduction: A configuration with many parallel-connected boostflyback converters sharing a single active clamp has
Analysis of the Interleaved Isolated Boost Converter with Coupled Inductors Abstract Introduction: A configuration with many parallel-connected boostflyback converters sharing a single active clamp has
EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 6 Diodes: Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Converting AC to DC
 EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 6 Diodes: Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Converting C to DC The process of converting a sinusoidal C voltage to a
EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 6 Diodes: Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Converting C to DC The process of converting a sinusoidal C voltage to a
Lab 9: 3 phase Inverters and Snubbers
 Lab 9: 3 phase Inverters and Snubbers Name: Pre Lab 3 phase inverters: Three phase inverters can be realized in two ways: three single phase inverters operating together, or one three phase inverter. The
Lab 9: 3 phase Inverters and Snubbers Name: Pre Lab 3 phase inverters: Three phase inverters can be realized in two ways: three single phase inverters operating together, or one three phase inverter. The
New lossless clamp for single ended converters
 New lossless clamp for single ended converters Nigel Machin & Jurie Dekter Rectifier Technologies Pacific 24 Harker St Burwood, Victoria, 3125 Australia information@rtp.com.au Abstract A clamp for single
New lossless clamp for single ended converters Nigel Machin & Jurie Dekter Rectifier Technologies Pacific 24 Harker St Burwood, Victoria, 3125 Australia information@rtp.com.au Abstract A clamp for single
Implementation of Resistor based Protection Scheme for the Fault Conditions and Closed Loop Operation of a Three-Level DC-DC Converter
 Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347-5161 2014 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Implementation
Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347-5161 2014 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Implementation
ISSN: X Impact factor: (Volume 3, Issue 6) Available online at Modeling and Analysis of Transformer
 ISSN: 2454-132X Impact factor: 4.295 (Volume 3, Issue 6) Available online at www.ijariit.com Modeling and Analysis of Transformer Divyapradeepa.T Department of Electrical and Electronics, Rajalakshmi Engineering
ISSN: 2454-132X Impact factor: 4.295 (Volume 3, Issue 6) Available online at www.ijariit.com Modeling and Analysis of Transformer Divyapradeepa.T Department of Electrical and Electronics, Rajalakshmi Engineering
Fundamentals of Microelectronics
 Fundamentals of Microelectronics CH1 Why Microelectronics? CH2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors CH3 Diode Circuits CH4 Physics of Bipolar Transistors CH5 Bipolar Amplifiers CH6 Physics of MOS Transistors
Fundamentals of Microelectronics CH1 Why Microelectronics? CH2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors CH3 Diode Circuits CH4 Physics of Bipolar Transistors CH5 Bipolar Amplifiers CH6 Physics of MOS Transistors
Diode Characteristics and Applications
 Diode Characteristics and Applications Topics covered in this presentation: Diode Characteristics Diode Clamp Protecting Against Back-EMF Half-Wave Rectifier The Zener Diode 1 of 18 Diode Characteristics
Diode Characteristics and Applications Topics covered in this presentation: Diode Characteristics Diode Clamp Protecting Against Back-EMF Half-Wave Rectifier The Zener Diode 1 of 18 Diode Characteristics
CHAPTER 3 DC-DC CONVERTER TOPOLOGIES
 47 CHAPTER 3 DC-DC CONVERTER TOPOLOGIES 3.1 INTRODUCTION In recent decades, much research efforts are directed towards finding an isolated DC-DC converter with high volumetric power density, low electro
47 CHAPTER 3 DC-DC CONVERTER TOPOLOGIES 3.1 INTRODUCTION In recent decades, much research efforts are directed towards finding an isolated DC-DC converter with high volumetric power density, low electro
POWER ELECTRONICS. Converters, Applications, and Design. NED MOHAN Department of Electrical Engineering University of Minnesota Minneapolis, Minnesota
 POWER ELECTRONICS Converters, Applications, and Design THIRD EDITION NED MOHAN Department of Electrical Engineering University of Minnesota Minneapolis, Minnesota TORE M. UNDELAND Department of Electrical
POWER ELECTRONICS Converters, Applications, and Design THIRD EDITION NED MOHAN Department of Electrical Engineering University of Minnesota Minneapolis, Minnesota TORE M. UNDELAND Department of Electrical
Differential-Mode Emissions
 Differential-Mode Emissions In Fig. 13-5, the primary purpose of the capacitor C F, however, is to filter the full-wave rectified ac line voltage. The filter capacitor is therefore a large-value, high-voltage
Differential-Mode Emissions In Fig. 13-5, the primary purpose of the capacitor C F, however, is to filter the full-wave rectified ac line voltage. The filter capacitor is therefore a large-value, high-voltage
Electronic Circuits I Laboratory 03 Rectifiers
 Electronic Circuits I Laboratory 03 Rectifiers # Student ID Student Name Grade (10) 1 Instructor signature 2 3 4 5 Delivery Date -1 / 18 - Objectives In this experiment, you will get to know a group of
Electronic Circuits I Laboratory 03 Rectifiers # Student ID Student Name Grade (10) 1 Instructor signature 2 3 4 5 Delivery Date -1 / 18 - Objectives In this experiment, you will get to know a group of
Lecture 19 - Single-phase square-wave inverter
 Lecture 19 - Single-phase square-wave inverter 1. Introduction Inverter circuits supply AC voltage or current to a load from a DC supply. A DC source, often obtained from an AC-DC rectifier, is converted
Lecture 19 - Single-phase square-wave inverter 1. Introduction Inverter circuits supply AC voltage or current to a load from a DC supply. A DC source, often obtained from an AC-DC rectifier, is converted
Exercise 12. Semiconductors EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. Introduction to semiconductors. The diode
 Exercise 12 Semiconductors EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the operation of a diode. You will learn how to use a diode to rectify ac voltage to produce
Exercise 12 Semiconductors EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the operation of a diode. You will learn how to use a diode to rectify ac voltage to produce
DOWNLOAD PDF POWER ELECTRONICS DEVICES DRIVERS AND APPLICATIONS
 Chapter 1 : Power Electronics Devices, Drivers, Applications, and Passive theinnatdunvilla.com - Google D Download Power Electronics: Devices, Drivers and Applications By B.W. Williams - Provides a wide
Chapter 1 : Power Electronics Devices, Drivers, Applications, and Passive theinnatdunvilla.com - Google D Download Power Electronics: Devices, Drivers and Applications By B.W. Williams - Provides a wide
Matrix Drives Boost Power Quality and Energy Savings
 Matrix Drives Boost Power Quality and Energy Savings How It s Done: An Overview of Matrix Drive Technology yaskawa.com Introduction Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) are electronic devices used to regulate
Matrix Drives Boost Power Quality and Energy Savings How It s Done: An Overview of Matrix Drive Technology yaskawa.com Introduction Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) are electronic devices used to regulate
Large-Capacity, High-Efficiency 3-Level UPS for North America 7000HX-T3U
 Large-Capacity, High-Efficiency 3-Level for North America 7000HX-T3U KAWASAKI, Daisuke HAMADA, Ippei SATO, Atsushi ABSTRACT Due to the development of information and communications systems in the information
Large-Capacity, High-Efficiency 3-Level for North America 7000HX-T3U KAWASAKI, Daisuke HAMADA, Ippei SATO, Atsushi ABSTRACT Due to the development of information and communications systems in the information
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Introduction Power semiconductor devices constitute the heart of the modern power electronics, and are being extensively used in power electronic converters in the form of a
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Introduction Power semiconductor devices constitute the heart of the modern power electronics, and are being extensively used in power electronic converters in the form of a
Applications of Diode
 Applications of Diode Diode Approximation: (Large signal operations): 1. Ideal Diode: When diode is forward biased, resistance offered is zero, When it is reverse biased resistance offered is infinity.
Applications of Diode Diode Approximation: (Large signal operations): 1. Ideal Diode: When diode is forward biased, resistance offered is zero, When it is reverse biased resistance offered is infinity.
CHAPTER 3. SINGLE-STAGE PFC TOPOLOGY GENERALIZATION AND VARIATIONS
 CHAPTER 3. SINGLE-STAGE PFC TOPOLOG GENERALIATION AND VARIATIONS 3.1. INTRODUCTION The original DCM S 2 PFC topology offers a simple integration of the DCM boost rectifier and the PWM DC/DC converter.
CHAPTER 3. SINGLE-STAGE PFC TOPOLOG GENERALIATION AND VARIATIONS 3.1. INTRODUCTION The original DCM S 2 PFC topology offers a simple integration of the DCM boost rectifier and the PWM DC/DC converter.
Chapter 6: Converter circuits
 Chapter 6. Converter Circuits 6.1. Circuit manipulations 6.2. A short list of converters 6.3. Transformer isolation 6.4. Converter evaluation and design 6.5. Summary of key points Where do the boost, buck-boost,
Chapter 6. Converter Circuits 6.1. Circuit manipulations 6.2. A short list of converters 6.3. Transformer isolation 6.4. Converter evaluation and design 6.5. Summary of key points Where do the boost, buck-boost,
Power Protection and Conditioning
 2/50 Voltage Wave Attenuation CBEMA Constant Voltage Power Supply Voltage surge with a virtual front time of 1.2 ms and a time to half-value of 50 ms delivered across an open circuit. 8/20 Current Wave
2/50 Voltage Wave Attenuation CBEMA Constant Voltage Power Supply Voltage surge with a virtual front time of 1.2 ms and a time to half-value of 50 ms delivered across an open circuit. 8/20 Current Wave
CHOICE OF HIGH FREQUENCY INVERTERS AND SEMICONDUCTOR SWITCHES
 Chapter-3 CHOICE OF HIGH FREQUENCY INVERTERS AND SEMICONDUCTOR SWITCHES This chapter is based on the published articles, 1. Nitai Pal, Pradip Kumar Sadhu, Dola Sinha and Atanu Bandyopadhyay, Selection
Chapter-3 CHOICE OF HIGH FREQUENCY INVERTERS AND SEMICONDUCTOR SWITCHES This chapter is based on the published articles, 1. Nitai Pal, Pradip Kumar Sadhu, Dola Sinha and Atanu Bandyopadhyay, Selection
BUCK-BOOST CONVERTER:
 BUCK-BOOST CONVERTER: The buck boost converter is a type of DC-DC converter that has an output voltage magnitude that is either greater than or less than the input voltage magnitude. Two different topologies
BUCK-BOOST CONVERTER: The buck boost converter is a type of DC-DC converter that has an output voltage magnitude that is either greater than or less than the input voltage magnitude. Two different topologies
A Novel Single-Stage Push Pull Electronic Ballast With High Input Power Factor
 770 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, VOL. 48, NO. 4, AUGUST 2001 A Novel Single-Stage Push Pull Electronic Ballast With High Input Power Factor Chang-Shiarn Lin, Member, IEEE, and Chern-Lin
770 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, VOL. 48, NO. 4, AUGUST 2001 A Novel Single-Stage Push Pull Electronic Ballast With High Input Power Factor Chang-Shiarn Lin, Member, IEEE, and Chern-Lin
2.1 Performance Standards The UPS is designed with the applicable sections of UL, CUL, and ISO The UPS has UL and CUL listing.
 1.0 Scope This document describes the specification for Toshiba 1000 Series On-Line Uninterruptible Power System (UPS). The UPS will supply a computer grade AC output sine wave which is unaffected by the
1.0 Scope This document describes the specification for Toshiba 1000 Series On-Line Uninterruptible Power System (UPS). The UPS will supply a computer grade AC output sine wave which is unaffected by the
Fundamentals of Microelectronics
 Fundamentals of Microelectronics CH1 Why Microelectronics? CH2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors CH3 Diode Circuits CH4 Physics of Bipolar Transistors CH5 Bipolar Amplifiers CH6 Physics of MOS Transistors
Fundamentals of Microelectronics CH1 Why Microelectronics? CH2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors CH3 Diode Circuits CH4 Physics of Bipolar Transistors CH5 Bipolar Amplifiers CH6 Physics of MOS Transistors
Improvements of LLC Resonant Converter
 Chapter 5 Improvements of LLC Resonant Converter From previous chapter, the characteristic and design of LLC resonant converter were discussed. In this chapter, two improvements for LLC resonant converter
Chapter 5 Improvements of LLC Resonant Converter From previous chapter, the characteristic and design of LLC resonant converter were discussed. In this chapter, two improvements for LLC resonant converter
CHAPTER 2 A SERIES PARALLEL RESONANT CONVERTER WITH OPEN LOOP CONTROL
 14 CHAPTER 2 A SERIES PARALLEL RESONANT CONVERTER WITH OPEN LOOP CONTROL 2.1 INTRODUCTION Power electronics devices have many advantages over the traditional power devices in many aspects such as converting
14 CHAPTER 2 A SERIES PARALLEL RESONANT CONVERTER WITH OPEN LOOP CONTROL 2.1 INTRODUCTION Power electronics devices have many advantages over the traditional power devices in many aspects such as converting
TOSHIBA International Corp
 TOSHIBA International Corp GUIDE SPECIFICATIONS THREE PHASE UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SYSTEM TOSHIBA 4200FA 30 kva CT Internal Battery UPS GUIDE SPECIFICATIONS 1 (30 kva CT) 1.0 SCOPE 1.1 System This specification
TOSHIBA International Corp GUIDE SPECIFICATIONS THREE PHASE UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SYSTEM TOSHIBA 4200FA 30 kva CT Internal Battery UPS GUIDE SPECIFICATIONS 1 (30 kva CT) 1.0 SCOPE 1.1 System This specification
R. W. Erickson. Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder
 R. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder 6.3.5. Boost-derived isolated converters A wide variety of boost-derived isolated dc-dc converters
R. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder 6.3.5. Boost-derived isolated converters A wide variety of boost-derived isolated dc-dc converters
Open-Delta Systems Affect Variable Frequency Drives
 Open-Delta Systems Affect Variable Frequency Drives To avoid premature drive failure, proper precautions must be taken when installing VFDs on open-delta supplies. Written by: Dan Peters, Yaskawa America,
Open-Delta Systems Affect Variable Frequency Drives To avoid premature drive failure, proper precautions must be taken when installing VFDs on open-delta supplies. Written by: Dan Peters, Yaskawa America,
FINALTERM EXAMINATION. Spring PHY301- Circuit Theory
 Date 14/2/2013 Eini FINALTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 PHY301- Circuit Theory Time: 90 min Marks: 60 Question No: 1 If we connect 3 capacitors in parallel, the combined effect of all these capacitors will
Date 14/2/2013 Eini FINALTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 PHY301- Circuit Theory Time: 90 min Marks: 60 Question No: 1 If we connect 3 capacitors in parallel, the combined effect of all these capacitors will
Recent Approaches to Develop High Frequency Power Converters
 The 1 st Symposium on SPC (S 2 PC) 17/1/214 Recent Approaches to Develop High Frequency Power Converters Location Fireworks Much snow Tokyo Nagaoka University of Technology, Japan Prof. Jun-ichi Itoh Dr.
The 1 st Symposium on SPC (S 2 PC) 17/1/214 Recent Approaches to Develop High Frequency Power Converters Location Fireworks Much snow Tokyo Nagaoka University of Technology, Japan Prof. Jun-ichi Itoh Dr.
Half bridge converter with LCL filter for battery charging application using DC-DC converter topology
 Half bridge converter with LCL filter for battery charging application using DC-DC converter topology Manasa.B 1, Kalpana S 2 Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Electronics PESITM, Shivamogga
Half bridge converter with LCL filter for battery charging application using DC-DC converter topology Manasa.B 1, Kalpana S 2 Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Electronics PESITM, Shivamogga
EE 105. Diode Circuits. Prof. Ali M. Niknejad and Prof. Rikky Muller. March 2, U.C. Berkeley Copyright 2017 by Ali M.
 EE 105 Diode Circuits Prof. Ali M. Niknejad and Prof. Rikky Muller U.C. Berkeley Copyright 2017 by Ali M. Niknejad March 2, 2017 1/ 23 Diode Introduction A diode is a non-linear element. To a very good
EE 105 Diode Circuits Prof. Ali M. Niknejad and Prof. Rikky Muller U.C. Berkeley Copyright 2017 by Ali M. Niknejad March 2, 2017 1/ 23 Diode Introduction A diode is a non-linear element. To a very good
Conventional Single-Switch Forward Converter Design
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Amplifier and Comparator Circuits > APP 3983 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Power-Supply Circuits
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Amplifier and Comparator Circuits > APP 3983 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Power-Supply Circuits
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Power Diode EE2301 POWER ELECTRONICS UNIT I POWER SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES PART A 1. What is meant by fast recovery
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Power Diode EE2301 POWER ELECTRONICS UNIT I POWER SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES PART A 1. What is meant by fast recovery
A New Three-Phase Interleaved Isolated Boost Converter With Solar Cell Application. K. Srinadh
 A New Three-Phase Interleaved Isolated Boost Converter With Solar Cell Application K. Srinadh Abstract In this paper, a new three-phase high power dc/dc converter with an active clamp is proposed. The
A New Three-Phase Interleaved Isolated Boost Converter With Solar Cell Application K. Srinadh Abstract In this paper, a new three-phase high power dc/dc converter with an active clamp is proposed. The
Diodes and Applications
 Diodes and Applications Diodes and Applications 2 1 Diode Operation 2 2 Voltage-Current (V-I) Characteristics 2 3 Diode Models 2 4 Half-Wave Rectifiers 2 5 Full-Wave Rectifiers 2 6 Power Supply Filters
Diodes and Applications Diodes and Applications 2 1 Diode Operation 2 2 Voltage-Current (V-I) Characteristics 2 3 Diode Models 2 4 Half-Wave Rectifiers 2 5 Full-Wave Rectifiers 2 6 Power Supply Filters
After performing this experiment, you should be able to:
 Objectives: After performing this experiment, you should be able to: Demonstrate the strengths and weaknesses of the two basic rectifier circuits. Draw the output waveforms for the two basic rectifier
Objectives: After performing this experiment, you should be able to: Demonstrate the strengths and weaknesses of the two basic rectifier circuits. Draw the output waveforms for the two basic rectifier
High Efficiency Power Conversion Using a Matrix Converter
 High Efficiency Power Conversion Using a Converter Jun-ichi Itoh Akihiro Odaka Ikuya Sato 1. Introduction As demands for energy savings have increased in recent years, inverters are being used in a wider
High Efficiency Power Conversion Using a Converter Jun-ichi Itoh Akihiro Odaka Ikuya Sato 1. Introduction As demands for energy savings have increased in recent years, inverters are being used in a wider
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. AN120 An overview of switched-mode power supplies Dec
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS An overview of switched-mode power supplies 1988 Dec Conceptually, three basic approaches exist for obtaining regulated DC voltage from an AC power source. These are: Shunt regulation
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS An overview of switched-mode power supplies 1988 Dec Conceptually, three basic approaches exist for obtaining regulated DC voltage from an AC power source. These are: Shunt regulation
Modern Concepts of Energy Control Technology through VVVF Propulsion Drive
 Modern Concepts of Energy Control Technology through VVVF Propulsion Drive Satoru OZAKI, Fuji Electric Systems Co., Ltd. Ken-ichi URUGA, Toyo Denki Seizo K.K. Dr. D.P. Bhatt, Autometers Alliance Ltd ABSTRACT
Modern Concepts of Energy Control Technology through VVVF Propulsion Drive Satoru OZAKI, Fuji Electric Systems Co., Ltd. Ken-ichi URUGA, Toyo Denki Seizo K.K. Dr. D.P. Bhatt, Autometers Alliance Ltd ABSTRACT
NJWA - Harmonics and Drives Proper System Design
 Session Goals Larry Stanley, Sr. Regional Business Development Engineer, Water Segment Matthew LaRue, ABB Drives Product Manager Philadelphia District, Baldor of Philadelphia NJWA - Harmonics and Drives
Session Goals Larry Stanley, Sr. Regional Business Development Engineer, Water Segment Matthew LaRue, ABB Drives Product Manager Philadelphia District, Baldor of Philadelphia NJWA - Harmonics and Drives
CHAPTER 2 EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT MODELING OF CONDUCTED EMI BASED ON NOISE SOURCES AND IMPEDANCES
 29 CHAPTER 2 EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT MODELING OF CONDUCTED EMI BASED ON NOISE SOURCES AND IMPEDANCES A simple equivalent circuit modeling approach to describe Conducted EMI coupling system for the SPC is described
29 CHAPTER 2 EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT MODELING OF CONDUCTED EMI BASED ON NOISE SOURCES AND IMPEDANCES A simple equivalent circuit modeling approach to describe Conducted EMI coupling system for the SPC is described
A Single Phase Single Stage AC/DC Converter with High Input Power Factor and Tight Output Voltage Regulation
 638 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 A Single Phase Single Stage AC/DC Converter with High Input Power Factor and Tight Output Voltage Regulation A. K.
638 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 A Single Phase Single Stage AC/DC Converter with High Input Power Factor and Tight Output Voltage Regulation A. K.
Soft switching of multioutput flyback converter with active clamp circuit
 Soft switching of multioutput flyback converter with active clamp circuit Aruna N S 1, Dr S G Srivani 2, Balaji P 3 PG Student, Dept. of EEE, R.V. College of Engineering, Bangalore, Karnataka, India 1
Soft switching of multioutput flyback converter with active clamp circuit Aruna N S 1, Dr S G Srivani 2, Balaji P 3 PG Student, Dept. of EEE, R.V. College of Engineering, Bangalore, Karnataka, India 1
High Voltage DC Transmission 2
 High Voltage DC Transmission 2 1.0 Introduction Interconnecting HVDC within an AC system requires conversion from AC to DC and inversion from DC to AC. We refer to the circuits which provide conversion
High Voltage DC Transmission 2 1.0 Introduction Interconnecting HVDC within an AC system requires conversion from AC to DC and inversion from DC to AC. We refer to the circuits which provide conversion
A Series-Resonant Half-Bridge Inverter for Induction-Iron Appliances
 IEEE PEDS 2011, Singapore, 5-8 December 2011 A Series-Resonant Half-Bridge Inverter for Induction-Iron Appliances N. Sanajit* and A. Jangwanitlert ** * Department of Electrical Power Engineering, Faculty
IEEE PEDS 2011, Singapore, 5-8 December 2011 A Series-Resonant Half-Bridge Inverter for Induction-Iron Appliances N. Sanajit* and A. Jangwanitlert ** * Department of Electrical Power Engineering, Faculty
Power Converters. Neil Marks. STFC ASTeC/ Cockcroft Institute/ U. of Liverpool, Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington WA4 4AD, U.K.
 Power Converters Neil Marks STFC ASTeC/ Cockcroft Institute/ U. of Liverpool, Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington WA4 4AD, U.K. n.marks@dl.ac.uk Contents 1. Requirements. 2. Basic elements of power supplies.
Power Converters Neil Marks STFC ASTeC/ Cockcroft Institute/ U. of Liverpool, Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington WA4 4AD, U.K. n.marks@dl.ac.uk Contents 1. Requirements. 2. Basic elements of power supplies.
Switching and Semiconductor Switches
 1 Switching and Semiconductor Switches 1.1 POWER FLOW CONTROL BY SWITCHES The flow of electrical energy between a fixed voltage supply and a load is often controlled by interposing a controller, as shown
1 Switching and Semiconductor Switches 1.1 POWER FLOW CONTROL BY SWITCHES The flow of electrical energy between a fixed voltage supply and a load is often controlled by interposing a controller, as shown
SERIES ACTIVE power filters have proved to be an interesting
 928 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 14, NO. 5, SEPTEMBER 1999 A Fault Protection Scheme for Series Active Power Filters Luis A. Morán, Senior Member, IEEE, Ivar Pastorini, Juan Dixon, Senior
928 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 14, NO. 5, SEPTEMBER 1999 A Fault Protection Scheme for Series Active Power Filters Luis A. Morán, Senior Member, IEEE, Ivar Pastorini, Juan Dixon, Senior
ECE514 Power Electronics Converter Topologies. Part 2 [100 pts] Design of an RDC snubber for flyback converter
![ECE514 Power Electronics Converter Topologies. Part 2 [100 pts] Design of an RDC snubber for flyback converter ECE514 Power Electronics Converter Topologies. Part 2 [100 pts] Design of an RDC snubber for flyback converter](/thumbs/72/67440195.jpg) ECE514 Power Electronics Converter Topologies Homework Assignment #4 Due date October 31, 2014, beginning of the lecture Part 1 [100 pts] Redo Term Test 1 (attached) Part 2 [100 pts] Design of an RDC snubber
ECE514 Power Electronics Converter Topologies Homework Assignment #4 Due date October 31, 2014, beginning of the lecture Part 1 [100 pts] Redo Term Test 1 (attached) Part 2 [100 pts] Design of an RDC snubber
Design, Control and Application of Modular Multilevel Converters for HVDC Transmission Systems by Kamran Sharifabadi, Lennart Harnefors, Hans-Peter
 1 Design, Control and Application of Modular Multilevel Converters for HVDC Transmission Systems by Kamran Sharifabadi, Lennart Harnefors, Hans-Peter Nee, Staffan Norrga, Remus Teodorescu ISBN-10: 1118851560
1 Design, Control and Application of Modular Multilevel Converters for HVDC Transmission Systems by Kamran Sharifabadi, Lennart Harnefors, Hans-Peter Nee, Staffan Norrga, Remus Teodorescu ISBN-10: 1118851560
A Double ZVS-PWM Active-Clamping Forward Converter: Analysis, Design, and Experimentation
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 16, NO. 6, NOVEMBER 2001 745 A Double ZVS-PWM Active-Clamping Forward Converter: Analysis, Design, and Experimentation René Torrico-Bascopé, Member, IEEE, and
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 16, NO. 6, NOVEMBER 2001 745 A Double ZVS-PWM Active-Clamping Forward Converter: Analysis, Design, and Experimentation René Torrico-Bascopé, Member, IEEE, and
EXPERIMENT 5 : DIODES AND RECTIFICATION
 EXPERIMENT 5 : DIODES AND RECTIFICATION Component List Resistors, one of each o 2 1010W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (Imax = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6Vpp, 12.6 VRMS) 100 F Electrolytic
EXPERIMENT 5 : DIODES AND RECTIFICATION Component List Resistors, one of each o 2 1010W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (Imax = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6Vpp, 12.6 VRMS) 100 F Electrolytic
An Interleaved High Step-Up Boost Converter With Voltage Multiplier Module for Renewable Energy System
 An Interleaved High Step-Up Boost Converter With Voltage Multiplier Module for Renewable Energy System Vahida Humayoun 1, Divya Subramanian 2 1 P.G. Student, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
An Interleaved High Step-Up Boost Converter With Voltage Multiplier Module for Renewable Energy System Vahida Humayoun 1, Divya Subramanian 2 1 P.G. Student, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
1 Diodes. 1.1 Diode Models Ideal Diode. ELEN 236 Diodes
 ELEN 236 Diodes 1 Diodes 1.1 Diode Models 1.1.1 Ideal Diode Current through diode is zero for any voltage less than zero i.e. reverse biased case Current through diode is not limited by diode if voltage
ELEN 236 Diodes 1 Diodes 1.1 Diode Models 1.1.1 Ideal Diode Current through diode is zero for any voltage less than zero i.e. reverse biased case Current through diode is not limited by diode if voltage
HIGH VOLTAGE ENGINEERING(FEEE6402) LECTURER-24
 LECTURER-24 GENERATION OF HIGH ALTERNATING VOLTAGES When test voltage requirements are less than about 300kV, a single transformer can be used for test purposes. The impedance of the transformer should
LECTURER-24 GENERATION OF HIGH ALTERNATING VOLTAGES When test voltage requirements are less than about 300kV, a single transformer can be used for test purposes. The impedance of the transformer should
Control of buck-boost chopper type AC voltage regulator
 International Journal of Research in Advanced Engineering and Technology ISSN: 2455-0876; Impact Factor: RJIF 5.44 www.engineeringresearchjournal.com Volume 2; Issue 3; May 2016; Page No. 52-56 Control
International Journal of Research in Advanced Engineering and Technology ISSN: 2455-0876; Impact Factor: RJIF 5.44 www.engineeringresearchjournal.com Volume 2; Issue 3; May 2016; Page No. 52-56 Control
Industrial Electrician Level 3
 Industrial Electrician Level 3 Industrial Electrician Unit: C1 Industrial Electrical Code I Level: Three Duration: 77 hours Theory: Practical: 77 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit is designed to provide
Industrial Electrician Level 3 Industrial Electrician Unit: C1 Industrial Electrical Code I Level: Three Duration: 77 hours Theory: Practical: 77 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit is designed to provide
Power Conditioning Equipment for Improvement of Power Quality in Distribution Systems M. Weinhold R. Zurowski T. Mangold L. Voss
 Power Conditioning Equipment for Improvement of Power Quality in Distribution Systems M. Weinhold R. Zurowski T. Mangold L. Voss Siemens AG, EV NP3 P.O. Box 3220 91050 Erlangen, Germany e-mail: Michael.Weinhold@erls04.siemens.de
Power Conditioning Equipment for Improvement of Power Quality in Distribution Systems M. Weinhold R. Zurowski T. Mangold L. Voss Siemens AG, EV NP3 P.O. Box 3220 91050 Erlangen, Germany e-mail: Michael.Weinhold@erls04.siemens.de
VLA574-01R V I + V CC DETECT C trip V O V I - F O C S V EE TIMER & RESET LATCH DETECT. 1kΩ INTERFACE UVL 240Ω GATE SHUT DOWN BLOCK DIAGRAM DESCRIPTION
 DESCRIPTION VLA74 is a hybrid integrated circuit designed for driving n-channel IGBT modules in any gate-amplifier application. OUTLINE DRAWING Dimensions : mm This device operates as an isolation amplifier
DESCRIPTION VLA74 is a hybrid integrated circuit designed for driving n-channel IGBT modules in any gate-amplifier application. OUTLINE DRAWING Dimensions : mm This device operates as an isolation amplifier
Module 4. AC to AC Voltage Converters. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 4 AC to AC Voltage Converters Version EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 9 Introduction to Cycloconverters Version EE IIT, Kharagpur Instructional Objectives Study of the following: The cyclo-converter
Module 4 AC to AC Voltage Converters Version EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 9 Introduction to Cycloconverters Version EE IIT, Kharagpur Instructional Objectives Study of the following: The cyclo-converter
ENG2210 Electronic Circuits. Chapter 3 Diodes
 ENG2210 Electronic Circuits Mokhtar A. Aboelaze York University Chapter 3 Diodes Objectives Learn the characteristics of ideal diode and how to analyze and design circuits containing multiple diodes Learn
ENG2210 Electronic Circuits Mokhtar A. Aboelaze York University Chapter 3 Diodes Objectives Learn the characteristics of ideal diode and how to analyze and design circuits containing multiple diodes Learn
Experiment DC-DC converter
 POWER ELECTRONIC LAB Experiment-7-8-9 DC-DC converter Power Electronics Lab Ali Shafique, Ijhar Khan, Dr. Syed Abdul Rahman Kashif 10/11/2015 This manual needs to be completed before the mid-term examination.
POWER ELECTRONIC LAB Experiment-7-8-9 DC-DC converter Power Electronics Lab Ali Shafique, Ijhar Khan, Dr. Syed Abdul Rahman Kashif 10/11/2015 This manual needs to be completed before the mid-term examination.
CHAPTER 4 FULL WAVE RECTIFIER. AC DC Conversion
 CHAPTER 4 FULL WAVE RECTIFIER AC DC Conversion SINGLE PHASE FULL-WAVE RECTIFIER The objective of a full wave rectifier is to produce a voltage or current which is purely dc or has some specified dc component.
CHAPTER 4 FULL WAVE RECTIFIER AC DC Conversion SINGLE PHASE FULL-WAVE RECTIFIER The objective of a full wave rectifier is to produce a voltage or current which is purely dc or has some specified dc component.
Power Electronics. Prof. B. G. Fernandes. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay.
 Power Electronics Prof. B. G. Fernandes Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 28 So far we have studied 4 different DC to DC converters. They are; first
Power Electronics Prof. B. G. Fernandes Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 28 So far we have studied 4 different DC to DC converters. They are; first
Three Phase Power Factor Corrected Isolated Buck for 48V/100A Rectifier with Secondary Active Clamp
 7- Three Phase Power Factor Corrected solated Buck for 48V/100A Rectifier with Secondary Active Clamp Robert Sheehy, Jurien Dekter and Nigel Machin Rectifier Technologies, Melbourne, Australia mail: information@rtp.com.au
7- Three Phase Power Factor Corrected solated Buck for 48V/100A Rectifier with Secondary Active Clamp Robert Sheehy, Jurien Dekter and Nigel Machin Rectifier Technologies, Melbourne, Australia mail: information@rtp.com.au
UPS Uninterruptible Power System
 UPS Uninterruptible Power System Handling items Uninterruptible Power System (UPS) Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) Frequency Converter (F/C) Rectifier Battery Charge Transformer UPS Outline Definition
UPS Uninterruptible Power System Handling items Uninterruptible Power System (UPS) Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) Frequency Converter (F/C) Rectifier Battery Charge Transformer UPS Outline Definition
STK A-E. Applications Air conditioner three-phase compressor motor driver.
 Ordering number : EN*A1339A STK621-043A-E Thick-Film Hybrid IC Air Conditioner Three-Phase Compressor Motor Driver IMST Inverter Power Hybrid IC Overview The STK621-043A-E is a 3-phase inverter power hybrid
Ordering number : EN*A1339A STK621-043A-E Thick-Film Hybrid IC Air Conditioner Three-Phase Compressor Motor Driver IMST Inverter Power Hybrid IC Overview The STK621-043A-E is a 3-phase inverter power hybrid
Analysis, Design and Implementation of Snubberless Bidirectional Current Fed Full Bridge Voltage Doubler
 Analysis, Design and Implementation of Snubberless Bidirectional Current Fed Full Bridge Voltage Doubler Vinay.K.V 1, Raju Yanamshetti 2, Ravindra.Y.N 3 PG Student [Power Electronics], Dept. of EEE, PDA
Analysis, Design and Implementation of Snubberless Bidirectional Current Fed Full Bridge Voltage Doubler Vinay.K.V 1, Raju Yanamshetti 2, Ravindra.Y.N 3 PG Student [Power Electronics], Dept. of EEE, PDA
IGBT based Multiport Bidirectional DC-DC Converter with Renewable Energy Source
 IGBT based Multiport Bidirectional DC-DC Converter with Renewable Energy Source S.Gautham Final Year, UG student, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, P. B. College of Engineering, Chennai
IGBT based Multiport Bidirectional DC-DC Converter with Renewable Energy Source S.Gautham Final Year, UG student, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, P. B. College of Engineering, Chennai
Modeling and Simulation of STATCOM
 Modeling and Simulation of STATCOM Parimal Borse, India Dr. A. G. Thosar Associate Professor, India Samruddhi Shaha, India Abstract:- This paper attempts to model and simulate Flexible Alternating Current
Modeling and Simulation of STATCOM Parimal Borse, India Dr. A. G. Thosar Associate Professor, India Samruddhi Shaha, India Abstract:- This paper attempts to model and simulate Flexible Alternating Current
PQ for Industrial Benchmarking with various methods to improve. Tushar Mogre.
 General PQ: Power Quality has multiple issues involved. Thus, need to have some benchmarking standards. Very little is spoken about the LT supply installation within an industry. There is need to understand
General PQ: Power Quality has multiple issues involved. Thus, need to have some benchmarking standards. Very little is spoken about the LT supply installation within an industry. There is need to understand
ACS 1000 Transformer Failure Investigation. Nathan Schachter, Peng
 Investigation Nathan Schachter, Peng Objectives Learn what happened Explain why it happened Discuss solutions Suggest remedies so it does not happen again Prevention is the key to success 2 ACS 1000 VFD
Investigation Nathan Schachter, Peng Objectives Learn what happened Explain why it happened Discuss solutions Suggest remedies so it does not happen again Prevention is the key to success 2 ACS 1000 VFD
POWER FACTOR CORRECTION USING AN IMPROVED SINGLE-STAGE SINGLE- SWITCH (S 4 ) TECHNIQUE
 International Journal of Power Systems and Microelectronics (IJMPS) Vol. 1, Issue 1, Jun 2016, 45-52 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd POWER FACTOR CORRECTION USING AN IMPROVED SINGLE-STAGE SINGLE- SWITCH (S 4 ) TECHNIQUE
International Journal of Power Systems and Microelectronics (IJMPS) Vol. 1, Issue 1, Jun 2016, 45-52 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd POWER FACTOR CORRECTION USING AN IMPROVED SINGLE-STAGE SINGLE- SWITCH (S 4 ) TECHNIQUE
Open Access Research on Fast Response Characteristic of Magnetic Control Reactor
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 966 The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 2014, 6, 966-974 Open Access Research on Fast Response Characteristic of Magnetic Control Reactor
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 966 The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 2014, 6, 966-974 Open Access Research on Fast Response Characteristic of Magnetic Control Reactor
International Journal of Research. Available at
 Pi Controller Based Soft-Switching Two-Switch Resonant Ac Dc Converter with High Power Factor C.Sukumar & Dr.Chidhambaraiah Setty #1M.Tech Student, #2professor, Department of EEE St.Johns College of Engineering
Pi Controller Based Soft-Switching Two-Switch Resonant Ac Dc Converter with High Power Factor C.Sukumar & Dr.Chidhambaraiah Setty #1M.Tech Student, #2professor, Department of EEE St.Johns College of Engineering
Exercise 3: EXERCISE OBJECTIVE
 Exercise 3: EXERCISE OBJECTIVE voltage equal to double the peak ac input voltage by using a voltage doubler circuit. You will verify your results with a multimeter and an oscilloscope. DISCUSSION times
Exercise 3: EXERCISE OBJECTIVE voltage equal to double the peak ac input voltage by using a voltage doubler circuit. You will verify your results with a multimeter and an oscilloscope. DISCUSSION times
1. The current-doubler rectifier can be used to double the load capability of isolated dc dc converters with bipolar secondaryside
 Highlights of the Chapter 4 1. The current-doubler rectifier can be used to double the load capability of isolated dc dc converters with bipolar secondaryside voltage. Some industry-generated papers recommend
Highlights of the Chapter 4 1. The current-doubler rectifier can be used to double the load capability of isolated dc dc converters with bipolar secondaryside voltage. Some industry-generated papers recommend
RECTIFIERS POWER SUPPLY AND VOLTAGE REGULATION. Rectifier. Basic DC Power Supply. Filter. Regulator
 RECTIFIERS POWER SUPPLY AND OLTAGE REGULATION Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Electronic Devices by Thomas L. Floyd Because of their ability to conduct current in one direction and block current
RECTIFIERS POWER SUPPLY AND OLTAGE REGULATION Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Electronic Devices by Thomas L. Floyd Because of their ability to conduct current in one direction and block current
Hardware Implementation of Interleaved Converter with Voltage Multiplier Cell for PV System
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 12 June 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Hardware Implementation of Interleaved Converter with Voltage Multiplier Cell for
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 12 June 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Hardware Implementation of Interleaved Converter with Voltage Multiplier Cell for
Courseware Sample F0
 Electric Power / Controls Courseware Sample 85822-F0 A ELECTRIC POWER / CONTROLS COURSEWARE SAMPLE by the Staff of Lab-Volt Ltd. Copyright 2009 Lab-Volt Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Electric Power / Controls Courseware Sample 85822-F0 A ELECTRIC POWER / CONTROLS COURSEWARE SAMPLE by the Staff of Lab-Volt Ltd. Copyright 2009 Lab-Volt Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
CHAPTER 4 MODIFIED H- BRIDGE MULTILEVEL INVERTER USING MPD-SPWM TECHNIQUE
 58 CHAPTER 4 MODIFIED H- BRIDGE MULTILEVEL INVERTER USING MPD-SPWM TECHNIQUE 4.1 INTRODUCTION Conventional voltage source inverter requires high switching frequency PWM technique to obtain a quality output
58 CHAPTER 4 MODIFIED H- BRIDGE MULTILEVEL INVERTER USING MPD-SPWM TECHNIQUE 4.1 INTRODUCTION Conventional voltage source inverter requires high switching frequency PWM technique to obtain a quality output
Lecture 5: Diode, Rectifier and Capacitor. Bo Wang Division of Information & Computing Technology Hamad Bin Khalifa University
 Lecture 5: Diode, Rectifier and Capacitor Bo Wang Division of Information & Computing Technology Hamad Bin Khalifa University bwang@hbku.edu.qa 1 Why Rectifying? Voltage and current delivered from the
Lecture 5: Diode, Rectifier and Capacitor Bo Wang Division of Information & Computing Technology Hamad Bin Khalifa University bwang@hbku.edu.qa 1 Why Rectifying? Voltage and current delivered from the
results at the output, disrupting safe, precise measurements.
 H Common-Mode Noise: Sources and Solutions Application Note 1043 Introduction Circuit designers often encounter the adverse effects of commonmode noise on a design. Once a common-mode problem is identified,
H Common-Mode Noise: Sources and Solutions Application Note 1043 Introduction Circuit designers often encounter the adverse effects of commonmode noise on a design. Once a common-mode problem is identified,
S. General Topological Properties of Switching Structures, IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, 1979 Record, pp , June 1979.
 Problems 179 [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] [30] J. N. PARK and T. R. ZALOUM, A Dual Mode Forward/Flyback Converter, IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, 1982 Record, pp. 3-13, June
Problems 179 [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] [30] J. N. PARK and T. R. ZALOUM, A Dual Mode Forward/Flyback Converter, IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, 1982 Record, pp. 3-13, June
3.4. Operation in the Reverse Breakdown
 3.4. peration in the Reverse Breakdown Under certain circumstances, diodes may be intentionally used in the reverse breakdown region These are referred to as Zener Diode or Breakdown Diode Voltage regulator
3.4. peration in the Reverse Breakdown Under certain circumstances, diodes may be intentionally used in the reverse breakdown region These are referred to as Zener Diode or Breakdown Diode Voltage regulator
[High side bias challenges and solutions in half bridge gate drivers] [Ritesh Oza]
![[High side bias challenges and solutions in half bridge gate drivers] [Ritesh Oza] [High side bias challenges and solutions in half bridge gate drivers] [Ritesh Oza]](/thumbs/77/74996773.jpg) [High side bias challenges and solutions in half bridge gate drivers] [Ritesh Oza] 1 What will I get out of this session? Purpose: Understand various challenges associated with high side bias design in
[High side bias challenges and solutions in half bridge gate drivers] [Ritesh Oza] 1 What will I get out of this session? Purpose: Understand various challenges associated with high side bias design in
Power Supplies and Circuits. Bill Sheets K2MQJ Rudolf F. Graf KA2CWL
 Power Supplies and Circuits Bill Sheets K2MQJ Rudolf F. Graf KA2CWL The power supply is an often neglected important item for any electronics experimenter. No one seems to get very excited about mundane
Power Supplies and Circuits Bill Sheets K2MQJ Rudolf F. Graf KA2CWL The power supply is an often neglected important item for any electronics experimenter. No one seems to get very excited about mundane
LM MHz Cuk Converter
 LM2611 1.4MHz Cuk Converter General Description The LM2611 is a current mode, PWM inverting switching regulator. Operating from a 2.7-14V supply, it is capable of producing a regulated negative output
LM2611 1.4MHz Cuk Converter General Description The LM2611 is a current mode, PWM inverting switching regulator. Operating from a 2.7-14V supply, it is capable of producing a regulated negative output
EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE
 EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE Component List Resistors, one of each o 1 10 10W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (Imax = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6Vpp, 12.6 VRMS) 100 F Electrolytic Capacitor
EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE Component List Resistors, one of each o 1 10 10W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (Imax = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6Vpp, 12.6 VRMS) 100 F Electrolytic Capacitor
Harmonic Mitigation for Variable Frequency Drives. HWEA Conference February 15, Kelvin J. Hurdle Rockwell Bus. Dev. Mgr.
 Harmonic Mitigation for Variable Frequency Drives HWEA Conference February 15, 2011 Kelvin J. Hurdle Rockwell Bus. Dev. Mgr. 1 OVERVIEW Linear vs. Non- Linear Load Definitions AC Drive Input Current Harmonics
Harmonic Mitigation for Variable Frequency Drives HWEA Conference February 15, 2011 Kelvin J. Hurdle Rockwell Bus. Dev. Mgr. 1 OVERVIEW Linear vs. Non- Linear Load Definitions AC Drive Input Current Harmonics
Student Department of EEE (M.E-PED), 2 Assitant Professor of EEE Selvam College of Technology Namakkal, India
 Design and Development of Single Phase Bridgeless Three Stage Interleaved Boost Converter with Fuzzy Logic Control System M.Pradeep kumar 1, M.Ramesh kannan 2 1 Student Department of EEE (M.E-PED), 2 Assitant
Design and Development of Single Phase Bridgeless Three Stage Interleaved Boost Converter with Fuzzy Logic Control System M.Pradeep kumar 1, M.Ramesh kannan 2 1 Student Department of EEE (M.E-PED), 2 Assitant
Chapter 6 Soft-Switching dc-dc Converters Outlines
 Chapter 6 Soft-Switching dc-dc Converters Outlines Classification of soft-switching resonant converters Advantages and disadvantages of ZCS and ZVS Zero-current switching topologies The resonant switch
Chapter 6 Soft-Switching dc-dc Converters Outlines Classification of soft-switching resonant converters Advantages and disadvantages of ZCS and ZVS Zero-current switching topologies The resonant switch
