PERCEIVING SCENES. Visual Perception
|
|
|
- Arnold Richardson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PERCEIVING SCENES Visual Perception
2 Occlusion Face it in everyday life We can do a pretty good job in the face of occlusion Need to complete parts of the objects we cannot see Slide 2
3 Visual Completion Perceive partly occluded surface as complete Slide 3
4 Visual Completion Multiple possible perception Only one is dominant How might it happen? Figural familiarity Figural similarity Ecological Constraint Slide 4
5 Figural Familiarity Slide 5
6 Cannot Explain We can complete novel shapes Theory still holds Slide 6
7 Figural Simplicity Complete as the simplest figures What is simple? Is simplicity number of sides or number of axes of symmetry? Slide 7
8 Ecological Constraints Based on ecological evidence of occluded contours E.g. T- Junction Slide 8
9 Relatibility Theory Edge discontinuities are necessary Relatable Discontinuities Intersect at 90 degree Smoothly Connected Slide 9
10 Relatibility Theory Edge discontinuities are necessary Relatable Discontinuities Intersect at 90 degree Smoothly Connected Form a enclosed Area Infer position in depth Slide 10
11 Let us take an example Can you almost perceive depth? Slide 11
12 Illusory Contours Come with Visual Completion Enclosed space is important Slide 12
13 Alternative Perception Slide 13
14 Alternative Perception Slide 14
15 Perceived Translucency Perceived as being viewed through a closer translucent object Slide 15
16 Translucency Slide 16
17 Multistability More than one perception Spontaneously alternate between more than one perception Necker Cube Slide 17
18 Network Model Slide 18
19 Why only one interpretation at a time? Slide 19
20 Why does alteration happen? Neural Fatigue Theory Slide 20
21 Why does alteration happen? Neural Fatigue Theory Not the only one Role of eye fixation or instructions Slide 21
22 Perceivable Properties Shape Orientation Size Position Slide 22
23 Shape Constancy Perceive objects to be of same shape despite being viewed from different viewpoints Slide 23
24 Size and Shape is related Slide 24
25 2D objects Slide 25
26 3D objects Slide 26
27 3D objects Slide 27
28 Shape Illusions Cicle/Ellipse Ponzo Ames Room Slide 28
29 Orientation Constancy Objects don t tilt when our heads tilt Slide 29
30 Proprioceptive System Slide 30
31 Tilted Room Illusion K4-AI Slide 31
32 Zollner Illusion Slide 32
33 Zollner Illusion Slide 33
34 How much can we adapt? Slide 34
35 How much can we adapt? Slide 35
36 How much can we adapt? Slide 36
37 Retinal Un-Inversion Experiment Slide 37
38 Parts Perceive shape, size and orientation by parts Linguistic and phenomenological evidence Refer by parts: Palm, toe, shin, ankle All over the world in all cultures Slide 38
39 Which comes first? Whole or parts? Slide 39
40 Global Precedence Global advantage Responds faster to global letters Global to local interference Inconsistency slows local letter identification Lack of local to global interference Inconsistency does not slow down the global letter identification Processed in different halves of brain Slide 40
41 In two different parts of brain Preferences : Local on left, global on right Slide 41
Object Perception. 23 August PSY Object & Scene 1
 Object Perception Perceiving an object involves many cognitive processes, including recognition (memory), attention, learning, expertise. The first step is feature extraction, the second is feature grouping
Object Perception Perceiving an object involves many cognitive processes, including recognition (memory), attention, learning, expertise. The first step is feature extraction, the second is feature grouping
Today. Pattern Recognition. Introduction. Perceptual processing. Feature Integration Theory, cont d. Feature Integration Theory (FIT)
 Today Pattern Recognition Intro Psychology Georgia Tech Instructor: Dr. Bruce Walker Turning features into things Patterns Constancy Depth Illusions Introduction We have focused on the detection of features
Today Pattern Recognition Intro Psychology Georgia Tech Instructor: Dr. Bruce Walker Turning features into things Patterns Constancy Depth Illusions Introduction We have focused on the detection of features
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception. Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation
 Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Bottom-up and Top-down Perception Bottom-up perception
 Bottom-up and Top-down Perception Bottom-up perception Physical characteristics of stimulus drive perception Realism Top-down perception Knowledge, expectations, or thoughts influence perception Constructivism:
Bottom-up and Top-down Perception Bottom-up perception Physical characteristics of stimulus drive perception Realism Top-down perception Knowledge, expectations, or thoughts influence perception Constructivism:
Gestalt and Picture Organization
 Perceptual and Artistic Principles for Effective Computer Depiction Grouping by color Georgia O Keeffe Gestalt and Picture Organization Fredo Durand MIT- Lab for Computer Science Grouping, illusory contour
Perceptual and Artistic Principles for Effective Computer Depiction Grouping by color Georgia O Keeffe Gestalt and Picture Organization Fredo Durand MIT- Lab for Computer Science Grouping, illusory contour
Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Perception. How we interpret the information our senses receive. Overview Perception
 Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Visual Rules. Why are they necessary?
 Visual Rules Why are they necessary? Because the image on the retina has just two dimensions, a retinal image allows countless interpretations of a visual object in three dimensions. Underspecified Poverty
Visual Rules Why are they necessary? Because the image on the retina has just two dimensions, a retinal image allows countless interpretations of a visual object in three dimensions. Underspecified Poverty
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See
 Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction. Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc.
 Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
Human Vision and Human-Computer Interaction Much content from Jeff Johnson, UI Wizards, Inc. are these guidelines grounded in perceptual psychology and how can we apply them intelligently? Mach bands:
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation
 IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects
 4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects Chapter 4 4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects Finding edges Grouping and texture segmentation Figure Ground assignment Edges, parts, and wholes Object recognition
4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects Chapter 4 4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects Finding edges Grouping and texture segmentation Figure Ground assignment Edges, parts, and wholes Object recognition
Our visual system always has to compute a solid object given definite limitations in the evidence that the eye is able to obtain from the world, by
 Perceptual Rules Our visual system always has to compute a solid object given definite limitations in the evidence that the eye is able to obtain from the world, by inferring a third dimension. We can
Perceptual Rules Our visual system always has to compute a solid object given definite limitations in the evidence that the eye is able to obtain from the world, by inferring a third dimension. We can
Sensation & Perception
 Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Sensation & Perception What is sensation & perception? Detection of emitted or reflected by Done by sense organs Process by which the and sensory information Done by the How does work? receptors detect
Vision: Distance & Size Perception
 Vision: Distance & Size Perception Useful terms: Egocentric distance: distance from you to an object. Relative distance: distance between two objects in the environment. 3-d structure: Objects appear three-dimensional,
Vision: Distance & Size Perception Useful terms: Egocentric distance: distance from you to an object. Relative distance: distance between two objects in the environment. 3-d structure: Objects appear three-dimensional,
Fun with visual illusions. Professor William Ayliffe Gresham Professor of Physic
 Gresham Lecture, Wednesday 13 October 2010 Fun with visual illusions Professor William Ayliffe Gresham Professor of Physic There are many definitions of what constitutes a visual illusion. We commonly
Gresham Lecture, Wednesday 13 October 2010 Fun with visual illusions Professor William Ayliffe Gresham Professor of Physic There are many definitions of what constitutes a visual illusion. We commonly
Motion perception PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 24. Aperture problem
 Motion perception PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 24 How do you see motion here? Aperture problem A detector that only sees part of a scene cannot precisely identify the motion direction or speed of an edge
Motion perception PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 24 How do you see motion here? Aperture problem A detector that only sees part of a scene cannot precisely identify the motion direction or speed of an edge
You ve heard about the different types of lines that can appear in line drawings. Now we re ready to talk about how people perceive line drawings.
 You ve heard about the different types of lines that can appear in line drawings. Now we re ready to talk about how people perceive line drawings. 1 Line drawings bring together an abundance of lines to
You ve heard about the different types of lines that can appear in line drawings. Now we re ready to talk about how people perceive line drawings. 1 Line drawings bring together an abundance of lines to
the dimensionality of the world Travelling through Space and Time Learning Outcomes Johannes M. Zanker
 Travelling through Space and Time Johannes M. Zanker http://www.pc.rhul.ac.uk/staff/j.zanker/ps1061/l4/ps1061_4.htm 05/02/2015 PS1061 Sensation & Perception #4 JMZ 1 Learning Outcomes at the end of this
Travelling through Space and Time Johannes M. Zanker http://www.pc.rhul.ac.uk/staff/j.zanker/ps1061/l4/ps1061_4.htm 05/02/2015 PS1061 Sensation & Perception #4 JMZ 1 Learning Outcomes at the end of this
Outline 2/21/2013. The Retina
 Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Outline 2/21/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception 2 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Simple Figures and Perceptions in Depth (2): Stereo Capture
 59 JSL, Volume 2 (2006), 59 69 Simple Figures and Perceptions in Depth (2): Stereo Capture Kazuo OHYA Following previous paper the purpose of this paper is to collect and publish some useful simple stimuli
59 JSL, Volume 2 (2006), 59 69 Simple Figures and Perceptions in Depth (2): Stereo Capture Kazuo OHYA Following previous paper the purpose of this paper is to collect and publish some useful simple stimuli
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Size perception PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 22 Why the cars look like toys. Our visual system is useful for identifying the properties of objects in the world Surface (color, texture) Location (depth)
Size perception PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 22 Why the cars look like toys. Our visual system is useful for identifying the properties of objects in the world Surface (color, texture) Location (depth)
Human Vision. Human Vision - Perception
 1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
PERCEIVING MOVEMENT. Ways to create movement
 PERCEIVING MOVEMENT Ways to create movement Perception More than one ways to create the sense of movement Real movement is only one of them Slide 2 Important for survival Animals become still when they
PERCEIVING MOVEMENT Ways to create movement Perception More than one ways to create the sense of movement Real movement is only one of them Slide 2 Important for survival Animals become still when they
Learning Targets. Module 19
 Learning Targets Module 19 Visual Organization and Interpretation 19-1 Describe the Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles
Learning Targets Module 19 Visual Organization and Interpretation 19-1 Describe the Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles
Sensation and Perception. Sensation. Sensory Receptors. Sensation. General Properties of Sensory Systems
 Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Sensation and Perception Psychology I Sjukgymnastprogrammet May, 2012 Joel Kaplan, Ph.D. Dept of Clinical Neuroscience Karolinska Institute joel.kaplan@ki.se General Properties of Sensory Systems Sensation:
Perception: From Biology to Psychology
 Perception: From Biology to Psychology What do you see? Perception is a process of meaning-making because we attach meanings to sensations. That is exactly what happened in perceiving the Dalmatian Patterns
Perception: From Biology to Psychology What do you see? Perception is a process of meaning-making because we attach meanings to sensations. That is exactly what happened in perceiving the Dalmatian Patterns
the human chapter 1 Traffic lights the human User-centred Design Light Vision part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) Information i/o
 Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Traffic lights chapter 1 the human part 1 (modified extract for AISD 2005) http://www.baddesigns.com/manylts.html User-centred Design Bad design contradicts facts pertaining to human capabilities Usability
Part III: Line Drawings and Perception
 Part III: Line Drawings and Perception Doug DeCarlo Line Drawings from 3D Models SIGGRAPH 2005 Course Notes 1 Line drawings cross-hatching hatching contour crease Albrecht Dürer,, The Presentation in the
Part III: Line Drawings and Perception Doug DeCarlo Line Drawings from 3D Models SIGGRAPH 2005 Course Notes 1 Line drawings cross-hatching hatching contour crease Albrecht Dürer,, The Presentation in the
Occlusion. Atmospheric Perspective. Height in the Field of View. Seeing Depth The Cue Approach. Monocular/Pictorial
 Seeing Depth The Cue Approach Occlusion Monocular/Pictorial Cues that are available in the 2D image Height in the Field of View Atmospheric Perspective 1 Linear Perspective Linear Perspective & Texture
Seeing Depth The Cue Approach Occlusion Monocular/Pictorial Cues that are available in the 2D image Height in the Field of View Atmospheric Perspective 1 Linear Perspective Linear Perspective & Texture
Sensation. Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes
 Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
P rcep e t p i t on n a s a s u n u c n ons n c s ious u s i nf n e f renc n e L ctur u e 4 : Recogni n t i io i n
 Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Face Perception. The Thatcher Illusion. The Thatcher Illusion. Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Face Inversion Effect
 The Thatcher Illusion Face Perception Did you notice anything odd about the upside-down image of Margaret Thatcher that you saw before? Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Thatcher Illusion
The Thatcher Illusion Face Perception Did you notice anything odd about the upside-down image of Margaret Thatcher that you saw before? Can you recognize these upside-down faces? The Thatcher Illusion
Sensation and Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Sensation
 Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Sensation and Perception Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney 2/18/2009 Sensation.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Psychophysics Sensations Hearing Vision Touch Taste Smell Kinesthetic Perception 2/18/2009
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex
 Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Lecture 4 Foundations and Cognitive Processes in Visual Perception From the Retina to the Visual Cortex 1.Vision Science 2.Visual Performance 3.The Human Visual System 4.The Retina 5.The Visual Field and
Chapter 3: Psychophysical studies of visual object recognition
 BEWARE: These are preliminary notes. In the future, they will become part of a textbook on Visual Object Recognition. Chapter 3: Psychophysical studies of visual object recognition We want to understand
BEWARE: These are preliminary notes. In the future, they will become part of a textbook on Visual Object Recognition. Chapter 3: Psychophysical studies of visual object recognition We want to understand
Humans used a web interface to say same person or different person for a large set of faces. Several computer programs made the same comparisons
 OPTO 6124 Perception Scott Stevenson Image Segmentation What is really behind so many perception demos? Perception demos show us that our visual understanding of the world involves a lot of filling in
OPTO 6124 Perception Scott Stevenson Image Segmentation What is really behind so many perception demos? Perception demos show us that our visual understanding of the world involves a lot of filling in
Module 2. Lecture-1. Understanding basic principles of perception including depth and its representation.
 Module 2 Lecture-1 Understanding basic principles of perception including depth and its representation. Initially let us take the reference of Gestalt law in order to have an understanding of the basic
Module 2 Lecture-1 Understanding basic principles of perception including depth and its representation. Initially let us take the reference of Gestalt law in order to have an understanding of the basic
AUDITORY ILLUSIONS & LAB REPORT FORM
 01/02 Illusions - 1 AUDITORY ILLUSIONS & LAB REPORT FORM NAME: DATE: PARTNER(S): The objective of this experiment is: To understand concepts such as beats, localization, masking, and musical effects. APPARATUS:
01/02 Illusions - 1 AUDITORY ILLUSIONS & LAB REPORT FORM NAME: DATE: PARTNER(S): The objective of this experiment is: To understand concepts such as beats, localization, masking, and musical effects. APPARATUS:
An Introduction to 3D Computer Graphics, Stereoscopic Image, and Animation in OpenGL and C/C++ Fore June
 An Introduction to 3D Computer Graphics, Stereoscopic Image, and Animation in OpenGL and C/C++ Fore June Chapter 8 Depth Perception 8.1 Stereoscopic Depth Perception When we observe the three dimensional
An Introduction to 3D Computer Graphics, Stereoscopic Image, and Animation in OpenGL and C/C++ Fore June Chapter 8 Depth Perception 8.1 Stereoscopic Depth Perception When we observe the three dimensional
Chapter 4 PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
3D Space Perception. (aka Depth Perception)
 3D Space Perception (aka Depth Perception) 3D Space Perception The flat retinal image problem: How do we reconstruct 3D-space from 2D image? What information is available to support this process? Interaction
3D Space Perception (aka Depth Perception) 3D Space Perception The flat retinal image problem: How do we reconstruct 3D-space from 2D image? What information is available to support this process? Interaction
Perception: Pattern and object recognition. Chapter 3
 Perception: Pattern and object recognition Chapter 3 Pattern recognition theories How do we interpret lines and patterns as objects? Why is object perception so difficult for computers? Start simple: How
Perception: Pattern and object recognition Chapter 3 Pattern recognition theories How do we interpret lines and patterns as objects? Why is object perception so difficult for computers? Start simple: How
Perception of structure 2: Impossible Objects
 Perception of structure 2: Impossible Objects (Aaron Sloman, University of Birmingham) This is a sequel to the presentation of a challenge to vision researchers here: http://www.cs.bham.ac.uk/research/projects/cogaff/challenge.pdf
Perception of structure 2: Impossible Objects (Aaron Sloman, University of Birmingham) This is a sequel to the presentation of a challenge to vision researchers here: http://www.cs.bham.ac.uk/research/projects/cogaff/challenge.pdf
Introduction to Psychology Prof. Braj Bhushan Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Introduction to Psychology Prof. Braj Bhushan Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 10 Perception Role of Culture in Perception Till now we have
Introduction to Psychology Prof. Braj Bhushan Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 10 Perception Role of Culture in Perception Till now we have
Perceptual Organization
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Perceptual Organization Module 16 2 Perceptual Organization Perceptual
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Perceptual Organization Module 16 2 Perceptual Organization Perceptual
CAN WE BELIEVE OUR OWN EYES?
 Reading Practice CAN WE BELIEVE OUR OWN EYES? A. An optical illusion refers to a visually perceived image that is deceptive or misleading in that information transmitted from the eye to the brain is processed
Reading Practice CAN WE BELIEVE OUR OWN EYES? A. An optical illusion refers to a visually perceived image that is deceptive or misleading in that information transmitted from the eye to the brain is processed
Sensation. Perception. Perception
 Ch 4D depth and gestalt 1 Sensation Basic principles in perception o Absolute Threshold o Difference Threshold o Weber s Law o Sensory Adaptation Description Examples Color Perception o Trichromatic Theory
Ch 4D depth and gestalt 1 Sensation Basic principles in perception o Absolute Threshold o Difference Threshold o Weber s Law o Sensory Adaptation Description Examples Color Perception o Trichromatic Theory
the human chapter 1 the human Overview Perception Limitations of poor interface design Why do we need to understand users?
 the human chapter 1 the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied problem solving Emotion influences
the human chapter 1 the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied problem solving Emotion influences
7Motion Perception. 7 Motion Perception. 7 Computation of Visual Motion. Chapter 7
 7Motion Perception Chapter 7 7 Motion Perception Computation of Visual Motion Eye Movements Using Motion Information The Man Who Couldn t See Motion 7 Computation of Visual Motion How would you build a
7Motion Perception Chapter 7 7 Motion Perception Computation of Visual Motion Eye Movements Using Motion Information The Man Who Couldn t See Motion 7 Computation of Visual Motion How would you build a
B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION. Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh
 B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh 2 The Perception of Movement Where is it going? 3 Biological Functions of Motion Perception
B.A. II Psychology Paper A MOVEMENT PERCEPTION Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh 2 The Perception of Movement Where is it going? 3 Biological Functions of Motion Perception
Vision Defect Identification System (VDIS) using Knowledge Base and Image Processing Framework
 Vishal Dahiya* et al. / (IJRCCT) INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN COMPUTER AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY Vol No. 1, Issue No. 1 Vision Defect Identification System (VDIS) using Knowledge Base and Image
Vishal Dahiya* et al. / (IJRCCT) INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN COMPUTER AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY Vol No. 1, Issue No. 1 Vision Defect Identification System (VDIS) using Knowledge Base and Image
Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 10. Neurophysiology
 Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 10 A continuous surface infolded on itself. Neurophysiology We are working under the following hypothesis What we see is determined by the pattern of neural
Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 10 A continuous surface infolded on itself. Neurophysiology We are working under the following hypothesis What we see is determined by the pattern of neural
Constancy PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 19. Brightness illusions
 Constancy PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 19 It s all an illusion! Brightness illusions Most people think of visual perception as a measurement of light As it reflects off of objects 1 Object identification
Constancy PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 19 It s all an illusion! Brightness illusions Most people think of visual perception as a measurement of light As it reflects off of objects 1 Object identification
268 Index. Ecological validity, 44 45, 73, 90, , 233. See also Brunswick; Gibson
 Index Accommodation cue, 44, 57 Accuracy of shape perception, 16 18, 23, 25 of slant perception, 23, 25 Affine. See Transformation; Invariants Afterimage, 10, 36 Alhazen, 9 13. See also Taking into account
Index Accommodation cue, 44, 57 Accuracy of shape perception, 16 18, 23, 25 of slant perception, 23, 25 Affine. See Transformation; Invariants Afterimage, 10, 36 Alhazen, 9 13. See also Taking into account
Motion Perception II Chapter 8
 Motion Perception II Chapter 8 Lecture 14 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2019 Eye movements: also give rise to retinal motion. important to distinguish motion due to
Motion Perception II Chapter 8 Lecture 14 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2019 Eye movements: also give rise to retinal motion. important to distinguish motion due to
Perception. The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events.
 Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. At any moment our awareness focuses, like a flashlight beam, on only
Perception The process of organizing and interpreting information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events. At any moment our awareness focuses, like a flashlight beam, on only
2. How does the brain cope with the blind spot? What does the author mean when he says that brain is hallucinating?
 NAME: Read Camels and Cops and answer the following: 1. What is the optic disk? 2. How does the brain cope with the blind spot? What does the author mean when he says that brain is hallucinating? 3. Explain
NAME: Read Camels and Cops and answer the following: 1. What is the optic disk? 2. How does the brain cope with the blind spot? What does the author mean when he says that brain is hallucinating? 3. Explain
D) visual capture. E) perceptual adaptation.
 1. Our inability to consciously perceive all the sensory information available to us at any single point in time best illustrates the necessity of: A) selective attention. B) perceptual adaptation. C)
1. Our inability to consciously perceive all the sensory information available to us at any single point in time best illustrates the necessity of: A) selective attention. B) perceptual adaptation. C)
Plan. Vision Solves Problems. Distal vs. proximal stimulus. Vision as an inverse problem. Unconscious inference (Helmholtz)
 The Art and Science of Depiction Vision Solves Problems Plan Vision as an cognitive process Computational theory of vision Constancy, invariants Fredo Durand MIT- Lab for Computer Science Intro to Visual
The Art and Science of Depiction Vision Solves Problems Plan Vision as an cognitive process Computational theory of vision Constancy, invariants Fredo Durand MIT- Lab for Computer Science Intro to Visual
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception All Senses have 3 Characteristics Sense organs: Eyes, Nose, Ears, Skin, Tongue gather information about your environment 1. Transduction 2. Adaptation 3. Sensation/Perception
Resolving Perceptual Ambiguity Visual Rules & Other Factors
 Resolving Perceptual Ambiguity Visual Rules & Other Factors Dr Joseph L Brooks School of Psychology & Centre for Cognitive Neuroscience & Cognitive Systems University of Kent What do you see? Depth ambiguity
Resolving Perceptual Ambiguity Visual Rules & Other Factors Dr Joseph L Brooks School of Psychology & Centre for Cognitive Neuroscience & Cognitive Systems University of Kent What do you see? Depth ambiguity
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
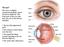 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2010 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Sensor Array
Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2010 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Sensor Array
Salient features make a search easy
 Chapter General discussion This thesis examined various aspects of haptic search. It consisted of three parts. In the first part, the saliency of movability and compliance were investigated. In the second
Chapter General discussion This thesis examined various aspects of haptic search. It consisted of three parts. In the first part, the saliency of movability and compliance were investigated. In the second
Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2)
 Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2) Dorsal and Ventral visual pathways Figure 4.15 The dorsal and ventral streams in the cortex originate with the magno and parvo ganglion cells and
Parvocellular layers (3-6) Magnocellular layers (1 & 2) Dorsal and Ventral visual pathways Figure 4.15 The dorsal and ventral streams in the cortex originate with the magno and parvo ganglion cells and
A Vestibular Sensation: Probabilistic Approaches to Spatial Perception (II) Presented by Shunan Zhang
 A Vestibular Sensation: Probabilistic Approaches to Spatial Perception (II) Presented by Shunan Zhang Vestibular Responses in Dorsal Visual Stream and Their Role in Heading Perception Recent experiments
A Vestibular Sensation: Probabilistic Approaches to Spatial Perception (II) Presented by Shunan Zhang Vestibular Responses in Dorsal Visual Stream and Their Role in Heading Perception Recent experiments
Articulation: brightness, apparent illumination, and contrast ratios
 Perception, 2, volume 31, pages 161 ^ 169 DOI:.68/p9sp Articulation: brightness, apparent illumination, and contrast ratios James A Schirillo Department of Psychology, Wake Forest University, PO Box 7778
Perception, 2, volume 31, pages 161 ^ 169 DOI:.68/p9sp Articulation: brightness, apparent illumination, and contrast ratios James A Schirillo Department of Psychology, Wake Forest University, PO Box 7778
The occlusion illusion: Partial modal completion or apparent distance?
 Perception, 2007, volume 36, pages 650 ^ 669 DOI:10.1068/p5694 The occlusion illusion: Partial modal completion or apparent distance? Stephen E Palmer, Joseph L Brooks, Kevin S Lai Department of Psychology,
Perception, 2007, volume 36, pages 650 ^ 669 DOI:10.1068/p5694 The occlusion illusion: Partial modal completion or apparent distance? Stephen E Palmer, Joseph L Brooks, Kevin S Lai Department of Psychology,
Munker ^ White-like illusions without T-junctions
 Perception, 2002, volume 31, pages 711 ^ 715 DOI:10.1068/p3348 Munker ^ White-like illusions without T-junctions Arash Yazdanbakhsh, Ehsan Arabzadeh, Baktash Babadi, Arash Fazl School of Intelligent Systems
Perception, 2002, volume 31, pages 711 ^ 715 DOI:10.1068/p3348 Munker ^ White-like illusions without T-junctions Arash Yazdanbakhsh, Ehsan Arabzadeh, Baktash Babadi, Arash Fazl School of Intelligent Systems
Understanding Optical Illusions. Mohit Gupta
 Understanding Optical Illusions Mohit Gupta What are optical illusions? Perception: I see Light (Sensing) Truth: But this is an! Oracle Optical Illusion in Nature Image Courtesy: http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/classes/met130/notes/chapter19/graphics/infer_mirage_road.jpg
Understanding Optical Illusions Mohit Gupta What are optical illusions? Perception: I see Light (Sensing) Truth: But this is an! Oracle Optical Illusion in Nature Image Courtesy: http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/classes/met130/notes/chapter19/graphics/infer_mirage_road.jpg
Neuro-Fuzzy and Soft Computing: Fuzzy Sets. Chapter 1 of Neuro-Fuzzy and Soft Computing by Jang, Sun and Mizutani
 Chapter 1 of Neuro-Fuzzy and Soft Computing by Jang, Sun and Mizutani Outline Introduction Soft Computing (SC) vs. Conventional Artificial Intelligence (AI) Neuro-Fuzzy (NF) and SC Characteristics 2 Introduction
Chapter 1 of Neuro-Fuzzy and Soft Computing by Jang, Sun and Mizutani Outline Introduction Soft Computing (SC) vs. Conventional Artificial Intelligence (AI) Neuro-Fuzzy (NF) and SC Characteristics 2 Introduction
The peripheral drift illusion: A motion illusion in the visual periphery
 Perception, 1999, volume 28, pages 617-621 The peripheral drift illusion: A motion illusion in the visual periphery Jocelyn Faubert, Andrew M Herbert Ecole d'optometrie, Universite de Montreal, CP 6128,
Perception, 1999, volume 28, pages 617-621 The peripheral drift illusion: A motion illusion in the visual periphery Jocelyn Faubert, Andrew M Herbert Ecole d'optometrie, Universite de Montreal, CP 6128,
Computer Vision Introduction
 Computer Vision Introduction Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines Vision What and Why? Human vision Computer vision General computer vision applications Course Outlines Administrative
Computer Vision Introduction Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines Vision What and Why? Human vision Computer vision General computer vision applications Course Outlines Administrative
The horizon line, linear perspective, interposition, and background brightness as determinants of the magnitude of the pictorial moon illusion
 Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics 2009, 71 (1), 131-142 doi:10.3758/app.71.1.131 The horizon line, linear perspective, interposition, and background brightness as determinants of the magnitude of
Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics 2009, 71 (1), 131-142 doi:10.3758/app.71.1.131 The horizon line, linear perspective, interposition, and background brightness as determinants of the magnitude of
Sensation and Perception
 Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Page 94 Check syllabus! We are starting with Section 6-7 in book. Sensation and Perception Our Link With the World Shorter wavelengths give us blue experience Longer wavelengths give us red experience
Perceiving the Present and a Systematization of Illusions
 Cognitive Science 32 (2008) 459 503 Copyright C 2008 Cognitive Science Society, Inc. All rights reserved. ISSN: 0364-0213 print / 1551-6709 online DOI: 10.1080/03640210802035191 Perceiving the Present
Cognitive Science 32 (2008) 459 503 Copyright C 2008 Cognitive Science Society, Inc. All rights reserved. ISSN: 0364-0213 print / 1551-6709 online DOI: 10.1080/03640210802035191 Perceiving the Present
Cognition and Perception
 Cognition and Perception 2/10/10 4:25 PM Scribe: Katy Ionis Today s Topics Visual processing in the brain Visual illusions Graphical perceptions vs. graphical cognition Preattentive features for design
Cognition and Perception 2/10/10 4:25 PM Scribe: Katy Ionis Today s Topics Visual processing in the brain Visual illusions Graphical perceptions vs. graphical cognition Preattentive features for design
Computational Vision and Picture. Plan. Computational Vision and Picture. Distal vs. proximal stimulus. Vision as an inverse problem
 Perceptual and Artistic Principles for Effective Computer Depiction Perceptual and Artistic Principles for Effective Computer Depiction Computational Vision and Picture Fredo Durand MIT- Lab for Computer
Perceptual and Artistic Principles for Effective Computer Depiction Perceptual and Artistic Principles for Effective Computer Depiction Computational Vision and Picture Fredo Durand MIT- Lab for Computer
Perception of 3D Structure. How does the visual system reconstruct a 3D world from the FLAT, 2D retinal image? Our depth perception: far from flawless
 Perception of 3D Structure Depth perception is crucially important for everyday activities Getting out of bed in the morning Reaching for nearby objects (such as the alarm clock) Pouring coffee into your
Perception of 3D Structure Depth perception is crucially important for everyday activities Getting out of bed in the morning Reaching for nearby objects (such as the alarm clock) Pouring coffee into your
Dan Kersten Computational Vision Lab Psychology Department, U. Minnesota SUnS kersten.org
 How big is it? Dan Kersten Computational Vision Lab Psychology Department, U. Minnesota SUnS 2009 kersten.org NIH R01 EY015261 NIH P41 008079, P30 NS057091 and the MIND Institute Huseyin Boyaci Bilkent
How big is it? Dan Kersten Computational Vision Lab Psychology Department, U. Minnesota SUnS 2009 kersten.org NIH R01 EY015261 NIH P41 008079, P30 NS057091 and the MIND Institute Huseyin Boyaci Bilkent
"Illusions of motion perception" Stuart Anstis (Dept of Psychology, University of California, San Diego, USA)
 INVITED TALKS "Illusions of motion perception" Stuart Anstis (Dept of Psychology, University of California, San Diego, USA) I have discovered various illusions that demonstrate how luminance, contrast,
INVITED TALKS "Illusions of motion perception" Stuart Anstis (Dept of Psychology, University of California, San Diego, USA) I have discovered various illusions that demonstrate how luminance, contrast,
Color, Vision, & Perception. Outline
 Color, Vision, & Perception CS 160, Fall 97 Professor James Landay September 24, 1997 9/24/97 1 Outline Administrivia Review Human visual system Color perception Color deficiency Guidelines for design
Color, Vision, & Perception CS 160, Fall 97 Professor James Landay September 24, 1997 9/24/97 1 Outline Administrivia Review Human visual system Color perception Color deficiency Guidelines for design
Analysis of Gaze on Optical Illusions
 Analysis of Gaze on Optical Illusions Thomas Rapp School of Computing Clemson University Clemson, South Carolina 29634 tsrapp@g.clemson.edu Abstract A comparison of human gaze patterns on illusions before
Analysis of Gaze on Optical Illusions Thomas Rapp School of Computing Clemson University Clemson, South Carolina 29634 tsrapp@g.clemson.edu Abstract A comparison of human gaze patterns on illusions before
GROUPING BASED ON PHENOMENAL PROXIMITY
 Journal of Experimental Psychology 1964, Vol. 67, No. 6, 531-538 GROUPING BASED ON PHENOMENAL PROXIMITY IRVIN ROCK AND LEONARD BROSGOLE l Yeshiva University The question was raised whether the Gestalt
Journal of Experimental Psychology 1964, Vol. 67, No. 6, 531-538 GROUPING BASED ON PHENOMENAL PROXIMITY IRVIN ROCK AND LEONARD BROSGOLE l Yeshiva University The question was raised whether the Gestalt
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e. Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst
 Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Sensation and Perception Chapter Module 9 Perception Perception While sensation is the process by
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Sensation and Perception Chapter Module 9 Perception Perception While sensation is the process by
T-junctions in inhomogeneous surrounds
 Vision Research 40 (2000) 3735 3741 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres T-junctions in inhomogeneous surrounds Thomas O. Melfi *, James A. Schirillo Department of Psychology, Wake Forest Uni ersity, Winston
Vision Research 40 (2000) 3735 3741 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres T-junctions in inhomogeneous surrounds Thomas O. Melfi *, James A. Schirillo Department of Psychology, Wake Forest Uni ersity, Winston
Shape Constancy and Polar Perspective
 Journal of Experimental Psychology: Copyright 1986 by the Ammican Psycholosical Association, Inc. Human Perception and Performance 0096-1523/86/$00.75 1986, Vol. 12, No. 3, 338-342 Shape Constancy and
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Copyright 1986 by the Ammican Psycholosical Association, Inc. Human Perception and Performance 0096-1523/86/$00.75 1986, Vol. 12, No. 3, 338-342 Shape Constancy and
Introduction to Vision. Alan L. Yuille. UCLA.
 Introduction to Vision Alan L. Yuille. UCLA. IPAM Summer School 2013 3 weeks of online lectures on Vision. What papers do I read in computer vision? There are so many and they are so different. Main Points
Introduction to Vision Alan L. Yuille. UCLA. IPAM Summer School 2013 3 weeks of online lectures on Vision. What papers do I read in computer vision? There are so many and they are so different. Main Points
AS Psychology Activity 4
 AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2014 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2014 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
THE POGGENDORFF ILLUSION WITH ANOMALOUS SURFACES: MANAGING PAC-MANS, PARALLELS LENGTH AND TYPE OF TRANSVERSAL.
 THE POGGENDORFF ILLUSION WITH ANOMALOUS SURFACES: MANAGING PAC-MANS, PARALLELS LENGTH AND TYPE OF TRANSVERSAL. Spoto, A. 1, Massidda, D. 1, Bastianelli, A. 1, Actis-Grosso, R. 2 and Vidotto, G. 1 1 Department
THE POGGENDORFF ILLUSION WITH ANOMALOUS SURFACES: MANAGING PAC-MANS, PARALLELS LENGTH AND TYPE OF TRANSVERSAL. Spoto, A. 1, Massidda, D. 1, Bastianelli, A. 1, Actis-Grosso, R. 2 and Vidotto, G. 1 1 Department
CS 559: Computer Vision. Lecture 1
 CS 559: Computer Vision Lecture 1 Prof. Sinisa Todorovic sinisa@eecs.oregonstate.edu 1 Outline Gestalt laws for grouping 2 Perceptual Grouping -- Gestalt Laws Gestalt laws are summaries of image properties
CS 559: Computer Vision Lecture 1 Prof. Sinisa Todorovic sinisa@eecs.oregonstate.edu 1 Outline Gestalt laws for grouping 2 Perceptual Grouping -- Gestalt Laws Gestalt laws are summaries of image properties
Embodiment illusions via multisensory integration
 Embodiment illusions via multisensory integration COGS160: sensory systems and neural coding presenter: Pradeep Shenoy 1 The illusory hand Botvinnik, Science 2004 2 2 This hand is my hand An illusion of
Embodiment illusions via multisensory integration COGS160: sensory systems and neural coding presenter: Pradeep Shenoy 1 The illusory hand Botvinnik, Science 2004 2 2 This hand is my hand An illusion of
Chapter 1: Introduction to Neuro-Fuzzy (NF) and Soft Computing (SC)
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Neuro-Fuzzy (NF) and Soft Computing (SC) Introduction (1.1) SC Constituants and Conventional Artificial Intelligence (AI) (1.2) NF and SC Characteristics (1.3) Jyh-Shing Roger
Chapter 1: Introduction to Neuro-Fuzzy (NF) and Soft Computing (SC) Introduction (1.1) SC Constituants and Conventional Artificial Intelligence (AI) (1.2) NF and SC Characteristics (1.3) Jyh-Shing Roger
Orientation Illusions and Crosstalk. University of Ulm Faculty of Natural Sciences
 Orientation Illusions and Crosstalk W.A. Kreiner University of Ulm Faculty of Natural Sciences 1. The Problem 2. Orientation illusions due to small angle patterns 2.1 Target line oriented vertically or
Orientation Illusions and Crosstalk W.A. Kreiner University of Ulm Faculty of Natural Sciences 1. The Problem 2. Orientation illusions due to small angle patterns 2.1 Target line oriented vertically or
Vision. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 13. Vision. Vision
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Perception. Selective Attention focus of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus. Cocktail Party Effect
 Perception Aoccudrnig to rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn t mttaer in what oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoetnt tihng is that the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae.
Perception Aoccudrnig to rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn t mttaer in what oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoetnt tihng is that the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae.
CHAPTER 8: THE PSYCHOLOGY OF VISION QUICK GUIDE TO INSTRUCTOR S RESOURCES CHAPTER OBJECTIVES CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 8 1
 CHAPTER 8: THE PSYCHOLOGY OF VISION QUICK GUIDE TO INSTRUCTOR S RESOURCES CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 8 1 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS FROM PETER GRAY AND DAVID BJORKLUND 8 2 FOCUS QUESTIONS 8 2 CLASSROOM ACTIVITIES/DEMONSTRATIONS
CHAPTER 8: THE PSYCHOLOGY OF VISION QUICK GUIDE TO INSTRUCTOR S RESOURCES CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 8 1 TEACHING SUGGESTIONS FROM PETER GRAY AND DAVID BJORKLUND 8 2 FOCUS QUESTIONS 8 2 CLASSROOM ACTIVITIES/DEMONSTRATIONS
Planes and Frames: Spatial Layering in Josef Albers Homage to the Square Paintings
 Bridges Finland Conference Proceedings Planes and Frames: Spatial Layering in Josef Albers Homage to the Square Paintings James Mai School of Art / Campus Box 5620 Illinois State University Normal, IL
Bridges Finland Conference Proceedings Planes and Frames: Spatial Layering in Josef Albers Homage to the Square Paintings James Mai School of Art / Campus Box 5620 Illinois State University Normal, IL
