Islamic Constructions: The Geometry Needed by Craftsmen
|
|
|
- Julia Rose
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
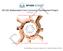
1 ISAMA The International Society of the Arts, Mathematics, and Architecture BRIDGEs Mathematical Connections in Art, Music, and Science Islamic Constructions: The Geometry Needed by Craftsmen Raymond Tennant Department of Natural and Quantitative Sciences Zayed University P.O. Box 4783 Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates Abstract The Islamic world has a.rich artistic tradition of creating highly geometric and symmetric ornamentation. Over the centuries, the process of creating Islamic tilings was refined from the J5'h Century ornamentation in the Alhambra Palace in Granada, Spain to the exquisite tilings, which are seen in mosques, mausoleums and minarets throughout the world today. The contemporary mathematics of group theory and knot theory combined with computer programs provide tools for creating modem day variations of these historical tilings. The title of this paper is motivated by the Id h Century treatise On Those Parts of Geometry Needed by Craftsmen written by the Khorasan mathematician and astronomer Abu'I-WajQ Bul,jiini who described several constructions made with the aid of straightedge and "rusty compass", a compass with a fixed angle. He was one of a long line of Islamic mathematicians who developed geometric techniques that proved useful to artisans in creating the highly symmetrical. omamentationfound in architecture around the world today. This paper looks at the geometry of Abu'I-WqfQ BUQiini with an eye toward determining geometric methods for reproducing Islamic tilings with students in the classroom. 1. Islamic Ornamentation The Islamic world has a rich heritage of incorporating geometry in the construction of intricate designs that appear on architecture, tile walkways as well as patterns on fabric. This highly stylized form of art has evolved over the centuries from simple designs to fairly complex geometry involving a high degree of mathematical symmetry (Figure 1). The Alhambra Palace in Granada, Spain contains many excellent examples of these Islamic constructions used to ornament this 15 th Century Moorish architectural wonder. Figure 1: Islamic Tiling from the Alhambra The interplay between mathematics and art involved in constructing these patterns has a rich history of liaisons between mathematicians and artisans. These collaborations point out the similarities and differences in the ways in which these creative individuals approach their crafts. On the one hand, geometers use proof and rigor to verify that constructions are exact while; artisans use constructions, which are not exact to appeal to a sense of aesthetic. Consider a simple construction of an isosceles right 459
2 triangle with legs each one unit in length. The geometer would appeal to the Pythagorean theorem to conclude that the hypotenuse has a length of.fi. The artisan may be completely unaware of this fact and further, the very act of constructing such a triangle in clay, wood, or some other material makes such accuracy of little importance. This interdisciplinary relationship between mathematics and art also serves as a powerful tool for teachers in the classroom. These elaborate visual designs provide motivating examples for exciting students to the wonderful artistic applications of symmetry and geometry. It is with this backdrop that we focus on a historical example of such a collaboration followed by construction examples for the classroom. 2. Historical Example of Collaboration The history of geometric design contains many instances of collaborations between mathematicians and artists and the continuing evolution of Islamic ornamentation is no exception. During the 10 th Century, the Islamic mathematician and astronomer Abu'l-Wata Buzjani, who was born in the Khorasan province of Persia (Iran) and moved to Baghdad when he was twenty, participated in meetings which served as a forum for artisans and mathematicians to discuss methods for constructing ornamental designs in wood, tile, and other materials. In his treatise, On Those Parts of Geometry Needed by Craftsmen, Abu'l-Wata Buzjani discussed mistakes that craftsmen make in constructing geometric designs. These mistakes point out the differences between the aesthetic considerations of the artisan and the precise calculations of the mathematician. In chapter, On Assembling and Dividing Squares, Abu'l-Wata Buzjani describes the techniques by which artisans mask slight imperfections in their constructions. In fact, the tools of the artisan, no matter how fine usually will contain a certain degree of approximation when used to construct a design. Fi re 5: Divided as Two S uares Fi e 6: Additional S uare 460
3 Abu'l-Warn Buzjfuli described several constructions with a straightedge and "rusty compass" [2] having one fixed radius. These included constructing a perpendicular at the endpoint of a line segment, dividing segments in equal parts, bisecting angles, constructing a square in a circle and, constructing a regular pentagon. These constructions form the basis for creating many of the symmetric patterns of the artisans at that time. In one example, a method for dividing a square begins by constructing semicircles on the four sides of a square (Figure 2). A point is chosen on each semicircle and a line is drawn from the point to a vertex of the square (Figure 3). Since any triangle inscribed in a semicircle must be a right triangle, it follows that the central polygon is a square regardless of where the initial point is chosen on the semicircle. In this figure, the point is chosen so that the longer leg of the right triangle is twice as long as the shorter leg. Removing the semicircles (Figure 4) reveals a square, which may be divided into two smaller squares (Figure 5). Adding four right triangles produces a larger square (Figure 6). Once this square tile was constructed, the artisan could extend the pattern in two perpendicular directions (Figure 7). Figure 7: Tiling by Translations In subsequent centuries, many other Islamic mathematicians sought to apply geometry to solving problems that were important to artisans. In the 11th Century, Omar Khayyam used a cubic equation to construct a right triangle whose hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the short side and the perpendicular to the hypotenuse. 3. Construction Examples for the Classroom A useful tool in teaching mathematics lies in describing cultural connections to the mathematics that is being discussed. This is particularly powerful if the connection being made is to the student's own personal history and culture. For students in the Middle East, these historical references of mathematicians interacting with artisans serve as a springboard for developing the more theoretical ideas of constructions, transformation geometry, and group theory. In looking at any particular Islamic tiling, it is interesting to investigate methods for constructing it with straightedge and compass or by a computer program like Geometer's Sketchpad or Mathematica. Here is a construction for the fundamental tile that generates the tiling shown in Figure 8. It involves only basic constructions of the type described by Abu'l-Wata Buzjani in his treatise. First, concentric squares are drawn (Figure 9) and a circle is constructed in the center of the squares (Figure 10). A square is inscribed 461
4 in the smaller circle and the lines extended to the large square (Figure 11). Lines ate' drawn connecting vertices of the inscribed square to midpoints of the large square (Figures 12 and 13). The circle is removed (Figure 14). The lines are widened to form the latticework (Figure 15). All intersecting lines are eliminated from the tile (Figure 16). The overlapping detail of the tiles is created by alternating crossings of the latticework between over and under Figure 17). Figure 8: Islamic Pattern o 462
5 Another approach to constructing the tiling is to determine the smallest part of this tile, which could be transformed around so as to create the entire tiling. For this particular tile (Figure 18), the. isosceles triangle (Figure 19) would generate the tile by 90-degree rotations. If the overlapping of the latticework were eliminated, the tile could be generated by the smaller triangle (Figure 20). 4. Conclusion The construction of Islamic tilings lies on the interesting boundary between mathematics and art. These constructions have a rich history involving both mathematicians and artisans and this history provides motivation to increase student interest and excitement in mathematics. References [1[Alpay Ozdural, Mathematics and Art: Connections between Theory and Practice in the Medieval Islamic World, Historia Mathematica, Vol. 27, pp ,2000. [2] J.L. Berggren, Episodes in the Mathematics o/medievaiislam, Springer-Verlag,
6
Constructing and Classifying Designs of al-andalus
 ISAMA The International Society of the Arts, Mathematics, and Architecture Constructing and Classifying Designs of al-andalus BRIDGES Mathematical Connections in Art, Music, and Science B. Lynn Bodner
ISAMA The International Society of the Arts, Mathematics, and Architecture Constructing and Classifying Designs of al-andalus BRIDGES Mathematical Connections in Art, Music, and Science B. Lynn Bodner
Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry
 Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry This Guide Belongs to: Date: Table of Contents Using Sketchpad - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry This Guide Belongs to: Date: Table of Contents Using Sketchpad - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Modularity in Medieval Persian Mosaics: Textual, Empirical, Analytical, and Theoretical Considerations
 Modularity in Medieval Persian Mosaics: Textual, Empirical, Analytical, and Theoretical Considerations Reza Sarhangi Mathematics Department Towson University Towson, MD 21252, USA rsarhangi@towson.edu
Modularity in Medieval Persian Mosaics: Textual, Empirical, Analytical, and Theoretical Considerations Reza Sarhangi Mathematics Department Towson University Towson, MD 21252, USA rsarhangi@towson.edu
Dividing and Composing the Squares
 The Lamar University Electronic Journal of Student Research Fall, 2008 Dividing and Composing the Squares Narges Assarzadegan Chahar bagh khajou Street Mirza karim, Mohammad Hasan Hedayat Postal Code 81537-t74491
The Lamar University Electronic Journal of Student Research Fall, 2008 Dividing and Composing the Squares Narges Assarzadegan Chahar bagh khajou Street Mirza karim, Mohammad Hasan Hedayat Postal Code 81537-t74491
Challenges from Ancient Greece
 Challenges from ncient Greece Mathematical goals Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods. Use congruent triangles to justify geometric constructions. Common Core State Standards
Challenges from ncient Greece Mathematical goals Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods. Use congruent triangles to justify geometric constructions. Common Core State Standards
Copying a Line Segment
 Copying a Line Segment Steps 1 4 below show you how to copy a line segment. Step 1 You are given line segment AB to copy. A B Step 2 Draw a line segment that is longer than line segment AB. Label one of
Copying a Line Segment Steps 1 4 below show you how to copy a line segment. Step 1 You are given line segment AB to copy. A B Step 2 Draw a line segment that is longer than line segment AB. Label one of
Welcome Booklet. Version 5
 Welcome Booklet Version 5 Visit the Learning Center Find all the resources you need to learn and use Sketchpad videos, tutorials, tip sheets, sample activities, and links to online resources, services,
Welcome Booklet Version 5 Visit the Learning Center Find all the resources you need to learn and use Sketchpad videos, tutorials, tip sheets, sample activities, and links to online resources, services,
Constructions. Unit 9 Lesson 7
 Constructions Unit 9 Lesson 7 CONSTRUCTIONS Students will be able to: Understand the meanings of Constructions Key Vocabulary: Constructions Tools of Constructions Basic geometric constructions CONSTRUCTIONS
Constructions Unit 9 Lesson 7 CONSTRUCTIONS Students will be able to: Understand the meanings of Constructions Key Vocabulary: Constructions Tools of Constructions Basic geometric constructions CONSTRUCTIONS
UNIT 1 SIMILARITY, CONGRUENCE, AND PROOFS Lesson 3: Constructing Polygons Instruction
 rerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: using a compass copying and bisecting line segments constructing perpendicular lines constructing circles of a given radius Introduction
rerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: using a compass copying and bisecting line segments constructing perpendicular lines constructing circles of a given radius Introduction
Geometry, Aperiodic tiling, Mathematical symmetry.
 Conference of the International Journal of Arts & Sciences, CD-ROM. ISSN: 1943-6114 :: 07(03):343 348 (2014) Copyright c 2014 by UniversityPublications.net Tiling Theory studies how one might cover the
Conference of the International Journal of Arts & Sciences, CD-ROM. ISSN: 1943-6114 :: 07(03):343 348 (2014) Copyright c 2014 by UniversityPublications.net Tiling Theory studies how one might cover the
Step 2: Extend the compass from the chosen endpoint so that the width of the compass is more than half the distance between the two points.
 Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Miami-Dade County Public Schools Test: 9_12 Mathematics Geometry Exam 1 Description: GEO Topic 1 Test: Tools of Geometry Form: 201 1. A student followed the given
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Miami-Dade County Public Schools Test: 9_12 Mathematics Geometry Exam 1 Description: GEO Topic 1 Test: Tools of Geometry Form: 201 1. A student followed the given
8.2 Slippery Slopes. A Solidify Understanding Task
 7 8.2 Slippery Slopes A Solidify Understanding Task CC BY https://flic.kr/p/kfus4x While working on Is It Right? in the previous module you looked at several examples that lead to the conclusion that the
7 8.2 Slippery Slopes A Solidify Understanding Task CC BY https://flic.kr/p/kfus4x While working on Is It Right? in the previous module you looked at several examples that lead to the conclusion that the
Geometry by Jurgensen, Brown and Jurgensen Postulates and Theorems from Chapter 1
 Postulates and Theorems from Chapter 1 Postulate 1: The Ruler Postulate 1. The points on a line can be paired with the real numbers in such a way that any two points can have coordinates 0 and 1. 2. Once
Postulates and Theorems from Chapter 1 Postulate 1: The Ruler Postulate 1. The points on a line can be paired with the real numbers in such a way that any two points can have coordinates 0 and 1. 2. Once
Geometry For Technical Drawing Chapter 4
 Geometry For Technical Drawing Chapter 4 Sacramento City College EDT 300/ENGR 306 EDT 300/ENGR 306 1 Objectives Identify and describe geometric shapes and constructions used by drafters. Construct various
Geometry For Technical Drawing Chapter 4 Sacramento City College EDT 300/ENGR 306 EDT 300/ENGR 306 1 Objectives Identify and describe geometric shapes and constructions used by drafters. Construct various
is formed where the diameters intersect? Label the center.
 E 26 Get Into Shape Hints or notes: A circle will be folded into a variety of geometric shapes. This activity provides the opportunity to assess the concepts, vocabulary and knowledge of relationships
E 26 Get Into Shape Hints or notes: A circle will be folded into a variety of geometric shapes. This activity provides the opportunity to assess the concepts, vocabulary and knowledge of relationships
Objective: Use a compass and straight edge to construct congruent segments and angles.
 CONSTRUCTIONS Objective: Use a compass and straight edge to construct congruent segments and angles. Introduction to Constructions Constructions: The drawing of various shapes using only a pair of compasses
CONSTRUCTIONS Objective: Use a compass and straight edge to construct congruent segments and angles. Introduction to Constructions Constructions: The drawing of various shapes using only a pair of compasses
University of Houston High School Mathematics Contest Geometry Exam Spring 2016
 University of Houston High School Mathematics ontest Geometry Exam Spring 016 nswer the following. Note that diagrams may not be drawn to scale. 1. In the figure below, E, =, = 4 and E = 0. Find the length
University of Houston High School Mathematics ontest Geometry Exam Spring 016 nswer the following. Note that diagrams may not be drawn to scale. 1. In the figure below, E, =, = 4 and E = 0. Find the length
Objective: Use a compass and straight edge to construct congruent segments and angles.
 CONSTRUCTIONS Objective: Use a compass and straight edge to construct congruent segments and angles. Oct 1 8:33 AM Oct 2 7:42 AM 1 Introduction to Constructions Constructions: The drawing of various shapes
CONSTRUCTIONS Objective: Use a compass and straight edge to construct congruent segments and angles. Oct 1 8:33 AM Oct 2 7:42 AM 1 Introduction to Constructions Constructions: The drawing of various shapes
Construction Junction, What s your Function?
 Construction Junction, What s your Function? Brian Shay Teacher and Department Chair Canyon Crest Academy Brian.Shay@sduhsd.net @MrBrianShay Session Goals Familiarize ourselves with CCSS and the GSE Geometry
Construction Junction, What s your Function? Brian Shay Teacher and Department Chair Canyon Crest Academy Brian.Shay@sduhsd.net @MrBrianShay Session Goals Familiarize ourselves with CCSS and the GSE Geometry
7th Grade Drawing Geometric Figures
 Slide 1 / 53 Slide 2 / 53 7th Grade Drawing Geometric Figures 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 53 Topics Table of Contents Determining if a Triangle is Possible Click on a topic to go to that section
Slide 1 / 53 Slide 2 / 53 7th Grade Drawing Geometric Figures 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 53 Topics Table of Contents Determining if a Triangle is Possible Click on a topic to go to that section
Title: Quadrilaterals Aren t Just Squares
 Title: Quadrilaterals ren t Just Squares Brief Overview: This is a collection of the first three lessons in a series of seven lessons studying characteristics of quadrilaterals, including trapezoids, parallelograms,
Title: Quadrilaterals ren t Just Squares Brief Overview: This is a collection of the first three lessons in a series of seven lessons studying characteristics of quadrilaterals, including trapezoids, parallelograms,
The Texas Education Agency and the Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board Geometry Module Pre-/Post-Test. U x T'
 Pre-/Post-Test The Texas Education Agency and the Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board Geometry Module Pre-/Post-Test 1. Triangle STU is rotated 180 clockwise to form image STU ' ' '. Determine the
Pre-/Post-Test The Texas Education Agency and the Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board Geometry Module Pre-/Post-Test 1. Triangle STU is rotated 180 clockwise to form image STU ' ' '. Determine the
Geometric Puzzle Medley
 Geometric Puzzle Medley (16 August 2018) Jim Stevenson This is a collection of simple but elegant puzzles, mostly from a British high school math teacher Catriona Shearer @Cshearer41 (https://twitter.com/cshearer41),
Geometric Puzzle Medley (16 August 2018) Jim Stevenson This is a collection of simple but elegant puzzles, mostly from a British high school math teacher Catriona Shearer @Cshearer41 (https://twitter.com/cshearer41),
June 2016 Regents GEOMETRY COMMON CORE
 1 A student has a rectangular postcard that he folds in half lengthwise. Next, he rotates it continuously about the folded edge. Which three-dimensional object below is generated by this rotation? 4) 2
1 A student has a rectangular postcard that he folds in half lengthwise. Next, he rotates it continuously about the folded edge. Which three-dimensional object below is generated by this rotation? 4) 2
The Geometer s Sketchpad Unit 1. Meet Geometer s Sketchpad
 Trainer/Instructor Notes: Geometer s Sketchpad Training Meet Geometer s Sketchpad The Geometer s Sketchpad Unit 1 Meet Geometer s Sketchpad Overview: Objective: In this unit, participants become familiar
Trainer/Instructor Notes: Geometer s Sketchpad Training Meet Geometer s Sketchpad The Geometer s Sketchpad Unit 1 Meet Geometer s Sketchpad Overview: Objective: In this unit, participants become familiar
Sec Geometry - Constructions
 Sec 2.2 - Geometry - Constructions Name: 1. [COPY SEGMENT] Construct a segment with an endpoint of C and congruent to the segment AB. A B C **Using a ruler measure the two lengths to make sure they have
Sec 2.2 - Geometry - Constructions Name: 1. [COPY SEGMENT] Construct a segment with an endpoint of C and congruent to the segment AB. A B C **Using a ruler measure the two lengths to make sure they have
Geometry 2001 part 1
 Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
8.2 Slippery Slopes. A Solidify Understanding Task
 SECONDARY MATH I // MODULE 8 7 8.2 Slippery Slopes A Solidify Understanding Task CC BY https://flic.kr/p/kfus4x While working on Is It Right? in the previous module you looked at several examples that
SECONDARY MATH I // MODULE 8 7 8.2 Slippery Slopes A Solidify Understanding Task CC BY https://flic.kr/p/kfus4x While working on Is It Right? in the previous module you looked at several examples that
Print n Play Collection. Of the 12 Geometrical Puzzles
 Print n Play Collection Of the 12 Geometrical Puzzles Puzzles Hexagon-Circle-Hexagon by Charles W. Trigg Regular hexagons are inscribed in and circumscribed outside a circle - as shown in the illustration.
Print n Play Collection Of the 12 Geometrical Puzzles Puzzles Hexagon-Circle-Hexagon by Charles W. Trigg Regular hexagons are inscribed in and circumscribed outside a circle - as shown in the illustration.
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Geometry SOL G.4 Constructions Name Date Block. Constructions
 Geometry SOL G.4 Constructions Mrs. Grieser Name Date Block Constructions Grab your compass and straight edge - it s time to learn about constructions!! On the following pages you will find instructions
Geometry SOL G.4 Constructions Mrs. Grieser Name Date Block Constructions Grab your compass and straight edge - it s time to learn about constructions!! On the following pages you will find instructions
THINGS TO DO WITH A GEOBOARD
 THINGS TO DO WITH A GEOBOARD The following list of suggestions is indicative of exercises and examples that can be worked on the geoboard. Simpler, as well as, more difficult suggestions can easily be
THINGS TO DO WITH A GEOBOARD The following list of suggestions is indicative of exercises and examples that can be worked on the geoboard. Simpler, as well as, more difficult suggestions can easily be
Name: Date: Chapter 2 Quiz Geometry. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Date: Chapter 2 Quiz Geometry Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the value of x? Identify the missing justifications.,, and.
Name: Date: Chapter 2 Quiz Geometry Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the value of x? Identify the missing justifications.,, and.
Standards of Learning Guided Practice Suggestions. For use with the Mathematics Tools Practice in TestNav TM 8
 Standards of Learning Guided Practice Suggestions For use with the Mathematics Tools Practice in TestNav TM 8 Table of Contents Change Log... 2 Introduction to TestNav TM 8: MC/TEI Document... 3 Guided
Standards of Learning Guided Practice Suggestions For use with the Mathematics Tools Practice in TestNav TM 8 Table of Contents Change Log... 2 Introduction to TestNav TM 8: MC/TEI Document... 3 Guided
6.00 Trigonometry Geometry/Circles Basics for the ACT. Name Period Date
 6.00 Trigonometry Geometry/Circles Basics for the ACT Name Period Date Perimeter and Area of Triangles and Rectangles The perimeter is the continuous line forming the boundary of a closed geometric figure.
6.00 Trigonometry Geometry/Circles Basics for the ACT Name Period Date Perimeter and Area of Triangles and Rectangles The perimeter is the continuous line forming the boundary of a closed geometric figure.
Geometric Constructions
 Geometric onstructions (1) opying a segment (a) Using your compass, place the pointer at Point and extend it until reaches Point. Your compass now has the measure of. (b) Place your pointer at, and then
Geometric onstructions (1) opying a segment (a) Using your compass, place the pointer at Point and extend it until reaches Point. Your compass now has the measure of. (b) Place your pointer at, and then
TIalgebra.com Algebra 1
 Perpendicular Slopes ID: 8973 Time required 45 minutes Topic: Linear Functions Graph lines whose slopes are negative reciprocals and measure the angles to verify they are perpendicular. Activity Overview
Perpendicular Slopes ID: 8973 Time required 45 minutes Topic: Linear Functions Graph lines whose slopes are negative reciprocals and measure the angles to verify they are perpendicular. Activity Overview
9.1 and 9.2 Introduction to Circles
 Date: Secondary Math 2 Vocabulary 9.1 and 9.2 Introduction to Circles Define the following terms and identify them on the circle: Circle: The set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given
Date: Secondary Math 2 Vocabulary 9.1 and 9.2 Introduction to Circles Define the following terms and identify them on the circle: Circle: The set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given
CONSTRUCTION #1: Segment Copy
 CONSTRUCTION #1: Segment Copy Objective: Given a line segment, construct a line segment congruent to the given one. Procedure: After doing this Your work should look like this Start with a line segment
CONSTRUCTION #1: Segment Copy Objective: Given a line segment, construct a line segment congruent to the given one. Procedure: After doing this Your work should look like this Start with a line segment
(1) Page 482 #1 20. (2) Page 488 #1 14. (3) Page # (4) Page 495 #1 10. (5) Page #12 30,
 Geometry/Trigonometry Unit 8: Circles Notes Name: Date: Period: # (1) Page 482 #1 20 (2) Page 488 #1 14 (3) Page 488 489 #15 26 (4) Page 495 #1 10 (5) Page 495 496 #12 30, 37 39 (6) Page 502 #1 7 (7) Page
Geometry/Trigonometry Unit 8: Circles Notes Name: Date: Period: # (1) Page 482 #1 20 (2) Page 488 #1 14 (3) Page 488 489 #15 26 (4) Page 495 #1 10 (5) Page 495 496 #12 30, 37 39 (6) Page 502 #1 7 (7) Page
Underlying Tiles in a 15 th Century Mamluk Pattern
 Bridges Finland Conference Proceedings Underlying Tiles in a 15 th Century Mamluk Pattern Ron Asherov Israel rasherov@gmail.com Abstract An analysis of a 15 th century Mamluk marble mosaic pattern reveals
Bridges Finland Conference Proceedings Underlying Tiles in a 15 th Century Mamluk Pattern Ron Asherov Israel rasherov@gmail.com Abstract An analysis of a 15 th century Mamluk marble mosaic pattern reveals
Chapter 5. Drawing a cube. 5.1 One and two-point perspective. Math 4520, Spring 2015
 Chapter 5 Drawing a cube Math 4520, Spring 2015 5.1 One and two-point perspective In Chapter 5 we saw how to calculate the center of vision and the viewing distance for a square in one or two-point perspective.
Chapter 5 Drawing a cube Math 4520, Spring 2015 5.1 One and two-point perspective In Chapter 5 we saw how to calculate the center of vision and the viewing distance for a square in one or two-point perspective.
TERRA Environmental Research Institute
 TERRA Environmental Research Institute MATHEMATICS FCAT PRACTICE STRAND 3 Geometry and Spatial Sense Angle Relationships Lines and Transversals Plane Figures The Pythagorean Theorem The Coordinate Plane
TERRA Environmental Research Institute MATHEMATICS FCAT PRACTICE STRAND 3 Geometry and Spatial Sense Angle Relationships Lines and Transversals Plane Figures The Pythagorean Theorem The Coordinate Plane
Euclid s Muse MATERIALS VOCABULARY. area perimeter triangle quadrilateral rectangle line point plane. TIME: 40 minutes
 Euclid s Muse In this activity, participants match geometry terms to definitions and definitions to words. MATERIALS Transparency: Euclid s Muse Directions Transparency/Page: Euclid s Muse Transparency/Page:
Euclid s Muse In this activity, participants match geometry terms to definitions and definitions to words. MATERIALS Transparency: Euclid s Muse Directions Transparency/Page: Euclid s Muse Transparency/Page:
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Rowan. Assessment: 9_12 T and I IC61 - Drafting I Test 1. Form: 501
 Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Rowan Assessment: 9_12 T and I IC61 - Drafting I Test 1 Description: Test 4 A (Diagrams) Form: 501 Please use the following figure for this question. 1. In the GEOMETRIC
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Rowan Assessment: 9_12 T and I IC61 - Drafting I Test 1 Description: Test 4 A (Diagrams) Form: 501 Please use the following figure for this question. 1. In the GEOMETRIC
PENNSYLVANIA. List properties, classify, draw, and identify geometric figures in two dimensions.
 Know: Understand: Do: CC.2.3.4.A.1 -- Draw lines and angles and identify these in two-dimensional figures. CC.2.3.4.A.2 -- Classify twodimensional figures by properties of their lines and angles. CC.2.3.4.A.3
Know: Understand: Do: CC.2.3.4.A.1 -- Draw lines and angles and identify these in two-dimensional figures. CC.2.3.4.A.2 -- Classify twodimensional figures by properties of their lines and angles. CC.2.3.4.A.3
16. DOK 1, I will succeed." In this conditional statement, the underlined portion is
 Geometry Semester 1 REVIEW 1. DOK 1 The point that divides a line segment into two congruent segments. 2. DOK 1 lines have the same slope. 3. DOK 1 If you have two parallel lines and a transversal, then
Geometry Semester 1 REVIEW 1. DOK 1 The point that divides a line segment into two congruent segments. 2. DOK 1 lines have the same slope. 3. DOK 1 If you have two parallel lines and a transversal, then
What role does the central angle play in helping us find lengths of arcs and areas of regions within the circle?
 Middletown Public Schools Mathematics Unit Planning Organizer Subject Geometry Grade/Course 10 Unit 5 Circles and other Conic Sections Duration 16 instructional + 4 days for reteaching/enrichment Big Idea
Middletown Public Schools Mathematics Unit Planning Organizer Subject Geometry Grade/Course 10 Unit 5 Circles and other Conic Sections Duration 16 instructional + 4 days for reteaching/enrichment Big Idea
Measuring and Drawing Angles and Triangles
 NME DTE Measuring and Drawing ngles and Triangles Measuring an angle 30 arm origin base line 0 180 0 If the arms are too short to reach the protractor scale, lengthen them. Step 1: lace the origin of the
NME DTE Measuring and Drawing ngles and Triangles Measuring an angle 30 arm origin base line 0 180 0 If the arms are too short to reach the protractor scale, lengthen them. Step 1: lace the origin of the
ACT Coordinate Geometry Review
 ACT Coordinate Geometry Review Here is a brief review of the coordinate geometry concepts tested on the ACT. Note: there is no review of how to graph an equation on this worksheet. Questions testing this
ACT Coordinate Geometry Review Here is a brief review of the coordinate geometry concepts tested on the ACT. Note: there is no review of how to graph an equation on this worksheet. Questions testing this
3 In the diagram below, the vertices of DEF are the midpoints of the sides of equilateral triangle ABC, and the perimeter of ABC is 36 cm.
 1 In the diagram below, ABC XYZ. 3 In the diagram below, the vertices of DEF are the midpoints of the sides of equilateral triangle ABC, and the perimeter of ABC is 36 cm. Which two statements identify
1 In the diagram below, ABC XYZ. 3 In the diagram below, the vertices of DEF are the midpoints of the sides of equilateral triangle ABC, and the perimeter of ABC is 36 cm. Which two statements identify
MODELING AND DESIGN C H A P T E R F O U R
 MODELING AND DESIGN C H A P T E R F O U R OBJECTIVES 1. Identify and specify basic geometric elements and primitive shapes. 2. Select a 2D profile that best describes the shape of an object. 3. Identify
MODELING AND DESIGN C H A P T E R F O U R OBJECTIVES 1. Identify and specify basic geometric elements and primitive shapes. 2. Select a 2D profile that best describes the shape of an object. 3. Identify
SELECTED GEOMETRICAL CONSTRUCTIONS
 FACULTY OF NATURAL SCIENCES CONSTANTINE THE PHILOSOPHER UNIVERSITY IN NITRA ACTA MATHEMATICA 17 SELECTED GEOMETRICAL CONSTRUCTIONS ABSTRACT. This article deals with selected classical geometric constructions
FACULTY OF NATURAL SCIENCES CONSTANTINE THE PHILOSOPHER UNIVERSITY IN NITRA ACTA MATHEMATICA 17 SELECTED GEOMETRICAL CONSTRUCTIONS ABSTRACT. This article deals with selected classical geometric constructions
DIRECTIONS FOR GEOMETRY CONSTRUCTION PROJECT
 Name Period DIRECTIONS FOR GEOMETRY CONSTRUCTION PROJECT Materials needed: Objective: Standards: 8 pieces of unlined white computer paper (8.5 in. by 11in.), compass, ruler, protractor, pencil, and markers/colored
Name Period DIRECTIONS FOR GEOMETRY CONSTRUCTION PROJECT Materials needed: Objective: Standards: 8 pieces of unlined white computer paper (8.5 in. by 11in.), compass, ruler, protractor, pencil, and markers/colored
!"#$ %&& ' ( ) * ' ) * !"#$!%&&'
 !"#$ %&& ' ( ) * ' ) *!"#$!%&&' (+'* ',, '!-.,!!! #,,!,.!! -!, '!*!!,,,!!-. *!'*,-!-,./ From an article written by J.J. O'Connor and E.F. Robertson located at: http://www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk/mathematicians/hippocrates.html
!"#$ %&& ' ( ) * ' ) *!"#$!%&&' (+'* ',, '!-.,!!! #,,!,.!! -!, '!*!!,,,!!-. *!'*,-!-,./ From an article written by J.J. O'Connor and E.F. Robertson located at: http://www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk/mathematicians/hippocrates.html
Geometry. Teacher s Guide
 Geometry Teacher s Guide WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher.......................................................... vi Classroom Management..................................................
Geometry Teacher s Guide WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher.......................................................... vi Classroom Management..................................................
Basic Mathematics Review 5232
 Basic Mathematics Review 5232 Symmetry A geometric figure has a line of symmetry if you can draw a line so that if you fold your paper along the line the two sides of the figure coincide. In other words,
Basic Mathematics Review 5232 Symmetry A geometric figure has a line of symmetry if you can draw a line so that if you fold your paper along the line the two sides of the figure coincide. In other words,
h r c On the ACT, remember that diagrams are usually drawn to scale, so you can always eyeball to determine measurements if you get stuck.
 ACT Plane Geometry Review Let s first take a look at the common formulas you need for the ACT. Then we ll review the rules for the tested shapes. There are also some practice problems at the end of this
ACT Plane Geometry Review Let s first take a look at the common formulas you need for the ACT. Then we ll review the rules for the tested shapes. There are also some practice problems at the end of this
Elementary Geometric Drawings Angles. Angle Bisector. Perpendicular Bisector
 Lessons and Activities GEOMETRY Elementary Geometric Drawings Angles Angle Bisector Perpendicular Bisector 1 Lessons and Activities POLYGONS are PLANE SHAPES (figures) with at least 3 STRAIGHT sides and
Lessons and Activities GEOMETRY Elementary Geometric Drawings Angles Angle Bisector Perpendicular Bisector 1 Lessons and Activities POLYGONS are PLANE SHAPES (figures) with at least 3 STRAIGHT sides and
Unit 4: Geometric Construction (Chapter4: Geometry For Modeling and Design)
 Unit 4: Geometric Construction (Chapter4: Geometry For Modeling and Design) DFTG-1305 Technical Drafting Instructor: Jimmy Nhan OBJECTIVES 1. Identify and specify basic geometric elements and primitive
Unit 4: Geometric Construction (Chapter4: Geometry For Modeling and Design) DFTG-1305 Technical Drafting Instructor: Jimmy Nhan OBJECTIVES 1. Identify and specify basic geometric elements and primitive
Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures. Grade 9 Mathematics
 Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures Grade 9 Mathematics For each of the answers below, we give the steps to complete the task given. We ve used the following resources if you would
Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures Grade 9 Mathematics For each of the answers below, we give the steps to complete the task given. We ve used the following resources if you would
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
3. Given the similarity transformation shown below; identify the composition:
 Midterm Multiple Choice Practice 1. Based on the construction below, which statement must be true? 1 1) m ABD m CBD 2 2) m ABD m CBD 3) m ABD m ABC 1 4) m CBD m ABD 2 2. Line segment AB is shown in the
Midterm Multiple Choice Practice 1. Based on the construction below, which statement must be true? 1 1) m ABD m CBD 2 2) m ABD m CBD 3) m ABD m ABC 1 4) m CBD m ABD 2 2. Line segment AB is shown in the
6.1 Justifying Constructions
 Name lass ate 6.1 Justifying onstructions Essential Question: How can you be sure that the result of a construction is valid? Resource Locker Explore 1 Using a Reflective evice to onstruct a erpendicular
Name lass ate 6.1 Justifying onstructions Essential Question: How can you be sure that the result of a construction is valid? Resource Locker Explore 1 Using a Reflective evice to onstruct a erpendicular
MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY TOPIC: Learning to construct using Geometer s Sketchpad
 AGENDAS FOR WEEK 1 OF 4 WEEKS FOR PROJECT BASED UNIT MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY TOPIC: Learning to construct using Geometer s Sketchpad TOPIC: Applying Geometer Sketchpad Skills construct
AGENDAS FOR WEEK 1 OF 4 WEEKS FOR PROJECT BASED UNIT MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY TOPIC: Learning to construct using Geometer s Sketchpad TOPIC: Applying Geometer Sketchpad Skills construct
Constructing Angle Bisectors and Parallel Lines
 Name: Date: Period: Constructing Angle Bisectors and Parallel Lines TASK A: 1) Complete the following steps below. a. Draw a circle centered on point P. b. Mark any two points on the circle that are not
Name: Date: Period: Constructing Angle Bisectors and Parallel Lines TASK A: 1) Complete the following steps below. a. Draw a circle centered on point P. b. Mark any two points on the circle that are not
3 Kevin s work for deriving the equation of a circle is shown below.
 June 2016 1. A student has a rectangular postcard that he folds in half lengthwise. Next, he rotates it continuously about the folded edge. Which three-dimensional object below is generated by this rotation?
June 2016 1. A student has a rectangular postcard that he folds in half lengthwise. Next, he rotates it continuously about the folded edge. Which three-dimensional object below is generated by this rotation?
9.3 Properties of Chords
 9.3. Properties of Chords www.ck12.org 9.3 Properties of Chords Learning Objectives Find the lengths of chords in a circle. Discover properties of chords and arcs. Review Queue 1. Draw a chord in a circle.
9.3. Properties of Chords www.ck12.org 9.3 Properties of Chords Learning Objectives Find the lengths of chords in a circle. Discover properties of chords and arcs. Review Queue 1. Draw a chord in a circle.
Activity: Islamic Mosaics
 Activity: Islamic Mosaics Materials Printed template(s) Compass or bull s eye Straight edge Colour pencils Skills Motor Drawing a circle with a compass Tracing a straight line Affective/metacognitive Persevering
Activity: Islamic Mosaics Materials Printed template(s) Compass or bull s eye Straight edge Colour pencils Skills Motor Drawing a circle with a compass Tracing a straight line Affective/metacognitive Persevering
1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: and. b. Use a straightedge to draw.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 Problem Set 4 Name Date 1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: and. b. Use a straightedge to draw.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 Problem Set 4 Name Date 1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: and. b. Use a straightedge to draw.
DIRECTIONS FOR GEOMETRY HONORS CONSTRUCTION PROJECT
 Name Period DIRECTIONS FOR GEOMETRY HONORS CONSTRUCTION PROJECT Materials needed: Objective: Standards: 8 pieces of unlined white computer / copy paper (8.5 in. by 11in.), compass, ruler, protractor, pencil,
Name Period DIRECTIONS FOR GEOMETRY HONORS CONSTRUCTION PROJECT Materials needed: Objective: Standards: 8 pieces of unlined white computer / copy paper (8.5 in. by 11in.), compass, ruler, protractor, pencil,
Slopes of Lines Notes What is slope?
 Slopes of Lines Notes What is slope? Find the slope of each line. 1 Find the slope of each line. Find the slope of the line containing the given points. 6, 2!!"#! 3, 5 4, 2!!"#! 4, 3 Find the slope of
Slopes of Lines Notes What is slope? Find the slope of each line. 1 Find the slope of each line. Find the slope of the line containing the given points. 6, 2!!"#! 3, 5 4, 2!!"#! 4, 3 Find the slope of
A PROOF OF EUCLID'S 47th PROPOSITION Using the Figure of The Point Within a Circle and With the Kind Assistance of President James A. Garfield.
 A PROOF OF EUCLID'S 47th PROPOSITION Using the Figure of The Point Within a Circle and With the Kind Assistance of President James A. Garfield. by Bro. William Steve Burkle KT, 32 Scioto Lodge No. 6, Chillicothe,
A PROOF OF EUCLID'S 47th PROPOSITION Using the Figure of The Point Within a Circle and With the Kind Assistance of President James A. Garfield. by Bro. William Steve Burkle KT, 32 Scioto Lodge No. 6, Chillicothe,
SFUSD Mathematics Core Curriculum Development Project
 1 SFUSD Mathematics Core Curriculum Development Project 2014 2015 Creating meaningful transformation in mathematics education Developing learners who are independent, assertive constructors of their own
1 SFUSD Mathematics Core Curriculum Development Project 2014 2015 Creating meaningful transformation in mathematics education Developing learners who are independent, assertive constructors of their own
Big Ideas Math: A Common Core Curriculum Geometry 2015 Correlated to Common Core State Standards for High School Geometry
 Common Core State s for High School Geometry Conceptual Category: Geometry Domain: The Number System G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment,
Common Core State s for High School Geometry Conceptual Category: Geometry Domain: The Number System G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment,
Session 1 What Is Geometry?
 Key Terms for This Session Session 1 What Is Geometry? New in This Session altitude angle bisector concurrent line line segment median midline perpendicular bisector plane point ray Introduction In this
Key Terms for This Session Session 1 What Is Geometry? New in This Session altitude angle bisector concurrent line line segment median midline perpendicular bisector plane point ray Introduction In this
0810ge. Geometry Regents Exam y # (x $ 3) 2 % 4 y # 2x $ 5 1) (0,%4) 2) (%4,0) 3) (%4,%3) and (0,5) 4) (%3,%4) and (5,0)
 0810ge 1 In the diagram below, ABC! XYZ. 3 In the diagram below, the vertices of DEF are the midpoints of the sides of equilateral triangle ABC, and the perimeter of ABC is 36 cm. Which two statements
0810ge 1 In the diagram below, ABC! XYZ. 3 In the diagram below, the vertices of DEF are the midpoints of the sides of equilateral triangle ABC, and the perimeter of ABC is 36 cm. Which two statements
E G 2 3. MATH 1012 Section 8.1 Basic Geometric Terms Bland
 MATH 1012 Section 8.1 Basic Geometric Terms Bland Point A point is a location in space. It has no length or width. A point is represented by a dot and is named by writing a capital letter next to the dot.
MATH 1012 Section 8.1 Basic Geometric Terms Bland Point A point is a location in space. It has no length or width. A point is represented by a dot and is named by writing a capital letter next to the dot.
Challenging Students to Discover the Pythagorean Relationship
 Brought to you by YouthBuild USA Teacher Fellows! Challenging Students to Discover the Pythagorean Relationship A Common Core-Aligned Lesson Plan to use in your Classroom Author Richard Singer, St. Louis
Brought to you by YouthBuild USA Teacher Fellows! Challenging Students to Discover the Pythagorean Relationship A Common Core-Aligned Lesson Plan to use in your Classroom Author Richard Singer, St. Louis
Circles Assignment Answer the following questions.
 Answer the following questions. 1. Define constructions. 2. What are the basic tools that are used to draw geometric constructions? 3. What is the use of constructions? 4. What is Compass? 5. What is Straight
Answer the following questions. 1. Define constructions. 2. What are the basic tools that are used to draw geometric constructions? 3. What is the use of constructions? 4. What is Compass? 5. What is Straight
1. Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment. 1. Begin with line segment XY.
 1. onstruct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment. 1. egin with line segment. 2. lace the compass at point. djust the compass radius so that it is more
1. onstruct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment. 1. egin with line segment. 2. lace the compass at point. djust the compass radius so that it is more
The 7* Basic Constructions Guided Notes
 Name: The 7* asic Constructions Guided Notes Included: 1. Given an segment, construct a 2 nd segment congruent to the original. (ctually not included!) 2. Given an angle, construct a 2 nd angle congruent
Name: The 7* asic Constructions Guided Notes Included: 1. Given an segment, construct a 2 nd segment congruent to the original. (ctually not included!) 2. Given an angle, construct a 2 nd angle congruent
SESSION ONE GEOMETRY WITH TANGRAMS AND PAPER
 SESSION ONE GEOMETRY WITH TANGRAMS AND PAPER Outcomes Develop confidence in working with geometrical shapes such as right triangles, squares, and parallelograms represented by concrete pieces made of cardboard,
SESSION ONE GEOMETRY WITH TANGRAMS AND PAPER Outcomes Develop confidence in working with geometrical shapes such as right triangles, squares, and parallelograms represented by concrete pieces made of cardboard,
Unit 1 Foundations of Geometry: Vocabulary, Reasoning and Tools
 Number of Days: 34 9/5/17-10/20/17 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: Using building blocks from Algebra 1, students will use a variety of tools and techniques to construct, understand, and prove geometric
Number of Days: 34 9/5/17-10/20/17 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: Using building blocks from Algebra 1, students will use a variety of tools and techniques to construct, understand, and prove geometric
Tangents to Circles. The distance across the circle, through its center, is the diameter of the circle. The diameter is twice the radius.
 ircles Tangents to ircles circle is the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point called the center of the circle. circle with center P is called circle P. The distance from
ircles Tangents to ircles circle is the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point called the center of the circle. circle with center P is called circle P. The distance from
The Basics: Geometric Structure
 Trinity University Digital Commons @ Trinity Understanding by Design: Complete Collection Understanding by Design Summer 6-2015 The Basics: Geometric Structure Danielle Kendrick Trinity University Follow
Trinity University Digital Commons @ Trinity Understanding by Design: Complete Collection Understanding by Design Summer 6-2015 The Basics: Geometric Structure Danielle Kendrick Trinity University Follow
LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII. Mathematics Laboratory
 LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII Mathematics Laboratory The concept of Mathematics Laboratory has been introduced by the Board in its affiliated schools with the objective
LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII Mathematics Laboratory The concept of Mathematics Laboratory has been introduced by the Board in its affiliated schools with the objective
Grades 3-5. Robert Smith. Author
 Editors Polly Hoffman Gisela Lee Editorial Manager Karen J. Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Editor-in-Chief Sharon Coan, M.S. Ed. Cover Artist Jessica Orlando Grades 3-5 Art Coordinator Kevin Barnes Creative Director
Editors Polly Hoffman Gisela Lee Editorial Manager Karen J. Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Editor-in-Chief Sharon Coan, M.S. Ed. Cover Artist Jessica Orlando Grades 3-5 Art Coordinator Kevin Barnes Creative Director
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important
 Many artists use geometric concepts in their work. Think about what you have learned in geometry. How do these examples of First Nations art and architecture show geometry ideas? What You ll Learn Identify
Many artists use geometric concepts in their work. Think about what you have learned in geometry. How do these examples of First Nations art and architecture show geometry ideas? What You ll Learn Identify
Properties of Chords
 Properties of Chords Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org
Properties of Chords Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org
INTERMEDIATE LEVEL MEASUREMENT
 INTERMEDIATE LEVEL MEASUREMENT TABLE OF CONTENTS Format & Background Information...3-6 Learning Experience 1- Getting Started...6-7 Learning Experience 2 - Cube and Rectangular Prisms...8 Learning Experience
INTERMEDIATE LEVEL MEASUREMENT TABLE OF CONTENTS Format & Background Information...3-6 Learning Experience 1- Getting Started...6-7 Learning Experience 2 - Cube and Rectangular Prisms...8 Learning Experience
TRIANGLES. Unit 3. Teacher Notes
 Unit 3 TRIANGLES Teacher Notes Activities Altitudes Area Angles Exploring Properties of Exploring Types of Exploring the Pythagorean Theorem Triangle Search The Real Real Numer Line Projects Slice It,
Unit 3 TRIANGLES Teacher Notes Activities Altitudes Area Angles Exploring Properties of Exploring Types of Exploring the Pythagorean Theorem Triangle Search The Real Real Numer Line Projects Slice It,
Name. Ms. Nong. Due on: Per: Geometry 2 nd semester Math packet # 2 Standards: 8.0 and 16.0
 Name FRIDAY, FEBRUARY 24 Due on: Per: TH Geometry 2 nd semester Math packet # 2 Standards: 8.0 and 16.0 8.0 Students know, derive, and solve problems involving the perimeter, circumference, area, volume
Name FRIDAY, FEBRUARY 24 Due on: Per: TH Geometry 2 nd semester Math packet # 2 Standards: 8.0 and 16.0 8.0 Students know, derive, and solve problems involving the perimeter, circumference, area, volume
9.5 Properties and Conditions for Kites and Trapezoids
 Name lass ate 9.5 Properties and onditions for Kites and Trapezoids ssential uestion: What are the properties of kites and trapezoids? Resource Locker xplore xploring Properties of Kites kite is a quadrilateral
Name lass ate 9.5 Properties and onditions for Kites and Trapezoids ssential uestion: What are the properties of kites and trapezoids? Resource Locker xplore xploring Properties of Kites kite is a quadrilateral
Project Maths Geometry Notes
 The areas that you need to study are: Project Maths Geometry Notes (i) Geometry Terms: (ii) Theorems: (iii) Constructions: (iv) Enlargements: Axiom, theorem, proof, corollary, converse, implies The exam
The areas that you need to study are: Project Maths Geometry Notes (i) Geometry Terms: (ii) Theorems: (iii) Constructions: (iv) Enlargements: Axiom, theorem, proof, corollary, converse, implies The exam
The Magic Circle Basic Lesson. Developed by The Alexandria Seaport Foundation
 The Magic Circle Basic Lesson Developed by The Alexandria Seaport Foundation The Tools Needed Compass Straightedge Pencil Paper (not graph paper, 8.5 x 11 is fine) Your Brain (the most important tool!)
The Magic Circle Basic Lesson Developed by The Alexandria Seaport Foundation The Tools Needed Compass Straightedge Pencil Paper (not graph paper, 8.5 x 11 is fine) Your Brain (the most important tool!)
JMG. Review Module 1 Lessons 1-20 for Mid-Module. Prepare for Endof-Unit Assessment. Assessment. Module 1. End-of-Unit Assessment.
 Lesson Plans Lesson Plan WEEK 161 December 5- December 9 Subject to change 2016-2017 Mrs. Whitman 1 st 2 nd Period 3 rd Period 4 th Period 5 th Period 6 th Period H S Mathematics Period Prep Geometry Math
Lesson Plans Lesson Plan WEEK 161 December 5- December 9 Subject to change 2016-2017 Mrs. Whitman 1 st 2 nd Period 3 rd Period 4 th Period 5 th Period 6 th Period H S Mathematics Period Prep Geometry Math
0809ge. Geometry Regents Exam Based on the diagram below, which statement is true?
 0809ge 1 Based on the diagram below, which statement is true? 3 In the diagram of ABC below, AB # AC. The measure of!b is 40. 1) a! b 2) a! c 3) b! c 4) d! e What is the measure of!a? 1) 40 2) 50 3) 70
0809ge 1 Based on the diagram below, which statement is true? 3 In the diagram of ABC below, AB # AC. The measure of!b is 40. 1) a! b 2) a! c 3) b! c 4) d! e What is the measure of!a? 1) 40 2) 50 3) 70
and Transitional Comprehensive Curriculum. Geometry Unit 3: Parallel and Perpendicular Relationships
 Geometry Unit 3: Parallel and Perpendicular Relationships Time Frame: Approximately three weeks Unit Description This unit demonstrates the basic role played by Euclid s fifth postulate in geometry. Euclid
Geometry Unit 3: Parallel and Perpendicular Relationships Time Frame: Approximately three weeks Unit Description This unit demonstrates the basic role played by Euclid s fifth postulate in geometry. Euclid
Geometry Unit 3 Note Sheets Date Name of Lesson. Slopes of Lines. Partitioning a Segment. Equations of Lines. Quiz
 Date Name of Lesson Slopes of Lines Partitioning a Segment Equations of Lines Quiz Introduction to Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Slopes and Parallel Lines Slopes and Perpendicular Lines Perpendicular
Date Name of Lesson Slopes of Lines Partitioning a Segment Equations of Lines Quiz Introduction to Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Slopes and Parallel Lines Slopes and Perpendicular Lines Perpendicular
