62. Teaching Sustainability through Living Labs in Architecture: The case study of the UPC-LOW3 prototype solar house
|
|
|
- Edgar McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 62. Teaching Sustainability through Living Labs in Architecture: The case study of the UPC-LOW3 prototype solar house T. Masseck ETSAV School of Architecture, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, UPC-Barcelona Tech Abstract Sustainability is currently one of the most important issues to be integrated at all levels of teaching from kindergarten through to university up to lifelong learning activities of society as a whole. Specific disciplinary knowledge should be taught by adopting a holistic method, with a transdisciplinary approach towards the environmental, economic and social aspects of sustainability. The term Sustainability Science describes the corresponding concepts and methodologies. Within the career of Architecture and Architecture-related disciplines, new teaching formats are needed for this holistic approach for knowledge generation and transmission. Living Labs in architecture can be tools towards achieving a holistic approach in teaching sustainability, using real built environments for user-centred research and collaborative learning in a university campus. LOW3 is the 2010 Solar Decathlon Europe solar house of UPC Barcelona Tech that since 2011 serves as Living Lab at the ETSAV campus at Sant Cugat del Vallés (Barcelona). As a Net Zero Energy Building (NZEB), Living Lab LOW3 allows active teaching, research and innovation activities in the field of sustainable architecture and lifestyle. The present article describes the different stages of implementation of Living Lab LOW3 at the campus, a first evaluation of teaching and applied research activities through questionnaires and interviews with the participants and a critical analysis of the overall project concept. It shows that after 2 years of step-by-step implementation, Living Lab LOW3 has greatly contributed to a holistic-based sustainability education at the ETSAV School of Architecture. The knowledge generated was broadly disseminated and important generic competences were fostered through the project. Living Lab LOW3 is an ongoing project, which aims to innovate in sustainability education. Its outcomes and lessons learned can serve as an example for similar activities at other universities. Key words: Solar Architecture, Teaching, Sustainability, Living Labs, Net Zero Energy Buildings, Collaborative Learning Environments, User-centred Research and Innovation 1 Introduction Our society nowadays needs a redefinition of its productive model that integrates bottom-up environmental, economical and social aspects of sustainability. Radical changes towards Net Zero Energy Buildings and consideration for much more energy efficient lifestyles are urgently required. Holistic thinking professionals with well-developed generic competences are needed to solve complex problems. By employing a holistic view to our complex environmental, economical and societal systems and their corresponding interrelations, Sustainability Science a new holistic and scientific model could be the right approach to address the problems of today s society. Sustainability Science focuses on the 1
2 Engineering Education for Sustainable Development, Cambridge, UK. September 22 25, complex and dynamic interactions between society and nature and is based on transdisciplinarity, integrated analysis and the development of knowledge for action (Komiyama et al. 2011). In order to transfer this new scientific approach to the academic world, multi-stakeholder collaborations between university, society and companies must be intensified thereby fostering synergies in the fields of learning, research and innovation in the field of sustainability. 1.1 State of the art Living Labs for Architecture and Lifestyle Existing laboratories for building construction, building physics or technological research and development traditionally focus on specific areas of knowledge and less on a holistic multidisciplinary approach. They therefore have limited capacity to generate relevant output in fields of research where user interaction is an important factor. For example, regarding the user acceptance of technology, usertechnology interaction or the field of a holistic impact analysis of technological innovations on lifestyle and society. The development of Living Labs has been a step forward in bridging this gap. Living Labs or living laboratories are defined as real world environments which focus on user-centred research and user co-creation with the aim of accelerating innovation processes (Almirall & Wareham, 2008). In the late 1990 s the term Living Lab was first used for innovation activities related to ICT, such as mobile appliances for improving elderly healthcare or improvements in proceedings and work flows in city administrations. Using real world environments for implementation, evaluation and improvement cycles they then allowed the development of the first solutions within an iterative process towards a final product, application or service (Almirall & Wareham, 2008). With regard to the Living Lab approach, several Living Lab networks and platforms have been founded since approximately the year One of the fastest growing networks of Living Labs is the ENoLL (European Network of Living Labs). It was founded in 2006 and today (May 2013) has more than 450 Living Lab initiatives linked to it. EnOLL describes the need for Living Labs with the necessity of fastening the market availability of innovations through user-centred research and user co-creation (Open Living Labs. The First Step Towards a New Innovation System, 2013). These concepts are based on the idea that, through immediate user feedback in real world environments, researchers and developers in collaboration with users are able to create and improve innovations and assure market viability within very short periods. This is an efficient alternative to traditional research and innovation processes. Only a small part of the ENoLL initiatives are focused on sustainable architecture and lifestyle, with a strong emphasis on social research and a culture of change. In the last years, specific research and innovation infrastructures and projects have been created that focus on Net Zero Energy Buildings (NZEB) and Sustainable Lifestyle. One is the Norwegian Research Centre on Zero Emission Buildings at NTNU (Trondheim, Norway). It focuses not only on zero emission technologies but also on user behaviour and lifestyle (ZEB - the Research Centre of Zero Emission Buildings, 2013). Another important initiative is the LIVING LAB project, a funded European FP7 project for Living Labs, directed by the Wupperthal Institute which had the idea of creating a network of standardized living labs in different climatic and social-economic environments in Europe, thereby allowing the comparison of results through similar physical settings (Liedtke et al, 2012). Since 2002, the international Solar Decathlon competition promotes the development of energy selfsufficient solar houses by universities; fostering during the latest competitions, especially in Europe, a holistic view on sustainable architecture, including the aspects of urban density, shared facilities and
3 Engineering Education for Sustainable Development, Cambridge, UK. September 22 25, infrastructure as well as energetic renovation processes. More than 120 prototypes have been developed and built during the last decade (Solar Decathlon 2010: UPC, 2010). The efficiency of the Living Lab approach, together with the transdisciplinary and holistic concept of the Solar Decathlon solar houses, invite one to analyze the potential of these prototypes being converted into living laboratories in the field of sustainable architecture and lifestyle. The present article describes the case study of a widened concept for a Living Lab in architecture: linking innovation to collaborative learning and co-creation activities, fostering synergies between the knowledge triangle of teaching, research and innovation in the field of sustainable housing and lifestyle. 1.2 Background The ETSAV School of Architecture of UPC-Barcelona Tech regularly contributes to important innovations in teaching strategies towards participating models. They, in turn, foster the generic competences of students and look for interaction with the local socio-economic environment of the school. Since 2008, one of the projects with a mayor impact has been participation in the Solar Decathlon Europe competition, starting with the 2010 prototype solar house LOW3. Today LOW3 is a Living Lab at the campus and serves as a place for implementing Living Lab strategies and activities, integrating all three fields of teaching, research, and innovation. The main hypothesis of the Living Lab LOW3 project is that the establishment of Living Labs in architecture as collaborative learning environments, innovation arenas, and places of social interchange, learning and progress can be a mayor contribution to a holistic and effective education in sustainability at schools of architecture and beyond. 1.3 Research Questions Considering Living Labs based on prototype buildings as new tools or infrastructures within academia, with a special focus on architecture and architecture-related disciplines, the main questions for this ongoing research work are the following: Is the use of Living Labs in architecture useful and efficient for education in sustainability and a holistic knowledge about architecture, technology and lifestyle? Which activities can be efficiently linked to a Living Lab, and which generic and specific competences can be better attended to through the Living Lab approach compared to traditional teaching formats? How can a teaching and research infrastructure like a Living Lab be created, financed, managed and maintained within the administrative and academic context of a university? What are the lessons learned and future recommendations of the Living Lab LOW3 project at UPC Barcelona Tech? 2 Methodology 2.1 Type of research The methodology applied for analysing the Living Lab approach of the LOW3 project is based on participatory action research with a regular analysis of activities, evolution, and outcomes. This way,
4 Engineering Education for Sustainable Development, Cambridge, UK. September 22 25, we can evaluate the success of all related initiatives and their contribution to the holistic overall Living Lab concept. The documentation of activities, enquiries and interviews of participants and stakeholders, as well as the development of Living Lab indicators, are further tools for the analysis of progress and outcomes. A comparison with similar projects - such as the HOME+ prototype of Hochschule für Technik (HfT) Stuttgart, or the 2007 and 2009 SD solar houses of Universität Darmstadt as well as other similar Living Lab projects all over the world - will allow a critical discussion of the achieved results. 2.2 Object of research living lab activities The main focus of the present research work is the analysis of the development, implementation and activation of the Living Lab LOW3 project since the end of the SDE 2010 competition. Three official Living Lab LOW3 courses and several complementary activities have been completed since then. Figure 1 shows the development over time of Living Lab LOW3 project and its related activities. Figure 1: Development over time of the Living Lab concept of Living Lab LOW3 Main activities since 2011: Living Lab LOW3 course 2011: re-construction, installation works, analysis, first measurements of the LOW3 prototype solar house at the campus Living Lab LOW3 course 2011/12: installation works, bioclimatic measurements, holistic evaluation, knowledge dissemination Living Lab course 2012: LIVE AT LOW3 experiment activity based on user-centred research: house occupation with 2 students during 2 weeks and holistic evaluation of their lifestyle and impact through the participating student team Related final career projects, Master and PhD thesis work: Natural ventilation in buildings (2011), The house management system of LOW3 (2012), Personal Learning Environments (2012), Grey water recycling materials (2012) and Living Labs in Architecture (2012) 1 st co-creation and innovation seminar: activities platform for new student projects, initiatives and participatory research activities (2013) Collaboration in industrial research project on concentrated solar power systems and energy storage in buildings (2013) Several other activities related to teaching, projects and dissemination with more than 1200 participants in more than 2 years
5 Engineering Education for Sustainable Development, Cambridge, UK. September 22 25, Figure 2 shows the diverse activities linked to the Living Lab LOW3 project, from formal teaching and applied research activities, to social events, knowledge dissemination and less formal co-learning activities. Figure 2: Living Lab LOW: Teaching, research and Innovation activities regarding sustainable architecture and lifestyle Each activity has been documented. An individual analysis and evaluation has been carried out in order to evaluate the success of each initiative, analyse the lessons learned, and gather information about possible improvements. 2.3 Indicators One important issue for the comparison and the overall evaluation of the success of the Living Lab initiatives is to find the right indicators for the evaluation of a Living Lab approach in Architecture as a holistic project for teaching, research and innovation. During the analysis of similar projects, with a special focus on the post-competition use of Solar Decathlon solar houses, the following main indicators for success and impact of Architecture Living Labs have been identified: Total amount of stakeholders involved: number of persons, companies and public institutions linked to the project Transdisciplinarity: number of different disciplines involved into the project User-centred innovation and co-creation activities: Type and amount of activities linked Outcome: Publications of results such as communications in congresses, thesis work related, articles Financial concept and support: total amount of funding and type of stakeholder contracts These indicators are a first approach for the analysis and comparison of Living Lab initiatives and will be further developed, weighted and discussed in future research.
6 Engineering Education for Sustainable Development, Cambridge, UK. September 22 25, Regular questionnaires of students Regular questionnaires were given to students at the start and after finishing the Living Lab courses. These serve to: obtain and analyse the feedback about the concept of each course, determine which competences students consider important at the start of the course, and to see whether these identified competences became strengthened through the Living Lab approach. Opinions given about deficits perceived by students regarding their regular studies and possible improvements through the use of Living Lab completed the questionnaires. Table 1 shows an example of the initial questionnaire of the 2011 and 2012 Living Lab courses. Table 1: Extract of participant initial questionnaire Living Lab LOW and 2012 A. For your future work life, which Teamwork abilities and communication skills competences, abilities and Transdisciplinary communication and understanding knowledge do you think are most important? Holistic view and specific knowledge on sustainability Use of virtual learning environments and resources B. What do you think a Living Lab in Architecture could stand for? Collaborative and participatory learning environment Transdisciplinary teaching and research in sustainability Holistic education on sustainable construction and energy efficiency Platform for user co-creation and innovation C. What aspects of your current studies do you think could be significantly improved through a Living Lab at the campus? Practical construction and evaluation experience Transdisciplinary work experience Project based learning on a real building Interactive Learning Platform virtual/presential After finishing the course, Living Lab students were asked to which degree (1-5 scale) the course would have attended the previously identified competences, knowledge and other aspects. Figure 3 shows an example of answers given by the 38 participating students of the 2011/12 and 2012 Living Lab courses regarding competences in teamwork, leadership and decision-making. Figure 3: Example of results of participant s enquiries about the Living Lab course and the attended competences regarding teamwork, leadership and decision-making
7 Engineering Education for Sustainable Development, Cambridge, UK. September 22 25, Interviews were conducted with the participants to discuss special issues such as their personal learning environments. Additionally, open group conversations were held after concluding each activity for feedback on its success, critics and proposals for improvement. 3 Results The following results of the research conducted show the outcomes of the Living Lab LOW3 project within its university context. 3.1 Teaching Sustainability through Living Lab courses All three Living Lab courses held since 2011 proved to be highly participative, developing many generic competences, skills and knowledge of students that had to collaborate and co-design the individual objectives and working plans for each course. The questionnaires confirmed that competences such as transdisciplinary collaboration and understanding (valued 3,46 in a 1 to 5 scale), a holistic view and specific knowledge on sustainability (valued 3,86) and especially teamwork and communication skills (valued 4,05) have been fostered broadly throughout the course. The students identified the following special qualities common to all Living Lab courses, differentiating them from other regular teaching formats: The transdisciplinary teaching and research approach (3,84), and especially the collaborative and participatory learning environment (valued 4,22). They further valued positively the project-based learning approach related to a real building (valued 3,86) and the practical construction and evaluation experience (3,92). Self-organization of different construction and installation works as well as monitoring activities demanded a real commitment from each participant. This caused minor conflicts due to time intensive nature of works out of regular schedule, for example regarding the collaboration with external experts or installers. Different individual attitudes of students towards the common goal of the courses also caused some tensions. 3.2 Live-at-LOW3 Experiment The Live-at-LOW3 experiment of the 2012 course needed a special commitment of the participating students. No regular timetable could be guaranteed during the course. The house-occupation experiment has been a holistic approach to user-centred research. A pair of students evaluated and tested the prototype solar house during 14 days with the participating course students accompanying and evaluating the experiment through monitoring and lifestyle evaluation of the inhabitants with a holistic view on housing, consumption, food and mobility. Results were published in research documents, the experiment was filmed and published through a documentary as well as local newspapers and television showed interest in the experiment and its outcomes. A holistic learning and user-centred research process could be conducted with interesting results. A wider engagement of the academic community, as well as society in general, could be achieved through open door days, media interest (national and local TV and radio emissions, digital newspapers) and the use of social networks and ICT (youtube channel for video diary, documentary, live webcam). 3.3 Management, financing, stakeholder participation and indicators A Living Lab like LOW3 at a university campus is a complex infrastructure that needs regular funding for its installation, maintenance and management. Stakeholders like local, public administration and
8 Engineering Education for Sustainable Development, Cambridge, UK. September 22 25, private companies are ideal partners to contribute to their diversity and the necessary funding. Organizational difficulties can arise regarding responsibility, university regulations, maintenance costs, property rights, and many other aspects. LOW3, as with many other Solar Decathlon projects, lacked resources. After the competition voluntary student collaborations, interest from the university, and media attention retreated, accompanied by a peak of exhaustion of administrative staff and collaborators. No clear planning for the after use of the project was developed before and during the SDE competition. All stakeholder participations, teaching and applied research activities as well as co-creation seminars and additional initiatives have been organized step-by-step after the competition. Indicators are important instruments to assess the performance of a Living Lab. The number of students, teaching staff, researchers and stakeholders involved, number of projects and activities linked, documents generated (reports, documentaries), people reached (open doors day, news on television, publications in newspapers, visits on website and blog, newsletters etc.) are some of the indicators that really confirm the contribution of the project to the school s academic profile, and will help to compare Living Lab LOW3 with other similar living lab projects. 4 Discussion After more than 2 years of implementation, field experience and continuous evaluation, the following lessons could be learned from the Living Lab LOW3 project: SDE prototype houses like LOW3 are ideal objects to be converted into Living Labs for sustainable architecture and lifestyle at universities, but proven methodologies and documented experiences on strategies, tools and outcomes are still rare. Students value positively the innovative teaching approach and especially the participatory teaching model of the Living Lab LOW3 courses, but also ask for clear course structures. Living Lab LOW3 facilitates the generation of participatory co-learning activities that allow collectively generating and distributing new knowledge. A dynamic learning environment with formal and informal activities from workshops and seminars up to co-creation sessions, usercentred research activities and knowledge dissemination for the general public has been created. The development of ICT technologies and societal changes are happening today very fast and universities need to respond to these phenomena (new teaching subjects like NZEBs or smart cities, collaborative learning environments, e-learning, MOOCs, social media, social networks). Living Lab LOW3 shows itself to be an ideal infrastructure for experimenting and integrating these issues into the academic agenda. University organizations need to adjust some of their organizational structures and administrative mechanisms to handle smoothly activities like SDE, Living Labs or similar projects regarding organization, financing, management and integration in curricula. Indicators are needed to describe and compare Living Lab projects and their structure, allowing benchmarking of different Living Lab initiatives. 5 Conclusions Sustainability science in research and education is still a young discipline and it is in constant flux and evolution. Transdisciplinary thinking and collaboration are fields yet to be developed within our disciplinary-organized universities. Collaboration, co-creation or synergies cannot be forced to happen within the diverse academic context of universities. Nevertheless, places and infrastructures can be created that facilitate these
9 Engineering Education for Sustainable Development, Cambridge, UK. September 22 25, essential educational processes. This seems to be one of the most important contributions that Living Labs can make to Architecture. Further development of this relatively new Living Lab approach is necessary. Methodologies and tools are in constant change, and experiences on a national and an international level will generate new knowledge that helps evolve the initial concepts. 6 Acknowledgements The project has been possible due to the collaboration of UPC, ETSAV, IS.UPC, KIC InnoEnergy, IDAE 10Action Intelligent Energy Europe, City of Sant Cugat del Vallès, Schneider Electric, TU/e, LOW3 and Living Lab LOW3 students as well as many other institutions, companies, individuals and colleagues. 7 References Solar Decathlon 2010: UPC (last update: 2010). Available: ALMIRALL, ESTEVE; WAREHAM, JONATHAN (2008). "Living Labs and Open Innovation: Roles and Aplicability" in ejov - the Journal for Networks and Virtual Organizations, vol.10, nº. "Special Issue on Living Labs" [viewed: 12 april 2011]. Available: ISBN: ALMIRALL, ESTEVE; WAREHAM, JONATHAN (2008). "The Role of Living Labs in Open Innovation" in European Living Labs. A new approach for human centric regional innovation. p ed.wissenschaftlicher Verlag Berlin. ISBN: CHRISTA LIEDTKE, MARIA JOLANTA WELFENS, HOLGER ROHN, JULIA NORDMANN (2012). "Design study for the living lab research Infrastructure, to research human interaction with, and stimulate the adoption of, sustainable, smart and healthy innovations around the home " in International Journal of Sustainability in Higher Education, vol.13, nº. 2. p [viewed: may 2013] dx.doi.org/ / European Union. Open Living Labs. the First Step Towards a New Innovation System (last update: 2013). Available: Gunnarshaug Lien, Anne. ZEB - the Research Centre of Zero Emission Buildings (last update: 2013). Available: KOMIYAMA, HIROSHI; et al. (ed.) (2011). Sustainability Science: A Multidisciplinary Approach. (pub.) UNITED NATIONS UNIVERSITY PRESS. ISBN:
Higher Education for Science, Technology and Innovation. Accelerating Africa s Aspirations. Communique. Kigali, Rwanda.
 Higher Education for Science, Technology and Innovation Accelerating Africa s Aspirations Communique Kigali, Rwanda March 13, 2014 We, the Governments here represented Ethiopia, Mozambique, Rwanda, Senegal,
Higher Education for Science, Technology and Innovation Accelerating Africa s Aspirations Communique Kigali, Rwanda March 13, 2014 We, the Governments here represented Ethiopia, Mozambique, Rwanda, Senegal,
Action Line Cyber-Physical Systems Addressing the challenges and fostering innovation in Cyber-Physical Systems
 Action Line Cyber-Physical Systems Addressing the challenges and fostering innovation in Cyber-Physical Systems Dr. Holger Pfeifer Technische Universität München EIT ICT Labs Action Line Lead Cyber-Physical
Action Line Cyber-Physical Systems Addressing the challenges and fostering innovation in Cyber-Physical Systems Dr. Holger Pfeifer Technische Universität München EIT ICT Labs Action Line Lead Cyber-Physical
ALCOTRA INNOVATION. Transnational Workshop July 8th 2011 Genova
 1 ALCOTRA INNOVATION Transnational Workshop July 8th 2011 Genova 1 2 Tha Apollon and SmartIES Projects Marita Holst Center for Distance-spanning Technology 2 Botnia Living Lab - hosted by Centre for Distance-spanning
1 ALCOTRA INNOVATION Transnational Workshop July 8th 2011 Genova 1 2 Tha Apollon and SmartIES Projects Marita Holst Center for Distance-spanning Technology 2 Botnia Living Lab - hosted by Centre for Distance-spanning
International comparison of education systems: a European model? Paris, November 2008
 International comparison of education systems: a European model? Paris, 13-14 November 2008 Workshop 2 Higher education: Type and ranking of higher education institutions Interim results of the on Assessment
International comparison of education systems: a European model? Paris, 13-14 November 2008 Workshop 2 Higher education: Type and ranking of higher education institutions Interim results of the on Assessment
Future of Cities. Harvard GSD. Smart[er] Citizens Bergamo University
![Future of Cities. Harvard GSD. Smart[er] Citizens Bergamo University Future of Cities. Harvard GSD. Smart[er] Citizens Bergamo University](/thumbs/72/66409025.jpg) Future of Cities Harvard GSD Smart[er] Citizens Bergamo University Future of Cities Harvard GSD Smart[er] Citizens Bergamo University SMART[ER] CITIES Harvard Graduate School of Design SCI 0637100 Spring
Future of Cities Harvard GSD Smart[er] Citizens Bergamo University Future of Cities Harvard GSD Smart[er] Citizens Bergamo University SMART[ER] CITIES Harvard Graduate School of Design SCI 0637100 Spring
COST FP9 Position Paper
 COST FP9 Position Paper 7 June 2017 COST 047/17 Key position points The next European Framework Programme for Research and Innovation should provide sufficient funding for open networks that are selected
COST FP9 Position Paper 7 June 2017 COST 047/17 Key position points The next European Framework Programme for Research and Innovation should provide sufficient funding for open networks that are selected
Creating a Mindset for Innovation
 Creating a Mindset for Innovation Paul Skaggs Richard Fry Geoff Wright To stay ahead of the development of new technology, we believe engineers need to understand what it means to be innovative. This research
Creating a Mindset for Innovation Paul Skaggs Richard Fry Geoff Wright To stay ahead of the development of new technology, we believe engineers need to understand what it means to be innovative. This research
CREATING A MINDSET FOR INNOVATION Paul Skaggs, Richard Fry, and Geoff Wright Brigham Young University /
 CREATING A MINDSET FOR INNOVATION Paul Skaggs, Richard Fry, and Geoff Wright Brigham Young University paul_skaggs@byu.edu / rfry@byu.edu / geoffwright@byu.edu BACKGROUND In 1999 the Industrial Design program
CREATING A MINDSET FOR INNOVATION Paul Skaggs, Richard Fry, and Geoff Wright Brigham Young University paul_skaggs@byu.edu / rfry@byu.edu / geoffwright@byu.edu BACKGROUND In 1999 the Industrial Design program
Pacts for Europe 2020: Good Practices and Views from EU Cities and Regions
 1 EU Committee of the Regions CoR Territorial Dialogue on "Territorial Pacts to implement Europe 2020" Brussels, 22 February, 2011 Markku Markkula, Member of the Espoo City Council, CoR member, Rapporteur
1 EU Committee of the Regions CoR Territorial Dialogue on "Territorial Pacts to implement Europe 2020" Brussels, 22 February, 2011 Markku Markkula, Member of the Espoo City Council, CoR member, Rapporteur
LIVING LAB OF GLOBAL CHANGE RESEARCH
 LIVING LAB OF GLOBAL CHANGE RESEARCH PhD Tanja Suni, Secretary General Future Earth Finland www.futureearthfinland.fi OUTLINE Our pilot Answers to session questions Lessons learned IMPROVING UTILISATION
LIVING LAB OF GLOBAL CHANGE RESEARCH PhD Tanja Suni, Secretary General Future Earth Finland www.futureearthfinland.fi OUTLINE Our pilot Answers to session questions Lessons learned IMPROVING UTILISATION
European Rail Research Advisory Council
 MARKET IMPACT EVALUATION ERRAC was set up in 2001 and is the single European body with the competence and capability to help revitalise the European rail sector : To make it more competitive To foster
MARKET IMPACT EVALUATION ERRAC was set up in 2001 and is the single European body with the competence and capability to help revitalise the European rail sector : To make it more competitive To foster
Water, Energy and Environment in the scope of the Circular Economy
 Water, Energy and Environment in the scope of the Circular Economy Maria da Graça Carvalho 11th SDEWES Conference Lisbon 2016 Contents of the Presentation 1. The Circular Economy 2. The Horizon 2020 Program
Water, Energy and Environment in the scope of the Circular Economy Maria da Graça Carvalho 11th SDEWES Conference Lisbon 2016 Contents of the Presentation 1. The Circular Economy 2. The Horizon 2020 Program
The 45 Adopted Recommendations under the WIPO Development Agenda
 The 45 Adopted Recommendations under the WIPO Development Agenda * Recommendations with an asterisk were identified by the 2007 General Assembly for immediate implementation Cluster A: Technical Assistance
The 45 Adopted Recommendations under the WIPO Development Agenda * Recommendations with an asterisk were identified by the 2007 General Assembly for immediate implementation Cluster A: Technical Assistance
COUNTRY: Questionnaire. Contact person: Name: Position: Address:
 Questionnaire COUNTRY: Contact person: Name: Position: Address: Telephone: Fax: E-mail: The questionnaire aims to (i) gather information on the implementation of the major documents of the World Conference
Questionnaire COUNTRY: Contact person: Name: Position: Address: Telephone: Fax: E-mail: The questionnaire aims to (i) gather information on the implementation of the major documents of the World Conference
Digitisation Plan
 Digitisation Plan 2016-2020 University of Sydney Library University of Sydney Library Digitisation Plan 2016-2020 Mission The University of Sydney Library Digitisation Plan 2016-20 sets out the aim and
Digitisation Plan 2016-2020 University of Sydney Library University of Sydney Library Digitisation Plan 2016-2020 Mission The University of Sydney Library Digitisation Plan 2016-20 sets out the aim and
WIPO Development Agenda
 WIPO Development Agenda 2 The WIPO Development Agenda aims to ensure that development considerations form an integral part of WIPO s work. As such, it is a cross-cutting issue which touches upon all sectors
WIPO Development Agenda 2 The WIPO Development Agenda aims to ensure that development considerations form an integral part of WIPO s work. As such, it is a cross-cutting issue which touches upon all sectors
PROJECT FACT SHEET GREEK-GERMANY CO-FUNDED PROJECT. project proposal to the funding measure
 PROJECT FACT SHEET GREEK-GERMANY CO-FUNDED PROJECT project proposal to the funding measure Greek-German Bilateral Research and Innovation Cooperation Project acronym: SIT4Energy Smart IT for Energy Efficiency
PROJECT FACT SHEET GREEK-GERMANY CO-FUNDED PROJECT project proposal to the funding measure Greek-German Bilateral Research and Innovation Cooperation Project acronym: SIT4Energy Smart IT for Energy Efficiency
Service Science: A Key Driver of 21st Century Prosperity
 Service Science: A Key Driver of 21st Century Prosperity Dr. Bill Hefley Carnegie Mellon University The Information Technology and Innovation Foundation Washington, DC April 9, 2008 Topics Why a focus
Service Science: A Key Driver of 21st Century Prosperity Dr. Bill Hefley Carnegie Mellon University The Information Technology and Innovation Foundation Washington, DC April 9, 2008 Topics Why a focus
WHY ACCOUNTANCY & SOCIAL DESIGN
 OPEN DESIGN STUDIO WHY ACCOUNTANCY & SOCIAL DESIGN Last year, we launched a ground-breaking partnership with the Royal Society of Art, which explored the future of our society and outlined a vision for
OPEN DESIGN STUDIO WHY ACCOUNTANCY & SOCIAL DESIGN Last year, we launched a ground-breaking partnership with the Royal Society of Art, which explored the future of our society and outlined a vision for
e-care Living Lab - 5 avenue du Grand Sablon La Tronche - FRANCE Tel: +33 (0)
 e-care Living Lab e-care Living Lab in Rhône-Alpes Region e-care got the Living Lab label in 2010 from ENoLL e-care Living Lab objectives (1/2) To promote the Living Lab approach in the healthcare sector
e-care Living Lab e-care Living Lab in Rhône-Alpes Region e-care got the Living Lab label in 2010 from ENoLL e-care Living Lab objectives (1/2) To promote the Living Lab approach in the healthcare sector
Brief to the. Senate Standing Committee on Social Affairs, Science and Technology. Dr. Eliot A. Phillipson President and CEO
 Brief to the Senate Standing Committee on Social Affairs, Science and Technology Dr. Eliot A. Phillipson President and CEO June 14, 2010 Table of Contents Role of the Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI)...1
Brief to the Senate Standing Committee on Social Affairs, Science and Technology Dr. Eliot A. Phillipson President and CEO June 14, 2010 Table of Contents Role of the Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI)...1
COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION. Brussels, 9 December 2008 (16.12) (OR. fr) 16767/08 RECH 410 COMPET 550
 COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Brussels, 9 December 2008 (16.12) (OR. fr) 16767/08 RECH 410 COMPET 550 OUTCOME OF PROCEEDINGS of: Competitiveness Council on 1 and 2 December 2008 No. prev. doc. 16012/08
COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Brussels, 9 December 2008 (16.12) (OR. fr) 16767/08 RECH 410 COMPET 550 OUTCOME OF PROCEEDINGS of: Competitiveness Council on 1 and 2 December 2008 No. prev. doc. 16012/08
April 2015 newsletter. Efficient Energy Planning #3
 STEEP (Systems Thinking for Efficient Energy Planning) is an innovative European project delivered in a partnership between the three cities of San Sebastian (Spain), Bristol (UK) and Florence (Italy).
STEEP (Systems Thinking for Efficient Energy Planning) is an innovative European project delivered in a partnership between the three cities of San Sebastian (Spain), Bristol (UK) and Florence (Italy).
Socio-Economic Sciences and Humanities. First Call for proposals. Nikos Kastrinos. Unit L1 Coordination and Horizontal Aspects
 Socio-Economic Sciences and Humanities First Call for proposals Nikos Kastrinos Unit L1 Coordination and Horizontal Aspects Information Day Socio-economic Sciences & the Humanities Thessaloniki 29 March
Socio-Economic Sciences and Humanities First Call for proposals Nikos Kastrinos Unit L1 Coordination and Horizontal Aspects Information Day Socio-economic Sciences & the Humanities Thessaloniki 29 March
10246/10 EV/ek 1 DG C II
 COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Brussels, 28 May 2010 10246/10 RECH 203 COMPET 177 OUTCOME OF PROCEEDINGS from: General Secretariat of the Council to: Delegations No. prev. doc.: 9451/10 RECH 173 COMPET
COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Brussels, 28 May 2010 10246/10 RECH 203 COMPET 177 OUTCOME OF PROCEEDINGS from: General Secretariat of the Council to: Delegations No. prev. doc.: 9451/10 RECH 173 COMPET
Roadmap for European Universities in Energy December 2016
 Roadmap for European Universities in Energy December 2016 1 Project partners This project has received funding from the European Union s Seventh Framework Programme for research, technological development
Roadmap for European Universities in Energy December 2016 1 Project partners This project has received funding from the European Union s Seventh Framework Programme for research, technological development
Twenty years of Ibero American Science and Education Consortium (ISTEC): Past, Present and Future of a Collaborative Work
 Twenty years of Ibero American Science and Education Consortium (ISTEC): Past, Present and Future of a Collaborative Work Authors: Marisa De Giusti, Comisión de Investigaciones Científicas de la provincia
Twenty years of Ibero American Science and Education Consortium (ISTEC): Past, Present and Future of a Collaborative Work Authors: Marisa De Giusti, Comisión de Investigaciones Científicas de la provincia
6.0 RESEARCH. 6.1 Overview LESSONS LEARNED
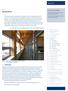 6.0 RESEARCH Thinking of a new building that would demonstrate [sustainability] was a way for us to think about making tangible our goals, we d been doing all this research a lot of participatory research
6.0 RESEARCH Thinking of a new building that would demonstrate [sustainability] was a way for us to think about making tangible our goals, we d been doing all this research a lot of participatory research
Smart Cities and Infrastructure
 Smart Cities and Infrastructure Introduction of the Issues Paper Mr. Arun Jacob Science and Technology Section UNCTAD United Nations Commission on Science and Technology for Development, Inter-sessional
Smart Cities and Infrastructure Introduction of the Issues Paper Mr. Arun Jacob Science and Technology Section UNCTAD United Nations Commission on Science and Technology for Development, Inter-sessional
Transportation Education in the New Millennium
 Transportation Education in the New Millennium As the world enters the 21 st Century, the quality of education continues to be a major factor in the success of a nation's ability to succeed and to excel.
Transportation Education in the New Millennium As the world enters the 21 st Century, the quality of education continues to be a major factor in the success of a nation's ability to succeed and to excel.
Strategic Plan for CREE Oslo Centre for Research on Environmentally friendly Energy
 September 2012 Draft Strategic Plan for CREE Oslo Centre for Research on Environmentally friendly Energy This strategic plan is intended as a long-term management document for CREE. Below we describe the
September 2012 Draft Strategic Plan for CREE Oslo Centre for Research on Environmentally friendly Energy This strategic plan is intended as a long-term management document for CREE. Below we describe the
FET Flagships in Horizon 2020
 HORIZON 2020 - Future & Emerging Technologies (FET) Paris, 21 st December 2017 FET Flagships in Horizon 2020 Aymard de Touzalin Deputy Head of Unit, Flagships DG Connect, European Commission 1 Horizon
HORIZON 2020 - Future & Emerging Technologies (FET) Paris, 21 st December 2017 FET Flagships in Horizon 2020 Aymard de Touzalin Deputy Head of Unit, Flagships DG Connect, European Commission 1 Horizon
PROGRAMME SYLLABUS Sustainable Building Information Management (master),
 PROGRAMME SYLLABUS Sustainable Building Information Management (master), 120 Programmestart: Autumn 2017 School of Engineering, Box 1026, SE-551 11 Jönköping VISIT Gjuterigatan 5, Campus PHONE +46 (0)36-10
PROGRAMME SYLLABUS Sustainable Building Information Management (master), 120 Programmestart: Autumn 2017 School of Engineering, Box 1026, SE-551 11 Jönköping VISIT Gjuterigatan 5, Campus PHONE +46 (0)36-10
Conclusions concerning various issues related to the development of the European Research Area
 COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Conclusions concerning various issues related to the development of the European Research Area The Council adopted the following conclusions: "THE COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN
COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Conclusions concerning various issues related to the development of the European Research Area The Council adopted the following conclusions: "THE COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN
Multi-level third space for systemic urban research and innovation
 EU POLICY LAB & DG RTD MAY 17, 2017 LAB CONNECTIONS KICKSTARTER Multi-level third space for systemic urban research and innovation V 0.1 CITIES AS COMPLEX ECOSYSTEMS MULTI-LEVEL, MULTI-DIMENSIONAL, MULTI-
EU POLICY LAB & DG RTD MAY 17, 2017 LAB CONNECTIONS KICKSTARTER Multi-level third space for systemic urban research and innovation V 0.1 CITIES AS COMPLEX ECOSYSTEMS MULTI-LEVEL, MULTI-DIMENSIONAL, MULTI-
FP7 ICT Call 6: Cognitive Systems and Robotics
 FP7 ICT Call 6: Cognitive Systems and Robotics Information day Luxembourg, January 14, 2010 Libor Král, Head of Unit Unit E5 - Cognitive Systems, Interaction, Robotics DG Information Society and Media
FP7 ICT Call 6: Cognitive Systems and Robotics Information day Luxembourg, January 14, 2010 Libor Král, Head of Unit Unit E5 - Cognitive Systems, Interaction, Robotics DG Information Society and Media
Written response to the public consultation on the European Commission Green Paper: From
 EABIS THE ACADEMY OF BUSINESS IN SOCIETY POSITION PAPER: THE EUROPEAN UNION S COMMON STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK FOR FUTURE RESEARCH AND INNOVATION FUNDING Written response to the public consultation on the European
EABIS THE ACADEMY OF BUSINESS IN SOCIETY POSITION PAPER: THE EUROPEAN UNION S COMMON STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK FOR FUTURE RESEARCH AND INNOVATION FUNDING Written response to the public consultation on the European
Research strategy
 Department of People & Technology Research strategy 2017-2020 Introduction The Department of People and Technology was established on 1 January 2016 through an integration of academic environments from
Department of People & Technology Research strategy 2017-2020 Introduction The Department of People and Technology was established on 1 January 2016 through an integration of academic environments from
KNOWLEDGE & MEET EFFICIENCY SCIENCE TURNED INTO SUCCESS
 KNOWLEDGE & CREATIVITY MEET EFFICIENCY FORERUNNING EXPERTISE Developed at TUAS, the novel concept of innovation pedagogy, INNOPEDA, is designed to encourage innovative thinking. Thus, cooperation with
KNOWLEDGE & CREATIVITY MEET EFFICIENCY FORERUNNING EXPERTISE Developed at TUAS, the novel concept of innovation pedagogy, INNOPEDA, is designed to encourage innovative thinking. Thus, cooperation with
Report on the Results of. Questionnaire 1
 Report on the Results of Questionnaire 1 (For Coordinators of the EU-U.S. Programmes, Initiatives, Thematic Task Forces, /Working Groups, and ERA-Nets) BILAT-USA G.A. n 244434 - Task 1.2 Deliverable 1.3
Report on the Results of Questionnaire 1 (For Coordinators of the EU-U.S. Programmes, Initiatives, Thematic Task Forces, /Working Groups, and ERA-Nets) BILAT-USA G.A. n 244434 - Task 1.2 Deliverable 1.3
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering. Five-Year Strategic Plan: Improving Lives. Transforming Louisiana. Changing the World.
 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Five-Year Strategic Plan: 2010-2015 Improving Lives. Transforming Louisiana. Changing the World. Engineering is intertwined with our very own way of life.
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Five-Year Strategic Plan: 2010-2015 Improving Lives. Transforming Louisiana. Changing the World. Engineering is intertwined with our very own way of life.
SCIENCE IN THE CENTRE STRATEGIC PLAN
 SCIENCE IN THE CENTRE STRATEGIC PLAN 2017-2021 CONTACT Telephone: +47 73 59 21 45 Email address: post@vm.ntnu.no Street address: Erling Skakkes gate 47A, Trondheim Mailing address: NTNU Vitenskapsmuseet,
SCIENCE IN THE CENTRE STRATEGIC PLAN 2017-2021 CONTACT Telephone: +47 73 59 21 45 Email address: post@vm.ntnu.no Street address: Erling Skakkes gate 47A, Trondheim Mailing address: NTNU Vitenskapsmuseet,
Please send your responses by to: This consultation closes on Friday, 8 April 2016.
 CONSULTATION OF STAKEHOLDERS ON POTENTIAL PRIORITIES FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION IN THE 2018-2020 WORK PROGRAMME OF HORIZON 2020 SOCIETAL CHALLENGE 5 'CLIMATE ACTION, ENVIRONMENT, RESOURCE EFFICIENCY AND
CONSULTATION OF STAKEHOLDERS ON POTENTIAL PRIORITIES FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION IN THE 2018-2020 WORK PROGRAMME OF HORIZON 2020 SOCIETAL CHALLENGE 5 'CLIMATE ACTION, ENVIRONMENT, RESOURCE EFFICIENCY AND
Conclusions on the future of information and communication technologies research, innovation and infrastructures
 COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Conclusions on the future of information and communication technologies research, innovation and infrastructures 2982nd COMPETITIVESS (Internal market, Industry and Research)
COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Conclusions on the future of information and communication technologies research, innovation and infrastructures 2982nd COMPETITIVESS (Internal market, Industry and Research)
G20 Initiative #eskills4girls
 Annex to G20 Leaders Declaration G20 Initiative #eskills4girls Transforming the future of women and girls in the digital economy A gender inclusive digital economy 1. During their meeting in Hangzhou in
Annex to G20 Leaders Declaration G20 Initiative #eskills4girls Transforming the future of women and girls in the digital economy A gender inclusive digital economy 1. During their meeting in Hangzhou in
Integrated Transformational and Open City Governance Rome May
 Integrated Transformational and Open City Governance Rome May 9-11 2016 David Ludlow University of the West of England, Bristol Workshop Aims Key question addressed - how do we advance towards a smart
Integrated Transformational and Open City Governance Rome May 9-11 2016 David Ludlow University of the West of England, Bristol Workshop Aims Key question addressed - how do we advance towards a smart
Position Paper. CEN-CENELEC Response to COM (2010) 546 on the Innovation Union
 Position Paper CEN-CENELEC Response to COM (2010) 546 on the Innovation Union Introduction CEN and CENELEC very much welcome the overall theme of the Communication, which is very much in line with our
Position Paper CEN-CENELEC Response to COM (2010) 546 on the Innovation Union Introduction CEN and CENELEC very much welcome the overall theme of the Communication, which is very much in line with our
Framework Programme 7
 Framework Programme 7 1 Joining the EU programmes as a Belarusian 1. Introduction to the Framework Programme 7 2. Focus on evaluation issues + exercise 3. Strategies for Belarusian organisations + exercise
Framework Programme 7 1 Joining the EU programmes as a Belarusian 1. Introduction to the Framework Programme 7 2. Focus on evaluation issues + exercise 3. Strategies for Belarusian organisations + exercise
Science with Arctic Attitude
 Science with Arctic Attitude 04 07 08 11 Pushing the boundaries of the known for a more sustainable, healthy and intelligent world We make a significant contribution to solving global challenges in five
Science with Arctic Attitude 04 07 08 11 Pushing the boundaries of the known for a more sustainable, healthy and intelligent world We make a significant contribution to solving global challenges in five
Consultancy on Technological Foresight
 Consultancy on Technological Foresight A Product of the Technical Cooperation Agreement Strategic Roadmap for Productive Development in Trinidad and Tobago Policy Links, IfM Education and Consultancy Services
Consultancy on Technological Foresight A Product of the Technical Cooperation Agreement Strategic Roadmap for Productive Development in Trinidad and Tobago Policy Links, IfM Education and Consultancy Services
Inclusively Creative
 In Bandung, Indonesia, December 5 th to 7 th 2017, over 100 representatives from the government, civil society, the private sector, think-tanks and academia, international organization as well as a number
In Bandung, Indonesia, December 5 th to 7 th 2017, over 100 representatives from the government, civil society, the private sector, think-tanks and academia, international organization as well as a number
From FP7 towards Horizon 2020 Workshop on " Research performance measurement and the impact of innovation in Europe" IPERF, Luxembourg, 31/10/2013
 From FP7 towards Horizon 2020 Workshop on " Research performance measurement and the impact of innovation in Europe" IPERF, Luxembourg, 31/10/2013 Lucilla Sioli, European Commission, DG CONNECT Overview
From FP7 towards Horizon 2020 Workshop on " Research performance measurement and the impact of innovation in Europe" IPERF, Luxembourg, 31/10/2013 Lucilla Sioli, European Commission, DG CONNECT Overview
Creative Informatics Research Fellow - Job Description Edinburgh Napier University
 Creative Informatics Research Fellow - Job Description Edinburgh Napier University Edinburgh Napier University is appointing a full-time Post Doctoral Research Fellow to contribute to the delivery and
Creative Informatics Research Fellow - Job Description Edinburgh Napier University Edinburgh Napier University is appointing a full-time Post Doctoral Research Fellow to contribute to the delivery and
Fistera Delphi Austria
 Fistera Delphi Austria Carsten Orwat Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe and Systems Analysis Outline 1. Overview 2. Objectives and Approach 3. Innovative Features 4. Elements 5. IST Coverage 6. Analysis: Results
Fistera Delphi Austria Carsten Orwat Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe and Systems Analysis Outline 1. Overview 2. Objectives and Approach 3. Innovative Features 4. Elements 5. IST Coverage 6. Analysis: Results
ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL RESEARCH COUNCIL IMPACT REPORT
 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL RESEARCH COUNCIL IMPACT REPORT For awards ending on or after 1 November 2009 This Impact Report should be completed and submitted using the grant reference as the email subject to reportsofficer@esrc.ac.uk
ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL RESEARCH COUNCIL IMPACT REPORT For awards ending on or after 1 November 2009 This Impact Report should be completed and submitted using the grant reference as the email subject to reportsofficer@esrc.ac.uk
KIC EIT Raw Materials
 KIC EIT Raw Materials Text Text Dr. Lisa Maria T. O Donoghue Dublin 18.10.17 Picture source http://www.falconautoonline.com/incoming-material/ What is a EIT-KIC KIC (acronym of Knowledge Innovation Community)
KIC EIT Raw Materials Text Text Dr. Lisa Maria T. O Donoghue Dublin 18.10.17 Picture source http://www.falconautoonline.com/incoming-material/ What is a EIT-KIC KIC (acronym of Knowledge Innovation Community)
EU expert briefing: Thematic context of the Seminar: Overall strategic approach
 EU-China experts seminar on developing a joint initiative for cooperation in research and innovation on Food, Agriculture and Biotechnologies (FAB), Beijing 10-11 October 2013 EU expert briefing: Thematic
EU-China experts seminar on developing a joint initiative for cooperation in research and innovation on Food, Agriculture and Biotechnologies (FAB), Beijing 10-11 October 2013 EU expert briefing: Thematic
D8.1 PROJECT PRESENTATION
 D8.1 PROJECT PRESENTATION Approval Status AUTHOR(S) NAME AND SURNAME ROLE IN THE PROJECT PARTNER Daniela De Lucia, Gaetano Cascini PoliMI APPROVED BY Gaetano Cascini Project Coordinator PoliMI History
D8.1 PROJECT PRESENTATION Approval Status AUTHOR(S) NAME AND SURNAME ROLE IN THE PROJECT PARTNER Daniela De Lucia, Gaetano Cascini PoliMI APPROVED BY Gaetano Cascini Project Coordinator PoliMI History
Interoperable systems that are trusted and secure
 Government managers have critical needs for models and tools to shape, manage, and evaluate 21st century services. These needs present research opportunties for both information and social scientists,
Government managers have critical needs for models and tools to shape, manage, and evaluate 21st century services. These needs present research opportunties for both information and social scientists,
The function is assumed by technology management, usually the Technological Development Committee.
 Integrated Report 6.8 Innovation 167 The ACS Group is a continuously evolving organisation that responds to the growing demand for improvements in processes, technological advances and quality of service
Integrated Report 6.8 Innovation 167 The ACS Group is a continuously evolving organisation that responds to the growing demand for improvements in processes, technological advances and quality of service
demonstrator approach real market conditions would be useful to provide a unified partner search instrument for the CIP programme
 Contribution by the Ministry of Industry and Trade of the Czech Republic to the public consultations on a successor programme to the Competitiveness and Innovation Framework Programme (CIP) 2007-2013 Given
Contribution by the Ministry of Industry and Trade of the Czech Republic to the public consultations on a successor programme to the Competitiveness and Innovation Framework Programme (CIP) 2007-2013 Given
Towards a Consumer-Driven Energy System
 IEA Committee on Energy Research and Technology EXPERTS GROUP ON R&D PRIORITY-SETTING AND EVALUATION Towards a Consumer-Driven Energy System Understanding Human Behaviour Workshop Summary 12-13 October
IEA Committee on Energy Research and Technology EXPERTS GROUP ON R&D PRIORITY-SETTING AND EVALUATION Towards a Consumer-Driven Energy System Understanding Human Behaviour Workshop Summary 12-13 October
Priority Theme 1: Science, Technology and Innovation (STI) for the Post-2015 Agenda
 UN Commission on Science and Technology for Development 2013-2014 Inter-sessional Panel 2-4 December 2013 Washington D.C., United States of America Priority Theme 1: Science, Technology and Innovation
UN Commission on Science and Technology for Development 2013-2014 Inter-sessional Panel 2-4 December 2013 Washington D.C., United States of America Priority Theme 1: Science, Technology and Innovation
Innovation for Defence Excellence and Security (IDEaS)
 ASSISTANT DEPUTY MINISTER (SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY) Innovation for Defence Excellence and Security (IDEaS) Department of National Defence November 2017 Innovative technology, knowledge, and problem solving
ASSISTANT DEPUTY MINISTER (SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY) Innovation for Defence Excellence and Security (IDEaS) Department of National Defence November 2017 Innovative technology, knowledge, and problem solving
Smart City Indicators
 Smart City Indicators meanings of indicators in a place based understanding Rudolf Giffinger TU Wien Centre of Regional Science - SRF EERA JP Smart Cities Symposium on Key Performance Indicators for Smart
Smart City Indicators meanings of indicators in a place based understanding Rudolf Giffinger TU Wien Centre of Regional Science - SRF EERA JP Smart Cities Symposium on Key Performance Indicators for Smart
BUILDING DIGITAL COMPETENCIES TO BENEFIT FROM EXISTING AND EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES, WITH A SPECIAL FOCUS ON GENDER AND YOUTH DIMENSIONS
 BUILDING DIGITAL COMPETENCIES TO BENEFIT FROM EXISTING AND EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES, WITH A SPECIAL FOCUS ON GENDER AND YOUTH DIMENSIONS Introduction of the Report of the Secretary-General Shamika N. Sirimanne
BUILDING DIGITAL COMPETENCIES TO BENEFIT FROM EXISTING AND EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES, WITH A SPECIAL FOCUS ON GENDER AND YOUTH DIMENSIONS Introduction of the Report of the Secretary-General Shamika N. Sirimanne
Evaluation of Strategic Research Initiatives at Roskilde University Guidelines for the evaluator s report
 ROSKILDE UNIVERSITY Communication and Rector s Office Evaluation of Strategic Research Initiatives at Roskilde University Guidelines for the evaluator s report The strategic research initiatives grew out
ROSKILDE UNIVERSITY Communication and Rector s Office Evaluation of Strategic Research Initiatives at Roskilde University Guidelines for the evaluator s report The strategic research initiatives grew out
THE ROLE OF TRANSPORT TECHNOLOGY PLATFORMS IN FOSTERING EXPLOITATION. Josef Mikulík Transport Research Centre - CDV
 THE ROLE OF TRANSPORT TECHNOLOGY PLATFORMS IN FOSTERING EXPLOITATION Josef Mikulík Transport Research Centre - CDV Outlines European Technology Platforms ERTRAC Czech ERTRAC Other national TP Technology
THE ROLE OF TRANSPORT TECHNOLOGY PLATFORMS IN FOSTERING EXPLOITATION Josef Mikulík Transport Research Centre - CDV Outlines European Technology Platforms ERTRAC Czech ERTRAC Other national TP Technology
Horizon the new EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation
 Horizon 2020 - the new EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation Dr. Ulrike Trojahn, European Research and Project Office GmbH Seminar: Anträge für EU Förderungsprogramme February 6, 2014, htw
Horizon 2020 - the new EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation Dr. Ulrike Trojahn, European Research and Project Office GmbH Seminar: Anträge für EU Förderungsprogramme February 6, 2014, htw
What is backcasting & why do we need it
 What is backcasting & why do we need it Tools for complexity studies We need tools to find options to solve complex problems like Sustainable Development Long term Great uncertainties Great number of stakeholders
What is backcasting & why do we need it Tools for complexity studies We need tools to find options to solve complex problems like Sustainable Development Long term Great uncertainties Great number of stakeholders
New Approaches to Innovation Ener2i Training Workshop Minsk, 15 October 2014
 New Approaches to Innovation Ener2i Training Workshop Minsk, 15 October 2014 Manfred Spiesberger Centre for Social Innovation ZSI Vienna, Austria spiesberger@zsi.at Table of contents 1. Centre for Social
New Approaches to Innovation Ener2i Training Workshop Minsk, 15 October 2014 Manfred Spiesberger Centre for Social Innovation ZSI Vienna, Austria spiesberger@zsi.at Table of contents 1. Centre for Social
Committee on Development and Intellectual Property (CDIP)
 E CDIP/6/4 REV. ORIGINAL: ENGLISH DATE: NOVEMBER 26, 2010 Committee on Development and Intellectual Property (CDIP) Sixth Session Geneva, November 22 to 26, 2010 PROJECT ON INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND TECHNOLOGY
E CDIP/6/4 REV. ORIGINAL: ENGLISH DATE: NOVEMBER 26, 2010 Committee on Development and Intellectual Property (CDIP) Sixth Session Geneva, November 22 to 26, 2010 PROJECT ON INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND TECHNOLOGY
Robotics: from FP7 to Horizon Libor Král, Head of Unit Unit A2 - Robotics DG Communication Networks, Content and Technology European Commission
 Robotics: from FP7 to Horizon 2020 Libor Král, Head of Unit Unit A2 - Robotics DG Communication Networks, Content and Technology European Commission Robotics in Regions 30 October 2013 Key issues research
Robotics: from FP7 to Horizon 2020 Libor Král, Head of Unit Unit A2 - Robotics DG Communication Networks, Content and Technology European Commission Robotics in Regions 30 October 2013 Key issues research
Lithuania: Pramonė 4.0
 Digital Transformation Monitor Lithuania: Pramonė 4.0 February 2018 Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs Lithuania:Pramonė 4.0 Lithuania: Pramonė 4.0 istock.com Fact box for Lithuania s
Digital Transformation Monitor Lithuania: Pramonė 4.0 February 2018 Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs Lithuania:Pramonė 4.0 Lithuania: Pramonė 4.0 istock.com Fact box for Lithuania s
Funding opportunities for BigSkyEarth projects. Darko Jevremović Brno, April
 Funding opportunities for BigSkyEarth projects Darko Jevremović Brno, April 14 2016 OUTLINE H2020 ESIF http://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/en/policy/them es/research-innovation/ http://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/index.cfm/en/p
Funding opportunities for BigSkyEarth projects Darko Jevremović Brno, April 14 2016 OUTLINE H2020 ESIF http://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/en/policy/them es/research-innovation/ http://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/index.cfm/en/p
Enabling ICT for. development
 Enabling ICT for development Interview with Dr M-H Carolyn Nguyen, who explains why governments need to start thinking seriously about how to leverage ICT for their development goals, and why an appropriate
Enabling ICT for development Interview with Dr M-H Carolyn Nguyen, who explains why governments need to start thinking seriously about how to leverage ICT for their development goals, and why an appropriate
Terms of Reference. Call for Experts in the field of Foresight and ICT
 Terms of Reference Call for Experts in the field of Foresight and ICT Title Work package Lead: Related Workpackage: Related Task: Author(s): Project Number Instrument: Call for Experts in the field of
Terms of Reference Call for Experts in the field of Foresight and ICT Title Work package Lead: Related Workpackage: Related Task: Author(s): Project Number Instrument: Call for Experts in the field of
Media Literacy Expert Group Draft 2006
 Page - 2 Media Literacy Expert Group Draft 2006 INTRODUCTION The media are a very powerful economic and social force. The media sector is also an accessible instrument for European citizens to better understand
Page - 2 Media Literacy Expert Group Draft 2006 INTRODUCTION The media are a very powerful economic and social force. The media sector is also an accessible instrument for European citizens to better understand
CyPhers Project: Main Results
 CyPhers Project: Main Results Saddek Bensalem / shortened Presentation by Sebastian Engell (CPSoS) SoS Open Workshop, Florence May 28, 2015 fortiss (Munich) KTH (Stockholm) U. Joseph Fourier (Grenoble)
CyPhers Project: Main Results Saddek Bensalem / shortened Presentation by Sebastian Engell (CPSoS) SoS Open Workshop, Florence May 28, 2015 fortiss (Munich) KTH (Stockholm) U. Joseph Fourier (Grenoble)
TECHNOLOGY, ARTS AND MEDIA (TAM) CERTIFICATE PROPOSAL. November 6, 1999
 TECHNOLOGY, ARTS AND MEDIA (TAM) CERTIFICATE PROPOSAL November 6, 1999 ABSTRACT A new age of networked information and communication is bringing together three elements -- the content of business, media,
TECHNOLOGY, ARTS AND MEDIA (TAM) CERTIFICATE PROPOSAL November 6, 1999 ABSTRACT A new age of networked information and communication is bringing together three elements -- the content of business, media,
DELIVERABLE SEPE Exploitation Plan
 2016 DELIVERABLE 6.1.3 SEPE Exploitation Plan Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 1. Description of the Project... 4 2. Aims & Objectives of the Deliverable... 5 3. SEPE s role in Exploitation...
2016 DELIVERABLE 6.1.3 SEPE Exploitation Plan Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 1. Description of the Project... 4 2. Aims & Objectives of the Deliverable... 5 3. SEPE s role in Exploitation...
Professional Competences beyond Technical Know-How : A Perspective from a Technology Company
 Professional Competences beyond Technical Know-How : A Perspective from a Technology Company Should Innovation Trainning at The University be Oriented to Teach Students About Market Competences or They
Professional Competences beyond Technical Know-How : A Perspective from a Technology Company Should Innovation Trainning at The University be Oriented to Teach Students About Market Competences or They
Humanities for a Digital Society, Towards The Tilburg School of Humanities and Digital Sciences
 Humanities for a Digital Society, 2018-2021 Towards The Tilburg School of Humanities and Digital Sciences Version 4.0, dd 23 November 2017, approved by Faculty Council Vision Human identities and responsibilities,
Humanities for a Digital Society, 2018-2021 Towards The Tilburg School of Humanities and Digital Sciences Version 4.0, dd 23 November 2017, approved by Faculty Council Vision Human identities and responsibilities,
Vice Chancellor s introduction
 H O R I Z O N 2 0 2 0 2 Vice Chancellor s introduction Since its formation in 1991, the University of South Australia has pursued high aspirations with enthusiasm and success. This journey is ongoing and
H O R I Z O N 2 0 2 0 2 Vice Chancellor s introduction Since its formation in 1991, the University of South Australia has pursued high aspirations with enthusiasm and success. This journey is ongoing and
EC-Egypt Science and Technology Cooperation Agreement. Road Map
 EC-Egypt Science and Technology Cooperation Agreement Road Map 2007-2008 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS pp. INTRODUCTION... 3 FACILITATING COOPERATION... 3-4 ENERGY... 4 ENVIRONMENT (INCLUDING CLIMATE CHANGE)...
EC-Egypt Science and Technology Cooperation Agreement Road Map 2007-2008 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS pp. INTRODUCTION... 3 FACILITATING COOPERATION... 3-4 ENERGY... 4 ENVIRONMENT (INCLUDING CLIMATE CHANGE)...
A manifesto for global sustainable health. Sustainable Health Symposium Cambridge, UK 25th July 2017
 A manifesto for global sustainable health Sustainable Health Symposium Cambridge, UK 25th July 2017 Introduction Across the globe, the health of individuals, their communities and the planet is in crisis
A manifesto for global sustainable health Sustainable Health Symposium Cambridge, UK 25th July 2017 Introduction Across the globe, the health of individuals, their communities and the planet is in crisis
DANUBE INNOVATION PARTNERSHIP
 Horizontal flagship support activity: DANUBE INNOVATION PARTNERSHIP 1. RATIONALE As part of the Europe 2020 Strategy, the 'Innovation Union' flagship initiative sets out a comprehensive innovation strategy
Horizontal flagship support activity: DANUBE INNOVATION PARTNERSHIP 1. RATIONALE As part of the Europe 2020 Strategy, the 'Innovation Union' flagship initiative sets out a comprehensive innovation strategy
Technology Platforms: champions to leverage knowledge for growth
 SPEECH/04/543 Janez POTOČNIK European Commissioner for Science and Research Technology Platforms: champions to leverage knowledge for growth Seminar of Industrial Leaders of Technology Platforms Brussels,
SPEECH/04/543 Janez POTOČNIK European Commissioner for Science and Research Technology Platforms: champions to leverage knowledge for growth Seminar of Industrial Leaders of Technology Platforms Brussels,
Research Infrastructures and Innovation
 Research Infrastructures and Innovation Octavi Quintana Principal Adviser European Commission DG Research & Innovation The presentation shall neither be binding nor construed as constituting commitment
Research Infrastructures and Innovation Octavi Quintana Principal Adviser European Commission DG Research & Innovation The presentation shall neither be binding nor construed as constituting commitment
Reputation enhanced by innovation - Call for proposals in module 3
 Reputation enhanced by innovation - Call for proposals in module 3 The Nordic Innovation Centre on behalf of the Nordic partners of the programme Innovation in the Nordic marine sector invites to submit
Reputation enhanced by innovation - Call for proposals in module 3 The Nordic Innovation Centre on behalf of the Nordic partners of the programme Innovation in the Nordic marine sector invites to submit
Academic Program IIT Rajasthan
 Academic Program IIT Rajasthan Prem K Kalra 28 October 2009 IIT Rajasthan 1 Challenges of the 21 st century Inclusive & sustainable development Global thinking & approach Building capacity, capability
Academic Program IIT Rajasthan Prem K Kalra 28 October 2009 IIT Rajasthan 1 Challenges of the 21 st century Inclusive & sustainable development Global thinking & approach Building capacity, capability
Knowledge Exchange Strategy ( )
 UNIVERSITY OF ST ANDREWS Knowledge Exchange Strategy (2012-2017) This document lays out our strategy for Knowledge Exchange founded on the University s Academic Strategy and in support of the University
UNIVERSITY OF ST ANDREWS Knowledge Exchange Strategy (2012-2017) This document lays out our strategy for Knowledge Exchange founded on the University s Academic Strategy and in support of the University
The Riga Declaration on e-skills A call to action on digital skills and job creation in Europe
 The Riga Declaration on e-skills A call to action on digital skills and job creation in Europe Riga, 13 March 2015: Representatives from governments, industry, academia, NGOs, and other key stakeholders
The Riga Declaration on e-skills A call to action on digital skills and job creation in Europe Riga, 13 March 2015: Representatives from governments, industry, academia, NGOs, and other key stakeholders
Europe how to become No. 1!
 Science2 Society Europe how to become No. 1! Science2Society starts to boost innovation efficiency across Europe This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation
Science2 Society Europe how to become No. 1! Science2Society starts to boost innovation efficiency across Europe This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation
Engaging Stakeholders
 Engaging Stakeholders Users, providers and the climate science community JPI Climate WG2 Workshop: National Dialogues in Europe Thursday, 08 th May 2014 Roger B Street Module 2 Lessons Learned Users Needs
Engaging Stakeholders Users, providers and the climate science community JPI Climate WG2 Workshop: National Dialogues in Europe Thursday, 08 th May 2014 Roger B Street Module 2 Lessons Learned Users Needs
MILAN DECLARATION Joining Forces for Investment in the Future of Europe
 MILAN DECLARATION Joining Forces for Investment in the Future of Europe We, the political leaders and representatives of the Vanguard Initiative for New Growth through Smart Specialisation, call upon the
MILAN DECLARATION Joining Forces for Investment in the Future of Europe We, the political leaders and representatives of the Vanguard Initiative for New Growth through Smart Specialisation, call upon the
Seoul Initiative on the 4 th Industrial Revolution
 ASEM EMM Seoul, Korea, 21-22 Sep. 2017 Seoul Initiative on the 4 th Industrial Revolution Presented by Korea 1. Background The global economy faces unprecedented changes with the advent of disruptive technologies
ASEM EMM Seoul, Korea, 21-22 Sep. 2017 Seoul Initiative on the 4 th Industrial Revolution Presented by Korea 1. Background The global economy faces unprecedented changes with the advent of disruptive technologies
Empirical Research on Systems Thinking and Practice in the Engineering Enterprise
 Empirical Research on Systems Thinking and Practice in the Engineering Enterprise Donna H. Rhodes Caroline T. Lamb Deborah J. Nightingale Massachusetts Institute of Technology April 2008 Topics Research
Empirical Research on Systems Thinking and Practice in the Engineering Enterprise Donna H. Rhodes Caroline T. Lamb Deborah J. Nightingale Massachusetts Institute of Technology April 2008 Topics Research
Sustainable Society Network+ Research Call
 Sustainable Society Network+ Research Call Call for Pilot Studies and Challenge Fellowships Closing date: 17:00 on 31 st October2012 Summary Applicants are invited to apply for short- term pilot study
Sustainable Society Network+ Research Call Call for Pilot Studies and Challenge Fellowships Closing date: 17:00 on 31 st October2012 Summary Applicants are invited to apply for short- term pilot study
Belgian Position Paper
 The "INTERNATIONAL CO-OPERATION" COMMISSION and the "FEDERAL CO-OPERATION" COMMISSION of the Interministerial Conference of Science Policy of Belgium Belgian Position Paper Belgian position and recommendations
The "INTERNATIONAL CO-OPERATION" COMMISSION and the "FEDERAL CO-OPERATION" COMMISSION of the Interministerial Conference of Science Policy of Belgium Belgian Position Paper Belgian position and recommendations
