Time evolution of face recognition in accessible scenarios
|
|
|
- Bartholomew Barber
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI /s REVIEW Open Access Time evolution of face recognition in accessible scenarios Ramon Blanco Gonzalo 1*, Norman Poh 2, Rita Wong 2 and Raul Sanchez Reillo 1 *Correspondence: rbgonzal@ing.uc3m.es 1 University Carlos III, Madrid, Avda. de la Universidad, 30, Leganes, Spain Full list of author information is available at the end of the article Abstract Up to now, biometric recognition has shown significant advantages as to be considered a reliable solution for security systems in mobile environments. Nevertheless, due to the short lifetime of biometrics in mobile devices, a handful of concerns regarding usability and accessibility need to be covered in order to meet users requirements. This work is focused on analysing the usability and accessibility of a face recognition system used by visually impaired people, focusing on the time spent in the process, which is a critical aspect. Specifically, we cover different key questions including which kind of feedback is more useful for visually impaired users and beneficial for performance and how is the performance evolution in contrast with the time spent in the recognition. Our findings suggest that several parameters improve along with the time spent in the process, including performance. The audio feedback provided in real time involves also better performance and user experience than instructions given previously. Background Biometrics in mobile environments The amount of sensitive data that needs to be protected, not only at institutions or companies levels but also for ordinary people, is increasing exponentially [10] [23]. Nowadays, it is common to use the smartphone to access bank accounts [20], make payments or handle important information in general [7, 8], which leads to the necessity of increase the security in those devices [17, 24]. Usually, the applied methods to assure security in mobile devices are based on PINs or passwords, which can be easy to forget and forge, so that, other approaches are arising. In particular, biometric recognition is suggested to be embedded in mobile devices for many reasons. The first one is the large amount of devices already deployed, which has reached the situation that it is difficult to find someone that does not possess and use daily devices such as smartphones or tablets. The second one is that for some biometric modalities, the capture device is already included within the mobile device (e.g., camera for face recognition, touch screen for handwritten signature recognition, microphone for speaker recognition, or the inclusion of some swipe sensors for fingerprint verification). Handwritten signature, voice and face recognition has been suggested as the most suitable modalities [19]. This leads to an important reduction in the cost of the deployment, as users already have those devices and they should only acquire the application. Other important factors are the necessity of having ID portable devices by security forces (e.g., for suspects 2015 Blanco-Gonzalo et al. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
2 Page 2 of 11 identification) or for signing documents on the spot. Also, as users are already familiar with this kind of devices, the usability level achieved could be improved, although, as it will be mentioned below, mobility also creates new usability challenges. Due to marketing needs, mobile devices are improving every day, which will allow powerful biometric algorithms in the near future. As an important drawback, mobile devices present security concerns related to how the operating system controls the way that installed applications access memory data and communication buffers. A lack of a strict control compromises the integration of biometrics as sensitive data may be endangered. Usability and accessibility concerns One of the major drawbacks when using biometrics in mobile devices is the lack of usability being this technology a challenge for users in many cases. Almost all the work done in biometrics is devoted to improve algorithms performance and bringing the Equal Error Rate (EER) close to zero. But while this kind of research is necessary, working on improving user interaction with systems is also extremely important, as a lack of usability could mean not only the rejection of the system by the users, but also a reduction in the expected performance of the biometric system. In order to increase the easiness and encourage the use of biometrics it is necessary to improve its usability and accessibility, making it reachable for a wider percent of population. One of the collectives usually excluded at the time of design security systems is the disabled people, who are around 15 % of the world population [35]. Furthermore, it is important to highlight that every individual is potentially dependent (illnesses, age, pregnancy, etc.). Improving biometrics designs would be beneficial not only for disabled people but for many others who find the technology complicated to use. It could be thought that biometric recognition is challenging for disabled people but we show in this work that a correct design can make the process easy for everyone. Specifically, we focus on face recognition for visually impaired users, providing audio feedback and instructions. Face recognition has shown to have a good acceptation and it is one of the less intrusive modalities for users. There are several works in the literature embedding face recognition in mobile environments [4, 29, 30]. Nevertheless, the amount of works in biometrics accessibility is scarce yet. One of the first approaches is a universal access control to mobile devices through fingerprint and handwritten signature developed by authors [22]. Other recent works in biometrics accessibility show the advantages against other alternatives such as PIN or passwords [37]. These researches point the necessity of reliable solutions which could ease several procedures to people with accessibility concerns. State of the art in biometrics usability There are several usability works in biometrics in the literature and most of them come from the usability definition given by the ISO 9241:2010 [1]: The extent to which a product can be used by specified users to achieve specified goals with effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction in a specified context of use. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) made some experiments emphasizing in ergonomics to better capture user traits. For instance, in [27] an experiment analysing the optimal device position regarding height or in [28] where they measured the usability of the face image capturing system at the US ports of entry. One of the first usability studies in biometrics
3 Page 3 of 11 was an enrolment trial in the UK [3] conducted by Atos. Kukula et al. designed a model, the HBSI (Human Biometric System Interaction) [15], where the interaction between the user and the system is studied through ergonomics, usability and signal processing. In Kukula et al. [33] analysed the different kinds of possible errors when applying hand geometry recognition. Another example is [16] where an extensive analysis on the fingerprint devices ergonomics is done. Authors have carried out several experiments analysing various factors which affect usability in biometrics. In [5] the use of different styluses in dynamic signature verification on an ipad was studied reaching interesting outcomes regarding ergonomics. The stress as a key usability factor in biometric recognition was analysed in [6], where authors showed that mobile biometrics are reliable even when the user is under stressful situations (banks, shops, post office, etc.). The most relevant works providing feedback to users in biometrics are the experiments made by NIST. In [11] and [9] they present a quality-driven interactive real-time user feedback mechanism for unattended fingerprint kiosk, where the application shows pictures (visual feedback) to users helping them to better place their fingertips on the sensor. In our case, we suggest a new feedback mode providing audio feedback in order to guide visually impaired users through the biometric process. Study of the time evolution Several visually impaired people participated in this usability evaluation of face recognition, where they were asked to take self-photos with a mobile device. We prepared different experiments with different kinds of feedback divided into two sessions. Once all the images had been taken we analysed the face recognition performance in contrast with the time employed in the process. In mobile environments, one of the most critical aspects is the time employed in the authentication process because long times would lead to users rejection and/or security concerns. On the contrary, quick interactions could involve misuses and errors in recognition. Then, in this work we have focused on the efficiency (as defined by ISO 9241:2010, the time spent in tasks) of biometrics in mobile devices. There are not too many works on accessibility in biometrics [21] and there is not a standard methodology yet. In this work, we compare instructions with audio feedback in real time following the state of the art in interfaces [31] accessibility and applying them to biometrics [2]. This work comprises an extensive analysis of the time influence in face recognition for visually impaired users both in performance and usability, obtaining several important outcomes regarding: the importance of the received feedback, the variability of the performance and the usable images rates along with the time spent in the process. This paper is divided as follows: in Evaluation set up the evaluation set up is provided. We explain the methodology and the experimentation in the Methodology and experimentation. The results are in Results and discussion and the conclusions and future work are in Conclusions and future work. Evaluation set up This evaluation was carried out in the Saint Nicholas Home centre for visually impaired people (Penang, Malaysia). The scenario was a quiet room where the user was only
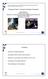
4 Page 4 of 11 accompanied by the operator and the ambient conditions were normal (e.g. lightning, temperature and humidity). In all the experiments the user was sat at a table and was requested to hold the camera by himself and try to focus his face in order to obtain a face image as centred as possible. The process was scheduled in two sessions and each one consisted of four different experiments (from this point forward E ) and completed in this order: E1, E2, E3 and E4 (explained in Experiments ). The camera used for capturing the face images is an Advent Slim 300K web cam connected to a PC, easily manageable for users. The images taken have a resolution in grayscale. Each experiment takes as much time as the user needs (until a timeout set at 45 s) to obtain a good image (in quality given by the face detector confidence) of his face. The evaluation crew was composed of 40 users (29 men and 11 woman) with different range of age and impairment (Fig. 1). The users general degree of vision is really low as many of them can barely distinguish light. Each user has different knowledge about the technology and none of them have used a biometric system previously. Experiments The experiments made were planned in order to meet the initial requirements regarding usability and accessibility. The users receive different kinds of feedback in each experiment being the final goal is to focus their face at the camera in all of them. The experiments are: E1: The user does not receive any information or feedback about how to take the selfphoto. E2: An audio feedback consisting of a sinusoidal wave sound is given by the computer. The sound is set at three different frequencies according to the face detection confidence of the acquired image. Higher face confidence involves higher frequency. E3: The user receives information before starting about how to take the self-photo, regarding the correct distance and camera handling. E4: The user receives the audio feedback and information about how to take the selfphoto (E2+E3). Each experiment was recorded as a video and each video comprises several images (some of them contain a face and others not, depending on the user skills at the time employed to take the self-photo). An example of the experiments images is in Fig. 2. Fig. 1 Level of vision and ages of the participants.
5 Page 5 of 11 Fig. 2 Images of the same user in the E1, E2, E2 and E4 from left to right (session 1). An ideal way to carry out the experiments is by using RCT (Randomized Controlled Trial), whereby a user is subject to one of the four modes of feedback. However, we were concerned with two issues with this approach. The first is the fact that biometric performance is subject-dependent. Therefore, if one conducts the same experiment (the same mode of feedback) on two different disjoint populations, one will get two different results. The effect of the subject variability might be higher than the effect due to the mode of feedback. The second concern is that the number of blind subjects is limited, which is about 40. For this reason, deploying RCT would mean that one has to divide the population into a smaller set with 10 subjects for each mode of feedback. This is arguably not the best use of limited samples available to us. We have therefore, opted for subjecting every volunteers to all the four modes of feedback, but doing so carefully so that the effect of one feedback does not influence that of another. One way to achieve this is by exploiting the natural ordering of the modes of feedback. For example, the E1 setting does not have any feedback and so should be carried out first. E2 and E3 are each independent of each other because the audio feedback does not convey any information about the instruction. However, the instruction (E3) mode should take place after. A potential weakness of the above approach is that the volunteer may have become more familiar with the device after each experiment which are conducted sequentially. After a post experimental analysis, we found that this is not a concern. Methodology and experimentation The main target of this work is to contrast several hypotheses related to the efficiency in the biometric recognition context and to do so a whole biometric recognition process was designed. Next, the suggested hypotheses, the algorithms used and the methodology followed to process the data are described. Hypotheses On the basis of the literature about efficiency [26] and face recognition [12] we had suggested several hypotheses that are all derived in the Results and discussion. Those are the following: 1. Performance results are better in the last experiments (i.e. E4 > E3 > E2 > E1) because (a) the user has already acquired more habituation and (b) the user has received more information about the process. This should involve better images quality and therefore, better results.
6 Page 6 of The audio feedback is more useful than the information because it is provided in real time and the users can correct bad postures on the spot. 3. There are less performance variations in the last experiments (i.e. E4 < E3 < E2 < E1) because the user is more habituated to the system and makes less mistakes. 4. The number of valid images is higher in the last experiments because of the habituation because (a) the user has already acquired more habituation and (b) the user has received more information about the process. Algorithms applied We describe the face recognition system designed according to the well-known biometric recognition schema (Fig. 3). These algorithms were applied once all the images had been collected except the face detector used for giving audio feedback in real time. The database acquired contains self-images of visual impaired individuals, then many of them are generally rotated, blurred or not centred [36]. In order to overcome this problem we have normalized the images and applied a face detection algorithm. Furthermore we have used an alignment-free based face recognition algorithm. Audio feedback The audio feedback was provided to the users as a function of the face detection confidence, applying a Viola-Jones based algorithm (an example is shown in Fig. 4). The feedback consisted of three different sinusoidal wave sounds with three different frequencies: the lowest (1.5 khz) indicates non face/partial face detected, the medium (4.5 khz) indicates non frontal face and the highest (7.5 khz) indicates frontal face. These sounds are intended to alert the users about the current quality of image and encourage them to better locate the face. Pre processing One of the most prejudicial factors for face recognition is lightning [14], so that we have applied a lightning normalization to improve the performance [25]. Then, in order to use only the images that contain faces we have used a Viola-Jones based [32] implementation for face detection and finally the face images were cropped to delete noise and normalize the size. An example of the final images is in Fig. 3. Fig. 3 Biometric Recognition process in the evaluation. Examples of the images obtained are over the Capture and Pre-process boxes. Over the Matching box is an example of the SIFT application.
7 Page 7 of 11 Fig. 4 Illustration of audio feedback on image quality assessment [34]. Feature extraction The application of the classic alignment-based algorithms (e.g. PCA, LDA, etc.) could involve poor results with this particular set of images because the landmarks used as references for the alignment are in many cases occluded or distorted. For instance, in many of them could be difficult to differentiate the eyes from the eyebrows. Thus, we have used SIFT [18], an alignment-free-based method initially developed for object recognition but also used in face recognition approaches [13]. This algorithm extracts several keypoints from the high contrast regions of the image reducing local variations errors and then being resistant to distortion, orientation, changes in the image scale and noise (then accomplishing all our requirements). Once the SIFT had been applied, each face image was divided in several descriptors making up the template. Matching The SIFT algorithm returns the number of matches between two images. A match is obtained when the distance between the first and the second nearest neighbour between 2 descriptors is under a given threshold. Notice that comparing image A with image B can return a different number of matches than comparing image B with image A. Then, once the SIFT had returned the number of matches between two images, they were normalized to the number of descriptors of both to obtain a score: ( matchesab Score = mean (1) descriptorsa + matchesba ). descriptorsb Applying this kind of normalization the score will be low as the number of matches between two images is always too much lower than the number of descriptors. In order to calculate genuine and impostor rates we have obtained the templates from the session 1, being the image with the highest confidence the template for each combination of user-experiment. The genuine rates were computed matching each user-experiment template with all the images from the same user-experiment of the session 2. Methodology applied to process the data A first approach to the genuine scores has shown meaningful differences from some users to others representing no consistence as to obtain broad conclusions (Fig. 5, left).
8 Page 8 of 11 Fig. 5 Four random users performance results in the four experiments. The x axis is the time and the y axis is the genuine score. The red lines are the scores mean for each time slot (μ R). Thus it is necessary to normalize the results on a user by user basis with the baseline in order to obtain reliable results. To obtain the scores evolution in time, we have divided each user interaction (each user-experiment) into three parts of the same length, namely t1 (first part), t2 (second part) and t3 (third part). Then, we have calculated the mean score per each user-part and normalized it (μ R) to the same part in the baseline (E1) (Fig. 5, right). µ t k =µt k µt 1 µ t 1 for k {2, 3, 4}, for t {1, 2, 3}. (2) Then, we have measured the differences in the genuine scores between t1 and t3 (the beginning and the end of the interactions). Results and discussion In this section we contrast and discuss all the suggested hypotheses with the results obtained. First, we have used the t test between the pairs t1 t3 for each experiment (except for Experiment 1 which is not normalized) to validate the data. The t test showed these p values: pexp2 = 0.12, pexp3 = 0.09, pexp4 = Authors conclude that the database size should be increased in order to obtain more reliable and statistically significant results. Using the current database and following the initial order of hypotheses: 1. According to the results obtained, the experiments order (according to the performance evolution in time) is not as expected and the correct order is E4 > E2 > E3 > E1 as shown in Fig. 6. The fact that the results in E2 outperform those of E3 points out that the audio feedback could be more useful than the previous instructions. As E2 has obtained better scores, we also suggest that the audio feedback is even more effective than the habituation. 2. The audio feedback was more successful than the instructions given: as shown in Fig. 6, E2 and E4 (those experiments where the audio feedback was provided) are better in performance.
9 Page 9 of 11 Fig. 6 A boxplot of normalized genuine scores values for the four experiments for t1 (a) and t3 (b). The y axis is the genuine score and the x axis is the experiment. 3. The Fig. 6, where the variance is represented by the boxplots, shows that there is not an experiment dependency regarding the performance variance as it does not tend to change in any experiment. This fact shows that users did not get habituated to the system as much as to gain consistency in the results. 4. The experiments order with regards to the amount of valid images in this case is as expected (according to the number of valid images): E > E > E > E Figure 6 shows also that performance increases in time in all cases. Therefore, though the performance evolution is not consistent in all users, its tendency is to increase in time. Conclusions and future work This work shows the high influence of the time on usability concerns in biometrics, specifically for visually impaired people: the longer the interaction the better the performance. It also covers a gap as we did not find in the literature any other study of the time spent in the face recognition for disabled people (the accessibility studies are scarce in biometrics). Regarding the feedback, the previous works in biometrics (mainly carried out by NIST) were based on provide images to users. In this experiment, we have successfully applied audio feedback in real time and we suggest that it is more effective than previous instructions, but even more effective is to use both modes of feedback jointly. Regarding accessibility, we have found big variations from one user to another when processing the received feedback. Then, for some of the users the audio is more helpful and other users process the previous instructions better. This fact strengthen our suggestion of provide both feedback modes at the same time (E4). We have also found that users acquired skills on taking self-photos during the process because the number of valid images increases from one experiment to another. Nevertheless, it is not consistent with the performance as we have obtained more valid images in E3 than in E2 but the performance in E2 is better. This fact reinforces our suggestion that audio feedback is more effective than instructions and even that habituation. The performance results obtained are under the state of the art as expected due to evident reasons.
10 Page 10 of 11 Although our findings suggest that a continuous use of this technology by visually impaired people would lead to improve the final results. It is necessary to extend this work including other different kinds of feedback (e.g. mobile vibration, different sounds, etc.). Another future project could be to implement this work in a real application for common mobile devices including both feedback modes. Authors contributions RB made the data analysis and the experiments planning. Furthermore he wrote the paper. NP directed the whole experiment. RW has gathered the database. RS has reviewed the paper and gave a final approval of it. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Author details 1 University Carlos III, Madrid, Avda. de la Universidad, 30, Leganes, Spain. 2 University of Surrey, Surrey GU2 7XH, UK. Acknowledgements This work has been supported by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness by the project TEC : URBE-Universal Access through Biometrics in Mobile Scenarios. Compliance with ethical guidelines Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Received: 14 October 2014 Accepted: 31 July 2015 References 1. International Organization for Standardization (1999 ) ISO 13407:1999. Human-centred design processes for interactive systems 2. Abidin A, Xie H, Wong KW (2013) Touch screen with audio feedback: Content analysis and the effect of spatial ability on blind people s sense of position of web pages. In: Research and Innovation in Information Systems (ICRIIS), 2013 International Conference, pp Atos: Ukps biometric enrolment trial (2005) 4. Barra S, De Marsico M, Galdi C, Riccio D, Wechsler H (2013) Fame: face authentication for mobile encounter. In: Biometric Measurements and Systems for Security and Medical Applications (BIOMS), IEEE Workshop, pp Blanco-Gonzalo R, Diaz-Fernandez L, Miguel-Hurtado O, Sanchez-Reillo R (2014) Usability evaluation of biometrics in mobile environments. In: Hippe ZS, Kulikowski JL, Mroczek T, Wtorek J (eds.) Human-computer systems interaction: backgrounds and applications 3, advances in intelligent systems and computing, vol 300. Springer International Publishing, New York, pp doi: / _24 6. Blanco-Gonzalo R, Sanchez-Reillo R, Miguel-Hurtado O, Bella-Pulgarin E (2014) Automatic usability and stress analysis in mobile biometrics, Image Vision Comput 32(12): Chagnaadorj O, Tanaka J (2014) Gesture input as an out-of-band channel. J Inform Process Syst 10(1): Cho H, Choy M (2014) Personal mobile album/diary application development. J Converg 5(1): Choong YY, Theofanos M, Guan H (2012) Fingerprint self-captures: Usability of a fingerprint system with real-time feedback. In: Biometrics: theory, applications and systems (BTAS), 2012 IEEE Fifth International Conference, pp Cisco: Cisco visual networking index (2014) Global mobile data traffic forecast update, cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/serviceprovider/visual-networking-index-vni/white_paper_c html. Accessed 5 Aug Guan H, Theofanos M, Choong YY, Stanton B (2011) Real-time feedback for usable fingerprint systems. In: Biometrics (IJCB), 2011 International Joint Conference, pp Jain AK, Li SZ (2005) Handbook of Face Recognition. Springer-Verlag New York Inc, Secaucus 13. Kamencay P, Breznan M, Jelsovka D, Zachariasova M (2012) Improved face recognition method based on segmentation algorithm using sift-pca. In: Telecommunications and signal processing (TSP) th International Conference, pp Kim H, Lee SH, Sohn MK, Kim DJ (2014) Illumination invariant head pose estimation using random forests classifier and binary pattern run length matrix. Human-Centric Comput Inform Sci 4(1):9 15. Kukula E (2008) Design and evaluation of the human-biometric sensor interaction method. PhD thesis, Purdue University, USA 16. Kukula E, Sutton M, Elliott S (2010) The human biometric-sensor interaction evaluation method: Biometric performance and usability measurements. Instrum Measurement IEEE Trans 59(4): Lee IY, Park SW (2013) Anonymous authentication scheme based on NTRU for the protection of payment information in NFC mobile environment. J Inform Process Syst 9(3): Lowe D (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vision 60(2): Marcel S, McCool C, Matějka P, Ahonen T, Černocký J, Chakraborty S et al (2010) On the results of the first mobile biometry (mobio) face and speaker verification evaluation. In: Nay D, Ataltepe Z, Aksoy S (eds) Recognizing Patterns in Signals, Speech, Images and Videos, vol 6388., Lecture notes in computer sciencespringer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp
11 Page 11 of Ravi V, Nishanth K (2013) A computational intelligence based online data imputation method: An application for banking. J Converg 9(4): Riley C, McCracken H, Buckner K (2007) Fingers, veins and the grey pound: Accessibility of biometric technology. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Cognitive Ergonomics: Invent! Explore!, ECCE 07, ACM, New York, pp Sanchez-Reillo R, Blanco-Gonzalo R, Liu-Jimenez J, Lopez M, Canto E (2013) Universal access through biometrics in mobile scenarios. In: Proceedings ICCST2013: 47th annual IEEE International Carnahan Conference on Security Technology 23. Seo H, Choy Y (2014) Id credit scoring system based on application scoring system: Conceptual online id credit for id integrated environment. J Converg 5(1): Singh R, Singh P, Duhan M (2014) An effective implementation of security based algorithmic approach in mobile adhoc networks. Human-Centric Comput Inform Sci 4(1):7 25. Tan X, Triggs B (2010) Enhanced local texture feature sets for face recognition under difficult lighting conditions. Image Process IEEE Trans 19(6): Theofanos MF, Stanton BC, Wolfson C (2008) Usability and biometrics: Ensuring successful biometric systems. In: International Workshop on Usability and Biometrics, p Theofanos MF, Stanton BC, Orandi S, Micheals R (2007) Effects of scanner height on fingerprint capture. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg NISTIT 7382 (2006) 28. Theofanos MF, Stanton BC, Micheals R Usability testing of face image capture for us ports of entry. In: 2nd IEEE International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems. BTAS, pp Tresadern P, Cootes T, Poh N, Matejka P, Hadid A, Levy C (2013) Mobile biometrics: Combined face and voice verification for a mobile platform. Pervasive Comput IEEE 12(1): Vazquez-Fernandez E, Garcia-Pardo H, Gonzalez-Jimenez D, Perez-Freire L (2011) Built-in face recognition for smart photo sharing in mobile devices. In: Multimedia and Expo (ICME), 2011 IEEE International Conference, pp Verma P, Singh R, Singh A (2013) A framework to integrate speech based interface for blind web users on the websites of public interest. Human-Centric Comput Inform Sci 3(1): Viola P, Jones M (2001) Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference, vol. 1, pp I-511 I Wamsley A, Elliott S, Dunkelberger C, Mershon M (2011) Analysis of slap segmentation and HBSI errors across different force levels. In: Security Technology (ICCST), 2011 IEEE International Carnahan Conference, pp Wong R, Poh N, Kittler J, Frohlich D (2010) Interactive quality-driven feedback for biometric systems. In: Biometrics: Theory Applications and Systems (BTAS), 2010 Fourth IEEE International Conference, pp World Health Organization: WHO ((2011)) World report on disability, Yang X, Peng G, Cai Z, Zeng K (2013) Occluded and low resolution face detection with hierarchical deformable model. J Converg 4(2): Kowtko MA (2014) Biometric authentication for older adults. Systems, Applications and Technology Conference (LISAT), 2014 IEEE Long Island, pp 1 6
About user acceptance in hand, face and signature biometric systems
 About user acceptance in hand, face and signature biometric systems Aythami Morales, Miguel A. Ferrer, Carlos M. Travieso, Jesús B. Alonso Instituto Universitario para el Desarrollo Tecnológico y la Innovación
About user acceptance in hand, face and signature biometric systems Aythami Morales, Miguel A. Ferrer, Carlos M. Travieso, Jesús B. Alonso Instituto Universitario para el Desarrollo Tecnológico y la Innovación
Biometric Recognition: How Do I Know Who You Are?
 Biometric Recognition: How Do I Know Who You Are? Anil K. Jain Department of Computer Science and Engineering, 3115 Engineering Building, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA jain@cse.msu.edu
Biometric Recognition: How Do I Know Who You Are? Anil K. Jain Department of Computer Science and Engineering, 3115 Engineering Building, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA jain@cse.msu.edu
Biometric Signature for Mobile Devices
 Chapter 13 Biometric Signature for Mobile Devices Maria Villa and Abhishek Verma CONTENTS 13.1 Biometric Signature Recognition 309 13.2 Introduction 310 13.2.1 How Biometric Signature Works 310 13.2.2
Chapter 13 Biometric Signature for Mobile Devices Maria Villa and Abhishek Verma CONTENTS 13.1 Biometric Signature Recognition 309 13.2 Introduction 310 13.2.1 How Biometric Signature Works 310 13.2.2
PERFORMANCE TESTING EVALUATION REPORT OF RESULTS
 COVER Page 1 / 139 PERFORMANCE TESTING EVALUATION REPORT OF RESULTS Copy No.: 1 CREATED BY: REVIEWED BY: APPROVED BY: Dr. Belen Fernandez Saavedra Dr. Raul Sanchez-Reillo Dr. Raul Sanchez-Reillo Date:
COVER Page 1 / 139 PERFORMANCE TESTING EVALUATION REPORT OF RESULTS Copy No.: 1 CREATED BY: REVIEWED BY: APPROVED BY: Dr. Belen Fernandez Saavedra Dr. Raul Sanchez-Reillo Dr. Raul Sanchez-Reillo Date:
SVC2004: First International Signature Verification Competition
 SVC2004: First International Signature Verification Competition Dit-Yan Yeung 1, Hong Chang 1, Yimin Xiong 1, Susan George 2, Ramanujan Kashi 3, Takashi Matsumoto 4, and Gerhard Rigoll 5 1 Hong Kong University
SVC2004: First International Signature Verification Competition Dit-Yan Yeung 1, Hong Chang 1, Yimin Xiong 1, Susan George 2, Ramanujan Kashi 3, Takashi Matsumoto 4, and Gerhard Rigoll 5 1 Hong Kong University
Title Goes Here Algorithms for Biometric Authentication
 Title Goes Here Algorithms for Biometric Authentication February 2003 Vijayakumar Bhagavatula 1 Outline Motivation Challenges Technology: Correlation filters Example results Summary 2 Motivation Recognizing
Title Goes Here Algorithms for Biometric Authentication February 2003 Vijayakumar Bhagavatula 1 Outline Motivation Challenges Technology: Correlation filters Example results Summary 2 Motivation Recognizing
Evaluation of Biometric Systems. Christophe Rosenberger
 Evaluation of Biometric Systems Christophe Rosenberger Outline GREYC research lab Evaluation: a love story Evaluation of biometric systems Quality of biometric templates Conclusions & perspectives 2 GREYC
Evaluation of Biometric Systems Christophe Rosenberger Outline GREYC research lab Evaluation: a love story Evaluation of biometric systems Quality of biometric templates Conclusions & perspectives 2 GREYC
Challenging areas:- Hand gesture recognition is a growing very fast and it is I. INTRODUCTION
 Hand gesture recognition for vehicle control Bhagyashri B.Jakhade, Neha A. Kulkarni, Sadanand. Patil Abstract: - The rapid evolution in technology has made electronic gadgets inseparable part of our life.
Hand gesture recognition for vehicle control Bhagyashri B.Jakhade, Neha A. Kulkarni, Sadanand. Patil Abstract: - The rapid evolution in technology has made electronic gadgets inseparable part of our life.
Feature Extraction Techniques for Dorsal Hand Vein Pattern
 Feature Extraction Techniques for Dorsal Hand Vein Pattern Pooja Ramsoful, Maleika Heenaye-Mamode Khan Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Mauritius Mauritius pooja.ramsoful@umail.uom.ac.mu,
Feature Extraction Techniques for Dorsal Hand Vein Pattern Pooja Ramsoful, Maleika Heenaye-Mamode Khan Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Mauritius Mauritius pooja.ramsoful@umail.uom.ac.mu,
EFFICIENT ATTENDANCE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM USING FACE DETECTION AND RECOGNITION
 EFFICIENT ATTENDANCE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM USING FACE DETECTION AND RECOGNITION 1 Arun.A.V, 2 Bhatath.S, 3 Chethan.N, 4 Manmohan.C.M, 5 Hamsaveni M 1,2,3,4,5 Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
EFFICIENT ATTENDANCE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM USING FACE DETECTION AND RECOGNITION 1 Arun.A.V, 2 Bhatath.S, 3 Chethan.N, 4 Manmohan.C.M, 5 Hamsaveni M 1,2,3,4,5 Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
Haptic presentation of 3D objects in virtual reality for the visually disabled
 Haptic presentation of 3D objects in virtual reality for the visually disabled M Moranski, A Materka Institute of Electronics, Technical University of Lodz, Wolczanska 211/215, Lodz, POLAND marcin.moranski@p.lodz.pl,
Haptic presentation of 3D objects in virtual reality for the visually disabled M Moranski, A Materka Institute of Electronics, Technical University of Lodz, Wolczanska 211/215, Lodz, POLAND marcin.moranski@p.lodz.pl,
Second Symposium & Workshop on ICAO-Standard MRTDs, Biometrics and Security
 Second Symposium & Workshop on ICAO-Standard MRTDs, Biometrics and Security Face Biometric Capture & Applications Terry Hartmann Director and Global Solution Lead Secure Identification & Biometrics UNISYS
Second Symposium & Workshop on ICAO-Standard MRTDs, Biometrics and Security Face Biometric Capture & Applications Terry Hartmann Director and Global Solution Lead Secure Identification & Biometrics UNISYS
Biometric Authentication for secure e-transactions: Research Opportunities and Trends
 Biometric Authentication for secure e-transactions: Research Opportunities and Trends Fahad M. Al-Harby College of Computer and Information Security Naif Arab University for Security Sciences (NAUSS) fahad.alharby@nauss.edu.sa
Biometric Authentication for secure e-transactions: Research Opportunities and Trends Fahad M. Al-Harby College of Computer and Information Security Naif Arab University for Security Sciences (NAUSS) fahad.alharby@nauss.edu.sa
An Un-awarely Collected Real World Face Database: The ISL-Door Face Database
 An Un-awarely Collected Real World Face Database: The ISL-Door Face Database Hazım Kemal Ekenel, Rainer Stiefelhagen Interactive Systems Labs (ISL), Universität Karlsruhe (TH), Am Fasanengarten 5, 76131
An Un-awarely Collected Real World Face Database: The ISL-Door Face Database Hazım Kemal Ekenel, Rainer Stiefelhagen Interactive Systems Labs (ISL), Universität Karlsruhe (TH), Am Fasanengarten 5, 76131
3D Face Recognition System in Time Critical Security Applications
 Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research 25 (7): 1619-1623, 2017 ISSN 1990-9233 IDOSI Publications, 2017 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.mejsr.2017.1619.1623 3D Face Recognition System in Time Critical Security Applications
Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research 25 (7): 1619-1623, 2017 ISSN 1990-9233 IDOSI Publications, 2017 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.mejsr.2017.1619.1623 3D Face Recognition System in Time Critical Security Applications
Distinguishing Identical Twins by Face Recognition
 Distinguishing Identical Twins by Face Recognition P. Jonathon Phillips, Patrick J. Flynn, Kevin W. Bowyer, Richard W. Vorder Bruegge, Patrick J. Grother, George W. Quinn, and Matthew Pruitt Abstract The
Distinguishing Identical Twins by Face Recognition P. Jonathon Phillips, Patrick J. Flynn, Kevin W. Bowyer, Richard W. Vorder Bruegge, Patrick J. Grother, George W. Quinn, and Matthew Pruitt Abstract The
Technology offer. Aerial obstacle detection software for the visually impaired
 Technology offer Aerial obstacle detection software for the visually impaired Technology offer: Aerial obstacle detection software for the visually impaired SUMMARY The research group Mobile Vision Research
Technology offer Aerial obstacle detection software for the visually impaired Technology offer: Aerial obstacle detection software for the visually impaired SUMMARY The research group Mobile Vision Research
Automatic Licenses Plate Recognition System
 Automatic Licenses Plate Recognition System Garima R. Yadav Dept. of Electronics & Comm. Engineering Marathwada Institute of Technology, Aurangabad (Maharashtra), India yadavgarima08@gmail.com Prof. H.K.
Automatic Licenses Plate Recognition System Garima R. Yadav Dept. of Electronics & Comm. Engineering Marathwada Institute of Technology, Aurangabad (Maharashtra), India yadavgarima08@gmail.com Prof. H.K.
Experiments with An Improved Iris Segmentation Algorithm
 Experiments with An Improved Iris Segmentation Algorithm Xiaomei Liu, Kevin W. Bowyer, Patrick J. Flynn Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556, U.S.A.
Experiments with An Improved Iris Segmentation Algorithm Xiaomei Liu, Kevin W. Bowyer, Patrick J. Flynn Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556, U.S.A.
A Proposal for Security Oversight at Automated Teller Machine System
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 10, Issue 6 (June 2014), PP.18-25 A Proposal for Security Oversight at Automated
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 10, Issue 6 (June 2014), PP.18-25 A Proposal for Security Oversight at Automated
ENHANCHED PALM PRINT IMAGES FOR PERSONAL ACCURATE IDENTIFICATION
 ENHANCHED PALM PRINT IMAGES FOR PERSONAL ACCURATE IDENTIFICATION Prof. Rahul Sathawane 1, Aishwarya Shende 2, Pooja Tete 3, Naina Chandravanshi 4, Nisha Surjuse 5 1 Prof. Rahul Sathawane, Information Technology,
ENHANCHED PALM PRINT IMAGES FOR PERSONAL ACCURATE IDENTIFICATION Prof. Rahul Sathawane 1, Aishwarya Shende 2, Pooja Tete 3, Naina Chandravanshi 4, Nisha Surjuse 5 1 Prof. Rahul Sathawane, Information Technology,
Student Attendance Monitoring System Via Face Detection and Recognition System
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 2 Issue 11 May 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Student Attendance Monitoring System Via Face Detection and Recognition System Pinal
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 2 Issue 11 May 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Student Attendance Monitoring System Via Face Detection and Recognition System Pinal
Specific Sensors for Face Recognition
 Specific Sensors for Face Recognition Walid Hizem, Emine Krichen, Yang Ni, Bernadette Dorizzi, and Sonia Garcia-Salicetti Département Electronique et Physique, Institut National des Télécommunications,
Specific Sensors for Face Recognition Walid Hizem, Emine Krichen, Yang Ni, Bernadette Dorizzi, and Sonia Garcia-Salicetti Département Electronique et Physique, Institut National des Télécommunications,
Vein and Fingerprint Identification Multi Biometric System: A Novel Approach
 Vein and Fingerprint Identification Multi Biometric System: A Novel Approach Hatim A. Aboalsamh Abstract In this paper, a compact system that consists of a Biometrics technology CMOS fingerprint sensor
Vein and Fingerprint Identification Multi Biometric System: A Novel Approach Hatim A. Aboalsamh Abstract In this paper, a compact system that consists of a Biometrics technology CMOS fingerprint sensor
Introduction to Biometrics 1
 Introduction to Biometrics 1 Gerik Alexander v.graevenitz von Graevenitz Biometrics, Bonn, Germany May, 14th 2004 Introduction to Biometrics Biometrics refers to the automatic identification of a living
Introduction to Biometrics 1 Gerik Alexander v.graevenitz von Graevenitz Biometrics, Bonn, Germany May, 14th 2004 Introduction to Biometrics Biometrics refers to the automatic identification of a living
Face Detection: A Literature Review
 Face Detection: A Literature Review Dr.Vipulsangram.K.Kadam 1, Deepali G. Ganakwar 2 Professor, Department of Electronics Engineering, P.E.S. College of Engineering, Nagsenvana Aurangabad, Maharashtra,
Face Detection: A Literature Review Dr.Vipulsangram.K.Kadam 1, Deepali G. Ganakwar 2 Professor, Department of Electronics Engineering, P.E.S. College of Engineering, Nagsenvana Aurangabad, Maharashtra,
LabVIEW based Intelligent Frontal & Non- Frontal Face Recognition System
 LabVIEW based Intelligent Frontal & Non- Frontal Face Recognition System Muralindran Mariappan, Manimehala Nadarajan, and Karthigayan Muthukaruppan Abstract Face identification and tracking has taken a
LabVIEW based Intelligent Frontal & Non- Frontal Face Recognition System Muralindran Mariappan, Manimehala Nadarajan, and Karthigayan Muthukaruppan Abstract Face identification and tracking has taken a
Iris Recognition-based Security System with Canny Filter
 Canny Filter Dr. Computer Engineering Department, University of Technology, Baghdad-Iraq E-mail: hjhh2007@yahoo.com Received: 8/9/2014 Accepted: 21/1/2015 Abstract Image identification plays a great role
Canny Filter Dr. Computer Engineering Department, University of Technology, Baghdad-Iraq E-mail: hjhh2007@yahoo.com Received: 8/9/2014 Accepted: 21/1/2015 Abstract Image identification plays a great role
Book Cover Recognition Project
 Book Cover Recognition Project Carolina Galleguillos Department of Computer Science University of California San Diego La Jolla, CA 92093-0404 cgallegu@cs.ucsd.edu Abstract The purpose of this project
Book Cover Recognition Project Carolina Galleguillos Department of Computer Science University of California San Diego La Jolla, CA 92093-0404 cgallegu@cs.ucsd.edu Abstract The purpose of this project
Real-Time Face Detection and Tracking for High Resolution Smart Camera System
 Digital Image Computing Techniques and Applications Real-Time Face Detection and Tracking for High Resolution Smart Camera System Y. M. Mustafah a,b, T. Shan a, A. W. Azman a,b, A. Bigdeli a, B. C. Lovell
Digital Image Computing Techniques and Applications Real-Time Face Detection and Tracking for High Resolution Smart Camera System Y. M. Mustafah a,b, T. Shan a, A. W. Azman a,b, A. Bigdeli a, B. C. Lovell
The Role of Biometrics in Virtual Communities. and Digital Governments
 The Role of Biometrics in Virtual Communities and Digital Governments Chang-Tsun Li Department of Computer Science University of Warwick Coventry CV4 7AL UK Tel: +44 24 7657 3794 Fax: +44 24 7657 3024
The Role of Biometrics in Virtual Communities and Digital Governments Chang-Tsun Li Department of Computer Science University of Warwick Coventry CV4 7AL UK Tel: +44 24 7657 3794 Fax: +44 24 7657 3024
User Awareness of Biometrics
 Advances in Networks, Computing and Communications 4 User Awareness of Biometrics B.J.Edmonds and S.M.Furnell Network Research Group, University of Plymouth, Plymouth, United Kingdom e-mail: info@network-research-group.org
Advances in Networks, Computing and Communications 4 User Awareness of Biometrics B.J.Edmonds and S.M.Furnell Network Research Group, University of Plymouth, Plymouth, United Kingdom e-mail: info@network-research-group.org
License Plate Localisation based on Morphological Operations
 License Plate Localisation based on Morphological Operations Xiaojun Zhai, Faycal Benssali and Soodamani Ramalingam School of Engineering & Technology University of Hertfordshire, UH Hatfield, UK Abstract
License Plate Localisation based on Morphological Operations Xiaojun Zhai, Faycal Benssali and Soodamani Ramalingam School of Engineering & Technology University of Hertfordshire, UH Hatfield, UK Abstract
Effective and Efficient Fingerprint Image Postprocessing
 Effective and Efficient Fingerprint Image Postprocessing Haiping Lu, Xudong Jiang and Wei-Yun Yau Laboratories for Information Technology 21 Heng Mui Keng Terrace, Singapore 119613 Email: hplu@lit.org.sg
Effective and Efficient Fingerprint Image Postprocessing Haiping Lu, Xudong Jiang and Wei-Yun Yau Laboratories for Information Technology 21 Heng Mui Keng Terrace, Singapore 119613 Email: hplu@lit.org.sg
Biometrics 2/23/17. the last category for authentication methods is. this is the realm of biometrics
 CSC362, Information Security the last category for authentication methods is Something I am or do, which means some physical or behavioral characteristic that uniquely identifies the user and can be used
CSC362, Information Security the last category for authentication methods is Something I am or do, which means some physical or behavioral characteristic that uniquely identifies the user and can be used
Toward a Non-Intrusive, Physio- Behavioral Biometric for Smartphones
 Toward a Non-Intrusive, Physio- Behavioral Biometric for Smartphones Esther Vasiete Vishal Patel Department of Computer Science UMIACS University of Colorado Boulder University of Maryland esther.vasiete@colorado.edu
Toward a Non-Intrusive, Physio- Behavioral Biometric for Smartphones Esther Vasiete Vishal Patel Department of Computer Science UMIACS University of Colorado Boulder University of Maryland esther.vasiete@colorado.edu
An Overview of Biometrics. Dr. Charles C. Tappert Seidenberg School of CSIS, Pace University
 An Overview of Biometrics Dr. Charles C. Tappert Seidenberg School of CSIS, Pace University What are Biometrics? Biometrics refers to identification of humans by their characteristics or traits Physical
An Overview of Biometrics Dr. Charles C. Tappert Seidenberg School of CSIS, Pace University What are Biometrics? Biometrics refers to identification of humans by their characteristics or traits Physical
TECHNICAL AND OPERATIONAL NOTE ON CHANGE MANAGEMENT OF GAMBLING TECHNICAL SYSTEMS AND APPROVAL OF THE SUBSTANTIAL CHANGES TO CRITICAL COMPONENTS.
 TECHNICAL AND OPERATIONAL NOTE ON CHANGE MANAGEMENT OF GAMBLING TECHNICAL SYSTEMS AND APPROVAL OF THE SUBSTANTIAL CHANGES TO CRITICAL COMPONENTS. 1. Document objective This note presents a help guide for
TECHNICAL AND OPERATIONAL NOTE ON CHANGE MANAGEMENT OF GAMBLING TECHNICAL SYSTEMS AND APPROVAL OF THE SUBSTANTIAL CHANGES TO CRITICAL COMPONENTS. 1. Document objective This note presents a help guide for
Card IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence
 2015 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence Cynthia Sthembile Mlambo Council for Scientific and Industrial Research Information Security Pretoria, South Africa smlambo@csir.co.za Distortion
2015 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence Cynthia Sthembile Mlambo Council for Scientific and Industrial Research Information Security Pretoria, South Africa smlambo@csir.co.za Distortion
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 12, December ISSN IJSER
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 12, December-2016 192 A Novel Approach For Face Liveness Detection To Avoid Face Spoofing Attacks Meenakshi Research Scholar,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 12, December-2016 192 A Novel Approach For Face Liveness Detection To Avoid Face Spoofing Attacks Meenakshi Research Scholar,
Image Extraction using Image Mining Technique
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) e-issn: 2250-3021, p-issn: 2278-8719 Vol. 3, Issue 9 (September. 2013), V2 PP 36-42 Image Extraction using Image Mining Technique Prof. Samir Kumar Bandyopadhyay,
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) e-issn: 2250-3021, p-issn: 2278-8719 Vol. 3, Issue 9 (September. 2013), V2 PP 36-42 Image Extraction using Image Mining Technique Prof. Samir Kumar Bandyopadhyay,
Face Recognition Based Attendance System with Student Monitoring Using RFID Technology
 Face Recognition Based Attendance System with Student Monitoring Using RFID Technology Abhishek N1, Mamatha B R2, Ranjitha M3, Shilpa Bai B4 1,2,3,4 Dept of ECE, SJBIT, Bangalore, Karnataka, India Abstract:
Face Recognition Based Attendance System with Student Monitoring Using RFID Technology Abhishek N1, Mamatha B R2, Ranjitha M3, Shilpa Bai B4 1,2,3,4 Dept of ECE, SJBIT, Bangalore, Karnataka, India Abstract:
Using a Game Development Platform to Improve Advanced Programming Skills
 Journal of Reviews on Global Economics, 2017, 6, 328-334 328 Using a Game Development Platform to Improve Advanced Programming Skills Banyapon Poolsawas 1 and Winyu Niranatlamphong 2,* 1 Department of
Journal of Reviews on Global Economics, 2017, 6, 328-334 328 Using a Game Development Platform to Improve Advanced Programming Skills Banyapon Poolsawas 1 and Winyu Niranatlamphong 2,* 1 Department of
IRIS Biometric for Person Identification. By Lakshmi Supriya.D M.Tech 04IT6002 Dept. of Information Technology
 IRIS Biometric for Person Identification By Lakshmi Supriya.D M.Tech 04IT6002 Dept. of Information Technology What are Biometrics? Why are Biometrics used? How Biometrics is today? Iris Iris is the area
IRIS Biometric for Person Identification By Lakshmi Supriya.D M.Tech 04IT6002 Dept. of Information Technology What are Biometrics? Why are Biometrics used? How Biometrics is today? Iris Iris is the area
Identity and Message recognition by biometric signals
 Identity and Message recognition by biometric signals J. Bigun, F. Alonso-Fernandez, S. M. Karlsson, A. Mikaelyan Abstract The project addresses visual information representation, and extraction. The problem
Identity and Message recognition by biometric signals J. Bigun, F. Alonso-Fernandez, S. M. Karlsson, A. Mikaelyan Abstract The project addresses visual information representation, and extraction. The problem
Face Detection System on Ada boost Algorithm Using Haar Classifiers
 Vol.2, Issue.6, Nov-Dec. 2012 pp-3996-4000 ISSN: 2249-6645 Face Detection System on Ada boost Algorithm Using Haar Classifiers M. Gopi Krishna, A. Srinivasulu, Prof (Dr.) T.K.Basak 1, 2 Department of Electronics
Vol.2, Issue.6, Nov-Dec. 2012 pp-3996-4000 ISSN: 2249-6645 Face Detection System on Ada boost Algorithm Using Haar Classifiers M. Gopi Krishna, A. Srinivasulu, Prof (Dr.) T.K.Basak 1, 2 Department of Electronics
Empirical Evaluation of Visible Spectrum Iris versus Periocular Recognition in Unconstrained Scenario on Smartphones
 Empirical Evaluation of Visible Spectrum Iris versus Periocular Recognition in Unconstrained Scenario on Smartphones Kiran B. Raja * R. Raghavendra * Christoph Busch * * Norwegian Biometric Laboratory,
Empirical Evaluation of Visible Spectrum Iris versus Periocular Recognition in Unconstrained Scenario on Smartphones Kiran B. Raja * R. Raghavendra * Christoph Busch * * Norwegian Biometric Laboratory,
A Comparison Study of Image Descriptors on Low- Resolution Face Image Verification
 A Comparison Study of Image Descriptors on Low- Resolution Face Image Verification Gittipat Jetsiktat, Sasipa Panthuwadeethorn and Suphakant Phimoltares Advanced Virtual and Intelligent Computing (AVIC)
A Comparison Study of Image Descriptors on Low- Resolution Face Image Verification Gittipat Jetsiktat, Sasipa Panthuwadeethorn and Suphakant Phimoltares Advanced Virtual and Intelligent Computing (AVIC)
MAV-ID card processing using camera images
 EE 5359 MULTIMEDIA PROCESSING SPRING 2013 PROJECT PROPOSAL MAV-ID card processing using camera images Under guidance of DR K R RAO DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT ARLINGTON
EE 5359 MULTIMEDIA PROCESSING SPRING 2013 PROJECT PROPOSAL MAV-ID card processing using camera images Under guidance of DR K R RAO DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT ARLINGTON
An Evaluation of Automatic License Plate Recognition Vikas Kotagyale, Prof.S.D.Joshi
 An Evaluation of Automatic License Plate Recognition Vikas Kotagyale, Prof.S.D.Joshi Department of E&TC Engineering,PVPIT,Bavdhan,Pune ABSTRACT: In the last decades vehicle license plate recognition systems
An Evaluation of Automatic License Plate Recognition Vikas Kotagyale, Prof.S.D.Joshi Department of E&TC Engineering,PVPIT,Bavdhan,Pune ABSTRACT: In the last decades vehicle license plate recognition systems
Postprint.
 http://www.diva-portal.org Postprint This is the accepted version of a paper presented at IEEE Conf. on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems, BTAS, Washington DC, USA, 27-29 Sept., 27. Citation
http://www.diva-portal.org Postprint This is the accepted version of a paper presented at IEEE Conf. on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems, BTAS, Washington DC, USA, 27-29 Sept., 27. Citation
Near Infrared Face Image Quality Assessment System of Video Sequences
 2011 Sixth International Conference on Image and Graphics Near Infrared Face Image Quality Assessment System of Video Sequences Jianfeng Long College of Electrical and Information Engineering Hunan University
2011 Sixth International Conference on Image and Graphics Near Infrared Face Image Quality Assessment System of Video Sequences Jianfeng Long College of Electrical and Information Engineering Hunan University
Controlling Humanoid Robot Using Head Movements
 Volume-5, Issue-2, April-2015 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 648-652 Controlling Humanoid Robot Using Head Movements S. Mounica 1, A. Naga bhavani 2, Namani.Niharika
Volume-5, Issue-2, April-2015 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 648-652 Controlling Humanoid Robot Using Head Movements S. Mounica 1, A. Naga bhavani 2, Namani.Niharika
Edge Histogram Descriptor for Finger Vein Recognition
 Edge Histogram Descriptor for Finger Vein Recognition Yu Lu 1, Sook Yoon 2, Daegyu Hwang 1, and Dong Sun Park 2 1 Division of Electronic and Information Engineering, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju,
Edge Histogram Descriptor for Finger Vein Recognition Yu Lu 1, Sook Yoon 2, Daegyu Hwang 1, and Dong Sun Park 2 1 Division of Electronic and Information Engineering, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju,
Travel Photo Album Summarization based on Aesthetic quality, Interestingness, and Memorableness
 Travel Photo Album Summarization based on Aesthetic quality, Interestingness, and Memorableness Jun-Hyuk Kim and Jong-Seok Lee School of Integrated Technology and Yonsei Institute of Convergence Technology
Travel Photo Album Summarization based on Aesthetic quality, Interestingness, and Memorableness Jun-Hyuk Kim and Jong-Seok Lee School of Integrated Technology and Yonsei Institute of Convergence Technology
Segmentation of Fingerprint Images
 Segmentation of Fingerprint Images Asker M. Bazen and Sabih H. Gerez University of Twente, Department of Electrical Engineering, Laboratory of Signals and Systems, P.O. box 217-75 AE Enschede - The Netherlands
Segmentation of Fingerprint Images Asker M. Bazen and Sabih H. Gerez University of Twente, Department of Electrical Engineering, Laboratory of Signals and Systems, P.O. box 217-75 AE Enschede - The Netherlands
Proposed Method for Off-line Signature Recognition and Verification using Neural Network
 e-issn: 2349-9745 p-issn: 2393-8161 Scientific Journal Impact Factor (SJIF): 1.711 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com Proposed Method for Off-line Signature
e-issn: 2349-9745 p-issn: 2393-8161 Scientific Journal Impact Factor (SJIF): 1.711 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com Proposed Method for Off-line Signature
Biometrics - A Tool in Fraud Prevention
 Biometrics - A Tool in Fraud Prevention Agenda Authentication Biometrics : Need, Available Technologies, Working, Comparison Fingerprint Technology About Enrollment, Matching and Verification Key Concepts
Biometrics - A Tool in Fraud Prevention Agenda Authentication Biometrics : Need, Available Technologies, Working, Comparison Fingerprint Technology About Enrollment, Matching and Verification Key Concepts
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Computer Science 56 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 56 (2015 ) 538 543 International Workshop on Communication for Humans, Agents, Robots, Machines and Sensors (HARMS 2015)
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 56 (2015 ) 538 543 International Workshop on Communication for Humans, Agents, Robots, Machines and Sensors (HARMS 2015)
A Study on the control Method of 3-Dimensional Space Application using KINECT System Jong-wook Kang, Dong-jun Seo, and Dong-seok Jung,
 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.11 No.9, September 2011 55 A Study on the control Method of 3-Dimensional Space Application using KINECT System Jong-wook Kang,
IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.11 No.9, September 2011 55 A Study on the control Method of 3-Dimensional Space Application using KINECT System Jong-wook Kang,
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
 Pertanika J. Sci. & Technol. 25 (S): 163-172 (2017) SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Journal homepage: http://www.pertanika.upm.edu.my/ Performance Comparison of Min-Max Normalisation on Frontal Face Detection Using
Pertanika J. Sci. & Technol. 25 (S): 163-172 (2017) SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Journal homepage: http://www.pertanika.upm.edu.my/ Performance Comparison of Min-Max Normalisation on Frontal Face Detection Using
Copyright: Conference website: Date deposited:
 Coleman M, Ferguson A, Hanson G, Blythe PT. Deriving transport benefits from Big Data and the Internet of Things in Smart Cities. In: 12th Intelligent Transport Systems European Congress 2017. 2017, Strasbourg,
Coleman M, Ferguson A, Hanson G, Blythe PT. Deriving transport benefits from Big Data and the Internet of Things in Smart Cities. In: 12th Intelligent Transport Systems European Congress 2017. 2017, Strasbourg,
Recognition System for Pakistani Paper Currency
 World Applied Sciences Journal 28 (12): 2069-2075, 2013 ISSN 1818-4952 IDOSI Publications, 2013 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wasj.2013.28.12.300 Recognition System for Pakistani Paper Currency 1 2 Ahmed Ali and
World Applied Sciences Journal 28 (12): 2069-2075, 2013 ISSN 1818-4952 IDOSI Publications, 2013 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wasj.2013.28.12.300 Recognition System for Pakistani Paper Currency 1 2 Ahmed Ali and
Presentation Attack Detection Algorithms for Finger Vein Biometrics: A Comprehensive Study
 215 11th International Conference on Signal-Image Technology & Internet-Based Systems Presentation Attack Detection Algorithms for Finger Vein Biometrics: A Comprehensive Study R. Raghavendra Christoph
215 11th International Conference on Signal-Image Technology & Internet-Based Systems Presentation Attack Detection Algorithms for Finger Vein Biometrics: A Comprehensive Study R. Raghavendra Christoph
Biometric Recognition Techniques
 Biometric Recognition Techniques Anjana Doshi 1, Manisha Nirgude 2 ME Student, Computer Science and Engineering, Walchand Institute of Technology Solapur, India 1 Asst. Professor, Information Technology,
Biometric Recognition Techniques Anjana Doshi 1, Manisha Nirgude 2 ME Student, Computer Science and Engineering, Walchand Institute of Technology Solapur, India 1 Asst. Professor, Information Technology,
Combined Approach for Face Detection, Eye Region Detection and Eye State Analysis- Extended Paper
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 10, Issue 9 (September 2014), PP.57-68 Combined Approach for Face Detection, Eye
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 10, Issue 9 (September 2014), PP.57-68 Combined Approach for Face Detection, Eye
Do-It-Yourself Object Identification Using Augmented Reality for Visually Impaired People
 Do-It-Yourself Object Identification Using Augmented Reality for Visually Impaired People Atheer S. Al-Khalifa 1 and Hend S. Al-Khalifa 2 1 Electronic and Computer Research Institute, King Abdulaziz City
Do-It-Yourself Object Identification Using Augmented Reality for Visually Impaired People Atheer S. Al-Khalifa 1 and Hend S. Al-Khalifa 2 1 Electronic and Computer Research Institute, King Abdulaziz City
Toward an Augmented Reality System for Violin Learning Support
 Toward an Augmented Reality System for Violin Learning Support Hiroyuki Shiino, François de Sorbier, and Hideo Saito Graduate School of Science and Technology, Keio University, Yokohama, Japan {shiino,fdesorbi,saito}@hvrl.ics.keio.ac.jp
Toward an Augmented Reality System for Violin Learning Support Hiroyuki Shiino, François de Sorbier, and Hideo Saito Graduate School of Science and Technology, Keio University, Yokohama, Japan {shiino,fdesorbi,saito}@hvrl.ics.keio.ac.jp
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL IN ADVANCED ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IRJAET)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL IN ADVANCED ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IRJAET) www.irjaet.com ISSN (PRINT) : 2454-4744 ISSN (ONLINE): 2454-4752 Vol. 1, Issue 4, pp.240-245, November, 2015 IRIS RECOGNITION
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL IN ADVANCED ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IRJAET) www.irjaet.com ISSN (PRINT) : 2454-4744 ISSN (ONLINE): 2454-4752 Vol. 1, Issue 4, pp.240-245, November, 2015 IRIS RECOGNITION
Postprint.
 http://www.diva-portal.org Postprint This is the accepted version of a paper presented at IEEE Intl. Conf. on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision, ICARCV, Special Session on Biometrics, Singapore,
http://www.diva-portal.org Postprint This is the accepted version of a paper presented at IEEE Intl. Conf. on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision, ICARCV, Special Session on Biometrics, Singapore,
Modern Biometric Technologies: Technical Issues and Research Opportunities
 Modern Biometric Technologies: Technical Issues and Research Opportunities Mandeep Singh Walia (Electronics and Communication Engg, Panjab University SSG Regional Centre, India) Abstract : A biometric
Modern Biometric Technologies: Technical Issues and Research Opportunities Mandeep Singh Walia (Electronics and Communication Engg, Panjab University SSG Regional Centre, India) Abstract : A biometric
Classification of Features into Strong and Weak Features for an Intelligent Online Signature Verification System
 Classification of Features into Strong and Weak Features for an Intelligent Online Signature Verification System Saad Tariq, Saqib Sarwar & Waqar Hussain Department of Electrical Engineering Air University
Classification of Features into Strong and Weak Features for an Intelligent Online Signature Verification System Saad Tariq, Saqib Sarwar & Waqar Hussain Department of Electrical Engineering Air University
Image Averaging for Improved Iris Recognition
 Image Averaging for Improved Iris Recognition Karen P. Hollingsworth, Kevin W. Bowyer, and Patrick J. Flynn University of Notre Dame Abstract. We take advantage of the temporal continuity in an iris video
Image Averaging for Improved Iris Recognition Karen P. Hollingsworth, Kevin W. Bowyer, and Patrick J. Flynn University of Notre Dame Abstract. We take advantage of the temporal continuity in an iris video
Linear Gaussian Method to Detect Blurry Digital Images using SIFT
 IJCAES ISSN: 2231-4946 Volume III, Special Issue, November 2013 International Journal of Computer Applications in Engineering Sciences Special Issue on Emerging Research Areas in Computing(ERAC) www.caesjournals.org
IJCAES ISSN: 2231-4946 Volume III, Special Issue, November 2013 International Journal of Computer Applications in Engineering Sciences Special Issue on Emerging Research Areas in Computing(ERAC) www.caesjournals.org
MATLAB DIGITAL IMAGE/SIGNAL PROCESSING TITLES
 MATLAB DIGITAL IMAGE/SIGNAL PROCESSING TITLES -2018 S.NO PROJECT CODE 1 ITIMP01 2 ITIMP02 3 ITIMP03 4 ITIMP04 5 ITIMP05 6 ITIMP06 7 ITIMP07 8 ITIMP08 9 ITIMP09 `10 ITIMP10 11 ITIMP11 12 ITIMP12 13 ITIMP13
MATLAB DIGITAL IMAGE/SIGNAL PROCESSING TITLES -2018 S.NO PROJECT CODE 1 ITIMP01 2 ITIMP02 3 ITIMP03 4 ITIMP04 5 ITIMP05 6 ITIMP06 7 ITIMP07 8 ITIMP08 9 ITIMP09 `10 ITIMP10 11 ITIMP11 12 ITIMP12 13 ITIMP13
Design a Model and Algorithm for multi Way Gesture Recognition using Motion and Image Comparison
 e-issn 2455 1392 Volume 2 Issue 10, October 2016 pp. 34 41 Scientific Journal Impact Factor : 3.468 http://www.ijcter.com Design a Model and Algorithm for multi Way Gesture Recognition using Motion and
e-issn 2455 1392 Volume 2 Issue 10, October 2016 pp. 34 41 Scientific Journal Impact Factor : 3.468 http://www.ijcter.com Design a Model and Algorithm for multi Way Gesture Recognition using Motion and
ZKTECO COLLEGE- FUNDAMENTAL OF FINGER VEIN RECOGNITION
 ZKTECO COLLEGE- FUNDAMENTAL OF FINGER VEIN RECOGNITION What are Finger Veins? Veins are blood vessels which present throughout the body as tubes that carry blood back to the heart. As its name implies,
ZKTECO COLLEGE- FUNDAMENTAL OF FINGER VEIN RECOGNITION What are Finger Veins? Veins are blood vessels which present throughout the body as tubes that carry blood back to the heart. As its name implies,
Outdoor Face Recognition Using Enhanced Near Infrared Imaging
 Outdoor Face Recognition Using Enhanced Near Infrared Imaging Dong Yi, Rong Liu, RuFeng Chu, Rui Wang, Dong Liu, and Stan Z. Li Center for Biometrics and Security Research & National Laboratory of Pattern
Outdoor Face Recognition Using Enhanced Near Infrared Imaging Dong Yi, Rong Liu, RuFeng Chu, Rui Wang, Dong Liu, and Stan Z. Li Center for Biometrics and Security Research & National Laboratory of Pattern
Manuscript Investigation in the Sinai II Project
 Manuscript Investigation in the Sinai II Project Fabian Hollaus, Ana Camba, Stefan Fiel, Sajid Saleem, Robert Sablatnig Institute of Computer Aided Automation Computer Vision Lab Vienna University of Technology
Manuscript Investigation in the Sinai II Project Fabian Hollaus, Ana Camba, Stefan Fiel, Sajid Saleem, Robert Sablatnig Institute of Computer Aided Automation Computer Vision Lab Vienna University of Technology
Computer Vision in Human-Computer Interaction
 Invited talk in 2010 Autumn Seminar and Meeting of Pattern Recognition Society of Finland, M/S Baltic Princess, 26.11.2010 Computer Vision in Human-Computer Interaction Matti Pietikäinen Machine Vision
Invited talk in 2010 Autumn Seminar and Meeting of Pattern Recognition Society of Finland, M/S Baltic Princess, 26.11.2010 Computer Vision in Human-Computer Interaction Matti Pietikäinen Machine Vision
International Journal of Engineering and Emerging Technology, Vol. 2, No. 1, January June 2017
 Measurement of Face Detection Accuracy Using Intensity Normalization Method and Homomorphic Filtering I Nyoman Gede Arya Astawa [1]*, I Ketut Gede Darma Putra [2], I Made Sudarma [3], and Rukmi Sari Hartati
Measurement of Face Detection Accuracy Using Intensity Normalization Method and Homomorphic Filtering I Nyoman Gede Arya Astawa [1]*, I Ketut Gede Darma Putra [2], I Made Sudarma [3], and Rukmi Sari Hartati
Content Based Image Retrieval Using Color Histogram
 Content Based Image Retrieval Using Color Histogram Nitin Jain Assistant Professor, Lokmanya Tilak College of Engineering, Navi Mumbai, India. Dr. S. S. Salankar Professor, G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering,
Content Based Image Retrieval Using Color Histogram Nitin Jain Assistant Professor, Lokmanya Tilak College of Engineering, Navi Mumbai, India. Dr. S. S. Salankar Professor, G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering,
The 2019 Biometric Technology Rally
 DHS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY The 2019 Biometric Technology Rally Kickoff Webinar, November 5, 2018 Arun Vemury -- DHS S&T Jake Hasselgren, John Howard, and Yevgeniy Sirotin -- The Maryland Test Facility
DHS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY The 2019 Biometric Technology Rally Kickoff Webinar, November 5, 2018 Arun Vemury -- DHS S&T Jake Hasselgren, John Howard, and Yevgeniy Sirotin -- The Maryland Test Facility
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF VARIOUS BIOMETRIC APPROACHES
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF VARIOUS BIOMETRIC APPROACHES Ramandeep Chahal Department of CSE GVIET, Banur, Punjab, India ABSTRACT Biometric is the science for recognizing an individual on the basis of his or
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF VARIOUS BIOMETRIC APPROACHES Ramandeep Chahal Department of CSE GVIET, Banur, Punjab, India ABSTRACT Biometric is the science for recognizing an individual on the basis of his or
Effects of the Unscented Kalman Filter Process for High Performance Face Detector
 Effects of the Unscented Kalman Filter Process for High Performance Face Detector Bikash Lamsal and Naofumi Matsumoto Abstract This paper concerns with a high performance algorithm for human face detection
Effects of the Unscented Kalman Filter Process for High Performance Face Detector Bikash Lamsal and Naofumi Matsumoto Abstract This paper concerns with a high performance algorithm for human face detection
City Research Online. Permanent City Research Online URL:
 Lugini, L., Marasco, E., Cukic, B. & Gashi, I. (0). Interoperability in Fingerprint Recognition: A Large-Scale Empirical Study. Paper presented at the rd Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable
Lugini, L., Marasco, E., Cukic, B. & Gashi, I. (0). Interoperability in Fingerprint Recognition: A Large-Scale Empirical Study. Paper presented at the rd Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable
Multi-sensory Tracking of Elders in Outdoor Environments on Ambient Assisted Living
 Multi-sensory Tracking of Elders in Outdoor Environments on Ambient Assisted Living Javier Jiménez Alemán Fluminense Federal University, Niterói, Brazil jjimenezaleman@ic.uff.br Abstract. Ambient Assisted
Multi-sensory Tracking of Elders in Outdoor Environments on Ambient Assisted Living Javier Jiménez Alemán Fluminense Federal University, Niterói, Brazil jjimenezaleman@ic.uff.br Abstract. Ambient Assisted
Improved SIFT Matching for Image Pairs with a Scale Difference
 Improved SIFT Matching for Image Pairs with a Scale Difference Y. Bastanlar, A. Temizel and Y. Yardımcı Informatics Institute, Middle East Technical University, Ankara, 06531, Turkey Published in IET Electronics,
Improved SIFT Matching for Image Pairs with a Scale Difference Y. Bastanlar, A. Temizel and Y. Yardımcı Informatics Institute, Middle East Technical University, Ankara, 06531, Turkey Published in IET Electronics,
A New Fake Iris Detection Method
 A New Fake Iris Detection Method Xiaofu He 1, Yue Lu 1, and Pengfei Shi 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Technology, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China {xfhe,ylu}@cs.ecnu.edu.cn
A New Fake Iris Detection Method Xiaofu He 1, Yue Lu 1, and Pengfei Shi 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Technology, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China {xfhe,ylu}@cs.ecnu.edu.cn
Wadehra Kartik, Kathpalia Mukul, Bahl Vasudha, International Journal of Advance Research, Ideas and Innovations in Technology
 ISSN: 2454-132X Impact factor: 4.295 (Volume 4, Issue 1) Available online at www.ijariit.com Hand Detection and Gesture Recognition in Real-Time Using Haar-Classification and Convolutional Neural Networks
ISSN: 2454-132X Impact factor: 4.295 (Volume 4, Issue 1) Available online at www.ijariit.com Hand Detection and Gesture Recognition in Real-Time Using Haar-Classification and Convolutional Neural Networks
An Efficient Approach for Iris Recognition by Improving Iris Segmentation and Iris Image Compression
 An Efficient Approach for Iris Recognition by Improving Iris Segmentation and Iris Image Compression K. N. Jariwala, SVNIT, Surat, India U. D. Dalal, SVNIT, Surat, India Abstract The biometric person authentication
An Efficient Approach for Iris Recognition by Improving Iris Segmentation and Iris Image Compression K. N. Jariwala, SVNIT, Surat, India U. D. Dalal, SVNIT, Surat, India Abstract The biometric person authentication
IMPACT OF SIGNATURE LEGIBILITY AND SIGNATURE TYPE IN OFF-LINE SIGNATURE VERIFICATION.
 IMPACT OF SIGNATURE LEGIBILITY AND SIGNATURE TYPE IN OFF-LINE SIGNATURE VERIFICATION F. Alonso-Fernandez a, M.C. Fairhurst b, J. Fierrez a and J. Ortega-Garcia a. a Biometric Recognition Group - ATVS,
IMPACT OF SIGNATURE LEGIBILITY AND SIGNATURE TYPE IN OFF-LINE SIGNATURE VERIFICATION F. Alonso-Fernandez a, M.C. Fairhurst b, J. Fierrez a and J. Ortega-Garcia a. a Biometric Recognition Group - ATVS,
Evaluating the Biometric Sample Quality of Handwritten Signatures
 Evaluating the Biometric Sample Quality of Handwritten Signatures Sascha Müller 1 and Olaf Henniger 2 1 Technische Universität Darmstadt, Darmstadt, Germany mueller@sec.informatik.tu-darmstadt.de 2 Fraunhofer
Evaluating the Biometric Sample Quality of Handwritten Signatures Sascha Müller 1 and Olaf Henniger 2 1 Technische Universität Darmstadt, Darmstadt, Germany mueller@sec.informatik.tu-darmstadt.de 2 Fraunhofer
Little Fingers. Big Challenges.
 Little Fingers. Big Challenges. How Image Quality and Sensor Technology Are Key for Fast, Accurate Mobile Fingerprint Recognition for Children The Challenge of Children s Identity While automated fingerprint
Little Fingers. Big Challenges. How Image Quality and Sensor Technology Are Key for Fast, Accurate Mobile Fingerprint Recognition for Children The Challenge of Children s Identity While automated fingerprint
BIOMETRICS BY- VARTIKA PAUL 4IT55
 BIOMETRICS BY- VARTIKA PAUL 4IT55 BIOMETRICS Definition Biometrics is the identification or verification of human identity through the measurement of repeatable physiological and behavioral characteristics
BIOMETRICS BY- VARTIKA PAUL 4IT55 BIOMETRICS Definition Biometrics is the identification or verification of human identity through the measurement of repeatable physiological and behavioral characteristics
Face Recognition System Based on Infrared Image
 International Journal of Engineering Inventions e-issn: 2278-7461, p-issn: 2319-6491 Volume 6, Issue 1 [October. 217] PP: 47-56 Face Recognition System Based on Infrared Image Yong Tang School of Electronics
International Journal of Engineering Inventions e-issn: 2278-7461, p-issn: 2319-6491 Volume 6, Issue 1 [October. 217] PP: 47-56 Face Recognition System Based on Infrared Image Yong Tang School of Electronics
Incorporating Touch Biometrics to Mobile One-Time Passwords: Exploration of Digits
 Incorporating Touch Biometrics to Mobile One-Time Passwords: Exploration of Digits Ruben Tolosana, Ruben Vera-Rodriguez, Julian Fierrez and Javier Ortega-Garcia Biometrics and Data Pattern Analtics (BiDA)
Incorporating Touch Biometrics to Mobile One-Time Passwords: Exploration of Digits Ruben Tolosana, Ruben Vera-Rodriguez, Julian Fierrez and Javier Ortega-Garcia Biometrics and Data Pattern Analtics (BiDA)
Iris Recognition using Histogram Analysis
 Iris Recognition using Histogram Analysis Robert W. Ives, Anthony J. Guidry and Delores M. Etter Electrical Engineering Department, U.S. Naval Academy Annapolis, MD 21402-5025 Abstract- Iris recognition
Iris Recognition using Histogram Analysis Robert W. Ives, Anthony J. Guidry and Delores M. Etter Electrical Engineering Department, U.S. Naval Academy Annapolis, MD 21402-5025 Abstract- Iris recognition
An Effective Method for Removing Scratches and Restoring Low -Quality QR Code Images
 An Effective Method for Removing Scratches and Restoring Low -Quality QR Code Images Ashna Thomas 1, Remya Paul 2 1 M.Tech Student (CSE), Mahatma Gandhi University Viswajyothi College of Engineering and
An Effective Method for Removing Scratches and Restoring Low -Quality QR Code Images Ashna Thomas 1, Remya Paul 2 1 M.Tech Student (CSE), Mahatma Gandhi University Viswajyothi College of Engineering and
Iris Segmentation & Recognition in Unconstrained Environment
 www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume - 3 Issue -8 August, 2014 Page No. 7514-7518 Iris Segmentation & Recognition in Unconstrained Environment ABSTRACT
www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume - 3 Issue -8 August, 2014 Page No. 7514-7518 Iris Segmentation & Recognition in Unconstrained Environment ABSTRACT
