Fight Risk with Risk: Relexivity of Risk and Globalization in IS
|
|
|
- Emery Burns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) ECIS 2004 Proceedings European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS) Fight Risk with Risk: Relexivity of Risk and Globalization in IS Edoardo Jacucci University of Oslo, Miria Grisot University of Oslo, Ole Hanseth University of Oslo, Follow this and additional works at: Recommended Citation Jacucci, Edoardo; Grisot, Miria; and Hanseth, Ole, "Fight Risk with Risk: Relexivity of Risk and Globalization in IS" (2004). ECIS 2004 Proceedings. Paper This material is brought to you by the European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS) at AIS Electronic Library (AISeL). It has been accepted for inclusion in ECIS 2004 Proceedings by an authorized administrator of AIS Electronic Library (AISeL). For more information, please contact
2 FIGHT RISK WITH RISK: REFLEXIVITY OF RISK AND GLOBALIZATION IN IS Jacucci, Edoardo, University of Oslo, P.O.Box 1080, Blindern, Oslo, Norway Grisot, Miria, University of Oslo, P.O.Box 1080, Blindern, Oslo, Norway Hanseth, Ole, University of Oslo, P.O.Box 1080, Blindern, Oslo, Norway Abstract In this paper, we address the following research question: How can we understand the nature of risk in IS projects in the context of globalization? Based on a case study conducted over a period of two years in a Norwegian hospital on the development and implementation of a Electronic Patient Record (EPR), the paper contributes to the current discussion on the conceptualization of risk in IS projects. Drawing upon the concept of reflexive modernization (Beck 1999) the paper makes two key contributions: firstly, it shows the limits of current risk management approaches in understanding the nature of new risks in IS generated by globalization processes; secondly, it suggest a possible theoretical framework for analyzing such nature. The research question is addressed by providing a historical and contingent analysis of the risk management dynamics emerging from the case. Keywords: Risk, Globalization, Information Systems, Electronic Patient Record, Reflexive Modernization.
3 1 INTRODUCTION As the process of globalization of our society intensifies, local IS projects face new opportunities of expansion in new geographical dimensions. The engagement in these new dimensions considerably changes the nature and scope of risks involved in the development of IS applications. In this new scenario, risk management approaches need to be reshaped and readapted to meet the new challenges. Traditional risk management studies have provided useful analytical and management tools to address the challenge of an IS project and possibly of its change (see Lyytinen et al. (1998) for an extensive overview). Yet they may come short in describing how and why local projects (and their risks) may escalate from a local to a global scope. It is the aim of this paper to address this theoretical gap and provide empirical evidence of the need of extending traditional studies. Based on a case study conducted at a major Norwegian hospital (referred to as Norhospital) regarding the development of an Electronic Patient Record system (EPR) the paper analyses the dynamics of escalation of the project from a local to a global scope. Adopting the concept of reflexive modernization as theorized by Beck (Beck 1999; Beck et al. 1994), the paper then discusses the nature of the process of globalization of the risks of the EPR project. We are not engaging in the debate on globalization as such; rather we focus on the concept of risk and its recent theorization. Our aim is to contribute to the IS field by looking at how the nature of risk has changed in the context of globalization. We believe IS research needs to question traditional risk management approaches. Specifically the paper addresses the following research question: How should we understand the nature of risk in IS projects in the context of globalization? The paper is structured as follows: first, we look at the main limits of the traditional approach to risk management and introduce an alternative perspective. Secondly, we describe the methodology adopted in the research. Thirdly, we introduce the case and provide the empirical evidence. Then, we engage in the analysis and discussion of the collected data, providing possible insights in to the relation between risk and globalization in IS. Finally we will conclude the paper by summarizing the main points. 2 THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK Overall in the IS literature, we can identify two main theoretical approaches dealing with the concept of risk and its management. The aim of this section is to introduce such approaches, and discuss their characteristics. The first can be considered a more traditional approach to interpreting and managing risk, and it has been accurately summarized by Lyytinen et al. (1998). The second approach is more recent, and adopts a perspective on risk inspired by the sociological contribution of Beck (1999) and Giddens (1990) to the debate on globalization. By means of the analysis of the main limits of the traditional approach, we suggest that ideas developed by Beck and Giddens give new insights into the conceptualization of risk and its interpretation in relation to IS development projects. Specifically, we will focus on reflexive modernization and the reflexive nature of risk. 2.1 The Traditional Risk Management Literature and its limitations Risk management approaches have traditionally focused their attention on identifying specific sources of risk and developing appropriate management techniques to control it (Alter & Ginzberg 1978; Davis 1982; McFarlan 1982; Boehm 1991; Lyytinen et al. 1998). In this literature risk is defined and analyzed within the particular context of the project, organization, and artifact to be developed. Accordingly, various management techniques and heuristics are developed in order to manage, control, or reduce risk (see Lyytinen et al for a comprehensive overview). While striving to
4 provide rich analyses and detailed prescriptions on how to deal with risk involved in IS development, these approaches seem to come short in providing a larger perspective on the source of the risks we are dealing with and why it is increasingly difficult to manage them. In risk management approaches the nature of risk is considered as being connected to peculiarities of particular projects or organizational contexts. Consequently, traditional approaches tend to provide analytical tools and solutions which apply and are limited to a micro level dimension of risk management. Acknowledging their value in providing rich and detailed cases, we believe it is critical for IS development projects to further dig into the complexities of the risk phenomena. Our motivation is twofold: first, as the case study will empirically illustrate, in large IS development projects, managers are not in control of the sources of risk, which are also not predictable; second, the very nature of risk and its propagation mode has changed with the intensification of global dynamics in terms of integration, interconnectivity and interdependency, and this has in turn heavily challenged traditional risk management. Instances of such change are well illustrated by the work of Hanseth et al. on the development of an ERP solution (Hanseth et al. 2001), and by the work of Rolland on the side-effects of globalization in the development and use of a survey management system (Rolland, 2003). 2.2 An alternative approach: Reflexivity of Risk in our Modern Society In this paragraph, we suggest an alternative theoretical framework to understand risk dynamics. In particular, we suggest that local risk management is intermingled with macro realities of our modern society. With such aim, we will first introduce the concept of Risk Society and Reflexive Modernization as theorized by Beck (1999). Risk society is the metaphor Beck uses to indicate the direction that the industrial society is taking. Precisely, he argues, contemporary western societies are living in a transitional period, in which industrial society is becoming a risk society, marked by a shifting of old relationships, rise of new uncertainties, individualism, and basic changes in major social institutions. Risk is not an invention of modernity, but in modernity it assumes a new nature: it no longer has a personal dimension, but its nature and magnitude has changed and tends to escape institutional monitoring for quantification, prevention and protection. In particular, Beck argues, our society is characterized by a process of reflexive modernization (Beck 1999; Beck et al. 1994). According to Beck, reflexive modernization means that modernity feeds back to itself, exacerbating and possibly undermining its own foundations. More clearly, as our modern society deploys its weapons of control, rationalization and integration, the society itself becomes increasingly interconnected and interdependent. In this scenario, actions taken in a local setting may have effects that propagate in an unexpected way. Thus, unintended consequences and side-effects challenge the initial aims of increased control and rationalization. From this perspective, risk does not originate within a specific confined setting, but is the very result of the modern ongoing process of rationalization and control undermined by reflexivity. The process of globalization just intensifies these dynamics, by increasing the number of interdependencies and relations. As Giddens puts it, globalization is [ ] the intensification of worldwide social relations which link distant localities in such a way that local happenings are shaped by events occurring many miles away and vice versa[ ] (Giddens 1990: 64). Hence, local events (like the IS project presented in this paper) when put in contact with processes of globalization (like the one pursued by the multinational vendor s marketing strategy) suddenly become linked and interdependent with a variety of new actors around the globe, drastically reshaping the nature and distribution of risk involved in the project.
5 2.3 Risk and Reflexivity in IS Beck is a sociologist, and technology is not explicitly considered in his work. However, it is evident that technological development plays a crucial role in the process of transformation of society. In fact, this theoretical framework to understand modern society has been interestingly applied to the analysis of studies of IT implementation and use in different organizations and work situations. In particular, specific aspects of the reflexive modernization theory have been applied to the analysis of how IT supports and enables the very process of modernization, and which consequences this creates in organizational realities. The use of this framework is quite a recent topic in IS literature. Scott (2000) builds on risk society and reflexive modernization to look at how IT and new related forms of organizational rationalization are transforming the standard spatial and temporal traditional assumptions about work and work life. As to our interests, she does not analyze issues of risk and reflexivity related to the management of the IT implementation process, but focuses the analysis on the very use of the technology. In the IS literature, few studies deal explicitly with issues of risk, reflexivity and side effects. Such concern is an explicit aim of a theoretical chapter by Hanseth and Braa (2000). The authors report issues from the reflexive modernization theory, and explore the role that IT may play. They suggest that the role of IT can be explained by the way it supports and enables, for instance, time and space distantiation, intensifying one of the dynamics of modernity. Specifically, they frame the understanding of technological development as development of control technologies which enable organizations to be distributed globally, and at the same time enable control of global logistics. Such large technologies or infrastructures emerge as interconnected systems, thus increasing the risks of transferring side effects faster and wider. This framework is applied in a later paper to the analysis of SAP implementation in a Norwegian company (Hanseth, Ciborra, Braa, 2001). Here it is discussed how events, deviations and breakdowns in the implementation process are apparitions embedded in the dynamics of modernity and globalization with its side effects. Dynamics of reflexivity and the propagation of side effects is also the topic of a study on the implementation of a new infrastructure in a global maritime classification company (Rolland, 2003). Rolland focuses on the role of disembedding mechanisms and new definitions of trust, to explore how information infrastructures are not just configured to adjust to local practices, but initiate a process of reinvention that takes place in situated practices of use. In using the reflexive modernization theory, we are interested in unfolding the dynamics shaping the socio-technical process of the implementation of the EPR. Aspects of such complex processes will be addressed at different levels of granularity. 3 METHODOLOGY The research reported in this paper is grounded in the interpretive approach to case studies (Klein and Myers, 1999; Walsham, 1993, 1995). For data collection, we employed ethnographically inspired methods conducting 32 interviews, 8 instances of observations of daily work and user training sessions, documents analysis, and participation in several discussions and meetings. The head of research of the IT department of the hospital has regularly joined these meeting to provide updates regarding the implementation project, and to suggest interesting areas for further research. Our fieldwork is part of a long term research cooperation between our Department of Informatics at the University of Oslo and the IT department of the hospital. Between 1996 and 1999, the implementation of the EPR has been the topic for a project in an Advanced Systems Development course. Each year around 5 groups of 5-7 Master students studied and reported on some aspects of the design and implementation process in the hospital. The process of writing this paper from the perspective of complexity and risk has helped us to look both at micro and macro level phenomena, and at the intertwining of the two. Beck s theory on
6 reflexive modernization has guided us to the understanding of the mechanisms of appropriation and reproduction of risks. The reflexive modernization theory has directed our attention to the central role of side effects, and their mechanisms of production, in creating a situation perceived as risky and out of control. 4 CASE DESCRIPTION In the following sections, we will introduce the case study of the development of an Electronic Patient Record (EPR) system at Norhospital. The EPR is a clinical system used for storing clinical information related to the treatment of the patient. It may be specific to a particular clinical department (e.g. cardiology) or, as in our case, regard the clinical information of all clinical departments in the hospital. We will first provide some background information about the hospital and the EPR project. We will then describe the process of globalization of the EPR project. Finally we will conduct a preliminary analysis of the globalization process along several analytical dimensions. 4.1 Background Today Norhospital is the second largest hospital in Norway, with approximately 600 beds, 4000 employees and an annual budget of 2.5 billion NOK (around 360 million US Dollars). In 2002 more than patients were treated. The IT department of Norhospital currently has a staff of over 80 people and an annual budget of ca. 80 MNOK, while just ten years ago only 7 people were on the staff. The role of the department has considerably changed from providing technical support and maintenance for mainframes and networks, to developing hospital-wide clinical information systems. At the time the EPR project started (1996), the information infrastructure of the hospital consisted mainly of a centralized paper-based patient record, numerous local clinical systems including local EPR solutions, central administrative systems (e.g. PAS: patient administrative system), and a LAN with PCs for office automation. Besides local EPR implementations in particular clinical departments, no hospital wide EPR implementation was ongoing in Norway. One exception was the Medina project: a bottom-up development project of an EPR solution partly funded by the Norwegian Research Fund (see Ellingsen & Monteiro 2002, for details). In 1996, Norhospital and other four regional hospitals became interested in developing a hospital wide EPR solution. In order to share costs and reduce risk of failure, they decided to join into a common project merging requirements and splitting costs; the project was called Medakis. In the particular case of Norhospital, the system had to reach 3500 potential users (mainly doctors, nurses and secretaries) substituting the centralized paper record and either integrating or replacing local clinical systems. 4.2 From Local to Global For the development of the EPR, the Medakis consortium of hospitals needed to chose a vendor. In mid 1990s, the main provider of EPR solutions in Norway was a company we will here call MedInfo (a European high-tech diversified multinational company), which had also acquired the local project Medina (Ellingsen and Monteiro, 2002). At that point of time, it was the opinion of the IT managers at Norhospital that a large international company with the appropriate financial resources was needed for the development of such a complex product. MedInfo seemed to have the right credentials. Nevertheless, at that time, the involvement of MedInfo was limited to its local Norwegian subsidiary, and both the development and the target market were Norwegian. The timeframe of the project was set between 1996 and The vendor was supposed to implement a preliminary version of the EPR (which we will name NorEPR) in 1996 with the aim to substitute it with a final version at the end of the project. The target of both the vendor and the hospital was to obtain a paperless hospital with automated support for workflow and statistics.
7 A first critical step in the evolution of the project occurred when the IT managers of Norhospital discovered, while attending a presentation at a conference on IT and Healthcare in the UK, that MedInfo UK was also engaged in a project of EPR development. Asking MedInfo Norway for more clarification, they discovered that within MedInfo there was more than one EPR development project: at least five of them were ongoing in Sweden, UK, Germany, India, and Norway. The IT managers realized that Norway was representing the smallest market, and had the risk of being overrun by another internal project driven by a more profitable market. As a consequence, the Medakis consortium together with MedInfo Norway agreed to take the first step and internationalize the project first to a Scandinavian dimension, and later to a European one. Accordingly, requirements from other EPR projects inside MedInfo had to be merged, and a new architecture had to be designed. Furthermore, since the original deadline for the final delivery (1999) was approaching, Medakis agreed with MedInfo to extend it in favor of the new internationalized EPR solution (which we will call IntEPR). A second major step in the project occurred when MedInfo acquired a large IT & Healthcare organization in the US, and consequently changed the scope, resources, and balance of its Medical division. As a result, the division s headquarters were moved from Europe to the US, and running projects gained the opportunity and resources to reach a global scope. In this scenario, Medakis supported MedInfo in widening development and marketing range of IntEPR. As a consequence, the new IntEPR architecture was dropped in favor of a new one (GlobEPR), and Medakis obtained the basic requirements already defined for the Norwegian customer to be partly inscribed in the new architecture. 4.3 On Development, Requirements, and Control The historical evolution of the project from the local to the global context has three interesting dimensions: the organization of the software development, the scope and complexity of the requirements, and the influence of Norhospital on the trajectory of the project. As to the first dimension, previous to Medakis the development of local EPR solutions was carried out by amateur doctors-programmers in single clinical departments. With Medakis and NorEPR, the development was carried out in Norway by the Norwegian subsidiary of MedInfo. IntEPR internationalized the development as other MedInfo Scandinavian sites were involved. Finally, the development of GlobEPR became truly global, with development sites in the US, Norway, Sweden, Germany, and India. Thus, the number of sites grew with the process of internationalization, making coordination and cooperation dynamics increasingly difficult and complex. As to the second dimension, in the development of local EPR solutions, the definition of requirements was done for each single clinical department. Accordingly, requirements were confined and easily controllable. The creation of Medakis made requirements the result of negotiations and agreements among several Norwegian hospitals. With IntEPR, and even more with GlobEPR, Norwegian requirements were marginalized, as the new product had to satisfy a larger customer base. In particular with GlobEPR, Norhospital initiated a struggle with MedInfo to make sure that Norwegian requirements were not marginalized or even abandoned in favor of the ones of the more profitable US customer base. As to the third dimension, in the progressive project internationalization, the control of Norhospital over the trajectory of development decreased drastically. The senior managers at the IT department were aware of this side-effect of going global, nevertheless they assumed they would get greater benefits that would compensate for the loss of control. The main points related to the three dimensions are summarized in the following table:
8 Organization of SW development Customer and requirements base Control of Norhospital over the project Table 1 Departmental EPR NorEPR IntEPR GlobEPR Amateur, confined in the clinical department Single clinical department Norhospital is initially not interested in controlling local developments Norwegian: development by Norwegian subsidiary of MedInfo 5 regional hospitals (requirements for the whole hospital) 20%: Norhospital is one of five customers Development, requirements, and control on the project European: involving subsidiaries in Norway, Sweden, and Germany First Scandinavia, then European customer Still consistent: the design of IntEPR has the Norwegian Requirements inscribed in its architecture Global: development sites in US, Norway, Sweden, Germany, and India Potentially customers all over the world Marginal: Norway is seen as a marginal market; larger emphasis is given to US customers (the largest potential customer base) 5 DISCUSSION The aim of this section is to analyze and discuss the empirical material, emphasizing the dynamics of risk generation; once more, we would like to remind that we do not aim to engage in a discussion on risk management techniques, rather we will focus on how risk management decisions generate new risks. Our discussion unfolds in three analytical steps: (1) we analyze the mechanism of risk management, and identify a pattern in the decision making process of the project; (2) we identify the logic behind the pattern, and describe it as a process of risk escalation in terms of range and scope; (3) finally, we interpret escalation as the risk management process generating new risks. We will underline how analysis and understanding of risks involved in complex IS projects should not be limited to the confined spatial and temporal boundaries of a particular stage in the project management. Rather, the mechanism of new risk generation by means of risk management decisions should also be considered. This latter aspect, we will submit, is increasingly relevant as complexity and globalization of IS projects intensifies. Finally, we will provide a theoretical interpretation of the observed risk dynamics by using the framework of reflexive modernization as proposed by Beck (et al. 1994). 5.1 The Recurring Pattern of Risk Management Decisions In this section, we will highlight a recurring pattern of how decisions to increase size, scope, customer base, and budget of the project were made. The starting point of the project was the decision of a single hospital to develop a hospital-wide EPR. In this context, the EPR was clearly a technology aimed at rationalizing the production and consumption of information in the organization, by integrating sources and use practices of information. By rationalizing and integrating through the EPR, the hospital (specifically the IT department and the management) could gain control over the information in the organization. In this sense, the implementation of an EPR could help avoid the risk of a too fragmented and uncoordinated, thus potentially inefficient and ineffective, information system. The decision to develop a hospital-wide EPR, in turn, raised questions of feasibility and sustainability. The five hospitals in Medakis estimated that the task was too complex and risky to be achieved independently. On the other hand, alongside complexity, the IT managers of the five hospitals considered that the design of an EPR could be standardized; that is, the requirements could be merged
9 and aligned and the EPR easily adapted to local contexts of each hospital. This latter reasoning was triggered by the belief that economies of scale could be achieved through standardization. To assure the feasibility and sustainability of the development and to achieve the needed economies of scale, Medakis intentionally looked for a vendor with abundant resources and an international background. At this stage, the decision to address the risk of fragmentation and inefficiencies in the information system inside the hospital produced the need to evaluate another risk management decision. Accordingly, pushed by the same principles of rationalization, integration, and control through standardization, the EPR project gained a national scope. The decision to involve an international partner opened up the horizon of NorEPR. The Medakis consortium immediately realized that NorEPR was just a tiny project in the international arena. It was soon assessed that Norway was representing a too small market and risked being crushed by lager projects. In this scenario, there were two alternatives: (1) either passively becoming sooner or later part of an international project with little or no decision-making power; (2) or take the first step by anticipating this likely scenario, and by actively inscribing the needed requirements in the new architecture. Interestingly, the joint decision of Medakis and MedInfo to internationalize the project followed the same logic of rationalization, integration, and control. From the point of view of Norhospital as part of Medakis, the new project (IntEPR) was a mean to rationalize the international distributed development of similar products. This was achieved by integrating requirements from the various countries. By doing so, Norhospital could gain control over the future trajectory of EPR developments in MedInfo by inscribing its requirements in the design. In other terms, the influence that Norhospital or the whole of Medakis had on the new project decreased, as the new product had to satisfy a larger customer base. Yet, in this new integrated scenario, Norway could have an international influence which was lacking before. The next step, from IntEPR to GlobEPR, basically followed the same pattern. With MedInfo expanding in the global market through acquisitions, the horizon of IntEPR widened once again. Norhospital saw the growth and globalization of the medical division inside MedInfo as a positive sign, despite the decrease of influence on the project. Even more resources in fact could be allocated to the EPR project, in a way reassuring the Norwegian customers that the complexity of the development could be overcome. At the same time, MedInfo aimed for a global customer base, on the one side potentially increasing economies of scale, on the other side increasing the complexity of management and coordination of development processes and requirements handling. Throughout the trajectory of the project, the actors involved in the decision-making process seemed to have followed a recurring pattern. At each stage of the project, the decision to go to the next stage by increasing its scope and range seems to follow the same quest for increased rationalization, integration, and control. At the first stage, these principles apply to the information generated and used in the hospital. At the second stage (creation of Medakis), the principles are applied to the gathering of requirements, the organization of the development process, and the control over costs. The same pattern applied with the internationalization of NorEPR to IntEPR, and subsequently to GlobEPR. Certainly, many other factors have influenced the decision analyzed in this case. Moreover, the pattern we have identified is also a rather obvious rationale behind most IT projects; in this respect it is nothing new. What we aim to underline is that under certain conditions the quest for rationalization and greater control can produce opposite effects: increased complexity and loss of control. It is therefore relevant to investigate further in this dynamic in order to understand how the perception and redistribution of risk is affected. 5.2 The Logic of Escalation So far, we have described the trajectory of the project along particular dimensions (requirements, development, and control). Moreover, we have highlighted a recurring pattern in each step of the trajectory of how decisions were met. We can now observe how iterative attempts to address the problem of developing an EPR brought about an unplanned creation of a larger problem which
10 contained the initial one. More specifically, the initial quest for rationalization and integration through the EPR created a problem of a certain complexity. In order to address this problem, the five Norwegian hospitals teamed together and transformed a local problem to a national problem. If, on the one hand, more resource were guaranteed for the initial problem (one hospital), the increased complexity of the new problem (standardization of five hospitals in NorEPR) required the search for more resources. MedInfo provided the new resources, but also reshaped the problem once again. Being an international player, the contextualization of NorEPR in the international arena redefined the original problem by increasing the scope of the development and marketing at European level. The same logic then applied for the transition from IntEPR to GlobEPR. If we put the trajectory of the project in perspective, we see how the recurring decisions followed a logic of escalation. Consequently, the escalation of the problem setting generated an escalation of the risks involved as well, as the number of actors involved and size and complexity of the project grew exponentially. We can identify two sources of this logic of escalation: (1) a mechanism of re-appropriation of the complexity of the problem; (2) the role of MedInfo as a global amplifier of the setting of the project. Regarding the first source, iteratively a more complex situation is created at each decision making step in the process. The increased complexity then triggers the need of the redefinition of the project at a new level. Regarding the second source, the escalation from a Norwegian to a global level could not be possible if the chosen vendor was not as global as MedInfo. Being a multinational with globalized networks of innovation, production, and marketing, MedInfo simply enabled the amplification of the project on a global scale with its existing infrastructure. Finally, we can observe how the two sources drive escalation in different ways. At each iteration, the increased complexity of the development constrains the project to search for greater resources; while the global infrastructure of MedInfo enables the escalation to happen. In this sense, the escalation is pushed by the increasing complexity of the project, and pulled by the opportunity of standardization and economies of scale. Alongside with the project, its risks were also enhanced with the complexity, and amplified on a global scale. Thus, the risk management of the project at one level, required the creation and involvement of new risks at a next level, with greater scope. 5.3 On Globalization, Reflexivity and Risk The case presented in this paper is an example of how local IS projects can be reinterpreted in a global context. As we have discussed, by being marginally connected to a global network, a local project like NorEPR is reshaped and deeply redefined: the locality of Norhospital becomes one of the elements of a wide global network. Moreover, interests and requirements are disembedded and reembedded in the global environment (Giddens 1990). In this global scenario, the IT department of Norhospital saw its interests less and less represented, and the risk of having delivered an unsatisfactory product increased. Paradoxically, the decisions taken by the IT department in the project have actively contributed to the creation of such risky situation. This reflexive mechanism has lead to a scenario that, from the perspective of Norhospital, is out of control. The concept of reflexivity provides a theoretical interpretation to the micro-dynamics of the escalation process. Applied to our case, it explains how the production of greater complexity and less control, has its source in the attempt to rationalize and control a less complex problem. Moreover, the reflexive mechanism in our case regards a process of modernization, as, in fact, the aim behind the development of the EPR is rationalization and control. In terms of risk, the reflexive logic of risk management in the EPR project is paradoxically the following: in order to fight risk involved in the project, a more complex project involving greater risk is created. While it is true that for each new iteration of the project, risks are distributed in a different way, it is also true that the overall risk involved in the
11 project in greater, as greater numbers of actors can be affected to a greater extent. Moreover, those actors have less and less control over the project. The concept of reflexive modernization, applied to the analysis of risk, provides a framework to understand how new risks can be generated in the process of globalization of the EPR project. The new risks are related to possible side-effects and unintended consequences which can occur in a so tightly integrated global network. 6 CONCLUSIONS In this paper, we have investigated the relation between generation of risk in IS projects and the process of globalization. Based on a case of globalization of an IS development project, we analyze and discuss how new risks are generated and distributed at each step of the globalization process. In particular, we have highlighted how decisions which increased the size and scope of the project were guided by the same pattern of principles: rationalization, integration, and control. Furthermore, we have shown how the project moved along a trajectory of escalation. The escalation, we submit, was due to the need to address an increased complexity of the original problem, and due to the opportunity of globalization, enabled by actors in the project, such as the vendor. Finally, we observed how the nature and distribution of risk changed at each iteration of the escalation process. The case and the analysis put an emphasis on the need to extend current studies on risk in IS project to include an understanding of the role of globalization. Indeed, traditional studies tend to focus the analysis of risk to confined temporal and spatial boundaries. We have shown that, in order to understand the escalation of risk in the case at study, a new framework is needed, which can relate to processes of globalization. With this purpose, we have proposed and applied the concept of reflexive modernization (Beck, 1999). We claim that this concept provides new insights to the study of risk dynamics in IS development in contexts of globalization. References Alter, M., and Ginzberg, M. (1978). Managing Uncertainty in MIS Implementation. Sloan Management Review, Fall (1978), pp Beck, U., Giddens, A., Lash, S.(1994). Reflexive Modernization. Politics, Tradition and Aesthetics in the Modern Social Order, Polity Press, Beck, U. (1999). World Risk Society, Polity Press, Boehm, B. W. (1991). Software Risk Management: Principles and Practices. IEEE Software, January (1991), pp Davis, G. B. (1982). Strategies for Information Requirements Determination. IBM Systems Journal, 21, 1 (1982), pp Ellingsen, G., Monteiro, E. (2002). Big is Beautiful: electronic patient records in large Norwegian hospitals 1980s Scandinavian Journal of Information Systems. (accepted for publication). Giddens, A. (1990). The Consequences of Modernity, Polity Press. Hanseth, O., Braa, K. (2000). Globalization and Risk Society. Chapter in From Control to Drift: the dynamics of corporate information infrastructures, C. U. Ciborra and Associates editors, Oxford University Press. Hanseth, O., Ciborra, C., Braa, K. (2001). The Control Devolution: EPR and the Side-effects of Globalization. The Data Base for Advances in Information Systems, special issues on EPR systems, Fall 2001, Vol. 32, No. 4, pp Klein, H.K., and Myers, M.D. (1999). A set of principles for conducting and evaluating interpretive field studies in information systems, MIS Quarterly, vol.23, no.1, 1999, pp Lyytinen, K., Mathiassen, L., Ropponen, J. (1998). Attention Shaping and Software Risk A Categorical Analysis of Four Classical Risk Management Approaches. Information Systems Research, Vol. 9, No. 3, September 1998, pp
12 McFarlan, W. (1982). Portfolio Approach to Information Systems. Journal of Systems Management, January (1982), pp Rolland, K. (2003). Re-inventing Information Infrastructure in Situated Practices of Use, PhD Thesis, University of Oslo. Scott, V.S., (2000), IT-enabled credit risk modernization: a revolution under the cloak of normality, Accounting Management and Information Technologies, 10, Walsham, G. (1993). Interpreting Information Systems in Organizations, Wiley, Walsham, G. (1995). Interpretive case study in IS research: nature and method, European Journal of Information Systems, Vol.4, 1995, pp.74-81
A Case Study on Actor Roles in Systems Development
 Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) ECIS 2003 Proceedings European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS) 2003 A Case Study on Actor Roles in Systems Development Vincenzo
Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) ECIS 2003 Proceedings European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS) 2003 A Case Study on Actor Roles in Systems Development Vincenzo
Information Sociology
 Information Sociology Educational Objectives: 1. To nurture qualified experts in the information society; 2. To widen a sociological global perspective;. To foster community leaders based on Christianity.
Information Sociology Educational Objectives: 1. To nurture qualified experts in the information society; 2. To widen a sociological global perspective;. To foster community leaders based on Christianity.
Generification in change: the complexity of modelling the healthcare domain.
 Line Silsand and Bente Christensen (2017): Generification in change: the complexity of modelling the healthcare domain. 6th International Workshop on Infrastructures for Healthcare: Infrastructures for
Line Silsand and Bente Christensen (2017): Generification in change: the complexity of modelling the healthcare domain. 6th International Workshop on Infrastructures for Healthcare: Infrastructures for
MEDIA AND INFORMATION
 MEDIA AND INFORMATION MI Department of Media and Information College of Communication Arts and Sciences 101 Understanding Media and Information Fall, Spring, Summer. 3(3-0) SA: TC 100, TC 110, TC 101 Critique
MEDIA AND INFORMATION MI Department of Media and Information College of Communication Arts and Sciences 101 Understanding Media and Information Fall, Spring, Summer. 3(3-0) SA: TC 100, TC 110, TC 101 Critique
Compendium Overview. By John Hagel and John Seely Brown
 Compendium Overview By John Hagel and John Seely Brown Over four years ago, we began to discern a new technology discontinuity on the horizon. At first, it came in the form of XML (extensible Markup Language)
Compendium Overview By John Hagel and John Seely Brown Over four years ago, we began to discern a new technology discontinuity on the horizon. At first, it came in the form of XML (extensible Markup Language)
ty of solutions to the societal needs and problems. This perspective links the knowledge-base of the society with its problem-suite and may help
 SUMMARY Technological change is a central topic in the field of economics and management of innovation. This thesis proposes to combine the socio-technical and technoeconomic perspectives of technological
SUMMARY Technological change is a central topic in the field of economics and management of innovation. This thesis proposes to combine the socio-technical and technoeconomic perspectives of technological
MULTIPLE LOGICS AT WORK IN INFORMATION INFRASTRUCTURE IN USE: A CASE STUDY ON HEART TRANSPLANTATION
 Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) MCIS 2008 Proceedings Mediterranean Conference on Information Systems (MCIS) 10-2008 MULTIPLE LOGICS AT WORK IN INFORMATION INFRASTRUCTURE
Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) MCIS 2008 Proceedings Mediterranean Conference on Information Systems (MCIS) 10-2008 MULTIPLE LOGICS AT WORK IN INFORMATION INFRASTRUCTURE
Managing the process towards a new library building. Experiences from Utrecht University. Bas Savenije. Abstract
 Managing the process towards a new library building. Experiences from Utrecht University. Bas Savenije Abstract In September 2004 Utrecht University will open a new building for the university library.
Managing the process towards a new library building. Experiences from Utrecht University. Bas Savenije Abstract In September 2004 Utrecht University will open a new building for the university library.
Strategic Plan for CREE Oslo Centre for Research on Environmentally friendly Energy
 September 2012 Draft Strategic Plan for CREE Oslo Centre for Research on Environmentally friendly Energy This strategic plan is intended as a long-term management document for CREE. Below we describe the
September 2012 Draft Strategic Plan for CREE Oslo Centre for Research on Environmentally friendly Energy This strategic plan is intended as a long-term management document for CREE. Below we describe the
Enhancing industrial processes in the industry sector by the means of service design
 ServDes2018 - Service Design Proof of Concept Politecnico di Milano 18th-19th-20th, June 2018 Enhancing industrial processes in the industry sector by the means of service design giuseppe@attoma.eu, peter.livaudais@attoma.eu
ServDes2018 - Service Design Proof of Concept Politecnico di Milano 18th-19th-20th, June 2018 Enhancing industrial processes in the industry sector by the means of service design giuseppe@attoma.eu, peter.livaudais@attoma.eu
A review of the role and costs of clinical commissioning groups
 A picture of the National Audit Office logo Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General NHS England A review of the role and costs of clinical commissioning groups HC 1783 SESSION 2017 2019 18 DECEMBER
A picture of the National Audit Office logo Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General NHS England A review of the role and costs of clinical commissioning groups HC 1783 SESSION 2017 2019 18 DECEMBER
A Three Cycle View of Design Science Research
 Scandinavian Journal of Information Systems Volume 19 Issue 2 Article 4 2007 A Three Cycle View of Design Science Research Alan R. Hevner University of South Florida, ahevner@usf.edu Follow this and additional
Scandinavian Journal of Information Systems Volume 19 Issue 2 Article 4 2007 A Three Cycle View of Design Science Research Alan R. Hevner University of South Florida, ahevner@usf.edu Follow this and additional
Roadmapping. Market Products Technology. People Process. time, ca 5 years
 - drives, requires supports, enables Customer objectives Application Functional Conceptual Realization Market Products Technology People Marketing Architect technology, process people manager time, ca
- drives, requires supports, enables Customer objectives Application Functional Conceptual Realization Market Products Technology People Marketing Architect technology, process people manager time, ca
The Tool Box of the System Architect
 - number of details 10 9 10 6 10 3 10 0 10 3 10 6 10 9 enterprise context enterprise stakeholders systems multi-disciplinary design parts, connections, lines of code human overview tools to manage large
- number of details 10 9 10 6 10 3 10 0 10 3 10 6 10 9 enterprise context enterprise stakeholders systems multi-disciplinary design parts, connections, lines of code human overview tools to manage large
If These Crawls Could Talk: Studying and Documenting Web Archives Provenance
 If These Crawls Could Talk: Studying and Documenting Web Archives Provenance Emily Maemura, PhD Candidate Faculty of Information, University of Toronto NetLab Forum February 27, 2018 The Team Nich Worby
If These Crawls Could Talk: Studying and Documenting Web Archives Provenance Emily Maemura, PhD Candidate Faculty of Information, University of Toronto NetLab Forum February 27, 2018 The Team Nich Worby
Imagine your future lab. Designed using Virtual Reality and Computer Simulation
 Imagine your future lab Designed using Virtual Reality and Computer Simulation Bio At Roche Healthcare Consulting our talented professionals are committed to optimising patient care. Our diverse range
Imagine your future lab Designed using Virtual Reality and Computer Simulation Bio At Roche Healthcare Consulting our talented professionals are committed to optimising patient care. Our diverse range
Revista Economică 68:5 (2016) PUBLIC PERCEPTION OF THE ROLE OF SCIENCE AND INNOVATION IN SOLVING THE PROBLEMS EXPERIENCED BY CONTEMPORARY ECONOMY
 PUBLIC PERCEPTION OF THE ROLE OF SCIENCE AND INNOVATION IN SOLVING THE PROBLEMS EXPERIENCED BY CONTEMPORARY ECONOMY DURALIA Oana 1 Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu Abstract: In the context of contemporary
PUBLIC PERCEPTION OF THE ROLE OF SCIENCE AND INNOVATION IN SOLVING THE PROBLEMS EXPERIENCED BY CONTEMPORARY ECONOMY DURALIA Oana 1 Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu Abstract: In the context of contemporary
A SYSTEMIC APPROACH TO KNOWLEDGE SOCIETY FORESIGHT. THE ROMANIAN CASE
 A SYSTEMIC APPROACH TO KNOWLEDGE SOCIETY FORESIGHT. THE ROMANIAN CASE Expert 1A Dan GROSU Executive Agency for Higher Education and Research Funding Abstract The paper presents issues related to a systemic
A SYSTEMIC APPROACH TO KNOWLEDGE SOCIETY FORESIGHT. THE ROMANIAN CASE Expert 1A Dan GROSU Executive Agency for Higher Education and Research Funding Abstract The paper presents issues related to a systemic
Activity-Centric Configuration Work in Nomadic Computing
 Activity-Centric Configuration Work in Nomadic Computing Steven Houben The Pervasive Interaction Technology Lab IT University of Copenhagen shou@itu.dk Jakob E. Bardram The Pervasive Interaction Technology
Activity-Centric Configuration Work in Nomadic Computing Steven Houben The Pervasive Interaction Technology Lab IT University of Copenhagen shou@itu.dk Jakob E. Bardram The Pervasive Interaction Technology
White paper The Quality of Design Documents in Denmark
 White paper The Quality of Design Documents in Denmark Vers. 2 May 2018 MT Højgaard A/S Knud Højgaards Vej 7 2860 Søborg Denmark +45 7012 2400 mth.com Reg. no. 12562233 Page 2/13 The Quality of Design
White paper The Quality of Design Documents in Denmark Vers. 2 May 2018 MT Højgaard A/S Knud Højgaards Vej 7 2860 Søborg Denmark +45 7012 2400 mth.com Reg. no. 12562233 Page 2/13 The Quality of Design
FP 8 in a new European research and innovation landscape. A reflection paper
 FP 8 in a new European research and innovation landscape A reflection paper FP 8 in a new European research and innovation landscape A reflection paper The Research Council of Norway 2010 The Research
FP 8 in a new European research and innovation landscape A reflection paper FP 8 in a new European research and innovation landscape A reflection paper The Research Council of Norway 2010 The Research
Issue Article Vol.30 No.2, April 1998 Article Issue
 Issue Article Vol.30 No.2, April 1998 Article Issue Tailorable Groupware Issues, Methods, and Architectures Report of a Workshop held at GROUP'97, Phoenix, AZ, 16th November 1997 Anders Mørch, Oliver Stiemerlieng,
Issue Article Vol.30 No.2, April 1998 Article Issue Tailorable Groupware Issues, Methods, and Architectures Report of a Workshop held at GROUP'97, Phoenix, AZ, 16th November 1997 Anders Mørch, Oliver Stiemerlieng,
Socio-cognitive Engineering
 Socio-cognitive Engineering Mike Sharples Educational Technology Research Group University of Birmingham m.sharples@bham.ac.uk ABSTRACT Socio-cognitive engineering is a framework for the human-centred
Socio-cognitive Engineering Mike Sharples Educational Technology Research Group University of Birmingham m.sharples@bham.ac.uk ABSTRACT Socio-cognitive engineering is a framework for the human-centred
THE GENERATIVE MECHANISMS OF DIGITAL INFRASTRUCTURE EVOLUTION. Bendik Bygstad University of Oslo IFIP 8.6 Aalborg 2.June 2014
 THE GENERATIVE MECHANISMS OF DIGITAL INFRASTRUCTURE EVOLUTION Bendik Bygstad University of Oslo IFIP 8.6 Aalborg 2.June 2014 Research question Which mechanisms contingently cause digital infrastructure
THE GENERATIVE MECHANISMS OF DIGITAL INFRASTRUCTURE EVOLUTION Bendik Bygstad University of Oslo IFIP 8.6 Aalborg 2.June 2014 Research question Which mechanisms contingently cause digital infrastructure
250 Introduction to Applied Programming Fall. 3(2-2) Creation of software that responds to user input. Introduces
 MEDIA AND INFORMATION MI Department of Media and Information College of Communication Arts and Sciences 101 Understanding Media and Information Fall, Spring, Summer. 3(3-0) SA: TC 100, TC 110, TC 101 Critique
MEDIA AND INFORMATION MI Department of Media and Information College of Communication Arts and Sciences 101 Understanding Media and Information Fall, Spring, Summer. 3(3-0) SA: TC 100, TC 110, TC 101 Critique
Research with Impact Aalto Research Day, 26th of September, 2013 Mikko Kosonen, President, Sitra
 Research with Impact Aalto Research Day, 26th of September, 2013 Mikko Kosonen, President, Sitra Megatrends of the interconnected world Superseniors X-Events Data as a source of power and wealth Race for
Research with Impact Aalto Research Day, 26th of September, 2013 Mikko Kosonen, President, Sitra Megatrends of the interconnected world Superseniors X-Events Data as a source of power and wealth Race for
Exploring the Nature of Virtuality An Interplay of Global and Local Interactions
 25 Exploring the Nature of Virtuality An Interplay of Global and Local Interactions Niki Panteli^ Mike Chiasson^, Lin Yan^, Angeliki Poulymenakou'*, Anthony Papargyris^ 1 University of Bath, UK; N.Panteli@bath.ac.uk
25 Exploring the Nature of Virtuality An Interplay of Global and Local Interactions Niki Panteli^ Mike Chiasson^, Lin Yan^, Angeliki Poulymenakou'*, Anthony Papargyris^ 1 University of Bath, UK; N.Panteli@bath.ac.uk
SME Adoption of Wireless LAN Technology: Applying the UTAUT Model
 Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) SAIS 2004 Proceedings Southern (SAIS) 3-1-2004 SME Adoption of Wireless LAN Technology: Applying the UTAUT Model John E. Anderson andersonj@mail.ecu.edu
Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) SAIS 2004 Proceedings Southern (SAIS) 3-1-2004 SME Adoption of Wireless LAN Technology: Applying the UTAUT Model John E. Anderson andersonj@mail.ecu.edu
Issues and Challenges in Coupling Tropos with User-Centred Design
 Issues and Challenges in Coupling Tropos with User-Centred Design L. Sabatucci, C. Leonardi, A. Susi, and M. Zancanaro Fondazione Bruno Kessler - IRST CIT sabatucci,cleonardi,susi,zancana@fbk.eu Abstract.
Issues and Challenges in Coupling Tropos with User-Centred Design L. Sabatucci, C. Leonardi, A. Susi, and M. Zancanaro Fondazione Bruno Kessler - IRST CIT sabatucci,cleonardi,susi,zancana@fbk.eu Abstract.
An Ontology for Modelling Security: The Tropos Approach
 An Ontology for Modelling Security: The Tropos Approach Haralambos Mouratidis 1, Paolo Giorgini 2, Gordon Manson 1 1 University of Sheffield, Computer Science Department, UK {haris, g.manson}@dcs.shef.ac.uk
An Ontology for Modelling Security: The Tropos Approach Haralambos Mouratidis 1, Paolo Giorgini 2, Gordon Manson 1 1 University of Sheffield, Computer Science Department, UK {haris, g.manson}@dcs.shef.ac.uk
MedTech Europe position on future EU cooperation on Health Technology Assessment (21 March 2017)
 MedTech Europe position on future EU cooperation on Health Technology Assessment (21 March 2017) Table of Contents Executive Summary...3 The need for healthcare reform...4 The medical technology industry
MedTech Europe position on future EU cooperation on Health Technology Assessment (21 March 2017) Table of Contents Executive Summary...3 The need for healthcare reform...4 The medical technology industry
End-to-End Infrastructure for Usability Evaluation of ehealth Applications and Services
 End-to-End Infrastructure for Usability Evaluation of ehealth Applications and Services Martin Gerdes, Berglind Smaradottir, Rune Fensli Department of Information and Communication Systems, University
End-to-End Infrastructure for Usability Evaluation of ehealth Applications and Services Martin Gerdes, Berglind Smaradottir, Rune Fensli Department of Information and Communication Systems, University
Science, Technology, and Innovation for Sustainable Development: National Policy Frameworks in Asia and the Pacific Apiwat Ratanawaraha
 Science, Technology, and Innovation for Sustainable Development: National Policy Frameworks in Asia and the Pacific Apiwat Ratanawaraha Background Paper for the Second Regional workshop on Harnessing Science,
Science, Technology, and Innovation for Sustainable Development: National Policy Frameworks in Asia and the Pacific Apiwat Ratanawaraha Background Paper for the Second Regional workshop on Harnessing Science,
THE CONSTRUCTION- AND FACILITIES MANAGEMENT PROCESS FROM AN END USERS PERSPECTIVE - ProFacil
 CEC 99 Björk, Bo-Christer, Nilsson, Anders, Lundgren, Berndt Page of 9 THE CONSTRUCTION- AND FACILITIES MANAGEMENT PROCESS FROM AN END USERS PERSPECTIVE - ProFacil Björk, Bo-Christer, Nilsson, Anders,
CEC 99 Björk, Bo-Christer, Nilsson, Anders, Lundgren, Berndt Page of 9 THE CONSTRUCTION- AND FACILITIES MANAGEMENT PROCESS FROM AN END USERS PERSPECTIVE - ProFacil Björk, Bo-Christer, Nilsson, Anders,
European Creative Synergy: Application for Energy Transition Efficiency. 6th European Conference on Corporate R&D and Innovation: CONCORDi 2017
 European Creative Synergy: Application for Energy Transition Efficiency 6th European Conference on Corporate R&D and Innovation: CONCORDi 2017 Energy Transition in our Industry a multi-actor value chain
European Creative Synergy: Application for Energy Transition Efficiency 6th European Conference on Corporate R&D and Innovation: CONCORDi 2017 Energy Transition in our Industry a multi-actor value chain
Towards a Software Engineering Research Framework: Extending Design Science Research
 Towards a Software Engineering Research Framework: Extending Design Science Research Murat Pasa Uysal 1 1Department of Management Information Systems, Ufuk University, Ankara, Turkey ---------------------------------------------------------------------***---------------------------------------------------------------------
Towards a Software Engineering Research Framework: Extending Design Science Research Murat Pasa Uysal 1 1Department of Management Information Systems, Ufuk University, Ankara, Turkey ---------------------------------------------------------------------***---------------------------------------------------------------------
Fostering Innovative Ideas and Accelerating them into the Market
 Fostering Innovative Ideas and Accelerating them into the Market Dr. Mikel SORLI 1, Dr. Dragan STOKIC 2, Ana CAMPOS 2, Antonio SANZ 3 and Miguel A. LAGOS 1 1 Labein, Cta. de Olabeaga, 16; 48030 Bilbao;
Fostering Innovative Ideas and Accelerating them into the Market Dr. Mikel SORLI 1, Dr. Dragan STOKIC 2, Ana CAMPOS 2, Antonio SANZ 3 and Miguel A. LAGOS 1 1 Labein, Cta. de Olabeaga, 16; 48030 Bilbao;
Research and Change Call for abstracts Nr. 2
 Research and Change Call for abstracts Nr. 2 Theme: What kinds of knowledge are needed in the professions, and what kinds of research are necessary? In the wake of public sector reforms and other societal
Research and Change Call for abstracts Nr. 2 Theme: What kinds of knowledge are needed in the professions, and what kinds of research are necessary? In the wake of public sector reforms and other societal
POSITION OF THE NATIONAL RESEARCH COUNCIL OF ITALY (CNR) ON HORIZON 2020
 POSITION OF THE NATIONAL RESEARCH COUNCIL OF ITALY (CNR) ON HORIZON 2020 General view CNR- the National Research Council of Italy welcomes the architecture designed by the European Commission for Horizon
POSITION OF THE NATIONAL RESEARCH COUNCIL OF ITALY (CNR) ON HORIZON 2020 General view CNR- the National Research Council of Italy welcomes the architecture designed by the European Commission for Horizon
Proposal for Workshop
 The 26th European Conference on Information Systems 23 28 June 2018 Proposal for Workshop Title of the workshop Platformization in the Public Sector: Please visit: www.platformization.org Main Contact
The 26th European Conference on Information Systems 23 28 June 2018 Proposal for Workshop Title of the workshop Platformization in the Public Sector: Please visit: www.platformization.org Main Contact
Transferring knowledge from operations to the design and optimization of work systems: bridging the offshore/onshore gap
 Transferring knowledge from operations to the design and optimization of work systems: bridging the offshore/onshore gap Carolina Conceição, Anna Rose Jensen, Ole Broberg DTU Management Engineering, Technical
Transferring knowledge from operations to the design and optimization of work systems: bridging the offshore/onshore gap Carolina Conceição, Anna Rose Jensen, Ole Broberg DTU Management Engineering, Technical
The Research Project Portfolio of the Humanistic Management Center
 The Research Project Portfolio of the Humanistic Our Pipeline of Research Projects Contents 1 2 3 4 5 Myths and Misunderstandings in the CR Debate Humanistic Case Studies The Makings of Humanistic Corporate
The Research Project Portfolio of the Humanistic Our Pipeline of Research Projects Contents 1 2 3 4 5 Myths and Misunderstandings in the CR Debate Humanistic Case Studies The Makings of Humanistic Corporate
Constants and Variables in 30 Years of Science and Technology Policy. Luke Georghiou University of Manchester Presentation for NISTEP 30 Symposium
 Constants and Variables in 30 Years of Science and Technology Policy Luke Georghiou University of Manchester Presentation for NISTEP 30 Symposium Some personal highlights working with NISTEP Science policy
Constants and Variables in 30 Years of Science and Technology Policy Luke Georghiou University of Manchester Presentation for NISTEP 30 Symposium Some personal highlights working with NISTEP Science policy
European Charter for Access to Research Infrastructures - DRAFT
 13 May 2014 European Charter for Access to Research Infrastructures PREAMBLE - DRAFT Research Infrastructures are at the heart of the knowledge triangle of research, education and innovation and therefore
13 May 2014 European Charter for Access to Research Infrastructures PREAMBLE - DRAFT Research Infrastructures are at the heart of the knowledge triangle of research, education and innovation and therefore
Infrastructure for Systematic Innovation Enterprise
 Valeri Souchkov ICG www.xtriz.com This article discusses why automation still fails to increase innovative capabilities of organizations and proposes a systematic innovation infrastructure to improve innovation
Valeri Souchkov ICG www.xtriz.com This article discusses why automation still fails to increase innovative capabilities of organizations and proposes a systematic innovation infrastructure to improve innovation
ServDes Service Design Proof of Concept
 ServDes.2018 - Service Design Proof of Concept Call for Papers Politecnico di Milano, Milano 18 th -20 th, June 2018 http://www.servdes.org/ We are pleased to announce that the call for papers for the
ServDes.2018 - Service Design Proof of Concept Call for Papers Politecnico di Milano, Milano 18 th -20 th, June 2018 http://www.servdes.org/ We are pleased to announce that the call for papers for the
Corporate Mind 2015 Corporate Responsibility Report
 Corporate Mind 2015 Corporate Responsibility Report Artwork: Artist s rendering of the components of a cell. Corporate Mind Promega s corporate responsibility program not only helps our life sciences industry
Corporate Mind 2015 Corporate Responsibility Report Artwork: Artist s rendering of the components of a cell. Corporate Mind Promega s corporate responsibility program not only helps our life sciences industry
How Books Travel. Translation Flows and Practices of Dutch Acquiring Editors and New York Literary Scouts, T.P. Franssen
 How Books Travel. Translation Flows and Practices of Dutch Acquiring Editors and New York Literary Scouts, 1980-2009 T.P. Franssen English Summary In this dissertation I studied the development of translation
How Books Travel. Translation Flows and Practices of Dutch Acquiring Editors and New York Literary Scouts, 1980-2009 T.P. Franssen English Summary In this dissertation I studied the development of translation
PROJECT FACT SHEET GREEK-GERMANY CO-FUNDED PROJECT. project proposal to the funding measure
 PROJECT FACT SHEET GREEK-GERMANY CO-FUNDED PROJECT project proposal to the funding measure Greek-German Bilateral Research and Innovation Cooperation Project acronym: SIT4Energy Smart IT for Energy Efficiency
PROJECT FACT SHEET GREEK-GERMANY CO-FUNDED PROJECT project proposal to the funding measure Greek-German Bilateral Research and Innovation Cooperation Project acronym: SIT4Energy Smart IT for Energy Efficiency
Research group self-assessment:
 Evaluation of social science research in Norway Research group self-assessment: Research group title: TIK-STS (The Science, Technology and Society group) Research group leader: Kristin Asdal Research group
Evaluation of social science research in Norway Research group self-assessment: Research group title: TIK-STS (The Science, Technology and Society group) Research group leader: Kristin Asdal Research group
Business Environment, User Involvement, and Information System Success:A Case Study
 Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) AMCIS 1995 Proceedings Americas Conference on Information Systems (AMCIS) 8-25-1995 Business Environment, User Involvement, and Information
Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) AMCIS 1995 Proceedings Americas Conference on Information Systems (AMCIS) 8-25-1995 Business Environment, User Involvement, and Information
MULTIPLEX Foundational Research on MULTIlevel complex networks and systems
 MULTIPLEX Foundational Research on MULTIlevel complex networks and systems Guido Caldarelli IMT Alti Studi Lucca node leaders Other (not all!) Colleagues The Science of Complex Systems is regarded as
MULTIPLEX Foundational Research on MULTIlevel complex networks and systems Guido Caldarelli IMT Alti Studi Lucca node leaders Other (not all!) Colleagues The Science of Complex Systems is regarded as
A Research and Innovation Agenda for a global Europe: Priorities and Opportunities for the 9 th Framework Programme
 A Research and Innovation Agenda for a global Europe: Priorities and Opportunities for the 9 th Framework Programme A Position Paper by the Young European Research Universities Network About YERUN The
A Research and Innovation Agenda for a global Europe: Priorities and Opportunities for the 9 th Framework Programme A Position Paper by the Young European Research Universities Network About YERUN The
December Rules for Digital-Proofing Your Technology Strategy
 December 2017 5 Rules for Digital-Proofing Your Technology Strategy AT A GLANCE No development in modern times has been as pervasive and formative as the digital revolution. Digitalization repeatedly rewrites
December 2017 5 Rules for Digital-Proofing Your Technology Strategy AT A GLANCE No development in modern times has been as pervasive and formative as the digital revolution. Digitalization repeatedly rewrites
Scenario Development Process
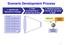 Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
Higher Education Institutions and Networked Knowledge Societies
 1 Higher Education Institutions and Networked Knowledge Societies Jussi Välimaa 2 Main Challenges How to understand & explain contemporary societies? How to explain theoretically the roles Higher education
1 Higher Education Institutions and Networked Knowledge Societies Jussi Välimaa 2 Main Challenges How to understand & explain contemporary societies? How to explain theoretically the roles Higher education
Science Impact Enhancing the Use of USGS Science
 United States Geological Survey. 2002. "Science Impact Enhancing the Use of USGS Science." Unpublished paper, 4 April. Posted to the Science, Environment, and Development Group web site, 19 March 2004
United States Geological Survey. 2002. "Science Impact Enhancing the Use of USGS Science." Unpublished paper, 4 April. Posted to the Science, Environment, and Development Group web site, 19 March 2004
Intellectual Property Management Strategies of Enterprises Based on Open Innovation Model
 1378 Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Innovation & Management Intellectual Property Management Strategies of Enterprises Based on Open Innovation Model Tu Wenjuan, Zhao Lei School of
1378 Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Innovation & Management Intellectual Property Management Strategies of Enterprises Based on Open Innovation Model Tu Wenjuan, Zhao Lei School of
Chapter 4. Research Objectives and Hypothesis Formulation
 Chapter 4 Research Objectives and Hypothesis Formulation 77 Chapter 4: Research Objectives and Hypothesis Formulation 4.1 Introduction and Relevance of the Topic The present study aims at examining the
Chapter 4 Research Objectives and Hypothesis Formulation 77 Chapter 4: Research Objectives and Hypothesis Formulation 4.1 Introduction and Relevance of the Topic The present study aims at examining the
Welcome to the future of energy
 Welcome to the future of energy Sustainable Innovation Jobs The Energy Systems Catapult - why now? Our energy system is radically changing. The challenges of decarbonisation, an ageing infrastructure and
Welcome to the future of energy Sustainable Innovation Jobs The Energy Systems Catapult - why now? Our energy system is radically changing. The challenges of decarbonisation, an ageing infrastructure and
Globalisation increasingly affects how companies in OECD countries
 ISBN 978-92-64-04767-9 Open Innovation in Global Networks OECD 2008 Executive Summary Globalisation increasingly affects how companies in OECD countries operate, compete and innovate, both at home and
ISBN 978-92-64-04767-9 Open Innovation in Global Networks OECD 2008 Executive Summary Globalisation increasingly affects how companies in OECD countries operate, compete and innovate, both at home and
Committee on Development and Intellectual Property (CDIP)
 E CDIP/6/4 REV. ORIGINAL: ENGLISH DATE: NOVEMBER 26, 2010 Committee on Development and Intellectual Property (CDIP) Sixth Session Geneva, November 22 to 26, 2010 PROJECT ON INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND TECHNOLOGY
E CDIP/6/4 REV. ORIGINAL: ENGLISH DATE: NOVEMBER 26, 2010 Committee on Development and Intellectual Property (CDIP) Sixth Session Geneva, November 22 to 26, 2010 PROJECT ON INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND TECHNOLOGY
Constructing Technology-in-use Practices: EPR-adaptation in Canada and Norway
 In association with Simon Fraser University & the Vancouver Coastal Health Research Institute NOT FOR CIRCULATION FOR INTERNAL CIRCULATION FOR PUBLIC CIRCULATION X Constructing Technology-in-use Practices:
In association with Simon Fraser University & the Vancouver Coastal Health Research Institute NOT FOR CIRCULATION FOR INTERNAL CIRCULATION FOR PUBLIC CIRCULATION X Constructing Technology-in-use Practices:
Modeling Enterprise Systems
 Modeling Enterprise Systems A summary of current efforts for the SERC November 14 th, 2013 Michael Pennock, Ph.D. School of Systems and Enterprises Stevens Institute of Technology Acknowledgment This material
Modeling Enterprise Systems A summary of current efforts for the SERC November 14 th, 2013 Michael Pennock, Ph.D. School of Systems and Enterprises Stevens Institute of Technology Acknowledgment This material
Introduction to the Special Section. Character and Citizenship: Towards an Emerging Strong Program? Andrea M. Maccarini *
 . Character and Citizenship: Towards an Emerging Strong Program? Andrea M. Maccarini * Author information * Department of Political Science, Law and International Studies, University of Padova, Italy.
. Character and Citizenship: Towards an Emerging Strong Program? Andrea M. Maccarini * Author information * Department of Political Science, Law and International Studies, University of Padova, Italy.
Patenting Strategies. The First Steps. Patenting Strategies / Bernhard Nussbaumer, 12/17/2009 1
 Patenting Strategies The First Steps Patenting Strategies / Bernhard Nussbaumer, 12/17/2009 1 Contents 1. The pro-patent era 2. Main drivers 3. The value of patents 4. Patent management 5. The strategic
Patenting Strategies The First Steps Patenting Strategies / Bernhard Nussbaumer, 12/17/2009 1 Contents 1. The pro-patent era 2. Main drivers 3. The value of patents 4. Patent management 5. The strategic
AGILE USER EXPERIENCE
 AGILE USER EXPERIENCE Tina Øvad Radiometer Medical ApS and Aalborg University tina.oevad.pedersen@radiometer.dk ABSTRACT This paper describes a PhD project, exploring the opportunities of integrating the
AGILE USER EXPERIENCE Tina Øvad Radiometer Medical ApS and Aalborg University tina.oevad.pedersen@radiometer.dk ABSTRACT This paper describes a PhD project, exploring the opportunities of integrating the
Research strategy
 Department of People & Technology Research strategy 2017-2020 Introduction The Department of People and Technology was established on 1 January 2016 through an integration of academic environments from
Department of People & Technology Research strategy 2017-2020 Introduction The Department of People and Technology was established on 1 January 2016 through an integration of academic environments from
Advances and Perspectives in Health Information Standards
 Advances and Perspectives in Health Information Standards HL7 Brazil June 14, 2018 W. Ed Hammond. Ph.D., FACMI, FAIMBE, FIMIA, FHL7, FIAHSI Director, Duke Center for Health Informatics Director, Applied
Advances and Perspectives in Health Information Standards HL7 Brazil June 14, 2018 W. Ed Hammond. Ph.D., FACMI, FAIMBE, FIMIA, FHL7, FIAHSI Director, Duke Center for Health Informatics Director, Applied
~. a.\\ l. å ~ t 1 ~ ~, Department of Cultural Anthropology and Ethnology
 ~. a.\\ l '` y ", I' i ~ -' ~I å ~ t 1 ~ ~, w Department of Cultural Anthropology and Ethnology The MA in Cultural Anthropology is an international degree program taught in English. The program is offered
~. a.\\ l '` y ", I' i ~ -' ~I å ~ t 1 ~ ~, w Department of Cultural Anthropology and Ethnology The MA in Cultural Anthropology is an international degree program taught in English. The program is offered
PREFACE. Introduction
 PREFACE Introduction Preparation for, early detection of, and timely response to emerging infectious diseases and epidemic outbreaks are a key public health priority and are driving an emerging field of
PREFACE Introduction Preparation for, early detection of, and timely response to emerging infectious diseases and epidemic outbreaks are a key public health priority and are driving an emerging field of
FRAMEWORK Advances in biomedical technology are
 TECHNOLOGY FRAMEWORK Advances in biomedical technology are occurring so rapidly that healthcare professionals can barely keep abreast of the changes. And these advances have cost hospitals dearly. They
TECHNOLOGY FRAMEWORK Advances in biomedical technology are occurring so rapidly that healthcare professionals can barely keep abreast of the changes. And these advances have cost hospitals dearly. They
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
 Editorial Special issue on Collaborative Work and Social Innovation by Elisabeth Willumsen Professor of Social Work Department of Health Studies, University of Stavanger, Norway E-mail: elisabeth.willumsen@uis.no
Editorial Special issue on Collaborative Work and Social Innovation by Elisabeth Willumsen Professor of Social Work Department of Health Studies, University of Stavanger, Norway E-mail: elisabeth.willumsen@uis.no
TENTATIVE REFLECTIONS ON A FRAMEWORK FOR STI POLICY ROADMAPS FOR THE SDGS
 TENTATIVE REFLECTIONS ON A FRAMEWORK FOR STI POLICY ROADMAPS FOR THE SDGS STI Roadmaps for the SDGs, EGM International Workshop 8-9 May 2018, Tokyo Michal Miedzinski, UCL Institute for Sustainable Resources,
TENTATIVE REFLECTIONS ON A FRAMEWORK FOR STI POLICY ROADMAPS FOR THE SDGS STI Roadmaps for the SDGs, EGM International Workshop 8-9 May 2018, Tokyo Michal Miedzinski, UCL Institute for Sustainable Resources,
MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATIONS MARKET INNOVATION: THE TRANSFORMATION FROM 2G TO 3G 1
 MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATIONS MARKET INNOVATION: THE TRANSFORMATION FROM 2G TO 3G 1 Damsgaard, Jan, Department of Informatics, Copenhagen Business School, Howitzvej 60, DK-2000 Fredriksberg, Denmark, jd.inf@cbs.dk
MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATIONS MARKET INNOVATION: THE TRANSFORMATION FROM 2G TO 3G 1 Damsgaard, Jan, Department of Informatics, Copenhagen Business School, Howitzvej 60, DK-2000 Fredriksberg, Denmark, jd.inf@cbs.dk
STRATEGIC DIRECTIONS A world-class and innovative information service and learning space
 STRATEGIC DIRECTIONS 2016 2020 A world-class and innovative information service and learning space Table of contents Introduction...3 Vision...5 Mission...5 Values...6 Strategic Objectives & Actions...6
STRATEGIC DIRECTIONS 2016 2020 A world-class and innovative information service and learning space Table of contents Introduction...3 Vision...5 Mission...5 Values...6 Strategic Objectives & Actions...6
HTA Position Paper. The International Network of Agencies for Health Technology Assessment (INAHTA) defines HTA as:
 HTA Position Paper The Global Medical Technology Alliance (GMTA) represents medical technology associations whose members supply over 85 percent of the medical devices and diagnostics purchased annually
HTA Position Paper The Global Medical Technology Alliance (GMTA) represents medical technology associations whose members supply over 85 percent of the medical devices and diagnostics purchased annually
Belgian Position Paper
 The "INTERNATIONAL CO-OPERATION" COMMISSION and the "FEDERAL CO-OPERATION" COMMISSION of the Interministerial Conference of Science Policy of Belgium Belgian Position Paper Belgian position and recommendations
The "INTERNATIONAL CO-OPERATION" COMMISSION and the "FEDERAL CO-OPERATION" COMMISSION of the Interministerial Conference of Science Policy of Belgium Belgian Position Paper Belgian position and recommendations
Working together to deliver on Europe 2020
 Lithuanian Position Paper on the Green Paper From Challenges to Opportunities: Towards a Common Strategic Framework for EU Research and Innovation Funding Lithuania considers Common Strategic Framework
Lithuanian Position Paper on the Green Paper From Challenges to Opportunities: Towards a Common Strategic Framework for EU Research and Innovation Funding Lithuania considers Common Strategic Framework
Space Assets and the Sustainable Development Goals
 Space Assets and the Sustainable Development Goals Michael Simpson, Secure World Foundation In cooperation with Krystal Wilson Breakout Session #2 - Space Society Monday, November 21, 2016 United Nations/United
Space Assets and the Sustainable Development Goals Michael Simpson, Secure World Foundation In cooperation with Krystal Wilson Breakout Session #2 - Space Society Monday, November 21, 2016 United Nations/United
Current state of the debate regarding the role of Social Sciences and Humanities in Research and Innovation in the EU 1
 AUG 18 Current state of the debate regarding the role of Social Sciences and Humanities in Research and Innovation in the EU 1 The role of social sciences and humanities (SSH) in European research and
AUG 18 Current state of the debate regarding the role of Social Sciences and Humanities in Research and Innovation in the EU 1 The role of social sciences and humanities (SSH) in European research and
"Working Groups for Harmonisation and Alignment in Brain Imaging Methods for Neurodegeneration" Final version
 Page 1 of 5 Call for Proposals for "Working Groups for Harmonisation and Alignment in Brain Imaging Methods for Neurodegeneration" Final version January 2016 Submission deadline for proposals: 10 th March
Page 1 of 5 Call for Proposals for "Working Groups for Harmonisation and Alignment in Brain Imaging Methods for Neurodegeneration" Final version January 2016 Submission deadline for proposals: 10 th March
Management Consultancy
 University Press Scholarship Online You are looking at 1-9 of 9 items for: keywords : management innovation Management Consultancy Andrew Sturdy, Karen Handley, Timothy Clark, and Robin Fincham Published
University Press Scholarship Online You are looking at 1-9 of 9 items for: keywords : management innovation Management Consultancy Andrew Sturdy, Karen Handley, Timothy Clark, and Robin Fincham Published
Almost by definition, issues of risk are both complex and complicated.
 E d itorial COMPLEXITY, RISK AND EMERGENCE: ELEMENTS OF A MANAGEMENT DILEMMA Risk Management (2006) 8, 221 226. doi: 10.1057/palgrave.rm.8250024 Introduction Almost by definition, issues of risk are both
E d itorial COMPLEXITY, RISK AND EMERGENCE: ELEMENTS OF A MANAGEMENT DILEMMA Risk Management (2006) 8, 221 226. doi: 10.1057/palgrave.rm.8250024 Introduction Almost by definition, issues of risk are both
Please send your responses by to: This consultation closes on Friday, 8 April 2016.
 CONSULTATION OF STAKEHOLDERS ON POTENTIAL PRIORITIES FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION IN THE 2018-2020 WORK PROGRAMME OF HORIZON 2020 SOCIETAL CHALLENGE 5 'CLIMATE ACTION, ENVIRONMENT, RESOURCE EFFICIENCY AND
CONSULTATION OF STAKEHOLDERS ON POTENTIAL PRIORITIES FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION IN THE 2018-2020 WORK PROGRAMME OF HORIZON 2020 SOCIETAL CHALLENGE 5 'CLIMATE ACTION, ENVIRONMENT, RESOURCE EFFICIENCY AND
Empirical Study of the Formation Processes of Energy Scenarios
 Empirical Study of the Formation Processes of Energy Scenarios Name: Institution: Christian Dieckhoff Institute for Technology Assessment and Systems Analysis (ITAS), Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe GmbH Address:
Empirical Study of the Formation Processes of Energy Scenarios Name: Institution: Christian Dieckhoff Institute for Technology Assessment and Systems Analysis (ITAS), Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe GmbH Address:
Integrated Transformational and Open City Governance Rome May
 Integrated Transformational and Open City Governance Rome May 9-11 2016 David Ludlow University of the West of England, Bristol Workshop Aims Key question addressed - how do we advance towards a smart
Integrated Transformational and Open City Governance Rome May 9-11 2016 David Ludlow University of the West of England, Bristol Workshop Aims Key question addressed - how do we advance towards a smart
Development and Integration of Artificial Intelligence Technologies for Innovation Acceleration
 Development and Integration of Artificial Intelligence Technologies for Innovation Acceleration Research Supervisor: Minoru Etoh (Professor, Open and Transdisciplinary Research Initiatives, Osaka University)
Development and Integration of Artificial Intelligence Technologies for Innovation Acceleration Research Supervisor: Minoru Etoh (Professor, Open and Transdisciplinary Research Initiatives, Osaka University)
Epilogue. Simona Rocchi Erasmus University, Centre for Environmental Studies, Rotterdam
 Simona Rocchi Erasmus University, Centre for Environmental Studies, Rotterdam Epilogue Enhancing Sustainable Innovation by Design An Approach to the Co-creation of Economic, Social and Environmental Value
Simona Rocchi Erasmus University, Centre for Environmental Studies, Rotterdam Epilogue Enhancing Sustainable Innovation by Design An Approach to the Co-creation of Economic, Social and Environmental Value
Research Development Request - Profile Template. European Commission
 Research Development Request - Profile Template European Commission Research Development Request Profile The following table can be used as a template for drafting a Research Development Request profile.
Research Development Request - Profile Template European Commission Research Development Request Profile The following table can be used as a template for drafting a Research Development Request profile.
Building National Infrastructures for Patientcentred
 Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) ECIS 2015 Completed Research Papers ECIS 2015 Proceedings Spring 5-29-2015 Building National Infrastructures for Patientcentred Digital
Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) ECIS 2015 Completed Research Papers ECIS 2015 Proceedings Spring 5-29-2015 Building National Infrastructures for Patientcentred Digital
The workspace design concept: A new framework of participatory ergonomics
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 16, 2017 The workspace design concept: A new framework of participatory ergonomics Broberg, Ole Published in: Ergonomics for a future Publication date: 2007 Document
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 16, 2017 The workspace design concept: A new framework of participatory ergonomics Broberg, Ole Published in: Ergonomics for a future Publication date: 2007 Document
Software Project Management 4th Edition. Chapter 3. Project evaluation & estimation
 Software Project Management 4th Edition Chapter 3 Project evaluation & estimation 1 Introduction Evolutionary Process model Spiral model Evolutionary Process Models Evolutionary Models are characterized
Software Project Management 4th Edition Chapter 3 Project evaluation & estimation 1 Introduction Evolutionary Process model Spiral model Evolutionary Process Models Evolutionary Models are characterized
SITUATED CREATIVITY INSPIRED IN PARAMETRIC DESIGN ENVIRONMENTS
 The 2nd International Conference on Design Creativity (ICDC2012) Glasgow, UK, 18th-20th September 2012 SITUATED CREATIVITY INSPIRED IN PARAMETRIC DESIGN ENVIRONMENTS R. Yu, N. Gu and M. Ostwald School
The 2nd International Conference on Design Creativity (ICDC2012) Glasgow, UK, 18th-20th September 2012 SITUATED CREATIVITY INSPIRED IN PARAMETRIC DESIGN ENVIRONMENTS R. Yu, N. Gu and M. Ostwald School
About Software Engineering.
 About Software Engineering pierre-alain.muller@uha.fr What is Software Engineering? Software Engineering Software development Engineering Let s s have a look at ICSE International Conference on Software
About Software Engineering pierre-alain.muller@uha.fr What is Software Engineering? Software Engineering Software development Engineering Let s s have a look at ICSE International Conference on Software
OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 2008: Highlights
 OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 2008: Highlights Global dynamics in science, technology and innovation Investment in science, technology and innovation has benefited from strong economic
OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 2008: Highlights Global dynamics in science, technology and innovation Investment in science, technology and innovation has benefited from strong economic
Architectural assumptions and their management in software development Yang, Chen
 University of Groningen Architectural assumptions and their management in software development Yang, Chen IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Architectural assumptions and their management in software development Yang, Chen IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
Cooperation and Control in Innovation Networks
 Cooperation and Control in Innovation Networks Ilkka Tuomi @ meaningprocessing. com I. Tuomi 9 September 2010 page: 1 Agenda A brief introduction to the multi-focal downstream innovation model and why
Cooperation and Control in Innovation Networks Ilkka Tuomi @ meaningprocessing. com I. Tuomi 9 September 2010 page: 1 Agenda A brief introduction to the multi-focal downstream innovation model and why
4 WHAT DO WE MEAN BY INFORMATION
 4 WHAT DO WE MEAN BY INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY? PERSPECTIVES ON STUDYING COMPUTING Steve Sawyer School of Information Sciences and Technology The Pennsylvania State University Steven Haynes School of Information
4 WHAT DO WE MEAN BY INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY? PERSPECTIVES ON STUDYING COMPUTING Steve Sawyer School of Information Sciences and Technology The Pennsylvania State University Steven Haynes School of Information
Written response to the public consultation on the European Commission Green Paper: From
 EABIS THE ACADEMY OF BUSINESS IN SOCIETY POSITION PAPER: THE EUROPEAN UNION S COMMON STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK FOR FUTURE RESEARCH AND INNOVATION FUNDING Written response to the public consultation on the European
EABIS THE ACADEMY OF BUSINESS IN SOCIETY POSITION PAPER: THE EUROPEAN UNION S COMMON STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK FOR FUTURE RESEARCH AND INNOVATION FUNDING Written response to the public consultation on the European
