(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
|
|
|
- Charles Gregory
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1 Harris et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2007 (54) SPIRAL INDUCTOR FORMED IN A Publication Classification SEMCONDUCTOR SUBSTRATE AND A METHOD FOR FORMING THE INDUCTOR (51) Int. Cl. HOIF 7/06 ( ) (76) Inventors: Edward B. Harris, Orlando, FL (US); H05K 3/02 ( ) Stephen W. Downey, Orlando, FL (US) (52) U.S. Cl /602.1; 29/846; 29/606 Correspondence Address: HITT GAINES, PC AGERE SYSTEMS INC. (57) ABSTRACT PO BOX RICHARDSON, TX (US) (21) Appl. No.: 11A An inductor formed on a semiconductor Substrate, compris y x ing active device regions. The inductor comprises conduc (22) Filed: May 19, 2006 tive lines formed on a dielectric layer overlying the semi conductor Substrate. The conductive lines are patterned and Related U.S. Application Data etched into the desired shape, in one embodiment a planar (62) Division of application No. 10/646,997, filed on Aug. 22, 2003, now Pat. No. 7,075,167. spiral. A region of the substrate below the inductor are removed to lower the inductive Q factor ? \
2
3
4
5
6 ((N) Patent Application Publication May 17, 2007 Sheet 5 of 12 09gg 090 ZGZ9 ( 09 - US 2007/ A1
7 Patent Application Publication May 17, 2007 Sheet 6 of 12 US 2007/ A1 89 /19 9 "SDI Z9
8 Patent Application Publication May 17, 2007 Sheet 7 of 12 US 2007/ A A 76 FIG 7 80 FIG. 8
9 Patent Application Publication May 17, 2007 Sheet 8 of 12 US 2007/ A1 97
10 Patent Application Publication May 17, 2007 Sheet 9 of 12 US 2007/ A A
11 Patent Application Publication May 17, 2007 Sheet 10 of 12 US 2007/ A1
12 Patent Application Publication May 17, 2007 Sheet 11 of 12 US 2007/ A1 N Z/ 99 gg ~
13
14 US 2007/ A1 May 17, 2007 SPIRAL INDUCTOR FORMED IN A SEMCONDUCTOR SUBSTRATE AND A METHOD FOR FORMING THE INDUCTOR This patent application is a divisional of Ser. No. 10/646,997 filed on Aug. 22, FIELD OF THE INVENTION 0002 This invention relates generally to inductors, and more specifically, to spiral inductors formed in a semicon ductor substrate. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION The current revolution in wireless communications and the need for Smaller wireless communications devices has spawned significant efforts directed to the optimization and miniaturization of radio communications electronic devices. Passive components (such as inductors, capacitors and transformers), play a necessary role in the operation of these devices and thus efforts are directed toward reducing the size and improving the performance and fabrication efficiency of Such passive components Discrete inductors and capacitors are electromag netic components employed in alternating current and radio frequency applications, such as oscillators, amplifiers and signal filters, to provide frequency dependent effects. Spe cifically, the Voltage across the inductor is a function of the product of the inductance and the time derivative of the current through the inductor. A conventional inductor com prises a plurality of windings enclosing a core constructed of a ferromagnetic or an insulating material. Although an inductor core is not required, use of a ferromagnetic core, for example, increases the inductance value. The inductance is also a function of the number of coil turns (specifically, the inductance is proportional to the square of the number of turns) and the core area. Conventional discrete inductors are formed as a helix (also referred to as a Solenoidal shape) or a torroid. The core is typically formed of iron, cobalt or nickel (or a ferromagnetic alloy) comprising a plurality of magnetic domains. The current Supplied to the inductor induces a magnetic field in the core material, causing domain alignment and a resulting increase in the material permeability, which in turn increases the inductance Developments in the semiconductor industry have over the years been directed at fabricating higher perfor mance devices of decreasing size. One challenge of semi conductor circuit design and fabrication is the integration of high performance capacitors and inductors into the semi conductor device. Ideally, these components are formed on a relatively small Surface area of a semiconductor Substrate, using methods and procedures that are conventional in the semiconductor fabrication art. However, compared with the feature sizes and line widths of active devices, inductors and capacitors are large and not easily integrated into semicon ductor devices that typically have feature sizes in the sub micron range Most inductors formed on a semiconductor sub strate surface have a spiral shape, where the plane of the spiral is parallel to the Substrate Surface. Many techniques are known for forming the spiral inductor, such as by masking, patterning and etching a layer of conductive mate rial formed on the substrate surface. Multiple interconnected spiral inductors can also be formed to provide the desired inductive properties and/or to simplify the fabrication pro cess. See for example, U.S. Pat. No. 6,429,504 describing a multi-layer spiral inductor and U.S. Pat. No. 5,610,433 disclosing a high value inductor with a high Q factor formed from a plurality of layers with each layer comprising two or more coils. The coils in the various layers are interconnected in series The Q (or quality factor), an important inductor figure of merit, is defined as the ratio of inductive reactance to resistance. High-Q inductors (e.g., having a low resis tance) present a narrow Q peak as a function of the input signal frequency, where the peak occurs at the inductor resonant frequency. High-Q inductors are especially impor tant for use in frequency-dependent circuits operating with narrow bandwidths. For example, increasing the Q for an inductor operating in an oscillator decreases the oscillator phase noise, and confines the oscillator frequency to a narrower band of frequencies. Because the Q value is an inverse function of inductor resistance, minimizing the resistance increases the Q. One known technique for mini mizing the resistance increases the cross-sectional area of the conductive material forming the inductor. However, such conductors can present difficulties during the etching, clean ing, and passivating steps, and consume valuable space on the semiconductor substrate. Also, difficulties arise when gaps form in the dielectric material between the metal conductors, creating device reliability problems, as the gaps can promote local dielectric breakdown and consequent shorting of the inductor turns The magnetic field of a spiral inductor formed on the Surface of a semiconductor Substrate is perpendicular to the substrate. The field induces eddy currents within the semiconductor Substrate and the conductive interconnect structures formed in the Substrate to connect active semi conductor regions. Since these eddy currents represent a loss mechanism, they increase the inductor resistance and thus lower the inductor Q factor. To avoid such losses, at rela tively low operational frequencies the inductive effect can be achieved by simulating an inductor with active devices. But active devices have a finite dynamic range, can inject unwanted noise into the operating circuits and cannot pro vide acceptable inductive effects at higher operational fre quencies One known technique for limiting eddy current losses places a conductive shield parallel to and underlying the inductor. The conductor shorts the magnetic field lines, reducing the eddy currents in the underlying semiconductor substrate material. Eddy currents can also be reduced by using deep trench technology to remove a region of silicon below the inductor. This technique, which can be used to form isolation regions in an integrated circuit comprising both bipolar and CMOS transistors (complementary metal oxide silicon field effect transistors), removes the silicon from the front or top surface of the wafer. Increasing the distance between the inductor and the underlying silicon also lowers the eddy current losses. Marginal improvement in the Q factor have been noted when these techniques are employed. BRIEF SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION To provide further advances in the fabrication of inductors in conjunction with active devices on a semicon
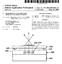
15 US 2007/ A1 May 17, 2007 ductor Substrate, an architecture and processes are provided for forming Such an inductor comprising a semiconductor Substrate and a dielectric layer overlying the Substrate. Conductive lines, comprising the inductor, are formed on an upper Surface of the dielectric layer. A region of the semi conductor Substrate under the conductive lines is removed ) A semiconductor device comprises a semiconduc tor Substrate and a dielectric layer overlying the semicon ductor Substrate. A continuous conductor is disposed on the dielectric layer. The semiconductor substrate defines an aperture therein in at least a portion of a region underlying the continuous conductor. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The present invention can be more easily under stood and the advantages and uses thereof more readily apparent, when considered in view of the following detailed description of when read in conjunction with the following figures wherein: 0013 FIGS illustrate a semiconductor structure and inductor following the completion of various process steps according to the invention In accordance with common practice, the various described device features are not drawn to scale, but are drawn to emphasize specific features relevant to the inven tion. Reference characters denote like elements throughout the figures and text. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION One process for forming an inductor according to the present invention begins as shown in FIG. 1, illustrating an integrated circuit semiconductor Substrate 10, which conventionally includes a plurality of active elements (not shown). According to one embodiment of the present inven tion, to accommodate the inductor no active elements are formed within regions 12 and A dielectric layer 40 (typically 3-5 microns thick) is formed over an upper surface 42 of the silicon substrate 10, followed by formation of windows 44 extending through the dielectric layer 40 to active elements in regions 46 and 48 of the substrate 10. The windows 44 are formed using known photolithographic masking, patterning and etching processes. In Subsequent processing steps a conductive material layer is formed overlying an upper Surface 45. In the region of the silicon substrate illustrated in FIG. 1 an inductor is formed in the conductive material layer, and interconnecting elements (e.g., tungsten plugs) are formed in the windows 44 for connecting the inductor to the active elements in the regions 46 and As illustrated in FIG. 2, a titanium layer 50 is deposited in the windows 44 and on a field region 52, i.e., an upper surface of the dielectric layer 40. At a bottom surface 53 of the windows 44, the titanium layer 50 reacts with the underlying silicon of the active regions to form a localized titanium silicide region. This silicide region pro vides improved conductivity between the active regions and the interconnecting tungsten plugs formed later in the win dows ) Next a titanium-nitride (TiN) layer 58 is deposited within the windows 44 and on the field region 52. It is known that titanium-nitride can delaminate from oxide based materials such as the dielectric layer 40. The titanium layer 50 serves as an adhesion layer to promote bonding between the titanium-nitride layer 58 and the underlying dielectric material of the field region 52, sidewalls 56 and bottom surfaces 53. The TiN layer 58 serves as a barrier between the underlying titanium layer and the fluorine-based gas used during the tungsten deposition step described below, as the fluorine-based gas is highly reactive with titanium As shown in FIG. 3, a tungsten layer 60 is formed in the windows 44 and in the field region 52 by a chemical vapor deposition process involving tungsten hexafluoride (WF) and silane (SiH). The silicon substrate 10 then undergoes a chemical-mechanical polishing step, forming tungsten plugs 62. See FIG As illustrated in FIG. 5, an aluminum stack 66 comprising, from bottom to top, a titanium layer 67, a titanium nitride layer 68, an aluminum layer 69 and an anti-reflective cap layer 70, is deposited over the field region 52. The titanium layer 67 and the titanium-nitride layer 68 of the aluminum stack 66 serve the same purposes as the titanium and titanium nitride layers 50 and 58 described above Certain regions of the aluminum stack 66 are removed using conventional masking, patterning and etch ing steps, to form, in one region of the Substrate 10, the desired conductor shape for an inductor 71, comprising a plurality of aluminum conductive lines 66A as shown in FIG In other regions of the substrate 10 not shown in FIG. 6, conductive interconnect structures are formed in the aluminum stack 66 by masking, patterning and etching steps, and underlying conductive tungsten plugs are formed in contact with active regions in the substrate 10. The interconnect structures, referred to as a metal-1 layer or first metallization layer, connect to the underlying tungsten plugs. AS is known to those skilled in the art, additional interconnect structures, conductive Vias and intermetallic dielectric layers are formed overlying the aluminum stack 66 to form a complete interconnect system for the integrated circuit. Thus formation of the inductor 71 is conveniently integrated into the process for forming device interconnects, as the inductor can be formed simultaneously with formation of the interconnect structures As can be seen from the plan view of FIG. 7 (FIG. 6 is a cross-sectional view take along the lines 6-6 of FIG. 7), in this embodiment the conductive lines 66A are linear and intersect at about a 90 angle, forming a linear spiral shaped inductor 71. Terminal ends 76 of the inductor 71 may be connected to underlying active devices in the regions 46 and 48 by the tungsten plugs A curved spiral inductor 80 as shown in FIG. 8 can also be formed by appropriate masking, patterning and etching of material regions of the aluminum stack 66. An inductor having a desired inductance value can be formed by appropriate selection of the size and geometrical pattern of the conductors forming the inductor In the embodiment of the present invention illus trated in FIG. 6, the inductor 71 is formed in a metal-1 layer
16 US 2007/ A1 May 17, 2007 or a first metallization layer. In other embodiments illus trated below, the inductor is formed in upper level metalli Zation layers According to the present invention the regions 12 and 14 of the substrate 10 underlying the inductor 71 (referred to as the backside of the wafer) are removed after formation of the inductor 71, forming voids 82. The result ing structure is illustrated in the cross-sectional view of FIG. 9 and the plan view of FIG. 10. Material etching processes or laser micro-machining are known techniques that can be employed to remove the regions 12 and 14, which are typically about microns thick. Although the voids 82 have a rectangular shape in FIG. 10, this is merely exemplary. The void for a circular spiral inductor, for example, would typically be circular. In one embodiment the voids 82 are filled with a non-conductive, dielectric or packaging material Such as epoxy or polyimide. In another embodiment the voids 82 are formed in the substrate 10 prior to formation of the inductor 71, although such a technique may be more difficult as it may be necessary to fill the void with a dielectric material. Such as silicon dioxide, to allow Subsequent formation of overlying layers As discussed above, the absence of semiconductor and conductive material below the inductor 71 lowers induc tor-induced eddy currents and raises the inductor Q factor FIG. 11 illustrates an embodiment of an inductor 89 comprising a conductive element 90 in the same metal lization layer as the conductive lines 66A.for extending the terminal end 76. In this embodiment the void 82 is larger than in the embodiment of FIG. 9, thus increasing the Q factor of the inductor 89, when compared with the inductor 71 of FIG FIG. 12 is a plan view of the inductor 89 of FIG. 11, with the cross-sectional view of FIG. 11 taken along the plane of FIG FIG. 13 is a cross-sectional view of an inductor 92, wherein both terminal ends 76 are spaced apart from the inductor 71 to allow the formation of a larger void 82 than present in the embodiments described heretofore. To form this embodiment an intermetallic dielectric layer 94 is disposed over the conductive lines 66A, and a second metallization layer overlying the intermetallic dielectric layer 94 comprises a conductive element 98 formed therein. A tungsten plug 100 connects the terminal end 76 to the conductive element 98. A tungsten plug 102 connects the conductive line 98 to an active region in the substrate 10. With both terminal ends 76 connected to an active region outside the footprint of the inductor 92, the void 82 can encompass Substantially the entire region below the inductor As is known to those skilled in the art, an integrated circuit generally comprises a plurality of metallization layers for interconnecting device active regions formed within the semiconductor substrate. These layers are typically referred to with a numerical indicator preceded by the letter M, for metallization, such as metallization layer one (M1). In one embodiment of the present invention an inductor is formed in an upper metallization layer (i.e., above M1), with upwardly and/or downwardly extending tungsten plugs for connecting inductor terminal ends to device active regions or other conductive structures Typically a fifth metallization layer (M5) is about 5 microns from the semiconductor substrate 10. An inductor formed therein is therefore about 5 microns from the sub strate 10. It has been observed that removal of underlying Substrate material (according to the teachings of the present invention) with a 5 micron separation between the inductor and the substrate improves the inductor Q. The known lossy substrate effects discussed above are observed up to an inductor-substrate separation distance equal to at least the diameter of the inductor. Typical inductor diameters may be in the range of microns. Thus the teachings of the present invention may be advantageously employed where the inductor is formed in any of the metallization layers, since all the metallization layers are within 100 microns of the semiconductor Substrate FIG. 14 is a cross-sectional view illustrating an embodiment of the present invention wherein an inductor 120 is formed in the third metallization layer or M3 of an integrated circuit device. FIG. 14 does not illustrate certain ancillary layers (e.g., titanium and titanium-nitride) shown in the embodiments above. A semiconductor substrate 122 comprises a plurality of active devices (not shown) formed according to known prior art techniques. Conductive Vias 124 are formed in a dielectric layer 126. A first metallization layer (M1) comprises conductive structures 128 for inter connecting the conductive Vias 124 to overlying conductive vias 130 formed in an intermetallic dielectric layer 132. As is known in the art, the conductive structures also extend into and outwardly from the plane of the FIG. 14 cross section A second metallization layer (M2) comprises con ductive structures 140 overlying the conductive vias 130 and connected to conductive vias 142 formed in an intermetallic dielectric layer 144. The third metallization layer comprises the inductor 120 and a conductive structure 146, which are formed simultaneously by known masking, patterning and etching steps performed on a conductive layer formed overlying the intermetallic dielectric later 144. Additional metallization layers and intermetallic dielectric layers (not shown in FIG. 14) can be formed over the illustrated Structure. 0035) Prior to formation of the intermetallic dielectric layer 144 voids are formed in regions 150, underlying the inductor 120, using conventional masking, patterning and etching steps. The voids are filled with silicon dioxide (a dielectric material) or another relatively low loss material prior to formation of the intermetallic dielectric layer 144 thereover. In another embodiment (not shown in FIG. 14) a region of the substrate 122 below the inductor 120 is also removed, according to the teachings above. As in the pre vious embodiment, the absence of semiconductor and met allization layers below the inductor 120 reduces eddy cur rent loses and improves the inductor Q factor. 0036) An architecture and process have been described as useful for forming an inductor on a semiconductor Substrate. While specific applications of the invention have been illustrated, the principals disclosed herein provide a basis for practicing the invention in a variety of ways and in a variety of circuit structures. Numerous variations are possible within the scope of the invention. The invention is limited only by the claims that follow.
17 US 2007/ A1 May 17, 2007 What is claimed is: 1. A method for forming an inductor, comprising: forming a semiconductor Substrate; forming a dielectric layer overlying the Substrate, wherein the dielectric layer comprises an upper Surface; forming conductive lines on the upper Surface, wherein the conductive lines exhibit an inductive effect; and removing a region of the semiconductor Substrate under lying at least a portion of the conductive lines. 2. The method of claim 1 further comprising forming active regions in the semiconductor Substrate. 3. The method of claim 1 wherein the conductive lines comprise first and second terminal ends, further comprising forming conductive interconnects through the dielectric layer for connecting the first and the second terminals to active regions. 4. The method of claim 1 wherein the step of removing a region of the semiconductor Substrate comprises etching the semiconductor Substrate. 5. The method of claim 1 wherein the step of removing a region of the semiconductor Substrate comprises micro machining the semiconductor Substrate. 6. A method for forming an inductor, comprising: forming a semiconductor Substrate; forming one or more dielectric layers overlying the Sub strate, wherein an upper layer of the one or more dielectric layers comprises an upper Surface; forming conductive lines on the upper Surface, wherein the conductive lines exhibit an inductive effect; and defining an aperture by removing a region of one or more of the dielectric layers underlying at least a portion of the conductive lines. 7. The method of claim 6 further comprising depositing a dielectric material in the aperture.
y y (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1 (19) United States (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, C 410C 422b 4200
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0255300 A1 He et al. US 201502553.00A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) DENSELY SPACED FINS FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0255300 A1 He et al. US 201502553.00A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) DENSELY SPACED FINS FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006
 (19) United States US 200601 19753A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01 19753 A1 Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006 (54) STACKED STORAGE CAPACITOR STRUCTURE FOR A THIN FILM
(19) United States US 200601 19753A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01 19753 A1 Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006 (54) STACKED STORAGE CAPACITOR STRUCTURE FOR A THIN FILM
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,770,955 B1
 USOO6770955B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Coccioli et al. () Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 2004 (54) SHIELDED ANTENNA INA 6,265,774 B1 * 7/2001 Sholley et al.... 7/728 SEMCONDUCTOR PACKAGE 6,282,095
USOO6770955B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Coccioli et al. () Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 2004 (54) SHIELDED ANTENNA INA 6,265,774 B1 * 7/2001 Sholley et al.... 7/728 SEMCONDUCTOR PACKAGE 6,282,095
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030091084A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091084A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) INTEGRATION OF VCSEL ARRAY AND Publication Classification
US 20030091084A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091084A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) INTEGRATION OF VCSEL ARRAY AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
(19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,211,068 B1
 USOO6211068B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,211,068 B1 Huang (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) DUAL DAMASCENE PROCESS FOR 5,981,377 * 11/1999 Koyama... 438/633 MANUFACTURING INTERCONNECTS
USOO6211068B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,211,068 B1 Huang (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) DUAL DAMASCENE PROCESS FOR 5,981,377 * 11/1999 Koyama... 438/633 MANUFACTURING INTERCONNECTS
A///X 2. N N-14. NetNNNNNNN N. / Et EY / E \ \ (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060055032A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0055032A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 16, 2006 (54) PACKAGING WITH METAL STUDS FORMED ON SOLDER PADS
(19) United States US 20060055032A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0055032A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 16, 2006 (54) PACKAGING WITH METAL STUDS FORMED ON SOLDER PADS
(12) United States Patent
 US009 159725B2 (12) United States Patent Forghani-Zadeh et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) CONTROLLED ON AND OFF TIME SCHEME FORMONOLTHC
US009 159725B2 (12) United States Patent Forghani-Zadeh et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) CONTROLLED ON AND OFF TIME SCHEME FORMONOLTHC
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 LLP 57)
 III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 201502272O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0227202 A1 BACKMAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 13, 2015 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 201502272O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0227202 A1 BACKMAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 13, 2015 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0043209A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0043209 A1 Zhu (43) Pub. Date: (54) COIL DECOUPLING FORAN RF COIL (52) U.S. Cl.... 324/322 ARRAY (57) ABSTRACT
(19) United States US 2011 0043209A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0043209 A1 Zhu (43) Pub. Date: (54) COIL DECOUPLING FORAN RF COIL (52) U.S. Cl.... 324/322 ARRAY (57) ABSTRACT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 2007014.8968A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/014.8968 A1 KWOn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) METHOD OF FORMING SELF-ALIGNED (30) Foreign Application
US 2007014.8968A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/014.8968 A1 KWOn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) METHOD OF FORMING SELF-ALIGNED (30) Foreign Application
III. United States Patent (19) Hutter et al. N- BURED AYER P SUBSTRATE. A vertical PNP structure for use in a merged bipolar/cmos
 United States Patent (19) Hutter et al. III US00447A 11 Patent Number: 5,5,447 ) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 1995 54) 75 73 21 22 63) 51 (52) 58) 56) VERTICAL PNP TRANSISTOR IN MERGED BIPOLAR/CMOS TECHNOLOGY
United States Patent (19) Hutter et al. III US00447A 11 Patent Number: 5,5,447 ) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 1995 54) 75 73 21 22 63) 51 (52) 58) 56) VERTICAL PNP TRANSISTOR IN MERGED BIPOLAR/CMOS TECHNOLOGY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130256528A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0256528A1 XIAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 3, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (57) ABSTRACT DETECTING BURED
(19) United States US 20130256528A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0256528A1 XIAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 3, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (57) ABSTRACT DETECTING BURED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 20040070460A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0070460 A1 Norton (43) Pub. Date: (54) MICROWAVE OSCILLATOR Publication Classification (76) Inventor: Philip
US 20040070460A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0070460 A1 Norton (43) Pub. Date: (54) MICROWAVE OSCILLATOR Publication Classification (76) Inventor: Philip
United States Patent Patent Number: 5,683,539 Qian et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 1997
 USOO5683539A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: Qian et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 1997 54 NDUCTIVELY COUPLED RF PLASMA 5,458,732 10/1995 Butler et al.... 216/61 REACTORWTH FLOATING COL 5,525,159
USOO5683539A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: Qian et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 1997 54 NDUCTIVELY COUPLED RF PLASMA 5,458,732 10/1995 Butler et al.... 216/61 REACTORWTH FLOATING COL 5,525,159
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140097081A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0097081 A1 Morrissey et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHODS OF FORMING ATHIN FILM (52) U.S. Cl. RESISTOR USPC...
(19) United States US 20140097081A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0097081 A1 Morrissey et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHODS OF FORMING ATHIN FILM (52) U.S. Cl. RESISTOR USPC...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
a gif (12) United States Patent 2OO US 6,355,502 B1 Mar. 12, 2002 Kang et al. (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (54) SEMICONDUCTOR PACKAGE AND
 (12) United States Patent Kang et al. USOO63555O2B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,355,502 B1 Mar. 12, 2002 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR PACKAGE AND METHOD FOR MAKING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Kun-A Kang;
(12) United States Patent Kang et al. USOO63555O2B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,355,502 B1 Mar. 12, 2002 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR PACKAGE AND METHOD FOR MAKING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Kun-A Kang;
III IIHIH III. United States Patent (19) Brandt CURRENT. 5,534,837 Jul. 9, Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent:
 United States Patent (19) Brandt 54 ORTHOGONAL-FIELD ELECTRICALLY VARABLE MAGNETIC DEVICE I75) Inventor: Randy L. Brandt, Orange, Calif. 73 Assignee: Rockwell International, Seal Beach, Calif. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Brandt 54 ORTHOGONAL-FIELD ELECTRICALLY VARABLE MAGNETIC DEVICE I75) Inventor: Randy L. Brandt, Orange, Calif. 73 Assignee: Rockwell International, Seal Beach, Calif. 21 Appl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 (19) United States US 2006OOO1503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0001503 A1 Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (54) MICROSTRIP TO WAVEGUIDE LAUNCH (52) U.S. Cl.... 333/26
(19) United States US 2006OOO1503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0001503 A1 Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (54) MICROSTRIP TO WAVEGUIDE LAUNCH (52) U.S. Cl.... 333/26
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,791,072 B1. Prabhu (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2004
 USOO6791072B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,791,072 B1 Prabhu (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FORMING 2001/0020671 A1 * 9/2001 Ansorge et al.... 250/208.1
USOO6791072B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,791,072 B1 Prabhu (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FORMING 2001/0020671 A1 * 9/2001 Ansorge et al.... 250/208.1
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1. Dong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2017
 (19) United States US 20170214216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0214216 A1 Dong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HYBRID SEMICONDUCTOR LASERS (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... HOIS 5/1014 (2013.01);
(19) United States US 20170214216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0214216 A1 Dong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HYBRID SEMICONDUCTOR LASERS (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... HOIS 5/1014 (2013.01);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003.01225O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0122502 A1 Clauberg et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 3, 2003 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE DRIVER (52) U.S. Cl....
US 2003.01225O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0122502 A1 Clauberg et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 3, 2003 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE DRIVER (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004O155237A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0155237 A1 Kerber (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 12, 2004 (54) SELF-ALIGNED JUNCTION PASSIVATION Publication Classification
US 2004O155237A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0155237 A1 Kerber (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 12, 2004 (54) SELF-ALIGNED JUNCTION PASSIVATION Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0098.554A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0098554 A1 Chhatre et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) WINDOW AND MOUNTING ARRANGEMENT (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2013 0098.554A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0098554 A1 Chhatre et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 25, 2013 (54) WINDOW AND MOUNTING ARRANGEMENT (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O279458A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0279458 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 4, 2010 (54) PROCESS FOR MAKING PARTIALLY Related U.S. Application
(19) United States US 2010O279458A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0279458 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 4, 2010 (54) PROCESS FOR MAKING PARTIALLY Related U.S. Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O2325O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0232502 A1 Asakawa (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 18, 2003 (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING Publication Classification SEMCONDUCTOR
US 2003O2325O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0232502 A1 Asakawa (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 18, 2003 (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING Publication Classification SEMCONDUCTOR
(12) United States Patent
 US007 153067B2 (12) United States Patent GreenW00d et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2006 (54) ROTARY CUTTING TOOL HAVING MULTIPLE HELICAL CUTTING EDGES WITH DIFFERING HELIX ANGLES (76)
US007 153067B2 (12) United States Patent GreenW00d et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2006 (54) ROTARY CUTTING TOOL HAVING MULTIPLE HELICAL CUTTING EDGES WITH DIFFERING HELIX ANGLES (76)
United States Patent (19) (11) 4,130,822
 34.3a700 MS AU 26 EX l9/78 OR 4 gl30,822 United States Patent (19) (11) 4,130,822 Conroy Dec. 19, 1978 l2/ - (4) S A FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (7 Inventor: Peter J. Conroy, Scottsdale, Ariz. 10083 9/193
34.3a700 MS AU 26 EX l9/78 OR 4 gl30,822 United States Patent (19) (11) 4,130,822 Conroy Dec. 19, 1978 l2/ - (4) S A FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (7 Inventor: Peter J. Conroy, Scottsdale, Ariz. 10083 9/193
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9463468B2 () Patent No.: Hiley (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2016 (54) COMPACT HIGH VOLTAGE RF BO3B 5/08 (2006.01) GENERATOR USING A SELF-RESONANT GOIN 27/62 (2006.01) INDUCTOR
(12) United States Patent USOO9463468B2 () Patent No.: Hiley (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2016 (54) COMPACT HIGH VOLTAGE RF BO3B 5/08 (2006.01) GENERATOR USING A SELF-RESONANT GOIN 27/62 (2006.01) INDUCTOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,278,340 B1. Liu (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 21, 2001
 USOO627834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,278,340 B1 Liu (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 21, 2001 (54) MINIATURIZED BROADBAND BALUN 5,574,411 11/1996 Apel et al.... 333/25 TRANSFORMER HAVING
USOO627834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,278,340 B1 Liu (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 21, 2001 (54) MINIATURIZED BROADBAND BALUN 5,574,411 11/1996 Apel et al.... 333/25 TRANSFORMER HAVING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004
 (19) United States US 2004.0058664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0058664 A1 Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004 (54) SAW FILTER (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2004.0058664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0058664 A1 Yamamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 25, 2004 (54) SAW FILTER (30) Foreign Application Priority
Publication number: A2. Int. CI.5: H01 L 29/ Meadowridge Drive Garland, Texas 75044(US)
 Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets Publication number: 0 562 352 A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 93103748.5 Int. CI.5: H01 L 29/784 @ Date of filing:
Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets Publication number: 0 562 352 A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 93103748.5 Int. CI.5: H01 L 29/784 @ Date of filing:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Ironside et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004
 US 2004O247218A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0247218 A1 Ironside et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) OPTOELECTRONIC DEVICE Publication Classification
US 2004O247218A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0247218 A1 Ironside et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) OPTOELECTRONIC DEVICE Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) Morris
 United States Patent (19) Morris 54 CMOS INPUT BUFFER WITH HIGH SPEED AND LOW POWER 75) Inventor: Bernard L. Morris, Allentown, Pa. 73) Assignee: AT&T Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, N.J. 21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Morris 54 CMOS INPUT BUFFER WITH HIGH SPEED AND LOW POWER 75) Inventor: Bernard L. Morris, Allentown, Pa. 73) Assignee: AT&T Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, N.J. 21 Appl. No.:
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,777,539 Folker et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1998
 III USOO5777539A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,777,539 Folker et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1998 54 INDUCTOR USING MULTILAYERED 5,521,573 5/1996 Inoh et al.... 336,200 PRINTED CIRCUIT
III USOO5777539A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,777,539 Folker et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1998 54 INDUCTOR USING MULTILAYERED 5,521,573 5/1996 Inoh et al.... 336,200 PRINTED CIRCUIT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012
 US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
(12) United States Patent
 US008193047B2 (12) United States Patent Ryoo et al. (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE HAVING SUFFICIENT PROCESS MARGIN AND METHOD OF FORMING SAME (75) Inventors: Man-Hyoung Ryoo, Gyeonggi-do (KR): Gi-Sung Yeo,
US008193047B2 (12) United States Patent Ryoo et al. (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE HAVING SUFFICIENT PROCESS MARGIN AND METHOD OF FORMING SAME (75) Inventors: Man-Hyoung Ryoo, Gyeonggi-do (KR): Gi-Sung Yeo,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O151875A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0151875 A1 Lehr et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) LAMINATE INLAY PROCESS FOR SPORTS BOARDS (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2004O151875A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0151875 A1 Lehr et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) LAMINATE INLAY PROCESS FOR SPORTS BOARDS (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,602,001 B2. Gonzalez (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2009
 -. USOO7602001 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,602,001 B2 Gonzalez (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2009 (54) CAPACITORLESS ONE TRANSISTOR DRAM CELL, INTEGRATED CIRCUITRY 5,753,947 A 6,005,273
-. USOO7602001 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,602,001 B2 Gonzalez (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2009 (54) CAPACITORLESS ONE TRANSISTOR DRAM CELL, INTEGRATED CIRCUITRY 5,753,947 A 6,005,273
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Street et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006
 (19) United States US 2006.00354O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0035402 A1 Street et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) MICROELECTRONIC IMAGING UNITS AND METHODS OF
(19) United States US 2006.00354O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0035402 A1 Street et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) MICROELECTRONIC IMAGING UNITS AND METHODS OF
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,673,522 B2
 USOO6673522B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,673,522 B2 Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 6, 2004 (54) METHOD OF FORMING CAPILLARY 2002/0058209 A1 5/2002 Kim et al.... 430/321 DISCHARGE
USOO6673522B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,673,522 B2 Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 6, 2004 (54) METHOD OF FORMING CAPILLARY 2002/0058209 A1 5/2002 Kim et al.... 430/321 DISCHARGE
ve: 146 (12) United States Patent - D ( c10onsec GATE 132 (10) Patent No.: US 9,379,022 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 28, 2016 Pendharkar et al.
 US009379022B2 (12) United States Patent Pendharkar et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (62) (51) (52) PROCESS FOR FORMING DRIVER FOR NORMALLY ON II-NITRIDE
US009379022B2 (12) United States Patent Pendharkar et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (62) (51) (52) PROCESS FOR FORMING DRIVER FOR NORMALLY ON II-NITRIDE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 20050207013A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0207013 A1 Kanno et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2005 (54) PHOTOELECTRIC ENCODER AND (30) Foreign Application
US 20050207013A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0207013 A1 Kanno et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2005 (54) PHOTOELECTRIC ENCODER AND (30) Foreign Application
United States Patent 19 Lee et al.
 United States Patent 19 Lee et al. USOO5796586A 11 Patent umber: 5,796,586 45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1998 54 75 73) 21 22 51 52 58 SUBSTRATE BOARD HAVIG A ATI ADHESWE SOLDIER MASK Inventors: Shaw Wei
United States Patent 19 Lee et al. USOO5796586A 11 Patent umber: 5,796,586 45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1998 54 75 73) 21 22 51 52 58 SUBSTRATE BOARD HAVIG A ATI ADHESWE SOLDIER MASK Inventors: Shaw Wei
United States Patent (19) Price, Jr.
 United States Patent (19) Price, Jr. 11 4) Patent Number: Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 1986 4) (7) (73) 21) 22 1) 2 8) NPN BAND GAP VOLTAGE REFERENCE Inventor: John J. Price, Jr., Mesa, Ariz. Assignee: Motorola,
United States Patent (19) Price, Jr. 11 4) Patent Number: Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 1986 4) (7) (73) 21) 22 1) 2 8) NPN BAND GAP VOLTAGE REFERENCE Inventor: John J. Price, Jr., Mesa, Ariz. Assignee: Motorola,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. BOrthakur et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2009
 (19) United States US 20090017576A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0017576A1 BOrthakur et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2009 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR PROCESSING METHODS (57) ABSTRACT
(19) United States US 20090017576A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0017576A1 BOrthakur et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2009 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR PROCESSING METHODS (57) ABSTRACT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090103787A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0103787 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2009 (54) SLIDING TYPE THIN FINGERPRINT SENSOR PACKAGE (75)
(19) United States US 20090103787A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0103787 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2009 (54) SLIDING TYPE THIN FINGERPRINT SENSOR PACKAGE (75)
79 Hists air sigtais is a sign 83 r A. 838 EEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEE
 US 20060011813A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0011813 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A PASSIVATION (22) Filed: Jan.
US 20060011813A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0011813 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2006 (54) IMAGE SENSOR HAVING A PASSIVATION (22) Filed: Jan.
(12) Patent Application Publication
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Ryken et al. US 2003.0076261A1 (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0076261 A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIPURPOSE MICROSTRIPANTENNA FOR USE ON MISSILE (76) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Ryken et al. US 2003.0076261A1 (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0076261 A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIPURPOSE MICROSTRIPANTENNA FOR USE ON MISSILE (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,387,795 B1
 USOO6387795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shao (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) WAFER-LEVEL PACKAGING 5,045,918 A * 9/1991 Cagan et al.... 357/72 (75) Inventor: Tung-Liang Shao, Taoyuan
USOO6387795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shao (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) WAFER-LEVEL PACKAGING 5,045,918 A * 9/1991 Cagan et al.... 357/72 (75) Inventor: Tung-Liang Shao, Taoyuan
United States Patent (19) Rannou et al.
 United States Patent (19) Rannou et al. (54) (75) 73 22) (21) 30) 52 (51) (58) (56) WIDE-BAND OMNIDIRECTIONAL ANTENNA Inventors: Jean Rannou; William Luther, both of Paris, France Assignee: Thomson-CSF,
United States Patent (19) Rannou et al. (54) (75) 73 22) (21) 30) 52 (51) (58) (56) WIDE-BAND OMNIDIRECTIONAL ANTENNA Inventors: Jean Rannou; William Luther, both of Paris, France Assignee: Thomson-CSF,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. FOSS (43) Pub. Date: May 27, 2010
 US 2010O126550A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0126550 A1 FOSS (43) Pub. Date: May 27, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHODS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
US 2010O126550A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0126550 A1 FOSS (43) Pub. Date: May 27, 2010 (54) APPARATUS AND METHODS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
E3, ES 2.ÉAN 27 Asiaz
 (19) United States US 2014001 4915A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0014.915 A1 KOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) DUAL MODE DISPLAY DEVICES AND Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2014001 4915A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0014.915 A1 KOO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) DUAL MODE DISPLAY DEVICES AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 O155810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0155810 A1 TANGUCH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2011 (54) ANTENNA DEVICE AND RADIO (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2011 O155810A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0155810 A1 TANGUCH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2011 (54) ANTENNA DEVICE AND RADIO (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Schwab et al. US006335619B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR COMPRISING ARESONANT OSCILLATORY CIRCUIT RESPONDING TO CHANGES IN
(12) United States Patent Schwab et al. US006335619B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR COMPRISING ARESONANT OSCILLATORY CIRCUIT RESPONDING TO CHANGES IN
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Eklund (54) HIGH VOLTAGE MOS TRANSISTORS 75) Inventor: Klas H. Eklund, Los Gatos, Calif. 73) Assignee: Power Integrations, Inc., Mountain View, Calif. (21) Appl. No.: 41,994 22
United States Patent (19) Eklund (54) HIGH VOLTAGE MOS TRANSISTORS 75) Inventor: Klas H. Eklund, Los Gatos, Calif. 73) Assignee: Power Integrations, Inc., Mountain View, Calif. (21) Appl. No.: 41,994 22
52 U.S. Cl /587, 206/592: 229/87.02 planar Surfaces on which imprinting can appear. The molded
 USOO5806683A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Gale (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 15, 1998 54 WRAPPED PACKAGE AND METHOD USING Primary Examiner Paul T. Sewell MOLDED FIBER INNER STRUCTURE ASSistant
USOO5806683A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Gale (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 15, 1998 54 WRAPPED PACKAGE AND METHOD USING Primary Examiner Paul T. Sewell MOLDED FIBER INNER STRUCTURE ASSistant
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O134516A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Du (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) DUAL BAND SLEEVE ANTENNA (52) U.S. Cl.... 3437790 (75) Inventor: Xin Du, Schaumburg,
(19) United States US 2005O134516A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Du (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) DUAL BAND SLEEVE ANTENNA (52) U.S. Cl.... 3437790 (75) Inventor: Xin Du, Schaumburg,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090146763A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0146763 A1 Hershtig (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 11, 2009 (54) HIGH Q SURFACE MOUNTTECHNOLOGY Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20090146763A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0146763 A1 Hershtig (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 11, 2009 (54) HIGH Q SURFACE MOUNTTECHNOLOGY Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1
 USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,955,771 Kurtz et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 21, 1999
 USOO5955771A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,955,771 Kurtz et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 21, 1999 54). SENSORS FOR USE IN HIGH VIBRATIONAL 5,780,885 7/1998 Diem et al.... 257/254 EATSNMETHODs
USOO5955771A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,955,771 Kurtz et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 21, 1999 54). SENSORS FOR USE IN HIGH VIBRATIONAL 5,780,885 7/1998 Diem et al.... 257/254 EATSNMETHODs
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Su US 2005O127853A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) MULTI-LEVEL DC BUS INVERTER FOR PROVIDING SNUSODAL AND PWM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Su US 2005O127853A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) MULTI-LEVEL DC BUS INVERTER FOR PROVIDING SNUSODAL AND PWM
In this lecture we will begin a new topic namely the Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor.
 Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 38 MOS Field Effect Transistor In this lecture we will begin
Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 38 MOS Field Effect Transistor In this lecture we will begin
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,804,867. Leighton et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 8, 1998
 USOO5804867A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,804,867 Leighton et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 8, 1998 54) THERMALLY BALANCED RADIO 5,107,326 4/1992 Hargasser... 257/579 FREQUENCY POWER TRANSISTOR
USOO5804867A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,804,867 Leighton et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 8, 1998 54) THERMALLY BALANCED RADIO 5,107,326 4/1992 Hargasser... 257/579 FREQUENCY POWER TRANSISTOR
(12) United States Patent
 USOO964O656B2 (12) United States Patent Mayuzumi et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) TRANSISTORS HAVING STRAINED CHANNEL UNDER GATE
USOO964O656B2 (12) United States Patent Mayuzumi et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) TRANSISTORS HAVING STRAINED CHANNEL UNDER GATE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,928,083 B2
 US008928O83B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,928,083 B2 Chang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 6, 2015 (54) DIODESTRUCTURE AND METHOD FOR USPC... 257/350, 370,586,347, 392:438/202, FINFETTECHNOLOGES
US008928O83B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,928,083 B2 Chang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 6, 2015 (54) DIODESTRUCTURE AND METHOD FOR USPC... 257/350, 370,586,347, 392:438/202, FINFETTECHNOLOGES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O1893.99A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0189399 A1 Hu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) BIAS CIRCUIT FOR A RADIO FREQUENCY (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2004O1893.99A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0189399 A1 Hu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) BIAS CIRCUIT FOR A RADIO FREQUENCY (30) Foreign Application
United States Patent (19) Wrathal
 United States Patent (19) Wrathal (54) VOLTAGE REFERENCE CIRCUIT (75) Inventor: Robert S. Wrathall, Tempe, Ariz. 73) Assignee: Motorola, Inc., Schaumburg, Ill. (21) Appl. No.: 219,797 (22 Filed: Dec. 24,
United States Patent (19) Wrathal (54) VOLTAGE REFERENCE CIRCUIT (75) Inventor: Robert S. Wrathall, Tempe, Ariz. 73) Assignee: Motorola, Inc., Schaumburg, Ill. (21) Appl. No.: 219,797 (22 Filed: Dec. 24,
(51) Int. Cl... HoH 316 trolling a state of conduction of AC current between the
 USOO58599A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,8,599 ROSenbaum () Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54 GROUND FAULT CIRCUIT INTERRUPTER 57 ABSTRACT SYSTEM WITH UNCOMMITTED CONTACTS A ground fault
USOO58599A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,8,599 ROSenbaum () Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54 GROUND FAULT CIRCUIT INTERRUPTER 57 ABSTRACT SYSTEM WITH UNCOMMITTED CONTACTS A ground fault
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 19, 2004
 US 004OO301A1 (19) United States (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/00301 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 19, 004 (54) HERMETICALLY PACKAGING A () Filed: Aug. 14, 00 MICROELECTROMECHANICAL
US 004OO301A1 (19) United States (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 004/00301 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 19, 004 (54) HERMETICALLY PACKAGING A () Filed: Aug. 14, 00 MICROELECTROMECHANICAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (76) I ViOS t SUHAL ANWAR, San a Jose, OSC CA C23C I6/505 (2006.
 (19) United States US 20090101069A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0101069 A1 AWAR et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2009 (54) RF RETUR PLATES FOR BACKIG PLATE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20090101069A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0101069 A1 AWAR et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2009 (54) RF RETUR PLATES FOR BACKIG PLATE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United S tates US 20020003503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0003503 A1 Justice (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 10, 2002 (54) TWIN COILA NTENNA (76) Inventor: Christopher M. Justice,
(19) United S tates US 20020003503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0003503 A1 Justice (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 10, 2002 (54) TWIN COILA NTENNA (76) Inventor: Christopher M. Justice,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 US 2002O189352A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0189352 A1 Reeds, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2002 (54) MEMS SENSOR WITH SINGLE CENTRAL Publication
US 2002O189352A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0189352 A1 Reeds, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2002 (54) MEMS SENSOR WITH SINGLE CENTRAL Publication
us/ (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1 (19) United States / 112 / 108 Frederick et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb.
 (19) United States US 20080030263A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0030263 A1 Frederick et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2008 (54) CONTROLLER FOR ORING FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR
(19) United States US 20080030263A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0030263 A1 Frederick et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2008 (54) CONTROLLER FOR ORING FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Crawford 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 1990 54 (76) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) 56 LASERRANGEFINDER RECEIVER. PREAMPLETER Inventor: Ian D. Crawford, 1805 Meadowbend
United States Patent (19) Crawford 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 1990 54 (76) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) 56 LASERRANGEFINDER RECEIVER. PREAMPLETER Inventor: Ian D. Crawford, 1805 Meadowbend
(12) United States Patent
 US008549731B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,549,731 B2 Lim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OFA 5,111,382 A 5/1992 Jones et a1. VARIABLE INDUCTANCE
US008549731B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,549,731 B2 Lim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OFA 5,111,382 A 5/1992 Jones et a1. VARIABLE INDUCTANCE
United States Patent (19) Davis
 United States Patent (19) Davis 54 ACTIVE TERMINATION FOR A TRANSMISSION LINE 75 Inventor: 73 Assignee: Thomas T. Davis, Bartlesville, Okla. Phillips Petroleum Company, Bartlesville, Okla. 21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Davis 54 ACTIVE TERMINATION FOR A TRANSMISSION LINE 75 Inventor: 73 Assignee: Thomas T. Davis, Bartlesville, Okla. Phillips Petroleum Company, Bartlesville, Okla. 21 Appl. No.:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160090275A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0090275 A1 Piech et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2016 (54) WIRELESS POWER SUPPLY FOR SELF-PROPELLED ELEVATOR
(19) United States US 20160090275A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0090275 A1 Piech et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2016 (54) WIRELESS POWER SUPPLY FOR SELF-PROPELLED ELEVATOR
July 18, 1967 T. W. MOORE 3,331,967 TIME DELAY CIRCUIT EMPLOYING SCR CONTROLLED BY TIMING-CAPACITOR HAVING PLURAL CURRENT
 July 18, 1967 T. W. MOORE TIME DELAY CIRCUIT EMPLOYING SCR CONTROLLED BY TIMING-CAPACITOR HAVING PLURAL CURRENT PATHS FOR TOTAL DISCHARGING THEREOF Filed May 31, l963 1.7 d 8 M 23 s 24 Š5 22 7 s 9 wastin
July 18, 1967 T. W. MOORE TIME DELAY CIRCUIT EMPLOYING SCR CONTROLLED BY TIMING-CAPACITOR HAVING PLURAL CURRENT PATHS FOR TOTAL DISCHARGING THEREOF Filed May 31, l963 1.7 d 8 M 23 s 24 Š5 22 7 s 9 wastin
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,995,467 B2
 USOO699.5467B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,995,467 B2 Herfurth et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2006 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR COMPONENT 5,789.311 8/1998 Ueno et al.... 438/573 5,801,570
USOO699.5467B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,995,467 B2 Herfurth et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2006 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR COMPONENT 5,789.311 8/1998 Ueno et al.... 438/573 5,801,570
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.00200O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0020002 A1 FENG (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 21, 2016 (54) CABLE HAVING ASIMPLIFIED CONFIGURATION TO REALIZE SHIELDING
(19) United States US 2016.00200O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0020002 A1 FENG (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 21, 2016 (54) CABLE HAVING ASIMPLIFIED CONFIGURATION TO REALIZE SHIELDING
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Pfeffer et al. 11 (45 Oct. 5, 1976 54) (75) 73) 22) 21 (52) 51) 58) ALTERNATOR-RECTFER UNIT WITH PHASE WINDING AND RECTIFIER SETS SUBJECT TO SERIES-PARALLEL SWITCHING Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Pfeffer et al. 11 (45 Oct. 5, 1976 54) (75) 73) 22) 21 (52) 51) 58) ALTERNATOR-RECTFER UNIT WITH PHASE WINDING AND RECTIFIER SETS SUBJECT TO SERIES-PARALLEL SWITCHING Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013
 (19) United States US 20130279282A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0279282 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013 (54) E-FUSE ARRAY CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... GI IC 17/16 (2013.01);
(19) United States US 20130279282A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0279282 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013 (54) E-FUSE ARRAY CIRCUIT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... GI IC 17/16 (2013.01);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0188326 A1 Lee et al. US 2011 0188326A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) DUAL RAIL STATIC RANDOMACCESS MEMORY (75) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0188326 A1 Lee et al. US 2011 0188326A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) DUAL RAIL STATIC RANDOMACCESS MEMORY (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 2015 0096785A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0096785 A1 HAYASHSHTA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 9, 2015 (54) MULTICORE CABLE Publication Classification
US 2015 0096785A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0096785 A1 HAYASHSHTA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 9, 2015 (54) MULTICORE CABLE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014.0062180A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0062180 A1 Demmerle et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH-VOLTAGE INTERLOCK LOOP (52) U.S. Cl. ("HVIL") SWITCH
(19) United States US 2014.0062180A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0062180 A1 Demmerle et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH-VOLTAGE INTERLOCK LOOP (52) U.S. Cl. ("HVIL") SWITCH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
(19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
United States Patent (19) Nilssen
 United States Patent (19) Nilssen (4) HIGH-EFFICIENCY SINGLE-ENDED INVERTER CRCUIT 76) Inventor: Ole K. Nilssen, Caesar Dr. Rte. 4, Barrington, Ill. 60010 21 Appl. No.: 33,33 (22) Filed: Apr. 2, 1979 (1)
United States Patent (19) Nilssen (4) HIGH-EFFICIENCY SINGLE-ENDED INVERTER CRCUIT 76) Inventor: Ole K. Nilssen, Caesar Dr. Rte. 4, Barrington, Ill. 60010 21 Appl. No.: 33,33 (22) Filed: Apr. 2, 1979 (1)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0018076 A1 Chen et al. US 200700 18076A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) ELECTROMAGNETIC DIGITIZER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0018076 A1 Chen et al. US 200700 18076A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) ELECTROMAGNETIC DIGITIZER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006O151349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0151349 A1 Andrews et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) TRADING CARD AND CONTAINER (76) Inventors: Robert
(19) United States US 2006O151349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0151349 A1 Andrews et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) TRADING CARD AND CONTAINER (76) Inventors: Robert
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Sternbergh 54 75 73 21 22 63 51 52 58 56 MULTILAYER ANT-REFLECTIVE AND ULTRAWOLET BLOCKNG COATNG FOR SUNGLASSES Inventor: James H. Sternbergh, Webster, N.Y. Assignee: Bausch &
United States Patent (19) Sternbergh 54 75 73 21 22 63 51 52 58 56 MULTILAYER ANT-REFLECTIVE AND ULTRAWOLET BLOCKNG COATNG FOR SUNGLASSES Inventor: James H. Sternbergh, Webster, N.Y. Assignee: Bausch &
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0334265A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0334265 A1 AVis0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) BRASTORAGE DEVICE Publication Classification
US 2013 0334265A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0334265 A1 AVis0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) BRASTORAGE DEVICE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007035123B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,035,123 B2 Schreiber et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2006 (54) FREQUENCY CONVERTER AND ITS (56) References Cited CONTROL METHOD FOREIGN
(12) United States Patent US007035123B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,035,123 B2 Schreiber et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2006 (54) FREQUENCY CONVERTER AND ITS (56) References Cited CONTROL METHOD FOREIGN
