7. Parameteric amplifiers are very low noise. They are common as the on-the-antenna amplifier of satellite signal receiver systems.
|
|
|
- Damian McCormick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction Rather than try to give you the material so that you can answer the questions from first principles," I will provide enough information that you can recognize the correct answer to each question. Chapter 6 Notes In no particular order, the necessary nuggets: 1. Junction transistors are current controlled and therefore have relatively low input impedance. Field effect devices, including vacuum tubes, are voltage controlled and therefore have relatively high input impedance. Vacuum tubes are implicitly diodes as well. Transistor input and output elements can be reversed and the device would operate somewhat. 2. See attached amplifier circuits sheet. Another phrase for common word" amplifer is grounded word" amplifer. The key is determining which lead is at signal ground level. The lead may not be at DC ground for bias reasons. If a lead is connected to the power supply via a capacitor in parallel with a resistor then that lead is at signal ground. 3. See attached oscillators circuits sheet. Oscillators can be built using any type of amplifier. All that is required is a gain greater than 1 with positive feed back. The major classes of oscillators are named according to the method of providing that feedback. If the feedback circuit is a divided capacitor, then the oscillator is a Colpitts oscillator. The memory key is C for capacitance. If the feedback circuit is a divided inductor, then the oscillator is a Hartley oscillator. The memory key is H for Henries of inductance. If the feedback circuit is a crystal, then the oscillator os a Pierce oscillator. A crystal is a piezo-electric device. The memory key is P for piezo-electric. It is difficult to significantly modify the frequency of a Pierce (crystal) oscillator. Properly doped diodes properly biased into their negative resistance region of operation can be used as the amplifier section of an oscillator. Common such devices are Gunn and tunnel diodes, which can be made to oscillate into the THz range. 4. To stabilize an amplifier, provide negative feedback. 5. Distortion causes unintended (spurious) signals. Unintended signals are a violation of FCC regulations. Spurious signals can be wide bandwidth and result in transmissions outside the permitted amateur radio bands. 6. Common (grounded) control (grid, base or gate) element amplifiers have low output impedance. Linear power regulator circuits tend to use such amplifiers. Another common use is direct drive (transformerless) loudspeaker amplifiers. 7. Parameteric amplifiers are very low noise. They are common as the on-the-antenna amplifier of satellite signal receiver systems. 8. The opposite to a digital to analog converter (DAC) is an analog to digital converter. Most ADCs work by sampling a voltage (signal) and generating a match using a over-under procedure using a DAC working from the high order (largest value bit) to the low order (smallest value bit) and giving the digital value of a DAC s input. Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 1 of 17
2 9. AM implies changing the power of the signal. Often AM modulation is done using a mixer circuit. A 100Hz carrier modulated with a 6HZ and a 4HZ signal. sin(100t)(1 + sin(6t)/2 + sin(4t)/3)/1.8 The modulation signal: The transmitted signal: The Discrete Fourier Transform Power Spectrum: Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 2 of 17
3 10. FM implies changing frequencies. In a Colpitts or Hartley oscillator, one changes the frequency by modulating the reactance of something in the resonant circuit of the oscillator. sin(100t + 6 sin(t) The modulation signal: The transmitted signal (carrier at 10Hz for illustration): The Discrete Fourier Transform Power Spectrum: FM implies PM modulation and vis-a-vis. If an amplifier has a resonant circuit in it and that resonant circuit is modulated by a reactance modulator, the phase of the signal is affected. Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 3 of 17
4 Question by question explanations: E6E01 What is a crystal lattice filter? A filter with narrow bandwidth and steep skirts made using quartz crystals. It is a signal filter and not a power supply filter nor an audio filter. E6E02 Which of the following factors has the greatest effect in helping determine the bandwidth and response shape of a crystal ladder filter? The relative frequencies of the individual crystals. E6E03 What is one aspect of the piezoelectric effect? Physical deformation of a crystal by the application of a voltage. The other principal effect is a voltage generated by the physical deformation of a crystal. E6E09 Which of the following must be done to insure that a crystal oscillator provides the frequency specified by the crystal manufacturer? Provide the crystal with a specified parallel capacitance. E6E10 What is the equivalent circuit of a quartz crystal? Motional capacitance, motional inductance and loss resistance in series, with a shunt capacitance representing electrode and stray capacitance. Motional series tuned circuit Loss resistance Electrode and stray capacitance E6E12 What is a "Jones filter" as used as part of a HF receiver IF stage? A variable bandwidth crystal lattice filter. Patent assigned to Ten-tec. Amplifier classes (as compared to amplifier types) are determined by what portion of the input signal is present in the output. A The entire 360 of the the input is represented in the output. Such amplifiers can be quite linear. They are less than 50% efficient. AB More than 180 but less than 360 of the input is represented in the output. They are between class A and class B in efficiency. B Exactly 180 of the input is represented in the output. They are about 75% efficient. C Less than 180 of the input is represented in the output. Such amplifier are quite nonlinear (i.e., cause considerable distortion) and can be quite efficient. D Basically, a switching power supply whose output voltage is controlled by the signal being amplified. They can be extremely efficient; but, require extreme output filtering. Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 4 of 17
5 E7B01 For what portion of a signal cycle does a Class AB amplifier operate? More than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees. They are between class A and class B in efficiency. E7B02 What is a Class D amplifier? A type of amplifier that uses switching technology to achieve high efficiency. E7B03 Which of the following forms the output of a class D amplifier circuit? A low-pass filter to remove switching signal components. E7B04 Where on the load line of a Class A common emitter amplifier would bias normally be set? Approximately half-way between saturation and cutoff. This usually is the operating region where the amplifier is most linear. E7B05 What can be done to prevent unwanted oscillations in an RF power amplifier? Install parasitic suppressors and/or neutralize the stage. E7B06 Which of the following amplifier types reduces or eliminates even-order harmonics? Push-pull. Push-push" does not exist under that label. It is possible and practical to operate several devices in parallel for greater power handling; that might be called push-push. Classes AB and C have considerable distortion. Push-pull" amplifiers are coupled class B amplifiers, each of which handle half the signal. Even harmonics are reduced. E7B07 Which of the following amplifier types reduces or eliminates even-order harmonics? Signal distortion and excessive bandwidth. Class C amplifiers have considerable distortion which causes unintended (spurious) signals. See nuggets above. E7B08 How can an RF power amplifier be neutralized? By feeding a 180-degree out-of-phase portion of the output back to the input. Negative feedback stabilzes amplifers. Out-of-phase output feed back to the input provides negative feedback. E7B09 Which of the following describes how the loading and tuning capacitors are to be adjusted when tuning a vacuum tube RF power amplifier that employs a pi-network output circuit? The tuning capacitor is adjusted for minimum plate current, while the loading capacitor is adjusted for maximum permissible plate current Tune for minimum plate current. Load for maximum plate current. The issues are minimum resting plate current and maximum coupling to the antenna and its feedline. Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 5 of 17
6 E7B10 In Figure E7-1, what is the purpose of R1 and R2? Fixed bias. The load resistor is the resistor from the collector to the power supply. The changing currents through the load resistor creates the varying output voltage. R3 provides self bias, a bias proportional to the current through the transistor which protects the transistor from thermal run-away. It is not feed back as it is feed directly from the power supply. E7B11 Figure E7-1, what is the purpose of R3? Self bias. See E7B10 s discussion of R3. E7B12 What type of circuit is shown in Figure E7-1? Common emitter amplifier. Common emitter as the emitter is at signal ground because of C3. E7B13 In Figure E7-2, what is the purpose of R? Emitter load. This circuit is a common collector amplifier as the collector is at signal ground caused by C1. E7B14 In Figure E7-2, what is the purpose of C2? Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 6 of 17
7 Output coupling. Note that this is a common (grounded) collector amplifier circuit because of C1. E7B15 What is one way to prevent thermal runaway in a bipolar transistor amplifier? Use a resistor in series with the emitter. You want negative feedback that is dependent on the current into the emitter. Even though neutralization is negative feedback, it is not negative feedback that is dependent on the emitter current. That is the purpose of R3 in E7-1. The emitter bias resistor should be signal bypassed by a capacitor to leave the transistor s emitter at signal ground. That is the purpose of C3 in E7-1. E7B16 What is the effect of intermodulation products in a linear power amplifier? Transmission of spurious signals. Whereas all of the answers are technically correct, the primary effect is the creation of spurious signals. A linear amplifier is inherently low efficiency. Intermodulation products do not ncessarily cause oscillations. This leaves [t]ransmission of spurious signals" as the best answer. E7B17 Why are third-order intermodulation distortion products of particular concern in linear power amplifiers? Because they are relatively close in frequency to the desired signal. They are likely to become transmitted. E7B18 Which of the following is a characteristic of a grounded-grid amplifier? Low input impedance. E7B19 What is a klystron? A VHF, UHF, or microwave vacuum tube that uses velocity modulation. Klystrons and magnetrons are VHF or higher power devices. Think microwave oven. E7B20 What is a parametric amplifier? A low-noise VHF or UHF amplifier relying on varying reactance for amplification. Parameteric amplifiers are very low noise. They are common as the on-the-antenna amplifier of a satellite signal receiver system. A varactor diode is a diode used in a back biased and blocking mode. It can be used in a variable reactance modulator or a parametric amplifier. E7B20 Which of the following devices is generally best suited for UHF or microwave power amplifier applications? Field effect transistor. FETs (field effect transistors) can be built to operate at high power and at UHF and SHF frequencies. Silicon controlled rectifiers and Triacs are switched devices. Nuvistors are UHF and higher signal vacuum tubes. Usually, Nuvistors are triodes although some tetrodes were made. Typical diameter is on the order 1.5cm and height is on the order of 2cm. Since time of flight of electron within the device is a significant limiting factor in their frequency response, the small size helps them operate at high frequencies than conventionally sized vacuum tubes. E7C01 How are the capacitors and inductors of a low-pass filter Pi-network arranged between the network s input and output? A capacitor is connected between the input and ground, another capacitor is connected between the output and ground, and an inductor is connected between input and output. The purpose of a low pass filter is to block passage or to shunt to ground high frequencies. Therefore, in a pi (Π) low pass filter the legs" should be capacitors to shunt the high frequencies to ground and the top" should be an inductor to block the same high frequencies. The component types would be reversed for a high pass filter. Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 7 of 17
8 E7C02 A T-network with series capacitors and a parallel shunt inductor has which of the following properties? It is a high-pass filter. The purpose of a high pass filter is to block passage or to shunt to ground low frequencies. Therefore, in a T high pass filter the leg" should be an inductor to shunt the low frequencies to ground and the tops" should be capacitors to block the same low frequencies. The component types would be reversed for a low pass filter. E7C03 What advantage does a Pi-L-network have over a Pi-network for impedance matching between the final amplifier of a vacuum-tube transmitter and an antenna? Greater harmonic suppression. The Pi-L filter has two filtering stages which makes it more effective at removing undesired frequencies. E7C04 How does an impedance-matching circuit transform a complex impedance to a resistive impedance? It cancels the reactive part of the impedance and changes the resistive part to a desired value. A network which transforms a complex impedance does so by supplying corrective complex impedances (capacitors and inductors) and transforms the resistive component to the desired value. E7C05 Which filter type is described as having ripple in the passband and a sharp cutoff? A Chebyshev filter. E7C06 What are the distinguishing features of an elliptical filter? Extremely sharp cutoff with one or more notches in the stop band. An elliptical filter has ripple in both the pass and stop bands. Its sides are sharp. E7C07 What kind of filter would you use to attenuate an interfering carrier signal while receiving an SSB transmission? A notch filter. You want to notch out the undesired carrier frequency. E7C08 What kind of digital signal processing audio filter might be used to remove unwanted noise from a received SSB signal? An adaptive filter. You want a filter which discovers constantly present frequencies and removes them: an adaptive filter. E7C09 What type of digital signal processing filter might be used to generate an SSB signal? A Hilbert-transform filter. It is usually implemented in a Digital Signal Processor (DSP). The other filter types in the answer selection are all easily implemented in analog form. It takes several pages in the ARRL handbook to try to describe how Hilbert transform filter works. A brief explanation is that the audio is converted to a frequency domain description, displaced to the carrier frequency by adding the audio frequencies to form the positive (USB) or by subtracting the audio frequencies to form the negative (LSB) signal description and converting the result back to a time domain signal. E7C10 Which of the following filters would be the best choice for use in a 2 meter repeater duplexer? A cavity filter. A cavity filter or a circulator is a three or four port device. A signal coming in on one port leaves out the next port around the device. With correct connections, an antenna can be connected to one port, a receiver to another and a transmitter to a third and both the receiver and transmitter can be in operation at the same time without harm to either. Received signals would be routed to the receiver and transmitted signals would be routed to the antenna. Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 8 of 17
9 E7C11 Which of the following is the common name for a filter network which is equivalent to two L networks connected back-to-back with the inductors in series and the capacitors in shunt at the input and output? Pi E7C12 Which of the following describes a Pi-L network used for matching a vacuum-tube final amplifier to a 50-ohm unbalanced output? A Pi network with an additional series inductor on the output. A Pi-L network has four components. A low pass Pi-L network has two inductors in series and two capacitors shunting from the inductors to ground. E7C13 What is one advantage of a Pi matching network over an L matching network consisting of a single inductor and a single capacitor? The Q of Pi networks can be varied by changing the component values chosen. E7C14 Which of these modes is most affected by non-linear phase response in a receiver IF filter? Digital. Digital signal modes require that the phase relationships of various signal components remain unchanged. E7D01 What is one characteristic of a linear electronic voltage regulator? The conduction of a control element is varied to maintain a constant output voltage Normally, the control element is active. E7D02 What is one characteristic of a switching electronic voltage regulator? The control device s duty cycle is controlled to produce a constant average output voltage. In a switching power supply, the control element is switched on and off rapidly to supply high frequency pulsed power at the appropriate average power for the load. That pulsed power is then supplied to an appropriate low pass filter to create a constant output voltage. E7D03 What device is typically used as a stable reference voltage in a linear voltage regulator? A Zener diode. 1. A Zener diode is a common voltage reference source. it has a stable breakdown voltage when biased in the reverse direction. If the current through the diode is appropriately limited, then the device is not damaged in this mode of operation. 2. A tunnel diode is a negative resistance device used as signal amplifier or oscillator un the UHF and higher frequencies. It can be used in the THz range. 3. A silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) is a power handling device which can be switched into operation by a small control signal. These devices can handles multiple megawatts. 4. A varactor diode is a diode used in a back biased and blocking mode. Depending on the back voltage on the diode, its capacitance varies. It can be used in a variable reactance modulator or a parametric amplifier. E7D04 Which of the following types of linear voltage regulator usually make the most efficient use of the primary power source? A series regulator. Shunt circuits throw away unneeded power. Constant current sources always supply some current. Only a series regulator turns on" as needed. E7D05 Which of the following types of linear voltage regulator places a constant load on the unregulated voltage source? A shunt regulator. A shunt regulator throws away the current unneeded by the load. Neither the voltage nor the current change at the power source. Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 9 of 17
10 E7D06 What is the purpose of Q1 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-3? It increases the current-handling capability of the regulator. E7D07 What is the purpose of C2 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-3? It bypasses hum around D1. The bypass capacitor provides a high pass filtering function to the Zener voltage reference diode. E7D08 What type of circuit is shown in Figure E7-3? Linear voltage regulator. This circuit operates constantly and not in pulses. This circuit operates in a common base configuration. E7D09 What is the purpose of C1 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-3? It filters the supply voltage. E7D10 What is the purpose of C3 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-3? It prevents self-oscillation. C3 is too small to be an output filter. C3 brings the output collector to signal ground. E7D11 What is the purpose of R1 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-3? It supplies current to D1. R1 supplies a small amount of current to the Zener diode so that it can operate and limits the maximum current that the Zener diode can draw so that the Zener diode does not damage itself. E7D12 What is the purpose of R2 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-3? It provides a constant minimum load for Q1. It helps the regulator circuit stay in its linear range of operation. E7D13 What is the purpose of D1 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-3? To provide a voltage reference. E7D14 What is one purpose of a "bleeder" resistor in a conventional (unregulated) power supply? To improve output voltage regulation. E7D15 What is the purpose of a "step-start" circuit in a high-voltage power supply? To allow the filter capacitors to charge gradually. A step circuit reduces the size of the charging currents to the output filtering capacitors when the power supply is turned on. Otherwise, these surge currents could destroy the regulator circuit. Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 10 of 17
11 E7D16 When several electrolytic filter capacitors are connected in series to increase the operating voltage of a power supply filter circuit, why should resistors be connected across each capacitor? All of these choices are correct. E7D17 What is the primary reason that a high-frequency inverter type high-voltage power supply can be both less expensive and lighter in weight than a conventional power supply? The high frequency inverter design uses much smaller transformers and filter components for an equivalent power output. E7E01 Which of the following can be used to generate FM phone emissions? Reactance modulation of the oscillator. Modulating amplifiers does not make much sense. A balanced modulator creates a double sideband suppressed carrier signal. E7E02 What is the function of a reactance modulator? To produce PM signals by using an electrically variable inductance or capacitance A varying reactance creates FM (frequency modulated) or PM (phase modulated) signals. In this case, the main effect is generating FM modulation of the signal oscillator. It does not create an AM (amplitude modulated) signal. E7E03 How does an analog phase modulator function? By varying the tuning of an amplifier tank circuit to produce PM signals. A varying reactance creates FM (frequency modulated) or PM (phase modulated) signals. In this case, the main effect is generating PM modulation of the signal signal being generated. It does not create an AM (amplitude modulated) signal. E7E04 What is one way a single-sideband phone signal can be generated? By using a balanced modulator followed by a filter. A balanced modulator creates a double sideband suppressed carrier signal. The desired sideband can then be selected by filtering and amplified as needed. Or, a DSP implementing a Hilbert transform filter can generate the SSB signal directly. E7E05 What circuit is added to an FM transmitter to boost the higher audio frequencies? A pre-emphasis network. Pre-emphasis on the transmitter side. De-emphasis on the receiver side. This is also done in phonograph and magnetic sound recordings. Pre-emphasis when recording; de-emphasis when playing. E7E06 Why is de-emphasis commonly used in FM communications receivers? For compatibility with transmitters using phase modulation. See E7E05 for the correct answer. The best available answer is the one given above. E7E07 What is meant by the term baseband in radio communications? The frequency components present in the modulating signal. Note in the modulating signal. E7E08 What are the principal frequencies that appear at the output of a mixer circuit? The two input frequencies along with their sum and difference frequencies. In the frequency domain, mixers do not multiply; they only Only one answer has only sums and differences. E7E09 What occurs when an excessive amount of signal energy reaches a mixer circuit? Spurious mixer products are generated. A excessive input power drives the circuit into saturation and distortion. The distortion causes harmonics. The harmonics create spurious signals. Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 11 of 17
12 E7E10 How does a diode detector function? By rectification and filtering of RF signals. E7E11 Which of the following types of detector is well suited for demodulating SSB signals? Product detector. A product detector is a product mixer which reduces the implicit carrier frequency to 0. E7E12 What is a frequency discriminator stage in a FM receiver? A circuit for detecting FM signals. A frequency discriminator has a output proportional to the input frequency. It can be used to demodulate a FM signal. E7E13 Which of the following describes a common means of generating an SSB signal when using digital signal processing? The quadrature method. As previously noted, the Hamiliton transform filter method might also be sued. E7E14 What is meant by direct conversion when referring to a software defined receiver? Incoming RF is mixed to "baseband" for analog-to-digital conversion and subsequent processing. Direct conversion in any case is the conversion of a RF signal directly to baseband." In this question, the mention of software-defined radio is a spurious signal" (a red herring). The other answers are nonsense. E7G01 What primarily determines the gain and frequency characteristics of an op-amp RC active filter? The values of capacitors and resistors external to the op-amp. The external components around the operational amplifier form a pontentially complex feedback circuit. E7G02 What is the effect of ringing in a filter? Undesired oscillations added to the desired signal. Ringing in an active filter occurs when there is positive feedback almost sufficient to cause oscillation at some frequencies. The filter effectively has a high Q. Ringing in a passive filter occurs when the components have sufficiently high Q at some frequencies so that the signal decays slowly at those frequencies. E7G03 Which of the following is an advantage of using an op-amp instead of LC elements in an audio filter? Op-amps exhibit gain rather than insertion loss. E7G04 Which of the following is a type of capacitor best suited for use in high-stability op-amp RC active filter circuits? Polystyrene. E7G05 How can unwanted ringing and audio instability be prevented in a multi-section op-amp RC audio filter circuit? Restrict both gain and Q. See E7G02. E7G06 Which of the following is the most appropriate use of an op-amp active filter? As an audio filter in a receiver. Generally, operational amplifiers are not power devices. Radio frequency interference (RFI) is generally done with passive components. Therefore, of the answer selections given, the audio receiving filter is the proper choice. Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 12 of 17
13 E7G07 What magnitude of voltage gain can be expected from the circuit in Figure E7-4 when R1 is 10 ohms and RF is 470 ohms? = 47 Gain is defined as being an absolute number and therefore is not negative. E7G08 How does the gain of an ideal operational amplifier vary with frequency? It does not vary with frequency. A theoretically ideal operational is just that: ideal. It has no frequncy dependentt characteristics. E7G09 RF R = 10K 1K 0.23 = 2.3. Signals are signed. See E7E07. E7G11 What absolute voltage gain can be expected from the circuit in Figure E7-4 when R1 is 3300 ohms and RF is 47 kilohms? 14.. R F = R E7G12 What is an integrated circuit operational amplifier? A high-gain, direct-coupled differential amplifier with very high input and very low output impedance A high-gain, direct coupled differential amplifier whose characteristics are determined by components external to the amplifier. The Wikipedia article on Operational amplifiers" provides a good description. E7G13 What is meant by the term op-amp input-offset voltage? The input voltage needed to bring the open-loop output voltage to zero. The Wikipedia answer is: the voltage difference between the differential inputs which causes the output to be at ground in a single output operational amplifier E7G14 What is the typical input impedance of an integrated circuit op-amp? Very high. E7G17 What is the typical output impedance of an integrated circuit op-amp? Very low. Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 13 of 17
14 E7H01 What are three oscillator circuits used in Amateur Radio equipment? Colpitts, Hartley and Pierce. See oscillator nugget above. Example shematics follow. E7H02 What condition must exist for a circuit to oscillate? It must have positive feedback with a gain greater than 1. See oscillator nugget above. Example shematic follows. E7H03 How is positive feedback supplied in a Hartley oscillator? Through a tapped coil. See oscillator nugget above. Example shematic follows. E7H04 How is positive feedback supplied in a Colpitts oscillator? Through a capacitive divider. See oscillator nugget above. Example shematic follows. E7H05 How is positive feedback supplied in a Pierce oscillator? Through a quartz crystal. See oscillator nugget above. Example shematic follows. E7H06 Which of the following oscillator circuits are commonly used in VFOs? Colpitts and Hartley. See varactor diode nugget above. E7H07 What is a magnetron oscillator? A UHF or microwave oscillator consisting of a diode vacuum tube with a specially shaped anode, surrounded by an external magnet. Usually used at frequencies of 100s of MHz to 10s of GHz. E7H08 What is a Gunn diode oscillator? An oscillator based on the negative resistance properties of properly-doped semiconductors. E7H09 What type of frequency synthesizer circuit uses a phase accumulator, lookup table, digital to analog converter and a low-pass anti-alias filter? A phase locked loop synthesizer. E7H10 What information is contained in the lookup table of a direct digital frequency synthesizer? The amplitude values that represent a sine-wave output. E7H11 What are the major spectral impurity components of direct digital synthesizers? Spurious signals at discrete frequencies. The spurious signals are usually at harmonics of the table step frequency. E7H12 Which of the following is a principal component of a direct digital synthesizer (DDS)? Phase accumulator. E7H13 What is the capture range of a phase-locked loop circuit? The frequency range over which the circuit can lock. E7H14 What is a phase-locked loop circuit? An electronic servo loop consisting of a phase detector, a low-pass filter, a voltage-controlled oscillator, and a stable reference oscillator. Note that a DDS could be used instead of the voltage-controlled oscillator. E7H15 Which of these functions can be performed by a phase-locked loop? Frequency synthesis, FM demodulation. Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 14 of 17
15 E7H16 Why is the short-term stability of the reference oscillator important in the design of a phase locked loop (PLL) frequency synthesizer? Any phase variations in the reference oscillator signal will produce phase noise in the synthesizer output. E7H17 Why is a phase-locked loop often used as part of a variable frequency synthesizer for receivers and transmitters? It makes it possible for a VFO to have the same degree of frequency stability as a crystal oscillator. the stability of a crystal oscillator. E7H18 What are the major spectral impurity components of phase-locked loop synthesizers? Phase noise. E8A14 Which of these methods is commonly used to convert analog signals to digital signals? Sequential sampling. This is followed analog to digital voltage conversion at the sampling frequency. Legalese NCVEC Extra Class Question Pool 2012 declared public domain by NCVEC NCVEC , Randolph J. Herber, W9HE. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 United States License (see Include this notice in any derivative works, preferably with your own copyright notices. Wolfram Mathematica 8 used to create some of the illustrations. Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 15 of 17
16 + + + Common Emitter Common Base Common Collector High voltage gain Inverted output Low input impedance Unity current gain Low output impedance Unity Voltage gain + R C R E For NPN bipolar transistors, reverse the power supply voltage. From top to bottom bottom, collector, base and emitter. This is the symbol for a N channel JFET. For a P channel, the arrow points away from the device. From top to bottom, the connections are drain, gate and source. Voltage is about RC/RE because of the degenerative or negative of RE This is a vacuum tube triode, which behaves much like a N channel JFET. The connections from top to bottom are plate or anode, grid, cathode and heater (which is not part of signal processing; but is necessary for operation. Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 16 of 17
17 150nH 10K + 6V 100nf 10K 2N pF 100pF + approximately 50MHz common base Colpitts oscillator with a series resonant circuit. Hartley common gate oscillator with at parallel resonant circuit. Mnemonic: Capacitor feedback is Colpitts. Mnemonic: Inductive feedback in Henrys is Hartley. + common source Peirce oscillator with the ctystal provides phase reverse at resonant frequencey. In general, oscillators are amplifiers with some form positive feedback at the desired frequency. The amplifiers can be of any type and the feedback can be done with series or parallel resonant circuits. The collary is to stablize an amplifier provide negative feedback (degenerative feedback). Mnemonic: Piezoelectric feedback is Peirce Randolph J. Herber, W9HE, Extra chapter 6 Page 17 of 17
Introduction. Chapter 6 Notes
 Introduction Rather than try to give you the material so that you can answer the questions from first principles, I will provide enough information that you can recognize the correct answer to each question.
Introduction Rather than try to give you the material so that you can answer the questions from first principles, I will provide enough information that you can recognize the correct answer to each question.
CHAPTER 6 Radio Circuits and Systems
 6.1 AMPLIFIERS (page 6-1) CHAPTER 6 Radio Circuits and Systems AMPLIFIER GAIN (page 6-2) INPUT AND OUTPUT IMPEDANCE (page 6-2) DISCRETE DEVICE AMPLIFIERS (page 6-2) BASIC CIRCUITS (page 6-2) COMMON-EMITTER
6.1 AMPLIFIERS (page 6-1) CHAPTER 6 Radio Circuits and Systems AMPLIFIER GAIN (page 6-2) INPUT AND OUTPUT IMPEDANCE (page 6-2) DISCRETE DEVICE AMPLIFIERS (page 6-2) BASIC CIRCUITS (page 6-2) COMMON-EMITTER
4/30/2012. General Class Element 3 Course Presentation. Practical Circuits. Practical Circuits. Subelement G7. 2 Exam Questions, 2 Groups
 General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G7 2 Exam Questions, 2 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures G3 Radio Wave Propagation
General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G7 2 Exam Questions, 2 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures G3 Radio Wave Propagation
PRACTICE. Amateur Radio Operator Certificate Examination. Advanced Qualification
 Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada Innovation, Sciences et Développement économique Canada Amateur Radio Operator Certificate Examination Advanced Qualification 2018-06-30 To pass this
Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada Innovation, Sciences et Développement économique Canada Amateur Radio Operator Certificate Examination Advanced Qualification 2018-06-30 To pass this
PRACTICE. Amateur Radio Operator Certificate Examination. Advanced Qualification
 Amateur Radio Operator ertificate Examination Advanced Qualification 2019-04-03 To pass this exam, you must correctly answer 35 out of 50 questions Exam Number: 115916 1. (A-007-008-002) Why would one
Amateur Radio Operator ertificate Examination Advanced Qualification 2019-04-03 To pass this exam, you must correctly answer 35 out of 50 questions Exam Number: 115916 1. (A-007-008-002) Why would one
General Class License Theory II. Dick Grote K6PBF
 General Class License Theory II Dick Grote K6PBF k6pbfdick@gmail.com 1 Introduction In the first theory class we talked about basic electrical principles and components. Now we will build on this to learn
General Class License Theory II Dick Grote K6PBF k6pbfdick@gmail.com 1 Introduction In the first theory class we talked about basic electrical principles and components. Now we will build on this to learn
Chapter.8: Oscillators
 Chapter.8: Oscillators Objectives: To understand The basic operation of an Oscillator the working of low frequency oscillators RC phase shift oscillator Wien bridge Oscillator the working of tuned oscillator
Chapter.8: Oscillators Objectives: To understand The basic operation of an Oscillator the working of low frequency oscillators RC phase shift oscillator Wien bridge Oscillator the working of tuned oscillator
EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS. Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi
 EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi 2.1 INTRODUCTION An electronic circuit which is designed to generate a periodic waveform continuously at
EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi 2.1 INTRODUCTION An electronic circuit which is designed to generate a periodic waveform continuously at
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
 OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
Chapter 6. FM Circuits
 Chapter 6 FM Circuits Topics Covered 6-1: Frequency Modulators 6-2: Frequency Demodulators Objectives You should be able to: Explain the operation of an FM modulators and demodulators. Compare and contrast;
Chapter 6 FM Circuits Topics Covered 6-1: Frequency Modulators 6-2: Frequency Demodulators Objectives You should be able to: Explain the operation of an FM modulators and demodulators. Compare and contrast;
The steeper the phase shift as a function of frequency φ(ω) the more stable the frequency of oscillation
 It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION. Model Answer. 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the
 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17213 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17213 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Lesson Four Lesson Five PREVIEW COPY
 Oscillators Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Introduction to Oscillators...3 Flip-Flops...19 Logic Clocks...37 Lesson Four Filters and Waveforms...53 Lesson Five Troubleshooting Oscillators...69
Oscillators Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Introduction to Oscillators...3 Flip-Flops...19 Logic Clocks...37 Lesson Four Filters and Waveforms...53 Lesson Five Troubleshooting Oscillators...69
Module 04.(B1) Electronic Fundamentals
 1.1a. Semiconductors - Diodes. Module 04.(B1) Electronic Fundamentals Question Number. 1. What gives the colour of an LED?. Option A. The active element. Option B. The plastic it is encased in. Option
1.1a. Semiconductors - Diodes. Module 04.(B1) Electronic Fundamentals Question Number. 1. What gives the colour of an LED?. Option A. The active element. Option B. The plastic it is encased in. Option
Crystal Oscillators and Circuits
 Crystal Oscillators and Circuits It is often required to produce a signal whose frequency or pulse rate is very stable and exactly known. This is important in any application where anything to do with
Crystal Oscillators and Circuits It is often required to produce a signal whose frequency or pulse rate is very stable and exactly known. This is important in any application where anything to do with
HF Receivers, Part 2
 HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
Radio Receivers. Al Penney VO1NO
 Radio Receivers Al Penney VO1NO Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is
Radio Receivers Al Penney VO1NO Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits. Module 7
 Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
LBI-30398N. MAINTENANCE MANUAL MHz PHASE LOCK LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 DESCRIPTION TABLE OF CONTENTS. Page. DESCRIPTION...
 MAINTENANCE MANUAL 138-174 MHz PHASE LOCK LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 LBI-30398N TABLE OF CONTENTS DESCRIPTION...Front Cover CIRCUIT ANALYSIS... 1 MODIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS... 4 PARTS LIST AND PRODUCTION
MAINTENANCE MANUAL 138-174 MHz PHASE LOCK LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 LBI-30398N TABLE OF CONTENTS DESCRIPTION...Front Cover CIRCUIT ANALYSIS... 1 MODIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS... 4 PARTS LIST AND PRODUCTION
High Frequency VCO Design and Schematics
 High Frequency VCO Design and Schematics Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, http://www.qsl.net/va3iul/ This note will review the process by which VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator) designers choose their oscillator
High Frequency VCO Design and Schematics Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, http://www.qsl.net/va3iul/ This note will review the process by which VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator) designers choose their oscillator
FCC Technician License Course
 FCC Technician License Course 2014-2018 FCC Element 2 Technician Class Question Pool Presented by: Tamiami Amateur Radio Club (TARC) WELCOME To the SECOND of 4, 3-hour classes presented by TARC to prepare
FCC Technician License Course 2014-2018 FCC Element 2 Technician Class Question Pool Presented by: Tamiami Amateur Radio Club (TARC) WELCOME To the SECOND of 4, 3-hour classes presented by TARC to prepare
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks)
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks) 1. What is meant by tuned amplifiers? Tuned amplifiers are amplifiers that are designed to reject a certain
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks) 1. What is meant by tuned amplifiers? Tuned amplifiers are amplifiers that are designed to reject a certain
ERICSSONZ LBI-30398P. MAINTENANCE MANUAL MHz PHASE LOCKED LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 DESCRIPTION TABLE OF CONTENTS
 MAINTENANCE MANUAL 138-174 MHz PHASE LOCKED LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DESCRIPTION... Front Cover CIRCUIT ANALYSIS...1 MODIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS...4 PARTS LIST...5 PRODUCTION
MAINTENANCE MANUAL 138-174 MHz PHASE LOCKED LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DESCRIPTION... Front Cover CIRCUIT ANALYSIS...1 MODIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS...4 PARTS LIST...5 PRODUCTION
The G4EGQ RAE COURSE Lesson 9 Transmitters Lesson 8 looked at a simple transmitter exciter comprising of oscillator, buffer and multiplier stages.
 Lesson 8 looked at a simple transmitter exciter comprising of oscillator, buffer and multiplier stages. The power amplifier The output from the exciter is usually very low and it is necessary to amplify
Lesson 8 looked at a simple transmitter exciter comprising of oscillator, buffer and multiplier stages. The power amplifier The output from the exciter is usually very low and it is necessary to amplify
Chapter 2. The Fundamentals of Electronics: A Review
 Chapter 2 The Fundamentals of Electronics: A Review Topics Covered 2-1: Gain, Attenuation, and Decibels 2-2: Tuned Circuits 2-3: Filters 2-4: Fourier Theory 2-1: Gain, Attenuation, and Decibels Most circuits
Chapter 2 The Fundamentals of Electronics: A Review Topics Covered 2-1: Gain, Attenuation, and Decibels 2-2: Tuned Circuits 2-3: Filters 2-4: Fourier Theory 2-1: Gain, Attenuation, and Decibels Most circuits
RF Power Amplifier (RFPA) Designing a 'Output Tank Circuit'
 RF Power Amplifier (RFPA) Designing a 'Output Tank Circuit' By Larry E. Gugle K4RFE, RF Design, Manufacture, Test & Service Engineer (Retired) Figure-1 Output 'Tank' Circuit Network in Low-Pass Filter
RF Power Amplifier (RFPA) Designing a 'Output Tank Circuit' By Larry E. Gugle K4RFE, RF Design, Manufacture, Test & Service Engineer (Retired) Figure-1 Output 'Tank' Circuit Network in Low-Pass Filter
Operational Amplifiers
 Operational Amplifiers Table of contents 1. Design 1.1. The Differential Amplifier 1.2. Level Shifter 1.3. Power Amplifier 2. Characteristics 3. The Opamp without NFB 4. Linear Amplifiers 4.1. The Non-Inverting
Operational Amplifiers Table of contents 1. Design 1.1. The Differential Amplifier 1.2. Level Shifter 1.3. Power Amplifier 2. Characteristics 3. The Opamp without NFB 4. Linear Amplifiers 4.1. The Non-Inverting
1. What is the unit of electromotive force? (a) volt (b) ampere (c) watt (d) ohm. 2. The resonant frequency of a tuned (LRC) circuit is given by
 Department of Examinations, Sri Lanka EXAMINATION FOR THE AMATEUR RADIO OPERATORS CERTIFICATE OF PROFICIENCY ISSUED BY THE DIRECTOR GENERAL OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS, SRI LANKA 2004 (NOVICE CLASS) Basic Electricity,
Department of Examinations, Sri Lanka EXAMINATION FOR THE AMATEUR RADIO OPERATORS CERTIFICATE OF PROFICIENCY ISSUED BY THE DIRECTOR GENERAL OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS, SRI LANKA 2004 (NOVICE CLASS) Basic Electricity,
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 10MHz to 1050MHz Integrated RF Oscillator with Buffered Outputs. Typical Operating Circuit. 10nH 1000pF MAX2620 BIAS SUPPLY
 19-1248; Rev 1; 5/98 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 10MHz to 1050MHz Integrated General Description The combines a low-noise oscillator with two output buffers in a low-cost, plastic surface-mount, ultra-small
19-1248; Rev 1; 5/98 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 10MHz to 1050MHz Integrated General Description The combines a low-noise oscillator with two output buffers in a low-cost, plastic surface-mount, ultra-small
Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent
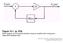 Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent feedback path. Figure 12-2 (p. 579) General circuit for a transistor oscillator. The transistor
Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent feedback path. Figure 12-2 (p. 579) General circuit for a transistor oscillator. The transistor
Amateur Radio Examination EXAMINATION PAPER No. 275 MARKER S COPY
 01-6-(d) An Amateur Station is quoted in the regulations as a station: a for training new radio operators b using amateur equipment for commercial purposes c for public emergency purposes d in the Amateur
01-6-(d) An Amateur Station is quoted in the regulations as a station: a for training new radio operators b using amateur equipment for commercial purposes c for public emergency purposes d in the Amateur
Power Amplifiers. Class A Amplifier
 Power Amplifiers The Power amplifiers amplify the power level of the signal. This amplification is done in the last stage in audio applications. The applications related to radio frequencies employ radio
Power Amplifiers The Power amplifiers amplify the power level of the signal. This amplification is done in the last stage in audio applications. The applications related to radio frequencies employ radio
EE12: Laboratory Project (Part-2) AM Transmitter
 EE12: Laboratory Project (Part-2) AM Transmitter ECE Department, Tufts University Spring 2008 1 Objective This laboratory exercise is the second part of the EE12 project of building an AM transmitter in
EE12: Laboratory Project (Part-2) AM Transmitter ECE Department, Tufts University Spring 2008 1 Objective This laboratory exercise is the second part of the EE12 project of building an AM transmitter in
Chapter 13 Oscillators and Data Converters
 Chapter 13 Oscillators and Data Converters 13.1 General Considerations 13.2 Ring Oscillators 13.3 LC Oscillators 13.4 Phase Shift Oscillator 13.5 Wien-Bridge Oscillator 13.6 Crystal Oscillators 13.7 Chapter
Chapter 13 Oscillators and Data Converters 13.1 General Considerations 13.2 Ring Oscillators 13.3 LC Oscillators 13.4 Phase Shift Oscillator 13.5 Wien-Bridge Oscillator 13.6 Crystal Oscillators 13.7 Chapter
UNIT-3. Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation
 UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) paper 2
 Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) paper 2 1. VSWR on a transmission line is always 1. Equal to 1 2. Equal to 0 3. Less than 1 4. Greater than 1 2. In a amplitude modulated wave, the value of Vmax is 10V and
Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) paper 2 1. VSWR on a transmission line is always 1. Equal to 1 2. Equal to 0 3. Less than 1 4. Greater than 1 2. In a amplitude modulated wave, the value of Vmax is 10V and
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 2016 EXAMINATIONS.
 Summer 2016 EXAMINATIONS Subject Code: 17321 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the answer scheme. 2) The
Summer 2016 EXAMINATIONS Subject Code: 17321 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the answer scheme. 2) The
Devices and Op-Amps p. 1 Introduction to Diodes p. 3 Introduction to Diodes p. 4 Inside the Diode p. 6 Three Diode Models p. 10 Computer Circuit
 Contents p. v Preface p. ix Devices and Op-Amps p. 1 Introduction to Diodes p. 3 Introduction to Diodes p. 4 Inside the Diode p. 6 Three Diode Models p. 10 Computer Circuit Analysis p. 16 MultiSIM Lab
Contents p. v Preface p. ix Devices and Op-Amps p. 1 Introduction to Diodes p. 3 Introduction to Diodes p. 4 Inside the Diode p. 6 Three Diode Models p. 10 Computer Circuit Analysis p. 16 MultiSIM Lab
BASIC ELECTRONICS/ ELECTRONICS
 BASIC ELECTRONICS/ ELECTRONICS PREAMBLE The syllabus is intended to equip candidates with broad understanding of the technology of manufacturing, maintenance and repair of domestic and industrial equipment.
BASIC ELECTRONICS/ ELECTRONICS PREAMBLE The syllabus is intended to equip candidates with broad understanding of the technology of manufacturing, maintenance and repair of domestic and industrial equipment.
Glossary + - A BNC plug that shorts the inner wire in a coax cable to the outer shield through a
 50Ω Terminator AC Active Alligator Clip Back Bias Base Battery Bias + - Bipolar Transistor BJT Black Box BNC BNC Cable A BNC plug that shorts the inner wire in a coax cable to the outer shield through
50Ω Terminator AC Active Alligator Clip Back Bias Base Battery Bias + - Bipolar Transistor BJT Black Box BNC BNC Cable A BNC plug that shorts the inner wire in a coax cable to the outer shield through
High Frequency VCO Design and Schematics
 High Frequency VCO Design and Schematics Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, http://www.qsl.net/va3iul/ This note will review the process by which VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator) designers choose their oscillator
High Frequency VCO Design and Schematics Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, http://www.qsl.net/va3iul/ This note will review the process by which VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator) designers choose their oscillator
GLOSSARY. A connector used to T together two BNC coax cables and a BNC jack. The transfer function vs. frequency plotted on Log Log axis.
 GLOSSARY 50ΩTerminator AC Active Alligator Clip Back Bias Base Battery Bias + - Bipolar Transistor BJT Black Box BNC BNC Cable A BNC plug that shorts the inner wire in a coax cable to the outer shield
GLOSSARY 50ΩTerminator AC Active Alligator Clip Back Bias Base Battery Bias + - Bipolar Transistor BJT Black Box BNC BNC Cable A BNC plug that shorts the inner wire in a coax cable to the outer shield
Radio Receivers. Al Penney VO1NO
 Radio Receivers Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is usually very weak
Radio Receivers Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is usually very weak
Oscillators. An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier.
 Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
UNIT V - RECTIFIERS AND POWER SUPPLIES
 UNIT V - RECTIFIERS AND POWER SUPPLIES OBJECTIVE On the completion of this unit the student will understand CLASSIFICATION OF POWER SUPPLY HALF WAVE, FULL WAVE, BRIDGE RECTIFER AND ITS RIPPLE FACTOR C,
UNIT V - RECTIFIERS AND POWER SUPPLIES OBJECTIVE On the completion of this unit the student will understand CLASSIFICATION OF POWER SUPPLY HALF WAVE, FULL WAVE, BRIDGE RECTIFER AND ITS RIPPLE FACTOR C,
KWM-2/2A Transceiver THE COLLINS KWM-2/2A TRANSCEIVER
 KWM-2/2A Transceiver Click the photo to see a larger photo Click "Back" button on browser to return Courtesy of Norm - WA3KEY THE COLLINS KWM-2/2A TRANSCEIVER Unmatched for versatility, dependability and
KWM-2/2A Transceiver Click the photo to see a larger photo Click "Back" button on browser to return Courtesy of Norm - WA3KEY THE COLLINS KWM-2/2A TRANSCEIVER Unmatched for versatility, dependability and
Introduction Introduction to radio frequencies p. 3 What are the 'radio frequencies'? p. 3 Why are radio frequencies different? p.
 Foreword p. xi Preface p. xiii Introduction Introduction to radio frequencies p. 3 What are the 'radio frequencies'? p. 3 Why are radio frequencies different? p. 3 What this book covers p. 3 Signals and
Foreword p. xi Preface p. xiii Introduction Introduction to radio frequencies p. 3 What are the 'radio frequencies'? p. 3 Why are radio frequencies different? p. 3 What this book covers p. 3 Signals and
MISCELLANEOUS. Figure 1.
 Reading 41 Ron Bertrand VK2DQ http://www.radioelectronicschool.com MISCELLANEOUS The purpose of this reading is to catch anything that may have slipped through the previous forty readings or just does
Reading 41 Ron Bertrand VK2DQ http://www.radioelectronicschool.com MISCELLANEOUS The purpose of this reading is to catch anything that may have slipped through the previous forty readings or just does
RF Integrated Circuits
 Introduction and Motivation RF Integrated Circuits The recent explosion in the radio frequency (RF) and wireless market has caught the semiconductor industry by surprise. The increasing demand for affordable
Introduction and Motivation RF Integrated Circuits The recent explosion in the radio frequency (RF) and wireless market has caught the semiconductor industry by surprise. The increasing demand for affordable
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13)
 GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
G5A07 (D) What happens when the impedance of an electrical load is equal to the internal impedance of the power source?
 G5A07 (D) What happens when the impedance of an electrical load is equal to the internal impedance of the power source? A. The source delivers minimum power to the load B. The electrical load is shorted
G5A07 (D) What happens when the impedance of an electrical load is equal to the internal impedance of the power source? A. The source delivers minimum power to the load B. The electrical load is shorted
WASSCE / WAEC BASIC ELECTRONICS / ELECTRONICS SYLLABUS
 WASSCE / WAEC BASIC ELECTRONICS / ELECTRONICS SYLLABUS WWW.LARNEDU.COM Visit www.larnedu.com for WASSCE / WAEC syllabus on different subjects and more great stuff to help you ace the WASSCE in flying colours.
WASSCE / WAEC BASIC ELECTRONICS / ELECTRONICS SYLLABUS WWW.LARNEDU.COM Visit www.larnedu.com for WASSCE / WAEC syllabus on different subjects and more great stuff to help you ace the WASSCE in flying colours.
Results for sample general2015 test paper
 1 / 8 2016/09/22 15:51 Your answers are marked like this: A. You got this question right, this is your correct answer. A. You got this question wrong, this is your incorrect answer. A. You got this question
1 / 8 2016/09/22 15:51 Your answers are marked like this: A. You got this question right, this is your correct answer. A. You got this question wrong, this is your incorrect answer. A. You got this question
10MHz to 1050MHz Integrated RF Oscillator with Buffered Outputs
 9-24; Rev 2; 2/02 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 0MHz to 050MHz Integrated General Description The combines a low-noise oscillator with two output buffers in a low-cost, plastic surface-mount, ultra-small µmax
9-24; Rev 2; 2/02 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 0MHz to 050MHz Integrated General Description The combines a low-noise oscillator with two output buffers in a low-cost, plastic surface-mount, ultra-small µmax
Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator
 Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator Modeling the Piezo Electric Quartz Crystal Most oscillators employed for RF and microwave applications use a resonator to set the frequency of oscillation. It is desirable to
Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator Modeling the Piezo Electric Quartz Crystal Most oscillators employed for RF and microwave applications use a resonator to set the frequency of oscillation. It is desirable to
4/30/2012. General Class Element 3 Course Presentation. Circuit CoCircuit Componentsmponents. Subelement G6. 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups
 General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G6 Circuit Components 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures G3
General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G6 Circuit Components 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures G3
SUMMER 13 EXAMINATION Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: / N
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT-I - PN DIODEAND ITSAPPLICATIONS 1. What is depletion region in PN junction?
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT-I - PN DIODEAND ITSAPPLICATIONS 1. What is depletion region in PN junction?
PESIT - BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS PART A
 PESIT - BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS LESSON - PLAN FOR BASIC ELECTRONICS ENGG. Name of Faculty: Percentage of course Periods Reference/ Text books Topics covered Reference chapter covered Cumulative PART A Unit
PESIT - BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS LESSON - PLAN FOR BASIC ELECTRONICS ENGG. Name of Faculty: Percentage of course Periods Reference/ Text books Topics covered Reference chapter covered Cumulative PART A Unit
Difference between BJTs and FETs. Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFET)
 Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Advanced Qualification Question Bank for Amateur Radio Operator Certificate Examinations
 RIC-8 Issue 3 April 2007 Spectrum Management and Telecommunications Radiocommunication Information Circular Advanced Qualification Question Bank for Amateur Radio Operator Certificate Examinations Aussi
RIC-8 Issue 3 April 2007 Spectrum Management and Telecommunications Radiocommunication Information Circular Advanced Qualification Question Bank for Amateur Radio Operator Certificate Examinations Aussi
Chapter 6: Power Amplifiers
 Chapter 6: Power Amplifiers Contents Class A Class B Class C Power Amplifiers Class A, B and C amplifiers are used in transmitters Tuned with a band width wide enough to pass all information sidebands
Chapter 6: Power Amplifiers Contents Class A Class B Class C Power Amplifiers Class A, B and C amplifiers are used in transmitters Tuned with a band width wide enough to pass all information sidebands
Electronics Interview Questions
 Electronics Interview Questions 1. What is Electronic? The study and use of electrical devices that operate by controlling the flow of electrons or other electrically charged particles. 2. What is communication?
Electronics Interview Questions 1. What is Electronic? The study and use of electrical devices that operate by controlling the flow of electrons or other electrically charged particles. 2. What is communication?
AM Generation High Level Low Level
 AM Generation High Level Low Level Low-level generation In modern radio systems, modulated signals are generated via digital signal processing (DSP). With DSP many types of AM modulation are possible with
AM Generation High Level Low Level Low-level generation In modern radio systems, modulated signals are generated via digital signal processing (DSP). With DSP many types of AM modulation are possible with
Expect to be successful, expect to be liked,
 Thought of the Day Expect to be successful, expect to be liked, expect to be popular everywhere you go. Oscillators 1 Oscillators D.C. Kulshreshtha Oscillators 2 Need of an Oscillator An oscillator circuit
Thought of the Day Expect to be successful, expect to be liked, expect to be popular everywhere you go. Oscillators 1 Oscillators D.C. Kulshreshtha Oscillators 2 Need of an Oscillator An oscillator circuit
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17213 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17213 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION
 CPC H H03 COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION ELECTRICITY (NOTE omitted) BASIC ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY H03B GENERATION OF OSCILLATIONS, DIRECTLY OR BY FREQUENCY-CHANGING, BY CIRCUITS EMPLOYING ACTIVE ELEMENTS
CPC H H03 COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION ELECTRICITY (NOTE omitted) BASIC ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY H03B GENERATION OF OSCILLATIONS, DIRECTLY OR BY FREQUENCY-CHANGING, BY CIRCUITS EMPLOYING ACTIVE ELEMENTS
Glossary of VCO terms
 Glossary of VCO terms VOLTAGE CONTROLLED OSCILLATOR (VCO): This is an oscillator designed so the output frequency can be changed by applying a voltage to its control port or tuning port. FREQUENCY TUNING
Glossary of VCO terms VOLTAGE CONTROLLED OSCILLATOR (VCO): This is an oscillator designed so the output frequency can be changed by applying a voltage to its control port or tuning port. FREQUENCY TUNING
HOW DIODES WORK CONTENTS. Solder plated Part No. Lot No Cathode mark. Solder plated 0.
 www.joeknowselectronics.com Joe Knows, Inc. 1930 Village Center Circle #3-8830 Las Vegas, NV 89134 How Diodes Work Copyright 2013 Joe Knows Electronics HOW DIODES WORK Solder plated 0.4 1.6 There are several
www.joeknowselectronics.com Joe Knows, Inc. 1930 Village Center Circle #3-8830 Las Vegas, NV 89134 How Diodes Work Copyright 2013 Joe Knows Electronics HOW DIODES WORK Solder plated 0.4 1.6 There are several
4.2.2 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)
 4.2.2 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) The Metal Oxide Semitonductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) has two modes of operation, the depletion mode, and the enhancement mode.
4.2.2 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) The Metal Oxide Semitonductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) has two modes of operation, the depletion mode, and the enhancement mode.
Feedback Amplifier & Oscillators
 256 UNIT 5 Feedback Amplifier & Oscillators 5.1 Learning Objectives Study definations of positive /negative feedback. Study the camparions of positive and negative feedback. Study the block diagram and
256 UNIT 5 Feedback Amplifier & Oscillators 5.1 Learning Objectives Study definations of positive /negative feedback. Study the camparions of positive and negative feedback. Study the block diagram and
4/29/2012. General Class Element 3 Course Presentation. Signals and Emissions. SignalSignals and Emissionsissions. Subelement G8
 General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G8 Signals and Emissions 2 Exam Questions, 2 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures
General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G8 Signals and Emissions 2 Exam Questions, 2 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures
The Hartley Oscillator
 The Hartley Oscillator One of the main disadvantages of the basic LC Oscillator circuit we looked at in the previous tutorial is that they have no means of controlling the amplitude of the oscillations
The Hartley Oscillator One of the main disadvantages of the basic LC Oscillator circuit we looked at in the previous tutorial is that they have no means of controlling the amplitude of the oscillations
onlinecomponents.com FET Circuit Applications FET Circuit Applications AN-32 National Semiconductor Application Note 32 February 1970
 FET Circuit Applications National Semiconductor Application Note 32 February 1970 Polycarbonate dielectric Sample and Hold With Offset Adjustment TL H 6791 1 Long Time Comparator TL H 6791 2 The 2N4393
FET Circuit Applications National Semiconductor Application Note 32 February 1970 Polycarbonate dielectric Sample and Hold With Offset Adjustment TL H 6791 1 Long Time Comparator TL H 6791 2 The 2N4393
State the application of negative feedback and positive feedback (one in each case)
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Subject Code: 073 Model wer Page No: / N Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Subject Code: 073 Model wer Page No: / N Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
TUNED AMPLIFIERS. Tank circuits.
 Tank circuits. TUNED AMPLIFIERS Analysis of single tuned amplifier, Double tuned, stagger tuned amplifiers. Instability of tuned amplifiers, stabilization techniques, Narrow band neutralization using coil,
Tank circuits. TUNED AMPLIFIERS Analysis of single tuned amplifier, Double tuned, stagger tuned amplifiers. Instability of tuned amplifiers, stabilization techniques, Narrow band neutralization using coil,
BASIC ELECTRONICS CERTIFICATION COMPETENCIES
 ANALOG BASICS (EM3) of the Associate C.E.T. BASIC ELECTRONICS CERTIFICATION COMPETENCIES (As suggested from segmenting the Associate CET Competencies into 6 BASIC areas: DC; AC; Analog; Digital; Comprehensive;
ANALOG BASICS (EM3) of the Associate C.E.T. BASIC ELECTRONICS CERTIFICATION COMPETENCIES (As suggested from segmenting the Associate CET Competencies into 6 BASIC areas: DC; AC; Analog; Digital; Comprehensive;
Amateur Radio Examination EXAMINATION PAPER No. 276 MARKER S COPY
 01-3-(a) The Amateur Service in New Zealand is administered through this prime document: a the New Zealand Radiocommunications Regulations b the Broadcasting Act c the Telecommunications Act d the Radio
01-3-(a) The Amateur Service in New Zealand is administered through this prime document: a the New Zealand Radiocommunications Regulations b the Broadcasting Act c the Telecommunications Act d the Radio
VCO Design Project ECE218B Winter 2011
 VCO Design Project ECE218B Winter 2011 Report due 2/18/2011 VCO DESIGN GOALS. Design, build, and test a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). 1. Design VCO for highest center frequency (< 400 MHz). 2. At
VCO Design Project ECE218B Winter 2011 Report due 2/18/2011 VCO DESIGN GOALS. Design, build, and test a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). 1. Design VCO for highest center frequency (< 400 MHz). 2. At
f o Fig ECE 6440 Frequency Synthesizers P.E. Allen Frequency Magnitude Spectral impurity Frequency Fig010-03
 Lecture 010 Introduction to Synthesizers (5/5/03) Page 010-1 LECTURE 010 INTRODUCTION TO FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZERS (References: [1,5,9,10]) What is a Synthesizer? A frequency synthesizer is the means by which
Lecture 010 Introduction to Synthesizers (5/5/03) Page 010-1 LECTURE 010 INTRODUCTION TO FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZERS (References: [1,5,9,10]) What is a Synthesizer? A frequency synthesizer is the means by which
Norfolk Amateur Radio Club
 Norfolk Amateur Radio Club The Transmitter & Transmitter Interference Nick M0HGU & Steve G3PND Plan for the Day The Transmitter Introduction, Block diagrams Oscillators, Buffers & Multipliers Modulation
Norfolk Amateur Radio Club The Transmitter & Transmitter Interference Nick M0HGU & Steve G3PND Plan for the Day The Transmitter Introduction, Block diagrams Oscillators, Buffers & Multipliers Modulation
EXPERIMENT #2 CARRIER OSCILLATOR
 EXPERIMENT #2 CARRIER OSCILLATOR INTRODUCTION: The oscillator is usually the first stage of any transmitter. Its job is to create a radio-frequency carrier that can be amplified and modulated before being
EXPERIMENT #2 CARRIER OSCILLATOR INTRODUCTION: The oscillator is usually the first stage of any transmitter. Its job is to create a radio-frequency carrier that can be amplified and modulated before being
Circuit Components Lesson 4 From: Emergency Management Ontario
 4.1 Amplifier Fundamentals The role of a amplifier is to produce an output which is an enlarged reproduction of the features of the signal fed into the input. The increase in signal by an amplifier is
4.1 Amplifier Fundamentals The role of a amplifier is to produce an output which is an enlarged reproduction of the features of the signal fed into the input. The increase in signal by an amplifier is
Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: / N
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Acknowledgments Introduction
 Acknowledgments Introduction xiii xi 1 Electronic meters 1 1.1 Digital meters 2 1.2 Nondigital (analog) meters 6 1.3 Differential meters 14 1.4 Digital meter displays and ranges 16 1.5 Nondigital meter
Acknowledgments Introduction xiii xi 1 Electronic meters 1 1.1 Digital meters 2 1.2 Nondigital (analog) meters 6 1.3 Differential meters 14 1.4 Digital meter displays and ranges 16 1.5 Nondigital meter
070 ELECTRONICS WORKS EXAMINATION STRUCTURE
 070 ELECTRONICS WORKS EXAMINATION STRUCTURE The trade will be examined under the following components or subject grouping: Electronic Devices and Circuit, Radio Communication and Television. EXAMINATION
070 ELECTRONICS WORKS EXAMINATION STRUCTURE The trade will be examined under the following components or subject grouping: Electronic Devices and Circuit, Radio Communication and Television. EXAMINATION
PRINCIPLES OF RADAR. By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Third Edition by J.
 PRINCIPLES OF RADAR By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology Third Edition by J. Francis Reintjes ASSISTANT PBOFESSOR OF COMMUNICATIONS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
PRINCIPLES OF RADAR By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology Third Edition by J. Francis Reintjes ASSISTANT PBOFESSOR OF COMMUNICATIONS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
Interference & Suppression Page 59
 INTERFERENCE Interference & Suppression Page 59 Front-End Overload, Cross-Modulation What is meant by receiver overload? Interference caused by strong signals from a nearby transmitter What is one way
INTERFERENCE Interference & Suppression Page 59 Front-End Overload, Cross-Modulation What is meant by receiver overload? Interference caused by strong signals from a nearby transmitter What is one way
LINEAR IC APPLICATIONS
 1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-2012 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
Receiver Design. Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21
 Receiver Design Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21 MW & RF Design / Prof. T. -L. Wu 1 The receiver mush be very sensitive to -110dBm
Receiver Design Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21 MW & RF Design / Prof. T. -L. Wu 1 The receiver mush be very sensitive to -110dBm
Communication Circuit Lab Manual
 German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 3 Crystal Oscillator Eng. Anas Alashqar
German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 3 Crystal Oscillator Eng. Anas Alashqar
i. At the start-up of oscillation there is an excess negative resistance (-R)
 OSCILLATORS Andrew Dearn * Introduction The designers of monolithic or integrated oscillators usually have the available process dictated to them by overall system requirements such as frequency of operation
OSCILLATORS Andrew Dearn * Introduction The designers of monolithic or integrated oscillators usually have the available process dictated to them by overall system requirements such as frequency of operation
Contents. 1. Essential Electronics 1. Preface Acknowledgements
 Contents Preface Acknowledgements ix xi 1. Essential Electronics 1 1.1: Current 2 1.2: Voltage 5 1.3: Power 6 1.4: Signals and Averages 7 1.4.1: Mean Average 7 1.4.2: Rectified Average 8 1.4.3: RMS Average
Contents Preface Acknowledgements ix xi 1. Essential Electronics 1 1.1: Current 2 1.2: Voltage 5 1.3: Power 6 1.4: Signals and Averages 7 1.4.1: Mean Average 7 1.4.2: Rectified Average 8 1.4.3: RMS Average
 Code No: Y0221/R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2013 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
Code No: Y0221/R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2013 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering)
 Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter
 SSB Reception Analog Communications Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION On the circuit board, you will set up the SSB transmitter to transmit a 1000 khz SSB signal
SSB Reception Analog Communications Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION On the circuit board, you will set up the SSB transmitter to transmit a 1000 khz SSB signal
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS UNIT-1 SUBJECT : ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE : EC6202 BRANCH: EEE PART -A 1. What is meant by diffusion current in a semi conductor? (APR/MAY 2010, 2011, NOV/DEC
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS UNIT-1 SUBJECT : ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE : EC6202 BRANCH: EEE PART -A 1. What is meant by diffusion current in a semi conductor? (APR/MAY 2010, 2011, NOV/DEC
Amateur Wireless Station Operators License Exam
 Amateur Wireless Station Operators License Exam Study material 2017 South India Amateur Radio Society, Chennai CHAPTER 5 1 Chapter 5 Amateur Wireless Station Operators License Exam Study Material Chapter
Amateur Wireless Station Operators License Exam Study material 2017 South India Amateur Radio Society, Chennai CHAPTER 5 1 Chapter 5 Amateur Wireless Station Operators License Exam Study Material Chapter
Downloaded from Downloaded from
 IV SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 The figure in the margin indicates full marks. [i] (110111) 2 = (?) 16 [ii] (788) 10 = (?) 8 Q. [1] [a] Explain the types of extrinsic semiconductors with the help of
IV SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 The figure in the margin indicates full marks. [i] (110111) 2 = (?) 16 [ii] (788) 10 = (?) 8 Q. [1] [a] Explain the types of extrinsic semiconductors with the help of
