Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition
|
|
|
- Chester Holt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Powerpoint slides copied from or based upon: Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition Connally, Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, Et Al. Copyright 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
2 CHAPTER 6 TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS SECTION 6.5 SINUSOIDAL FUNCTIONS
3 Transformations of the sine and cosine are called sinusoidal functions, and can be expressed in the form: y asin( B( t h)) k and y acos( B( t h)) k where A, B, h, and k are constants. Their graphs resemble the graphs of sine and cosine, but may also be shifted, flipped, or stretched. Page 269 3
4 These transformations may change the period, amplitude, and midline of the function as well as its value at t = 0. y asin( B( t h)) k and y acos( B( t h)) k Page 269 4
5 We already know: The functions of y = A sin t and y = A cos t have amplitude A. The midline of the functions y = sin t + k and y = cos t + k is the horizontal line y = k. Page 269 5
6 Graph y = sin t and y = sin 2t for 0 t 2π. Describe any similarities and differences. What are their periods? Page 269 Example #1 6
7 Using our calculator, let's graph the following: y1 = sin(x) y2 = sin(2x) Page 269 Example #1 Window Value Xmin 0 Xmax 2π Xscl 1 Ymin -1.5 Ymax 1.5 Yscl 1 7
8 y1 sin( x) 0.5 y2 sin(2 x) x Page 269 Example #1 8
9 Graph y = sin t and y = sin 2t for 0 t 2π. Describe any similarities and differences. Page 269 Example #1 9
10 We already know: The functions of y = A sin t and y = A cos t have amplitude A. The midline of the functions y = sin t + k and y = cos t + k is the horizontal line y = k. Page
11 y1 sin( x) 0.5 y2 sin(2 x) x Page 269 Example #1 11
12 Amplitude = 1, Midline = y1 sin( x) 0.5 y2 sin(2 x) x Page 269 Example #1 12
13 Graph y = sin t and y = sin 2t for 0 t 2π. What are their periods? Page 269 Example #1 13
14 y1 sin( x) 0.5 y2 sin(2 x) x Page 269 Example #1 14
15 sin(x) has period = 2π, sin(2x) has 1.5 period = π 1.0 y1 sin( x) 0.5 y2 sin(2 x) x Page 269 Example #1 15
16 sin(x) has period = 2π, sin(2x) has period = π Page 269 Example #1 16
17 If f is a function and k a positive constant, then the graph of y = f(kx) is the graph of f Horizontally compressed by a factor of 1/k if k > 1, Horizontally stretched by a factor of 1/k if k < 1. Page 221 Blue Box (Section 5.4) 17
18 sin(x) has period = 2π, sin(2x) has period = π Page 269 Example #1 18
19 This is because the factor of 2 causes a horizontal compression ( ), squeezing the graph twice as close to the y-axis. Page 269 Example #1 19
20 If B > 0 the function y = sin(bt) resembles the function y = sin t except that it is stretched or compressed horizontally. The constant B determines how many cycles the function completes on an interval of length 2π. For example, we saw that the function y = sin 2t completes two cycles on the interval 0 t 2π. Page
21 Since, for B > 0, the graph of y = sin(bt) completes B cycles on the interval 0 t 2π, each cycle has length 2π/B. The period is thus 2π/B. Page
22 In our example, since sin(2x) completes 2 cycles on the interval 0 x 2π, each cycle has length 2π/2, which equals π. Therefore, the period equals: 2π/B = 2π/2 = π. Page
23 In general, for B of any sign, we have: The functions y = sin(bt) and y = cos(bt) have period P = 2π/ B. Page 270 Blue Box 23
24 In general, for B of any sign, we have: The functions y = sin(bt) and y = cos(bt) have period P = 2π/ B. The number of cycles in one unit of time is B /2π, the frequency. Page 270 Blue Box 24
25 In our example, since sin(2x) completes 2 cycles on the interval 0 x 2π, each cycle has length 2π/2, which equals π. Therefore, the period equals: 2π/B = 2π/2 = π. The number of cycles in one unit of time is B /2π, the frequency. Here we have: 2 /2π = 2/2π = 1/π Page
26 The number of cycles in one unit of time is B /2π, the frequency. Here we have: 2 /2π = 2/2π = 1/π Ask yourself: How many cycles in 2π? 2 cycles per 2π, or 1 cycle per π. Page
27 Again, for sin(2x), how many cycles in 2π? 2 cycles per 2π, or 1 cycle per π (freq). Page
28 Another example: sin(3x) Period? Frequency? Page N/A 28
29 Another example: sin(3x) Since sin(3x) completes 3 cycles on the interval 0 x 2π, each cycle has length 2π/3, which equals (2/3) π. Therefore, the period equals: 2π/3 = (2/3) π. Page
30 The number of cycles in one unit of time is B /2π, the frequency. Here we have: 3 /2π = 3/2π Ask yourself: How many cycles in 2π? 3 cycles per 2π, or 1.5 cycles per π. Page
31 Find possible formulas for the functions f and g shown in Figures 6.56 and Page 270 Example #2 31
32 Page 270 Example #2 32
33 The graph of f resembles the graph of y = sin t except that its period is P = 4π. Page 270 Example #2 33
34 The graph of f resembles the graph of y = sin t except that its period is P = 4π. Using P = 2π/B gives Page 270 Example #2 34
35 The graph of f resembles the graph of y = sin t except that its period is P = 4π. Using P = 2π/B gives 4 2 B 4 B 2 B Page 270 Example #2 35
36 Therefore: 1 f ( t) sin 2 t Page 270 Example #2 36
37 Let's use our calculator and graph: 1 y1 sin x 2 Page 270 Example #2 Window Value Xmin 0 Xmax 14 Xscl 2 Ymin -2 Ymax 2 Yscl 1 37
38 Find possible formulas for the functions f and g shown in Figures 6.56 and Page 270 Example #2 38
39 Page 270 Example #2 39
40 The graph of g resembles the graph of y = cos t except that its period is P = 20. Using P = 2π/B gives Page 270 Example #2 40
41 The graph of g resembles the graph of y = cos t except that its period is P = 20. Using P = 2π/B gives 20 2 B 20B 2 B Page 270 Example #2 41
42 Therefore: g( t) cos 10 t Page 270 Example #2 42
43 Let's use our calculator and graph: y1 cos 10 x Page 270 Example #2 Window Value Xmin 0 Xmax 60 Xscl 20 Ymin -2 Ymax 2 Yscl 1 43
44 Horizontal Shift Figure 6.59 shows the graphs of two trigonometric functions, f and g, with period P = 12. Page
45 Horizontal Shift The graph of f resembles a sine function, so a possible formula for f is f(t) = sin Bt. Since the period of f is 12, what is B? Page
46 Horizontal Shift The graph of f resembles a sine function, so a possible formula for f is f(t) = sin Bt B 12B 2 Page 271 B
47 Horizontal Shift t f( t) sin 6 Page
48 If y = g(x) is a function and k is a constant, then the graph of y = g(x) + k is the graph of y = g(x) shifted vertically k units. If k > 0, the shift is up; if k < 0, the shift is down. y = g(x + k) is the graph of y = g(x) shifted horizontally k units. If k > 0, the shift is to the left; if k < 0, the shift is to the right. Page 196 Blue Box (Section 5.1) 48
49 Page
50 Horizontal Shift The graph of g looks like the graph of f shifted to the right by 2 units. Thus a possible formula for g is g( t) f ( t 2) Page
51 Horizontal Shift The graph of g looks like the graph of f shifted to the right by 2 units. Thus a possible formula for g is g( t) sin ( t 2) 6 (Wherever you see t, you substitute t-2.) Page
52 Horizontal Shift We can rewrite the functions as: g( t) sin t 6 3 Page
53 Horizontal Shift BUT... g( t) sin t 6 3 Page
54 Horizontal Shift BUT... g( t) sin t 6 3 the horizontal shift is not 3 Page
55 Horizontal Shift To pick out the horizontal shift from the formula, we must write the formula in factored form, that is, as sin(b(t h)). g( t) sin ( t 2) 6 Page
56 Horizontal Shift The graphs of: y = sin(b(t h)) & y = cos(b(t h)) are the graphs of y = sin Bt and y = cos Bt shifted horizontally by h units. Page 271 Blue Box 56
57 Describe in words the graph of the function: g( t) cos 3t 4 Page 272 Example #5 57
58 Write the formula for g in the form cos(b(t h)) by factoring 3 out from the expression 3t π/4 to get g(t) = cos(3(t π/12)). What is the period? Page 272 Example #5 58
59 Since cos(3x) completes 3 cycles on the interval 0 x 2π, each cycle has length 2π/3, which equals (2/3) π. Therefore, the period equals: 2π/3 = (2/3) π. Page
60 g(t) = cos(3(t π/12)). The graph is the graph of f = cos 3t shifted π/12 units to the right, as shown in Figure Page 272 Example #5 60
61 g(t) = cos(3(t π/12)) Page 272 Example #5 61
62 Let's use our calculator and graph: y1 cos(3 x) and y2 cos 3x Page 272 Example #5 Window Value Xmin -π/2 Xmax 3 Xscl 1 Ymin -1.5 Ymax 1.5 Yscl
63 Page 272 Example #5 Now add: y3 cos 3 x 12 Window Value Xmin -π/2 Xmax 3 Xscl 1 Ymin -1.5 Ymax 1.5 Yscl 1 63
64 Since: cos( B( t h)) cos 3 x 12 B 3, h 12 Page 272 Example #5 64
65 Summary of Transformations The parameters a, B, h, and k determine the graph of a transformed sine or cosine function. Page 272 Blue Box 65
66 Summary of Transformations For the sinusoidal functions y asin( B( t h)) k and y acos( B( t h)) k a is the amplitude 2π/ B is the period h is the horizontal shift y = k is the midline B /2π is the frequency; that is, the number of cycles completed in unit time. Page 272 Blue Box 66
67 Phase Shift In Example 5, we factored (3t π/4) to write the function as g(t) = cos(3(t π/12)). This allowed us to recognize the horizontal shift, π/12. However, in most physical applications, the quantity π/4, known as the phase shift, is more important than the horizontal shift. We define: Phase Shift = Fraction of pd x 2π Page
68 Phase Shift Phase Shift (π/4) = Fraction of pd x 2π Now solve for "Fraction of pd": Fraction of pd = (π/4) / 2π Page
69 Phase Shift Fraction of pd = (π/4) / 2π = 1/8 (of a full period) Page
70 Phase Shift In example #5 the graph of f(t) = cos 3t is shifted 1/8 of its period to the right. Page
71 Phase Shift In example #5 the graph of f(t) = cos 3t is shifted 1/8 of its period to the right. Page
72 Phase Shift In example #5 the graph of f(t) = cos 3t is shifted 1/8 of its period to the right. cos 3 x cos 3x 12 4 Horizontal shift Phase shift Page
73 Phase Shift Phase shift is significant because in many applications, such as optical interference, we want to know if two waves reinforce or cancel each other. Page
74 Phase Shift For two waves of the same period, a phase shift of 0 or 2π tells us that the two waves reinforce each other; a phase shift of π tells us that the two waves cancel. Thus, the phase shift tells us the relative positions of two waves of the same period. Page
75 Phase Shift For the sinusoidal functions written in the form: y asin( Bt ) and y acos( Bt ) is the phase shift. Page
76 Using the Transformed Sine and Cosine Functions Page
77 Use the sinusoidal function f(t) = a sin(b(t h)) + k to represent your height above ground at time t while riding the ferris wheel. Page 275 Example #9 77
78 Page 275 Example #9 78
79 Summary of Transformations For the sinusoidal functions y asin( B( t h)) k a is the amplitude 2π/ B is the period h is the horizontal shift y = k is the midline B /2π is the frequency; that is, the number of cycles completed in unit time. Page 272 Blue Box 79
80 The diameter of the ferris wheel is 450 feet, so the midline is k = 225 and the amplitude, A, is also 225. The period of the ferris wheel is 30 minutes, so B 2 = Page 275 Example #9 80
81 The sine graph is shifted 7.5 minutes to the right because we reach y = 225 (the 3 o'clock position) when t = 7.5. Thus, the horizontal shift is h = 7.5, so f ( t) 225sin ( t 7.5) Page 275 Example #9 81
82 We can rewrite: f ( t) 225sin ( t ) 225 f ( t) 225sin t Page 275 Example #9 82
83 f ( t) 225sin t Let's substitute equivalent values: Page 275 Example #9 83
84 225sin t Page 275 Example #9 84
85 Page 275 Example #9 85
86 You will recall from Section 6.1 our sine regression experiment: Page 275 Example #9 86
87 y=a * sin(bx+c)+d a=225 b= c= d=225 Page N/A 87
88 We utilzed the sin regression function to fit a sin curve to the set of points. Here is the result: y=a * sin(bx+c)+d y = 225sin( x )+225 Page N/A 88
89 End of Section
Section 8.4: The Equations of Sinusoidal Functions
 Section 8.4: The Equations of Sinusoidal Functions In this section, we will examine transformations of the sine and cosine function and learn how to read various properties from the equation. Transformed
Section 8.4: The Equations of Sinusoidal Functions In this section, we will examine transformations of the sine and cosine function and learn how to read various properties from the equation. Transformed
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y
Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions We know from previously studying the periodicity of the trigonometric functions that the sine and cosine functions repeat themselves after 2 radians.
Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions We know from previously studying the periodicity of the trigonometric functions that the sine and cosine functions repeat themselves after 2 radians.
Section 8.4 Equations of Sinusoidal Functions soln.notebook. May 17, Section 8.4: The Equations of Sinusoidal Functions.
 Section 8.4: The Equations of Sinusoidal Functions Stop Sine 1 In this section, we will examine transformations of the sine and cosine function and learn how to read various properties from the equation.
Section 8.4: The Equations of Sinusoidal Functions Stop Sine 1 In this section, we will examine transformations of the sine and cosine function and learn how to read various properties from the equation.
WARM UP. 1. Expand the expression (x 2 + 3) Factor the expression x 2 2x Find the roots of 4x 2 x + 1 by graphing.
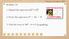 WARM UP Monday, December 8, 2014 1. Expand the expression (x 2 + 3) 2 2. Factor the expression x 2 2x 8 3. Find the roots of 4x 2 x + 1 by graphing. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Objectives Distinguish between
WARM UP Monday, December 8, 2014 1. Expand the expression (x 2 + 3) 2 2. Factor the expression x 2 2x 8 3. Find the roots of 4x 2 x + 1 by graphing. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Objectives Distinguish between
You analyzed graphs of functions. (Lesson 1-5)
 You analyzed graphs of functions. (Lesson 1-5) LEQ: How do we graph transformations of the sine and cosine functions & use sinusoidal functions to solve problems? sinusoid amplitude frequency phase shift
You analyzed graphs of functions. (Lesson 1-5) LEQ: How do we graph transformations of the sine and cosine functions & use sinusoidal functions to solve problems? sinusoid amplitude frequency phase shift
5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions.notebook. Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs
 Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs 1 Chapter 5 5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Pages 222 237 Complete the following table using your calculator. Round answers to the nearest tenth. 2
Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs 1 Chapter 5 5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Pages 222 237 Complete the following table using your calculator. Round answers to the nearest tenth. 2
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide Section 8.2 and 8.3-1
 8.3-1 Transformation of sine and cosine functions Sections 8.2 and 8.3 Revisit: Page 142; chapter 4 Section 8.2 and 8.3 Graphs of Transformed Sine and Cosine Functions Graph transformations of y = sin
8.3-1 Transformation of sine and cosine functions Sections 8.2 and 8.3 Revisit: Page 142; chapter 4 Section 8.2 and 8.3 Graphs of Transformed Sine and Cosine Functions Graph transformations of y = sin
Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 A Periodic Function and Its Period Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions A nonconstant function f is said to be periodic if there is a number p > 0 such that f(x + p) = f(x) for all x in
A Periodic Function and Its Period Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions A nonconstant function f is said to be periodic if there is a number p > 0 such that f(x + p) = f(x) for all x in
Pre-Calculus Notes: Chapter 6 Graphs of Trigonometric Functions
 Name: Pre-Calculus Notes: Chapter Graphs of Trigonometric Functions Section 1 Angles and Radian Measure Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. Radian measure is based on the circumference
Name: Pre-Calculus Notes: Chapter Graphs of Trigonometric Functions Section 1 Angles and Radian Measure Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. Radian measure is based on the circumference
Graphs of sin x and cos x
 Graphs of sin x and cos x One cycle of the graph of sin x, for values of x between 0 and 60, is given below. 1 0 90 180 270 60 1 It is this same shape that one gets between 60 and below). 720 and between
Graphs of sin x and cos x One cycle of the graph of sin x, for values of x between 0 and 60, is given below. 1 0 90 180 270 60 1 It is this same shape that one gets between 60 and below). 720 and between
6.1 - Introduction to Periodic Functions
 6.1 - Introduction to Periodic Functions Periodic Functions: Period, Midline, and Amplitude In general: A function f is periodic if its values repeat at regular intervals. Graphically, this means that
6.1 - Introduction to Periodic Functions Periodic Functions: Period, Midline, and Amplitude In general: A function f is periodic if its values repeat at regular intervals. Graphically, this means that
Algebra and Trig. I. The graph of
 Algebra and Trig. I 4.5 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions The graph of The graph of. The trigonometric functions can be graphed in a rectangular coordinate system by plotting points whose coordinates
Algebra and Trig. I 4.5 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions The graph of The graph of. The trigonometric functions can be graphed in a rectangular coordinate system by plotting points whose coordinates
5.3-The Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 5.3-The Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions Objectives: 1. Graph the sine and cosine functions. 2. Determine the amplitude, period and phase shift of the sine and cosine functions. 3. Find equations
5.3-The Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions Objectives: 1. Graph the sine and cosine functions. 2. Determine the amplitude, period and phase shift of the sine and cosine functions. 3. Find equations
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
Amplitude, Reflection, and Period
 SECTION 4.2 Amplitude, Reflection, and Period Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1 2 3 4 Find the amplitude of a sine or cosine function. Find the period of a sine or
SECTION 4.2 Amplitude, Reflection, and Period Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1 2 3 4 Find the amplitude of a sine or cosine function. Find the period of a sine or
Extra Practice for Section I: Chapter 4
 Haberman MTH 112 Extra Practice for Section I: Chapter You should complete all of these problems without a calculator in order to prepare for the Midterm which is a no-calculator exam. 1. Find two different
Haberman MTH 112 Extra Practice for Section I: Chapter You should complete all of these problems without a calculator in order to prepare for the Midterm which is a no-calculator exam. 1. Find two different
Section 7.6 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 4 Section 7. Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions In this section, we will look at the graphs of the sine and cosine function. The input values will be the angle in radians so we will be using x is
4 Section 7. Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions In this section, we will look at the graphs of the sine and cosine function. The input values will be the angle in radians so we will be using x is
2.5 Amplitude, Period and Frequency
 2.5 Amplitude, Period and Frequency Learning Objectives Calculate the amplitude and period of a sine or cosine curve. Calculate the frequency of a sine or cosine wave. Graph transformations of sine and
2.5 Amplitude, Period and Frequency Learning Objectives Calculate the amplitude and period of a sine or cosine curve. Calculate the frequency of a sine or cosine wave. Graph transformations of sine and
5.3 Trigonometric Graphs. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 5.3 Trigonometric Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Graphs of Sine and Cosine Graphs of Transformations of Sine and Cosine Using Graphing Devices to Graph Trigonometric
5.3 Trigonometric Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Graphs of Sine and Cosine Graphs of Transformations of Sine and Cosine Using Graphing Devices to Graph Trigonometric
6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions. The smallest number p with the above property is called the period of the function.
 Math 160 www.timetodare.com Periods of trigonometric functions Definition A function y f ( t) f ( t p) f ( t) 6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions = is periodic if there is a positive number p such
Math 160 www.timetodare.com Periods of trigonometric functions Definition A function y f ( t) f ( t p) f ( t) 6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions = is periodic if there is a positive number p such
3. Use your unit circle and fill in the exact values of the cosine function for each of the following angles (measured in radians).
 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Desmos Activity 1. Use your unit circle and fill in the exact values of the sine function for each of the following angles (measured in radians). sin 0 sin π 2 sin π
Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Desmos Activity 1. Use your unit circle and fill in the exact values of the sine function for each of the following angles (measured in radians). sin 0 sin π 2 sin π
4-4 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions
 Describe how the graphs of f (x) and g(x) are related. Then find the amplitude of g(x), and sketch two periods of both functions on the same coordinate axes. 1. f (x) = sin x; g(x) = sin x The graph of
Describe how the graphs of f (x) and g(x) are related. Then find the amplitude of g(x), and sketch two periods of both functions on the same coordinate axes. 1. f (x) = sin x; g(x) = sin x The graph of
Graph of the Sine Function
 1 of 6 8/6/2004 6.3 GRAPHS OF THE SINE AND COSINE 6.3 GRAPHS OF THE SINE AND COSINE Periodic Functions Graph of the Sine Function Graph of the Cosine Function Graphing Techniques, Amplitude, and Period
1 of 6 8/6/2004 6.3 GRAPHS OF THE SINE AND COSINE 6.3 GRAPHS OF THE SINE AND COSINE Periodic Functions Graph of the Sine Function Graph of the Cosine Function Graphing Techniques, Amplitude, and Period
1. Measure angle in degrees and radians 2. Find coterminal angles 3. Determine the arc length of a circle
 Pre- Calculus Mathematics 12 5.1 Trigonometric Functions Goal: 1. Measure angle in degrees and radians 2. Find coterminal angles 3. Determine the arc length of a circle Measuring Angles: Angles in Standard
Pre- Calculus Mathematics 12 5.1 Trigonometric Functions Goal: 1. Measure angle in degrees and radians 2. Find coterminal angles 3. Determine the arc length of a circle Measuring Angles: Angles in Standard
Unit 8 Trigonometry. Math III Mrs. Valentine
 Unit 8 Trigonometry Math III Mrs. Valentine 8A.1 Angles and Periodic Data * Identifying Cycles and Periods * A periodic function is a function that repeats a pattern of y- values (outputs) at regular intervals.
Unit 8 Trigonometry Math III Mrs. Valentine 8A.1 Angles and Periodic Data * Identifying Cycles and Periods * A periodic function is a function that repeats a pattern of y- values (outputs) at regular intervals.
Chapter #2 test sinusoidal function
 Chapter #2 test sinusoidal function Sunday, October 07, 2012 11:23 AM Multiple Choice [ /10] Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. For the function y = sin x,
Chapter #2 test sinusoidal function Sunday, October 07, 2012 11:23 AM Multiple Choice [ /10] Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. For the function y = sin x,
 http://www.math.utah.edu/~palais/sine.html http://www.ies.co.jp/math/java/trig/index.html http://www.analyzemath.com/function/periodic.html http://math.usask.ca/maclean/sincosslider/sincosslider.html http://www.analyzemath.com/unitcircle/unitcircle.html
http://www.math.utah.edu/~palais/sine.html http://www.ies.co.jp/math/java/trig/index.html http://www.analyzemath.com/function/periodic.html http://math.usask.ca/maclean/sincosslider/sincosslider.html http://www.analyzemath.com/unitcircle/unitcircle.html
Graphing Sine and Cosine
 The problem with average monthly temperatures on the preview worksheet is an example of a periodic function. Periodic functions are defined on p.254 Periodic functions repeat themselves each period. The
The problem with average monthly temperatures on the preview worksheet is an example of a periodic function. Periodic functions are defined on p.254 Periodic functions repeat themselves each period. The
Please grab the warm up off of the chair in the front of the room and begin working!
 Please grab the warm up off of the chair in the front of the room and begin working! add the x! #2 Fix to y = 5cos (2πx 2) + 9 Have your homework out on your desk to be checked. (Pre requisite for graphing
Please grab the warm up off of the chair in the front of the room and begin working! add the x! #2 Fix to y = 5cos (2πx 2) + 9 Have your homework out on your desk to be checked. (Pre requisite for graphing
The Sine Function. Precalculus: Graphs of Sine and Cosine
 Concepts: Graphs of Sine, Cosine, Sinusoids, Terminology (amplitude, period, phase shift, frequency). The Sine Function Domain: x R Range: y [ 1, 1] Continuity: continuous for all x Increasing-decreasing
Concepts: Graphs of Sine, Cosine, Sinusoids, Terminology (amplitude, period, phase shift, frequency). The Sine Function Domain: x R Range: y [ 1, 1] Continuity: continuous for all x Increasing-decreasing
Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions
 Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions Now we will look at other types of graphs: secant. tan x, cot x, csc x, sec x. We will start with the cosecant and y csc x In order to draw this graph we will first
Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions Now we will look at other types of graphs: secant. tan x, cot x, csc x, sec x. We will start with the cosecant and y csc x In order to draw this graph we will first
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y values
Section 8.1 Radians and Arc Length
 Section 8. Radians and Arc Length Definition. An angle of radian is defined to be the angle, in the counterclockwise direction, at the center of a unit circle which spans an arc of length. Conversion Factors:
Section 8. Radians and Arc Length Definition. An angle of radian is defined to be the angle, in the counterclockwise direction, at the center of a unit circle which spans an arc of length. Conversion Factors:
Graphing Trig Functions. Objectives: Students will be able to graph sine, cosine and tangent functions and translations of these functions.
 Graphing Trig Functions Name: Objectives: Students will be able to graph sine, cosine and tangent functions and translations of these functions. y = sinx (0,) x 0 sinx (,0) (0, ) (,0) /2 3/2 /2 3/2 2 x
Graphing Trig Functions Name: Objectives: Students will be able to graph sine, cosine and tangent functions and translations of these functions. y = sinx (0,) x 0 sinx (,0) (0, ) (,0) /2 3/2 /2 3/2 2 x
Unit 6 Test REVIEW Algebra 2 Honors
 Unit Test REVIEW Algebra 2 Honors Multiple Choice Portion SHOW ALL WORK! 1. How many radians are in 1800? 10 10π Name: Per: 180 180π 2. On the unit circle shown, which radian measure is located at ( 2,
Unit Test REVIEW Algebra 2 Honors Multiple Choice Portion SHOW ALL WORK! 1. How many radians are in 1800? 10 10π Name: Per: 180 180π 2. On the unit circle shown, which radian measure is located at ( 2,
2.4 Translating Sine and Cosine Functions
 www.ck1.org Chapter. Graphing Trigonometric Functions.4 Translating Sine and Cosine Functions Learning Objectives Translate sine and cosine functions vertically and horizontally. Identify the vertical
www.ck1.org Chapter. Graphing Trigonometric Functions.4 Translating Sine and Cosine Functions Learning Objectives Translate sine and cosine functions vertically and horizontally. Identify the vertical
5.4 Graphs of the Sine & Cosine Functions Objectives
 Objectives 1. Graph Functions of the Form y = A sin(wx) Using Transformations. 2. Graph Functions of the Form y = A cos(wx) Using Transformations. 3. Determine the Amplitude & Period of Sinusoidal Functions.
Objectives 1. Graph Functions of the Form y = A sin(wx) Using Transformations. 2. Graph Functions of the Form y = A cos(wx) Using Transformations. 3. Determine the Amplitude & Period of Sinusoidal Functions.
7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS
 7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS Ferris Wheel Height As a Function of Time The London Eye Ferris Wheel measures 450 feet in diameter and turns continuously, completing a single rotation once every
7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS Ferris Wheel Height As a Function of Time The London Eye Ferris Wheel measures 450 feet in diameter and turns continuously, completing a single rotation once every
MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) (sin x + cos x) 1 + sin x cos x =? 1) ) sec 4 x + sec x tan x - tan 4 x =? ) ) cos
MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) (sin x + cos x) 1 + sin x cos x =? 1) ) sec 4 x + sec x tan x - tan 4 x =? ) ) cos
1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine
 1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Exercise 1 Sketch a graph of y = cos(t). Label the multiples of π 2 and π 4 on your plot, as well as the amplitude and the period of the function. (Feel free to sketch the unit
1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Exercise 1 Sketch a graph of y = cos(t). Label the multiples of π 2 and π 4 on your plot, as well as the amplitude and the period of the function. (Feel free to sketch the unit
Chapter 14 Trig Graphs and Reciprocal Functions Algebra II Common Core
 Chapter 14 Trig Graphs and Reciprocal Functions Algebra II Common Core LESSON 1: BASIC GRAPHS OF SINE AND COSINE LESSON : VERTICAL SHIFTING OF SINUSOIDAL GRAPHS LESSON 3 : THE FREQUENCY AND PERIOD OF A
Chapter 14 Trig Graphs and Reciprocal Functions Algebra II Common Core LESSON 1: BASIC GRAPHS OF SINE AND COSINE LESSON : VERTICAL SHIFTING OF SINUSOIDAL GRAPHS LESSON 3 : THE FREQUENCY AND PERIOD OF A
Pythagorean Identity. Sum and Difference Identities. Double Angle Identities. Law of Sines. Law of Cosines
 Review for Math 111 Final Exam The final exam is worth 30% (150/500 points). It consists of 26 multiple choice questions, 4 graph matching questions, and 4 short answer questions. Partial credit will be
Review for Math 111 Final Exam The final exam is worth 30% (150/500 points). It consists of 26 multiple choice questions, 4 graph matching questions, and 4 short answer questions. Partial credit will be
Math 1330 Precalculus Electronic Homework (EHW 6) Sections 5.1 and 5.2.
 Math 0 Precalculus Electronic Homework (EHW 6) Sections 5. and 5.. Work the following problems and choose the correct answer. The problems that refer to the Textbook may be found at www.casa.uh.edu in
Math 0 Precalculus Electronic Homework (EHW 6) Sections 5. and 5.. Work the following problems and choose the correct answer. The problems that refer to the Textbook may be found at www.casa.uh.edu in
6.6. Investigating Models of Sinusoidal Functions. LEARN ABOUT the Math. Sasha s Solution Investigating Models of Sinusoidal Functions
 6.6 Investigating Models of Sinusoidal Functions GOAL Determine the equation of a sinusoidal function from a graph or a table of values. LEARN ABOUT the Math A nail located on the circumference of a water
6.6 Investigating Models of Sinusoidal Functions GOAL Determine the equation of a sinusoidal function from a graph or a table of values. LEARN ABOUT the Math A nail located on the circumference of a water
Section 7.7 Graphs of the Tangent, Cotangent, Cosecant, and Secant Functions
 Section 7.7 Graphs of the Tangent, Cotangent, Cosecant, and Secant Functions In this section, we will look at the graphs of the other four trigonometric functions. We will start by examining the tangent
Section 7.7 Graphs of the Tangent, Cotangent, Cosecant, and Secant Functions In this section, we will look at the graphs of the other four trigonometric functions. We will start by examining the tangent
Secondary Math Amplitude, Midline, and Period of Waves
 Secondary Math 3 7-6 Amplitude, Midline, and Period of Waves Warm UP Complete the unit circle from memory the best you can: 1. Fill in the degrees 2. Fill in the radians 3. Fill in the coordinates in the
Secondary Math 3 7-6 Amplitude, Midline, and Period of Waves Warm UP Complete the unit circle from memory the best you can: 1. Fill in the degrees 2. Fill in the radians 3. Fill in the coordinates in the
How to Graph Trigonometric Functions
 How to Graph Trigonometric Functions This handout includes instructions for graphing processes of basic, amplitude shifts, horizontal shifts, and vertical shifts of trigonometric functions. The Unit Circle
How to Graph Trigonometric Functions This handout includes instructions for graphing processes of basic, amplitude shifts, horizontal shifts, and vertical shifts of trigonometric functions. The Unit Circle
TRANSFORMING TRIG FUNCTIONS
 Chapter 7 TRANSFORMING TRIG FUNCTIONS 7.. 7..4 Students appl their knowledge of transforming parent graphs to the trigonometric functions. The will generate general equations for the famil of sine, cosine
Chapter 7 TRANSFORMING TRIG FUNCTIONS 7.. 7..4 Students appl their knowledge of transforming parent graphs to the trigonometric functions. The will generate general equations for the famil of sine, cosine
ALGEBRA 2 ~ Lessons 1 13
 ALGEBRA 2 ~ Lessons 1 13 Remember to write the original problem and show all of your steps! All work should be done on a separate piece of paper. ASSIGNMENT 1 Arithmetic (No calculator.) Add, subtract
ALGEBRA 2 ~ Lessons 1 13 Remember to write the original problem and show all of your steps! All work should be done on a separate piece of paper. ASSIGNMENT 1 Arithmetic (No calculator.) Add, subtract
Math 3 Trigonometry Part 2 Waves & Laws
 Math 3 Trigonometry Part 2 Waves & Laws GRAPHING SINE AND COSINE Graph of sine function: Plotting every angle and its corresponding sine value, which is the y-coordinate, for different angles on the unit
Math 3 Trigonometry Part 2 Waves & Laws GRAPHING SINE AND COSINE Graph of sine function: Plotting every angle and its corresponding sine value, which is the y-coordinate, for different angles on the unit
7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS
 7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS *SECTION: 6.1 DCP List: periodic functions period midline amplitude Pg 247- LECTURE EXAMPLES: Ferris wheel, 14,16,20, eplain 23, 28, 32 *SECTION: 6.2 DCP List: unit
7.1 INTRODUCTION TO PERIODIC FUNCTIONS *SECTION: 6.1 DCP List: periodic functions period midline amplitude Pg 247- LECTURE EXAMPLES: Ferris wheel, 14,16,20, eplain 23, 28, 32 *SECTION: 6.2 DCP List: unit
Trig functions are examples of periodic functions because they repeat. All periodic functions have certain common characteristics.
 Trig functions are examples of periodic functions because they repeat. All periodic functions have certain common characteristics. The sine wave is a common term for a periodic function. But not all periodic
Trig functions are examples of periodic functions because they repeat. All periodic functions have certain common characteristics. The sine wave is a common term for a periodic function. But not all periodic
What is a Sine Function Graph? U4 L2 Relate Circle to Sine Activity.pdf
 Math 3 Unit 6, Trigonometry L04: Amplitude and Period of Sine and Cosine AND Translations of Sine and Cosine Functions WIMD: What I must do: I will find the amplitude and period from a graph of the sine
Math 3 Unit 6, Trigonometry L04: Amplitude and Period of Sine and Cosine AND Translations of Sine and Cosine Functions WIMD: What I must do: I will find the amplitude and period from a graph of the sine
the input values of a function. These are the angle values for trig functions
 SESSION 8: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: Graphs of Trigonometric Functions y = sin θ y = cos θ y = tan θ Properties of Graphs Shape Intercepts Domain and Range Minimum and maximum values Period
SESSION 8: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: Graphs of Trigonometric Functions y = sin θ y = cos θ y = tan θ Properties of Graphs Shape Intercepts Domain and Range Minimum and maximum values Period
Chapter 7 Repetitive Change: Cyclic Functions
 Chapter 7 Repetitive Change: Cyclic Functions 7.1 Cycles and Sine Functions Data that is periodic may often be modeled by trigonometric functions. This chapter will help you use Excel to deal with periodic
Chapter 7 Repetitive Change: Cyclic Functions 7.1 Cycles and Sine Functions Data that is periodic may often be modeled by trigonometric functions. This chapter will help you use Excel to deal with periodic
The GC s standard graphing window shows the x-axis from -10 to 10 and the y-axis from -10 to 10.
 Name Date TI-84+ GC 17 Changing the Window Objectives: Adjust Xmax, Xmin, Ymax, and/or Ymin in Window menu Understand and adjust Xscl and/or Yscl in Window menu The GC s standard graphing window shows
Name Date TI-84+ GC 17 Changing the Window Objectives: Adjust Xmax, Xmin, Ymax, and/or Ymin in Window menu Understand and adjust Xscl and/or Yscl in Window menu The GC s standard graphing window shows
Seeing Music, Hearing Waves
 Seeing Music, Hearing Waves NAME In this activity, you will calculate the frequencies of two octaves of a chromatic musical scale in standard pitch. Then, you will experiment with different combinations
Seeing Music, Hearing Waves NAME In this activity, you will calculate the frequencies of two octaves of a chromatic musical scale in standard pitch. Then, you will experiment with different combinations
When interpreting a word problem, graphing the situation, and writing a cosine and sine equation to model the data, use the following steps:
 Modeling with Sinusoidal Functions Name Date PD When interpreting a word problem, graphing the situation, and writing a cosine and sine equation to model the data, use the following steps: 1) Identify
Modeling with Sinusoidal Functions Name Date PD When interpreting a word problem, graphing the situation, and writing a cosine and sine equation to model the data, use the following steps: 1) Identify
Math 1205 Trigonometry Review
 Math 105 Trigonometry Review We begin with the unit circle. The definition of a unit circle is: x + y =1 where the center is (0, 0) and the radius is 1. An angle of 1 radian is an angle at the center of
Math 105 Trigonometry Review We begin with the unit circle. The definition of a unit circle is: x + y =1 where the center is (0, 0) and the radius is 1. An angle of 1 radian is an angle at the center of
Section 2.4 General Sinusoidal Graphs
 Section. General Graphs Objective: any one of the following sets of information about a sinusoid, find the other two: ) the equation ) the graph 3) the amplitude, period or frequency, phase displacement,
Section. General Graphs Objective: any one of the following sets of information about a sinusoid, find the other two: ) the equation ) the graph 3) the amplitude, period or frequency, phase displacement,
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a polar equation is given. Select the polar
Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a polar equation is given. Select the polar
Trigonometry, Exam 2 Review, Spring (b) y 4 cos x
 Trigonometr, Eam Review, Spring 8 Section.A: Basic Sine and Cosine Graphs. Sketch the graph indicated. Remember to label the aes (with numbers) and to carefull sketch the five points. (a) sin (b) cos Section.B:
Trigonometr, Eam Review, Spring 8 Section.A: Basic Sine and Cosine Graphs. Sketch the graph indicated. Remember to label the aes (with numbers) and to carefull sketch the five points. (a) sin (b) cos Section.B:
Trigonometric Equations
 Chapter Three Trigonometric Equations Solving Simple Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Solving Complicated Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions Solving Trigonometric
Chapter Three Trigonometric Equations Solving Simple Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Solving Complicated Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions Solving Trigonometric
GRAPHING TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
 GRAPHING TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Section.6B Precalculus PreAP/Dual, Revised 7 viet.dang@humbleisd.net 8//8 : AM.6B: Graphing Trig Functions REVIEW OF GRAPHS 8//8 : AM.6B: Graphing Trig Functions A. Equation:
GRAPHING TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Section.6B Precalculus PreAP/Dual, Revised 7 viet.dang@humbleisd.net 8//8 : AM.6B: Graphing Trig Functions REVIEW OF GRAPHS 8//8 : AM.6B: Graphing Trig Functions A. Equation:
Practice Test Chapter 8 Sinusoidal Functions
 FOM 12 Practice Test Chapter 8 Sinusoidal Functions Name: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Block: _ 1. Convert 120 into radians. A. 2 3 B.
FOM 12 Practice Test Chapter 8 Sinusoidal Functions Name: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Block: _ 1. Convert 120 into radians. A. 2 3 B.
Name: Date: Group: Learning Target: I can determine amplitude, period, frequency, and phase shift, given a graph or equation of a periodic function.
 Pre-Lesson Assessment Unit 2: Trigonometric Functions Periodic Functions Diagnostic Exam: Page 1 Name: Date: Group: Learning Target: I can determine amplitude, period, frequency, and phase shift, given
Pre-Lesson Assessment Unit 2: Trigonometric Functions Periodic Functions Diagnostic Exam: Page 1 Name: Date: Group: Learning Target: I can determine amplitude, period, frequency, and phase shift, given
of the whole circumference.
 TRIGONOMETRY WEEK 13 ARC LENGTH AND AREAS OF SECTORS If the complete circumference of a circle can be calculated using C = 2πr then the length of an arc, (a portion of the circumference) can be found by
TRIGONOMETRY WEEK 13 ARC LENGTH AND AREAS OF SECTORS If the complete circumference of a circle can be calculated using C = 2πr then the length of an arc, (a portion of the circumference) can be found by
Vocabulary. A Graph of the Cosine Function. Lesson 10-6 The Cosine and Sine Functions. Mental Math
 Lesson 10-6 The Cosine and Sine Functions Vocabular periodic function, period sine wave sinusoidal BIG IDEA The graphs of the cosine and sine functions are sine waves with period 2π. Remember that when
Lesson 10-6 The Cosine and Sine Functions Vocabular periodic function, period sine wave sinusoidal BIG IDEA The graphs of the cosine and sine functions are sine waves with period 2π. Remember that when
Trigonometric Integrals Section 5.7
 A B I L E N E C H R I S T I A N U N I V E R S I T Y Department of Mathematics Trigonometric Integrals Section 5.7 Dr. John Ehrke Department of Mathematics Spring 2013 Eliminating Powers From Trig Functions
A B I L E N E C H R I S T I A N U N I V E R S I T Y Department of Mathematics Trigonometric Integrals Section 5.7 Dr. John Ehrke Department of Mathematics Spring 2013 Eliminating Powers From Trig Functions
5-5 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Identities
 Find the values of sin 2, cos 2, tan 2 1 cos for the given value interval, (270, 360 ) Since on the interval (270, 360 ), one point on the terminal side of θ has x-coordinate 3 a distance of 5 units from
Find the values of sin 2, cos 2, tan 2 1 cos for the given value interval, (270, 360 ) Since on the interval (270, 360 ), one point on the terminal side of θ has x-coordinate 3 a distance of 5 units from
Unit 5 Investigating Trigonometry Graphs
 Mathematics IV Frameworks Student Edition Unit 5 Investigating Trigonometry Graphs 1 st Edition Table of Contents INTRODUCTION:... 3 What s Your Temperature? Learning Task... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Mathematics IV Frameworks Student Edition Unit 5 Investigating Trigonometry Graphs 1 st Edition Table of Contents INTRODUCTION:... 3 What s Your Temperature? Learning Task... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Name Date Class. Identify whether each function is periodic. If the function is periodic, give the period
 Name Date Class 14-1 Practice A Graphs of Sine and Cosine Identify whether each function is periodic. If the function is periodic, give the period. 1.. Use f(x) = sinx or g(x) = cosx as a guide. Identify
Name Date Class 14-1 Practice A Graphs of Sine and Cosine Identify whether each function is periodic. If the function is periodic, give the period. 1.. Use f(x) = sinx or g(x) = cosx as a guide. Identify
The Cartesian Coordinate System
 The Cartesian Coordinate System The xy-plane Although a familiarity with the xy-plane, or Cartesian coordinate system, is expected, this worksheet will provide a brief review. The Cartesian coordinate
The Cartesian Coordinate System The xy-plane Although a familiarity with the xy-plane, or Cartesian coordinate system, is expected, this worksheet will provide a brief review. The Cartesian coordinate
Chapter 8: SINUSODIAL FUNCTIONS
 Chapter 8 Math 0 Chapter 8: SINUSODIAL FUNCTIONS Section 8.: Understanding Angles p. 8 How can we measure things? Eamples: Length - meters (m) or ards (d.) Temperature - degrees Celsius ( o C) or Fahrenheit
Chapter 8 Math 0 Chapter 8: SINUSODIAL FUNCTIONS Section 8.: Understanding Angles p. 8 How can we measure things? Eamples: Length - meters (m) or ards (d.) Temperature - degrees Celsius ( o C) or Fahrenheit
5-5 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Identities
 Find the values of sin 2, cos 2, and tan 2 for the given value and interval. 1. cos =, (270, 360 ) Since on the interval (270, 360 ), one point on the terminal side of θ has x-coordinate 3 and a distance
Find the values of sin 2, cos 2, and tan 2 for the given value and interval. 1. cos =, (270, 360 ) Since on the interval (270, 360 ), one point on the terminal side of θ has x-coordinate 3 and a distance
Chapter 4/5 Part 2- Trig Identities and Equations
 Chapter 4/5 Part 2- Trig Identities and Equations Lesson Package MHF4U Chapter 4/5 Part 2 Outline Unit Goal: By the end of this unit, you will be able to solve trig equations and prove trig identities.
Chapter 4/5 Part 2- Trig Identities and Equations Lesson Package MHF4U Chapter 4/5 Part 2 Outline Unit Goal: By the end of this unit, you will be able to solve trig equations and prove trig identities.
Math 102 Key Ideas. 1 Chapter 1: Triangle Trigonometry. 1. Consider the following right triangle: c b
 Math 10 Key Ideas 1 Chapter 1: Triangle Trigonometry 1. Consider the following right triangle: A c b B θ C a sin θ = b length of side opposite angle θ = c length of hypotenuse cosθ = a length of side adjacent
Math 10 Key Ideas 1 Chapter 1: Triangle Trigonometry 1. Consider the following right triangle: A c b B θ C a sin θ = b length of side opposite angle θ = c length of hypotenuse cosθ = a length of side adjacent
Name: Which equation is represented in the graph? Which equation is represented by the graph? 1. y = 2 sin 2x 2. y = sin x. 1.
 Name: Print Close Which equation is represented in the graph? Which equation is represented by the graph? y = 2 sin 2x y = sin x y = 2 sin x 4. y = sin 2x Which equation is represented in the graph? 4.
Name: Print Close Which equation is represented in the graph? Which equation is represented by the graph? y = 2 sin 2x y = sin x y = 2 sin x 4. y = sin 2x Which equation is represented in the graph? 4.
c. Using the conditions described in Part b, how far does Mario travel each minute?
 Trig. Modeling Short Answer 1. Mario's bicycle has 42 teeth in the crankset attached to the pedals. It has three sprockets of differing sizes connected to the rear wheel. The three sprockets at the rear
Trig. Modeling Short Answer 1. Mario's bicycle has 42 teeth in the crankset attached to the pedals. It has three sprockets of differing sizes connected to the rear wheel. The three sprockets at the rear
Outline. Drawing the Graph. 1 Homework Review. 2 Introduction. 3 Histograms. 4 Histograms on the TI Assignment
 Lecture 14 Section 4.4.4 on Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Sep 18, 2009 Outline 1 on 2 3 4 on 5 6 Even-numbered on Exercise 4.25, p. 249. The following is a list of homework scores for two students: Student
Lecture 14 Section 4.4.4 on Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Sep 18, 2009 Outline 1 on 2 3 4 on 5 6 Even-numbered on Exercise 4.25, p. 249. The following is a list of homework scores for two students: Student
Do You See What I See?
 Concept Geometry and measurement Activity 5 Skill Calculator skills: coordinate graphing, creating lists, ' Do You See What I See? Students will discover how pictures formed by graphing ordered pairs can
Concept Geometry and measurement Activity 5 Skill Calculator skills: coordinate graphing, creating lists, ' Do You See What I See? Students will discover how pictures formed by graphing ordered pairs can
Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas
 Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas By: OpenStaxCollege Bicycle ramps for advanced riders have a steeper incline than those designed for novices. Bicycle ramps made for competition (see [link])
Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas By: OpenStaxCollege Bicycle ramps for advanced riders have a steeper incline than those designed for novices. Bicycle ramps made for competition (see [link])
Sinusoidal Applications
 Sinusoidal Applications A package of 5 activities Problems dealing with graphing and determining the equations of sinusoidal functions for real world situations Fractal image generated by MathWiz Created
Sinusoidal Applications A package of 5 activities Problems dealing with graphing and determining the equations of sinusoidal functions for real world situations Fractal image generated by MathWiz Created
Precalculus ~ Review Sheet
 Period: Date: Precalculus ~ Review Sheet 4.4-4.5 Multiple Choice 1. The screen below shows the graph of a sound recorded on an oscilloscope. What is the period and the amplitude? (Each unit on the t-axis
Period: Date: Precalculus ~ Review Sheet 4.4-4.5 Multiple Choice 1. The screen below shows the graph of a sound recorded on an oscilloscope. What is the period and the amplitude? (Each unit on the t-axis
Section 5.1 Angles and Radian Measure. Ever Feel Like You re Just Going in Circles?
 Section 5.1 Angles and Radian Measure Ever Feel Like You re Just Going in Circles? You re riding on a Ferris wheel and wonder how fast you are traveling. Before you got on the ride, the operator told you
Section 5.1 Angles and Radian Measure Ever Feel Like You re Just Going in Circles? You re riding on a Ferris wheel and wonder how fast you are traveling. Before you got on the ride, the operator told you
Trigonometry. An Overview of Important Topics
 Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics 1 Contents Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics... 4 UNDERSTAND HOW ANGLES ARE MEASURED... 6 Degrees... 7 Radians... 7 Unit Circle... 9 Practice Problems...
Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics 1 Contents Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics... 4 UNDERSTAND HOW ANGLES ARE MEASURED... 6 Degrees... 7 Radians... 7 Unit Circle... 9 Practice Problems...
Unit 5 Graphing Trigonmetric Functions
 HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 5 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 5 Graphing Trigonmetric Functions This is a BASIC CALCULATORS ONLY unit. (2) Periodic Functions (3) Graph of the Sine Function (4) Graph of the Cosine Function
HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 5 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 5 Graphing Trigonmetric Functions This is a BASIC CALCULATORS ONLY unit. (2) Periodic Functions (3) Graph of the Sine Function (4) Graph of the Cosine Function
Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.
 MAT 115 Spring 2015 Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) Part I: No Calculators. Show work. 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.) a.
MAT 115 Spring 2015 Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) Part I: No Calculators. Show work. 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.) a.
2. Be able to evaluate a trig function at a particular degree measure. Example: cos. again, just use the unit circle!
 Study Guide for PART II of the Fall 18 MAT187 Final Exam NO CALCULATORS are permitted on this part of the Final Exam. This part of the Final exam will consist of 5 multiple choice questions. You will be
Study Guide for PART II of the Fall 18 MAT187 Final Exam NO CALCULATORS are permitted on this part of the Final Exam. This part of the Final exam will consist of 5 multiple choice questions. You will be
Introduction to Trigonometry. Algebra 2
 Introduction to Trigonometry Algebra 2 Angle Rotation Angle formed by the starting and ending positions of a ray that rotates about its endpoint Use θ to represent the angle measure Greek letter theta
Introduction to Trigonometry Algebra 2 Angle Rotation Angle formed by the starting and ending positions of a ray that rotates about its endpoint Use θ to represent the angle measure Greek letter theta
C H A P T E R 4 Trigonometric Functions
 C H A P T E R Trigonometric Functions Section. Radian and Degree Measure................ 7 Section. Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle........ 8 Section. Right Triangle Trigonometr................
C H A P T E R Trigonometric Functions Section. Radian and Degree Measure................ 7 Section. Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle........ 8 Section. Right Triangle Trigonometr................
- go over homework #2 on applications - Finish Applications Day #3 - more applications... tide problems, start project
 10/20/15 ALICATIONS DAY #3 HOMEWORK TC2 WARM U! Agenda Homework - go over homework #2 on applications - Finish Applications Day #3 - more applications... tide problems, start project UCOMING: OW #6 Quiz
10/20/15 ALICATIONS DAY #3 HOMEWORK TC2 WARM U! Agenda Homework - go over homework #2 on applications - Finish Applications Day #3 - more applications... tide problems, start project UCOMING: OW #6 Quiz
Objectives. Materials
 . Objectives Activity 8 To plot a mathematical relationship that defines a spiral To use technology to create a spiral similar to that found in a snail To use technology to plot a set of ordered pairs
. Objectives Activity 8 To plot a mathematical relationship that defines a spiral To use technology to create a spiral similar to that found in a snail To use technology to plot a set of ordered pairs
How to Graph Trigonometric Functions for Sine and Cosine. Amplitudes Midlines Periods Oh My! Kyle O. Linford
 How to Graph Trigonometric Functions for Sine and Cosine Amplitudes Midlines Periods Oh My! Kyle O. Linford Linford 1 For all of my future students, May this text help you understand the power and beauty
How to Graph Trigonometric Functions for Sine and Cosine Amplitudes Midlines Periods Oh My! Kyle O. Linford Linford 1 For all of my future students, May this text help you understand the power and beauty
Fungus Farmers LEAF CUTTING ANTS A C T I V I T Y. Activity Overview. How much leaf do leaf cutter ants chew?
 How much leaf do leaf cutter ants chew? Activity Overview Leaf cutting ants carry away leaf pieces that are up to 30 times their weight. They sometimes carry these pieces 100-200 meters (about 2 football
How much leaf do leaf cutter ants chew? Activity Overview Leaf cutting ants carry away leaf pieces that are up to 30 times their weight. They sometimes carry these pieces 100-200 meters (about 2 football
SECTION 1.5: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
 SECTION.5: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS The Unit Circle The unit circle is the set of all points in the xy-plane for which x + y =. Def: A radian is a unit for measuring angles other than degrees and is measured
SECTION.5: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS The Unit Circle The unit circle is the set of all points in the xy-plane for which x + y =. Def: A radian is a unit for measuring angles other than degrees and is measured
Unit 3 Unit Circle and Trigonometry + Graphs
 HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 3 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 3 Unit Circle and Trigonometry + Graphs (2) The Unit Circle (3) Displacement and Terminal Points (5) Significant t-values Coterminal Values of t (7) Reference
HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 3 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 3 Unit Circle and Trigonometry + Graphs (2) The Unit Circle (3) Displacement and Terminal Points (5) Significant t-values Coterminal Values of t (7) Reference
Section 7.1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine
 Section 7.1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine OBJECTIVE 1: Understanding the Graph of the Sine Function and its Properties In Chapter 7, we will use a rectangular coordinate system for a different purpose. We
Section 7.1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine OBJECTIVE 1: Understanding the Graph of the Sine Function and its Properties In Chapter 7, we will use a rectangular coordinate system for a different purpose. We
Unit Circle: Sine and Cosine
 Unit Circle: Sine and Cosine Functions By: OpenStaxCollege The Singapore Flyer is the world s tallest Ferris wheel. (credit: Vibin JK /Flickr) Looking for a thrill? Then consider a ride on the Singapore
Unit Circle: Sine and Cosine Functions By: OpenStaxCollege The Singapore Flyer is the world s tallest Ferris wheel. (credit: Vibin JK /Flickr) Looking for a thrill? Then consider a ride on the Singapore
