D-STATE RADIOMETER. I. Switch Driver
|
|
|
- Neal Jason Robertson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NATIONAL RADIO ASTRONOMY OBSERVATORY Green Bank, West Virginia Electronics Division Internal Report No. 13 A SOLID-STATE RADIOMETER James L. Dolan August 1963 Rerun 11/10/ 66: 50
2 D-STATE RADIOMETER Work is now being done at ITRAO that will lead to a completely solid-s ate standard receiver that will eventually replace the standard vacuum tube version now seeing wide use at the Observatory. So far, the work has progressed very well although relatively small effort has been applied in this direction, but a solid-state receiver is well within the realm of possibility. The major objective is to insure that the radiometer is noise limited instead of stability limited. As with any system development, some design constants should be chosen that are common to all components. The radiometer system consists of a number of sub systems, such as the gain modulator, intermediate frequency amplifier, audio amplifier, switch driver, and phase detector. First, the selection of transistors becomes very important. Such factors as frequency cut-off, power dissipation, collector ratings, small signal current gain, and cost must be considered. On the basis of these considerations, the Philco 2N1742 MADT (micro alloy diffused-base transistor) was selected for all radio frequency circuits. The audio and phase detector circuits are not so demanding, and there are a number of transistors that can be.used. The primary voltage to be used is of considerable practical importance. Since the 2N1742 collector rating is -20 V DC, a voltage of -18 volts was chosen This voltage is slightly higher than was desired, because the transistor is very sensitive to over voltage. The -18 volts was selected because it is a multiple of 6 (used in digital circuits), and it is high enough to allow nominal power output without a heavy collector current. A voltage of 12 or 15 volts would be better if the 2N1742 was the only component using the primary power. A bandwidth of megacycles, centered on 50 megacycles, Is being attempted up to the diode detector. Since this is a post-amplifier, noise figure is of secondary importance, and no attempt will be made to keep the noise figure less than 7 or 8 db. I. Switch Driver A solid-state switch has been designed and tested that will deliver more than enough 400 cycle power to drive the entire receiver. In fact, it is intended that the 400 cycle unit will he capable of driving at least two standard receivers. The 400 cycle switch is simply a triggered multivibrator running at 400 cycles/sec. It is possible to construct a free running multivibrator, but the frequency stability is dependent on the RC feedback
3 loop, and the free running unit tends to drift about ± 5 cycles. With a narrow 400 cycles filter In the audio circuit, this drift cannot be tolerated. Therefore, the synchronizing trigger seems advisable at this time. The multivibrator circuit is inherently very inefficient because of the large feed-back power required to switch the opposite transistor On or off, as the case may be. There are two ways to achieve the desired power from the multivibrator. One way is to use large components and high power and use only a small portion of the dissipated power, This is a very inefficient method. The second method is to use small components and low power, and feed the vibrator output into a high impedance =Oilier, and amplify the signal by conventional means. This method requires more components, but the circuit is more efficient. Another factor to consider with switch drivers is the possibility of operation at more than one frequency. For instance, the AIL maser system is switched at 20 cycles/second, whereas the standard receiver is switched at 400 cycles/second. If a monostable or bistable circuit is used, it can be triggered at any frequency from a fraction of a cycle/second to more than one megacycle. If an Astable circuit is used, it will run at only the design frequency. In this system the bistame circuit was chosen. This circuit can be modified quickly to astable operation if the need should arise. The general circuit is shown in Figure 2. The theory of operation is straightforward. The transistor Q i is used in the emitter follower configuration in order to present a high impedance to the reference source. In some cases the transistor may not be necessary, depending on the internal Impedance of the reference oscillator. Transistors Q and i Q 2 are connected in the conventional bistable multivibrator circuit, using 2N242 transistors. This is a relatively inefficient circuit, and can be improved upon. The transistor Q 4 is used as a Class A power amplifier, capable of approximately 4 waits output power. Improvements in the circuit could be made by reducing the size of the transistors Q z and (4. 3 in the multi vibrator, thereby increasing circuit efficiency. This will be done in the finished circuit. One problem not immediately seen is AC coupling at low frequencies (such as 20 cycles/second) and low impedance. A future project will be to design and test a hybrid circuit using analog and digital techniques which should avoid the AC coupling difficulties.
4 ne Gain Modulator The gain modulator designed for the solid state receiver has been tested with Posttive results. This unit is the first RF circuit in the standard system, and uses 2N1742 transistors throughout (see Figure 3). Transistor Q serves two purposes. First, it serves as a constant current source for the transistor switches, Q i and Q 2, and second. it provides a means of inserting the RF signal into the switches. Transistors Q 2 and Q. are emitter coupled and transistor Q is driven by the 400 cycles/second square wave alternately into saturation and to cut-off. Q 2 follows Q i exactly out of phase. Therefore, the signal is effectively switched from one attenuator to another. These attenuators can be adjusted to provide radiometer balance. After the signal passes through the attenuators the two channels are recombined in a summing circuit and fed on to the intermediate ampli fier. The problems encountered in the gain modulator have been limited to the attenuators, and to bandwidth. The attenuator problem has been of a physical nature; simply, the attenuators have been approximately 2 or 3 times as large as the remainder of the circuit. Some consideration has been given to this problem, and on the final configuration it will have been eliminated. Since we are attempting to maintain a bandwidth of about 100 Mcis through the system, the gain modulator must be capable of this bandwidth. The limiting factor now is the coupling transformers between the switching transistors and their associated attenuators. In the final design, the circuit will use the wide-band transmission line transformers. These transformers will be discussed more fully under the IF amplifier. The gain modulator as shown in Figure 3 has a 3 db bandwidth of 15 Mc/s, and co-channel separation of about 40 db. This can probably be improved by a different layout and better RF shielding. Also shown in Figure 3 is the DC biasing circuit, and the switch locking network, providing a method to lock the gain modulator in either the signal or comparison position. There are other means by which gain modulation can be accomplished, such as a voltage controlled stage in the IF strip, the gain changing in synchronization with a drive voltage. The radiometer would be balanced by changing the amplitude of the drive voltage. A system such as this, while theoretically possible, introduces a number of variables into the system that must be controlled very closely. As for now, the circuit of Figure 3 works well and has been used in the prototype radiometers.
5 *e The Intermediate frequency (IF) amplifier in the so1idstate receiver should have an overall gain of about 60 db a bandwidth of about 100 Mc/s, and a power output of approximately 50 mw. Noise figure is not so important and 7 or 8 db would be adequate. Figure 4 shows the preliminary design of the unit as built and tested in the laboratory As in the gain modulator, the transmission line transformeits are the deciding factor in *gain and bandwidth. The transformers that have been built did not meet design specifications and, consequently, the IF amplifier did not approach the desired specifications. As shown in Figure 4, the gain was only about 15 db, and 3 db bandwidth was 40 Mc with about 6 to db ripple. These difficulties have been attributed to the transformer, and specifically to the toroid core material.. Since the prototyp circuit was built and tested no further circuit design has been done. Further investigation has been made into the transmission line transformers, and we are now in the process of obtaining new core material to be used In the next bread board prototype. If the interstage transformers can be considered as ideal, the design is relatively simple and straightforward. Transistor Q i is used in the input impedance matching dr cult, and in conjunction with resistor R i provides a nominal input impedance of 50 ohms. Capacitor Q i is used as a peaking capacitor for frequency adjustment. Resistor 11 2 and transformer T make up the interstage coupling network. R is used for the same reason 1 2 as capacitor C i, to boost the high frequency response of the circuit. The following stages are identical up to the output stage which is designed as a power amplifier. Theoretically, the current gain per stage should be 6 db, obtained across the transformer. Practically, the gain that can be obtained is limited by the biasing circuit and stray L and C. Actual gain per stage approaches 5 db. There are minor adjustments that can be made to enhance frequency response, such as increasing bias current or adding a variable inductance in the transistor base lead. A new amplifier will be built in the near future using a new type of core material for the toroidal transformers. In the bread-board test set-up a commercial IF amplifier was used. The bandwidth of this amplifier was approximately 90 Mc/s.
6 The 400 cycle signal from the detector must be filtered and amplified. This is accomplished by the circuit configuration as shown in Figure 5. Any good qu ty audio ransistor can be used, and the circuit constants can be adjusted accordingly. The circuit as shown will deliver about 20 db gain but it is a simple matter to add stages to increase this figure. The circuit is a narrow bandwidth s twin-tee feed-back amplifier, tuned to the switch frequency of 400 cycles per second. The transistors are used as straight cascaded audio amplifiers, and the bandpass characteristics are determined by the twin tee feed-back loop. The theory of operation is simply this: The twin-tee presents a low impedance to all frequencies except 400 cycles, and thus gives almost 100 percent feed-back. The remaining amplifier signal is the 400 cycle sine wave that is desired. By this means, the low power 400 cycle square wave signal is converted to a higher power sine wave signal that maintains phase relation with the 400 cycle driving signal, and the phase detector is protected from overload by noise on the 400 cycle signal.. V. Phase Sensitive Detector In order to separate the desired signal from the undesired random signal some sort of phase sensitive device is required. The circuit used in the prototype receiver is shown in Figure 6. Circuit operation is as follows: The 400 cycle signal is introduced by means of transformer T i. Q i and Q. are solid-state choppers built specifically to obtain low offset voltage. The offset voltage from the integrated choppers is extremely low, usually less than 50 V. These solid-state devices are used in this case as switches driven alternately on and off by the 400 cycle switching signal. The result is a simple, effective phase sensitive detector. The output signal can be used directly, or if the level is too low, it can be amplified by means of a DC amplifier. From this pointion, the signal can be handled by digital means. Physical size is secondary in most cases but it is worth noting that a system built along these lines would occupy about 30 inches of standard 19-inch panel. Since the transistor is a low power device, heat problems would be minimized and thermal instability would be less than that for vacuum tubes. The tran sistor is also insensitive to microphonics. Although the standard tube receiver has shown good results, it is believed that the solid state receiver will eventually make the tube version obsolete.
7
8
9 NOIVCINILIV NOSI8Vd WOO Oi
10 , BROAD BAND TRANSFORMER (TYPICAL) INPUT R1 2N1742 MI, OWN....ft.0IMt. 2N1742 TRIMMER OMNI APPROXIMATELY 12 STAGES 5db GAIN/STAGE R Rs 2K (BLOCKING RESISTANCE) -- - EL (BIAS RESISTORS) le,.ol Mt. F GURE-4
11
12
Operational Amplifiers
 Operational Amplifiers Table of contents 1. Design 1.1. The Differential Amplifier 1.2. Level Shifter 1.3. Power Amplifier 2. Characteristics 3. The Opamp without NFB 4. Linear Amplifiers 4.1. The Non-Inverting
Operational Amplifiers Table of contents 1. Design 1.1. The Differential Amplifier 1.2. Level Shifter 1.3. Power Amplifier 2. Characteristics 3. The Opamp without NFB 4. Linear Amplifiers 4.1. The Non-Inverting
LINEAR IC APPLICATIONS
 1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
PAiA 4780 Twelve Stage Analog Sequencer Design Analysis Originally published 1974
 PAiA 4780 Twelve Stage Analog Sequencer Design Analysis Originally published 1974 DESIGN ANALYSIS: CLOCK As is shown in the block diagram of the sequencer (fig. 1) and the schematic (fig. 2), the clock
PAiA 4780 Twelve Stage Analog Sequencer Design Analysis Originally published 1974 DESIGN ANALYSIS: CLOCK As is shown in the block diagram of the sequencer (fig. 1) and the schematic (fig. 2), the clock
Summer 2015 Examination
 Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
EC202- ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS II Unit- I -FEEEDBACK AMPLIFIER
 EC202- ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS II Unit- I -FEEEDBACK AMPLIFIER 1. What is feedback? What are the types of feedback? 2. Define positive feedback. What are its merits and demerits? 3. Define negative feedback.
EC202- ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS II Unit- I -FEEEDBACK AMPLIFIER 1. What is feedback? What are the types of feedback? 2. Define positive feedback. What are its merits and demerits? 3. Define negative feedback.
The steeper the phase shift as a function of frequency φ(ω) the more stable the frequency of oscillation
 It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
TUNED AMPLIFIERS. Tank circuits.
 Tank circuits. TUNED AMPLIFIERS Analysis of single tuned amplifier, Double tuned, stagger tuned amplifiers. Instability of tuned amplifiers, stabilization techniques, Narrow band neutralization using coil,
Tank circuits. TUNED AMPLIFIERS Analysis of single tuned amplifier, Double tuned, stagger tuned amplifiers. Instability of tuned amplifiers, stabilization techniques, Narrow band neutralization using coil,
Multivibrators. Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Amrita School of Engineering
 Multivibrators Multivibrators Multivibrator is an electronic circuit that generates square, rectangular, pulse waveforms. Also called as nonlinear oscillators or function generators. Multivibrator is basically
Multivibrators Multivibrators Multivibrator is an electronic circuit that generates square, rectangular, pulse waveforms. Also called as nonlinear oscillators or function generators. Multivibrator is basically
ERICSSONZ LBI-30398P. MAINTENANCE MANUAL MHz PHASE LOCKED LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 DESCRIPTION TABLE OF CONTENTS
 MAINTENANCE MANUAL 138-174 MHz PHASE LOCKED LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DESCRIPTION... Front Cover CIRCUIT ANALYSIS...1 MODIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS...4 PARTS LIST...5 PRODUCTION
MAINTENANCE MANUAL 138-174 MHz PHASE LOCKED LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DESCRIPTION... Front Cover CIRCUIT ANALYSIS...1 MODIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS...4 PARTS LIST...5 PRODUCTION
LBI-30398N. MAINTENANCE MANUAL MHz PHASE LOCK LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 DESCRIPTION TABLE OF CONTENTS. Page. DESCRIPTION...
 MAINTENANCE MANUAL 138-174 MHz PHASE LOCK LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 LBI-30398N TABLE OF CONTENTS DESCRIPTION...Front Cover CIRCUIT ANALYSIS... 1 MODIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS... 4 PARTS LIST AND PRODUCTION
MAINTENANCE MANUAL 138-174 MHz PHASE LOCK LOOP EXCITER 19D423249G1 & G2 LBI-30398N TABLE OF CONTENTS DESCRIPTION...Front Cover CIRCUIT ANALYSIS... 1 MODIFICATION INSTRUCTIONS... 4 PARTS LIST AND PRODUCTION
Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers
 Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers Second Edition ROBERT E. SIMPSON University of New Hampshire Allyn and Bacon, Inc. Boston London Sydney Toronto Contents Preface xiü 1 Direct Current
Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers Second Edition ROBERT E. SIMPSON University of New Hampshire Allyn and Bacon, Inc. Boston London Sydney Toronto Contents Preface xiü 1 Direct Current
The Hartley Oscillator
 The Hartley Oscillator One of the main disadvantages of the basic LC Oscillator circuit we looked at in the previous tutorial is that they have no means of controlling the amplitude of the oscillations
The Hartley Oscillator One of the main disadvantages of the basic LC Oscillator circuit we looked at in the previous tutorial is that they have no means of controlling the amplitude of the oscillations
A Simplified Test Set for Op Amp Characterization
 A Simplified Test Set for Op Amp Characterization INTRODUCTION The test set described in this paper allows complete quantitative characterization of all dc operational amplifier parameters quickly and
A Simplified Test Set for Op Amp Characterization INTRODUCTION The test set described in this paper allows complete quantitative characterization of all dc operational amplifier parameters quickly and
CHAPTER - 3 PIN DIODE RF ATTENUATORS
 CHAPTER - 3 PIN DIODE RF ATTENUATORS 2 NOTES 3 PIN DIODE VARIABLE ATTENUATORS INTRODUCTION An Attenuator [1] is a network designed to introduce a known amount of loss when functioning between two resistive
CHAPTER - 3 PIN DIODE RF ATTENUATORS 2 NOTES 3 PIN DIODE VARIABLE ATTENUATORS INTRODUCTION An Attenuator [1] is a network designed to introduce a known amount of loss when functioning between two resistive
onlinecomponents.com FET Circuit Applications FET Circuit Applications AN-32 National Semiconductor Application Note 32 February 1970
 FET Circuit Applications National Semiconductor Application Note 32 February 1970 Polycarbonate dielectric Sample and Hold With Offset Adjustment TL H 6791 1 Long Time Comparator TL H 6791 2 The 2N4393
FET Circuit Applications National Semiconductor Application Note 32 February 1970 Polycarbonate dielectric Sample and Hold With Offset Adjustment TL H 6791 1 Long Time Comparator TL H 6791 2 The 2N4393
A Simple Notch Type Harmonic Distortion Analyzer
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Nov. 28, 2009, rev. Nov. 29, 2009 Introduction This note describes a simple notch type harmonic distortion analyzer that can be constructed with basic parts. It is intended for use in
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Nov. 28, 2009, rev. Nov. 29, 2009 Introduction This note describes a simple notch type harmonic distortion analyzer that can be constructed with basic parts. It is intended for use in
A U.H.F. amplifier and distribution unit
 RESEARCH DEPARTMENT A U.H.F. amplifier and distribution unit TECHNOLOGICAL REPORT No.G-089 1964/16 THE BRITISH BROADCASTING CORPORATION ENGINEERING DIVISION RESEARCH DEPARTMENT A U.H.F. AMPLIFIER AND DISTRIBUTION
RESEARCH DEPARTMENT A U.H.F. amplifier and distribution unit TECHNOLOGICAL REPORT No.G-089 1964/16 THE BRITISH BROADCASTING CORPORATION ENGINEERING DIVISION RESEARCH DEPARTMENT A U.H.F. AMPLIFIER AND DISTRIBUTION
 PREFACE xvii PRACTICAL TRANSISTOR CIRCUIT THEORY 1.1 Iterated Circuits 1.2 Symbols 1.3 Feedback 1.4 The Miller Effect 1.5 Transistors 1.6 The transistor gain-impedance relation 1.7 Ohm's law and dc current-voltage
PREFACE xvii PRACTICAL TRANSISTOR CIRCUIT THEORY 1.1 Iterated Circuits 1.2 Symbols 1.3 Feedback 1.4 The Miller Effect 1.5 Transistors 1.6 The transistor gain-impedance relation 1.7 Ohm's law and dc current-voltage
HEATHKIT ELECTRONIC KEYER HD-10
 HEATHKIT ELECTRONIC KEYER HD-10 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM The letter-number designations on the Schematic Diagram are used to identify resistors, capacitors and diodes. Each designation is
HEATHKIT ELECTRONIC KEYER HD-10 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM The letter-number designations on the Schematic Diagram are used to identify resistors, capacitors and diodes. Each designation is
Op Amp Booster Designs
 Op Amp Booster Designs Although modern integrated circuit operational amplifiers ease linear circuit design, IC processing limits amplifier output power. Many applications, however, require substantially
Op Amp Booster Designs Although modern integrated circuit operational amplifiers ease linear circuit design, IC processing limits amplifier output power. Many applications, however, require substantially
TONE DECODER / PHASE LOCKED LOOP PIN FUNCTION 1 OUTPUT FILTER 2 LOW-PASS FILTER 3 INPUT 4 V + 5 TIMING R 6 TIMING CR 7 GROUND 8 OUTPUT
 TONE DECODER / PHASE LOCKED LOOP GENERAL DESCRIPTION The NJM567 tone and frequency decoder is a highly stable phase locked loop with synchronous AM lock detection and power output circuitry. Its primary
TONE DECODER / PHASE LOCKED LOOP GENERAL DESCRIPTION The NJM567 tone and frequency decoder is a highly stable phase locked loop with synchronous AM lock detection and power output circuitry. Its primary
EE301 Electronics I , Fall
 EE301 Electronics I 2018-2019, Fall 1. Introduction to Microelectronics (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Introduction, Historical Background, Basic Consepts 2. Rewiev of Semiconductors (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Semiconductor materials
EE301 Electronics I 2018-2019, Fall 1. Introduction to Microelectronics (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Introduction, Historical Background, Basic Consepts 2. Rewiev of Semiconductors (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Semiconductor materials
Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Lesson Four Lesson Five PREVIEW COPY
 Oscillators Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Introduction to Oscillators...3 Flip-Flops...19 Logic Clocks...37 Lesson Four Filters and Waveforms...53 Lesson Five Troubleshooting Oscillators...69
Oscillators Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Introduction to Oscillators...3 Flip-Flops...19 Logic Clocks...37 Lesson Four Filters and Waveforms...53 Lesson Five Troubleshooting Oscillators...69
ATF High Intercept Low Noise Amplifier for the MHz PCS Band using the Enhancement Mode PHEMT
 ATF-54143 High Intercept Low Noise Amplifier for the 185 191 MHz PCS Band using the Enhancement Mode PHEMT Application Note 1222 Introduction Avago Technologies ATF-54143 is a low noise enhancement mode
ATF-54143 High Intercept Low Noise Amplifier for the 185 191 MHz PCS Band using the Enhancement Mode PHEMT Application Note 1222 Introduction Avago Technologies ATF-54143 is a low noise enhancement mode
United States Patent Office
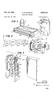 United States Patent Office Patented Feb. 14, 1961 1 AJ."\IPLIFIER CIRCUIT Richard Silberbach, Chicago, m., assignor to Motorola, Ine., Chicago, m., a corporation of Dlinois Filed Dec. 23, 1957, Ser. No.
United States Patent Office Patented Feb. 14, 1961 1 AJ."\IPLIFIER CIRCUIT Richard Silberbach, Chicago, m., assignor to Motorola, Ine., Chicago, m., a corporation of Dlinois Filed Dec. 23, 1957, Ser. No.
Lab 4 : Transistor Oscillators
 Objective: Lab 4 : Transistor Oscillators In this lab, you will learn how to design and implement a colpitts oscillator. In part II you will implement a RC phase shift oscillator Hardware Required : Pre
Objective: Lab 4 : Transistor Oscillators In this lab, you will learn how to design and implement a colpitts oscillator. In part II you will implement a RC phase shift oscillator Hardware Required : Pre
Gechstudentszone.wordpress.com
 8.1 Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) UNIT 8: Operational Amplifier An operational amplifier ("op-amp") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended
8.1 Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) UNIT 8: Operational Amplifier An operational amplifier ("op-amp") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended
Sub Code & Name: EC2251- ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS II Unit : I Branch : ECE Year:II
 Unit : I Branch : ECE Year:II Page 01 of 06 UNIT 1 FEEDBACK AMPLIFIERS 9 Block diagram, Loop gain, Gain with feedback, Effects of negative feedback Sensitivity and desensitivity of gain, Cut-off frequencies,
Unit : I Branch : ECE Year:II Page 01 of 06 UNIT 1 FEEDBACK AMPLIFIERS 9 Block diagram, Loop gain, Gain with feedback, Effects of negative feedback Sensitivity and desensitivity of gain, Cut-off frequencies,
Power Amplifiers. Class A Amplifier
 Power Amplifiers The Power amplifiers amplify the power level of the signal. This amplification is done in the last stage in audio applications. The applications related to radio frequencies employ radio
Power Amplifiers The Power amplifiers amplify the power level of the signal. This amplification is done in the last stage in audio applications. The applications related to radio frequencies employ radio
B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics
 B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics Sr. No. Date TITLE To From Marks Sign 1 To verify the application of op-amp as an Inverting Amplifier 2 To
B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics Sr. No. Date TITLE To From Marks Sign 1 To verify the application of op-amp as an Inverting Amplifier 2 To
UNIT-I CIRCUIT CONFIGURATION FOR LINEAR
 UNIT-I CIRCUIT CONFIGURATION FOR LINEAR ICs 2 marks questions 1.Mention the advantages of integrated circuits. *Miniaturisation and hence increased equipment density. *Cost reduction due to batch processing.
UNIT-I CIRCUIT CONFIGURATION FOR LINEAR ICs 2 marks questions 1.Mention the advantages of integrated circuits. *Miniaturisation and hence increased equipment density. *Cost reduction due to batch processing.
Analog Electronic Circuits Lab-manual
 2014 Analog Electronic Circuits Lab-manual Prof. Dr Tahir Izhar University of Engineering & Technology LAHORE 1/09/2014 Contents Experiment-1:...4 Learning to use the multimeter for checking and indentifying
2014 Analog Electronic Circuits Lab-manual Prof. Dr Tahir Izhar University of Engineering & Technology LAHORE 1/09/2014 Contents Experiment-1:...4 Learning to use the multimeter for checking and indentifying
LECTURE NOTES ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS II SYLLABUS
 FATIMA MICHAEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Madurai Sivagangai Main Road Madurai - 625 020. [An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution] LECTURE NOTES EC6401 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS - II SEMESTER: IV /
FATIMA MICHAEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Madurai Sivagangai Main Road Madurai - 625 020. [An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution] LECTURE NOTES EC6401 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS - II SEMESTER: IV /
An active filter offers the following advantages over a passive filter:
 ACTIVE FILTERS An electric filter is often a frequency-selective circuit that passes a specified band of frequencies and blocks or attenuates signals of frequencies outside this band. Filters may be classified
ACTIVE FILTERS An electric filter is often a frequency-selective circuit that passes a specified band of frequencies and blocks or attenuates signals of frequencies outside this band. Filters may be classified
HIGH LOW Astable multivibrators HIGH LOW 1:1
 1. Multivibrators A multivibrator circuit oscillates between a HIGH state and a LOW state producing a continuous output. Astable multivibrators generally have an even 50% duty cycle, that is that 50% of
1. Multivibrators A multivibrator circuit oscillates between a HIGH state and a LOW state producing a continuous output. Astable multivibrators generally have an even 50% duty cycle, that is that 50% of
Audio Noise Figure Meter
 Audio Noise Figure Meter Abstract Low noise amplifiers in the audio range are used in many applications. The definition of 'lownoise' is very flexible and poorly defined so any experimenter in this field
Audio Noise Figure Meter Abstract Low noise amplifiers in the audio range are used in many applications. The definition of 'lownoise' is very flexible and poorly defined so any experimenter in this field
Specify Gain and Phase Margins on All Your Loops
 Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, power supply, gain and phase margins, feedback loop, open-loop gain, output capacitance, stability margins, oscillator, power electronics circuits, voltmeter,
Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, power supply, gain and phase margins, feedback loop, open-loop gain, output capacitance, stability margins, oscillator, power electronics circuits, voltmeter,
LM2900 LM3900 LM3301 Quad Amplifiers
 LM2900 LM3900 LM3301 Quad Amplifiers General Description The LM2900 series consists of four independent dual input internally compensated amplifiers which were designed specifically to operate off of a
LM2900 LM3900 LM3301 Quad Amplifiers General Description The LM2900 series consists of four independent dual input internally compensated amplifiers which were designed specifically to operate off of a
THE SIMPLE HIGH-VOLTAGE REGULATOR
 THE SIMPLE HIGH-VOLTAGE REGULATOR Eugene V. Karpov NexTube The English variant is edited by Alex Shekhter In article the availability of a semi-conductor regulator for a feed of the tube amplifiers is
THE SIMPLE HIGH-VOLTAGE REGULATOR Eugene V. Karpov NexTube The English variant is edited by Alex Shekhter In article the availability of a semi-conductor regulator for a feed of the tube amplifiers is
Common-emitter amplifier, no feedback, with reference waveforms for comparison.
 Feedback If some percentage of an amplifier's output signal is connected to the input, so that the amplifier amplifies part of its own output signal, we have what is known as feedback. Feedback comes in
Feedback If some percentage of an amplifier's output signal is connected to the input, so that the amplifier amplifies part of its own output signal, we have what is known as feedback. Feedback comes in
WESTREX RA-1712 PHOTOGRAPHIC SOUND RECORD ELECTRONICS
 INTRODUCTION The RA-1712 solid state Record Electronics is an integrated system for recording photographic sound tracks on a Westrex photographic sound recorder. It accepts a 600Ω input signal level from
INTRODUCTION The RA-1712 solid state Record Electronics is an integrated system for recording photographic sound tracks on a Westrex photographic sound recorder. It accepts a 600Ω input signal level from
CHAPTER 6 Radio Circuits and Systems
 6.1 AMPLIFIERS (page 6-1) CHAPTER 6 Radio Circuits and Systems AMPLIFIER GAIN (page 6-2) INPUT AND OUTPUT IMPEDANCE (page 6-2) DISCRETE DEVICE AMPLIFIERS (page 6-2) BASIC CIRCUITS (page 6-2) COMMON-EMITTER
6.1 AMPLIFIERS (page 6-1) CHAPTER 6 Radio Circuits and Systems AMPLIFIER GAIN (page 6-2) INPUT AND OUTPUT IMPEDANCE (page 6-2) DISCRETE DEVICE AMPLIFIERS (page 6-2) BASIC CIRCUITS (page 6-2) COMMON-EMITTER
A 50-CHANNEL MULTIFILTER RECEIVER (250 khz BANDWIDTH PER CHANNEL) Michael Balister NOVEMBER 1971
 NATIONAL RADIO ASTRONOMY OBSERVATORY Green Bank, West Virginia Electronics Division Internal Report No, 112 A 50-CHANNEL MULTIFILTER RECEIVER (250 khz BANDWIDTH PER CHANNEL) Michael Balister NOVEMBER 1971
NATIONAL RADIO ASTRONOMY OBSERVATORY Green Bank, West Virginia Electronics Division Internal Report No, 112 A 50-CHANNEL MULTIFILTER RECEIVER (250 khz BANDWIDTH PER CHANNEL) Michael Balister NOVEMBER 1971
LM110 LM210 LM310 Voltage Follower
 LM110 LM210 LM310 Voltage Follower General Description The LM110 series are monolithic operational amplifiers internally connected as unity-gain non-inverting amplifiers They use super-gain transistors
LM110 LM210 LM310 Voltage Follower General Description The LM110 series are monolithic operational amplifiers internally connected as unity-gain non-inverting amplifiers They use super-gain transistors
Optimization of an OTA Based Sine Waveshaper
 1 Optimization of an OTA Based Sine Waveshaper openmusiclabs February, 017 I. INTRODUCTION The most common analog Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) cores are sawtooth and triangle wave generators. This
1 Optimization of an OTA Based Sine Waveshaper openmusiclabs February, 017 I. INTRODUCTION The most common analog Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) cores are sawtooth and triangle wave generators. This
Exam Booklet. Pulse Circuits
 Exam Booklet Pulse Circuits Pulse Circuits STUDY ASSIGNMENT This booklet contains two examinations for the six lessons entitled Pulse Circuits. The material is intended to provide the last training sought
Exam Booklet Pulse Circuits Pulse Circuits STUDY ASSIGNMENT This booklet contains two examinations for the six lessons entitled Pulse Circuits. The material is intended to provide the last training sought
High Current MOSFET Toggle Switch with Debounced Push Button
 Set/Reset Flip Flop This is an example of a set/reset flip flop using discrete components. When power is applied, only one of the transistors will conduct causing the other to remain off. The conducting
Set/Reset Flip Flop This is an example of a set/reset flip flop using discrete components. When power is applied, only one of the transistors will conduct causing the other to remain off. The conducting
Pb-free lead plating; RoHS compliant
 Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Pb-free lead plating; RoHS compliant SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone,
Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Pb-free lead plating; RoHS compliant SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone,
NOORUL ISLAM COLLEGE OF ENGG, KUMARACOIL. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGG. SUBJECT CODE: EC 1251 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS-II
 NOORUL ISLAM COLLEGE OF ENGG, KUMARACOIL. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGG. SUBJECT CODE: EC 1251 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS-II Prepared by, C.P.SREE BALA LEKSHMI (Lect/ECE) ELECTRONICS
NOORUL ISLAM COLLEGE OF ENGG, KUMARACOIL. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGG. SUBJECT CODE: EC 1251 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS-II Prepared by, C.P.SREE BALA LEKSHMI (Lect/ECE) ELECTRONICS
ELC224 Final Review (12/10/2009) Name:
 ELC224 Final Review (12/10/2009) Name: Select the correct answer to the problems 1 through 20. 1. A common-emitter amplifier that uses direct coupling is an example of a dc amplifier. 2. The frequency
ELC224 Final Review (12/10/2009) Name: Select the correct answer to the problems 1 through 20. 1. A common-emitter amplifier that uses direct coupling is an example of a dc amplifier. 2. The frequency
Design and Layout of a X-Band MMIC Power Amplifier in a Phemt Technology
 Design and Layout of a X-Band MMIC Power Amplifier in a Phemt Technology Renbin Dai, and Rana Arslan Ali Khan Abstract The design of Class A and Class AB 2-stage X band Power Amplifier is described in
Design and Layout of a X-Band MMIC Power Amplifier in a Phemt Technology Renbin Dai, and Rana Arslan Ali Khan Abstract The design of Class A and Class AB 2-stage X band Power Amplifier is described in
Audio Applications of Linear Integrated Circuits
 Audio Applications of Linear Integrated Circuits Although operational amplifiers and other linear ICs have been applied as audio amplifiers relatively little documentation has appeared for other audio
Audio Applications of Linear Integrated Circuits Although operational amplifiers and other linear ICs have been applied as audio amplifiers relatively little documentation has appeared for other audio
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT-I - PN DIODEAND ITSAPPLICATIONS 1. What is depletion region in PN junction?
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT-I - PN DIODEAND ITSAPPLICATIONS 1. What is depletion region in PN junction?
UNIT 2. Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator. Ans. Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation
 UNIT 2 Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator Ans. STANDARD SIGNAL GENERATOR A standard signal generator produces known and controllable voltages. It is used as power source for the
UNIT 2 Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator Ans. STANDARD SIGNAL GENERATOR A standard signal generator produces known and controllable voltages. It is used as power source for the
Chapter 6: Power Amplifiers
 Chapter 6: Power Amplifiers Contents Class A Class B Class C Power Amplifiers Class A, B and C amplifiers are used in transmitters Tuned with a band width wide enough to pass all information sidebands
Chapter 6: Power Amplifiers Contents Class A Class B Class C Power Amplifiers Class A, B and C amplifiers are used in transmitters Tuned with a band width wide enough to pass all information sidebands
CLD Application Notes Connection Options
 CLD Application Notes Connection Options Series Higher voltages may be obtained by connecting identical CLDs in series (Figure 4). Voltage balancing resistors are recommended. Since the resistors shunt
CLD Application Notes Connection Options Series Higher voltages may be obtained by connecting identical CLDs in series (Figure 4). Voltage balancing resistors are recommended. Since the resistors shunt
AND ITS APPLICATIONS M.C.SHARMA
 AND ITS APPLICATIONS M.C.SHARMA 555 TIMER AND ITS APPLICATIONS BY M. C. SHARMA, M. Sc. PUBLISHERS: BUSINESS PROMOTION PUBLICATIONS 376, Lajpat Rai Market, Delhi-110006 By the same author Transistor Novelties
AND ITS APPLICATIONS M.C.SHARMA 555 TIMER AND ITS APPLICATIONS BY M. C. SHARMA, M. Sc. PUBLISHERS: BUSINESS PROMOTION PUBLICATIONS 376, Lajpat Rai Market, Delhi-110006 By the same author Transistor Novelties
ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL
 ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL AIMS The general aims of the subject are : 1. to foster an interest in and an enjoyment of electronics as a practical and intellectual discipline; 2. to develop
ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL AIMS The general aims of the subject are : 1. to foster an interest in and an enjoyment of electronics as a practical and intellectual discipline; 2. to develop
CH85CH2202-0/85/ $1.00
 SYNCHRONIZATION AND TRACKING WITH SYNCHRONOUS OSCILLATORS Vasil Uzunoglu and Marvin H. White Fairchild Industries Germantown, Maryland Lehigh University Bethlehem, Pennsylvania ABSTRACT A Synchronous Oscillator
SYNCHRONIZATION AND TRACKING WITH SYNCHRONOUS OSCILLATORS Vasil Uzunoglu and Marvin H. White Fairchild Industries Germantown, Maryland Lehigh University Bethlehem, Pennsylvania ABSTRACT A Synchronous Oscillator
c. Battery Charger c Volt Supply TL MICROWAVE RADIO DESCRIPTION POWER SUPPLY H. Battery Voltage Alarm Circuit.
 BELL SYSTEM PRACTCES Plant Series 2. OPERATNG PRNCPLES CONTENTS PAGE B. Klystron Supply Regulator and nverter. D. Battery Voltage Alarm Circuit. 3. CRCUT DESCRPTON. A. Klystron Supply Regulator and nverter.
BELL SYSTEM PRACTCES Plant Series 2. OPERATNG PRNCPLES CONTENTS PAGE B. Klystron Supply Regulator and nverter. D. Battery Voltage Alarm Circuit. 3. CRCUT DESCRPTON. A. Klystron Supply Regulator and nverter.
A Low Noise Amplifier with HF Selectivity
 A Low Noise Amplifier with HF Selectivity Johan Karlsson Mikael Grudd Radio project 2008 Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University Supervisor: Göran Jönsson Abstract This report
A Low Noise Amplifier with HF Selectivity Johan Karlsson Mikael Grudd Radio project 2008 Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University Supervisor: Göran Jönsson Abstract This report
Question Paper Code: 21398
 Reg. No. : Question Paper Code: 21398 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY/JUNE 2013 Fourth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE2254 LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS AND APPLICATIONS (Regulation
Reg. No. : Question Paper Code: 21398 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY/JUNE 2013 Fourth Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE2254 LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS AND APPLICATIONS (Regulation
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING* DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING* DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUB.NAME : LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS SUB CODE: EC1254 YEAR / SEMESTER : II / IV UNIT- I IC FABRICATION
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING* DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUB.NAME : LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS SUB CODE: EC1254 YEAR / SEMESTER : II / IV UNIT- I IC FABRICATION
Unit WorkBook 1 Level 4 ENG U22 Electronic Circuits and Devices 2018 UniCourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sample
 Pearson BTEC Level 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 22: Electronic Circuits and Devices Unit Workbook 1 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 1 Operational Amplifiers Page 1 of 23
Pearson BTEC Level 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 22: Electronic Circuits and Devices Unit Workbook 1 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 1 Operational Amplifiers Page 1 of 23
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks)
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks) 1. What is meant by tuned amplifiers? Tuned amplifiers are amplifiers that are designed to reject a certain
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks) 1. What is meant by tuned amplifiers? Tuned amplifiers are amplifiers that are designed to reject a certain
PartIIILectures. Multistage Amplifiers
 University of missan Electronic II, Second year 2015-2016 PartIIILectures Assistant Lecture: 1 Multistage and Compound Amplifiers Basic Definitions: 1- Gain of Multistage Amplifier: Fig.(1-1) A general
University of missan Electronic II, Second year 2015-2016 PartIIILectures Assistant Lecture: 1 Multistage and Compound Amplifiers Basic Definitions: 1- Gain of Multistage Amplifier: Fig.(1-1) A general
A 40 MHz Programmable Video Op Amp
 A 40 MHz Programmable Video Op Amp Conventional high speed operational amplifiers with bandwidths in excess of 40 MHz introduce problems that are not usually encountered in slower amplifiers such as LF356
A 40 MHz Programmable Video Op Amp Conventional high speed operational amplifiers with bandwidths in excess of 40 MHz introduce problems that are not usually encountered in slower amplifiers such as LF356
Chapter 13: Comparators
 Chapter 13: Comparators So far, we have used op amps in their normal, linear mode, where they follow the op amp Golden Rules (no input current to either input, no voltage difference between the inputs).
Chapter 13: Comparators So far, we have used op amps in their normal, linear mode, where they follow the op amp Golden Rules (no input current to either input, no voltage difference between the inputs).
A Low Noise GHz Amplifier
 A Low Noise 3.4-4.6 GHz Amplifier C. Risacher*, M. Dahlgren*, V. Belitsky* * GARD, Radio & Space Science Department with Onsala Space Observatory, Microtechnology Centre at Chalmers (MC2), Chalmers University
A Low Noise 3.4-4.6 GHz Amplifier C. Risacher*, M. Dahlgren*, V. Belitsky* * GARD, Radio & Space Science Department with Onsala Space Observatory, Microtechnology Centre at Chalmers (MC2), Chalmers University
LM125 Precision Dual Tracking Regulator
 LM125 Precision Dual Tracking Regulator INTRODUCTION The LM125 is a precision, dual, tracking, monolithic voltage regulator. It provides separate positive and negative regulated outputs, thus simplifying
LM125 Precision Dual Tracking Regulator INTRODUCTION The LM125 is a precision, dual, tracking, monolithic voltage regulator. It provides separate positive and negative regulated outputs, thus simplifying
LM389 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier with NPN Transistor Array
 LM389 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier with NPN Transistor Array General Description The LM389 is an array of three NPN transistors on the same substrate with an audio power amplifier similar to the LM386
LM389 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier with NPN Transistor Array General Description The LM389 is an array of three NPN transistors on the same substrate with an audio power amplifier similar to the LM386
AN-1098 APPLICATION NOTE
 APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 9106 Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.4700 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com Methodology for Narrow-Band Interface Design Between High Performance
APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 9106 Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.4700 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com Methodology for Narrow-Band Interface Design Between High Performance
PRACTICE. Amateur Radio Operator Certificate Examination. Advanced Qualification
 Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada Innovation, Sciences et Développement économique Canada Amateur Radio Operator Certificate Examination Advanced Qualification 2018-06-30 To pass this
Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada Innovation, Sciences et Développement économique Canada Amateur Radio Operator Certificate Examination Advanced Qualification 2018-06-30 To pass this
ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS - II BY A P GODSE, U A BAKSHI DOWNLOAD EBOOK : ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS - II BY A P GODSE, U A BAKSHI PDF
 Read Online and Download Ebook ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS - II BY A P GODSE, U A BAKSHI DOWNLOAD EBOOK : ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS - II BY A P GODSE, U A BAKSHI Click link bellow and free register to download ebook:
Read Online and Download Ebook ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS - II BY A P GODSE, U A BAKSHI DOWNLOAD EBOOK : ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS - II BY A P GODSE, U A BAKSHI Click link bellow and free register to download ebook:
HOME ASSIGNMENT. Figure.Q3
 HOME ASSIGNMENT 1. For the differential amplifier circuit shown below in figure.q1, let I=1 ma, V CC =5V, v CM = -2V, R C =3kΩ and β=100. Assume that the BJTs have v BE =0.7 V at i C =1 ma. Find the voltage
HOME ASSIGNMENT 1. For the differential amplifier circuit shown below in figure.q1, let I=1 ma, V CC =5V, v CM = -2V, R C =3kΩ and β=100. Assume that the BJTs have v BE =0.7 V at i C =1 ma. Find the voltage
Tone decoder/phase-locked loop
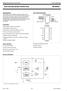 NE/SE DESCRIPTION The NE/SE tone and frequency decoder is a highly stable phase-locked loop with synchronous AM lock detection and power output circuitry. Its primary function is to drive a load whenever
NE/SE DESCRIPTION The NE/SE tone and frequency decoder is a highly stable phase-locked loop with synchronous AM lock detection and power output circuitry. Its primary function is to drive a load whenever
UNIT-3. Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation
 UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
HF Receivers, Part 2
 HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS. Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100
 EC 40 MODEL TEST PAPER - 1 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, any two from Group B and all from Group C. All parts of a question
EC 40 MODEL TEST PAPER - 1 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, any two from Group B and all from Group C. All parts of a question
Oscillators. An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier.
 Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) paper 2
 Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) paper 2 1. VSWR on a transmission line is always 1. Equal to 1 2. Equal to 0 3. Less than 1 4. Greater than 1 2. In a amplitude modulated wave, the value of Vmax is 10V and
Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) paper 2 1. VSWR on a transmission line is always 1. Equal to 1 2. Equal to 0 3. Less than 1 4. Greater than 1 2. In a amplitude modulated wave, the value of Vmax is 10V and
Lecture #2 Operational Amplifiers
 Spring 2015 Benha University Faculty of Engineering at Shoubra ECE-322 Electronic Circuits (B) Lecture #2 Operational Amplifiers Instructor: Dr. Ahmad El-Banna Agenda Introduction Op-Amps Input Modes and
Spring 2015 Benha University Faculty of Engineering at Shoubra ECE-322 Electronic Circuits (B) Lecture #2 Operational Amplifiers Instructor: Dr. Ahmad El-Banna Agenda Introduction Op-Amps Input Modes and
 11. What is fall time (tf) in transistor? The time required for the collector current to fall from 90% to 10% of its DEPARTMENT OF ECE EC 6401 Electronic Circuits II UNIT-IV WAVE SHAPING AND MULTIVIBRATOR
11. What is fall time (tf) in transistor? The time required for the collector current to fall from 90% to 10% of its DEPARTMENT OF ECE EC 6401 Electronic Circuits II UNIT-IV WAVE SHAPING AND MULTIVIBRATOR
Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT Real Time Wireless Electrocardiogram (ECG) Monitoring System Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Guilherme K. Kolotelo, Rogers G. Reichert Cambridge, MA
Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT Real Time Wireless Electrocardiogram (ECG) Monitoring System Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Guilherme K. Kolotelo, Rogers G. Reichert Cambridge, MA
IAM-8 Series Active Mixers. Application Note S013
 IAM-8 Series Active Mixers Application Note S013 Introduction Hewlett-Packard s IAM-8 products are Gilbert cell based double balanced active mixers capable of accepting RF inputs up to 5 GHz and producing
IAM-8 Series Active Mixers Application Note S013 Introduction Hewlett-Packard s IAM-8 products are Gilbert cell based double balanced active mixers capable of accepting RF inputs up to 5 GHz and producing
1 Lock-in Amplifier Introduction
 1 Lock-in Amplifier Introduction The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce the student to the lock-in amplifier. A lock-in amplifier is a nearly ubiquitous piece of laboratory equipment, and can serve
1 Lock-in Amplifier Introduction The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce the student to the lock-in amplifier. A lock-in amplifier is a nearly ubiquitous piece of laboratory equipment, and can serve
LM125 Precision Dual Tracking Regulator
 LM125 Precision Dual Tracking Regulator INTRODUCTION The LM125 is a precision dual tracking monolithic voltage regulator It provides separate positive and negative regulated outputs thus simplifying dual
LM125 Precision Dual Tracking Regulator INTRODUCTION The LM125 is a precision dual tracking monolithic voltage regulator It provides separate positive and negative regulated outputs thus simplifying dual
Function Generator Using Op Amp Ic 741 Theory
 Function Generator Using Op Amp Ic 741 Theory Note: Op-Amps ua741, LM 301, LM311, LM 324 & AD 633 may be used To design an Inverting Amplifier for the given specifications using Op-Amp IC 741. THEORY:
Function Generator Using Op Amp Ic 741 Theory Note: Op-Amps ua741, LM 301, LM311, LM 324 & AD 633 may be used To design an Inverting Amplifier for the given specifications using Op-Amp IC 741. THEORY:
Difference between BJTs and FETs. Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFET)
 Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
LESSON PLAN. SUBJECT: LINEAR IC S AND APPLICATION NO OF HOURS: 52 FACULTY NAME: Mr. Lokesh.L, Hema. B DEPT: ECE. Portions to be covered
 LESSON PLAN SUBJECT: LINEAR IC S AND APPLICATION SUB CODE: 15EC46 NO OF HOURS: 52 FACULTY NAME: Mr. Lokesh.L, Hema. B DEPT: ECE Class# Chapter title/reference literature Portions to be covered MODULE I
LESSON PLAN SUBJECT: LINEAR IC S AND APPLICATION SUB CODE: 15EC46 NO OF HOURS: 52 FACULTY NAME: Mr. Lokesh.L, Hema. B DEPT: ECE Class# Chapter title/reference literature Portions to be covered MODULE I
ASTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR
 555 TIMER ASTABLE MULTIIBRATOR MONOSTABLE MULTIIBRATOR 555 TIMER PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) 555 TIMER Introduction The 555 timer is an integrated circuit (chip) implementing a variety of
555 TIMER ASTABLE MULTIIBRATOR MONOSTABLE MULTIIBRATOR 555 TIMER PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) 555 TIMER Introduction The 555 timer is an integrated circuit (chip) implementing a variety of
Project (02) Dc 2 AC Inverter
 Project (02) Dc 2 AC Inverter By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee 1 12v DC to 220v AC Converter Circuit Using Astable Multivibrator Inverter circuits can either use thyristors as switching devices or transistors. Normally
Project (02) Dc 2 AC Inverter By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee 1 12v DC to 220v AC Converter Circuit Using Astable Multivibrator Inverter circuits can either use thyristors as switching devices or transistors. Normally
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. AN109 Microprocessor-compatible DACs Dec
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS 1988 Dec DAC products are designed to convert a digital code to an analog signal. Since a common source of digital signals is the data bus of a microprocessor, DAC circuits that are
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS 1988 Dec DAC products are designed to convert a digital code to an analog signal. Since a common source of digital signals is the data bus of a microprocessor, DAC circuits that are
G.PULLAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY II B.Tech II-SEM MID -I EXAM Branch: EEE Sub: Analog Electronic Circuits Date:
 G.PULLAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY II B.Tech II-SEM MID -I EXAM Branch: EEE Sub: Analog Electronic Circuits Date: 08-03-18 Time: 20 minutes Max.Marks:10 1. The amplifier that gives unity current
G.PULLAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY II B.Tech II-SEM MID -I EXAM Branch: EEE Sub: Analog Electronic Circuits Date: 08-03-18 Time: 20 minutes Max.Marks:10 1. The amplifier that gives unity current
note application Measurement of Frequency Stability and Phase Noise by David Owen
 application Measurement of Frequency Stability and Phase Noise note by David Owen The stability of an RF source is often a critical parameter for many applications. Performance varies considerably with
application Measurement of Frequency Stability and Phase Noise note by David Owen The stability of an RF source is often a critical parameter for many applications. Performance varies considerably with
Communication Circuit Lab Manual
 German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 3 Crystal Oscillator Eng. Anas Alashqar
German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 3 Crystal Oscillator Eng. Anas Alashqar
Balanced Line Driver & Receiver
 Balanced Line Driver & Receiver Rod Elliott (ESP) Introduction Sometimes, you just can't get rid of that %$#*& hum, no matter what you do. Especially with long interconnects (such as to a powered sub-woofer),
Balanced Line Driver & Receiver Rod Elliott (ESP) Introduction Sometimes, you just can't get rid of that %$#*& hum, no matter what you do. Especially with long interconnects (such as to a powered sub-woofer),
The Ins and Outs of Audio Transformers. How to Choose them and How to Use them
 The Ins and Outs of Audio Transformers How to Choose them and How to Use them Steve Hogan Product Development Engineer, Jensen Transformers 1983 1989 Designed new products and provided application assistance
The Ins and Outs of Audio Transformers How to Choose them and How to Use them Steve Hogan Product Development Engineer, Jensen Transformers 1983 1989 Designed new products and provided application assistance
e base generators Tim 1
 Time base generators 1 LINEAR TIME BASE GENERATORS Circuits thatprovide An Output Waveform Which Exhibits Linear Variation Of Voltage or current With Time. Linear variation of Voltage :Voltage time base
Time base generators 1 LINEAR TIME BASE GENERATORS Circuits thatprovide An Output Waveform Which Exhibits Linear Variation Of Voltage or current With Time. Linear variation of Voltage :Voltage time base
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. AN120 An overview of switched-mode power supplies Dec
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS An overview of switched-mode power supplies 1988 Dec Conceptually, three basic approaches exist for obtaining regulated DC voltage from an AC power source. These are: Shunt regulation
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS An overview of switched-mode power supplies 1988 Dec Conceptually, three basic approaches exist for obtaining regulated DC voltage from an AC power source. These are: Shunt regulation
