IPSO Algorithm for Maximization of System Loadability, Voltage Stability and Loss Minimisation by Optimal DG Placement
|
|
|
- Ralph Shelton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Algorithm for Maximization of System Loadability, Voltage Stability and Loss Minimisation by Optimal DG Placement N. Prema Kumar 1, K. Mercy Rosalina Associate Professor, Department of Electrical Engineering, Andhra University 1 Research Scholar, Department of Electrical Engineering, Andhra University, Visahapatnam Abstract: Under constantly increased electricity demands and power transactions, it is becoming more essential to enhance the system loadability of existing distribution networs such that more power transfers can be accommodated with less networ expansion cost. Instead of building new distribution substations or lines, proper installation of distribution generation units can mae the distribution networs accommodate more power transfers with less expansion cost. In this paper, the problem to maximize power system loadability by optimally installing DG units is formulated as an optimization problem. To reduce the complexity of the problem, the locations suitable for DG installations are first investigated with multi objective optimisation based on inertia weighted particle swam optimisation () method with power loss index (PLI) and voltage stability index (VSI). The size of the DG is to be installed is determined from the standard analytical methods. The proposed algorithms is tested on two standard test systems, i.e. 33-, and 69- bus radial distribution systems. The proposed algorithms has been implemented using MATLAB R010a running on Intel Core Duo processor.93 GHz, 1.96 GB of RAM. All evaluations were carried out with self developed MATLAB codes. Keywords: Distributed generation, Power loss index (PLI), Voltage stability index (VSI), System loadability,. I. INTRODUCTION It is expectable that the future economic developments will result in large electric demands regionally and, in the deregulated power systems, due to open access to the transmission networs a great numbers of various power transactions will incur huge changing power flows, stability and loadability of the system. In this view, serious threats to power system security might occur. Distribution generation can be used to balance the distribution line flows and system voltage, leading to lower system losses, higher loadability and improved voltage regulation. Most of the studies on optimal DG installations are oriented to technical, economic or both concerns. The problem of the voltage stability has risen since the beginning due to large difference in generation and load demands, and to the limited expansion because of high investment cost of equipments, of distribution systems. In order to meet the load demand distribution company usually integrate the distributed resources to the existing system. Distributed resources are the power sources (active or reactive) that can be connected to a distribution system by a distribution company or by the customer at the customer side of the meter [1]. The distributed resources, if strategically located and operated, defer or eliminate system upgrades by improving various energy efficiency defining parameters lie voltage profile, power losses and loadability limit. However, for better energy performance the simultaneous improvement in these parameters is required. Here, voltage stability is the major concern as it improves the reliability of supplying power to the consumers. The improvement in system performance by networ reconfiguration is limited to the load balancing, as the resultant power flow remains the same [8]. Therefore, in order to meet the growing load demand the power utilities integrate the distributed resources with the existing system. However, this is a big challenge to find the optimal size and location of these resources as the load varies with time, weather condition and the state of economy. There exists an extensive effort to find the optimal placement of distributed resources in []-[13]. The effect of load behavior using the different load models has been presented in [9] and [10] while finding the optimal size and location of the distributed resources using multi-objective approach. On the other hand, in [11] the size of the distributed resource for voltage support is obtained under particular loading conditions. The effect of capacitor placement while finding the optimal configuration for different loading patterns is presented in [1]. Authors in [13] and [14] achieve the same objective for distributed generator (DG) placement. Also, a voltage quality index is developed, in order to find the optimal location for DG in distribution system. Using the recursive load flow equations, paper [15] presents the expression for the calculation of the size of DG and optimizes the system operation for maximum loss reduction with single and multi placement of DG. From the literature, it can be observed that the different approach uses voltage profile as main objective in order to improve the system performance. However, the improvement in voltage profile does not guarantee that the system can serve more loads at the respective node. Therefore, in order to improve the reliability of supplying power the distribution company need to enhance the voltage stability rather Copyright to IJIREEICE DOI /IJIREEICE
2 considering the node voltage profile, as the distribution system usually operate on the verge of its loadability limit. II. PROBLEM FORMATION The problem is to determine optimal location and size of DG units which minimizes the total real power losses and to improve the voltage profile, stability and lodability of the system under different system operating constraints. The operating constraints are voltage profile of the system, radial structure of the distribution system, real and reactive power generation limits and power balance constraint. LF i+1 = r i P i +x i Q i + r i +xi P i +Qi x i P i r i Q i V i (1) Here, LFi+1 is the loadability factor at node i+1 which when multiply with the existing load demand (in VA) at respective node defines its loadability, i.e. the load that can be connected before voltage collapses at respective node. Equation (1) also represents that the loadability factor depends upon the load demands therefore; it can vary significantly with the placement of distributed resources as they alter load demand at respective node. However, the placement of these resources at a particular node doesn t guarantee for simultaneous improvement in any other energy efficiency defining parameters. This paper finds the location and size of distributed resources for improvement of voltage stability, in order to serve as maximum as possible number of consumers at a node having worst level of loadability limit, in the system configuration. In order to evaluate the loss reduction, improved voltage regulation and system voltage stability, power utilities need to now the possible load that can be connected at a respective node. This can be easily defined by nowing the loadability factor at the respective node, as described in []. Formation of the multi-objective function is as follows: Objective-I The objective function of the problem is formulated to maximize the lodability of the sytem by improving the loading factor which is a function of the voltage profile of radial distribution system, which is given by Maximize f = max V i () The above expression can also be written as minimization voltage deviation index in the radial distribution system, which is given by Minimize f = min( abs i= VDI ) (3) Where, n is number of buses in the radial distribution system and VDI is called voltage deviation index is expressed as follows VDI = abs n n V ref V i i= (4) V ref Where, Vref is reference voltage of the ith bus usually it is taen as Vref = 1.0 p.u. and Vi is the voltage magnitude of ith bus after DG unit placement. Objective-II The objective function of the problem is formulated to maximize the realpower loss reduction in radial distribution system, which is given by DG Maximize f = max P Loss (5) The expression can also be written as minimization power loss in the radial distribution system, which is given by inimize n 1 f = min i=1 P Loss i, i + 1 (6) Where, n is number of buses in the radial distribution system or this can also expressed as follows Minimize f = min (PLI) (7) PLI = P LWDG P LWODG (8) Where, PLI is called power loss index, P LWDG is power loss with DG and P LWODG is power loss without DG Conversion of multi objective functions into single objective functions f 1 = min PLI (9) f = min(vdi) (10) f 1, f are two different objective functions, using weight factor method multi objective function is expressed as follows f mo = W 1 f 1 + W f (11) Where, W1 and W are called weight factors W1= 0.8; W=0. Minimize f = min(f mo ) (1) Subjected to constraints: Power balance constraints P DGi P Di (13) Voltage limits V min V i V max (14) Vmin and Vmax is minimum and maximum voltage limits of ith bus Real power generation limits P DGmin P DGi P DGmax (15) Reactive power generation limits Q DGmin Q DGi Q DGmax (16) A. Solution techniques for placement of distributed resources for improved voltage stability and loadability The computational steps involved in the solution technique for improvement in voltage stability of radial distribution system, based upon the mathematical formulation presented are as follows: Step1: Run the load flow program by assuming flat voltage profile, and calculate active and reactive load demand at each node. Step: Compute the node voltage, loadability factor, power loss and distributed resource size at each node for base case. Step3: Place a distributed resource, one at a time, as DG of size equal to active component of load demand. Step4: Run the load flow and re-calculate the node voltage and loadability limit at each node. Step5: Print the size of the distributed resources for which the system can serve as maximum as possible number of consumers at a node having worst level of loadability limit. Also, print system power loss, minimum node voltage and worst level of loadability limit. Copyright to IJIREEICE DOI /IJIREEICE
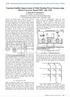
3 III. IMPLEMENTATION OF ALGORITHM TO DG PLACEMENT PROBLEM This algorithm handles a population of individuals, in parallel, to probe capable areas of a multidimensional space where the optimal solution is searched. The individual are called particles and the population is called swam (solution matrix contains DG sizes and locations). Each particle in swam moves towards the optimal point with adaptive velocity. Each particle in the population is treated as a mass less and volume less point in a n- dimensional search space. Mathematically, the position and velocity of the particle, in a n-dimensional vector is represented as: Xm = (xm,1, xm,, xm,3, xm,n) (16) Vm = (vm,1, vm,, vm,3, vm,n) (17) Alternatively, the best position related to the lowest value of the objective function for each particle is: pbestm = (pbestm,1, pbestm,, pbestm,3, pbestm,n), and the global best position among all the particles or best pbest is denoted as: gbestm = (gbestm,1, gbestm,, gbestm,3, gbestm,n), during the iteration procedure, the velocity and position of the particles are updated. It should be noticed that the value of DG size varies between 0 to 70% of the loads plus losses. A large inertia weight (w) facilitates a global search while a small inertia weight facilitates a local search. This is regarded as the position of a particle during the optimization process. The steps used in proposed algorithm are given below. A. Steps followed in algorithm Step 1: Read the input system data and initialize population, number of particles, limits of DG size, voltage limits, parameters of algorithm etc. Step : Calculation of objective function by using Forward-Bacward sweep based distribution load flow. Step 3: Calculate pbest i.e. objective function value of each particle in the population of the current iteration is compared with its previous iteration and the position of the particle having a lower objective function value as pbest for the current iteration is recorded: pbest +1 m = pbest m if f +1 m f m +1 x m if f +1 m f (18) m Where, is the number of iterations, and f is objective function evaluated for the particle. Step 4: Calculation of gbest i.e. the best objective function associated with the pbest among all particles in the current iteration is compared with that in the previous iteration and the lower value is selected as the current overall gbest. gbest m +1 = gbest m if f m +1 f m pbest m +1 if f m +1 f m (19) Step 5: Velocity updating, after calculation of the pbest and gbest the velocity of particles for the next iteration should be modified by using equation: V m +1 + V m + C 1 rand pbest m X m + C rand gbest X m (0) Where, the parameters of the above equation should be determined in advance and is the inertia weight factor, defined as follows: = max max min iter max iter (1) C1, C are the acceleration coefficients usually in range [1, ]. A large inertia weight (w) facilitates a global search while a small inertia weight facilitates a local search. Step 6: Chec the velocity components constraints occurring in the limits from the following conditions, If Vid >Vmax, then Vid = Vmax (or) If Vid < - Vmax then Vid = -Vmax () Step 7: Position updating, the position of each particle at the next iteration (+1) is modified as follows: X j +1 = X j + V j +1 (3) Step 8: If the number of iterations reaches the maximum i.e. iter = itermax, then go to step 9. Otherwise, go to step. Step 9: The individual that generates the latest gbest is the optimal locations and sizes of DGs with minimum power loss. B. Description of parameters for ipso algorithm Algorithm parameter selection plays major role for any optimization algorithms in terms of performance. Hence, parameter tuning is required for optimization techniques. The values assigned for these parameters are selected by the number of trails on the performance of the proposed method. The parameter description and assigned values for are furnished in the Table 1. TABLE I Parameter description for algorithm Type Parameter Description Assigned value P Population size 150 Wmax Maximum inertia weight factor Minimum inertia Wmin weight factor 0.4 C1, C Cognitive parameters, Iter max Maximum no of iterations 150 IV. SIMULATION RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS The proposed algorithms is tested on two standard test systems, i.e. 33-, and 69- bus radial distribution systems. The proposed algorithms has been implemented using MATLAB R010a running on Intel Core Duo processor.93 GHz, 1.96 GB of RAM. All evaluations were carried out with self developed MATLAB codes. The optimal parameters setting for the proposed algorithm are given in Table 1 for all systems. It is assumed that Maximum DG size is considered in the range of 0-70% of the total real power load and the maximum number of DGs that are to be connected is restricted to three for 33- bus and 69-bus systems in this study. It is also assumed that all loads are constant power loads and the system load curve is fixed (pea load). In this study, DGs are modelled as Type-1(p.f = 1) DGs. Copyright to IJIREEICE DOI /IJIREEICE
4 Voltage in pu Voltage in pu Real power loss in W Real power loss in W ISSN (Online) The 33-bus radial distribution system consists of 33 buses and 3 branches; total load of 3.7 MW,.3 Mvar and the real and reactive power losses in the system is W and 143 var. The 69-bus radial distribution system have 69 buses and 68 branches, total load of 3.80 MW,.69 Mvar and the real and reactive power losses in the system is 4.7 W and var x x number of iterations Fig.1 Convergence characteristics for 33-bus RDS number of iterations Fig. 5 Convergence characteristics for 69-bus RDS 1.0 without DG 1.05 without DG with DG with DG Bus number Fig. Voltage profile correction for 33-bus RDS Bus number Fig. 6 Voltage profile correction for 69-bus RDS Fig. 7 Loadability (Lambda) characteristics of 33 bus RDS Fig. 3 Loadability (Lambda) characteristics of 33 bus RDS Fig. 4 Optimal size of DG at all busses in 33 bus system Fig. 8 Optimal size of DG at all busses in 69 bus system TABLE II Numerical results of proposed algorithms for 33- and 69-bus system Type of RDS 33 Bus 66 Bus P Loss(MW) Before After DGs DG % Loss reduction Optimal Bus No. DG size PDG (MW) SI Loading Factor Max. Load ability VPI CPU time (s) Copyright to IJIREEICE DOI /IJIREEICE
5 The effect of optimal access point and capacity of Type-1 DGs on the real power loss of the system, percentage loss reduction, various performance indices, lodability and computation time are given in Table. It is evident that the reduction in line current could reduce the line losses in turn reduces line voltage drop and improves the overall voltage profile. The effect of inserting DGs on the voltage profile of the system, loadability and DG sizes are shown in Figures 1 to 8, improvement in system performance parameters under Type-1 DGs is very significant. V. CONCLUSION In this paper, an efficient DG installation strategy is proposed to enhance the system loadability such that the existing transmission networs can accommodate more power transfers. The application of algorithm has been proposed to solve optimal location and size of DGs radial distribution systems for minimum real power loss and improved system lodability excluding load models. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithms has been investigated on radial power distribution systems having 33- and 69-buses. From the numerical results of the two test systems has shown that, proposed algorithm is succeeded in achieving the goal of real power loss minimization and loadbility. The efficiency of the proposed method is validated with the test results of the DG installation scheme suggested for transmission system loadability enhancement properly consistent with specific technical concerns. REFERENCES [1] E G Carrano, et.al.,, Electric Distribution Networ Multi objective Design using a Problem-Specific Genetic Algorithm, IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, Volume 1, Number, 006, pp [] M H Nehrir and C Wang, Analytical Approaches for Optimal Placement of Distributed Generation sources in Power Systems, IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, Volume 19, Number 4, 004, pp [3] G. W. Chang, Senior Member, IEEE, S. Y. Chu, Student Member, IEEE, and H. L. Wang, Student Member, IEEE, An Improved Bacward/Forward Sweep Load Flow Algorithm for Radial Distribution Systems, IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, vol., no., may 007, pp [4] Pavlos S. Georgilais, Senior Member, IEEE, and Nios D. Hatziargyriou, Fellow, IEEE, Optimal Distributed Generation Placement in Power Distribution Networs: Models, Methods, and Future Research, IEEE Transaction on Power Systems, December 4, 01, p.p [5] T. N. Shula, S.P. Singh, K. B. Nai, Allocation of optimal distributed generation using Genetic Algorithm for minimum system losses in radial distribution networs, International Journal of Engineering, Science and Technology Vol., No. 3, 010, pp [6] T. Xiao-bo, W. Xue-hong, A New Method of Distributed Generation Optimal Placement Based on Load Centroid, IEEE Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC), 011, pp.1-5. [7] Dr. Ganga Agnihotri, Jitendra Singh Bhadoriya, Optimal Placement and Sizing of Multi-Distributed Generation (DG) Including Different Load Models using Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) [8] S. Kumar Injeti, Dr. Navuri P Kumar, Optimal Planning of Distributed Generation for Improved Voltage Stability and Loss Reduction, International Journal of Computer Applications ( ) Volume 15 No.1, February 011, pp [9] D. Singh, D. Singh, and R.K. Misra. "Effect of Load Models in Distributed Generation Planning" IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, vol., no. 4 pp. 04 1, Nov [10] D. Singh, D. Singh, and K. S. Verma, Multiobjective Optimization for DG Planning With Load Models, IEEE Trans. on Power Systems, Vol. 4, no. 1,pp. 7-36, Feb [11] K. Zou, A.P. Agalgaonar, K.M. Muttaqi, and S. Perera, Voltage support by distributed generation units and shunt capacitors in distributed system IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting. pp [1] D Singh, et.al., GA based Optimal Sizing & Placement of Distributed Generation for Loss Minimization, In Proc. of Word Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, Volume. 6, 007, pp [13] D Singh, et.al., Multi-objective Optimization for DG Planning With Load Models, IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, Volume 4, Number 1, 009, pp [14] M Gandomar, et.al. A Genetic Based Tabu Search Algorithm for Optimal DG Allocation in Distribution Networs, Elect. Power Comp. and Syst., Volume 33, 005, pp [15] D Singh, et.al., Effect of Load Models in Distributed Generation Planning, IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, Volume, Number 4, 007, pp [16] N Acharya, et.al. An analytical approach for DG allocation in primary distribution networ, Int. J. of Elect. Power and Ener. Syst. Volume 8, 006, pp [17] V. Farahani, B. Vahidi, and H. A. Abyaneh, "Reconfiguration and capacitor placement simultaneously for energy loss reduction based on an improved reconfiguration method," IEEE Trans. Power Systems, vol. 7, no., pp , May 01. [18] V. F. Martins and C. L. T. Borges, "Active Distribution Networ Integrated Planning Incorporating Distributed Generation and Load Response Uncertainties," IEEE Trans. Power Systems, vol. 6, no. 4, pp , Nov.011. BIOGRAPHIES Dr. N. Prema Kumar is woring with department of Electrical Engineering, Andhra University as Associate Professor. His current research interests include Power systems, Electrical drives, high voltage engineering and signal processing techniques. K. Mercy Rosalina is pursuing her Ph.D. in Electrical Engineering from Andhra University, Andhra Pradesh. She obtained her M. Tech in Power Systems from NIE, Mysore. Currently she is associate Professor of EEE, St. Martin s College of Engineering, Hyderabad. Her research interests include distribution system studies, signal processing and AI techniques to power system. Copyright to IJIREEICE DOI /IJIREEICE
Voltage Controller for Radial Distribution Networks with Distributed Generation
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 3, March 2014 1 Voltage Controller for Radial Distribution Networks with Distributed Generation Christopher Kigen *, Dr. Nicodemus
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 3, March 2014 1 Voltage Controller for Radial Distribution Networks with Distributed Generation Christopher Kigen *, Dr. Nicodemus
OPTIMAL PLACEMENT OF UNIFIED POWER QUALITY CONDITIONER IN DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS USING PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION METHOD
 OPTIMAL PLACEMENT OF UNIFIED POWER QUALITY CONDITIONER IN DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS USING PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION METHOD M. Laxmidevi Ramanaiah and M. Damodar Reddy Department of E.E.E., S.V. University,
OPTIMAL PLACEMENT OF UNIFIED POWER QUALITY CONDITIONER IN DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS USING PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION METHOD M. Laxmidevi Ramanaiah and M. Damodar Reddy Department of E.E.E., S.V. University,
Optimal Voltage Regulators Placement in Radial Distribution System Using Fuzzy Logic
 Optimal Voltage Regulators Placement in Radial Distribution System Using Fuzzy Logic K.Sandhya 1, Dr.A.Jaya Laxmi 2, Dr.M.P.Soni 3 1 Research Scholar, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
Optimal Voltage Regulators Placement in Radial Distribution System Using Fuzzy Logic K.Sandhya 1, Dr.A.Jaya Laxmi 2, Dr.M.P.Soni 3 1 Research Scholar, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
Analysis and Enhancement of Voltage Stability using Shunt Controlled FACTs Controller
 Volume 1, Issue 2, October-December, 2013, pp. 25-33, IASTER 2013 www.iaster.com, Online: 2347-5439, Print: 2348-0025 Analysis and Enhancement of Voltage Stability using Shunt Controlled FACTs Controller
Volume 1, Issue 2, October-December, 2013, pp. 25-33, IASTER 2013 www.iaster.com, Online: 2347-5439, Print: 2348-0025 Analysis and Enhancement of Voltage Stability using Shunt Controlled FACTs Controller
Whale Optimization Algorithm Based Technique for Distributed Generation Installation in Distribution System
 Bulletin of Electrical Engineering and Informatics Vol. 7, No. 3, September 2018, pp. 442~449 ISSN: 2302-9285, DOI: 10.11591/eei.v7i3.1276 442 Whale Optimization Algorithm Based Technique for Distributed
Bulletin of Electrical Engineering and Informatics Vol. 7, No. 3, September 2018, pp. 442~449 ISSN: 2302-9285, DOI: 10.11591/eei.v7i3.1276 442 Whale Optimization Algorithm Based Technique for Distributed
Minimization of Power Loss and Improvement of Voltage Profile in a Distribution System Using Harmony Search Algorithm
 Minimization of Power Loss and Improvement of Voltage Profile in a Distribution System Using Harmony Search Algorithm M. Madhavi 1, Sh. A. S. R Sekhar 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of Electrical and Electronics
Minimization of Power Loss and Improvement of Voltage Profile in a Distribution System Using Harmony Search Algorithm M. Madhavi 1, Sh. A. S. R Sekhar 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of Electrical and Electronics
Optimal Allocation of TCSC Devices Using Genetic Algorithms
 Proceedings of the 14 th International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON 10), Cairo University, Egypt, December 19-21, 2010, Paper ID 195. Optimal Allocation of TCSC Devices Using Genetic Algorithms
Proceedings of the 14 th International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON 10), Cairo University, Egypt, December 19-21, 2010, Paper ID 195. Optimal Allocation of TCSC Devices Using Genetic Algorithms
Identification of weak buses using Voltage Stability Indicator and its voltage profile improvement by using DSTATCOM in radial distribution systems
 IOSR Journal of Electrical And Electronics Engineering (IOSRJEEE) ISSN : 2278-1676 Volume 2, Issue 4 (Sep.-Oct. 2012), PP 17-23 Identification of weak buses using Voltage Stability Indicator and its voltage
IOSR Journal of Electrical And Electronics Engineering (IOSRJEEE) ISSN : 2278-1676 Volume 2, Issue 4 (Sep.-Oct. 2012), PP 17-23 Identification of weak buses using Voltage Stability Indicator and its voltage
Annamacharya Institute of Technology and Sciences, Tirupathi, A.P, India
 Active Power Loss Minimization Using Simultaneous Network Reconfiguration and DG Placement with AGPSO Algorithm K.Sandhya,Venkata Supura Vemulapati 2,2 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
Active Power Loss Minimization Using Simultaneous Network Reconfiguration and DG Placement with AGPSO Algorithm K.Sandhya,Venkata Supura Vemulapati 2,2 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
OPTIMAL SITING AND SIZING OF DISTRIBUTED GENERATION IN RADIAL DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS
 OPTIMAL SITING AND SIZING OF DISTRIBUTED GENERATION IN RADIAL DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS Ms. Shilpa Kotwal, Ms. Amandeep Kaur Research Scholar, E-Max Institute of Engineering and Technology, Ambala, Haryana,
OPTIMAL SITING AND SIZING OF DISTRIBUTED GENERATION IN RADIAL DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS Ms. Shilpa Kotwal, Ms. Amandeep Kaur Research Scholar, E-Max Institute of Engineering and Technology, Ambala, Haryana,
Optimal Sizing and Placement of DG in a Radial Distribution Network using Sensitivity based Methods
 Optimal Sizing and Placement of DG in a Radial Distribution Network using Sensitivity based Methods Nitin Singh 1, Smarajit Ghosh 2, Krishna Murari 3 EIED, Thapar university, Patiala-147004, India Email-
Optimal Sizing and Placement of DG in a Radial Distribution Network using Sensitivity based Methods Nitin Singh 1, Smarajit Ghosh 2, Krishna Murari 3 EIED, Thapar university, Patiala-147004, India Email-
DISTRIBUTION NETWORK RECONFIGURATION FOR LOSS MINIMISATION USING DIFFERENTIAL EVOLUTION ALGORITHM
 DISTRIBUTION NETWORK RECONFIGURATION FOR LOSS MINIMISATION USING DIFFERENTIAL EVOLUTION ALGORITHM K. Sureshkumar 1 and P. Vijayakumar 2 1 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Velammal
DISTRIBUTION NETWORK RECONFIGURATION FOR LOSS MINIMISATION USING DIFFERENTIAL EVOLUTION ALGORITHM K. Sureshkumar 1 and P. Vijayakumar 2 1 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Velammal
Madurai, Tamilnadu, India *Corresponding author. Madurai, Tamilnadu, India ABSTRACT
 International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2158 Volume 7, Number 2 (2014), pp. 211-226 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Power Quality Improvement of Distribution
International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2158 Volume 7, Number 2 (2014), pp. 211-226 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Power Quality Improvement of Distribution
ATC ENHANCEMENT THROUGH OPTIMAL PLACEMENT OF TCSC USING WIPSO TECHNIQUE
 ATC ENHANCEMENT THROUGH OPTIMAL PLACEMENT OF TCSC USING WIPSO TECHNIQUE R. Sripriya and R. Neela Department of Electrical Enneering, Annamalai University, India E-Mail: sripriyavineeth@gmail.com ABSTRACT
ATC ENHANCEMENT THROUGH OPTIMAL PLACEMENT OF TCSC USING WIPSO TECHNIQUE R. Sripriya and R. Neela Department of Electrical Enneering, Annamalai University, India E-Mail: sripriyavineeth@gmail.com ABSTRACT
Optimal Positioning and Sizing of DG Units Using Differential Evolution Algorithm
 Optimal Positioning and Sizing of DG Units Using Differential Evolution Algorithm Ravi 1, Himanshu Sangwan 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical Engineering, D C R University of Science & Technology,
Optimal Positioning and Sizing of DG Units Using Differential Evolution Algorithm Ravi 1, Himanshu Sangwan 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical Engineering, D C R University of Science & Technology,
FOUR TOTAL TRANSFER CAPABILITY. 4.1 Total transfer capability CHAPTER
 CHAPTER FOUR TOTAL TRANSFER CAPABILITY R structuring of power system aims at involving the private power producers in the system to supply power. The restructured electric power industry is characterized
CHAPTER FOUR TOTAL TRANSFER CAPABILITY R structuring of power system aims at involving the private power producers in the system to supply power. The restructured electric power industry is characterized
Application of DE & PSO Algorithm For The Placement of FACTS Devices For Economic Operation of a Power System
 Application DE & PSO Algorithm For The Placement Devices For Economic Operation a Power System B. BHATTACHARYYA, VIKASH KUMAR GUPTA 2 Department Electrical Engineering, Indian School Mines, Dhanbad, Jharkhanbd
Application DE & PSO Algorithm For The Placement Devices For Economic Operation a Power System B. BHATTACHARYYA, VIKASH KUMAR GUPTA 2 Department Electrical Engineering, Indian School Mines, Dhanbad, Jharkhanbd
Optimal Solar Photovoltaic Placement as a Distributed Generation in Radial Distribution Networks using Particle Swarm Optimization
 Nigerian Journal of Solar Energy, Vol. 26, 2015. Solar Energy Society of Nigeria (SESN) 2015. All rights reserved. Optimal Solar Photovoltaic as a Distributed Generation in Radial Distribution Networks
Nigerian Journal of Solar Energy, Vol. 26, 2015. Solar Energy Society of Nigeria (SESN) 2015. All rights reserved. Optimal Solar Photovoltaic as a Distributed Generation in Radial Distribution Networks
OPTIMAL ALLOCATION AND CONTINGENCY ANALYSIS WITH MULTIPLE EMBEDDED GENERATION UNITS IN RADIAL DISTRIBUTION NETWORK USING GA
 International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Research (IJEEER) ISSN(P): 2250-155X; ISSN(E): 2278-943X Vol. 5, Issue 2, Apr 2015, 41-50 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. OPTIMAL ALLOCATION AND CONTINGENCY
International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Research (IJEEER) ISSN(P): 2250-155X; ISSN(E): 2278-943X Vol. 5, Issue 2, Apr 2015, 41-50 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. OPTIMAL ALLOCATION AND CONTINGENCY
Optimal PMU Placement in Power System Considering the Measurement Redundancy
 Advance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 4, Number 6 (2014), pp. 593-598 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Optimal PMU Placement in Power System
Advance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 4, Number 6 (2014), pp. 593-598 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Optimal PMU Placement in Power System
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Computer Science 92 (2016 ) 36 41
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 92 (2016 ) 36 41 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Communication & Convergence (ICCC-2016) Srikanta
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 92 (2016 ) 36 41 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Communication & Convergence (ICCC-2016) Srikanta
Sensitivity Analysis for 14 Bus Systems in a Distribution Network With Distributed Generators
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 10, Issue 3 Ver. I (May Jun. 2015), PP 21-27 www.iosrjournals.org Sensitivity Analysis for
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 10, Issue 3 Ver. I (May Jun. 2015), PP 21-27 www.iosrjournals.org Sensitivity Analysis for
Analysis of Voltage Rise Effect on Distribution Network with Distributed Generation
 Analysis of Voltage ise Effect on Distribution Network with Distributed Generation M. A. Mahmud, M. J. Hossain, H.. Pota The University of New South Wales at the Australian Defence Force Academy, Northcott
Analysis of Voltage ise Effect on Distribution Network with Distributed Generation M. A. Mahmud, M. J. Hossain, H.. Pota The University of New South Wales at the Australian Defence Force Academy, Northcott
Voltage Drop Compensation and Congestion Management by Optimal Placement of UPFC
 P P Assistant P International Journal of Automation and Power Engineering, 2012, 1: 29-36 - 29 - Published Online May 2012 www.ijape.org Voltage Drop Compensation and Congestion Management by Optimal Placement
P P Assistant P International Journal of Automation and Power Engineering, 2012, 1: 29-36 - 29 - Published Online May 2012 www.ijape.org Voltage Drop Compensation and Congestion Management by Optimal Placement
COST EFFECTIVE SOLUTION FOR OPTIMAL PLACEMENT AND SIZE OF MULTIPLE STATCOM USING PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION
 2005-204 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved. ISSN: 992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 87-395 COST EFFECTIVE SOLUTION FOR OPTIMAL PLACEMENT AND SIZE OF MULTIPLE STATCOM USING PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION K. KUMARASAMY,
2005-204 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved. ISSN: 992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 87-395 COST EFFECTIVE SOLUTION FOR OPTIMAL PLACEMENT AND SIZE OF MULTIPLE STATCOM USING PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION K. KUMARASAMY,
GENETIC ALGORITHM BASED CONGESTION MANAGEMENT BY USING OPTIMUM POWER FLOW TECHNIQUE TO INCORPORATE FACTS DEVICES IN DEREGULATED ENVIRONMENT
 GENETIC ALGORITHM BASED CONGESTION MANAGEMENT BY USING OPTIMUM POWER FLOW TECHNIQUE TO INCORPORATE FACTS DEVICES IN DEREGULATED ENVIRONMENT S.Vinod Kumar 1, J.Sreenivasulu 2, K.Vimala Kumar 3 PG Student,
GENETIC ALGORITHM BASED CONGESTION MANAGEMENT BY USING OPTIMUM POWER FLOW TECHNIQUE TO INCORPORATE FACTS DEVICES IN DEREGULATED ENVIRONMENT S.Vinod Kumar 1, J.Sreenivasulu 2, K.Vimala Kumar 3 PG Student,
OPTIMAL PASSIVE FILTER LOCATION BASED POWER LOSS MINIMIZING IN HARMONICS DISTORTED ENVIRONMENT
 OPTIMAL PASSIVE FILTER LOCATION BASED POWER LOSS MINIMIZING IN HARMONICS DISTORTED ENVIRONMENT * Mohammadi M., Mohammadi Rozbahani A., Montazeri M. and Memarinezhad H. Department of Electrical Engineering,
OPTIMAL PASSIVE FILTER LOCATION BASED POWER LOSS MINIMIZING IN HARMONICS DISTORTED ENVIRONMENT * Mohammadi M., Mohammadi Rozbahani A., Montazeri M. and Memarinezhad H. Department of Electrical Engineering,
Design Of PID Controller In Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) System Using PSO Technique
 Design Of PID Controller In Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) System Using PSO Technique Vivek Kumar Bhatt 1, Dr. Sandeep Bhongade 2 1,2 Department of Electrical Engineering, S. G. S. Institute of Technology
Design Of PID Controller In Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) System Using PSO Technique Vivek Kumar Bhatt 1, Dr. Sandeep Bhongade 2 1,2 Department of Electrical Engineering, S. G. S. Institute of Technology
WITH THE advent of advanced power-electronics technologies,
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 29, NO. 4, AUGUST 2014 1859 Impact of Unified Power-Quality Conditioner Allocation on Line Loading, Losses, and Voltage Stability of Radial Distribution Systems
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 29, NO. 4, AUGUST 2014 1859 Impact of Unified Power-Quality Conditioner Allocation on Line Loading, Losses, and Voltage Stability of Radial Distribution Systems
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Computer Science 92 (2016 ) 30 35
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 92 (2016 ) 30 35 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Communication & Convergence (ICCC-2016) Srikanta
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 92 (2016 ) 30 35 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Communication & Convergence (ICCC-2016) Srikanta
Distributed Generation Placement in Distribution Network using Selective Particle Swarm Optimization
 2018 IJSRST Volume 4 Issue 5 Print ISSN: 2395-6011 Online ISSN: 2395-602X Themed Section: Science and Technology Distributed Generation Placement in Distribution Network using Selective Particle Swarm
2018 IJSRST Volume 4 Issue 5 Print ISSN: 2395-6011 Online ISSN: 2395-602X Themed Section: Science and Technology Distributed Generation Placement in Distribution Network using Selective Particle Swarm
Keyword: conductors, feeders, genetic algorithm, conventional method, real power loss, reactive power loss, distributed load flow, cost and savings.
 Optimal Conductor Selection Using Genetic Algorithm Deepak Sharma 1, Priya Jha 2,S.Vidyasagar 3 1 PG Student, SRM University, Chennai, India 2 PG Student, SRM University, Chennai, India 3 Assistant Professor,
Optimal Conductor Selection Using Genetic Algorithm Deepak Sharma 1, Priya Jha 2,S.Vidyasagar 3 1 PG Student, SRM University, Chennai, India 2 PG Student, SRM University, Chennai, India 3 Assistant Professor,
Optimal Placement of Multi DG in 33 Bus System Using PSO
 Optimal Placement of Multi in 33 Bus System Using PSO Rohit Fanish 1, Jitendra Singh Bhadoriya 2 PG Scholar, Department of EEE, NRI Institute of Info.Science and Tech, Bhopal, (MP), India 1 Assistant Professor,
Optimal Placement of Multi in 33 Bus System Using PSO Rohit Fanish 1, Jitendra Singh Bhadoriya 2 PG Scholar, Department of EEE, NRI Institute of Info.Science and Tech, Bhopal, (MP), India 1 Assistant Professor,
Particle Swarm Based Optimization of Power Losses in Network Using STATCOM
 International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ 14) Cordoba (Spain), 8 th to 10 th April, 2014 Renewable Energy and Power Quality Journal (RE&PQJ) ISSN 2172-038 X, No.12, April
International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ 14) Cordoba (Spain), 8 th to 10 th April, 2014 Renewable Energy and Power Quality Journal (RE&PQJ) ISSN 2172-038 X, No.12, April
A Novel Approach for Reducing Proximity to Voltage Instability of Multibus Power System with Line Outage Using Shunt Compensation and Modal Analysis
 A Novel Approach for Reducing Proximity to Voltage Instability of Multibus Power System with Line Outage Using Shunt Compensation and Modal Analysis S.D.Naik Department of Electrical Engineering Shri Ramdeobaba
A Novel Approach for Reducing Proximity to Voltage Instability of Multibus Power System with Line Outage Using Shunt Compensation and Modal Analysis S.D.Naik Department of Electrical Engineering Shri Ramdeobaba
PID Controller Tuning using Soft Computing Methodologies for Industrial Process- A Comparative Approach
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 7(S7), 140 145, November 2014 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 PID Controller Tuning using Soft Computing Methodologies for Industrial Process-
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 7(S7), 140 145, November 2014 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 PID Controller Tuning using Soft Computing Methodologies for Industrial Process-
Power System Stability Enhancement Using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC)
 Vol. 3, Issue. 4, Jul - Aug. 2013 pp-2530-2536 ISSN: 2249-6645 Power System Stability Enhancement Using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC) B. M. Naveen Kumar Reddy 1, Mr. G. V. Rajashekar 2,
Vol. 3, Issue. 4, Jul - Aug. 2013 pp-2530-2536 ISSN: 2249-6645 Power System Stability Enhancement Using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC) B. M. Naveen Kumar Reddy 1, Mr. G. V. Rajashekar 2,
NSGA Based Optimal Volt / Var Control in Distribution System with Dispersed Generation
 NSGA Based Optimal Volt / Var Control in Distribution System with Dispersed Generation P. N. Hrisheekesha, and Jaydev Sharma Abstract In this paper, a method based on Non-Dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm
NSGA Based Optimal Volt / Var Control in Distribution System with Dispersed Generation P. N. Hrisheekesha, and Jaydev Sharma Abstract In this paper, a method based on Non-Dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm
SuperOPF and Global-OPF : Design, Development, and Applications
 SuperOPF and Global-OPF : Design, Development, and Applications Dr. Hsiao-Dong Chiang Professor, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA School of electrical
SuperOPF and Global-OPF : Design, Development, and Applications Dr. Hsiao-Dong Chiang Professor, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA School of electrical
Neural Network Based Loading Margin Approximation for Static Voltage Stability in Power Systems
 Neural Network Based Loading Margin Approximation for Static Voltage Stability in Power Systems Arthit Sode-Yome, Member, IEEE, and Kwang Y. Lee, Fellow, IEEE Abstract Approximate loading margin methods
Neural Network Based Loading Margin Approximation for Static Voltage Stability in Power Systems Arthit Sode-Yome, Member, IEEE, and Kwang Y. Lee, Fellow, IEEE Abstract Approximate loading margin methods
Optimal Placement of AVR in RDS Using Modified Cuckoo Search Algorithm
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 11, Issue 2 Ver. I (Mar. Apr. 2016), PP 54-65 www.iosrjournals.org Optimal Placement of AVR
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 11, Issue 2 Ver. I (Mar. Apr. 2016), PP 54-65 www.iosrjournals.org Optimal Placement of AVR
Harmony Search and Nonlinear Programming Based Hybrid Approach to Enhance Power System Performance with Wind Penetration
 Abstract Wind generation existence in power system greatly affects power system transient stability and it also greatly affects steady state conditions. FACTS devices are proposed as a solution to this
Abstract Wind generation existence in power system greatly affects power system transient stability and it also greatly affects steady state conditions. FACTS devices are proposed as a solution to this
Enhancement of Voltage Stability by SVC and TCSC Using Genetic Algorithm
 ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 3, Special Issue 3, March 2014 2014 International Conference
ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 3, Special Issue 3, March 2014 2014 International Conference
Implementation of Line Stability Index for Contingency Analysis and Screening in Power Systems
 Journal of Computer Science 8 (4): 585-590, 2012 ISSN 1549-3636 2012 Science Publications Implementation of Line Stability Index for Contingency Analysis and Screening in Power Systems Subramani, C., Subhransu
Journal of Computer Science 8 (4): 585-590, 2012 ISSN 1549-3636 2012 Science Publications Implementation of Line Stability Index for Contingency Analysis and Screening in Power Systems Subramani, C., Subhransu
Effect of Parameter Tuning on Performance of Cuckoo Search Algorithm for Optimal Reactive Power Dispatch
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Effect of Parameter Tuning on Performance of Cuckoo Search Algorithm for Optimal Reactive Power Dispatch Tejaswini Sharma Laxmi Srivastava Department of Electrical Engineering
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Effect of Parameter Tuning on Performance of Cuckoo Search Algorithm for Optimal Reactive Power Dispatch Tejaswini Sharma Laxmi Srivastava Department of Electrical Engineering
Fuzzy Approach to Critical Bus Ranking under Normal and Line Outage Contingencies
 Fuzzy Approach to Critical Bus Ranking under Normal and Line Outage Shobha Shankar *, Dr. T. Ananthapadmanabha ** * Research Scholar and Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
Fuzzy Approach to Critical Bus Ranking under Normal and Line Outage Shobha Shankar *, Dr. T. Ananthapadmanabha ** * Research Scholar and Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
SIMPLE ROBUST POWER FLOW METHOD FOR RADIAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS
 SIMPLE ROBUST POWER FLOW METHOD FOR RADIAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS 1 NITIN MALIK, 2 SHUBHAM SWAPNIL, 3 JAIMIN D. SHAH, 4 VAIBHAV A. MAHESHWARI 1 ITM University, Gurgaon, India, 2 School of Electrical Engg,
SIMPLE ROBUST POWER FLOW METHOD FOR RADIAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS 1 NITIN MALIK, 2 SHUBHAM SWAPNIL, 3 JAIMIN D. SHAH, 4 VAIBHAV A. MAHESHWARI 1 ITM University, Gurgaon, India, 2 School of Electrical Engg,
Genetic Algorithm based Voltage Regulator Placement in Unbalanced Radial Distribution Systems
 Volume 50, Number 4, 2009 253 Genetic Algorithm based Voltage Regulator in Unbalanced Radial Distribution Systems Ganesh VULASALA, Sivanagaraju SIRIGIRI and Ramana THIRUVEEDULA Abstract: In rural power
Volume 50, Number 4, 2009 253 Genetic Algorithm based Voltage Regulator in Unbalanced Radial Distribution Systems Ganesh VULASALA, Sivanagaraju SIRIGIRI and Ramana THIRUVEEDULA Abstract: In rural power
Optimal Voltage Control using Singular Value Decomposition of Fast Decoupled Load Flow Jacobian
 Optimal Voltage Control using Singular Value Decomposition of Fast Decoupled Load Flow Jacobian Talha Iqbal, Ali Dehghan Banadaki, Ali Feliachi Lane Department of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering
Optimal Voltage Control using Singular Value Decomposition of Fast Decoupled Load Flow Jacobian Talha Iqbal, Ali Dehghan Banadaki, Ali Feliachi Lane Department of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering
Optimal Allocation of TCSC Using Heuristic Optimization Technique
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijssI/2017/132 Optimal Allocation of TCSC Using Heuristic Optimization Technique M Nafar, A Ramezanpour Department of Electrical
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijssI/2017/132 Optimal Allocation of TCSC Using Heuristic Optimization Technique M Nafar, A Ramezanpour Department of Electrical
A NEW EVALUTIONARY ALGORITHMS USED FOR OPTIMAL LOCATION OF UPFC ON POWER SYSTEM
 A NEW EVALUTIONARY ALGORITHMS USED FOR OPTIMAL LOCATION OF ON POWER SYSTEM 1 K. VENKATESWARLU, 2 CH. SAIBABU 1 Associate professor in EEE Dept., M L Engg. College. S.Konda, Prakasam (Dt.), A.P.,India.
A NEW EVALUTIONARY ALGORITHMS USED FOR OPTIMAL LOCATION OF ON POWER SYSTEM 1 K. VENKATESWARLU, 2 CH. SAIBABU 1 Associate professor in EEE Dept., M L Engg. College. S.Konda, Prakasam (Dt.), A.P.,India.
Optimal Location and Parameter Setting of UPFC based on PSO for Enhancing Power System Security under Single Contingencies
 Optimal Location and Parameter Setting of UPFC based on PSO for Enhancing Power System Security under Single Contingencies 1 Nedunuri Vineela, 2 Chunduri Rambabu 1 Sri Vasavi Engineering College, Tadepalligudem,
Optimal Location and Parameter Setting of UPFC based on PSO for Enhancing Power System Security under Single Contingencies 1 Nedunuri Vineela, 2 Chunduri Rambabu 1 Sri Vasavi Engineering College, Tadepalligudem,
Optimal placement of different DG units type in distribution networks based on voltage stability maximization and minimization of power losses
 8th International Conference on Modelling, Identification and Control (ICMIC-26) Algiers, Algeria- November -7, 26 Optimal placement of different DG units type in distribution networks based on voltage
8th International Conference on Modelling, Identification and Control (ICMIC-26) Algiers, Algeria- November -7, 26 Optimal placement of different DG units type in distribution networks based on voltage
AS the power distribution networks become more and more
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 21, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2006 153 A Unified Three-Phase Transformer Model for Distribution Load Flow Calculations Peng Xiao, Student Member, IEEE, David C. Yu, Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 21, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2006 153 A Unified Three-Phase Transformer Model for Distribution Load Flow Calculations Peng Xiao, Student Member, IEEE, David C. Yu, Member,
Analysis The IIR Filter Design Using Particle Swarm Optimization Method
 Xxxxxxx IJSRRS: International I Journal of Scientific Research in Recent Sciences Research Paper Vol-1, Issue-1 ISSN: XXXX-XXXX Analysis The IIR Filter Design Using Particle Swarm Optimization Method Neha
Xxxxxxx IJSRRS: International I Journal of Scientific Research in Recent Sciences Research Paper Vol-1, Issue-1 ISSN: XXXX-XXXX Analysis The IIR Filter Design Using Particle Swarm Optimization Method Neha
Harmonic Minimization for Cascade Multilevel Inverter based on Genetic Algorithm
 Harmonic Minimization for Cascade Multilevel Inverter based on Genetic Algorithm Ranjhitha.G 1, Padmanaban.K 2 PG Scholar, Department of EEE, Gnanamani College of Engineering, Namakkal, India 1 Assistant
Harmonic Minimization for Cascade Multilevel Inverter based on Genetic Algorithm Ranjhitha.G 1, Padmanaban.K 2 PG Scholar, Department of EEE, Gnanamani College of Engineering, Namakkal, India 1 Assistant
Maximum Allowable PV Penetration by Feeder Reconfiguration Considering Harmonic Distortion Limits
 Maximum Allowable PV Penetration by Feeder Reconfiguration Considering Harmonic Distortion Limits Vemula Mahesh Veera Venkata Prasad #1, R. Madhusudhana Rao *, Mrutyunjay Mohanty #3 #1 M.Tech student,
Maximum Allowable PV Penetration by Feeder Reconfiguration Considering Harmonic Distortion Limits Vemula Mahesh Veera Venkata Prasad #1, R. Madhusudhana Rao *, Mrutyunjay Mohanty #3 #1 M.Tech student,
Voltage Stability Index of Radial Distribution Networks with Distributed Generation
 International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2158 Volume 5, Number 6 (2012), pp. 791-803 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Voltage Stability Index of Radial
International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2158 Volume 5, Number 6 (2012), pp. 791-803 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Voltage Stability Index of Radial
DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM PLANNING USING NETWORK RECONFIGURATION FOR LOSS REDUCTION
 DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM PLANNING USING NETWORK RECONFIGURATION FOR LOSS REDUCTION Raval Vivek 1, Sanjay R. Vyas 2 1PG Scholar, EE Dept., LDRP-ITR, Gandhinagar, Gujarat, India. 2Head of Department, EE Dept.,
DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM PLANNING USING NETWORK RECONFIGURATION FOR LOSS REDUCTION Raval Vivek 1, Sanjay R. Vyas 2 1PG Scholar, EE Dept., LDRP-ITR, Gandhinagar, Gujarat, India. 2Head of Department, EE Dept.,
Optimal Placement of Unified Power Flow Controller for Minimization of Power Transmission Line Losses
 Optimal Placement of Unified Power Flow Controller for inimization of Power Transmission Line Losses Sreerama umar R., Ibrahim. Jomoah, and Abdullah Omar Bafail Abstract This paper proposes the application
Optimal Placement of Unified Power Flow Controller for inimization of Power Transmission Line Losses Sreerama umar R., Ibrahim. Jomoah, and Abdullah Omar Bafail Abstract This paper proposes the application
Smart Grid Reconfiguration Using Genetic Algorithm and NSGA-II
 Smart Grid Reconfiguration Using Genetic Algorithm and NSGA-II 1 * Sangeeta Jagdish Gurjar, 2 Urvish Mewada, 3 * Parita Vinodbhai Desai 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, AIT, Gujarat Technical University,
Smart Grid Reconfiguration Using Genetic Algorithm and NSGA-II 1 * Sangeeta Jagdish Gurjar, 2 Urvish Mewada, 3 * Parita Vinodbhai Desai 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, AIT, Gujarat Technical University,
THERE has been a growing interest in the optimal operation
 648 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 22, NO. 2, MAY 2007 A New Optimal Routing Algorithm for Loss Minimization and Voltage Stability Improvement in Radial Power Systems Joong-Rin Shin, Member,
648 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 22, NO. 2, MAY 2007 A New Optimal Routing Algorithm for Loss Minimization and Voltage Stability Improvement in Radial Power Systems Joong-Rin Shin, Member,
DIGITAL SIMULATION OF MULTILEVEL INVERTER BASED STATCOM
 DIGITAL SIMULATION OF MULTILEVEL INVERTER BASED STATCOM G.SUNDAR, S.RAMAREDDY Research Scholar, Bharath University Chenna Professor Jerusalam College of Engg. Chennai ABSTRACT This paper deals with simulation
DIGITAL SIMULATION OF MULTILEVEL INVERTER BASED STATCOM G.SUNDAR, S.RAMAREDDY Research Scholar, Bharath University Chenna Professor Jerusalam College of Engg. Chennai ABSTRACT This paper deals with simulation
Optimal Placement and Sizing of FACTS Devices for Loadability Enhancement in Deregulated Power Systems
 Optimal Placement and Sizing of FACTS Devices for Enhancement in Deregulated Power Systems Mahmoud Mohammadi, Dr.Alireza Rezazadeh, Dr.Mostafa Sedighizadeh Beheshti University Beheshti University, Evin,
Optimal Placement and Sizing of FACTS Devices for Enhancement in Deregulated Power Systems Mahmoud Mohammadi, Dr.Alireza Rezazadeh, Dr.Mostafa Sedighizadeh Beheshti University Beheshti University, Evin,
Voltage Control of Distribution Networks with Distributed Generation using Reactive Power Compensation
 Voltage Control of Distribution Networks with Distributed Generation using Reactive Power Compensation Author Mahmud, M., Hossain, M., Pota, H., M Nasiruzzaman, A. Published 2011 Conference Title Proceedings
Voltage Control of Distribution Networks with Distributed Generation using Reactive Power Compensation Author Mahmud, M., Hossain, M., Pota, H., M Nasiruzzaman, A. Published 2011 Conference Title Proceedings
International Journal on Technical and Physical Problems of Engineering (IJTPE) Published by International Organization of IOTPE
 International Journal on Technical and Physical Problems of Engineering (IJTPE) Published by International Organization of IOTPE ISSN 2077-3528 IJTPE Journal www.iotpe.com ijtpe@iotpe.com June 2013 Issue
International Journal on Technical and Physical Problems of Engineering (IJTPE) Published by International Organization of IOTPE ISSN 2077-3528 IJTPE Journal www.iotpe.com ijtpe@iotpe.com June 2013 Issue
Volume 2, Number 4, 2016 Pages Jordan Journal of Electrical Engineering ISSN (Print): , ISSN (Online):
 JJEE Volume, Number 4, 6 Pages - Jordan Journal of Electrical Engineering ISSN (Print): 49-96, ISSN (Online): 49-969 Enhancement of Voltage Stability and Line Loadability by Reconfiguration of Radial Electrical
JJEE Volume, Number 4, 6 Pages - Jordan Journal of Electrical Engineering ISSN (Print): 49-96, ISSN (Online): 49-969 Enhancement of Voltage Stability and Line Loadability by Reconfiguration of Radial Electrical
I. INTRODUCTION. Keywords:- FACTS, TCSC, TCPAR,UPFC,ORPD
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 11, Issue 11 (November 2015), PP.13-18 Modelling Of Various Facts Devices for Optimal
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 11, Issue 11 (November 2015), PP.13-18 Modelling Of Various Facts Devices for Optimal
Identification of Critical Bus and Optimal Allocation of Facts Device
 Identification of Critical Bus and Optimal Allocation of Facts Device Dipali Kiratsata 1, Gaurav Gangil 2 M.Tech Scholar, Department of Electrical, Sobhasaria Group of Institutions Sikar, India Assistant
Identification of Critical Bus and Optimal Allocation of Facts Device Dipali Kiratsata 1, Gaurav Gangil 2 M.Tech Scholar, Department of Electrical, Sobhasaria Group of Institutions Sikar, India Assistant
Load Flow Analysis for Radial Distribution Networks Using Backward/Forward Sweep Method
 Open Access Journal Journal of Sustainable Research in Engineering Vol. 3 (3) 2016, 82-87 Journal homepage: http://sri.jkuat.ac.ke/ojs/index.php/sri Load Flow Analysis for Radial Distribution Networks
Open Access Journal Journal of Sustainable Research in Engineering Vol. 3 (3) 2016, 82-87 Journal homepage: http://sri.jkuat.ac.ke/ojs/index.php/sri Load Flow Analysis for Radial Distribution Networks
Load Frequency and Voltage Control of Two Area Interconnected Power System using PID Controller. Kavita Goswami 1 and Lata Mishra 2
 e t International Journal on Emerging Technologies (Special Issue NCETST-2017) 8(1): 722-726(2017) (Published by Research Trend, Website: www.researchtrend.net) ISSN No. (Print) : 0975-8364 ISSN No. (Online)
e t International Journal on Emerging Technologies (Special Issue NCETST-2017) 8(1): 722-726(2017) (Published by Research Trend, Website: www.researchtrend.net) ISSN No. (Print) : 0975-8364 ISSN No. (Online)
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 29, NO. 4, JULY
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 29, NO. 4, JULY 2014 1801 Multi-Objective Planning for Reactive Power Compensation of Radial Distribution Networks With Unified Power Quality Conditioner Allocation
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 29, NO. 4, JULY 2014 1801 Multi-Objective Planning for Reactive Power Compensation of Radial Distribution Networks With Unified Power Quality Conditioner Allocation
Damping Power system Oscillation using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC)
 Damping Power system Oscillation using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC) Girish Kumar Prasad 1, Dr. Malaya S Dash 2 1M-Tech Scholar, Dept. of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Technocrats
Damping Power system Oscillation using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC) Girish Kumar Prasad 1, Dr. Malaya S Dash 2 1M-Tech Scholar, Dept. of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Technocrats
CHAPTER 5 PSO AND ACO BASED PID CONTROLLER
 128 CHAPTER 5 PSO AND ACO BASED PID CONTROLLER 5.1 INTRODUCTION The quality and stability of the power supply are the important factors for the generating system. To optimize the performance of electrical
128 CHAPTER 5 PSO AND ACO BASED PID CONTROLLER 5.1 INTRODUCTION The quality and stability of the power supply are the important factors for the generating system. To optimize the performance of electrical
On Using Fuzzy Logic Based Automatic Voltage Relay In Distribution Network
 On Using Fuzzy Logic Based Automatic Voltage Relay In Distribution Network 1 Uchegbu C.E 2, Ekulibe James 2. Ilo F.U 1 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Enugu state University of science
On Using Fuzzy Logic Based Automatic Voltage Relay In Distribution Network 1 Uchegbu C.E 2, Ekulibe James 2. Ilo F.U 1 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Enugu state University of science
OPTIMAL PLACEMENT AND SIZING OF UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER USING HEURISTIC TECHNIQUES FOR ELECTRICAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM
 OPTIMAL PLACEMENT AND SIZING OF UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER USING HEURISTIC TECHNIQUES FOR ELECTRICAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM R. Siva Subramanyam Reddy 1, T. Gowri Manohar 2 and Moupuri Satish Kumar Reddy
OPTIMAL PLACEMENT AND SIZING OF UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER USING HEURISTIC TECHNIQUES FOR ELECTRICAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM R. Siva Subramanyam Reddy 1, T. Gowri Manohar 2 and Moupuri Satish Kumar Reddy
STATCOM Optimal Allocation in Transmission Grids Considering Contingency Analysis in OPF Using BF-PSO Algorithm
 Journal of Operation and Automation in Power Engineering, Vol., No., March 03 STATCOM Optimal Allocation in Transmission Grids Considering Contingency Analysis in OPF Using BF-PSO Algorithm R. Kazemzadeh*,
Journal of Operation and Automation in Power Engineering, Vol., No., March 03 STATCOM Optimal Allocation in Transmission Grids Considering Contingency Analysis in OPF Using BF-PSO Algorithm R. Kazemzadeh*,
Aggregated Rooftop PV Sizing in Distribution Feeder Considering Harmonic Distortion Limit
 Aggregated Rooftop PV Sizing in Distribution Feeder Considering Harmonic Distortion Limit Mrutyunjay Mohanty Power Research & Development Consultant Pvt. Ltd., Bangalore, India Student member, IEEE mrutyunjay187@gmail.com
Aggregated Rooftop PV Sizing in Distribution Feeder Considering Harmonic Distortion Limit Mrutyunjay Mohanty Power Research & Development Consultant Pvt. Ltd., Bangalore, India Student member, IEEE mrutyunjay187@gmail.com
Available Transfer Capability Enhancement with FACTS Devices in the Deregulated Electricity Market
 14 Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. 14~24, 2011 DOI: 10.5370/JEET.2011.6.1.014 Available Transfer Capability Enhancement with FACTS Devices in the Deregulated Electricity
14 Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. 14~24, 2011 DOI: 10.5370/JEET.2011.6.1.014 Available Transfer Capability Enhancement with FACTS Devices in the Deregulated Electricity
Optimal PMU Placement in Power System Networks Using Integer Linear Programming
 ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 3, Special Issue 3, March 2014 2014 International Conference
ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 3, Special Issue 3, March 2014 2014 International Conference
Resonant Controller to Minimize THD for PWM Inverter
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 10, Issue 3 Ver. III (May Jun. 2015), PP 49-53 www.iosrjournals.org Resonant Controller to
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 10, Issue 3 Ver. III (May Jun. 2015), PP 49-53 www.iosrjournals.org Resonant Controller to
Application Of Power System Stabilizer At Serir Power Plant
 Vol. 3 Issue 4, April - 27 Application Of Power System Stabilizer At Serir Power Plant *T. Hussein, **A. Shameh Electrical and Electronics Dept University of Benghazi Benghazi- Libya *Tawfiq.elmenfy@uob.edu.ly
Vol. 3 Issue 4, April - 27 Application Of Power System Stabilizer At Serir Power Plant *T. Hussein, **A. Shameh Electrical and Electronics Dept University of Benghazi Benghazi- Libya *Tawfiq.elmenfy@uob.edu.ly
Max Covering Phasor Measurement Units Placement for Partial Power System Observability
 Engineering Management Research; Vol. 2, No. 1; 2013 ISSN 1927-7318 E-ISSN 1927-7326 Published by Canadian Center o Science and Education Max Covering Phasor Measurement Units Placement or Partial Power
Engineering Management Research; Vol. 2, No. 1; 2013 ISSN 1927-7318 E-ISSN 1927-7326 Published by Canadian Center o Science and Education Max Covering Phasor Measurement Units Placement or Partial Power
Identifying Long Term Voltage Stability Caused by Distribution Systems vs Transmission Systems
 Identifying Long Term Voltage Stability Caused by Distribution Systems vs Transmission Systems Amarsagar Reddy Ramapuram M. Ankit Singhal Venkataramana Ajjarapu amar@iastate.edu ankit@iastate.edu vajjarapu@iastate.edu
Identifying Long Term Voltage Stability Caused by Distribution Systems vs Transmission Systems Amarsagar Reddy Ramapuram M. Ankit Singhal Venkataramana Ajjarapu amar@iastate.edu ankit@iastate.edu vajjarapu@iastate.edu
The Selective Harmonic Elimination Technique for Harmonic Reduction of Multilevel Inverter Using PSO Algorithm
 The Selective Harmonic Elimination Technique for Harmonic Reduction of Multilevel Inverter Using PSO Algorithm Maruthupandiyan. R 1, Brindha. R 2 1,2. Student, M.E Power Electronics and Drives, Sri Shakthi
The Selective Harmonic Elimination Technique for Harmonic Reduction of Multilevel Inverter Using PSO Algorithm Maruthupandiyan. R 1, Brindha. R 2 1,2. Student, M.E Power Electronics and Drives, Sri Shakthi
Optimal sizing and placement of Static and Dynamic VAR devices through Imperialist Competitive Algorithm for minimization of Transmission Power Loss
 Optimal sizing and placement of Static and Dynamic VAR devices through Imperialist Competitive Algorithm for minimization of Transmission Power Loss Pramod Kumar Gouda #1, P K Hota *2, K. Chandrasekar
Optimal sizing and placement of Static and Dynamic VAR devices through Imperialist Competitive Algorithm for minimization of Transmission Power Loss Pramod Kumar Gouda #1, P K Hota *2, K. Chandrasekar
Optimal Location and Design of TCSC controller For Improvement of Stability
 Optimal Location and Design of TCSC controller For Improvement of Stability Swathi Kommamuri & P. Sureshbabu Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, NEC Narasaraopet,India E-mail : swathikommamuri@gmail.com,
Optimal Location and Design of TCSC controller For Improvement of Stability Swathi Kommamuri & P. Sureshbabu Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, NEC Narasaraopet,India E-mail : swathikommamuri@gmail.com,
An efficient power flow algorithm for distribution systems with polynomial load
 An efficient power flow algorithm for distribution systems with polynomial load Jianwei Liu, M. M. A. Salama and R. R. Mansour Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Waterloo,
An efficient power flow algorithm for distribution systems with polynomial load Jianwei Liu, M. M. A. Salama and R. R. Mansour Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Waterloo,
Interline Power Quality Conditioner for Power Quality Improvement
 Interline Power Quality Conditioner for Power Quality Improvement K.Sandhya 1, Dr.A.Jaya Laxmi 2 and Dr.M.P.Soni 3 1 Research Scholar, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, JNTU College
Interline Power Quality Conditioner for Power Quality Improvement K.Sandhya 1, Dr.A.Jaya Laxmi 2 and Dr.M.P.Soni 3 1 Research Scholar, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, JNTU College
Generator Capability Curve Constraint for PSO Based Optimal Power Flow
 World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology 53 29 Generator Capability Curve Constraint for PSO Based Optimal Power Flow Mat Syai in, Adi Soeprijanto, and Takashi Hiyama Abstract An optimal power
World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology 53 29 Generator Capability Curve Constraint for PSO Based Optimal Power Flow Mat Syai in, Adi Soeprijanto, and Takashi Hiyama Abstract An optimal power
Optimum Design of Multi-band Transformer with Multi-section for Two Arbitrary Complex Frequency-dependent Impedances
 Chinese Journal of Electronics Vol.21, No.1, Jan. 2012 Optimum Design of Multi-band Transformer with Multi-section for Two Arbitrary Complex Frequency-dependent Impedances CHEN Ming (Institute of Microwave
Chinese Journal of Electronics Vol.21, No.1, Jan. 2012 Optimum Design of Multi-band Transformer with Multi-section for Two Arbitrary Complex Frequency-dependent Impedances CHEN Ming (Institute of Microwave
Margin Adaptive Resource Allocation for Multi user OFDM Systems by Particle Swarm Optimization and Differential Evolution
 Margin Adaptive Resource Allocation for Multi user OFDM Systems by Particle Swarm Optimization and Differential Evolution Imran Ahmed, Sonia Sadeque, and Suraiya Pervin Northern University Bangladesh,
Margin Adaptive Resource Allocation for Multi user OFDM Systems by Particle Swarm Optimization and Differential Evolution Imran Ahmed, Sonia Sadeque, and Suraiya Pervin Northern University Bangladesh,
OPTIMAL UTILIZATION OF GENERATORS USING HARMONY SEARCH ALGORITHM FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CONTINGENCY
 International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information and Control ICIC International c 2018 ISSN 1349-4198 Volume 14, Number 3, June 2018 pp. 1159 1168 OPTIMAL UTILIZATION OF GENERATORS USING HARMONY
International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information and Control ICIC International c 2018 ISSN 1349-4198 Volume 14, Number 3, June 2018 pp. 1159 1168 OPTIMAL UTILIZATION OF GENERATORS USING HARMONY
Impact of various load models in distribution system with DG using Harmony and Backtracking Search Algorithms
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 6 Issue 11 November 2017 PP 34-42 Impact of various load models in distribution system with
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 6 Issue 11 November 2017 PP 34-42 Impact of various load models in distribution system with
LOW FREQUENCY OSCILLATION DAMPING BY DISTRIBUTED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER WITH A ROBUST FUZZY SUPPLEMENTARY CONTROLLER
 LOW FREQUENCY OSCILLATION DAMPING BY DISTRIBUTED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER WITH A ROBUST FUZZY SUPPLEMENTARY CONTROLLER C. Narendra Raju 1, V.Naveen 2 1PG Scholar, Department of EEE, JNTU Anantapur, Andhra
LOW FREQUENCY OSCILLATION DAMPING BY DISTRIBUTED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER WITH A ROBUST FUZZY SUPPLEMENTARY CONTROLLER C. Narendra Raju 1, V.Naveen 2 1PG Scholar, Department of EEE, JNTU Anantapur, Andhra
OPTIMAL ALLOCATION OF PMU CONSIDERING CONTROLLED ISLANDING OF POWER SYSTEM USING HYBRID OPTIMIZATION ALGORITHM
 OPTIMAL ALLOCATION OF PMU CONSIDERING CONTROLLED ISLANDING OF POWER SYSTEM USING HYBRID OPTIMIZATION ALGORITHM 1 Deebiga Kandasamy, 2 Raqib Hussain A 1 PG scholar, Assistant Professor, 2 Department of
OPTIMAL ALLOCATION OF PMU CONSIDERING CONTROLLED ISLANDING OF POWER SYSTEM USING HYBRID OPTIMIZATION ALGORITHM 1 Deebiga Kandasamy, 2 Raqib Hussain A 1 PG scholar, Assistant Professor, 2 Department of
Control of Load Frequency of Power System by PID Controller using PSO
 Website: www.ijrdet.com (ISSN 2347-6435(Online) Volume 5, Issue 6, June 206) Control of Load Frequency of Power System by PID Controller using PSO Shiva Ram Krishna, Prashant Singh 2, M. S. Das 3,2,3 Dept.
Website: www.ijrdet.com (ISSN 2347-6435(Online) Volume 5, Issue 6, June 206) Control of Load Frequency of Power System by PID Controller using PSO Shiva Ram Krishna, Prashant Singh 2, M. S. Das 3,2,3 Dept.
IMPLEMENTATION OF NETWORK RECONFIGURATION TECHNIQUE FOR LOSS MINIMIZATION ON A 11KV DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM OF MRS SHIMOGA-A CASE STUDY
 IMPLEMENTATION OF NETWORK RECONFIGURATION TECHNIQUE FOR LOSS MINIMIZATION ON A 11KV DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM OF MRS SHIMOGA-A CASE STUDY PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S0848 COLLEGE : PES INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
IMPLEMENTATION OF NETWORK RECONFIGURATION TECHNIQUE FOR LOSS MINIMIZATION ON A 11KV DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM OF MRS SHIMOGA-A CASE STUDY PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S0848 COLLEGE : PES INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter Based UPFC with ANN
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 04, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 04, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter
Optimal Power flow with FACTS devices using Genetic Algorithm
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume, Issue 8, August 2013 Optimal Power flow with FACTS devices using Genetic Algorithm Serene C Kurian, Jo Joy Abstract Increasing demands
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume, Issue 8, August 2013 Optimal Power flow with FACTS devices using Genetic Algorithm Serene C Kurian, Jo Joy Abstract Increasing demands
