Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators
|
|
|
- Bruno Boone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. Senior Technical Expert Motorola Automotive Government & Enterprise Mobility Solutions September 15, 2005 Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
2 1 Introduction 2 Voltage References 3 Linear Regulators 4 Switching Regulators 5 Switched-Capacitor Voltage Converters Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
3 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Voltage References 3 Linear Regulators 4 Switching Regulators 5 Switched-Capacitor Voltage Converters Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
4 Introduction Goals of the Seminar Series Provide an overview of power conversion techniques Power supplies are common subsystems in most of our products Present follow-up seminars in related areas switching regulator topologies/compensation, simulation Offer refresher seminars in fundamental areas mathematical modeling, circuit analysis, control design Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
5 Power Supplies Every electronic system needs a source of energy to operate Power supplies provide circuits with ac/dc voltages/currents Power management refers to strategies to generate and control regulated voltages The regulation/control of energy from source to the consumer is accomplished using power electronics Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
6 Types of Power Conversion Type Process Name Processor dc dc conversion converter ac dc rectification rectifier dc ac inversion inverter ac ac cycloconversion cycloconverter Most of the coverage will be devoted to dc/dc converters Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
7 Types of dc/dc Converters Voltage Reference V BE -based voltage reference circuit Linear Regulator Three-terminal circuit with a pass transistor (linear region) Switching Regulator Regulator with a switching transistor and inductive storage Switched-Capacitor Converter Inductorless voltage converter using capacitive charge transfer Battery Charger Specialized converter with voltage/temperature monitoring All converters except the battery charger will be covered Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
8 Example 1: Notebook Computer Requirements High performance Light weight Long battery life Fast charging Power System Battery: Lithium-ion Charger: Switching rectifier µp: Buck converter Disk drive: Boost converter Display: High-voltage inverter Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
9 Example 2: Mobile Phone Requirements High performance Small size Light weight Long battery life Fast charging Low cost Power System Battery: Lithium-ion Charger: Switching rectifier Transmitter: Switching regulator Power Management: Linear regulator Power Management: Voltage reference Display: Regulated charge pump Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
10 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Voltage References 3 Linear Regulators 4 Switching Regulators 5 Switched-Capacitor Voltage Converters Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
11 Introduction to Voltage References Characteristics Voltage reference and regulators have much in common Voltage references have great impact on accuracy of analog systems Drifting (temp/aging) may be more important than absolute accuracy VR must be chosen to account for temp. coefficient and aging Noise can also be an issue Dynamics (behavior at startup and transient loads) Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
12 Introduction to Voltage References General types of Voltage References Two-terminal [diodes, Zener diodes] Flexible polarity Restrictive loading conditions Increased power dissipation with source resistor Non-standard voltages (6.2V) Three-terminal [TL431] Positive polarity Lower, more stable quiescent current Standard output voltages Relatively high output current Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
13 Diode Reference Simple diode reference +V s I D R s I L D + V ref Characteristics Current-driven forward-biased diode Junction drop independent of V s Strong tempco of 2mV/ C Sensitive to loading Inflexible output voltages (n 600mV) Polarity is reversible Load current << drive current Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
14 Zener Reference Zener reference +V s I D R s I L D 1 D 2 + V ref Characteristics D 1 avalanche 5-8V with +tempco Forward biased D 2 has tempco Net tempco is 100ppm/ C Limited loading Must be driven by a source > 6V Noisy due to zener breakdown 1N821 1N829 temp. comp. zener Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
15 Bandgap Reference Simplified bandgap reference (LM109/LM113) +V s R 2 R 1 6kΩ 600Ω Q 1 Q 2 R 3 600Ω I z + + R 2 R 3 V BE + + V BE V BE Q 3 V ref Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
16 Bandgap Reference V BE Different emitter current densities (J 1 10J 2 ) produce V BE V BE = kt q ln J 1 J 2 = T (at T = T 0 = 300 K, V BE = 60mV) V BE V BE = kt q ln i E Is but I s is a strong function of temperature V BE V g0 (1 T T 0 )+V BE0 ( T T 0 ) = 1.2(1 T T 0 )+0.6( T T 0 ) V ref V ref = R 2 R 3 V BE +V BE 1.2V (see plots) V ref varies < 0.5% from 55 C to +125 C (see LM113 graph) Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
17 Bandgap Reference V ref V g0 1.2V V BE = 1.2(1 T T 0 )+0.6( T T 0 ) V BE0 0.6V R 2 R 3 V BE = (T T 0) T 0 0V 273 C 27 C 327 C 0 K 300 K 600 K T Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
18 Bandgap Reference Characteristics (LM113) Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
19 Three-terminal reference TL431-based reference +V s I D TL431 R s R 1 V ref V out Characteristics V out = (1+R 1 /R 2 )V ref R 1, R 2 should be precision resistors R s is chosen to make I D 1mA at V s,min Reference voltage is ± 0.055V Typically used as V ref for linear regulators R 2 Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
20 TL431-based 5V regulator V batt R s R 1 Q I out V out TL431 V ref R 2 Choose R 1 = R 2 to make V out = 5V Select R s to make TL431 cathode current 1mA Choose transistor Q to handle I out Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
21 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Voltage References 3 Linear Regulators 4 Switching Regulators 5 Switched-Capacitor Voltage Converters Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
22 Introduction to Linear Regulators Three-terminal devices input, output, common (ground) Linear regulators may be classified by their series (pass) transistor Series element may consist of bipolar of field-effect transistors Bipolar outputs Darlington NPN, PNP, NPN-PNP Majority of regulators use bipolars (FET-based regulators $) Series transistor structure determines V dropout, I bias, I q, P diss Frequency compensation and protection circuity also important V dropout minimum input-output voltage difference to stay in regulation I bias bias current for the pass transistor I q regulator quiescent current of which I bias is one component P diss regulator power dissipation Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
23 NPN Regulator NPN Regulator V in Iload R 1 Error Amp I bias + V ref + R 2 V out GND Characteristics NPN Darlington pass PNP driver Used in 78xx series I bias I load /β 3 Smallest chip area Small comp. capacitor Least expensive V do = 2V BE +V sat 2.0V No reverse battery protection Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
24 PNP Low Dropout (LDO) Regulator PNP (LDO) Regulator V in R 1 Error Amp + I bias V ref + R 2 V out GND Characteristics PNP pass NPN or EA direct drive V do = V sat 600mV Inherent reverse battery protection I bias I load /β pnp Large chip area Large comp. capacitor More expensive Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
25 Composite (Quasi-LDO) Regulator Composite Regulator V in R 1 Error Amp + I bias V ref + R 2 V out GND Characteristics NPN pass PNP driver V do = V BE +V sat 1.3V I bias I load /β 2 Compromise between NPN and PNP Larger chip area than NPN Large comp. capacitor No reverse battery protection Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
26 Summary of Linear Regulator Advantages/Disadvantages Topology Advantages Disadvantages NPN smallest die size large dropout voltage fastest transient response no rev. batt. protection smallest comp. capacitor PNP low dropout voltage high quiescent current rev. battery protection large comp. capacitor large die size NPN/PNP moderate dropout voltage large comp. capacitor lower I q than PNP no rev. batttery protection Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
27 Linear Regulator Performance Comparison I load Power Dissipation V in V out P diss = (V in V out )I load +V in I q I q Linear Regulators for V out = 5V and I load = 100mA at 25 C Topology Part V do I q P diss at V in = 12V NPN LM V 5.15mA (700+62) mw PNP CS V 45.0mA ( )mW NPN/PNP CS V 2.50mA (700+30) mw Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
28 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Voltage References 3 Linear Regulators 4 Switching Regulators 5 Switched-Capacitor Voltage Converters Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
29 Introduction to Switching Regulators Switching converters are often referred to as switchers Conversion based on inductive storage and lowpass filtering Basic topology has one switch, diode, inductor and capacitor Input current ripple must not get on supply line (input capacitance) Output voltage ripple depends on L, C and switching frequency Theoretical efficiency is 100% (elements in box are lossless) V in + S D L C load V out Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
30 Advantages/Disadvantages Linear Simple, inexpensive Electrically quiet V in > V out Poor efficiency (< 60%) Physically large Single output Switch-mode Complex, expensive Electrically noisy Wide V in range High efficiency (> 90%) Compact Multiple outputs Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
31 Buck Converter Buck Converter S L V out V in + D C load DT s T s V out V in = D Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
32 Buck Converter Steady-State Analysis Buck Converter Circuit Modes S L S L V in D v L V out V in D v L V out Mode 1, duration: DT s Mode 2, duration: (1 D)T s Steady-state operation requires v L = 1 T s Ts 0 v L dt = 0 This is referred to as volt-second balance or flux balance Mode 1 v L = V in V out ; Mode 2 v L = V out v L = 1 T s [(V in V out )DT s +( V out )(1 D)T s ] = 0 Vout V in = D Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
33 Boost Converter Boost Converter L D V out V in + S C load DT s T s V out V in = 1 1 D Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
34 Buck/Boost Converter Buck/Boost Converter S D V out V in + L C load DT s T s V out V in = D 1 D Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
35 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Voltage References 3 Linear Regulators 4 Switching Regulators 5 Switched-Capacitor Voltage Converters Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
36 Switched-Capacitor Voltage Converters (SCVC) Characteristics SCVCs transfer energy and convert voltage without inductors Voltage conversion accomplished by capacitive charge transfer SCVC Inverter V in + I in A B C 1 C 2 A B I out load V out V in Steady-State Operation AA : V in applied to C 1 BB : V in inverted & applied to C 2 and load Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
37 Switched-Capacitor Voltage Converters (SCVC) Advantages/Disadvantages Elimination of inductor & related design issues Low noise, minimal radiated EMI Simple implementation (2 3 external capacitors) Low cost, low profile, compact design Efficiency > 90% Optimized for doubling or inverting supply voltage Limited current output (typically mA) Basic SCVCs have no output voltage regulation Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
38 Voltage Inverter Voltage Inverter I in A B V in + C 1 C 2 load A B I out V out V in C 1 charged to V in during 1st half of switching cycle During 2nd half, voltage is inverted and applied to C 2 and load V out V in, I in I out After startup transient, C 1 provides small amount of charge to output Charge transfer depends on I load and f sw When C 1 is being charged, C 2 supplies load current voltage droop For same voltage droop, smaller caps can be used if f sw is increased Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
39 Voltage Inverter Implementation Voltage Inverter S 1 S 3 V in + S 2 C 1 S 4 V out V in Oscillator & Drive Circuit C 2 load Each SPDT switch can be implemented with 2 SPST switches SPST switches can be implemented with a bipolar or CMOS process IC SCVCs contain all the switches, oscillator and control circuits Pump capacitor (C 1 ), load capacitor (C 2 ) are external Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
40 Voltage Doubler Voltage Doubler I in A B I out V out 2V in V in + A C 1 C 2 B load Operation if very similar to the inverter C 1 charged to V in during 1st half of switching cycle During 2nd half, C 1 is placed in series with C 2 and load V out 2V in, I in 2I out Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
41 Voltage Doubler Implementation Voltage Doubler S 1 S 3 V out 2V in V in + C 1 C 2 load S 2 S 4 Oscillator & Drive Circuit V in Implementation of inverter and doubler uses a common structure Most ICs allow implementation of either structure (ADM660/ADM8660) Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
42 Conclusion Reference circuits used in many designs Linear regulators utilized when low-noise is important Switching regulators are more flexible and efficient Charge-pumps usually designed into ICs External components (e.g. filtering) are critical to performance Frequency response analysis essential in avoiding oscillations Modeling/simulation key to avoiding power supply design issues Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
43 References W. Kester. Practical Design Techniques for Power & Thermal Management. Analog Devices, Norwood, MA, National Semiconductor. Application Note AN-56, 1.2V Reference. Santa Clara, CA, December National Semiconductor. Application Note AN 1188, Linear Regulators: Theory of Operation and Compensation. Santa Clara, CA, May ON Semiconductor. Application Note SR0003AN/D, Compensation for Linear Regulators. Phoenix, AZ, April ON Semiconductor. Application Note SR0004AN/D, Linear Regulator Output Structures. Phoenix, AZ, April Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
44 Sources of information on the web Analog Devices Infineon Technologies Linear Technology Maxim National Semiconductor ON Semiconductor Texas Instruments Vahe Caliskan, Sc.D. (g17823) Overview of Linear & Switching Regulators September 15, / 44
Linear Voltage Regulators Power supplies and chargers SMM Alavi, SBU, Fall2017
 Linear Voltage Regulator LVRs can be classified based on the type of the transistor that is used as the pass element. The bipolar junction transistor (BJT), field effect transistor (FET), or metal oxide
Linear Voltage Regulator LVRs can be classified based on the type of the transistor that is used as the pass element. The bipolar junction transistor (BJT), field effect transistor (FET), or metal oxide
Linear Regulator APPLICATION NOTE
 Kieran O Malley ON Semiconductor 2000 South County Trail East Greenwich, RI 02818 APPLICATION NOTE Choosing a linear regulator for an application involves more than looking for the part with the lowest
Kieran O Malley ON Semiconductor 2000 South County Trail East Greenwich, RI 02818 APPLICATION NOTE Choosing a linear regulator for an application involves more than looking for the part with the lowest
Power Management. Introduction. Courtesy of Dr. Sanchez-Sinencio s Group. ECEN 489: Power Management Circuits and Systems
 Power Management Introduction Courtesy of Dr. Sanchez-Sinencio s Group 1 Today What is power management? Big players Market Types of converters Pros and cons Specifications Selection of converters 2 Motivation
Power Management Introduction Courtesy of Dr. Sanchez-Sinencio s Group 1 Today What is power management? Big players Market Types of converters Pros and cons Specifications Selection of converters 2 Motivation
Chapter 1: Introduction
 1.1. Introduction to power processing 1.2. Some applications of power electronics 1.3. Elements of power electronics Summary of the course 2 1.1 Introduction to Power Processing Power input Switching converter
1.1. Introduction to power processing 1.2. Some applications of power electronics 1.3. Elements of power electronics Summary of the course 2 1.1 Introduction to Power Processing Power input Switching converter
Concepts to be Covered
 Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Analog Circuits Part 2 Semiconductors, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota Concepts to be Covered Semiconductors
Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Analog Circuits Part 2 Semiconductors, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota Concepts to be Covered Semiconductors
Not Recommended for New Designs
 Not Recommended for New Designs This product was manufactured for Maxim by an outside wafer foundry using a process that is no longer available. It is not recommended for new designs. The data sheet remains
Not Recommended for New Designs This product was manufactured for Maxim by an outside wafer foundry using a process that is no longer available. It is not recommended for new designs. The data sheet remains
TS6001. A 7ppm/ C, 0.08% Precision +2.5V Voltage Reference in SOT23 FEATURES DESCRIPTION APPLICATIONS TYPICAL APPLICATION CIRCUIT
 VOLTAGE - Volt TS6001 A 7ppm/ C, 0.08% Precision +2.5V Voltage Reference in SOT23 FEATURES Improved Electrical Performance over MAX6025 Initial Accuracy: 0.08% (max) TS6001A 0.16% (max) TS6001B Temperature
VOLTAGE - Volt TS6001 A 7ppm/ C, 0.08% Precision +2.5V Voltage Reference in SOT23 FEATURES Improved Electrical Performance over MAX6025 Initial Accuracy: 0.08% (max) TS6001A 0.16% (max) TS6001B Temperature
LM , -8.2, -8.4, -12.6, Lithium-Ion Battery Charge Controller
 LM3420-4.2, -8.2, -8.4, -12.6, -16.8 Lithium-Ion Battery Charge Controller General Description The LM3420 series of controllers are monolithic integrated circuits designed for charging and end-of-charge
LM3420-4.2, -8.2, -8.4, -12.6, -16.8 Lithium-Ion Battery Charge Controller General Description The LM3420 series of controllers are monolithic integrated circuits designed for charging and end-of-charge
Power Management for Computer Systems. Prof. C Wang
 ECE 5990 Power Management for Computer Systems Prof. C Wang Fall 2010 Course Outline Fundamental of Power Electronics cs for Computer Systems, Handheld Devices, Laptops, etc More emphasis in DC DC converter
ECE 5990 Power Management for Computer Systems Prof. C Wang Fall 2010 Course Outline Fundamental of Power Electronics cs for Computer Systems, Handheld Devices, Laptops, etc More emphasis in DC DC converter
Driving High Intensity LED Strings in DC to DC Applications D. Solley, ON Semiconductor, Phoenix, AZ
 Driving High Intensity LED Strings in DC to DC Applications D. Solley, ON Semiconductor, Phoenix, AZ Abstract Improvements in high brightness LED technology offer enhanced energy efficient lighting solutions
Driving High Intensity LED Strings in DC to DC Applications D. Solley, ON Semiconductor, Phoenix, AZ Abstract Improvements in high brightness LED technology offer enhanced energy efficient lighting solutions
High-Efficiency, 26V Step-Up Converters for Two to Six White LEDs
 19-2731; Rev 1; 10/03 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE High-Efficiency, 26V Step-Up Converters General Description The step-up converters drive up to six white LEDs with a constant current to provide backlight
19-2731; Rev 1; 10/03 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE High-Efficiency, 26V Step-Up Converters General Description The step-up converters drive up to six white LEDs with a constant current to provide backlight
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 28V, PWM, Step-Up DC-DC Converter PART V IN 3V TO 28V
 19-1462; Rev ; 6/99 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 28V, PWM, Step-Up DC-DC Converter General Description The CMOS, PWM, step-up DC-DC converter generates output voltages up to 28V and accepts inputs from +3V
19-1462; Rev ; 6/99 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 28V, PWM, Step-Up DC-DC Converter General Description The CMOS, PWM, step-up DC-DC converter generates output voltages up to 28V and accepts inputs from +3V
Linear Regulators: Theory of Operation and Compensation
 Linear Regulators: Theory of Operation and Compensation Introduction The explosive proliferation of battery powered equipment in the past decade has created unique requirements for a voltage regulator
Linear Regulators: Theory of Operation and Compensation Introduction The explosive proliferation of battery powered equipment in the past decade has created unique requirements for a voltage regulator
High Precision 10 V IC Reference AD581*
 a FEATURES Laser Trimmed to High Accuracy: 10.000 Volts 5 mv (L and U) Trimmed Temperature Coefficient: 5 ppm/ C max, 0 C to +70 C (L) 10 ppm/ C max, 55 C to +125 C (U) Excellent Long-Term Stability: 25
a FEATURES Laser Trimmed to High Accuracy: 10.000 Volts 5 mv (L and U) Trimmed Temperature Coefficient: 5 ppm/ C max, 0 C to +70 C (L) 10 ppm/ C max, 55 C to +125 C (U) Excellent Long-Term Stability: 25
Analog Circuits Part 2 Semiconductors
 Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Analog Circuits Part 2 Semiconductors, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota Concepts to be Covered Semiconductors
Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Analog Circuits Part 2 Semiconductors, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota Concepts to be Covered Semiconductors
Diodes (non-linear devices)
 C H A P T E R 4 Diodes (non-linear devices) Ideal Diode Figure 4.2 The two modes of operation of ideal diodes and the use of an external circuit to limit (a) the forward current and (b) the reverse voltage.
C H A P T E R 4 Diodes (non-linear devices) Ideal Diode Figure 4.2 The two modes of operation of ideal diodes and the use of an external circuit to limit (a) the forward current and (b) the reverse voltage.
Fast IC Power Transistor with Thermal Protection
 Fast IC Power Transistor with Thermal Protection Introduction Overload protection is perhaps most necessary in power circuitry. This is shown by recent trends in power transistor technology. Safe-area,
Fast IC Power Transistor with Thermal Protection Introduction Overload protection is perhaps most necessary in power circuitry. This is shown by recent trends in power transistor technology. Safe-area,
LM340 Series Three Terminal Positive Regulators
 LM340 Series Three Terminal Positive Regulators Introduction The LM340-XX are three terminal 1.0A positive voltage regulators, with preset output voltages of 5.0V or 15V. The LM340 regulators are complete
LM340 Series Three Terminal Positive Regulators Introduction The LM340-XX are three terminal 1.0A positive voltage regulators, with preset output voltages of 5.0V or 15V. The LM340 regulators are complete
PART* PART. Maxim Integrated Products 1
 19-1704; Rev 0; 4/00 Improved Precision Micropower General Description The is a precision two-terminal shunt mode, bandgap voltage reference with a fixed reverse breakdown voltage of 1.225V. Ideal for
19-1704; Rev 0; 4/00 Improved Precision Micropower General Description The is a precision two-terminal shunt mode, bandgap voltage reference with a fixed reverse breakdown voltage of 1.225V. Ideal for
55:141 Advanced Circuit Techniques Switching Regulators
 55:141 Advanced Circuit Techniques Switching Regulators Material: ecture Notes, Handouts, and Sections of Chapter 11 of Franco A. Kruger 55:141: Advanced Circuit Techniques The University of Iowa Switching
55:141 Advanced Circuit Techniques Switching Regulators Material: ecture Notes, Handouts, and Sections of Chapter 11 of Franco A. Kruger 55:141: Advanced Circuit Techniques The University of Iowa Switching
LM125 Precision Dual Tracking Regulator
 LM125 Precision Dual Tracking Regulator INTRODUCTION The LM125 is a precision, dual, tracking, monolithic voltage regulator. It provides separate positive and negative regulated outputs, thus simplifying
LM125 Precision Dual Tracking Regulator INTRODUCTION The LM125 is a precision, dual, tracking, monolithic voltage regulator. It provides separate positive and negative regulated outputs, thus simplifying
HY2596A 3A 150kHz DC-DC BUCK REGULATOR
 Description of regulators provides all the active functions for a step-down (buck) switching regulator, and drives 3A load with excellent line and load regulation. is available in fixed output voltages
Description of regulators provides all the active functions for a step-down (buck) switching regulator, and drives 3A load with excellent line and load regulation. is available in fixed output voltages
Features MIC2193BM. Si9803 ( 2) 6.3V ( 2) VDD OUTP COMP OUTN. Si9804 ( 2) Adjustable Output Synchronous Buck Converter
 MIC2193 4kHz SO-8 Synchronous Buck Control IC General Description s MIC2193 is a high efficiency, PWM synchronous buck control IC housed in the SO-8 package. Its 2.9V to 14V input voltage range allows
MIC2193 4kHz SO-8 Synchronous Buck Control IC General Description s MIC2193 is a high efficiency, PWM synchronous buck control IC housed in the SO-8 package. Its 2.9V to 14V input voltage range allows
Assume availability of the following components to DESIGN and DRAW the circuits of the op. amp. applications listed below:
 ========================================================================================== UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN MAINE Dept. of Electrical Engineering TEST #3 Prof. M.G.Guvench ELE343/02 ==========================================================================================
========================================================================================== UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN MAINE Dept. of Electrical Engineering TEST #3 Prof. M.G.Guvench ELE343/02 ==========================================================================================
Lecture 3: Transistors
 Lecture 3: Transistors Now that we know about diodes, let s put two of them together, as follows: collector base emitter n p n moderately doped lightly doped, and very thin heavily doped At first glance,
Lecture 3: Transistors Now that we know about diodes, let s put two of them together, as follows: collector base emitter n p n moderately doped lightly doped, and very thin heavily doped At first glance,
MAX889TESA -40 C to +85 C 8 SO 2MHz MAX889SESA -40 C to +85 C 8 SO 1MHz MAX889RESA -40 C to +85 C 8 SO 0.5MHz. Maxim Integrated Products 1
 19-1774; Rev ; 7/ EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE High-Frequency, Regulated, General Description The inverting charge pump delivers a regulated negative output voltage at loads of up to 2. The device operates
19-1774; Rev ; 7/ EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE High-Frequency, Regulated, General Description The inverting charge pump delivers a regulated negative output voltage at loads of up to 2. The device operates
FAN MHz TinyBoost Regulator with 33V Integrated FET Switch
 FAN5336 1.5MHz TinyBoost Regulator with 33V Integrated FET Switch Features 1.5MHz Switching Frequency Low Noise Adjustable Output Voltage Up to 1.5A Peak Switch Current Low Shutdown Current:
FAN5336 1.5MHz TinyBoost Regulator with 33V Integrated FET Switch Features 1.5MHz Switching Frequency Low Noise Adjustable Output Voltage Up to 1.5A Peak Switch Current Low Shutdown Current:
LM2685 Dual Output Regulated Switched Capacitor Voltage Converter
 Dual Output Regulated Switched Capacitor Voltage Converter General Description The LM2685 CMOS charge-pump voltage converter operates as an input voltage doubler, +5V regulator and inverter for an input
Dual Output Regulated Switched Capacitor Voltage Converter General Description The LM2685 CMOS charge-pump voltage converter operates as an input voltage doubler, +5V regulator and inverter for an input
List of Figures and Photos
 List of Figures and Photos p. xiii List of Tables p. xxv Acknowledgements p. xxix A Short History of References p. 1 Introduction p. 1 The first JFETs and op amps p. 3 The first bandgaps p. 5 The buried-zener
List of Figures and Photos p. xiii List of Tables p. xxv Acknowledgements p. xxix A Short History of References p. 1 Introduction p. 1 The first JFETs and op amps p. 3 The first bandgaps p. 5 The buried-zener
An LDO Primer. Part III: A Review on PSRR and Output Noise
 An LDO Primer Part III: A Review on PSRR and Output Noise Qi Deng Senior Product Marketing Engineer, Analog and Interface Products Division Microchip Technology Inc. In Parts I and II of this article series,
An LDO Primer Part III: A Review on PSRR and Output Noise Qi Deng Senior Product Marketing Engineer, Analog and Interface Products Division Microchip Technology Inc. In Parts I and II of this article series,
LM2662/LM2663 Switched Capacitor Voltage Converter
 LM2662/LM2663 Switched Capacitor Voltage Converter General Description The LM2662/LM2663 CMOS charge-pump voltage converter inverts a positive voltage in the range of 1.5V to 5.5V to the corresponding
LM2662/LM2663 Switched Capacitor Voltage Converter General Description The LM2662/LM2663 CMOS charge-pump voltage converter inverts a positive voltage in the range of 1.5V to 5.5V to the corresponding
Orister Corporation. LDO Thesis
 Orister Corporation LDO Thesis AGENDA What is a Linear egulator LDO ntroductions LDO S Terms and Definitions LDO S LAYOUT What s a Linear egulator A linear regulator operates by using a voltage-controlled
Orister Corporation LDO Thesis AGENDA What is a Linear egulator LDO ntroductions LDO S Terms and Definitions LDO S LAYOUT What s a Linear egulator A linear regulator operates by using a voltage-controlled
4.5V to 32V Input High Current LED Driver IC For Buck or Buck-Boost Topology CN5816. Features: SHDN COMP OVP CSP CSN
 4.5V to 32V Input High Current LED Driver IC For Buck or Buck-Boost Topology CN5816 General Description: The CN5816 is a current mode fixed-frequency PWM controller for high current LED applications. The
4.5V to 32V Input High Current LED Driver IC For Buck or Buck-Boost Topology CN5816 General Description: The CN5816 is a current mode fixed-frequency PWM controller for high current LED applications. The
EEL 646 POWER ELECTRONICS II. Issa Batarseh. January 13, 2015
 EEL 646 POWER ELECTRONICS II Issa Batarseh January 13, 2015 Agenda About the course Syllabus Review Course Topics Review of Power Electronics I Questions Introduction (cont d) Introduction (cont d) 5
EEL 646 POWER ELECTRONICS II Issa Batarseh January 13, 2015 Agenda About the course Syllabus Review Course Topics Review of Power Electronics I Questions Introduction (cont d) Introduction (cont d) 5
55:141 Advanced Circuit Techniques Switching Regulators
 55:141 Advanced Circuit Techniques Switching Regulators Material: ecture Notes, Handouts, and Sections of Chapter 11 of Franco A. Kruger 55:141: Advanced Circuit Techniques The University of Iowa Switching
55:141 Advanced Circuit Techniques Switching Regulators Material: ecture Notes, Handouts, and Sections of Chapter 11 of Franco A. Kruger 55:141: Advanced Circuit Techniques The University of Iowa Switching
SGM mA Buck/Boost Charge Pump LED Driver
 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The SGM3140 is a current-regulated charge pump ideal for powering high brightness LEDs for camera flash applications. The charge pump can be set to regulate two current levels for FLASH
GENERAL DESCRIPTION The SGM3140 is a current-regulated charge pump ideal for powering high brightness LEDs for camera flash applications. The charge pump can be set to regulate two current levels for FLASH
The FMMT718 Range, Features and Applications
 The Range, Features and Applications Replacing SOT89, SOT223 and D-Pak Products with High Current SOT23 Bipolar Transistors. David Bradbury Neil Chadderton Designers of surface mount products wishing to
The Range, Features and Applications Replacing SOT89, SOT223 and D-Pak Products with High Current SOT23 Bipolar Transistors. David Bradbury Neil Chadderton Designers of surface mount products wishing to
PART MAX1658C/D MAX1659C/D TOP VIEW
 19-1263; Rev 0; 7/97 350mA, 16.5V Input, General Description The linear regulators maximize battery life by combining ultra-low supply currents and low dropout voltages. They feature Dual Mode operation,
19-1263; Rev 0; 7/97 350mA, 16.5V Input, General Description The linear regulators maximize battery life by combining ultra-low supply currents and low dropout voltages. They feature Dual Mode operation,
High-Efficiency Step-Up Converters for White LED Main and Subdisplay Backlighting MAX1582/MAX1582Y
 19-2783; Rev 2; 8/05 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE High-Efficiency Step-Up Converters General Description The drive up to six white LEDs in series with a constant current to provide display backlighting for
19-2783; Rev 2; 8/05 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE High-Efficiency Step-Up Converters General Description The drive up to six white LEDs in series with a constant current to provide display backlighting for
Semiconductors, ICs and Digital Fundamentals
 Semiconductors, ICs and Digital Fundamentals The Diode The semiconductor phenomena. Diode performance with ac and dc currents. Diode types: General purpose LED Zener The Diode The semiconductor phenomena
Semiconductors, ICs and Digital Fundamentals The Diode The semiconductor phenomena. Diode performance with ac and dc currents. Diode types: General purpose LED Zener The Diode The semiconductor phenomena
REV. B. NOTES 1 At Pin 1. 2 Calculated as average over the operating temperature range. 3 H = Hermetic Metal Can; N = Plastic DIP.
 SPECIFICATIONS (@ V IN = 15 V and 25 C unless otherwise noted.) Model AD584J AD584K AD584L Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit OUTPUT VOLTAGE TOLERANCE Maximum Error 1 for Nominal Outputs of: 10.000
SPECIFICATIONS (@ V IN = 15 V and 25 C unless otherwise noted.) Model AD584J AD584K AD584L Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit OUTPUT VOLTAGE TOLERANCE Maximum Error 1 for Nominal Outputs of: 10.000
EECS 473 Advanced Embedded Systems
 EECS 473 Advanced Embedded Systems Lecture 15: Power review & Switching power supplies (again) A number of slides taken from UT-Austin s EE462L power electronics class. http://users.ece.utexas.edu/~kwasinski/ee462ls14.html
EECS 473 Advanced Embedded Systems Lecture 15: Power review & Switching power supplies (again) A number of slides taken from UT-Austin s EE462L power electronics class. http://users.ece.utexas.edu/~kwasinski/ee462ls14.html
Precision, Micropower, Low-Dropout Voltage References MAX6190 MAX6195/MAX6198
 19-108; Rev 3; /10 Precision, Micropower, General Description The precision, micropower, low-dropout voltage references offer high initial accuracy and very low temperature coefficient through a proprietary
19-108; Rev 3; /10 Precision, Micropower, General Description The precision, micropower, low-dropout voltage references offer high initial accuracy and very low temperature coefficient through a proprietary
Low-Cost, Low-Power, Low-Dropout, SOT23-3 Voltage References
 13-1395; Rev 1; /99 Low-Cost, Low-Power, Low-Dropout, General Description The family of SOT23, low-cost series voltage references meets the cost advantage of shunt references and offers the power-saving
13-1395; Rev 1; /99 Low-Cost, Low-Power, Low-Dropout, General Description The family of SOT23, low-cost series voltage references meets the cost advantage of shunt references and offers the power-saving
MAX8863T/S/R, MAX8864T/S/R. Low-Dropout, 120mA Linear Regulators. General Description. Benefits and Features. Ordering Information.
 General Description The MAX8863T/S/R and low-dropout linear regulators operate from a +2.5V to +6.5V input range and deliver up to 12mA. A PMOS pass transistor allows the low, 8μA supply current to remain
General Description The MAX8863T/S/R and low-dropout linear regulators operate from a +2.5V to +6.5V input range and deliver up to 12mA. A PMOS pass transistor allows the low, 8μA supply current to remain
DT V 400KHz Boost DC-DC Controller FEATURES GENERAL DESCRIPTION APPLICATIONS ORDER INFORMATION
 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The DT9150 is a 5V step-up DC/DC controller designed capable of deliver over 50V Output with proper external N-MOSFET devices. The DT9150 can work with most Power N-MOSFET devices,
GENERAL DESCRIPTION The DT9150 is a 5V step-up DC/DC controller designed capable of deliver over 50V Output with proper external N-MOSFET devices. The DT9150 can work with most Power N-MOSFET devices,
LM386 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier
 LM386 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier General Description The LM386 is a power amplifier designed for use in low voltage consumer applications. The gain is internally set to 20 to keep external part
LM386 Low Voltage Audio Power Amplifier General Description The LM386 is a power amplifier designed for use in low voltage consumer applications. The gain is internally set to 20 to keep external part
A Low Voltage Bandgap Reference Circuit With Current Feedback
 A Low Voltage Bandgap Reference Circuit With Current Feedback Keywords: Bandgap reference, current feedback, FinFET, startup circuit, VDD variation as a low voltage source or uses the differences between
A Low Voltage Bandgap Reference Circuit With Current Feedback Keywords: Bandgap reference, current feedback, FinFET, startup circuit, VDD variation as a low voltage source or uses the differences between
Op Amp Booster Designs
 Op Amp Booster Designs Although modern integrated circuit operational amplifiers ease linear circuit design, IC processing limits amplifier output power. Many applications, however, require substantially
Op Amp Booster Designs Although modern integrated circuit operational amplifiers ease linear circuit design, IC processing limits amplifier output power. Many applications, however, require substantially
Chapter 11 Output Stages
 1 Chapter 11 Output Stages Learning Objectives 2 1) The classification of amplifier output stages 2) Analysis and design of a variety of output-stage types 3) Overview of power amplifiers Introduction
1 Chapter 11 Output Stages Learning Objectives 2 1) The classification of amplifier output stages 2) Analysis and design of a variety of output-stage types 3) Overview of power amplifiers Introduction
LM134/LM234/LM334 3-Terminal Adjustable Current Sources
 3-Terminal Adjustable Current Sources General Description The are 3-terminal adjustable current sources featuring 10,000:1 range in operating current, excellent current regulation and a wide dynamic voltage
3-Terminal Adjustable Current Sources General Description The are 3-terminal adjustable current sources featuring 10,000:1 range in operating current, excellent current regulation and a wide dynamic voltage
FAN5602 Universal (Step-Up/Step-Down) Charge Pump Regulated DC/DC Converter
 August 2009 FAN5602 Universal (Step-Up/Step-Down) Charge Pump Regulated DC/DC Converter Features Low-Noise, Constant-Frequency Operation at Heavy Load High-Efficiency, Pulse-Skip (PFM) Operation at Light
August 2009 FAN5602 Universal (Step-Up/Step-Down) Charge Pump Regulated DC/DC Converter Features Low-Noise, Constant-Frequency Operation at Heavy Load High-Efficiency, Pulse-Skip (PFM) Operation at Light
Low-Power, Low-Drift, +2.5V/+5V/+10V Precision Voltage References
 19-38; Rev 3; 6/7 Low-Power, Low-Drift, +2.5V/+5V/+1V General Description The precision 2.5V, 5V, and 1V references offer excellent accuracy and very low power consumption. Extremely low temperature drift
19-38; Rev 3; 6/7 Low-Power, Low-Drift, +2.5V/+5V/+1V General Description The precision 2.5V, 5V, and 1V references offer excellent accuracy and very low power consumption. Extremely low temperature drift
Non-Synchronous PWM Boost Controller for LED Driver
 Non-Synchronous PWM Boost Controller for LED Driver General Description The is boost topology switching regulator for LED driver. It provides built-in gate driver pin for driving external N-MOSFET. The
Non-Synchronous PWM Boost Controller for LED Driver General Description The is boost topology switching regulator for LED driver. It provides built-in gate driver pin for driving external N-MOSFET. The
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904 Low Power Dual Operational Amplifiers
 LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904 Low Power Dual Operational Amplifiers General Description The LM158 series consists of two independent, high gain, internally frequency compensated operational amplifiers which
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904 Low Power Dual Operational Amplifiers General Description The LM158 series consists of two independent, high gain, internally frequency compensated operational amplifiers which
2A, 23V, 380KHz Step-Down Converter
 2A, 23V, 380KHz Step-Down Converter General Description The is a buck regulator with a built-in internal power MOSFET. It achieves 2A continuous output current over a wide input supply range with excellent
2A, 23V, 380KHz Step-Down Converter General Description The is a buck regulator with a built-in internal power MOSFET. It achieves 2A continuous output current over a wide input supply range with excellent
TOP VIEW. OUTPUT PRESET 2.5V TO 5V 200mA SHDN 3 4 BP GND. Maxim Integrated Products 1
 19-2584; Rev ; 1/2 Low-Noise, Low-Dropout, 2mA General Description The low-noise, low-dropout linear regulator operates from a 2.5V to 6.5V input and delivers up to 2mA. Typical output noise is 3µV RMS,
19-2584; Rev ; 1/2 Low-Noise, Low-Dropout, 2mA General Description The low-noise, low-dropout linear regulator operates from a 2.5V to 6.5V input and delivers up to 2mA. Typical output noise is 3µV RMS,
Positive to Negative Buck-Boost Converter Using LM267X SIMPLE SWITCHER Regulators
 Positive to Negative Buck-Boost Converter Using LM267X SIMPLE SWITCHER Regulators Abstract The 3rd generation Simple Switcher LM267X series of regulators are monolithic integrated circuits with an internal
Positive to Negative Buck-Boost Converter Using LM267X SIMPLE SWITCHER Regulators Abstract The 3rd generation Simple Switcher LM267X series of regulators are monolithic integrated circuits with an internal
Linear DC-DC Conversion Topology and Component Selection
 ECE 480 Application Note Team 7 November 14, 2014 Linear DC-DC Conversion Topology and Component Selection Jacob Brettrager Compact DC-AC Inverter ABSTRACT It is often necessary to convert direct current
ECE 480 Application Note Team 7 November 14, 2014 Linear DC-DC Conversion Topology and Component Selection Jacob Brettrager Compact DC-AC Inverter ABSTRACT It is often necessary to convert direct current
OUTPUT UP TO 300mA C2 TOP VIEW FAULT- DETECT OUTPUT. Maxim Integrated Products 1
 19-1422; Rev 2; 1/1 Low-Dropout, 3mA General Description The MAX886 low-noise, low-dropout linear regulator operates from a 2.5 to 6.5 input and is guaranteed to deliver 3mA. Typical output noise for this
19-1422; Rev 2; 1/1 Low-Dropout, 3mA General Description The MAX886 low-noise, low-dropout linear regulator operates from a 2.5 to 6.5 input and is guaranteed to deliver 3mA. Typical output noise for this
AL8811. Description. Pin Assignments. Features. Applications. Typical Application Diagram. Boost/Buck/Inverting DC-DC CONVERTER AL8811
 Boost/Buck/Inverting DC-DC CONVERTER Description The is a monolithic control circuit containing the primary functions required for DC-to-DC converters. These devices consist of an internal temperature
Boost/Buck/Inverting DC-DC CONVERTER Description The is a monolithic control circuit containing the primary functions required for DC-to-DC converters. These devices consist of an internal temperature
Power Supplies Bandgap Reference Case Study Spring 2017 Lecture 9 1
 Power Supplies Bandgap Reference Case Study 6.101 Spring 2017 Lecture 9 1 Power Supply Designs AC to DC power supplies Linear Switch mode DC to DC power supplies Linear Switch mode Bandgap reference Case
Power Supplies Bandgap Reference Case Study 6.101 Spring 2017 Lecture 9 1 Power Supply Designs AC to DC power supplies Linear Switch mode DC to DC power supplies Linear Switch mode Bandgap reference Case
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE PWM Buck Converters with Bypass FET for N-CDMA/W-CDMA Handsets DAC. Maxim Integrated Products 1
 19-2641; Rev 0; 10/02 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE PWM Buck Converters with Bypass FET General Description The PWM DC-to-DC buck converters are optimized with integrated bypass FET (0.25Ω typ) to provide power
19-2641; Rev 0; 10/02 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE PWM Buck Converters with Bypass FET General Description The PWM DC-to-DC buck converters are optimized with integrated bypass FET (0.25Ω typ) to provide power
LM193/LM293/LM393/LM2903 Low Power Low Offset Voltage Dual Comparators
 LM193/LM293/LM393/LM2903 Low Power Low Offset Voltage Dual Comparators General Description The LM193 series consists of two independent precision voltage comparators with an offset voltage specification
LM193/LM293/LM393/LM2903 Low Power Low Offset Voltage Dual Comparators General Description The LM193 series consists of two independent precision voltage comparators with an offset voltage specification
High Precision 10 V IC Reference AD581
 High Precision 0 V IC Reference FEATURES Laser trimmed to high accuracy 0.000 V ±5 mv (L and U models) Trimmed temperature coefficient 5 ppm/ C maximum, 0 C to 70 C (L model) 0 ppm/ C maximum, 55 C to
High Precision 0 V IC Reference FEATURES Laser trimmed to high accuracy 0.000 V ±5 mv (L and U models) Trimmed temperature coefficient 5 ppm/ C maximum, 0 C to 70 C (L model) 0 ppm/ C maximum, 55 C to
A LDO PRIMER Part I: A REVIEW ON PASS ELEMENT
 A LDO PRIMER Part I: A REVIEW ON PASS ELEMENT Qi Deng Senior Product Marketing Engineer, Analog and Interface Products Division Microchip Technology Inc. A Low Drop Out regulator (LDO) is a linear regulator
A LDO PRIMER Part I: A REVIEW ON PASS ELEMENT Qi Deng Senior Product Marketing Engineer, Analog and Interface Products Division Microchip Technology Inc. A Low Drop Out regulator (LDO) is a linear regulator
Pb-free lead plating; RoHS compliant
 Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Pb-free lead plating; RoHS compliant SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone,
Programmable Single-/Dual-/Triple- Tone Gong Pb-free lead plating; RoHS compliant SAE 800 Bipolar IC Features Supply voltage range 2.8 V to 18 V Few external components (no electrolytic capacitor) 1 tone,
Single Supply, Rail to Rail Low Power FET-Input Op Amp AD820
 a FEATURES True Single Supply Operation Output Swings Rail-to-Rail Input Voltage Range Extends Below Ground Single Supply Capability from + V to + V Dual Supply Capability from. V to 8 V Excellent Load
a FEATURES True Single Supply Operation Output Swings Rail-to-Rail Input Voltage Range Extends Below Ground Single Supply Capability from + V to + V Dual Supply Capability from. V to 8 V Excellent Load
150mA, Low-Dropout Linear Regulator with Power-OK Output
 9-576; Rev ; /99 5mA, Low-Dropout Linear Regulator General Description The low-dropout (LDO) linear regulator operates from a +2.5V to +6.5V input voltage range and delivers up to 5mA. It uses a P-channel
9-576; Rev ; /99 5mA, Low-Dropout Linear Regulator General Description The low-dropout (LDO) linear regulator operates from a +2.5V to +6.5V input voltage range and delivers up to 5mA. It uses a P-channel
Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3.
 Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3. What is difference between electron and hole? 4. Why electrons have
Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3. What is difference between electron and hole? 4. Why electrons have
1.5MHz, 800mA Synchronous Step-Down Regulator
 1.5MHz, 800mA Synchronous Step-Down Regulator General Description The is a high efficiency current mode synchronous buck PWM DC-DC regulator. The internal generated 0.6V precision feedback reference voltage
1.5MHz, 800mA Synchronous Step-Down Regulator General Description The is a high efficiency current mode synchronous buck PWM DC-DC regulator. The internal generated 0.6V precision feedback reference voltage
AT V Synchronous Buck Converter
 38V Synchronous Buck Converter FEATURES DESCRIPTION Wide 8V to 38V Operating Input Range Integrated two 140mΩ Power MOSFET Switches Feedback Voltage : 220mV Internal Soft-Start / VFB Over Voltage Protection
38V Synchronous Buck Converter FEATURES DESCRIPTION Wide 8V to 38V Operating Input Range Integrated two 140mΩ Power MOSFET Switches Feedback Voltage : 220mV Internal Soft-Start / VFB Over Voltage Protection
2A, 23V, 380KHz Step-Down Converter
 2A, 23V, 380KHz Step-Down Converter FP6182 General Description The FP6182 is a buck regulator with a built in internal power MOSFET. It achieves 2A continuous output current over a wide input supply range
2A, 23V, 380KHz Step-Down Converter FP6182 General Description The FP6182 is a buck regulator with a built in internal power MOSFET. It achieves 2A continuous output current over a wide input supply range
LM2660/LM2661 Switched Capacitor Voltage Converter
 LM2660/LM2661 Switched Capacitor Voltage Converter General Description The LM2660/LM2661 CMOS charge-pump voltage converter inverts a positive voltage in the range of 1.5V to 5.5V to the corresponding
LM2660/LM2661 Switched Capacitor Voltage Converter General Description The LM2660/LM2661 CMOS charge-pump voltage converter inverts a positive voltage in the range of 1.5V to 5.5V to the corresponding
Input Stage Concerns. APPLICATION NOTE 656 Design Trade-Offs for Single-Supply Op Amps
 Maxim/Dallas > App Notes > AMPLIFIER AND COMPARATOR CIRCUITS Keywords: single-supply, op amps, amplifiers, design, trade-offs, operational amplifiers Apr 03, 2000 APPLICATION NOTE 656 Design Trade-Offs
Maxim/Dallas > App Notes > AMPLIFIER AND COMPARATOR CIRCUITS Keywords: single-supply, op amps, amplifiers, design, trade-offs, operational amplifiers Apr 03, 2000 APPLICATION NOTE 656 Design Trade-Offs
PHYS 3152 Methods of Experimental Physics I E2. Diodes and Transistors 1
 Part I Diodes Purpose PHYS 3152 Methods of Experimental Physics I E2. In this experiment, you will investigate the current-voltage characteristic of a semiconductor diode and examine the applications of
Part I Diodes Purpose PHYS 3152 Methods of Experimental Physics I E2. In this experiment, you will investigate the current-voltage characteristic of a semiconductor diode and examine the applications of
2A, 23V, 340KHz Synchronous Step-Down Converter
 2A, 23, 340KHz Synchronous Step-Down Converter FP6188 General Description The FP6188 is a synchronous buck regulator with integrated two 0.13Ω power MOSFETs. It achieves 2A continuous output current over
2A, 23, 340KHz Synchronous Step-Down Converter FP6188 General Description The FP6188 is a synchronous buck regulator with integrated two 0.13Ω power MOSFETs. It achieves 2A continuous output current over
Features. Applications. Adjustable Regulator Application. (*See Minimum Load Current Section)
 3A, Low Voltage µcap LDO Regulator General Description The is a 3A low-dropout linear voltage regulator that provides a low voltage, high current output with a minimum of external components. It offers
3A, Low Voltage µcap LDO Regulator General Description The is a 3A low-dropout linear voltage regulator that provides a low voltage, high current output with a minimum of external components. It offers
10µA, Low-Dropout, Precision Voltage References MAX872/MAX874. General Description. Features. Applications. Ordering Information
 9-; Rev 2; 6/97, Low-Dropout, General Description The / precision 2. and 4.96 micropower voltage references consume a maximum of only and operate from supply voltages up to. The combination of ultra-low
9-; Rev 2; 6/97, Low-Dropout, General Description The / precision 2. and 4.96 micropower voltage references consume a maximum of only and operate from supply voltages up to. The combination of ultra-low
LM2596 SIMPLE SWITCHER Power Converter 150 khz 3A Step-Down Voltage Regulator
 SIMPLE SWITCHER Power Converter 150 khz 3A Step-Down Voltage Regulator General Description The series of regulators are monolithic integrated circuits that provide all the active functions for a step-down
SIMPLE SWITCHER Power Converter 150 khz 3A Step-Down Voltage Regulator General Description The series of regulators are monolithic integrated circuits that provide all the active functions for a step-down
(a) BJT-OPERATING MODES & CONFIGURATIONS
 (a) BJT-OPERATING MODES & CONFIGURATIONS 1. The leakage current I CBO flows in (a) The emitter, base and collector leads (b) The emitter and base leads. (c) The emitter and collector leads. (d) The base
(a) BJT-OPERATING MODES & CONFIGURATIONS 1. The leakage current I CBO flows in (a) The emitter, base and collector leads (b) The emitter and base leads. (c) The emitter and collector leads. (d) The base
PS7516. Description. Features. Applications. Pin Assignments. Functional Pin Description
 Description The PS756 is a high efficiency, fixed frequency 550KHz, current mode PWM boost DC/DC converter which could operate battery such as input voltage down to.9.. The converter output voltage can
Description The PS756 is a high efficiency, fixed frequency 550KHz, current mode PWM boost DC/DC converter which could operate battery such as input voltage down to.9.. The converter output voltage can
LM193/LM293/LM393/LM2903 Low Power Low Offset Voltage Dual Comparators
 Low Power Low Offset Voltage Dual Comparators General Description The LM193 series consists of two independent precision voltage comparators with an offset voltage specification as low as 2.0 mv max for
Low Power Low Offset Voltage Dual Comparators General Description The LM193 series consists of two independent precision voltage comparators with an offset voltage specification as low as 2.0 mv max for
SUN MHz, 800mA Synchronous Step-Down Converter GENERAL DESCRIPTION EVALUATION BOARD APPLICATIONS. Typical Application
 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a 1.5MHz constant frequency, slope compensated current mode PWM stepdown converter. The device integrates a main switch and a synchronous rectifier for high efficiency without
GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a 1.5MHz constant frequency, slope compensated current mode PWM stepdown converter. The device integrates a main switch and a synchronous rectifier for high efficiency without
PB63 PB63A. Dual Power Booster Amplifier PB63
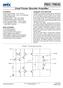 Dual Power Booster Amplifier A FEATURES Wide Supply Range ± V to ±75 V High Output Current Up to 2 A Continuous Programmable Gain High Slew Rate 1 V/µs Typical Programmable Output Current Limit High Power
Dual Power Booster Amplifier A FEATURES Wide Supply Range ± V to ±75 V High Output Current Up to 2 A Continuous Programmable Gain High Slew Rate 1 V/µs Typical Programmable Output Current Limit High Power
LM2686 Regulated Switched Capacitor Voltage Converter
 LM2686 Regulated Switched Capacitor Voltage Converter General Description The LM2686 CMOS charge-pump voltage converter operates as an input voltage doubler and a +5V regulator for an input voltage in
LM2686 Regulated Switched Capacitor Voltage Converter General Description The LM2686 CMOS charge-pump voltage converter operates as an input voltage doubler and a +5V regulator for an input voltage in
Switching vs Linear Regulators
 MICROPOWER DIRECT Even small electronic systems often require a wide variety of DC voltage levels to operate correctly. A system of any complexity will require a power distribution system to insure that
MICROPOWER DIRECT Even small electronic systems often require a wide variety of DC voltage levels to operate correctly. A system of any complexity will require a power distribution system to insure that
AT2596 3A Step Down Voltage Switching Regulators
 FEATURES Standard PSOP-8/TO-220-5L /TO-263-5L Package Adjustable Output Versions Adjustable Version Output Voltage Range 1.23V to 37V V OUT Accuracy is to ± 3% Under Specified Input Voltage the Output
FEATURES Standard PSOP-8/TO-220-5L /TO-263-5L Package Adjustable Output Versions Adjustable Version Output Voltage Range 1.23V to 37V V OUT Accuracy is to ± 3% Under Specified Input Voltage the Output
MP2314S 2A, 24V, 500kHz, High-Efficiency, Synchronous, Step-Down Converter
 The Future of Analog IC Technology DESCRIPTION The MP2314S is a high-efficiency, synchronous, rectified, step-down, switch mode converter with built-in, internal power MOSFETs. It is a next generation
The Future of Analog IC Technology DESCRIPTION The MP2314S is a high-efficiency, synchronous, rectified, step-down, switch mode converter with built-in, internal power MOSFETs. It is a next generation
1.2 V Ultralow Power High PSRR Voltage Reference ADR280
 1.2 V Ultralow Power High PSRR Voltage Reference FEATURES 1.2 V precision output Excellent line regulation: 2 ppm/v typical High power supply ripple rejection: 80 db at 220 Hz Ultralow power supply current:
1.2 V Ultralow Power High PSRR Voltage Reference FEATURES 1.2 V precision output Excellent line regulation: 2 ppm/v typical High power supply ripple rejection: 80 db at 220 Hz Ultralow power supply current:
EXPERIMENT 5 CURRENT AND VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS OF BJT
 EXPERIMENT 5 CURRENT AND VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS OF BJT 1. OBJECTIVES 1.1 To practice how to test NPN and PNP transistors using multimeter. 1.2 To demonstrate the relationship between collector current
EXPERIMENT 5 CURRENT AND VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS OF BJT 1. OBJECTIVES 1.1 To practice how to test NPN and PNP transistors using multimeter. 1.2 To demonstrate the relationship between collector current
EUP A,30V,500KHz Step-Down Converter DESCRIPTION FEATURES APPLICATIONS. Typical Application Circuit
 5A,30V,500KHz Step-Down Converter DESCRIPTION The is current mode, step-down switching regulator capable of driving 5A continuous load with excellent line and load regulation. The operates with an input
5A,30V,500KHz Step-Down Converter DESCRIPTION The is current mode, step-down switching regulator capable of driving 5A continuous load with excellent line and load regulation. The operates with an input
4.2.2 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)
 4.2.2 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) The Metal Oxide Semitonductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) has two modes of operation, the depletion mode, and the enhancement mode.
4.2.2 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) The Metal Oxide Semitonductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) has two modes of operation, the depletion mode, and the enhancement mode.
1A Buck/Boost Charge Pump LED Driver
 1A Buck/Boost Charge Pump LED Driver Description The Buck/Boost charge pump LED driver is designed for powering high brightness white LEDs for camera flash applications. The automatically switches modes
1A Buck/Boost Charge Pump LED Driver Description The Buck/Boost charge pump LED driver is designed for powering high brightness white LEDs for camera flash applications. The automatically switches modes
SGM mA Buck/Boost Charge Pump LED Driver
 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The SGM3140 is a current-regulated charge pump ideal for powering high brightness LEDs for camera flash applications. The charge pump can be set to regulate two current levels for Flash
GENERAL DESCRIPTION The SGM3140 is a current-regulated charge pump ideal for powering high brightness LEDs for camera flash applications. The charge pump can be set to regulate two current levels for Flash
LM2576/LM2576HV Series 3A Step-Down Switching Regulator
 /H /H Series 3A Step-Down Switching Regulator DESCRIPTION The series of regulators are monolithic integrated circuits that provide all the active functions for a step-down (buck) switching regulator, capable
/H /H Series 3A Step-Down Switching Regulator DESCRIPTION The series of regulators are monolithic integrated circuits that provide all the active functions for a step-down (buck) switching regulator, capable
LM78S40 Switching Voltage Regulator Applications
 LM78S40 Switching Voltage Regulator Applications Contents Introduction Principle of Operation Architecture Analysis Design Inductor Design Transistor and Diode Selection Capacitor Selection EMI Design
LM78S40 Switching Voltage Regulator Applications Contents Introduction Principle of Operation Architecture Analysis Design Inductor Design Transistor and Diode Selection Capacitor Selection EMI Design
MICROCONTROLLER BASED BOOST PID MUNAJAH BINTI MOHD RUBAEE
 MICROCONTROLLER BASED BOOST PID MUNAJAH BINTI MOHD RUBAEE This thesis is submitted as partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of Bachelor of Electrical Engineering (Power System) Faculty of
MICROCONTROLLER BASED BOOST PID MUNAJAH BINTI MOHD RUBAEE This thesis is submitted as partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of Bachelor of Electrical Engineering (Power System) Faculty of
The First Step to Success Selecting the Optimal Topology Brian King
 The First Step to Success Selecting the Optimal Topology Brian King 1 What will I get out of this session? Purpose: Inside the Box: General Characteristics of Common Topologies Outside the Box: Unique
The First Step to Success Selecting the Optimal Topology Brian King 1 What will I get out of this session? Purpose: Inside the Box: General Characteristics of Common Topologies Outside the Box: Unique
MP A, 36V, 700KHz Step-Down Converter with Programmable Output Current Limit
 The Future of Analog IC Technology MP2490 1.5A, 36V, 700KHz Step-Down Converter with Programmable Output Current Limit DESCRIPTION The MP2490 is a monolithic step-down switch mode converter with a programmable
The Future of Analog IC Technology MP2490 1.5A, 36V, 700KHz Step-Down Converter with Programmable Output Current Limit DESCRIPTION The MP2490 is a monolithic step-down switch mode converter with a programmable
