Lab Equipment EECS 311 Fall 2009
|
|
|
- Naomi Gilmore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab Equipment EECS 311 Fall 2009 Contents Lab Equipment Overview pg. 1 Lab Components.. pg. 4 Probe Compensation... pg. 8 Finite Instrumentation Impedance. pg.10 Simulation Tools..... pg Laboratory Equipment 1.1 Proto-boards A proto-board provides a fast way of hooking up circuits with no soldering. The protoboard consists of an array of interconnected holes. Connections are made by pushing leads into the holes. When using a proto-board, only straight wires of small diameter (a resistor lead or smaller) should be inserted into the holes. In general, when building a proto-board circuit, a good rule is "the fewer the wires, the better." A messy circuit is likely to perform poorly and be a pain to debug. Some of the labs (the design labs in particular) may require more than one testing session to complete. For these labs, it is advantageous to be able to keep your circuits constructed between testing sessions. For this purpose, you may check out a proto-board from your lab GSI. Note that this proto-board must be returned prior to the final. If it is not returned before the final, you will receive a grade of "incomplete" for the course.
2 Page 2 of Oscilloscopes General An oscilloscope is the most useful piece of test equipment in the laboratory. Basically, it is a device which graphically displays time-varying voltage signals. In particular, it is most often used to display voltages as a function of time. Each of the stations in the EECS 311 laboratory is equipped with an oscilloscope. You should already be familiar with the use of oscilloscopes from previous required courses (e.g., EECS 215). To best familiarize yourself with the oscilloscope used in the EECS 311 laboratory, browse through the "User's Guide" located in the lab. Some Helpful Pointers. The following usage pointers are helpful in insuring the most accurate circuit measurements in the EECS 311 laboratory: (i) Use an oscilloscope probe whenever possible. The probe may or may not have a built in attenuator, and the oscilloscope has a setting that will scale the measured voltage accordingly. This feature is under Utilities. (ii) Make sure each probe is grounded. (iii) Compensate the oscilloscope probe frequently (see page 8). (iv) Always know the location of the ground reference located on the display. (v) Use an external trigger whenever possible. 1.3 Digital Multimeters (DMM's) Voltage Measurements. A DMM can be used to make measurements of both AC and DC voltages. The measurement procedure involves setting the DMM to the appropriate scale, selecting AC or DC volts, and connecting the probe between the two points to be measured. If set to the wrong scale, the display will usually flash or give some other error indication. Some points to keep in mind: (i) The EECS 311 DMM's will usually not load the circuit excessively, because they have an input impedance of several MΩ's. (ii) Voltage measurements are made in parallel. (iii) When reading AC volts, most meters will read true RMS only if the AC voltage is a sine wave. Some DMM's, usually marked "True RMS", will read the RMS voltage of arbitrary waveforms. (iv) When reading AC volts, the DMM has a fairly low upper frequency limit, usually a couple of khz or less. Consult the instruction manual for further details.
3 Page 3 of 10 Resistance Measurements To measure resistance, set the DMM to ohms and select the appropriate scale. Connect the probes across the resistance to be measured. Some fine points: (i) When taking data using the high resistance scale, make sure not to handle the probe tips. Handling will add your skin resistance in parallel with the resistance to be measured, which will cause the DMM to read a value lower than the actual resistance. (ii) Only certain scales will supply enough current to forward bias a diode. These are marked with a diode symbol. (iii) Resistance measurements should be made outside of the circuit whenever possible. Any in-circuit measurements made should be considered suspect. Current Measurements When measuring current, it is necessary to set the DMM to ma and to select the appropriate scale. Note that the probes are connected to a different set of jacks for current measurements. One must always remember to make current measurements in SERIES, not parallel. Connecting the meter across a voltage is likely to blow a fuse in the meter. Both AC and DC current can be measured. The same limitations as those on AC voltage measurements apply here. 1.4 Function Generators Function generators are so named because they produce various voltage waveforms. The most common are square, sine, and triangle. The function generators in the EECS 311 lab have various triggering and gating functions. To adjust the peak-to-peak voltage of the output signal, AMPLITUDE controls are provided. The DC level of the signal can also be adjusted with the OFFSET control. To adjust the frequency, use the FREQUENCY button. There are three ways to adjust the output of the function generator. First, press the button of the parameter you would like to change. To change the value (ie frequency, amplitude, or offset) either: (ii) Turn the knob value. clockwise to increase the value or counterclockwise to decrease the (ii) Use the arrow buttons on the function generator: ( ) up arrow = increase value ( ) down arrow = decease value ( ) left and right arrows, select digit to change
4 Page 4 of 10 (iii) Enter the desired value directly using the Enter Number button. To do this, press Enter Number. Then enter the value you want using the numeric keypad. When you are done, press Enter. Of particular interest is the external triggering output. Whenever possible, this signal should be directly connected to the external triggering input of the oscilloscope. 1.5 Capacitance Meters In EECS 311, we will only be concerned with simple capacitance meters. To use a capacitance meter: (i) Depress the measurement button without anything connected and use the OFFSET or ZERO control to zero the display. (ii) Insert the device to be tested into the slots on the front of the capacitance meter. Keep any leads as short as possible. (iii) Depress the measurement button. 1.6 Electronic Components Resistors The resistors used in the EECS 311 lab are all 5%, 1/4 Watt carbon film resistors. "5%" refers to the resistance tolerance at room temperature (i.e., how far off from the stated value it may be), "1/4 Watt" refers to the maximum safe power dissipation, and "carbon film" refers to the resistor construction. The resistance value is indicated by color coded bands. Learning to read the color code will save you both grief and time in the lab (since you will not have to use the DMM to measure every time you need to know an approximate resistor value). The colors represent digits as indicated in Table I.
5 Page 5 of 10 The actual value of the bands depends on their relative position. The right most band indicates tolerance. To read the color code, hold the resistor so the gold or silver tolerance band is on the right. (20% resistors do not have a gold or silver tolerance color band, however, they have a space where the band would be). Now, reading from left to right, the first two color bands are read directly as numerals. The third band (sometimes called the multiplier band) indicates the number of zeros to be concatenated on the first two digits. For example, if you read BROWN-GREEN-ORANGE-GOLD, the resistor would be of 5% tolerance and would have the value 15000, or 15 kω. In other words, "1", "5", and 3 zeros (for orange) following. BROWN-BLACK-YELLOW-SILVER would be a 10% , or 100 kω resistor. In other words, "1", "0", and 4 zeros (for yellow) following. Capacitors The marking for capacitors is not nearly as standardized as that for resistors. The most -12 common method is to mark the capacitor in picofarads (pf = 10 Farads) using the same format as resistors, but with numerals instead of colors. For example, 101 indicates 100 pf ("1", "0", and 1 zero following), 100 would be 10 pf. Ask your GSI for help in identifying capacitors. We will use two basic types of capacitors in the EECS 311 lab: ceramic and electrolytic. Ceramic caps are relatively temperature stable and have the advantage of being nonpolarized; that is, they can be charged to either polarity. Electrolytic capacitors, on the other hand, can only be subjected to a specific DC voltage polarity. The polarity is marked on the
6 Page 6 of 10 outside of the capacitor. DO NOT hook up an electrolytic capacitor backwards, as this will almost certainly damage the capacitor. (It could possibly explode.) Electrolytic capacitors have the advantage of possessing a high capacitance per unit volume; i.e., the largest valued capacitors will often be electrolytic. Semiconductor Diodes and Transistors. The diodes used in the EECS 311 lab are general purpose signal diodes and are marked as shown in Fig. 1. Transistors do not have standard markings or pinouts. Ask your GSI for help in identifying transistor pinouts.
7 Page 7 of 10 Integrated Circuits. The only integrated circuit used in the EECS 311 lab is the 741 op amp. Different manufacturers make 741's with different prefixes. To name a few, ua741 indicates that the chip was manufactured by Fairchild Semiconductor, NE741 indicates Signetics, and LM741 indicates National Semiconductor. Despite different manufacturers, all of these chips are functionally identical. The 741 comes in an 8- or 14-pin DIP (Dual In-line Package). The pinout for a 741 is given in Fig. 2. The pin numbers in any DIP package can be determined by first looking down on the IC such that the notch or dot is facing left. Pin 1 is now in the lower left hand corner. The pin numbers increase as you count counterclockwise around the IC starting at pin 1. This is illustrated in the example sketches of the 741 in Fig. 2. More information on the actual 741 op amps to be used in the lab, as well as all of the other electronic components used, can be found in the data sheets presented in Appendix A. Make sure you consult the data sheet whenever you are unsure of the pinout for a particular device.
8 Page 8 of 10 2 Probe Compensation Whenever measurements of a physical system are made, the act of measurement alters the system of interest, thus, altering the value of the desired parameter. For the case of the laboratory measurements to be made in EECS 311, all of the measurement equipment exhibits finite input/output impedance, which can load the circuits being measured, changing their properties and altering the actual values being measured. Resistive loading of amplifiers is a topic for EECS 311 lecture. As will be seen in this lab, capacitors can also significantly load circuits (as can inductors). As an example of loading by measurement, consider the use of an oscilloscope to measure the output of a low-pass filter consisting of R 1 and C 1. The required experimental setup for this measurement is depicted in Fig. PL1.2(a) below. Figure PL1.1 Figure PL1.2 Figure PL1.2(b) is an equivalent circuit schematic for the experimental set-up of Fig. PL1.2(a). The combined capacitance of the oscilloscope and the coaxial cable is represented by C2 = 50 pf, and the input resistance of the oscilloscope is modeled by Rosc = 1 MΩ.
9 Page 9 of 10 To minimize the effects of loading, oscilloscope probes are often built as compensated attenuators. The equivalent circuit schematic for a typical compensated attenuator is shown in Fig. PL1.3. Note that V i in Fig. PL1.3 is not the V i in Fig. PL1.1 and Fig. PL1.2. The voltage Vi in Fig. PL1.3 is the voltage across C 1 in Fig. PL1.1 and Fig. PL1.2. To Test Circuit (a) Derive an expression for the rise time of the compensated attenuator for the case when Ccomp = 0. (b) Derive an expression for Ccomp based on the values of Rbuff, R osc, and C 2 to yield the following transfer function: Note that due to the addition of Ccomp, the rise time of the circuit can theoretically be made zero. Compensating the Oscilloscope Probe The first step in any lab is to organize the required equipment and to COMPENSATE THE OSCILLOSCOPE PROBE. The probe can be easily compensated in the following way: (i) Connect the probe to the test point located on the front of the HP oscilloscope. The test point provides a square wave of known properties. The scope must be DC coupled for this operation. (ii) Set the triggering to normal and adjust the trigger level for a stable display. (iii) Adjust the sweep time and vertical sensitivity to display about two cycles of the square wave. (iv) With an adjustment tool, gently adjust the compensation control on the probe while observing the image displayed on the screen. Continue to adjust the probe until the square wave has "as flat a top as possible", as indicated in the far right of Fig. L1.1.
10 Page 10 of Finite Instrumentation Impedance Depending on the user defined load impedance, the function generator will scale the output voltage it generates to achieve the desired Vout. For instance, if the load is defined to be 50 ohms and the generator is set to output 1V, then it will in reality output 2V assuming that Rgen is also 50 ohms. However, if the load is defined to be in high-z, then Vgen will only be 1V. 4 - Simulation Tools As mentioned in lecture, EECS 311 will utilize the Cadence software package for schematic entry and simulation of circuits. Virtuoso is the package for circuit schematic entry, while Spectre is the package for circuit simulation. Feel free to ask your GSI for help in using the Cadence tools. Within this Laboratory Manual there are many references to the word SPICE. SPICE is the first extensive circuit simulator created in the 70's. Today, virtually all circuit simulator programs, including Spectre, use SPICE within their kernels. Thus, the device models used by Spectre and other circuit simulation tools are basically SPICE models, as they conform to the strict SPICE format. You will be provided with a tutorial covering basic use of the Cadence software.
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 2 BASIC CIRCUIT ELEMENTS OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to familiarize the student with
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 2 BASIC CIRCUIT ELEMENTS OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to familiarize the student with
AME140 Lab #2 INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRONIC TEST EQUIPMENT AND BASIC ELECTRONICS MEASUREMENTS
 INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRONIC TEST EQUIPMENT AND BASIC ELECTRONICS MEASUREMENTS The purpose of this document is to guide students through a few simple activities to increase familiarity with basic electronics
INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRONIC TEST EQUIPMENT AND BASIC ELECTRONICS MEASUREMENTS The purpose of this document is to guide students through a few simple activities to increase familiarity with basic electronics
LAB 1: Familiarity with Laboratory Equipment (_/10)
 LAB 1: Familiarity with Laboratory Equipment (_/10) PURPOSE o gain familiarity with basic laboratory equipment oscilloscope, oscillator, multimeter and electronic components. EQUIPMEN (i) Oscilloscope
LAB 1: Familiarity with Laboratory Equipment (_/10) PURPOSE o gain familiarity with basic laboratory equipment oscilloscope, oscillator, multimeter and electronic components. EQUIPMEN (i) Oscilloscope
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. EEC 180A DIGITAL SYSTEMS I Winter 2015
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC 180A DIGITAL SYSTEMS I Winter 2015 LAB 2: INTRODUCTION TO LAB INSTRUMENTS The purpose of this lab is to introduce the
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EEC 180A DIGITAL SYSTEMS I Winter 2015 LAB 2: INTRODUCTION TO LAB INSTRUMENTS The purpose of this lab is to introduce the
LAB I. INTRODUCTION TO LAB EQUIPMENT
 1. OBJECTIVE LAB I. INTRODUCTION TO LAB EQUIPMENT In this lab you will learn how to properly operate the oscilloscope Agilent MSO6032A, the Keithley Source Measure Unit (SMU) 2430, the function generator
1. OBJECTIVE LAB I. INTRODUCTION TO LAB EQUIPMENT In this lab you will learn how to properly operate the oscilloscope Agilent MSO6032A, the Keithley Source Measure Unit (SMU) 2430, the function generator
Laboratory Equipment Instruction Manual 2011
 University of Toronto Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Instrumentation Laboratory GB341 Laboratory Equipment Instruction Manual 2011 Page 1. Wires and Cables A-2 2. Protoboard A-3 3. DC
University of Toronto Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Instrumentation Laboratory GB341 Laboratory Equipment Instruction Manual 2011 Page 1. Wires and Cables A-2 2. Protoboard A-3 3. DC
Bring your textbook to lab.
 Bring your textbook to lab. Electrical & Computer Engineering Department ECE 2100 Experiment No. 11 Introduction to MOSFET Transistors A. Stolp, 4/3/01 rev,4/6/03 Minimum required points = 46 Recommend
Bring your textbook to lab. Electrical & Computer Engineering Department ECE 2100 Experiment No. 11 Introduction to MOSFET Transistors A. Stolp, 4/3/01 rev,4/6/03 Minimum required points = 46 Recommend
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 4 SINGLE STAGE AMPLIFIER
 University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 4 SINGLE STAGE AMPLIFIER Issued 10/27/2008 Report due in Lecture 11/10/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize a 2N3904 NPN
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 4 SINGLE STAGE AMPLIFIER Issued 10/27/2008 Report due in Lecture 11/10/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize a 2N3904 NPN
Group: Names: Resistor Band Colors Measured Value ( ) R 1 : 1k R 2 : 1k R 3 : 2k R 4 : 1M R 5 : 1M
 2.4 Laboratory Procedure / Summary Sheet Group: Names: (1) Select five separate resistors whose nominal values are listed below. Record the band colors for each resistor in the table below. Then connect
2.4 Laboratory Procedure / Summary Sheet Group: Names: (1) Select five separate resistors whose nominal values are listed below. Record the band colors for each resistor in the table below. Then connect
CHAPTER 6. Motor Driver
 CHAPTER 6 Motor Driver In this lab, we will construct the circuitry that your robot uses to drive its motors. However, before testing the motor circuit we will begin by making sure that you are able to
CHAPTER 6 Motor Driver In this lab, we will construct the circuitry that your robot uses to drive its motors. However, before testing the motor circuit we will begin by making sure that you are able to
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARIZATION WITH COMMONLY USED INSTRUMENTATION
 Objectives: ME 365 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARIZATION WITH COMMONLY USED INSTRUMENTATION The primary goal of this laboratory is to study the operation and limitations of several commonly used pieces of instrumentation:
Objectives: ME 365 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARIZATION WITH COMMONLY USED INSTRUMENTATION The primary goal of this laboratory is to study the operation and limitations of several commonly used pieces of instrumentation:
ECE 2274 Lab 1 (Intro)
 ECE 2274 Lab 1 (Intro) Richard Dumene: Spring 2018 Revised: Richard Cooper: Spring 2018 Forward (DO NOT TURN IN) The purpose of this lab course is to familiarize you with high-end lab equipment, and train
ECE 2274 Lab 1 (Intro) Richard Dumene: Spring 2018 Revised: Richard Cooper: Spring 2018 Forward (DO NOT TURN IN) The purpose of this lab course is to familiarize you with high-end lab equipment, and train
Chapter 1: DC circuit basics
 Chapter 1: DC circuit basics Overview Electrical circuit design depends first and foremost on understanding the basic quantities used for describing electricity: Voltage, current, and power. In the simplest
Chapter 1: DC circuit basics Overview Electrical circuit design depends first and foremost on understanding the basic quantities used for describing electricity: Voltage, current, and power. In the simplest
Electric Circuit II Lab Manual Session #1
 Department of Electrical Engineering Electric Circuit II Lab Manual Session #1 Subject Lecturer Dr. Yasser Hegazy Name:-------------------------------------------------- Group:--------------------------------------------------
Department of Electrical Engineering Electric Circuit II Lab Manual Session #1 Subject Lecturer Dr. Yasser Hegazy Name:-------------------------------------------------- Group:--------------------------------------------------
Physics 323. Experiment # 1 - Oscilloscope and Breadboard
 Physics 323 Experiment # 1 - Oscilloscope and Breadboard Introduction In order to familiarise yourself with the laboratory equipment, a few simple experiments are to be performed. References: XYZ s of
Physics 323 Experiment # 1 - Oscilloscope and Breadboard Introduction In order to familiarise yourself with the laboratory equipment, a few simple experiments are to be performed. References: XYZ s of
Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks
 OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
EE 368 Electronics Lab. Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2)
 EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
Precalculations Individual Portion Introductory Lab: Basic Operation of Common Laboratory Instruments
 Name: Date of lab: Section number: M E 345. Lab 1 Precalculations Individual Portion Introductory Lab: Basic Operation of Common Laboratory Instruments Precalculations Score (for instructor or TA use only):
Name: Date of lab: Section number: M E 345. Lab 1 Precalculations Individual Portion Introductory Lab: Basic Operation of Common Laboratory Instruments Precalculations Score (for instructor or TA use only):
ECE 53A: Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering I
 ECE 53A: Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Assignment #1: Instrument Operation, Basic Resistor Measurements and Kirchhoff s Laws Fall 2007 General Guidelines: - Record data and observations
ECE 53A: Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Assignment #1: Instrument Operation, Basic Resistor Measurements and Kirchhoff s Laws Fall 2007 General Guidelines: - Record data and observations
Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06)
 Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06) Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied
Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06) Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied
Chapter 9: Operational Amplifiers
 Chapter 9: Operational Amplifiers The Operational Amplifier (or op-amp) is the ideal, simple amplifier. It is an integrated circuit (IC). An IC contains many discrete components (resistors, capacitors,
Chapter 9: Operational Amplifiers The Operational Amplifier (or op-amp) is the ideal, simple amplifier. It is an integrated circuit (IC). An IC contains many discrete components (resistors, capacitors,
Prepare for this experiment!
 Notes on Experiment #10 Prepare for this experiment! Read the P-Amp Tutorial before going on with this experiment. For any Ideal p Amp with negative feedback you may assume: V - = V + (But not necessarily
Notes on Experiment #10 Prepare for this experiment! Read the P-Amp Tutorial before going on with this experiment. For any Ideal p Amp with negative feedback you may assume: V - = V + (But not necessarily
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2009 LAB 2 NON IDEAL OPAMPS
 University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2009 LAB 2 NON IDEAL OPAMPS Issued 10/5/2008 Pre Lab Completed 10/12/2008 Lab Due in Lecture 10/21/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2009 LAB 2 NON IDEAL OPAMPS Issued 10/5/2008 Pre Lab Completed 10/12/2008 Lab Due in Lecture 10/21/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize
The University of Jordan Mechatronics Engineering Department Electronics Lab.( ) Experiment 1: Lab Equipment Familiarization
 The University of Jordan Mechatronics Engineering Department Electronics Lab.(0908322) Experiment 1: Lab Equipment Familiarization Objectives To be familiar with the main blocks of the oscilloscope and
The University of Jordan Mechatronics Engineering Department Electronics Lab.(0908322) Experiment 1: Lab Equipment Familiarization Objectives To be familiar with the main blocks of the oscilloscope and
Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization
 Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied to the
Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied to the
EGR Laboratory 3 - Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps)
 EGR 215 - Laboratory 3 - Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps) Authors C. Ramon, R.D. Christie, K.F. Böhringer of the University of Washington Objectives At the end of this lab, you will be able to: Construct
EGR 215 - Laboratory 3 - Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps) Authors C. Ramon, R.D. Christie, K.F. Böhringer of the University of Washington Objectives At the end of this lab, you will be able to: Construct
Equipment: You will use the bench power supply, function generator and oscilloscope.
 EE203 Lab #0 Laboratory Equipment and Measurement Techniques Purpose Your objective in this lab is to gain familiarity with the properties and effective use of the lab power supply, function generator
EE203 Lab #0 Laboratory Equipment and Measurement Techniques Purpose Your objective in this lab is to gain familiarity with the properties and effective use of the lab power supply, function generator
Physics 120 Lab 6 (2018) - Field Effect Transistors: Ohmic Region
 Physics 120 Lab 6 (2018) - Field Effect Transistors: Ohmic Region The field effect transistor (FET) is a three-terminal device can be used in two extreme ways as an active element in a circuit. One is
Physics 120 Lab 6 (2018) - Field Effect Transistors: Ohmic Region The field effect transistor (FET) is a three-terminal device can be used in two extreme ways as an active element in a circuit. One is
DC Circuits, Ohm's Law and Multimeters Physics 246
 DC Circuits, Ohm's Law and Multimeters Physics 246 Theory: In this lab we will learn the use of multimeters, verify Ohm s law, and study series and parallel combinations of resistors and capacitors. For
DC Circuits, Ohm's Law and Multimeters Physics 246 Theory: In this lab we will learn the use of multimeters, verify Ohm s law, and study series and parallel combinations of resistors and capacitors. For
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING
 ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING Objectives: To familiarize the student with the concepts of signal conditioning. At the end of the lab, the student should be able to: Understand the
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING Objectives: To familiarize the student with the concepts of signal conditioning. At the end of the lab, the student should be able to: Understand the
Name: Resistors and Basic Resistive Circuits. Objective: To gain experience with data acquisition proto-boards physical resistors. Table of Contents:
 Objective: To gain experience with data acquisition proto-boards physical resistors Table of Contents: Name: Resistors and Basic Resistive Circuits Pre-Lab Assignment 1 Background 2 National Instruments
Objective: To gain experience with data acquisition proto-boards physical resistors Table of Contents: Name: Resistors and Basic Resistive Circuits Pre-Lab Assignment 1 Background 2 National Instruments
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department. EE 204 Electrical Engineering Lab
 University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 204 Electrical Engineering Lab EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT DEVICES Prepared by: Prof. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 204 Electrical Engineering Lab EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT DEVICES Prepared by: Prof. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT
Practical 2P12 Semiconductor Devices
 Practical 2P12 Semiconductor Devices What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some points from the lecture courses on Semiconductor Materials and Semiconductor Devices
Practical 2P12 Semiconductor Devices What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some points from the lecture courses on Semiconductor Materials and Semiconductor Devices
Experiment A8 Electronics III Procedure
 Experiment A8 Electronics III Procedure Deliverables: checked lab notebook, plots Overview Electronics have come a long way in the last century. Using modern fabrication techniques, engineers can now print
Experiment A8 Electronics III Procedure Deliverables: checked lab notebook, plots Overview Electronics have come a long way in the last century. Using modern fabrication techniques, engineers can now print
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 02139
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No. READING ASSIGNMENT
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No. READING ASSIGNMENT
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II
 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II LAB 5 INTRO: INTRODUCTION TO INVERTING AMPLIFIERS AND OTHER OP-AMP CIRCUITS GOALS In this lab, you will characterize the gain and frequency dependence of inverting op-amp
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II LAB 5 INTRO: INTRODUCTION TO INVERTING AMPLIFIERS AND OTHER OP-AMP CIRCUITS GOALS In this lab, you will characterize the gain and frequency dependence of inverting op-amp
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 Name: MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.091 Hands-On Introduction to EE Lab Skills Laboratory No. 1 Oscilloscopes, Multimeter, Function Generator IAP 2008 1 Objective In this laboratory, you will
Name: MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.091 Hands-On Introduction to EE Lab Skills Laboratory No. 1 Oscilloscopes, Multimeter, Function Generator IAP 2008 1 Objective In this laboratory, you will
Physics 310 Lab 2 Circuit Transients and Oscilloscopes
 Physics 310 Lab 2 Circuit Transients and Oscilloscopes Equipment: function generator, oscilloscope, two BNC cables, BNC T connector, BNC banana adapter, breadboards, wire packs, some banana cables, three
Physics 310 Lab 2 Circuit Transients and Oscilloscopes Equipment: function generator, oscilloscope, two BNC cables, BNC T connector, BNC banana adapter, breadboards, wire packs, some banana cables, three
ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics
 ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics 1 Linear System Characteristics The first part of this experiment will serve as an introduction to the use of the spectrum analyzer in making absolute
ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics 1 Linear System Characteristics The first part of this experiment will serve as an introduction to the use of the spectrum analyzer in making absolute
10: AMPLIFIERS. Circuit Connections in the Laboratory. Op-Amp. I. Introduction
 10: AMPLIFIERS Circuit Connections in the Laboratory From now on you will construct electrical circuits and test them. The usual way of constructing circuits would be to solder each electrical connection
10: AMPLIFIERS Circuit Connections in the Laboratory From now on you will construct electrical circuits and test them. The usual way of constructing circuits would be to solder each electrical connection
A Manual explaining the basic Components, Devices and Experimental Methods employed in an Electronic Instrumentation Lab for Scientists. MULTIMETER.
 A Manual explaining the basic Components, Devices and Experimental Methods employed in an Electronic Instrumentation ab for Scientists. MUTIMETER. Digital Multi Meters (or DMMs abbreviated) and Digital
A Manual explaining the basic Components, Devices and Experimental Methods employed in an Electronic Instrumentation ab for Scientists. MUTIMETER. Digital Multi Meters (or DMMs abbreviated) and Digital
EECE 2413 Electronics Laboratory
 EECE 2413 Electronics Laboratory Lab #2: Diode Circuits Goals In this lab you will become familiar with several different types of pn-junction diodes. These include silicon and germanium junction diodes,
EECE 2413 Electronics Laboratory Lab #2: Diode Circuits Goals In this lab you will become familiar with several different types of pn-junction diodes. These include silicon and germanium junction diodes,
Physics 120 Lab 1 (2018) - Instruments and DC Circuits
 Physics 120 Lab 1 (2018) - Instruments and DC Circuits Welcome to the first laboratory exercise in Physics 120. Your state-of-the art equipment includes: Digital oscilloscope w/usb output for SCREENSHOTS.
Physics 120 Lab 1 (2018) - Instruments and DC Circuits Welcome to the first laboratory exercise in Physics 120. Your state-of-the art equipment includes: Digital oscilloscope w/usb output for SCREENSHOTS.
Introduction to basic laboratory instruments
 BEE 233 Laboratory-1 Introduction to basic laboratory instruments 1. Objectives To learn safety procedures in the laboratory. To learn how to use basic laboratory instruments: power supply, function generator,
BEE 233 Laboratory-1 Introduction to basic laboratory instruments 1. Objectives To learn safety procedures in the laboratory. To learn how to use basic laboratory instruments: power supply, function generator,
EK307 Introduction to the Lab
 EK307 Introduction to the Lab Learning to Use the Test Equipment Laboratory Goal: Become familiar with the test equipment in the electronics laboratory (PHO105). Learning Objectives: Voltage source and
EK307 Introduction to the Lab Learning to Use the Test Equipment Laboratory Goal: Become familiar with the test equipment in the electronics laboratory (PHO105). Learning Objectives: Voltage source and
Practical 2P12 Semiconductor Devices
 Practical 2P12 Semiconductor Devices What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some points from the lecture courses on Semiconductor Materials and Semiconductor Devices
Practical 2P12 Semiconductor Devices What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some points from the lecture courses on Semiconductor Materials and Semiconductor Devices
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 02139
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019 Spring Term 00.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No.
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019 Spring Term 00.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No.
Laboratory 2 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore)
 Laboratory 2 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore) Instrument Familiarization and Basic Electrical Relations Required Components: 2 1k resistors 2 1M resistors 1 2k resistor Objectives This exercise is designed
Laboratory 2 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore) Instrument Familiarization and Basic Electrical Relations Required Components: 2 1k resistors 2 1M resistors 1 2k resistor Objectives This exercise is designed
Notes on Experiment #1
 Notes on Experiment #1 Bring graph paper (cm cm is best) From this week on, be sure to print a copy of each experiment and bring it with you to lab. There will not be any experiment copies available in
Notes on Experiment #1 Bring graph paper (cm cm is best) From this week on, be sure to print a copy of each experiment and bring it with you to lab. There will not be any experiment copies available in
Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response
 ES 3: Introduction to Electrical Systems Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response I. GOALS: In this laboratory, you will build an audio amplifier using an LM386 integrated circuit.
ES 3: Introduction to Electrical Systems Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response I. GOALS: In this laboratory, you will build an audio amplifier using an LM386 integrated circuit.
LAB II. INTRODUCTION TO LAB EQUIPMENT
 1. OBJECTIVE LAB II. INTRODUCTION TO LAB EQUIPMENT In this lab you will learn how to properly operate the oscilloscope Keysight DSOX1102A, the Keithley Source Measure Unit (SMU) 2430, the function generator
1. OBJECTIVE LAB II. INTRODUCTION TO LAB EQUIPMENT In this lab you will learn how to properly operate the oscilloscope Keysight DSOX1102A, the Keithley Source Measure Unit (SMU) 2430, the function generator
Experiment 3 Ohm s Law
 Experiment 3 Ohm s Law The goals of Experiment 3 are: To identify resistors based upon their color code. To construct a two-resistor circuit using proper wiring techniques. To measure the DC voltages and
Experiment 3 Ohm s Law The goals of Experiment 3 are: To identify resistors based upon their color code. To construct a two-resistor circuit using proper wiring techniques. To measure the DC voltages and
BME 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers
 BME 351 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers Learning Objectives: Be familiar with the operation of a basic op-amp circuit. Be familiar with the characteristics of both ideal and real
BME 351 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers Learning Objectives: Be familiar with the operation of a basic op-amp circuit. Be familiar with the characteristics of both ideal and real
Combinational logic: Breadboard adders
 ! ENEE 245: Digital Circuits & Systems Lab Lab 1 Combinational logic: Breadboard adders ENEE 245: Digital Circuits and Systems Laboratory Lab 1 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are the following:
! ENEE 245: Digital Circuits & Systems Lab Lab 1 Combinational logic: Breadboard adders ENEE 245: Digital Circuits and Systems Laboratory Lab 1 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are the following:
LAB I. INTRODUCTION TO LAB EQUIPMENT
 LAB I. INTRODUCTION TO LAB EQUIPMENT 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you will learn how to properly operate the basic bench equipment used for characterizing active devices: 1. Oscilloscope (Keysight DSOX 1102A),
LAB I. INTRODUCTION TO LAB EQUIPMENT 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you will learn how to properly operate the basic bench equipment used for characterizing active devices: 1. Oscilloscope (Keysight DSOX 1102A),
Penrose Quantizer Assembly Guide
 Penrose Quantizer Assembly Guide Schematic and BOM The schematic can be found here: www.sonic-potions.com/public/penrosequantizerschematic.pdf The BOM is available at google docs: Link to BOM Prepare the
Penrose Quantizer Assembly Guide Schematic and BOM The schematic can be found here: www.sonic-potions.com/public/penrosequantizerschematic.pdf The BOM is available at google docs: Link to BOM Prepare the
Lab #1 Lab Introduction
 Cir cuit s 212 Lab Lab #1 Lab Introduction Special Information for this Lab s Report Because this is a one-week lab, please hand in your lab report for this lab at the beginning of next week s lab. The
Cir cuit s 212 Lab Lab #1 Lab Introduction Special Information for this Lab s Report Because this is a one-week lab, please hand in your lab report for this lab at the beginning of next week s lab. The
Chapter 1: DC circuit basics
 Chapter 1: DC circuit basics Overview Electrical circuit design depends first and foremost on understanding the basic quantities used for describing electricity: voltage, current, and power. In the simplest
Chapter 1: DC circuit basics Overview Electrical circuit design depends first and foremost on understanding the basic quantities used for describing electricity: voltage, current, and power. In the simplest
Electronics. RC Filter, DC Supply, and 555
 Electronics RC Filter, DC Supply, and 555 0.1 Lab Ticket Each individual will write up his or her own Lab Report for this two-week experiment. You must also submit Lab Tickets individually. You are expected
Electronics RC Filter, DC Supply, and 555 0.1 Lab Ticket Each individual will write up his or her own Lab Report for this two-week experiment. You must also submit Lab Tickets individually. You are expected
Experiment A8 Electronics III Procedure
 Experiment A8 Electronics III Procedure Deliverables: checked lab notebook, plots Overview Electronics have come a long way in the last century. Using modern fabrication techniques, engineers can now print
Experiment A8 Electronics III Procedure Deliverables: checked lab notebook, plots Overview Electronics have come a long way in the last century. Using modern fabrication techniques, engineers can now print
ECE 201 LAB 8 TRANSFORMERS & SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE ANALYSIS
 Version 1.1 1 of 8 ECE 201 LAB 8 TRANSFORMERS & SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE ANALYSIS BEFORE YOU BEGIN PREREQUISITE LABS Introduction to MATLAB Introduction to Lab Equipment Introduction to Oscilloscope Capacitors,
Version 1.1 1 of 8 ECE 201 LAB 8 TRANSFORMERS & SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE ANALYSIS BEFORE YOU BEGIN PREREQUISITE LABS Introduction to MATLAB Introduction to Lab Equipment Introduction to Oscilloscope Capacitors,
BME/ISE 3512 Bioelectronics. Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers
 BME/ISE 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers Learning Objectives: Be familiar with the operation of a basic op-amp circuit. Be familiar with the characteristics of both ideal and
BME/ISE 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers Learning Objectives: Be familiar with the operation of a basic op-amp circuit. Be familiar with the characteristics of both ideal and
Experiment 8 Frequency Response
 Experiment 8 Frequency Response W.T. Yeung, R.A. Cortina, and R.T. Howe UC Berkeley EE 105 Spring 2005 1.0 Objective This lab will introduce the student to frequency response of circuits. The student will
Experiment 8 Frequency Response W.T. Yeung, R.A. Cortina, and R.T. Howe UC Berkeley EE 105 Spring 2005 1.0 Objective This lab will introduce the student to frequency response of circuits. The student will
UNIVERSITY OF UTAH ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
 UNIVERSITY OF UTAH ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ECE 3110 LAB EXPERIMENT NO. 4 CLASS AB POWER OUTPUT STAGE Objective: In this laboratory exercise you will build and characterize a class AB power output
UNIVERSITY OF UTAH ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ECE 3110 LAB EXPERIMENT NO. 4 CLASS AB POWER OUTPUT STAGE Objective: In this laboratory exercise you will build and characterize a class AB power output
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department. EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab
 University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab EXPERIMENT 4 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 4 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab EXPERIMENT 4 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 4 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS
Laboratory 2. Lab 2. Instrument Familiarization and Basic Electrical Relations. Required Components: 2 1k resistors 2 1M resistors 1 2k resistor
 Laboratory 2 nstrument Familiarization and Basic Electrical Relations Required Components: 2 1k resistors 2 1M resistors 1 2k resistor 2.1 Objectives This exercise is designed to acquaint you with the
Laboratory 2 nstrument Familiarization and Basic Electrical Relations Required Components: 2 1k resistors 2 1M resistors 1 2k resistor 2.1 Objectives This exercise is designed to acquaint you with the
Design and Technology
 E.M.F, Voltage and P.D E.M F This stands for Electromotive Force (e.m.f) A battery provides Electromotive Force An e.m.f can make an electric current flow around a circuit E.m.f is measured in volts (v).
E.M.F, Voltage and P.D E.M F This stands for Electromotive Force (e.m.f) A battery provides Electromotive Force An e.m.f can make an electric current flow around a circuit E.m.f is measured in volts (v).
EXAMPLE. Use this jack for the red test lead when measuring. current from 0 to 200mA. Figure P-1
 Digital Multimeters ON / OFF power switch Continuity / Diode Test Function Resistance Function Ranges from 200Ω to 200MΩ Transistor Test Function DC Current Function Ranges from 2mA to 20A. AC Current
Digital Multimeters ON / OFF power switch Continuity / Diode Test Function Resistance Function Ranges from 200Ω to 200MΩ Transistor Test Function DC Current Function Ranges from 2mA to 20A. AC Current
ECE 2274 Lab 2. Your calculator will have a setting that will automatically generate the correct format.
 ECE 2274 Lab 2 Forward (DO NOT TURN IN) You are expected to use engineering exponents for all answers (p,n,µ,m, N/A, k, M, G) and to give each with a precision between one and three leading digits and
ECE 2274 Lab 2 Forward (DO NOT TURN IN) You are expected to use engineering exponents for all answers (p,n,µ,m, N/A, k, M, G) and to give each with a precision between one and three leading digits and
EET140/3 ELECTRIC CIRCUIT I
 SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL SYSTEM ENGINEERING UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS EET140/3 ELECTRIC CIRCUIT I MODULE 1 PART I: INTRODUCTION TO BASIC LABORATORY EQUIPMENT PART II: OHM S LAW PART III: SERIES PARALEL CIRCUIT
SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL SYSTEM ENGINEERING UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS EET140/3 ELECTRIC CIRCUIT I MODULE 1 PART I: INTRODUCTION TO BASIC LABORATORY EQUIPMENT PART II: OHM S LAW PART III: SERIES PARALEL CIRCUIT
CPE 100L DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN I DESIGN LABORATORY LABORATORY 1 LAB SAFETY QUIZ & LAB EQUIPMENT USE TUTORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA, LAS VEGAS GOALS:
 CPE 100L DESIGN LABORATORY LABORATORY 1 LAB SAFETY QUIZ & LAB EQUIPMENT USE TUTORIAL DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA, LAS VEGAS GOALS: Introduce laboratory safety
CPE 100L DESIGN LABORATORY LABORATORY 1 LAB SAFETY QUIZ & LAB EQUIPMENT USE TUTORIAL DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA, LAS VEGAS GOALS: Introduce laboratory safety
ECE 2274 Lab 2 (Network Theorems)
 ECE 2274 Lab 2 (Network Theorems) Forward (DO NOT TURN IN) You are expected to use engineering exponents for all answers (p,n,µ,m, N/A, k, M, G) and to give each with a precision between one and three
ECE 2274 Lab 2 (Network Theorems) Forward (DO NOT TURN IN) You are expected to use engineering exponents for all answers (p,n,µ,m, N/A, k, M, G) and to give each with a precision between one and three
On-Line Students Analog Discovery 2: Arbitrary Waveform Generator (AWG). Two channel oscilloscope
 EET 150 Introduction to EET Lab Activity 5 Oscilloscope Introduction Required Parts, Software and Equipment Parts Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 Component /Value Quantity Resistor 10 kω, ¼ Watt, 5% Tolerance
EET 150 Introduction to EET Lab Activity 5 Oscilloscope Introduction Required Parts, Software and Equipment Parts Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 Component /Value Quantity Resistor 10 kω, ¼ Watt, 5% Tolerance
On-Line Students Analog Discovery 2: Arbitrary Waveform Generator (AWG). Two channel oscilloscope
 EET 150 Introduction to EET Lab Activity 8 Function Generator Introduction Required Parts, Software and Equipment Parts Figure 1 Component /Value Quantity Resistor 10 kω, ¼ Watt, 5% Tolerance 1 Resistor
EET 150 Introduction to EET Lab Activity 8 Function Generator Introduction Required Parts, Software and Equipment Parts Figure 1 Component /Value Quantity Resistor 10 kω, ¼ Watt, 5% Tolerance 1 Resistor
EGR Laboratory 9 - Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps) Team Names
 EG 1301 - Laboratory 9 - Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps) Team Names Objectives At the end of this lab, you will be able to: Construct and test inverting and non-inverting op amp circuits Compute calculated
EG 1301 - Laboratory 9 - Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps) Team Names Objectives At the end of this lab, you will be able to: Construct and test inverting and non-inverting op amp circuits Compute calculated
electrical noise and interference, environmental changes, instrument resolution, or uncertainties in the measurement process itself.
 MUST 382 / EELE 491 Spring 2014 Basic Lab Equipment and Measurements Electrical laboratory work depends upon various devices to supply power to a circuit, to generate controlled input signals, and for
MUST 382 / EELE 491 Spring 2014 Basic Lab Equipment and Measurements Electrical laboratory work depends upon various devices to supply power to a circuit, to generate controlled input signals, and for
Instrument Usage in Circuits Lab
 Instrument Usage in Circuits Lab This document contains descriptions of the various components and instruments that will be used in Circuit Analysis laboratory. Descriptions currently exist for the following
Instrument Usage in Circuits Lab This document contains descriptions of the various components and instruments that will be used in Circuit Analysis laboratory. Descriptions currently exist for the following
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
University of Portland EE 271 Electrical Circuits Laboratory. Experiment: Op Amps
 University of Portland EE 271 Electrical Circuits Laboratory Experiment: Op Amps I. Objective The objective of this experiment is to learn how to use an op amp circuit to prevent loading and to amplify
University of Portland EE 271 Electrical Circuits Laboratory Experiment: Op Amps I. Objective The objective of this experiment is to learn how to use an op amp circuit to prevent loading and to amplify
ECE ECE285. Electric Circuit Analysis I. Spring Nathalia Peixoto. Rev.2.0: Rev Electric Circuits I
 ECE285 Electric Circuit Analysis I Spring 2014 Nathalia Peixoto Rev.2.0: 140124. Rev 2.1. 140813 1 Lab reports Background: these 9 experiments are designed as simple building blocks (like Legos) and students
ECE285 Electric Circuit Analysis I Spring 2014 Nathalia Peixoto Rev.2.0: 140124. Rev 2.1. 140813 1 Lab reports Background: these 9 experiments are designed as simple building blocks (like Legos) and students
ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis
 ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis All circuit simulation packages that use the Pspice engine allow users to do complex analysis that were once impossible to
ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis All circuit simulation packages that use the Pspice engine allow users to do complex analysis that were once impossible to
Breadboard Primer. Experience. Objective. No previous electronics experience is required.
 Breadboard Primer Experience No previous electronics experience is required. Figure 1: Breadboard drawing made using an open-source tool from fritzing.org Objective A solderless breadboard (or protoboard)
Breadboard Primer Experience No previous electronics experience is required. Figure 1: Breadboard drawing made using an open-source tool from fritzing.org Objective A solderless breadboard (or protoboard)
Pre-Laboratory Assignment
 Measurement of Electrical Resistance and Ohm's Law PreLaboratory Assignment Read carefully the entire description of the laboratory and answer the following questions based upon the material contained
Measurement of Electrical Resistance and Ohm's Law PreLaboratory Assignment Read carefully the entire description of the laboratory and answer the following questions based upon the material contained
ELR 4202C Project: Finger Pulse Display Module
 EEE 4202 Project: Finger Pulse Display Module Page 1 ELR 4202C Project: Finger Pulse Display Module Overview: The project will use an LED light source and a phototransistor light receiver to create an
EEE 4202 Project: Finger Pulse Display Module Page 1 ELR 4202C Project: Finger Pulse Display Module Overview: The project will use an LED light source and a phototransistor light receiver to create an
Intro To Engineering II for ECE: Lab 7 The Op Amp Erin Webster and Dr. Jay Weitzen, c 2014 All rights reserved.
 Lab 7: The Op Amp Laboratory Objectives: 1) To introduce the operational amplifier or Op Amp 2) To learn the non-inverting mode 3) To learn the inverting mode 4) To learn the differential mode Before You
Lab 7: The Op Amp Laboratory Objectives: 1) To introduce the operational amplifier or Op Amp 2) To learn the non-inverting mode 3) To learn the inverting mode 4) To learn the differential mode Before You
ECE 480: SENIOR DESIGN LABORATORY
 ECE 480: SENIOR DESIGN LABORATORY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING MICHIGAN STATE UNIVERSITY I. TITLE: Lab I - Introduction to the Oscilloscope, Function Generator, Digital Multimeter
ECE 480: SENIOR DESIGN LABORATORY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING MICHIGAN STATE UNIVERSITY I. TITLE: Lab I - Introduction to the Oscilloscope, Function Generator, Digital Multimeter
1-1. Kirchoff s Laws A. Construct the circuit shown below. R 1 =1 kω. = 2.7 kω R 3 R 2 5 V
 Physics 310 Lab 1: DC Circuits Equipment: Digital Multimeter, 5V Supply, Breadboard, two 1 kω, 2.7 kω, 5.1 kω, 10 kω, two, Decade Resistor Box, potentiometer, 10 kω Thermistor, Multimeter Owner s Manual
Physics 310 Lab 1: DC Circuits Equipment: Digital Multimeter, 5V Supply, Breadboard, two 1 kω, 2.7 kω, 5.1 kω, 10 kω, two, Decade Resistor Box, potentiometer, 10 kω Thermistor, Multimeter Owner s Manual
EXPERIMENT 1 PRELIMINARY MATERIAL
 EXPERIMENT 1 PRELIMINARY MATERIAL BREADBOARD A solderless breadboard, like the basic model in Figure 1, consists of a series of square holes, and those columns of holes are connected to each other via
EXPERIMENT 1 PRELIMINARY MATERIAL BREADBOARD A solderless breadboard, like the basic model in Figure 1, consists of a series of square holes, and those columns of holes are connected to each other via
APPENDIX D DISCUSSION OF ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTS
 APPENDIX D DISCUSSION OF ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTS DC POWER SUPPLIES We will discuss these instruments one at a time, starting with the DC power supply. The simplest DC power supplies are batteries which
APPENDIX D DISCUSSION OF ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTS DC POWER SUPPLIES We will discuss these instruments one at a time, starting with the DC power supply. The simplest DC power supplies are batteries which
University of Utah Electrical Engineering Department ECE 2100 Experiment No. 2 Linear Operational Amplifier Circuits II
 University of Utah Electrical Engineering Department ECE 2100 Experiment No. 2 Linear Operational Amplifier Circuits II Minimum required points = 51 Grade base, 100% = 85 points Recommend parts should
University of Utah Electrical Engineering Department ECE 2100 Experiment No. 2 Linear Operational Amplifier Circuits II Minimum required points = 51 Grade base, 100% = 85 points Recommend parts should
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering. ESE 206: Electrical Circuits and Systems II - Lab
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE 206: Electrical Circuits and Systems II - Lab AC POWER ANALYSIS AND DESIGN I. Purpose and Equipment: Provide experimental
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE 206: Electrical Circuits and Systems II - Lab AC POWER ANALYSIS AND DESIGN I. Purpose and Equipment: Provide experimental
Sept 13 Pre-lab due Sept 12; Lab memo due Sept 19 at the START of lab time, 1:10pm
 Sept 13 Pre-lab due Sept 12; Lab memo due Sept 19 at the START of lab time, 1:10pm EGR 220: Engineering Circuit Theory Lab 1: Introduction to Laboratory Equipment Pre-lab Read through the entire lab handout
Sept 13 Pre-lab due Sept 12; Lab memo due Sept 19 at the START of lab time, 1:10pm EGR 220: Engineering Circuit Theory Lab 1: Introduction to Laboratory Equipment Pre-lab Read through the entire lab handout
Lab 11: 555 Timer/Oscillator Circuits
 Page 1 of 6 Laboratory Goals Familiarize students with the 555 IC and its uses Design a free-running oscillator Design a triggered one-shot circuit Compare actual to theoretical values for the circuits
Page 1 of 6 Laboratory Goals Familiarize students with the 555 IC and its uses Design a free-running oscillator Design a triggered one-shot circuit Compare actual to theoretical values for the circuits
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5)
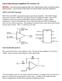 Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING ELECTRONIC WORKSHOP # 03. Resistors
 MEHRAN UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, JAMSHORO DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING ELECTRONIC WORKSHOP # 03 Resistors Roll. No: Checked by: Date: Grade: Object: To become familiar with resistors,
MEHRAN UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, JAMSHORO DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING ELECTRONIC WORKSHOP # 03 Resistors Roll. No: Checked by: Date: Grade: Object: To become familiar with resistors,
AC/DC ELECTRONICS LABORATORY
 Includes Teacher's Notes and Typical Experiment Results Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model EM-8656 012-05892A 1/96 AC/DC ELECTRONICS LABORATORY 1995 PASCO scientific
Includes Teacher's Notes and Typical Experiment Results Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model EM-8656 012-05892A 1/96 AC/DC ELECTRONICS LABORATORY 1995 PASCO scientific
Lab 1: Basic Lab Equipment and Measurements
 Abstract: Lab 1: Basic Lab Equipment and Measurements This lab exercise introduces the basic measurement instruments that will be used throughout the course. These instruments include multimeters, oscilloscopes,
Abstract: Lab 1: Basic Lab Equipment and Measurements This lab exercise introduces the basic measurement instruments that will be used throughout the course. These instruments include multimeters, oscilloscopes,
Test No. 1. Introduction to Scope Measurements. Report History. University of Applied Sciences Hamburg. Last chance!! EEL2 No 1
 University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L: in charge of the report Test No. Date: Assistant A2: Professor:
University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L: in charge of the report Test No. Date: Assistant A2: Professor:
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Electrical Engineering Department. EE SOPHOMORE LABORATORY Experiment 3 The Oscilloscope
 POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Electrical Engineering Department EE SOPHOMORE LABORATORY Experiment 3 The Oscilloscope Modified for Physics 18, Brooklyn College I. Overview of the Experiment The main objective
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Electrical Engineering Department EE SOPHOMORE LABORATORY Experiment 3 The Oscilloscope Modified for Physics 18, Brooklyn College I. Overview of the Experiment The main objective
Experiment 2. Ohm s Law. Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current.
 Experiment 2 Ohm s Law 2.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
Experiment 2 Ohm s Law 2.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
