Physics 3 Lab 5 Normal Modes and Resonance
|
|
|
- Christian Rice
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physics 3 Lab 5 Normal Modes and Resonance 1 Physics 3 Lab 5 Normal Modes and Resonance INTRODUCTION Earlier in the semester you did an experiment with the simplest possible vibrating object, the simple harmonic oscillator. Real vibrating objects, such as are used to construct musical instruments, are more complicated, but all vibrating objects have some basic behavior in common which you re going to investigate in this experiment. BACKGROUND Nearly all musical instruments that have distinctive sounds (which is pretty much all of them) depend on the idea of normal modes: any vibrating object more complicated than a single mass on a spring or its equivalent has two or more simple motions, called normal modes, at which it wants to vibrate. Typically the more moving parts the object has, the more normal modes. A single mass on a spring has only one moving part and a single normal mode, while a vibrating string, which you can think of as a very large number of very small masses connected by very small springs, has a very large number of normal modes. We re going to keep the number of normal modes manageable in this experment by working with two or three gliders on an air track, where the number of modes will turn out to be equal to the number of gliders. Any actual vibration of the object can be regarded as a combination of those natural motions. Equally important to the operation of musical instruments is a property of vibrating objects called resonance: if you shake or drive an object at one of its normal frequencies, the object will vibrate much more strongly (specifically, its vibration will have a much larger amplitude) than if you drove the object at some randomly-chosen frequency. This phenomenon explains how the sound production in a musical instrument can start with something as disorganized as a brass player s buzzing lips and still produce tones built from a harmonic series. EQUIPMENT Air track with mounted metric scale and air compressor Glider connected with springs to the ends of the air track Additional gliders and springs Computer running Data Studio PROCEDURE Part 1. Measuring the natural frequency of a single glider. A schematic of the apparatus is given on the next page. Data Studio should already be set up and running, if it isn t, instructions for getting it started are given in the appendix at the end of this file. If necessary, add or remove gliders and springs so that you have a single glider connected to each end of the air track by a spring, the same as your setup for the simple harmonic oscillator and similar to the schematic above. One spring will actually be connected to
2 Physics 3 Lab 5 Normal Modes and Resonance 2 a piston that you will use to drive the glider at a frequency that you can set. The computer at your station should have a file called SHOFit.ds already loaded and the Sonic Ranger set up. You should see two open windows, one a graph of the position of the glider as a function of time, although it will probably be labelled something like Graph 1. The other window is labeled Curve Fit, and that s where the heavy lifting will take place. Schematic of air track Driver Spring Sail Spring Glider Intake for hose from compressor Start the glider oscillating and then click the Start button, which has a green rightpointing triangle on it. You will notice that Start now changes to Stop and the green triangle changes to a red square. Let it run for 5-10 seconds and then click the Stop button, which will display all the data you took for that run. Your data should look oscillatory, although the amplitude of oscillation will decrease over time because the air resistance of the sail is pretty substantial. We can t get rid of the sail, though, because that s what reflects the pulses from the Sonic Ranger back to its detector. You will need to know the frequency of your single-glider system to study resonance. In the earlier experiment on the simple harmonic oscillator, you measured the period off the graph, and you can calculate the frequency once you know the period. There s actually a more precise way to measure the period, which for devious reasons of my own I didn t have you use last time. Start by taking a data run with the single glider if you haven t already. If you do have a previous run with more than one glider, delete it by going to Experiment in the top menu, and choose Delete last data run. Then go to the Curve Fit box and choose Sine Fit from the pull-down menu. Although your run will show some drop in the amplitude because of air resistance, if your run is only a few oscillations long the effect of air resistance will be pretty minimal and you will get an accurate measurement of the period. From the period you can calculate the frequency of the oscillator (in Hz). Part 2. Resonance and the single glider. In the Introduction, I claimed that driving a vibrating system at one of its natural or normal frequencies will produce a much larger response than driving the system at some arbitrary frequency. This sensitivity to the driving frequency is what physicists call resonance, and you can test my claim quite easily. Notice that the function generator is wired to a cylindrical box with a sort of piston in it, and the piston is connected to one of the springs connected to the glider. Set the amplitude knob about one-quarter of the way between its
3 Physics 3 Lab 5 Normal Modes and Resonance 3 minimum and maximum settings, and notice that now the pistion moves in and out, stretching and compressing the spring, which in turn exerts a (sinusoically varying) force on the glider. How far the piston moves depends on the setting of the amplitude knob, and the frequency with which the piston is moving, and hence the frequency at which you are driving the oscillator, is determined by the frequency setting. Nothing else should be happening, though, because the compressed air is turned off. Take your measurement of the natural frequency that you found above and set the function generator attached to the driver to that frequency. Now you are driving the oscillator at its natural frequency. Finally you can turn on the compressed air! Start taking data right away so that you can see the transient, which is the initial motion of the glider, a combination of the oscillation you would get if you just gave it a shove and the motion you get from driving it. After a minute or so, you should see the motion settle down and become genuinely periodic, reaching its steady-state motion which is determined by the driving force but is independent of how the oscillator got started. Once the steady-state motion is established, stop the current data run, delete it from the graph, and then start a new one that you ll use to measure the amplitude and frequency of the oscillation. Get about 10 seconds of data for your fit. You can either measure the amplitude and period of the oscillation directly from the graph, or you can use the Fit button for this data. If you use the Fit button to find the period, choose Sine Fit. With either method, record the period and the amplitude of the oscillation. From the period, calculate the frequency of the oscillation. Then delete the run and the fit, and also turn off the compressed air and put the glider approximately at its equilbrium position. Next set your function generator to a driving frequency about 20% lower than the natural frequency, repeat the experiment above, and measure the frequency and amplitude of the new oscillation. (Remember that the driving frequency is the frequency you read off the function generator, while the natural frequency is the frequency you measured in Part 1 for the undriven oscillator.) Do this again for a driving frequency about 20% higher than the natural frequency. What happens to the amplitude of oscillation when you drive the system at a frequency noticeably different from the natural frequency of oscillation? How is the frequency of the resulting motion related to the natural frequency of the oscillator and/or the driving frequency? In answering the questions above (which appear on the data summary sheet), it s important to remember that there are conceptually three different frequencies you need to keep straight. (They may not all have different numerical values, but they have three different roles in this experiment.) The first is the natural frequency of the undriven oscillator: that s the frequency you measured in the first part of the experiment, with the function generator turned off (or at least the amplitude knob turned down to zero). The second is the driving frequency: that s the setting on the function generator. Since the natural frequency is set by the spring constant and the glider mass, while the driving frequency is set by you to whatever value you choose, those two frequencies need not have the same value (although of course if you set the value of the driving frequency value to the number you measured for the natural frequency, they will have the same value). The third frequency is the frequency of the driven oscillation, the frequency at which the oscillator actually oscillates, and one question you will want to think about and test experimentally is whether or not the frequency of the driven oscillation is always equal to one of the other two frequencies.
4 Physics 3 Lab 5 Normal Modes and Resonance 4 Part 3. The two-glider system. Now add a second glider and a spring so that you have two gliders and three connecting springs on the air track. The glider closer to the motion sensor should have the sail mounted on it. You will probably also have to move the ring stand which is connected to one of the springs so that all three springs are under tension. Turn on the compressed air to the air track and measure the equilibrium positions of both gliders, where each glider is at rest because the forces exerted on it by the two springs balance each other. It doesn t matter what point on the gliders you use as long as you re consistent, so pick some point that s convenient. Take one run (if you haven t already) that you start by displacing one of the gliders from equilibrium and then letting go. Get about ten seconds worth of data. Probably your graph will be more or less oscillatory but not really periodic, because you started the system randomly. Since the two gliders are connected by a spring, in addition to being connected to the two ends of the air track, when one of the gliders moves it will exert a force on the other glider and cause it to move as well. The result is motion that looks pretty complicated, at least to the casual observer. Just for laughs (and also to make a point), run a Sine Fit on your data. Data Studio will almost certainly come up with a set of fit parameters. The resulting sine wave just won t look very much like your data. The point to running this fit is to notice that you can (try to) fit any function you want to any data you have, and the procedure will come up with a best fit. There s no guarantee, though, that this best fit is actually any good. And in this case, the best fit single sine wave is probably a pretty terrible fit because the motion of your two-glider system is more complicated than a single sine wave. (One hazard to these built-in fitting routines is that finding a fit is so easy that you often forget that the fit may or may not mean anything. When people had to fit functions by hand, they were pretty careful to start with a sensible guess for the function they were trying to fit.) However, if you go one step more complicated, you can get a pretty good fit. Instead of fitting a single sine wave, try the next item in the list of fitting functions, Sine Series. The Sine Series will try to fit the sum of two sine waves, with different periods and probably different amplitudes, to your data. This time, you should get a function that looks quite a bit like the motion of the glider with the sail, and you can read the periods for both sine waves right off the fit. From the periods you can calculate the two normal frequencies for your system of oscillators. Once you ve found the two normal frequencies, one for each normal mode, see if you can get your two-glider system to go into resonance. Set the function generator to one of your two normal frequencies and turn on the compressed air. While in principle this should work no matter how the gliders get started, in practice you can save a lot of time by starting with the gliders at rest and close to their equilibrium positions. Even so, you may have to wait a minute or so for the transient motion (which does depend on how the gliders get started) to damp out. Do you get the single mode (or close to it) that you would expect from the frequency? Now suppose you set the frequency counter either 20% above or below the normal frequency. What does the motion look like now? You can use the Sine Series fit to measure the amplitudes of the two modes. If you really are driving the system at one of its resonant frequencies, one of the amplitudes should be much larger than the other. Is this the case? Is the frequency of the largeamplitude motion the one you would expect?
5 Physics 3 Lab 5 Normal Modes and Resonance 5 Repeat this process with the other normal frequency. (Turn off the compressed air and start the gliders over.) Do you now get motion at the mode associated with that frequency? What happens when you set the frequency 20% high or low? (Setting the frequency to some frequency different from one of the normal frequencies is sometimes called de-tuning, or going off-resonance. ) Measuring the amplitudes and frequencies in this case is trickier because you re really driving the system in both modes at once. The amplitudes in your Sine Series fit should be consistent with this statement. Appendix. Setting up Data Studio. A shortcut for Data Studio should appear on the desktop; double-click the icon to start. When the program starts you will be asked, How would you like to use Data Studio? Choose Create Experiment. You will get a window called Experiment Setup, which will include a picture of the black box (more precisely, the ScienceWorkshop 750 Interface) which connects your computer with the motion sensor. That black box should have two cables, one with a yellow plug and one with a black plug, plugged into it. Point the cursor at the picture of one of those two sockets and click on it. You should get a menu of sensors: choose the motion sensor and click the OK button. If you get a Help window that says something like, Data Studio could not connect, that probably means that the black box isn t turned on. Its on/off switch is in back on the right. After you ve turned it on, you ll get a yellow triangle with an exclamation point and the instructions to click to connect. After doing so, the Help window should now tell you, The interface is ready for use. After you ve connected the motion sensor you can close the Experiment Setup window. For displaying your data, you will want a graph of the position of the sail-equipped glider as a function of time. The left side of the field should contain two small tables, one labeled Data and the other labeled Displays. Select Position, Ch 1 & 2 from the Data table and drag it down to Graph in the Displays table. (If you don t have those two tables, click the Summary button near the top of the window on the left.) You now get a graphing area which at the moment has no data in it. With luck you ll have one or more gliders on your air track, one of them with a sail. Turn on the compressed air, get that glider moving, and then click the Start button, which you encountered earlier in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator experiment. The motion sensor will start to collect data and graph it. You can scale the graph so your data fill the screen by clicking the left-most button in the graphing window. That s the Scale to fit button but it looks like a tiny baseball field to me. Now you re ready to start the experiment.
Lab 11. Vibrating Strings
 Lab 11. Vibrating Strings Goals To experimentally determine relationships between fundamental resonant of a vibrating string and its length, its mass per unit length, and tension in string. To introduce
Lab 11. Vibrating Strings Goals To experimentally determine relationships between fundamental resonant of a vibrating string and its length, its mass per unit length, and tension in string. To introduce
Figure AC circuit to be analyzed.
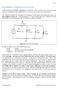 7.2(1) MULTISIM DEMO 7.2: INTRODUCTION TO AC ANALYSIS In this section, we ll introduce AC Analysis in Multisim. This is perhaps one of the most useful Analyses that Multisim offers, and we ll use it in
7.2(1) MULTISIM DEMO 7.2: INTRODUCTION TO AC ANALYSIS In this section, we ll introduce AC Analysis in Multisim. This is perhaps one of the most useful Analyses that Multisim offers, and we ll use it in
Activity P40: Driven Harmonic Motion - Mass on a Spring (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor, Power Amplifier)
 Name Class Date Activity P40: Driven Harmonic Motion - Mass on a Spring (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor, Power Amplifier) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Harmonic motion P40
Name Class Date Activity P40: Driven Harmonic Motion - Mass on a Spring (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor, Power Amplifier) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Harmonic motion P40
Sonometer CAUTION. 1 Introduction. 2 Theory
 Sonometer Equipment Capstone, sonometer (with detector coil but not driver coil), voltage sensor, BNC to double banana plug adapter, set of hook masses, and 2 set of wires CAUTION In this experiment a
Sonometer Equipment Capstone, sonometer (with detector coil but not driver coil), voltage sensor, BNC to double banana plug adapter, set of hook masses, and 2 set of wires CAUTION In this experiment a
3A: PROPERTIES OF WAVES
 3A: PROPERTIES OF WAVES Int roduct ion Your ear is complicated device that is designed to detect variations in the pressure of the air at your eardrum. The reason this is so useful is that disturbances
3A: PROPERTIES OF WAVES Int roduct ion Your ear is complicated device that is designed to detect variations in the pressure of the air at your eardrum. The reason this is so useful is that disturbances
Lab 12. Vibrating Strings
 Lab 12. Vibrating Strings Goals To experimentally determine relationships between fundamental resonant of a vibrating string and its length, its mass per unit length, and tension in string. To introduce
Lab 12. Vibrating Strings Goals To experimentally determine relationships between fundamental resonant of a vibrating string and its length, its mass per unit length, and tension in string. To introduce
3. Draw a side-view picture of the situation below, showing the ringstand, rubber band, and your hand when the rubber band is fully stretched.
 1 Forces and Motion In the following experiments, you will investigate how the motion of an object is related to the forces acting on it. For our purposes, we ll use the everyday definition of a force
1 Forces and Motion In the following experiments, you will investigate how the motion of an object is related to the forces acting on it. For our purposes, we ll use the everyday definition of a force
Experiment P20: Driven Harmonic Motion - Mass on a Spring (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor, Power Amplifier)
 PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P20-1 Experiment P20: - Mass on a Spring (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor, Power Amplifier) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file harmonic motion 45 m 700
PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P20-1 Experiment P20: - Mass on a Spring (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor, Power Amplifier) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file harmonic motion 45 m 700
Experiment 9 : Pulse Width Modulation
 Name/NetID: Experiment 9 : Pulse Width Modulation Laboratory Outline In experiment 5 we learned how to control the speed of a DC motor using a variable resistor. This week, we will learn an alternative
Name/NetID: Experiment 9 : Pulse Width Modulation Laboratory Outline In experiment 5 we learned how to control the speed of a DC motor using a variable resistor. This week, we will learn an alternative
Physics 2310 Lab #2 Speed of Sound & Resonance in Air
 Physics 2310 Lab #2 Speed of Sound & Resonance in Air Objective: The objectives of this experiment are a) to measure the speed of sound in air, and b) investigate resonance within air. Apparatus: Pasco
Physics 2310 Lab #2 Speed of Sound & Resonance in Air Objective: The objectives of this experiment are a) to measure the speed of sound in air, and b) investigate resonance within air. Apparatus: Pasco
Experiment 18: Driven RLC Circuit
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8. Spring 3 Experiment 8: Driven LC Circuit OBJECTIVES To measure the resonance frequency and the quality factor of a driven LC circuit INTODUCTION
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8. Spring 3 Experiment 8: Driven LC Circuit OBJECTIVES To measure the resonance frequency and the quality factor of a driven LC circuit INTODUCTION
PHYSICS 107 LAB #3: WAVES ON STRINGS
 Section: Monday / Tuesday (circle one) Name: Partners: Total: /40 PHYSICS 107 LAB #3: WAVES ON STRINGS Equipment: Function generator, amplifier, driver, elastic string, pulley and clamp, rod and table
Section: Monday / Tuesday (circle one) Name: Partners: Total: /40 PHYSICS 107 LAB #3: WAVES ON STRINGS Equipment: Function generator, amplifier, driver, elastic string, pulley and clamp, rod and table
Experiment 8: An AC Circuit
 Experiment 8: An AC Circuit PART ONE: AC Voltages. Set up this circuit. Use R = 500 Ω, L = 5.0 mh and C =.01 μf. A signal generator built into the interface provides the emf to run the circuit from Output
Experiment 8: An AC Circuit PART ONE: AC Voltages. Set up this circuit. Use R = 500 Ω, L = 5.0 mh and C =.01 μf. A signal generator built into the interface provides the emf to run the circuit from Output
Resonance Tube Lab 9
 HB 03-30-01 Resonance Tube Lab 9 1 Resonance Tube Lab 9 Equipment SWS, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads
HB 03-30-01 Resonance Tube Lab 9 1 Resonance Tube Lab 9 Equipment SWS, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads
Experiment: P34 Resonance Modes 1 Resonance Modes of a Stretched String (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P34-1 Experiment: P34 Resonance Modes 1 Resonance Modes of a Stretched String (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P34-1 Experiment: P34 Resonance Modes 1 Resonance Modes of a Stretched String (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows
(i) node [1] (ii) antinode...
![(i) node [1] (ii) antinode... (i) node [1] (ii) antinode...](/thumbs/96/126586647.jpg) 1 (a) When used to describe stationary (standing) waves explain the terms node...... [1] (ii) antinode....... [1] (b) Fig. 5.1 shows a string fixed at one end under tension. The frequency of the mechanical
1 (a) When used to describe stationary (standing) waves explain the terms node...... [1] (ii) antinode....... [1] (b) Fig. 5.1 shows a string fixed at one end under tension. The frequency of the mechanical
Activity P52: LRC Circuit (Voltage Sensor)
 Activity P52: LRC Circuit (Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) AC circuits P52 LRC Circuit.DS (See end of activity) (See end of activity) Equipment Needed Qty
Activity P52: LRC Circuit (Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) AC circuits P52 LRC Circuit.DS (See end of activity) (See end of activity) Equipment Needed Qty
Auntie Spark s Guide to creating a Data Collection VI
 Auntie Spark s Guide to creating a Data Collection VI Suppose you wanted to gather data from an experiment. How would you create a VI to do so? For sophisticated data collection and experimental control,
Auntie Spark s Guide to creating a Data Collection VI Suppose you wanted to gather data from an experiment. How would you create a VI to do so? For sophisticated data collection and experimental control,
Resonance Tube. 1 Purpose. 2 Theory. 2.1 Air As A Spring. 2.2 Traveling Sound Waves in Air
 Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adapters, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adapters, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Activity P07: Acceleration of a Cart (Acceleration Sensor, Motion Sensor)
 Name Class Date Activity P07: Acceleration of a Cart (Acceleration Sensor, Motion Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Linear motion P07 Accelerate Cart.ds (See end of
Name Class Date Activity P07: Acceleration of a Cart (Acceleration Sensor, Motion Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Linear motion P07 Accelerate Cart.ds (See end of
Experiment P55: Light Intensity vs. Position (Light Sensor, Motion Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P55-1 Experiment P55: (Light Sensor, Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file illuminance 30 m 500/700 P55 Light vs. Position P55_LTVM.SWS
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P55-1 Experiment P55: (Light Sensor, Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file illuminance 30 m 500/700 P55 Light vs. Position P55_LTVM.SWS
Oscillations II: Damped and/or Driven Oscillations
 Oscillations II: Damped and/or Driven Oscillations Michael Fowler 3/4/9 Introducing Damping We ll assume the damping force is proportional to the velocity, and, of course, in the opposite direction. Then
Oscillations II: Damped and/or Driven Oscillations Michael Fowler 3/4/9 Introducing Damping We ll assume the damping force is proportional to the velocity, and, of course, in the opposite direction. Then
INTRODUCTION TO DATA STUDIO
 1 INTRODUCTION TO DATA STUDIO PART I: FAMILIARIZATION OBJECTIVE To become familiar with the operation of the Passport/Xplorer digital instruments and the DataStudio software. INTRODUCTION We will use the
1 INTRODUCTION TO DATA STUDIO PART I: FAMILIARIZATION OBJECTIVE To become familiar with the operation of the Passport/Xplorer digital instruments and the DataStudio software. INTRODUCTION We will use the
AC Circuits. "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert ( )
 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits use varying
AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits use varying
Properties of Sound. Goals and Introduction
 Properties of Sound Goals and Introduction Traveling waves can be split into two broad categories based on the direction the oscillations occur compared to the direction of the wave s velocity. Waves where
Properties of Sound Goals and Introduction Traveling waves can be split into two broad categories based on the direction the oscillations occur compared to the direction of the wave s velocity. Waves where
8A. ANALYSIS OF COMPLEX SOUNDS. Amplitude, loudness, and decibels
 8A. ANALYSIS OF COMPLEX SOUNDS Amplitude, loudness, and decibels Last week we found that we could synthesize complex sounds with a particular frequency, f, by adding together sine waves from the harmonic
8A. ANALYSIS OF COMPLEX SOUNDS Amplitude, loudness, and decibels Last week we found that we could synthesize complex sounds with a particular frequency, f, by adding together sine waves from the harmonic
H. Pipes. Open Pipes. Fig. H-1. Simplest Standing Wave on a Slinky. Copyright 2012 Prof. Ruiz, UNCA H-1
 H. Pipes We proceed now to the study of standing waves in pipes. The standing waves in the pipe are actually sound waves. We cannot see sound waves in air. However, we can readily hear the tones. The advantage
H. Pipes We proceed now to the study of standing waves in pipes. The standing waves in the pipe are actually sound waves. We cannot see sound waves in air. However, we can readily hear the tones. The advantage
Key Vocabulary: Wave Interference Standing Wave Node Antinode Harmonic Destructive Interference Constructive Interference
 Key Vocabulary: Wave Interference Standing Wave Node Antinode Harmonic Destructive Interference Constructive Interference 1. Work with two partners. Two will operate the Slinky and one will record the
Key Vocabulary: Wave Interference Standing Wave Node Antinode Harmonic Destructive Interference Constructive Interference 1. Work with two partners. Two will operate the Slinky and one will record the
MAKE SURE TA & TI STAMPS EVERY PAGE BEFORE YOU START
 Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 11 Velocity of Waves 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1.) What is the longest wavelength at which a sound wave will
Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 11 Velocity of Waves 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1.) What is the longest wavelength at which a sound wave will
PURPOSE: To understand the how position-time and velocity-time graphs describe motion in the real world.
 PURPOSE: To understand the how position-time and velocity-time graphs describe motion in the real world. INTRODUCTION In this lab you ll be performing four activities that will allow you to compare motion
PURPOSE: To understand the how position-time and velocity-time graphs describe motion in the real world. INTRODUCTION In this lab you ll be performing four activities that will allow you to compare motion
2 Oscilloscope Familiarization
 Lab 2 Oscilloscope Familiarization What You Need To Know: Voltages and currents in an electronic circuit as in a CD player, mobile phone or TV set vary in time. Throughout the course you will investigate
Lab 2 Oscilloscope Familiarization What You Need To Know: Voltages and currents in an electronic circuit as in a CD player, mobile phone or TV set vary in time. Throughout the course you will investigate
LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit
 LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit Equipment: Voltage Sensor 1 Multimeter 1 Patch Cords 2 AC/DC Electronics Lab (100 μf capacitor; 10 Ω resistor; Inductor Coil; Iron core; 5 inch wire lead) The purpose of
LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit Equipment: Voltage Sensor 1 Multimeter 1 Patch Cords 2 AC/DC Electronics Lab (100 μf capacitor; 10 Ω resistor; Inductor Coil; Iron core; 5 inch wire lead) The purpose of
Resonance Tube. 1 Purpose. 2 Theory. 2.1 Air As A Spring. 2.2 Traveling Sound Waves in Air
 Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Resonance in Circuits
 Resonance in Circuits Purpose: To map out the analogy between mechanical and electronic resonant systems To discover how relative phase depends on driving frequency To gain experience setting up circuits
Resonance in Circuits Purpose: To map out the analogy between mechanical and electronic resonant systems To discover how relative phase depends on driving frequency To gain experience setting up circuits
AP PHYSICS WAVE BEHAVIOR
 AP PHYSICS WAVE BEHAVIOR NAME: HB: ACTIVITY I. BOUNDARY BEHAVIOR As a wave travels through a medium, it will often reach the end of the medium and encounter an obstacle or perhaps another medium through
AP PHYSICS WAVE BEHAVIOR NAME: HB: ACTIVITY I. BOUNDARY BEHAVIOR As a wave travels through a medium, it will often reach the end of the medium and encounter an obstacle or perhaps another medium through
Physics 1021 Experiment 3. Sound and Resonance
 1 Physics 1021 Sound and Resonance 2 Sound and Resonance Introduction In today's experiment, you will examine beat frequency using tuning forks, a microphone and LoggerPro. You will also produce resonance
1 Physics 1021 Sound and Resonance 2 Sound and Resonance Introduction In today's experiment, you will examine beat frequency using tuning forks, a microphone and LoggerPro. You will also produce resonance
First Tutorial Orange Group
 First Tutorial Orange Group The first video is of students working together on a mechanics tutorial. Boxed below are the questions they re discussing: discuss these with your partners group before we watch
First Tutorial Orange Group The first video is of students working together on a mechanics tutorial. Boxed below are the questions they re discussing: discuss these with your partners group before we watch
Standing waves in a string
 Standing waves in a string Introduction When you shake a string, a pulse travels down its length. When it reaches the end, the pulse can be reflected. A series of regularly occurring pulses will generate
Standing waves in a string Introduction When you shake a string, a pulse travels down its length. When it reaches the end, the pulse can be reflected. A series of regularly occurring pulses will generate
Analog Discovery Arbitrary Function Generator for Windows 7 by Mr. David Fritz and Ms. Ellen Robertson
 Analog Discovery Arbitrary Function Generator for Windows 7 by Mr. David Fritz and Ms. Ellen Robertson Financial support to develop this tutorial was provided by the Bradley Department of Electrical and
Analog Discovery Arbitrary Function Generator for Windows 7 by Mr. David Fritz and Ms. Ellen Robertson Financial support to develop this tutorial was provided by the Bradley Department of Electrical and
FORCED HARMONIC MOTION Ken Cheney
 FORCED HARMONIC MOTION Ken Cheney ABSTRACT The motion of an object under the influence of a driving force, a restoring force, and a friction force is investigated using a mass on a spring driven by a variable
FORCED HARMONIC MOTION Ken Cheney ABSTRACT The motion of an object under the influence of a driving force, a restoring force, and a friction force is investigated using a mass on a spring driven by a variable
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science MOCK EXAMINATION PHY207H1S. Duration 3 hours NO AIDS ALLOWED
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science MOCK EXAMINATION PHY207H1S Duration 3 hours NO AIDS ALLOWED Instructions: Please answer all questions in the examination booklet(s) provided. Completely
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science MOCK EXAMINATION PHY207H1S Duration 3 hours NO AIDS ALLOWED Instructions: Please answer all questions in the examination booklet(s) provided. Completely
Lab 6 Instrument Familiarization
 Lab 6 Instrument Familiarization What You Need To Know: Voltages and currents in an electronic circuit as in a CD player, mobile phone or TV set vary in time. Throughout todays lab you will investigate
Lab 6 Instrument Familiarization What You Need To Know: Voltages and currents in an electronic circuit as in a CD player, mobile phone or TV set vary in time. Throughout todays lab you will investigate
The Series RLC Circuit and Resonance
 Purpose Theory The Series RLC Circuit and Resonance a. To study the behavior of a series RLC circuit in an AC current. b. To measure the values of the L and C using the impedance method. c. To study the
Purpose Theory The Series RLC Circuit and Resonance a. To study the behavior of a series RLC circuit in an AC current. b. To measure the values of the L and C using the impedance method. c. To study the
CNC Using the FlexiCam CNC and HMI Software. Guldbergsgade 29N, P0 E: T:
 CNC Using the FlexiCam CNC and HMI Software Guldbergsgade 29N, P0 E: makerlab@kea.dk T: +46 46 03 90 This grey box is the NC controller. Let s start by turning the red switch to the ON position, then press
CNC Using the FlexiCam CNC and HMI Software Guldbergsgade 29N, P0 E: makerlab@kea.dk T: +46 46 03 90 This grey box is the NC controller. Let s start by turning the red switch to the ON position, then press
(a) What is the tension in the rope? (b) With what frequency must the rope vibrate to create a traveling wave with a wavelength of 2m?
 1. A rope is stretched between two vertical supports. The points where it s attached (P and Q) are fixed. The linear density of the rope, μ, is 0.4kg/m, and the speed of a transverse wave on the rope is
1. A rope is stretched between two vertical supports. The points where it s attached (P and Q) are fixed. The linear density of the rope, μ, is 0.4kg/m, and the speed of a transverse wave on the rope is
Standing Waves. Equipment
 rev 12/2016 Standing Waves Equipment Qty Items Parts Number 1 String Vibrator WA-9857 1 Mass and Hanger Set ME-8967 1 Pulley ME-9448B 1 Universal Table Clamp ME-9376B 1 Small Rod ME-8988 2 Patch Cords
rev 12/2016 Standing Waves Equipment Qty Items Parts Number 1 String Vibrator WA-9857 1 Mass and Hanger Set ME-8967 1 Pulley ME-9448B 1 Universal Table Clamp ME-9376B 1 Small Rod ME-8988 2 Patch Cords
Interference & Superposition. Creating Complex Wave Forms
 Interference & Superposition Creating Complex Wave Forms Waves & Interference I. Definitions and Types II. Parameters and Equations III. Sound IV. Graphs of Waves V. Interference - superposition - standing
Interference & Superposition Creating Complex Wave Forms Waves & Interference I. Definitions and Types II. Parameters and Equations III. Sound IV. Graphs of Waves V. Interference - superposition - standing
SUMMARY. ) f s Shock wave Sonic boom UNIT. Waves transmit energy. Sound is a longitudinal mechanical wave. KEY CONCEPTS CHAPTER SUMMARY
 UNIT D SUMMARY KEY CONCEPTS CHAPTER SUMMARY 9 Waves transmit energy. Crest, trough, amplitude, wavelength Longitudinal and transverse waves Cycle Period, frequency f 1_ T Universal wave equation v fλ Wave
UNIT D SUMMARY KEY CONCEPTS CHAPTER SUMMARY 9 Waves transmit energy. Crest, trough, amplitude, wavelength Longitudinal and transverse waves Cycle Period, frequency f 1_ T Universal wave equation v fλ Wave
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring Experiment 11: Driven RLC Circuit
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.2 Spring 24 Experiment 11: Driven LC Circuit OBJECTIVES 1. To measure the resonance frequency and the quality factor of a driven LC circuit.
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.2 Spring 24 Experiment 11: Driven LC Circuit OBJECTIVES 1. To measure the resonance frequency and the quality factor of a driven LC circuit.
Lab 1B LabVIEW Filter Signal
 Lab 1B LabVIEW Filter Signal Due Thursday, September 12, 2013 Submit Responses to Questions (Hardcopy) Equipment: LabVIEW Setup: Open LabVIEW Skills learned: Create a low- pass filter using LabVIEW and
Lab 1B LabVIEW Filter Signal Due Thursday, September 12, 2013 Submit Responses to Questions (Hardcopy) Equipment: LabVIEW Setup: Open LabVIEW Skills learned: Create a low- pass filter using LabVIEW and
Introduction to project hardware
 ECE2883 HP: Lab 2- nonsme Introduction to project hardware Using the oscilloscope, solenoids, audio transducers, motors In the following exercises, you will use some of the project hardware devices, which
ECE2883 HP: Lab 2- nonsme Introduction to project hardware Using the oscilloscope, solenoids, audio transducers, motors In the following exercises, you will use some of the project hardware devices, which
SDOF System: Obtaining the Frequency Response Function
 University Consortium on Instructional Shake Tables SDOF System: Obtaining the Frequency Response Function Developed By: Dr. Shirley Dyke and Xiuyu Gao Purdue University [updated July 6, 2010] SDOF System:
University Consortium on Instructional Shake Tables SDOF System: Obtaining the Frequency Response Function Developed By: Dr. Shirley Dyke and Xiuyu Gao Purdue University [updated July 6, 2010] SDOF System:
G54GAM Lab Session 1
 G54GAM Lab Session 1 The aim of this session is to introduce the basic functionality of Game Maker and to create a very simple platform game (think Mario / Donkey Kong etc). This document will walk you
G54GAM Lab Session 1 The aim of this session is to introduce the basic functionality of Game Maker and to create a very simple platform game (think Mario / Donkey Kong etc). This document will walk you
The Beauty and Joy of Computing Lab Exercise 10: Shall we play a game? Objectives. Background (Pre-Lab Reading)
 The Beauty and Joy of Computing Lab Exercise 10: Shall we play a game? [Note: This lab isn t as complete as the others we have done in this class. There are no self-assessment questions and no post-lab
The Beauty and Joy of Computing Lab Exercise 10: Shall we play a game? [Note: This lab isn t as complete as the others we have done in this class. There are no self-assessment questions and no post-lab
BoomTschak User s Guide
 BoomTschak User s Guide Audio Damage, Inc. 1 November 2016 The information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of Audio Damage, Inc. No
BoomTschak User s Guide Audio Damage, Inc. 1 November 2016 The information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of Audio Damage, Inc. No
Voltage Current and Resistance II
 Voltage Current and Resistance II Equipment: Capstone with 850 interface, analog DC voltmeter, analog DC ammeter, voltage sensor, RLC circuit board, 8 male to male banana leads 1 Purpose This is a continuation
Voltage Current and Resistance II Equipment: Capstone with 850 interface, analog DC voltmeter, analog DC ammeter, voltage sensor, RLC circuit board, 8 male to male banana leads 1 Purpose This is a continuation
Chapter PREPTEST: SHM & WAVE PROPERTIES
 2 4 Chapter 13-14 PREPTEST: SHM & WAVE PROPERTIES Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A load of 45 N attached to a spring that is hanging vertically
2 4 Chapter 13-14 PREPTEST: SHM & WAVE PROPERTIES Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A load of 45 N attached to a spring that is hanging vertically
26 Sep. 10 PHYS102 2
 RESONANCE IN STRINGS INTRODUCTION A sine wave generator drives a string vibrator to create a standing wave pattern in a stretched string. The driving frequency and the length, density, and tension of the
RESONANCE IN STRINGS INTRODUCTION A sine wave generator drives a string vibrator to create a standing wave pattern in a stretched string. The driving frequency and the length, density, and tension of the
Smoking and any food or drinks are not permitted in the Applications Lab!
 Pre-Lab Activities: None 220 Lab A Electrical Properties of Transmission Systems and the Local Loop Purpose of the experiment: Experiment with a telephone and view its properties under various different
Pre-Lab Activities: None 220 Lab A Electrical Properties of Transmission Systems and the Local Loop Purpose of the experiment: Experiment with a telephone and view its properties under various different
Dynamic Vibration Absorber
 Part 1B Experimental Engineering Integrated Coursework Location: DPO Experiment A1 (Short) Dynamic Vibration Absorber Please bring your mechanics data book and your results from first year experiment 7
Part 1B Experimental Engineering Integrated Coursework Location: DPO Experiment A1 (Short) Dynamic Vibration Absorber Please bring your mechanics data book and your results from first year experiment 7
2809 CAD TRAINING: Part 1 Sketching and Making 3D Parts. Contents
 Contents Getting Started... 2 Lesson 1:... 3 Lesson 2:... 13 Lesson 3:... 19 Lesson 4:... 23 Lesson 5:... 25 Final Project:... 28 Getting Started Get Autodesk Inventor Go to http://students.autodesk.com/
Contents Getting Started... 2 Lesson 1:... 3 Lesson 2:... 13 Lesson 3:... 19 Lesson 4:... 23 Lesson 5:... 25 Final Project:... 28 Getting Started Get Autodesk Inventor Go to http://students.autodesk.com/
Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance
 E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
Name EET 1131 Lab #2 Oscilloscope and Multisim
 Name EET 1131 Lab #2 Oscilloscope and Multisim Section 1. Oscilloscope Introduction Equipment and Components Safety glasses Logic probe ETS-7000 Digital-Analog Training System Fluke 45 Digital Multimeter
Name EET 1131 Lab #2 Oscilloscope and Multisim Section 1. Oscilloscope Introduction Equipment and Components Safety glasses Logic probe ETS-7000 Digital-Analog Training System Fluke 45 Digital Multimeter
SAVING, LOADING AND REUSING LAYER STYLES
 SAVING, LOADING AND REUSING LAYER STYLES In this Photoshop tutorial, we re going to learn how to save, load and reuse layer styles! Layer styles are a great way to create fun and interesting photo effects
SAVING, LOADING AND REUSING LAYER STYLES In this Photoshop tutorial, we re going to learn how to save, load and reuse layer styles! Layer styles are a great way to create fun and interesting photo effects
PHYSICS 107 LAB #9: AMPLIFIERS
 Section: Monday / Tuesday (circle one) Name: Partners: PHYSICS 107 LAB #9: AMPLIFIERS Equipment: headphones, 4 BNC cables with clips at one end, 3 BNC T connectors, banana BNC (Male- Male), banana-bnc
Section: Monday / Tuesday (circle one) Name: Partners: PHYSICS 107 LAB #9: AMPLIFIERS Equipment: headphones, 4 BNC cables with clips at one end, 3 BNC T connectors, banana BNC (Male- Male), banana-bnc
PHYSICS 326 LAB # 1: The Oscilloscope and Signal Generators 1/6
 PHYSICS 326 LAB # 1: The Oscilloscope and Signal Generators 1/6 PURPOSE: To be sure that each student begins the course with at least the minimum required knowledge of two instruments which we will be
PHYSICS 326 LAB # 1: The Oscilloscope and Signal Generators 1/6 PURPOSE: To be sure that each student begins the course with at least the minimum required knowledge of two instruments which we will be
Computer Tools for Data Acquisition
 Computer Tools for Data Acquisition Introduction to Capstone You will be using a computer to assist in taking and analyzing data throughout this course. The software, called Capstone, is made specifically
Computer Tools for Data Acquisition Introduction to Capstone You will be using a computer to assist in taking and analyzing data throughout this course. The software, called Capstone, is made specifically
Teacher s Guide - Activity P51: LR Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor)
 Teacher s Guide - Activity P51: LR Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Circuits P51 LR Circuit.DS (See end of activity) (See end of activity)
Teacher s Guide - Activity P51: LR Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Circuits P51 LR Circuit.DS (See end of activity) (See end of activity)
Experiment P24: Motor Efficiency (Photogate, Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P24-1 Experiment P24: Motor Efficiency (Photogate, Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh File Windows File energy 30 m 700 P24 Motor
PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P24-1 Experiment P24: Motor Efficiency (Photogate, Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh File Windows File energy 30 m 700 P24 Motor
Experiment P31: Waves on a String (Power Amplifier)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P31-1 Experiment P31: (Power Amplifier) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file Waves 45 m 700 P31 P31_WAVE.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED Interface Pulley
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P31-1 Experiment P31: (Power Amplifier) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file Waves 45 m 700 P31 P31_WAVE.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED Interface Pulley
Activity P51: LR Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor)
 Activity P51: LR Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Circuits P51 LR Circuit.DS (See end of activity) (See end of activity) Equipment Needed
Activity P51: LR Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Circuits P51 LR Circuit.DS (See end of activity) (See end of activity) Equipment Needed
Affiliate Millions - How To Create Money Magnets
 Michael Cheney s Affiliate Millions 1 Now it s time to talk about how to create your money magnets. What are money magnets? Well, as the name suggests, it s just anything that you can put on your website
Michael Cheney s Affiliate Millions 1 Now it s time to talk about how to create your money magnets. What are money magnets? Well, as the name suggests, it s just anything that you can put on your website
Term Definition Introduced in:
 60 Minutes of Access Secrets Key Terms Term Definition Introduced in: Calculated Field A field that displays the results of a calculation. Introduced in Access 2010, this field allows you to make calculations
60 Minutes of Access Secrets Key Terms Term Definition Introduced in: Calculated Field A field that displays the results of a calculation. Introduced in Access 2010, this field allows you to make calculations
The Oscilloscope. Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift ( ) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope.
 The Oscilloscope Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift (1667-1745) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope. THEORY The oscilloscope, or scope for short, is a device for drawing
The Oscilloscope Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift (1667-1745) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope. THEORY The oscilloscope, or scope for short, is a device for drawing
Practicing with Ableton: Click Tracks and Reference Tracks
 Practicing with Ableton: Click Tracks and Reference Tracks Why practice our instruments with Ableton? Using Ableton in our practice can help us become better musicians. It offers Click tracks that change
Practicing with Ableton: Click Tracks and Reference Tracks Why practice our instruments with Ableton? Using Ableton in our practice can help us become better musicians. It offers Click tracks that change
PHYSICS 220 LAB #1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL MOTION
 /53 pts Name: Partners: PHYSICS 22 LAB #1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES 1. To learn about three complementary ways to describe motion in one dimension words, graphs, and vector diagrams. 2. To acquire
/53 pts Name: Partners: PHYSICS 22 LAB #1: ONE-DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES 1. To learn about three complementary ways to describe motion in one dimension words, graphs, and vector diagrams. 2. To acquire
// Parts of a Multimeter
 Using a Multimeter // Parts of a Multimeter Often you will have to use a multimeter for troubleshooting a circuit, testing components, materials or the occasional worksheet. This section will cover how
Using a Multimeter // Parts of a Multimeter Often you will have to use a multimeter for troubleshooting a circuit, testing components, materials or the occasional worksheet. This section will cover how
sin(wt) y(t) Exciter Vibrating armature ENME599 1
 ENME599 1 LAB #3: Kinematic Excitation (Forced Vibration) of a SDOF system Students must read the laboratory instruction manual prior to the lab session. The lab report must be submitted in the beginning
ENME599 1 LAB #3: Kinematic Excitation (Forced Vibration) of a SDOF system Students must read the laboratory instruction manual prior to the lab session. The lab report must be submitted in the beginning
3. Apparatus/ Materials 1) Computer 2) Vernier board circuit
 Experiment 3 RLC Circuits 1. Introduction You have studied the behavior of capacitors and inductors in simple direct-current (DC) circuits. In alternating current (AC) circuits, these elements act somewhat
Experiment 3 RLC Circuits 1. Introduction You have studied the behavior of capacitors and inductors in simple direct-current (DC) circuits. In alternating current (AC) circuits, these elements act somewhat
RLC Circuits Building An AM Radio
 RLC Circuits Building An AM Radio (Left) An AM radio station antenna tower; (Right) A circuit that tunes for AM frequencies. You will build this circuit in lab to receive AM transmissions from towers such
RLC Circuits Building An AM Radio (Left) An AM radio station antenna tower; (Right) A circuit that tunes for AM frequencies. You will build this circuit in lab to receive AM transmissions from towers such
RLC Circuits Building An AM Radio
 1 RLC Circuits Building An AM Radio (Left) An AM radio station antenna tower; (Right) A circuit that tunes for AM frequencies. You will build this circuit in lab to receive AM transmissions from towers
1 RLC Circuits Building An AM Radio (Left) An AM radio station antenna tower; (Right) A circuit that tunes for AM frequencies. You will build this circuit in lab to receive AM transmissions from towers
Physics 4B, Lab # 2 Circuit Tools and Voltage Waveforms
 Physics 4B, Lab # 2 Circuit Tools and Voltage Waveforms OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar with a DC power supply and setting the output voltage. 2. Learn how to measure voltages & currents using a Digital
Physics 4B, Lab # 2 Circuit Tools and Voltage Waveforms OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar with a DC power supply and setting the output voltage. 2. Learn how to measure voltages & currents using a Digital
Experiment P01: Understanding Motion I Distance and Time (Motion Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P01-1 Experiment P01: Understanding Motion I Distance and Time (Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file linear motion 30 m 500 or 700 P01
PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P01-1 Experiment P01: Understanding Motion I Distance and Time (Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file linear motion 30 m 500 or 700 P01
Laboratory 1: Motion in One Dimension
 Phys 131L Spring 2018 Laboratory 1: Motion in One Dimension Classical physics describes the motion of objects with the fundamental goal of tracking the position of an object as time passes. The simplest
Phys 131L Spring 2018 Laboratory 1: Motion in One Dimension Classical physics describes the motion of objects with the fundamental goal of tracking the position of an object as time passes. The simplest
PHYSICS LAB. Sound. Date: GRADE: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JAMES MADISON UNIVERSITY
 PHYSICS LAB Sound Printed Names: Signatures: Date: Lab Section: Instructor: GRADE: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JAMES MADISON UNIVERSITY Revision August 2003 Sound Investigations Sound Investigations 78 Part I -
PHYSICS LAB Sound Printed Names: Signatures: Date: Lab Section: Instructor: GRADE: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JAMES MADISON UNIVERSITY Revision August 2003 Sound Investigations Sound Investigations 78 Part I -
Experiment 3 Topic: Dynamic System Response Week A Procedure
 Experiment 3 Topic: Dynamic System Response Week A Procedure Laboratory Assistant: Email: Office Hours: LEX-3 Website: Brock Hedlund bhedlund@nd.edu 11/05 11/08 5 pm to 6 pm in B14 http://www.nd.edu/~jott/measurements/measurements_lab/e3
Experiment 3 Topic: Dynamic System Response Week A Procedure Laboratory Assistant: Email: Office Hours: LEX-3 Website: Brock Hedlund bhedlund@nd.edu 11/05 11/08 5 pm to 6 pm in B14 http://www.nd.edu/~jott/measurements/measurements_lab/e3
In this video tutorial, we re going to take a look at continuity editing and how we can use editing techniques to compress time.
 Digital Film School Continuity editing In this video tutorial, we re going to take a look at continuity editing and how we can use editing techniques to compress time. Rick and John have given me the rushes
Digital Film School Continuity editing In this video tutorial, we re going to take a look at continuity editing and how we can use editing techniques to compress time. Rick and John have given me the rushes
Principles of Technology DUE one week from your lab day. Lab 2: Measuring Forces
 Lab 2: Measuring Forces Principles of Technology DUE one week from your lab day Lab Objectives When you ve finished this lab, you should be able to do the following: Measure forces by using appropriate
Lab 2: Measuring Forces Principles of Technology DUE one week from your lab day Lab Objectives When you ve finished this lab, you should be able to do the following: Measure forces by using appropriate
STAB22 section 2.4. Figure 2: Data set 2. Figure 1: Data set 1
 STAB22 section 2.4 2.73 The four correlations are all 0.816, and all four regressions are ŷ = 3 + 0.5x. (b) can be answered by drawing fitted line plots in the four cases. See Figures 1, 2, 3 and 4. Figure
STAB22 section 2.4 2.73 The four correlations are all 0.816, and all four regressions are ŷ = 3 + 0.5x. (b) can be answered by drawing fitted line plots in the four cases. See Figures 1, 2, 3 and 4. Figure
Momentum and Impulse. Objective. Theory. Investigate the relationship between impulse and momentum.
 [For International Campus Lab ONLY] Objective Investigate the relationship between impulse and momentum. Theory ----------------------------- Reference -------------------------- Young & Freedman, University
[For International Campus Lab ONLY] Objective Investigate the relationship between impulse and momentum. Theory ----------------------------- Reference -------------------------- Young & Freedman, University
An Inclined Plane. Experiment OBJECTIVES MATERIALS
 Dual-Range Force Sensor An Inclined Plane Experiment 22 An inclined plane is a slanted surface used to raise objects. The sloping floor of a theater, a road over a mountain, and a ramp into a building
Dual-Range Force Sensor An Inclined Plane Experiment 22 An inclined plane is a slanted surface used to raise objects. The sloping floor of a theater, a road over a mountain, and a ramp into a building
Physics 334 Notes for Lab 2 Capacitors
 Physics 334 Notes for Lab 2 Capacitors January 19, 2009 Do the Lab Manual sections in the following order 2-1, 2-3, 2-4, 2-2, 2-5, 2-6, 2-8 (Skip 2-7 and 2-9). First, here s a review of some important
Physics 334 Notes for Lab 2 Capacitors January 19, 2009 Do the Lab Manual sections in the following order 2-1, 2-3, 2-4, 2-2, 2-5, 2-6, 2-8 (Skip 2-7 and 2-9). First, here s a review of some important
Activity P57: Transistor Lab 3 Common-Emitter Amplifier (Voltage Sensor)
 Activity P57: Transistor Lab 3 Common-Emitter Amplifier (Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Semiconductors P57 Common Emitter.DS (See end of activity) (See end
Activity P57: Transistor Lab 3 Common-Emitter Amplifier (Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Semiconductors P57 Common Emitter.DS (See end of activity) (See end
EENG-201 Experiment # 4: Function Generator, Oscilloscope
 EENG-201 Experiment # 4: Function Generator, Oscilloscope I. Objectives Upon completion of this experiment, the student should be able to 1. To become familiar with the use of a function generator. 2.
EENG-201 Experiment # 4: Function Generator, Oscilloscope I. Objectives Upon completion of this experiment, the student should be able to 1. To become familiar with the use of a function generator. 2.
Time-Varying Signals
 Time-Varying Signals Objective This lab gives a practical introduction to signals that varies with time using the components such as: 1. Arbitrary Function Generator 2. Oscilloscopes The grounding issues
Time-Varying Signals Objective This lab gives a practical introduction to signals that varies with time using the components such as: 1. Arbitrary Function Generator 2. Oscilloscopes The grounding issues
EXPERIMENT 8: LRC CIRCUITS
 EXPERIMENT 8: LRC CIRCUITS Equipment List S 1 BK Precision 4011 or 4011A 5 MHz Function Generator OS BK 2120B Dual Channel Oscilloscope V 1 BK 388B Multimeter L 1 Leeds & Northrup #1532 100 mh Inductor
EXPERIMENT 8: LRC CIRCUITS Equipment List S 1 BK Precision 4011 or 4011A 5 MHz Function Generator OS BK 2120B Dual Channel Oscilloscope V 1 BK 388B Multimeter L 1 Leeds & Northrup #1532 100 mh Inductor
Lab 2b: Dynamic Response of a Rotor with Shaft Imbalance
 Lab 2b: Dynamic Response of a Rotor with Shaft Imbalance OBJECTIVE: To calibrate an induction position/displacement sensor using a micrometer To calculate and measure the natural frequency of a simply-supported
Lab 2b: Dynamic Response of a Rotor with Shaft Imbalance OBJECTIVE: To calibrate an induction position/displacement sensor using a micrometer To calculate and measure the natural frequency of a simply-supported
Part 1. Using LabVIEW to Measure Current
 NAME EET 2259 Lab 11 Studying Characteristic Curves with LabVIEW OBJECTIVES -Use LabVIEW to measure DC current. -Write LabVIEW programs to display the characteristic curves of resistors, diodes, and transistors
NAME EET 2259 Lab 11 Studying Characteristic Curves with LabVIEW OBJECTIVES -Use LabVIEW to measure DC current. -Write LabVIEW programs to display the characteristic curves of resistors, diodes, and transistors
16.3 Standing Waves on a String.notebook February 16, 2018
 Section 16.3 Standing Waves on a String A wave pulse traveling along a string attached to a wall will be reflected when it reaches the wall, or the boundary. All of the wave s energy is reflected; hence
Section 16.3 Standing Waves on a String A wave pulse traveling along a string attached to a wall will be reflected when it reaches the wall, or the boundary. All of the wave s energy is reflected; hence
Ph 2306 Experiment 2: A Look at Sound
 Name ID number Date Lab CRN Lab partner Lab instructor Ph 2306 Experiment 2: A Look at Sound Objective Because sound is something that we can only hear, it is difficult to analyze. You have probably seen
Name ID number Date Lab CRN Lab partner Lab instructor Ph 2306 Experiment 2: A Look at Sound Objective Because sound is something that we can only hear, it is difficult to analyze. You have probably seen
