+1 (479)
|
|
|
- Horatio Sanders
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to VLSI Design +1 (479)
2 Invention of the Transistor Vacuum tubes ruled in first half of 20th century Large, expensive, power-hungry, unreliable 1947: first point contact transistor John Bardeen and Walter Brattain at Bell Labs Read Crystal Fire by Riordan, Hoddeson 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 2
3 Transistor Types Bipolar transistors npn or pnp silicon structure Small current into very thin base layer controls large currents between emitter and collector Base currents limit integration density Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors nmos and pmos MOSFETS Voltage applied to insulated gate controls current between source and drain Low power allows very high integration 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 3
4 MOS Integrated Circuits 1970 s processors usually had only nmos transistors Inexpensive, but consume power while idle Intel bit SRAM Intel bit mproc 1980s-present: CMOS (Complementary MOS) processes for low idle power 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 4
5 Moore s Law Original (1965) Gordon Moore (Fairchild) The number of transistors on an IC would double every year. Revised (1975) Gordon Moore (Intel) A doubling every two years, rather than every year. Moore: "Cramming more components onto integrated circuits" Electronics, Vol. 38, No. 8, 1965 IEEE, IEDM Tech Digest (1975) 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 5
6 Moore s Law Moore's law suggests exponential growth (2x every 18 months) Is not about performance, not about chip size Hinted about the cost reduction Exponential transistor count Exponential complexity 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 6
7 Silicon Lattice Transistors are built on a silicon substrate Silicon is a Group IV material Forms crystal lattice with bonds to four neighbors Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 7
8 Dopants Silicon is a semiconductor Pure silicon has no free carriers and conducts poorly Adding dopants increases the conductivity Group V: extra electron (n-type) Group III: missing electron, called hole (p-type) Si Si - Si Si Si + Si Si + As Si Si B - Si Si Si Si Si Si Si 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 8
9 P-N Junctions A junction between p-type and n-type semiconductor forms a diode. Current flows only in one direction p-type n-type anode cathode 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 9
10 nmos Transistor Four terminals: gate, source, drain, body Gate oxide body stack looks like a capacitor Gate and body are conductors SiO 2 (oxide) is a very good insulator Called metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) capacitor Even though gate may not be made of metal Source Gate Drain Polysilicon SiO 2 n+ n+ p bulk Si 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 10
11 nmos Operation Body is commonly tied to ground (0 V) When the gate is at a low voltage: P-type body is at low voltage Source-body and drain-body diodes are OFF No current flows, transistor is OFF Source Gate Drain Polysilicon SiO 2 n+ p n+ bulk Si S 0 D 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 11
12 nmos Operation When the gate is at a high voltage: Positive charge on gate of MOS capacitor Negative charge attracted to body Inverts a channel under gate to n-type Now current can flow through n-type silicon from source through channel to drain, transistor is ON Source Gate Drain Polysilicon SiO 2 n+ p n+ bulk Si S 1 D 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 12
13 pmos Transistor Similar, but doping and voltages reversed Body tied to high voltage (V DD ) Gate low: transistor ON Gate high: transistor OFF Bubble indicates inverted behavior Polysilicon Source Gate Drain SiO 2 p+ p+ n bulk Si 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 13
14 CMOS Inverter A Y A Y V DD ON A=0 Y=1 OFF GND 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 14
15 CMOS NAND Gate A B Y A=1 OFF OFF Y=0 ON B=1 ON 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 15
16 CMOS NOR Gate A B Y A B Y 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 16
17 From Logic Symbol to Circuit Recall what you learned in CSCE2114 NAND Vdd IN1 IN2 OUT IN1 IN2 OUT IN1 IN2 OUT GND Logic Symbol Truth table Schematic 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 17
18 From Circuit to Layout Transistors are formed when poly is drawn over active/diffusion layer Vdd IN1 IN2 OUT IN1 IN2 OUT Contact Metal layer Poly layer Diffusion layer N-Well PMOS GND NMOS 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 18
19 Standard Cells Layout in out in1 in2 out VDD VDD n+ (n-implant) n-well p-well p-well n-well p+ (p-implant) contact poly (gate) in out in1 in2 metal 1 out cell bounrary p-well n-well p-well n-well GND GND INV NAND2 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 19
20 Standard Cells Layout Abstract The layout abstract hides details about standard cells and macros, leaves only interface geometries and connections Pins, obstacles, nets in out in1 in2 out VDD VDD metal 1 cell bounrary in out in1 out in2 GND INV GND NAND2 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 20
21 From Layout to Silicon Once the layout is done, it is send to foundries for fabrication Top-down view Side view 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 21
22 CMOS Fabrication CMOS transistors are fabricated on silicon wafer Lithography process similar to printing press On each step, different materials are deposited or etched Easiest to understand by viewing both top and cross-section of wafer in a simplified manufacturing process Video from Intel: 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 22
23 Inverter Mask Set Transistors and wires are defined by masks Cross-section taken along dashed line A Y GND V DD substrate tap nmos transistor pmos transistor well tap 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 23
24 Inverter Cross-Section Typically use p-type substrate for nmos transistors Requires n-well for body of pmos transistors A GND Y V DD SiO 2 n+ diffusion n+ n+ p+ p substrate n well p+ p+ diffusion polysilicon metal1 nmos transistor pmos transistor 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 24
25 Well and Substrate Contacts Substrate must be tied to GND and n-well to V DD Metal to lightly-doped semiconductor forms poor connection (used for Schottky Diode) Use heavily doped well and substrate contacts / taps A GND Y V DD p+ n+ n+ p+ p+ n+ p substrate n well substrate tap well tap 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 25
26 Detailed Mask Views Six masks n-well Polysilicon n+ diffusion p+ diffusion Contact n well Polysilicon n+ Diffusion p+ Diffusion Contact Metal Metal 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 26
27 Fabrication Steps Start with blank wafer Build inverter from the bottom up First step will be to form the n-well Cover wafer with protective layer of SiO 2 (oxide) Remove layer where n-well should be built Implant or diffuse n dopants into exposed wafer Strip off SiO 2 p substrate 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 27
28 Oxidation Grow SiO 2 on top of Si wafer C with H 2 O or O 2 in oxidation furnace SiO 2 p substrate 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 28
29 Photoresist Spin on photoresist Photoresist is a light-sensitive organic polymer Softens where exposed to light Photoresist SiO 2 p substrate 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 29
30 Lithography Expose photoresist through n-well mask Strip off exposed photoresist Top View Cross-section Photoresist SiO 2 p substrate 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 30
31 Etch Etch oxide with hydrofluoric acid (HF) Seeps through skin and eats bone; nasty stuff!!! Only attacks oxide where resist has been exposed Photoresist SiO 2 p substrate 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 31
32 Strip Photoresist Strip off remaining photoresist Use mixture of acids called piranha etch (H 2 SO 4 + H 2 O 2 ) Necessary so resist doesn t melt in next step SiO 2 p substrate 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 32
33 n-well n-well is formed with diffusion or ion implantation Diffusion Place wafer in furnace with arsenic gas Heat until As atoms diffuse into exposed Si Ion Implantation Blast wafer with beam of As ions Ions blocked by SiO 2, only enter exposed Si SiO 2 n well 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 33
34 Strip Oxide Strip off the remaining oxide using HF Back to bare wafer with n-well Subsequent steps involve similar series of steps p substrate n well 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 34
35 Polysilicon Deposit very thin layer of gate oxide < 20 Å (6-7 atomic layers) Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) of silicon layer Place wafer in furnace with Silane gas (SiH 4 ) Forms many small crystals called polysilicon Heavily doped to be good conductor Polysilicon Thin gate oxide p substrate n well 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 35
36 Polysilicon Patterning Use same lithography process to pattern polysilicon Top View Polysilicon Cross-section Polysilicon Thin gate oxide p substrate n well 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 36
37 N-diffusion Use oxide and masking to expose where n+ dopants should be diffused or implanted N-diffusion forms nmos source, drain, and n-well contact p substrate n well 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 37
38 N-diffusion (cont.) Pattern oxide and form n+ regions n+ Diffusion p substrate n well 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 38
39 N-diffusion (cont.) Historically dopants were diffused Usually ion implantation today But regions are still called diffusion n+ n+ n+ p substrate n well 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 39
40 N-diffusion (cont.) Strip off oxide to complete patterning step n+ n+ n+ p substrate n well 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 40
41 P-Diffusion Similar set of steps form p+ diffusion regions for pmos source and drain and substrate contact p+ Diffusion p+ n+ n+ p+ p+ n+ p substrate n well 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 41
42 Contacts Now we need to wire together the devices Cover chip with thick field oxide Etch oxide where contact cuts are needed Contact p+ n+ n+ p+ p+ n+ Thick field oxide p substrate n well 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 42
43 Metalization Sputter on copper / aluminum over whole wafer Pattern to remove excess metal, leaving wires Metal p+ n+ n+ p+ p+ n+ Metal Thick field oxide p substrate n well 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 43
44 Layout Chips are specified with set of masks Minimum dimensions of masks determine transistor size (and hence speed, cost, and power) Feature size f = minimum distance between source and drain Set by minimum width of polysilicon Feature size scales ~0.7x every 2 years both lateral and vertical Moore s law Normalize feature size when describing design rules Express rules in terms of λ= f/2 E.g. λ = 90 nm in 180 nm process 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 44
45 Design Rule Design rules ensure the layout is manufacturable. VDD 1 n-well 7 3 p-well 1: Min dist. (poly, contact) 2: Min dist. (metal 1) 3: Min dist. (active, well boundary) : Min width (poly) in out 5: Min width (metal 1) 6: Min dist. (contact) p-well n-well 7: Min dist. (contact, well bounrary) 6 GND 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 45
46 Types of Design Rules Size rules such as min/max width: The dimensions of any component (shape), e.g., length of a boundary edge or area of the shape, cannot be smaller than given min/max values. Separation rules such as min separation: Two shapes, either on the same layer or on adjacent layers, must be a minimum distance apart. Overlap rules such as min overlap: Two connected shapes on adjacent layers must have a certain amount of overlap due to inaccuracy of mask alignment to previously-made patterns on the wafer. Other rules Min/max area, min density etc 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 46
47 Types of Design Constraint Technology constraints Enable fabrication for a specific technology node and are derived from technology restrictions. Examples include minimum layout widths and spacing values between layout shapes. Electrical constraints Ensure the desired electrical behavior of the design. Examples include meeting maximum timing constraints for signal delay and staying below maximum coupling capacitances. Design methodology constraints Introduced to reduce the overall complexity of the design process. Examples include the use of preferred wiring directions during routing, and the placement of standard cells in rows. 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 47
48 VLSI Design Full-Custom Design Mostly used for microprocessor, memory and FPGAs Few design constraint: as long as it can be manufactured, it is allowed High performance, low power, small silicon area, and highly optimized High cost, time consuming, error-prone, and difficult to test Semi-Custom Design Uses standard cells and macro blocks as building materials Regularly place the cells in rows and arrays Need to add wires and vias for interconnection Standard flow exists with silicon-verified tools. Can be easily verified and tested. Short design cycle and time-to-market (Reduce cost) A slight degradation in performance and area (Increase cost) FPGA, PLA 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 48
49 VLSI Design Full-Custom Design Semi-Custom Design 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 49
50 Full-Custom Design (CPU) CPU Specification Comparison CPU Process Cores Transistor Count Die Size AMD Bulldozer 8C 32nm 8 1.2B 315mm 2 Intel Ivy Bridge 4C 22nm 4 1.4B 160mm 2 Intel Sandy Bridge E (6C) 32nm B 435mm 2 Intel Sandy Bridge 4C 32nm B 216mm 2 Intel Lynnfield 4C 45nm 4 774M 296mm 2 Intel Sandy Bridge 2C (GT2) 32nm 2 624M 149mm 2 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 50
51 Full-Custom Design (SRAM) SRAM cells are highly compact CMOS transistor arrays 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 51
52 Full-Custom Design (DRAM) DRAM unit cells are made of one NMOS and one capacitor Layout is highly vendor dependent 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 52
53 Standard-Cell-Based Design Macro Standard cells I/O cell 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 53
54 Custom vs. Synthesis 8-bit Implementations 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 54
55 FPGA Design In FPGA, logic elements and switch boxes as well as interconnect resources are pre-fabricated into the chip The logic elements and connections are programmable 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 55
56 Comparisons of Design Styles VLSI Design comparison FPGA provides fastest design time, with highest constraint on the cells and interconnects Semi-custom designs are extremely popular with application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC), allowing designing high performance chips with automated tools (Our focus) Full-Custom Standard-cell FPGA Cell size Variable Fixed height Fixed Cell type Variable Variable Programmable Cell placement Variable In row Fixed Interconnection Variable Variable Programmable Area Compact Compact to moderate Large Performance High High to moderate Low 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 56
57 Design Styles Tradeoffs 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 57
58 VLSI Semi-Custom Design Flow System Specification Architecture Design Logic/Circuit Design 64-bit Processor System Model RTL Netlist Freq Area Power 2GHz / 50mm 2 / 10W Synthesis Gate-level Netlist Physical Design Layout Verification Tape-out Fabrication Bare die Packaging & Testing Chip 9/5/2017 CSCE/ELEG 4914: Advnaced Digital Design 58
420 Intro to VLSI Design
 Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering 420 Intro to VLSI Design Lecture 0: Course Introduction and Overview Valencia M. Joyner Spring 2005 Getting Started Syllabus About the Instructor Labs, Problem
Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering 420 Intro to VLSI Design Lecture 0: Course Introduction and Overview Valencia M. Joyner Spring 2005 Getting Started Syllabus About the Instructor Labs, Problem
Lecture 0: Introduction
 Lecture 0: Introduction Introduction Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): bucketloads! Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Fast, cheap, low power
Lecture 0: Introduction Introduction Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): bucketloads! Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Fast, cheap, low power
VLSI Design. Introduction
 VLSI Design Introduction Outline Introduction Silicon, pn-junctions and transistors A Brief History Operation of MOS Transistors CMOS circuits Fabrication steps for CMOS circuits Introduction Integrated
VLSI Design Introduction Outline Introduction Silicon, pn-junctions and transistors A Brief History Operation of MOS Transistors CMOS circuits Fabrication steps for CMOS circuits Introduction Integrated
VLSI Design. Introduction
 Tassadaq Hussain VLSI Design Introduction Outcome of this course Problem Aims Objectives Outcomes Data Collection Theoretical Model Mathematical Model Validate Development Analysis and Observation Pseudo
Tassadaq Hussain VLSI Design Introduction Outcome of this course Problem Aims Objectives Outcomes Data Collection Theoretical Model Mathematical Model Validate Development Analysis and Observation Pseudo
EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis. Lecture 1 Introduction Zhuo Feng
 EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Lecture 1 Introduction Zhuo Feng 1.1 Prof. Zhuo Feng Office: EERC 730 Phone: 487-3116 Email: zhuofeng@mtu.edu Class Website http://www.ece.mtu.edu/~zhuofeng/ee4800fall2010.html
EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Lecture 1 Introduction Zhuo Feng 1.1 Prof. Zhuo Feng Office: EERC 730 Phone: 487-3116 Email: zhuofeng@mtu.edu Class Website http://www.ece.mtu.edu/~zhuofeng/ee4800fall2010.html
FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. Dr. Mohammed M. Farag
 FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Outline Overview of CMOS Fabrication Processes The CMOS Fabrication Process Flow Design Rules Reference: Uyemura, John P. "Introduction to
FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Outline Overview of CMOS Fabrication Processes The CMOS Fabrication Process Flow Design Rules Reference: Uyemura, John P. "Introduction to
Basic Fabrication Steps
 Basic Fabrication Steps and Layout Somayyeh Koohi Department of Computer Engineering Adapted with modifications from lecture notes prepared by author Outline Fabrication steps Transistor structures Transistor
Basic Fabrication Steps and Layout Somayyeh Koohi Department of Computer Engineering Adapted with modifications from lecture notes prepared by author Outline Fabrication steps Transistor structures Transistor
Topic 3. CMOS Fabrication Process
 Topic 3 CMOS Fabrication Process Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: p.cheung@ic.ac.uk Lecture 3-1 Layout of a Inverter
Topic 3 CMOS Fabrication Process Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: p.cheung@ic.ac.uk Lecture 3-1 Layout of a Inverter
Introduction. Reading: Chapter 1. Courtesy of Dr. Dansereau, Dr. Brown, Dr. Vranesic, Dr. Harris, and Dr. Choi.
 Introduction Reading: Chapter 1 Courtesy of Dr. Dansereau, Dr. Brown, Dr. Vranesic, Dr. Harris, and Dr. Choi http://csce.uark.edu +1 (479) 575-6043 yrpeng@uark.edu Why study logic design? Obvious reasons
Introduction Reading: Chapter 1 Courtesy of Dr. Dansereau, Dr. Brown, Dr. Vranesic, Dr. Harris, and Dr. Choi http://csce.uark.edu +1 (479) 575-6043 yrpeng@uark.edu Why study logic design? Obvious reasons
Layout of a Inverter. Topic 3. CMOS Fabrication Process. The CMOS Process - photolithography (2) The CMOS Process - photolithography (1) v o.
 Layout of a Inverter Topic 3 CMOS Fabrication Process V DD Q p Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London v i v o Q n URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: p.cheung@ic.ac.uk
Layout of a Inverter Topic 3 CMOS Fabrication Process V DD Q p Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London v i v o Q n URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: p.cheung@ic.ac.uk
EMT 251 Introduction to IC Design
 EMT 251 Introduction to IC Design (Pengantar Rekabentuk Litar Terkamir) Semester II 2011/2012 Introduction to IC design and Transistor Fundamental Some Keywords! Very-large-scale-integration (VLSI) is
EMT 251 Introduction to IC Design (Pengantar Rekabentuk Litar Terkamir) Semester II 2011/2012 Introduction to IC design and Transistor Fundamental Some Keywords! Very-large-scale-integration (VLSI) is
Spiral 1 / Unit 8. Transistor Implementations CMOS Logic Gates
 18.1 Spiral 1 / Unit 8 Transistor Implementations CMOS Logic Gates 18.2 Spiral Content Mapping Spiral Theory Combinational Design Sequential Design System Level Design Implementation and Tools Project
18.1 Spiral 1 / Unit 8 Transistor Implementations CMOS Logic Gates 18.2 Spiral Content Mapping Spiral Theory Combinational Design Sequential Design System Level Design Implementation and Tools Project
Transistor was first invented by William.B.Shockley, Walter Brattain and John Bardeen of Bell Labratories. In 1961, first IC was introduced.
 Unit 1 Basic MOS Technology Transistor was first invented by William.B.Shockley, Walter Brattain and John Bardeen of Bell Labratories. In 1961, first IC was introduced. Levels of Integration:- i) SSI:-
Unit 1 Basic MOS Technology Transistor was first invented by William.B.Shockley, Walter Brattain and John Bardeen of Bell Labratories. In 1961, first IC was introduced. Levels of Integration:- i) SSI:-
ECE 5745 Complex Digital ASIC Design Topic 2: CMOS Devices
 ECE 5745 Complex Digital ASIC Design Topic 2: CMOS Devices Christopher Batten School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University http://www.csl.cornell.edu/courses/ece5950 Simple Transistor
ECE 5745 Complex Digital ASIC Design Topic 2: CMOS Devices Christopher Batten School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University http://www.csl.cornell.edu/courses/ece5950 Simple Transistor
EE 434 ASIC and Digital Systems. Prof. Dae Hyun Kim School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University.
 EE 434 ASIC and Digital Systems Prof. Dae Hyun Kim School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Preliminaries VLSI Design System Specification Functional Design RTL
EE 434 ASIC and Digital Systems Prof. Dae Hyun Kim School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Preliminaries VLSI Design System Specification Functional Design RTL
Jack Keil Wolf Lecture. ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals. Lecture Outline. MOSFET N-Type, P-Type.
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Jack Keil Wolf Lecture Lec 3: January 24, 2019 MOS Fabrication pt. 2: Design Rules and Layout http://www.ese.upenn.edu/about-ese/events/wolf.php
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Jack Keil Wolf Lecture Lec 3: January 24, 2019 MOS Fabrication pt. 2: Design Rules and Layout http://www.ese.upenn.edu/about-ese/events/wolf.php
CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits Lec 2 Fabrication of MOSFETs
 CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits Lec 2 Fabrication of MOSFETs 1 CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits 3 rd Edition Categories of Materials Materials can be categorized into three main groups regarding their
CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits Lec 2 Fabrication of MOSFETs 1 CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits 3 rd Edition Categories of Materials Materials can be categorized into three main groups regarding their
Lecture 0: Introduction
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture : Introduction David Harris Steven Levitan Harvey Mudd College University of Pittsburgh Spring 24 Fall 28 Administrivia Professor Steven Levitan TA: Bo Zhao Syllabus
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture : Introduction David Harris Steven Levitan Harvey Mudd College University of Pittsburgh Spring 24 Fall 28 Administrivia Professor Steven Levitan TA: Bo Zhao Syllabus
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 3: January 24, 2019 MOS Fabrication pt. 2: Design Rules and Layout Penn ESE 570 Spring 2019 Khanna Jack Keil Wolf Lecture http://www.ese.upenn.edu/about-ese/events/wolf.php
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 3: January 24, 2019 MOS Fabrication pt. 2: Design Rules and Layout Penn ESE 570 Spring 2019 Khanna Jack Keil Wolf Lecture http://www.ese.upenn.edu/about-ese/events/wolf.php
Chapter 3: Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing 2006/9/27 1. Topics
 Chapter 3: Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing 2006/9/27 1 Topics What is semiconductor Basic semiconductor devices Basics of IC processing CMOS technologies 2006/9/27 2 1 What is Semiconductor
Chapter 3: Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing 2006/9/27 1 Topics What is semiconductor Basic semiconductor devices Basics of IC processing CMOS technologies 2006/9/27 2 1 What is Semiconductor
Outcomes. Spiral 1 / Unit 8. DeMorgan s Theorem DEMORGAN'S THEOREM. Transistor Implementations CMOS Logic Gates
 18.1 18.2 Spiral 1 / Unit 8 Transistor Implementations MOS Logic Gates Mark Redekopp Outcomes I know the difference between combinational and sequential logic and can name examples of each. I understand
18.1 18.2 Spiral 1 / Unit 8 Transistor Implementations MOS Logic Gates Mark Redekopp Outcomes I know the difference between combinational and sequential logic and can name examples of each. I understand
2009 Spring CS211 Digital Systems & Lab 1 CHAPTER 3: TECHNOLOGY (PART 2)
 1 CHAPTER 3: IMPLEMENTATION TECHNOLOGY (PART 2) Whatwillwelearninthischapter? we learn in this 2 How transistors operate and form simple switches CMOS logic gates IC technology FPGAs and other PLDs Basic
1 CHAPTER 3: IMPLEMENTATION TECHNOLOGY (PART 2) Whatwillwelearninthischapter? we learn in this 2 How transistors operate and form simple switches CMOS logic gates IC technology FPGAs and other PLDs Basic
Chapter 3 Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing
 Chapter 3 Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing 1 Objectives Identify at least two semiconductor materials from the periodic table of elements List n-type and p-type dopants Describe a diode and
Chapter 3 Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing 1 Objectives Identify at least two semiconductor materials from the periodic table of elements List n-type and p-type dopants Describe a diode and
EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02
 EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall 2014 Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02 1 Lecture Outline Review on semiconductor materials Review on microelectronic devices Example of microelectronic
EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall 2014 Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02 1 Lecture Outline Review on semiconductor materials Review on microelectronic devices Example of microelectronic
INTRODUCTION TO MOS TECHNOLOGY
 INTRODUCTION TO MOS TECHNOLOGY 1. The MOS transistor The most basic element in the design of a large scale integrated circuit is the transistor. For the processes we will discuss, the type of transistor
INTRODUCTION TO MOS TECHNOLOGY 1. The MOS transistor The most basic element in the design of a large scale integrated circuit is the transistor. For the processes we will discuss, the type of transistor
EE 330 Lecture 7. Design Rules. IC Fabrication Technology Part 1
 EE 330 Lecture 7 Design Rules IC Fabrication Technology Part 1 Review from Last Time Technology Files Provide Information About Process Process Flow (Fabrication Technology) Model Parameters Design Rules
EE 330 Lecture 7 Design Rules IC Fabrication Technology Part 1 Review from Last Time Technology Files Provide Information About Process Process Flow (Fabrication Technology) Model Parameters Design Rules
! Review: MOS IV Curves and Switch Model. ! MOS Device Layout. ! Inverter Layout. ! Gate Layout and Stick Diagrams. ! Design Rules. !
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 3: January 21, 2017 MOS Fabrication pt. 2: Design Rules and Layout Lecture Outline! Review: MOS IV Curves and Switch Model! MOS Device Layout!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 3: January 21, 2017 MOS Fabrication pt. 2: Design Rules and Layout Lecture Outline! Review: MOS IV Curves and Switch Model! MOS Device Layout!
! Review: MOS IV Curves and Switch Model. ! MOS Device Layout. ! Inverter Layout. ! Gate Layout and Stick Diagrams. ! Design Rules. !
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 3: January 21, 2016 MOS Fabrication pt. 2: Design Rules and Layout Lecture Outline! Review: MOS IV Curves and Switch Model! MOS Device Layout!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 3: January 21, 2016 MOS Fabrication pt. 2: Design Rules and Layout Lecture Outline! Review: MOS IV Curves and Switch Model! MOS Device Layout!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 3: January 21, 2016 MOS Fabrication pt. 2: Design Rules and Layout Penn ESE 570 Spring 2016 Khanna Adapted from GATech ESE3060 Slides Lecture
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 3: January 21, 2016 MOS Fabrication pt. 2: Design Rules and Layout Penn ESE 570 Spring 2016 Khanna Adapted from GATech ESE3060 Slides Lecture
Microelectronics, BSc course
 Microelectronics, BSc course MOS circuits: CMOS circuits, construction http://www.eet.bme.hu/~poppe/miel/en/14-cmos.pptx http://www.eet.bme.hu The abstraction level of our study: SYSTEM + MODULE GATE CIRCUIT
Microelectronics, BSc course MOS circuits: CMOS circuits, construction http://www.eet.bme.hu/~poppe/miel/en/14-cmos.pptx http://www.eet.bme.hu The abstraction level of our study: SYSTEM + MODULE GATE CIRCUIT
PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. Dr. Mohammed M. Farag
 PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Outline Integrated Circuit Layers MOSFETs CMOS Layers Designing FET Arrays EE 432 VLSI Modeling and Design 2 Integrated Circuit Layers
PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Outline Integrated Circuit Layers MOSFETs CMOS Layers Designing FET Arrays EE 432 VLSI Modeling and Design 2 Integrated Circuit Layers
Integrated diodes. The forward voltage drop only slightly depends on the forward current. ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI
 1 Integrated diodes pn junctions of transistor structures can be used as integrated diodes. The choice of the junction is limited by the considerations of switching speed and breakdown voltage. The forward
1 Integrated diodes pn junctions of transistor structures can be used as integrated diodes. The choice of the junction is limited by the considerations of switching speed and breakdown voltage. The forward
Device Technologies. Yau - 1
 Device Technologies Yau - 1 Objectives After studying the material in this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Identify differences between analog and digital devices and passive and active components. Explain
Device Technologies Yau - 1 Objectives After studying the material in this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Identify differences between analog and digital devices and passive and active components. Explain
Chapter 2 : Semiconductor Materials & Devices (II) Feb
 Chapter 2 : Semiconductor Materials & Devices (II) 1 Reference 1. SemiconductorManufacturing Technology: Michael Quirk and Julian Serda (2001) 3. Microelectronic Circuits (5/e): Sedra & Smith (2004) 4.
Chapter 2 : Semiconductor Materials & Devices (II) 1 Reference 1. SemiconductorManufacturing Technology: Michael Quirk and Julian Serda (2001) 3. Microelectronic Circuits (5/e): Sedra & Smith (2004) 4.
MICROPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY
 MICROPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY Assis. Prof. Hossam El-Din Moustafa Lecture 3 Ch.1 The Evolution of The Microprocessor 17-Feb-15 1 Chapter Objectives Introduce the microprocessor evolution from transistors to
MICROPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY Assis. Prof. Hossam El-Din Moustafa Lecture 3 Ch.1 The Evolution of The Microprocessor 17-Feb-15 1 Chapter Objectives Introduce the microprocessor evolution from transistors to
Notes. (Subject Code: 7EC5)
 COMPUCOM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & MANAGEMENT, JAIPUR (DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION) Notes VLSI DESIGN NOTES (Subject Code: 7EC5) Prepared By: MANVENDRA SINGH Class: B. Tech. IV Year, VII
COMPUCOM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & MANAGEMENT, JAIPUR (DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION) Notes VLSI DESIGN NOTES (Subject Code: 7EC5) Prepared By: MANVENDRA SINGH Class: B. Tech. IV Year, VII
EECS 151/251A Spring 2019 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits. Instructors: Wawrzynek. Lecture 8 EE141
 EECS 151/251A Spring 2019 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructors: Wawrzynek Lecture 8 EE141 From the Bottom Up IC processing CMOS Circuits (next lecture) EE141 2 Overview of Physical Implementations
EECS 151/251A Spring 2019 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructors: Wawrzynek Lecture 8 EE141 From the Bottom Up IC processing CMOS Circuits (next lecture) EE141 2 Overview of Physical Implementations
2.8 - CMOS TECHNOLOGY
 CMOS Technology (6/7/00) Page 1 2.8 - CMOS TECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Illustrate the fabrication sequence for a typical MOS transistor 2.) Show the physical
CMOS Technology (6/7/00) Page 1 2.8 - CMOS TECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Illustrate the fabrication sequence for a typical MOS transistor 2.) Show the physical
Layers. Layers. Layers. Transistor Manufacturing COMP375 1
 Layers VLSI COMP370 Intro to Computer Architecture t Applications Middleware other CS classes High level languages Machine Language Microcode Logic circuits Gates Transistors Silicon structures Layers
Layers VLSI COMP370 Intro to Computer Architecture t Applications Middleware other CS classes High level languages Machine Language Microcode Logic circuits Gates Transistors Silicon structures Layers
TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR (DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING) QUESTION BANK- 2018
 TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR (DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING) QUESTION BANK- 2018 Paper Setter Detail Name Designation Mobile No. E-mail ID Raina Modak Assistant Professor 6290025725 raina.modak@tib.edu.in
TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR (DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING) QUESTION BANK- 2018 Paper Setter Detail Name Designation Mobile No. E-mail ID Raina Modak Assistant Professor 6290025725 raina.modak@tib.edu.in
Introduction to VLSI ASIC Design and Technology
 Introduction to VLSI ASIC Design and Technology Paulo Moreira CERN - Geneva, Switzerland Paulo Moreira Introduction 1 Outline Introduction Is there a limit? Transistors CMOS building blocks Parasitics
Introduction to VLSI ASIC Design and Technology Paulo Moreira CERN - Geneva, Switzerland Paulo Moreira Introduction 1 Outline Introduction Is there a limit? Transistors CMOS building blocks Parasitics
Layers. Layers. Layers. Transistor Manufacturing COMP375 1
 VLSI COMP375 Computer Architecture Middleware other CS classes Machine Language Microcode Logic circuits Transistors Middleware Machine Language - earlier Microcode Logic circuits Transistors Middleware
VLSI COMP375 Computer Architecture Middleware other CS classes Machine Language Microcode Logic circuits Transistors Middleware Machine Language - earlier Microcode Logic circuits Transistors Middleware
Design cycle for MEMS
 Design cycle for MEMS Design cycle for ICs IC Process Selection nmos CMOS BiCMOS ECL for logic for I/O and driver circuit for critical high speed parts of the system The Real Estate of a Wafer MOS Transistor
Design cycle for MEMS Design cycle for ICs IC Process Selection nmos CMOS BiCMOS ECL for logic for I/O and driver circuit for critical high speed parts of the system The Real Estate of a Wafer MOS Transistor
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices
 EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 11/6/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 6 BJTs- Lecture 1 Reading Assignment: Chapter 10 More Scalable Device Structures Vertical Scaling is important. For example,
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 11/6/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 6 BJTs- Lecture 1 Reading Assignment: Chapter 10 More Scalable Device Structures Vertical Scaling is important. For example,
Semiconductor Devices
 Semiconductor Devices - 2014 Lecture Course Part of SS Module PY4P03 Dr. P. Stamenov School of Physics and CRANN, Trinity College, Dublin 2, Ireland Hilary Term, TCD 3 th of Feb 14 MOSFET Unmodified Channel
Semiconductor Devices - 2014 Lecture Course Part of SS Module PY4P03 Dr. P. Stamenov School of Physics and CRANN, Trinity College, Dublin 2, Ireland Hilary Term, TCD 3 th of Feb 14 MOSFET Unmodified Channel
Advantage of Having Large Numbers of Function on a Single Chip. Less Area occupied Less power Consumption Higher Speed Higher Reliability Economical
 VLSI DESIGN(UNIT 1) Introduction Some History Invention of the transistor (BJT) 1947 Single-transistor integrated circuit 1958 Invention of CMOS logic gates 1963 First microprocessor (Intel 4004)1970 Very
VLSI DESIGN(UNIT 1) Introduction Some History Invention of the transistor (BJT) 1947 Single-transistor integrated circuit 1958 Invention of CMOS logic gates 1963 First microprocessor (Intel 4004)1970 Very
APPLICATION TRAINING GUIDE
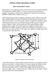 APPLICATION TRAINING GUIDE Basic Semiconductor Theory Semiconductor is an appropriate name for the device because it perfectly describes the material from which it's made -- not quite a conductor, and
APPLICATION TRAINING GUIDE Basic Semiconductor Theory Semiconductor is an appropriate name for the device because it perfectly describes the material from which it's made -- not quite a conductor, and
Progress due to: Feature size reduction - 0.7X/3 years (Moore s Law). Increasing chip size - 16% per year. Creativity in implementing functions.
 Introduction - Chapter 1 Evolution of IC Fabrication 1960 and 1990 integrated t circuits. it Progress due to: Feature size reduction - 0.7X/3 years (Moore s Law). Increasing chip size - 16% per year. Creativity
Introduction - Chapter 1 Evolution of IC Fabrication 1960 and 1990 integrated t circuits. it Progress due to: Feature size reduction - 0.7X/3 years (Moore s Law). Increasing chip size - 16% per year. Creativity
ESE370: Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems. Today. Variation. Variation. Process Corners.
 ESE370: Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Day 13: October 3, 2012 Layout and Area Today Coping with Variation (from last time) Layout Transistors Gates Design rules Standard
ESE370: Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Day 13: October 3, 2012 Layout and Area Today Coping with Variation (from last time) Layout Transistors Gates Design rules Standard
EC0306 INTRODUCTION TO VLSI DESIGN
 EC0306 INTRODUCTION TO VLSI DESIGN UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO MOS CIRCUITS Why VLSI? Integration improves the design: o lower parasitics = higher speed; o lower power; o physically smaller. Integration reduces
EC0306 INTRODUCTION TO VLSI DESIGN UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO MOS CIRCUITS Why VLSI? Integration improves the design: o lower parasitics = higher speed; o lower power; o physically smaller. Integration reduces
Engr354: Digital Logic Circuits
 Engr354: Digital Logic Circuits Chapter 3: Implementation Technology Curtis Nelson Chapter 3 Overview In this chapter you will learn about: How transistors are used as switches; Integrated circuit technology;
Engr354: Digital Logic Circuits Chapter 3: Implementation Technology Curtis Nelson Chapter 3 Overview In this chapter you will learn about: How transistors are used as switches; Integrated circuit technology;
Chapter 1, Introduction
 Introduction to Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology Chapter 1, Introduction hxiao89@hotmail.com 1 Objective After taking this course, you will able to Use common semiconductor terminology Describe a
Introduction to Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology Chapter 1, Introduction hxiao89@hotmail.com 1 Objective After taking this course, you will able to Use common semiconductor terminology Describe a
Student Lecture by: Giangiacomo Groppi Joel Cassell Pierre Berthelot September 28 th 2004
 Student Lecture by: Giangiacomo Groppi Joel Cassell Pierre Berthelot September 28 th 2004 Lecture outline Historical introduction Semiconductor devices overview Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Field
Student Lecture by: Giangiacomo Groppi Joel Cassell Pierre Berthelot September 28 th 2004 Lecture outline Historical introduction Semiconductor devices overview Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Field
Power MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017,
 ECE442 Power Semiconductor Devices and Integrated Circuits Power MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) Evolution of low-voltage (
ECE442 Power Semiconductor Devices and Integrated Circuits Power MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) Evolution of low-voltage (
Sticks Diagram & Layout. Part II
 Sticks Diagram & Layout Part II Well and Substrate Taps Substrate must be tied to GND and n-well to V DD Metal to lightly-doped semiconductor forms poor connection called Shottky Diode Use heavily doped
Sticks Diagram & Layout Part II Well and Substrate Taps Substrate must be tied to GND and n-well to V DD Metal to lightly-doped semiconductor forms poor connection called Shottky Diode Use heavily doped
College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley
 College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Below are your weekly quizzes. You should print out a copy of the quiz and complete it before your lab section. Bring in the completed quiz
College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Below are your weekly quizzes. You should print out a copy of the quiz and complete it before your lab section. Bring in the completed quiz
Session 3: Solid State Devices. Silicon on Insulator
 Session 3: Solid State Devices Silicon on Insulator 1 Outline A B C D E F G H I J 2 Outline Ref: Taurand Ning 3 SOI Technology SOl materials: SIMOX, BESOl, and Smart Cut SIMOX : Synthesis by IMplanted
Session 3: Solid State Devices Silicon on Insulator 1 Outline A B C D E F G H I J 2 Outline Ref: Taurand Ning 3 SOI Technology SOl materials: SIMOX, BESOl, and Smart Cut SIMOX : Synthesis by IMplanted
1 FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS What is Noise Coupling 1
 Contents 1 FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS 1 1.1 What is Noise Coupling 1 1.2 Resistance 3 1.2.1 Resistivity and Resistance 3 1.2.2 Wire Resistance 4 1.2.3 Sheet Resistance 5 1.2.4 Skin Effect 6 1.2.5 Resistance
Contents 1 FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS 1 1.1 What is Noise Coupling 1 1.2 Resistance 3 1.2.1 Resistivity and Resistance 3 1.2.2 Wire Resistance 4 1.2.3 Sheet Resistance 5 1.2.4 Skin Effect 6 1.2.5 Resistance
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
 Metal-Semiconductor and Semiconductor Heterojunctions The Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) is one of two major types of transistors. The MOSFET is used in digital circuit, because
Metal-Semiconductor and Semiconductor Heterojunctions The Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) is one of two major types of transistors. The MOSFET is used in digital circuit, because
Module-3: Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) & Emitter coupled logic (ECL) families
 1 Module-3: Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) & Emitter coupled logic (ECL) families 1. Introduction 2. Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) logic 2.1. Enhancement and depletion mode 2.2. NMOS and PMOS inverter
1 Module-3: Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) & Emitter coupled logic (ECL) families 1. Introduction 2. Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) logic 2.1. Enhancement and depletion mode 2.2. NMOS and PMOS inverter
Digital Systems Laboratory
 2012 Fall CSE140L Digital Systems Laboratory Lecture #2 by Dr. Choon Kim CSE Department, UCSD chk034@eng.ucsd.edu Lecture #2 1 Digital Technologies CPU(Central Processing Unit) GPU(Graphics Processing
2012 Fall CSE140L Digital Systems Laboratory Lecture #2 by Dr. Choon Kim CSE Department, UCSD chk034@eng.ucsd.edu Lecture #2 1 Digital Technologies CPU(Central Processing Unit) GPU(Graphics Processing
! MOS Device Layout. ! Inverter Layout. ! Gate Layout and Stick Diagrams. ! Design Rules. ! Standard Cells. ! CMOS Process Enhancements
 EE 570: igital Integrated Circuits and VLI Fundamentals Lec 3: January 18, 2018 MO Fabrication pt. 2: esign Rules and Layout Lecture Outline! MO evice Layout! Inverter Layout! Gate Layout and tick iagrams!
EE 570: igital Integrated Circuits and VLI Fundamentals Lec 3: January 18, 2018 MO Fabrication pt. 2: esign Rules and Layout Lecture Outline! MO evice Layout! Inverter Layout! Gate Layout and tick iagrams!
Lecture #29. Moore s Law
 Lecture #29 ANNOUNCEMENTS HW#15 will be for extra credit Quiz #6 (Thursday 5/8) will include MOSFET C-V No late Projects will be accepted after Thursday 5/8 The last Coffee Hour will be held this Thursday
Lecture #29 ANNOUNCEMENTS HW#15 will be for extra credit Quiz #6 (Thursday 5/8) will include MOSFET C-V No late Projects will be accepted after Thursday 5/8 The last Coffee Hour will be held this Thursday
ECE520 VLSI Design. Lecture 2: Basic MOS Physics. Payman Zarkesh-Ha
 ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 2: Basic MOS Physics Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review of Last Lecture Semiconductor
ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 2: Basic MOS Physics Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review of Last Lecture Semiconductor
Homework 10 posted just for practice. Office hours next week, schedule TBD. HKN review today. Your feedback is important!
 EE141 Fall 2005 Lecture 26 Memory (Cont.) Perspectives Administrative Stuff Homework 10 posted just for practice No need to turn in Office hours next week, schedule TBD. HKN review today. Your feedback
EE141 Fall 2005 Lecture 26 Memory (Cont.) Perspectives Administrative Stuff Homework 10 posted just for practice No need to turn in Office hours next week, schedule TBD. HKN review today. Your feedback
Physical Design of Digital Integrated Circuits (EN0291 S40) Sherief Reda Division of Engineering, Brown University Fall 2006
 Physical Design of Digital Integrated Circuits (EN0291 S40) Sherief Reda Division of Engineering, Brown University Fall 2006 Lecture 01: the big picture Course objective Brief tour of IC physical design
Physical Design of Digital Integrated Circuits (EN0291 S40) Sherief Reda Division of Engineering, Brown University Fall 2006 Lecture 01: the big picture Course objective Brief tour of IC physical design
LSI ON GLASS SUBSTRATES
 LSI ON GLASS SUBSTRATES OUTLINE Introduction: Why System on Glass? MOSFET Technology Low-Temperature Poly-Si TFT Technology System-on-Glass Technology Issues Conclusion System on Glass CPU SRAM DRAM EEPROM
LSI ON GLASS SUBSTRATES OUTLINE Introduction: Why System on Glass? MOSFET Technology Low-Temperature Poly-Si TFT Technology System-on-Glass Technology Issues Conclusion System on Glass CPU SRAM DRAM EEPROM
Spiral Content Mapping. Spiral 1 / Unit 8. Outcomes DEMORGAN'S THEOREM. Transistor Implementations CMOS Logic Gates
 18.1 18.2 Spiral ontent Mapping Spiral Theory ombinational esign Sequential esign System Level esign Implementation and Tools Project Spiral 1 / Unit 8 Transistor Implementations MOS Logic Gates Performance
18.1 18.2 Spiral ontent Mapping Spiral Theory ombinational esign Sequential esign System Level esign Implementation and Tools Project Spiral 1 / Unit 8 Transistor Implementations MOS Logic Gates Performance
Lecture 020 ECE4430 Review II (1/5/04) Page 020-1
 Lecture 020 ECE4430 Review II (1/5/04) Page 020-1 LECTURE 020 ECE 4430 REVIEW II (READING: GHLM - Chap. 2) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Identify the prerequisite material as taught
Lecture 020 ECE4430 Review II (1/5/04) Page 020-1 LECTURE 020 ECE 4430 REVIEW II (READING: GHLM - Chap. 2) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Identify the prerequisite material as taught
ECE 340 Lecture 37 : Metal- Insulator-Semiconductor FET Class Outline:
 ECE 340 Lecture 37 : Metal- Insulator-Semiconductor FET Class Outline: Metal-Semiconductor Junctions MOSFET Basic Operation MOS Capacitor Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What is the
ECE 340 Lecture 37 : Metal- Insulator-Semiconductor FET Class Outline: Metal-Semiconductor Junctions MOSFET Basic Operation MOS Capacitor Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What is the
Lecture 020 ECE4430 Review II (1/5/04) Page 020-1
 Lecture 020 ECE4430 Review II (1/5/04) Page 020-1 LECTURE 020 ECE 4430 REVIEW II (READING: GHLM - Chap. 2) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Identify the prerequisite material as taught
Lecture 020 ECE4430 Review II (1/5/04) Page 020-1 LECTURE 020 ECE 4430 REVIEW II (READING: GHLM - Chap. 2) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Identify the prerequisite material as taught
CMOS VLSI IC Design. A decent understanding of all tasks required to design and fabricate a chip takes years of experience
 CMOS VLSI IC Design A decent understanding of all tasks required to design and fabricate a chip takes years of experience 1 Commonly used keywords INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (IC) many transistors on one chip VERY
CMOS VLSI IC Design A decent understanding of all tasks required to design and fabricate a chip takes years of experience 1 Commonly used keywords INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (IC) many transistors on one chip VERY
VLSI Designed Low Power Based DPDT Switch
 International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering. ISSN 0974-2166 Volume 8, Number 1 (2015), pp. 81-86 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com VLSI Designed Low
International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering. ISSN 0974-2166 Volume 8, Number 1 (2015), pp. 81-86 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com VLSI Designed Low
Digital Integrated Circuits 1: Fundamentals
 Digital Integrated Circuits 1: Fundamentals Atsushi Takahashi Department of Information and Communications Engineering School of Engineering Tokyo Institute of Technology 1 VLSI and Computer System VLSI
Digital Integrated Circuits 1: Fundamentals Atsushi Takahashi Department of Information and Communications Engineering School of Engineering Tokyo Institute of Technology 1 VLSI and Computer System VLSI
ENG2410 Digital Design CMOS Technology. Fall 2017 S. Areibi School of Engineering University of Guelph
 ENG2410 Digital Design CMOS Technology Fall 2017 S. reibi School of Engineering University of Guelph The Transistor Revolution First transistor Bell Labs, 1948 Bipolar logic 1960 s Intel 4004 processor
ENG2410 Digital Design CMOS Technology Fall 2017 S. reibi School of Engineering University of Guelph The Transistor Revolution First transistor Bell Labs, 1948 Bipolar logic 1960 s Intel 4004 processor
Digital Design and System Implementation. Overview of Physical Implementations
 Digital Design and System Implementation Overview of Physical Implementations CMOS devices CMOS transistor circuit functional behavior Basic logic gates Transmission gates Tri-state buffers Flip-flops
Digital Design and System Implementation Overview of Physical Implementations CMOS devices CMOS transistor circuit functional behavior Basic logic gates Transmission gates Tri-state buffers Flip-flops
CS/ECE 5710/6710. Composite Layout
 CS/ECE 5710/6710 Introduction to Layout Inverter Layout Example Layout Design Rules Composite Layout Drawing the mask layers that will be used by the fabrication folks to make the devices Very different
CS/ECE 5710/6710 Introduction to Layout Inverter Layout Example Layout Design Rules Composite Layout Drawing the mask layers that will be used by the fabrication folks to make the devices Very different
Laboratory #5 BJT Basics and MOSFET Basics
 Laboratory #5 BJT Basics and MOSFET Basics I. Objectives 1. Understand the physical structure of BJTs and MOSFETs. 2. Learn to measure I-V characteristics of BJTs and MOSFETs. II. Components and Instruments
Laboratory #5 BJT Basics and MOSFET Basics I. Objectives 1. Understand the physical structure of BJTs and MOSFETs. 2. Learn to measure I-V characteristics of BJTs and MOSFETs. II. Components and Instruments
CMOS Technology. 1. Why CMOS 2. Qualitative MOSFET model 3. Building a MOSFET 4. CMOS logic gates. Handouts: Lecture Slides. metal ndiff.
 CMOS Technology 1. Why CMOS 2. Qualitative MOSFET model 3. Building a MOSFET 4. CMOS logic gates poly pdiff metal ndiff Handouts: Lecture Slides L03 - CMOS Technology 1 Building Bits from Atoms V in V
CMOS Technology 1. Why CMOS 2. Qualitative MOSFET model 3. Building a MOSFET 4. CMOS logic gates poly pdiff metal ndiff Handouts: Lecture Slides L03 - CMOS Technology 1 Building Bits from Atoms V in V
Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits. Lecture 2: Scaling Trends. Announcements. No office hour next Monday. Extra office hour Tuesday 2-3pm
 EE241 - Spring 20 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 2: Scaling Trends and Features of Modern Technologies Announcements No office hour next Monday Extra office hour Tuesday 2-3pm 2 1 Outline
EE241 - Spring 20 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 2: Scaling Trends and Features of Modern Technologies Announcements No office hour next Monday Extra office hour Tuesday 2-3pm 2 1 Outline
Lecture Integrated circuits era
 Lecture 1 1.1 Integrated circuits era Transistor was first invented by William.B.Shockley, Walter Brattain and John Bardeen of Bell laboratories. In 1961, first IC was introduced. Levels of Integration:-
Lecture 1 1.1 Integrated circuits era Transistor was first invented by William.B.Shockley, Walter Brattain and John Bardeen of Bell laboratories. In 1961, first IC was introduced. Levels of Integration:-
Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI)
 Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Lecture 6 Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Ah_madian@hotmail.com Dr. Ahmed H. Madian-VLSI 1 Contents Array subsystems Gate arrays technology Sea-of-gates Standard cell Macrocell
Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Lecture 6 Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Ah_madian@hotmail.com Dr. Ahmed H. Madian-VLSI 1 Contents Array subsystems Gate arrays technology Sea-of-gates Standard cell Macrocell
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization
 ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 2018 CMOS Logic Lecture 4: 1 NAND Logic Gate X Y (X Y) = NAND Using De Morgan s Law: (X Y) = X +Y X X X +Y = Y Y Also a NAND We can build circuits
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 2018 CMOS Logic Lecture 4: 1 NAND Logic Gate X Y (X Y) = NAND Using De Morgan s Law: (X Y) = X +Y X X X +Y = Y Y Also a NAND We can build circuits
Shorthand Notation for NMOS and PMOS Transistors
 Shorthand Notation for NMOS and PMOS Transistors Terminal Voltages Mode of operation depends on V g, V d, V s V gs = V g V s V gd = V g V d V ds = V d V s = V gs - V gd Source and drain are symmetric diffusion
Shorthand Notation for NMOS and PMOS Transistors Terminal Voltages Mode of operation depends on V g, V d, V s V gs = V g V s V gd = V g V d V ds = V d V s = V gs - V gd Source and drain are symmetric diffusion
ECE/CoE 0132: FETs and Gates
 ECE/CoE 0132: FETs and Gates Kartik Mohanram September 6, 2017 1 Physical properties of gates Over the next 2 lectures, we will discuss some of the physical characteristics of integrated circuits. We will
ECE/CoE 0132: FETs and Gates Kartik Mohanram September 6, 2017 1 Physical properties of gates Over the next 2 lectures, we will discuss some of the physical characteristics of integrated circuits. We will
Review: CMOS Logic Gates
 Review: CMOS Logic Gates INV Schematic NOR Schematic NAND Schematic + Vsg - pmos x x Vin Vout = Vin y + Vgs - nmos CMOS inverts functions CMOS Combinational Logic x g(x,y) = x + y use DeMorgan relations
Review: CMOS Logic Gates INV Schematic NOR Schematic NAND Schematic + Vsg - pmos x x Vin Vout = Vin y + Vgs - nmos CMOS inverts functions CMOS Combinational Logic x g(x,y) = x + y use DeMorgan relations
CMOS Digital Logic Design with Verilog. Chapter1 Digital IC Design &Technology
 CMOS Digital Logic Design with Verilog Chapter1 Digital IC Design &Technology Chapter Overview: In this chapter we study the concept of digital hardware design & technology. This chapter deals the standard
CMOS Digital Logic Design with Verilog Chapter1 Digital IC Design &Technology Chapter Overview: In this chapter we study the concept of digital hardware design & technology. This chapter deals the standard
PAPER SOLUTION_DECEMBER_2014_VLSI_DESIGN_ETRX_SEM_VII Prepared by Girish Gidaye
 Q1a) The MOS System under External Bias Depending on the polarity and the magnitude of V G, three different operating regions can be observed for the MOS system: 1) Accumulation 2) Depletion 3) Inversion
Q1a) The MOS System under External Bias Depending on the polarity and the magnitude of V G, three different operating regions can be observed for the MOS system: 1) Accumulation 2) Depletion 3) Inversion
VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 39 Latch up in CMOS We have been discussing about the problems in CMOS, basic
VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 39 Latch up in CMOS We have been discussing about the problems in CMOS, basic
Power Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs)
 ECE442 Power Semiconductor Devices and Integrated Circuits Power Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) Power Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Background The
ECE442 Power Semiconductor Devices and Integrated Circuits Power Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) Power Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Background The
Intel s High-k/Metal Gate Announcement. November 4th, 2003
 Intel s High-k/Metal Gate Announcement November 4th, 2003 1 What are we announcing? Intel has made significant progress in future transistor materials Two key parts of this new transistor are: The gate
Intel s High-k/Metal Gate Announcement November 4th, 2003 1 What are we announcing? Intel has made significant progress in future transistor materials Two key parts of this new transistor are: The gate
Basic Electronics. Introductory Lecture Course for. Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011
 Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory Session 3
Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory Session 3
This Week s Subject. DRAM & Flexible RRAM. p-channel MOSFET (PMOS) CMOS: Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
 DRAM & Flexible RRAM This Week s Subject p-channel MOSFET (PMOS) CMOS: Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor CMOS Logic Inverter NAND gate NOR gate CMOS Integration & Layout GaAs MESFET (JFET) 1 Flexible
DRAM & Flexible RRAM This Week s Subject p-channel MOSFET (PMOS) CMOS: Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor CMOS Logic Inverter NAND gate NOR gate CMOS Integration & Layout GaAs MESFET (JFET) 1 Flexible
Power Semiconductor Devices
 TRADEMARK OF INNOVATION Power Semiconductor Devices Introduction This technical article is dedicated to the review of the following power electronics devices which act as solid-state switches in the circuits.
TRADEMARK OF INNOVATION Power Semiconductor Devices Introduction This technical article is dedicated to the review of the following power electronics devices which act as solid-state switches in the circuits.
Solid State Devices- Part- II. Module- IV
 Solid State Devices- Part- II Module- IV MOS Capacitor Two terminal MOS device MOS = Metal- Oxide- Semiconductor MOS capacitor - the heart of the MOSFET The MOS capacitor is used to induce charge at the
Solid State Devices- Part- II Module- IV MOS Capacitor Two terminal MOS device MOS = Metal- Oxide- Semiconductor MOS capacitor - the heart of the MOSFET The MOS capacitor is used to induce charge at the
Mathematics and Science in Schools in Sub-Saharan Africa
 Mathematics and Science in Schools in Sub-Saharan Africa SEMICONDUCTORS What is a Semiconductor? What is a Semiconductor? Microprocessors LED Transistors Capacitors Range of Conduciveness The semiconductors
Mathematics and Science in Schools in Sub-Saharan Africa SEMICONDUCTORS What is a Semiconductor? What is a Semiconductor? Microprocessors LED Transistors Capacitors Range of Conduciveness The semiconductors
UNIT III VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN PROCESSES. In this chapter we will be studying how to get the schematic into stick diagrams or layouts.
 UNIT III VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN PROCESSES In this chapter we will be studying how to get the schematic into stick diagrams or layouts. MOS circuits are formed on four basic layers: N-diffusion P-diffusion
UNIT III VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN PROCESSES In this chapter we will be studying how to get the schematic into stick diagrams or layouts. MOS circuits are formed on four basic layers: N-diffusion P-diffusion
Low-Power VLSI. Seong-Ook Jung VLSI SYSTEM LAB, YONSEI University School of Electrical & Electronic Engineering
 Low-Power VLSI Seong-Ook Jung 2013. 5. 27. sjung@yonsei.ac.kr VLSI SYSTEM LAB, YONSEI University School of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Contents 1. Introduction 2. Power classification & Power performance
Low-Power VLSI Seong-Ook Jung 2013. 5. 27. sjung@yonsei.ac.kr VLSI SYSTEM LAB, YONSEI University School of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Contents 1. Introduction 2. Power classification & Power performance
FPGA Based System Design
 FPGA Based System Design Reference Wayne Wolf, FPGA-Based System Design Pearson Education, 2004 Why VLSI? Integration improves the design: higher speed; lower power; physically smaller. Integration reduces
FPGA Based System Design Reference Wayne Wolf, FPGA-Based System Design Pearson Education, 2004 Why VLSI? Integration improves the design: higher speed; lower power; physically smaller. Integration reduces
Semiconductor Memory: DRAM and SRAM. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore
 Semiconductor Memory: DRAM and SRAM Outline Introduction Random Access Memory (RAM) DRAM SRAM Non-volatile memory UV EPROM EEPROM Flash memory SONOS memory QD memory Introduction Slow memories Magnetic
Semiconductor Memory: DRAM and SRAM Outline Introduction Random Access Memory (RAM) DRAM SRAM Non-volatile memory UV EPROM EEPROM Flash memory SONOS memory QD memory Introduction Slow memories Magnetic
