THE USE OF POLARIZATION EFFECTS IN SEMICONDUCTOR OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS TO PERFORM ALL-OPTICAL SIGNAL PROCESSING
|
|
|
- Shawn Hill
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ingeniare. Kennedy, Revista Surre, chilena Philippe, de ingeniería, Bradley vol. and 15 Landais: Nº 3, 2007, The pp. use of polarization effects in semiconductor optical amplifiers to perform all-optical THE USE OF POLARIZATION EFFECTS IN SEMICONDUCTOR OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS TO PERFORM ALL-OPTICAL SIGNAL PROCESSING EL USO DE EFECTOS DE POLARIZACIÓN EN AMPLIFICADORES ÓPTICOS SEMICONDUCTORES PARA REALIZAR EL PROCESAMIENTO DE SEÑALES EN EL DOMINIO ÓPTICO Brendan F. Kennedy 1 Frederic Surre 2,3 Severine Philippe 3 Louise Bradley 3 Pascal Landais 2 Recibido 9 de agosto de 2007, aceptado 10 de octubre de 2007 Received: August 9, 2007 Accepted: October 10, 2007 RESUMEN En los servicios de telecomunicaciones, la necesidad de hacer uso intensivo de las aplicaciones ha presionado por un constante incremento del ancho de banda. Particularmente una de las tecnologías más promisorias, que ha permitido estos incrementos de ancho de banda, son los elementos ópticos, de tal manera que en las redes de comunicación los elementos electrónicos sean sustituidos por dichos elementos ópticos. En esta publicación se discute una técnica basada en la rotación no lineal del estado de polarización de una señal óptica conectada al amplificador semiconductor óptico. Se presenta un experimento, basado en este efecto, para realizar la conversión a 2,5 Gbits/s. La característica del conversor de longitud onda es probada en propagación directa e inversa. Se ha encontrado que conversión de la longitud de onda es independiente de longitud de onda (la conversión no depende del valor de la longitud de onda) en la modalidad de propagación directa no invertida. Palabras clave: Amplificador semiconductor óptico, conversión de la longitud de onda, rotación no lineal del estado de polarización. ABSTRACT As the need for higher and higher bandwidths in telecommunication systems continues, it is widely predicted that at some point in the future optical processing will need to be performed all-optically. Several techniques have been proposed to perform such all-optical signal processing. In this paper a technique based on the nonlinear rotation in the state of polarization of an optical signal injected into a bulk semiconductor optical amplifier is discussed. An experiment to perform wavelength conversion at 2.5 Gbit/s based on this effect is presented. The performance of the wavelength converter is tested in both co-and counter-propagation, and wavelength independent wavelength conversion is found in the non-inverted co-propagation setup. Keywords: Nonlinear polarization rotation, semiconductor optical amplifier, wavelength conversion. INTRODUCTION The recent explosive growth in internet traffic continues to increase with no sign of a levelling off in internet usage. In Chile, for example, the user penetration is the highest in South America with over 42% of the population using the internet. This represents a growth rate of over 200% in the last 5 years, and is a prime example of the exponential growth in internet usage in the world today. Densely populated countries with rapidly developing economies, for example India and China, will fuel the continued development of the internet. In the same five year period between 2000 and 2005, India s user growth was 684% resulting in a user penetration of only 3% whilst China s user growth was 358% resulting in a user penetration of only 7.9% [1]. As well as this, there is a continued rapid growth in the demand for new bandwidth hungry multimedia services. These facts indicate a future demand for faster switching capabilities than existing network infrastructure can provide. 1 Departamento de Ingeniería Eléctrica. Universidad de Santiago de Chile. Santiago, Chile. bkennedy@lauca.usach.cl 2 Department of Electronic Engineering. Dublin City University. Ireland. 3 Physics Department. Trinity College Dublin. Ireland 313 Libro INGENIERIA.indb 313 8/1/08 16:45:08
2 In long-haul telecommunications systems data propagates along optical fibre in optical format. The current systems, however, do not operate solely in the optical domain, as switching needs to be performed in the electronic domain. This involves conversion of the optical data to electronic data in order for the switching to take place and then conversion back to optical data after the switching operation has been performed. Commercial systems are currently restricted by the maximum speed at which the electronics can operate, which is 10Gb/s (OC-192) [2], with the latest improved electronics operating at 40Gb/s (OC-768) [3]. As the overall data transmission obtainable in the optical domain far exceeds this maximum, electronic bottlenecks may occur in future systems at the multiplexer, electronic to optical converter, optical to electronic converter and at the demultiplexer. This would have the effect of limiting the maximum transmission rate of the system. In order to avoid these bottlenecks, at some point it will likely be necessary for high-speed telecommunication networks to operate solely in the optical domain. In order for this to be realized, techniques to perform this all-optical switching need to be developed. The Semiconductor Optical Amplifier (SOA) has received extensive study as a potential device to implement all-optical signal processing. The SOA is a single-pass device, which is similar to a semiconductor laser operating below threshold. The device is kept below threshold by applying Anti-Reflection (AR) coatings and by tilting the waveguide of the device. Several techniques can be implemented using the SOA, namely Cross-Gain Modulation (XGM), Cross-Phase Modulation (XPM) and Four-Wave Mixing (FWM) [4]. These techniques take advantage of a modulation of either the gain or the phase of the device in order to perform all-optical signal processing, however, each one is limited by the polarization sensitivity in the SOA. The technique presented in this paper aims to take advantage of this inherent polarization sensitivity using the Nonlinear Polarization Rotation (NPR) effect in the device to perform Cross-Polarization Modulation (XPolM) [5, 6]. This effect occurs when a signal with a known state of polarization is injected into an SOA. Due to several effects in the device the state of polarization at the output of the device becomes rotated. This rotation is a nonlinear effect and may be used to perform all-optical signal processing such as wavelength conversion, where the data on a high intensity pump signal is transferred to a low intensity CW signal at a different wavelength. Experiments are presented in this paper in which wavelength conversion is performed in both co- and counter-propagation in order to determine which is the most efficient for the experimental setup under test. From these experiments it is found that for non-inverted conversion in the co-propagation setup it is possible to achieve wavelength conversion that is independent of the wavelength of the probe signal. This paper is organized as follows: Firstly, the causes of the NPR effect are introduced. After this an experiment is presented which demonstrates XPolM based on NPR in a bulk SOA at a data rate of 2.5 Gbit/s. THE CAUSES OF NPR IN A BULK SOA DEVICE NPR in the SOA is caused by several effects. One of the principle causes is due to waveguide asymmetry in the device. If the device is not perfectly square the result is that the confinement factor,, is different for the Transverse Electric (TE) and Transverse Magnetic (TM) Modes. This results in a polarization dependence of the device gain due to the equation (1): G ( g ) L (1) m where represents the confinement factor, g m represents the material gain, represents the optical losses and L is the length of the device. Another significant type of polarization dependence present in an SOA with an asymmetric waveguide is due to the birefringence introduced to the device. This asymmetry causes two propagation constants to exist corresponding to the orthogonal TE and TM modes. The effective refractive indices typically differ by 2x10-2 [7]. The difference in refractive index causes the TE and TM modes to propagate through the device at different speeds causing a phase difference to be introduced between the signals. An index difference as small as 2x10-4 has been reported as being sufficiently high to induce a phase shift between the TE and TM modes of 90 o [6]. Many of the initial publications based on NPR justified the effect as being solely due to the asymmetric waveguide [5, 6]. These papers also report an increase in the NPR due to birefringence as a function of injected power in the SOA. This modulation of the refractive index through modulation of the gain of the device is defined by the Self-phase Modulation (SPM) [8] and is quantified using the Linewidth Enhancement Factor (LEF) [9]. Because of the fact that the overall device gain is generally larger for the case of TE polarization, due to the difficulties in designing a completely square waveguide [10], a technique generally used is to introduce tensile strain to enhance the Light-Hole (LH) transitions, and therefore 314 Libro INGENIERIA.indb 314 8/1/08 16:45:09
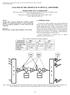
3 Kennedy, Surre, Philippe, Bradley and Landais: The use of polarization effects in semiconductor optical amplifiers to perform all-optical the TM transitions, in order to minimize the variation in gain between TE and TM axes. In this way the TM gain is increased to a level where it compensates for the higher TE gain. This balancing of the gains can be understood by considering the following expression [11]: G TM g db ( ) 1 TE g TE TM TM TE GTE db ( ) (2) Where G TE/TM represents the modal gain, TE/TM represents the confinement factor and g TE/TM represents the material gain. From this expression it is clear that increasing g TM over g TE can compensate for the larger confinement along the TE axis. This is effective and although complete polarization insensitivity has never been achieved, it is an effective technique in compensating for the higher TE gain. However, it should be noted that the measurements performed to test this technique, from the literature, only consider the static steady-state gain and not the dynamic gain processes, which are governed by the material gain. This is of vital importance, as it is the response of the gain to data signals that is of interest for optical signal processing. These are considered to be the strongest effects behind the NPR effect. One groups results also point to the modification of the eigenmodes of the device as being a cause of NPR [6]. This modification of the waveguide is brought about by a high intensity signal injected into the device causing a nonlinear birefringence effect. It was noticed that the TE and TM eigenmodes of the device at low injection powers were no longer the eigenmodes when the power was increased to high intensity values. Finally, in early SOA devices the polarization dependence of the AR coatings had a large effect, with a polarization dependence of over 10 db being measured. Since this time, multi-layer coatings have been developed to reduce the polarization dependency due to AR coatings to below 10-4 [12]. amplifier structure with a gain spectral bandwidth of 75 nm, centred at 1535 nm. It is biased at 200 ma and temperature controlled at 23 o. Both optical signals are generated using external cavity tunable lasers. The wavelength of the pump signal is 1538 nm and the wavelength of the probe signal is varied between 1535 nm and 1570 nm. The span was limited to 35 nm due to the spectral bandwidth of the EDFAs, which operate in the C-band. The pump signal is modulated at 2.5 Gb/s and then amplified through EDFA 2 to an average power of approximately 7 dbm at the input of the SOA, which saturates the gain of the device. A Band- Pass Filter (BPF 2) is used to remove noise introduced by the EDFA. The probe signal is injected with a power of -3.6 dbm. The signals are launched into the device in copropagation using a 50:50 coupler. The states of polarization, of both the pump and probe signals, are controlled using Polarization Controllers (PCs), which are adjusted in order to optimize the wavelength conversion. At the output of the SOA the combination of PC 3 and the PBS act to control the transmission of the amplified signal, based on the polarization of the signal. It is the combination of these two components that distinguishes this setup from that of XGM. The PBS used has an extinction ratio of 20 db and an insertion loss of 0.4 db. The wavelength conversion due to XPolM is based on the fact that the polarization rotation is a nonlinear process. Both inverted and non-inverted XPolM can be performed using this setup by adjusting PC3 to maximize or minimize the transmission of the probe signal, in the absence of the pump signal. In the case of inverted XPolM, for example, the probe transmission is maximized before injection of the pump. It is necessary to include BPF 1 after the PBS in order to select the probe signal wavelength. This BPF has a 3 db bandwidth of 1 nm and a wavelength tuning range of 40 nm. EDFA 1 is used to amplify the wavelength converted signal and an attenuator is used to vary the received power falling on the photodetector. The signal can then be observed on an oscilloscope and Bit Error Rate Tester (BERT). EXPERIMENTAL DEMONSTRATION OF XPOLM AT 2.5 GBIT/S After establishing the main causes of the NPR effect in a bulk SOA device, an experiment to perform wavelength conversion based on XPolM is now presented. Wavelength conversion is performed using XPolM at a data rate of 2.5 Gbit/s and a Pseudo Random Bit Sequence (PBRS) of This data rate is limited by the speed of the pseudo-random data generator and the error detector. The co-propagation setup is shown in figure 1. Two optical signals are simultaneously injected into the SOA. The SOA under test is an Avanex A1901, a tensile strained bulk Figure 1. Co-propagation XPolM experimental setup. Bold lines represent electrical connections. 315 Libro INGENIERIA.indb 315 8/1/08 16:45:11
4 The counter-propagation setup is shown in figure 2. The operating conditions of the device and the pump and probe powers are the same as for the co-propagation setup. The pump and probe are injected into the device in opposite directions. A circulator with 35 db isolation is used to inject the pump signal and to collect the converted signal. An isolator is used at the probe end of the device to ensure that the pump signal is not injected into the probe laser. Using this setup it is possible to convert data to the same wavelength. Because the signals are injected at opposite ends of the device it is not necessary to select the correct wavelength using BPF 1, but this filter is included to remove any Amplified Spontaneous Emission (ASE) that may have been transmitted through the PBS. Other than the opposite propagation direction of the data signal, the co- and counter-propagation setups operate in the same manner. In order to make a comparison between both techniques it is important to ensure that the pump and probe signals are injected into the device with the same level of intensity. It should be noted that both co- and counter-propagation setups can be easily changed to a XGM setup by removing PC 3 and the PBS, respectively. The wavelength dependence of XPolM is determined in both experimental setups for inverted and non-inverted conversion. The probe signal is varied from 1535 nm to 1570 nm, whilst the pump signal is maintained at 1538 nm. The pump wavelength is fixed as its main function is to deplete the carrier density in order that the device operates in the nonlinear regime. The probe wavelength is varied in order to measure the range of operation of the wavelength conversion scheme. Figure 2. Counter-propagation XPolM experimental setup. Bold lines represent electrical connections. A parameter known as the Q-factor is used to assess the performance of the wavelength conversion in this paper. The Q-factor is defined as: Q I 1 I where I 1 and I 0 represent the mean signal level at 1 and 0, and and represent the standard deviation of the noise on the 1 and 0 level. It is measured using an oscilloscope. It should also be stated that the Q-factor is not directly related to the BER because of the non-gaussian distribution of the intensity after the wavelength conversion. However, an approximation of the BER can be obtained from the Q-factor. The BER is measured in this experiment using a Bit Error Rate Tester (BERT) as illustrated in figure 1 and figure 2. ANALYSIS OF WAVELENGTH CONVERSION The Bit Error Rate (BER) as a function of received power for inverted and non-inverted XPolM, as well as XGM, is shown in figure 3 for both co- and counterpropagation schemes. The back-to-back data is also shown for comparison. In the co-propagation setup a penalty of approximately 1 db is introduced for both inverted XPolM and XGM as can be seen in figure 3(a). However, a larger penalty of approximately 5.5 db is introduced using the non-inverted XPolM in the co-propagation setup. This poor performance is a consequence of XGM, which occurs simultaneously with XPolM. XGM leads to inverted conversion and therefore opposes the effect of non-inverted conversion, because the converted signal experiences reduced gain. The opposite occurs for inverted XPolM, in which the signal inversion is enhanced by XGM. Figure 3(b) shows the results obtained from the counter-propagation setup. The penalty introduced to the inverted XPolM and XGM is reduced to approximately 0.5 db. This penalty is negligible if the insertion loss of the PBS in the counter-propagation setup is taken into consideration. However, the most significant variation between the co- and counter-propagation setups is in terms of the non-inverted XPolM. There is a reduction of approximately 4.5 db in the power penalty for this technique between the two experimental setups. This result indicates that the NPR effect is present with less power in the counter-propagation configuration. This improvement in penalty was not found for inverted XPolM. This may be due to the PBS, which has an extinction ratio limited to 20 db. If the conversion has reached this limit then any improvement in the conversion, due to an increase in the NPR, will be undetected. The results presented in figure 5 are in contrast to those presented in [13], where the smallest power penalty was found to be in the non-inverted setup. This discrepancy may be (3) 316 Libro INGENIERIA.indb 316 8/1/08 16:45:13
5 Kennedy, Surre, Philippe, Bradley and Landais: The use of polarization effects in semiconductor optical amplifiers to perform all-optical due to the different relationships between the gain and polarization nonlinearities in the two devices. It should be noted that whilst the results presented in figure 5 are in contrast to [13], they are in agreement with the results presented in [14]. Figure 4. Eye diagrams for back-to-back, XGM, noninverted XPolM and inverted XPolM in counter-propagation. WAVELENGTH DEPENDENCE OF WAVELENGTH CONVERSION Figure 3. BER as a function of received converted power for XGM, inverted XPolM and non-inverted XPolM in (a) co- and (b) counter-propagation. Pump wavelength = 1538 nm, probe wavelength = 1535 nm. The eye diagrams measured for the counter-propagation setup are shown in figure 4, along with the back-to-back measurement. The Q-factor measured for each setup is also shown. It can be seen that the Q-factor obtained for both inverted XPolM and XGM is practically the same as for the back-to-back case. From figure 4 it can be seen that a slow rising edge and a fast falling edge is present in the back-to-back eye diagram. It is logical to assume that the eye diagrams for the inverted configurations of XGM and inverted XPolM should therefore have a fast rising edge and a slow falling edge. Likewise, it is logical to assume the non-inverted XPolM configuration should have a slow rising edge and a fast falling edge, like the back-to-back eye diagram. However, from observation of figure 4 it appears that the opposite is true. This is caused by the presence of an inverted electrical amplifier used in the receiver. The pump power was also varied in both setups in order to optimize its value. The highest available pump power of 7 dbm consistently led to the best XPolM performance. This is expected, once the device has not reached its NPR saturation point. The BER as a function of received power for various probe signal wavelengths is shown in figure 5. From this figure it can be seen that the effect of varying the probe wavelength is strongly dependent on the system configuration. Wavelength independent conversion is found for non-inverted XPolM in the co-propagation setup, for BERs as low as 10-12, as can be seen from Fig. 5(a). For BERs lower than this a small wavelength dependence is introduced. The cause of the insensitivity to wavelength may be explained from the relationship between XGM and XPolM. In the non-inverted co-propagation setup the NPR acts to increase the extinction ratio of the converted signal. However, the suppressed gain causes a reduction of the extinction ratio, as it results in a lower amplification of the 1 level. As the probe wavelength is moved away from the gain peak of the SOA there are two effects on the wavelength conversion. Firstly, the NPR is reduced due to its intensity dependence. Secondly, the gain suppression is reduced. The result is that there is a balance in the contribution from these effects in the case of non-inverted XPolM in the co-propagation setup. Non-inverted XPolM is also obtained for the counterpropagation setup and is shown in figure 5(b). It has already been established that the NPR effect is larger for counter-propagation, which results in a wavelength dependence of the BER as the NPR and gain suppression mechanisms are no longer balanced. The increase in NPR in the counter-propagation setup results in a much larger contribution of NPR than of XGM. This leads to a wavelength dependence of 2.5 db over the 35 nm span. Further comparison between figure 5(a) and figure 5(b) reveals that the wavelength insensitivity in co-propagation is at the expense of a larger power penalty. 317 Libro INGENIERIA.indb 317 8/1/08 16:45:18
6 CONCLUSIONS Figure 5. BER as a function of received power for various probe signals wavelengths, where (a)-(b) represent non-inverted XPolM and (c)-(d) represent inverted XPolM in co and counter-propagation, respectively. The wavelength dependence of inverted XPolM is also analyzed. Obviously, wavelength insensitivity is not possible for inverted XPolM, as the NPR and gain suppression both increase the extinction ratio of the converted signal. In the co-propagation setup, as the wavelength is increased the power penalty increases by 1 db, as can be seen in figure 5(c). Similarly, in counter-propagation, the power penalty over the same wavelength range increases by approximately 3.5 db as shown in figure 5(d). For both inverted and non-inverted conversion it can be seen that the wavelength dependence of the XPolM is smallest in co-propagation. In both cases the cause of the larger wavelength dependence in counter-propagation is the increase in the contribution of the wavelength dependent NPR effect. The insensitivity to wavelength is at the cost of a penalty of over 5 db whereas inverted conversion in the counter-propagation setup has a minimum penalty of 0.26 db. The same trends are observed in the analysis of the Q-factor as a function of probe wavelength. The Q-factor in the co-propagation setup, for non-inverted XPolM, and for a received power of 10-9 was measured as 6.4 at 1535nm. The value at 1570 nm was measured to be 6.2, a difference of only 0.2 in the Q-factor over a range of 35 nm. In the non-inverted counter-propagation setup for the same experimental conditions a wavelength dependence in the Q-factor of 3.3 was measured over the same wavelength range. In each setup the highest Q-factor was measured for a probe wavelength of 1535 nm. The effect of NPR in bulk SOAs has been introduced in this paper. The main contributing factors have been discussed. This effect has been used to perform wavelength conversion based on XPolM. A comparison is made between co- and counter-propagation setups, in order to establish advantages and disadvantages of each. Both inverted and non-inverted XPolM were performed. The results indicate that the XPolM effect is larger in counterpropagation, with a 4.5 db improvement in the penalty introduced for non-inverted conversion. The wavelength dependence of the conversion is determined over a span of 35 nm. It is shown that wavelength insensitive conversion is possible for non-inverted XPolM in the copropagation setup over the accessible wavelength range, although a larger penalty is introduced in this case. The cause of this wavelength insensitivity is attributed to a balancing between NPR and gain suppression in the non-inverted case. It may be concluded that the question of whether to use a co- or counter-propagation setup for XPolM is dependent on the exact requirements of the system. If wavelength insensitivity is desired then co-propagation is more suitable, whereas if the power penalty is a crucial parameter then counter-propagation should be used. REFERENCES [1] E. de Argaez. Internet world stats. August URLs: [2] S. Tariq, M.K. Dhodhi, J.C. Palais and R.E. Ahmed. Next generation DWDM networks: Demands, capabilities and limitations. IEEE Canadian Conf. on Elec. and Comp. Eng Vol. 2, pp [3] G. Held. On the road to OC-768. IT Professional. Vol. 3, pp [4] D. Cotter, R.J. Manning, K.J. Blow, A.D. Ellis, A.E. Kelly, D. Nesset, I.D. Phillips, A.J. Poustie and D.C. Rogers. Nonlinear optics for high-speed digital information processing. Science. Vol. 286, pp [5] D.M. Patrick, A.D. Ellis, D.A.O. Davies, M.C. Tatham and G. Sherlock. Demultiplexing using polarization rotation in a semiconductor laser amplifier. IEE Electronic Letters. Vol. 30, pp Libro INGENIERIA.indb 318 8/1/08 16:45:20
7 Kennedy, Surre, Philippe, Bradley and Landais: The use of polarization effects in semiconductor optical amplifiers to perform all-optical [6] H. Soto, D. Erasme and G. Guekos. Cross polarization modulation in semiconductor optical amplifiers. IEEE Photonic Tech. Letters. Vol. 9, pp [7] R.J. Manning, A. Antonopoulos, R. Le Roux and A.E. Kelly. Experimental measurement of nonlinear polarization rotation in semiconductor optical amplifiers. IEE Electronic Letters. Vol. 37, pp [8] G.P. Agrawal, N.A. Olsson. Self-phase modulation and spectral broadening of optical pulses in semiconductor laser amplifiers. IEEE J. Quantum Electronics. Vol. 25, pp [9] C.H. Henry. Theory of the linewidth of semiconductor lasers. IEEE J. Quantum Electronics. Vol. 18, pp [10] P. Dousiere, P. Garabedian, C. Graver, D. Bonnevie, T. Fillion, E. Derouin, M. Monnot, J.G. Provost, D. Leclerc and M. Klenk. 1.55μm polarization independent semiconductor optical amplifier with 25 db fiber to fiber gain. IEEE Photonic Tech. Letters. Vol. 6, pp [11] M. Itoh, Y. Shibata, T. Kakitsuka, Y. Kadota, and Y. Tohmori. Polarization-insensitive SOA with a strained bulk active layer for network device application. IEEE Photonic Tech. Letters. Vol. 14, pp [12] C. Vassallo. Polarization-independent antireflection coatings for semiconductor optical amplifiers. IEE Electronic Letters. Vol. 24, pp [13] Y. Liu, M.T. Hill, E. Tangdiongga, H. de Waardt, N. Calabretta, G.D. Khoe and H.J.S. Dorren. Wavelength conversion using nonlinear polarization rotation in a single semiconductor optical amplifier. IEEE Photonic Tech. Letters. Vol. 15, pp [14] L. Guo and M.J. Connelly. Signal induced birefringence and dichroism in a tensile-strained bulk semiconductor optical amplifier and its application to wavelength conversion. IEEE J. Light. Technology. Vol. 23, pp December Libro INGENIERIA.indb 319 8/1/08 16:45:20
All-optical AND gate with improved extinction ratio using signal induced nonlinearities in a bulk semiconductor optical amplifier
 All-optical AND gate with improved extinction ratio using signal induced nonlinearities in a bulk semiconductor optical amplifier L. Q. Guo, and M. J. Connelly Optical Communications Research Group, Department
All-optical AND gate with improved extinction ratio using signal induced nonlinearities in a bulk semiconductor optical amplifier L. Q. Guo, and M. J. Connelly Optical Communications Research Group, Department
Simulation of All-Optical XOR, AND, OR gate in Single Format by Using Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers
 Simulation of All-Optical XOR, AND, OR gate in Single Format by Using Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers Chang Wan Son* a,b, Sang Hun Kim a, Young Min Jhon a, Young Tae Byun a, Seok Lee a, Deok Ha Woo a,
Simulation of All-Optical XOR, AND, OR gate in Single Format by Using Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers Chang Wan Son* a,b, Sang Hun Kim a, Young Min Jhon a, Young Tae Byun a, Seok Lee a, Deok Ha Woo a,
All-optical clock division at 40 GHz using a semiconductor amplifier. nonlinear interferometer
 All-optical clock division at 40 GHz using a semiconductor amplifier nonlinear interferometer R. J. Manning, I. D. Phillips, A. D. Ellis, A. E. Kelly, A. J. Poustie, K.J. Blow BT Laboratories, Martlesham
All-optical clock division at 40 GHz using a semiconductor amplifier nonlinear interferometer R. J. Manning, I. D. Phillips, A. D. Ellis, A. E. Kelly, A. J. Poustie, K.J. Blow BT Laboratories, Martlesham
To investigate effects of extinction ratio on SOA based wavelength Converters for all Optical Networks
 289 To investigate effects of extinction ratio on SOA based wavelength Converters for all Optical Networks Areet Aulakh 1, Kulwinder Singh Malhi 2 1 Student, M.Tech, ECE department, Punjabi University,
289 To investigate effects of extinction ratio on SOA based wavelength Converters for all Optical Networks Areet Aulakh 1, Kulwinder Singh Malhi 2 1 Student, M.Tech, ECE department, Punjabi University,
Implementation of All-Optical Logic AND Gate using XGM based on Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers
 Implementation of All-Optical Logic AND Gate using XGM based on Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers Sang H. Kim 1, J. H. Kim 1,2, C. W. Son 1, G. Kim 1, Y. T. yun 1, Y. M. Jhon 1, S. Lee 1, D. H. Woo 1, and
Implementation of All-Optical Logic AND Gate using XGM based on Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers Sang H. Kim 1, J. H. Kim 1,2, C. W. Son 1, G. Kim 1, Y. T. yun 1, Y. M. Jhon 1, S. Lee 1, D. H. Woo 1, and
All-optical logic gates using a semiconductor optical amplifier assisted by an optical filter
 All-optical logic gates using a semiconductor optical amplifier assisted by an optical filter Z. Li, Y. Liu, S. Zhang, H. Ju, H. de Waardt, G.D. Khoe H.J.S. Dorren and D. Lenstra Abstract: A simple all-optical
All-optical logic gates using a semiconductor optical amplifier assisted by an optical filter Z. Li, Y. Liu, S. Zhang, H. Ju, H. de Waardt, G.D. Khoe H.J.S. Dorren and D. Lenstra Abstract: A simple all-optical
Study of All-Optical Wavelength Conversion and Regeneration Subsystems for use in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Telecommunication Networks.
 Study of All-Optical Wavelength Conversion and Regeneration Subsystems for use in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Telecommunication Networks. Hercules Simos * National and Kapodistrian University
Study of All-Optical Wavelength Conversion and Regeneration Subsystems for use in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Telecommunication Networks. Hercules Simos * National and Kapodistrian University
Performance Analysis of SOA-MZI based All-Optical AND & XOR Gate
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2016 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Utkarsh
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2016 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Utkarsh
Application Instruction 001. The Enhanced Functionalities of Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers and their Role in Advanced Optical Networking
 The Enhanced Functionalities of Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers and their Role in Advanced Optical Networking I. Introduction II. III. IV. SOA Fundamentals Wavelength Conversion based on SOAs The Role
The Enhanced Functionalities of Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers and their Role in Advanced Optical Networking I. Introduction II. III. IV. SOA Fundamentals Wavelength Conversion based on SOAs The Role
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 27 EDFA In the last lecture, we talked about wavelength
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 27 EDFA In the last lecture, we talked about wavelength
Simultaneous Four-Wave Mixing and Cross-Gain Modulation for Implementing All Optical Full Adder without Assist Light
 Simultaneous Four-Wave Mixing and Cross-Gain Modulation for Implementing All Optical Full Adder without Assist Light Jaspreet Kaur 1, Naveen Dhillon 2, Rupinder Kaur 3 1 Lecturer, ECE, LPU, Punjab, India
Simultaneous Four-Wave Mixing and Cross-Gain Modulation for Implementing All Optical Full Adder without Assist Light Jaspreet Kaur 1, Naveen Dhillon 2, Rupinder Kaur 3 1 Lecturer, ECE, LPU, Punjab, India
All-optical NRZ to RZ format and wavelength converter by dual-wavelength injection locking
 15 August 2002 Optics Communications 209 (2002) 329 334 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom All-optical NRZ to RZ format and wavelength converter by dual-wavelength injection locking C.W. Chow, C.S. Wong *,
15 August 2002 Optics Communications 209 (2002) 329 334 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom All-optical NRZ to RZ format and wavelength converter by dual-wavelength injection locking C.W. Chow, C.S. Wong *,
Optimisation of DSF and SOA based Phase Conjugators. by Incorporating Noise-Suppressing Fibre Gratings
 Optimisation of DSF and SOA based Phase Conjugators by Incorporating Noise-Suppressing Fibre Gratings Paper no: 1471 S. Y. Set, H. Geiger, R. I. Laming, M. J. Cole and L. Reekie Optoelectronics Research
Optimisation of DSF and SOA based Phase Conjugators by Incorporating Noise-Suppressing Fibre Gratings Paper no: 1471 S. Y. Set, H. Geiger, R. I. Laming, M. J. Cole and L. Reekie Optoelectronics Research
SOA-BASED NOISE SUPPRESSION IN SPECTRUM-SLICED PONs: IMPACT OF BIT-RATE AND SOA GAIN RECOVERY TIME
 SOA-BASED NOISE SUPPRESSION IN SPECTRUM-SLICED PONs: IMPACT OF BIT-RATE AND SOA GAIN RECOVERY TIME Francesco Vacondio, Walid Mathlouthi, Pascal Lemieux, Leslie Ann Rusch Centre d optique photonique et
SOA-BASED NOISE SUPPRESSION IN SPECTRUM-SLICED PONs: IMPACT OF BIT-RATE AND SOA GAIN RECOVERY TIME Francesco Vacondio, Walid Mathlouthi, Pascal Lemieux, Leslie Ann Rusch Centre d optique photonique et
Study of Multiwavelength Fiber Laser in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber
 Study of Multiwavelength Fiber Laser in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber I. H. M. Nadzar 1 and N. A.Awang 1* 1 Faculty of Science, Technology and Human Development, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Johor,
Study of Multiwavelength Fiber Laser in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber I. H. M. Nadzar 1 and N. A.Awang 1* 1 Faculty of Science, Technology and Human Development, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Johor,
Performance Evaluation of Wavelength Conversion Using a Wideband Semiconductor Optical Amplifier at 40 Gbit/s
 The Open Optics Journal, 2010, 4, 21-28 21 Open Access Performance Evaluation of Wavelength Conversion Using a Wideband Semiconductor Optical Amplifier at 40 Gbit/s Y. Said *, H. Rezig and A. Bouallegue
The Open Optics Journal, 2010, 4, 21-28 21 Open Access Performance Evaluation of Wavelength Conversion Using a Wideband Semiconductor Optical Amplifier at 40 Gbit/s Y. Said *, H. Rezig and A. Bouallegue
Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks
 363 Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks CHAOUI Fahd 3, HAJAJI Anas 1, AGHZOUT Otman 2,4, CHAKKOUR Mounia 3, EL YAKHLOUFI Mounir
363 Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks CHAOUI Fahd 3, HAJAJI Anas 1, AGHZOUT Otman 2,4, CHAKKOUR Mounia 3, EL YAKHLOUFI Mounir
Optical Amplifiers Photonics and Integrated Optics (ELEC-E3240) Zhipei Sun Photonics Group Department of Micro- and Nanosciences Aalto University
 Photonics Group Department of Micro- and Nanosciences Aalto University Optical Amplifiers Photonics and Integrated Optics (ELEC-E3240) Zhipei Sun Last Lecture Topics Course introduction Ray optics & optical
Photonics Group Department of Micro- and Nanosciences Aalto University Optical Amplifiers Photonics and Integrated Optics (ELEC-E3240) Zhipei Sun Last Lecture Topics Course introduction Ray optics & optical
Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber
 Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber H. Ahmad 1, S. Shahi 1 and S. W. Harun 1,2* 1 Photonics Research Center, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2 Department
Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber H. Ahmad 1, S. Shahi 1 and S. W. Harun 1,2* 1 Photonics Research Center, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2 Department
ELSEVIER FIRST PROOFS
 OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS / Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers 1 OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS A5 S5 P5 P1 Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers M J Connelly, University of Limerick, Limerick, Ireland q 24, Elsevier Ltd. All Rights
OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS / Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers 1 OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS A5 S5 P5 P1 Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers M J Connelly, University of Limerick, Limerick, Ireland q 24, Elsevier Ltd. All Rights
Gigabit Transmission in 60-GHz-Band Using Optical Frequency Up-Conversion by Semiconductor Optical Amplifier and Photodiode Configuration
 22 Gigabit Transmission in 60-GHz-Band Using Optical Frequency Up-Conversion by Semiconductor Optical Amplifier and Photodiode Configuration Jun-Hyuk Seo, and Woo-Young Choi Department of Electrical and
22 Gigabit Transmission in 60-GHz-Band Using Optical Frequency Up-Conversion by Semiconductor Optical Amplifier and Photodiode Configuration Jun-Hyuk Seo, and Woo-Young Choi Department of Electrical and
CHAPTER 5 SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY IN DWDM
 61 CHAPTER 5 SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY IN DWDM 5.1 SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY IN DWDM Due to the ever-expanding Internet data traffic, telecommunication networks are witnessing a demand for high-speed data transfer.
61 CHAPTER 5 SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY IN DWDM 5.1 SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY IN DWDM Due to the ever-expanding Internet data traffic, telecommunication networks are witnessing a demand for high-speed data transfer.
A proposal for two-input arbitrary Boolean logic gates using single semiconductor optical amplifier by picosecond pulse injection
 A proposal for two-input arbitrary Boolean logic gates using single semiconductor optical amplifier by picosecond pulse injection Jianji Dong,,* Xinliang Zhang, and Dexiu Huang Wuhan National Laboratory
A proposal for two-input arbitrary Boolean logic gates using single semiconductor optical amplifier by picosecond pulse injection Jianji Dong,,* Xinliang Zhang, and Dexiu Huang Wuhan National Laboratory
S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique
 S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique Chien-Hung Yeh 1, *, Ming-Ching Lin 3, Ting-Tsan Huang 2, Kuei-Chu Hsu 2 Cheng-Hao Ko 2, and Sien Chi
S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique Chien-Hung Yeh 1, *, Ming-Ching Lin 3, Ting-Tsan Huang 2, Kuei-Chu Hsu 2 Cheng-Hao Ko 2, and Sien Chi
Module 19 : WDM Components
 Module 19 : WDM Components Lecture : WDM Components - II Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following OADM Optical Circulators Bidirectional OADM using Optical Circulators and FBG Optical Cross
Module 19 : WDM Components Lecture : WDM Components - II Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following OADM Optical Circulators Bidirectional OADM using Optical Circulators and FBG Optical Cross
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF APPLIED ENGINEERING RESEARCH, DINDIGUL Volume 1, No 3, 2010
 All Optical Half Adder Design Using Equations Governing XGM and FWM Effect in Semiconductor Optical Amplifier V. K. Srivastava, V. Priye Indian School of Mines University, Dhanbad srivastavavikrant@hotmail.com
All Optical Half Adder Design Using Equations Governing XGM and FWM Effect in Semiconductor Optical Amplifier V. K. Srivastava, V. Priye Indian School of Mines University, Dhanbad srivastavavikrant@hotmail.com
Prabhjeet Singh a, Narwant Singh b, Amandeep Singh c
 ISSN : 2250-3021 Investigation of DWDM System for Different Modulation Formats Prabhjeet Singh a, Narwant Singh b, Amandeep Singh c a B.G.I.E.T. Sangrur, India b G.N.D.E.C. Ludhiana, India c R.I.E.T, Ropar,
ISSN : 2250-3021 Investigation of DWDM System for Different Modulation Formats Prabhjeet Singh a, Narwant Singh b, Amandeep Singh c a B.G.I.E.T. Sangrur, India b G.N.D.E.C. Ludhiana, India c R.I.E.T, Ropar,
Analysis of Techniques for Wavelength Conversion in Semiconductor Optical Amplifier
 Global Journal of researches in engineering Electrical and electronical engineering Volume 11 Issue 5 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of researches in engineering Electrical and electronical engineering Volume 11 Issue 5 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Experimental demonstration of both inverted and non-inverted wavelength conversion based on transient cross phase modulation of SOA
 Experimental demonstration of both inverted and non-inverted wavelength conversion based on transient cross phase modulation of SOA Songnian Fu, Jianji Dong *, P. Shum, and Liren Zhang (1) Network Technology
Experimental demonstration of both inverted and non-inverted wavelength conversion based on transient cross phase modulation of SOA Songnian Fu, Jianji Dong *, P. Shum, and Liren Zhang (1) Network Technology
All-Optical Clock Division Using Period-one Oscillation of Optically Injected Semiconductor Laser
 International Conference on Logistics Engineering, Management and Computer Science (LEMCS 2014) All-Optical Clock Division Using Period-one Oscillation of Optically Injected Semiconductor Laser Shengxiao
International Conference on Logistics Engineering, Management and Computer Science (LEMCS 2014) All-Optical Clock Division Using Period-one Oscillation of Optically Injected Semiconductor Laser Shengxiao
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF WDM AND EDFA IN C-BAND FOR OPTICAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
 www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol13issue1/ijrras_13_1_26.pdf PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF WDM AND EDFA IN C-BAND FOR OPTICAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM M.M. Ismail, M.A. Othman, H.A. Sulaiman, M.H. Misran & M.A. Meor
www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol13issue1/ijrras_13_1_26.pdf PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF WDM AND EDFA IN C-BAND FOR OPTICAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM M.M. Ismail, M.A. Othman, H.A. Sulaiman, M.H. Misran & M.A. Meor
Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion
 Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion M. A. Khayer Azad and M. S. Islam Institute of Information and Communication
Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion M. A. Khayer Azad and M. S. Islam Institute of Information and Communication
The non-linear behaviour of laser diodes integrated with semiconductor optical amplifiers.
 The non-linear behaviour of laser diodes integrated with semiconductor optical amplifiers. Geert Morthier, Senior Member, IEEE, Wouter D Oosterlinck, Student Member, IEEE, Sam Verspurten, Student Member,
The non-linear behaviour of laser diodes integrated with semiconductor optical amplifiers. Geert Morthier, Senior Member, IEEE, Wouter D Oosterlinck, Student Member, IEEE, Sam Verspurten, Student Member,
Design of Ultra High Capacity DWDM System with Different Modulation Formats
 Design of Ultra High Capacity DWDM System with Different Modulation Formats A. Nandhini 1, K. Gokulakrishnan 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Regional Center, Anna
Design of Ultra High Capacity DWDM System with Different Modulation Formats A. Nandhini 1, K. Gokulakrishnan 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Regional Center, Anna
SIMULATIVE INVESTIGATION OF SINGLE-TONE ROF SYSTEM USING VARIOUS DUOBINARY MODULATION FORMATS
 SIMULATIVE INVESTIGATION OF SINGLE-TONE ROF SYSTEM USING VARIOUS DUOBINARY MODULATION FORMATS Namita Kathpal 1 and Amit Kumar Garg 2 1,2 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Deenbandhu
SIMULATIVE INVESTIGATION OF SINGLE-TONE ROF SYSTEM USING VARIOUS DUOBINARY MODULATION FORMATS Namita Kathpal 1 and Amit Kumar Garg 2 1,2 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Deenbandhu
Performance Analysis of dispersion compensation using Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) in Optical Communication
 Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347-5161 214 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Performance
Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347-5161 214 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Performance
Suppression of Stimulated Brillouin Scattering
 Suppression of Stimulated Brillouin Scattering 42 2 5 W i de l y T u n a b l e L a s e r T ra n s m i t te r www.lumentum.com Technical Note Introduction This technical note discusses the phenomenon and
Suppression of Stimulated Brillouin Scattering 42 2 5 W i de l y T u n a b l e L a s e r T ra n s m i t te r www.lumentum.com Technical Note Introduction This technical note discusses the phenomenon and
optoel 2013 VIII REUNIÓN ESPAÑOLA DE Optoelectrónica Julio de 2013 Alcalá de Henares Madrid LIBRO DE COMUNICACIONES
 optoel 213 VIII REUNIÓN ESPAÑOLA DE Optoelectrónica www.optoel213.fgua.es 1-12 Julio de 213 Alcalá de Henares Madrid LIBRO DE COMUNICACIONES Publicado por: Grupo de Ingeniería Fotónica Departamento de
optoel 213 VIII REUNIÓN ESPAÑOLA DE Optoelectrónica www.optoel213.fgua.es 1-12 Julio de 213 Alcalá de Henares Madrid LIBRO DE COMUNICACIONES Publicado por: Grupo de Ingeniería Fotónica Departamento de
Optical Fiber Amplifiers
 Optical Fiber Amplifiers Yousif Ahmed Omer 1 and Dr. Hala Eldaw Idris 2 1,2 Department of communication Faculty of Engineering, AL-Neelain University, Khartoum, Sudan Publishing Date: June 15, 2016 Abstract
Optical Fiber Amplifiers Yousif Ahmed Omer 1 and Dr. Hala Eldaw Idris 2 1,2 Department of communication Faculty of Engineering, AL-Neelain University, Khartoum, Sudan Publishing Date: June 15, 2016 Abstract
Introduction Fundamental of optical amplifiers Types of optical amplifiers
 ECE 6323 Introduction Fundamental of optical amplifiers Types of optical amplifiers Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers Semiconductor optical amplifier Others: stimulated Raman, optical parametric Advanced application:
ECE 6323 Introduction Fundamental of optical amplifiers Types of optical amplifiers Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers Semiconductor optical amplifier Others: stimulated Raman, optical parametric Advanced application:
Performance analysis of Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier at different pumping configurations
 Performance analysis of Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier at different pumping configurations Mayur Date M.E. Scholar Department of Electronics and Communication Ujjain Engineering College, Ujjain (M.P.) datemayur3@gmail.com
Performance analysis of Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier at different pumping configurations Mayur Date M.E. Scholar Department of Electronics and Communication Ujjain Engineering College, Ujjain (M.P.) datemayur3@gmail.com
ANALYSIS OF FWM POWER AND EFFICIENCY IN DWDM SYSTEMS BASED ON CHROMATIC DISPERSION AND CHANNEL SPACING
 ANALYSIS OF FWM POWER AND EFFICIENCY IN DWDM SYSTEMS BASED ON CHROMATIC DISPERSION AND CHANNEL SPACING S Sugumaran 1, Manu Agarwal 2, P Arulmozhivarman 3 School of Electronics Engineering, VIT University,
ANALYSIS OF FWM POWER AND EFFICIENCY IN DWDM SYSTEMS BASED ON CHROMATIC DISPERSION AND CHANNEL SPACING S Sugumaran 1, Manu Agarwal 2, P Arulmozhivarman 3 School of Electronics Engineering, VIT University,
EDFA Applications in Test & Measurement
 EDFA Applications in Test & Measurement White Paper PN 200-0600-00 Revision 1.1 September 2003 Calmar Optcom, Inc www.calamropt.com Overview Erbium doped fiber amplifiers (EDFAs) amplify optical pulses
EDFA Applications in Test & Measurement White Paper PN 200-0600-00 Revision 1.1 September 2003 Calmar Optcom, Inc www.calamropt.com Overview Erbium doped fiber amplifiers (EDFAs) amplify optical pulses
Characterization of the Semiconductor Optical Amplifier for Amplification and Photonic Switching Employing the Segmentation Model
 Characterization of the Semiconductor Optical Amplifier for Amplification and Photonic Switching Employing the Segmentation Model Abd El Aziz 1, W. P. Ng 1, Member, IEEE, Z. Ghassemlooy 1, Senior Member,
Characterization of the Semiconductor Optical Amplifier for Amplification and Photonic Switching Employing the Segmentation Model Abd El Aziz 1, W. P. Ng 1, Member, IEEE, Z. Ghassemlooy 1, Senior Member,
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology. April 11, Name: Student ID number: OCT1 1: OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade:
 Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Fiber Parametric Amplifiers for Wavelength Band Conversion
 IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 8, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2002 527 Fiber Parametric Amplifiers for Wavelength Band Conversion Mohammed N. Islam and Özdal Boyraz, Student Member, IEEE
IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 8, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2002 527 Fiber Parametric Amplifiers for Wavelength Band Conversion Mohammed N. Islam and Özdal Boyraz, Student Member, IEEE
Polarization Mode Dispersion compensation in WDM system using dispersion compensating fibre
 Polarization Mode Dispersion compensation in WDM system using dispersion compensating fibre AMANDEEP KAUR (Assist. Prof.) ECE department GIMET Amritsar Abstract: In this paper, the polarization mode dispersion
Polarization Mode Dispersion compensation in WDM system using dispersion compensating fibre AMANDEEP KAUR (Assist. Prof.) ECE department GIMET Amritsar Abstract: In this paper, the polarization mode dispersion
Emerging Subsea Networks
 EVALUATION OF NONLINEAR IMPAIRMENT FROM NARROW- BAND UNPOLARIZED IDLERS IN COHERENT TRANSMISSION ON DISPERSION-MANAGED SUBMARINE CABLE SYSTEMS Masashi Binkai, Keisuke Matsuda, Tsuyoshi Yoshida, Naoki Suzuki,
EVALUATION OF NONLINEAR IMPAIRMENT FROM NARROW- BAND UNPOLARIZED IDLERS IN COHERENT TRANSMISSION ON DISPERSION-MANAGED SUBMARINE CABLE SYSTEMS Masashi Binkai, Keisuke Matsuda, Tsuyoshi Yoshida, Naoki Suzuki,
Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion
 36 Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion Supreet Singh 1, Kulwinder Singh 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi
36 Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion Supreet Singh 1, Kulwinder Singh 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi
Performance of A Multicast DWDM Network Applied to the Yemen Universities Network using Quality Check Algorithm
 Performance of A Multicast DWDM Network Applied to the Yemen Universities Network using Quality Check Algorithm Khaled O. Basulaim, Samah Ali Al-Azani Dept. of Information Technology Faculty of Engineering,
Performance of A Multicast DWDM Network Applied to the Yemen Universities Network using Quality Check Algorithm Khaled O. Basulaim, Samah Ali Al-Azani Dept. of Information Technology Faculty of Engineering,
Performance Comparison of Pre-, Post-, and Symmetrical Dispersion Compensation for 96 x 40 Gb/s DWDM System using DCF
 Performance Comparison of Pre-, Post-, and Symmetrical Dispersion Compensation for 96 x 40 Gb/s DWDM System using Sabina #1, Manpreet Kaur *2 # M.Tech(Scholar) & Department of Electronics & Communication
Performance Comparison of Pre-, Post-, and Symmetrical Dispersion Compensation for 96 x 40 Gb/s DWDM System using Sabina #1, Manpreet Kaur *2 # M.Tech(Scholar) & Department of Electronics & Communication
International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT) ISSN: Vol. 2 Issue 9, September
 Performance Enhancement of WDM-ROF Networks With SOA-MZI Shalu (M.Tech), Baljeet Kaur (Assistant Professor) Department of Electronics and Communication Guru Nanak Dev Engineering College, Ludhiana Abstract
Performance Enhancement of WDM-ROF Networks With SOA-MZI Shalu (M.Tech), Baljeet Kaur (Assistant Professor) Department of Electronics and Communication Guru Nanak Dev Engineering College, Ludhiana Abstract
Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor
 Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor P. S. Chan, C. Y. Chow, and H. K. Tsang Department of Electronic Engineering, The
Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor P. S. Chan, C. Y. Chow, and H. K. Tsang Department of Electronic Engineering, The
The effect of the input energy on the SOA gain with non-uniform biasing
 The effect of the input energy on the SOA gain with non-uniform biasing A. Abd El Aziz, W. P. Ng, Z. Ghassemlooy, Moustafa Aly, R. Ngah 3, M. F. Chiang Optical Communications Research Group, NCRLab Northumbria
The effect of the input energy on the SOA gain with non-uniform biasing A. Abd El Aziz, W. P. Ng, Z. Ghassemlooy, Moustafa Aly, R. Ngah 3, M. F. Chiang Optical Communications Research Group, NCRLab Northumbria
Performance Analysis of EDFA for Different Pumping Configurations at High Data Rate
 Global Journal of Researches in Engineering Electrical and Electronics Engineering Volume 13 Issue 9 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global
Global Journal of Researches in Engineering Electrical and Electronics Engineering Volume 13 Issue 9 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global
Performance analysis of semiconductor optical amplifier using four wave mixing based wavelength Converter for all Optical networks.
 Performance analysis of semiconductor optical amplifier using four wave mixing based wavelength Converter for all Optical networks. Anupjeet Kaur 1, Kulwinder Singh 2,Bhawna Utreja 3 1 Student, 2 Associate
Performance analysis of semiconductor optical amplifier using four wave mixing based wavelength Converter for all Optical networks. Anupjeet Kaur 1, Kulwinder Singh 2,Bhawna Utreja 3 1 Student, 2 Associate
Rogério Nogueira Instituto de Telecomunicações Pólo de Aveiro Departamento de Física Universidade de Aveiro
 Fiber Bragg Gratings for DWDM Optical Networks Rogério Nogueira Instituto de Telecomunicações Pólo de Aveiro Departamento de Física Universidade de Aveiro Overview Introduction. Fabrication. Physical properties.
Fiber Bragg Gratings for DWDM Optical Networks Rogério Nogueira Instituto de Telecomunicações Pólo de Aveiro Departamento de Física Universidade de Aveiro Overview Introduction. Fabrication. Physical properties.
SOAs Nonlinearities and Their Applications for Next Generation of Optical Networks
 SOAs Nonlinearities and Their Applications for Next Generation of Optical Networks 2 Youssef Said and Houria Rezig Sys Com Laboratory, National Engineering School of Tunis (ENIT) Tunisia 1. Introduction
SOAs Nonlinearities and Their Applications for Next Generation of Optical Networks 2 Youssef Said and Houria Rezig Sys Com Laboratory, National Engineering School of Tunis (ENIT) Tunisia 1. Introduction
Lecture 6 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 6, Slide 1
 Lecture 6 Optical transmitters Photon processes in light matter interaction Lasers Lasing conditions The rate equations CW operation Modulation response Noise Light emitting diodes (LED) Power Modulation
Lecture 6 Optical transmitters Photon processes in light matter interaction Lasers Lasing conditions The rate equations CW operation Modulation response Noise Light emitting diodes (LED) Power Modulation
Improved Analysis of Hybrid Optical Amplifier in CWDM System
 Improved Analysis of Hybrid Optical Amplifier in CWDM System 1 Bandana Mallick, 2 Reeta Kumari, 3 Anirban Mukherjee, 4 Kunwar Parakram 1. Asst Proffesor in Dept. of ECE, GIET Gunupur 2, 3,4. Student in
Improved Analysis of Hybrid Optical Amplifier in CWDM System 1 Bandana Mallick, 2 Reeta Kumari, 3 Anirban Mukherjee, 4 Kunwar Parakram 1. Asst Proffesor in Dept. of ECE, GIET Gunupur 2, 3,4. Student in
An approach for Realization of all optical NAND gate using Nonlinear Effect in SOA
 An approach for Realization of all optical NAND gate using Nonlinear Effect in Ankur Saharia #1, Astt.professer PIET & M.Tech Scholar, MNIT, Jaipur, India Email ankursaharia@poornima.org Dr. Ritu Sharma
An approach for Realization of all optical NAND gate using Nonlinear Effect in Ankur Saharia #1, Astt.professer PIET & M.Tech Scholar, MNIT, Jaipur, India Email ankursaharia@poornima.org Dr. Ritu Sharma
SUBMARINE SYSTEM UPGRADES WITH 25 GHZ CHANNEL SPACING USING DRZ AND RZ-DPSK MODULATION FORMATS
 SUBMARINE SYSTEM UPGRADES WITH 25 GHZ CHANNEL SPACING USING DRZ AND RZ-DPSK MODULATION FORMATS Jiping Wen, Chunmei Yu, Tiegang Zhou, Xiaoyan Fan, Liping Ma (Huawei Marine Networks Co Ltd) Email:
SUBMARINE SYSTEM UPGRADES WITH 25 GHZ CHANNEL SPACING USING DRZ AND RZ-DPSK MODULATION FORMATS Jiping Wen, Chunmei Yu, Tiegang Zhou, Xiaoyan Fan, Liping Ma (Huawei Marine Networks Co Ltd) Email:
New pumping scheme for high gain and low noise figure in an erbium-doped fiber amplifier
 New pumping scheme for high gain and low noise figure in an erbium-doped fiber amplifier V. Sinivasagam, 1,3a) Mustafa A. G. Abushagur, 1,2 K. Dimyati, 3 and F. Tumiran 1 1 Photronix (M) Sdn. Bhd., G05,
New pumping scheme for high gain and low noise figure in an erbium-doped fiber amplifier V. Sinivasagam, 1,3a) Mustafa A. G. Abushagur, 1,2 K. Dimyati, 3 and F. Tumiran 1 1 Photronix (M) Sdn. Bhd., G05,
Investigation of Performance Analysis of EDFA Amplifier. Using Different Pump Wavelengths and Powers
 Investigation of Performance Analysis of EDFA Amplifier Using Different Pump Wavelengths and Powers Ramandeep Kaur, Parkirti, Rajandeep Singh ABSTRACT In this paper, an investigation of the performance
Investigation of Performance Analysis of EDFA Amplifier Using Different Pump Wavelengths and Powers Ramandeep Kaur, Parkirti, Rajandeep Singh ABSTRACT In this paper, an investigation of the performance
ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS
 MANDEEP SINGH AND S K RAGHUWANSHI: ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS DOI: 10.1917/ijct.013.0106 ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS Mandeep Singh 1 and S. K. Raghuwanshi 1 Department
MANDEEP SINGH AND S K RAGHUWANSHI: ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS DOI: 10.1917/ijct.013.0106 ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS Mandeep Singh 1 and S. K. Raghuwanshi 1 Department
2-R REGENERATION EXPLOITING SELF-PHASE MODULATION IN A SEMICONDUCTOR OPTICAL AMPLIFIER
 2-R REGENERATION EXPLOITING SELF-PHASE MODULATION IN A SEMICONDUCTOR OPTICAL AMPLIFIER Gianluca Meloni,^ Antonella Bogoni,^ and Luca Poti^ Scuola Superiore Sunt'Anna, P.zza dei Martin della Libertd 33,
2-R REGENERATION EXPLOITING SELF-PHASE MODULATION IN A SEMICONDUCTOR OPTICAL AMPLIFIER Gianluca Meloni,^ Antonella Bogoni,^ and Luca Poti^ Scuola Superiore Sunt'Anna, P.zza dei Martin della Libertd 33,
Optical Transport Tutorial
 Optical Transport Tutorial 4 February 2015 2015 OpticalCloudInfra Proprietary 1 Content Optical Transport Basics Assessment of Optical Communication Quality Bit Error Rate and Q Factor Wavelength Division
Optical Transport Tutorial 4 February 2015 2015 OpticalCloudInfra Proprietary 1 Content Optical Transport Basics Assessment of Optical Communication Quality Bit Error Rate and Q Factor Wavelength Division
Simulation and Performance Analysis of Optical Wavelength Converters based on Cross Gain Modulation (XGM) in SOA
 Simulation and Performance Analysis of Optical Wavelength Converters based on Cross Gain Modulation (XGM) in SOA Anju M.R. 1, Vipin V.R. 2 P.G Scholar 1, Asst. Professor 2, Dept. of ECE, T.K.M. Institute
Simulation and Performance Analysis of Optical Wavelength Converters based on Cross Gain Modulation (XGM) in SOA Anju M.R. 1, Vipin V.R. 2 P.G Scholar 1, Asst. Professor 2, Dept. of ECE, T.K.M. Institute
The Reduction of FWM effects using Duobinary Modulation in a Two-Channel D-WDM System
 The Reduction of FWM effects using Duobinary Modulation in a Two-Channel D-WDM System Laxman Tawade 1, Balasaheb Deokate 2 Department of Electronic and Telecommunication Vidya Pratishthan s College of
The Reduction of FWM effects using Duobinary Modulation in a Two-Channel D-WDM System Laxman Tawade 1, Balasaheb Deokate 2 Department of Electronic and Telecommunication Vidya Pratishthan s College of
Optical Amplifiers (Chapter 6)
 Optical Amplifiers (Chapter 6) General optical amplifier theory Semiconductor Optical Amplifier (SOA) Raman Amplifiers Erbium-doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFA) Read Chapter 6, pp. 226-266 Loss & dispersion
Optical Amplifiers (Chapter 6) General optical amplifier theory Semiconductor Optical Amplifier (SOA) Raman Amplifiers Erbium-doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFA) Read Chapter 6, pp. 226-266 Loss & dispersion
Comparative Analysis of Various Optimization Methodologies for WDM System using OptiSystem
 Comparative Analysis of Various Optimization Methodologies for WDM System using OptiSystem Koushik Mukherjee * Department of Electronics and Communication, Dublin Institute of Technology, Ireland E-mail:
Comparative Analysis of Various Optimization Methodologies for WDM System using OptiSystem Koushik Mukherjee * Department of Electronics and Communication, Dublin Institute of Technology, Ireland E-mail:
Design and Implementation of All-optical Demultiplexer using Four-Wave Mixing (FWM) in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber (HNLF)
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 5, May 2014 1 Design and Implementation of All-optical Demultiplexer using Four-Wave Mixing (FWM) in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 5, May 2014 1 Design and Implementation of All-optical Demultiplexer using Four-Wave Mixing (FWM) in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber
High Speed VCSEL Transmission at 1310 nm and 1550 nm Transmission Wavelengths
 American Journal of Optics and Photonics 01; (): - http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajop doi: 10.11/j.ajop.0100.1 ISSN: 0- (Print); ISSN: 0- (Online) High Speed VCSEL Transmission at 110 nm and
American Journal of Optics and Photonics 01; (): - http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajop doi: 10.11/j.ajop.0100.1 ISSN: 0- (Print); ISSN: 0- (Online) High Speed VCSEL Transmission at 110 nm and
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Computer Science 93 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 93 (016 ) 647 654 6th International Conference On Advances In Computing & Communications, ICACC 016, 6-8 September 016,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 93 (016 ) 647 654 6th International Conference On Advances In Computing & Communications, ICACC 016, 6-8 September 016,
Setup of the four-wavelength Doppler lidar system with feedback controlled pulse shaping
 Setup of the four-wavelength Doppler lidar system with feedback controlled pulse shaping Albert Töws and Alfred Kurtz Cologne University of Applied Sciences Steinmüllerallee 1, 51643 Gummersbach, Germany
Setup of the four-wavelength Doppler lidar system with feedback controlled pulse shaping Albert Töws and Alfred Kurtz Cologne University of Applied Sciences Steinmüllerallee 1, 51643 Gummersbach, Germany
EDFA-WDM Optical Network Analysis
 EDFA-WDM Optical Network Analysis Narruvala Lokesh, kranthi Kumar Katam,Prof. Jabeena A Vellore Institute of Technology VIT University, Vellore, India Abstract : Optical network that apply wavelength division
EDFA-WDM Optical Network Analysis Narruvala Lokesh, kranthi Kumar Katam,Prof. Jabeena A Vellore Institute of Technology VIT University, Vellore, India Abstract : Optical network that apply wavelength division
RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 25 33, 2009 RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, C.-H. Lee,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 25 33, 2009 RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, C.-H. Lee,
Comparison of Various Configurations of Hybrid Raman Amplifiers
 IJCST Vo l. 3, Is s u e 4, Oc t - De c 2012 ISSN : 0976-8491 (Online) ISSN : 2229-4333 (Print) Comparison of Various Configurations of Hybrid Raman Amplifiers Sunil Gautam Dept. of ECE, Shaheed Bhagat
IJCST Vo l. 3, Is s u e 4, Oc t - De c 2012 ISSN : 0976-8491 (Online) ISSN : 2229-4333 (Print) Comparison of Various Configurations of Hybrid Raman Amplifiers Sunil Gautam Dept. of ECE, Shaheed Bhagat
Module 12 : System Degradation and Power Penalty
 Module 12 : System Degradation and Power Penalty Lecture : System Degradation and Power Penalty Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Degradation during Propagation Modal Noise Dispersion
Module 12 : System Degradation and Power Penalty Lecture : System Degradation and Power Penalty Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Degradation during Propagation Modal Noise Dispersion
Suppression of Four Wave Mixing Based on the Pairing Combinations of Differently Linear-Polarized Optical Signals in WDM System
 The Quarterly Journal of Optoelectronical Nanostructures Islamic Azad University Spring 2016 / Vol. 1, No.1 Suppression of Four Wave Mixing Based on the Pairing Combinations of Differently Linear-Polarized
The Quarterly Journal of Optoelectronical Nanostructures Islamic Azad University Spring 2016 / Vol. 1, No.1 Suppression of Four Wave Mixing Based on the Pairing Combinations of Differently Linear-Polarized
Performance Evaluation of 32 Channel DWDM System Using Dispersion Compensation Unit at Different Bit Rates
 Performance Evaluation of 32 Channel DWDM System Using Dispersion Compensation Unit at Different Bit Rates Simarpreet Kaur Gill 1, Gurinder Kaur 2 1Mtech Student, ECE Department, Rayat- Bahra University,
Performance Evaluation of 32 Channel DWDM System Using Dispersion Compensation Unit at Different Bit Rates Simarpreet Kaur Gill 1, Gurinder Kaur 2 1Mtech Student, ECE Department, Rayat- Bahra University,
DBR based passively mode-locked 1.5m semiconductor laser with 9 nm tuning range Moskalenko, V.; Williams, K.A.; Bente, E.A.J.M.
 DBR based passively mode-locked 1.5m semiconductor laser with 9 nm tuning range Moskalenko, V.; Williams, K.A.; Bente, E.A.J.M. Published in: Proceedings of the 20th Annual Symposium of the IEEE Photonics
DBR based passively mode-locked 1.5m semiconductor laser with 9 nm tuning range Moskalenko, V.; Williams, K.A.; Bente, E.A.J.M. Published in: Proceedings of the 20th Annual Symposium of the IEEE Photonics
Chapter 8. Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (WDM) Part II: Amplifiers
 Chapter 8 Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (WDM) Part II: Amplifiers Introduction Traditionally, when setting up an optical link, one formulates a power budget and adds repeaters when the path loss exceeds
Chapter 8 Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (WDM) Part II: Amplifiers Introduction Traditionally, when setting up an optical link, one formulates a power budget and adds repeaters when the path loss exceeds
Power Transients in Hybrid Optical Amplifier (EDFA + DFRA) Cascades
 Power Transients in Hybrid Optical Amplifier (EDFA + DFRA) Cascades Bárbara Dumas and Ricardo Olivares Electronic Engineering Department Universidad Técnica Federico Santa María Valparaíso, Chile bpilar.dumas@gmail.com,
Power Transients in Hybrid Optical Amplifier (EDFA + DFRA) Cascades Bárbara Dumas and Ricardo Olivares Electronic Engineering Department Universidad Técnica Federico Santa María Valparaíso, Chile bpilar.dumas@gmail.com,
Fiber-Optic Communication Systems
 Fiber-Optic Communication Systems Second Edition GOVIND P. AGRAWAL The Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY A WILEY-iNTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. NEW YORK / CHICHESTER
Fiber-Optic Communication Systems Second Edition GOVIND P. AGRAWAL The Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY A WILEY-iNTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. NEW YORK / CHICHESTER
Performance Analysis Of Hybrid Optical OFDM System With High Order Dispersion Compensation
 Performance Analysis Of Hybrid Optical OFDM System With High Order Dispersion Compensation Manpreet Singh Student, University College of Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India. Abstract Orthogonal
Performance Analysis Of Hybrid Optical OFDM System With High Order Dispersion Compensation Manpreet Singh Student, University College of Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India. Abstract Orthogonal
AN EFFICIENT L-BAND ERBIUM-DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIER WITH ZIRCONIA-YTTRIA-ALUMINUM CO-DOPED SILICA FIBER
 Journal of Non - Oxide Glasses Vol. 10, No. 3, July - September 2018, p. 65-70 AN EFFICIENT L-BAND ERBIUM-DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIER WITH ZIRCONIA-YTTRIA-ALUMINUM CO-DOPED SILICA FIBER A. A. ALMUKHTAR a, A.
Journal of Non - Oxide Glasses Vol. 10, No. 3, July - September 2018, p. 65-70 AN EFFICIENT L-BAND ERBIUM-DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIER WITH ZIRCONIA-YTTRIA-ALUMINUM CO-DOPED SILICA FIBER A. A. ALMUKHTAR a, A.
Elements of Optical Networking
 Bruckner Elements of Optical Networking Basics and practice of optical data communication With 217 Figures, 13 Tables and 93 Exercises Translated by Patricia Joliet VIEWEG+ TEUBNER VII Content Preface
Bruckner Elements of Optical Networking Basics and practice of optical data communication With 217 Figures, 13 Tables and 93 Exercises Translated by Patricia Joliet VIEWEG+ TEUBNER VII Content Preface
Analyzing the Non-Linear Effects in DWDM Optical Network Using MDRZ Modulation Format
 Analyzing the Non-Linear Effects in DWDM Optical Network Using MDRZ Modulation Format Ami R. Lavingia Electronics & Communication Dept. SAL Institute of Technology & Engineering Research Gujarat Technological
Analyzing the Non-Linear Effects in DWDM Optical Network Using MDRZ Modulation Format Ami R. Lavingia Electronics & Communication Dept. SAL Institute of Technology & Engineering Research Gujarat Technological
OFC SYSTEMS Performance & Simulations. BC Choudhary NITTTR, Sector 26, Chandigarh
 OFC SYSTEMS Performance & Simulations BC Choudhary NITTTR, Sector 26, Chandigarh High Capacity DWDM OFC Link Capacity of carrying enormous rates of information in THz 1.1 Tb/s over 150 km ; 55 wavelengths
OFC SYSTEMS Performance & Simulations BC Choudhary NITTTR, Sector 26, Chandigarh High Capacity DWDM OFC Link Capacity of carrying enormous rates of information in THz 1.1 Tb/s over 150 km ; 55 wavelengths
Performance Analysis of Multi-format WDM-RoF Links Based on Low Cost Laser and SOA
 Performance Analysis of Multi-format WDM-RoF Links Based on Low Cost Laser and SOA Carlos Almeida 1,2, António Teixeira 1,2, and Mário Lima 1,2 1 Instituto de Telecomunicações, University of Aveiro, Campus
Performance Analysis of Multi-format WDM-RoF Links Based on Low Cost Laser and SOA Carlos Almeida 1,2, António Teixeira 1,2, and Mário Lima 1,2 1 Instituto de Telecomunicações, University of Aveiro, Campus
A PIECE WISE LINEAR SOLUTION FOR NONLINEAR SRS EFFECT IN DWDM FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 9 A PIECE WISE LINEAR SOLUION FOR NONLINEAR SRS EFFEC IN DWDM FIBER OPIC COMMUNICAION SYSEMS M. L. SINGH and I. S. HUDIARA Department of Electronics echnology Guru Nanak Dev University Amritsar-005, India
9 A PIECE WISE LINEAR SOLUION FOR NONLINEAR SRS EFFEC IN DWDM FIBER OPIC COMMUNICAION SYSEMS M. L. SINGH and I. S. HUDIARA Department of Electronics echnology Guru Nanak Dev University Amritsar-005, India
Downstream Transmission in a WDM-PON System Using a Multiwavelength SOA-Based Fiber Ring Laser Source
 JOURNAL OF L A TEX CLASS FILES, VOL. X, NO. XX, XXXX XXX 1 Downstream Transmission in a WDM-PON System Using a Multiwavelength SOA-Based Fiber Ring Laser Source Jérôme Vasseur, Jianjun Yu Senior Member,
JOURNAL OF L A TEX CLASS FILES, VOL. X, NO. XX, XXXX XXX 1 Downstream Transmission in a WDM-PON System Using a Multiwavelength SOA-Based Fiber Ring Laser Source Jérôme Vasseur, Jianjun Yu Senior Member,
Fiberoptic Communication Systems By Dr. M H Zaidi. Optical Amplifiers
 Optical Amplifiers Optical Amplifiers Optical signal propagating in fiber suffers attenuation Optical power level of a signal must be periodically conditioned Optical amplifiers are a key component in
Optical Amplifiers Optical Amplifiers Optical signal propagating in fiber suffers attenuation Optical power level of a signal must be periodically conditioned Optical amplifiers are a key component in
Performance Analysis of Gb/s DWDM Metropolitan Area Network using SMF-28 and MetroCor Optical Fibres
 Research Cell: An International Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN: 2229-6913 Issue Sept 2011, Vol. 4 11 Performance Analysis of 32 2.5 Gb/s DWDM Metropolitan Area Network using SMF-28 and MetroCor Optical
Research Cell: An International Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN: 2229-6913 Issue Sept 2011, Vol. 4 11 Performance Analysis of 32 2.5 Gb/s DWDM Metropolitan Area Network using SMF-28 and MetroCor Optical
Performance Analysis Of An Ultra High Capacity 1 Tbps DWDM-RoF System For Very Narrow Channel Spacing
 Performance Analysis Of An Ultra High Capacity 1 Tbps DWDM-RoF System For Very Narrow Channel Spacing Viyoma Sarup* and Amit Gupta Chandigarh University Punjab, India *viyoma123@gmail.com Abstract A RoF
Performance Analysis Of An Ultra High Capacity 1 Tbps DWDM-RoF System For Very Narrow Channel Spacing Viyoma Sarup* and Amit Gupta Chandigarh University Punjab, India *viyoma123@gmail.com Abstract A RoF
All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration
 1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
All optical wavelength converter based on fiber cross-phase modulation and fiber Bragg grating
 All optical wavelength converter based on fiber cross-phase modulation and fiber Bragg grating Pavel Honzatko a, a Institute of Photonics and Electronics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, v.v.i.,
All optical wavelength converter based on fiber cross-phase modulation and fiber Bragg grating Pavel Honzatko a, a Institute of Photonics and Electronics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, v.v.i.,
Power penalty caused by Stimulated Raman Scattering in WDM Systems
 Paper Power penalty caused by Stimulated Raman Scattering in WDM Systems Sławomir Pietrzyk, Waldemar Szczęsny, and Marian Marciniak Abstract In this paper we present results of an investigation into the
Paper Power penalty caused by Stimulated Raman Scattering in WDM Systems Sławomir Pietrzyk, Waldemar Szczęsny, and Marian Marciniak Abstract In this paper we present results of an investigation into the
Comparative Analysis Of Different Dispersion Compensation Techniques On 40 Gbps Dwdm System
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF TECHNOLOGY ENHANCEMENTS AND EMERGING ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOL 3, ISSUE 06 34 Comparative Analysis Of Different Dispersion Compensation Techniques On 40 Gbps Dwdm System Meenakshi,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF TECHNOLOGY ENHANCEMENTS AND EMERGING ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOL 3, ISSUE 06 34 Comparative Analysis Of Different Dispersion Compensation Techniques On 40 Gbps Dwdm System Meenakshi,
