The CHIP64 digital mode by Antonino Porcino, IZ8BLY
|
|
|
- Erik Elliott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The CHIP64 digital mode by Antonino Porcino, IZ8BLY Introduction The selection of the baudrate figure to adopt for a particular HF digital mode, is the result of a compromise between sensitivity and stability. In fact, while low baudrates guarantee low S/N thresholds, they suffer a great phase instability because of the propagation disturbances present on the HF channels. Indeed, at low baudrates, small variations in the ionosphere produce abrupt phase jumps that interfere with good reception. By increasing the baudrate, the effect of the ionosphere is diminished but the noise level increases thus requiring more power to establish the contact at the same conditions. Spread spectrum allows to overcome this compromise obtaining the noise levels of low speeds and the stability of high baudrates. When it comes to Spread Spectrum, people usually think of bandwidths too wide to be used on the HF, and maybe for that, the field has remained widely unexplored as regards amateur communications. I propose the design of a Spread Spectrum system reduced to fit to the HF channels that can provide similar or better performances than actual narrowband modes. A brief description of this design as well its software implementation is discussed below. What is Spread Spectrum Spread spectrum (SS) is a family of modulation techniques in which the transmitted signal occupies a bandwidth greatly wider than normally required to transmit the bare information. The are several reasons for doing this, ranging from exploiting maximum available bandwidth to making transmission hidden. Among the different possible implementations of SS, Chip64 uses the so called Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS). In a DSSS transmission, the low speed signal containing the data bits to be transmitted is mixed (multiplied) with a greatly higher speed signal called code. The result of this mixing operation, named spreading, is a high-speed bit stream which is then transmitted as a normal D- BPSK. Indeed, a DSSS signal looks like nothing else than a wideband BPSK. Considering the fact that data can be get back by the inverse operation, the mix of the data with the code has the purpose of transferring on the data stream some of the properties of the code. These properties are then exploited in the receive process allowing a different and advantageous decoding system than traditional BPSK. The code used in the spreading process is a sequence of bits which has the properties of randomness, autocorrelation and cross-correlation.
2 Randomness is the property to look like a random bit sequence, with no recurring pattern. It guarantees that the output power of the signal distributes evenly over all the bandwidth, generating a low density power spectrum. On the contrary, a bit sequence with recurring patterns generates spectrum spikes (for example, in PSK31 the idle signal 0000 generates a spectrum made of only two main peaks). The advantage of having a power spectrum well distributed over the whole bandwidth is essential to go below (or at least to keep close to ) the S/N level, thus passing unobserved and causing minimal interference to narrowband transmissions. Indeed, within its receive window, a narrow band mode listener notices only a slight increase of white noise when a spread spectrum station is transmitting. The property of autocorrelation is the most important as it allows to identify the code within the arriving bit sequence. With a simple operation of multiplication, called despreading, it s possible, instant by instant, to determine if the code is presenting on the receive bit stream. Despreading operations are done in a block called correlator, whose output indicates the likelihood that the code has arrived in that particular instant. Codes of greater length have better autocorrelation properties with less chance of false guesses. With the use of the correlator, there is no need to maintain the synchrony with the transmitter and it s unnecessary to recognize the single incoming symbol. Often indeed, symbols are below the noise threshold and it s not possible to distinguish them. The correlator can instead identify the whole group of symbols that form the code (called chips) indicating the exact instant they present to the receiver. The position of the single chip within the code can be later derived by offset, assuming that the transmitter has maintained the synchrony at least for all the duration of the code (which is a reasonable hypothesis). The property of cross-correlation, is the capability of the code to be distinguished from other possible codes employed. The use of different codes that are also orthogonal allows, to a certain extent, several Spread Spectrum signals to coexist on the same channel at the same time, if each one uses a different code. Thus, a good cross-correlation guarantees a minimal interference among the different spread spectrum signals that are sharing the same band. In Chip64 the use of codes is exploited in a rather different way: instead of allowing more transmissions on the same channel, all available codes are assigned to only one station, allowing it alone to exist on the channel, but nonetheless giving it a greater data speed. This choice is justified by the fact that HF hamradio bandwidths are too narrow and allow a very limited throughput when spread spectrum is used. CHIP64 design The design constraints that have been followed consider several factors: the maximum baudrate speed allowed on HF (300 baud); the average user keyboard typing speed (evaluated around 30 bps, as in PSK31); the common CPU speed in use among radio amateur stations (approximately 1 GHz at the date of this writing). After evaluating all the various parameters during laboratory and on-air tests, the length of the spreading code was fixed in n=64, reserving a further n=128 for slower but more reliable transmissions. Every spreading code has been conceived to be long exactly one data bit, so after the spreading operation a data bit will be 64 chips long. Initially, a classical approach to DSSS was followed, with the use of m-sequences and gold codes (msequences are the basic codes with which all other codes are built). The result was a system with a data
3 speed too slow to be usable. Indeed, with 64 chips long gold codes and using D-BPSK at 300 bauds, a modest 4.7 bps throughput is achieved; a speed which is too lower than our compare term of 30 bps. The next step was to use more gold codes at the same time as to form an alphabet, but discovering too soon that there weren t enough 64 chips long gold codes. Indeed, the number of gold codes, and their goodness, is very limited for n=64. The solution came with the use of Walsh-Hadamard codes, already known to radio amateurs because also used in MT63. These codes are a full set of 64 codes which are mutually orthogonal (each one is easily discernible from all the others) but that have a very poor autocorrelation. Indeed, Walsh- Hadamard codes are highly repetitive and contain a great number of recurring patterns. While in MT63 the bits of the code present in parallel to the receiver (one on every of the 64 tones), in our DSSS system they present serially, therefore good autocorrelation properties are required to make possible the identification of the starting point of the code. Walsh-Hadamard codes can be improved in autocorrelation by mixing them with an m-sequence. A new set of codes, which I named WHP codes (Walsh-Hadamard-Porcino), can be thus derived by simply multiplying each code with a generating m-sequence. The new codes show features of autocorrelation and orthogonality of their parent codes and they can be used to form an alphabet that encodes 6 bits words (2 6 =64). With the purpose of further increasing the total bit rate which was still too low, it was chosen to use two tables of WHP codes, each one obtained by multiplication with a different m-sequence. While this operation lowers the quality of the codes, it permits to double the data speed. Each of the WHP codes can be also transmitted with positive or negative polarity that can be directly detected by the correlator, providing one additional data bit. In total, we have a WHP codes alphabet which encodes 8 bit words. The total data rate is calculated as: chiprate 300 datarate= nbits = 8 = 37. 5bps codelength 64 The parameters of the system can be summed in the following table: Mode Chip 64 Chip 128 Modulation chips/s chips/s Code length 64 chips 128 chips Alphabet length 128 (2x64 WHP codes) 256 (2x128 WHP codes) Generating m-sequences (zero padded at end) M 63 =x 6 + x 5 M 63 = x 6 + x 5 + x 2 + x 1 M 127 =x 7 + x 3 M 127 = x 7 + x 3 + x 2 + x 1 Data bits encoded by the alphabet 8 bits 9 bits Total data rate 37.5 bps bps Rather than fixed 8-bit ASCII, a variable-length encoding (also known as Varicode) is used for characters. The Varicode has two functions: first it provides a sort of Huffman compression when lowercase English language is used. Second, it gives a character-to-character synchronization because each character has its ending delimiter, making possible faster recovers without needing an higher level layer of synchronization. The Varicode system featured in Chip64 is the enhanced version that also
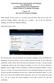
4 appears in MFSK16, which provides a more accurate probability distribution among letters and a reuse of bit sequences containing more than two zeros ( 00 ). The whole message transmission is also delimited with special non-printable characters allowing both station identification and message framing. The format is the following: <SOH> callsign <STX> message <EOT> Where <SOH>, <STX> and <EOT> are respectively varicode ASCII character #1, #2 and #4. <NUL> (#0) is used to flush the buffer at start/end of the transmission and as fill-in during keyboard empty buffer times. The transmitter / receiver software Chip64 signals can be transmitted and received with a specific client software written for Windows and soundcard. It can be freely downloaded from: The program features a special display called correloscope. It shows the presence of the code by displaying its time-offset. The correloscope plots in a graphical way the output of the correlator. On the horizontal axis, the time frame of a code-length is represented (1/300 sec). At each sampling step, one dot is drawn: the more the correlation confidence, the whiter the dot plotted. By plotting the correloscope in a waterfall fashion, the user is able to perceive how the offset of the received codes moves over time. A disturbed signal will plot an unsteady vertical trace (where the shape of this trace depends on the propagation conditions ). A weak signal will plot a steady but faint vertical trace. The correloscope can also show possible clock drifts between the transmitter and the receiver, which are seen as slanted traces. CCIR Poor +0.1% clock drift Fig. 1 the correloscope trace under two different conditions The output of the correlator also controls the squelch of the receiver which is turned off when the confidence falls below a certain threshold. The software has also the option to turn off the correlator and demodulate the signal as a traditional BPSK transmission (referred in the program as clocked decoding ). Its purpose is to show the differences between the two decoding systems under different conditions.
5 By averaging chips phase errors, a very smooth frequency tuning is possible. This is indeed another advantage of Spread Spectrum. The averaged phase errors, constitute a stable frequency error correction signal that can be put in feedback to the main NCO allowing an automatic and precise frequency tuning. The correlator In the decoding process, each receiving sequence has to be matched with the WHP codes from the alphabet, that is, the despreading process has to be repeated for every WHP code. This is necessary because in this system we haven t just a single code as in plain DSSS, but multiple codes present serially and randomly at the receiver. Thus, each chip from the arriving sequence is compared with the corresponding chip of the reference WHP code in the table. If the chip sign matches, confidence is augmented; otherwise if the sign doesn t match, confidence is decreased. At the end of the chips, the resulting confidence for that code is obtained and the matching work is repeated for all the other WHP codes in the table. The time-offset of the arriving code sequence is calculated as the point with best confidence over a code duration, and the corresponding code is used for decoding into text. For better performances, soft chips are processed. A soft chip is a chip that does not represents discrete states (+1 or -1) but represents the likelihood of the chip of being +1. This likelihood system provides a better accuracy giving a continuous range in the confidence values, rather than discrete steps of 1/64. The soft bit information is derived directly from the phase error output of the BPSK detector. Soft bit values range linearly from 0.0 (0 angle) to 1.0 (180 angle). To avoid in between chip synchronization, the despreading work has to be done in time steps smaller than one chip, thus picking with greater precision the offset point of the code. This is done by working with an oversampled signal respect to the chiprate. Depending on the CPU speed, three oversampling figures are provided: 21x, 7x and 3x; these apparently odd figures, are all divisors of Hz, the samplerate used by the soundcard. An higher oversample gives to the correlator a better resolution, but has an heavier load on the CPU. The CPU load is an actual limitation, as it can be too high to let the program run on some old PC workstations. The load is proportional to the number of elementary chip matching operations that can be executed in the time unit. Since these elementary operations translate into simple ADD and SUB register machine code instructions, they can be executed in just one CPUclock cycle, therefore the total CPU load (lower bound) can be approximately calculated as: nop = chiprate oversample chiplength ncodes For Chip64: For Chip128: nop = = 51,609, Mips nop = = 206,438, Mips With current CPU clocks in the range of few GHz, it s necessary that the correlator has the maximum possible performance. For this reason, integer math was used as it guarantees faster execution speeds than floating point math. In particular, the correlation routine was written in pure assembler doing all operations in CPU registers and interlacing the machine language instructions to take advantage of the processor s execution pipeline.
6 Performance of the system Chip64 and Chip128 have been extensively tested on air during the year 2004 by me and a restricted group of people: Murray Greenman ZL1BPU (who also contributed in the design of the system), Chris Gerber HB9BDM and Manfred Salzwedel OH/DK4ZC. The system proved to be efficient and we found it comparable to the other modern digital modes. Being totally different in its architecture, it shows better performance during certain circumstances, while in others it shows no actual gain. In particular, it performs better under multipath where normal BPSK can t track arriving symbols, but in quiet environments it doesn t show any improvement over plain BPSK. This is expected because of the losses that occur due to the imperfect autocorrelation of the codes. Conclusions The design of this new digital mode served to introduce the Spread Spectrum technology among radio amateurs by providing a communication tool to experiment with. Its purpose was to prove that it s possible to take advantage of the Spread Spectrum techniques even on the HF channels, making the communication possible under conditions where traditional narrowband modes fail. All accurate performance tests and possible fields of application are left for future studies. If you are interested in the Chip64 project you might want to join the Chip64 mailing list at the address: chip64@yahoogroups.com.
CHAPTER 2. Instructor: Mr. Abhijit Parmar Course: Mobile Computing and Wireless Communication ( )
 CHAPTER 2 Instructor: Mr. Abhijit Parmar Course: Mobile Computing and Wireless Communication (2170710) Syllabus Chapter-2.4 Spread Spectrum Spread Spectrum SS was developed initially for military and intelligence
CHAPTER 2 Instructor: Mr. Abhijit Parmar Course: Mobile Computing and Wireless Communication (2170710) Syllabus Chapter-2.4 Spread Spectrum Spread Spectrum SS was developed initially for military and intelligence
Spread Spectrum. Chapter 18. FHSS Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum DSSS Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum DSSS using CDMA Code Division Multiple Access
 Spread Spectrum Chapter 18 FHSS Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum DSSS Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum DSSS using CDMA Code Division Multiple Access Single Carrier The traditional way Transmitted signal
Spread Spectrum Chapter 18 FHSS Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum DSSS Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum DSSS using CDMA Code Division Multiple Access Single Carrier The traditional way Transmitted signal
Amateur Radio Digital Modes
 Amateur Radio Digital Modes An introduction to PSK31, MFSK16, MT63, and Hellschreiber John DeGood NU3E Trenton Computer Festival Sat 5 May 2001 Acknowledgement: figures and illustrations from http://www.qsl.net/zl1bpu/
Amateur Radio Digital Modes An introduction to PSK31, MFSK16, MT63, and Hellschreiber John DeGood NU3E Trenton Computer Festival Sat 5 May 2001 Acknowledgement: figures and illustrations from http://www.qsl.net/zl1bpu/
Lecture 9: Spread Spectrum Modulation Techniques
 Lecture 9: Spread Spectrum Modulation Techniques Spread spectrum (SS) modulation techniques employ a transmission bandwidth which is several orders of magnitude greater than the minimum required bandwidth
Lecture 9: Spread Spectrum Modulation Techniques Spread spectrum (SS) modulation techniques employ a transmission bandwidth which is several orders of magnitude greater than the minimum required bandwidth
Some Notes on STANAG A DXer s View
 Some Notes on STANAG 4285 - A DXer s View STANAG 4285 is a single-tone modem, agreed upon by NATO member states in the 1980 s. The unclassified specification can be downloaded here. Until today, there
Some Notes on STANAG 4285 - A DXer s View STANAG 4285 is a single-tone modem, agreed upon by NATO member states in the 1980 s. The unclassified specification can be downloaded here. Until today, there
RTTY: an FSK decoder program for Linux. Jesús Arias (EB1DIX)
 RTTY: an FSK decoder program for Linux. Jesús Arias (EB1DIX) June 15, 2001 Contents 1 rtty-2.0 Program Description. 2 1.1 What is RTTY........................................... 2 1.1.1 The RTTY transmissions.................................
RTTY: an FSK decoder program for Linux. Jesús Arias (EB1DIX) June 15, 2001 Contents 1 rtty-2.0 Program Description. 2 1.1 What is RTTY........................................... 2 1.1.1 The RTTY transmissions.................................
COMMON CHARACTERISTICS. Patrick Lindecker (F6CTE) the 8 of may 2004 (mail:
 Patrick Lindecker (F6CTE) the 8 of may 2004 (mail: f6cte@aol.com) In this paper, I will describe two digital modes "keyboard to keyboard" of PSK (Phase Shift Keying) type: the PSKFEC31 and the PSK63F,
Patrick Lindecker (F6CTE) the 8 of may 2004 (mail: f6cte@aol.com) In this paper, I will describe two digital modes "keyboard to keyboard" of PSK (Phase Shift Keying) type: the PSKFEC31 and the PSK63F,
Laboratory 5: Spread Spectrum Communications
 Laboratory 5: Spread Spectrum Communications Cory J. Prust, Ph.D. Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Department Milwaukee School of Engineering Last Update: 19 September 2018 Contents 0 Laboratory
Laboratory 5: Spread Spectrum Communications Cory J. Prust, Ph.D. Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Department Milwaukee School of Engineering Last Update: 19 September 2018 Contents 0 Laboratory
Module 3: Physical Layer
 Module 3: Physical Layer Dr. Associate Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 Phone: 601-979-3661 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu 1 Topics 3.1 Signal Levels: Baud
Module 3: Physical Layer Dr. Associate Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 Phone: 601-979-3661 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu 1 Topics 3.1 Signal Levels: Baud
Spread Spectrum (SS) is a means of transmission in which the signal occupies a
 SPREAD-SPECTRUM SPECTRUM TECHNIQUES: A BRIEF OVERVIEW SS: AN OVERVIEW Spread Spectrum (SS) is a means of transmission in which the signal occupies a bandwidth in excess of the minimum necessary to send
SPREAD-SPECTRUM SPECTRUM TECHNIQUES: A BRIEF OVERVIEW SS: AN OVERVIEW Spread Spectrum (SS) is a means of transmission in which the signal occupies a bandwidth in excess of the minimum necessary to send
Spread Spectrum Techniques
 0 Spread Spectrum Techniques Contents 1 1. Overview 2. Pseudonoise Sequences 3. Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Systems 4. Frequency Hopping Systems 5. Synchronization 6. Applications 2 1. Overview Basic
0 Spread Spectrum Techniques Contents 1 1. Overview 2. Pseudonoise Sequences 3. Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Systems 4. Frequency Hopping Systems 5. Synchronization 6. Applications 2 1. Overview Basic
Wireless Transmission & Media Access
 Wireless Transmission & Media Access Signals and Signal Propagation Multiplexing Modulation Media Access 1 Significant parts of slides are based on original material by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller,
Wireless Transmission & Media Access Signals and Signal Propagation Multiplexing Modulation Media Access 1 Significant parts of slides are based on original material by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller,
CDMA Principle and Measurement
 CDMA Principle and Measurement Concepts of CDMA CDMA Key Technologies CDMA Air Interface CDMA Measurement Basic Agilent Restricted Page 1 Cellular Access Methods Power Time Power Time FDMA Frequency Power
CDMA Principle and Measurement Concepts of CDMA CDMA Key Technologies CDMA Air Interface CDMA Measurement Basic Agilent Restricted Page 1 Cellular Access Methods Power Time Power Time FDMA Frequency Power
Telegraphic alphabet for data communication by phase shift keying at 31 Bd in the amateur and amateur-satellite services. Recommendation ITU-R M.
 Recommendation ITU-R M.2034 (02/2013) Telegraphic alphabet for data communication by phase shift keying at 31 Bd in the amateur and amateur-satellite services M Series Mobile, radiodetermination, amateur
Recommendation ITU-R M.2034 (02/2013) Telegraphic alphabet for data communication by phase shift keying at 31 Bd in the amateur and amateur-satellite services M Series Mobile, radiodetermination, amateur
Chapter 2 Direct-Sequence Systems
 Chapter 2 Direct-Sequence Systems A spread-spectrum signal is one with an extra modulation that expands the signal bandwidth greatly beyond what is required by the underlying coded-data modulation. Spread-spectrum
Chapter 2 Direct-Sequence Systems A spread-spectrum signal is one with an extra modulation that expands the signal bandwidth greatly beyond what is required by the underlying coded-data modulation. Spread-spectrum
ECE 5325/6325: Wireless Communication Systems Lecture Notes, Spring 2013
 ECE 5325/6325: Wireless Communication Systems Lecture Notes, Spring 2013 Lecture 17 Today: Spread Spectrum: (1) Frequency Hopping, (2) Direct Sequence Reading: Today Molisch 18.1, 18.2. Thu: MUSE Channel
ECE 5325/6325: Wireless Communication Systems Lecture Notes, Spring 2013 Lecture 17 Today: Spread Spectrum: (1) Frequency Hopping, (2) Direct Sequence Reading: Today Molisch 18.1, 18.2. Thu: MUSE Channel
Costas Loop. Modules: Sequence Generator, Digital Utilities, VCO, Quadrature Utilities (2), Phase Shifter, Tuneable LPF (2), Multiplier
 Costas Loop Modules: Sequence Generator, Digital Utilities, VCO, Quadrature Utilities (2), Phase Shifter, Tuneable LPF (2), Multiplier 0 Pre-Laboratory Reading Phase-shift keying that employs two discrete
Costas Loop Modules: Sequence Generator, Digital Utilities, VCO, Quadrature Utilities (2), Phase Shifter, Tuneable LPF (2), Multiplier 0 Pre-Laboratory Reading Phase-shift keying that employs two discrete
Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 2: Wireless Transmission (2/2)
 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 2: Wireless Transmission (2/2) [Schiller, Section 2.6 & 2.7] [Reader Part 1: OFDM: An architecture for the fourth generation] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 2: Wireless Transmission (2/2) [Schiller, Section 2.6 & 2.7] [Reader Part 1: OFDM: An architecture for the fourth generation] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture
Chapter 7. Multiple Division Techniques
 Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques 1 Outline Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Comparison of FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA Walsh
Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques 1 Outline Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Comparison of FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA Walsh
2. TELECOMMUNICATIONS BASICS
 2. TELECOMMUNICATIONS BASICS The purpose of any telecommunications system is to transfer information from the sender to the receiver by a means of a communication channel. The information is carried by
2. TELECOMMUNICATIONS BASICS The purpose of any telecommunications system is to transfer information from the sender to the receiver by a means of a communication channel. The information is carried by
Multiple Access Schemes
 Multiple Access Schemes Dr Yousef Dama Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology An-Najah National University 2016-2017 Why Multiple access schemes Multiple access schemes are used to allow many
Multiple Access Schemes Dr Yousef Dama Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology An-Najah National University 2016-2017 Why Multiple access schemes Multiple access schemes are used to allow many
- 1 - Rap. UIT-R BS Rep. ITU-R BS.2004 DIGITAL BROADCASTING SYSTEMS INTENDED FOR AM BANDS
 - 1 - Rep. ITU-R BS.2004 DIGITAL BROADCASTING SYSTEMS INTENDED FOR AM BANDS (1995) 1 Introduction In the last decades, very few innovations have been brought to radiobroadcasting techniques in AM bands
- 1 - Rep. ITU-R BS.2004 DIGITAL BROADCASTING SYSTEMS INTENDED FOR AM BANDS (1995) 1 Introduction In the last decades, very few innovations have been brought to radiobroadcasting techniques in AM bands
Cross Spectral Density Analysis for Various Codes Suitable for Spread Spectrum under AWGN conditions with Error Detecting Code
 Cross Spectral Density Analysis for Various Codes Suitable for Spread Spectrum under AWG conditions with Error Detecting Code CH.ISHATHI 1, R.SUDAR RAJA 2 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,
Cross Spectral Density Analysis for Various Codes Suitable for Spread Spectrum under AWG conditions with Error Detecting Code CH.ISHATHI 1, R.SUDAR RAJA 2 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,
Lecture 3. Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Systems. COMM 907:Spread Spectrum Communications
 COMM 907: Spread Spectrum Communications Lecture 3 Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Systems Performance of DSSSS with BPSK Modulation in presence of Interference (Jamming) Broadband Interference (Jamming):
COMM 907: Spread Spectrum Communications Lecture 3 Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum Systems Performance of DSSSS with BPSK Modulation in presence of Interference (Jamming) Broadband Interference (Jamming):
CDMA Example with MATLAB
 CDMA Example with MATLAB Firstly we generate a small random sequence of binary data, that we represent as a sampled waveform with 64 samples per bit. % CDMA example clear all data = randint(1,15,2); for
CDMA Example with MATLAB Firstly we generate a small random sequence of binary data, that we represent as a sampled waveform with 64 samples per bit. % CDMA example clear all data = randint(1,15,2); for
Part 3. Multiple Access Methods. p. 1 ELEC6040 Mobile Radio Communications, Dept. of E.E.E., HKU
 Part 3. Multiple Access Methods p. 1 ELEC6040 Mobile Radio Communications, Dept. of E.E.E., HKU Review of Multiple Access Methods Aim of multiple access To simultaneously support communications between
Part 3. Multiple Access Methods p. 1 ELEC6040 Mobile Radio Communications, Dept. of E.E.E., HKU Review of Multiple Access Methods Aim of multiple access To simultaneously support communications between
Implementation of DSSS System using Chaotic Sequence using MATLAB and VHDL
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 5, May 2015, pg.598
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 5, May 2015, pg.598
Chapter 2 Overview - 1 -
 Chapter 2 Overview Part 1 (last week) Digital Transmission System Frequencies, Spectrum Allocation Radio Propagation and Radio Channels Part 2 (today) Modulation, Coding, Error Correction Part 3 (next
Chapter 2 Overview Part 1 (last week) Digital Transmission System Frequencies, Spectrum Allocation Radio Propagation and Radio Channels Part 2 (today) Modulation, Coding, Error Correction Part 3 (next
CDMA - QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
 CDMA - QUESTIONS & ANSWERS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/cdma/questions_and_answers.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com 1. What is CDMA? CDMA stands for Code Division Multiple Access. It is a wireless technology
CDMA - QUESTIONS & ANSWERS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/cdma/questions_and_answers.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com 1. What is CDMA? CDMA stands for Code Division Multiple Access. It is a wireless technology
Wireless Intro : Computer Networking. Wireless Challenges. Overview
 Wireless Intro 15-744: Computer Networking L-17 Wireless Overview TCP on wireless links Wireless MAC Assigned reading [BM09] In Defense of Wireless Carrier Sense [BAB+05] Roofnet (2 sections) Optional
Wireless Intro 15-744: Computer Networking L-17 Wireless Overview TCP on wireless links Wireless MAC Assigned reading [BM09] In Defense of Wireless Carrier Sense [BAB+05] Roofnet (2 sections) Optional
Performance Analysis of DSSS and FHSS Techniques over AWGN Channel
 Performance Analysis of DSSS and FHSS Techniques over AWGN Channel M. Katta Swamy, M.Deepthi, V.Mounika, R.N.Saranya Vignana Bharathi Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, and Andhra Pradesh, India. Corresponding
Performance Analysis of DSSS and FHSS Techniques over AWGN Channel M. Katta Swamy, M.Deepthi, V.Mounika, R.N.Saranya Vignana Bharathi Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, and Andhra Pradesh, India. Corresponding
SC - Single carrier systems One carrier carries data stream
 Digital modulation SC - Single carrier systems One carrier carries data stream MC - Multi-carrier systems Many carriers are used for data transmission. Data stream is divided into sub-streams and each
Digital modulation SC - Single carrier systems One carrier carries data stream MC - Multi-carrier systems Many carriers are used for data transmission. Data stream is divided into sub-streams and each
1. INTRODUCTION II. SPREADING USING WALSH CODE. International Journal of Advanced Networking & Applications (IJANA) ISSN:
 Analysis of DWT OFDM using Rician Channel and Comparison with ANN based OFDM Geeta S H1, Smitha B2, Shruthi G, Shilpa S G4 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, DBIT, Bangalore, Visvesvaraya
Analysis of DWT OFDM using Rician Channel and Comparison with ANN based OFDM Geeta S H1, Smitha B2, Shruthi G, Shilpa S G4 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, DBIT, Bangalore, Visvesvaraya
ECS455: Chapter 4 Multiple Access
 ECS455: Chapter 4 Multiple Access 4.4 DS/SS 1 Dr.Prapun Suksompong prapun.com/ecs455 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Wednesday 15:30-16:30 Friday 9:30-10:30 Spread spectrum (SS) Historically spread spectrum was
ECS455: Chapter 4 Multiple Access 4.4 DS/SS 1 Dr.Prapun Suksompong prapun.com/ecs455 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Wednesday 15:30-16:30 Friday 9:30-10:30 Spread spectrum (SS) Historically spread spectrum was
GNSS Technologies. GNSS Acquisition Dr. Zahidul Bhuiyan Finnish Geospatial Research Institute, National Land Survey
 GNSS Acquisition 25.1.2016 Dr. Zahidul Bhuiyan Finnish Geospatial Research Institute, National Land Survey Content GNSS signal background Binary phase shift keying (BPSK) modulation Binary offset carrier
GNSS Acquisition 25.1.2016 Dr. Zahidul Bhuiyan Finnish Geospatial Research Institute, National Land Survey Content GNSS signal background Binary phase shift keying (BPSK) modulation Binary offset carrier
SPREAD SPECTRUM (SS) SIGNALS FOR DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS
 Dr. Ali Muqaibel SPREAD SPECTRUM (SS) SIGNALS FOR DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS VERSION 1.1 Dr. Ali Hussein Muqaibel 1 Introduction Narrow band signal (data) In Spread Spectrum, the bandwidth W is much greater
Dr. Ali Muqaibel SPREAD SPECTRUM (SS) SIGNALS FOR DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS VERSION 1.1 Dr. Ali Hussein Muqaibel 1 Introduction Narrow band signal (data) In Spread Spectrum, the bandwidth W is much greater
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
 Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
Zipping Characterization of Chaotic Sequences Used in Spread Spectrum Communication Systems
 Zipping Characterization of Chaotic Sequences Used in Spread Spectrum Communication Systems L. De Micco, C. M. Arizmendi and H. A. Larrondo Facultad de Ingenieria, Universidad de Mar del Plata (UNMDP).
Zipping Characterization of Chaotic Sequences Used in Spread Spectrum Communication Systems L. De Micco, C. M. Arizmendi and H. A. Larrondo Facultad de Ingenieria, Universidad de Mar del Plata (UNMDP).
CDMA Mobile Radio Networks
 - 1 - CDMA Mobile Radio Networks Elvino S. Sousa Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Canada ECE1543S - Spring 1999 - 2 - CONTENTS Basic principle of direct sequence
- 1 - CDMA Mobile Radio Networks Elvino S. Sousa Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Canada ECE1543S - Spring 1999 - 2 - CONTENTS Basic principle of direct sequence
Chapter 2 Overview - 1 -
 Chapter 2 Overview Part 1 (last week) Digital Transmission System Frequencies, Spectrum Allocation Radio Propagation and Radio Channels Part 2 (today) Modulation, Coding, Error Correction Part 3 (next
Chapter 2 Overview Part 1 (last week) Digital Transmission System Frequencies, Spectrum Allocation Radio Propagation and Radio Channels Part 2 (today) Modulation, Coding, Error Correction Part 3 (next
T325 Summary T305 T325 B BLOCK 3 4 PART III T325. Session 11 Block III Part 3 Access & Modulation. Dr. Saatchi, Seyed Mohsen.
 T305 T325 B BLOCK 3 4 PART III T325 Summary Session 11 Block III Part 3 Access & Modulation [Type Dr. Saatchi, your address] Seyed Mohsen [Type your phone number] [Type your e-mail address] Prepared by:
T305 T325 B BLOCK 3 4 PART III T325 Summary Session 11 Block III Part 3 Access & Modulation [Type Dr. Saatchi, your address] Seyed Mohsen [Type your phone number] [Type your e-mail address] Prepared by:
Physical Layer: Modulation, FEC. Wireless Networks: Guevara Noubir. S2001, COM3525 Wireless Networks Lecture 3, 1
 Wireless Networks: Physical Layer: Modulation, FEC Guevara Noubir Noubir@ccsneuedu S, COM355 Wireless Networks Lecture 3, Lecture focus Modulation techniques Bit Error Rate Reducing the BER Forward Error
Wireless Networks: Physical Layer: Modulation, FEC Guevara Noubir Noubir@ccsneuedu S, COM355 Wireless Networks Lecture 3, Lecture focus Modulation techniques Bit Error Rate Reducing the BER Forward Error
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS. MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications
 DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications Bandpass binary signalling The common techniques of bandpass binary signalling are: - On-off keying (OOK), also known as
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications Bandpass binary signalling The common techniques of bandpass binary signalling are: - On-off keying (OOK), also known as
QUESTION BANK EC 1351 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION YEAR / SEM : III / VI UNIT I- PULSE MODULATION PART-A (2 Marks) 1. What is the purpose of sample and hold
 QUESTION BANK EC 1351 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION YEAR / SEM : III / VI UNIT I- PULSE MODULATION PART-A (2 Marks) 1. What is the purpose of sample and hold circuit 2. What is the difference between natural sampling
QUESTION BANK EC 1351 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION YEAR / SEM : III / VI UNIT I- PULSE MODULATION PART-A (2 Marks) 1. What is the purpose of sample and hold circuit 2. What is the difference between natural sampling
EE 400L Communications. Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation
 EE 400L Communications Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, at Las Vegas PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in
EE 400L Communications Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, at Las Vegas PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in
Comparative Study of OFDM & MC-CDMA in WiMAX System
 IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 9, Issue 1, Ver. IV (Jan. 2014), PP 64-68 Comparative Study of OFDM & MC-CDMA in WiMAX
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 9, Issue 1, Ver. IV (Jan. 2014), PP 64-68 Comparative Study of OFDM & MC-CDMA in WiMAX
I-Q transmission. Lecture 17
 I-Q Transmission Lecture 7 I-Q transmission i Sending Digital Data Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK): sending binary data over a single frequency band Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK): sending twice
I-Q Transmission Lecture 7 I-Q transmission i Sending Digital Data Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK): sending binary data over a single frequency band Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK): sending twice
MODULATION AND MULTIPLE ACCESS TECHNIQUES
 1 MODULATION AND MULTIPLE ACCESS TECHNIQUES Networks and Communication Department Dr. Marwah Ahmed Outlines 2 Introduction Digital Transmission Digital Modulation Digital Transmission of Analog Signal
1 MODULATION AND MULTIPLE ACCESS TECHNIQUES Networks and Communication Department Dr. Marwah Ahmed Outlines 2 Introduction Digital Transmission Digital Modulation Digital Transmission of Analog Signal
EE 460L University of Nevada, Las Vegas ECE Department
 EE 460L PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in the context of digital communications is a modulation process which imparts to a sinusoid two or more discrete amplitude levels. These are related
EE 460L PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in the context of digital communications is a modulation process which imparts to a sinusoid two or more discrete amplitude levels. These are related
Evolution of the WSJT Digital Modes
 Evolution of the WSJT Digital Modes Mike Hasselbeck WB2FKO New Mexico TechFest 25 February 2017 WSJT: A software package for digital radio communication Weak Signal communication by Professor Joe Taylor
Evolution of the WSJT Digital Modes Mike Hasselbeck WB2FKO New Mexico TechFest 25 February 2017 WSJT: A software package for digital radio communication Weak Signal communication by Professor Joe Taylor
Efficient UMTS. 1 Introduction. Lodewijk T. Smit and Gerard J.M. Smit CADTES, May 9, 2003
 Efficient UMTS Lodewijk T. Smit and Gerard J.M. Smit CADTES, email:smitl@cs.utwente.nl May 9, 2003 This article gives a helicopter view of some of the techniques used in UMTS on the physical and link layer.
Efficient UMTS Lodewijk T. Smit and Gerard J.M. Smit CADTES, email:smitl@cs.utwente.nl May 9, 2003 This article gives a helicopter view of some of the techniques used in UMTS on the physical and link layer.
Study on the UWB Rader Synchronization Technology
 Study on the UWB Rader Synchronization Technology Guilin Lu Guangxi University of Technology, Liuzhou 545006, China E-mail: lifishspirit@126.com Shaohong Wan Ari Force No.95275, Liuzhou 545005, China E-mail:
Study on the UWB Rader Synchronization Technology Guilin Lu Guangxi University of Technology, Liuzhou 545006, China E-mail: lifishspirit@126.com Shaohong Wan Ari Force No.95275, Liuzhou 545005, China E-mail:
Spread Spectrum Communications and Jamming Prof. Debarati Sen G S Sanyal School of Telecommunications Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Spread Spectrum Communications and Jamming Prof. Debarati Sen G S Sanyal School of Telecommunications Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 07 Slow and Fast Frequency Hopping Hello students,
Spread Spectrum Communications and Jamming Prof. Debarati Sen G S Sanyal School of Telecommunications Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 07 Slow and Fast Frequency Hopping Hello students,
CHAPTER 4. DESIGN OF ADAPTIVE MODULATION SYSTEM BY USING 1/3 RATE TURBO CODER (SNR Vs BER)
 112 CHAPTER 4 DESIGN OF ADAPTIVE MODULATION SYSTEM BY USING 1/3 RATE TURBO CODER (SNR Vs BER) 4.1 NECESSITY FOR SYSTEM DESIGN The improved BER was achieved by inhibiting 1/3 rated Turbo coder instead of
112 CHAPTER 4 DESIGN OF ADAPTIVE MODULATION SYSTEM BY USING 1/3 RATE TURBO CODER (SNR Vs BER) 4.1 NECESSITY FOR SYSTEM DESIGN The improved BER was achieved by inhibiting 1/3 rated Turbo coder instead of
IFH SS CDMA Implantation. 6.0 Introduction
 6.0 Introduction Wireless personal communication systems enable geographically dispersed users to exchange information using a portable terminal, such as a handheld transceiver. Often, the system engineer
6.0 Introduction Wireless personal communication systems enable geographically dispersed users to exchange information using a portable terminal, such as a handheld transceiver. Often, the system engineer
OFDMA and MIMO Notes
 OFDMA and MIMO Notes EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 14 Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) is a digital multi-carrier modulation technique extending the concept of single subcarrier modulation
OFDMA and MIMO Notes EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 14 Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) is a digital multi-carrier modulation technique extending the concept of single subcarrier modulation
Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques for Traffic Channels
 Introduction to Wireless & Mobile Systems Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques for Traffic Channels Outline Introduction Concepts and Models for Multiple Divisions Frequency Division Multiple Access
Introduction to Wireless & Mobile Systems Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques for Traffic Channels Outline Introduction Concepts and Models for Multiple Divisions Frequency Division Multiple Access
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 3: Antennas, Propagation, and Spread Spectrum September 30, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Antennas and
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 3: Antennas, Propagation, and Spread Spectrum September 30, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Antennas and
ECS455: Chapter 4 Multiple Access
 ECS455: Chapter 4 Multiple Access 4.4 DS/SS 1 Dr.Prapun Suksompong prapun.com/ecs455 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 9:30-10:30 Tuesday 13:30-14:30 Thursday 13:30-14:30 Spread spectrum (SS) Historically
ECS455: Chapter 4 Multiple Access 4.4 DS/SS 1 Dr.Prapun Suksompong prapun.com/ecs455 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 9:30-10:30 Tuesday 13:30-14:30 Thursday 13:30-14:30 Spread spectrum (SS) Historically
Weak Signal Digital Modes. 9V1KG Klaus Aug 2016
 Weak Signal Digital Modes 9V1KG Klaus Aug 2016 Content Introduction What makes these modes so popular? Station setup and interfacing Digital Modulation PSK 31 JT-65/JT-9 PSK Reporter 9V1KG - Weak Signal
Weak Signal Digital Modes 9V1KG Klaus Aug 2016 Content Introduction What makes these modes so popular? Station setup and interfacing Digital Modulation PSK 31 JT-65/JT-9 PSK Reporter 9V1KG - Weak Signal
What is it? What do I need? How do I use it? Randy Hall K7AGE
 PSK-31 What is it? What do I need? How do I use it? Randy Hall K7AGE First, a little bit about me I was first licensed in 1968 I ve been around video since high school Built a TV camera as high school
PSK-31 What is it? What do I need? How do I use it? Randy Hall K7AGE First, a little bit about me I was first licensed in 1968 I ve been around video since high school Built a TV camera as high school
(Refer Slide Time: 2:23)
 Data Communications Prof. A. Pal Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11B Multiplexing (Contd.) Hello and welcome to today s lecture on multiplexing
Data Communications Prof. A. Pal Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture-11B Multiplexing (Contd.) Hello and welcome to today s lecture on multiplexing
Performance Evaluation of STBC-OFDM System for Wireless Communication
 Performance Evaluation of STBC-OFDM System for Wireless Communication Apeksha Deshmukh, Prof. Dr. M. D. Kokate Department of E&TC, K.K.W.I.E.R. College, Nasik, apeksha19may@gmail.com Abstract In this paper
Performance Evaluation of STBC-OFDM System for Wireless Communication Apeksha Deshmukh, Prof. Dr. M. D. Kokate Department of E&TC, K.K.W.I.E.R. College, Nasik, apeksha19may@gmail.com Abstract In this paper
K.NARSING RAO(08R31A0425) DEPT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING (NOVH).
 Smart Antenna K.NARSING RAO(08R31A0425) DEPT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING (NOVH). ABSTRACT:- One of the most rapidly developing areas of communications is Smart Antenna systems. This paper
Smart Antenna K.NARSING RAO(08R31A0425) DEPT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING (NOVH). ABSTRACT:- One of the most rapidly developing areas of communications is Smart Antenna systems. This paper
Amplitude Frequency Phase
 Chapter 4 (part 2) Digital Modulation Techniques Chapter 4 (part 2) Overview Digital Modulation techniques (part 2) Bandpass data transmission Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) Phase Shift Keying (PSK) Frequency
Chapter 4 (part 2) Digital Modulation Techniques Chapter 4 (part 2) Overview Digital Modulation techniques (part 2) Bandpass data transmission Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) Phase Shift Keying (PSK) Frequency
Mobile Computing. Chapter 3: Medium Access Control
 Mobile Computing Chapter 3: Medium Access Control Prof. Sang-Jo Yoo Contents Motivation Access methods SDMA/FDMA/TDMA Aloha Other access methods Access method CDMA 2 1. Motivation Can we apply media access
Mobile Computing Chapter 3: Medium Access Control Prof. Sang-Jo Yoo Contents Motivation Access methods SDMA/FDMA/TDMA Aloha Other access methods Access method CDMA 2 1. Motivation Can we apply media access
Wireless Medium Access Control and CDMA-based Communication Lesson 08 Auto-correlation and Barker Codes
 Wireless Medium Access Control and CDMA-based Communication Lesson 08 Auto-correlation and Barker Codes 1 Coding Methods in CDMA Use distinctive spreading codes to spread the symbols before transmission
Wireless Medium Access Control and CDMA-based Communication Lesson 08 Auto-correlation and Barker Codes 1 Coding Methods in CDMA Use distinctive spreading codes to spread the symbols before transmission
QSY Society Field Day 2011 PSK31 Training By KC2QFR - Fred Lauricella Introduction:
 QSY Society Field Day 2011 PSK31 Training By KC2QFR - Fred Lauricella Introduction: The Digital mode PSK31 was the creation of Peter Martinez. Introduced in a 1998 RSGB article by G3PLX in the societies
QSY Society Field Day 2011 PSK31 Training By KC2QFR - Fred Lauricella Introduction: The Digital mode PSK31 was the creation of Peter Martinez. Introduced in a 1998 RSGB article by G3PLX in the societies
Data transmission - Transmission modes
 Data transmission - Transmission modes Transmission modes A given transmission on a communications channel between two machines can occur in several different ways. The transmission is characterised by:
Data transmission - Transmission modes Transmission modes A given transmission on a communications channel between two machines can occur in several different ways. The transmission is characterised by:
Prof. P. Subbarao 1, Veeravalli Balaji 2
 Performance Analysis of Multicarrier DS-CDMA System Using BPSK Modulation Prof. P. Subbarao 1, Veeravalli Balaji 2 1 MSc (Engg), FIETE, MISTE, Department of ECE, S.R.K.R Engineering College, A.P, India
Performance Analysis of Multicarrier DS-CDMA System Using BPSK Modulation Prof. P. Subbarao 1, Veeravalli Balaji 2 1 MSc (Engg), FIETE, MISTE, Department of ECE, S.R.K.R Engineering College, A.P, India
Spread Spectrum: Definition
 Spread Spectrum: Definition refers to the expansion of signal bandwidth, by several orders of magnitude in some cases, which occurs when a key is attached to the communication channel an RF communications
Spread Spectrum: Definition refers to the expansion of signal bandwidth, by several orders of magnitude in some cases, which occurs when a key is attached to the communication channel an RF communications
Rec. ITU-R F RECOMMENDATION ITU-R F *,**
 Rec. ITU-R F.240-6 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R F.240-6 *,** SIGNAL-TO-INTERFERENCE PROTECTION RATIOS FOR VARIOUS CLASSES OF EMISSION IN THE FIXED SERVICE BELOW ABOUT 30 MHz (Question 143/9) Rec. ITU-R F.240-6
Rec. ITU-R F.240-6 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R F.240-6 *,** SIGNAL-TO-INTERFERENCE PROTECTION RATIOS FOR VARIOUS CLASSES OF EMISSION IN THE FIXED SERVICE BELOW ABOUT 30 MHz (Question 143/9) Rec. ITU-R F.240-6
Communications I (ELCN 306)
 Communications I (ELCN 306) c Samy S. Soliman Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department Cairo University, Egypt Email: samy.soliman@cu.edu.eg Website: http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/samysoliman
Communications I (ELCN 306) c Samy S. Soliman Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department Cairo University, Egypt Email: samy.soliman@cu.edu.eg Website: http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/samysoliman
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61)
 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61) Module 1 1. Explain Digital communication system with a neat block diagram. 2. What are the differences between digital and analog communication systems?
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61) Module 1 1. Explain Digital communication system with a neat block diagram. 2. What are the differences between digital and analog communication systems?
Assignment 1: Solutions to Problems on Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
 G. S. Sanyal School of Telecommunications Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur MOOC: Spread Spectrum Communications & Jamming Assignment 1: Solutions to Problems on Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
G. S. Sanyal School of Telecommunications Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur MOOC: Spread Spectrum Communications & Jamming Assignment 1: Solutions to Problems on Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
Code Division Multiple Access.
 Code Division Multiple Access Mobile telephony, using the concept of cellular architecture, are built based on GSM (Global System for Mobile communication) and IS-95(Intermediate Standard-95). CDMA allows
Code Division Multiple Access Mobile telephony, using the concept of cellular architecture, are built based on GSM (Global System for Mobile communication) and IS-95(Intermediate Standard-95). CDMA allows
Wireless Communication: Concepts, Techniques, and Models. Hongwei Zhang
 Wireless Communication: Concepts, Techniques, and Models Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Outline Digital communication over radio channels Channel capacity MIMO: diversity and parallel channels
Wireless Communication: Concepts, Techniques, and Models Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Outline Digital communication over radio channels Channel capacity MIMO: diversity and parallel channels
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R F *, ** Signal-to-interference protection ratios for various classes of emission in the fixed service below about 30 MHz
 Rec. ITU-R F.240-7 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R F.240-7 *, ** Signal-to-interference protection ratios for various classes of emission in the fixed service below about 30 MHz (Question ITU-R 143/9) (1953-1956-1959-1970-1974-1978-1986-1990-1992-2006)
Rec. ITU-R F.240-7 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R F.240-7 *, ** Signal-to-interference protection ratios for various classes of emission in the fixed service below about 30 MHz (Question ITU-R 143/9) (1953-1956-1959-1970-1974-1978-1986-1990-1992-2006)
Spread Spectrum Signal for Digital Communications
 Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Spread Spectrum Signal for Digital Communications Institute of Communications Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Multiple Access Schemes Table of
Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Spread Spectrum Signal for Digital Communications Institute of Communications Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Multiple Access Schemes Table of
Chapter 7 Spread-Spectrum Modulation
 Chapter 7 Spread-Spectrum Modulation Spread Spectrum Technique simply consumes spectrum in excess of the minimum spectrum necessary to send the data. 7.1 Introduction o Definition of spread-spectrum modulation
Chapter 7 Spread-Spectrum Modulation Spread Spectrum Technique simply consumes spectrum in excess of the minimum spectrum necessary to send the data. 7.1 Introduction o Definition of spread-spectrum modulation
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R F ARRANGEMENT OF VOICE-FREQUENCY, FREQUENCY-SHIFT TELEGRAPH CHANNELS OVER HF RADIO CIRCUITS. (Question ITU-R 145/9)
 Rec. ITU-R F.436-4 1 9E4: HF radiotelegraphy RECOMMENDATION ITU-R F.436-4 ARRANGEMENT OF VOICE-FREQUENCY, FREQUENCY-SHIFT TELEGRAPH CHANNELS OVER HF RADIO CIRCUITS (Question ITU-R 145/9) (1966-1970-1978-1994-1995)
Rec. ITU-R F.436-4 1 9E4: HF radiotelegraphy RECOMMENDATION ITU-R F.436-4 ARRANGEMENT OF VOICE-FREQUENCY, FREQUENCY-SHIFT TELEGRAPH CHANNELS OVER HF RADIO CIRCUITS (Question ITU-R 145/9) (1966-1970-1978-1994-1995)
This tutorial describes the principles of 24-bit recording systems and clarifies some common mis-conceptions regarding these systems.
 This tutorial describes the principles of 24-bit recording systems and clarifies some common mis-conceptions regarding these systems. This is a general treatment of the subject and applies to I/O System
This tutorial describes the principles of 24-bit recording systems and clarifies some common mis-conceptions regarding these systems. This is a general treatment of the subject and applies to I/O System
Lecture 3 Concepts for the Data Communications and Computer Interconnection
 Lecture 3 Concepts for the Data Communications and Computer Interconnection Aim: overview of existing methods and techniques Terms used: -Data entities conveying meaning (of information) -Signals data
Lecture 3 Concepts for the Data Communications and Computer Interconnection Aim: overview of existing methods and techniques Terms used: -Data entities conveying meaning (of information) -Signals data
Mobile Communications TCS 455
 Mobile Communications TCS 455 Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th Lecture 21 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30 Announcements Read Chapter 9: 9.1 9.5 HW5 is posted.
Mobile Communications TCS 455 Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th Lecture 21 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30 Announcements Read Chapter 9: 9.1 9.5 HW5 is posted.
Fundamentals of Digital Communication
 Fundamentals of Digital Communication Network Infrastructures A.A. 2017/18 Digital communication system Analog Digital Input Signal Analog/ Digital Low Pass Filter Sampler Quantizer Source Encoder Channel
Fundamentals of Digital Communication Network Infrastructures A.A. 2017/18 Digital communication system Analog Digital Input Signal Analog/ Digital Low Pass Filter Sampler Quantizer Source Encoder Channel
ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION DATA AND PULSE COMMUNICATION HISTORY OF DATA COMMUNICATION, STANDARDS ORGANIZATIONS FOR DATA COMMUNICATION.
 UNIT III DATA AND PULSE COMMUNICATION 3.1 DATA COMMUNICATION: HISTORY OF DATA COMMUNICATION, STANDARDS ORGANIZATIONS FOR DATA COMMUNICATION. Data communication can be defined as two personal computers
UNIT III DATA AND PULSE COMMUNICATION 3.1 DATA COMMUNICATION: HISTORY OF DATA COMMUNICATION, STANDARDS ORGANIZATIONS FOR DATA COMMUNICATION. Data communication can be defined as two personal computers
An Improved VLSI Architecture Using Galois Sequence for High Speed DSSS Signal Acquisition at Low SNR
 International Journal of Engineering Inventions ISSN: 2278-7461, www.ijeijournal.com Volume 1, Issue 9 (November2012) PP: 42-48 An Improved VLSI Architecture Using Galois Sequence for High Speed DSSS Signal
International Journal of Engineering Inventions ISSN: 2278-7461, www.ijeijournal.com Volume 1, Issue 9 (November2012) PP: 42-48 An Improved VLSI Architecture Using Galois Sequence for High Speed DSSS Signal
Wireless Networks (PHY): Design for Diversity
 Wireless Networks (PHY): Design for Diversity Y. Richard Yang 9/20/2012 Outline Admin and recap Design for diversity 2 Admin Assignment 1 questions Assignment 1 office hours Thursday 3-4 @ AKW 307A 3 Recap:
Wireless Networks (PHY): Design for Diversity Y. Richard Yang 9/20/2012 Outline Admin and recap Design for diversity 2 Admin Assignment 1 questions Assignment 1 office hours Thursday 3-4 @ AKW 307A 3 Recap:
STANAG 4529 CONFORMANCE TEST PROCEDURES
 DEFENSE INFORMATION SYSTEMS AGENCY JOINT INTEROPERABILITY TEST COMMAND FORT HUACHUCA, ARIZONA STANAG 4529 CONFORMANCE TEST PROCEDURES APRIL 2004 Downloaded from http://www.everyspec.com (This page intentionally
DEFENSE INFORMATION SYSTEMS AGENCY JOINT INTEROPERABILITY TEST COMMAND FORT HUACHUCA, ARIZONA STANAG 4529 CONFORMANCE TEST PROCEDURES APRIL 2004 Downloaded from http://www.everyspec.com (This page intentionally
SPREADING CODES PERFORMANCE FOR CORRELATION FUNCTION USING MATLAB
 International Journal of Electronics, Communication & Instrumentation Engineering Research and Development (IJECIERD) ISSN 2249-684X Vol. 3, Issue 2, Jun 2013, 15-24 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. SPREADING CODES PERFORMANCE
International Journal of Electronics, Communication & Instrumentation Engineering Research and Development (IJECIERD) ISSN 2249-684X Vol. 3, Issue 2, Jun 2013, 15-24 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. SPREADING CODES PERFORMANCE
March, 2003 IEEE P /131r0. IEEE P Wireless Personal Area Networks
 Project Title IEEE P802.15 Wireless Personal rea Networks IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal rea Networks (WPNs) PHY Proposal Using Dual Independent Single Sideband, Non-coherent M and Defined
Project Title IEEE P802.15 Wireless Personal rea Networks IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal rea Networks (WPNs) PHY Proposal Using Dual Independent Single Sideband, Non-coherent M and Defined
ICT 5305 Mobile Communications. Lecture - 3 April Dr. Hossen Asiful Mustafa
 ICT 5305 Mobile Communications Lecture - 3 April 2016 Dr. Hossen Asiul Mustaa Advanced Phase Shit Keying Q BPSK (Binary Phase Shit Keying): bit value 0: sine wave bit value 1: inverted sine wave very simple
ICT 5305 Mobile Communications Lecture - 3 April 2016 Dr. Hossen Asiul Mustaa Advanced Phase Shit Keying Q BPSK (Binary Phase Shit Keying): bit value 0: sine wave bit value 1: inverted sine wave very simple
Point-to-Point Communications
 Point-to-Point Communications Key Aspects of Communication Voice Mail Tones Alphabet Signals Air Paper Media Language English/Hindi English/Hindi Outline of Point-to-Point Communication 1. Signals basic
Point-to-Point Communications Key Aspects of Communication Voice Mail Tones Alphabet Signals Air Paper Media Language English/Hindi English/Hindi Outline of Point-to-Point Communication 1. Signals basic
Implementation of Different Interleaving Techniques for Performance Evaluation of CDMA System
 Implementation of Different Interleaving Techniques for Performance Evaluation of CDMA System Anshu Aggarwal 1 and Vikas Mittal 2 1 Anshu Aggarwal is student of M.Tech. in the Department of Electronics
Implementation of Different Interleaving Techniques for Performance Evaluation of CDMA System Anshu Aggarwal 1 and Vikas Mittal 2 1 Anshu Aggarwal is student of M.Tech. in the Department of Electronics
Frequency-Hopped Spread-Spectrum
 Chapter Frequency-Hopped Spread-Spectrum In this chapter we discuss frequency-hopped spread-spectrum. We first describe the antijam capability, then the multiple-access capability and finally the fading
Chapter Frequency-Hopped Spread-Spectrum In this chapter we discuss frequency-hopped spread-spectrum. We first describe the antijam capability, then the multiple-access capability and finally the fading
Channel Capacity. Tom McDermott, N5EG June 1997
 Channel Capacity Tom McDermott, N5EG June 1997 Why Spread Spectrum? Data transmission can occur with or without SS modulation - why use it? SS can be more resistant to multipath SS can be more resistant
Channel Capacity Tom McDermott, N5EG June 1997 Why Spread Spectrum? Data transmission can occur with or without SS modulation - why use it? SS can be more resistant to multipath SS can be more resistant
IEEE P Wireless Access Method and Physical Layer Specification
 doc: IEEE P802.11 93/5 IEEE P802.11 Wireless Access Method and Physical Layer Specification Comparison between 3-channel FDMA and CDMA Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum System. Jan Boer, Rajeev Krishnamoorthy
doc: IEEE P802.11 93/5 IEEE P802.11 Wireless Access Method and Physical Layer Specification Comparison between 3-channel FDMA and CDMA Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum System. Jan Boer, Rajeev Krishnamoorthy
Quick Introduction to Communication Systems
 Quick Introduction to Communication Systems p. 1/26 Quick Introduction to Communication Systems Aly I. El-Osery, Ph.D. elosery@ee.nmt.edu Department of Electrical Engineering New Mexico Institute of Mining
Quick Introduction to Communication Systems p. 1/26 Quick Introduction to Communication Systems Aly I. El-Osery, Ph.D. elosery@ee.nmt.edu Department of Electrical Engineering New Mexico Institute of Mining
VARA HF Modem Specification Revision Oct30, 2017 Jose Alberto Nieto Ros, EA5HVK
 VARA HF Modem Specification Revision 1.0.0 Oct30, 2017 Jose Alberto Nieto Ros, EA5HVK 1.0 Overview: VARA HF Modem is a propietary system developed by Jose Alberto Nieto Ros EA5HVK and can be used under
VARA HF Modem Specification Revision 1.0.0 Oct30, 2017 Jose Alberto Nieto Ros, EA5HVK 1.0 Overview: VARA HF Modem is a propietary system developed by Jose Alberto Nieto Ros EA5HVK and can be used under
Simple Algorithm in (older) Selection Diversity. Receiver Diversity Can we Do Better? Receiver Diversity Optimization.
 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 6: Physical Layer Diversity and Coding Peter Steenkiste Carnegie Mellon University Spring Semester 2017 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss17/
18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 6: Physical Layer Diversity and Coding Peter Steenkiste Carnegie Mellon University Spring Semester 2017 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss17/
