Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College
|
|
|
- Jessie Floyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College Laboratory Manual Network Theory For Second Year Students JNEC, Aurangabad
2 FOREWORD It is my great pleasure to present this laboratory manual for second year engineering students for the subject of Network Theory, keeping in view the vast coverage required to visualize the basic concepts of various networks using basic components. NT covers designing a network for specific input/output requirements. This being a core subject, it becomes very essential to have clear theoretical and practical designing aspects. This lab manual provides a platform to the students for understanding the basic concepts of network theory. This practical background will help students to gain confidence in qualitative and quantitative approach to electronic networks. Good Luck for your Enjoyable Laboratory Sessions. 2
3 LABORATORY MANUAL CONTENTS This manual is intended for the second year students of engineering branches in the subject of network theory. This manual typically contains practical/lab Sessions related to Network Theory covering various aspects related the subject to enhance understanding. In this manual we have made the efforts to cover various experiments on network theory with detailed circuit diagrams, detailed procedure and graphs wherever required. Students are advised to thoroughly go through this manual rather than only topics mentioned in the syllabus as practical aspects are the key to understanding and conceptual visualization of theoretical aspects covered in the books. Good Luck for your Enjoyable Laboratory Sessions 3
4 SUBJECT INDEX 1.Do s and Don ts 2. Lab exercise: 1. Verification of Superposition Theorem. 2. Verification of Thevenin s Theorem. 3. Verification of Norton s theorem. 4. Verification of Maximum power transfer theorem. 5. To measure input impedance and output impedance of a given two port network. 6. Design of a High Pass Filter. 7. Design of a Low Pass Filter. 8. To observe and analyze the waveform across a capacitor of a series RC circuit exited by a unit step function. 4
5 Dos and Don ts in Laboratory: 1. Do not handle any equipment before reading the instructions/instruction manuals. 2. Apply proper voltage to the circuit as given in procedure. 3. Check CRO probe before connecting it. 4. Strictly observe the instructions given by the teacher/lab Instructor. Instruction for Laboratory Teachers: 1. Submission related to whatever lab work has been completed should be done during the next lab session. 2. The promptness of submission should be encouraged by way of marking and evaluation patterns that will benefit the sincere students. 5
6 EXPERIMENT.NO. 1 AIM: - To verify Superposition theorem. APPARATUS: - Breadboard, Resistors, Milliammeter, connecting wires, etc. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:- V1 R R I1 I2 R3 I3 V2 10 VOLTS 15 VOLTS l l 2 1 THEORY: - If network contains two or more than two sources, then principle of superposition theorem is used to simplify network calculations. It may be stated as follows. In a bilateral network if two or more than two energy sources are present, then the current which flows at any point is the vector sum of all currents which would flow at that point if each source was considered separately and all other sources replaced at the time by impedance equal to their internal impedances. PROCEDURE:- 1. Connect D. C. power supply across terminals 1-1 l and apply voltage of say V1=10 volts and similarly across terminals 2-2 l apply voltage of say V2=15 volts 2. Measure current flowing through all branches, say these currents are I1, I2, and I3. 3. Now connect only V1=10 volts across terminals1-1 l and short circuit terminals 2-2 l that is V2=0 volts. 4. Measure currents flowing through all branches for V1=10 volts V2=0 volts using a milliameter, say these currents are I 1, I2, I3. 5. Similarly connect only V2 =15 volts across terminals 2-2 l and short circuit terminals 1-1 l that is V1=0 volts. 6. Measure current flowing through all branches for V1=0 volts and V2=15 volts using a milliameter, say these currents are I1, I2, I3. 7. For verifying superposition theorem I 1 = I 1 + I 1, I 2 = I 2 + I 2, I3=I3 +I3. 8. Calculate theoretical values of currents, these values should be approximately equal to measured values of currents. 6
7 OBSERVATION TABLE:- V1=10VOLTS V1=10VOLTS V1=0VOLTS V2=15VOLTS V2=0 VOLTS V2=15VOLTS I1= I1 = I1 = I2= I2 = I2 = I3= I3 = I3 = V1 R1 R2 1 2 I1 I2 R3 I3 V2 10V 15V 1 2 V1 R1 R2 1 2 I1 I2 R3 I3 V2 10V 15V 2 CONCLUSION: - The branch current is the algebraic sum of currents due to individual voltage source when all other voltage sources are short circuited; hence superposition theorem has been verified. 7
8 EXPERIMENT. NO. 2 AIM: - To verify Thevenin s theorem. APPARATUS: - Bread board, resistors, D.C. power supply, multimeter, connecting wires, etc. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:- 1 R1 R2 2 R3 RL 1 2 THEORY:- The current flowing through the load impedance R L connected across the terminals 2 & 2 l of a network containing impedance & energy sources is the same as it would flow if this load impedance were connected across a simple constant voltage source whose generated emf is an open circuited voltage, measured across the network terminals 2 & 2 l. Its internal impedance is the same as the impedance of the network looking back into the terminals 2 & 2 l, when all sources have been replaced by impedances and sources with output terminals 2 & 2 l. across which load impedance R L is connected. PROCEDURE:- 1. Apply dc voltage across terminals 1-1 l, call this voltage as Vdc. 2. Connect voltmeter across terminals 2-2 l and measure voltage on voltmeter. This voltage is known as open circuit voltage or Thevenin s voltage (Vth). 3. Vary the dc voltage across terminals 1-1 l and repeat step 2, take two/three readings. 4. Disconnect the applied voltage at terminals 1-1 l and voltmeter at terminals 2-2 l. 5. Now short terminals 1-1 l and connect multimeter across terminals 2-2 l. With the help of multimeter measure resistance between terminals 2-2 l. This is known as Thevenin s resistance (Rth). 6. Calculate Vth and Rth by theoretical calculations, the theoretical values and measured values of Vth and Rth should be approximately equal. 7. Connect load resistor RL across terminals 2-2 l and measure IL for applied dc voltage. 8
9 OBSERVATION TABLE:- Sr.No. Vdc Measured values Theoretical values Rth Vth I L Rth Vth I L CONCLUSION: - The theoretical values and measured values of Vth and Rth and IL are approximately equal, hence Thevenin s theorem has been verified. 9
10 EXPERIMENT NO. 3 AIM: - To verify Norton s theorem. APPARATUS: - Breadboard, milliammeter (0-50mA), D.C. power supply (0-30V), multimeter, resistors, connecting wires, etc. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:- 1 R1 R2 2 R3 RL 1 2 THEORY:- Any two terminal linear network, consisting of generators and impedances, can be replaced with an equivalent circuit consisting of a current source Isc in parallel with an admittance Y AB. The Isc is short circuit current between the network and Y AB is the admittance measured between the terminals, with all energy sources eliminated except their internal impedances. PROCEDURE:- 1. Apply d. c. voltage across terminals 1-1 l called this voltage Vdc. 2. Connect milliammeter across terminals 2-2 l and measure current, this is the short circuit (Isc) current. 3. Vary the d. c. voltage across terminals 1-1 l and repeat step 2, take three readings. 4. Disconnect the applied voltage at terminals 1-1 l and milliammeter at terminals 2-2 l. 5. Short terminals 1-1 l and connect Multimeter (keep it on resistance range) across terminals 2-2 l, and note down the reading, this resistance is known as Req. 6. Calculate Isc and Req by using formulae, the calculated values and measured values of Isc and Rth should be approximately equal. 7. Connect RL across terminals 2-2 l and measure IL by milliammeter for applied D.C. voltage. 10
11 OBSERVATION TABLE:- Sr.No. Vdc Measured values Calculated values Isc Req I L Isc Req I L CONCLUSION: - The Calculated values and measured values of Isc, IL, Req are approximately equal; hence Norton s theorem has been verified. 11
12 EXPERIMENT. NO. 4 AIM: - To verify maximum power transfer theorem. APPARATUS: - Breadboard, resistance, potentiometer, milliammeter, multimeter, etc. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:- 1 R1 R2 2 + ma Vdc R3 + V RL _ 1 l 2 l THEORY:- Maximum power will be delivered by a network to an impedance Z R if the impedance of Z R is the conjugate of the impedance Z l of the network, measured looking back into the terminals of the network. Z l E ZL PROCEDURE:- 1. Make the connections according to circuit diagram. 1. Connect d.c. power supply of say Vdc=20 volts across terminal 1-1 l. 2. Connect variable load RL across terminals 2-2 l. 3. Vary RL gradually from minimum value and measure corresponding load current IL. 4. Find load power for each value of RL and IL. 5. Draw the graph of power v/s load resistances. 6. From the graph note peak power point and correspondingly load resistance. Verify the same using calculations. 7. Remove the d.c.power supply and short circuit the terminals 1-1 l. Remove load resistance connected across terminals 2-2 l and measure the resistance with the help of Multimeter. This resistance is approximately equal to the load resistance found in step 6. 12
13 OBSERVATION TABLE:- Sr.No. Load resistance = Load current I L Power = V L. I L R L =V L /I L CONCLUSION: - The maximum power transfer takes place from the network to the load when equivalent resistance of the network between terminals 2-2 l is equal to the load resistance. IL RL MAX POWER RL 13
14 EXPERIMENT NO.5 AIM :- To measure input impedance and output impedance of a given two port network APPARATUS :- Breadboard, resistance, multimeter, connecting wires, etc. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:- 1 I1 R1 R2 2 + V2 V1 R3 R4 _ 1 l 2 l THEORY:- In two port network port variables are port currents and port voltages. To describe relationship between ports voltages and currents, two linear equations are required. In the two port network, there are four variables. These are the voltages and currents at the input and output ports, namely V1, I1 and V2, I2. From this two are independent and two are dependent variables. By expressing V1 and V2 in terms of I1 and I2 V1=Z11.I1+ Z22.I2 V2=Z21.I2+Z22.I2 From these equations we can find out all Z parameters. PROCEDURE :- 1. Connect dc power supply Va =5V at port 1-1 and keep output port open circuited i.e. I2=0. 2. Measure the current I1 by connecting milliammeter in series with R1. 3. Measure voltage V2 across R4 by Multimeter. 4. From these values of V1, V2, I1 and I2 (I2=0) find input driving point impedance where V1=Va. i.e. Z11 = V1/I1 I2=0 & Find forward transfer impedance i.e. Z21 = V2/I1 I2=0 14
15 5. Connect dc power supply Vb= 5v at port 2-2 and keep input port open circuited i.e. I1=0. 6. Measure the current I2 by connecting milliammeter in series with supply. 7. Measure the voltage V1 across R3 by multimeter. 8. From this value of V2, V1, I2 and I1( I1=0) find output driving point impedance that is & Z22 = V2/I2 Z12 = V1/I2 I1=0 I1=0 9. Calculate z-parameters theoretically. These values should be approximately equal to the practical values of z-parameters. CONCLUSION:-Since Z12=Z21 the circuit is reciprocal and since Z11 = Z22 the circuit is not symmetrical. 15
16 EXPERIMENT NO. 6 AIM :- To study high pass filter. APPARTUS :-Signal Generator, CRO(dual trace), Connecting Wires THEORY :- An electric wave filter or simply filter is one electric network which passes or allowed unattenuated transmission of electric signal within certain frequency range & stops transmission of electric signal outside this range. PARAMETERS OF HIGH PASS FILTER:- 1. What is Characteristic impedance. 2. What is pass band. 3. What is stop band. 4. What is cut-off frequency. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM :- C 1uF C 1uF L 1uH PROCEDURE: Connect function generator as shown in circuit diagram. Set the function generator output voltage to say Vs=10 Volts. Increase the function generator output signal frequency from minimum say 10 Hz to a maximum signal frequency of 1MHz in decade steps(10,20, ,200,..1000, k,20k.). For applied signal frequency measure voltage. Calculate gain for the frequency. Plot the graph of frequency v/s gain. Find cutoff freq and Ro. 16
17 OBSERVATION:- S.No. Frequency f Vi Vo Gain = 20 log Vo/ Vi FORMULAS Cut- off frequency F c = 1 / 4Π (LC) 1/2 R O = (L / C ) 1/ 2 CONCLUSION:- In this way, we have studied high pass flter. 17
18 EXPERIMENT NO. 7 AIM :- To study Low pass filter. APPARTUS :-Signal Generator, CRO(dual trace), Connecting Wires THEORY :- An electric wave filter or simply filter is one electric network which passes or allowed attenuated transmission of electric signal within certain frequency range & stops transmission of electric signal outside this range. PARAMETERS OF LOW PASS FILTER:- 1. What is Characteristic impedance. 2. What is pass band. 3. What is stop band. 4. What is cut-off frequency. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM :- L1 1uH L2 1uH C1 1uF PROCEDURE :- Connect function generator as shown in circuit diagram. Set the function generator output voltage to say Vs=10 Volts. Increase the function generator output signal frequency from minimum say 10 Hz to a maximum signal frequency of 1MHz in decade steps(10,20, ,200,..1000, k,20k.). For applied signal frequency measure voltage. Calculate gain for the frequency. Plot the graph of frequency v/s gain. Find cutoff freq and Ro. 18
19 OBSERVATIONS :- S.No. Frequency f Vi Vo Gain = 20 log Vo/ Vi FORMULAS Cut- off frequency F c = 1 / 2Π (LC) 1/2 R O = (L / C ) 1/ 2 CONCLUSION :- In this way we study Low Pass Filter. 19
20 EXPERIMENT NO. 8 AIM: - To observe and analyze the waveform across capacitor of a series RC circuit excited by a unit step function. APPARATUS: - Function generator, CRO, breadboard, resistor, capacitor and connecting wires. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:- V() 1 0 t Input Excitation + s + _ vs --1µ Circuit diagram CRO THEORY:- The basic switching equation that applies any RC circuit is: V = vi + (vf vi )(1 e -t/rc ) Where V = instantaneous capacitor voltage vi = initial capacitor voltage (i.e. = 0) vf = target capacitor voltage (i.e.= vcc) t = charging time RC = time constant. Therefore Vc V = Vcc (1 e -t/rc ) t 20
21 PROCEDURE:- 1. Connect the setup as shown in diagram. 2. Calculate the RC time constant α (Z=RC) of the circuit and record it. 3. Set the function generator at pulse of Vp-p and pulse tme tp= 1ms 4. For the circuit setup calculate and record the voltage across capacitor on CRO CONCLUSION :- If we excite the capacitor by unit step function capacitor will charge for period Γ=RC time constant of the ckt.
22 PDF to Word
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY MANUAL (II SEMESTER)
 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY MANUAL (II SEMESTER) LIST OF EXPERIMENTS. Verification of Ohm s laws and Kirchhoff s laws. 2. Verification of Thevenin s and Norton s Theorem. 3. Verification of Superposition
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY MANUAL (II SEMESTER) LIST OF EXPERIMENTS. Verification of Ohm s laws and Kirchhoff s laws. 2. Verification of Thevenin s and Norton s Theorem. 3. Verification of Superposition
Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College
 Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College Laboratory Manual EDC-I For Second Year Students Manual made by A.A.Sayar Author JNEC, Aurangabad 1 MGM S Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College N-6, CIDCO, Aurangabad
Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College Laboratory Manual EDC-I For Second Year Students Manual made by A.A.Sayar Author JNEC, Aurangabad 1 MGM S Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College N-6, CIDCO, Aurangabad
Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College
 Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College Laboratory Manual Elements of Electronics For First Year Students Manual made by Prof. P.R.Shirpewar Author JNEC, Aurangabad MGM S Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College
Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College Laboratory Manual Elements of Electronics For First Year Students Manual made by Prof. P.R.Shirpewar Author JNEC, Aurangabad MGM S Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS CMPE 253 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING LABORATORY MANUAL ISHIK UNIVERSITY
 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS CMPE 253 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING LABORATORY MANUAL ISHIK UNIVERSITY 2017-2018 1 WEEK EXPERIMENT TITLE NUMBER OF EXPERIMENT No Meeting Instructional Objective 2 Tutorial 1 3
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS CMPE 253 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING LABORATORY MANUAL ISHIK UNIVERSITY 2017-2018 1 WEEK EXPERIMENT TITLE NUMBER OF EXPERIMENT No Meeting Instructional Objective 2 Tutorial 1 3
DRONACHARYA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING GREATER NOIDA LAB MANUAL NETWORK LABORATORY EEE-452
 DRONACHARYA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING GREATER NOIDA LAB MANUAL NETWORK LABORATORY EEE-452 Syllabus 1. Verification of principle of superposition with dc and ac sources. 2. Verification of Thevenin, Norton
DRONACHARYA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING GREATER NOIDA LAB MANUAL NETWORK LABORATORY EEE-452 Syllabus 1. Verification of principle of superposition with dc and ac sources. 2. Verification of Thevenin, Norton
Geethanjali College of Engineering & Technology
 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY LAB Geethanjali College of Engineering & Technology ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY LAB MANUAL II-B.Tech II-SEMESTER(ECE),2015-2016 Prepared By B.RAMESH BABU, M.Pradeep manjul khare pooja raani
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY LAB Geethanjali College of Engineering & Technology ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY LAB MANUAL II-B.Tech II-SEMESTER(ECE),2015-2016 Prepared By B.RAMESH BABU, M.Pradeep manjul khare pooja raani
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE8261-ELECTRIC CIRCUITS LABORATORY LABORATORY MANUAL 1 ST YEAR EEE (REGULATION 2017)
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE8261-ELECTRIC CIRCUITS LABORATORY LABORATORY MANUAL 1 ST YEAR EEE (REGULATION 2017)
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology. EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments. Masood Ejaz
 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments Masood Ejaz Experiment # 1 DC Measurements of a Resistive Circuit and Proof of Thevenin Theorem
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments Masood Ejaz Experiment # 1 DC Measurements of a Resistive Circuit and Proof of Thevenin Theorem
ECE ECE285. Electric Circuit Analysis I. Spring Nathalia Peixoto. Rev.2.0: Rev Electric Circuits I
 ECE285 Electric Circuit Analysis I Spring 2014 Nathalia Peixoto Rev.2.0: 140124. Rev 2.1. 140813 1 Lab reports Background: these 9 experiments are designed as simple building blocks (like Legos) and students
ECE285 Electric Circuit Analysis I Spring 2014 Nathalia Peixoto Rev.2.0: 140124. Rev 2.1. 140813 1 Lab reports Background: these 9 experiments are designed as simple building blocks (like Legos) and students
LABORATORY MODULE. ENT 163 Fundamental of Electrical Engineering Semester 1 (2006/2007) EXPERIMENT 4: Thevenin s and Norton s Theorem
 LABORATORY MODULE ENT 163 Fundamental of Electrical Engineering Semester 1 (2006/2007) EXPERIMENT 4: Thevenin s and Norton s Theorem Name Matrix No. : : School of Mechatronic Engineering Northern Malaysia
LABORATORY MODULE ENT 163 Fundamental of Electrical Engineering Semester 1 (2006/2007) EXPERIMENT 4: Thevenin s and Norton s Theorem Name Matrix No. : : School of Mechatronic Engineering Northern Malaysia
Announcements. To stop blowing fuses in the lab, note how the breadboards are wired. EECS 42, Spring 2005 Week 3a 1
 Announcements New topics: Mesh (loop) method of circuit analysis Superposition method of circuit analysis Equivalent circuit idea (Thevenin, Norton) Maximum power transfer from a circuit to a load To stop
Announcements New topics: Mesh (loop) method of circuit analysis Superposition method of circuit analysis Equivalent circuit idea (Thevenin, Norton) Maximum power transfer from a circuit to a load To stop
Questions Bank of Electrical Circuits
 Questions Bank of Electrical Circuits 1. If a 100 resistor and a 60 XL are in series with a 115V applied voltage, what is the circuit impedance? 2. A 50 XC and a 60 resistance are in series across a 110V
Questions Bank of Electrical Circuits 1. If a 100 resistor and a 60 XL are in series with a 115V applied voltage, what is the circuit impedance? 2. A 50 XC and a 60 resistance are in series across a 110V
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY LAB MANUAL. Prepared by
 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY LAB MANUAL Year : 2016-2017 Subject Code : AEE102 Regulations : R16 Class : I B.Tech II Semester Branch : ECE / EEE Prepared by Mr.P.Sridhar (Professor/HOD) Mr.G.Hari krishna
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY LAB MANUAL Year : 2016-2017 Subject Code : AEE102 Regulations : R16 Class : I B.Tech II Semester Branch : ECE / EEE Prepared by Mr.P.Sridhar (Professor/HOD) Mr.G.Hari krishna
Announcements. To stop blowing fuses in the lab, note how the breadboards are wired. EECS 42, Spring 2005 Week 3a 1
 Announcements New topics: Mesh (loop) method of circuit analysis Superposition method of circuit analysis Equivalent circuit idea (Thevenin, Norton) Maximum power transfer from a circuit to a load To stop
Announcements New topics: Mesh (loop) method of circuit analysis Superposition method of circuit analysis Equivalent circuit idea (Thevenin, Norton) Maximum power transfer from a circuit to a load To stop
Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College
 Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College Laboratory Manual COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING For Author JNEC, Aurangabad. Second Year Students Lab manual made by PROF. S.A. ANNANDATE PROF. P. B. MURMUDE PROF. P.B.YADAV
Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College Laboratory Manual COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING For Author JNEC, Aurangabad. Second Year Students Lab manual made by PROF. S.A. ANNANDATE PROF. P. B. MURMUDE PROF. P.B.YADAV
UNIT 1 CIRCUIT ANALYSIS 1 What is a graph of a network? When all the elements in a network is replaced by lines with circles or dots at both ends.
 UNIT 1 CIRCUIT ANALYSIS 1 What is a graph of a network? When all the elements in a network is replaced by lines with circles or dots at both ends. 2 What is tree of a network? It is an interconnected open
UNIT 1 CIRCUIT ANALYSIS 1 What is a graph of a network? When all the elements in a network is replaced by lines with circles or dots at both ends. 2 What is tree of a network? It is an interconnected open
EE 241 Experiment #7: NETWORK THEOREMS, LINEARITY, AND THE RESPONSE OF 1 ST ORDER RC CIRCUITS 1
 EE 241 Experiment #7: NETWORK THEOREMS, LINEARITY, AND THE RESPONSE OF 1 ST ORDER RC CIRCUITS 1 PURPOSE: To verify the validity of Thevenin and maximum power transfer theorems. To demonstrate the linear
EE 241 Experiment #7: NETWORK THEOREMS, LINEARITY, AND THE RESPONSE OF 1 ST ORDER RC CIRCUITS 1 PURPOSE: To verify the validity of Thevenin and maximum power transfer theorems. To demonstrate the linear
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6211-ELECTRIC CIRCUITS LABORATORY LABORATORY MANUAL 1ST YEAR EEE (REGULATION 2013)
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE62-ELECTRIC CIRCUITS LABORATORY LABORATORY MANUAL ST YEAR EEE (REGULATION 203) EE62 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS LABORATORY LTPC0032 LIST OF EXPERIMENTS. Experimental
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE62-ELECTRIC CIRCUITS LABORATORY LABORATORY MANUAL ST YEAR EEE (REGULATION 203) EE62 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS LABORATORY LTPC0032 LIST OF EXPERIMENTS. Experimental
Question Paper Profile
 I Scheme Question Paper Profile Program Name : Electrical Engineering Program Group Program Code : EE/EP/EU Semester : Third Course Title : Electrical Circuits Max. Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hrs. Instructions:
I Scheme Question Paper Profile Program Name : Electrical Engineering Program Group Program Code : EE/EP/EU Semester : Third Course Title : Electrical Circuits Max. Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hrs. Instructions:
Circuit Models. Lab 5
 Circuit Models Lab 5 1 Equipment List DC power supply Decade resistance box (2) 1.5kΩ, 2.2kΩ, 560Ω 2 Circuit Models Any circuit can be modeled by either a Thevenin or a Norton model Any circuit whose output
Circuit Models Lab 5 1 Equipment List DC power supply Decade resistance box (2) 1.5kΩ, 2.2kΩ, 560Ω 2 Circuit Models Any circuit can be modeled by either a Thevenin or a Norton model Any circuit whose output
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET
 Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET LABORATORY MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO. ISSUE NO. : ISSUE DATE: REV. NO. : REV. DATE : PAGE:
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET LABORATORY MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO. ISSUE NO. : ISSUE DATE: REV. NO. : REV. DATE : PAGE:
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET REV. NO. : REV.
 Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET LABORATORY MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO. ISSUE NO. : ISSUE DATE: July 200 REV. NO. : REV.
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET LABORATORY MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO. ISSUE NO. : ISSUE DATE: July 200 REV. NO. : REV.
Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College, Aurangabad.
 Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College, Aurangabad. Laboratory Manual ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT & TEACHNIQUES [EMT] For Second Year (EEP) Students Manual made by- Prof. J.S.Solanke FORWARD It is my great pleasure
Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College, Aurangabad. Laboratory Manual ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT & TEACHNIQUES [EMT] For Second Year (EEP) Students Manual made by- Prof. J.S.Solanke FORWARD It is my great pleasure
EE6211 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS LAB
 SEMBODAI RUKMANI VARATHARAJAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, SEMBODAI, NAGAPATTINAM. DEPARTMENT OF SCIENCE AND HUMANITIES II- Semester B.E (EEE) EE6211 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS LAB Prepared by, Mr.R.Dhineshkumar M.E.,
SEMBODAI RUKMANI VARATHARAJAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, SEMBODAI, NAGAPATTINAM. DEPARTMENT OF SCIENCE AND HUMANITIES II- Semester B.E (EEE) EE6211 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS LAB Prepared by, Mr.R.Dhineshkumar M.E.,
Department of Electronics &Electrical Engineering
 Department of Electronics &Electrical Engineering Question Bank- 3rd Semester, (Network Analysis & Synthesis) EE-201 Electronics & Communication Engineering TWO MARKS OUSTIONS: 1. Differentiate between
Department of Electronics &Electrical Engineering Question Bank- 3rd Semester, (Network Analysis & Synthesis) EE-201 Electronics & Communication Engineering TWO MARKS OUSTIONS: 1. Differentiate between
For input: Peak to peak amplitude of the input = volts. Time period for 1 full cycle = sec
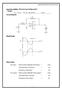 Inverting amplifier: [Closed Loop Configuration] Design: A CL = V o /V in = - R f / R in ; Assume R in = ; Gain = ; Circuit Diagram: RF +10V F.G ~ + Rin 2 3 7 IC741 + 4 6 v0-10v CRO Model Graph Inverting
Inverting amplifier: [Closed Loop Configuration] Design: A CL = V o /V in = - R f / R in ; Assume R in = ; Gain = ; Circuit Diagram: RF +10V F.G ~ + Rin 2 3 7 IC741 + 4 6 v0-10v CRO Model Graph Inverting
LAB MANUAL NETWORK THEORY (EC-316-F) III SEMESTER ECS
 LAB MANUAL NETWORK THEORY (EC-316-F) III SEMESTER ECS Department of Electronics & Communication Engg. Dronacharya College of Engineering Khentawas, Gurgaon 123506 LIST OF EXPERIMENTS A: Simulation based
LAB MANUAL NETWORK THEORY (EC-316-F) III SEMESTER ECS Department of Electronics & Communication Engg. Dronacharya College of Engineering Khentawas, Gurgaon 123506 LIST OF EXPERIMENTS A: Simulation based
ANALOG ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS LABORATORY MANUAL (CODE: EEE - 228)
 ANALOG ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS LABORATORY MANUAL (CODE: EEE - 228) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ANIL NEERUKONDA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCES (Affiliated to AU, Approved by AICTE
ANALOG ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS LABORATORY MANUAL (CODE: EEE - 228) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ANIL NEERUKONDA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCES (Affiliated to AU, Approved by AICTE
ECE 215 Lecture 8 Date:
 ECE 215 Lecture 8 Date: 28.08.2017 Phase Shifter, AC bridge AC Circuits: Steady State Analysis Phase Shifter the circuit current I leads the applied voltage by some phase angle θ, where 0 < θ < 90 ο depending
ECE 215 Lecture 8 Date: 28.08.2017 Phase Shifter, AC bridge AC Circuits: Steady State Analysis Phase Shifter the circuit current I leads the applied voltage by some phase angle θ, where 0 < θ < 90 ο depending
EEE 2101 Circuit Theory I - Laboratory 1 Kirchoff s Laws, Series-Parallel Circuits
 ame & Surname: D: Date: EEE 20 Circuit Theory - Laboratory Kirchoff s Laws, Series-Parallel Circuits List of topics for this laboratory: Ohm s Law Kirchoff s Current Law(KCL) Kirchoff s Voltage Law(KVL)
ame & Surname: D: Date: EEE 20 Circuit Theory - Laboratory Kirchoff s Laws, Series-Parallel Circuits List of topics for this laboratory: Ohm s Law Kirchoff s Current Law(KCL) Kirchoff s Voltage Law(KVL)
Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology
 Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering AU ST /E EE LABORATORY MANUAL FOR ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC SESSIONAL COURSE Student Name : Student ID
Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering AU ST /E EE LABORATORY MANUAL FOR ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC SESSIONAL COURSE Student Name : Student ID
EE 105 Discussion #1: Fundamentals of Circuit Analysis
 EE 105 Discussion #1: Fundamentals of Circuit Analysis 1.1 Ohm s Law V = ir i = V/R 1.2 KCL & KVL Kirchoff s Current Law (KCL) Kirchoff s Voltage Law (KVL) The algebraic sum of all currents entering a
EE 105 Discussion #1: Fundamentals of Circuit Analysis 1.1 Ohm s Law V = ir i = V/R 1.2 KCL & KVL Kirchoff s Current Law (KCL) Kirchoff s Voltage Law (KVL) The algebraic sum of all currents entering a
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 1 MAXIMUM POWER TRANSFER OBJECTIVES In this experiment the student will investigate the circuit requirements
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 1 MAXIMUM POWER TRANSFER OBJECTIVES In this experiment the student will investigate the circuit requirements
EQUIVALENT EQUIPMENT CIRCUITS
 INTRODUCTION EQUIVALENT EQUIPMENT CIRCUITS The student will analyze the internal properties of the equipment used in lab. The input resistance of the oscilloscope and digital multimeter when used as a
INTRODUCTION EQUIVALENT EQUIPMENT CIRCUITS The student will analyze the internal properties of the equipment used in lab. The input resistance of the oscilloscope and digital multimeter when used as a
Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance
 Objective Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance To understand how the reactance of inductors and capacitors change with frequency, and how the two can cancel each other to leave
Objective Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance To understand how the reactance of inductors and capacitors change with frequency, and how the two can cancel each other to leave
EMT1250 LABORATORY EXPERIMENT. EXPERIMENT # 4: Combinational Logic Circuits. Name: Date:
 EXPERIMENT # 4: Combinational Logic Circuits Name: Date: Equipment/Parts Needed: 5V DC Power Supply Digital Trainer (Logic Probe) Breadboard DIP Switch 7400 NAND gate 7402 NOR gate 7404 Inverter 7408 AND
EXPERIMENT # 4: Combinational Logic Circuits Name: Date: Equipment/Parts Needed: 5V DC Power Supply Digital Trainer (Logic Probe) Breadboard DIP Switch 7400 NAND gate 7402 NOR gate 7404 Inverter 7408 AND
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 7 BJT AMPLIFIER CONFIGURATIONS AND INPUT/OUTPUT IMPEDANCE OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 7 BJT AMPLIFIER CONFIGURATIONS AND INPUT/OUTPUT IMPEDANCE OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment
Welcome to your second Electronics Laboratory Session. In this session you will learn about how to use resistors, capacitors and inductors to make
 Welcome to your second Electronics Laboratory Session. In this session you will learn about how to use resistors, capacitors and inductors to make simple circuits. You will find out how these circuits
Welcome to your second Electronics Laboratory Session. In this session you will learn about how to use resistors, capacitors and inductors to make simple circuits. You will find out how these circuits
Equivalent Equipment Circuits
 1. Introduction Equivalent Equipment Circuits The student will analyze the internal properties of the equipment used in lab. The input resistance of the oscilloscope and Digital MultiMeter (DMM) when used
1. Introduction Equivalent Equipment Circuits The student will analyze the internal properties of the equipment used in lab. The input resistance of the oscilloscope and Digital MultiMeter (DMM) when used
Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits
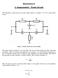 Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits This laboratory session involves circuits which contain a double-t (or TT), a passive RC circuit: Figure 1. Double T passive RC circuit module The upper
Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits This laboratory session involves circuits which contain a double-t (or TT), a passive RC circuit: Figure 1. Double T passive RC circuit module The upper
1. LINEAR WAVE SHAPING
 Aim: 1. LINEAR WAVE SHAPING i) To design a low pass RC circuit for the given cutoff frequency and obtain its frequency response. ii) To observe the response of the designed low pass RC circuit for the
Aim: 1. LINEAR WAVE SHAPING i) To design a low pass RC circuit for the given cutoff frequency and obtain its frequency response. ii) To observe the response of the designed low pass RC circuit for the
Unit-1(A) Circuit Analysis Techniques
 Unit-1(A Circuit Analysis Techniques Basic Terms used in a Circuit 1. Node :- It is a point in a circuit where two or more circuit elements are connected together. 2. Branch :- It is that part of a network
Unit-1(A Circuit Analysis Techniques Basic Terms used in a Circuit 1. Node :- It is a point in a circuit where two or more circuit elements are connected together. 2. Branch :- It is that part of a network
BME (311) Electric Circuits lab
 Summer 2016 Facility of Engineering Department of Biomedical Engineering BME (311) Electric Circuits lab Prepared By: Eng. Hala Amari Supervised By: Dr. Areen AL-Bashir Table of Contents Experiment # 1
Summer 2016 Facility of Engineering Department of Biomedical Engineering BME (311) Electric Circuits lab Prepared By: Eng. Hala Amari Supervised By: Dr. Areen AL-Bashir Table of Contents Experiment # 1
Lab 1: Basic RL and RC DC Circuits
 Name- Surname: ID: Department: Lab 1: Basic RL and RC DC Circuits Objective In this exercise, the DC steady state response of simple RL and RC circuits is examined. The transient behavior of RC circuits
Name- Surname: ID: Department: Lab 1: Basic RL and RC DC Circuits Objective In this exercise, the DC steady state response of simple RL and RC circuits is examined. The transient behavior of RC circuits
MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND. Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science. Laboratory Manual for. Eng Circuit Analysis (2013)
 MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Laboratory Manual for Eng. 3821 Circuit Analysis (2013) Instructor: E. W. Gill PREFACE The laboratory exercises in this manual
MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Laboratory Manual for Eng. 3821 Circuit Analysis (2013) Instructor: E. W. Gill PREFACE The laboratory exercises in this manual
The Series RLC Circuit and Resonance
 Purpose Theory The Series RLC Circuit and Resonance a. To study the behavior of a series RLC circuit in an AC current. b. To measure the values of the L and C using the impedance method. c. To study the
Purpose Theory The Series RLC Circuit and Resonance a. To study the behavior of a series RLC circuit in an AC current. b. To measure the values of the L and C using the impedance method. c. To study the
Lab #5 Steady State Power Analysis
 Lab #5 Steady State Power Analysis Steady state power analysis refers to the power analysis of circuits that have one or more sinusoid stimuli. This lab covers the concepts of RMS voltage, maximum power
Lab #5 Steady State Power Analysis Steady state power analysis refers to the power analysis of circuits that have one or more sinusoid stimuli. This lab covers the concepts of RMS voltage, maximum power
PHYS 1112L - Introductory Physics Laboratory II
 PHYS 1112L - Introductory Physics Laboratory II Laboratory Advanced Sheet dc Circuits 1. Objectives. The objectives of this laboratory are a. to be able to construct dc circuits given a circuit diagram
PHYS 1112L - Introductory Physics Laboratory II Laboratory Advanced Sheet dc Circuits 1. Objectives. The objectives of this laboratory are a. to be able to construct dc circuits given a circuit diagram
Exercise 2: High-Pass Filters
 Exercise 2: High-Pass Filters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to calculate and measure the cutoff frequencies oscilloscope. DISCUSSION of inductors, capacitors,
Exercise 2: High-Pass Filters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to calculate and measure the cutoff frequencies oscilloscope. DISCUSSION of inductors, capacitors,
FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIER
 Exp. No #5 FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIER Date: OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to analyze and plot the frequency response of a common collector amplifier. EQUIPMENT AND COMPONENTS
Exp. No #5 FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIER Date: OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to analyze and plot the frequency response of a common collector amplifier. EQUIPMENT AND COMPONENTS
LABORATORY MANUAL. Network Theory Lab EE-223-F
 Electrical & Electronics Engineering Department BRCM COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY BAHAL 127028 ( Distt. Bhiwani ) Haryana, India Laboratory LABORATORY MANUAL Network Theory Lab EE-223-F (3 rd Semester)
Electrical & Electronics Engineering Department BRCM COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY BAHAL 127028 ( Distt. Bhiwani ) Haryana, India Laboratory LABORATORY MANUAL Network Theory Lab EE-223-F (3 rd Semester)
Network Analysis I Laboratory EECS 70LA
 Network Analysis I Laboratory EECS 70LA Spring 2018 Edition Written by: Franco De Flaviis, P. Burke Table of Contents Page no. Foreword...3 Summary...4 Report Guidelines and Grading Policy...5 Introduction
Network Analysis I Laboratory EECS 70LA Spring 2018 Edition Written by: Franco De Flaviis, P. Burke Table of Contents Page no. Foreword...3 Summary...4 Report Guidelines and Grading Policy...5 Introduction
PHY203: General Physics III Lab page 1 of 5 PCC-Cascade. Lab: AC Circuits
 PHY203: General Physics III Lab page 1 of 5 Lab: AC Circuits OBJECTIVES: EQUIPMENT: Universal Breadboard (Archer 276-169) 2 Simpson Digital Multimeters (464) Function Generator (Global Specialties 2001)*
PHY203: General Physics III Lab page 1 of 5 Lab: AC Circuits OBJECTIVES: EQUIPMENT: Universal Breadboard (Archer 276-169) 2 Simpson Digital Multimeters (464) Function Generator (Global Specialties 2001)*
Lab 8 - INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOLTAGES
 08-1 Name Date Partners ab 8 - INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOTAGES OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase, reactance, and impedance in AC circuits. To observe the behavior
08-1 Name Date Partners ab 8 - INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOTAGES OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase, reactance, and impedance in AC circuits. To observe the behavior
Ohm s Law and Electrical Circuits
 Ohm s Law and Electrical Circuits INTRODUCTION In this experiment, you will measure the current-voltage characteristics of a resistor and check to see if the resistor satisfies Ohm s law. In the process
Ohm s Law and Electrical Circuits INTRODUCTION In this experiment, you will measure the current-voltage characteristics of a resistor and check to see if the resistor satisfies Ohm s law. In the process
VTU NOTES QUESTION PAPERS NEWS RESULTS FORUMS TESTING OF DIODE CLIPPING CIRCUITS
 TESTING OF DIODE CLIPPING CIRCUITS Aim: Testing of diode clipping circuits. Apparatus required: Diode (1N4007/BY127), Resistor, DC regulated power supply, signal generator and CRO. Theory: The circuit
TESTING OF DIODE CLIPPING CIRCUITS Aim: Testing of diode clipping circuits. Apparatus required: Diode (1N4007/BY127), Resistor, DC regulated power supply, signal generator and CRO. Theory: The circuit
AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE
 July 22, 2008 AC Currents, Voltages, Filters, Resonance 1 Name Date Partners AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE V(volts) t(s) OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase,
July 22, 2008 AC Currents, Voltages, Filters, Resonance 1 Name Date Partners AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE V(volts) t(s) OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase,
Exercise 1: Thevenin to Norton Conversion
 Exercise 1: Thevenin to Norton Conversion EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to convert a voltage source to a current source. You will verify your results by comparing
Exercise 1: Thevenin to Norton Conversion EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to convert a voltage source to a current source. You will verify your results by comparing
BASIC ELECTRONICS PROF. T.S. NATARAJAN DEPT OF PHYSICS IIT MADRAS
 BASIC ELECTRONICS PROF. T.S. NATARAJAN DEPT OF PHYSICS IIT MADRAS LECTURE-13 Basic Characteristic of an Amplifier Simple Transistor Model, Common Emitter Amplifier Hello everybody! Today in our series
BASIC ELECTRONICS PROF. T.S. NATARAJAN DEPT OF PHYSICS IIT MADRAS LECTURE-13 Basic Characteristic of an Amplifier Simple Transistor Model, Common Emitter Amplifier Hello everybody! Today in our series
POWER ELECTRONICS LAB MANUAL
 JIS College of Engineering (An Autonomous Institution) Department of Electrical Engineering POWER ELECTRONICS LAB MANUAL Exp-1. Study of characteristics of an SCR AIM: To obtain the V-I characteristics
JIS College of Engineering (An Autonomous Institution) Department of Electrical Engineering POWER ELECTRONICS LAB MANUAL Exp-1. Study of characteristics of an SCR AIM: To obtain the V-I characteristics
INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING AND LABORATORY EXPERIENCE Spring, 2015
 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING AND LABORATORY EXPERIENCE Spring, 2015 Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Jack Ou, Ph.D. Engineering Science Sonoma State University A SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY PUBLICATION CONTENTS 1 Electronic
INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING AND LABORATORY EXPERIENCE Spring, 2015 Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Jack Ou, Ph.D. Engineering Science Sonoma State University A SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY PUBLICATION CONTENTS 1 Electronic
BEST BMET CBET STUDY GUIDE MODULE ONE
 BEST BMET CBET STUDY GUIDE MODULE ONE 1 OCTOBER, 2008 1. The phase relation for pure capacitance is a. current leads voltage by 90 degrees b. current leads voltage by 180 degrees c. current lags voltage
BEST BMET CBET STUDY GUIDE MODULE ONE 1 OCTOBER, 2008 1. The phase relation for pure capacitance is a. current leads voltage by 90 degrees b. current leads voltage by 180 degrees c. current lags voltage
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA SCHOOL OF ENGENEERING. Electrical Engineering Science. Laboratory Manual
 UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA SCHOOL OF ENGENEERING Electrical Engineering Science Laboratory Manual Table of Contents Experiment #1 OHM S LAW... 3 Experiment # 2 SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS... 8
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA SCHOOL OF ENGENEERING Electrical Engineering Science Laboratory Manual Table of Contents Experiment #1 OHM S LAW... 3 Experiment # 2 SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS... 8
10. Introduction and Chapter Objectives
 Real Analog - Circuits Chapter 0: Steady-state Sinusoidal Analysis 0. Introduction and Chapter Objectives We will now study dynamic systems which are subjected to sinusoidal forcing functions. Previously,
Real Analog - Circuits Chapter 0: Steady-state Sinusoidal Analysis 0. Introduction and Chapter Objectives We will now study dynamic systems which are subjected to sinusoidal forcing functions. Previously,
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING I-YEAR/II-SEMESTER- EEE&ECE EE6201- CIRCUIT THEORY Two Marks with Answers PREPARED BY: Mr.A.Thirukkumaran,
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING I-YEAR/II-SEMESTER- EEE&ECE EE6201- CIRCUIT THEORY Two Marks with Answers PREPARED BY: Mr.A.Thirukkumaran,
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA School of Engineering -
 UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA School of Engineering - Electrical Engineering Science Laboratory Manual Table of Contents Safety Rules and Operating Procedures... 3 Troubleshooting Hints... 4 Experiment
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, JAMAICA School of Engineering - Electrical Engineering Science Laboratory Manual Table of Contents Safety Rules and Operating Procedures... 3 Troubleshooting Hints... 4 Experiment
LAB 4 : FET AMPLIFIERS
 LEARNING OUTCOME: LAB 4 : FET AMPLIFIERS In this lab, students design and implement single-stage FET amplifiers and explore the frequency response of the real amplifiers. Breadboard and the Analog Discovery
LEARNING OUTCOME: LAB 4 : FET AMPLIFIERS In this lab, students design and implement single-stage FET amplifiers and explore the frequency response of the real amplifiers. Breadboard and the Analog Discovery
Department of Electronic Engineering NED University of Engineering & Technology. LABORATORY WORKBOOK For the Course SIGNALS & SYSTEMS (TC-202)
 Department of Electronic Engineering NED University of Engineering & Technology LABORATORY WORKBOOK For the Course SIGNALS & SYSTEMS (TC-202) Instructor Name: Student Name: Roll Number: Semester: Batch:
Department of Electronic Engineering NED University of Engineering & Technology LABORATORY WORKBOOK For the Course SIGNALS & SYSTEMS (TC-202) Instructor Name: Student Name: Roll Number: Semester: Batch:
STUDY OF RC AND RL CIRCUITS Venue: Microelectronics Laboratory in E2 L2
 EXPERIMENT #1 STUDY OF RC AND RL CIRCUITS Venue: Microelectronics Laboratory in E2 L2 I. INTRODUCTION This laboratory is about verifying the transient behavior of RC and RL circuits. You need to revise
EXPERIMENT #1 STUDY OF RC AND RL CIRCUITS Venue: Microelectronics Laboratory in E2 L2 I. INTRODUCTION This laboratory is about verifying the transient behavior of RC and RL circuits. You need to revise
PART ONE: DC Circuits
 SEE ONLINE COURSE ON: http://users.utcluj.ro/~denisad PART ONE: DC Circuits Chapter 4. Circuit Theorems Monday, March 12, 2018 1 Contents 1. Superposition Theorem 2. Source Transformation 3. Thevenin s
SEE ONLINE COURSE ON: http://users.utcluj.ro/~denisad PART ONE: DC Circuits Chapter 4. Circuit Theorems Monday, March 12, 2018 1 Contents 1. Superposition Theorem 2. Source Transformation 3. Thevenin s
Lab 2: Common Base Common Collector Design Exercise
 CSUS EEE 109 Lab - Section 01 Lab 2: Common Base Common Collector Design Exercise Author: Bogdan Pishtoy / Lab Partner: Roman Vermenchuk Lab Report due March 26 th Lab Instructor: Dr. Kevin Geoghegan 2016-03-25
CSUS EEE 109 Lab - Section 01 Lab 2: Common Base Common Collector Design Exercise Author: Bogdan Pishtoy / Lab Partner: Roman Vermenchuk Lab Report due March 26 th Lab Instructor: Dr. Kevin Geoghegan 2016-03-25
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
Exercise 3: Power in a Series/Parallel Circuit
 DC Fundamentals Power in DC Circuits Exercise 3: Power in a Series/Parallel Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to determine the power dissipated in a series/
DC Fundamentals Power in DC Circuits Exercise 3: Power in a Series/Parallel Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to determine the power dissipated in a series/
ES330 Laboratory Experiment No. 9 Bipolar Differential Amplifier [Reference: Sedra/Smith (Chapter 9; Section 9.2; pp )]
![ES330 Laboratory Experiment No. 9 Bipolar Differential Amplifier [Reference: Sedra/Smith (Chapter 9; Section 9.2; pp )] ES330 Laboratory Experiment No. 9 Bipolar Differential Amplifier [Reference: Sedra/Smith (Chapter 9; Section 9.2; pp )]](/thumbs/84/89341671.jpg) ES330 Laboratory Experiment No. 9 Bipolar Differential Amplifier [Reference: Sedra/Smith (Chapter 9; Section 9.2; pp. 614-627)] Objectives: 1. Explore the operation of a bipolar junction transistor differential
ES330 Laboratory Experiment No. 9 Bipolar Differential Amplifier [Reference: Sedra/Smith (Chapter 9; Section 9.2; pp. 614-627)] Objectives: 1. Explore the operation of a bipolar junction transistor differential
AC : A CIRCUITS COURSE FOR MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING
 AC 2010-2256: A CIRCUITS COURSE FOR MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING L. Brent Jenkins, Southern Polytechnic State University American Society for Engineering Education, 2010 Page 15.14.1 A Circuits Course for
AC 2010-2256: A CIRCUITS COURSE FOR MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING L. Brent Jenkins, Southern Polytechnic State University American Society for Engineering Education, 2010 Page 15.14.1 A Circuits Course for
LIC & COMMUNICATION LAB MANUAL
 LIC & Communication Lab Manual LIC & COMMUNICATION LAB MANUAL FOR V SEMESTER B.E (E& ( E&C) (For private circulation only) NAME: DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION SRI SIDDHARTHA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
LIC & Communication Lab Manual LIC & COMMUNICATION LAB MANUAL FOR V SEMESTER B.E (E& ( E&C) (For private circulation only) NAME: DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION SRI SIDDHARTHA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
ET1210: Module 5 Inductance and Resonance
 Part 1 Inductors Theory: When current flows through a coil of wire, a magnetic field is created around the wire. This electromagnetic field accompanies any moving electric charge and is proportional to
Part 1 Inductors Theory: When current flows through a coil of wire, a magnetic field is created around the wire. This electromagnetic field accompanies any moving electric charge and is proportional to
Group: Names: Resistor Band Colors Measured Value ( ) R 1 : 1k R 2 : 1k R 3 : 2k R 4 : 1M R 5 : 1M
 2.4 Laboratory Procedure / Summary Sheet Group: Names: (1) Select five separate resistors whose nominal values are listed below. Record the band colors for each resistor in the table below. Then connect
2.4 Laboratory Procedure / Summary Sheet Group: Names: (1) Select five separate resistors whose nominal values are listed below. Record the band colors for each resistor in the table below. Then connect
MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND. Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science. Laboratory Manual for. Eng Circuit Analysis (2011)
 MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Laboratory Manual for Eng. 3821 Circuit Analysis (2011) Instructor: E. Gill PREFACE The laboratory exercises in this manual
MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Laboratory Manual for Eng. 3821 Circuit Analysis (2011) Instructor: E. Gill PREFACE The laboratory exercises in this manual
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK UNIT I BASIC CIRCUITS ANALYSIS PART A (2-MARKS)
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK YEAR / SEM : I / II SUBJECT CODE & NAME : EE 1151 CIRCUIT THEORY UNIT I BASIC CIRCUITS ANALYSIS PART A (2-MARKS)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK YEAR / SEM : I / II SUBJECT CODE & NAME : EE 1151 CIRCUIT THEORY UNIT I BASIC CIRCUITS ANALYSIS PART A (2-MARKS)
Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters
 BEE 233 Laboratory-4 Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters 1. Objectives Analyze and measure characteristics of circuits built with opamps. Design and test circuits with opamps. Plot gain vs.
BEE 233 Laboratory-4 Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters 1. Objectives Analyze and measure characteristics of circuits built with opamps. Design and test circuits with opamps. Plot gain vs.
UNIT - 1 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FUNDAMENTALS
 UNIT - 1 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FUNDAMENTALS 1.1 Basic operational amplifier circuit- hte basic circuit of an operational amplifier is as shown in above fig. has a differential amplifier input stage and
UNIT - 1 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FUNDAMENTALS 1.1 Basic operational amplifier circuit- hte basic circuit of an operational amplifier is as shown in above fig. has a differential amplifier input stage and
Experiment #2 Half Wave Rectifier
 PURPOSE: ELECTRONICS 224 ETR620S Experiment #2 Half Wave Rectifier This laboratory session acquaints you with the operation of a diode power supply. You will study the operation of half-wave and the effect
PURPOSE: ELECTRONICS 224 ETR620S Experiment #2 Half Wave Rectifier This laboratory session acquaints you with the operation of a diode power supply. You will study the operation of half-wave and the effect
THIRD SEMESTER ELECTRONICS - II BASIC ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS LAB DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 THIRD SEMESTER ELECTRONICS - II BASIC ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS LAB DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Prepared By: Checked By: Approved By: Engr. Saqib Riaz Engr. M.Nasim Khan Dr.Noman Jafri Lecturer
THIRD SEMESTER ELECTRONICS - II BASIC ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS LAB DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Prepared By: Checked By: Approved By: Engr. Saqib Riaz Engr. M.Nasim Khan Dr.Noman Jafri Lecturer
NETWORK THEORY (EE 223 F) LAB MANUAL
 NETWORK THEORY (EE 223 F) LAB MANUAL III SEMESTER Department Of Electrical & Electronics Engg Dronacharya College Of Engineering Khentawas, Gurgaon 123506 LIST OF EXPERIMENTS EXP NO. NAME OF THE EXPERIMENT
NETWORK THEORY (EE 223 F) LAB MANUAL III SEMESTER Department Of Electrical & Electronics Engg Dronacharya College Of Engineering Khentawas, Gurgaon 123506 LIST OF EXPERIMENTS EXP NO. NAME OF THE EXPERIMENT
ECE 2006 University of Minnesota Duluth Lab 11. AC Circuits
 1. Objective AC Circuits In this lab, the student will study sinusoidal voltages and currents in order to understand frequency, period, effective value, instantaneous power and average power. Also, the
1. Objective AC Circuits In this lab, the student will study sinusoidal voltages and currents in order to understand frequency, period, effective value, instantaneous power and average power. Also, the
ENGR 201 Homework, Fall 2018
 Chapter 1 Voltage, Current, Circuit Laws (Selected contents from Chapter 1-3 in the text book) 1. What are the following instruments? Draw lines to match them to their cables: Fig. 1-1 2. Complete the
Chapter 1 Voltage, Current, Circuit Laws (Selected contents from Chapter 1-3 in the text book) 1. What are the following instruments? Draw lines to match them to their cables: Fig. 1-1 2. Complete the
Communication Circuit Lab Manual
 German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 2 Tuned Amplifier Eng. Anas Alashqar
German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 2 Tuned Amplifier Eng. Anas Alashqar
Lab 2: DC Circuits Lab Assignment
 2 class days 1. I-V curve for various components Source: Curtis, 1.2.1. (HH 1.1, 1.2, 1.3) Lab 2: DC Circuits Lab Assignment A passive element is a two-contact device that contains no source of power or
2 class days 1. I-V curve for various components Source: Curtis, 1.2.1. (HH 1.1, 1.2, 1.3) Lab 2: DC Circuits Lab Assignment A passive element is a two-contact device that contains no source of power or
ELEN 140 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS II Winter 2013
 ELEN 140 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS II Winter 2013 Professor: Stephen O Loughlin Prerequisite: ELEN 130 Office: C234B Co-requisite: none Office Ph: (250) 762-5445 ext 4376 Lecture: 3.0 hrs/week Email: soloughlin@okanagan.bc.ca
ELEN 140 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS II Winter 2013 Professor: Stephen O Loughlin Prerequisite: ELEN 130 Office: C234B Co-requisite: none Office Ph: (250) 762-5445 ext 4376 Lecture: 3.0 hrs/week Email: soloughlin@okanagan.bc.ca
EE 2274 DIODE OR GATE & CLIPPING CIRCUIT
 EE 2274 DIODE OR GATE & CLIPPING CIRCUIT Prelab Part I: Wired Diode OR Gate LTspice use 1N4002 1. Design a diode OR gate, Figure 1 in which the maximum current thru R1 I R1 = 9mA assume Vin = 5Vdc. Design
EE 2274 DIODE OR GATE & CLIPPING CIRCUIT Prelab Part I: Wired Diode OR Gate LTspice use 1N4002 1. Design a diode OR gate, Figure 1 in which the maximum current thru R1 I R1 = 9mA assume Vin = 5Vdc. Design
PART B. t (sec) Figure 1
 Code No: R16128 R16 SET 1 I B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, April/May 217 ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT ANALYSIS I (Electrical and Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 7 Note: 1. Question
Code No: R16128 R16 SET 1 I B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, April/May 217 ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT ANALYSIS I (Electrical and Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 7 Note: 1. Question
Core Technology Group Application Note 1 AN-1
 Measuring the Impedance of Inductors and Transformers. John F. Iannuzzi Introduction In many cases it is necessary to characterize the impedance of inductors and transformers. For instance, power supply
Measuring the Impedance of Inductors and Transformers. John F. Iannuzzi Introduction In many cases it is necessary to characterize the impedance of inductors and transformers. For instance, power supply
Fundamental of Electrical Engineering Lab Manual
 Fundamental of Electrical Engineering Lab Manual EngE-111/318 Dr.Hidayath Mirza & Dr.Rais Ahmad Sheikh 1/9/19 EngE111 Testing Battery (DC) Testing AC Testing Wire 1 P a g e Resistor measurement Testing
Fundamental of Electrical Engineering Lab Manual EngE-111/318 Dr.Hidayath Mirza & Dr.Rais Ahmad Sheikh 1/9/19 EngE111 Testing Battery (DC) Testing AC Testing Wire 1 P a g e Resistor measurement Testing
Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institute of Technology INDEX
 Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institute of Technology Diploma EE Semester III 3330905: ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS AND CIRCUITS INDEX Sr. No. Title Page Date Sign Grade 1 Obtain I-V characteristic of Diode. 2 To
Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institute of Technology Diploma EE Semester III 3330905: ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS AND CIRCUITS INDEX Sr. No. Title Page Date Sign Grade 1 Obtain I-V characteristic of Diode. 2 To
ACTIVE FILTERS USING OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 ACTIVE FILTERS USING OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to design and compare the frequency plots of second order low pass and high pass active filters. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
ACTIVE FILTERS USING OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to design and compare the frequency plots of second order low pass and high pass active filters. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS. Third Edition JOSEPH EDMINISTER MAHMOOD NAHVI
 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Third Edition JOSEPH EDMINISTER MAHMOOD NAHVI Includes 364 solved problems --fully explained Complete coverage of the fundamental, core concepts of electric circuits All-new chapters
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Third Edition JOSEPH EDMINISTER MAHMOOD NAHVI Includes 364 solved problems --fully explained Complete coverage of the fundamental, core concepts of electric circuits All-new chapters
ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics
 ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics 1 Linear System Characteristics The first part of this experiment will serve as an introduction to the use of the spectrum analyzer in making absolute
ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics 1 Linear System Characteristics The first part of this experiment will serve as an introduction to the use of the spectrum analyzer in making absolute
Laboratory 2 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore)
 Laboratory 2 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore) Instrument Familiarization and Basic Electrical Relations Required Components: 2 1k resistors 2 1M resistors 1 2k resistor Objectives This exercise is designed
Laboratory 2 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore) Instrument Familiarization and Basic Electrical Relations Required Components: 2 1k resistors 2 1M resistors 1 2k resistor Objectives This exercise is designed
