U.S. Patent Sep. 16, 1997 Sheet 1 of 3 5,668,620 FIC. 1
|
|
|
- Ginger Anthony
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 United States Patent 19 Kurtin et al VARABLE FOCAL LENGTH LENSES WHICH HAVE ANARBITRARLY SHAPED PERPHERY Inventors: Stephen Kurtin, 3835 Kingswood Rd., Sherman Oaks, Calif ; Daniel E. Fedele, 3007 N. Arlington Ave., Simi Valley, Calif ; Saul Epstein, Deervale Pl. Sherman Oaks, Calif Appl. No.: 226,344 Fied: Apr. 12, 1994 Int. Cl.... G02C 1/00: G02B 1/06 U.S. Cl /158; 359/665; 359/666 Field of Search /666, 665, 359/832, 722, 672; 351/41, 158 References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 3,598,479 8/1971 Wright /159 4,261,655 4/1981 Honigsbaum A1 4,913,536 4/1990 Barnea /419 5,138,494 8/1992 Kurtin /666 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS /1926 United Kingdom. US A 11 Patent Number: 5,668, Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 1997 Primary Examiner-Hung X. Dang Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Saul Epstein 57 ABSTRACT A variable focal length lens whose peripheral shape can be arbitrarily specified, for use in spectacles, which includes a rigid lens to provide the wearer's distance correction, and a liquid-filled lens bounded by a stretched distensible elasto meric membrane to provide a variable near addition. The liquid, which has a fixed volume, is stored in the field of view between the elastomeric membrane and the rigid lens. Variation of the optical power of the liquid filled lens is achieved by displacement of a membrane support to which the outer periphery of the stretched elastomeric membrane is attached. The shape of the distended membrane is kept substantially spherical, despite the circumference of the membrane being non-circular, by making the free area of the membrane circular. This is accomplished by supporting the membrane on a transparent spacing member which has substantially the same refractive index as the liquid and which includes a circular opening which defines the free area of the membrane. A pair of spectacles is comprised of two variable focallength lenses mounted to a frame with an actuator for adjusting their focal lengths mounted on the frame between the lenses. The actuator is mechanically coupled to the lenses by point contacts which prevent twisting couples from being created in the lens structures. 9 Claims, 3 Drawing Sheets v a 2 3.N t 2.
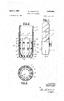
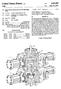
2 U.S. Patent Sep. 16, 1997 Sheet 1 of 3 5,668,620 FIC. 1 N s
3 U.S. Patent Sep. 16, 1997 Sheet 2 of 3 5,668, SGSN 72 se
4 U.S. Patent Sep. 16, 1997 Sheet 3 of 3 5,668,620 FIC. 7 FIC az Y2YZ
5 1. VARABLE FOCAL LENGTH LENSES WHICH HAVE AN ARBTRARLY SHAPED PERPHERY BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION This invention relates to spectacles which use variable focal length lenses. There are many other uses for such lenses, but there is a particular need for them as spectacle lenses. This need arises as people get older (generally about the age of forty five) because the lens in the human eye becomes incapable of Sufficient accommodation to focus on near objects. After the onset of this condition of limited focal accommodation, called presbyopia, a single set of fixed focus spectacles will be found to be unsatisfactory for both distant and near vision, irrespective of the wearer's general visual acuity. Whatever correction (if any) may be required to correct a person's vision for distance, an additional amount of optical power (up to about three diopters) will be found to be required to correct that person's eyesight for near vision. The required "near addition generally does not involve an astigmatic component. The usual solution to this problem is to fit persons suffering from presbyopia with spectacles having bifocal lenses. In the most common form of bifocal lens, the upper part is ground to provide the wearer with the proper correc tion (if any is needed) for distance vision, and the lower part is ground with the same correction plus a relatively small near addition, usually amounting to no more than a few diopters of additional optical power. Using bifocal lenses in a pair of spectacles allows a person to see distant objects clearly by looking straight ahead, and to see close objects clearly by looking downward. The bifocal solution is not entirely satisfactory for at least three reasons. Firstly, many people have difficulty in adapt ing to bifocals; secondly, there is often the need to see near objects which are on a level with, or above, the wearer; and finally, there is usually an intermediate distance range within which which neither part of the lens is satisfactory. Trifocals or progressive multifocal lenses are used to help alleviate this last problem, but the first two difficulties remain, and in any event, the in-focus field of view may be more limited than is desired. The foregoing problem was addressed in a prior patentissued to one of the present inventors. U.S. Pat. No This patent discloses a continuously variable focal length lens which can be adjusted by the wearer to focus on any object, irrespective of its distance from the Watc. In the aforementioned prior patent, a liquid-filled variable focallength lens was disclosed which includes a distensible transparent membrane spaced from a rigid lens, with the space between them filled with a liquid having a relatively high refractive index. The membrane is bonded to a mem brane Support, and the peripheries of the rigid lens and the membrane support are connected with a flexible sealing member. The rigid lens, the membrane, and the sealing member define a substantially fixed volume for the liquid filling. Changing the spacing between the membrane support and the rigid lens in such a structure causes the membrane to assume a curved form, either increasing the power of the lens or decreasing it, depending on the direction of the change in spacing. If the periphery of the membrane is circular, its shape, when distended, will be essentially spherical, and little or no optical distortion will be encoun tered in use. However, as noted, one substantial use of the lenses described in the previous patent is in variable focus spectacles. In spectacles, for reasons of style, lens shapes 5,668,620 5 O other than circular are often desired. It has been found that in Such cases, depending on the extent of the non-circularity of the lenses, the membrane shape may deviate significantly from the desired spherical shape, and greater than desired optical distortions may be encountered. It is therefore an object of the present invention to enable the production of a liquid filled variable focal length lens wherein optical distortion otherwise arising from non circularity of the lens may be minimized. It is a further object of the present invention to enable the production Of spectacles using such variable focal length lenses. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention uses a structure similar in many respects to the structure disclosed in the aforementioned 494 patent. Hence, the disclosures of U.S. Pat. No are incorporated herein by reference. The structures illustrated in FIGS. 5-9 of that patent are particularly relevant hereto. The presently preferred embodiment of this invention utilizes a structure similar to that described in connection with FIG. 9 of the prior invention, modified so as to minimize distortions which might otherwise arise from the use of a membrane having a noncircular periphery. As was noted in the previous section, the usual spectacle prescription for a person suffering from presbyopia (i.e., most people over the age of forty five) includes a distance correction to correct his or her vision at infinity (including, if needed, spherical and astigmatic corrections) plus an additional correction for close vision. The additional cor rection for close vision is almost always only spherical. Both the prior invention and the present invention basically involve means for providing close vision correction by varying the spherical power of the lens. The present inven tion is an improvement over the previous invention in that it minimizes distortions which may arise if the shape of the lenses is other than circular. As noted above, the 494 patent discloses a liquid filled variable focus lens in which a transparent membrane mounted on a membrane supportis moved in such away that the membrane distends to change the optical power of the lens. Also as noted above, depending on the shape of the periphery of the membrane, the distended surface may not be spherical. Hence, the present invention provides means to minimize any variation from sphericity as the optical power is changed. In the present invention, the free area of the distensible membrane is circular irrespective of the peripheral shape of the membrane Support. This is accomplished by making the membrane Support transparent, and providing a circular opening therein which defines the free area of the mem brane. Since the free area of the distensible membrane is circular, its distensions are spherical, and do not cause optical distortions. Also, the membrane support is made of a material which has substantially the same index of refrac tion as the liquid filling. This renders the support substan tially invisible, and hence it does not detract from the appearance or styling of the glasses. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a rear view (i.e., from the wearer's side) of a portion of a pair of spectacles using lenses according to a first embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a cross sectional view of the right eye lens from the spectacles shown in FIG. 1, taken at 2-2 of FIG. 1, and showing the lens adjusted for distance viewing.
6 3 FIG. 3 is a cross sectional view of the lens shown in FIG. 1, taken at the same section as FIG. 2, but showing the lens adjusted to focus on a near object. FIG. 4 is a rear view (i.e., from the wearer's side) of a portion of a pair of spectacles using lenses according to a second embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 5 is a cross sectional view of the right eye lens from the spectacles shown in FIG. 4, taken at 5-5 of FIG.4, and showing the lens adjusted for distance viewing. FIG. 6 is a fragmentary view showing a variant of the membrane support of FIG. 5. FIG. 7 is a rear view of an actuator assembly for use in connection with the invented variable focus lenses in the context of spectacles. FIG. 8 is a cross sectional view of the actuator of FIG. 6, taken at 8-8 of FIG. 7. FIG. 9 is a fragmentary view of the actuator of FIG. 6, taken at 99 of FIG. 7. DETALED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION FIG. 1 depicts a pair of spectacles which include variable focus lenses according to the present invention. Only the right lens is shown (the view being from the wearer's side of the spectacles), plus a small portion of the adjusting tab (19') of the left lens, sufficient to show the relationships between the parts. The following description will generally refer to only a single lens but, of course, it will be understood that there are actually two lenses in a pair of spectacles. Basically, the invented variable focus lens can be thought of as a fixed rigid lens plus aliquid lens which has a variable power. The liquid lens is bounded on one side by the rigid lens, and on the other by a distensible transparent membrane, the space between the membrane and the rigid lens being filled with a transparent liquid. If the rigid lens is moved closer to the membrane, the membrane will distend, becoming convex and increasing the optical power of the lens assembly. Conversely, if the lens is moved away from the membrane, the membrane will become concave, reduc ing the optical power of the assembly. The present invention involves means for assuring that the distension of the membrane is spherical when the shape of the membrane Support is not circular. As seen in FIG. 1, the spectacles include a frame 10 to which temples (not shown) are attached. The frame is generally symmetrical about a nasal region 10 Apair of lens assemblies 11 and 11" (a right hand and a lefthand assembly) are attached to the frame 10 by screws or other means (not shown) on either side of the nasal region 10" Only the adjusting tab. 19' of the left hand assembly 11" can be seen in FIG. 1. The lens assemblies are positioned so that the wearer's left eye sees through assembly 11", and his or her right eye sees through assembly 11. FIGS. 2 and 3 are cross sectional views of the right eye lens assembly 11, the assembly of FIG. 2 being adjusted for distance viewing, and the assembly of FIG. 3 being adjusted for near viewing. Front ring 14 of the lens assembly is the member attached to frame 10. Distensible membrane 15, under radial tension, is placed between front ring 14 and membrane support 16, and the three items cemented, or otherwise fastened together. The membrane support may have any peripheral shape as desired, but irrespective of its peripheral shape, the central portion includes a substantially circular opening 16 which defines the free area of membrane 15. The opening 16 as seen in FIGS. 2 and 3 extends completely through the 5,668, membrane support 16, however, the opening need only be deep enough to define the desired free area of the membrane. If the opening 16 does not extend through the thickness of the membrane support, it will be necessary to provide some other passage (such as a small hole) for the filling liquid to flow from one side of the membrane support to the other. Arigid lens 12 is cemented, or otherwise attached, to rear ring 17, and is spaced from frame 10 by flex hinges 22 and actuator 20, which will be described below. A flexible seal 13, preferably made of silicone rubber, is sealed to the rear ring 17, and also to front ring 14. As shown in the drawings, seal 13 is held in place by compression rings 18, but cementing or other sealing methods may be used if desired. The view of membrane support 16 with its central open ing 16 as shown in FIG. 1 is through rigid lens 12. Because, as will be discussed below, the rigid lens, the membrane support, the membrane, and the transparent liquid filling preferably all have substantially the same index of refraction, the membrane support actually will be difficult to see. For explanatory purposes, however, this element is shown in FIG. 1 as if it were clearly visible. The surface of membrane support 16 which contacts membrane 15 is preferably sufficiently convex so that mem brane 15 will remain in contact with the edge of opening 16, even when the membrane is distended to its maximum convexity. If such construction is used, membrane 15 need be attached to the membrane support only at its periphery. If the convexity of the top surface of the membrane support is made less than the amount which will assure contact between the membrane 15 and the edge of opening 16 at maximum distension, membrane 15 must be attached to the membrane support 16 around the periphery of opening 16, as by cementing, to assure that the free area of the membrane is circular, even at maximum distension. If cemented, the cement used should be transparent and index-matched so as to render it invisible in use. The construction with an adequately convex top surface of the membrane Support is presently preferred, since it avoids the need to attach the membrane to membrane support 16 in such a way that the interface is invisible. As will be appreciated by those skilled in the art, while it may be possible to fasten the membrane to the membrane support so as to achieve the desired results, avoiding this step is advantageous. The membrane 15 is comprised of a thin transparent distensible plastic film such as saran. The enclosed volume defined by membrane 15, membrane support 16, front ring 14, seal 13, rear ring 17, and rigid lens 12 is filled with a transparent liquid 21. The indexes of refraction of the liquid filling, the membrane support, the membrane and the rigid lens are all preferably the same or nearly the same. The rear ring 17 is attached to frame 10 via a pair of flex "hinges 22, one of which can be seen in FIGS. 2 and 3. Each of the hinges 22 is preferably comprised of a plastic tube which is relatively weak in bending so that the angle between the rearring 17 and the front ring 14 can be varied as desired. Other types of hinges can also be used, if desired. An adjusting tab 19 is attached to the rear ring 17, and extends outward from it at a point remote from the hinges. The adjusting tabs 19 and 19" (from both lenses of the spectacles, as can be seen in FIG. 1) are engaged by an actuator 20 located just above the nose of the wearer. The actuator 20 allows the wearer to adjust the distance between the frontring 14 and the rearring 17 adjacent to the actuator. This causes a change in the angle between front ring 14 and rear ring 17, changing the volume between the two rings. Since the liquid 21 is sensibly incompressible, membrane
7 5 15, the softest member enclosing the liquid, distends as needed to enclose a fixed volume. Flexible seal 13 is constructed so that the volume change due to its motion is relatively low. Moving the adjusting tabs 19 and 19" toward the frame 10 causes the membranes 15 to bulge outward, resulting in a convex membrane surface and an increased optical power. Assuming that the index of refraction of liquid 21 is equal to that of the rigid lens 12, the optical power of the lens assembly is determined by the refractive index and the shapes of the membrane 15 and the outer (rear) surface of rigid lens 12. The shape of the interface between the liquid 21 and lens 12 will have no effect. The shape of membrane 15 as shown in FIG. 2 is concave for purposes of illustration and explanation. Since FIG. 2 is intended to illustrate a distance viewing configuration, the outer (i.e., rear) surface of lens 12 would be ground so that, in combination with the concave membrane, the wearer's prescription for distance viewing is achieved. Adjusting actuator 20 so that adjusting tabs 19 and 19" are moved closer to frame 10 causes the membrane to become convex, adding to the power of the lens assembly so that the wearer can focus on nearer objects. Membrane 15 need not be concave in the distance view ing configuration, as shown, but could, for example, be flat (or even convex, if desired). The outer surface of lens 12, in such a case, should be ground to provide the wearer's distance prescription with whatever shape membrane is chosen. It is believed to be advantageous to use a concave membrane shape, as shown, for the distance configuration since it is then possible to minimize the membrane distension, and correspondingly the actuation forces, by causing the membrane shape go from concave, through flat, to convex as the spectacles are adjusted from distance to near viewing. Since the membrane support is transparent, and has sub stantially the same refractive index as does the liquid 21, it tends to be invisible to both the wearer and to persons observing the wearer, and there will be no degradation of the stylistic effect sought to be achieved by whatever outline shape is chosen. At the same time, because the free area of the membrane is circular, the distensions of the membrane will be spherical, and there will be no significant distortion of the images seen by the wearer over a wide solid angle of WieW. It may be noted, that as described herein, the membrane support 16 is fastened to the spectacles frame, while the rigid lens is moved with respect thereto. It will be understood by those skilled in the art that this construction is only a matter of convenience for purposes of explanation and illustration, and that the reverse construction whereby the rigid lens is attached to the frame, and the membrane support is moved with respect thereto, would achieve similar results. FIGS. 4 and 5 depict a second embodiment of a lens according to the invention (indicated by the numeral 40), which, for purposes of illustration, are according to the alternate construction mentioned in the previous paragraph; namely, the construction where the rigid lens 50, instead of being the movable member, is attached to a front ring 51. which in turn is attached to frame 10. The transparent membrane support 52, in this embodiment, is movable with respect to the frame 10 in the same manner as was the rigid lens in the first embodiment. In FIG. 5, where the lens is set for distance viewing, the optically active portion of the membrane is shown flat, for purposes of illustration, rather than concave as was shown in FIG. 2. This alternate mem brane configuration was discussed above. 5,668, The membrane 53 in this second embodiment is bonded around its periphery to the membrane Support 52 and to rear ring 54. A raised circular ridge 55 projects from the mem brane support 52 and supports the membrane away from the body of the membrane Support. The membrane may or may not be bonded to the ridge. Holes 56 through the membrane support allow the filling liquid 21 to pass through the membrane support as the support is moved. Channels 57 allow the filling liquid to pass in and out of the central area of the space between membrane support 52 and membrane 53. Since the raised ridge 55 is circular, distensions of the membrane will be essentially spherical irrespective of the shape of the periphery of the membrane. As illustrated in FIG. 4, there are four channels 57 separating four portions of the ridge 55. It will be understood that there could be few or many channels 57. and that the lands of ridge 55 could be large or relatively small, i.e., ridge 55 could, for example, be comprised of a series of small raised dots, or, on the other hand, of a continuous ridge. In the latter case, one or more holes 56 interior of the ridge could be used to allow liquid flow to and from the center portion. FIG. 6 illustrates a variant of the membrane support 52 shown in FIG. 5. The membrane support 52 of FIG. 6 is different from the membrane support 52 in three particulars. any one, or ones of which may be adopted in the construc tion of a variable focus lens according to the invention. The first difference is that the opening 55' extends completely through the membrane support, rather than merely part way; the second is that the opening is tapered, rather than cylin drical; and the third is that there is a lip on the periphery of the membrane support so that the membrane does not taper downward outside the ridge 55" as in the construction of FIG.S. Details of the presently preferred means for adjusting the focallength of the invented lenses in the context of a pair of spectacles (actuator 20) are shown in FIGS. 7 through 9. Linear motion which is imparted to adjusting tabs 19 and 19 by the actuator 20 is created by rotating nut 61 around threaded stud 62. Knurled finger-wheel 71, which is the element engaged by the wearer to adjust the focal length, is pressed onto nut 61. Two "point washers 63, a wave spring 64, and a shim65 are located in the space between the finger wheel 71 and flange 61' of nut 61. Each point washer 63 has two diametrically opposed points projecting from one of its faces which engage mating grooves in adjusting tabs 19 and 19" As nut 61 is rotated by the wearer's finger pressure on finger wheel 71, the point washers remain rotationally stationary, but move axially with respect to threaded stud 62. The linear axial motion is coupled to the adjusting tabs 19 and 19 through the points 63, and the focal length of each lens is thereby changed. Transmitting the displacement force to adjusting tabs 19 and 19" through the points 63' assures that no twisting couple (which would tend to twist the rear ring 17 and thereby introduce optical distortion) is trans mitted to the lens assembly. In addition, the point type of coupling between the actuator and the adjusting tabs mini mizes any uncertainty in the points of application of force to the lenses, which assures that they will track optically as their focal lengths are changed. The threaded stud 62 is held to frame 10 by screw 66. The angular position of stud 62 may be set on assembly to the position which locates adjusting tabs 19 and 19" as desired with respect to the angular position of finger wheel 71. It will be appreciated that the actuator as described above is capable of exerting actuation forces in either direction. and hence is suitable for use with a lens wherein the membrane shape changes from concave to convex within its
8 7 range of operation. If a construction is used wherein the membrane is always convex (or always concave), the actua tion force may not reverse direction during operation, and in Such case, only one point washer may be found to be Sufficient. What has been invented are spectacles which utilize liquid filled variable focus lenses wherein distortions, which might otherwise occur due to non-circularity of the lenses, are Substantially reduced. Various modifications and adaptations of the invention will no doubt occur to those skilled in the art. Such modifications and adaptations as are within the terms and spirit of the following claims are intended to be covered thereby. We claim: 1. A variable focal length lens which comprises: a rigid lens; a membrane support member positioned across the field of view of said rigid lens and spaced therefrom, said membrane support member having a central portion including Support means which supports a transparent distensible membrane whereby said membrane has a substantially circular free area, wherein said support means is in the form of a raised ridge projecting outward from a surface of said membrane support member, said membrane being positioned against said Support means and being maintained at all times in contact with said support means in the region of said support means adjacent to said free area of said mem brane; a transparent liquid filling the space between said rigid lens and said membrane; flexible sealing means for retaining said transparent liquid between said rigid lens and said membrane; and variable spacing means acting between said rigid lens and said membrane support member for adjusting the spac ing between said membrane support member and said rigid lens. 2. A variable focal length lens which comprises: a rigid lens; a membrane support member positioned across the field of view of said rigid lens and spaced therefrom, said membrane support member having a central portion including support means which supports a transparent distensible membrane whereby said membrane has a substantially circular free area, wherein said support means is comprised of the area surrounding a substan tially circular opening in a surface of said membrane support member and said membrane is not attached to the area of said membrane support member which comprises said support means, said membrane being positioned against said support means and being main tained at all times in contact with said support means in the region of said support means adjacent to said free area of said membrane; a transparent liquid filling the space between said rigid lens and said membrane; flexible sealingmeans for retaining said transparent liquid between said rigid lens and said membrane; and variable spacing means acting between said rigidlens and said membrane support member for adjusting the spac ing between said membrane support member and said rigid lens. 3. A variable focal length lens as recited in claim 2 wherein said surface of said membrane support member is convexly shaped. 5,668,620 O A variable focal length lens which comprises: a rigid lens; a membrane support member positioned across the field of view of said rigid lens and spaced therefrom, said membrane Support member having a central portion including support means which supports a transparent distensible membrane whereby said membrane has a substantially circular free area, where said central por tion of said membrane support is transparent and has substantially the same refractive index as said trans parent liquid, said membrane being positioned against said support means and being maintained at all times in contact with said support means in the region of said support means adjacent to said free area of said mem brane; a transparent liquid filling the space between said rigid lens and said membrane; flexible sealing means for retaining said transparent liquid between said rigid lens and said membrane; and variable spacing means acting between said rigidlens and said membrane support member for adjusting the spac ing between said membrane Support member and said rigid lens, said membrane Support member and said rigid lens being hingedly connected, and said variable spacing means acting between said membrane support and said rigid lens remote from said hinge. 5. A variable focal length lens which comprises: a rigid lens; a membrane support member positioned across the field of view of said rigid lens and spaced therefrom, said membrane support member having a central portion including Support means which supports a transparent distensible membrane whereby said membrane has a substantially circular free area, wherein said support means is in the form of a raised ridge projecting outward from a surface of said membrane support member, said membrane being positioned against said support means and being maintained at all times in contact with said support means in the region of said support means adjacent to said free area of said mem brane; a transparent liquid filling the space between said rigid lens and said membrane; flexible sealing means for retaining said transparent liquid between said rigid lens and said membrane; and variable spacing means acting between said rigid lens and said membrane Support member for adjusting the spac ing between said membrane support member and said rigid lens, said membrane Support member and said rigid lens being hingedly connected, and said variable spacing means acting between said membrane support and said rigid lens remote from said hinge. 6. A variable focal length lens as recited in claim 5 where said central portion of said membrane support is transparent and has substantially the same refractive index as said transparent liquid. 7. A variable focal length lens which comprises: a rigid lens; a membrane support member positioned across the field of View of said rigid lens and spaced therefrom, said membrane support member having a central portion including Support means which supports a transparent distensible membrane whereby said membrane has a substantially circular free area, wherein said support means is comprised of the area surrounding a substan
9 9 tially circular opening in a surface of said support member and said membrane is not attached to the area of said membrane support member which comprises said Support means, said membrane being positioned against said support means and being maintained at all times in contact with said support means in the region of said support means adjacent to said free area of said membrane; a transparent liquid filling the space between said rigid lens said membrane; flexible sealing means for retaining said transparent liquid between said rigid lens and said membrane; and variable spacing means acting between said rigid lens and said membrane support member for adjusting the spac 5,668, ing between said membrane support member and said rigid lens, said membrane support member and said rigid lens being hingedly connected, and said variable spacing means acting between said membrane support and said rigid lens remote from said hinge. 8. A variable focal length lens as recited in claim 7 wherein said surface of said membrane Support member is convexly shaped. 9. A variable focal length lens as recited in claim 8 where said central portion of said membrane support is transparent and has substantially the same refractive index as said transparent liquid.
10 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CERTFCATE OF CORRECTION PATENT NO. : 5,668,620 DATED September 16, 1997 NVENTOR(S) : Stephen Kurtin, et. al. it is certified that error appears in the above-identified patent and that said Letters Patent is hereby corrected as shown below: On title page, item (76) should read as follows: --Stephen Kurtin, 3835 Kingswood Rd., and Saul Epstein, Deervale Pl, both of Sherman Oaks, Calif Attest. Signed and Sealed this Sixteenth Day of December, 1997 (Sue (eam BRUCE LEHMAN Attesting Officer Connissioner of Patents and Trademarks
United States Patent (19) Prizzi
 United States Patent (19) Prizzi (54) TOWEL HOLDER 76 Inventor: Darin Prizzi, 8416 Mantanzas Rd., Fort Myers, Fla. 33912 (21) Appl. No.: 491,820 (22 Filed: Jun. 19, 1995 (51) Int. Cl.... A47H 13/00 (52)
United States Patent (19) Prizzi (54) TOWEL HOLDER 76 Inventor: Darin Prizzi, 8416 Mantanzas Rd., Fort Myers, Fla. 33912 (21) Appl. No.: 491,820 (22 Filed: Jun. 19, 1995 (51) Int. Cl.... A47H 13/00 (52)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,752,496 B2
 USOO6752496 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,752,496 B2 Conner (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 22, 2004 (54) PLASTIC FOLDING AND TELESCOPING 5,929.966 A * 7/1999 Conner... 351/118 EYEGLASS
USOO6752496 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,752,496 B2 Conner (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 22, 2004 (54) PLASTIC FOLDING AND TELESCOPING 5,929.966 A * 7/1999 Conner... 351/118 EYEGLASS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,663,057 B2
 USOO6663057B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,663,057 B2 Garelick et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADJUSTABLE PEDESTAL FOR BOAT 5,297.849 A * 3/1994 Chancellor... 297/344.
USOO6663057B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,663,057 B2 Garelick et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADJUSTABLE PEDESTAL FOR BOAT 5,297.849 A * 3/1994 Chancellor... 297/344.
United States Patent [15] 3,650,496 Svensson (45) Mar. 21, 1972
![United States Patent [15] 3,650,496 Svensson (45) Mar. 21, 1972 United States Patent [15] 3,650,496 Svensson (45) Mar. 21, 1972](/thumbs/91/105347464.jpg) United States Patent [15] 3,650,496 Svensson (45) Mar. 21, 1972 54. FOLDING FNS FOR MESSELES 3,273,500 9/1966 Kongelbeck... 244/3.28 (72) Inventor: Nils-Åke Birger Svensson, Karlskoga, Primary Examiner-Verlin
United States Patent [15] 3,650,496 Svensson (45) Mar. 21, 1972 54. FOLDING FNS FOR MESSELES 3,273,500 9/1966 Kongelbeck... 244/3.28 (72) Inventor: Nils-Åke Birger Svensson, Karlskoga, Primary Examiner-Verlin
April 1, 1969 W. JONAs ET AL 3,435,988. PAPER Cup DISPENSER. Filed March 20, 1968 Sheet / of 2 N S. INVENTORs WALTER JONAS. ADOLF PFUND. ATTORNEY.
 April 1, 1969 W. JONAs ET AL. PAPER Cup DISPENSER Filed March 20, 1968 Sheet / of 2 N S. N ) INVENTORs WALTER JONAS. ADOLF PFUND. ATTORNEY. April 1, 1969 filed March 20, 1968 Sºzzzzzzzz!,, ~~~~ FIG 5.
April 1, 1969 W. JONAs ET AL. PAPER Cup DISPENSER Filed March 20, 1968 Sheet / of 2 N S. N ) INVENTORs WALTER JONAS. ADOLF PFUND. ATTORNEY. April 1, 1969 filed March 20, 1968 Sºzzzzzzzz!,, ~~~~ FIG 5.
IN THE UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD
 IN THE UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD In re U.S. Patent No. 8,708,487 B2 Filed: September 4, 2013 Issued: April 29, 2014 Inventor: Assignee: Title: Stephen
IN THE UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD In re U.S. Patent No. 8,708,487 B2 Filed: September 4, 2013 Issued: April 29, 2014 Inventor: Assignee: Title: Stephen
III IIII. United States Patent (19) Hamilton et al. application of welds thereto for attaching the hub member to
 United States Patent (19) Hamilton et al. 54) EARTH SCREW ANCHOR ASSEMBLY HAVING ENHANCED PENETRATING CAPABILITY (75) Inventors: Daniel V. Hamilton; Robert M. Hoyt, both of Centralia; Patricia J. Halferty,
United States Patent (19) Hamilton et al. 54) EARTH SCREW ANCHOR ASSEMBLY HAVING ENHANCED PENETRATING CAPABILITY (75) Inventors: Daniel V. Hamilton; Robert M. Hoyt, both of Centralia; Patricia J. Halferty,
Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner. Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green
 III United States Patent (19) 11) US005230172A Patent Number: 5,230,172 Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 1993 54 PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner o Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green 76)
III United States Patent (19) 11) US005230172A Patent Number: 5,230,172 Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 1993 54 PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner o Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green 76)
United States Patent (19) Lieber
 United States Patent (19) Lieber 54 76 (21) 22 51 (52) 58) NOISE REDUCTION DEVICE FOR IMPACT TOOLS Inventor: Raymond S. Lieber, 1105 Alumni Ave., Las Cruces, N. Mex. 88003 Appl. No.: 676,878 Filed: Apr.
United States Patent (19) Lieber 54 76 (21) 22 51 (52) 58) NOISE REDUCTION DEVICE FOR IMPACT TOOLS Inventor: Raymond S. Lieber, 1105 Alumni Ave., Las Cruces, N. Mex. 88003 Appl. No.: 676,878 Filed: Apr.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,393,712 B1
 USOO6393712B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Jan SSOn (45) Date of Patent: May 28, 2002 (54) GRINDING JIG FOR GRINDING GOUGE 277,882 A 5/1883 Carr... 451/369 CHSELS 494,893 A 4/1893 Ross, Jr....
USOO6393712B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Jan SSOn (45) Date of Patent: May 28, 2002 (54) GRINDING JIG FOR GRINDING GOUGE 277,882 A 5/1883 Carr... 451/369 CHSELS 494,893 A 4/1893 Ross, Jr....
IIII. United States Patent 19 Delorme. 11 Patent Number: 5,894,701 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 20, Attorney, Agent, or Firn-Swabey Ogilvy Renault
 United States Patent 19 Delorme 54) WOODEN MODULARPANELING FOR INTERFOR DECORATION 76 Inventor: Claude Delorme, 9141 Pierre Elliott Trudeau, St-Léonard, Québec, Canada, HR 3WA. 21 Appl. No.: 08/910,667
United States Patent 19 Delorme 54) WOODEN MODULARPANELING FOR INTERFOR DECORATION 76 Inventor: Claude Delorme, 9141 Pierre Elliott Trudeau, St-Léonard, Québec, Canada, HR 3WA. 21 Appl. No.: 08/910,667
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090249965A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0249965 A1 Hauser (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIT REMOVER (75) Inventor: Lawrence M. Hauser, Auburn, WA (US) Correspondence
(19) United States US 20090249965A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0249965 A1 Hauser (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIT REMOVER (75) Inventor: Lawrence M. Hauser, Auburn, WA (US) Correspondence
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Roy et al. USOO6216409 B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,216,409 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 17, 2001 (54) CLADDING PANEL FOR FLOORS, WALLS OR THE LIKE (76) Inventors: Valerie Roy, 13,
(12) United States Patent Roy et al. USOO6216409 B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,216,409 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 17, 2001 (54) CLADDING PANEL FOR FLOORS, WALLS OR THE LIKE (76) Inventors: Valerie Roy, 13,
(12) United States Patent
 US008393237B2 (12) United States Patent Arenz et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 12, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) DRIVING DEVICE FOR A HATCH INA MOTOR VEHICLE
US008393237B2 (12) United States Patent Arenz et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 12, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) DRIVING DEVICE FOR A HATCH INA MOTOR VEHICLE
United States Patent (19) Blackburn et al.
 United States Patent (19) Blackburn et al. 11 Patent Number: (4) Date of Patent: 4,21,042 Jun. 4, 198 4 THREADED CONNECTION 7) Inventors: Jan W. Blackburn, Kingwood; Burl E. Baron, Houston, both of Tex.
United States Patent (19) Blackburn et al. 11 Patent Number: (4) Date of Patent: 4,21,042 Jun. 4, 198 4 THREADED CONNECTION 7) Inventors: Jan W. Blackburn, Kingwood; Burl E. Baron, Houston, both of Tex.
United States Patent (19) Schoonover et al.
 United States Patent (19) Schoonover et al. (54) 76 (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) 56) FLUID CONTAINER Inventors: Michael I. Schoonover, 1218 W. Atherton, Flint, Mich. 48507; James A. McFadden, 504 Kingswood,
United States Patent (19) Schoonover et al. (54) 76 (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) 56) FLUID CONTAINER Inventors: Michael I. Schoonover, 1218 W. Atherton, Flint, Mich. 48507; James A. McFadden, 504 Kingswood,
Warp length compensator for a triaxial weaving machine
 United States Patent: 4,170,249 2/15/03 8:18 AM ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 4,170,249 Trost October 9, 1979 Warp length compensator for a triaxial weaving machine Abstract A fixed cam located between
United States Patent: 4,170,249 2/15/03 8:18 AM ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 4,170,249 Trost October 9, 1979 Warp length compensator for a triaxial weaving machine Abstract A fixed cam located between
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,650,825 B1
 USOO7650825B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 26, 2010 (54) CASE TRIMMER AND CHAMFER TOOL 4.325,282 A 4, 1982 Schaenzer... 86,24 4.385,546 A 5/1983 Lee...
USOO7650825B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 26, 2010 (54) CASE TRIMMER AND CHAMFER TOOL 4.325,282 A 4, 1982 Schaenzer... 86,24 4.385,546 A 5/1983 Lee...
(12) United States Patent
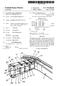 (12) United States Patent US007793.996 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.793,996 B2 Karlander (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2010 (54) CRASH BOX AND A METHOD OF (58) Field of Classification Search... 296/18703,
(12) United States Patent US007793.996 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.793,996 B2 Karlander (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2010 (54) CRASH BOX AND A METHOD OF (58) Field of Classification Search... 296/18703,
United States Patent
 United States Patent This PDF file contains a digital copy of a United States patent that relates to the Native American Flute. It is part of a collection of Native American Flute resources available at
United States Patent This PDF file contains a digital copy of a United States patent that relates to the Native American Flute. It is part of a collection of Native American Flute resources available at
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,156,854 B2
 US007 156854B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,156,854 B2 BrOWn et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2007 (54) LENS DELIVERY SYSTEM 5,944,725 A * 8/1999 Cicenas et al.... 606/107 6,241,737
US007 156854B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,156,854 B2 BrOWn et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2007 (54) LENS DELIVERY SYSTEM 5,944,725 A * 8/1999 Cicenas et al.... 606/107 6,241,737
United States Patent 19) 11 Patent Number: 5,442,436 Lawson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 1995
 I () US005442436A United States Patent 19) 11 Patent Number: Lawson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 1995 54 REFLECTIVE COLLIMATOR 4,109,304 8/1978 Khvalovsky et al.... 362/259 4,196,461 4/1980 Geary......
I () US005442436A United States Patent 19) 11 Patent Number: Lawson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 1995 54 REFLECTIVE COLLIMATOR 4,109,304 8/1978 Khvalovsky et al.... 362/259 4,196,461 4/1980 Geary......
United States Patent (19) Van Halen
 United States Patent (19) Van Halen 11) () Patent Number: Date of Patent: Apr. 14, 1987 54 MUSICAL INSTRUMENT SUPPORT 76 Inventor: Edward L. Van Halen, 1900 Ave. of Stars #1780, Los Angeles, Calif. 90067
United States Patent (19) Van Halen 11) () Patent Number: Date of Patent: Apr. 14, 1987 54 MUSICAL INSTRUMENT SUPPORT 76 Inventor: Edward L. Van Halen, 1900 Ave. of Stars #1780, Los Angeles, Calif. 90067
United States Patent (19) Lin
 United States Patent (19) Lin 11) 45) Dec. 22, 1981 54) (76) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) (56) BUILDING BLOCK SET Inventor: Wen-Ping Lin, 30, Chien-Yung St., Taichung, Taiwan Appl. No.: 187,618 Filed: Sep. 15,
United States Patent (19) Lin 11) 45) Dec. 22, 1981 54) (76) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) (56) BUILDING BLOCK SET Inventor: Wen-Ping Lin, 30, Chien-Yung St., Taichung, Taiwan Appl. No.: 187,618 Filed: Sep. 15,
United States Patent (19) Shahan
 United States Patent (19) Shahan 54, HEAVY DUTY SHACKLE 75 Inventor: James B. Shahan, Tulsa, Okla. (73) Assignee: American Hoist & Derrick Company, Tulsa, Okla. (21) Appl. No.: 739,056 22 Filed: Nov. 5,
United States Patent (19) Shahan 54, HEAVY DUTY SHACKLE 75 Inventor: James B. Shahan, Tulsa, Okla. (73) Assignee: American Hoist & Derrick Company, Tulsa, Okla. (21) Appl. No.: 739,056 22 Filed: Nov. 5,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,876 B1
 USOO6385876B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: McKenzie () Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) LOCKABLE LICENSE PLATE COVER 2,710,475 A 6/1955 Salzmann... /202 ASSEMBLY 3,304,642 A 2/1967 Dardis...
USOO6385876B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: McKenzie () Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) LOCKABLE LICENSE PLATE COVER 2,710,475 A 6/1955 Salzmann... /202 ASSEMBLY 3,304,642 A 2/1967 Dardis...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 2007025 1096A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0251096 A1 Smith (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 1, 2007 (54) EGG BREAKING DEVICE INCORPORATING A DURABLE AND RUBBERIZED
(19) United States US 2007025 1096A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0251096 A1 Smith (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 1, 2007 (54) EGG BREAKING DEVICE INCORPORATING A DURABLE AND RUBBERIZED
United States Patent (19)
 US006041720A 11 Patent Number: Hardy (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 2000 United States Patent (19) 54 PRODUCT MANAGEMENT DISPLAY 5,738,019 4/1998 Parker... 108/61 X SYSTEM FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS 75 Inventor:
US006041720A 11 Patent Number: Hardy (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 2000 United States Patent (19) 54 PRODUCT MANAGEMENT DISPLAY 5,738,019 4/1998 Parker... 108/61 X SYSTEM FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS 75 Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,880,737 B2
 USOO6880737B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bauer (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) CELL PHONE HOLSTER SUBSIDIARY 5,217,294 A 6/1993 Liston STRAP AND HOLDER 5,503,316 A 4/1996 Stewart
USOO6880737B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bauer (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) CELL PHONE HOLSTER SUBSIDIARY 5,217,294 A 6/1993 Liston STRAP AND HOLDER 5,503,316 A 4/1996 Stewart
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007 172314B2 () Patent No.: Currie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 6, 2007 (54) SOLID STATE ELECTRIC LIGHT BULB (58) Field of Classification Search... 362/2, 362/7, 800, 243,
(12) United States Patent US007 172314B2 () Patent No.: Currie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 6, 2007 (54) SOLID STATE ELECTRIC LIGHT BULB (58) Field of Classification Search... 362/2, 362/7, 800, 243,
Y 6a W SES. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States. Belinda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov.
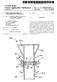 (19) United States US 2005O2521.52A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Belinda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 17, 2005 (54) STEELTRUSS FASTENERS FOR MULTI-POSITIONAL INSTALLATION (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O2521.52A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Belinda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 17, 2005 (54) STEELTRUSS FASTENERS FOR MULTI-POSITIONAL INSTALLATION (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120047754A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047754 A1 Schmitt (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2012 (54) ELECTRICSHAVER (52) U.S. Cl.... 30/527 (57) ABSTRACT
US 20120047754A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047754 A1 Schmitt (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2012 (54) ELECTRICSHAVER (52) U.S. Cl.... 30/527 (57) ABSTRACT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
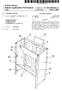 US 20030085640A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085640 A1 Chan (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) FOLDABLE CABINET Publication Classification (76) Inventor:
US 20030085640A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085640 A1 Chan (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) FOLDABLE CABINET Publication Classification (76) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2
 USOO6543599B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2 Jasinetzky (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) STEP FOR ESCALATORS 5,810,148 A * 9/1998 Schoeneweiss... 198/333 6,398,003 B1
USOO6543599B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2 Jasinetzky (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) STEP FOR ESCALATORS 5,810,148 A * 9/1998 Schoeneweiss... 198/333 6,398,003 B1
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,076,665 Petersen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 1991
 United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Petersen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 1991 (54 COMPUTER SCREEN MONITOR OPTIC 4,253,737 3/1981 Thomsen et al.... 350/276 R RELEF DEVICE 4,529,268 7/1985 Brown...
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Petersen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 1991 (54 COMPUTER SCREEN MONITOR OPTIC 4,253,737 3/1981 Thomsen et al.... 350/276 R RELEF DEVICE 4,529,268 7/1985 Brown...
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Sternbergh 54 75 73 21 22 63 51 52 58 56 MULTILAYER ANT-REFLECTIVE AND ULTRAWOLET BLOCKNG COATNG FOR SUNGLASSES Inventor: James H. Sternbergh, Webster, N.Y. Assignee: Bausch &
United States Patent (19) Sternbergh 54 75 73 21 22 63 51 52 58 56 MULTILAYER ANT-REFLECTIVE AND ULTRAWOLET BLOCKNG COATNG FOR SUNGLASSES Inventor: James H. Sternbergh, Webster, N.Y. Assignee: Bausch &
United States Patent (19) Lund
 United States Patent (19) Lund 54 BROACHING CUTTER 76 Inventor: David R. Lund, 1823 Cornish Ave., Charleston, S.C. 29412 21 Appl. No.: 903,157 22 Filed: Jul. 30, 1997 Related U.S. Application Data 62 Division
United States Patent (19) Lund 54 BROACHING CUTTER 76 Inventor: David R. Lund, 1823 Cornish Ave., Charleston, S.C. 29412 21 Appl. No.: 903,157 22 Filed: Jul. 30, 1997 Related U.S. Application Data 62 Division
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130270214A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0270214 A1 Huels et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2013 54) BOTTOM STRUCTURE FOR A PLASTC 3O Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20130270214A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0270214 A1 Huels et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2013 54) BOTTOM STRUCTURE FOR A PLASTC 3O Foreign Application
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A Approved for Public Release Distribution Unlimited
 Serial Number 09/152.477 Filing Date 11 September 1998 Inventor Anthony A. Ruffa NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed
Serial Number 09/152.477 Filing Date 11 September 1998 Inventor Anthony A. Ruffa NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed
United States Patent (19) Lacombe
 United States Patent (19) Lacombe (54) SPACER FOR GLASS SEALED UNT AND INTERLOCK MEMBER THEREFOR (75) Inventor: Gaetan Y. Lacombe, Duvernay, Canada 73 Assignee: D. C. Glass Limited, Anjou, Canada 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Lacombe (54) SPACER FOR GLASS SEALED UNT AND INTERLOCK MEMBER THEREFOR (75) Inventor: Gaetan Y. Lacombe, Duvernay, Canada 73 Assignee: D. C. Glass Limited, Anjou, Canada 21 Appl.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Berweiler USOO6328358B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) COVER PART LOCATED WITHIN THE BEAM PATH OF A RADAR (75) Inventor: Eugen Berweiler, Aidlingen (DE) (73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent Berweiler USOO6328358B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) COVER PART LOCATED WITHIN THE BEAM PATH OF A RADAR (75) Inventor: Eugen Berweiler, Aidlingen (DE) (73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,386,952 B1
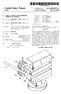 USOO6386952B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,386,952 B1 White (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) SINGLE STATION BLADE SHARPENING 2,692.457 A 10/1954 Bindszus METHOD AND APPARATUS 2,709,874
USOO6386952B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,386,952 B1 White (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) SINGLE STATION BLADE SHARPENING 2,692.457 A 10/1954 Bindszus METHOD AND APPARATUS 2,709,874
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,612,223 B2. Leonard et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 2003
 USOO6612223B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,612,223 B2 Leonard et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 2003 (54) PNEUMATIC ACTUATOR 5,178,367 A * 1/1993 Vaughen... 254/93 HP 5,461.207 A 10/1995
USOO6612223B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,612,223 B2 Leonard et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 2003 (54) PNEUMATIC ACTUATOR 5,178,367 A * 1/1993 Vaughen... 254/93 HP 5,461.207 A 10/1995
don, G.B. U.S. P. DOCUMENTS spaced by an air gap from the collecting lens. The widths of
 United States Patent (19) Wartmann III US005708532A 11 Patent Number: 5,708,532 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 13, 1998 (54) DOUBLE-SIDED TELECENTRC 573790 11/1977 U.S.S.R... 359/663 MEASUREMENT OBJECTIVE 1 248
United States Patent (19) Wartmann III US005708532A 11 Patent Number: 5,708,532 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 13, 1998 (54) DOUBLE-SIDED TELECENTRC 573790 11/1977 U.S.S.R... 359/663 MEASUREMENT OBJECTIVE 1 248
N St. Els"E"" (4) Atomy, Agent, or Firm Steina Brunda Garred &
 USOO6536045B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Wilson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 25, 2003 (54) TEAR-OFF OPTICAL STACK HAVING 4,716,601. A 1/1988 McNeal... 2/434 PERPHERAL SEAL MOUNT 5,420,649
USOO6536045B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Wilson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 25, 2003 (54) TEAR-OFF OPTICAL STACK HAVING 4,716,601. A 1/1988 McNeal... 2/434 PERPHERAL SEAL MOUNT 5,420,649
IIH. United States Patent (19) Chen. (11) Patent Number: 5,318,090 (45. Date of Patent: Jun. 7, 1994
 United States Patent (19) Chen 54) ROLLER ASSEMBLY FORVENETIAN BLIND 76 Inventor: Cheng-Hsiung Chen, No. 228, Sec. 2, Chung-Te Rd., Taichung City, Taiwan 21 Appl. No.: 60,278 22 Filed: May 11, 1993 51)
United States Patent (19) Chen 54) ROLLER ASSEMBLY FORVENETIAN BLIND 76 Inventor: Cheng-Hsiung Chen, No. 228, Sec. 2, Chung-Te Rd., Taichung City, Taiwan 21 Appl. No.: 60,278 22 Filed: May 11, 1993 51)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,189,225 B1
 USOO6189225B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,189,225 B1 Jan SSOn (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 20, 2001 (54) ANGLE GAUGE FOR GRINDING SHARP- 2,468.395 4/1949 Fredin... 33/628 EDGED TOOLS
USOO6189225B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,189,225 B1 Jan SSOn (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 20, 2001 (54) ANGLE GAUGE FOR GRINDING SHARP- 2,468.395 4/1949 Fredin... 33/628 EDGED TOOLS
4/ /hoe 2eceolónzee-zee-ee. E 6 Ée, S. 2&772zz, z/7%zz. J422/s, Feb. 22, s. MANDL 2,108,866. Avezzr. Filed April 17, Sheets-Sheet l. 2.
 Feb. 22, 1938. s. MANDL SOCKET WRENCH Filed April 17, 1936 2 Sheets-Sheet l. Se E 6 Ée, S. 2.72 N NS s Na w Avezzr. 2&772zz, z/7%zz 4/ /hoe 2eceolónzee-zee-ee J422/s, Feb. 22, 1938. S. MAND SOCKET WRENCH
Feb. 22, 1938. s. MANDL SOCKET WRENCH Filed April 17, 1936 2 Sheets-Sheet l. Se E 6 Ée, S. 2.72 N NS s Na w Avezzr. 2&772zz, z/7%zz 4/ /hoe 2eceolónzee-zee-ee J422/s, Feb. 22, 1938. S. MAND SOCKET WRENCH
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Parvin USOO6254209B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,254,209 B1 (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 3, 2001 (54) DRAWER SLIDE FLOATING BUMPER DETENT (75) Inventor: Jackie D. Parvin, Pomona, CA (US)
(12) United States Patent Parvin USOO6254209B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,254,209 B1 (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 3, 2001 (54) DRAWER SLIDE FLOATING BUMPER DETENT (75) Inventor: Jackie D. Parvin, Pomona, CA (US)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,571,916 B1. Swanson 45) Date of Patent: Jun. 3, 2003
 USOO6571916B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,571,916 B1 Swanson 45) Date of Patent: Jun. 3, 2003 9 (54) FULLY ADJUSTABLE HUNTING TREE 5,355.974. A * 10/1994 Miller... 182/187 STAND 5.439,074
USOO6571916B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,571,916 B1 Swanson 45) Date of Patent: Jun. 3, 2003 9 (54) FULLY ADJUSTABLE HUNTING TREE 5,355.974. A * 10/1994 Miller... 182/187 STAND 5.439,074
"62/.62.6 S3 ( A/27 AAZZZ, at a fic-12 SS SN IN June 26, 1962 H. W. KUP 3,040,420. NN TÉ 2, a87-zé g-g2 SNAP RING PLIERS
 June 26, 1962 H. W. KUP 3,040,420 SNAP RING PLIERS Filed Jan. 12, l960 2. Sheets-Sheet l AZY B 4f 32 30 NN TÉ 2, a87-zé g-g2 S3 (330 25 SS SN IN 76-. 26. at 72 62 44 a fic-12 4/7 47 32. 47 Saa1 Z 7 AZ670
June 26, 1962 H. W. KUP 3,040,420 SNAP RING PLIERS Filed Jan. 12, l960 2. Sheets-Sheet l AZY B 4f 32 30 NN TÉ 2, a87-zé g-g2 S3 (330 25 SS SN IN 76-. 26. at 72 62 44 a fic-12 4/7 47 32. 47 Saa1 Z 7 AZ670
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,848,291 B1
 USOO684.8291B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,848,291 B1 Johnson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) PRESS BRAKE TOOL AND TOOL HOLDER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO684.8291B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,848,291 B1 Johnson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) PRESS BRAKE TOOL AND TOOL HOLDER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Peterson, III
 United States Patent (19) Peterson, III (54) INSULATION WINDOW 76 Inventor: O. James Peterson, III, 2841 River Oaks Drive, Midlothian, Va. 23113 (21) Appl. No.: 7,221 22 Filed: Oct. 22, 1976 5ll Int. Cl?...
United States Patent (19) Peterson, III (54) INSULATION WINDOW 76 Inventor: O. James Peterson, III, 2841 River Oaks Drive, Midlothian, Va. 23113 (21) Appl. No.: 7,221 22 Filed: Oct. 22, 1976 5ll Int. Cl?...
USOO A United States Patent 19) 11 Patent Number: 5,528,855 Kapphahn (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 25, 1996
 USOO5528855A United States Patent 19) 11 Patent Number: 5,528,855 Kapphahn (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 25, 1996 54. FOLDABLE ARTEFICIAL MULCH COVER 2832460 2/1980 Germany... 47/25 HAVING SLT INSTALLATION
USOO5528855A United States Patent 19) 11 Patent Number: 5,528,855 Kapphahn (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 25, 1996 54. FOLDABLE ARTEFICIAL MULCH COVER 2832460 2/1980 Germany... 47/25 HAVING SLT INSTALLATION
Schaeff, LLP. 22 Filed: Nov. 2, 1998 (51) Int. Cl."... B21D 51/ U.S. Cl... 72/329; 72/ Field of Search... 72/327, 328, 329, 72/348
 United States Patent Turner et al. 19 USOO607.9249A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 27, 2000 54 METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR FORMING A BEADED CAN END 75 Inventors: Stephen B. Turner, Kettering;
United States Patent Turner et al. 19 USOO607.9249A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 27, 2000 54 METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR FORMING A BEADED CAN END 75 Inventors: Stephen B. Turner, Kettering;
Nitti. United States Patent (19) Dent et al. 4,619,082. Oct. 28, Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: (21) Appl. No.
 United States Patent (19) Dent et al. 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4,619,082 Oct. 28, 1986 (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING A CONTACT LENS (75) Inventors: Michael J. Dent, Chalfont St Giles; Ian L.
United States Patent (19) Dent et al. 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4,619,082 Oct. 28, 1986 (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING A CONTACT LENS (75) Inventors: Michael J. Dent, Chalfont St Giles; Ian L.
2x2 EARCEPOST APPROVED IMPORTANT SYSA NEX2 N - May 21, 1963 T, A, SULKE 3, (ZW, Filed Aug. 28, 196l AR MAIL RUBBER STAMP DEVICE ATTORNEYS
 May 21, 1963 T, A, SULKE 3,0904 RUBBER STAMP DEVICE Filed Aug. 28, 196l AR MAIL EARCEPOST APPROVED IMPORTANT 22 SN &KNS SYSA (ZW, SS NEX2 N - 2x2 S&N 2. A Ya Ya Y A SSSSSSSSSS INVENTOR Thomas Sulkie ATTORNEYS
May 21, 1963 T, A, SULKE 3,0904 RUBBER STAMP DEVICE Filed Aug. 28, 196l AR MAIL EARCEPOST APPROVED IMPORTANT 22 SN &KNS SYSA (ZW, SS NEX2 N - 2x2 S&N 2. A Ya Ya Y A SSSSSSSSSS INVENTOR Thomas Sulkie ATTORNEYS
United States Patent (19) Achatz et al.
 United States Patent (19) Achatz et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 1989 (54) MULTIFOCAL, ESPECIALLY BIFOCAL, INTRAOCULAR, ARTIFICIAL OPHTHALMIC LENS 76) Inventors: Manfred Achatz,
United States Patent (19) Achatz et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 1989 (54) MULTIFOCAL, ESPECIALLY BIFOCAL, INTRAOCULAR, ARTIFICIAL OPHTHALMIC LENS 76) Inventors: Manfred Achatz,
United States Patent (19) 11) 3,711,874 Gajer (45) Jan. 23, 1973
 United States Patent (19) 11) 3,711,874 Gajer (45) Jan. 23, 1973 54 BASKETSINK STRAINER 3,007, 179 1/1961 Bertulli... 4/287 3,096,527 7/1963 Eynon......41287 (75) Inventor: Israel Gajer, Wyandanch, N.Y.
United States Patent (19) 11) 3,711,874 Gajer (45) Jan. 23, 1973 54 BASKETSINK STRAINER 3,007, 179 1/1961 Bertulli... 4/287 3,096,527 7/1963 Eynon......41287 (75) Inventor: Israel Gajer, Wyandanch, N.Y.
(12) United States Patent
 US007 153067B2 (12) United States Patent GreenW00d et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2006 (54) ROTARY CUTTING TOOL HAVING MULTIPLE HELICAL CUTTING EDGES WITH DIFFERING HELIX ANGLES (76)
US007 153067B2 (12) United States Patent GreenW00d et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2006 (54) ROTARY CUTTING TOOL HAVING MULTIPLE HELICAL CUTTING EDGES WITH DIFFERING HELIX ANGLES (76)
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Garcia et al. USOO6540079B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 1, 2003 (54) PRODUCT PACKAGING UNDER FILMI-SEALED SHELL (75) Inventors: Firmin Garcia, Evreux (FR); Aline
(12) United States Patent Garcia et al. USOO6540079B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 1, 2003 (54) PRODUCT PACKAGING UNDER FILMI-SEALED SHELL (75) Inventors: Firmin Garcia, Evreux (FR); Aline
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O116153A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0116153 A1 Hataguchi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2005 (54) ENCODER UTILIZING A REFLECTIVE CYLINDRICAL SURFACE
(19) United States US 2005O116153A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0116153 A1 Hataguchi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2005 (54) ENCODER UTILIZING A REFLECTIVE CYLINDRICAL SURFACE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,729,834 B1
 USOO6729834B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,729,834 B1 McKinley (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) WAFER MANIPULATING AND CENTERING 5,788,453 A * 8/1998 Donde et al.... 414/751 APPARATUS
USOO6729834B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,729,834 B1 McKinley (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) WAFER MANIPULATING AND CENTERING 5,788,453 A * 8/1998 Donde et al.... 414/751 APPARATUS
United States Patent 9 Grant
 United States Patent 9 Grant 1 l) May 8, 1973 4 7) (73) GAME BOX HAVING AMAZE Inventor: Perry J. Grant, Pacific Palisades, Calif. Assignee: Reuben B. Kamer d/b/a Reugen Klamer & Associates, Beverly Hills,
United States Patent 9 Grant 1 l) May 8, 1973 4 7) (73) GAME BOX HAVING AMAZE Inventor: Perry J. Grant, Pacific Palisades, Calif. Assignee: Reuben B. Kamer d/b/a Reugen Klamer & Associates, Beverly Hills,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Wei USOO66160O2B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,616,002 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 9, 2003 (54) BARREL WITH TRAPDOOR (75) Inventor: William J. Weil, Waverly, OH (US) (73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent Wei USOO66160O2B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,616,002 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 9, 2003 (54) BARREL WITH TRAPDOOR (75) Inventor: William J. Weil, Waverly, OH (US) (73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Dekerle 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 1991 54 NIPPLE ADAPTER FOR A BOTTLE COMPRISING ASCREW RING 75) Inventor: 73) Assignee: Benoit Dekerle, Evian, France Societe
United States Patent (19) Dekerle 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 1991 54 NIPPLE ADAPTER FOR A BOTTLE COMPRISING ASCREW RING 75) Inventor: 73) Assignee: Benoit Dekerle, Evian, France Societe
Oct. 25, ,280,665. Filed April 8, ATToRNEYs H. BLOCK. 2 Sheets-Sheet NVENTOR HAROLD BLOCK TWEEZERS
 Oct. 25, 1966 Filed April 8, 1966 H. BLOCK 2 Sheets-Sheet NVENTOR HAROLD BLOCK ATToRNEYs Oct. 25, 1966 Filed April 8, 1966 H, BLOCK 2. Sheets-Sheet 2 ZZZZZZ Taseo (7 INVENTOR HAROLD BLOCK ATTORNEYS United
Oct. 25, 1966 Filed April 8, 1966 H. BLOCK 2 Sheets-Sheet NVENTOR HAROLD BLOCK ATToRNEYs Oct. 25, 1966 Filed April 8, 1966 H, BLOCK 2. Sheets-Sheet 2 ZZZZZZ Taseo (7 INVENTOR HAROLD BLOCK ATTORNEYS United
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/40
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 372 845 A1 (43) Date of publication: 05.10.2011 Bulletin 2011/40 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 11/28 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10425105.3 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 372 845 A1 (43) Date of publication: 05.10.2011 Bulletin 2011/40 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 11/28 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10425105.3 (22) Date of filing:
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,959,246 Gretz (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 28, 1999
 USOO5959246A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,959,246 Gretz (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 28, 1999 54 ELECTRIC BOX EXTENDER AND 3,770,873 11/1973 Brown... 174/58 SUPPLEMENTAL PART 4,044,908 8/1977
USOO5959246A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,959,246 Gretz (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 28, 1999 54 ELECTRIC BOX EXTENDER AND 3,770,873 11/1973 Brown... 174/58 SUPPLEMENTAL PART 4,044,908 8/1977
United States Statutory Invention Registration (19) Feb. 28, 1996 JP Japan (51) Int. Cl... GO2B 21/ U.S. Cl...
 USOO4(OO1763B2 United States Statutory Invention Registration (19) Mizusawa 54) MICROSCOPE OBJECTIVE LENS 75 Inventor: Masayuki Mizusawa, Yokohama, Japan 73 Assignee: Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan 21
USOO4(OO1763B2 United States Statutory Invention Registration (19) Mizusawa 54) MICROSCOPE OBJECTIVE LENS 75 Inventor: Masayuki Mizusawa, Yokohama, Japan 73 Assignee: Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan 21
Optical spray painting practice and training system
 University of Northern Iowa UNI ScholarWorks Patents (University of Northern Iowa) 9-14-1999 Optical spray painting practice and training system Richard J. Klein II Follow this and additional works at:
University of Northern Iowa UNI ScholarWorks Patents (University of Northern Iowa) 9-14-1999 Optical spray painting practice and training system Richard J. Klein II Follow this and additional works at:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Mack USOO686.0488B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2005 (54) DRILL CHUCK WITH FRONT-END SHIELD (75) Inventor: Hans-Dieter Mack, Sontheim (DE) (73) Assignee: Rohm
(12) United States Patent Mack USOO686.0488B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2005 (54) DRILL CHUCK WITH FRONT-END SHIELD (75) Inventor: Hans-Dieter Mack, Sontheim (DE) (73) Assignee: Rohm
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,187,032 B1
 US008187032B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,187,032 B1 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2012 (54) GUIDED MISSILE/LAUNCHER TEST SET (58) Field of Classification Search... 439/76.1.
US008187032B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,187,032 B1 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2012 (54) GUIDED MISSILE/LAUNCHER TEST SET (58) Field of Classification Search... 439/76.1.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,805,823 B2. Sembritzky et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 2010
 US007805823B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,805,823 B2 Sembritzky et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 2010 (54) AXIAL SWAGE ALIGNMENT TOOL (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: David
US007805823B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,805,823 B2 Sembritzky et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 2010 (54) AXIAL SWAGE ALIGNMENT TOOL (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: David
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,299,109. Grondal. (45. Date of Patent: Mar. 29, a. Assistant Examiner-Alan B.
 H HHHHHHH US005299.109A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,299,109 Grondal. (45. Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 1994 (54) LED EXIT LIGHT FIXTURE 5,138,782 8/1992 Mizobe... 40/219 75) Inventor: Daniel
H HHHHHHH US005299.109A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,299,109 Grondal. (45. Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 1994 (54) LED EXIT LIGHT FIXTURE 5,138,782 8/1992 Mizobe... 40/219 75) Inventor: Daniel
United States Patent (19) Putman
 United States Patent (19) Putman 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Sep. 4, 1990 54. RHEOMETER DIE ASSEMBLY 76 Inventor: John B. Putman, 4.638 Commodore Dr., Stow, Ohio 44224 21 Appl. No.: 416,025 22
United States Patent (19) Putman 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Sep. 4, 1990 54. RHEOMETER DIE ASSEMBLY 76 Inventor: John B. Putman, 4.638 Commodore Dr., Stow, Ohio 44224 21 Appl. No.: 416,025 22
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,068,465 B2
 USOO90684-65B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Keny et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 30, 2015 (54) TURBINE ASSEMBLY USPC... 416/215, 216, 217, 218, 248, 500 See application file for complete
USOO90684-65B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Keny et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 30, 2015 (54) TURBINE ASSEMBLY USPC... 416/215, 216, 217, 218, 248, 500 See application file for complete
United States Patent (19) Green et al.
 United States Patent (19) Green et al. (54. FOLDABLE BINOCULARS 76 Inventors: John R. Green, 3105 E. Harcourt St., Compton, Calif. 90221; Charles D. Turner, 48 Eastfield Dr., Rolling Hills, Calif. 90274
United States Patent (19) Green et al. (54. FOLDABLE BINOCULARS 76 Inventors: John R. Green, 3105 E. Harcourt St., Compton, Calif. 90221; Charles D. Turner, 48 Eastfield Dr., Rolling Hills, Calif. 90274
United States Patent Wondowski
 United States Patent Wondowski 4 TWEEZER WITH ADJUSTABLE PRECISION GRIP 72 Inventor: Raymond S. Wondowski, 17 B Hampton Arms, Hightstown, N.J. 08 22 Filed: Aug. 27, 19 (21) Appl. No.: 67,312 (2) U.S. Cl...
United States Patent Wondowski 4 TWEEZER WITH ADJUSTABLE PRECISION GRIP 72 Inventor: Raymond S. Wondowski, 17 B Hampton Arms, Hightstown, N.J. 08 22 Filed: Aug. 27, 19 (21) Appl. No.: 67,312 (2) U.S. Cl...
TEPZZ _ 59 _A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2017/09
 (19) TEPZZ _ 59 _A_T (11) EP 3 135 931 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/09 (51) Int Cl.: F16C 29/06 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 16190648.2 (22)
(19) TEPZZ _ 59 _A_T (11) EP 3 135 931 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/09 (51) Int Cl.: F16C 29/06 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 16190648.2 (22)
United States Patent (19) Morita et al.
 United States Patent (19) Morita et al. - - - - - 54. TEMPLATE 75 Inventors: Shiro Morita, Sakura; Kazuo Yoshitake, Tokyo, both of Japan 73 Assignee: Yoshitake Seisakujo Co., Inc., Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl.
United States Patent (19) Morita et al. - - - - - 54. TEMPLATE 75 Inventors: Shiro Morita, Sakura; Kazuo Yoshitake, Tokyo, both of Japan 73 Assignee: Yoshitake Seisakujo Co., Inc., Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Takekuma USOO6850001B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (75) Inventor: Akira Takekuma, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: Agilent Technologies,
(12) United States Patent Takekuma USOO6850001B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (75) Inventor: Akira Takekuma, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: Agilent Technologies,
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/50
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 261 890 A1 (43) Date of publication: 15.12.20 Bulletin 20/50 (51) Int Cl.: GD 13/02 (2006.01) GH 3/14 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 160308.2 (22) Date
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 261 890 A1 (43) Date of publication: 15.12.20 Bulletin 20/50 (51) Int Cl.: GD 13/02 (2006.01) GH 3/14 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 160308.2 (22) Date
Universal mounting bracket for laser targeting and feedback system
 University of Northern Iowa UNI ScholarWorks Patents (University of Northern Iowa) 5-6-2003 Universal mounting bracket for laser targeting and feedback system Richard J. Kelin II Follow this and additional
University of Northern Iowa UNI ScholarWorks Patents (University of Northern Iowa) 5-6-2003 Universal mounting bracket for laser targeting and feedback system Richard J. Kelin II Follow this and additional
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,884,014 B2. Stone et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005
 USOO6884O14B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Stone et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) TOLERANCE COMPENSATING MOUNTING 4,682,906. A 7/1987 Ruckert et al.... 403/409.1 DEVICE 4,846,614
USOO6884O14B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Stone et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2005 (54) TOLERANCE COMPENSATING MOUNTING 4,682,906. A 7/1987 Ruckert et al.... 403/409.1 DEVICE 4,846,614
United States Patent (19) Cobb
 United States Patent (19) Cobb 54 RAM-SHEAR AND SLIP DEVICE FOR WELL PIPE 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: A. Tom Cobb, Seabrook, Tex. Continental Oil Company, Ponca City, Okla. 21 Appl. No.: 671,464 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Cobb 54 RAM-SHEAR AND SLIP DEVICE FOR WELL PIPE 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: A. Tom Cobb, Seabrook, Tex. Continental Oil Company, Ponca City, Okla. 21 Appl. No.: 671,464 22 Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050O28668A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0028668A1 Teel (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 10, 2005 (54) WRIST POSITION TRAINING ASSEMBLY (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(19) United States US 20050O28668A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0028668A1 Teel (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 10, 2005 (54) WRIST POSITION TRAINING ASSEMBLY (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,890,073 B2
 USOO6890O73B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,890,073 B2 DiChiara et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 10, 2005 (54) IMPACT RESISTANT EYE WEAR FRAME FR 592.096 4/1925 ASSEMBLY HAVING ASPLT FRAME
USOO6890O73B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,890,073 B2 DiChiara et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 10, 2005 (54) IMPACT RESISTANT EYE WEAR FRAME FR 592.096 4/1925 ASSEMBLY HAVING ASPLT FRAME
IIIHIIII. United States Patent (19) Tannenbaum
 United States Patent (19) Tannenbaum (54) ROTARY SHAKER WITH FLEXIBLE STRAP SUSPENSION 75) Inventor: Myron Tannenbaum, Cranbury, N.J. 73) Assignee: New Brunswick Scientific Co., Inc., Edison, N.J. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Tannenbaum (54) ROTARY SHAKER WITH FLEXIBLE STRAP SUSPENSION 75) Inventor: Myron Tannenbaum, Cranbury, N.J. 73) Assignee: New Brunswick Scientific Co., Inc., Edison, N.J. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,673,489 Robel 45) Date of Patent: Oct. 7, 1997
 III USOO5673489A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,673,489 Robel 45) Date of Patent: Oct. 7, 1997 54 GRIDDED MEASUREMENT SYSTEM FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS CONSTRUCTION MATER ALS 529509 6/1955
III USOO5673489A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,673,489 Robel 45) Date of Patent: Oct. 7, 1997 54 GRIDDED MEASUREMENT SYSTEM FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS CONSTRUCTION MATER ALS 529509 6/1955
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0146172 A1 Maillard et al. US 2015O146172A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (86) (30) CURVED PROJECTORSCREEN
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0146172 A1 Maillard et al. US 2015O146172A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (86) (30) CURVED PROJECTORSCREEN
Ay:44, 444-, INven TOR HARVEY R. PLUMMER. Jan. 3, 1967 H. R. PLUMMER 3,295,187. ArTws, Filed March l, Sheets-Sheet
 Jan. 3, 1967 H. R. PLUMMER Filed March l, 1965 2 Sheets-Sheet INven TOR HARVEY R. PLUMMER Ay:44, 444-, 14-42--- ArTws, Jan. 3, 1967 H. R. PUMMER Filed March 1, 1965 2. Sheets-Sheet 2 INVENTOR HARVEY R.
Jan. 3, 1967 H. R. PLUMMER Filed March l, 1965 2 Sheets-Sheet INven TOR HARVEY R. PLUMMER Ay:44, 444-, 14-42--- ArTws, Jan. 3, 1967 H. R. PUMMER Filed March 1, 1965 2. Sheets-Sheet 2 INVENTOR HARVEY R.
United States Patent 19 Clifton
 United States Patent 19 Clifton (54) TAPE MEASURING SQUARE AND ADJUSTABLE TOOL GUIDE 76 Inventor: Norman L. Clifton, 49 S. 875 West, Orem, Utah 84058-5267 21 Appl. No.: 594,082 22 Filed: Jan. 30, 1996
United States Patent 19 Clifton (54) TAPE MEASURING SQUARE AND ADJUSTABLE TOOL GUIDE 76 Inventor: Norman L. Clifton, 49 S. 875 West, Orem, Utah 84058-5267 21 Appl. No.: 594,082 22 Filed: Jan. 30, 1996
United States Patent [191
 United States Patent [191 Henning [11] Patent Number: [45] Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1988 [54] TWIST-OFF BOTTLE CAP [75] Inventor: John C. Henning, Fairfield, Ohio [73] Assignee: Product Investment Incorporated,
United States Patent [191 Henning [11] Patent Number: [45] Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1988 [54] TWIST-OFF BOTTLE CAP [75] Inventor: John C. Henning, Fairfield, Ohio [73] Assignee: Product Investment Incorporated,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.704,201 B2
 USOO7704201B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.704,201 B2 Johnson (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2010 (54) ENVELOPE-MAKING AID 3,633,800 A * 1/1972 Wallace... 223/28 4.421,500 A * 12/1983...
USOO7704201B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.704,201 B2 Johnson (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2010 (54) ENVELOPE-MAKING AID 3,633,800 A * 1/1972 Wallace... 223/28 4.421,500 A * 12/1983...
United States Patent 19
 United States Patent 19 Swayney et al. USOO5743074A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 28, 1998 54) 76) 21) 22 51 (52) 58 LAWN MOWER DECK PROTECTING DEVICE Inventors: Ernest Edward Swayney; Norman
United States Patent 19 Swayney et al. USOO5743074A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 28, 1998 54) 76) 21) 22 51 (52) 58 LAWN MOWER DECK PROTECTING DEVICE Inventors: Ernest Edward Swayney; Norman
United States Patent (19) Fries
 4, 297 0 () () United States Patent (19) Fries 4). SOLAR LIGHTING SYSTEM 76) Inventor: James E. Fries, 7860 Valley View, Apt. 242, Buena Park, Calif. 90620 (21) Appl. No.: 2,620 22 Filed: Jan. 11, 1979
4, 297 0 () () United States Patent (19) Fries 4). SOLAR LIGHTING SYSTEM 76) Inventor: James E. Fries, 7860 Valley View, Apt. 242, Buena Park, Calif. 90620 (21) Appl. No.: 2,620 22 Filed: Jan. 11, 1979
Imaging Systems for Eyeglass-Based Display Devices
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Imaging Systems for Eyeglass-Based Display Devices 6-28-2011 Jannick Rolland University of Central Florida Ozan Cakmakci University of Central Florida Find
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Imaging Systems for Eyeglass-Based Display Devices 6-28-2011 Jannick Rolland University of Central Florida Ozan Cakmakci University of Central Florida Find
March 8, 1966 F. F. STUBBS 3,238,939 WRIST SUPPORT. Zas ZZ INVENTOR aa/a 277, S7 eveas " R attoane Y
 March 8, 1966 F. F. STUBBS 3,238,939 WRIST SUPPORT Filed Feb. 23, 1965 3 Sheets-Sheet l 2 Zas ZZ 17.1- INVENTOR. 3. 27 30 22 2 22aa/a 277, S7 eveas " R. 8-7. attoane Y March 8, 1966 F. F. SUBBS 3,238,939
March 8, 1966 F. F. STUBBS 3,238,939 WRIST SUPPORT Filed Feb. 23, 1965 3 Sheets-Sheet l 2 Zas ZZ 17.1- INVENTOR. 3. 27 30 22 2 22aa/a 277, S7 eveas " R. 8-7. attoane Y March 8, 1966 F. F. SUBBS 3,238,939
11 Patent Number: 5,584,458 Rando 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 17, (56) References Cited (54) SEAERS FOR U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
 United States Patent (19) III IIHIIII USOO5584458A 11 Patent Number: 5,584,458 Rando 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 17, 1996 (56) References Cited (54) SEAERS FOR U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,926,722 5/1990 Sorensen
United States Patent (19) III IIHIIII USOO5584458A 11 Patent Number: 5,584,458 Rando 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 17, 1996 (56) References Cited (54) SEAERS FOR U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,926,722 5/1990 Sorensen
