Activity P35: Light Intensity in Double-Slit and Single-Slit Diffraction Patterns (Light Sensor, Rotary Motion Sensor)
|
|
|
- Percival Hart
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Class Date Activity P35: Light Intensity in Double-Slit and Single-Slit Diffraction Patterns (Light Sensor, Rotary Motion Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Interference P35 Diffraction.ds P58 Diffraction Patterns P58_DIFF.SWS Equipment Needed Qty Equipment Needed Qty Light Sensor (CI-6504A) 1 Diode Laser (OS-8525) 1 Rotary Motion Sensor (CI-6538) 1 Linear Translator (OS-8535) 1 Aperture Bracket (OS-8534) 1 Slit Accessory (OS-8523) 1 Basic Optics System (OS-8515) 1 What Do You Think? The wave nature of light can be investigated by studying diffraction patterns. What is diffraction and just how can the observance of diffraction patterns be used to verify the wave nature of light? Take time to answer the What Do You Think? question(s) in the Lab Report section. Background: Part One In 1801, Thomas Young obtained convincing evidence of the wave nature of light. Light from a single source falls on a slide containing two closely spaced slits. If light consists of tiny particles (or corpuscles as described by Isaac Newton), we might expect to see two bright lines on a screen placed behind the slits. Young observed a series of bright lines. Young was able to explain this result as a wave interference phenomenon. Because of diffraction, the waves leaving the two small slits spread out from the edges of the slits. This is equivalent to the interference pattern of ripples produced when two rocks are thrown into a pond. In general, the distance between slits is very small compared to the distance from the slits to the screen where the diffraction pattern is observed. The rays from the edges of the slits are essentially parallel. Constructive interference will occur on the screen when the extra distance that rays from one slit travel is a whole number of wavelengths in difference from the distance that rays from the other slit travel. Destructive interference occurs when the distance difference is a whole number of half-wavelengths. For two slits, there should be several bright points (or maxima ) of constructive interference on either side of a line that is perpendicular to the point directly between the two slits. Background: Part Two The interference pattern created when monochromatic light passes through a single slit is similar to the pattern created by a double slit, but the central maximum is measurably brighter than the maxima on either side of the pattern. Compared to the double-slit pattern, most of the light intensity is in the central maximum and very little is in the rest of the pattern. The smaller the width of the slit, the more intense the central diffraction maximum. P PASCO scientific p. 259
2 Physics Labs with Computers, Vol. 1 Student Workbook P35: Diffraction Patterns A SAFETY REMINDER Follow all safety instructions. For You To Do In Part A of this activity, use the Light Sensor to measure the intensity of the maxima in a double-slit diffraction pattern created by monochromatic laser light passing through a double-slit. Use the Rotary Motion Sensor (RMS) to measure the relative positions of the maxima in the diffraction pattern. In Part B, use the Light Sensor to measure the intensity of the maxima in a single-slit diffraction pattern created by monochromatic laser light passing through a single-slit. Use the Rotary Motion Sensor (RMS) to measure the relative positions of the maxima in the diffraction pattern. Use DataStudio or ScienceWorkshop to record and display the light intensity and the relative position of the maxima in the pattern and to plot intensity versus position. PART IA: Computer Setup Double-Slit Diffraction Pattern 1. Connect the ScienceWorkshop interface to the computer, turn on the interface, and turn on the computer. 2. Connect the Light Sensor into Analog Channel A on the interface. 3. Connect the Rotary Motion Sensor stereo phone plugs to Digital Channels 1 and Open the document titled as shown: DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) P35 Diffraction.ds P58 Diffraction Patterns P58_DIFF.SWS The DataStudio document has a Workbook display. Read the instructions in the Workbook. The ScienceWorkshop document opens with a Graph display of light intensity vs. position. Data recording is set at 50 measurements per second (50 Hz). PART IIA: Sensor Calibration & Equipment Setup Double-Slit Diffraction Pattern You do not need to calibrate the sensors. Equipment Setup 1. Mount the Diode Laser on one end of the Optics Bench. Connect the power supply to the laser. p PASCO scientific P35
3 Name Class Date 2. Place the MULTIPLE SLIT SET into the Slit Accessory holder. Mount the Slit Accessory holder in front of the Diode Laser on the bench. P PASCO scientific p. 261
4 Physics Labs with Computers, Vol. 1 Student Workbook P35: Diffraction Patterns A 3. Put the rack from the Linear Translator through the slot in the side of the Rotary Motion Sensor. Put the rack clamp onto the rack and tighten its thumbscrew. 4. Place the rack with the sensor onto the Linear Translator so the back end of the sensor rests on the upright edge of the base of the Linear Translator. Use the thumbscrews to attach the rack to the translator. 5. Remove the O ring and thumbscrew from the Rotary Motion Sensor pulley so they will not interfere with the Aperture Bracket. 6. Mount the Light Sensor onto the Aperture Bracket by screwing the Aperture Bracket post into the threaded hole on the bottom of the Light Sensor. LIGHT SENSOR LIGHT SENSOR p PASCO scientific P35
5 Name Class Date 7. Put the post into the rod clamp on the end of the Rotary Motion Sensor. Tighten the rod clamp thumbscrew to hold the Aperture Bracket and Light Sensor in place. 8. Turn on the power switch on the back of the Diode Laser. Adjust the position of the laser and the MULTIPLE SLIT SET on the Slit Accessory so that the laser beam passes through one of the double-slit pairs on the SLIT SET and forms a clear, horizontal diffraction pattern on the white screen of the Aperture Bracket. Light Sensor Diode Laser Rotary Motion Sensor Slit Accessory 9. Record the slit width a and slit spacing d of the double-slit pattern you use in the Lab Report section. 10. Rotate the Aperture Disk on the front of the Aperture Bracket until the narrowest slit is in front of the Light Sensor opening. Preparing to Record Data Before recording any data for later analysis, you should experiment with the Rotary Motion Sensor and Light Sensor setup. Move the Rotary Motion Sensor/Light Sensor along the rack until the maximum at one edge of the diffraction pattern is next to the slit in front of the Light Sensor. Begin recording data. Slowly and smoothly, move the Rotary Motion Sensor/Light Sensor so that the maxima of the diffraction pattern move across the slit on the Aperture Disk. When the entire interference pattern has been measured, stop recording data. Run #1 will appear in the Data List. Rescale the Graph to fit the data. Examine the plot of light intensity versus position.. Erase your data. Select Run #1 in the Data List and press the Delete key on the keyboard. PART IIIA: Data Recording Double-Slit Diffraction Pattern Move the Rotary Motion Sensor/Light Sensor along the rack until the maximum at one edge of the diffraction pattern is next to the slit in front of the Light Sensor. P PASCO scientific p. 263
6 Physics Labs with Computers, Vol. 1 Student Workbook P35: Diffraction Patterns A 1. Begin recording data. 2. Slowly and smoothly, move the Rotary Motion Sensor/Light Sensor so that the maxima of the diffraction pattern move across the slit on the Aperture Disk. 3. When the entire diffraction pattern has been measured, stop recording data. p PASCO scientific P35
7 Name Class Date PART IB: Computer Setup Single-Slit Diffraction Pattern Use the same computer setup as in Part A. PART IIB: Sensor Calibration & Equipment Setup Single-Slit Diffraction Pattern 1. Replace the MULTIPLE SLIT SET with the SINGLE SLIT SET on the Slit Accessory Holder. 2. Record the slit width a of the single-slit pattern you use in the Lab Report section. 3. Re-align the laser beam with one of the single slits on the SINGLE SLIT SET. Adjust the positions of the laser and the Rotary Motion Sensor/Light Sensorif necessary so that the diffraction pattern is at the same height for the double-slit. PART IIIB: Data Recording Single-Slit Diffraction Pattern 1. Repeat the procedure for collecting data as in Part A. Run #2 will appear in the Data List in the Experiment Setup window. 2. Turn off the laser. Analyzing the Data 1. Rescale the Graph to fit the data. 2. Examine the shape of the plots of light intensity versus position for both the double-slit and the single-slit patterns. In ScienceWorkshop, the Graph will display the most recent run of data. Use the Add Plot Menu to create a second plot on the Graph. Click the Add Plot Menu button ( ) and select Analog A, Intensity from the Add Plot Menu. Both plots will show the most recent run (Run #2) of data. Use the DATA Menu in the top plot of the Graph to display Run #1. Click the DATA Menu button ( ) in the top plot of the Graph. Select No Data to clear Run #2. Click the DATA Menu button again and select Run #1. Result: The top plot will display Run #1 and the bottom plot will display Run #2. P PASCO scientific p. 265
8 Physics Labs with Computers, Vol. 1 Student Workbook P35: Diffraction Patterns A p PASCO scientific P35
9 Name Class Date Lab Report - Activity P58: Diffraction Patterns What Do You Think? The wave nature of light can be investigated by studying diffraction patterns. What is diffraction and just how can the observance of diffraction patterns be used to verify the wave nature of light? Data Part A Double-slit Part B Single-Slit Question Slit Width (a) Slit Spacing (d) 1. How does the plot of light intensity versus position for the double-slit diffraction pattern compare to the plot of light intensity versus position for the single-slit diffraction pattern? P PASCO scientific p. 267
10 Physics Labs with Computers, Vol. 1 Student Workbook P35: Diffraction Patterns A p PASCO scientific P35
Experiment P58: Light Intensity in Double-Slit and Single-Slit Diffraction Patterns (Light Sensor, Rotary Motion Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P58-1 Experiment P58: Light Intensity in Double-Slit and Single-Slit Diffraction Patterns (Light Sensor, Rotary Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P58-1 Experiment P58: Light Intensity in Double-Slit and Single-Slit Diffraction Patterns (Light Sensor, Rotary Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh
Single-Slit Diffraction. = m, (Eq. 1)
 Single-Slit Diffraction Experimental Objectives To observe the interference pattern formed by monochromatic light passing through a single slit. Compare the diffraction patterns of a single-slit and a
Single-Slit Diffraction Experimental Objectives To observe the interference pattern formed by monochromatic light passing through a single slit. Compare the diffraction patterns of a single-slit and a
Activity P07: Acceleration of a Cart (Acceleration Sensor, Motion Sensor)
 Name Class Date Activity P07: Acceleration of a Cart (Acceleration Sensor, Motion Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Linear motion P07 Accelerate Cart.ds (See end of
Name Class Date Activity P07: Acceleration of a Cart (Acceleration Sensor, Motion Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Linear motion P07 Accelerate Cart.ds (See end of
Single Slit Diffraction
 PC1142 Physics II Single Slit Diffraction 1 Objectives Investigate the single-slit diffraction pattern produced by monochromatic laser light. Determine the wavelength of the laser light from measurements
PC1142 Physics II Single Slit Diffraction 1 Objectives Investigate the single-slit diffraction pattern produced by monochromatic laser light. Determine the wavelength of the laser light from measurements
Experiment 10. Diffraction and interference of light
 Experiment 10. Diffraction and interference of light 1. Purpose Perform single slit and Young s double slit experiment by using Laser and computer interface in order to understand diffraction and interference
Experiment 10. Diffraction and interference of light 1. Purpose Perform single slit and Young s double slit experiment by using Laser and computer interface in order to understand diffraction and interference
Activity P56: Transistor Lab 2 Current Gain: The NPN Emitter-Follower Amplifier (Power Output, Voltage Sensor)
 Activity P56: Transistor Lab 2 Current Gain: The NPN Emitter-Follower Amplifier (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Semiconductors P56 Emitter
Activity P56: Transistor Lab 2 Current Gain: The NPN Emitter-Follower Amplifier (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Semiconductors P56 Emitter
Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System OS-8537 and OS-8539
 GAIN 1 10 Instruction Manual with Experiment Guide and Teachers Notes 012-06575C *012-06575* Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System OS-8537 and OS-8539 100 CI-6604A LIGHT SENSOR POLARIZER
GAIN 1 10 Instruction Manual with Experiment Guide and Teachers Notes 012-06575C *012-06575* Educational Spectrophotometer Accessory Kit and System OS-8537 and OS-8539 100 CI-6604A LIGHT SENSOR POLARIZER
EDUCATIONAL SPECTROPHOTOMETER ACCESSORY KIT AND EDUCATIONAL SPECTROPHOTOMETER SYSTEM
 GAIN 1 10 100 Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model OS-8537 and OS-8539 012-06575A 3/98 EDUCATIONAL SPECTROPHOTOMETER ACCESSORY KIT AND EDUCATIONAL SPECTROPHOTOMETER SYSTEM
GAIN 1 10 100 Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model OS-8537 and OS-8539 012-06575A 3/98 EDUCATIONAL SPECTROPHOTOMETER ACCESSORY KIT AND EDUCATIONAL SPECTROPHOTOMETER SYSTEM
Activity P40: Driven Harmonic Motion - Mass on a Spring (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor, Power Amplifier)
 Name Class Date Activity P40: Driven Harmonic Motion - Mass on a Spring (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor, Power Amplifier) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Harmonic motion P40
Name Class Date Activity P40: Driven Harmonic Motion - Mass on a Spring (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor, Power Amplifier) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Harmonic motion P40
Activity P52: LRC Circuit (Voltage Sensor)
 Activity P52: LRC Circuit (Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) AC circuits P52 LRC Circuit.DS (See end of activity) (See end of activity) Equipment Needed Qty
Activity P52: LRC Circuit (Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) AC circuits P52 LRC Circuit.DS (See end of activity) (See end of activity) Equipment Needed Qty
POLARIZATION ANALYZER
 nstruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model OS-8533A 012-09200A POLARZATON ANALYZER Polarization Analyzer @ 2005 PASCO scientific, :/: SCentfc,@ 10101 Foothilfs Blvd' Roseviile,
nstruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model OS-8533A 012-09200A POLARZATON ANALYZER Polarization Analyzer @ 2005 PASCO scientific, :/: SCentfc,@ 10101 Foothilfs Blvd' Roseviile,
Physics 248 Spring 2009 Lab 1: Interference and Diffraction
 Name Section Physics 248 Spring 2009 Lab 1: Interference and Diffraction Your TA will use this sheet to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. You must clearly explain your reasoning
Name Section Physics 248 Spring 2009 Lab 1: Interference and Diffraction Your TA will use this sheet to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. You must clearly explain your reasoning
Activity P55: Transistor Lab 1 The NPN Transistor as a Digital Switch (Power Output, Voltage Sensor)
 Activity P55: Transistor Lab 1 The NPN Transistor as a Digital Switch (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Semiconductors P55 Digital Switch.DS
Activity P55: Transistor Lab 1 The NPN Transistor as a Digital Switch (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Semiconductors P55 Digital Switch.DS
Experiment P31: Waves on a String (Power Amplifier)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P31-1 Experiment P31: (Power Amplifier) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file Waves 45 m 700 P31 P31_WAVE.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED Interface Pulley
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P31-1 Experiment P31: (Power Amplifier) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file Waves 45 m 700 P31 P31_WAVE.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED Interface Pulley
Activity P51: LR Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor)
 Activity P51: LR Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Circuits P51 LR Circuit.DS (See end of activity) (See end of activity) Equipment Needed
Activity P51: LR Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Circuits P51 LR Circuit.DS (See end of activity) (See end of activity) Equipment Needed
Experiment P11: Newton's Second Law Constant Force (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P11-1 Experiment P11: Newton's Second Law Constant Force (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file Newton s Laws 30 m 500
PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P11-1 Experiment P11: Newton's Second Law Constant Force (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file Newton s Laws 30 m 500
Experiment P55: Light Intensity vs. Position (Light Sensor, Motion Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P55-1 Experiment P55: (Light Sensor, Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file illuminance 30 m 500/700 P55 Light vs. Position P55_LTVM.SWS
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P55-1 Experiment P55: (Light Sensor, Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file illuminance 30 m 500/700 P55 Light vs. Position P55_LTVM.SWS
Teacher s Guide - Activity P51: LR Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor)
 Teacher s Guide - Activity P51: LR Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Circuits P51 LR Circuit.DS (See end of activity) (See end of activity)
Teacher s Guide - Activity P51: LR Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Circuits P51 LR Circuit.DS (See end of activity) (See end of activity)
Experiment P24: Motor Efficiency (Photogate, Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P24-1 Experiment P24: Motor Efficiency (Photogate, Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh File Windows File energy 30 m 700 P24 Motor
PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P24-1 Experiment P24: Motor Efficiency (Photogate, Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh File Windows File energy 30 m 700 P24 Motor
Activity P57: Transistor Lab 3 Common-Emitter Amplifier (Voltage Sensor)
 Activity P57: Transistor Lab 3 Common-Emitter Amplifier (Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Semiconductors P57 Common Emitter.DS (See end of activity) (See end
Activity P57: Transistor Lab 3 Common-Emitter Amplifier (Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Semiconductors P57 Common Emitter.DS (See end of activity) (See end
Spectroscopy Lab 2. Reading Your text books. Look under spectra, spectrometer, diffraction.
 1 Spectroscopy Lab 2 Reading Your text books. Look under spectra, spectrometer, diffraction. Consult Sargent Welch Spectrum Charts on wall of lab. Note that only the most prominent wavelengths are displayed
1 Spectroscopy Lab 2 Reading Your text books. Look under spectra, spectrometer, diffraction. Consult Sargent Welch Spectrum Charts on wall of lab. Note that only the most prominent wavelengths are displayed
Experiment P02: Understanding Motion II Velocity and Time (Motion Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P02-1 Experiment P02: Understanding Motion II Velocity and Time (Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file linear motion 30 m 500 or 700
PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P02-1 Experiment P02: Understanding Motion II Velocity and Time (Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file linear motion 30 m 500 or 700
Experiment P10: Acceleration of a Dynamics Cart II (Motion Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P10-1 Experiment P10: (Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file Newton s Laws 30 m 500 or 700 P10 Cart Acceleration II P10_CAR2.SWS EQUIPMENT
PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P10-1 Experiment P10: (Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file Newton s Laws 30 m 500 or 700 P10 Cart Acceleration II P10_CAR2.SWS EQUIPMENT
Lab 5: Brewster s Angle and Polarization. I. Brewster s angle
 Lab 5: Brewster s Angle and Polarization I. Brewster s angle CAUTION: The beam splitters are sensitive pieces of optical equipment; the oils on your fingertips if left there will degrade the coatings on
Lab 5: Brewster s Angle and Polarization I. Brewster s angle CAUTION: The beam splitters are sensitive pieces of optical equipment; the oils on your fingertips if left there will degrade the coatings on
PHYS 3153 Methods of Experimental Physics II O2. Applications of Interferometry
 Purpose PHYS 3153 Methods of Experimental Physics II O2. Applications of Interferometry In this experiment, you will study the principles and applications of interferometry. Equipment and components PASCO
Purpose PHYS 3153 Methods of Experimental Physics II O2. Applications of Interferometry In this experiment, you will study the principles and applications of interferometry. Equipment and components PASCO
BLACK BODY LIGHT SOURCE FOR THE OS-8539 EDUCATIONAL SPECTROPHOTOMETER
 Includes Teacher's Notes and Typical Experiment Results Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model OS-8542 012-07105B BLACK BODY LIGHT SOURCE FOR THE OS-8539 EDUCATIONAL SPECTROPHOTOMETER
Includes Teacher's Notes and Typical Experiment Results Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model OS-8542 012-07105B BLACK BODY LIGHT SOURCE FOR THE OS-8539 EDUCATIONAL SPECTROPHOTOMETER
Experiment P01: Understanding Motion I Distance and Time (Motion Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P01-1 Experiment P01: Understanding Motion I Distance and Time (Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file linear motion 30 m 500 or 700 P01
PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P01-1 Experiment P01: Understanding Motion I Distance and Time (Motion Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file linear motion 30 m 500 or 700 P01
Physics activities using the ScienceWorkshop program and interfaces from PASCO scientific
 ScienceWorkshop ScienceWorkshop Physics Labs with Computers Physics activities using the ScienceWorkshop program and interfaces from PASCO scientific Volume 2 10101 Foothills Boulevard Roseville, CA 95747-7100
ScienceWorkshop ScienceWorkshop Physics Labs with Computers Physics activities using the ScienceWorkshop program and interfaces from PASCO scientific Volume 2 10101 Foothills Boulevard Roseville, CA 95747-7100
Experiment 1: The Wave Model of light vs. the Quantum Model
 012-04049J h/e Apparatus and h/e Apparatus Accessory Kit Experiment 1: The Wave Model of light vs. the Quantum Model Setup According to the photon theory of light, the maximum kinetic energy, KE, of photoelectrons
012-04049J h/e Apparatus and h/e Apparatus Accessory Kit Experiment 1: The Wave Model of light vs. the Quantum Model Setup According to the photon theory of light, the maximum kinetic energy, KE, of photoelectrons
Experiment P41: Induction Magnet through a Coil (Photogate, Voltage Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P41-1 Experiment P41: Induction Magnet through a Coil (Photogate, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file circuits 30 m 500/700
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P41-1 Experiment P41: Induction Magnet through a Coil (Photogate, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file circuits 30 m 500/700
Experiment P49: Transistor Lab 2 Current Gain: The NPN Emitter-Follower Amplifier (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P49-1 Experiment P49: Transistor Lab 2 Current Gain: The NPN Emitter-Follower Amplifier (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P49-1 Experiment P49: Transistor Lab 2 Current Gain: The NPN Emitter-Follower Amplifier (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh
Part 1: Standing Waves - Measuring Wavelengths
 Experiment 7 The Microwave experiment Aim: This experiment uses microwaves in order to demonstrate the formation of standing waves, verifying the wavelength λ of the microwaves as well as diffraction from
Experiment 7 The Microwave experiment Aim: This experiment uses microwaves in order to demonstrate the formation of standing waves, verifying the wavelength λ of the microwaves as well as diffraction from
Physics 476LW. Advanced Physics Laboratory - Microwave Optics
 Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Microwave Radiation Introduction Setup The purpose of this lab is to better understand the various ways that interference of EM radiation manifests itself. However,
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Microwave Radiation Introduction Setup The purpose of this lab is to better understand the various ways that interference of EM radiation manifests itself. However,
Rotary Fixture M/V/X CLASS LASER SYSTEMS. Installation and Operation Instructions
 Rotary Fixture M/V/X CLASS LASER SYSTEMS Installation and Operation Instructions 02/01/2000 Introduction The Rotary Fixture controls in the Printer Driver are used along with the optional Rotary Fixture
Rotary Fixture M/V/X CLASS LASER SYSTEMS Installation and Operation Instructions 02/01/2000 Introduction The Rotary Fixture controls in the Printer Driver are used along with the optional Rotary Fixture
1 Diffraction of Microwaves
 1 Diffraction of Microwaves 1.1 Purpose In this lab you will investigate the coherent scattering of electromagnetic waves from a periodic structure. The experiment is a direct analog of the Bragg diffraction
1 Diffraction of Microwaves 1.1 Purpose In this lab you will investigate the coherent scattering of electromagnetic waves from a periodic structure. The experiment is a direct analog of the Bragg diffraction
Microwave Diffraction and Interference
 Microwave Diffraction and Interference Department of Physics Ryerson University rev.2014 1 Introduction The object of this experiment is to observe interference and diffraction of microwave radiation,
Microwave Diffraction and Interference Department of Physics Ryerson University rev.2014 1 Introduction The object of this experiment is to observe interference and diffraction of microwave radiation,
Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit
 Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit Purpose 1. To understand the theory of Fraunhofer diffraction of light at a single slit and at a circular aperture; 2. To learn how to measure
Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit Purpose 1. To understand the theory of Fraunhofer diffraction of light at a single slit and at a circular aperture; 2. To learn how to measure
FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION
 FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION Revised November 15, 2017 INTRODUCTION The simplest and most commonly described examples of diffraction and interference from two-dimensional apertures
FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION Revised November 15, 2017 INTRODUCTION The simplest and most commonly described examples of diffraction and interference from two-dimensional apertures
Ph 3455 The Photoelectric Effect
 Ph 3455 The Photoelectric Effect Required background reading Tipler, Llewellyn, section 3-3 Prelab Questions 1. In this experiment you will be using a mercury lamp as the source of photons. At the yellow
Ph 3455 The Photoelectric Effect Required background reading Tipler, Llewellyn, section 3-3 Prelab Questions 1. In this experiment you will be using a mercury lamp as the source of photons. At the yellow
Phy Ph s y 102 Lecture Lectur 22 Interference 1
 Phys 102 Lecture 22 Interference 1 Physics 102 lectures on light Light as a wave Lecture 15 EM waves Lecture 16 Polarization Lecture 22 & 23 Interference& diffraction Light as a ray Lecture 17 Introduction
Phys 102 Lecture 22 Interference 1 Physics 102 lectures on light Light as a wave Lecture 15 EM waves Lecture 16 Polarization Lecture 22 & 23 Interference& diffraction Light as a ray Lecture 17 Introduction
Experiment P42: Transformer (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P42-1 Experiment P42: (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh File Windows File basic electricity 30 m 700 P42 P42_XTRN.SWS EQUIPMENT
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P42-1 Experiment P42: (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh File Windows File basic electricity 30 m 700 P42 P42_XTRN.SWS EQUIPMENT
Physics 197 Lab 8: Interference
 Physics 197 Lab 8: Interference Equipment: Item Part # per Team # of Teams Bottle of Bubble Solution with dipper 1 8 8 Wine Glass 1 8 8 Straw 1 8 8 Optics Bench PASCO OS-8518 1 8 8 Red Diode Laser and
Physics 197 Lab 8: Interference Equipment: Item Part # per Team # of Teams Bottle of Bubble Solution with dipper 1 8 8 Wine Glass 1 8 8 Straw 1 8 8 Optics Bench PASCO OS-8518 1 8 8 Red Diode Laser and
Experiment P36: Resonance Modes and the Speed of Sound (Voltage Sensor, Power Amplifier)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P36-1 Experiment P36: Resonance Modes and the Speed of Sound (Voltage Sensor, Power Amplifier) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh File Windows File waves 45
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P36-1 Experiment P36: Resonance Modes and the Speed of Sound (Voltage Sensor, Power Amplifier) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh File Windows File waves 45
Measuring with Interference and Diffraction
 Team Physics 312 10B Lab #3 Date: Name: Table/Team: Measuring with Interference and Diffraction Purpose: In this activity you will accurately measure the width of a human hair using the interference and
Team Physics 312 10B Lab #3 Date: Name: Table/Team: Measuring with Interference and Diffraction Purpose: In this activity you will accurately measure the width of a human hair using the interference and
Film Holder Accessories
 Page 1 of 9 Film Holder Accessories For Cary 1/3/4/5/100/300/400/500/500i/4000/5000/6000i/Deep UV Part numbers: Cary 100/300-0010048500; Cary 400/500/500i/4000/5000/6000i - 0210125400 Contents This document
Page 1 of 9 Film Holder Accessories For Cary 1/3/4/5/100/300/400/500/500i/4000/5000/6000i/Deep UV Part numbers: Cary 100/300-0010048500; Cary 400/500/500i/4000/5000/6000i - 0210125400 Contents This document
PHYS2090 OPTICAL PHYSICS Laboratory Microwaves
 PHYS2090 OPTICAL PHYSICS Laboratory Microwaves Reference Hecht, Optics, (Addison-Wesley) 1. Introduction Interference and diffraction are commonly observed in the optical regime. As wave-particle duality
PHYS2090 OPTICAL PHYSICS Laboratory Microwaves Reference Hecht, Optics, (Addison-Wesley) 1. Introduction Interference and diffraction are commonly observed in the optical regime. As wave-particle duality
Copyright Black Box Corporation. All rights reserved Park Drive Lawrence, PA Fax
 Copyright 2004. Black Box Corporation. All rights reserved. 1000 Park Drive Lawrence, PA 15055-1018 724-746-5500 Fax 724-746-0746 JANUARY 2004 RF500A RF507A RF514A RF521A RF501A RF508A RF515A RF522A RF502A
Copyright 2004. Black Box Corporation. All rights reserved. 1000 Park Drive Lawrence, PA 15055-1018 724-746-5500 Fax 724-746-0746 JANUARY 2004 RF500A RF507A RF514A RF521A RF501A RF508A RF515A RF522A RF502A
Resonant Frequency of the LRC Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor)
 72 Resonant Frequency of the LRC Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Equipment List Qty Items Part Numbers 1 PASCO 750 Interface 1 Voltage Sensor CI-6503 1 AC/DC Electronics Laboratory EM-8656 2 Banana
72 Resonant Frequency of the LRC Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Equipment List Qty Items Part Numbers 1 PASCO 750 Interface 1 Voltage Sensor CI-6503 1 AC/DC Electronics Laboratory EM-8656 2 Banana
Momentum and Impulse. Objective. Theory. Investigate the relationship between impulse and momentum.
 [For International Campus Lab ONLY] Objective Investigate the relationship between impulse and momentum. Theory ----------------------------- Reference -------------------------- Young & Freedman, University
[For International Campus Lab ONLY] Objective Investigate the relationship between impulse and momentum. Theory ----------------------------- Reference -------------------------- Young & Freedman, University
Momentum and Impulse
 General Physics Lab Department of PHYSICS YONSEI University Lab Manual (Lite) Momentum and Impulse Ver.20180328 NOTICE This LITE version of manual includes only experimental procedures for easier reading
General Physics Lab Department of PHYSICS YONSEI University Lab Manual (Lite) Momentum and Impulse Ver.20180328 NOTICE This LITE version of manual includes only experimental procedures for easier reading
Diffraction at Circular Edges
 Diffraction at Circular Edges References: Equipment: Born and Wolf, Principles of Optics nd ed., Pergamon Press 1964 pp. 395-398. Giles, Robin A., Waves and Optics Simulations:The Consortium for Upper
Diffraction at Circular Edges References: Equipment: Born and Wolf, Principles of Optics nd ed., Pergamon Press 1964 pp. 395-398. Giles, Robin A., Waves and Optics Simulations:The Consortium for Upper
Experiment P20: Driven Harmonic Motion - Mass on a Spring (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor, Power Amplifier)
 PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P20-1 Experiment P20: - Mass on a Spring (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor, Power Amplifier) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file harmonic motion 45 m 700
PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P20-1 Experiment P20: - Mass on a Spring (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor, Power Amplifier) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file harmonic motion 45 m 700
Fresnel and Fraunhofer Diffraction: Development of an Advanced Laboratory Experiment
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Senior Theses and Projects Materials Physics 12-1990 Fresnel and Fraunhofer Diffraction: Development of an Advanced Laboratory Experiment Jeff Adams Utah State
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Senior Theses and Projects Materials Physics 12-1990 Fresnel and Fraunhofer Diffraction: Development of an Advanced Laboratory Experiment Jeff Adams Utah State
Laboratory 1: Motion in One Dimension
 Phys 131L Spring 2018 Laboratory 1: Motion in One Dimension Classical physics describes the motion of objects with the fundamental goal of tracking the position of an object as time passes. The simplest
Phys 131L Spring 2018 Laboratory 1: Motion in One Dimension Classical physics describes the motion of objects with the fundamental goal of tracking the position of an object as time passes. The simplest
Basic Optics System OS-8515C
 40 50 30 60 20 70 10 80 0 90 80 10 20 70 T 30 60 40 50 50 40 60 30 70 20 80 90 90 80 BASIC OPTICS RAY TABLE 10 0 10 70 20 60 50 40 30 Instruction Manual with Experiment Guide and Teachers Notes 012-09900B
40 50 30 60 20 70 10 80 0 90 80 10 20 70 T 30 60 40 50 50 40 60 30 70 20 80 90 90 80 BASIC OPTICS RAY TABLE 10 0 10 70 20 60 50 40 30 Instruction Manual with Experiment Guide and Teachers Notes 012-09900B
Experimental Question 2: An Optical Black Box
 Experimental Question 2: An Optical Black Box TV and computer screens have advanced significantly in recent years. Today, most displays consist of a color LCD filter matrix and a uniform white backlight
Experimental Question 2: An Optical Black Box TV and computer screens have advanced significantly in recent years. Today, most displays consist of a color LCD filter matrix and a uniform white backlight
Lecture Outline Chapter 28. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 28 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 28 Physical Optics: Interference and Diffraction Units of Chapter 28 Superposition and Interference Young s Two-Slit Experiment
Lecture Outline Chapter 28 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 28 Physical Optics: Interference and Diffraction Units of Chapter 28 Superposition and Interference Young s Two-Slit Experiment
7. Michelson Interferometer
 7. Michelson Interferometer In this lab we are going to observe the interference patterns produced by two spherical waves as well as by two plane waves. We will study the operation of a Michelson interferometer,
7. Michelson Interferometer In this lab we are going to observe the interference patterns produced by two spherical waves as well as by two plane waves. We will study the operation of a Michelson interferometer,
ECEN. Spectroscopy. Lab 8. copy. constituents HOMEWORK PR. Figure. 1. Layout of. of the
 ECEN 4606 Lab 8 Spectroscopy SUMMARY: ROBLEM 1: Pedrotti 3 12-10. In this lab, you will design, build and test an optical spectrum analyzer and use it for both absorption and emission spectroscopy. The
ECEN 4606 Lab 8 Spectroscopy SUMMARY: ROBLEM 1: Pedrotti 3 12-10. In this lab, you will design, build and test an optical spectrum analyzer and use it for both absorption and emission spectroscopy. The
12 Projectile Motion 12 - Page 1 of 9. Projectile Motion
 12 Projectile Motion 12 - Page 1 of 9 Equipment Projectile Motion 1 Mini Launcher ME-6825A 2 Photogate ME-9498A 1 Photogate Bracket ME-6821A 1 Time of Flight ME-6810 1 Table Clamp ME-9472 1 Rod Base ME-8735
12 Projectile Motion 12 - Page 1 of 9 Equipment Projectile Motion 1 Mini Launcher ME-6825A 2 Photogate ME-9498A 1 Photogate Bracket ME-6821A 1 Time of Flight ME-6810 1 Table Clamp ME-9472 1 Rod Base ME-8735
Chapter 17: Wave Optics. What is Light? The Models of Light 1/11/13
 Chapter 17: Wave Optics Key Terms Wave model Ray model Diffraction Refraction Fringe spacing Diffraction grating Thin-film interference What is Light? Light is the chameleon of the physical world. Under
Chapter 17: Wave Optics Key Terms Wave model Ray model Diffraction Refraction Fringe spacing Diffraction grating Thin-film interference What is Light? Light is the chameleon of the physical world. Under
Mercury 1200 and 1500P
 Mercury 200 and 500P M200-Analog Output Encoder Systems M500P-Digital Output Encoder Systems Installation Manual and Reference Guide Manual No. IM-M200 & M500P Rev i Introduction MicroE Systems was founded
Mercury 200 and 500P M200-Analog Output Encoder Systems M500P-Digital Output Encoder Systems Installation Manual and Reference Guide Manual No. IM-M200 & M500P Rev i Introduction MicroE Systems was founded
Physics 4C Chabot College Scott Hildreth
 Physics 4C Chabot College Scott Hildreth The Inverse Square Law for Light Intensity vs. Distance Using Microwaves Experiment Goals: Experimentally test the inverse square law for light using Microwaves.
Physics 4C Chabot College Scott Hildreth The Inverse Square Law for Light Intensity vs. Distance Using Microwaves Experiment Goals: Experimentally test the inverse square law for light using Microwaves.
PRINCIPLE PROCEDURE ACTIVITY. AIM To observe diffraction of light due to a thin slit.
 ACTIVITY 12 AIM To observe diffraction of light due to a thin slit. APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED Two razor blades, one adhesive tape/cello-tape, source of light (electric bulb/ laser pencil), a piece
ACTIVITY 12 AIM To observe diffraction of light due to a thin slit. APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED Two razor blades, one adhesive tape/cello-tape, source of light (electric bulb/ laser pencil), a piece
Interferometer. Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model OS /91 Revision B
 Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO Model OS-8501 012-02675 10/91 Revision B Interferometer MODEL OS-8501 INTERFEROMETER Copyright February 1986 $10.00 Interferometer 012-02675B Table
Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO Model OS-8501 012-02675 10/91 Revision B Interferometer MODEL OS-8501 INTERFEROMETER Copyright February 1986 $10.00 Interferometer 012-02675B Table
The Wave Nature of Light
 The Wave Nature of Light Physics 102 Lecture 7 4 April 2002 Pick up Grating & Foil & Pin 4 Apr 2002 Physics 102 Lecture 7 1 Light acts like a wave! Last week we saw that light travels from place to place
The Wave Nature of Light Physics 102 Lecture 7 4 April 2002 Pick up Grating & Foil & Pin 4 Apr 2002 Physics 102 Lecture 7 1 Light acts like a wave! Last week we saw that light travels from place to place
LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit
 LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit Equipment: Voltage Sensor 1 Multimeter 1 Patch Cords 2 AC/DC Electronics Lab (100 μf capacitor; 10 Ω resistor; Inductor Coil; Iron core; 5 inch wire lead) The purpose of
LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit Equipment: Voltage Sensor 1 Multimeter 1 Patch Cords 2 AC/DC Electronics Lab (100 μf capacitor; 10 Ω resistor; Inductor Coil; Iron core; 5 inch wire lead) The purpose of
Single Photon Interference Katelynn Sharma and Garrett West University of Rochester, Institute of Optics, 275 Hutchison Rd. Rochester, NY 14627
 Single Photon Interference Katelynn Sharma and Garrett West University of Rochester, Institute of Optics, 275 Hutchison Rd. Rochester, NY 14627 Abstract: In studying the Mach-Zender interferometer and
Single Photon Interference Katelynn Sharma and Garrett West University of Rochester, Institute of Optics, 275 Hutchison Rd. Rochester, NY 14627 Abstract: In studying the Mach-Zender interferometer and
INTRODUCTION TO DATA STUDIO
 1 INTRODUCTION TO DATA STUDIO PART I: FAMILIARIZATION OBJECTIVE To become familiar with the operation of the Passport/Xplorer digital instruments and the DataStudio software. INTRODUCTION We will use the
1 INTRODUCTION TO DATA STUDIO PART I: FAMILIARIZATION OBJECTIVE To become familiar with the operation of the Passport/Xplorer digital instruments and the DataStudio software. INTRODUCTION We will use the
MICROWAVE OPTICS. Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model WA-9314B G
 Includes Teacher's Notes and Typical Experiment Results Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model WA-9314B 012-04630G MICROWAVE OPTICS 10101 Foothills Blvd. Roseville, CA 95678-9011
Includes Teacher's Notes and Typical Experiment Results Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model WA-9314B 012-04630G MICROWAVE OPTICS 10101 Foothills Blvd. Roseville, CA 95678-9011
Week IX: INTERFEROMETER EXPERIMENTS
 Week IX: INTERFEROMETER EXPERIMENTS Notes on Adjusting the Michelson Interference Caution: Do not touch the mirrors or beam splitters they are front surface and difficult to clean without damaging them.
Week IX: INTERFEROMETER EXPERIMENTS Notes on Adjusting the Michelson Interference Caution: Do not touch the mirrors or beam splitters they are front surface and difficult to clean without damaging them.
18600 Angular Momentum
 18600 Angular Momentum Experiment 1 - Collisions Involving Rotation Setup: Place the kit contents on a laboratory bench or table. Refer to Figure 1, Section A. Tip the angular momentum apparatus base on
18600 Angular Momentum Experiment 1 - Collisions Involving Rotation Setup: Place the kit contents on a laboratory bench or table. Refer to Figure 1, Section A. Tip the angular momentum apparatus base on
Ohm s Law. Equipment. Setup
 rev 05/2018 Ohm s Law Equipment Qty Item Part Number 1 AC/DC Electronics Laboratory EM-8656 1 Current Sensor CI-6556 1 Multimeter 4 Patch Cords 2 Banana Clips 1 100Ω Resistor Purpose The purpose of this
rev 05/2018 Ohm s Law Equipment Qty Item Part Number 1 AC/DC Electronics Laboratory EM-8656 1 Current Sensor CI-6556 1 Multimeter 4 Patch Cords 2 Banana Clips 1 100Ω Resistor Purpose The purpose of this
Exp. No. 13 Measuring the runtime of light in the fiber
 Exp. No. 13 Measuring the runtime of light in the fiber Aim of Experiment The aim of experiment is measuring the runtime of light in optical fiber with length of 1 km and the refractive index of optical
Exp. No. 13 Measuring the runtime of light in the fiber Aim of Experiment The aim of experiment is measuring the runtime of light in optical fiber with length of 1 km and the refractive index of optical
End-of-Chapter Exercises
 End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions designed to see whether you understand the main concepts in the chapter. 1. Red laser light shines on a double slit, creating a pattern
End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions designed to see whether you understand the main concepts in the chapter. 1. Red laser light shines on a double slit, creating a pattern
±50N FORCE SENSOR. Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model CI A 6/ PASCO scientific $7.
 +50N Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model CI-6537 012-05804A 6/95 ±50N FORCE SENSOR CAUTION! -50N FORCE SENSOR 1995 PASCO scientific $7.50 012-05804A ±50N Force Sensor
+50N Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model CI-6537 012-05804A 6/95 ±50N FORCE SENSOR CAUTION! -50N FORCE SENSOR 1995 PASCO scientific $7.50 012-05804A ±50N Force Sensor
Microscopy. The dichroic mirror is an important component of the fluorescent scope: it reflects blue light while transmitting green light.
 Microscopy I. Before coming to lab Read this handout and the background. II. Learning Objectives In this lab, you'll investigate the physics of microscopes. The main idea is to understand the limitations
Microscopy I. Before coming to lab Read this handout and the background. II. Learning Objectives In this lab, you'll investigate the physics of microscopes. The main idea is to understand the limitations
Chapter 36: diffraction
 Chapter 36: diffraction Fresnel and Fraunhofer diffraction Diffraction from a single slit Intensity in the single slit pattern Multiple slits The Diffraction grating X-ray diffraction Circular apertures
Chapter 36: diffraction Fresnel and Fraunhofer diffraction Diffraction from a single slit Intensity in the single slit pattern Multiple slits The Diffraction grating X-ray diffraction Circular apertures
Experiment P48: Transistor Lab 1 The NPN Transistor as a Digital Switch (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P48-1 Experiment P48: Transistor Lab 1 The NPN Transistor as a Digital Switch (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P48-1 Experiment P48: Transistor Lab 1 The NPN Transistor as a Digital Switch (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. Just over two hundred years ago Thomas Young demonstrated the interference of light by illuminating two closely spaced narrow slits with light from a single light source.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. Just over two hundred years ago Thomas Young demonstrated the interference of light by illuminating two closely spaced narrow slits with light from a single light source.
PHYS General Physics II Lab Diffraction Grating
 1 PHYS 1040 - General Physics II Lab Diffraction Grating In this lab you will perform an experiment to understand the interference of light waves when they pass through a diffraction grating and to determine
1 PHYS 1040 - General Physics II Lab Diffraction Grating In this lab you will perform an experiment to understand the interference of light waves when they pass through a diffraction grating and to determine
Lab 12 Microwave Optics.
 b Lab 12 Microwave Optics. CAUTION: The output power of the microwave transmitter is well below standard safety levels. Nevertheless, do not look directly into the microwave horn at close range when the
b Lab 12 Microwave Optics. CAUTION: The output power of the microwave transmitter is well below standard safety levels. Nevertheless, do not look directly into the microwave horn at close range when the
Measuring the speed of light
 1 Purpose and comments Determine the speed of light by sending a laser beam through various mediums. Unless you want to see like Helen Keller, do not place your eyes in the beam path. Also, Switch the
1 Purpose and comments Determine the speed of light by sending a laser beam through various mediums. Unless you want to see like Helen Keller, do not place your eyes in the beam path. Also, Switch the
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET
 LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
Single Photon Interference Laboratory
 Single Photon Interference Laboratory Renald Dore Institute of Optics University of Rochester, Rochester, NY 14627, U.S.A Abstract The purpose of our laboratories was to observe the wave-particle duality
Single Photon Interference Laboratory Renald Dore Institute of Optics University of Rochester, Rochester, NY 14627, U.S.A Abstract The purpose of our laboratories was to observe the wave-particle duality
Modern Physics Laboratory MP4 Photoelectric Effect
 Purpose MP4 Photoelectric Effect In this experiment, you will investigate the photoelectric effect and determine Planck s constant and the work function. Equipment and components Photoelectric Effect Apparatus
Purpose MP4 Photoelectric Effect In this experiment, you will investigate the photoelectric effect and determine Planck s constant and the work function. Equipment and components Photoelectric Effect Apparatus
Experiment 19. Microwave Optics 1
 Experiment 19 Microwave Optics 1 1. Introduction Optical phenomena may be studied at microwave frequencies. Using a three centimeter microwave wavelength transforms the scale of the experiment. Microns
Experiment 19 Microwave Optics 1 1. Introduction Optical phenomena may be studied at microwave frequencies. Using a three centimeter microwave wavelength transforms the scale of the experiment. Microns
Component Assemblies. A Note on Handling Optics
 ~ Component Assemblies All ten experiments use a number of similar component assemblies. In order to simplify the experimental set up procedure we have included a section on building these assemblies.
~ Component Assemblies All ten experiments use a number of similar component assemblies. In order to simplify the experimental set up procedure we have included a section on building these assemblies.
PANalytical X pert Pro Gazing Incidence X-ray Reflectivity User Manual (Version: )
 University of Minnesota College of Science and Engineering Characterization Facility PANalytical X pert Pro Gazing Incidence X-ray Reflectivity User Manual (Version: 2012.10.17) The following instructions
University of Minnesota College of Science and Engineering Characterization Facility PANalytical X pert Pro Gazing Incidence X-ray Reflectivity User Manual (Version: 2012.10.17) The following instructions
Video. Part I. Equipment
 1 of 7 11/8/2013 11:32 AM There are two parts to this lab that can be done in either order. In Part I you will study the Laws of Reflection and Refraction, measure the index of refraction of glass and
1 of 7 11/8/2013 11:32 AM There are two parts to this lab that can be done in either order. In Part I you will study the Laws of Reflection and Refraction, measure the index of refraction of glass and
SatNOGS. SatNOGS Rotator v3 Mechanical Assembly. This is the assembly guide for the third version of the SatNOGS Rotator.
 SatNOGS SatNOGS Rotator v3 Mechanical Assembly This is the assembly guide for the third version of the SatNOGS Rotator. Written By: Pierros Papadeas 2017 satnogs.dozuki.com Page 1 of 19 INTRODUCTION Notes:
SatNOGS SatNOGS Rotator v3 Mechanical Assembly This is the assembly guide for the third version of the SatNOGS Rotator. Written By: Pierros Papadeas 2017 satnogs.dozuki.com Page 1 of 19 INTRODUCTION Notes:
Chapter Wave Optics. MockTime.com. Ans: (d)
 Chapter Wave Optics Q1. Which one of the following phenomena is not explained by Huygen s construction of wave front? [1988] (a) Refraction Reflection Diffraction Origin of spectra Q2. Which of the following
Chapter Wave Optics Q1. Which one of the following phenomena is not explained by Huygen s construction of wave front? [1988] (a) Refraction Reflection Diffraction Origin of spectra Q2. Which of the following
ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS RIGHT & LEFT HAND "J" TABLE
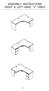 ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS RIGHT & LEFT HAND "J" TABLE (1) COMPONENT LIST FOR RIGHT & LEFT HAND "J" TABLE NOTE: Please count and inspect all pieces before disposing of any carton or packing materials. 24" x
ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS RIGHT & LEFT HAND "J" TABLE (1) COMPONENT LIST FOR RIGHT & LEFT HAND "J" TABLE NOTE: Please count and inspect all pieces before disposing of any carton or packing materials. 24" x
No Brain Too Small PHYSICS
 WAVES: WAVES BEHAVIOUR QUESTIONS No Brain Too Small PHYSICS DIFFRACTION GRATINGS (2016;3) Moana is doing an experiment in the laboratory. She shines a laser beam at a double slit and observes an interference
WAVES: WAVES BEHAVIOUR QUESTIONS No Brain Too Small PHYSICS DIFFRACTION GRATINGS (2016;3) Moana is doing an experiment in the laboratory. She shines a laser beam at a double slit and observes an interference
Automated Double Aperture Accessory
 For the Cary 1, 3, 100, 300, 4, 5, 400, 500, 500i, 4000, 5000, 6000i, Deep UV Installation Category II Pollution Degree 2 Equipment Class I Table of Contents Introduction Theory Operation Installation
For the Cary 1, 3, 100, 300, 4, 5, 400, 500, 500i, 4000, 5000, 6000i, Deep UV Installation Category II Pollution Degree 2 Equipment Class I Table of Contents Introduction Theory Operation Installation
HOLIDAY HOME WORK PHYSICS CLASS-12B AUTUMN BREAK 2018
 HOLIDAY HOME WK PHYSICS CLASS-12B AUTUMN BREAK 2018 NOTE: 1. THESE QUESTIONS ARE FROM PREVIOUS YEAR BOARD PAPERS FROM 2009-2018 CHAPTERS EMI,AC,OPTICS(BUT TRY TO SOLVE ONLY NON-REPEATED QUESTION) QUESTION
HOLIDAY HOME WK PHYSICS CLASS-12B AUTUMN BREAK 2018 NOTE: 1. THESE QUESTIONS ARE FROM PREVIOUS YEAR BOARD PAPERS FROM 2009-2018 CHAPTERS EMI,AC,OPTICS(BUT TRY TO SOLVE ONLY NON-REPEATED QUESTION) QUESTION
Removing the Z-Axis lead screw
 Page 1 of 8 TITLE: Sabre Z-Axis Lead Screw Replacement Procedure Gerber FastFact #: 5048 Supplied by: Gerber Hardware Support Last Modified: June 14, 2007 Summary: Tools used: The following procedure explains
Page 1 of 8 TITLE: Sabre Z-Axis Lead Screw Replacement Procedure Gerber FastFact #: 5048 Supplied by: Gerber Hardware Support Last Modified: June 14, 2007 Summary: Tools used: The following procedure explains
Lab 10: Lenses & Telescopes
 Physics 2020, Fall 2010 Lab 8 page 1 of 6 Circle your lab day and time. Your name: Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri TA name: 8-10 10-12 12-2 2-4 4-6 INTRODUCTION Lab 10: Lenses & Telescopes In this experiment, you
Physics 2020, Fall 2010 Lab 8 page 1 of 6 Circle your lab day and time. Your name: Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri TA name: 8-10 10-12 12-2 2-4 4-6 INTRODUCTION Lab 10: Lenses & Telescopes In this experiment, you
Instruction sheet VideoCom Retroreflecting Foil Falling Body for VideoCom. 1 Safety notes
 Physics Chemistry Biology Technics LEYBOLD DIDACTIC GMBH 8/97-Hund- Instruction sheet 337 47 337 471 337 472 VideoCom Retroreflecting Foil Falling Body for VideoCom Fig. 1 VideoCom (337 47) is a camera
Physics Chemistry Biology Technics LEYBOLD DIDACTIC GMBH 8/97-Hund- Instruction sheet 337 47 337 471 337 472 VideoCom Retroreflecting Foil Falling Body for VideoCom Fig. 1 VideoCom (337 47) is a camera
2. Refraction and Reflection
 2. Refraction and Reflection In this lab we will observe the displacement of a light beam by a parallel plate due to refraction. We will determine the refractive index of some liquids from the incident
2. Refraction and Reflection In this lab we will observe the displacement of a light beam by a parallel plate due to refraction. We will determine the refractive index of some liquids from the incident
