Index of Command Functions
|
|
|
- Albert Cannon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Index of Command Functions version 2.3 Command description [keyboard shortcut]:description including special instructions. Keyboard short for a Windows PC: the Control key AND the shortcut key. For a MacIntosh: the Meta or Command (Apple symbol) key AND a shortcut key. Note: lower case characters only! Under the MicroObservatoryImage menu (Mac OSX version only): 1. About MicroObservatoryImage: Program information, including program release version, contact information and Internet address for the software program and instructions. A toggle button allows the user to check for the most current version of the MicroObservatoryImage program. 2. Services: Not applicable. 3. Hide MicroObservatoryImage [Meta h]: Minimize the program. 4. Hide Others [Option Meta h]: Minimize all other programs. 5. Quit [Meta q] : Quit the program and closes all images. Note: The program will prompt you to save all open, unsaved images BEFORE quitting the program. Under the File menu:
2 1. Open an image on local disk [Meta o] : Open an image file from your local computer. The program only opens FITS and GIF formatted image files. The Drag and Drop feature allows you to drag an image, a file, or a URL address onto MicroObservatoryImage icon (Mac OSX version only) or into the application window (all versions) to open each. 2. Open an image on the Internet [n/a] : Open an image file directly from the Internet. Type or copy an URL address [copy to clipboard (Mac) or shortcut (PC) and then paste with Meta v or click on the Paste button] and click the OK button. The Drag and Drop feature allows you to drag an image, a file, or a URL address onto MicroObservatory Image icon (Mac OSX version only) or into the application window (all versions) to open each. 3. Open MicroObservatory Image Directory [n/a] : The Image Directory on the MicroObservatory web page is opened via your default internet web browser. Follow directions above to open an image file in the program. 4. Close [Meta w] : Close current image. 5. Save As / GIF : Save an image file in GIF format (graphics interchange format, a 256-brightness levels or 8-bit format). This data format may be gray scale or composite color image. Remember to type the.gif postfix to the end of each file name created. Save As / FITS : Save an image file in FITS format (flexible image transport system, the standard data format used in astronomy, which has basically an unlimited data size, but this program can manipulate signed 32-bit images or over 4 billion color/gray shades). Note: The original FITS header information is saved with the image, even if you have changed the image in anyway. Remember to type the.fits postfix to the end of each file name. Note: MicroObservatory images originally come from a 12-bit digital imaging device but they are stored using the 16-bit FITS data format standard. 12-bit means there are 4096 brightness levels or shades of gray between black and white. Black has a value of 0 and white equals Save As / Animated GIF : Save an image file in GIF format, similar to above but this contains several images in sequence which display as an animation. Note: only a Stacked image can be saved as an animated GIF, which is created from Process / Stack / Convert Images to Stack command. Remember to type the.gif postfix to each file name. 6. Print [Meta p] : Print the current image. Under the Edit menu:
3 (Note: all these commands are for text functions, NOT for image processing steps, except the Undo function.) 1. Undo [Meta z] : Undo last command performed. Works on Adjust Image, Color Table, Sharpen, Reduce Noise functions. 2. Cut [Meta x] : Highlight text with mouse then cuts or remove text. Cut text is saved in memory. 3. Copy [Meta c] : Highlight text with mouse then makes a copy without removing text. Copied text is saved in memory. 4. Paste [Meta v] : Text saved in memory from Cut or Copy command is pasted where the mouse cursor is located. 5. Select All [Meta a] : All text in current window is highlighted. Under the Process menu: 1. Adjust Image [n/a] : Rescales or remaps the brightness values of each picture element (pixel) of the displayed image to a different range of brightness values. A new window pops up with the title Adjust Image. You may choose either Linear (the default) or Log to scale the image values by clicking on the appropriate button. The maximum and minimum values of the image are initially displayed (as the default values) showing the full range of values. You may want to adjust the displayed range of brightness values to see detail not seen. You may adjust the maximum and minimum values either by clicking, holding and sliding the arrows to the right of the scale or by typing an integer value into the respective boxes on top and bottom. The Auto button automatically rescales the image with the optimized linear or logarithmic scaling method, depending on which button is chosen. Auto-Linear scaling sets the minimum and maximum values at two standard deviations from the mean pixel brightness value, then scaling 4095 brightness values between these established min-max values. Auto-Log scaling sets the minimum at the mode value and the maximum at five standard deviations then stretches the contrast scale logarithmically between these values to emphasize small changes in brightness near the mode (the most common pixel brightness value) while deemphasizing the brightest pixel values image components.
4 The Reset button returns the image to the default full-scale linear minimum and maximum display values. Linear rescaling is best for displaying bright objects like the Moon and planets. Logarithmic rescaling optimizes faint detailed features in nebulae and galaxies while still seeing the brighter details in the image. 2. Color Tables / various color options [n/a] : The image can be colorized, meaning that for each individual brightness level a specific color can be assigned to that value. The default color table is a gray scale where the smallest or faintest value is black and the highest or brightest value is white, with intermediate values being lighter shades of gray as pixel values increase. Matched the color table for filtered image is useful in creating RGB color imagery. See Stack command. Color Tables / Gray Scale: Different shades of gray represent pixel brightness values, black being faintest and white being the brightest. Color Tables / Red: Light red colors are bright high values, and darker red to black are low dimmer values. Use for red filtered images to create full color images. Color Tables / Green: Light green colors are bright high values, and darker green to black low dimmer values. Use for green filtered images to create full color images. Color Tables / Blue: Light blue colors are bright high values, and darker blue to black low dimmer values. Use for blue filtered images to create full color images. Color Tables / Spectrum: A multicolor (rainbow) table, where violet and blue are brighter pixel values and yellow to red are dimmer values. This table helps viewing low contrast images.
5 Color Tables / Fire: A different multicolor table. Brighter pixel values are yellow to red and fainter values are violet to blue. Color Tables / Ice: Another multicolor table, the reverse of Fire. Brighter pixel values are red to pink and fainter values are blue to green. Note: the brightness values for pixel in the image DO NOT change, only how they are represented or viewed on the display. 3. Invert Color [n/a] : Invert the brightness values of the images, converting the brightest high value to the lowest and the faintest value to the highest, and doing the same to all the intermediate values, to create a negative image of the original. 4. Sharpen [n/a] : Sharpen is a processing function that increases the brightness difference for a pixel as compared the all the surrounding pixels. This function increases the contrast, detail and noise of an image. Warning: The actual image data is changed with this function, unlike other functions in which the data is just displayed differently. 5. Reduce Noise [n/a] : Reduce noise is a function that averages a pixel s value with the surrounding pixels. This function reduces the noise viewed in an image but also reduces the detail or blurs the image, which can also reduce the contrast. This function is also called smoothing. Note: This function does not remove cosmic ray events but rather hides them in the background. Warning: The actual image data is changed with this function, unlike other functions in which the data is just displayed differently. 6. Crop [n/a] : Takes a portion of the image as highlighted by the box tool and creates a new image file. To use, open an image, select the box tool (located in the upper left corner of the image window), click and drag the mouse to create a box of the appropriate size and unclick. The box can be moved about the image by clicking and holding the mouse cursor inside the shape and repositioning the shape, unclicking the mouse to fix its position on the original image. Then choose crop and a new image of the highlighted region is created in a different window. 7. Measure [Meta m] : Measures the pixel statistics for all the pixels highlighted by the box or circle tools. Select the area of the image to be measured by choosing the box or circle tool (located in the upper left corner of the image), click and drag the mouse to create a box or circle of the appropriate size and unclick. The box or circle can be moved about the image by clicking and holding the mouse cursor inside the shape and repositioning the shape, unclicking the mouse to fix its position. The shape can also be positioned with precision by pressing the i, j, k, and l keyboard keys, which moves the box or circle pixel by pixel. Then choose Measure. A new window displaying a table of statistical values of the highlighted area is created. The first column of the table is the name of the highlighted area, which you can rename by clicking within that cell and typing a new name. The next columns display the area enclosed by the shape tool, mean value of all the pixels, total value of all the pixels, the minimum and maximum value found in all the pixels, as highlighted in the area. The contents of the table can be copied, either each row (click on the row) or all and successive rows (click AND also hold the Shift key, drag the cursor across the rows) or separate rows (click AND hold the Control key, then individually select each row of interest). Once selected, go to the Edit submenu and choose Copy. You can then paste the statistical values into any other text editing or spreadsheet program.
6 8. Image Calculator [n/a] : Performs arithmetic functions between two images. Select this command and a new window labeled Image Calculator is displayed. The most current image viewed is showed in both image registers. Only images currently open are listed in pull-down image registers. Select which image as Image 1, then either the add, subtract, multiply, divide function, and finally which image as Image 2. By default, a new image window is created by the operation. You must have more than one image frame open! Both images must have the same dimensions (width, height and bit depth). Add: Image1 is added to Image2 (Image1 + Image2). Subtract: Image2 is subtracted from Image 1 (Image1 Image2). Multiply: Image1 is multiplied by Image2 (Image1 x Image2). Divide: Image1 is divided by Image2 (Image1 / Image2). Useful for subtracting dark image frames from your image data. Experiment with the calculator. You might be surprised at the results from a simple calculation. The calculator performs only integer arithmetic and rounds values up or down to the nearest integer. The resultant values must remain within the range of values, 0 to 255 for 8-bit images and 0 to 4095 for 12-bit images. Overflowing or underflowing this range may produce severe rounding of pixel values and some very troublesome results. For example: Subtracting a high pixel value from a low pixel value will result in a zero value, not a negative value. Multiplying one image by another image can overflow the pixel value range, producing strange results. Caution: You cannot divide by zero! If you wish to divide one image by another image that has a zero pixel value, add 1 to the image with the zero pixel value by using the Math command. 9. Math [n/a] : Performs image arithmetic functions with integers to a single image. Similar to the Image Calculator in function but instead of an image operating on another image, an image is operated on by a constant value. The current image highlighted will be operated upon. Select command and a new window labeled as the arithmetic function (Add, Subtract, Multiply, Divide) is displayed. Type in an integer value and click OK. By default, a new image window is created by the operation.
7 Math / Add: An integer is added to the image. Math / Subtract: An integer is subtracted from the image. Math / Multiple: The image is multiplied by an integer. Math / Divide: The image is divided by an integer. Experiment with the arithmetic functions. Simple calculations are not always simple. The calculator performs only integer arithmetic and rounds values up or down to the nearest integer. The resultant values must remain within the range of values, 0 to 255 for 8-bit images and 0 to 4095 for 12-bit images, etc. Overflowing or underflowing this range may produce severe rounding of pixel values. For example: Subtracting a high pixel value from a low pixel value will result in a zero value, not a negative value. Multiplying an image by a high value can produce an overflowed high value. Caution: You cannot divide by zero! 10. Shift [n/a] : Aligns one image with another. Select this command and a new window opens, displaying a background and foreground pulldown image register, magnification pulldown selection menu and a display window with two views, an unmagnified and the magnified view of the images selected. Choose one image as the background (preferably the image with brighter objects, such as the red filtered image) and another image as the foreground. Only those images currently opened in the program are listed in the pulldown image registers. You need at least two images open to use this function. In the Shift display window, the unmagnified image is seen on the left and the magnified view is seen on the right. Magnification range is between 1 to 8 times the unmagnified view and is showed in the small window in the upper right corner. The magnified view is a portion of the unmagnified left image centered on the cursor position, as indicated by a crosshair cursor. You can use both the mouse for large position shifts (click and hold then release) and arrow keys on the keyboard for precise pixel by pixel movements (Meta up, Meta down, Meta left and Meta right arrows) to move the foreground image over the background image. Useful for creating RGB full color images from individual filtered images, or making an animated GIF movie, or adding several images together to create a longer exposed image. Refer to the Stack command.
8 Use the unmagnified view and mouse to approximately fit the two images together, then use the magnified view and arrow keys for fine alignment. You may want to initially begin with a lower magnification and then select progressively higher magnified views for more precise alignment. Once alignment is accomplished, click OK. The foreground image is repositioned using the background image coordinates. This command may be used with both GIF and FITS images, including aligning a GIF with a FITS image. Note: Any pixels from the foreground image that are not within the background image boundary are permanently lost. Conversely, due to the shifting operation, new area is created on the foreground image that was not there previously. This new area assumes a similar background pixel value (the mode) from the original foreground image but note that fake stars are not created! Experiment, because the process takes some practice. Note as to what part of the shifted foreground image is real and what is fake. Caution: Always save the new shifted image with a different file name than the origin. Best to use a copy of the origin data in any procedure that alters the data! 11. Stack [n/a] : Compiles of several images into one image to either create color RGB imagery or animations or a longer exposure. All the images to be stacked must be the same format, either all GIF or all FITS and have the same width, height and bit depth. Click on the image frame of interest; next choose Add Slice
9 to begin creating a stack. The image display changes, with a new window title labeled Stack, with a numerical counter at the bottom with forward and reverse directional arrows for sorting the slices. This numerical counter shows how many slices are in the stack. Continue adding slices until all the requested images are included. To remove an image, click the forward or reverse arrows at the bottom of the frame until the unwanted image is displayed, then select Delete Slice. Program functions can still operate on each individual slice within the Stack, such as Shift, Color, Crop, etc. even all the Tool Bar utilities, with the exception of the Process/Image Calculator and the Window/FITS Header functions. Stack / Add Slice: Add current active image frame to Stack. Stack / Delete Slice: Delete the displayed, specific image slice from Stack. Stack / Convert Images to Stack: Automatically add all open images within the program onto a Stack. Each image is added to the stack by order of most recent frame viewed to last frame viewed. Every image must have the same dimensions and bit depth. Stack / Convert Stack to Images: Automatically remove every slice from the Stack, creating a new image for each slice within the Stack. Data format is preserved from the original image when unstacked. Stack / Convert Stack to RGB: Convert three separate, colored images into a composite RGB color image. Begin procedure by adding only three images to
10 a stack. Select red, green or blue (by the Color Tables command) for each slice in stack (choose image frame by arrows at frame bottom). Each image may be colorized before adding the images to the stack also. Either method works. There must be only one red colored slice, one green slice and one blue slice in the stack or an error is displayed. Finally, choose the Convert Stack to RGB command. Note: This command converts all image formats to a 8-bit depth format, which can not be reversed. Higher bit depth image information will be lost permanently. Stack / Convert RGB to Stack: Converts a single RGB color image into three separate image slices within a Stack, one slice each of a red, green, blue color. If you unstuck the slices, each resulting image would be an 8-bit GIF formatted image. Stack / Start Animation: Begin animation sequence of stacked images. Review sequence prior to saving the image stack. Stack / Stop Animation: End animation sequence of stacked images. Stack / Animations Options : Set rate each frame in stack is displayed during animation sequence. Command shows a window entitled Stack Animation Settings and box where the frame rate, in frames per second (fps) can be adjusted. The slowest rate may be set to 1 fps and the fastest at 24 fps. Remember to save the converted RGB stack to GIF image as a GIF image by the command File / Save As / Gif. Use the command File / Save As / Animated GIF to save the stack as an animation file. Note, once a stack is saved as an animated GIF formatted file, the frame rate cannot be altered. Under the Window menu: 1. Image Info [Meta I] : Displays basic information on the FITS or GIF image and provides a zoomed (magnified) view of the current cursor location, indicated by a red crosshair. When the user starts the program, the Image Info window is opened in the top right of the program by default. Instructions stating Place Cursor Over Image, Use Up and Down Arrows to Zoom in and out of Image are shown to explain how image information can be viewed and is only displayed when the cursor is not positioned over an image. The image information shown: Data: 8 or 16-bit grayscale or color data image format standard. Image window name is displayed, if a Stack. Size: XX x YY (horizontal by vertical) numerical dimensions in pixels of the image. The origin (at the 0,0 position) is located in the upper left corner of the image. Window Mag: Magnification factor of the active image window. There are 1 to 16 levels of magnification centered on the present cursor position. Level 1 has no magnification and 16 the highest zoom factor. Refer to the Magnification Tool description in the Tool Bar section for more information about this feature. Image Info Mag: Magnification factor of smaller zoomed portion of active window shown in Image Info display window. There are 1 to 7 levels of zoom (magnification) available, centered on the cursor position. Level 1 is the lowest zoom factor and 7 the highest.
11 Level 1 = 100 x100 square array (no magnification) Level 2 = 50x50 square array Level 3 = 32x32 square array Level 4 = 24x24 square array Level 5 = 20x20 square array Level 6 = 16x16 square array Level 7 = 14x14 square array Cursor position and pixel value: X, Y, brightness value. The X value is the column or left to right position on the image. The Y value is the row or top to bottom position on the image. The pixel brightness value is measured brightness for the specific individual pixel the cursor is currently pointing to. To recall the Image Info window if closed, click on the command under the Windows menu. If the window cannot be seen amongst numerous open windows, click on the Image Info command, which will place the window in the uppermost right of the application window. 2. FITS Header [Meta f] : Displays information from a FITS (flexible image transport system) data file, called the FITS Header. Note: Edit menu functions
12 Select All and Copy can be used in this file window, to paste this data into another application. 3. Intensity Histogram [n/a] : Graph of pixel brightness values for the image data. The graph displays brightness level of pixels versus the number of pixels with that particular brightness value. The graph automatically sets the faintest brightness value on the left of the X-axis to the minimum pixel value found in the array and the brightest value to the maximum pixel value. A grey-scale bar is displayed below the X-axis to indicate darker to brighter scale of the represented values. The Y-axis values are automatically set to zero (no pixel with this brightness value) to the most frequent occurrence of a pixel brightness value in the image. Below the graph is displayed statistics for the image, including the image data file the histogram is calculated from, the minimum pixel brightness value, the maximum brightness value, the mode (most frequent value occurring within the image), the mean (average brightness value), the variance (the dispersion of brightness values from the mean value), the standard deviation (the square root of the variance) and the bin width (range of values). The variance can be used to characterize the noise and other factors of the digital detector. The standard deviation is another measure of noise characteristics. The bin width represents the frequency of pixel brightness values within a range of brightness values for the image data. This graph represents how many pixels within the image have those values. A histogram can be calculated for each image opened within the application, so you can compare different image histograms. 4. Windows Open Utility [n/a]: All the open images and histograms within the application are listed at the bottom of the Windows pull down menu. The active, topmost window is listed first and each successive image/histogram there after. Selecting any window from the list makes it the active, topmost window.
13 Under the Help menu: 1. About MicroObservatory Image [n/a] : Program information, including program release version, programmer contact and Internet address for the program and instructions. A toggle button allows the user to check for the most current version of the MicroObservatoryImage program. Note: The recommended computer memory (RAM) to run this program is 256MB.
14 The Tool Bar (in the upper left corner of every image window, below the file name): 1. Diagonal Line [n/a] : Measures separation between two points on the image. Select the diagonal line icon at the top left of the image window. Click and hold the mouse then drag and release at end point. To the right of the Tool Bar is displayed the starting point in X,Y (horizontal, vertical) image pixel coordinates and the length in pixels of the line. Remember the origin (or 0,0) position is the upper left corner of the image. Note: Use the Image Info/Zoom Window or the Magnification tool when selecting the beginning and ending point for more precise linear measures. 2. Box [n/a] : Measures the area enclosed by the scalable and moveable box. Select the square box icon at the top left of the image window. Click and hold the mouse then drag and release to define the box shape and size. Click and hold the mouse button within the box, then drag and release at the preferred location moves the box to a new location. Alternatively, for precise repositioning of the box, press the i, j, k, or l keys on the keyboard to move the shape a pixel at a time. To the right of the Tool Bar is shown the upper rightmost corner of the box in X,Y (horizontal, vertical) pixel coordinates and the width and height of the box, also in pixels. Remember the origin (or 0,0) position is the upper left corner of the image. This tool is used to define the area of the image to crop or measure pixel values, found under the Process menu. Note: Use of the Image Info/Zoom Window or the Magnification tool when making more precise area measures. 3. Circle [n/a] : Measures the area define within the circumference of a scalable and moveable circle. Select the circle icon at the top left of the image window. Click and hold the mouse then drag and release to set the radius. Click and hold the mouse button within the circle shape, then drag and release at the preferred location to reposition the circle. Alternatively, for precise repositioning of the circle, press the i, j, k, or l keys on the keyboard to move the shape a pixel at a time. To the right of the Tool Bar is shown the center of the circle in X,Y (horizontal, vertical) pixel coordinates and the radius of the circle in pixels. Remember the origin (or 0,0) position is the upper left corner of the image. Note: Use of the Image Info/Zoom Window or the Magnification tool when making precise area measures. 4. Magnification [n/a] : Full screen magnification utility. Select the magnifying glass icon at the top left of the image window. Position the mouse button within the image window and click to magnify the image window centered on this location. Each successive mouse button click doubles the magnification for this portion of the image, again, centered on where the mouse is clicked on the displayed image. Maximum zoom level is 16 times magnification (level 16). Click on the magnification icon in the Tool Bar to zoom in one magnification level or double click to return to an unmagnified image (level 1). 5. The Letter A [n/a] : A text writing utility for GIF images only. The image to be written on should be displayed in its original size and not magnified. Select the
15 letter A icon in the Tool Bar at the top left of the image window. Click and hold the mouse button then drag and release to define the text box. Click and hold the mouse button within the defined text box, then drag and release at the preferred location to reposition. Double clicking on the letter A in the Tool Bar allows you to adjust the font, size, style and color of the text. A sample text Type Text Here is shown. This text is deleted once one starts typing in the text box. Only one font, size, style, etc. is permitted in the text box. One space character is displayed between words, as multiple spaces do not add additional spacing. A space character can start a new line. The carriage return key is not available. The delete/back space key erases all mistakes. Long words are automatically repositioned on a new line and will overfill the boundaries of the defined text box if permitted. The text box can be resized but is of limited functional use. Double click outside of the text box to set the location of the text box on the image. Use the Edit menu command Undo to start over, if desired. Note: Experiment with this tool before altering a final processed image. Caution: Adding text will permanently alter the image, so save a copy of the origin GIF image file. 6. The Pencil [n/a] : This tool allows free-hand drawing of a single line on the image. Select the pencil icon at the top left of the image window. Click and hold the mouse to draw a line. To the right of the Tool Bar is the current location of the mouse cursor. Double clicking on the Pencil in the Tool Bar allows you to adjust the thickness and color of the line. The Edit command Undo will erase the last completed line only. Experiment with this tool before altering the image. Caution: Drawing lines on the image will permanently alter the image, so save a copy of the origin GIF image file. MicroObservatoryImage, version 2.2 can be selected as the default application to open FITS and/or GIF image files in Mac OSX. Choose the image file (FITS or GIF format) and select Get Info [Meta i]. A new window displaying the file information appears. Select the MicroObservatoryImage application from the Open with: pull down selection menu within the Get Info window. Written by Frank F. Sienkiewicz, Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory Updated September 24, 2010
Image Processing Tutorial Basic Concepts
 Image Processing Tutorial Basic Concepts CCDWare Publishing http://www.ccdware.com 2005 CCDWare Publishing Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Starting CCDStack... 4 Creating Calibration Frames... 5 Create
Image Processing Tutorial Basic Concepts CCDWare Publishing http://www.ccdware.com 2005 CCDWare Publishing Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Starting CCDStack... 4 Creating Calibration Frames... 5 Create
ImagesPlus Basic Interface Operation
 ImagesPlus Basic Interface Operation The basic interface operation menu options are located on the File, View, Open Images, Open Operators, and Help main menus. File Menu New The New command creates a
ImagesPlus Basic Interface Operation The basic interface operation menu options are located on the File, View, Open Images, Open Operators, and Help main menus. File Menu New The New command creates a
Adobe Photoshop CC 2018 Tutorial
 Adobe Photoshop CC 2018 Tutorial GETTING STARTED Adobe Photoshop CC 2018 is a popular image editing software that provides a work environment consistent with Adobe Illustrator, Adobe InDesign, Adobe Photoshop,
Adobe Photoshop CC 2018 Tutorial GETTING STARTED Adobe Photoshop CC 2018 is a popular image editing software that provides a work environment consistent with Adobe Illustrator, Adobe InDesign, Adobe Photoshop,
MEASUREMENT CAMERA USER GUIDE
 How to use your Aven camera s imaging and measurement tools Part 1 of this guide identifies software icons for on-screen functions, camera settings and measurement tools. Part 2 provides step-by-step operating
How to use your Aven camera s imaging and measurement tools Part 1 of this guide identifies software icons for on-screen functions, camera settings and measurement tools. Part 2 provides step-by-step operating
How to Create Website Banners
 How to Create Website Banners In the following instructions you will be creating banners in Adobe Photoshop Elements 6.0, using different images and fonts. The instructions will consist of finding images,
How to Create Website Banners In the following instructions you will be creating banners in Adobe Photoshop Elements 6.0, using different images and fonts. The instructions will consist of finding images,
Adobe Photoshop CS5 Tutorial
 Adobe Photoshop CS5 Tutorial GETTING STARTED Adobe Photoshop CS5 is a popular image editing software that provides a work environment consistent with Adobe Illustrator, Adobe InDesign, Adobe Photoshop
Adobe Photoshop CS5 Tutorial GETTING STARTED Adobe Photoshop CS5 is a popular image editing software that provides a work environment consistent with Adobe Illustrator, Adobe InDesign, Adobe Photoshop
We recommend downloading the latest core installer for our software from our website. This can be found at:
 Dusk Getting Started Installing the Software We recommend downloading the latest core installer for our software from our website. This can be found at: https://www.atik-cameras.com/downloads/ Locate and
Dusk Getting Started Installing the Software We recommend downloading the latest core installer for our software from our website. This can be found at: https://www.atik-cameras.com/downloads/ Locate and
Welcome to Photoshop CS
 Chapter 1 Welcome to Photoshop CS COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL Photoshop CS is the latest version of Photoshop, Adobe s powerful image-editing program. It s part of Adobe s Creative Suite, a package of design
Chapter 1 Welcome to Photoshop CS COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL Photoshop CS is the latest version of Photoshop, Adobe s powerful image-editing program. It s part of Adobe s Creative Suite, a package of design
Image Enhancement (from Chapter 13) (V6)
 Image Enhancement (from Chapter 13) (V6) Astronomical images often span a wide range of brightness, while important features contained in them span a very narrow range of brightness. Alternatively, interesting
Image Enhancement (from Chapter 13) (V6) Astronomical images often span a wide range of brightness, while important features contained in them span a very narrow range of brightness. Alternatively, interesting
Key Terms. Where is it Located Start > All Programs > Adobe Design Premium CS5> Adobe Photoshop CS5. Description
 Adobe Adobe Creative Suite (CS) is collection of video editing, graphic design, and web developing applications made by Adobe Systems. It includes Photoshop, InDesign, and Acrobat among other programs.
Adobe Adobe Creative Suite (CS) is collection of video editing, graphic design, and web developing applications made by Adobe Systems. It includes Photoshop, InDesign, and Acrobat among other programs.
Astronomy and Image Processing. Many thanks to Professor Kate Whitaker in the physics department for her help
 Astronomy and Image Processing Many thanks to Professor Kate Whitaker in the physics department for her help What is an image? An image is an array, or a matrix, of square pixels (picture elements) arranged
Astronomy and Image Processing Many thanks to Professor Kate Whitaker in the physics department for her help What is an image? An image is an array, or a matrix, of square pixels (picture elements) arranged
Using Adobe Photoshop
 Using Adobe Photoshop 4 Colour is important in most art forms. For example, a painter needs to know how to select and mix colours to produce the right tones in a picture. A Photographer needs to understand
Using Adobe Photoshop 4 Colour is important in most art forms. For example, a painter needs to know how to select and mix colours to produce the right tones in a picture. A Photographer needs to understand
5 Masks and Channels
 5 Masks and Channels Adobe Photoshop uses masks to isolate and manipulate specific parts of an image. A mask is like a stencil. The cutout portion of the mask can be altered, but the area surrounding the
5 Masks and Channels Adobe Photoshop uses masks to isolate and manipulate specific parts of an image. A mask is like a stencil. The cutout portion of the mask can be altered, but the area surrounding the
A guide to SalsaJ. This guide gives step-by-step instructions on how to use SalsaJ to carry out basic data analysis on astronomical data files.
 A guide to SalsaJ SalsaJ is free, student-friendly software developed originally for the European Hands- On Universe (EU-HOU) project. It is designed to be easy to install and use. It allows students to
A guide to SalsaJ SalsaJ is free, student-friendly software developed originally for the European Hands- On Universe (EU-HOU) project. It is designed to be easy to install and use. It allows students to
INSTRUCTION MANUAL MM-A209
 E INSTRUCTION MANUAL 9222-7300-11 MM-A209 2 BEFORE YOU BEGIN Before installing the DiMAGE Viewer software, read the data-transfer section in the camera manual. This section details how to connect the camera
E INSTRUCTION MANUAL 9222-7300-11 MM-A209 2 BEFORE YOU BEGIN Before installing the DiMAGE Viewer software, read the data-transfer section in the camera manual. This section details how to connect the camera
Photoshop: Manipulating Photos
 Photoshop: Manipulating Photos All Labs must be uploaded to the University s web server and permissions set properly. In this lab we will be manipulating photos using a very small subset of all of Photoshop
Photoshop: Manipulating Photos All Labs must be uploaded to the University s web server and permissions set properly. In this lab we will be manipulating photos using a very small subset of all of Photoshop
ArcSoft PhotoImpression Table of Contents:
 ArcSoft PhotoImpression Table of Contents: 1. Welcome to PhotoImpression 2. Highlights of PhotoImpression 3. System Requirements 4. Installing PhotoImpression 5. Working with PhotoImpression Getting Started
ArcSoft PhotoImpression Table of Contents: 1. Welcome to PhotoImpression 2. Highlights of PhotoImpression 3. System Requirements 4. Installing PhotoImpression 5. Working with PhotoImpression Getting Started
Table of Contents 1. Image processing Measurements System Tools...10
 Introduction Table of Contents 1 An Overview of ScopeImage Advanced...2 Features:...2 Function introduction...3 1. Image processing...3 1.1 Image Import and Export...3 1.1.1 Open image file...3 1.1.2 Import
Introduction Table of Contents 1 An Overview of ScopeImage Advanced...2 Features:...2 Function introduction...3 1. Image processing...3 1.1 Image Import and Export...3 1.1.1 Open image file...3 1.1.2 Import
IMPAX 6 DISPLAY TOOL LIST
 IMPAX 6 DISPLAY TOOL LIST IMPAX 6.0 TOOLS INDEX A Advance by Image Allows you to scroll from one image or frame to the next Advance by Page Pages through images in a large series, one screen at a time
IMPAX 6 DISPLAY TOOL LIST IMPAX 6.0 TOOLS INDEX A Advance by Image Allows you to scroll from one image or frame to the next Advance by Page Pages through images in a large series, one screen at a time
ASTRO 1050 MicroObservatory RGB Image (if cloudy)
 ASTRO 1050 MicroObservatory RGB Image (if cloudy) ABSTRACT For this assignment, you will be using the MicroObservatory Robotic Telescope Network, run by the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics
ASTRO 1050 MicroObservatory RGB Image (if cloudy) ABSTRACT For this assignment, you will be using the MicroObservatory Robotic Telescope Network, run by the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics
LAB 2: Sampling & aliasing; quantization & false contouring
 CEE 615: Digital Image Processing Spring 2016 1 LAB 2: Sampling & aliasing; quantization & false contouring A. SAMPLING: Observe the effects of the sampling interval near the resolution limit. The goal
CEE 615: Digital Image Processing Spring 2016 1 LAB 2: Sampling & aliasing; quantization & false contouring A. SAMPLING: Observe the effects of the sampling interval near the resolution limit. The goal
By Washan Najat Nawi
 By Washan Najat Nawi how to get started how to use the interface how to modify images with basic editing skills Adobe Photoshop: is a popular image-editing software. Two general usage of Photoshop Creating
By Washan Najat Nawi how to get started how to use the interface how to modify images with basic editing skills Adobe Photoshop: is a popular image-editing software. Two general usage of Photoshop Creating
Color and More. Color basics
 Color and More In this lesson, you'll evaluate an image in terms of its overall tonal range (lightness, darkness, and contrast), its overall balance of color, and its overall appearance for areas that
Color and More In this lesson, you'll evaluate an image in terms of its overall tonal range (lightness, darkness, and contrast), its overall balance of color, and its overall appearance for areas that
Enhancement of Multispectral Images and Vegetation Indices
 Enhancement of Multispectral Images and Vegetation Indices ERDAS Imagine 2016 Description: We will use ERDAS Imagine with multispectral images to learn how an image can be enhanced for better interpretation.
Enhancement of Multispectral Images and Vegetation Indices ERDAS Imagine 2016 Description: We will use ERDAS Imagine with multispectral images to learn how an image can be enhanced for better interpretation.
Photoshop CC 2018 Essential Skills
 Photoshop CC 2018 Essential Skills Adobe Photoshop Creative Cloud 2018 University Information Technology Services Learning Technology, Training, Audiovisual and Outreach Copyright 2018 KSU Division of
Photoshop CC 2018 Essential Skills Adobe Photoshop Creative Cloud 2018 University Information Technology Services Learning Technology, Training, Audiovisual and Outreach Copyright 2018 KSU Division of
Geometric Functions. The color channel toolbar buttons are disabled.
 Introduction to Geometric Transformations Geometric Functions The geometric transformation commands are used to shift, rotate, scale, and align images. For quick rotation by 90 or mirroring of an image,
Introduction to Geometric Transformations Geometric Functions The geometric transformation commands are used to shift, rotate, scale, and align images. For quick rotation by 90 or mirroring of an image,
Image Pro Ultra. Tel:
 Image Pro Ultra www.ysctech.com info@ysctech.com Tel: 510.226.0889 Instructions for installing YSC VIC-USB and IPU For software and manual download, please go to below links. http://ysctech.com/support/ysc_imageproultra_20111010.zip
Image Pro Ultra www.ysctech.com info@ysctech.com Tel: 510.226.0889 Instructions for installing YSC VIC-USB and IPU For software and manual download, please go to below links. http://ysctech.com/support/ysc_imageproultra_20111010.zip
Viewing Landsat TM images with Adobe Photoshop
 Viewing Landsat TM images with Adobe Photoshop Reformatting images into GeoTIFF format Of the several formats in which Landsat TM data are available, only a few formats (primarily TIFF or GeoTIFF) can
Viewing Landsat TM images with Adobe Photoshop Reformatting images into GeoTIFF format Of the several formats in which Landsat TM data are available, only a few formats (primarily TIFF or GeoTIFF) can
Motic Live Imaging Module. Windows OS User Manual
 Motic Live Imaging Module Windows OS User Manual Motic Live Imaging Module Windows OS User Manual CONTENTS (Linked) Introduction 05 Menus, bars and tools 06 Title bar 06 Menu bar 06 Status bar 07 FPS 07
Motic Live Imaging Module Windows OS User Manual Motic Live Imaging Module Windows OS User Manual CONTENTS (Linked) Introduction 05 Menus, bars and tools 06 Title bar 06 Menu bar 06 Status bar 07 FPS 07
Photoshop CC Editing Images
 Photoshop CC Editing Images Rotate a Canvas A canvas can be rotated 90 degrees Clockwise, 90 degrees Counter Clockwise, or rotated 180 degrees. Navigate to the Image Menu, select Image Rotation and then
Photoshop CC Editing Images Rotate a Canvas A canvas can be rotated 90 degrees Clockwise, 90 degrees Counter Clockwise, or rotated 180 degrees. Navigate to the Image Menu, select Image Rotation and then
Fuzzy Image Editor. User Manual
 Fuzzy Image Editor User Manual I. Installation To install the program, run Fuzzy Image Editor.msi and follow the prompts. Then go to your Program Files/Team6/FuzzyImageEditor folder, right click and run
Fuzzy Image Editor User Manual I. Installation To install the program, run Fuzzy Image Editor.msi and follow the prompts. Then go to your Program Files/Team6/FuzzyImageEditor folder, right click and run
ADOBE PHOTOSHOP CS TUTORIAL
 ADOBE PHOTOSHOP CS TUTORIAL A D O B E P H O T O S H O P C S Adobe Photoshop CS is a popular image editing software that provides a work environment consistent with Adobe Illustrator, Adobe InDesign, Adobe
ADOBE PHOTOSHOP CS TUTORIAL A D O B E P H O T O S H O P C S Adobe Photoshop CS is a popular image editing software that provides a work environment consistent with Adobe Illustrator, Adobe InDesign, Adobe
Photoshop CC: Essentials
 Photoshop CC: Essentials Summary Workspace Overview... 2 Exercise Files... 2 Selection Tools... 3 Select All, Deselect, And Reselect... 3 Adding, Subtracting, and Intersecting... 3 Working with Layers...
Photoshop CC: Essentials Summary Workspace Overview... 2 Exercise Files... 2 Selection Tools... 3 Select All, Deselect, And Reselect... 3 Adding, Subtracting, and Intersecting... 3 Working with Layers...
INSTRUCTION MANUAL 2.3
 GB INSTRUCTION MANUAL 2.3 Become a member of Konica Minolta Photo World today, free of charge, and enter the fascinating world of Konica Minolta photography. The ultimate gateway to knowledge for photo-fans:
GB INSTRUCTION MANUAL 2.3 Become a member of Konica Minolta Photo World today, free of charge, and enter the fascinating world of Konica Minolta photography. The ultimate gateway to knowledge for photo-fans:
GETTING STARTED. 0 P a g e B a s i c s o f A d o b e P h o t o s h o p A g a P r i v a t e I n s t i t u t e f o r c o m p u t e r s c i e n c e
 GETTING STARTED 0 P a g e B a s i c s o f A d o b e P h o t o s h o p Adobe Photoshop: is a popular image editing software that provides a work environment consistent with Adobe Illustrator, Adobe InDesign,
GETTING STARTED 0 P a g e B a s i c s o f A d o b e P h o t o s h o p Adobe Photoshop: is a popular image editing software that provides a work environment consistent with Adobe Illustrator, Adobe InDesign,
ScanGear CS-U 5.3 for CanoScan FB630U/FB636U Color Image Scanner User s Guide
 ScanGear CS-U 5.3 for CanoScan FB630U/FB636U Color Image Scanner User s Guide Copyright Notice 1999 Canon Inc. This manual is copyrighted with all rights reserved. Under the copyright laws, this manual
ScanGear CS-U 5.3 for CanoScan FB630U/FB636U Color Image Scanner User s Guide Copyright Notice 1999 Canon Inc. This manual is copyrighted with all rights reserved. Under the copyright laws, this manual
Visioneer OneTouch Scanner. Installation Guide FOR WINDOWS
 Visioneer OneTouch Scanner Installation Guide FOR WINDOWS TABLE OF CONTENTS i TABLE OF CONTENTS Getting Started with your new Scanner....................... 1 Step 1: Installing the Scanner Software.......................
Visioneer OneTouch Scanner Installation Guide FOR WINDOWS TABLE OF CONTENTS i TABLE OF CONTENTS Getting Started with your new Scanner....................... 1 Step 1: Installing the Scanner Software.......................
Lesson 16 Text, Layer Effects, & Filters
 Lesson 16 Text, Layer Effects, & Filters Digital Media I Susan M. Raymond West High School In this tutorial, you will: Create a Type Layer Add and Format Type within a Type Layer Apply Layer Effects Apply
Lesson 16 Text, Layer Effects, & Filters Digital Media I Susan M. Raymond West High School In this tutorial, you will: Create a Type Layer Add and Format Type within a Type Layer Apply Layer Effects Apply
Adobe Photoshop CS5 Layers and Masks
 Adobe Photoshop CS5 Layers and Masks Email: training@health.ufl.edu Web Page: http://training.health.ufl.edu Adobe Photoshop CS5: Layers and Masks 2.0 Hours The workshop will cover creating and manipulating
Adobe Photoshop CS5 Layers and Masks Email: training@health.ufl.edu Web Page: http://training.health.ufl.edu Adobe Photoshop CS5: Layers and Masks 2.0 Hours The workshop will cover creating and manipulating
Photoshop Elements Hints by Steve Miller
 2015 Elements 13 A brief tutorial for basic photo file processing To begin, click on the Elements 13 icon, click on Photo Editor in the first box that appears. We will not be discussing the Organizer portion
2015 Elements 13 A brief tutorial for basic photo file processing To begin, click on the Elements 13 icon, click on Photo Editor in the first box that appears. We will not be discussing the Organizer portion
Photoshop CS2. Step by Step Instructions Using Layers. Adobe. About Layers:
 About Layers: Layers allow you to work on one element of an image without disturbing the others. Think of layers as sheets of acetate stacked one on top of the other. You can see through transparent areas
About Layers: Layers allow you to work on one element of an image without disturbing the others. Think of layers as sheets of acetate stacked one on top of the other. You can see through transparent areas
Extended Studies - Intro to Adobe Photoshop
 Working with Curves Curves are the Swiss Army knife of Photoshop. They re great for adjusting both the contrast and color balance of an image in one window. They can lighten and darken areas without selections
Working with Curves Curves are the Swiss Army knife of Photoshop. They re great for adjusting both the contrast and color balance of an image in one window. They can lighten and darken areas without selections
Reflection Project. Please start by resetting all tools in Photoshop.
 Reflection Project You will be creating a floor and wall for your advertisement. Before you begin on the Reflection Project, create a new composition. File New: Width 720 Pixels / Height 486 Pixels. Resolution
Reflection Project You will be creating a floor and wall for your advertisement. Before you begin on the Reflection Project, create a new composition. File New: Width 720 Pixels / Height 486 Pixels. Resolution
When you shoot a picture the lighting is not always ideal, so pictures sometimes may be underor overexposed.
 GIMP Brightness and Contrast Exposure When you shoot a picture the lighting is not always ideal, so pictures sometimes may be underor overexposed. A well-exposed image will have a good spread of tones
GIMP Brightness and Contrast Exposure When you shoot a picture the lighting is not always ideal, so pictures sometimes may be underor overexposed. A well-exposed image will have a good spread of tones
Module All You Ever Need to Know About The Displace Filter
 Module 02-05 All You Ever Need to Know About The Displace Filter 02-05 All You Ever Need to Know About The Displace Filter [00:00:00] In this video, we're going to talk about the Displace Filter in Photoshop.
Module 02-05 All You Ever Need to Know About The Displace Filter 02-05 All You Ever Need to Know About The Displace Filter [00:00:00] In this video, we're going to talk about the Displace Filter in Photoshop.
Chlorophyll Fluorescence Imaging System
 Quick Start Guide Chlorophyll Fluorescence Imaging System Quick Start Guide for Technologica FluorImager software for use with Technlogica CFImager hardware Copyright 2006 2015 TECHNOLOGICA LIMITED. All
Quick Start Guide Chlorophyll Fluorescence Imaging System Quick Start Guide for Technologica FluorImager software for use with Technlogica CFImager hardware Copyright 2006 2015 TECHNOLOGICA LIMITED. All
μscope Microscopy Software
 μscope Microscopy Software Pixelink μscope Essentials (ES) Software is an easy-to-use robust image capture tool optimized for productivity. Pixelink μscope Standard (SE) Software had added features, making
μscope Microscopy Software Pixelink μscope Essentials (ES) Software is an easy-to-use robust image capture tool optimized for productivity. Pixelink μscope Standard (SE) Software had added features, making
Apple iphoto 4 ITS Technology & Learning Services Dr. Luanne Fose Revised April 29, 2004
 Apple iphoto 4 ITS Technology & Learning Services Dr. Luanne Fose Revised April 29, 2004 Table of Contents Introduction...1 Importing Photos From Your Digital Camera...1 Importing Photos From Other Sources...2
Apple iphoto 4 ITS Technology & Learning Services Dr. Luanne Fose Revised April 29, 2004 Table of Contents Introduction...1 Importing Photos From Your Digital Camera...1 Importing Photos From Other Sources...2
AmericaView EOD 2016 page 1 of 16
 Remote Sensing Flood Analysis Lesson Using MultiSpec Online By Larry Biehl Systems Manager, Purdue Terrestrial Observatory (biehl@purdue.edu) v Objective The objective of these exercises is to analyze
Remote Sensing Flood Analysis Lesson Using MultiSpec Online By Larry Biehl Systems Manager, Purdue Terrestrial Observatory (biehl@purdue.edu) v Objective The objective of these exercises is to analyze
W i n d o w s. ScanGear CS-S 4.3 for CanoScan FB1200S Color Image Scanner. User's Guide
 f o r W i n d o w s ScanGear CS-S 4.3 for CanoScan FB1200S Color Image Scanner User's Guide How to Make Best Use of the Manuals 2 When you open the box Printed Manual CanoScan FB1200S Quick Start Guide
f o r W i n d o w s ScanGear CS-S 4.3 for CanoScan FB1200S Color Image Scanner User's Guide How to Make Best Use of the Manuals 2 When you open the box Printed Manual CanoScan FB1200S Quick Start Guide
Adobe Photoshop CS2 Workshop
 COMMUNITY TECHNICAL SUPPORT Adobe Photoshop CS2 Workshop Photoshop CS2 Help For more technical assistance, open Photoshop CS2 and press the F1 key, or go to Help > Photoshop Help. Selection Tools - The
COMMUNITY TECHNICAL SUPPORT Adobe Photoshop CS2 Workshop Photoshop CS2 Help For more technical assistance, open Photoshop CS2 and press the F1 key, or go to Help > Photoshop Help. Selection Tools - The
Digital Imaging - Photoshop
 Digital Imaging - Photoshop A digital image is a computer representation of a photograph. It is composed of a grid of tiny squares called pixels (picture elements). Each pixel has a position on the grid
Digital Imaging - Photoshop A digital image is a computer representation of a photograph. It is composed of a grid of tiny squares called pixels (picture elements). Each pixel has a position on the grid
GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program) MANUAL
 Selection Tools Icon Tool Name Function Select Rectangle Select Ellipse Select Hand-drawn area (lasso tool) Select Contiguous Region (magic wand) Selects a rectangular area, drawn from upper left (or lower
Selection Tools Icon Tool Name Function Select Rectangle Select Ellipse Select Hand-drawn area (lasso tool) Select Contiguous Region (magic wand) Selects a rectangular area, drawn from upper left (or lower
ISCapture User Guide. advanced CCD imaging. Opticstar
 advanced CCD imaging Opticstar I We always check the accuracy of the information in our promotional material. However, due to the continuous process of product development and improvement it is possible
advanced CCD imaging Opticstar I We always check the accuracy of the information in our promotional material. However, due to the continuous process of product development and improvement it is possible
Reference Guide. Color Image Scanner
 Color Image Scanner All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording,
Color Image Scanner All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording,
UN-SCAN-IT gel TM Version 6.3. User's Manual for. Macintosh (OS X)
 UN-SCAN-IT gel TM Version 6.3 User's Manual for Macintosh (OS X) Silk Scientific Inc. software and manuals are copyrighted, which means that your right to copy any part of them is limited by copyright
UN-SCAN-IT gel TM Version 6.3 User's Manual for Macintosh (OS X) Silk Scientific Inc. software and manuals are copyrighted, which means that your right to copy any part of them is limited by copyright
Introduction to Photoshop
 Introduction to Photoshop Instructional Services at KU Libraries A Division of Information Services www.lib.ku.edu/instruction Abstract: This course covers the basics of Photoshop, including common tools
Introduction to Photoshop Instructional Services at KU Libraries A Division of Information Services www.lib.ku.edu/instruction Abstract: This course covers the basics of Photoshop, including common tools
Generations Automatic Stand-Alone Lace By Bernie Griffith Generations Software
 We are going to create an open Italian lace. Generations software products provide advanced image processing features allowing for the creation of stand-alone lace with just a few simple techniques. A
We are going to create an open Italian lace. Generations software products provide advanced image processing features allowing for the creation of stand-alone lace with just a few simple techniques. A
GIMP Layers. Creating a Blank Image
 GIMP Layers One of the most powerful features of modern imaging software is the ability to work with layers. If an image is made of layers, we can work on the part that is in one layer without affecting
GIMP Layers One of the most powerful features of modern imaging software is the ability to work with layers. If an image is made of layers, we can work on the part that is in one layer without affecting
Drawing Bode Plots (The Last Bode Plot You Will Ever Make) Charles Nippert
 Drawing Bode Plots (The Last Bode Plot You Will Ever Make) Charles Nippert This set of notes describes how to prepare a Bode plot using Mathcad. Follow these instructions to draw Bode plot for any transfer
Drawing Bode Plots (The Last Bode Plot You Will Ever Make) Charles Nippert This set of notes describes how to prepare a Bode plot using Mathcad. Follow these instructions to draw Bode plot for any transfer
Rendering a perspective drawing using Adobe Photoshop
 Rendering a perspective drawing using Adobe Photoshop This hand-out will take you through the steps to render a perspective line drawing using Adobe Photoshop. The first important element in this process
Rendering a perspective drawing using Adobe Photoshop This hand-out will take you through the steps to render a perspective line drawing using Adobe Photoshop. The first important element in this process
Toothbrush Holder. A drawing of the sheet metal part will also be created.
 Prerequisite Knowledge Previous knowledge of the following commands is required to complete this lesson; Sketch (Line, Centerline, Circle, Add Relations, Smart Dimension,), Extrude Boss/Base, and Edit
Prerequisite Knowledge Previous knowledge of the following commands is required to complete this lesson; Sketch (Line, Centerline, Circle, Add Relations, Smart Dimension,), Extrude Boss/Base, and Edit
AutoCAD Tutorial First Level. 2D Fundamentals. Randy H. Shih SDC. Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
 AutoCAD 2018 Tutorial First Level 2D Fundamentals Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites to
AutoCAD 2018 Tutorial First Level 2D Fundamentals Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites to
Software Reference. FlexColor 3.0 for Flextight Scanners. by imacon
 Software Reference FlexColor 3.0 for Flextight Scanners by imacon 2 2001 Imacon A/S. All rights reserved., revision X-X. The information in this manual is furnished for informational use only, is subject
Software Reference FlexColor 3.0 for Flextight Scanners by imacon 2 2001 Imacon A/S. All rights reserved., revision X-X. The information in this manual is furnished for informational use only, is subject
Infinity Software Manual
 Infinity Software Manual Version 1.5 - October 2017 1 Contents Introduction 4 Getting Started 5 Main Screen 6 Mode Selection 7 Replay Mode 7 Taking an Image 8 Play 8 Exposure Progress 8 Exposure Settings
Infinity Software Manual Version 1.5 - October 2017 1 Contents Introduction 4 Getting Started 5 Main Screen 6 Mode Selection 7 Replay Mode 7 Taking an Image 8 Play 8 Exposure Progress 8 Exposure Settings
Welcome to Corel DESIGNER, a comprehensive vector-based package for technical graphic users and technical illustrators.
 Workspace tour Welcome to Corel DESIGNER, a comprehensive vector-based package for technical graphic users and technical illustrators. This tutorial will help you become familiar with the terminology and
Workspace tour Welcome to Corel DESIGNER, a comprehensive vector-based package for technical graphic users and technical illustrators. This tutorial will help you become familiar with the terminology and
Photoshop: Manipulating Photos
 Photoshop: Manipulating Photos All Labs must be uploaded to the University s web server and permissions set properly. In this lab we will be manipulating photos using a very small subset of all of Photoshop
Photoshop: Manipulating Photos All Labs must be uploaded to the University s web server and permissions set properly. In this lab we will be manipulating photos using a very small subset of all of Photoshop
Scanning Setup Guide for TWAIN Datasource
 Scanning Setup Guide for TWAIN Datasource Starting the Scan Validation Tool... 2 The Scan Validation Tool dialog box... 3 Using the TWAIN Datasource... 4 How do I begin?... 5 Selecting Image settings...
Scanning Setup Guide for TWAIN Datasource Starting the Scan Validation Tool... 2 The Scan Validation Tool dialog box... 3 Using the TWAIN Datasource... 4 How do I begin?... 5 Selecting Image settings...
Photoshop: a Beginner s course. by: Charina Ong Centre for Development of Teaching and Learning National University of Singapore
 Photoshop: a Beginner s course by: Charina Ong Centre for Development of Teaching and Learning National University of Singapore Table of Contents About the Workshop... 1 Prerequisites... 1 Workshop Objectives...
Photoshop: a Beginner s course by: Charina Ong Centre for Development of Teaching and Learning National University of Singapore Table of Contents About the Workshop... 1 Prerequisites... 1 Workshop Objectives...
Recitation 2 Introduction to Photoshop
 Recitation 2 Introduction to Photoshop What is Adobe Photoshop? Adobe Photoshop is a tool for creating digital graphics either by starting with a scanned photograph or artwork or by creating the graphics
Recitation 2 Introduction to Photoshop What is Adobe Photoshop? Adobe Photoshop is a tool for creating digital graphics either by starting with a scanned photograph or artwork or by creating the graphics
Software Reference. FlexColor 4.0 for Camera Backs. by Hasselblad Imacon
 Software Reference FlexColor 4.0 for Camera Backs by Hasselblad Imacon 2 2004 Hasselblad A/S. All rights reserved., Part No 70030035 revision 1.0. The information in this manual is furnished for informational
Software Reference FlexColor 4.0 for Camera Backs by Hasselblad Imacon 2 2004 Hasselblad A/S. All rights reserved., Part No 70030035 revision 1.0. The information in this manual is furnished for informational
AutoCAD LT 2009 Tutorial
 AutoCAD LT 2009 Tutorial Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. AutoCAD LT 2009 Tutorial 1-1 Lesson
AutoCAD LT 2009 Tutorial Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. AutoCAD LT 2009 Tutorial 1-1 Lesson
5. SilverFast Tools Tools SilverFast Manual. 5. SilverFast Tools Image Auto-Adjust (Auto-Gradation) 114
 Chapter 5 Tools 5. SilverFast Tools 5. SilverFast Tools 106 5.1 Image Auto-Adjust (Auto-Gradation) 114 5.2 Highlight / Shadow Tool 123 5.3 The Histogram 133 5.4 Gradation Dialogue 147 5.5 Global Colour
Chapter 5 Tools 5. SilverFast Tools 5. SilverFast Tools 106 5.1 Image Auto-Adjust (Auto-Gradation) 114 5.2 Highlight / Shadow Tool 123 5.3 The Histogram 133 5.4 Gradation Dialogue 147 5.5 Global Colour
2. Advanced Image editing
 Aim: In this lesson, you will learn: 2. Advanced Image editing Tejas: We have some pictures with us. We want to insert these pictures in a story that we are writing. Jyoti: Some of the pictures need modification
Aim: In this lesson, you will learn: 2. Advanced Image editing Tejas: We have some pictures with us. We want to insert these pictures in a story that we are writing. Jyoti: Some of the pictures need modification
Photoshop Elements Week 1 - Photoshop Elements Work Environment
 Menu Bar Just like any computer program, you have several dropdown menus to work with. Explore them all! But, most importantly remember to SAVE! Photoshop Elements Toolbox (with keyboard shortcut) Photoshop
Menu Bar Just like any computer program, you have several dropdown menus to work with. Explore them all! But, most importantly remember to SAVE! Photoshop Elements Toolbox (with keyboard shortcut) Photoshop
DIGITAL-MICROSCOPY CAMERA SOLUTIONS USB 3.0
 DIGITAL-MICROSCOPY CAMERA SOLUTIONS USB 3.0 PixeLINK for Microscopy Applications PixeLINK will work with you to choose and integrate the optimal USB 3.0 camera for your microscopy project. Ideal for use
DIGITAL-MICROSCOPY CAMERA SOLUTIONS USB 3.0 PixeLINK for Microscopy Applications PixeLINK will work with you to choose and integrate the optimal USB 3.0 camera for your microscopy project. Ideal for use
2. Advanced Image Editing
 2. Advanced Image Editing Aim: In this lesson, you will learn: The different options and tools to edit an image. The different ways to change and/or add attributes of an image. Jyoti: I want to prepare
2. Advanced Image Editing Aim: In this lesson, you will learn: The different options and tools to edit an image. The different ways to change and/or add attributes of an image. Jyoti: I want to prepare
Nikon Scan Windows. Contents. TWAIN Driver. User s Manual
 Contents TWAIN Driver Nikon Scan Windows User s Manual 1. Overview 2. Before You Begin 2.1 System Requirements 2.2 Software Installation 3. Basic Operations 3.1 Launching and Quitting 3.2 Main Dialog Box
Contents TWAIN Driver Nikon Scan Windows User s Manual 1. Overview 2. Before You Begin 2.1 System Requirements 2.2 Software Installation 3. Basic Operations 3.1 Launching and Quitting 3.2 Main Dialog Box
Introduction to Photoshop: Basic Editing & Prepare Images for the Web
 Introduction to Photoshop: Basic Editing & Prepare Images for the Web 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Basic tools in Photoshop & Use of Bridge Prepare images for print and web use TOPICS COVERED Photoshop Interface
Introduction to Photoshop: Basic Editing & Prepare Images for the Web 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Basic tools in Photoshop & Use of Bridge Prepare images for print and web use TOPICS COVERED Photoshop Interface
Photoshop Elements 3 Graphics
 Photoshop Elements 3 Graphics So far we have concentrated on modifying photographs. Photoshop Elements also can be used to create and modify graphics images that do not necessarily begin with a photograph.
Photoshop Elements 3 Graphics So far we have concentrated on modifying photographs. Photoshop Elements also can be used to create and modify graphics images that do not necessarily begin with a photograph.
The Main Screen. Viewing Area - show the photos that were selected in the Source List.
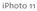 iphoto 11 The Main Screen Source List - This is where the Library, Events and Albums are identified. It is the place where photos can be organized and accessed. The Source List can also contain the slideshows,
iphoto 11 The Main Screen Source List - This is where the Library, Events and Albums are identified. It is the place where photos can be organized and accessed. The Source List can also contain the slideshows,
Applying mathematics to digital image processing using a spreadsheet
 Jeff Waldock Applying mathematics to digital image processing using a spreadsheet Jeff Waldock Department of Engineering and Mathematics Sheffield Hallam University j.waldock@shu.ac.uk Introduction When
Jeff Waldock Applying mathematics to digital image processing using a spreadsheet Jeff Waldock Department of Engineering and Mathematics Sheffield Hallam University j.waldock@shu.ac.uk Introduction When
Recovering highlight detail in over exposed NEF images
 Recovering highlight detail in over exposed NEF images Request I would like to compensate tones in overexposed RAW image, exhibiting a loss of detail in highlight portions. Response Highlight tones can
Recovering highlight detail in over exposed NEF images Request I would like to compensate tones in overexposed RAW image, exhibiting a loss of detail in highlight portions. Response Highlight tones can
2. Advanced Image Editing
 2. Advanced Image Editing Aim: In this lesson, you will learn: The different options and tools to edit an image. The different ways to change and/or add attributes of an image. Jyoti: I want to prepare
2. Advanced Image Editing Aim: In this lesson, you will learn: The different options and tools to edit an image. The different ways to change and/or add attributes of an image. Jyoti: I want to prepare
Version 4.2 For WINDOWS
 SIGMA Photo Pro User Guide Companion Processing Software for SIGMA Digital Cameras Version 4.2 For WINDOWS I M P O R T A N T : Please Read Before You Start Thank you very much for purchasing this SIGMA
SIGMA Photo Pro User Guide Companion Processing Software for SIGMA Digital Cameras Version 4.2 For WINDOWS I M P O R T A N T : Please Read Before You Start Thank you very much for purchasing this SIGMA
2. Picture Window Tutorial
 2. Picture Window Tutorial Copyright (c) Ken Deitcher, 1999 Original image Final image To get you started using Picture Window we present two short tutorials. Basic Image Editing This tutorial covers basic
2. Picture Window Tutorial Copyright (c) Ken Deitcher, 1999 Original image Final image To get you started using Picture Window we present two short tutorials. Basic Image Editing This tutorial covers basic
Digital Portable Overhead Document Camera LV-1010
 Digital Portable Overhead Document Camera LV-1010 Instruction Manual 1 Content I Product Introduction 1.1 Product appearance..3 1.2 Main functions and features of the product.3 1.3 Production specifications.4
Digital Portable Overhead Document Camera LV-1010 Instruction Manual 1 Content I Product Introduction 1.1 Product appearance..3 1.2 Main functions and features of the product.3 1.3 Production specifications.4
SDC. AutoCAD LT 2007 Tutorial. Randy H. Shih. Schroff Development Corporation Oregon Institute of Technology
 AutoCAD LT 2007 Tutorial Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com AutoCAD LT 2007 Tutorial 1-1 Lesson 1 Geometric
AutoCAD LT 2007 Tutorial Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com AutoCAD LT 2007 Tutorial 1-1 Lesson 1 Geometric
CSCI Lab 6. Part I: Simple Image Editing with Paint. Introduction to Personal Computing University of Georgia. Multimedia/Image Processing
 CSCI-1100 Introduction to Personal Computing University of Georgia Lab 6 Multimedia/Image Processing Purpose: The purpose of this lab is for you to gain experience performing image processing using some
CSCI-1100 Introduction to Personal Computing University of Georgia Lab 6 Multimedia/Image Processing Purpose: The purpose of this lab is for you to gain experience performing image processing using some
12. Creating a Product Mockup in Perspective
 12. Creating a Product Mockup in Perspective Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Understand perspective drawing. Use grid presets. Adjust the perspective grid. Draw and
12. Creating a Product Mockup in Perspective Lesson overview In this lesson, you ll learn how to do the following: Understand perspective drawing. Use grid presets. Adjust the perspective grid. Draw and
PATHTRACE MANUAL. Revision A Software Version 5.4 MatDesigner
 PATHTRACE MANUAL Revision A Software Version 5.4 MatDesigner Wizard International, Inc., 4600 116th St. SW, PO Box 66, Mukilteo, WA 98275 888/855-3335 Fax: 425/551-4350 wizardint.com NOTES: B- MatDesigner
PATHTRACE MANUAL Revision A Software Version 5.4 MatDesigner Wizard International, Inc., 4600 116th St. SW, PO Box 66, Mukilteo, WA 98275 888/855-3335 Fax: 425/551-4350 wizardint.com NOTES: B- MatDesigner
IT154 Midterm Study Guide
 IT154 Midterm Study Guide These are facts about the Adobe Photoshop CS4 application. If you know these facts, you should be able to do well on your midterm. Photoshop CS4 is part of the Adobe Creative
IT154 Midterm Study Guide These are facts about the Adobe Photoshop CS4 application. If you know these facts, you should be able to do well on your midterm. Photoshop CS4 is part of the Adobe Creative
Using Adobe Photoshop to enhance the image quality. Assistant course web site:
 Using Adobe Photoshop to enhance the image quality Assistant course web site: http://www.arches.uga.edu/~skwang/edit6170/course.htm Content Introduction 2 Unit1: Scan images 3 Lesson 1-1: Preparations
Using Adobe Photoshop to enhance the image quality Assistant course web site: http://www.arches.uga.edu/~skwang/edit6170/course.htm Content Introduction 2 Unit1: Scan images 3 Lesson 1-1: Preparations
Adobe Photoshop PS2, Part 3
 Adobe Photoshop PS2, Part 3 Basic Photo Corrections This guide steps you through the process of acquiring, resizing, and retouching a photo intended for posting on the Web as well as for a print layout.
Adobe Photoshop PS2, Part 3 Basic Photo Corrections This guide steps you through the process of acquiring, resizing, and retouching a photo intended for posting on the Web as well as for a print layout.
1 ImageBrowser Software User Guide 5.1
 1 ImageBrowser Software User Guide 5.1 Table of Contents (1/2) Chapter 1 What is ImageBrowser? Chapter 2 What Can ImageBrowser Do?... 5 Guide to the ImageBrowser Windows... 6 Downloading and Printing Images
1 ImageBrowser Software User Guide 5.1 Table of Contents (1/2) Chapter 1 What is ImageBrowser? Chapter 2 What Can ImageBrowser Do?... 5 Guide to the ImageBrowser Windows... 6 Downloading and Printing Images
CHROMACAL User Guide (v 1.1) User Guide
 CHROMACAL User Guide (v 1.1) User Guide User Guide Notice Hello and welcome to the User Guide for the Datacolor CHROMACAL Color Calibration System for Optical Microscopy, a cross-platform solution that
CHROMACAL User Guide (v 1.1) User Guide User Guide Notice Hello and welcome to the User Guide for the Datacolor CHROMACAL Color Calibration System for Optical Microscopy, a cross-platform solution that
Operating Procedures for MICROCT1 Nikon XTH 225 ST
 Operating Procedures for MICROCT1 Nikon XTH 225 ST Ensuring System is Ready (go through to ensure all windows and tasks below have been completed either by you or someone else prior to mounting and scanning
Operating Procedures for MICROCT1 Nikon XTH 225 ST Ensuring System is Ready (go through to ensure all windows and tasks below have been completed either by you or someone else prior to mounting and scanning
Ryan - Using the PhotoStitch Wizard
 Ryan - Using the PhotoStitch Wizard This exercise is taken from the PhotoStitch Wizard chapter of the PREMIER+ EMBROIDERY/PREMIER+ EXTRA Reference Guide. Using the PhotoStitch Wizard 1 - Load and Edit
Ryan - Using the PhotoStitch Wizard This exercise is taken from the PhotoStitch Wizard chapter of the PREMIER+ EMBROIDERY/PREMIER+ EXTRA Reference Guide. Using the PhotoStitch Wizard 1 - Load and Edit
Copyrights and Trademarks
 Mobile Copyrights and Trademarks Autodesk SketchBook Mobile (2.0) 2012 Autodesk, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Except as otherwise permitted by Autodesk, Inc., this publication, or parts thereof, may not be
Mobile Copyrights and Trademarks Autodesk SketchBook Mobile (2.0) 2012 Autodesk, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Except as otherwise permitted by Autodesk, Inc., this publication, or parts thereof, may not be
Excel 2003: Discos. 1. Open Excel. 2. Create Choose a new worksheet and save the file to your area calling it: Disco.xls
 Excel 2003: Discos 1. Open Excel 2. Create Choose a new worksheet and save the file to your area calling it: Disco.xls 3. Enter the following data into your spreadsheet: 4. Make the headings bold. Centre
Excel 2003: Discos 1. Open Excel 2. Create Choose a new worksheet and save the file to your area calling it: Disco.xls 3. Enter the following data into your spreadsheet: 4. Make the headings bold. Centre
