Objectives. Materials
|
|
|
- Ronald Crawford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 . Objectives Activity 8 To plot a mathematical relationship that defines a spiral To use technology to create a spiral similar to that found in a snail To use technology to plot a set of ordered pairs Materials At a Snail s Pace Introduction TI-73 Lead pencil Colored pencils - red and green Metric ruler Compass Tracing paper and graph paper It is hard to imagine a way to mathematically describe a spiral. Spirals are commonly seen in nature. There are a number of different types of spirals. Some interesting examples include the spiral arrangements of scales in pine cones, seeds in a sunflower, or the calcified layers of a snail s shell. One way of constructing a spiral is to use the Fibonacci sequence. This sequence was examined in Activity 4: The Calcumites Are Coming! The sequence starts with the following series of numbers: 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, and so on. Starting with the third number, each number is equal to the sum of the two numbers preceding it. This sequence can be applied to constructing a spiral resembling a snail s shell. Problem A snail shell is composed of a spiral of calcified layers that get wider with each turn. How can this spiral be mathematically modeled? Collecting the data 1. Place a piece of graph paper on your desk. Draw a set of x- and y-axes to include the four extreme points (0, 0), (34, 0), (0, 21), and (34, 21). 2. Draw a square by connecting the vertices (10, 5), (10, 6), (9, 6), and (9, 5). Lightly shade this square with a pencil.
2 102 Activities for Algebra with the TI Construct a square to the left of the original square by connecting vertices (8, 5), (8, 6), (9, 6), and (9, 5). Observe that the two squares together form a rectangle whose width is 1 and whose length is Construct a square above this rectangle by connecting the vertices (10, 6), (10, 8), (8, 8), and (8, 6). 5. Continue to add squares to the graph in a clockwise fashion (see diagram at right) connecting the vertices shown in the table below. The two rows are the 1 X 1 and 2 X 2 squares that you already constructed. The last row is a 21 X 21 square. Length of side of square Vertices 1 (8, 5) (8, 6) (9, 5) (9, 6) 2 (8, 6) (8, 8) (10, 6) (10, 8) 3 (10, 5) (10, 8) (13, 5) (13, 8) 5 (8, 0) (8, 5) (13, 0) (13, 5) 8 (0, 0) (0, 8) (8, 0) (8, 8) 13 (0, 8) (0, 21) (13, 8) (13, 21) 21 (13, 0) (13, 21) (0, 34) (34, 21) 6. Each time a square is added a new rectangle is formed. Record the dimensions of each rectangle on the Data Collection and Analysis page. Answer questions 1 and 2 on the Data Collection and Analysis page.
3 Activity 8: At a Snail s Pace Using a red pencil, mark each of the points shown in the table below on your graph paper. These points are each one of the corners of the squares in the graph. The dimensions of the sides of each square are also given in the table. Point (9, 6) (10, 6) (10, 5) (8, 5) (8, 8) (13, 8) (13, 0) (0, 0) Dimension of sides Using a compass, construct a ¼ circle in the square that measures 1 X 1. Place the point of the compass on the red point at vertices (9, 6) that you made in step 7. Open up the compass so that the pencil is on an adjacent vertex. Sweep an arc that goes to the opposite corner of the square. 9. Repeat this step with each of the squares, using the red marked points as the place to position the compass point. Observe that you are constructing a continuous curve that resembles a spiral a Fibonacci spiral. The result of the first three squares is shown to the right. Setting up the TI-73 Before starting your data collection, make sure that the TI-73 has the STAT PLOTS turned OFF, Y= functions turned OFF or cleared, the MODE and FORMAT set to their defaults, and the lists cleared. See the Appendix for a detailed description of the general setup steps. Setting up the window 1. Press π to set up the proper scale for the axes. 2. Set the Xmin value by identifying the minimum value. Choose a number that is less than the minimum. 3. Set the Xmax value by identifying the maximum value in each list. Choose a number that is greater than the maximum. Do Not Change the X Value. Set the Xscl to Set the Ymin value by identifying the minimum value in L2. Choose a number that is less than the minimum. 5. Set the Ymax value by identifying the maximum value in L2. Choose a number that is greater than the maximum. Set the Yscl to 0.
4 104 Activities for Algebra with the TI-73 Entering the data in the TI-73 Construct a Fibonacci spiral using the TI-73. You can construct circles using the same center points and radii that were used in the previous steps. Although you must draw full circles, you are only interested in one-fourth of each circle. Collectively, the circle segments will form the Fibonacci spiral. 1. Press - l to return to the Home screen. Press : to clear the Home screen. 2. The first circle has a center at point (9, 6) and a radius of 1. Press 2 to draw the circle. 3. Select 6:Circle( by pressing Type E. 5. Press b to draw the circle. A small circle is drawn as shown. The center of the circle is (9, 6) and the radius is 1.
5 Activity 8: At a Snail s Pace Repeat steps 1 through 4 for each circle. Change the center point and radius according to the table below each time step 4 is repeated. Center point Radius Home screen shows (10, 6) 2 Circle(10,6,2) (10, 5) 3 Circle(10,5,3) (8, 5) 5 Circle(8,5,5) (8, 8) 8 Circle(8,8,8) (13, 8) 13 Circle(13,8,13) (13, 0) 21 Circle(13,0,21) (0, 0) 34 Circle(0,0,34) Where is the spiral on the diagram shown at the right? The first circle that you constructed appears as a dot in the first quadrant of the graph. Remember that you only need one-fourth of each circle that was drawn. In the diagram shown at the right, threefourths of each circle that was constructed is erased, leaving a spiral. This action cannot be done on the TI Use tracing paper to help spot the spiral on the TI-73. Using a pencil, draw a set of axes on the tracing paper. Place the paper over the TI-73 screen so that the axes on the paper align with the axes on the screen. Using a red pencil, find and trace the spiral by finding the dark center of the spiral and proceeding clockwise around it. 8. Use the prior screens as guidelines. You should now have a spiral. How does this spiral compare with the spiral that you constructed on the graph paper? 9. Save the drawing. Press 2! to move the cursor to the STO menu.
6 106 Activities for Algebra with the TI Select 1:StorePic by pressing 1 or b. 11. Press - }. Select 4:Picture by pressing Select 1:Pic1 by pressing 1 or b. 13. Press b to save the picture for future use.
7 Data Collection and Analysis Name Date Activity 8: At a Snail s Pace Collecting the data Dimensions of Rectangles Width Length 1 2 Analyzing the data 1. Each square was added in a clockwise direction around the original shaded square. How many squares have to be added to the plot in order to draw one complete turn of the spiral? 2. The sequence of widths and lengths in the table above are part of a Fibonacci sequence. Determine the next five widths and lengths. Add those to the table below. Width Length
8 108 Activities for Algebra with the TI Give examples of Fibonacci sequences from this activity. Extension How much do the Fibonacci rectangles increase in area each time a square is added on? Look at how the areas of the rectangles change as you build larger and larger rectangles. Find out by what factor the area changes each time you increase the size of the rectangles. Two formulas can be used: L - S = S = Increase Factor where L is the area of the large rectangle, S is the area of the small rectangle, is the change in area. Is there a golden lesson in this activity? Does the graph generated in this exercise support your ideas about a Golden Ratio? Note: Activity 4: The Calcumites Are Coming! and this activity both dealt with the Golden Ratio of This ratio is obtained by dividing the numbers in a Fibonacci sequence by the preceding values in the sequence. Observe that the area of the rectangles increases by a factor of When using a spiral of squares to construct a spiral each quarter turn of the spiral increased in distance from the center by a factor of In a Fibonacci spiral, the distance from the center increases by a factor of with each complete turn of the spiral.
9 Teacher Notes Objectives To plot a mathematical relationship that defines a spiral Activity 8 To use technology to create a spiral similar to that found in a snail To use technology to plot a set of ordered pairs At a Snail s Pace Materials TI-73 Lead pencil Colored pencils - red and green Metric ruler Compass Tracing paper and graph paper Preparation For the first part of this activity it is important to select appropriate graph paper that allows students to visualize the spiral of squares and the spiral that they generate when drawing the arcs within the squares. Fibonacci sequences can be seen throughout this activity: 1) sides of the squares; 2) widths of the rectangles; 3) lengths of the rectangles; and 4) radii of the concentric circles that form the spiral. Golden Ratios are embedded within this activity, although only one is calculated. The one that the students calculated is the increase in the area of the Fibonacci rectangles. Other examples include: 1) the increase in distance from the center to subsequent turns in a Fibonacci spiral, and 2) the length of the rectangles divided by the width of the rectangles. The Fibonacci sequence is not the only sequence that approaches the Golden Ratio. Students can build a sequence by starting with any two numbers where, beginning with the third number, each number is equal to the sum of the preceding two numbers: 3, 7, 10, 17, 27, 44, 71, 115, and so on. The Golden Ratio is obtained by dividing each number by the preceding number in the sequence.
10 110 Activities for Algebra with the TI-73 Answers to Data Collection and Analysis questions Collecting the data Sample data: Dimensions of Rectangles Width Length Analyzing the data 1. Each square was added in a clockwise direction around the original shaded square. How many squares have to be added to the plot in order to draw one complete turn of the spiral? Four. Each square gives one-fourth of a turn of the spiral. 2. The sequence of widths and lengths in the table above are part of a Fibonacci sequence. Determine the next five widths and lengths. Add those to the table below. See chart. Width Length Give examples of Fibonacci sequences from this activity. Fibonacci sequences can be seen throughout this activity: 1) sides of the squares; 2) widths of the rectangles; 3) lengths of the rectangles; and 4) radii of the concentric circles that form the spiral.
Fungus Farmers LEAF CUTTING ANTS A C T I V I T Y. Activity Overview. How much leaf do leaf cutter ants chew?
 How much leaf do leaf cutter ants chew? Activity Overview Leaf cutting ants carry away leaf pieces that are up to 30 times their weight. They sometimes carry these pieces 100-200 meters (about 2 football
How much leaf do leaf cutter ants chew? Activity Overview Leaf cutting ants carry away leaf pieces that are up to 30 times their weight. They sometimes carry these pieces 100-200 meters (about 2 football
The GC s standard graphing window shows the x-axis from -10 to 10 and the y-axis from -10 to 10.
 Name Date TI-84+ GC 17 Changing the Window Objectives: Adjust Xmax, Xmin, Ymax, and/or Ymin in Window menu Understand and adjust Xscl and/or Yscl in Window menu The GC s standard graphing window shows
Name Date TI-84+ GC 17 Changing the Window Objectives: Adjust Xmax, Xmin, Ymax, and/or Ymin in Window menu Understand and adjust Xscl and/or Yscl in Window menu The GC s standard graphing window shows
Do You See What I See?
 Concept Geometry and measurement Activity 5 Skill Calculator skills: coordinate graphing, creating lists, ' Do You See What I See? Students will discover how pictures formed by graphing ordered pairs can
Concept Geometry and measurement Activity 5 Skill Calculator skills: coordinate graphing, creating lists, ' Do You See What I See? Students will discover how pictures formed by graphing ordered pairs can
6.1.2: Graphing Quadratic Equations
 6.1.: Graphing Quadratic Equations 1. Obtain a pair of equations from your teacher.. Press the Zoom button and press 6 (for ZStandard) to set the window to make the max and min on both axes go from 10
6.1.: Graphing Quadratic Equations 1. Obtain a pair of equations from your teacher.. Press the Zoom button and press 6 (for ZStandard) to set the window to make the max and min on both axes go from 10
Optical Illusion Sketchbook Project Art 1201
 Optical Illusion Sketchbook Project Art 1201 Before beginning our final optical illusion project, we need to practice drawing optical illusions so we will have a better understanding of how to construct
Optical Illusion Sketchbook Project Art 1201 Before beginning our final optical illusion project, we need to practice drawing optical illusions so we will have a better understanding of how to construct
Outline. Drawing the Graph. 1 Homework Review. 2 Introduction. 3 Histograms. 4 Histograms on the TI Assignment
 Lecture 14 Section 4.4.4 on Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Sep 18, 2009 Outline 1 on 2 3 4 on 5 6 Even-numbered on Exercise 4.25, p. 249. The following is a list of homework scores for two students: Student
Lecture 14 Section 4.4.4 on Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Sep 18, 2009 Outline 1 on 2 3 4 on 5 6 Even-numbered on Exercise 4.25, p. 249. The following is a list of homework scores for two students: Student
Name Date Class Practice A. 5. Look around your classroom. Describe a geometric pattern you see.
 Practice A Geometric Patterns Identify a possible pattern. Use the pattern to draw the next figure. 5. Look around your classroom. Describe a geometric pattern you see. 6. Use squares to create a geometric
Practice A Geometric Patterns Identify a possible pattern. Use the pattern to draw the next figure. 5. Look around your classroom. Describe a geometric pattern you see. 6. Use squares to create a geometric
Sketching Fundamentals
 Sketching Fundamentals Learning Outcome When you complete this module you will be able to: Make basic engineering sketches of plant equipment. Learning Objectives Here is what you will be able to do when
Sketching Fundamentals Learning Outcome When you complete this module you will be able to: Make basic engineering sketches of plant equipment. Learning Objectives Here is what you will be able to do when
Introduction to the Graphing Calculator for the TI-86
 Algebra 090 ~ Lecture Introduction to the Graphing Calculator for the TI-86 Copyright 1996 Sally J. Glover All Rights Reserved Grab your calculator and follow along. Note: BOLD FACE are used for calculator
Algebra 090 ~ Lecture Introduction to the Graphing Calculator for the TI-86 Copyright 1996 Sally J. Glover All Rights Reserved Grab your calculator and follow along. Note: BOLD FACE are used for calculator
The Magic Circle Basic Lesson. Developed by The Alexandria Seaport Foundation
 The Magic Circle Basic Lesson Developed by The Alexandria Seaport Foundation The Tools Needed Compass Straightedge Pencil Paper (not graph paper, 8.5 x 11 is fine) Your Brain (the most important tool!)
The Magic Circle Basic Lesson Developed by The Alexandria Seaport Foundation The Tools Needed Compass Straightedge Pencil Paper (not graph paper, 8.5 x 11 is fine) Your Brain (the most important tool!)
Chapter 4: Patterns and Relationships
 Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
Constructions. Unit 9 Lesson 7
 Constructions Unit 9 Lesson 7 CONSTRUCTIONS Students will be able to: Understand the meanings of Constructions Key Vocabulary: Constructions Tools of Constructions Basic geometric constructions CONSTRUCTIONS
Constructions Unit 9 Lesson 7 CONSTRUCTIONS Students will be able to: Understand the meanings of Constructions Key Vocabulary: Constructions Tools of Constructions Basic geometric constructions CONSTRUCTIONS
Maths lesson. Exploring sequences and the Fibonacci sequence. Learning objectives. Knowledge. Skills. Resources
 Exploring sequences and the Fibonacci sequence Learning objectives 1. Explore the exponential sequences, leading to negative powers. 2. Discover the Fibonacci sequence and the Golden Number or Golden Ratio.
Exploring sequences and the Fibonacci sequence Learning objectives 1. Explore the exponential sequences, leading to negative powers. 2. Discover the Fibonacci sequence and the Golden Number or Golden Ratio.
ALGEBRA 2 ~ Lessons 1 13
 ALGEBRA 2 ~ Lessons 1 13 Remember to write the original problem and show all of your steps! All work should be done on a separate piece of paper. ASSIGNMENT 1 Arithmetic (No calculator.) Add, subtract
ALGEBRA 2 ~ Lessons 1 13 Remember to write the original problem and show all of your steps! All work should be done on a separate piece of paper. ASSIGNMENT 1 Arithmetic (No calculator.) Add, subtract
AREA & PERIMETER LESSON 1 OBJ ECTIVE: OBJECTIVE: INVESTIGATE AND USE THE FORMULAS FOR AREA AND PERIMETER OF RECTANGLES.
 AREA & PERIMETER LESSON 1 OBJ ECTIVE: OBJECTIVE: INVESTIGATE AND USE THE FORMULAS FOR AREA AND PERIMETER OF RECTANGLES. Learning Goal By the end of the unit... students will apply the area and perimeter
AREA & PERIMETER LESSON 1 OBJ ECTIVE: OBJECTIVE: INVESTIGATE AND USE THE FORMULAS FOR AREA AND PERIMETER OF RECTANGLES. Learning Goal By the end of the unit... students will apply the area and perimeter
SHAPE level 2 questions. 1. Match each shape to its name. One is done for you. 1 mark. International School of Madrid 1
 SHAPE level 2 questions 1. Match each shape to its name. One is done for you. International School of Madrid 1 2. Write each word in the correct box. faces edges vertices 3. Here is half of a symmetrical
SHAPE level 2 questions 1. Match each shape to its name. One is done for you. International School of Madrid 1 2. Write each word in the correct box. faces edges vertices 3. Here is half of a symmetrical
Lesson 12: Unique Triangles Two Sides and a Non-Included Angle
 Lesson 12: Unique Triangles Two Sides and a Non-Included Angle Classwork Exploratory Challenge 1. Use your tools to draw, provided cm, cm, and. Continue with the rest of the problem as you work on your
Lesson 12: Unique Triangles Two Sides and a Non-Included Angle Classwork Exploratory Challenge 1. Use your tools to draw, provided cm, cm, and. Continue with the rest of the problem as you work on your
Lesson 3.2 Intercepts and Factors
 Lesson 3. Intercepts and Factors Activity 1 A Typical Quadratic Graph a. Verify that C œ ÐB (ÑÐB "Ñ is a quadratic equation. ( Hint: Expand the right side.) b. Graph C œ ÐB (ÑÐB "Ñ in the friendly window
Lesson 3. Intercepts and Factors Activity 1 A Typical Quadratic Graph a. Verify that C œ ÐB (ÑÐB "Ñ is a quadratic equation. ( Hint: Expand the right side.) b. Graph C œ ÐB (ÑÐB "Ñ in the friendly window
The Cartesian Coordinate System
 The Cartesian Coordinate System The xy-plane Although a familiarity with the xy-plane, or Cartesian coordinate system, is expected, this worksheet will provide a brief review. The Cartesian coordinate
The Cartesian Coordinate System The xy-plane Although a familiarity with the xy-plane, or Cartesian coordinate system, is expected, this worksheet will provide a brief review. The Cartesian coordinate
Austin and Sara s Game
 Austin and Sara s Game 1. Suppose Austin picks a random whole number from 1 to 5 twice and adds them together. And suppose Sara picks a random whole number from 1 to 10. High score wins. What would you
Austin and Sara s Game 1. Suppose Austin picks a random whole number from 1 to 5 twice and adds them together. And suppose Sara picks a random whole number from 1 to 10. High score wins. What would you
Moving Beyond Geometric Shapes: Other Connections Between Mathematics and the Arts for Elementary-grade Teachers
 Moving Beyond Geometric Shapes: Other Connections Between Mathematics and the Arts for Elementary-grade Teachers Virginia Usnick Marilyn Sue Ford Department of Curriculum and Instruction University of
Moving Beyond Geometric Shapes: Other Connections Between Mathematics and the Arts for Elementary-grade Teachers Virginia Usnick Marilyn Sue Ford Department of Curriculum and Instruction University of
YEAR 2 MID-PROGRAMME ENTRY EXAMINATIONS Time allowed: 2 hours
 YEAR 2 MID-PROGRAMME ENTRY EXAMINATIONS 2018 MATHEMATICS SATURDAY 2 nd JUNE 2018 Instructions to candidates Time allowed: 2 hours Answer the questions in the spaces provided there may be more space than
YEAR 2 MID-PROGRAMME ENTRY EXAMINATIONS 2018 MATHEMATICS SATURDAY 2 nd JUNE 2018 Instructions to candidates Time allowed: 2 hours Answer the questions in the spaces provided there may be more space than
FlashChart. Symbols and Chart Settings. Main menu navigation. Data compression and time period of the chart. Chart types.
 FlashChart Symbols and Chart Settings With FlashChart you can display several symbols (for example indices, securities or currency pairs) in an interactive chart. You can also add indicators and draw on
FlashChart Symbols and Chart Settings With FlashChart you can display several symbols (for example indices, securities or currency pairs) in an interactive chart. You can also add indicators and draw on
Standards of Learning Guided Practice Suggestions. For use with the Mathematics Tools Practice in TestNav TM 8
 Standards of Learning Guided Practice Suggestions For use with the Mathematics Tools Practice in TestNav TM 8 Table of Contents Change Log... 2 Introduction to TestNav TM 8: MC/TEI Document... 3 Guided
Standards of Learning Guided Practice Suggestions For use with the Mathematics Tools Practice in TestNav TM 8 Table of Contents Change Log... 2 Introduction to TestNav TM 8: MC/TEI Document... 3 Guided
Name: Class: Date: Around the Web
 Around the Web Directions: Plot the coordinate points in order. Connect the points with a straight line using a straightedge or a ruler. Draw the lines as you plot each point. (0, 15) (3, 13) (7, 11) (10,
Around the Web Directions: Plot the coordinate points in order. Connect the points with a straight line using a straightedge or a ruler. Draw the lines as you plot each point. (0, 15) (3, 13) (7, 11) (10,
Activity overview. Background. Concepts. Random Rectangles
 by: Bjørn Felsager Grade level: secondary (Years 9-12) Subject: mathematics Time required: 90 minutes Activity overview What variables characterize a rectangle? What kind of relationships exists between
by: Bjørn Felsager Grade level: secondary (Years 9-12) Subject: mathematics Time required: 90 minutes Activity overview What variables characterize a rectangle? What kind of relationships exists between
Folding Activity 3. Compass Colored paper Tape or glue stick
 Folding Activity 3 Part 1 You re not done until everyone in your group is done! If you finish before someone else, help them finish before starting on the next part. You ll need: Patty paper Ruler Sharpie
Folding Activity 3 Part 1 You re not done until everyone in your group is done! If you finish before someone else, help them finish before starting on the next part. You ll need: Patty paper Ruler Sharpie
Upper Primary Division Round 2. Time: 120 minutes
 3 rd International Mathematics Assessments for Schools (2013-2014 ) Upper Primary Division Round 2 Time: 120 minutes Printed Name Code Score Instructions: Do not open the contest booklet until you are
3 rd International Mathematics Assessments for Schools (2013-2014 ) Upper Primary Division Round 2 Time: 120 minutes Printed Name Code Score Instructions: Do not open the contest booklet until you are
Pascal Contest (Grade 9)
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Thursday, February 20, 201 (in North America and South America) Friday, February 21, 201 (outside of North
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Thursday, February 20, 201 (in North America and South America) Friday, February 21, 201 (outside of North
Drawing Bode Plots (The Last Bode Plot You Will Ever Make) Charles Nippert
 Drawing Bode Plots (The Last Bode Plot You Will Ever Make) Charles Nippert This set of notes describes how to prepare a Bode plot using Mathcad. Follow these instructions to draw Bode plot for any transfer
Drawing Bode Plots (The Last Bode Plot You Will Ever Make) Charles Nippert This set of notes describes how to prepare a Bode plot using Mathcad. Follow these instructions to draw Bode plot for any transfer
Hyperbolas Graphs, Equations, and Key Characteristics of Hyperbolas Forms of Hyperbolas p. 583
 C H A P T ER Hyperbolas Flashlights concentrate beams of light by bouncing the rays from a light source off a reflector. The cross-section of a reflector can be described as hyperbola with the light source
C H A P T ER Hyperbolas Flashlights concentrate beams of light by bouncing the rays from a light source off a reflector. The cross-section of a reflector can be described as hyperbola with the light source
CLEMSON MIDDLE SCHOOL MATHEMATICS PROJECT UNIT 5: GEOMETRIC RELATIONSHIPS
 CLEMSON MIDDLE SCHOOL MATHEMATICS PROJECT UNIT 5: GEOMETRIC RELATIONSHIPS PROBLEM 1: PERIMETER AND AREA TRAINS Let s define a train as the shape formed by congruent, regular polygons that share a side.
CLEMSON MIDDLE SCHOOL MATHEMATICS PROJECT UNIT 5: GEOMETRIC RELATIONSHIPS PROBLEM 1: PERIMETER AND AREA TRAINS Let s define a train as the shape formed by congruent, regular polygons that share a side.
TeleTrader FlashChart
 TeleTrader FlashChart Symbols and Chart Settings With TeleTrader FlashChart you can display several symbols (for example indices, securities or currency pairs) in an interactive chart. You can also add
TeleTrader FlashChart Symbols and Chart Settings With TeleTrader FlashChart you can display several symbols (for example indices, securities or currency pairs) in an interactive chart. You can also add
Exploring the Pythagorean Theorem
 Exploring the Pythagorean Theorem Lesson 11 Mathematics Objectives Students will analyze relationships to develop the Pythagorean Theorem. Students will find missing sides in right triangles using the
Exploring the Pythagorean Theorem Lesson 11 Mathematics Objectives Students will analyze relationships to develop the Pythagorean Theorem. Students will find missing sides in right triangles using the
Lesson 18: More Problems on Area and Circumference
 Lesson 18: More Problems on Area and Circumference Classwork Opening Exercise Draw a circle of diameter 12 cm and a square of side length 12 cm on grid paper. Determine the area of the square and the circle.
Lesson 18: More Problems on Area and Circumference Classwork Opening Exercise Draw a circle of diameter 12 cm and a square of side length 12 cm on grid paper. Determine the area of the square and the circle.
Chapter 2 Using Drawing Tools & Applied Geometry
 Chapter 2 Using Drawing Tools & Applied Geometry TOPICS Preparation of Tools. Using of Tools Applied Geometry PREPARATION OF TOOLS Fastening Paper to Drafting Board 1. Place the paper close to the table
Chapter 2 Using Drawing Tools & Applied Geometry TOPICS Preparation of Tools. Using of Tools Applied Geometry PREPARATION OF TOOLS Fastening Paper to Drafting Board 1. Place the paper close to the table
THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM
 Chapter 11 THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM The sinusoidal waveform or sine wave is the fundamental type of alternating current (ac) and alternating voltage. It is also referred to as a sinusoidal wave or, simply,
Chapter 11 THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM The sinusoidal waveform or sine wave is the fundamental type of alternating current (ac) and alternating voltage. It is also referred to as a sinusoidal wave or, simply,
Math Labs. Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates. Procedure
 Math Labs Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates Problem Statement Use the Cartesian coordinate system to draw rectangle ABCD. Use an x-y-z coordinate system to draw a rectangular
Math Labs Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates Problem Statement Use the Cartesian coordinate system to draw rectangle ABCD. Use an x-y-z coordinate system to draw a rectangular
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
GROWING UP IN MORECAMBE 2008 GROWING UP IN MORECAMBE The Mathematics of Shell Construction. and other patterns
 GROWING UP IN MORECAMBE 2008 GROWING UP IN MORECAMBE 2008 The Mathematics of Shell Construction and other patterns The Mathematics of Shell Construction and other patterns Contents 3 Fibonnaci Numbers
GROWING UP IN MORECAMBE 2008 GROWING UP IN MORECAMBE 2008 The Mathematics of Shell Construction and other patterns The Mathematics of Shell Construction and other patterns Contents 3 Fibonnaci Numbers
Algebra Mathematics S. J. Cooper
 THOMAS WHITHAM SIXTH FORM Algebra Mathematics S. J. Cooper Year 7 B U R N L E Y C@M P U S, B U R N L E Y, L A N C A S H I R E, B B 1 0 1 J D. T EL. 6 8 2 2 7 2 Algebra (1) Simplif each of the following
THOMAS WHITHAM SIXTH FORM Algebra Mathematics S. J. Cooper Year 7 B U R N L E Y C@M P U S, B U R N L E Y, L A N C A S H I R E, B B 1 0 1 J D. T EL. 6 8 2 2 7 2 Algebra (1) Simplif each of the following
Lesson 12: Unique Triangles Two Sides and a Non- Included Angle
 Lesson 12: Unique Triangles Two Sides and a Non- Included Angle Student Outcomes Students understand that two sides of a triangle and an acute angle, not included between the two sides, may not determine
Lesson 12: Unique Triangles Two Sides and a Non- Included Angle Student Outcomes Students understand that two sides of a triangle and an acute angle, not included between the two sides, may not determine
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet
 GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. a) Study: 6 units 6 tens 6 hundreds 6 thousands 6 ten-thousands 6 hundredthousands HTh T Th Th H T U 6 6 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. a) Study: 6 units 6 tens 6 hundreds 6 thousands 6 ten-thousands 6 hundredthousands HTh T Th Th H T U 6 6 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0
a. Sketch a wrapper like the one described above, using the actual size of your cone. Ignore any overlap required for assembly.
 Illustrative Mathematics G-MG Ice Cream Cone Alignment : G-MG.A.3 You have been hired by the owner of a local ice cream parlor to assist in his company s new venture. The company will soon sell its ice
Illustrative Mathematics G-MG Ice Cream Cone Alignment : G-MG.A.3 You have been hired by the owner of a local ice cream parlor to assist in his company s new venture. The company will soon sell its ice
5.3. Area of Polygons and Circles Play Area. My Notes ACTIVITY
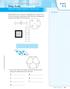 Area of Polygons and Circles SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Think/Pair/Share ACTIVITY 5.3 Pictured below is an aerial view of a playground. An aerial view is the view from above something. Decide what
Area of Polygons and Circles SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Think/Pair/Share ACTIVITY 5.3 Pictured below is an aerial view of a playground. An aerial view is the view from above something. Decide what
6.00 Trigonometry Geometry/Circles Basics for the ACT. Name Period Date
 6.00 Trigonometry Geometry/Circles Basics for the ACT Name Period Date Perimeter and Area of Triangles and Rectangles The perimeter is the continuous line forming the boundary of a closed geometric figure.
6.00 Trigonometry Geometry/Circles Basics for the ACT Name Period Date Perimeter and Area of Triangles and Rectangles The perimeter is the continuous line forming the boundary of a closed geometric figure.
Optimization Exploration: The Inscribed Rectangle. Learning Objectives: Materials:
 Optimization Exploration: The Inscribed Rectangle Lesson Information Written by Jonathan Schweig and Shira Sand Subject: Pre-Calculus Calculus Algebra Topic: Functions Overview: Students will explore some
Optimization Exploration: The Inscribed Rectangle Lesson Information Written by Jonathan Schweig and Shira Sand Subject: Pre-Calculus Calculus Algebra Topic: Functions Overview: Students will explore some
Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition
 Powerpoint slides copied from or based upon: Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition Connally, Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, Et Al. Copyright 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 CHAPTER
Powerpoint slides copied from or based upon: Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition Connally, Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, Et Al. Copyright 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 CHAPTER
Mathematical Construction
 Mathematical Construction Full illustrated instructions for the two bisectors: Perpendicular bisector Angle bisector Full illustrated instructions for the three triangles: ASA SAS SSS Note: These documents
Mathematical Construction Full illustrated instructions for the two bisectors: Perpendicular bisector Angle bisector Full illustrated instructions for the three triangles: ASA SAS SSS Note: These documents
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Mathematics Success Grade 6
 T428 Mathematics Success Grade 6 [OBJECTIVE] The students will plot ordered pairs containing rational values to identify vertical and horizontal lengths between two points in order to solve real-world
T428 Mathematics Success Grade 6 [OBJECTIVE] The students will plot ordered pairs containing rational values to identify vertical and horizontal lengths between two points in order to solve real-world
1 Sketching. Introduction
 1 Sketching Introduction Sketching is arguably one of the more difficult techniques to master in NX, but it is well-worth the effort. A single sketch can capture a tremendous amount of design intent, and
1 Sketching Introduction Sketching is arguably one of the more difficult techniques to master in NX, but it is well-worth the effort. A single sketch can capture a tremendous amount of design intent, and
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6355629826* MATHEMATICS 0580/03, 0581/03 Paper 3 (Core) October/November 2007 Candidates answer
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6355629826* MATHEMATICS 0580/03, 0581/03 Paper 3 (Core) October/November 2007 Candidates answer
Objective: Use varied protractors to distinguish angle measure from length
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 6 4 Lesson 6 Objective: Use varied protractors to distinguish angle measure from length Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 6 4 Lesson 6 Objective: Use varied protractors to distinguish angle measure from length Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept
How to Draw an Optimal Sri Yantra
 How to Draw an Optimal Sri Yantra The Optimal Sri Yantra The optimal Sri Yantra is the result of many years of research. Even though Sri Yantras look all the same they rarely are. There are hundreds if
How to Draw an Optimal Sri Yantra The Optimal Sri Yantra The optimal Sri Yantra is the result of many years of research. Even though Sri Yantras look all the same they rarely are. There are hundreds if
Building 3-D Initials with a Vanishing Point
 Grade level: 9-12 Building 3-D Initials with a Vanishing Point Tallahassee Activity overview Students will use a vanishing point for a one point perspective drawing of the initial of their choice. Concepts
Grade level: 9-12 Building 3-D Initials with a Vanishing Point Tallahassee Activity overview Students will use a vanishing point for a one point perspective drawing of the initial of their choice. Concepts
G 1 3 G13 BREAKING A STICK #1. Capsule Lesson Summary
 G13 BREAKING A STICK #1 G 1 3 Capsule Lesson Summary Given two line segments, construct as many essentially different triangles as possible with each side the same length as one of the line segments. Discover
G13 BREAKING A STICK #1 G 1 3 Capsule Lesson Summary Given two line segments, construct as many essentially different triangles as possible with each side the same length as one of the line segments. Discover
Catty Corner. Side Lengths in Two and. Three Dimensions
 Catty Corner Side Lengths in Two and 4 Three Dimensions WARM UP A 1. Imagine that the rectangular solid is a room. An ant is on the floor situated at point A. Describe the shortest path the ant can crawl
Catty Corner Side Lengths in Two and 4 Three Dimensions WARM UP A 1. Imagine that the rectangular solid is a room. An ant is on the floor situated at point A. Describe the shortest path the ant can crawl
7th Grade Drawing Geometric Figures
 Slide 1 / 53 Slide 2 / 53 7th Grade Drawing Geometric Figures 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 53 Topics Table of Contents Determining if a Triangle is Possible Click on a topic to go to that section
Slide 1 / 53 Slide 2 / 53 7th Grade Drawing Geometric Figures 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 53 Topics Table of Contents Determining if a Triangle is Possible Click on a topic to go to that section
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important
 Many artists use geometric concepts in their work. Think about what you have learned in geometry. How do these examples of First Nations art and architecture show geometry ideas? What You ll Learn Identify
Many artists use geometric concepts in their work. Think about what you have learned in geometry. How do these examples of First Nations art and architecture show geometry ideas? What You ll Learn Identify
with MultiMedia CD Randy H. Shih Jack Zecher SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation
 with MultiMedia CD Randy H. Shih Jack Zecher SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation WWW.SCHROFF.COM Lesson 1 Geometric Construction Basics AutoCAD LT 2002 Tutorial 1-1 1-2 AutoCAD LT 2002 Tutorial
with MultiMedia CD Randy H. Shih Jack Zecher SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation WWW.SCHROFF.COM Lesson 1 Geometric Construction Basics AutoCAD LT 2002 Tutorial 1-1 1-2 AutoCAD LT 2002 Tutorial
English 1 st Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: 1/13/14
 English 1 st Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: 1/13/14 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah State
English 1 st Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: 1/13/14 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah State
Locus Locus. Remarks
 4 4. The locus of a point is the path traced out by the point moving under given geometrical condition (or conditions). lternatively, the locus is the set of all those points which satisfy the given geometrical
4 4. The locus of a point is the path traced out by the point moving under given geometrical condition (or conditions). lternatively, the locus is the set of all those points which satisfy the given geometrical
Op Art Pinwheel Side 1 Choices
 Op Art Pinwheel Side 1 Choices 1. 1) Draw an X from corner to corner. Then draw a vertical line and horizontal line that match up in the center. 2) draw curved lines, spaced about 1/2" apart, between the
Op Art Pinwheel Side 1 Choices 1. 1) Draw an X from corner to corner. Then draw a vertical line and horizontal line that match up in the center. 2) draw curved lines, spaced about 1/2" apart, between the
Pre-Calculus Notes: Chapter 6 Graphs of Trigonometric Functions
 Name: Pre-Calculus Notes: Chapter Graphs of Trigonometric Functions Section 1 Angles and Radian Measure Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. Radian measure is based on the circumference
Name: Pre-Calculus Notes: Chapter Graphs of Trigonometric Functions Section 1 Angles and Radian Measure Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. Radian measure is based on the circumference
The activity looks at a sequence of growing patterns using sticks and blobs.
 Sticks and Blobs Key words: sequence, term Objectives Solve word problems and investigate in a range of contexts. Generate and describe sequences. Generate terms of a sequence using term-to-term and position-to-term
Sticks and Blobs Key words: sequence, term Objectives Solve word problems and investigate in a range of contexts. Generate and describe sequences. Generate terms of a sequence using term-to-term and position-to-term
You need to be really accurate at this before trying the next task. Keep practicing until you can draw a perfect regular hexagon.
 Starter 1: On plain paper practice constructing equilateral triangles using a ruler and a pair of compasses. Use a base of length 7cm. Measure all the sides and all the angles to check they are all the
Starter 1: On plain paper practice constructing equilateral triangles using a ruler and a pair of compasses. Use a base of length 7cm. Measure all the sides and all the angles to check they are all the
NUMBER PATTERNS. The first 3 triangular numbers can be illustrated as follows: 1 2 3
 1 NUMBER PATTERNS EXERCISE 1 1. Write down the first 20 Natural Numbers. 2. Provide answers to the following: a. What are the 4 th, 5 th and 6 th even numbers? b. What relationship is between an even number
1 NUMBER PATTERNS EXERCISE 1 1. Write down the first 20 Natural Numbers. 2. Provide answers to the following: a. What are the 4 th, 5 th and 6 th even numbers? b. What relationship is between an even number
UNIT PLAN. Grade Level: Unit #: 7 Unit Name: Circles
 UNIT PLAN Subject: Geometry Grade Level: 10-12 Unit #: 7 Unit Name: Circles Big Idea/Theme: The understanding of properties of circles, the lines that intersect them, and the use of their special segments
UNIT PLAN Subject: Geometry Grade Level: 10-12 Unit #: 7 Unit Name: Circles Big Idea/Theme: The understanding of properties of circles, the lines that intersect them, and the use of their special segments
MATHEMATICS TEST. Paper 1 calculator not allowed LEVEL 6 TESTS ANSWER BOOKLET. First name. Middle name. Last name. Date of birth Day Month Year
 2012 LEVEL 6 TESTS ANSWER BOOKLET Ma MATHEMATICS TEST LEVEL 6 TESTS Paper 1 calculator not allowed First name Middle name Last name Date of birth Day Month Year Please circle one Boy Girl Year group School
2012 LEVEL 6 TESTS ANSWER BOOKLET Ma MATHEMATICS TEST LEVEL 6 TESTS Paper 1 calculator not allowed First name Middle name Last name Date of birth Day Month Year Please circle one Boy Girl Year group School
AutoCAD LT 2009 Tutorial
 AutoCAD LT 2009 Tutorial Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. AutoCAD LT 2009 Tutorial 1-1 Lesson
AutoCAD LT 2009 Tutorial Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. AutoCAD LT 2009 Tutorial 1-1 Lesson
Analytic Geometry/ Trigonometry
 Analytic Geometry/ Trigonometry Course Numbers 1206330, 1211300 Lake County School Curriculum Map Released 2010-2011 Page 1 of 33 PREFACE Teams of Lake County teachers created the curriculum maps in order
Analytic Geometry/ Trigonometry Course Numbers 1206330, 1211300 Lake County School Curriculum Map Released 2010-2011 Page 1 of 33 PREFACE Teams of Lake County teachers created the curriculum maps in order
Isometric Drawings. Figure A 1
 A Isometric Drawings ISOMETRIC BASICS Isometric drawings are a means of drawing an object in picture form for better clarifying the object s appearance. These types of drawings resemble a picture of an
A Isometric Drawings ISOMETRIC BASICS Isometric drawings are a means of drawing an object in picture form for better clarifying the object s appearance. These types of drawings resemble a picture of an
AutoCAD LT 2012 Tutorial. Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS. Schroff Development Corporation
 AutoCAD LT 2012 Tutorial Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation AutoCAD LT 2012 Tutorial 1-1 Lesson 1 Geometric Construction
AutoCAD LT 2012 Tutorial Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation AutoCAD LT 2012 Tutorial 1-1 Lesson 1 Geometric Construction
GCSE style questions arranged by topic
 Write your name here Surname Other names In the style of: Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Mathematics Sequences GCSE style questions arranged by topic Candidate Number Higher Tier
Write your name here Surname Other names In the style of: Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Mathematics Sequences GCSE style questions arranged by topic Candidate Number Higher Tier
Downloaded from
 Understanding Elementary Shapes 1 1.In the given figure, lines l and m are.. to each other. (A) perpendicular (B) parallel (C) intersect (D) None of them. 2.a) If a clock hand starts from 12 and stops
Understanding Elementary Shapes 1 1.In the given figure, lines l and m are.. to each other. (A) perpendicular (B) parallel (C) intersect (D) None of them. 2.a) If a clock hand starts from 12 and stops
Using Google SketchUp
 Using Google SketchUp Opening sketchup 1. From the program menu click on the SketchUp 8 folder and select 3. From the Template Selection select Architectural Design Millimeters. 2. The Welcome to SketchUp
Using Google SketchUp Opening sketchup 1. From the program menu click on the SketchUp 8 folder and select 3. From the Template Selection select Architectural Design Millimeters. 2. The Welcome to SketchUp
UNC Charlotte 2012 Comprehensive
 March 5, 2012 1. In the English alphabet of capital letters, there are 15 stick letters which contain no curved lines, and 11 round letters which contain at least some curved segment. How many different
March 5, 2012 1. In the English alphabet of capital letters, there are 15 stick letters which contain no curved lines, and 11 round letters which contain at least some curved segment. How many different
AutoCAD 2018 Fundamentals
 Autodesk AutoCAD 2018 Fundamentals Elise Moss SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites to learn more about
Autodesk AutoCAD 2018 Fundamentals Elise Moss SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites to learn more about
Wordy Problems for MathyTeachers
 December 2012 Wordy Problems for MathyTeachers 1st Issue Buffalo State College 1 Preface When looking over articles that were submitted to our journal we had one thing in mind: How can you implement this
December 2012 Wordy Problems for MathyTeachers 1st Issue Buffalo State College 1 Preface When looking over articles that were submitted to our journal we had one thing in mind: How can you implement this
Figure 1: The Game of Fifteen
 1 FIFTEEN One player has five pennies, the other five dimes. Players alternately cover a number from 1 to 9. You win by covering three numbers somewhere whose sum is 15 (see Figure 1). 1 2 3 4 5 7 8 9
1 FIFTEEN One player has five pennies, the other five dimes. Players alternately cover a number from 1 to 9. You win by covering three numbers somewhere whose sum is 15 (see Figure 1). 1 2 3 4 5 7 8 9
Clarification of Standards for Parents Grade 3 Mathematics Unit 4
 Clarification of Standards for Parents Grade 3 Mathematics Unit 4 Dear Parents, We want to make sure that you have an understanding of the mathematics your child will be learning this year. Below you will
Clarification of Standards for Parents Grade 3 Mathematics Unit 4 Dear Parents, We want to make sure that you have an understanding of the mathematics your child will be learning this year. Below you will
Extra Practice 1. Name Date. Lesson 8.1: Parallel Lines. 1. Which line segments are parallel? How do you know? a) b) c) d)
 Master 8.24 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 8.1: Parallel Lines 1. Which line segments are parallel? How do you know? a) b) c) d) 2. Look at the diagram below. Find as many pairs of parallel line segments as you
Master 8.24 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 8.1: Parallel Lines 1. Which line segments are parallel? How do you know? a) b) c) d) 2. Look at the diagram below. Find as many pairs of parallel line segments as you
Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: May 23, 2011
 Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: May 23, 2011 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah State Board of Education,
Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: May 23, 2011 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah State Board of Education,
Make and Measure a Circle Without a Pattern
 Published on Sew4Home Make and Measure a Circle Without a Pattern Editor: Liz Johnson Thursday, 25 August 2016 1:00 The circle is, in my humble opinion, the Queen of the geometric shapes. Don't get me
Published on Sew4Home Make and Measure a Circle Without a Pattern Editor: Liz Johnson Thursday, 25 August 2016 1:00 The circle is, in my humble opinion, the Queen of the geometric shapes. Don't get me
UK SENIOR MATHEMATICAL CHALLENGE
 UK SENIOR MATHEMATICAL CHALLENGE Tuesday 8 November 2016 Organised by the United Kingdom Mathematics Trust and supported by Institute and Faculty of Actuaries RULES AND GUIDELINES (to be read before starting)
UK SENIOR MATHEMATICAL CHALLENGE Tuesday 8 November 2016 Organised by the United Kingdom Mathematics Trust and supported by Institute and Faculty of Actuaries RULES AND GUIDELINES (to be read before starting)
Excel Lab 2: Plots of Data Sets
 Excel Lab 2: Plots of Data Sets Excel makes it very easy for the scientist to visualize a data set. In this assignment, we learn how to produce various plots of data sets. Open a new Excel workbook, and
Excel Lab 2: Plots of Data Sets Excel makes it very easy for the scientist to visualize a data set. In this assignment, we learn how to produce various plots of data sets. Open a new Excel workbook, and
SolidWorks 95 User s Guide
 SolidWorks 95 User s Guide Disclaimer: The following User Guide was extracted from SolidWorks 95 Help files and was not originally distributed in this format. All content 1995, SolidWorks Corporation Contents
SolidWorks 95 User s Guide Disclaimer: The following User Guide was extracted from SolidWorks 95 Help files and was not originally distributed in this format. All content 1995, SolidWorks Corporation Contents
Trigonometric identities
 Trigonometric identities An identity is an equation that is satisfied by all the values of the variable(s) in the equation. For example, the equation (1 + x) = 1 + x + x is an identity. If you replace
Trigonometric identities An identity is an equation that is satisfied by all the values of the variable(s) in the equation. For example, the equation (1 + x) = 1 + x + x is an identity. If you replace
SDC. AutoCAD LT 2007 Tutorial. Randy H. Shih. Schroff Development Corporation Oregon Institute of Technology
 AutoCAD LT 2007 Tutorial Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com AutoCAD LT 2007 Tutorial 1-1 Lesson 1 Geometric
AutoCAD LT 2007 Tutorial Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com AutoCAD LT 2007 Tutorial 1-1 Lesson 1 Geometric
Using Geometry. 9.1 Earth Measure. 9.2 Angles and More Angles. 9.3 Special Angles. Introduction to Geometry and Geometric Constructions...
 Using Geometry Recognize these tools? The one on the right is a protractor, which has been used since ancient times to measure angles. The one on the left is a compass, used to create arcs and circles.
Using Geometry Recognize these tools? The one on the right is a protractor, which has been used since ancient times to measure angles. The one on the left is a compass, used to create arcs and circles.
GOAL Practise techniques for creating various types of geometric lines by constructing and reproducing figures. sheet of letter-sized white paper
 TECHNIQUE STUDENT BOOK Chapter 11, page 340 TOOLBOX Pages 62 67 GOAL Practise techniques for creating various types of geometric lines by constructing and reproducing figures. MATERIALS drawing board T-square
TECHNIQUE STUDENT BOOK Chapter 11, page 340 TOOLBOX Pages 62 67 GOAL Practise techniques for creating various types of geometric lines by constructing and reproducing figures. MATERIALS drawing board T-square
Progressive Primary Mathematics Book 6: Sample Schemes of Work: Term One
 Progressive Primary Mathematics Book 6: Sample : Term One WEEK 1 1 Whole Place values of pupils should be able to recognize identify the place values total values of, read write in words in figures up
Progressive Primary Mathematics Book 6: Sample : Term One WEEK 1 1 Whole Place values of pupils should be able to recognize identify the place values total values of, read write in words in figures up
Paper 2. Mathematics test. Calculator allowed. First name. Last name. School KEY STAGE TIER
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8 2004 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8 2004 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
This early Greek study was largely concerned with the geometric properties of conics.
 4.3. Conics Objectives Recognize the four basic conics: circle, ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola. Recognize, graph, and write equations of parabolas (vertex at origin). Recognize, graph, and write equations
4.3. Conics Objectives Recognize the four basic conics: circle, ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola. Recognize, graph, and write equations of parabolas (vertex at origin). Recognize, graph, and write equations
Autodesk AutoCAD 2013 Fundamentals
 Autodesk AutoCAD 2013 Fundamentals Elise Moss SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Visit the following websites to learn more
Autodesk AutoCAD 2013 Fundamentals Elise Moss SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Visit the following websites to learn more
Excel Tool: Plots of Data Sets
 Excel Tool: Plots of Data Sets Excel makes it very easy for the scientist to visualize a data set. In this assignment, we learn how to produce various plots of data sets. Open a new Excel workbook, and
Excel Tool: Plots of Data Sets Excel makes it very easy for the scientist to visualize a data set. In this assignment, we learn how to produce various plots of data sets. Open a new Excel workbook, and
3. The dimensioning SYMBOLS for arcs and circles should be given:
 Draft Student Name: Teacher: District: Date: Wake County Test: 9_12 T and I IC61 - Drafting I Test 2 Description: 4.08 Dimensioning Form: 501 1. The MINIMUM amount of space between two, ADJACENT DIMENSION
Draft Student Name: Teacher: District: Date: Wake County Test: 9_12 T and I IC61 - Drafting I Test 2 Description: 4.08 Dimensioning Form: 501 1. The MINIMUM amount of space between two, ADJACENT DIMENSION
How to Draw with a Grid
 Level: Beginner Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level: 8.3 Flesch-Kincaid Reading Ease: 67.5-6 Pages and 12 Illustrations How to Draw with a Grid Exploring the grid method to draw accurate outline drawings This resource
Level: Beginner Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level: 8.3 Flesch-Kincaid Reading Ease: 67.5-6 Pages and 12 Illustrations How to Draw with a Grid Exploring the grid method to draw accurate outline drawings This resource
Anna Gresham School of Landscape Design. CAD for Beginners. CAD 3: Using the Drawing Tools and Blocks
 Anna Gresham School of Landscape Design CAD for Beginners CAD 3: Using the Drawing Tools and Blocks Amended for DraftSight V4 October 2013 INDEX OF TOPICS for CAD 3 Pages ESnap 3-5 Essential drawing tools
Anna Gresham School of Landscape Design CAD for Beginners CAD 3: Using the Drawing Tools and Blocks Amended for DraftSight V4 October 2013 INDEX OF TOPICS for CAD 3 Pages ESnap 3-5 Essential drawing tools
