Additional Activity 1: A Kilometre of Dental Floss
|
|
|
- Joanna Alexander
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Master 9.6 Additional Activity 1: A Kilometre of Dental Floss Work on your own. You will need a package of dental floss, and paper and pencil. Suppose each member of your family flosses her or his teeth once a day. Do you think your family would use more or less than 1 km of dental floss in a year? Explain how you got your answer. Take It Further: Calculate about how many packages of dental floss equal 1 km. 50
2 Master 9.7 Additional Activity 2: Tangram Perimeters Work on your own. You will need a tangram, paper and pencil, and a ruler. Use the tangram pieces. Create a figure or a design. Trace the outline of your figure onto paper. You may need to have a classmate help you hold the pieces in place while you trace. Estimate first. Then measure to find the perimeter of your figure to the nearest tenth of a centimetre. Take It Further: Trade tracings with a classmate. Measure to find the perimeter of your classmate s figure. 51
3 Master 9.8 Additional Activity 3: Calculating Perimeter and Area Work with a partner. You will need 5 cardboard rectangles of various sizes, labelled A, B, C, D, and E, a ruler, and paper and pencil. Choose a rectangle. One of you estimates the perimeter of the rectangle. The other estimates its area. Record your estimates. Measure the length and the width of the rectangle. Record these measurements. Use the measurements to calculate the perimeter, then the area of the rectangle. Record these measurements. Repeat with the other rectangles. Take It Further: Order the rectangles from least to greatest perimeter. Then order them from least to greatest area. 52
4 Master 9.9 Additional Activity 4: Investigating Hands Work in a group of 4. You will need a pencil, 1-cm grid paper, string, and measuring tape. Hold out your right hands so they are near. Examine the 4 hands. Estimate to order them from least to greatest area. Each of you trace your right hand onto 1-cm grid paper. Find the approximate area of your hand. Order the hands from least to greatest area. Compare the results with your estimate. Take It Further: Estimate to order the hands from least to greatest perimeter. Use the string to find the perimeter of each hand. Compare the results with your estimate. 53
5 Master 9.10 Step-by-Step 1 Lesson 1, Question 6 Step 1 How many centimetres is 15 dm? Can you draw a length of 15 dm on this page? Step 2 Do you think a wingspan of 15 dm is reasonable for a pet bird? Explain. Step 3 25 cm is about 24 cm. Divide 24 cm into 4 equal lengths. Each length is cm. Step 4 Is each length of salmon large enough to feed one person? Is Pablo s statement reasonable? Explain. Step 5 About how long does it take you to walk 1 km? About how long would it take you to walk 5 km? Is Betty s statement reasonable? Explain. Step 6 The length of one shoelace is about 30 cm. How long would 2 shoelaces tied together be? Do you think this would equal the height of a small child? Explain. 54
6 Master 9.11 Step-by-Step 2 Lesson 2, Question 10 Step 1 How tall is Rico? What is Rico s height in centimetres? Step 2 How tall is Jeremy? What is Jeremy s height in centimetres? Step 3 How tall is Sasha? Step 4 Order the students from shortest to tallest, using their heights in centimetres. Step 5 Who is tallest? Step 6 Subtract the height of the second-tallest student from the height of the tallest student. Step 7 How much taller is the tallest student? 55
7 Master 9.12 Step-by-Step 3 Lesson 3, Question 4 Step 1 Find a table in your classroom. Cut a piece of string as long as the table. Step 2 How many times does the length of string fit along the length of the hallway? Step 3 Assume your classmates used a broom. Do you think your classmates will get the same result as you? Explain. 56
8 Master 9.13 Step-by-Step 4 Lesson 4, Question 7 Step 1 What is the circumference of the bracelet? Step 2 Cut a length of string equal to the circumference of your wrist. Measure the string with a ruler. What is the circumference of your wrist? Step 3 Is the circumference of your wrist greater than or less than the circumference of the bracelet? Step 4 Could you wear the bracelet? How do you know? 57
9 Master 9.14 Step-by-Step 5 Lesson 5, Question 6 Step 1 What is the perimeter of Miss Dahlia s flower garden? Step 2 Use1-cm grid paper. Let the length of 1 grid square represent 1 m. Draw a figure that is not a rectangle, with perimeter 28 m. The sides of the figure must be drawn on the lines of the grid paper. Step 3 Draw 2 other figures that are not rectangles, each with perimeter 28 m. Step 4 Count the squares in each of your 3 figures. How many squares are in the first figure? What is the area of the first figure? How many squares are in the second figure? What is the area of the second figure? How many squares are in the third figure? What is the area of the third figure? Step 5 Which figure has the greatest area? Step 6 Which figure will give Miss Dahlia the greatest amount of space for planting flowers? 58
10 Master 9.15 Step-by-Step 6 Lesson 6, Question 7 Step 1 Draw a rectangle. Label the lengths of two opposite sides 12.0 m. Add these lengths: Step 2 The perimeter is 55.0 m. Subtract to find the sum of the other two sides m m = m Step 3 We know the other two sides of the rectangle are of equal length. Divide your answer to Step 2 by 2 to find the length of each side. m 2 = m The dimensions of the garden are m by m. Step 4 Repeat the above calculations for side lengths of 12.1 m to 12.8 m. How many rectangles did you find? Step 5 Were you able to draw a rectangle with all 4 sides equal? 59
11 Master 9.16 Step-by-Step 7 Lesson 7, Question 9 Step 1 What is the perimeter of the rectangular garden? Step 2 Start with a pair of sides on the rectangle being equal to 1 m. All the side lengths will be whole numbers of metres. What will the length of the other two sides be? Step 3 Draw the rectangle on grip paper. Label all the dimensions. Check to make sure the perimeter is the same as in Step 1. Step 4 Increase the length of a pair of sides on the rectangle to 2 m. What will the lengths of the other two sides be? Draw the rectangle on grid paper. Step 5 Step 6 Step 7 Continue to increase the length of a pair of sides on the rectangle. Keep the same perimeter as in Step 1. Draw all your rectangles on grid paper. Count the number of squares in each of the rectangles. What is the greatest number of squares you can count? What is the area of that rectangle? Which garden would provide the most growing space? The least growing space? 60
12 Master 9.17 Step-by-Step 8 Lesson 8, Question 10 Step 1 Look at the rectangle. Step 2 What is its length? What is its width? What is the area of this rectangle? Step 3 Double the length of the rectangle. What is the new length? What is the area of the rectangle now? On grid paper, draw the rectangle with its length doubled. Step 4 Compare the area in Step 2 with the area in Step 3. What do you have to do to the area in Step 2 to get the area in Step 3? Step 5 Use the rectangle from Step 1. Double the length and double the width. What is the new length? What is the new width? What is the area of this rectangle? On grid paper, draw the rectangle with its length and width doubled. Step 6 Compare the area in Step 2 with the area in Step 5. What do you have to do to the area in Step 2 to get the area in Step 5? 61
13 Master 9.18 Step-by-Step 9 Lesson 9, Question 5 You will need square dot paper, a geoboard, and geobands. Step 1 On a geoboard, make each figure below. Step 2 Count the number of whole squares and half squares. What is the area of each figure? Figure A: Figure B: Figure C: Step 3 Use a geoband to divide each figure into 2 congruent parts. Count the number of whole squares and half squares. What is the area of each congruent part? Figure A: Figure B: Figure C: Record your work on dot paper. For each figure, check that the sum of the areas of the congruent parts is equal to the area of the whole figure in Step 2. Step 4 Divide each figure into as many congruent parts as you can. You can use whole squares or half squares or a combination of both. Check that each congruent part of a figure has the same area. Record your work on dot paper. 62
14 Master 9.19 Step-by-Step 10 Lesson 10, Question 3 Step 1 Trace a circular object on the grid below. Step 2 Cut a length of string equal to the circumference of the object. Measure the string with a ruler. What is the circumference of the object? Step 3 Draw a rectangle along grid lines around the tracing of the object. Count squares to find the area of the rectangle. Count the whole squares and part squares outside the tracing of the object, but inside the rectangle. Subtract this number from the area of the rectangle. = What is the area of the tracing of the object? 63
15 Master 9.20a Unit Test: Unit 9 Length, Perimeter, and Area Part A 1. Choose the most appropriate unit. Estimate, then measure. Use any materials you need to help you. What to Measure Estimate Measurement a) The height of the classroom door b) The thickness of a paper clip c) The circumference of your ankle d) The perimeter of your math book e) The area of this paper 2. Complete. Use >, <, or =. a) 0.7 m 7 dm b) 75 mm 6 cm c) 500 m 1 km 3. Complete. a) 75 mm = cm b) 0.24 m = cm c) 8 m = dm 4. Record each measure in millimetres, in centimetres, and in decimetres. a) 0.8 m b) 1.5 m 5. a) Find the perimeter and the area of each figure. Use any materials you need. b) For which figure are the answers approximate? Figure Perimeter Area A B C c) For which figures did you have to use a ruler? 64
16 Master 9.20b Unit Test continued Part B 6. Suppose you want to find how many benches lined up end to end will fit across the width of the gym floor. How could you do this without moving any benches? 7. a) Willa s rectangular patio has area 64 m 2, and whole-number side lengths. What might the length and width of the patio be? Give as many answers as you can. b) Willa enclosed her patio with 40 m of fence. What are the length and width of her patio? Explain how you know. 8. Use the data in the table. a) Which 2 fish are the same length? b) Which fish is shortest? c) Which fish is longest? Tropical Fish Name Length Guppy 2.5 cm Paradise fish 75 mm Red platy 0.4 dm Ruby barb 65 mm Neon tetra 4.0 cm Swordtail 8.2 cm d) Which fish is longer than the ruby barb but shorter than the swordtail? 65
17 Master 9.20c Unit Test continued 9. Pablo speed walks around the school playground every evening. The playground is 80 m long and 45 m wide. How many times would Pablo have to speed walk around the playground to walk 2 km? Use a diagram, words, or numbers to explain your answer. Part C 10. Albert has a rectangular garden with perimeter 48 m. The length and width of the garden are whole numbers of metres. What might the dimensions and area of Albert s garden be? Find all the possible answers. 66
18 Master 9.21 Sample Answers Unit Test Master 9.20 Part A 1. Estimates and measurements will vary. 2. a) 0.7 m = 7 dm b) 75 mm > 6 cm c) 500 m < 1 km 3. a) 7.5 cm b) 24 cm c) 80 dm 4. a) 800 mm, 80 cm, 8 dm b) 1500 mm, 150 cm, 15 dm 5. a) Figure Perimeter Area A 16 cm 8 cm 2 B About 11 cm About 12 cm 2 C 13.7 cm 8 cm 2 b) Figure B c) Figures B and C Part B 6. Sample answer: I would measure the length of one bench, then measure the width of the gym floor. Then I would divide the width of the floor by the length of a bench. This gives me the number of benches. 7. a) Possible answers: 1 m by 64 m; 2 m by 32 m, 4 m by 16 m, 8 m by 8 m b) Length: 16 m; width: 4 m Sample answer: If the length is 16 m and the width is 4 m, the perimeter is 40 m: (16 + 4) 2 = a) Red platy and neon tetra b) Guppy c) Swordtail d) Paradise fish 9. Sample answer: Perimeter: (80 m + 45 m) 2 = 250 m 2 km = 2000 m 250 m 4 = 1000 m So, 250 m 8 = 2000 m Pablo would have to walk around the playground 8 times. 80 m Part C 10. Possible ans wers: Length Width Area 23 m 1 m 23 m 2 22 m 2 m 44 m 2 21 m 3 m 63 m 2 20 m 4 m 80 m 2 19 m 5 m 95 m 2 18 m 6 m 108 m 2 17 m 7 m 119 m 2 16 m 8 m 128 m 2 15 m 9 m 135 m 2 14 m 10 m 140 m 2 13 m 11 m 143 m 2 12 m 12 m 144 m 2 45 m 67
19 Extra Practice Masters Go to the CD-ROM to access editable versions of these Extra Practice Masters. 68
20 Program Authors Peggy Morrow Ralph Connelly Bryn Keyes Jason Johnston Steve Thomas Jeananne Thomas Angela D Alessandro Maggie Martin Connell Don Jones Michael Davis Sharon Jeroski Trevor Brown Nora Alexander Cynthia Pratt Nicolson All Rights Reserved. This publication is protected by copyright, and permission should be obtained from the publisher prior to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise. For information regarding permission, write to the Permissions Department. Printed and bound in Canada TC
Step-by-Step 1. Lesson 1, Question 5
 Master 11.11a Step-by-Step 1 Lesson 1, Question 5 Step 1 Yellow is more likely, so there are more sectors than red. Red is more likely, so there are more sectors than blue. Look at the first spinner on
Master 11.11a Step-by-Step 1 Lesson 1, Question 5 Step 1 Yellow is more likely, so there are more sectors than red. Red is more likely, so there are more sectors than blue. Look at the first spinner on
Extra Practice 1. Lesson 1: Measuring Linear Dimensions
 Master 9.22 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 1: Measuring Linear Dimensions 1. Estimate each measure. Then measure to the nearest whole unit. a) The width of a door b) The length of your thumb c) The thickness
Master 9.22 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 1: Measuring Linear Dimensions 1. Estimate each measure. Then measure to the nearest whole unit. a) The width of a door b) The length of your thumb c) The thickness
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important. You see geometric figures all around you.
 You see geometric figures all around you. Look at these pictures. Identify a figure. What would you need to know to find the area of that figure? What would you need to know to find the perimeter of the
You see geometric figures all around you. Look at these pictures. Identify a figure. What would you need to know to find the area of that figure? What would you need to know to find the perimeter of the
Reflect & Share. Here is the same parallelogram. This is a parallelogram. The height is perpendicular to the base. Work with a partner.
 6.1 Area of a Parallelogram Focus Use a formula to find the area of a parallelogram. This is a parallelogram. How would you describe it? Here is the same parallelogram. Any side of the parallelogram is
6.1 Area of a Parallelogram Focus Use a formula to find the area of a parallelogram. This is a parallelogram. How would you describe it? Here is the same parallelogram. Any side of the parallelogram is
Released October 2017
 Released October 2017 Kilometres Perimeter on a grid Perimeter of a rectangle Perimeter of rectilinear shapes Measure and calculate the perimeter of a rectilinear figure (including squares) in centimetres
Released October 2017 Kilometres Perimeter on a grid Perimeter of a rectangle Perimeter of rectilinear shapes Measure and calculate the perimeter of a rectilinear figure (including squares) in centimetres
Released November /5. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 4: Length & Perimeter
 Released November 2017 4/5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Length & Perimeter Year 4/5 Autumn Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 4 Year 5 Kilometres Perimeter on a grid Perimeter
Released November 2017 4/5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Length & Perimeter Year 4/5 Autumn Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 4 Year 5 Kilometres Perimeter on a grid Perimeter
Squares and Square Roots
 Squares and Square Roots Focus on After this lesson, you will be able to... determine the square of a whole number determine the square root of a perfect square Literacy Link A square number is the product
Squares and Square Roots Focus on After this lesson, you will be able to... determine the square of a whole number determine the square root of a perfect square Literacy Link A square number is the product
Unit Rubric: Length, Perimeter, and Area
 Master 9.1 Unit Rubric: Length, Perimeter, and Area Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Problem solving chooses and carries out a range of strategies (estimating with a referent, using grid paper, using manipulatives,
Master 9.1 Unit Rubric: Length, Perimeter, and Area Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Problem solving chooses and carries out a range of strategies (estimating with a referent, using grid paper, using manipulatives,
Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem
 UNIT 1 Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem Just for Fun What Do You Notice? Follow the steps. An example is given. Example 1. Pick a 4-digit number with different digits. 3078 2. Find the greatest
UNIT 1 Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem Just for Fun What Do You Notice? Follow the steps. An example is given. Example 1. Pick a 4-digit number with different digits. 3078 2. Find the greatest
Problem solving Grade 4 GCSE 9-1
 Write your name here Surname Other names AQA Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Candidate Number Problem solving Grade 4 GCSE 9-1 www.themathsprofessor.com Higher Tier Paper Reference Time:
Write your name here Surname Other names AQA Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Candidate Number Problem solving Grade 4 GCSE 9-1 www.themathsprofessor.com Higher Tier Paper Reference Time:
Released January Years 3/4. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area
 Released January 208 Years 3/4 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area Year 3/4 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 3 Year 4 Measure length Equivalent lengths
Released January 208 Years 3/4 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area Year 3/4 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 3 Year 4 Measure length Equivalent lengths
1. 1 Square Numbers and Area Models (pp. 6-10)
 Math 8 Unit 1 Notes Name: 1. 1 Square Numbers and Area Models (pp. 6-10) square number: the product of a number multiplied by itself; for example, 25 is the square of 5 perfect square: a number that is
Math 8 Unit 1 Notes Name: 1. 1 Square Numbers and Area Models (pp. 6-10) square number: the product of a number multiplied by itself; for example, 25 is the square of 5 perfect square: a number that is
AREA See the Math Notes box in Lesson for more information about area.
 AREA..1.. After measuring various angles, students look at measurement in more familiar situations, those of length and area on a flat surface. Students develop methods and formulas for calculating the
AREA..1.. After measuring various angles, students look at measurement in more familiar situations, those of length and area on a flat surface. Students develop methods and formulas for calculating the
Representing Square Numbers. Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array.
 1.1 Student book page 4 Representing Square Numbers You will need counters a calculator Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array. 5 5 25 number
1.1 Student book page 4 Representing Square Numbers You will need counters a calculator Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array. 5 5 25 number
Number Relationships. Chapter GOAL
 Chapter 1 Number Relationships GOAL You will be able to model perfect squares and square roots use a variety of strategies to recognize perfect squares use a variety of strategies to estimate and calculate
Chapter 1 Number Relationships GOAL You will be able to model perfect squares and square roots use a variety of strategies to recognize perfect squares use a variety of strategies to estimate and calculate
Problem solving Grade 4 GCSE 9-1
 Write your name here Surname Other names AQA Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Candidate Number Problem solving Grade 4 GCSE 9-1 www.themathsprofessor.com Higher Tier Paper Reference Time:
Write your name here Surname Other names AQA Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Candidate Number Problem solving Grade 4 GCSE 9-1 www.themathsprofessor.com Higher Tier Paper Reference Time:
Geometry. Learning Goals U N I T
 U N I T Geometry Building Castles Learning Goals describe, name, and sort prisms construct prisms from their nets construct models of prisms identify, create, and sort symmetrical and non-symmetrical shapes
U N I T Geometry Building Castles Learning Goals describe, name, and sort prisms construct prisms from their nets construct models of prisms identify, create, and sort symmetrical and non-symmetrical shapes
E D C B A MS2.1. Correctly calculates the perimeter of most of the drawn shapes. Shapes are similarly drawn. Records lengths using cm.
 Stage 2 - Assessment Measurement Outcomes: MS2.1 Estimates, measures, compares and records lengths, distances and perimeters in metres, cm and mm MS2.2 Estimates, measures, compares and records the areas
Stage 2 - Assessment Measurement Outcomes: MS2.1 Estimates, measures, compares and records lengths, distances and perimeters in metres, cm and mm MS2.2 Estimates, measures, compares and records the areas
Mensuration. Chapter Introduction Perimeter
 Mensuration Chapter 10 10.1 Introduction When we talk about some plane figures as shown below we think of their regions and their boundaries. We need some measures to compare them. We look into these now.
Mensuration Chapter 10 10.1 Introduction When we talk about some plane figures as shown below we think of their regions and their boundaries. We need some measures to compare them. We look into these now.
Sub Strand Area 1. Booragul Public School NSW Syllabus for the Australian Curriculum Measurement and Geometry ~ 1 ~
 Booragul Public School NSW Syllabus for the Australian Curriculum Measurement and Geometry Sub Strand Area 1 Outcome Teaching and Learning Activities Notes/ Future Directions/Evaluation Date Stage 2 A
Booragul Public School NSW Syllabus for the Australian Curriculum Measurement and Geometry Sub Strand Area 1 Outcome Teaching and Learning Activities Notes/ Future Directions/Evaluation Date Stage 2 A
Length, Perimeter and Area
 E Student Book 4 Nae Series E Contents Topic Units of length (pp. 7) etres and centietres length and decial notation illietres convert it apply Date copleted Topic Perieter (pp. 8 4) easuring shapes calculating
E Student Book 4 Nae Series E Contents Topic Units of length (pp. 7) etres and centietres length and decial notation illietres convert it apply Date copleted Topic Perieter (pp. 8 4) easuring shapes calculating
Number Models for Area
 Number Models for Area Objectives To guide children as they develop the concept of area by measuring with identical squares; and to demonstrate how to calculate the area of rectangles using number models.
Number Models for Area Objectives To guide children as they develop the concept of area by measuring with identical squares; and to demonstrate how to calculate the area of rectangles using number models.
mentoringminds.com MATH LEVEL 3 Student Edition Sample Page Unit 24 Introduction 1. What is the perimeter of the figure outlined on this grid?
 Student Edition Sample Page Name 1. What is the perimeter of the figure outlined on this grid? Introduction 4. This figure is a quadrilateral with sides measured in centimeters. Write an equation that
Student Edition Sample Page Name 1. What is the perimeter of the figure outlined on this grid? Introduction 4. This figure is a quadrilateral with sides measured in centimeters. Write an equation that
The Grade 6 Common Core State Standards for Geometry specify that students should
 The focus for students in geometry at this level is reasoning about area, surface area, and volume. Students also learn to work with visual tools for representing shapes, such as graphs in the coordinate
The focus for students in geometry at this level is reasoning about area, surface area, and volume. Students also learn to work with visual tools for representing shapes, such as graphs in the coordinate
Constructions Practice
 1a) In the space below draw a parallelogram. Constructions Practice b) How many lines of symmetry has is got? c) What is the rotational symmetry of a parallelogram? 2. Label this circle correctly Radius
1a) In the space below draw a parallelogram. Constructions Practice b) How many lines of symmetry has is got? c) What is the rotational symmetry of a parallelogram? 2. Label this circle correctly Radius
Geometry Page 1 of 54
 TEST NAME: Geometry TEST ID: 115140 GRADE: 06 SUBJECT: Mathematics TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom Geometry Page 1 of 54 Student: Class: Date: 1. Lisa had two vases with dimensions as shown below. Which statement
TEST NAME: Geometry TEST ID: 115140 GRADE: 06 SUBJECT: Mathematics TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom Geometry Page 1 of 54 Student: Class: Date: 1. Lisa had two vases with dimensions as shown below. Which statement
Using the Standards Measurement
 IFG9959 Math Grade 5 Using the Standards Measurement, Gr. 5 Using the Standards Measurement Supports NCTM Standards Student-Created Problems Enhance Mastery Vocabulary Cards Reinforce Math Terms Includes
IFG9959 Math Grade 5 Using the Standards Measurement, Gr. 5 Using the Standards Measurement Supports NCTM Standards Student-Created Problems Enhance Mastery Vocabulary Cards Reinforce Math Terms Includes
Student Book SAMPLE CHAPTERS
 Student Book SAMPLE CHAPTERS Nelson Student Book Nelson Math Focus... Eas Each lesson starts with a Lesson Goal. Chapter 6 You will need base ten blocks GOAL Multiply using a simpler, related question.
Student Book SAMPLE CHAPTERS Nelson Student Book Nelson Math Focus... Eas Each lesson starts with a Lesson Goal. Chapter 6 You will need base ten blocks GOAL Multiply using a simpler, related question.
Grow your. Yellow 4. The wee Maths Book. Growth. of Big Brain. Guaranteed to make your brain grow, just add some effort and hard work
 Grow your Yellow 4 Guaranteed to make your brain grow, just add some effort and hard work Don t be afraid if you don t know how to do it, yet! The wee Maths Book of Big Brain Growth Length (including circumference)
Grow your Yellow 4 Guaranteed to make your brain grow, just add some effort and hard work Don t be afraid if you don t know how to do it, yet! The wee Maths Book of Big Brain Growth Length (including circumference)
Investigation. Triangle, Triangle, Triangle. Work with a partner.
 Investigation Triangle, Triangle, Triangle Work with a partner. Materials: centimetre ruler 1-cm grid paper scissors Part 1 On grid paper, draw a large right triangle. Make sure its base is along a grid
Investigation Triangle, Triangle, Triangle Work with a partner. Materials: centimetre ruler 1-cm grid paper scissors Part 1 On grid paper, draw a large right triangle. Make sure its base is along a grid
- Chapter 1: "Symmetry and Surface Area" -
 Mathematics 9 C H A P T E R Q U I Z Form P - Chapter 1: "Symmetry and Surface Area" - Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In the figure, the
Mathematics 9 C H A P T E R Q U I Z Form P - Chapter 1: "Symmetry and Surface Area" - Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In the figure, the
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important. Students in a grade 7 class were raising money for charity. Some students had a bowl-a-thon.
 Students in a grade 7 class were raising money for charity. Some students had a bowl-a-thon. This table shows the money that one student raised for different bowling times. Time (h) Money Raised ($) 1
Students in a grade 7 class were raising money for charity. Some students had a bowl-a-thon. This table shows the money that one student raised for different bowling times. Time (h) Money Raised ($) 1
Look carefully at the dimensions on each shape and find the perimeter. Express your answers in cm: 3 cm. Length, Perimeter and Area
 Perimeter measure perimeters Perimeter is the length around a shape. The word originates from Greek and literally means around measure. The boundary of this shape is the perimeter. Choose classroom objects.
Perimeter measure perimeters Perimeter is the length around a shape. The word originates from Greek and literally means around measure. The boundary of this shape is the perimeter. Choose classroom objects.
Model Perimeter. So, the perimeter of the figure is 16 units. centimeters. centimeters. centimeters. centimeters
 Lesson 11.1 Reteach Model Perimeter Perimeter is the distance around a figure. Find the perimeter of the figure. Step 1 Choose a unit to begin counting and label it 1. 1 1 unit Step 2 Count each unit around
Lesson 11.1 Reteach Model Perimeter Perimeter is the distance around a figure. Find the perimeter of the figure. Step 1 Choose a unit to begin counting and label it 1. 1 1 unit Step 2 Count each unit around
Measuring in Centimeters
 MD2-3 Measuring in Centimeters Pages 179 181 Standards: 2.MD.A.1 Goals: Students will measure pictures of objects in centimeters using centimeter cubes and then a centimeter ruler. Prior Knowledge Required:
MD2-3 Measuring in Centimeters Pages 179 181 Standards: 2.MD.A.1 Goals: Students will measure pictures of objects in centimeters using centimeter cubes and then a centimeter ruler. Prior Knowledge Required:
2 A rectangle 3 cm long and. Find the perimeter and area of each figure. Remember to include the correct units in your answers.
 5- Homework Draw each rectangle on the dot paper. Find the perimeter and area. A rectangle 5 cm long and cm wide A rectangle cm long and cm wide Perimeter = Area = Perimeter = Area = Find the perimeter
5- Homework Draw each rectangle on the dot paper. Find the perimeter and area. A rectangle 5 cm long and cm wide A rectangle cm long and cm wide Perimeter = Area = Perimeter = Area = Find the perimeter
The Pythagorean Theorem 8.6.C
 ? LESSON 8.1 The Pythagorean Theorem ESSENTIAL QUESTION Expressions, equations, and relationships 8.6.C Use models and diagrams to explain the Pythagorean Theorem. 8.7.C Use the Pythagorean Theorem...
? LESSON 8.1 The Pythagorean Theorem ESSENTIAL QUESTION Expressions, equations, and relationships 8.6.C Use models and diagrams to explain the Pythagorean Theorem. 8.7.C Use the Pythagorean Theorem...
(a) Write down the number marked by the arrow. Mark it with an arrow ( ). (1)
 Topic 3 Real-Life 5. 50 60 70 80 90 (a) Write down the number marked by the arrow.... (b) Find the number 530 on the number line. 300 400 500 600 700 800 Mark it with an arrow ( ). (c) Put these numbers
Topic 3 Real-Life 5. 50 60 70 80 90 (a) Write down the number marked by the arrow.... (b) Find the number 530 on the number line. 300 400 500 600 700 800 Mark it with an arrow ( ). (c) Put these numbers
Stage 3 Outcome Language square kilometre hectare dimensions length
 Stage 3 Outcome A student: describes and represents mathematical situations in a variety of ways using mathematical terminology and some conventions MA3-1WM selects and uses the appropriate unit to calculate
Stage 3 Outcome A student: describes and represents mathematical situations in a variety of ways using mathematical terminology and some conventions MA3-1WM selects and uses the appropriate unit to calculate
Exercise 2. Match. 2-2 Count Things Up to 5
 Exercise 2 Match. Using this page: Have students count and cross out the objects to help them keep track if needed, then match with the fiveframe card. Concept: One-to-one correspondence and cardinality.
Exercise 2 Match. Using this page: Have students count and cross out the objects to help them keep track if needed, then match with the fiveframe card. Concept: One-to-one correspondence and cardinality.
Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Grade 04
 Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Problem Solving Mathematical Process Expectations 4m1 develop, select, and apply problem-solving strategies as they pose and solve problems and conduct investigations, to
Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Problem Solving Mathematical Process Expectations 4m1 develop, select, and apply problem-solving strategies as they pose and solve problems and conduct investigations, to
The Measurement of LENGTH
 The Measurement of LENGTH What is Measuring? MEASUREMENT To measure, according to The Concise Oxford Dictionary is to ascertain extent or quantity of (thing) by comparison with fixed unit or with object
The Measurement of LENGTH What is Measuring? MEASUREMENT To measure, according to The Concise Oxford Dictionary is to ascertain extent or quantity of (thing) by comparison with fixed unit or with object
Covering and Surrounding Assessment. 1. (1 point) Find the area and perimeter of this rectangle. Explain how you found your answers.
 Name: Date: Score: /20 Covering and Surrounding Assessment Short Answer: Answer each question, making sure to show your work or provide an explanation or sketch to support your answer in the box. Make
Name: Date: Score: /20 Covering and Surrounding Assessment Short Answer: Answer each question, making sure to show your work or provide an explanation or sketch to support your answer in the box. Make
Pythagorean Theorem. 2.1 Soon You Will Determine the Right Triangle Connection The Pythagorean Theorem... 45
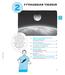 Pythagorean Theorem What is the distance from the Earth to the Moon? Don't let drawings or even photos fool you. A lot of them can be misleading, making the Moon appear closer than it really is, which
Pythagorean Theorem What is the distance from the Earth to the Moon? Don't let drawings or even photos fool you. A lot of them can be misleading, making the Moon appear closer than it really is, which
Unit 1, Lesson 1: What are Scaled Copies?
 Unit 1, Lesson 1: What are Scaled Copies? Let s explore scaled copies. 1.1: Printing Portraits m.openup.org/1/7-1-1-1 Here is a portrait of a student. 1. Look at Portraits A E. How is each one the same
Unit 1, Lesson 1: What are Scaled Copies? Let s explore scaled copies. 1.1: Printing Portraits m.openup.org/1/7-1-1-1 Here is a portrait of a student. 1. Look at Portraits A E. How is each one the same
Introduction Home : 0
 Introduction Home : 0 This topic is concerned with the mathematics of shape and space, both 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional. The main setting for much of the work is the home and, with that link, it would
Introduction Home : 0 This topic is concerned with the mathematics of shape and space, both 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional. The main setting for much of the work is the home and, with that link, it would
Angles and. Learning Goals U N I T
 U N I T Angles and Learning Goals name, describe, and classify angles estimate and determine angle measures draw and label angles provide examples of angles in the environment investigate the sum of angles
U N I T Angles and Learning Goals name, describe, and classify angles estimate and determine angle measures draw and label angles provide examples of angles in the environment investigate the sum of angles
Using the Standards Measurement
 Instructional Fair IFG99257 Math Grade 3 Using the Standards Measurement, Gr. 3 Using the Standards Measurement Supports NCTM Standards Student-Created Problems Enhance Mastery Vocabulary Cards Reinforce
Instructional Fair IFG99257 Math Grade 3 Using the Standards Measurement, Gr. 3 Using the Standards Measurement Supports NCTM Standards Student-Created Problems Enhance Mastery Vocabulary Cards Reinforce
BUILDING A VR VIEWER COMPLETE BUILD ASSEMBLY
 ACTIVITY 22: PAGE 1 ACTIVITY 22 BUILDING A VR VIEWER COMPLETE BUILD ASSEMBLY MATERIALS NEEDED One Rectangular Cardboard piece from 12-pack soda case Two round bi-convex lenses with a focal point of 45mm
ACTIVITY 22: PAGE 1 ACTIVITY 22 BUILDING A VR VIEWER COMPLETE BUILD ASSEMBLY MATERIALS NEEDED One Rectangular Cardboard piece from 12-pack soda case Two round bi-convex lenses with a focal point of 45mm
Lesson 20T ~ Parts of Circles
 Lesson 20T ~ Parts of Circles Name Period Date 1. Draw a diameter. 2. Draw a chord. 3. Draw a central angle. 4. Draw a radius. 5. Give two names for the line drawn in the circle. Given the radius, find
Lesson 20T ~ Parts of Circles Name Period Date 1. Draw a diameter. 2. Draw a chord. 3. Draw a central angle. 4. Draw a radius. 5. Give two names for the line drawn in the circle. Given the radius, find
Geometry Final Exam Review 2012 #
 1 PART 1: Multiple Choice (40 x 2 points = 80%). PART 2: Open Ended (2 x 10 = 20%) 1) Find the volume and surface area of the following rectangular prisms 2) Find the surface area of the following cylinders.
1 PART 1: Multiple Choice (40 x 2 points = 80%). PART 2: Open Ended (2 x 10 = 20%) 1) Find the volume and surface area of the following rectangular prisms 2) Find the surface area of the following cylinders.
AREA & PERIMETER LESSON 1 OBJ ECTIVE: OBJECTIVE: INVESTIGATE AND USE THE FORMULAS FOR AREA AND PERIMETER OF RECTANGLES.
 AREA & PERIMETER LESSON 1 OBJ ECTIVE: OBJECTIVE: INVESTIGATE AND USE THE FORMULAS FOR AREA AND PERIMETER OF RECTANGLES. Learning Goal By the end of the unit... students will apply the area and perimeter
AREA & PERIMETER LESSON 1 OBJ ECTIVE: OBJECTIVE: INVESTIGATE AND USE THE FORMULAS FOR AREA AND PERIMETER OF RECTANGLES. Learning Goal By the end of the unit... students will apply the area and perimeter
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *1846903511* MATHEMATICS 0580/31 Paper 3 (Core) October/November 2018 Candidates answer on the Question
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *1846903511* MATHEMATICS 0580/31 Paper 3 (Core) October/November 2018 Candidates answer on the Question
YuMi Deadly Maths Year 4 Teacher Resource: MG Make your own ruler
 YuMi Deadly Maths Year 4 Teacher Resource: MG Make your own ruler YuMi Deadly Maths Year 4 Teacher Resource: MG Make your own ruler Prepared by the YuMi Deadly Centre Faculty of Education, QUT ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
YuMi Deadly Maths Year 4 Teacher Resource: MG Make your own ruler YuMi Deadly Maths Year 4 Teacher Resource: MG Make your own ruler Prepared by the YuMi Deadly Centre Faculty of Education, QUT ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Area and Perimeter (F) Intervention Booklet
 Area and Perimeter (F) Intervention Booklet Area and Perimeter of Rectangles and Triangles Things to remember: Area of a rectangle = base x height Area of a triangle = ½ x base x height The perimeter is
Area and Perimeter (F) Intervention Booklet Area and Perimeter of Rectangles and Triangles Things to remember: Area of a rectangle = base x height Area of a triangle = ½ x base x height The perimeter is
7.3B STUDENT ACTIVITY #1
 E MAT I CS 7.3B STUDENT ACTIVITY #1 PROBLEM: Right triangles MNP and DEF are similar. Find the length in inches of side EF. D M 6 in. P 9 in. N 24 in. F x E Since the triangles are similar, their corresponding
E MAT I CS 7.3B STUDENT ACTIVITY #1 PROBLEM: Right triangles MNP and DEF are similar. Find the length in inches of side EF. D M 6 in. P 9 in. N 24 in. F x E Since the triangles are similar, their corresponding
Lesson 2. Measuring Length
 Math 5 Lesson 2 Measuring Length How Big is My Desk? Daksha needed to measure the length of his desk, but he did not have a ruler. He decided to use the width of his hand instead. He laid each hand side
Math 5 Lesson 2 Measuring Length How Big is My Desk? Daksha needed to measure the length of his desk, but he did not have a ruler. He decided to use the width of his hand instead. He laid each hand side
2018 national curriculum tests. Key stage 1. Mathematics. Paper 2: reasoning. First name. Middle name. Last name. Total marks
 2018 national curriculum tests Key stage 1 Mathematics Paper 2: reasoning First name Middle name Last name Total marks Amy Ajay Sam Ben Sita Kemi Page 2 of 32 Practice question Page 3 of 32 1 20 2 2 2
2018 national curriculum tests Key stage 1 Mathematics Paper 2: reasoning First name Middle name Last name Total marks Amy Ajay Sam Ben Sita Kemi Page 2 of 32 Practice question Page 3 of 32 1 20 2 2 2
Measurement 1 AP Book 4.1
 Measurement 1 AP Book 4.1 page 1 AP Book ME4-1 page 97 1. a) Answers may vary. b) Answers may vary. 2. Objects measured and lengths may vary. 3. a) 5 toonies toonies c) 10 toonies 4. a) Answers may vary.
Measurement 1 AP Book 4.1 page 1 AP Book ME4-1 page 97 1. a) Answers may vary. b) Answers may vary. 2. Objects measured and lengths may vary. 3. a) 5 toonies toonies c) 10 toonies 4. a) Answers may vary.
Stretch lesson: Constructions
 29 Stretch lesson: onstructions Stretch objectives efore you start this chapter, mark how confident you feel about each of the statements below: I can construct the perpendicular bisector of a given line.
29 Stretch lesson: onstructions Stretch objectives efore you start this chapter, mark how confident you feel about each of the statements below: I can construct the perpendicular bisector of a given line.
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9 1)
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9 1) *0123456789* MATHEMATICS 0626/01 Paper 1 (Core) For Examination from 2017 SPECIMEN PAPER Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9 1) *0123456789* MATHEMATICS 0626/01 Paper 1 (Core) For Examination from 2017 SPECIMEN PAPER Candidates
THOUSANDS TO MEASURE SUPPORT RESOURCES 1 INCH YARD METRE. Anna Quer Ceip Antoni Brusi
 SUPPORT RESOURCES 1 INCH YARD METRE CENTIMETRE MILLIMETRE LITER KILO TON FOOT POUND OUNCE SUPPORT RESOURCES 2 1. There are 100 millimeters in a metre. 2. Centi means one hundred. 3. Large measurements
SUPPORT RESOURCES 1 INCH YARD METRE CENTIMETRE MILLIMETRE LITER KILO TON FOOT POUND OUNCE SUPPORT RESOURCES 2 1. There are 100 millimeters in a metre. 2. Centi means one hundred. 3. Large measurements
Prepared by the YuMi Deadly Centre Faculty of Education, QUT. YuMi Deadly Maths Year 6 Teacher Resource: MG Fencing the yard
 YuMi Deadly Maths Year 6 Teacher Resource: MG Fencing the yard Prepared by the YuMi Deadly Centre Faculty of Education, QUT YuMi Deadly Maths Year 6 Teacher Resource: MG Fencing the yard ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
YuMi Deadly Maths Year 6 Teacher Resource: MG Fencing the yard Prepared by the YuMi Deadly Centre Faculty of Education, QUT YuMi Deadly Maths Year 6 Teacher Resource: MG Fencing the yard ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
WVDE Math 7 G Solve Real-life and Mathematical Problems involving Angle Measure, Area, Surface Area, and Volume Test
 WVDE Math 7 G Solve Real-life and Mathematical Problems involving Angle Measure, Area, Surface Area, and Volume Test 1 General Offline Instructions: Read each question carefully and decide which answer
WVDE Math 7 G Solve Real-life and Mathematical Problems involving Angle Measure, Area, Surface Area, and Volume Test 1 General Offline Instructions: Read each question carefully and decide which answer
FSA 7 th Grade Math. MAFS.7.G.1.1 Level 2. MAFS.7.G.1.1 Level 3. MAFS.7.G.1.1 Level 3. MAFS.7.G.1.2 Level 2. MAFS.7.G.1.1 Level 4
 FSA 7 th Grade Math Geometry This drawing shows a lawn in the shape of a trapezoid. The height of the trapezoidal lawn on the drawing is 1! inches. " What is the actual length, in feet, of the longest
FSA 7 th Grade Math Geometry This drawing shows a lawn in the shape of a trapezoid. The height of the trapezoidal lawn on the drawing is 1! inches. " What is the actual length, in feet, of the longest
Metric Measurement of Length
 CHAPTER 7 Metric Measurement of Length Lesson 1 Measuring in Meters Look at the pictures. Fill in the blanks with more or less. 1. meterstick 2. The length of the stick is meterstick than 1 meter. The
CHAPTER 7 Metric Measurement of Length Lesson 1 Measuring in Meters Look at the pictures. Fill in the blanks with more or less. 1. meterstick 2. The length of the stick is meterstick than 1 meter. The
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important
 Look at these pictures. What shapes do you see? What is a circle? Where do you see circles? What do you know about a circle? What might be useful to know about a circle? A parallelogram? A triangle? What
Look at these pictures. What shapes do you see? What is a circle? Where do you see circles? What do you know about a circle? What might be useful to know about a circle? A parallelogram? A triangle? What
2003 Exit 13) Use the information in each diagram to find the pair of similar polygons. A B C D
 2003 Exit 9) Use the ruler on the Mathematics hart to measure the dimensions of the composite figure to the nearest tenth of a centimeter. Which best represents the approximate area of this composite figure?
2003 Exit 9) Use the ruler on the Mathematics hart to measure the dimensions of the composite figure to the nearest tenth of a centimeter. Which best represents the approximate area of this composite figure?
Name Date Period STUDY GUIDE Summative Assessment #5 6 th Grade Math Covering and Surrounding
 Name Date Period STUDY GUIDE Summative Assessment #5 6 th Grade Math Covering and Surrounding 1) Mr. and Mrs. Hunter tiled their rectangular porch using 1ft. by 1ft. square tiles. The rectangular porch
Name Date Period STUDY GUIDE Summative Assessment #5 6 th Grade Math Covering and Surrounding 1) Mr. and Mrs. Hunter tiled their rectangular porch using 1ft. by 1ft. square tiles. The rectangular porch
New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning. Progressive Mathematics Initiative
 Slide 1 / 126 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
Slide 1 / 126 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
Math Labs. Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates. Procedure
 Math Labs Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates Problem Statement Use the Cartesian coordinate system to draw rectangle ABCD. Use an x-y-z coordinate system to draw a rectangular
Math Labs Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates Problem Statement Use the Cartesian coordinate system to draw rectangle ABCD. Use an x-y-z coordinate system to draw a rectangular
MEASURING SHAPES M.K. HOME TUITION. Mathematics Revision Guides. Level: GCSE Foundation Tier
 Mathematics Revision Guides Measuring Shapes Page 1 of 17 M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Foundation Tier MEASURING SHAPES Version: 2.2 Date: 16-11-2015 Mathematics Revision Guides
Mathematics Revision Guides Measuring Shapes Page 1 of 17 M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Foundation Tier MEASURING SHAPES Version: 2.2 Date: 16-11-2015 Mathematics Revision Guides
Eureka Math. Grade, Module. Student _B Contains Sprint and Fluency, Exit Ticket, and Assessment Materials
 A Story of Eureka Math Grade, Module Student _B Contains Sprint and Fluency,, and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 2015 Great Minds. All rights reserved. No part
A Story of Eureka Math Grade, Module Student _B Contains Sprint and Fluency,, and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 2015 Great Minds. All rights reserved. No part
3. Use words to write 26,615 and 92,980. Which number is greater?
 Chapter 10 Review Name: 1. Compare the fractions. Write >,
Chapter 10 Review Name: 1. Compare the fractions. Write >,
How to Draw with a Grid
 Level: Beginner Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level: 8.3 Flesch-Kincaid Reading Ease: 67.5-6 Pages and 12 Illustrations How to Draw with a Grid Exploring the grid method to draw accurate outline drawings This resource
Level: Beginner Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level: 8.3 Flesch-Kincaid Reading Ease: 67.5-6 Pages and 12 Illustrations How to Draw with a Grid Exploring the grid method to draw accurate outline drawings This resource
Objective. Materials. Find the lengths of diagonal geoboard segments. Find the perimeter of squares, rectangles, triangles, and other polygons.
 . Objective To find the perimeter of a variety of shapes (polygons) Activity 6 Materials TI-73 Student Activity pages (pp. 68 71) Walking the Fence Line In this activity you will Find the lengths of diagonal
. Objective To find the perimeter of a variety of shapes (polygons) Activity 6 Materials TI-73 Student Activity pages (pp. 68 71) Walking the Fence Line In this activity you will Find the lengths of diagonal
Measuring Parallelograms
 4 Measuring Parallelograms In this unit, you have developed ways to find the area and perimeter of rectangles and of triangles. In this investigation you will develop ways to find the area and perimeter
4 Measuring Parallelograms In this unit, you have developed ways to find the area and perimeter of rectangles and of triangles. In this investigation you will develop ways to find the area and perimeter
A vibration is one back-and-forth motion.
 Basic Skills Students who go to the park without mastering the following skills have difficulty completing the ride worksheets in the next section. To have a successful physics day experience at the amusement
Basic Skills Students who go to the park without mastering the following skills have difficulty completing the ride worksheets in the next section. To have a successful physics day experience at the amusement
Measuring Parallelograms
 4 Measuring Parallelograms In this unit, you have developed ways to find the area and perimeter of rectangles and of triangles. In this investigation you will develop ways to find the area and perimeter
4 Measuring Parallelograms In this unit, you have developed ways to find the area and perimeter of rectangles and of triangles. In this investigation you will develop ways to find the area and perimeter
Changing Area, Changing Perimeter
 2 Changing Area, Changing Perimeter Whether you make a floor plan for a bumper-car ride or a house, there are many options. You should consider the cost of materials and the use of a space to find the
2 Changing Area, Changing Perimeter Whether you make a floor plan for a bumper-car ride or a house, there are many options. You should consider the cost of materials and the use of a space to find the
1. Numbers & Operations Place Value Gr. 7 N-1a,b
 1. Numbers & Operations Place Value Gr. 7 N-1a,b Ghetto Blaster Cassette NUMBERS Student Recording Cassette answer sheet 1. On your answer sheet write the following as numbers: Whole numbers: a) eight
1. Numbers & Operations Place Value Gr. 7 N-1a,b Ghetto Blaster Cassette NUMBERS Student Recording Cassette answer sheet 1. On your answer sheet write the following as numbers: Whole numbers: a) eight
Year 1 Spring Term Week 8 to 9 Measurement: Length & Height
 1 Compare lengths and heights Measure length (1) Measure length (2) Measure and begin to record lengths and heights. Compare, describe and solve practical problems for: lengths and heights (for example,
1 Compare lengths and heights Measure length (1) Measure length (2) Measure and begin to record lengths and heights. Compare, describe and solve practical problems for: lengths and heights (for example,
Page 1 part 1 PART 2
 Page 1 part 1 PART 2 Page 2 Part 1 Part 2 Page 3 part 1 Part 2 Page 4 Page 5 Part 1 10. Which point on the curve y x 2 1 is closest to the point 4,1 11. The point P lies in the first quadrant on the graph
Page 1 part 1 PART 2 Page 2 Part 1 Part 2 Page 3 part 1 Part 2 Page 4 Page 5 Part 1 10. Which point on the curve y x 2 1 is closest to the point 4,1 11. The point P lies in the first quadrant on the graph
5Scale Representations
 231 Chapter 5Scale Representations Blueprints are an example of scale representation. Carpenters and contractors need to know how to read scale statements and scale diagrams to accurately construct buildings.
231 Chapter 5Scale Representations Blueprints are an example of scale representation. Carpenters and contractors need to know how to read scale statements and scale diagrams to accurately construct buildings.
Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2 (Calculator)
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics B Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2 (Calculator) Wednesday 6 March 2013 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics B Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2 (Calculator) Wednesday 6 March 2013 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
1. Geometry/Measurement Grade 9 Angles, Lines & Line Segments G/M-1e
 1. Geometry/Measurement Grade 9 Angles, Lines & Line Segments G/M-1e small rectangle or square of colored paper mira Geometry Set cardboard strips Your friend call you over the telephone and says, How
1. Geometry/Measurement Grade 9 Angles, Lines & Line Segments G/M-1e small rectangle or square of colored paper mira Geometry Set cardboard strips Your friend call you over the telephone and says, How
Student Outcomes. Lesson Notes. Classwork. Example 1 (10 minutes)
 Student Outcomes Students understand that a letter represents one number in an expression. When that number replaces the letter, the expression can be evaluated to one number. Lesson Notes Before this
Student Outcomes Students understand that a letter represents one number in an expression. When that number replaces the letter, the expression can be evaluated to one number. Lesson Notes Before this
UNIT 10 PERIMETER AND AREA
 UNIT 10 PERIMETER AND AREA INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will define basic geometric shapes and use definitions to categorize geometric figures. Then we will use the ideas of measuring length and area
UNIT 10 PERIMETER AND AREA INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will define basic geometric shapes and use definitions to categorize geometric figures. Then we will use the ideas of measuring length and area
GAP CLOSING. Powers and Roots. Intermediate / Senior Facilitator Guide
 GAP CLOSING Powers and Roots Intermediate / Senior Facilitator Guide Powers and Roots Diagnostic...5 Administer the diagnostic...5 Using diagnostic results to personalize interventions...5 Solutions...5
GAP CLOSING Powers and Roots Intermediate / Senior Facilitator Guide Powers and Roots Diagnostic...5 Administer the diagnostic...5 Using diagnostic results to personalize interventions...5 Solutions...5
1MA0/1F Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1MA0 Practice Paper 1F (Non-Calculator) Set C Foundation Tier Time: 1 hour 45 minutes
 1MA0/1F Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1MA0 Practice Paper 1F (Non-Calculator) Set C Foundation Tier Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required for examination Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres,
1MA0/1F Edexcel GCSE Mathematics (Linear) 1MA0 Practice Paper 1F (Non-Calculator) Set C Foundation Tier Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required for examination Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres,
1st Grade Length
 Slide 1 / 157 Slide 2 / 157 1st Grade Length 2015-11-30 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 157 Table of Contents Comparing Two Objects Comparing Three Objects Ordering Three Objects Using Blocks to Measure Lab: Comparison
Slide 1 / 157 Slide 2 / 157 1st Grade Length 2015-11-30 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 157 Table of Contents Comparing Two Objects Comparing Three Objects Ordering Three Objects Using Blocks to Measure Lab: Comparison
1st Grade. Slide 1 / 157. Slide 2 / 157. Slide 3 / 157. Length
 Slide 1 / 157 Slide 2 / 157 1st Grade Length 2015-11-30 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Comparing Two Objects Comparing Three Objects Ordering Three Objects Using Blocks to Measure Lab: Comparison Game
Slide 1 / 157 Slide 2 / 157 1st Grade Length 2015-11-30 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Comparing Two Objects Comparing Three Objects Ordering Three Objects Using Blocks to Measure Lab: Comparison Game
Mathematics Success Level F
 T598 [OBJECTIVE] The student will find the perimeter and area of rectangles and triangles. [MATERIALS] Student pages S204 S212 Transparencies T612, T614, T616, T618, T620, T622 Ruler Scissors Gridded index
T598 [OBJECTIVE] The student will find the perimeter and area of rectangles and triangles. [MATERIALS] Student pages S204 S212 Transparencies T612, T614, T616, T618, T620, T622 Ruler Scissors Gridded index
Unit 2: Number, Algebra, Geometry 1 (Non-Calculator) Foundation Tier
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics B Unit 2: Number, Algebra, Geometry 1 (Non-Calculator) Foundation Tier Thursday 4 June 2015 Morning
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics B Unit 2: Number, Algebra, Geometry 1 (Non-Calculator) Foundation Tier Thursday 4 June 2015 Morning
4 Allow time for students to use what they learned in Part 1 to estimate the perimeter of each planting bed.
 Teacher Information During this lesson students will: Estimate length to the nearest centimeter/inch. Accurately measure the length of the sides of each shape to the nearest centimeter/inch. Determine
Teacher Information During this lesson students will: Estimate length to the nearest centimeter/inch. Accurately measure the length of the sides of each shape to the nearest centimeter/inch. Determine
Paper Reference. Paper Reference(s) 5542F/7F Edexcel GCSE Mathematics. Unit 2 Stage 1 Foundation Tier Specimen Paper Time: 30 minutes
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Instructions to Candidates In the boxes above, write your centre number, candidate number, your surname, initials and signature. Check that you have the correct
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Instructions to Candidates In the boxes above, write your centre number, candidate number, your surname, initials and signature. Check that you have the correct
I think that all Ice Cream Cones are not scooped into cone shapes because. Recall 1. What is the formula to calculate the Volume of a Cylinder?
 Name: Date: Period: Why aren t all Ice Cream Cones Cones? Opening Question When you order an Ice Cream cone, why is it that you can choose between one that is actually shaped like a cone and one that is
Name: Date: Period: Why aren t all Ice Cream Cones Cones? Opening Question When you order an Ice Cream cone, why is it that you can choose between one that is actually shaped like a cone and one that is
Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests
 Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests 1 Equipment Required Printed question and answer sheet for the reader Printed blank answer page for child Stopwatch or timer Pencil No other equipment is required to complete
Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests 1 Equipment Required Printed question and answer sheet for the reader Printed blank answer page for child Stopwatch or timer Pencil No other equipment is required to complete
Lesson 18: More Problems on Area and Circumference
 Student Outcomes Students examine the meaning of quarter circle and semicircle. Students solve area and perimeter problems for regions made out of rectangles, quarter circles, semicircles, and circles,
Student Outcomes Students examine the meaning of quarter circle and semicircle. Students solve area and perimeter problems for regions made out of rectangles, quarter circles, semicircles, and circles,
GCSE Mathematics Specification (8300/2F)
 NEW SPECIMEN PAPERS PUBLISHED JUNE 2015 GCSE Mathematics Specification (8300/2F) Paper 2 Foundation tier F Date Morning 1 hour 30 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a calculator mathematical
NEW SPECIMEN PAPERS PUBLISHED JUNE 2015 GCSE Mathematics Specification (8300/2F) Paper 2 Foundation tier F Date Morning 1 hour 30 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a calculator mathematical
