Math Ready Unit 3. Measurement and Proportional Reasoning Student Manual
|
|
|
- Egbert Chambers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SREB Readiness Courses Transitioning to college and careers Math Ready Unit 3. Measurement and Proportional Reasoning Student Manual Version 2 Name 1
2 Math Ready. Unit 3. Student Manual Unit 3. Measurement and Proportional Reasoning Table of Contents Lesson Lesson Lesson Lesson Lesson Lesson
3 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 1 Task #1: Heart Rate Closing Activity 1. Find your pulse and count how many times it beats in 15 seconds. 2. Run (in place if necessary) for 2 minutes. Now take your pulse for 15 seconds. Record your result. 3. At this rate, how long would it take for your heart to beat 700,000 times? Express your answer in days. Now express your answer in days, hours, minutes, and seconds. (example: 2 days, 4 hours, 21 minutes, 15 seconds) 4. You are training for a 5K race. This morning you ran 8 miles in 1 hour. If you run the race at this speed, how many minutes will it take you to run a 5K race? 3
4 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 1 Task #2: Heart Rate Extension Activity Find a person 30 years old or older and record his/her approximate age. a. Measure his/her pulse for 15 seconds. What would it be in 1 minute? b. Have the person run in place for 2 minutes. Now take his/her pulse again for 15 seconds. What would it be in 1 minute? c. How many times would that person s heart beat if he/she ran a 5K race? (If you don t have a rate at which this person runs, assume the person can average 6 mph during the race.) Research to find a table of values for healthy heart rates to find out if your heart rate and the other person s heart rate are healthy. 4
5 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 2 Task #3: Fuel for Thought Student Activity Sheet Part 1 A Fuel-ish Question 1. Which of the following would save more fuel? a. Replacing a compact car that gets 34 miles per gallon (mpg) with a hybrid that gets 54 mpg. b. Replacing a sport utility vehicle (SUV) that gets 18 mpg with a sedan that gets 28 mpg. c. Both changes would save the same amount of fuel. 2. Explain your reasoning for your choice. 5
6 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 2 Task #4: Fuel for Thought Student Activity Sheet Part 2 Extending the Discussion MPG vs. Fuel Consumption 1. Complete the following chart comparing mpg and fuel consumption. MPG Fuel consumed to travel 100 miles 2. Use your values to sketch a graph. 6
7 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 2 3. Develop a written report explaining your observations and conclusions. 7
8 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 2 Task #5: Map Activity Sheet You are planning a trip from to on Highway. (city name) (city name) (Route) You want to determine the distance between these cities by using the map. On the map, locate the legend showing the scale of miles and answer the following questions. 1. How many miles are represented by 1 inch on the map? 2. How many inches represent 5 miles? How did you get your answer? 3. How many inches are there between the two cities listed above? 4. How many miles are there between these two cities? 8
9 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 2 Task #6: Unit Conversion Problems Medicine: A doctor orders 250 mg of Rocephin to be taken by a 19.8 lb infant every 8 hours. The medication label shows that mg/kg per day is the appropriate dosage range. Is this doctor s order within the desired range? Agriculture: You own an empty one acre lot. (640 acres = 1 mi 2 ; 1 mi = 5,280 ft) a. If 1 inch of rain fell over your one acre lot, how many cubic inches of water fell on your lot? b. How many cubic feet of water fell on your lot? c. If 1 cubic foot of water weighs about 62 pounds, what is the weight of the water that fell on your lot? d. If the weight of 1 gallon of water is approximately 8.3 pounds, how many gallons of water fell on your lot? Astronomy: Light travels 186,282 miles per second. a. How many miles will light travel in one year? (Use 365 days in a year) This unit of distance is called a light-year. b. Capella is the 6th brightest star in the sky and is 41 light-years from earth. How many miles will light from Capella travel on its way to earth? c. Neptune is 2,798,842,000 miles from the sun. How many hours does it take light to travel from the sun to Neptune? 9
10 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 4 Task #7: Scaling Activity Look at the two pictures below. The first picture is the Washington Monument in Washington DC. The second is of the Eiffel Tower in France. Washington Monument Eiffel Tower If you just look at the diagrams which appears to be the taller object? The scale for the Washington Monument is 1 unit feet. The scale for the Eiffel Tower is 1 unit 33.9 meters. Round your answers to the nearest whole number. A. Find the height of the Washington Monument. B. Find the height of the Eiffel Tower. Now let s think about the original question posed, which of the monuments is actually the taller? What will we have to do with our answers from A and B above to find the solution? Show and explain your work for this problem below. 10
11 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 4 Task #8: Scale Drawing Class Project Goal: To use scale drawing to recreate a card. Project: 1. Find two identical greeting cards or make a copy of the original card. 2. Draw a 1 cm grid on the back of the original card. 3. Number each of the squares this will be used to assemble the final project. 4. Cut the card into squares following the grid lines. 5. Place the cut squares into a container and chose one square, record which square you selected. 6. From the teacher, receive an 8" x 8" square of white paper. 7. Reproduce and color the square that you drew from the container onto the 8" x 8" sheet of paper using scale drawing. 8. Display the final drawing by placing the squares on a wall along with the original card. Questions: 1. Look at the finished product and evaluate the display. Did the lines match up? Which part looks the best? Which piece would have been the easiest to recreate? The hardest? Why? 2. What is the relationship of the perimeter and area between your original square and the square you created? What is the relationship of the perimeter and area of the original square to the final class project? 3. If we did the project using 4" x 4" squares how would that have affected the perimeter and area? 11
12 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 4 Task #9: Scale Drawing Individual Goal: To select a card and enlarge it to best fit an 8 ½ x 11 sheet of paper. To investigate how dimensions, perimeter and area are affected when doing scale drawings. Please include in your project: 1. The original picture 2. The enlarged picture (colored to match original) 3. Measurements of the original picture 4. The scale selected to enlarge the picture 5. Self-Completed Evaluation Design: Step 1: Measure the length and width of the picture in cm. (It does not matter which side you label the length and width; be consistent with your sides on the large paper) Length Width Step 2: Draw a 1 cm grid on the original card (Draw 1 cm tick marks going across the length and the width and then connect your marks to form a grid, these measurements need to be accurate) Step 3: Measure the paper in cm. Length Width Step 4: Select a scale (1 cm on card = cm on paper) To do this find the ratio of lengths and widths i.e.: Lp = = L c Wp = = W c Then pick the smallest of the two numbers to the nearest whole number (i.e. if you get 4.29 and 4.76 your scale should be 1 cm card = 4 cm on paper) Step 5: Draw the borders Multiply your length and width of the card by your scale factor and see how much of the paper you have left over for the border. Take this number and divide by two because the border should be on both sides. i.e. L c x Scale Factor = Then ( L p - )/2 = W c x Scale Factor = Then (W p - )/2 = 12
13 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 4 Step 6: Draw a grid on your paper using your scale. (i.e. If your scale is 1:4, your grid on your large paper will be 4 cm x 4 cm; therefore, you would draw 4 cm tick marks going across the length and width and then connect your marks to form a grid.) Step 7: Reconstruct drawing and color accordingly. Erase your grid marks on your final product before submitting the project! Higher scores will reflect a near-perfect representation of the smaller card frame. Colors, shading, and drawing should look identical! 1. What is the length and width of the squares of the small graph? Length = Width = 2. What is the length and width of the squares of the large graph? Length = Width = 3. What is the perimeter and area of each square on the small graph? Perimeter = Area = 4. What is the perimeter and area of each square on the large graph? Perimeter = Area = 5. How do the lengths of the small and large squares compare (answer as a fraction)? Answer: 6. How do the widths of the small and large squares compare (answer as a fraction)? Answer: 7. How do the perimeters compare (answer as a fraction)? Answer: 8. How do the areas compare (answer as a fraction)? Answer: 13
14 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 4 9. What is the length and width of the original card? Length = Width = 10. What is the length and width of the enlarged card? Length = Width = 11. What is the perimeter of the original card? Perimeter = 12. What is the perimeter of the enlarged card? Perimeter = 13. How do the two perimeters compare (answer as a fraction)? Answer: 14. What is the area of the original card? Area: 15. What is the area of the enlarged card? Area: 16. How do the two areas compare (answer as a fraction)? Answer: 17. Are the comparisons for perimeter and area the same? Explain why you think this happened. Yes or No 14
15 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 4 Scale Drawing Project Rubric NOTE: When you submit your project, you will first score yourself using this rubric. Be honest and thorough in your evaluation. Remember to include the following parts in your presentation: 1. The original picture 2. The enlarged picture (colored to match original) 3. Measurements of the original picture 4. The scale selected to enlarge the picture 5. Self-Completed Evaluation Scale Grids Reconstruction Presentation All calculations and proportions are shown. All grid lines can be seen on card (grid lines on enlarged picture should be erased, but should appear faintly). All lines are parallel and measured correctly. All proportions are accurate on the enlarged picture. The enlarged picture is colored neatly in the lines and colors match original card. Most calculations and proportions are shown. Most grid lines can be seen on card (grid lines on enlarged picture should be erased, but should appear faintly. Most lines are parallel and measured correctly. Most proportions are accurate on the enlarged picture. Most of the enlarged picture is colored neatly in the lines and most of the colors match original card. Few calculations and proportions are shown. Few grid lines can be seen on card (grid lines on enlarged picture should be erased, but should appear faintly). Few lines are parallel and measured correctly. Few proportions are accurate on the enlarged picture. Some of the enlarged picture is colored neatly in the lines and some of the colors match original card. No calculations and proportions are shown. No grid lines can be seen on card (grid lines on enlarged picture should be erased, but should appear faintly). No lines are parallel, nor measured correctly. No proportions are accurate on the enlarged picture. The enlarged picture is not colored neatly in the lines and does not match original card. Total Points Possible: 40 Self-Assessment: Teacher-Assessment: Scale: /10 Scale: /10 Grids: /10 Grids: /10 Reconstruction: /10 Reconstruction: /10 Presentation: /10 Presentation: /10 Total Points: /40 Total Points: /40 Comment on your level of effort Teacher Comments: and accuracy on this project: Adapted from the lesson Cartoons and Scale Drawings created by Sara Wheeler for the Alabama Learning Exchange. 15
16 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 5 Task #10: Comparing TV Areas Does an 80" TV Really Have More Than Twice the Area of a 55" TV? 1. What does the 80 inches represent in an 80" TV? 2. Find the area of an 80" TV if the ratio of the length to the height is 16:9. 3. Find the area of a 55" TV. The ratio of the length to the height is the same. 4. How much more area does the 80" TV have than the 55" TV? 5. Is the advertisement accurate? 16
17 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 5 Task #11: Area and Perimeter of Irregular Shapes Find the area and perimeter of each of the following shapes. 1. 7ft 4ft Perimeter = 3ft Area = 5ft 2. 6 mm Perimeter = 12 mm Area = 3. 6 m 4 m Perimeter = 5 m 10 m Area = 17
18 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson in Perimeter = 7 in 4 in Area = 14 in m 6 m 20 m 6 m Perimeter = 5 m Area = 16 m (Source: freemathsource.com) 18
19 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 5 Task #12: Area Problems Find the area and perimeter of each of the following shapes. 1. Find the largest possible rectangular area you can enclose with 96 meters of fencing. What is the (geometric) significance of the dimensions of this largest possible enclosure? What are the dimensions in meters? What are the dimensions in feet? What is the area in square feet? 2. The riding stables just received an unexpected rush of registrations for the next horse show, and quickly needs to create some additional paddock space. There is sufficient funding to rent 1200 feet of temporary chain-link fencing. The plan is to form two paddocks with one shared fence running down the middle. What is the maximum area that the stables can obtain, and what are the dimensions of each of the two paddocks? L W 19
20 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 5 3. A farmer has a square field that measures 100 m on a side. He wants to irrigate as much of the field as he possibly can using a circular irrigation system. a. Predict which irrigation system will irrigate more land? b. What percent of the field will be irrigated by the large system? c. What percent of the field will be irrigated by the four smaller systems? d. Which system will irrigate more land? e. What generalization can you draw from your answers? 20
21 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 5 Task #13: Paper Clip Activity This paper clip is just over 4 cm long. How many paper clips like this can be made from a straight piece of wire 10 meters long? Source: Illustrative Mathematics 21
22 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 5 Task #14: Race Track Problem A track has lanes that are 1 meter wide. The turn-radius of the inner lane is 24 meters and the straight parts are 80 meters long. In order to make the race fair, the starting lines are staggered so that each runner will run the same distance to the finish line. Finish Line Starting Lines a. Find the distances between the starting lines in neighboring lanes. b. Is the distance between the starting lanes for the first and second lane different from the distance between the starting lanes for the second and third lanes? c. What assumptions did you make in doing your calculations? 22
23 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 5 Task #15: Area & Perimeter Exit Slip DIRECTIONS: Calculate the perimeter and the area of each rectangle ' 12' Perimeter = Area = 2. 58' 36' Perimeter = Area = 3. 24' Perimeter = Area = a 4. A rectangle has an area of 2,130' and a width of 30', find its length and perimeter. 5. The perimeter of the triangle below is 52 cm. Find the length of each side of the triangle. Show your calculations. x 2x + 3 3x
24 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 7 Task #16: Quadrilateral Activity 1. Points A(1, 3), B(-3, 1), C(-1, -3), D(3, -1) form a square a. Graph the points and connect them. y x b. List as many properties of a square as you can. c. Show algebraically that the property assigned to your group is true for this square and all squares. d. Find the area and perimeter of ABCD. 24
25 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 7 2. Consider the points F(-4, -1), G(-2, -5), H(4, -2) and J(2,2). a. Graph the points. y x b. What type of quadrilateral is FGHJ? Justify your reasoning. 25
26 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 7 3. Consider the points K(-2, -1), L(-1, 2), M(2, 4) and N(1,1). a. Graph the points. y x b. What type of quadrilateral is KLMN? Show your work and justify your reasoning. 26
27 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 8 Task #17: Candy Bar Activity You are working for Amy s Candy World. You have been charged with creating new candy bars and the packaging for them. Since you are new to the company, you need to look at current products first. Phase I 1. Open a candy bar carefully. Measure the dimensions of the candy bar and record them. 2. What is the total area of the candy bar wrapper? 3. How much material just covers the candy bar (exclude the part that seals the edges)? 4. What is the surface area of the candy bar? 5. What is the relationship between the area of the wrapper and the surface area of the candy bar? 27
28 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 8 Phase II 6. Design two new candy bars that have the same surface area as the candy you opened, but have different dimensions. 7. What is the volume of the original candy bar? What are the volumes of the two new candy bars? 8. What would be the best dimensions of a candy bar that would have the same volume of your original candy bar, but would save money by using the least amount of wrapper? 28
29 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 8 Task #18: Can Label Activity Remove the label from a can. 1. What is the shape of the label? 2. What does the length of the rectangle represent on the can? 3. What does the width of the rectangle represent on the can? 4. Measure the dimensions of the can. 5. What is the perimeter of the label? What is the area of the label? 6. Without doing any additional measurements, find the radius of the top of the can. 7. Calculate the area of the top of the can. 8. What is the relationship between the area of the label and the surface area of the can? 9. Find the surface area of the can. 10. What is the volume of the can? 29
30 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 8 Task #19: Volume of a Candy Cylinder 1. Examine a roll of Lifesavers, Smarties, or any round, stacked candy. Measure the height of the package when all of the candies are in the package and record it. 2. What would a cross-section of the package look like if you cut the package between candies? 3. What is the area of the top of one of the candies? 4. What is the height of each individual candy? 5. How would you describe the volume of the package in relation to the area of one of the candies and the number of candies? Write it as a formula. 6. Now write a couple of sentences describing how the formula you created in #5 relates to the formula for the volume of a cylinder (V = Bh). 30
31 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 8 Task #20: Flower Vases My sister s birthday is in a few weeks and I would like to buy her a new vase to keep fresh flowers in her house. She often forgets to water her flowers and needs a vase that holds a lot of water. In a catalog there are three vases available and I want to purchase the one that holds the most water. The first vase is a cylinder with diameter 10 cm and height 40 cm. The second vase is a cone with base diameter 16 cm and height 45 cm. The third vase is a sphere with diameter 18 cm. 1. Which vase should I purchase? Cylinder Vase Show off your flowers inthis beautiful vase. 10cm x 40cm $9.95 4KE09 Cone Vase This vase holds your flowers in place! 16cm x 45cm $9.95 4KE08 Sphere Vase Does't get any more symmetric than this! 18cm x 18cm $9.95 4KE07 2. How much more water does the largest vase hold than the smallest vase? 3. Suppose the diameter of each vase decreases by 2 cm. Which vase would hold the most water? 4. The vase company designs a new vase that is shaped like a cylinder on bottom and a cone on top. The catalog states that the width is 12 cm and the total height is 42 cm. What would the height of the cylinder part have to be in order for the total volume to be 1224π cm 3? 5. Design your own vase with composite shapes, determine the volume, and write an ad for the catalog. (Source: Illustrative Mathematics) 31
32 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 8 Task #21: Gas Tank Problem The gas tank in my car has a total volume of 68 L. The manual says the gas gauge light will come on when there are only 5 L remaining in the tank and that the car will not be able to draw on the last 2 L in the tank. a. Practically speaking, what is the functional volume of the gas tank? b. My car stopped so I walked to the gas station to get gas. I purchased 5L of gas and put it into my tank. What is the total volume of gas in the tank? c. If 5 L of gas has a mass of 450 kg, what is the mass of the gas in my tank when it is full? d. What is the density of the gas? e. How many gallons does the gas tank hold? f. When will the gas gauge light come on? g. If my car gets 26 mpg on the highway and I am driving on the highway when my gas light comes on, how far can I drive before my car will stop? 32
33 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 8 Task #22: Propane Tank Activity Propane Tanks People who live in isolated or rural areas have their own tanks of natural gas to run appliances like stoves, washers, and water heaters. These tanks are made in the shape of a cylinder with hemispheres on the ends. r 10 feet The Insane Propane Tank Company makes tanks with this shape, in different sizes. The cylinder part of every tank is exactly 10 feet long, but the radius of the hemispheres, r, will be different depending on the size of the tank. The company want to double the capacity of their standard tank, which is 6 feet in diameter. What should the radius of the new tank be? Explain your thinking and show your calculations. 33
34 Math Ready. Unit 3. Lesson 8 Task #23: Toilet Roll Picture a roll of toilet paper; assume that the paper in the roll is very tightly rolled. Assuming that the paper in the roll is very thin, find a relationship between the thickness of the paper, the inner and outer radii of the roll, and the length of the paper in the roll. Express your answer as an algebraic formula involving the four listed variables. R i = inner radius R o = outer radius R o t = thickness of the toilet paper L = length of the toilet paper R i (Source: Illustrative Mathematics) 34
Math Ready Unit 3. Measurement and Proportional Reasoning Student Manual
 SREB Readiness Courses Transitioning to college and careers Math Ready Unit 3. Measurement and Proportional Reasoning Name 1 Math Ready. Unit 3. Unit 3. Measurement and Proportional Reasoning Table of
SREB Readiness Courses Transitioning to college and careers Math Ready Unit 3. Measurement and Proportional Reasoning Name 1 Math Ready. Unit 3. Unit 3. Measurement and Proportional Reasoning Table of
Math Ready Unit 3. Measurement and Proportional Reasoning Student Manual
 SREB Readiness Courses Transitioning to college and careers Math Ready Unit 3. Measurement and Proportional Reasoning Student Manual Name 1 Math Ready. Unit 3. Student Manual Unit 3. Measurement and Proportional
SREB Readiness Courses Transitioning to college and careers Math Ready Unit 3. Measurement and Proportional Reasoning Student Manual Name 1 Math Ready. Unit 3. Student Manual Unit 3. Measurement and Proportional
Bridge to College Mathematics Unit 3. Measurement and Proportional Reasoning Student Manual
 SREB Readiness Courses Transitioning to college and careers Bridge to College Mathematics Unit 3. Measurement and Proportional Reasoning Student Manual Name 1 Bridge to College Mathematics. Unit 3. Student
SREB Readiness Courses Transitioning to college and careers Bridge to College Mathematics Unit 3. Measurement and Proportional Reasoning Student Manual Name 1 Bridge to College Mathematics. Unit 3. Student
MATH MEASUREMENT AND GEOMETRY
 Students: 1. Students choose appropriate units of measure and use ratios to convert within and between measurement systems to solve problems. 1. Compare weights, capacities, geometric measures, time, and
Students: 1. Students choose appropriate units of measure and use ratios to convert within and between measurement systems to solve problems. 1. Compare weights, capacities, geometric measures, time, and
Unit 6, Activity 1, Measuring Scavenger Hunt
 Unit 6, Activity 1, Measuring Scavenger Hunt Name: Measurement Descriptions Object 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Blackline Masters, Mathematics, Grade 7 Page 6-1 Unit 6, Activity 4, Break it Down Name
Unit 6, Activity 1, Measuring Scavenger Hunt Name: Measurement Descriptions Object 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Blackline Masters, Mathematics, Grade 7 Page 6-1 Unit 6, Activity 4, Break it Down Name
Task: Pyramid. a. Below is a net for a three dimensional shape:
 Task: Cone You have been hired by the owner of a local ice cream parlor to assist in his company s new venture. The company will soon sell its ice cream cones in the freezer section of local grocery stores.
Task: Cone You have been hired by the owner of a local ice cream parlor to assist in his company s new venture. The company will soon sell its ice cream cones in the freezer section of local grocery stores.
2018 TAME Middle School Practice State Mathematics Test
 2018 TAME Middle School Practice State Mathematics Test (1) Noah bowled five games. He predicts the score of the next game he bowls will be 120. Which list most likely shows the scores of Kent s first
2018 TAME Middle School Practice State Mathematics Test (1) Noah bowled five games. He predicts the score of the next game he bowls will be 120. Which list most likely shows the scores of Kent s first
Name Date Period STUDY GUIDE Summative Assessment #5 6 th Grade Math Covering and Surrounding
 Name Date Period STUDY GUIDE Summative Assessment #5 6 th Grade Math Covering and Surrounding 1) Mr. and Mrs. Hunter tiled their rectangular porch using 1ft. by 1ft. square tiles. The rectangular porch
Name Date Period STUDY GUIDE Summative Assessment #5 6 th Grade Math Covering and Surrounding 1) Mr. and Mrs. Hunter tiled their rectangular porch using 1ft. by 1ft. square tiles. The rectangular porch
Essential Mathematics Practice Problems for Exam 5 Chapter 8
 Math 254B Essential Mathematics Practice Problems for Eam 5 Chapter 8 Name Date This eam is closed book and closed notes, ecept for the Geometry Formula sheet that is provided by the instructor. You can
Math 254B Essential Mathematics Practice Problems for Eam 5 Chapter 8 Name Date This eam is closed book and closed notes, ecept for the Geometry Formula sheet that is provided by the instructor. You can
Lesson 12: Ratios of Fractions and Their Unit Rates
 Student Outcomes Students use ratio tables and ratio reasoning to compute unit rates associated with ratios of fractions in the context of measured quantities, e.g., recipes, lengths, areas, and speed.
Student Outcomes Students use ratio tables and ratio reasoning to compute unit rates associated with ratios of fractions in the context of measured quantities, e.g., recipes, lengths, areas, and speed.
Name: Class: Assessment pack Semester 2 Grade 7
 Name: Class: Assessment pack Semester 2 Grade 7 Math Materials covered for Grade 7 Semester 2 exam Module 6 (Expressions and Equations) 6.1 algebraic expressions 6.2 one step equation with rational coefficient
Name: Class: Assessment pack Semester 2 Grade 7 Math Materials covered for Grade 7 Semester 2 exam Module 6 (Expressions and Equations) 6.1 algebraic expressions 6.2 one step equation with rational coefficient
Review. 3. Casey tossed a coin 25 times and recorded the results. What percent of the coin tosses came out heads?
 Name: Period: Review 1. Rectangle ABCD is 3 inches wide and 6 inches high. The rectangle is reduced to rectangle EFGH, which is 1 inch wide and 2 inches high. What is the scale factor for the reduction?
Name: Period: Review 1. Rectangle ABCD is 3 inches wide and 6 inches high. The rectangle is reduced to rectangle EFGH, which is 1 inch wide and 2 inches high. What is the scale factor for the reduction?
MEASURING IN THE PLANE AND SPACE G.MG.A.3: AREA AND SURFACE AREA
 MEASURING IN THE PLANE AND SPACE G.MG.A.3: AREA AND SURFACE AREA 95 A farmer has 64 feet of fence to enclose a rectangular vegetable garden. Which dimensions would result in the biggest area for this garden?
MEASURING IN THE PLANE AND SPACE G.MG.A.3: AREA AND SURFACE AREA 95 A farmer has 64 feet of fence to enclose a rectangular vegetable garden. Which dimensions would result in the biggest area for this garden?
Geometry. Practice Pack
 Geometry Practice Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents Unit 1: Lines and Angles Practice 1.1 What Is Geometry?........................ 1 Practice 1.2 What Is Geometry?........................ 2 Practice
Geometry Practice Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents Unit 1: Lines and Angles Practice 1.1 What Is Geometry?........................ 1 Practice 1.2 What Is Geometry?........................ 2 Practice
UNIT 10 PERIMETER AND AREA
 UNIT 10 PERIMETER AND AREA INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will define basic geometric shapes and use definitions to categorize geometric figures. Then we will use the ideas of measuring length and area
UNIT 10 PERIMETER AND AREA INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will define basic geometric shapes and use definitions to categorize geometric figures. Then we will use the ideas of measuring length and area
Unit 1, Lesson 1: What are Scaled Copies?
 Unit 1, Lesson 1: What are Scaled Copies? Let s explore scaled copies. 1.1: Printing Portraits m.openup.org/1/7-1-1-1 Here is a portrait of a student. 1. Look at Portraits A E. How is each one the same
Unit 1, Lesson 1: What are Scaled Copies? Let s explore scaled copies. 1.1: Printing Portraits m.openup.org/1/7-1-1-1 Here is a portrait of a student. 1. Look at Portraits A E. How is each one the same
Unit 3 Linear measurement
 Unit 3 Linear measurement Instructions: Using a pencil, complete the following questions as you work through the related lessons. Show ALL work as it is explained in the lessons. Do your best and ask your
Unit 3 Linear measurement Instructions: Using a pencil, complete the following questions as you work through the related lessons. Show ALL work as it is explained in the lessons. Do your best and ask your
Lesson 1 Area of Parallelograms
 NAME DATE PERIOD Lesson 1 Area of Parallelograms Words Formula The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any b and its h. Model Step 1: Write the Step 2: Replace letters with information from picture
NAME DATE PERIOD Lesson 1 Area of Parallelograms Words Formula The area A of a parallelogram is the product of any b and its h. Model Step 1: Write the Step 2: Replace letters with information from picture
Perimeters of Composite Figures
 8. Perimeters of Composite Figures How can you find the perimeter of a composite figure? ACTIVITY: Finding a Pattern Work with a partner. Describe the pattern of the perimeters. Use your pattern to find
8. Perimeters of Composite Figures How can you find the perimeter of a composite figure? ACTIVITY: Finding a Pattern Work with a partner. Describe the pattern of the perimeters. Use your pattern to find
Rosa Parks Middle School. Summer Math Packet C2.0 Algebra Student Name: Teacher Name: Date:
 Rosa Parks Middle School Summer Math Packet C2.0 Algebra Student Name: Teacher Name: Date: Dear Student and Parent, The purpose of this packet is to provide a review of objectives that were taught the
Rosa Parks Middle School Summer Math Packet C2.0 Algebra Student Name: Teacher Name: Date: Dear Student and Parent, The purpose of this packet is to provide a review of objectives that were taught the
Find the area and perimeter of any enlargement of the original rug above. Your work must include the following:
 7-1.Your friend Alonzo owns a rug manufacturing company, which is famous for its unique designs. Each rug design has an original size as well as enlargements that are exactly the same shape. Find the area
7-1.Your friend Alonzo owns a rug manufacturing company, which is famous for its unique designs. Each rug design has an original size as well as enlargements that are exactly the same shape. Find the area
Core Connections, Course 2 Checkpoint Materials
 Core Connections, Course Checkpoint Materials Notes to Students (and their Teachers) Students master different skills at different speeds. No two students learn exactly the same way at the same time. At
Core Connections, Course Checkpoint Materials Notes to Students (and their Teachers) Students master different skills at different speeds. No two students learn exactly the same way at the same time. At
Math 6/7 Unit 10 - GEOMETRY - Study Guide (SOL 6.10)
 Math 6/7 Unit 10 - GEOMETRY - Study Guide (SOL 6.10) Find the perimeter of the following (include the correct units): 1) 2) 5.3 cm 15 ft 15 ft 10.6 cm 18 ft P = P = Solve the following (include the correct
Math 6/7 Unit 10 - GEOMETRY - Study Guide (SOL 6.10) Find the perimeter of the following (include the correct units): 1) 2) 5.3 cm 15 ft 15 ft 10.6 cm 18 ft P = P = Solve the following (include the correct
3.3. You wouldn t think that grasshoppers could be dangerous. But they can damage
 Grasshoppers Everywhere! Area and Perimeter of Parallelograms on the Coordinate Plane. LEARNING GOALS In this lesson, you will: Determine the perimeter of parallelograms on a coordinate plane. Determine
Grasshoppers Everywhere! Area and Perimeter of Parallelograms on the Coordinate Plane. LEARNING GOALS In this lesson, you will: Determine the perimeter of parallelograms on a coordinate plane. Determine
ACTIVITY: Comparing Measurements
 7.5 Scale Drawings proportionally? How can you enlarge or reduce a drawing 1 ACTIVITY: Comparing Measurements Work with a partner. The diagram shows a food court at a shopping mall. Each centimeter in
7.5 Scale Drawings proportionally? How can you enlarge or reduce a drawing 1 ACTIVITY: Comparing Measurements Work with a partner. The diagram shows a food court at a shopping mall. Each centimeter in
Honors Geometry Summer Math Packet
 Honors Geometry Summer Math Packet Dear students, The problems in this packet will give you a chance to practice geometry-related skills from Grades 6 and 7. Do your best to complete each problem so that
Honors Geometry Summer Math Packet Dear students, The problems in this packet will give you a chance to practice geometry-related skills from Grades 6 and 7. Do your best to complete each problem so that
Foundations of Math 11: Unit 2 Proportions. The scale factor can be written as a ratio, fraction, decimal, or percentage
 Lesson 2.3 Scale Name: Definitions 1) Scale: 2) Scale Factor: The scale factor can be written as a ratio, fraction, decimal, or percentage Formula: Formula: Example #1: A small electronic part measures
Lesson 2.3 Scale Name: Definitions 1) Scale: 2) Scale Factor: The scale factor can be written as a ratio, fraction, decimal, or percentage Formula: Formula: Example #1: A small electronic part measures
Unit 3, Lesson 9: Applying Area of Circles
 Unit 3, Lesson 9: Applying Area of Circles Lesson Goals Use the formula Represent exact answers in terms of. to solve problems involving the areas of circles. Required Materials four-function calculators
Unit 3, Lesson 9: Applying Area of Circles Lesson Goals Use the formula Represent exact answers in terms of. to solve problems involving the areas of circles. Required Materials four-function calculators
G.MG.A.2: Density. Regents Exam Questions G.MG.A.2: Density
 Regents Exam Questions G.MG.A.: Density G.MG.A.: Density 1 A shipping container is in the shape of a right rectangular prism with a length of 1 feet, a width of 8.5 feet, and a height of 4 feet. The container
Regents Exam Questions G.MG.A.: Density G.MG.A.: Density 1 A shipping container is in the shape of a right rectangular prism with a length of 1 feet, a width of 8.5 feet, and a height of 4 feet. The container
G-MG.A: Geometric Measurement and Dimension Explain volume formulas and use them to solve problems
 Name: Date: G-MG.A: Geometric Measurement and Dimension Explain volume formulas and use them to solve problems 1. A shipping container is in the shape of a right rectangular prism with a length of 12 feet,
Name: Date: G-MG.A: Geometric Measurement and Dimension Explain volume formulas and use them to solve problems 1. A shipping container is in the shape of a right rectangular prism with a length of 12 feet,
Number Line: Comparing and Ordering Integers (page 6)
 LESSON Name 1 Number Line: Comparing and Ordering Integers (page 6) A number line shows numbers in order from least to greatest. The number line has zero at the center. Numbers to the right of zero are
LESSON Name 1 Number Line: Comparing and Ordering Integers (page 6) A number line shows numbers in order from least to greatest. The number line has zero at the center. Numbers to the right of zero are
UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet 24.1 The Pythagorean Theorem Explore the Pythagorean theorem numerically, algebraically, and geometrically. Understand a proof
Name Period Date UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet 24.1 The Pythagorean Theorem Explore the Pythagorean theorem numerically, algebraically, and geometrically. Understand a proof
Roberto Clemente Middle School
 Roberto Clemente Middle School Summer Math Packet for Students Entering Algebra I Name: 1. On the grid provided, draw a right triangle with whole number side lengths and a hypotenuse of 10 units. The
Roberto Clemente Middle School Summer Math Packet for Students Entering Algebra I Name: 1. On the grid provided, draw a right triangle with whole number side lengths and a hypotenuse of 10 units. The
Name Period Final Exam Review
 Name Period Final Exam Review 1. Given XXXXXX where X(0,6), Y(4, -2), and Z(-4, -2), use the grid to below to dilate the figure by a scale factor of 1. What are the new coordinates? 2 2. What is the slope
Name Period Final Exam Review 1. Given XXXXXX where X(0,6), Y(4, -2), and Z(-4, -2), use the grid to below to dilate the figure by a scale factor of 1. What are the new coordinates? 2 2. What is the slope
SIXTH GRADE MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 10 AREA AND PERIMETER TOPICS COVERED:
 SIXTH GRADE MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 10 AREA AND PERIMETER TOPICS COVERED: Perimeter of Polygons Area of Parallelograms Area of Triangles Area of a Trapezoid Area of Irregular Figures Activity 10-1: Sixth Grade
SIXTH GRADE MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 10 AREA AND PERIMETER TOPICS COVERED: Perimeter of Polygons Area of Parallelograms Area of Triangles Area of a Trapezoid Area of Irregular Figures Activity 10-1: Sixth Grade
Name Period No. Geometry Unit Review with Application Problems
 Name Period No. Geometry Unit Review with Application Problems For problems 1-3, find the area of each figure. Show all steps. 1) 2) 4) Draw a parallelogram with an area of 50 sq. units in the 3) coordinate
Name Period No. Geometry Unit Review with Application Problems For problems 1-3, find the area of each figure. Show all steps. 1) 2) 4) Draw a parallelogram with an area of 50 sq. units in the 3) coordinate
7. Geometry. Model Problem. The dimensions of a rectangular photograph are 4.5 inches by 6 inches. rubric.
 Table of Contents Letter to the Student............................................. 5 Chapter One: What Is an Open-Ended Math Question?.................... 6 Chapter Two: What Is a Rubric?...................................
Table of Contents Letter to the Student............................................. 5 Chapter One: What Is an Open-Ended Math Question?.................... 6 Chapter Two: What Is a Rubric?...................................
Students apply the Pythagorean Theorem to real world and mathematical problems in two dimensions.
 Student Outcomes Students apply the Pythagorean Theorem to real world and mathematical problems in two dimensions. Lesson Notes It is recommended that students have access to a calculator as they work
Student Outcomes Students apply the Pythagorean Theorem to real world and mathematical problems in two dimensions. Lesson Notes It is recommended that students have access to a calculator as they work
Area of Composite Figures. ESSENTIAL QUESTION do you find the area of composite figures? 7.9.C
 ? LESSON 9.4 Area of Composite Figures ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do you find the area of composite figures? Equations, expressions, and relationships Determine the area of composite figures containing combinations
? LESSON 9.4 Area of Composite Figures ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do you find the area of composite figures? Equations, expressions, and relationships Determine the area of composite figures containing combinations
5 th Grade MATH SUMMER PACKET ANSWERS Please attach ALL work
 NAME: 5 th Grade MATH SUMMER PACKET ANSWERS Please attach ALL work DATE: 1.) 26.) 51.) 76.) 2.) 27.) 52.) 77.) 3.) 28.) 53.) 78.) 4.) 29.) 54.) 79.) 5.) 30.) 55.) 80.) 6.) 31.) 56.) 81.) 7.) 32.) 57.)
NAME: 5 th Grade MATH SUMMER PACKET ANSWERS Please attach ALL work DATE: 1.) 26.) 51.) 76.) 2.) 27.) 52.) 77.) 3.) 28.) 53.) 78.) 4.) 29.) 54.) 79.) 5.) 30.) 55.) 80.) 6.) 31.) 56.) 81.) 7.) 32.) 57.)
GCSE MATHEMATICS (LINEAR) Foundation Tier Paper 2. Morning (JUN F01)
 Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature GCSE F MATHEMATICS (LINEAR) Foundation Tier Paper 2 Thursday 9 June 2016 Materials For this
Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature GCSE F MATHEMATICS (LINEAR) Foundation Tier Paper 2 Thursday 9 June 2016 Materials For this
Changing Area, Changing Perimeter
 2 Changing Area, Changing Perimeter Whether you make a floor plan for a bumper-car ride or a house, there are many options. You should consider the cost of materials and the use of a space to find the
2 Changing Area, Changing Perimeter Whether you make a floor plan for a bumper-car ride or a house, there are many options. You should consider the cost of materials and the use of a space to find the
Mathematics A *P49303RA0128* Pearson Edexcel GCSE P49303RA. Paper 2 (Calculator) Foundation Tier. Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes
 Write your name here Surname Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 2 (Calculator) Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Other names Candidate Number Foundation Tier Paper
Write your name here Surname Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 2 (Calculator) Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Other names Candidate Number Foundation Tier Paper
Geometry 2001 part 1
 Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
Mathematics, Grade 8
 Session 1, Multiple-Choice Questions 44084 C 1 13608 C 2 (0.5)(0.5)(0.5) is equal to which of the following? A. 0.000125 B. 0.00125 C. 0.125 D. 1.25 Reporting Category for Item 1: Number Sense and Operations
Session 1, Multiple-Choice Questions 44084 C 1 13608 C 2 (0.5)(0.5)(0.5) is equal to which of the following? A. 0.000125 B. 0.00125 C. 0.125 D. 1.25 Reporting Category for Item 1: Number Sense and Operations
INTERMEDIATE LEVEL MEASUREMENT
 INTERMEDIATE LEVEL MEASUREMENT TABLE OF CONTENTS Format & Background Information...3-6 Learning Experience 1- Getting Started...6-7 Learning Experience 2 - Cube and Rectangular Prisms...8 Learning Experience
INTERMEDIATE LEVEL MEASUREMENT TABLE OF CONTENTS Format & Background Information...3-6 Learning Experience 1- Getting Started...6-7 Learning Experience 2 - Cube and Rectangular Prisms...8 Learning Experience
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics tests KEY STAGE LEVEL. First name. Middle name. Last name. Date of birth Day Month Year.
 Ma KEY STAGE 2 Mathematics tests LEVEL 6 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Middle name 2013 Last name Date of birth Day Month Year School name DfE number 1 A box of crisps contains three different
Ma KEY STAGE 2 Mathematics tests LEVEL 6 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Middle name 2013 Last name Date of birth Day Month Year School name DfE number 1 A box of crisps contains three different
Paper 1. Mathematics test. Calculator not allowed. satspapers.org. First name. Last name. School KEY STAGE TIER
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 4 6 2003 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 4 6 2003 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Perimeter, Circumference, Area and Ratio Long-Term Memory Review Grade 6 Review 1
 Review 1 1. Which procedure is used to find the perimeter of any polygon? A) Add all the lengths B) Multiply length times width (l w) C) Add only one length and one width D) Multiply all of the lengths.
Review 1 1. Which procedure is used to find the perimeter of any polygon? A) Add all the lengths B) Multiply length times width (l w) C) Add only one length and one width D) Multiply all of the lengths.
Math 7 Mid-Winter Recess
 MOUNT VERNON CITY SCHOOL DISTRICT Children of Promise Math 7 Mid-Winter Recess Student Name: School Name: Teacher: Score: Module 1: Ratios and Proportional Relationships 1. It is a Saturday morning and
MOUNT VERNON CITY SCHOOL DISTRICT Children of Promise Math 7 Mid-Winter Recess Student Name: School Name: Teacher: Score: Module 1: Ratios and Proportional Relationships 1. It is a Saturday morning and
2017 Houston ISD Middle School Mathematics Test A Contest
 2017 Houston ISD Middle School Mathematics Test A Contest (1) 2 5 + 2 4 + 2 3 + 2 2 + 2 1 + 2 0 = A) 63 B) 62 C) 61 D) 56 E) 55 (2) Twenty-four percent of twenty-five is A) 60 B) 104 1 6 C) 96 D) 96 1
2017 Houston ISD Middle School Mathematics Test A Contest (1) 2 5 + 2 4 + 2 3 + 2 2 + 2 1 + 2 0 = A) 63 B) 62 C) 61 D) 56 E) 55 (2) Twenty-four percent of twenty-five is A) 60 B) 104 1 6 C) 96 D) 96 1
Summer Math Calendar
 Going into Third Grade Directions: Follow the daily activities to practice different math concepts. Feel free to extend any of the activities listed. When the work is completed, have a parent initial the
Going into Third Grade Directions: Follow the daily activities to practice different math concepts. Feel free to extend any of the activities listed. When the work is completed, have a parent initial the
WVDE Math 7 G Solve Real-life and Mathematical Problems involving Angle Measure, Area, Surface Area, and Volume Test
 WVDE Math 7 G Solve Real-life and Mathematical Problems involving Angle Measure, Area, Surface Area, and Volume Test 1 General Offline Instructions: Read each question carefully and decide which answer
WVDE Math 7 G Solve Real-life and Mathematical Problems involving Angle Measure, Area, Surface Area, and Volume Test 1 General Offline Instructions: Read each question carefully and decide which answer
Test Booklet. Subject: MA, Grade: 06 TAKS Grade 6 Math Student name:
 Test Booklet Subject: MA, Grade: 06 Student name: Author: Texas District: Texas Released Tests Printed: Wednesday July 11, 2012 1 Wayne is picking an outfit to wear to school. His choices are shown in
Test Booklet Subject: MA, Grade: 06 Student name: Author: Texas District: Texas Released Tests Printed: Wednesday July 11, 2012 1 Wayne is picking an outfit to wear to school. His choices are shown in
JK XY LJ LJ ZX KL KL YZ LJ KL YX KJ. Final Exam Review Modules 10 16, 18 19
 Geometry Final Exam Review Modules 10 16, 18 19 Use the following information for 1 3. The figure is symmetric about the x axis. Name: 6. In this figure ~. Which statement is not true? A JK XY LJ ZX C
Geometry Final Exam Review Modules 10 16, 18 19 Use the following information for 1 3. The figure is symmetric about the x axis. Name: 6. In this figure ~. Which statement is not true? A JK XY LJ ZX C
Topic. Easter Intervention. If you have any questions, feel free to
 Easter Intervention Foundation Questions Topic Angles Transformations Multiples, Factors, Primes Indices Algebra Area and Perimeter Factions, Decimals and Percentages Ratio Equations Probability Averages
Easter Intervention Foundation Questions Topic Angles Transformations Multiples, Factors, Primes Indices Algebra Area and Perimeter Factions, Decimals and Percentages Ratio Equations Probability Averages
WVDE Math 7 G Draw, Construct, and Describe Geometrical Figures and Describe the Relationsips between Them Test
 WVDE Math 7 G Draw, Construct, and Describe Geometrical Figures and Describe the Relationsips between Them Test 1 General Offline Instructions: Read each question carefully and decide which answer is correct.
WVDE Math 7 G Draw, Construct, and Describe Geometrical Figures and Describe the Relationsips between Them Test 1 General Offline Instructions: Read each question carefully and decide which answer is correct.
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 6th Grade Unit 8
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 6th Grade Unit 8 Unit 8 Geometry and Measurement MATH 608 Geometry and Measurement INTRODUCTION 3 1. PLANE FIGURES 5 PERIMETER 5 AREA OF PARALLELOGRAMS 11 AREA OF TRIANGLES 17 AREA OF
MATH STUDENT BOOK 6th Grade Unit 8 Unit 8 Geometry and Measurement MATH 608 Geometry and Measurement INTRODUCTION 3 1. PLANE FIGURES 5 PERIMETER 5 AREA OF PARALLELOGRAMS 11 AREA OF TRIANGLES 17 AREA OF
Student Answer Document STAAR Practice Test, Form A
 Student Answer Document STAAR Practice Test, Form A Sample A 3 3 Sample B Use grid BELOW. 4 37 Item 3 Use grid BELOW. 5 3 Item 39 4 Use grid BELOW. 40 5 7 4 3 4 4 7 9 43 5 30 44 9 3 45 7 0 3 4 Item 33
Student Answer Document STAAR Practice Test, Form A Sample A 3 3 Sample B Use grid BELOW. 4 37 Item 3 Use grid BELOW. 5 3 Item 39 4 Use grid BELOW. 40 5 7 4 3 4 4 7 9 43 5 30 44 9 3 45 7 0 3 4 Item 33
Performance Based Learning and Assessment Task Sand Castle I. ASSESSSMENT TASK OVERVIEW & PURPOSE: Students will find and compare the volumes of
 Performance Based Learning and Assessment Task Sand Castle I. ASSESSSMENT TASK OVERVIEW & PURPOSE: Students will find and compare the volumes of geometric solids including spheres, pyramids, cones, and
Performance Based Learning and Assessment Task Sand Castle I. ASSESSSMENT TASK OVERVIEW & PURPOSE: Students will find and compare the volumes of geometric solids including spheres, pyramids, cones, and
Math Mammoth Grade 6 End of the Year Test Notes
 Math Mammoth Grade 6 End of the Year Test Notes This test is very long, because it contains questions on all major topics covered in Math Mammoth Grade 6 Complete Curriculum. Its main purpose is to be
Math Mammoth Grade 6 End of the Year Test Notes This test is very long, because it contains questions on all major topics covered in Math Mammoth Grade 6 Complete Curriculum. Its main purpose is to be
1. An NFL playing field (not counting the end zones) is 300 feet long and 160 feet wide. What is the perimeter? What is the area?
 Geometry: Perimeter and Area Practice 24 Many sports require a rectangular field of play which is a specific length and width. Use the information given in the problems below to compute the perimeter and
Geometry: Perimeter and Area Practice 24 Many sports require a rectangular field of play which is a specific length and width. Use the information given in the problems below to compute the perimeter and
Daily Warmup. - x 2 + x x 2 + x Questions from HW?? (7x - 39) (3x + 17) 1. BD bisects ABC. Find the m ABC.
 Daily Warmup Questions from HW?? B 1. BD bisects ABC. Find the m ABC. (3x + 17) (7x - 39) C 2. The figure below is a regular polygon. Find the value of x. - x 2 + x + 43 A D 4x 2 + x - 37 3. The measure
Daily Warmup Questions from HW?? B 1. BD bisects ABC. Find the m ABC. (3x + 17) (7x - 39) C 2. The figure below is a regular polygon. Find the value of x. - x 2 + x + 43 A D 4x 2 + x - 37 3. The measure
VOLUME Judo Math Inc.
 VOLUME 2013 Judo Math Inc. 7 th grade Geometry Discipline: Black Belt Training Order of Mastery: Surface Area/Volume 1. 2D vs. 3D: slicing 3D shapes to get 2D shapes (7G3) 2. Surface Area 1 (7G6) 3. Volume
VOLUME 2013 Judo Math Inc. 7 th grade Geometry Discipline: Black Belt Training Order of Mastery: Surface Area/Volume 1. 2D vs. 3D: slicing 3D shapes to get 2D shapes (7G3) 2. Surface Area 1 (7G6) 3. Volume
Eighth Grade Test - Excellence in Mathematics Contest
 1. The sum of two natural numbers is 100 and their positive difference is 42. What is the positive difference of the squares of these two natural numbers?. 1600. 200. 600. 4200. 400 2. The sum of 16 consecutive
1. The sum of two natural numbers is 100 and their positive difference is 42. What is the positive difference of the squares of these two natural numbers?. 1600. 200. 600. 4200. 400 2. The sum of 16 consecutive
Sixteenth Annual Middle School Mathematics Contest
 Sixteenth Annual Middle School Mathematics Contest 7 th /8 th Grade Test Round Two, Spring 2018 Before you begin: 1. Please verify that the information on the sticker on your answer sheet is correct. If
Sixteenth Annual Middle School Mathematics Contest 7 th /8 th Grade Test Round Two, Spring 2018 Before you begin: 1. Please verify that the information on the sticker on your answer sheet is correct. If
WS Stilwell Practice 6-1
 Name Date Pd WS Stilwell Practice 6-1 Write each ratio in three different ways. Write your answer in simplest form. 1) 2) triangles to total circles to triangles 3) 4) all figures to circle triangles to
Name Date Pd WS Stilwell Practice 6-1 Write each ratio in three different ways. Write your answer in simplest form. 1) 2) triangles to total circles to triangles 3) 4) all figures to circle triangles to
Lesson 1: Understanding Proportional. Relationships
 Unit 3, Lesson 1: Understanding Proportional Relationships 1. Priya jogs at a constant speed. The relationship between her distance and time is shown on the graph. Diego bikes at a constant speed twice
Unit 3, Lesson 1: Understanding Proportional Relationships 1. Priya jogs at a constant speed. The relationship between her distance and time is shown on the graph. Diego bikes at a constant speed twice
Covering and Surrounding Assessment. 1. (1 point) Find the area and perimeter of this rectangle. Explain how you found your answers.
 Name: Date: Score: /20 Covering and Surrounding Assessment Short Answer: Answer each question, making sure to show your work or provide an explanation or sketch to support your answer in the box. Make
Name: Date: Score: /20 Covering and Surrounding Assessment Short Answer: Answer each question, making sure to show your work or provide an explanation or sketch to support your answer in the box. Make
Geometry. Warm Ups. Chapter 11
 Geometry Warm Ups Chapter 11 Name Period Teacher 1 1.) Find h. Show all work. (Hint: Remember special right triangles.) a.) b.) c.) 2.) Triangle RST is a right triangle. Find the measure of angle R. Show
Geometry Warm Ups Chapter 11 Name Period Teacher 1 1.) Find h. Show all work. (Hint: Remember special right triangles.) a.) b.) c.) 2.) Triangle RST is a right triangle. Find the measure of angle R. Show
Name: Period: !"#$. "%&'&()*
 Name: Period: Today you will extend your study of ratios by looking at enlargements and reductions of geometric figures. Think of a copy machine and what it does to a picture when the enlargement button
Name: Period: Today you will extend your study of ratios by looking at enlargements and reductions of geometric figures. Think of a copy machine and what it does to a picture when the enlargement button
Page 1 part 1 PART 2
 Page 1 part 1 PART 2 Page 2 Part 1 Part 2 Page 3 part 1 Part 2 Page 4 Page 5 Part 1 10. Which point on the curve y x 2 1 is closest to the point 4,1 11. The point P lies in the first quadrant on the graph
Page 1 part 1 PART 2 Page 2 Part 1 Part 2 Page 3 part 1 Part 2 Page 4 Page 5 Part 1 10. Which point on the curve y x 2 1 is closest to the point 4,1 11. The point P lies in the first quadrant on the graph
First Name: Last Name: Select the one best answer for each question. DO NOT use a calculator in completing this packet.
 5 Entering 5 th Grade Summer Math Packet First Name: Last Name: 5 th Grade Teacher: I have checked the work completed: Parent Signature Select the one best answer for each question. DO NOT use a calculator
5 Entering 5 th Grade Summer Math Packet First Name: Last Name: 5 th Grade Teacher: I have checked the work completed: Parent Signature Select the one best answer for each question. DO NOT use a calculator
Whirlygigs for Sale! Rotating Two-Dimensional Figures through Space. LESSON 4.1 Skills Practice. Vocabulary. Problem Set
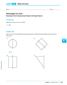 LESSON.1 Skills Practice Name Date Whirlygigs for Sale! Rotating Two-Dimensional Figures through Space Vocabulary Describe the term in your own words. 1. disc Problem Set Write the name of the solid figure
LESSON.1 Skills Practice Name Date Whirlygigs for Sale! Rotating Two-Dimensional Figures through Space Vocabulary Describe the term in your own words. 1. disc Problem Set Write the name of the solid figure
1. A maintenance technician sights the top of a telephone pole at a 25 angle of elevation as shown.
 Name 1. A maintenance technician sights the top of a telephone pole at a 25 angle of elevation as shown. Determine the horizontal distance between the technician and the base of the telephone pole to the
Name 1. A maintenance technician sights the top of a telephone pole at a 25 angle of elevation as shown. Determine the horizontal distance between the technician and the base of the telephone pole to the
2-6 Ratios and Proportions. Determine whether each pair of ratios are equivalent ratios. Write yes or no. SOLUTION: No, the ratios are not equivalent.
 Determine whether each pair of ratios are equivalent ratios. Write yes or no. 5. 1. No, the ratios are not equivalent. 6. 2. Yes, the ratios are equivalent. 3. 7. RACE Jennie ran the first 6 miles of a
Determine whether each pair of ratios are equivalent ratios. Write yes or no. 5. 1. No, the ratios are not equivalent. 6. 2. Yes, the ratios are equivalent. 3. 7. RACE Jennie ran the first 6 miles of a
Summer Solutions Problem Solving Level 4. Level 4. Problem Solving. Help Pages
 Level Problem Solving 6 General Terms acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 addend a number being added angle formed by two rays that share a common endpoint area the size of a surface; always expressed
Level Problem Solving 6 General Terms acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 addend a number being added angle formed by two rays that share a common endpoint area the size of a surface; always expressed
Summer Solutions Common Core Mathematics 4. Common Core. Mathematics. Help Pages
 4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
FSA 7 th Grade Math. MAFS.7.G.1.1 Level 2. MAFS.7.G.1.1 Level 3. MAFS.7.G.1.1 Level 3. MAFS.7.G.1.2 Level 2. MAFS.7.G.1.1 Level 4
 FSA 7 th Grade Math Geometry This drawing shows a lawn in the shape of a trapezoid. The height of the trapezoidal lawn on the drawing is 1! inches. " What is the actual length, in feet, of the longest
FSA 7 th Grade Math Geometry This drawing shows a lawn in the shape of a trapezoid. The height of the trapezoidal lawn on the drawing is 1! inches. " What is the actual length, in feet, of the longest
Grade 7 Mathematics Item Specifications Florida Standards Assessments
 Assessment Limit MAFS7.G.1 Draw, construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships between them. MAFS.7.G.1.1 Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including
Assessment Limit MAFS7.G.1 Draw, construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships between them. MAFS.7.G.1.1 Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including
Math 2 nd Grade GRADE LEVEL STANDARDS/DOK INDICATORS
 Number Properties and Operations Whole number sense and addition and subtraction are key concepts and skills developed in early childhood. Students build on their number sense and counting sense to develop
Number Properties and Operations Whole number sense and addition and subtraction are key concepts and skills developed in early childhood. Students build on their number sense and counting sense to develop
June 2016 Regents GEOMETRY COMMON CORE
 1 A student has a rectangular postcard that he folds in half lengthwise. Next, he rotates it continuously about the folded edge. Which three-dimensional object below is generated by this rotation? 4) 2
1 A student has a rectangular postcard that he folds in half lengthwise. Next, he rotates it continuously about the folded edge. Which three-dimensional object below is generated by this rotation? 4) 2
Area of Composite Figures. ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do you find the area of composite figures? 7.G.2.6
 LESSON 9.3 Area of Composite Figures Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, of objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons,. ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do you find the area
LESSON 9.3 Area of Composite Figures Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, of objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons,. ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do you find the area
Dear Parents and Students,
 Dear Parents and Students, We hope you will enjoy this Math Challenge packet and work hard to complete all problems on your own or with help from a parent or guardian. All projects in this packet are based
Dear Parents and Students, We hope you will enjoy this Math Challenge packet and work hard to complete all problems on your own or with help from a parent or guardian. All projects in this packet are based
RELEASED. End-of-Grade Alternate Assessment Mathematics. Grade 3. Student Booklet
 Released Form REDY NEXTEND End-of-Grade lternate ssessment Mathematics Grade Student ooklet cademic Services and Instructional Support Division of ccountability Services opyright 0 by the North arolina
Released Form REDY NEXTEND End-of-Grade lternate ssessment Mathematics Grade Student ooklet cademic Services and Instructional Support Division of ccountability Services opyright 0 by the North arolina
GRADE 4. M : Solve division problems without remainders. M : Recall basic addition, subtraction, and multiplication facts.
 GRADE 4 Students will: Operations and Algebraic Thinking Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems. 1. Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 7 as
GRADE 4 Students will: Operations and Algebraic Thinking Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems. 1. Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 7 as
Area and Perimeter. Practice 1 Area of a Rectangle. Find the area of each figure. Example. one-inch squares.
 Name: Date: Chapter Practice 1 Area of a Rectangle Find the area of each figure. Example There are 3 rows of one-inch squares. Each row has 4 one-inch squares. 3 3 4 5 12 There are 12 one-inch squares
Name: Date: Chapter Practice 1 Area of a Rectangle Find the area of each figure. Example There are 3 rows of one-inch squares. Each row has 4 one-inch squares. 3 3 4 5 12 There are 12 one-inch squares
Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts
 Meet #5 March 2009 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet #5 March 2009 Category 1 Mystery 1. Sam told Mike to pick any number, then double it, then add 5 to the new value, then
Meet #5 March 2009 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet #5 March 2009 Category 1 Mystery 1. Sam told Mike to pick any number, then double it, then add 5 to the new value, then
KS3 Revision work. Level 6 + = 1
 KS3 Revision work Level 6 1. Thinking fractions Write the missing numbers in these fraction sums. 1 + = 1 4 8 1 8 + = 1 3 2. Pi The value of correct to 7 decimal places is: 3.1415927 (a) Write the value
KS3 Revision work Level 6 1. Thinking fractions Write the missing numbers in these fraction sums. 1 + = 1 4 8 1 8 + = 1 3 2. Pi The value of correct to 7 decimal places is: 3.1415927 (a) Write the value
Grade 3: PA Academic Eligible Content and PA Common Core Crosswalk
 Grade 3: PA Academic Eligible and PA Common Core Crosswalk Alignment of Eligible : More than Just The crosswalk below is designed to show the alignment between the PA Academic Standard Eligible and the
Grade 3: PA Academic Eligible and PA Common Core Crosswalk Alignment of Eligible : More than Just The crosswalk below is designed to show the alignment between the PA Academic Standard Eligible and the
1. How many diagonals does a regular pentagon have? A diagonal is a 1. diagonals line segment that joins two non-adjacent vertices.
 Blitz, Page 1 1. How many diagonals does a regular pentagon have? A diagonal is a 1. diagonals line segment that joins two non-adjacent vertices. 2. Let N = 6. Evaluate N 2 + 6N + 9. 2. 3. How many different
Blitz, Page 1 1. How many diagonals does a regular pentagon have? A diagonal is a 1. diagonals line segment that joins two non-adjacent vertices. 2. Let N = 6. Evaluate N 2 + 6N + 9. 2. 3. How many different
Essentials. Week by. Week
 Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials After Marie s birthday party, there were pizzas left. Marie gave half of the leftover pizza to her friend to take home. Marie ate of what was left. How much pizza did
Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials After Marie s birthday party, there were pizzas left. Marie gave half of the leftover pizza to her friend to take home. Marie ate of what was left. How much pizza did
UNIT 5: RATIO, PROPORTION, AND PERCENT WEEK 20: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 5: RATIO, PROPORTION, AND PERCENT WEEK 20: Student Packet 20.1 Solving Proportions 1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational numbers. Use rates and proportions to solve problems.
Name Period Date UNIT 5: RATIO, PROPORTION, AND PERCENT WEEK 20: Student Packet 20.1 Solving Proportions 1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational numbers. Use rates and proportions to solve problems.
Adding & Subtracting Decimals. Multiplying Decimals. Dividing Decimals
 1. Write the problem vertically, lining up the decimal points. 2. Add additional zeroes at the end, if necessary, to make the numbers have the same number of decimal places. 3. Add/subtract as if the numbers
1. Write the problem vertically, lining up the decimal points. 2. Add additional zeroes at the end, if necessary, to make the numbers have the same number of decimal places. 3. Add/subtract as if the numbers
Modeling Geometric Figures. How can you apply geometry concepts to solve real-world problems? 1 cm in the drawing equals 7 feet in the actual yard.
 ? UNIT 4 Study Guide Review MODULE 8 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Modeling Geometric Figures How can you apply geometry concepts to solve real-world problems? EXAMPLE 1 Use the scale drawing to find the perimeter
? UNIT 4 Study Guide Review MODULE 8 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Modeling Geometric Figures How can you apply geometry concepts to solve real-world problems? EXAMPLE 1 Use the scale drawing to find the perimeter
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *5164933141* CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICS 0607/32 Paper 3 (Core) October/November 2017 1 hour
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *5164933141* CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICS 0607/32 Paper 3 (Core) October/November 2017 1 hour
Northern York County School District Curriculum
 Northern York County School District Curriculum Course Name Grade Level Mathematics Fourth grade Unit 1 Number and Operations Base Ten Time Frame 4-5 Weeks PA Common Core Standard (Descriptor) (Grades
Northern York County School District Curriculum Course Name Grade Level Mathematics Fourth grade Unit 1 Number and Operations Base Ten Time Frame 4-5 Weeks PA Common Core Standard (Descriptor) (Grades
Mathematics Concepts 2 Exam 2 Version 2 20 October 2017
 Mathematics Concepts 2 Exam 2 Version 2 20 October 2017 Name: Permissible Aides: The small ruler distributed by the proctor Prohibited: Class Notes Class Handouts Study Guides and Materials The Book Any
Mathematics Concepts 2 Exam 2 Version 2 20 October 2017 Name: Permissible Aides: The small ruler distributed by the proctor Prohibited: Class Notes Class Handouts Study Guides and Materials The Book Any
Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST INTEGRATED MATHEMATICS I. Student Name
 Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST INTEGRATED MATHEMATICS I Student Name The Ohio Department of Education does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, religion, age, or disability
Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST INTEGRATED MATHEMATICS I Student Name The Ohio Department of Education does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, religion, age, or disability
3 Kevin s work for deriving the equation of a circle is shown below.
 June 2016 1. A student has a rectangular postcard that he folds in half lengthwise. Next, he rotates it continuously about the folded edge. Which three-dimensional object below is generated by this rotation?
June 2016 1. A student has a rectangular postcard that he folds in half lengthwise. Next, he rotates it continuously about the folded edge. Which three-dimensional object below is generated by this rotation?
