The Grade 1 Common Core State Standards for Geometry specify that children should
|
|
|
- Agnes Blankenship
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 in the elementary classroom means more than recalling the names of shapes, measuring angles, and making tessellations it is closely linked to other mathematical concepts. For example, geometric representations can help children make sense of fractions and area. Children will also understand how parts are related to wholes as they begin to partition regions into equal shares and use words like halves, fourths, and quarter of. Such understanding is an essential learning component for more in-depth studies of fractions in later elementary years. Whether studying shapes and their attributes in the early years or working with geometric proofs in the secondary grades, geometry enables learners to interpret and describe their physical environment. It provides children opportunities to physically and mentally change the positions of objects, describe shapes and the relationships among them, and solve problems using special reasoning. The Grade 1 Common Core State Standards for specify that children should The following hands-on activities enable teachers to help children learn the concepts of geometry in a rich and meaningful way. It is important that teachers and children label terms and use such terminology appropriately. Doing so will enable children to develop the precision necessary for recognizing and describing similarities and differences among shapes. 120
2 Contents Lesson 1 Combining Shapes Objective: Combine geometric shapes to compose a copy of a given shape. Manipulative: Tangrams Lesson 2 Building Shapes Objective: Explore ways of combining different shapes to compose new shapes. Manipulative: Tangrams Lesson 3 Tangram Puzzles Objective: Use Tangrams to solve visual/spatial puzzles. Manipulative: Tangrams Lesson 4 Equal Shares of Rectangles Objective: Partition rectangles into equal shares. Manipulative: Color Tiles 121
3 1.G Objective Common Core State Standards Combining Shapes Giving children the opportunity to combine shapes helps them build important mathematical skills. In this activity, children will be placing shapes on top of other shapes. This will allow them a concrete exploration of how shapes can be combined to form new shapes. The hands-on approach to combining shapes will help children build congruence using the idea that the pieces coincide. This lesson also provides an introduction to tangrams. Familiarity with these shapes will help children work with puzzles in later activities. Talk About It Discuss the Try It! activity. Ask: What shapes did you use to cover the square? How many did you use? Was there more than one way to cover the square? Ask: What shapes did you use to cover the parallelogram? How many shapes did you use? Did you find more than one way to cover the parallelogram? Ask: What shapes did you use to cover the triangle? How many shapes did you use? Say: Describe the shapes you used for both ways you found to cover the triangle. Solve It With children, reread the problem. Have children experiment to find the answer (two triangles). Then have children draw a triangle made out of two smaller triangles and write a sentence telling what shapes Andrew used. More Ideas For other ways to teach about combining shapes to copy other shapes Distribute paper bags with Pattern Block squares and triangles to groups of three. Each child should reach into the bag and choose a shape without looking. The child then names the shape and builds it using two or more Tangram pieces. For children who need an additional challenge, introduce the trapezoid Pattern Block and ask them to build the shape with Tangram pieces. Have children work in pairs. Name a shape that can be built with Tangram pieces, such as a square, a triangle, or a parallelogram. Ask children to see if they can build the shapes using only triangles, or only squares and parallelograms. For an extra challenge, ask children if they can make a shape with five or six sides out of Tangram pieces. Formative Assessment Have children try the following problem. Draw a line through this shape to make two triangles.
4 Try It! 20 minutes Pairs Here is a problem about combining shapes to compose copies of other shapes. Andrew s class is building shapes using Tangram pieces. Andrew chose two shapes. He used them to make a square. What two shapes did Andrew use? Introduce the problem. Then have children do the activity to solve the problem. Draw a square, a triangle, and a parallelogram on the board. Tell children the name of each shape, and then have them practice saying the shape names. Distribute Tangrams to children. Materials Tangrams (2 sets per pair) 1. Instruct children to choose a square from their Tangrams. Ask children to use other shapes to cover the square. 2. Invite children to choose a parallelogram Tangram piece from the set. Instruct them to use other shapes to cover the surface of the parallelogram. 3. Have children repeat the activity by covering a large triangle with other Tangram pieces. Tell children that there is more than one way to do this. Ask them to find two different combinations of shapes that they can use. Children may be confused about the idea of covering up shapes. They may use Tangram pieces that do not fit exactly, causing the top shapes to overlap the bottom or leaving parts of the bottom shape uncovered. If this is the case, remind children that the pieces on top should make a shape that is exactly the same as the bottom shape. 123
5 Lesson 1 Name Answer Key Use Tangram pieces. Make each shape. Tell what pieces you used. (Check students work.) 1. square two small triangles Use Tangram pieces. Match the shape shown on the left using more than 1 piece. Draw the model in the shape on the right. 2. square and 2 other pieces 3. parallelogram and 2 other pieces ETA hand2mind 124 Hands-On Standards, Common Core Edition Download student pages at hand2mind.com/hosstudent.
6 Answer Name Key Challenge! How can you tell if two shapes are exactly the same size and shape? Challenge: (Sample) Place them on top of each other and make sure all of their sides match up. ETA hand2mind Download student pages at hand2mind.com/hosstudent. Hands-On Standards, Common Core Edition 125
7 2 Objective Building Shapes Giving children the opportunity to combine and take apart shapes helps them build several important mathematical skills. Such activities foster spatial reasoning and spatial visualization and deepen children s understanding of geometric properties. Open-ended activities like the one in this lesson encourage the development of problem-solving skills and logical thinking that will be applicable in a variety of experiences both in and out of the classroom environment. 1.G.2 Common Core State Standards Talk About It Discuss the Try It! activity. Ask: What shapes did you use to make a square? Say: Tell me something about your square. Ask: What shapes did you use to make the parallelogram? Say: Tell me something about your parallelogram. Ask: What shapes did you use to make the triangle? Say: Tell me something about your triangle. Ask: How is the triangle like the square you made? How is it different? How is the triangle like the parallelogram? How is it different? How are the parallelogram and the square alike? How are they different? Solve It With children, reread the problem. Then have children draw one way to make each shape out of Tangram pieces. More Ideas For other ways to teach about combining shapes to compose new shapes Have children use Snap Cubes to build composite shapes. Children can build cubes and prisms and combine them to build the composite shapes that you specify. Have children use Tangram pieces to play a guessing game. Ask them to build a rectangle. They then build the rectangle out of a square and two triangles or a parallelogram and two triangles. Ask them to build a parallelogram. They should then build a parallelogram out of a square and two triangles, or two triangles. Ask them to build a square. They can use two triangles. Formative Assessment Have children try the following problem. Divide this shape into six equal triangles and color each triangle a different color. 126
8 Try It! 20 minutes Pairs Here is a problem about combining shapes to compose new shapes. Juan s class is building shapes using Tangram pieces. Juan s teacher asks him to build a square, a triangle, and a parallelogram. How can Juan build these shapes using Tangram pieces? Introduce the problem. Then have children do the activity to solve the problem. Draw a square, a triangle, and a parallelogram on the board. Review the shape names, giving special attention to the parallelogram, which may be unfamiliar to children. Distribute Tangrams, paper, and pencils to children. Materials Tangrams (1 set per pair) paper (1 sheet per child) pencils (1 per child) 1. Instruct children to use Tangram pieces to build a square. Have them trace the shapes onto paper to show how they made the square. 2. Instruct children to use Tangram pieces to build a parallelogram. Have children trace the shapes onto paper to show how they made the parallelogram. 3. Have children repeat the activity by making a triangle with the Tangram pieces and tracing the result. Have children share their observations about the new shapes, including similarities and differences between them, and where they can see these shapes in the classroom, playground, school, home, store, and so on. Children may have trouble seeing how Tangram pieces fit together to make other shapes. You may wish to help them by drawing on the board the shape you are asking them to build, then drawing a line to show the silhouette of one smaller shape within it. For example, if you are asking children to build a parallelogram, you may want to draw it on the board and then draw a line to show one of the triangles that it is made of. Then ask children if they can see another triangle in the parallelogram. 127
9 Lesson 2 Name Answer Key Use Tangram pieces to model the shape shown on the left. Name the pieces you used to make the shape. (Check students work.) 1. parallelogram and small triangle Use Tangram pieces. Make the shape shown on the left using more than 1 piece. Sketch the model in the shape on the right. Name the pieces used. 2. two triangles 3. two small triangles and square ETA hand2mind 128 Hands-On Standards, Common Core Edition Download student pages at hand2mind.com/hosstudent.
10 Answer Name Key Challenge! When you join two Tangram shapes to make another shape, what parts of the shapes touch each other? Challenge: The sides must line up/touch to form a straight line. ETA hand2mind Download student pages at hand2mind.com/hosstudent. Hands-On Standards, Common Core Edition 129
11 3 Objective Tangram Puzzles While young children are often able to recognize and label a variety of simple geometric shapes, they have not yet developed a solid understanding of geometric concepts. Having the opportunity to solve puzzles using shapes will build a solid understanding of the shapes and foster the spatial and problemsolving skills needed to comprehend more involved geometric skills. 1.G.2 Common Core State Standards Talk About It Discuss the Try It! activity. Ask: Which shapes were already filled in for you on the first Tangram puzzle? Ask: Which shapes did you use to complete the first puzzle? Invite volunteers to list the combinations of shapes that they used. Ask: Did anyone use different shapes to finish the first puzzle? Allow children to compare the shapes they used. Repeat questions for the second puzzle and have children compare their results. Solve It With children, reread the problem. Then have children use the Tangram pieces to make their design. They can use any combination of Tangram pieces, as long as the end result is a square. Children will write to describe their designs and draw pictures of their designs on paper. More Ideas For other ways to teach about solving visual/spatial puzzles Have children create their own puzzles by putting all 7 Tangram pieces together to make pictures of their choice. Then children will outline their pictures and trade with a partner. Each partner will attempt to fill in the other s puzzle. Distribute Tangrams to children and have groups of four combine their sets. Have children use all of the small triangles to create a shape or design. Tell them to do the same for the other shapes. Then have children trace outlines of their shapes, exchange papers with another group, and then work to figure out which Tangram piece was used to make each larger shape. Formative Assessment Have children try the following problem. Which Tangram piece could be used to complete the square? 130 A. B. C.
12 Try It! 20 minutes Independent Here is a problem about solving visual/spatial puzzles. In Lora s classroom, there are tables that are different shapes. Some are triangles, some are squares, and some are parallelograms. Lora s teacher asks her to push some of the tables together to make a square. How can Lora figure out how to arrange the tables into a square? Introduce the problem. Then have children do the activity to solve the problem. Distribute Tangrams and Tangram Puzzles (BLM 9) to children. Materials Tangrams (1 set per child) Tangram Puzzles (BLM 9; 1 per child) 1. Tell children that they will be using Tangram pieces to fill in the Tangram Puzzles. Have children look at the first puzzle. Say: Some of the shapes you will use are already drawn on the worksheet to help you. Put the matching Tangram pieces on top of those shapes to start the puzzle. Have children place Tangram pieces over the shapes drawn on the first puzzle. 2. Say: Now fill in the rest of the pieces on the first puzzle. Allow children time to fill in the puzzle by experimenting with shapes to find out which will fit. 3. Once children have completed the first puzzle, allow them to complete the second puzzle on their own. Watch out for children whose Tangram pieces protrude outside the lines of the puzzle shape. Explain that the Tangram pieces must exactly fill in the puzzle shape, with no leftover space inside the lines and no Tangram parts outside the lines. Have children trace around their Tangram pieces with a crayon and then remove them from the puzzle template. Help children find any spots where the crayon tracing diverges from the puzzle outline. 131
13 Lesson 3 Name Answer Key Use Tangram pieces. Complete the model to make each shape. Draw the shapes in place. (Check students work.) ETA hand2mind 132 Hands-On Standards, Common Core Edition Download student pages at hand2mind.com/hosstudent.
14 Answer Name Key Challenge! How did you decide which Tangram pieces to place in the open spaces to complete the figures on the previous page? Challenge: (Sample) I tried putting the pieces in the places I thought. If they did not work, I tried a different way. ETA hand2mind Download student pages at hand2mind.com/hosstudent. Hands-On Standards, Common Core Edition 133
15 4 1.G.3 Objective Common Core State Standards Equal Shares of Rectangles A child s early understanding of fractions is usually based on the area model for partitioning a whole. Children start experimenting with this model by partitioning rectangles into two and four equal areas. As they experiment, they learn to use the words halves, fourths, and quarters. Building and partitioning rectangles helps children develop additional mathematical skills, as well. These include spatial reasoning and visualization and a sense of geometric properties. Talk About It Discuss the Try It! activity. Have children look at the top rectangle on the completed BLM. Ask: How many equal shares are shown? What are two equal shares called? Have children look at the bottom rectangle. Ask: How many equal shares are shown? What are four equal shares called? Have children compare the size of a half to the size of a fourth. Ask: When we make more equal shares of a rectangle, what happens to the size of the shares? Solve It With children, reread the problem. Have children draw a picture showing the whole graham cracker and then add a line to show where Marco could break the cracker to make two equal shares. More Ideas For other ways to teach partitioning rectangles into equal shares Have children use the Color Tiles to build different sized rectangles showing halves and fourths. Ask children to describe each rectangle using the terms equal shares, halves, fourths, and quarters. Have children use Deluxe Rainbow Fraction Squares to show halves and fourths and describe the equal shares. Encourage children to make up stories to go with the models they build. Have children use Geoboards to show halves and fourths and describe the equal shares. Formative Assessment Have children try the following problem. Which shows fourths? 134
16 Try It! 20 minutes Pairs Here is a problem about partitioning rectangles into equal shares. Marco has a graham cracker that is shaped like a rectangle. He wants to share it equally with his sister. How can Marco break the cracker into two equal shares? Introduce the problem. Then have children do the activity to solve the problem. Distribute Color Tiles and the Equal Shares of Rectangles (BLM 10) to children. Materials Color Tiles Equal Shares of Rectangles (BLM 10; 1 per pair) crayons (1 green, yellow, blue, and red per pair) 1. Have children place four green Color Tiles on the BLM in the top rectangle. Then have children fill in the remaining space in the rectangle with yellow Color Tiles. Tell students that if they did not already do so, you want them to arrange the tiles to form two squares inside the rectangle one green, one yellow. 2. Ask: Are the green and yellow parts equal in size? If necessary, elicit that they are equal in size and are therefore equal shares. Discuss the words half and halves. Point out that two halves make a whole. Have children take away the green tiles and color that half of the rectangle green; have them take away the yellow tiles and color that half yellow. Some children might be confused by using two or four Color Tiles to make each part of a rectangle. Have them focus on the colors as the parts and not on the individual Color Tiles. 3. Have children place two blue Color Tiles, two red Color Tiles, two green Color Tiles, and two yellow Color Tiles on the BLM in the bottom rectangle to form 4 equal parts. Ask: Are the four parts equal shares? Say: Four equal shares are called fourths, or quarters. Four fourths make a whole. Four quarters make a whole. Have children color in the fourths. 135
17 Lesson 4 Name Answer Key Use Color Tiles. Build the rectangle. Tell the number of equal shares equal shares (Check students work.) 2 2. equal shares Draw the rectangle. Tell if it shows halves or fourths. Circle the answer. 3. four red tiles and four blue tiles halves fourths halves two green tiles, two yellow tiles, two red tiles, and two blue tiles halves Hands-On Standards, Common Core Edition fourths fourths Download student pages at hand2mind.com/hosstudent. ETA hand2mind
18 Answer Name Key Challenge! Why are fourths smaller shares than halves? Challenge: (Sample) Fourths are smaller shares than halves because the whole is divided into four parts, not just two parts. ETA hand2mind Download student pages at hand2mind.com/hosstudent. Hands-On Standards, Common Core Edition 137
Building Shapes. Geometry. Objective. Common Core State Standards Talk About It. Solve It. More Ideas. Formative Assessment
 2 Objective Building Shapes Giving children the opportunity to combine and take apart shapes helps them build several important mathematical skills. Such activities foster spatial reasoning and spatial
2 Objective Building Shapes Giving children the opportunity to combine and take apart shapes helps them build several important mathematical skills. Such activities foster spatial reasoning and spatial
Multiplying Two Fractions
 Objective Multiplying Two Fractions Students will build upon their understanding of multiplying a fraction by a whole number to now multiply a fraction by a fraction. Using concrete models to build rectangles
Objective Multiplying Two Fractions Students will build upon their understanding of multiplying a fraction by a whole number to now multiply a fraction by a fraction. Using concrete models to build rectangles
Symmetrical Figures. Geometry. Objective. Common Core State Standards Talk About It. Solve It. More Ideas. Formative Assessment
 5 Objective Symmetrical Figures In this lesson, students solve problems involving symmetry. Because relationships across a line of symmetry correspond exactly in terms of size, form, and arrangement, students
5 Objective Symmetrical Figures In this lesson, students solve problems involving symmetry. Because relationships across a line of symmetry correspond exactly in terms of size, form, and arrangement, students
The Grade 6 Common Core State Standards for Geometry specify that students should
 The focus for students in geometry at this level is reasoning about area, surface area, and volume. Students also learn to work with visual tools for representing shapes, such as graphs in the coordinate
The focus for students in geometry at this level is reasoning about area, surface area, and volume. Students also learn to work with visual tools for representing shapes, such as graphs in the coordinate
1.G.1 Distinguish between defining attributes. Build and draw shapes that possess K.G.3 Identify shapes as 2-D (flat) or 3-D (solid)
 Identify and describe shapes, including squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres (Standards K.G.1 3). Standard K.G.1 Describe objects in the environment using
Identify and describe shapes, including squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres (Standards K.G.1 3). Standard K.G.1 Describe objects in the environment using
Area of a Parallelogram
 Area of a Parallelogram Objective In this activity, students reason about the area of a parallelogram by visualizing its relationship to a corresponding rectangle. Without a formula, the area of a rectangle
Area of a Parallelogram Objective In this activity, students reason about the area of a parallelogram by visualizing its relationship to a corresponding rectangle. Without a formula, the area of a rectangle
Measurement and Data. Finding Area. Talk About It. More Ideas. Formative Assessment. Have students try the following problem.
 Objective Common Core State Standards 3.MD.5a 3.MD.5b 3.MD.6 Finding Area Students have already had some experience with the ideas of shape, perimeter, and area in their geometry lessons, although they
Objective Common Core State Standards 3.MD.5a 3.MD.5b 3.MD.6 Finding Area Students have already had some experience with the ideas of shape, perimeter, and area in their geometry lessons, although they
Measurement and Data. Building Area. Talk About It. More Ideas. Formative Assessment. Have students try the following problem.
 13 Objective Common Core State Standards Building Area Students benefit from having concrete experiences working with measurement before being expected to comprehend measurement formulas, such as l w for
13 Objective Common Core State Standards Building Area Students benefit from having concrete experiences working with measurement before being expected to comprehend measurement formulas, such as l w for
Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD. We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential
 Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential Grade 2 Module 8 Parent Handbook The materials contained within this packet have been taken
Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential Grade 2 Module 8 Parent Handbook The materials contained within this packet have been taken
1. Choose two shapes. Combine the shapes to make a new shape. Make sure that the two shapes share a side. Draw your new shape.
 Name Unit 7 Shape Up!. Choose two shapes. Combine the shapes to make a new shape. Make sure that the two shapes share a side. Draw your new shape. 2. Describe each shape you used. Explain how your new
Name Unit 7 Shape Up!. Choose two shapes. Combine the shapes to make a new shape. Make sure that the two shapes share a side. Draw your new shape. 2. Describe each shape you used. Explain how your new
Measurement and Data. Bar Graphs. Talk About It. More Ideas. Formative Assessment. Have children try the following problem.
 4 1.MD.4 Objective Common Core State Standards Bar Graphs Counting and classifying provide a foundation for the gathering and analysis of data. Moving collected information from a tally chart to a graph
4 1.MD.4 Objective Common Core State Standards Bar Graphs Counting and classifying provide a foundation for the gathering and analysis of data. Moving collected information from a tally chart to a graph
Counting and Cardinality. More Ideas. Formative Assessment. Have children try the following problem.
 9 Counting and Cardinality Comparing Groups Objective This lesson extends children s investigations of numbers to 10 and takes on the additional focus of comparison. Children will count but will also be
9 Counting and Cardinality Comparing Groups Objective This lesson extends children s investigations of numbers to 10 and takes on the additional focus of comparison. Children will count but will also be
Day 2: Tangram Tune Up Grade 7
 Day 2: Tangram Tune Up Grade 7 Minds On... Action! Description Review geometric language. Introduce new geometric terminology. Construct tangram pieces and create 2-D composite shapes. Whole Class Reflection
Day 2: Tangram Tune Up Grade 7 Minds On... Action! Description Review geometric language. Introduce new geometric terminology. Construct tangram pieces and create 2-D composite shapes. Whole Class Reflection
Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS Math Guide 6-72 Overview NTCM Standards (Grades 3-5) 4-5 Lessons and Terms Vocabulary Flash Cards 45-72
 Contents shapes TABLE OF CONTENTS Math Guide 6-72 Overview 3 NTCM Standards (Grades 3-5) 4-5 Lessons and Terms Lesson 1: Introductory Activity 6-8 Lesson 2: Lines and Angles 9-12 Line and Angle Terms 11-12
Contents shapes TABLE OF CONTENTS Math Guide 6-72 Overview 3 NTCM Standards (Grades 3-5) 4-5 Lessons and Terms Lesson 1: Introductory Activity 6-8 Lesson 2: Lines and Angles 9-12 Line and Angle Terms 11-12
Parent Packet. HAUPPAUGE MATH DEPARTMENT CCLS Grade 1 MODULE 5
 Parent Packet HAUPPAUGE MATH DEPARTMENT CCLS Grade 1 MODULE 5 http://www.hauppauge.k12.ny.us/math 2014 2015 School Year Grade 1 Module 5 Identifying, Composing, and Partitioning Shapes In Module 5, students
Parent Packet HAUPPAUGE MATH DEPARTMENT CCLS Grade 1 MODULE 5 http://www.hauppauge.k12.ny.us/math 2014 2015 School Year Grade 1 Module 5 Identifying, Composing, and Partitioning Shapes In Module 5, students
Estimating and Measuring
 4 Objective Estimating and Measuring Measurement encompasses several areas of math. By this age, children will have experienced measuring objects with standard units. This exposure has formed a foundation
4 Objective Estimating and Measuring Measurement encompasses several areas of math. By this age, children will have experienced measuring objects with standard units. This exposure has formed a foundation
Whole Numbers as Lengths on a Number Line
 6 Objective Common Core State Standards Whole Numbers as Lengths on a Number Line As children continue to become familiar with the units and processes of measuring length, they can begin to see a ruler
6 Objective Common Core State Standards Whole Numbers as Lengths on a Number Line As children continue to become familiar with the units and processes of measuring length, they can begin to see a ruler
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Middle School Geometry. Session 2
 Middle School Geometry Session 2 Topic Activity Name Page Number Related SOL Spatial Square It 52 6.10, 6.13, Relationships 7.7, 8.11 Tangrams Soma Cubes Activity Sheets Square It Pick Up the Toothpicks
Middle School Geometry Session 2 Topic Activity Name Page Number Related SOL Spatial Square It 52 6.10, 6.13, Relationships 7.7, 8.11 Tangrams Soma Cubes Activity Sheets Square It Pick Up the Toothpicks
Arranging Sets of Objects
 7 Arranging Sets of Objects Objective In this lesson, children will learn that sets of objects with the same number of items can be arranged in different ways. A set of 8 items, for example, can be arranged
7 Arranging Sets of Objects Objective In this lesson, children will learn that sets of objects with the same number of items can be arranged in different ways. A set of 8 items, for example, can be arranged
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Space and Shape (Geometry)
 Space and Shape (Geometry) INTRODUCTION Geometry begins with play. (van Hiele, 1999) The activities described in this section of the study guide are informed by the research of Pierre van Hiele. According
Space and Shape (Geometry) INTRODUCTION Geometry begins with play. (van Hiele, 1999) The activities described in this section of the study guide are informed by the research of Pierre van Hiele. According
Pattern Block Pizza OVERVIEW THE BIG IDEA
 Math Tasks OVERVIEW OBJECTIVE Children will use to develop the concept of equivalence while working informally with halves, thirds, and sixths. They will develop an intuitive understanding of probability.
Math Tasks OVERVIEW OBJECTIVE Children will use to develop the concept of equivalence while working informally with halves, thirds, and sixths. They will develop an intuitive understanding of probability.
Space and Shape (Geometry)
 Space and Shape (Geometry) INTRODUCTION Geometry begins with play. (van Hiele, 1999) The activities described in this section of the study guide are informed by the research of Pierre van Hiele. According
Space and Shape (Geometry) INTRODUCTION Geometry begins with play. (van Hiele, 1999) The activities described in this section of the study guide are informed by the research of Pierre van Hiele. According
Penny, Nickel, and Dime
 9 Objective Penny, Nickel, and Dime With an understanding of the penny and the nickel and the relationship between them, children expand their work with money to include the dime. They perform counting,
9 Objective Penny, Nickel, and Dime With an understanding of the penny and the nickel and the relationship between them, children expand their work with money to include the dime. They perform counting,
Cut - Stretch - Fold. , by Karen Baicker; ISBN
 Cut - Stretch - Fold Summary This lesson will help students determine the area of a tangram piece without using formulas. After completing this activity students will use their knowledge to help them develop
Cut - Stretch - Fold Summary This lesson will help students determine the area of a tangram piece without using formulas. After completing this activity students will use their knowledge to help them develop
Please be sure to save a copy of this activity to your computer!
 Thank you for your purchase Please be sure to save a copy of this activity to your computer! This activity is copyrighted by AIMS Education Foundation. All rights reserved. No part of this work may be
Thank you for your purchase Please be sure to save a copy of this activity to your computer! This activity is copyrighted by AIMS Education Foundation. All rights reserved. No part of this work may be
learning about tangram shapes
 Introduction A Tangram is an ancient puzzle, invented in China and consisting of a square divided into seven geometric shapes: Two large right triangles One medium right triangle Tangram Two small right
Introduction A Tangram is an ancient puzzle, invented in China and consisting of a square divided into seven geometric shapes: Two large right triangles One medium right triangle Tangram Two small right
Objective: Create composite shapes from two-dimensional shapes.
 Lesson 4 1 5 Lesson 4 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (13 minutes) (7 minutes) (30 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Lesson 4 1 5 Lesson 4 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (13 minutes) (7 minutes) (30 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Foundations of Multiplication and Division
 Grade 2 Module 6 Foundations of Multiplication and Division OVERVIEW Grade 2 Module 6 lays the conceptual foundation for multiplication and division in Grade 3 and for the idea that numbers other than
Grade 2 Module 6 Foundations of Multiplication and Division OVERVIEW Grade 2 Module 6 lays the conceptual foundation for multiplication and division in Grade 3 and for the idea that numbers other than
Math Literature Connection
 Math Literature Connection Grandfather Tang s Story: A Tale Told with Tangrams By: Ann Tompert, Illustrated by Robert Andrew Parker About the Book: Two competitive fox fairies go through rapid physical
Math Literature Connection Grandfather Tang s Story: A Tale Told with Tangrams By: Ann Tompert, Illustrated by Robert Andrew Parker About the Book: Two competitive fox fairies go through rapid physical
Identifying Multiples
 4 Objective Identifying Multiples An understanding of multiples is useful to students when they work with multiplication, division, and equivalent fractions. Students also need to understand multiples
4 Objective Identifying Multiples An understanding of multiples is useful to students when they work with multiplication, division, and equivalent fractions. Students also need to understand multiples
Refer to Blackboard for Activities and/or Resources
 Lafayette Parish School System Curriculum Map Mathematics: Grade 5 Unit 4: Properties in Geometry (LCC Unit 5) Time frame: 16 Instructional Days Assess2know Testing Date: March 23, 2012 Refer to Blackboard
Lafayette Parish School System Curriculum Map Mathematics: Grade 5 Unit 4: Properties in Geometry (LCC Unit 5) Time frame: 16 Instructional Days Assess2know Testing Date: March 23, 2012 Refer to Blackboard
Enhanced Instructional Transition Guide
 Geometry: Coordinate Plane, Graphing Transformations, and Perspectives (9 days) Possible Lesson 01 (6 days) Possible Lesson 02 (3 days) POSSIBLE LESSON 02 (3 days) This lesson is one approach to teaching
Geometry: Coordinate Plane, Graphing Transformations, and Perspectives (9 days) Possible Lesson 01 (6 days) Possible Lesson 02 (3 days) POSSIBLE LESSON 02 (3 days) This lesson is one approach to teaching
angrams Algebra/Geometry Institute Summer 2005 Lesson Plan 3: Tangrams
 Algebra/Geometry Institute Summer 2005 Lesson Plan 3: Tangrams Faculty Name: Rayna McCarty School: Parks Elementary Grade Level: 5 1 Teaching objective(s) Students will use tangrams to identify, describe,
Algebra/Geometry Institute Summer 2005 Lesson Plan 3: Tangrams Faculty Name: Rayna McCarty School: Parks Elementary Grade Level: 5 1 Teaching objective(s) Students will use tangrams to identify, describe,
The learner will recognize and use geometric properties and relationships.
 The learner will recognize and use geometric properties and relationships. Notes 3and textbook 3.01 Use the coordinate system to describe the location and relative position of points and draw figures in
The learner will recognize and use geometric properties and relationships. Notes 3and textbook 3.01 Use the coordinate system to describe the location and relative position of points and draw figures in
First Grade Saxon Math Curriculum Guide Key Standards Addressed in Section
 Sections and Lessons First Grade Saxon Math Curriculum Guide MAP September 15 26, 2014 Section 1: Lessons 1-10 Making Sets of Tens & Ones with Concrete Objects, Numerals, Comparing Numbers, Using Graphs
Sections and Lessons First Grade Saxon Math Curriculum Guide MAP September 15 26, 2014 Section 1: Lessons 1-10 Making Sets of Tens & Ones with Concrete Objects, Numerals, Comparing Numbers, Using Graphs
Geometry. Learning Goals U N I T
 U N I T Geometry Building Castles Learning Goals describe, name, and sort prisms construct prisms from their nets construct models of prisms identify, create, and sort symmetrical and non-symmetrical shapes
U N I T Geometry Building Castles Learning Goals describe, name, and sort prisms construct prisms from their nets construct models of prisms identify, create, and sort symmetrical and non-symmetrical shapes
SESSION ONE GEOMETRY WITH TANGRAMS AND PAPER
 SESSION ONE GEOMETRY WITH TANGRAMS AND PAPER Outcomes Develop confidence in working with geometrical shapes such as right triangles, squares, and parallelograms represented by concrete pieces made of cardboard,
SESSION ONE GEOMETRY WITH TANGRAMS AND PAPER Outcomes Develop confidence in working with geometrical shapes such as right triangles, squares, and parallelograms represented by concrete pieces made of cardboard,
Multiplication and Area
 Grade 3 Module 4 Multiplication and Area OVERVIEW In this 20-day module students explore area as an attribute of two-dimensional figures and relate it to their prior understandings of multiplication. In
Grade 3 Module 4 Multiplication and Area OVERVIEW In this 20-day module students explore area as an attribute of two-dimensional figures and relate it to their prior understandings of multiplication. In
K Mathematics Curriculum. Analyzing, Comparing, and Composing Shapes. Module Overview... i
 K Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E Table of Contents GRADE K MODULE 6 Analyzing, Comparing, and Composing Shapes GRADE K MODULE 6 Module Overview... i Topic A: Building and Drawing Flat and Solid Shapes...
K Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E Table of Contents GRADE K MODULE 6 Analyzing, Comparing, and Composing Shapes GRADE K MODULE 6 Module Overview... i Topic A: Building and Drawing Flat and Solid Shapes...
Games for Young Mathematicians Pattern Block Puzzles HOW TO PLAY: PATTERN BLOCK PUZZLES
 HOW TO PLAY: PATTERN BLOCK PUZZLES Math children are practicing: Knowing names of familiar shapes Describing and comparing attributes of shapes using age-appropriate geometric language (corners/angles,
HOW TO PLAY: PATTERN BLOCK PUZZLES Math children are practicing: Knowing names of familiar shapes Describing and comparing attributes of shapes using age-appropriate geometric language (corners/angles,
Enduring Understanding Shapes can be divided into equal fractions, recombined into new shapes, and arranged in balance within artistic compositions.
 ARTS IMPACT LESSON PLAN Visual Arts and Math Infused Lesson Lesson Two: Balancing Shapes: Parts and Wholes Author: Meredith Essex Grade Level: First Enduring Understanding Shapes can be divided into equal
ARTS IMPACT LESSON PLAN Visual Arts and Math Infused Lesson Lesson Two: Balancing Shapes: Parts and Wholes Author: Meredith Essex Grade Level: First Enduring Understanding Shapes can be divided into equal
2.NBT.1 20) , 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, NBT.2
 Saxon Math 2 Class Description: Saxon mathematics is based on the principle of developing math skills incrementally and reviewing past skills daily. It also incorporates regular and cumulative assessments.
Saxon Math 2 Class Description: Saxon mathematics is based on the principle of developing math skills incrementally and reviewing past skills daily. It also incorporates regular and cumulative assessments.
Objective: Describe two-dimensional shapes based on attributes. (9 minutes) (60 minutes)
 Lesson 1 2 Lesson 1 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (6 minutes) (32 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Lesson 1 2 Lesson 1 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (6 minutes) (32 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Objective: Draw trapezoids to clarify their attributes, and define trapezoids based on those attributes.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 16 5 5 Lesson 16 Objective: Draw trapezoids to clarify their attributes, and define trapezoids based Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 16 5 5 Lesson 16 Objective: Draw trapezoids to clarify their attributes, and define trapezoids based Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application
(3 minutes) Materials: (T) Two-dimensional shape flash cards (Lesson 4 Fluency Template), three-dimensional shapes used in Lesson 3
 Lesson 5 1 Lesson 5 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice (13 minutes) Application Problem (5 minutes) Concept Development (32 minutes) Student Debrief (10 minutes) Total Time (60 minutes)
Lesson 5 1 Lesson 5 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice (13 minutes) Application Problem (5 minutes) Concept Development (32 minutes) Student Debrief (10 minutes) Total Time (60 minutes)
Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Grade 04
 Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Problem Solving Mathematical Process Expectations 4m1 develop, select, and apply problem-solving strategies as they pose and solve problems and conduct investigations, to
Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Problem Solving Mathematical Process Expectations 4m1 develop, select, and apply problem-solving strategies as they pose and solve problems and conduct investigations, to
Revised Elko County School District 2 nd Grade Math Learning Targets
 Elko County School District 2 nd Grade Math Learning Targets Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
Elko County School District 2 nd Grade Math Learning Targets Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
Thinking Kids. First Grade. NCTM Strands Covered: Number and Operations. Algebra. Geometry. Measurement. Data Analysis and Probability.
 Thinking Kids First Grade NCTM Strands Covered: Number and Operations Algebra Geometry Measurement Data Analysis and Probability Pretest How to Use This Assessment This Pretest introduces your students
Thinking Kids First Grade NCTM Strands Covered: Number and Operations Algebra Geometry Measurement Data Analysis and Probability Pretest How to Use This Assessment This Pretest introduces your students
Make 10. Operations and Algebraic Thinking. Objective. Common Core State Standards. Talk About It. Solve It. More Ideas. Formative Assessment
 9 Objective Common Core State Standards Make 10 To begin building a strong foundation for the base ten system and addition, children need to understand how two parts make up 10. By using concrete objects
9 Objective Common Core State Standards Make 10 To begin building a strong foundation for the base ten system and addition, children need to understand how two parts make up 10. By using concrete objects
Constant Perimeter and Changing Area
 Objective Common Core State Standards Constant Perimeter and Changing Area The concepts of perimeter and area are often misunderstood (and sometimes confused) by students who tend to lack real-world experience,
Objective Common Core State Standards Constant Perimeter and Changing Area The concepts of perimeter and area are often misunderstood (and sometimes confused) by students who tend to lack real-world experience,
Approximating Square Roots
 1 Objective The Number System Approximating Square Roots By now, students have studied various types of rational and irrational numbers, including square roots. In previous grades, students learned how
1 Objective The Number System Approximating Square Roots By now, students have studied various types of rational and irrational numbers, including square roots. In previous grades, students learned how
Correlation of Nelson Mathematics 2 to The Ontario Curriculum Grades 1-8 Mathematics Revised 2005
 Correlation of Nelson Mathematics 2 to The Ontario Curriculum Grades 1-8 Mathematics Revised 2005 Number Sense and Numeration: Grade 2 Section: Overall Expectations Nelson Mathematics 2 read, represent,
Correlation of Nelson Mathematics 2 to The Ontario Curriculum Grades 1-8 Mathematics Revised 2005 Number Sense and Numeration: Grade 2 Section: Overall Expectations Nelson Mathematics 2 read, represent,
5.3. Area of Polygons and Circles Play Area. My Notes ACTIVITY
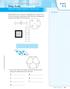 Area of Polygons and Circles SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Think/Pair/Share ACTIVITY 5.3 Pictured below is an aerial view of a playground. An aerial view is the view from above something. Decide what
Area of Polygons and Circles SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Think/Pair/Share ACTIVITY 5.3 Pictured below is an aerial view of a playground. An aerial view is the view from above something. Decide what
Grandfather Tang s Story by Ann Tompert. Upper ES / Math
 Grandfather Tang s Story by Ann Tompert Upper ES / Math Imagination, Transformation, Part and Whole, Polygon, Tangram During the week prior to seminar work with polygons and tangrams: Have students make
Grandfather Tang s Story by Ann Tompert Upper ES / Math Imagination, Transformation, Part and Whole, Polygon, Tangram During the week prior to seminar work with polygons and tangrams: Have students make
Planning Guide. Shape and Space (Transformations) Specific Outcomes 5, 6
 Mathematics Planning Guide Grade 4 Transformations Shape and Space (Transformations) Specific Outcomes 5, 6 This Planning Guide can be accessed online at: http://www.learnalberta.ca/content/mepg4/html/pg4_transformations/index.html
Mathematics Planning Guide Grade 4 Transformations Shape and Space (Transformations) Specific Outcomes 5, 6 This Planning Guide can be accessed online at: http://www.learnalberta.ca/content/mepg4/html/pg4_transformations/index.html
GRADE 1 SUPPLEMENT. Set A8 Number & Operations: Ordinal Numbers. Includes. Skills & Concepts
 GRADE 1 SUPPLEMENT Set A8 Number & Operations: Ordinal Numbers Includes Activity 1: The Train Station A8.1 Activity 2: Ten Cubes in a Box A8.5 Activity 3: Numeral Card Shuffle A8.9 Independent Worksheet
GRADE 1 SUPPLEMENT Set A8 Number & Operations: Ordinal Numbers Includes Activity 1: The Train Station A8.1 Activity 2: Ten Cubes in a Box A8.5 Activity 3: Numeral Card Shuffle A8.9 Independent Worksheet
6 th Grade Math. Skills and Knowledge: Division of Fractions Division of Fractions
 Title DESK L e s s o n Author / Source Submitted by Objectives What will students know and be able to do at the end of this lesson? Description Course: Davis Essential: 6 th Grade Math Number Sense/Fractions
Title DESK L e s s o n Author / Source Submitted by Objectives What will students know and be able to do at the end of this lesson? Description Course: Davis Essential: 6 th Grade Math Number Sense/Fractions
Standard 4.G.1 4.G.2 5.G.3 5.G.4 4.MD.5
 Draw and identify lines and angles, as well as classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles (Standards 4.G.1 3). Standard 4.G.1 Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute,
Draw and identify lines and angles, as well as classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles (Standards 4.G.1 3). Standard 4.G.1 Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute,
Shapes. Practice. Family Note. Unit. show 3-sided, 4-sided, 5-sided, and 6-sided shapes. Ask an adult for permission first. Add.
 Home Link 8-1 Shapes In this lesson children examined different shapes, such as triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and hexagons. They also discussed these shapes attributes or characteristics such as
Home Link 8-1 Shapes In this lesson children examined different shapes, such as triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and hexagons. They also discussed these shapes attributes or characteristics such as
Measuring in Centimeters
 MD2-3 Measuring in Centimeters Pages 179 181 Standards: 2.MD.A.1 Goals: Students will measure pictures of objects in centimeters using centimeter cubes and then a centimeter ruler. Prior Knowledge Required:
MD2-3 Measuring in Centimeters Pages 179 181 Standards: 2.MD.A.1 Goals: Students will measure pictures of objects in centimeters using centimeter cubes and then a centimeter ruler. Prior Knowledge Required:
Unit 5: Fractions Approximate Time Frame: 6-8 weeks Connections to Previous Learning: Focus of the Unit:
 Approximate Time Frame: 6-8 weeks Connections to Previous Learning: Grade 2 students have partitioned circles and rectangles into two, three, or four equal shares. They have used fractional language such
Approximate Time Frame: 6-8 weeks Connections to Previous Learning: Grade 2 students have partitioned circles and rectangles into two, three, or four equal shares. They have used fractional language such
E D C B A. divides rectangle into eight equal sections represents commonly used fractions within a rectangle
 Stage 2 - Assessment Rich Task Outcomes: NS2.4 Models, compares and represents commonly used fractions and decimals, adds and subtracts decimals to two decimal places, and interprets everyday percentages
Stage 2 - Assessment Rich Task Outcomes: NS2.4 Models, compares and represents commonly used fractions and decimals, adds and subtracts decimals to two decimal places, and interprets everyday percentages
8/22/2013 3:30:59 PM Adapted from UbD Framework Priority Standards Supporting Standards Additional Standards Page 1
 Approximate Time Frame: 6-8 weeks Connections to Previous Learning: Grade 2 students have partitioned circles and rectangles into two, three, or four equal shares. They have used fractional language such
Approximate Time Frame: 6-8 weeks Connections to Previous Learning: Grade 2 students have partitioned circles and rectangles into two, three, or four equal shares. They have used fractional language such
Go to Grade 3 Everyday Mathematics Sample Lesson
 McGraw-Hill makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy of any information contained in this McGraw-Hill Material, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular
McGraw-Hill makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy of any information contained in this McGraw-Hill Material, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular
Lesson 69 Putting shapes together
 Lesson 69 Putting Learning objectives Children will: fit 2D over larger 2D. compose 2D to make larger. copy a model composed of 3D objects. Australian Curriculum Content Descriptions Measurement and Geometry
Lesson 69 Putting Learning objectives Children will: fit 2D over larger 2D. compose 2D to make larger. copy a model composed of 3D objects. Australian Curriculum Content Descriptions Measurement and Geometry
MATH K-1 Common Core Assessments
 MATH K-1 Common Core Assessments Kindergarten/Grade 1 INTRODUCTION SHAPES KINDERGARTEN Describe and Compare Measurable Attributes Introduction to Shapes The assessments associated with the shape progression
MATH K-1 Common Core Assessments Kindergarten/Grade 1 INTRODUCTION SHAPES KINDERGARTEN Describe and Compare Measurable Attributes Introduction to Shapes The assessments associated with the shape progression
Games for Young Mathematicians Shape Card Games
 ABOUT THE MATH If you watch and listen to how students interact with the games, you can learn a lot about what they know and what they re ready to learn. Once you see what they can do, you can help them
ABOUT THE MATH If you watch and listen to how students interact with the games, you can learn a lot about what they know and what they re ready to learn. Once you see what they can do, you can help them
4 th Grade Mathematics Instructional Week 30 Geometry Concepts Paced Standards: 4.G.1: Identify, describe, and draw parallelograms, rhombuses, and
 4 th Grade Mathematics Instructional Week 30 Geometry Concepts Paced Standards: 4.G.1: Identify, describe, and draw parallelograms, rhombuses, and trapezoids using appropriate tools (e.g., ruler, straightedge
4 th Grade Mathematics Instructional Week 30 Geometry Concepts Paced Standards: 4.G.1: Identify, describe, and draw parallelograms, rhombuses, and trapezoids using appropriate tools (e.g., ruler, straightedge
Lesson 5: Area of Composite Shape Subject: Math Unit: Area Time needed: 60 minutes Grade: 6 th Date: 2 nd
 Lesson 5: Area of Composite Shape Subject: Math Unit: Area Time needed: 60 minutes Grade: 6 th Date: 2 nd Materials, Texts Needed, or advanced preparation: Lap tops or computer with Geogebra if possible
Lesson 5: Area of Composite Shape Subject: Math Unit: Area Time needed: 60 minutes Grade: 6 th Date: 2 nd Materials, Texts Needed, or advanced preparation: Lap tops or computer with Geogebra if possible
Grade: 3 Lesson Title: Equivalent Fractions
 Targeted Content Standard(s): Grade: 3 Lesson Title: Equivalent Fractions 3.NF.3 Explain equivalence of fractions in special cases and compare fractions by reasoning about their size. a. Understand two
Targeted Content Standard(s): Grade: 3 Lesson Title: Equivalent Fractions 3.NF.3 Explain equivalence of fractions in special cases and compare fractions by reasoning about their size. a. Understand two
PRACTICE TASK: Tangram Challenge Approximately 1 day
 Kindergarten Mathematics Unit 1 PRACTICE TASK: Tangram Challenge Approximately 1 day STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL CONTENT MCC.K.G.5. Model shapes in the world by building shapes from components (e.g., sticks
Kindergarten Mathematics Unit 1 PRACTICE TASK: Tangram Challenge Approximately 1 day STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL CONTENT MCC.K.G.5. Model shapes in the world by building shapes from components (e.g., sticks
A Shower of Shapes. Exemplars. Exemplars
 A Shower of Shapes Fold, and cut a 4-inch square of paper into 4 rectangles that are the same size and shape, and 4 triangles that are the same size and shape. Tell how you did this. Then arrange the pieces
A Shower of Shapes Fold, and cut a 4-inch square of paper into 4 rectangles that are the same size and shape, and 4 triangles that are the same size and shape. Tell how you did this. Then arrange the pieces
122 Taking Shape: Activities to Develop Geometric and Spatial Thinking, Grades K 2 P
 Game Rules The object of the game is to work together to completely cover each of the 6 hexagons with pattern blocks, according to the cards chosen. The game ends when all 6 hexagons are completely covered.
Game Rules The object of the game is to work together to completely cover each of the 6 hexagons with pattern blocks, according to the cards chosen. The game ends when all 6 hexagons are completely covered.
PRACTICE TASK: Tangram Challenge
 PRACTICE TASK: Tangram Challenge Approximately 1 day Back To Task Table STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL CONTENT MGSEK.G.5 Model shapes in the world by building shapes from components (e.g., sticks and clay
PRACTICE TASK: Tangram Challenge Approximately 1 day Back To Task Table STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL CONTENT MGSEK.G.5 Model shapes in the world by building shapes from components (e.g., sticks and clay
Rational Number Project
 Rational Number Project Initial Fraction Ideas Lesson : Overview Students use fraction circles to order fractions by comparing them to one-half. Materials Fraction Circles for students and teacher Student
Rational Number Project Initial Fraction Ideas Lesson : Overview Students use fraction circles to order fractions by comparing them to one-half. Materials Fraction Circles for students and teacher Student
Looking for Pythagoras An Investigation of the Pythagorean Theorem
 Looking for Pythagoras An Investigation of the Pythagorean Theorem I2t2 2006 Stephen Walczyk Grade 8 7-Day Unit Plan Tools Used: Overhead Projector Overhead markers TI-83 Graphing Calculator (& class set)
Looking for Pythagoras An Investigation of the Pythagorean Theorem I2t2 2006 Stephen Walczyk Grade 8 7-Day Unit Plan Tools Used: Overhead Projector Overhead markers TI-83 Graphing Calculator (& class set)
Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary. Correlations
 Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary Correlations Saxon Math Program Page Math K 2 Math 1 8 Math 2 14 California Math K 21 California Math 1 27 California Math 2 33 1 Saxon Math Manipulatives in
Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary Correlations Saxon Math Program Page Math K 2 Math 1 8 Math 2 14 California Math K 21 California Math 1 27 California Math 2 33 1 Saxon Math Manipulatives in
GRADE 1 SUPPLEMENT. December Calendar Pattern C4.1
 GRADE 1 SUPPLEMENT Set C4 Geometry: Symmetry Calendar Pattern Includes December Calendar Pattern C4.1 Skills & Concepts H recognize and create shapes that are congruent or have symmetry H identify a line
GRADE 1 SUPPLEMENT Set C4 Geometry: Symmetry Calendar Pattern Includes December Calendar Pattern C4.1 Skills & Concepts H recognize and create shapes that are congruent or have symmetry H identify a line
holiday math activities
 holiday math activities Materials: Stocking template ( attached) Part/Part/Whole (Three part) Mats (attached) Counters Scissors and Glue Math Concept: Compose and decompose a number as two parts using
holiday math activities Materials: Stocking template ( attached) Part/Part/Whole (Three part) Mats (attached) Counters Scissors and Glue Math Concept: Compose and decompose a number as two parts using
Grade 3, Module 5: Fractions as Number on the Number Line Mission: Fractions as Numbers
 Grade 3, Module 5: Fractions as Number on the Number Line Mission: Fractions as Numbers Lessons Table of Contents Lessons... 2-41 Topic A: Partitioning a Whole into Equal Parts... 2 Topic B: Unit Fractions
Grade 3, Module 5: Fractions as Number on the Number Line Mission: Fractions as Numbers Lessons Table of Contents Lessons... 2-41 Topic A: Partitioning a Whole into Equal Parts... 2 Topic B: Unit Fractions
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important. You see geometric figures all around you.
 You see geometric figures all around you. Look at these pictures. Identify a figure. What would you need to know to find the area of that figure? What would you need to know to find the perimeter of the
You see geometric figures all around you. Look at these pictures. Identify a figure. What would you need to know to find the area of that figure? What would you need to know to find the perimeter of the
Thinking Kids. First Grade. NCTM Strands Covered: Number and Operations. Algebra. Geometry. Measurement. Data Analysis and Probability.
 Thinking Kids First Grade NCTM Strands Covered: Number and Operations Algebra Geometry Measurement Data Analysis and Probability Posttest How to Use This Assessment This Posttest assesses your students
Thinking Kids First Grade NCTM Strands Covered: Number and Operations Algebra Geometry Measurement Data Analysis and Probability Posttest How to Use This Assessment This Posttest assesses your students
I've Seen That Shape Before Lesson Plan
 I've Seen That Shape Before Lesson Plan I) Overview II) Conducting the Lesson III) Teacher to Teacher IV) Handouts I. OVERVIEW Lesson Summary Students learn the names and explore properties of solid geometric
I've Seen That Shape Before Lesson Plan I) Overview II) Conducting the Lesson III) Teacher to Teacher IV) Handouts I. OVERVIEW Lesson Summary Students learn the names and explore properties of solid geometric
Grade 2 Arkansas Mathematics Standards. Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction
 Grade 2 Arkansas Mathematics Standards Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction AR.Math.Content.2.OA.A.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100
Grade 2 Arkansas Mathematics Standards Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction AR.Math.Content.2.OA.A.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100
Performance Assessment Task Quilt Making Grade 4. Common Core State Standards Math - Content Standards
 Performance Assessment Task Quilt Making Grade 4 The task challenges a student to demonstrate understanding of concepts of 2-dimensional shapes and ir properties. A student must be able to use characteristics,
Performance Assessment Task Quilt Making Grade 4 The task challenges a student to demonstrate understanding of concepts of 2-dimensional shapes and ir properties. A student must be able to use characteristics,
Shape, space and measures 4
 Shape, space and measures 4 contents There are three lessons in this unit, Shape, space and measures 4. S4.1 Rotation and rotation symmetry 3 S4.2 Reflection and line symmetry 6 S4.3 Problem solving 9
Shape, space and measures 4 contents There are three lessons in this unit, Shape, space and measures 4. S4.1 Rotation and rotation symmetry 3 S4.2 Reflection and line symmetry 6 S4.3 Problem solving 9
Objective: Draw polygons with specified attributes to solve problems. (3 minutes) (5 minutes) (60 minutes)
 Lesson 6 3 7 Lesson 6 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (8 minutes) (30 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Lesson 6 3 7 Lesson 6 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (8 minutes) (30 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Progressions for the Common Core State Standards in Mathematics
 Progressions for the Common Core State Standards in Mathematics c Common Core Standards Writing Team 8 The Progressions are published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license For information
Progressions for the Common Core State Standards in Mathematics c Common Core Standards Writing Team 8 The Progressions are published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license For information
The Tangram- A Chinese Puzzle
 1 The Tangram- A Chinese Puzzle A mini lesson plan for Chinese tangrams. By Stephanie Harrington for WWW.HIPHOMESCHOOLMOMS Lesson Objectives: To expose children to story telling with Tangrams. To introduce
1 The Tangram- A Chinese Puzzle A mini lesson plan for Chinese tangrams. By Stephanie Harrington for WWW.HIPHOMESCHOOLMOMS Lesson Objectives: To expose children to story telling with Tangrams. To introduce
Second Grade Mathematics Goals
 Second Grade Mathematics Goals Operations & Algebraic Thinking 2.OA.1 within 100 to solve one- and twostep word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart,
Second Grade Mathematics Goals Operations & Algebraic Thinking 2.OA.1 within 100 to solve one- and twostep word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart,
Objective: Draw rectangles and rhombuses to clarify their attributes, and define rectangles and rhombuses based on those attributes.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 18 5 5 Lesson 18 Objective: Draw rectangles and rhombuses to clarify their attributes, and define Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 18 5 5 Lesson 18 Objective: Draw rectangles and rhombuses to clarify their attributes, and define Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem
Thinking Kids. Second Grade. NCTM Strands Covered: Number and Operations. Algebra. Geometry. Measurement. Data Analysis and Probability.
 Thinking Kids Second Grade NCTM Strands Covered: Number and Operations Algebra Geometry Measurement Data Analysis and Probability Posttest 2.2 2.3 to another 6 5 4 3 2 1 N W E S How to Use This Assessment
Thinking Kids Second Grade NCTM Strands Covered: Number and Operations Algebra Geometry Measurement Data Analysis and Probability Posttest 2.2 2.3 to another 6 5 4 3 2 1 N W E S How to Use This Assessment
ARTS IMPACT ARTS-INFUSED INSTITUTE LESSON PLAN (YR2-AEMDD) LESSON TITLE: Locations and Transformations: Polygon Collages Visual Art and Math Lesson
 S IMPACT S-INFUSED INSTITUTE LESSON PLAN (YR2-AEMDD) LESSON TITLE: Locations and Transformations: Polygon Collages Visual Art and Math Lesson Artist-Mentor Meredith Essex Grade Level: Fifth Grade Enduring
S IMPACT S-INFUSED INSTITUTE LESSON PLAN (YR2-AEMDD) LESSON TITLE: Locations and Transformations: Polygon Collages Visual Art and Math Lesson Artist-Mentor Meredith Essex Grade Level: Fifth Grade Enduring
Content Area: Mathematics- 3 rd Grade
 Unit: Operations and Algebraic Thinking Topic: Multiplication and Division Strategies Multiplication is grouping objects into sets which is a repeated form of addition. What are the different meanings
Unit: Operations and Algebraic Thinking Topic: Multiplication and Division Strategies Multiplication is grouping objects into sets which is a repeated form of addition. What are the different meanings
Mouse House Riverdeep Interactive Learning Limited
 Mouse House I Spy Shapes Language s Review the characteristics of each geometric shape with your class: A triangle has three sides; a square has four equal sides, etc. Describe an object in the room to
Mouse House I Spy Shapes Language s Review the characteristics of each geometric shape with your class: A triangle has three sides; a square has four equal sides, etc. Describe an object in the room to
Essentials. Week by. Week
 Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials 9 4 23 3 2 Nifty Numbers Prepare a deck of cards with sets and numbers. See Blackline Masters. Play concentration, matching set and numeral. Look And See (.0g) Have
Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials 9 4 23 3 2 Nifty Numbers Prepare a deck of cards with sets and numbers. See Blackline Masters. Play concentration, matching set and numeral. Look And See (.0g) Have
Developing geometric thinking. A developmental series of classroom activities for Gr. 1-9
 Developing geometric thinking A developmental series of classroom activities for Gr. 1-9 Developing geometric thinking ii Contents Van Hiele: Developing Geometric Thinking... 1 Sorting objects using Geostacks...
Developing geometric thinking A developmental series of classroom activities for Gr. 1-9 Developing geometric thinking ii Contents Van Hiele: Developing Geometric Thinking... 1 Sorting objects using Geostacks...
Each diagram below is divided into equal sections. Shade three-quarters of each diagram. 2 marks. Page 1 of 27
 1 Each diagram below is divided into equal sections. Shade three-quarters of each diagram. 2 marks Page 1 of 27 2 Here are 21 apples. Put a ring around one third of them. Page 2 of 27 3 A line starts at
1 Each diagram below is divided into equal sections. Shade three-quarters of each diagram. 2 marks Page 1 of 27 2 Here are 21 apples. Put a ring around one third of them. Page 2 of 27 3 A line starts at
