Fun, Games, and AI. Conway's Game of Life. TSP Competition. Conway's Game of Life
|
|
|
- Audra Sanders
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
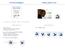
1 TSP Competition Fun, Games, and AI 1. Morgan Ong Zhihong Zu. 17, Mitchell Namias. 17, Smallest insertion Nearest insertion Best so far. Jeff Bagdis, Spring ' Introduction to Computer Science Sedgewick and Wayne Copyright Conway's Game of Life Conway's Game of Life Conway's game of life. Critters live and die in an infinite square grid. Time proceeds in discrete steps. Survival. Critter lives and dies depending on 8 neighbors: Too few? (0-1) die of loneliness just right? (2-3) survive to next generation too many? (4-8) die of overcrowding Birth. Critter born if exactly 3 neighbors. death birth John Conway hacker's emblem time t time t+1 3 4
2 Conway's Game of Life Conway's Game of Life Glider. Propagates a signal. Gosper glider gun. Generates gliders. time t time t+1 time t+2 time t+3 time t What Could This Be? Weak AI Can a machine appear intelligent? 7 8
3 Artificial Intelligence The Chess-Playing Turk Goal. [Turing 1950] Program computer to exhibit intelligent behavior. Every aspect of learning or any other feature of intelligence can in principle be so precisely described that a machine can be made to simulate it. J. McCarthy * s. Very optimistic predictions. Reality. Slow progress with some striking successes Tic-Tac-Toe Tic-Tac-Toe Tic tac toe. Two person game of skill. Minimax algorithm. Tic-tac-toe is solved. X will never lose; O will never lose. Number of possible games 255,168. assuming optimal play by X 11 12
4 Chess Kasparaov vs. Deep Blue Challenge. [Claude Shannon] Develop a computer program to play chess. Deep Blue. [IBM] Supercomputer, augmented by VLSI chess chips. 200 million board positions per second. Machine beats man. [February 1996] First computer program to win a chess game against reigning world champion. Number of possible games N-by-N version. EXPTIME-complete. 13 Chess 14 Checkers (Draughts) Number of possible games N-by-N version. EXPTIME-complete. Once again, man beats machine! 15 16
5 Checkers (Draughts) Backgammon Chinook. [Jon Schaeffer] Computer program for checkers. Backgammon. Two-player game of skill and luck. Man vs. machine. Chinook awarded world championship in 1994 after 6 draws with Marion Tinsley (who withdrew). TD gammon. [Gerry Tesauro 1980s] Program was given no expert backgammon knowledge. Learned strategy by playing itself 300,000 times. Among best backgammon players in the world. Checkers is solved! [Science, September 2007] Proof that black will never lose with optimal play. Proof that white will never lose with optimal play Poker Turing Test Poker. Multi-player game of skill and luck. Can a machine appear intelligent? If so, how could we tell? Poker bots. Not currently competitive with pros
6 Turing Test Eliza Judge types questions to both. Computer claims to be human. So does human. Eliza. [Weizenbaum 1966] Program imitates Rogerian psychiatrist. Works by generating scripted responses to keywords. Just 200 lines of code! Q. Does Eliza appear intelligent? A. You be the judge: Pass. If judge cannot tell which entity is human, we say computer has passed the test and is "intelligent." Prediction. [Turing] Computer would pass test by Eliza Pattern Matching Rules Parry key: perhaps decomp: * reasmb: You don't seem quite certain. reasmb: Why the uncertain tone? reasmb: Can't you be more positive? reasmb: You aren't sure? reasmb: Don't you know? Parry. [Colby 1972] Program imitates a paranoid schizophrenic. Q. What happens when Parry "meets" Eliza? A. You be the judge: key: francais decomp: * reasmb: goto xforeign reasmb: I told you before, I don't understand French. key: sorry decomp: * reasmb: Please don't apologise. reasmb: Apologies are not necessary. reasmb: I've told you that apologies are not required. key: apologise decomp: * reasmb: goto sorry 23 24
7 Turing Test Loebner Contest Dialogs Loebner Prize $100,000 to first program to pass restricted Turing Test. Annual competition held since Small awards given to best programs. Hello, Judge. My name is Ella. Please tell me your first name, or whatever I should call you." Call me Lisa. Am I male or female? Okay, I will call you 'Lisa. Am I Male Or Female?' I am here recently from Tainjin, China, so please be patient with me. I'm not a patient because I am not ill. Are you feeling well today? What do you think it means that you are not ill? Have you ever been ill? 'Have you ever been ill?' you say? That's it, Lisa Am I Male Or Female! I will schedule a whipping for you." Loebner Contest Dialogs Loebner Contest Dialogs "What do you think of Reading?" "I'm somewhat crazy about reading. I like to read mystery novels." "I meant the town." "Jones lives in the city and is a writer of children's books." "Does Jones live in Reading, then?" "Tomorrow is another day. We can only live today well." "Do you live, then?" "I live then a lot. Someday we will live on another planet." "I think you are already there." "What is it?" "What is what?" "A high-yield, perennial, four-lobed hybrid of wheat and rye whose root grain, triticale, can trace its ancestry to twentieth-century Canada." "At last. Another classic grain freak." "Lewis. Jim Lewis. Would you like for me to show you some poetry?" "No, thanks." "I didn't want to show you the stupid poetry anyway." 27 28
8 Knowledge Databases Twenty questions. Strong AI Question answering system. Can a machine be intelligent? Chinese Room Experiment (Searle 1980) Chinese Room Experiment (Searle 1980) Imagine that: You don't understand Chinese. You're alone in a room that has paper slots labeled "input" and "output". You have a big book of Chinese writing. You have English instructions (no translations) that tell you what to write on your output paper in response to various inputs. And then: Chinese speakers outside the room pass in pieces of paper with Chinese writing. They know these are questions (but you don't). You consult your manual of instructions, figure out the proper Chinese response, copy it down, and pass it out
9 Chinese Room Experiment (Searle 1980) Chinese Room Experiment Q. The folks outside think you understand Chinese. Do you? Q. If a computer did the same, would it understand Chinese? Weak AI. Can machines be programmed to exhibit intelligent behavior? A. Surely true: Deep Blue, Chinook, TD-Gammon, others. Strong AI. Can machines can be programmed to possess intelligence? Searle. Chinese Room is absolute refutation of strong AI. But many disagree! The question of whether a computer can think is no more interesting than the question of whether a submarine can swim. Edsger Dijkstra Is (Strong) AI Ultimately Possible? Reverse Turing Test Just as the Wright brothers at Kitty Hawk in 1903 were on the right track to the 747, so too is AI, with its attempts to formalize commonsense understanding, on its way to fully intelligent machines. Patrick Winston Believing that writing these types of programs will bring us closer to real artificial intelligence is like believing that someone climbing a tree is making progress toward reaching the moon. Hubert Dreyfus The brain happens to be a meat machine. Marvin Minsky, *54 Either artificial intelligence is possible...or we're not. Herb Simon 35 36
10 "Reverse" Turing Test Exploiting Intractability: Captcha's Standard Turing test. Judge is human. OCR. Given degraded text, find original text. Reverse Turing test. Judge is computer! CAPTCHA. [completely automated public Turing test to tell computers and humans apart] Why? Google allows each user 7GB storage. PayPal once offered $5 for each user who opens a new account. Both need to distinguish real humans from bots DARPA Grand Challenge DARPA Grand Challenge 2004 Grand Challenge. Navigate an autonomous vehicle through 142 mile course in Mohave Desert at military speed. Results. No team finished; CMU team finished 7.36 miles. Prospect Eleven Princeton team 39 40
11 DARPA Grand Challenge DARPA Grand Challenge 2005 Grand Challenge. Navigate an autonomous vehicle through 132 mile course in Mohave Desert at military speed Urban Challenge. Navigate an autonomous vehicle through 60 mile course in mock urban environment, obeying traffic laws and avoiding other vehicles. Results. Stanford team won in under 7 hours; $2 million prize. Stanley 41 42
Conway's Game of Life. Artificial Intelligence. Conway's Game of Life. Conway's Game of Life
 Artificial Intelligence Conway's Game of Life John Conway hacker's emblem Introduction to Computer Science Sedgewick and Wayne Copyright 2007 http://www.cs.princeton.edu/introcs 2 Conway's Game of Life
Artificial Intelligence Conway's Game of Life John Conway hacker's emblem Introduction to Computer Science Sedgewick and Wayne Copyright 2007 http://www.cs.princeton.edu/introcs 2 Conway's Game of Life
Artificial Intelligence. Conway's Game of Life. Conway's Game of Life
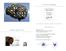 Artificial Intelligence Introduction to Computer Science Sedgewick and Wayne Copyright 2007 http://www.cs.princeton.edu/introcs Conway's Game of Life Conway's Game of Life Conway's game of life. Critters
Artificial Intelligence Introduction to Computer Science Sedgewick and Wayne Copyright 2007 http://www.cs.princeton.edu/introcs Conway's Game of Life Conway's Game of Life Conway's game of life. Critters
Final Lecture: Fun, mainly
 Today s Plan Final Lecture: Fun, mainly Minesweeper Conway s Game of Life The Busy-Beaver function Eliza The Turing Test: Can a machine be intelligent? The Chinese Room: Maybe not. A Story about a Barometer
Today s Plan Final Lecture: Fun, mainly Minesweeper Conway s Game of Life The Busy-Beaver function Eliza The Turing Test: Can a machine be intelligent? The Chinese Room: Maybe not. A Story about a Barometer
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #37: AI and Future of CS Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112 Acknowledgements:
CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #37: AI and Future of CS Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112 Acknowledgements:
4/20/12. Weak AI. CS 112 Introduction to Programming. Lecture #37: AI and Future of CS. Artificial Intelligence. (Spring 2012) Zhong Shao
 4/20/12 Artificial Intelligence CS 112 Introduction to Programming Fundamental questions. Is real life described by discrete rules, or not? Can we build a intelligent computer from living components? Can
4/20/12 Artificial Intelligence CS 112 Introduction to Programming Fundamental questions. Is real life described by discrete rules, or not? Can we build a intelligent computer from living components? Can
Overview. Origins. Idea of programming computers for "intelligent" behavior. First suggested by Alan Turing, 1950.
 Lecture S2: Artificial Intelligence Lecture S2: Artificial Intelligence Overview Origins A whirlwind tour of Artificial Intelligence. Idea of programming computers for "intelligent" behavior. First suggested
Lecture S2: Artificial Intelligence Lecture S2: Artificial Intelligence Overview Origins A whirlwind tour of Artificial Intelligence. Idea of programming computers for "intelligent" behavior. First suggested
Game Playing. Garry Kasparov and Deep Blue. 1997, GM Gabriel Schwartzman's Chess Camera, courtesy IBM.
 Game Playing Garry Kasparov and Deep Blue. 1997, GM Gabriel Schwartzman's Chess Camera, courtesy IBM. Game Playing In most tree search scenarios, we have assumed the situation is not going to change whilst
Game Playing Garry Kasparov and Deep Blue. 1997, GM Gabriel Schwartzman's Chess Camera, courtesy IBM. Game Playing In most tree search scenarios, we have assumed the situation is not going to change whilst
April 25, Competing and cooperating with AI. Pantelis P. Analytis. Human behavior in Chess. Competing with AI. Cooperative machines?
 April 25, 2018 1 / 47 1 2 3 4 5 6 2 / 47 The case of chess 3 / 47 chess The first stage was the orientation phase, in which the subject assessed the situation determined a very general idea of what to
April 25, 2018 1 / 47 1 2 3 4 5 6 2 / 47 The case of chess 3 / 47 chess The first stage was the orientation phase, in which the subject assessed the situation determined a very general idea of what to
Foundations of AI. 6. Adversarial Search. Search Strategies for Games, Games with Chance, State of the Art. Wolfram Burgard & Bernhard Nebel
 Foundations of AI 6. Adversarial Search Search Strategies for Games, Games with Chance, State of the Art Wolfram Burgard & Bernhard Nebel Contents Game Theory Board Games Minimax Search Alpha-Beta Search
Foundations of AI 6. Adversarial Search Search Strategies for Games, Games with Chance, State of the Art Wolfram Burgard & Bernhard Nebel Contents Game Theory Board Games Minimax Search Alpha-Beta Search
UNIT 13A AI: Games & Search Strategies. Announcements
 UNIT 13A AI: Games & Search Strategies 1 Announcements Do not forget to nominate your favorite CA bu emailing gkesden@gmail.com, No lecture on Friday, no recitation on Thursday No office hours Wednesday,
UNIT 13A AI: Games & Search Strategies 1 Announcements Do not forget to nominate your favorite CA bu emailing gkesden@gmail.com, No lecture on Friday, no recitation on Thursday No office hours Wednesday,
Quick work: Memory allocation
 Quick work: Memory allocation The OS is using a fixed partition algorithm. Processes place requests to the OS in the following sequence: P1=15 KB, P2=5 KB, P3=30 KB Draw the memory map at the end, if each
Quick work: Memory allocation The OS is using a fixed partition algorithm. Processes place requests to the OS in the following sequence: P1=15 KB, P2=5 KB, P3=30 KB Draw the memory map at the end, if each
Dr Rong Qu History of AI
 Dr Rong Qu History of AI AI Originated in 1956, John McCarthy coined the term very successful at early stage Within 10 years a computer will be a chess champion Herbert Simon, 1957 IBM Deep Blue on 11
Dr Rong Qu History of AI AI Originated in 1956, John McCarthy coined the term very successful at early stage Within 10 years a computer will be a chess champion Herbert Simon, 1957 IBM Deep Blue on 11
CS 440 / ECE 448 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Spring 2010 Lecture #5
 CS 440 / ECE 448 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Spring 2010 Lecture #5 Instructor: Eyal Amir Grad TAs: Wen Pu, Yonatan Bisk Undergrad TAs: Sam Johnson, Nikhil Johri Topics Game playing Game trees
CS 440 / ECE 448 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Spring 2010 Lecture #5 Instructor: Eyal Amir Grad TAs: Wen Pu, Yonatan Bisk Undergrad TAs: Sam Johnson, Nikhil Johri Topics Game playing Game trees
Computer Science 1400: Part #8: Where We Are: Artificial Intelligence WHAT IS ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)? AI IN SOCIETY RELATING WITH AI
 Computer Science 1400: Part #8: Where We Are: Artificial Intelligence WHAT IS ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)? AI IN SOCIETY RELATING WITH AI What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? Artificial Intelligence
Computer Science 1400: Part #8: Where We Are: Artificial Intelligence WHAT IS ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)? AI IN SOCIETY RELATING WITH AI What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence. Shobhanjana Kalita Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering Tezpur University
 Artificial Intelligence Shobhanjana Kalita Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering Tezpur University What is AI? What is Intelligence? The ability to acquire and apply knowledge and skills (definition
Artificial Intelligence Shobhanjana Kalita Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering Tezpur University What is AI? What is Intelligence? The ability to acquire and apply knowledge and skills (definition
Foundations of AI. 5. Board Games. Search Strategies for Games, Games with Chance, State of the Art. Wolfram Burgard and Luc De Raedt SA-1
 Foundations of AI 5. Board Games Search Strategies for Games, Games with Chance, State of the Art Wolfram Burgard and Luc De Raedt SA-1 Contents Board Games Minimax Search Alpha-Beta Search Games with
Foundations of AI 5. Board Games Search Strategies for Games, Games with Chance, State of the Art Wolfram Burgard and Luc De Raedt SA-1 Contents Board Games Minimax Search Alpha-Beta Search Games with
Foundations of AI. 6. Board Games. Search Strategies for Games, Games with Chance, State of the Art
 Foundations of AI 6. Board Games Search Strategies for Games, Games with Chance, State of the Art Wolfram Burgard, Andreas Karwath, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller SA-1 Contents Board Games Minimax
Foundations of AI 6. Board Games Search Strategies for Games, Games with Chance, State of the Art Wolfram Burgard, Andreas Karwath, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller SA-1 Contents Board Games Minimax
History and Philosophical Underpinnings
 History and Philosophical Underpinnings Last Class Recap game-theory why normal search won t work minimax algorithm brute-force traversal of game tree for best move alpha-beta pruning how to improve on
History and Philosophical Underpinnings Last Class Recap game-theory why normal search won t work minimax algorithm brute-force traversal of game tree for best move alpha-beta pruning how to improve on
Random Administrivia. In CMC 306 on Monday for LISP lab
 Random Administrivia In CMC 306 on Monday for LISP lab Artificial Intelligence: Introduction What IS artificial intelligence? Examples of intelligent behavior: Definitions of AI There are as many definitions
Random Administrivia In CMC 306 on Monday for LISP lab Artificial Intelligence: Introduction What IS artificial intelligence? Examples of intelligent behavior: Definitions of AI There are as many definitions
Lecture 1 What is AI?
 Lecture 1 What is AI? CSE 473 Artificial Intelligence Oren Etzioni 1 AI as Science What are the most fundamental scientific questions? 2 Goals of this Course To teach you the main ideas of AI. Give you
Lecture 1 What is AI? CSE 473 Artificial Intelligence Oren Etzioni 1 AI as Science What are the most fundamental scientific questions? 2 Goals of this Course To teach you the main ideas of AI. Give you
Adversarial Search (Game Playing)
 Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search (Game Playing) Chapter 5 Adapted from materials by Tim Finin, Marie desjardins, and Charles R. Dyer Outline Game playing State of the art and resources Framework
Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search (Game Playing) Chapter 5 Adapted from materials by Tim Finin, Marie desjardins, and Charles R. Dyer Outline Game playing State of the art and resources Framework
Artificial Intelligence Search III
 Artificial Intelligence Search III Lecture 5 Content: Search III Quick Review on Lecture 4 Why Study Games? Game Playing as Search Special Characteristics of Game Playing Search Ingredients of 2-Person
Artificial Intelligence Search III Lecture 5 Content: Search III Quick Review on Lecture 4 Why Study Games? Game Playing as Search Special Characteristics of Game Playing Search Ingredients of 2-Person
What is Artificial Intelligence? Alternate Definitions (Russell + Norvig) Human intelligence
 CSE 3401: Intro to Artificial Intelligence & Logic Programming Introduction Required Readings: Russell & Norvig Chapters 1 & 2. Lecture slides adapted from those of Fahiem Bacchus. What is AI? What is
CSE 3401: Intro to Artificial Intelligence & Logic Programming Introduction Required Readings: Russell & Norvig Chapters 1 & 2. Lecture slides adapted from those of Fahiem Bacchus. What is AI? What is
Adversarial Search and Game- Playing C H A P T E R 6 C M P T : S P R I N G H A S S A N K H O S R A V I
 Adversarial Search and Game- Playing C H A P T E R 6 C M P T 3 1 0 : S P R I N G 2 0 1 1 H A S S A N K H O S R A V I Adversarial Search Examine the problems that arise when we try to plan ahead in a world
Adversarial Search and Game- Playing C H A P T E R 6 C M P T 3 1 0 : S P R I N G 2 0 1 1 H A S S A N K H O S R A V I Adversarial Search Examine the problems that arise when we try to plan ahead in a world
CS 4700: Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
 CS 4700: Foundations of Artificial Intelligence selman@cs.cornell.edu Module: Adversarial Search R&N: Chapter 5 Part II 1 Outline Game Playing Optimal decisions Minimax α-β pruning Case study: Deep Blue
CS 4700: Foundations of Artificial Intelligence selman@cs.cornell.edu Module: Adversarial Search R&N: Chapter 5 Part II 1 Outline Game Playing Optimal decisions Minimax α-β pruning Case study: Deep Blue
UNIT 13A AI: Games & Search Strategies
 UNIT 13A AI: Games & Search Strategies 1 Artificial Intelligence Branch of computer science that studies the use of computers to perform computational processes normally associated with human intellect
UNIT 13A AI: Games & Search Strategies 1 Artificial Intelligence Branch of computer science that studies the use of computers to perform computational processes normally associated with human intellect
Overview. Pre AI developments. Birth of AI, early successes. Overwhelming optimism underwhelming results
 Help Overview Administrivia History/applications Modeling agents/environments What can we learn from the past? 1 Pre AI developments Philosophy: intelligence can be achieved via mechanical computation
Help Overview Administrivia History/applications Modeling agents/environments What can we learn from the past? 1 Pre AI developments Philosophy: intelligence can be achieved via mechanical computation
What is AI? Robert Platt Northeastern University
 Robert Platt Northeastern University Some material used from: 1. Russell/Norvig, AIMA 2. Stacy Marsella, CS4100 3. Seif El-Nasr, CS4100 4. Amy Hoover, CS4100 Historical perspective: Handbook of AI: the
Robert Platt Northeastern University Some material used from: 1. Russell/Norvig, AIMA 2. Stacy Marsella, CS4100 3. Seif El-Nasr, CS4100 4. Amy Hoover, CS4100 Historical perspective: Handbook of AI: the
Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search
 Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search Adversarial Search Adversarial search problems games They occur in multiagent competitive environments There is an opponent we can t control planning again us!
Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search Adversarial Search Adversarial search problems games They occur in multiagent competitive environments There is an opponent we can t control planning again us!
Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
 Foundations of Artificial Intelligence 6. Board Games Search Strategies for Games, Games with Chance, State of the Art Joschka Boedecker and Wolfram Burgard and Bernhard Nebel Albert-Ludwigs-Universität
Foundations of Artificial Intelligence 6. Board Games Search Strategies for Games, Games with Chance, State of the Art Joschka Boedecker and Wolfram Burgard and Bernhard Nebel Albert-Ludwigs-Universität
What's involved in Intelligence?
 AI Methodology Theoretical aspects Mathematical formalizations, properties, algorithms Engineering aspects The act of building (useful) machines Empirical science Experiments What's involved in Intelligence?
AI Methodology Theoretical aspects Mathematical formalizations, properties, algorithms Engineering aspects The act of building (useful) machines Empirical science Experiments What's involved in Intelligence?
CS 771 Artificial Intelligence. Adversarial Search
 CS 771 Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search Typical assumptions Two agents whose actions alternate Utility values for each agent are the opposite of the other This creates the adversarial situation
CS 771 Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search Typical assumptions Two agents whose actions alternate Utility values for each agent are the opposite of the other This creates the adversarial situation
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search Instructor: Stuart Russell University of California, Berkeley Game Playing State-of-the-Art Checkers: 1950: First computer player. 1959: Samuel s self-taught
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search Instructor: Stuart Russell University of California, Berkeley Game Playing State-of-the-Art Checkers: 1950: First computer player. 1959: Samuel s self-taught
Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
 Foundations of Artificial Intelligence 6. Board Games Search Strategies for Games, Games with Chance, State of the Art Joschka Boedecker and Wolfram Burgard and Frank Hutter and Bernhard Nebel Albert-Ludwigs-Universität
Foundations of Artificial Intelligence 6. Board Games Search Strategies for Games, Games with Chance, State of the Art Joschka Boedecker and Wolfram Burgard and Frank Hutter and Bernhard Nebel Albert-Ludwigs-Universität
What is AI? AI is the reproduction of human reasoning and intelligent behavior by computational methods. an attempt of. Intelligent behavior Computer
 What is AI? an attempt of AI is the reproduction of human reasoning and intelligent behavior by computational methods Intelligent behavior Computer Humans 1 What is AI? (R&N) Discipline that systematizes
What is AI? an attempt of AI is the reproduction of human reasoning and intelligent behavior by computational methods Intelligent behavior Computer Humans 1 What is AI? (R&N) Discipline that systematizes
Artificial Intelligence CS365. Amitabha Mukerjee
 Artificial Intelligence CS365 Amitabha Mukerjee What is intelligence Acting humanly: Turing Test Turing (1950) "Computing machinery and intelligence": "Can machines think?" Imitation Game Acting humanly:
Artificial Intelligence CS365 Amitabha Mukerjee What is intelligence Acting humanly: Turing Test Turing (1950) "Computing machinery and intelligence": "Can machines think?" Imitation Game Acting humanly:
Unit 8: Problems of Common Sense
 Unit 8: Problems of Common Sense AI is brain-dead Can a machine have intelligence? Difficulty of Endowing Common Sense to Computers Philosophical Objections Strong vs. Weak AI Reference copyright c 2013
Unit 8: Problems of Common Sense AI is brain-dead Can a machine have intelligence? Difficulty of Endowing Common Sense to Computers Philosophical Objections Strong vs. Weak AI Reference copyright c 2013
Adversarial Search Aka Games
 Adversarial Search Aka Games Chapter 5 Some material adopted from notes by Charles R. Dyer, U of Wisconsin-Madison Overview Game playing State of the art and resources Framework Game trees Minimax Alpha-beta
Adversarial Search Aka Games Chapter 5 Some material adopted from notes by Charles R. Dyer, U of Wisconsin-Madison Overview Game playing State of the art and resources Framework Game trees Minimax Alpha-beta
Game Playing. Philipp Koehn. 29 September 2015
 Game Playing Philipp Koehn 29 September 2015 Outline 1 Games Perfect play minimax decisions α β pruning Resource limits and approximate evaluation Games of chance Games of imperfect information 2 games
Game Playing Philipp Koehn 29 September 2015 Outline 1 Games Perfect play minimax decisions α β pruning Resource limits and approximate evaluation Games of chance Games of imperfect information 2 games
V. Adamchik Data Structures. Game Trees. Lecture 1. Apr. 05, Plan: 1. Introduction. 2. Game of NIM. 3. Minimax
 Game Trees Lecture 1 Apr. 05, 2005 Plan: 1. Introduction 2. Game of NIM 3. Minimax V. Adamchik 2 ü Introduction The search problems we have studied so far assume that the situation is not going to change.
Game Trees Lecture 1 Apr. 05, 2005 Plan: 1. Introduction 2. Game of NIM 3. Minimax V. Adamchik 2 ü Introduction The search problems we have studied so far assume that the situation is not going to change.
What's involved in Intelligence?
 AI Methodology Theoretical aspects Mathematical formalizations, properties, algorithms Engineering aspects The act of building (useful) machines Empirical science Experiments What's involved in Intelligence?
AI Methodology Theoretical aspects Mathematical formalizations, properties, algorithms Engineering aspects The act of building (useful) machines Empirical science Experiments What's involved in Intelligence?
Lecture 1 What is AI? EECS 348 Intro to Artificial Intelligence Doug Downey
 Lecture 1 What is AI? EECS 348 Intro to Artificial Intelligence Doug Downey Outline 1) What is AI: The Course 2) What is AI: The Field 3) Why to take the class (or not) 4) A Brief History of AI 5) Predict
Lecture 1 What is AI? EECS 348 Intro to Artificial Intelligence Doug Downey Outline 1) What is AI: The Course 2) What is AI: The Field 3) Why to take the class (or not) 4) A Brief History of AI 5) Predict
Contents. Foundations of Artificial Intelligence. Problems. Why Board Games?
 Contents Foundations of Artificial Intelligence 6. Board Games Search Strategies for Games, Games with Chance, State of the Art Wolfram Burgard, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller Albert-Ludwigs-Universität
Contents Foundations of Artificial Intelligence 6. Board Games Search Strategies for Games, Games with Chance, State of the Art Wolfram Burgard, Bernhard Nebel, and Martin Riedmiller Albert-Ludwigs-Universität
Adversarial search (game playing)
 Adversarial search (game playing) References Russell and Norvig, Artificial Intelligence: A modern approach, 2nd ed. Prentice Hall, 2003 Nilsson, Artificial intelligence: A New synthesis. McGraw Hill,
Adversarial search (game playing) References Russell and Norvig, Artificial Intelligence: A modern approach, 2nd ed. Prentice Hall, 2003 Nilsson, Artificial intelligence: A New synthesis. McGraw Hill,
Introduction and History of AI
 15-780 Introduction and History of AI J. Zico Kolter January 13, 2014 1 What is AI? 2 Some classic definitions Buildings computers that... Think like humans Act like humans Think rationally Act rationally
15-780 Introduction and History of AI J. Zico Kolter January 13, 2014 1 What is AI? 2 Some classic definitions Buildings computers that... Think like humans Act like humans Think rationally Act rationally
Programming Project 1: Pacman (Due )
 Programming Project 1: Pacman (Due 8.2.18) Registration to the exams 521495A: Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search (Min-Max) Lectured by Abdenour Hadid Adjunct Professor, CMVS, University of Oulu
Programming Project 1: Pacman (Due 8.2.18) Registration to the exams 521495A: Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search (Min-Max) Lectured by Abdenour Hadid Adjunct Professor, CMVS, University of Oulu
CPS331 Lecture: Search in Games last revised 2/16/10
 CPS331 Lecture: Search in Games last revised 2/16/10 Objectives: 1. To introduce mini-max search 2. To introduce the use of static evaluation functions 3. To introduce alpha-beta pruning Materials: 1.
CPS331 Lecture: Search in Games last revised 2/16/10 Objectives: 1. To introduce mini-max search 2. To introduce the use of static evaluation functions 3. To introduce alpha-beta pruning Materials: 1.
Foundations of Artificial Intelligence Introduction State of the Art Summary. classification: Board Games: Overview
 Foundations of Artificial Intelligence May 14, 2018 40. Board Games: Introduction and State of the Art Foundations of Artificial Intelligence 40. Board Games: Introduction and State of the Art 40.1 Introduction
Foundations of Artificial Intelligence May 14, 2018 40. Board Games: Introduction and State of the Art Foundations of Artificial Intelligence 40. Board Games: Introduction and State of the Art 40.1 Introduction
CS 380: ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
 CS 380: ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ADVERSARIAL SEARCH 10/23/2013 Santiago Ontañón santi@cs.drexel.edu https://www.cs.drexel.edu/~santi/teaching/2013/cs380/intro.html Recall: Problem Solving Idea: represent
CS 380: ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ADVERSARIAL SEARCH 10/23/2013 Santiago Ontañón santi@cs.drexel.edu https://www.cs.drexel.edu/~santi/teaching/2013/cs380/intro.html Recall: Problem Solving Idea: represent
Adversarial Search and Game Playing. Russell and Norvig: Chapter 5
 Adversarial Search and Game Playing Russell and Norvig: Chapter 5 Typical case 2-person game Players alternate moves Zero-sum: one player s loss is the other s gain Perfect information: both players have
Adversarial Search and Game Playing Russell and Norvig: Chapter 5 Typical case 2-person game Players alternate moves Zero-sum: one player s loss is the other s gain Perfect information: both players have
CSC 550: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence. Fall 2004
 CSC 550: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Fall 2004 See online syllabus at: http://www.creighton.edu/~davereed/csc550 Course goals: survey the field of Artificial Intelligence, including major areas
CSC 550: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Fall 2004 See online syllabus at: http://www.creighton.edu/~davereed/csc550 Course goals: survey the field of Artificial Intelligence, including major areas
Lecture 33: How can computation Win games against you? Chess: Mechanical Turk
 4/2/0 CS 202 Introduction to Computation " UNIVERSITY of WISCONSIN-MADISON Computer Sciences Department Lecture 33: How can computation Win games against you? Professor Andrea Arpaci-Dusseau Spring 200
4/2/0 CS 202 Introduction to Computation " UNIVERSITY of WISCONSIN-MADISON Computer Sciences Department Lecture 33: How can computation Win games against you? Professor Andrea Arpaci-Dusseau Spring 200
Adversarial Search and Game Playing
 Games Adversarial Search and Game Playing Russell and Norvig, 3 rd edition, Ch. 5 Games: multi-agent environment q What do other agents do and how do they affect our success? q Cooperative vs. competitive
Games Adversarial Search and Game Playing Russell and Norvig, 3 rd edition, Ch. 5 Games: multi-agent environment q What do other agents do and how do they affect our success? q Cooperative vs. competitive
Game-Playing & Adversarial Search
 Game-Playing & Adversarial Search This lecture topic: Game-Playing & Adversarial Search (two lectures) Chapter 5.1-5.5 Next lecture topic: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (two lectures) Chapter 6.1-6.4,
Game-Playing & Adversarial Search This lecture topic: Game-Playing & Adversarial Search (two lectures) Chapter 5.1-5.5 Next lecture topic: Constraint Satisfaction Problems (two lectures) Chapter 6.1-6.4,
CSC384 Intro to Artificial Intelligence* *The following slides are based on Fahiem Bacchus course lecture notes.
 CSC384 Intro to Artificial Intelligence* *The following slides are based on Fahiem Bacchus course lecture notes. Artificial Intelligence A branch of Computer Science. Examines how we can achieve intelligent
CSC384 Intro to Artificial Intelligence* *The following slides are based on Fahiem Bacchus course lecture notes. Artificial Intelligence A branch of Computer Science. Examines how we can achieve intelligent
CS 380: ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ADVERSARIAL SEARCH. Santiago Ontañón
 CS 380: ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ADVERSARIAL SEARCH Santiago Ontañón so367@drexel.edu Recall: Problem Solving Idea: represent the problem we want to solve as: State space Actions Goal check Cost function
CS 380: ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ADVERSARIAL SEARCH Santiago Ontañón so367@drexel.edu Recall: Problem Solving Idea: represent the problem we want to solve as: State space Actions Goal check Cost function
Creating a Poker Playing Program Using Evolutionary Computation
 Creating a Poker Playing Program Using Evolutionary Computation Simon Olsen and Rob LeGrand, Ph.D. Abstract Artificial intelligence is a rapidly expanding technology. We are surrounded by technology that
Creating a Poker Playing Program Using Evolutionary Computation Simon Olsen and Rob LeGrand, Ph.D. Abstract Artificial intelligence is a rapidly expanding technology. We are surrounded by technology that
Welcome to CompSci 171 Fall 2010 Introduction to AI.
 Welcome to CompSci 171 Fall 2010 Introduction to AI. http://www.ics.uci.edu/~welling/teaching/ics171spring07/ics171fall09.html Instructor: Max Welling, welling@ics.uci.edu Office hours: Wed. 4-5pm in BH
Welcome to CompSci 171 Fall 2010 Introduction to AI. http://www.ics.uci.edu/~welling/teaching/ics171spring07/ics171fall09.html Instructor: Max Welling, welling@ics.uci.edu Office hours: Wed. 4-5pm in BH
CSC321 Lecture 23: Go
 CSC321 Lecture 23: Go Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 23: Go 1 / 21 Final Exam Friday, April 20, 9am-noon Last names A Y: Clara Benson Building (BN) 2N Last names Z: Clara Benson Building (BN)
CSC321 Lecture 23: Go Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 23: Go 1 / 21 Final Exam Friday, April 20, 9am-noon Last names A Y: Clara Benson Building (BN) 2N Last names Z: Clara Benson Building (BN)
MA/CS 109 Computer Science Lectures. Wayne Snyder Computer Science Department Boston University
 MA/CS 109 Lectures Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today Artiificial Intelligence: Pro and Con Friday 12/9 AI Pro and Con continued The future of AI Artificial Intelligence Artificial Intelligence
MA/CS 109 Lectures Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today Artiificial Intelligence: Pro and Con Friday 12/9 AI Pro and Con continued The future of AI Artificial Intelligence Artificial Intelligence
6. Games. COMP9414/ 9814/ 3411: Artificial Intelligence. Outline. Mechanical Turk. Origins. origins. motivation. minimax search
 COMP9414/9814/3411 16s1 Games 1 COMP9414/ 9814/ 3411: Artificial Intelligence 6. Games Outline origins motivation Russell & Norvig, Chapter 5. minimax search resource limits and heuristic evaluation α-β
COMP9414/9814/3411 16s1 Games 1 COMP9414/ 9814/ 3411: Artificial Intelligence 6. Games Outline origins motivation Russell & Norvig, Chapter 5. minimax search resource limits and heuristic evaluation α-β
Last update: March 9, Game playing. CMSC 421, Chapter 6. CMSC 421, Chapter 6 1
 Last update: March 9, 2010 Game playing CMSC 421, Chapter 6 CMSC 421, Chapter 6 1 Finite perfect-information zero-sum games Finite: finitely many agents, actions, states Perfect information: every agent
Last update: March 9, 2010 Game playing CMSC 421, Chapter 6 CMSC 421, Chapter 6 1 Finite perfect-information zero-sum games Finite: finitely many agents, actions, states Perfect information: every agent
Artificial Intelligence. Topic 5. Game playing
 Artificial Intelligence Topic 5 Game playing broadening our world view dealing with incompleteness why play games? perfect decisions the Minimax algorithm dealing with resource limits evaluation functions
Artificial Intelligence Topic 5 Game playing broadening our world view dealing with incompleteness why play games? perfect decisions the Minimax algorithm dealing with resource limits evaluation functions
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence By Budditha Hettige Sources: Based on An Introduction to Multi-agent Systems by Michael Wooldridge, John Wiley & Sons, 2002 Artificial Intelligence A Modern Approach,
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence By Budditha Hettige Sources: Based on An Introduction to Multi-agent Systems by Michael Wooldridge, John Wiley & Sons, 2002 Artificial Intelligence A Modern Approach,
Introduction to AI. What is Artificial Intelligence?
 Introduction to AI Instructor: Dr. Wei Ding Fall 2009 1 What is Artificial Intelligence? Views of AI fall into four categories: Thinking Humanly Thinking Rationally Acting Humanly Acting Rationally The
Introduction to AI Instructor: Dr. Wei Ding Fall 2009 1 What is Artificial Intelligence? Views of AI fall into four categories: Thinking Humanly Thinking Rationally Acting Humanly Acting Rationally The
MITOCW Project: Backgammon tutor MIT Multicore Programming Primer, IAP 2007
 MITOCW Project: Backgammon tutor MIT 6.189 Multicore Programming Primer, IAP 2007 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue
MITOCW Project: Backgammon tutor MIT 6.189 Multicore Programming Primer, IAP 2007 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue
Adversarial Search. Chapter 5. Mausam (Based on slides of Stuart Russell, Andrew Parks, Henry Kautz, Linda Shapiro) 1
 Adversarial Search Chapter 5 Mausam (Based on slides of Stuart Russell, Andrew Parks, Henry Kautz, Linda Shapiro) 1 Game Playing Why do AI researchers study game playing? 1. It s a good reasoning problem,
Adversarial Search Chapter 5 Mausam (Based on slides of Stuart Russell, Andrew Parks, Henry Kautz, Linda Shapiro) 1 Game Playing Why do AI researchers study game playing? 1. It s a good reasoning problem,
Artificial Intelligence. Minimax and alpha-beta pruning
 Artificial Intelligence Minimax and alpha-beta pruning In which we examine the problems that arise when we try to plan ahead to get the best result in a world that includes a hostile agent (other agent
Artificial Intelligence Minimax and alpha-beta pruning In which we examine the problems that arise when we try to plan ahead to get the best result in a world that includes a hostile agent (other agent
Game Playing AI Class 8 Ch , 5.4.1, 5.5
 Game Playing AI Class Ch. 5.-5., 5.4., 5.5 Bookkeeping HW Due 0/, :59pm Remaining CSP questions? Cynthia Matuszek CMSC 6 Based on slides by Marie desjardin, Francisco Iacobelli Today s Class Clear criteria
Game Playing AI Class Ch. 5.-5., 5.4., 5.5 Bookkeeping HW Due 0/, :59pm Remaining CSP questions? Cynthia Matuszek CMSC 6 Based on slides by Marie desjardin, Francisco Iacobelli Today s Class Clear criteria
Games CSE 473. Kasparov Vs. Deep Junior August 2, 2003 Match ends in a 3 / 3 tie!
 Games CSE 473 Kasparov Vs. Deep Junior August 2, 2003 Match ends in a 3 / 3 tie! Games in AI In AI, games usually refers to deteristic, turntaking, two-player, zero-sum games of perfect information Deteristic:
Games CSE 473 Kasparov Vs. Deep Junior August 2, 2003 Match ends in a 3 / 3 tie! Games in AI In AI, games usually refers to deteristic, turntaking, two-player, zero-sum games of perfect information Deteristic:
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search Instructors: David Suter and Qince Li Course Delivered @ Harbin Institute of Technology [Many slides adapted from those created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel
Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search Instructors: David Suter and Qince Li Course Delivered @ Harbin Institute of Technology [Many slides adapted from those created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence CS482, CS682, MW 1 2:15, SEM 201, MS 227 Prerequisites: 302, 365 Instructor: Sushil Louis, sushil@cse.unr.edu, http://www.cse.unr.edu/~sushil Non-classical search - Path does not
Artificial Intelligence CS482, CS682, MW 1 2:15, SEM 201, MS 227 Prerequisites: 302, 365 Instructor: Sushil Louis, sushil@cse.unr.edu, http://www.cse.unr.edu/~sushil Non-classical search - Path does not
Overview. Introduction to Artificial Intelligence. What is Intelligence? What is Artificial Intelligence? Influential areas for AI
 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence By Budditha Hettige Sources: Based on An Introduction to Multi-agent Systems by Michael Wooldridge, John Wiley & Sons, 2002 Artificial Intelligence A Modern Approach,
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence By Budditha Hettige Sources: Based on An Introduction to Multi-agent Systems by Michael Wooldridge, John Wiley & Sons, 2002 Artificial Intelligence A Modern Approach,
These are the slides accompanying the book Artificial Intelligence and Games through the gameaibook.org website
 These are the slides accompanying the book Artificial Intelligence and Games through the gameaibook.org website 1 Some reasons why a course on game AI is time-relevant and important 2 Some potential learning
These are the slides accompanying the book Artificial Intelligence and Games through the gameaibook.org website 1 Some reasons why a course on game AI is time-relevant and important 2 Some potential learning
CS 5522: Artificial Intelligence II
 CS 5522: Artificial Intelligence II Adversarial Search Instructor: Alan Ritter Ohio State University [These slides were adapted from CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All materials available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.]
CS 5522: Artificial Intelligence II Adversarial Search Instructor: Alan Ritter Ohio State University [These slides were adapted from CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All materials available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.]
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence CS482, CS682, MW 1 2:15, SEM 201, MS 227 Prerequisites: 302, 365 Instructor: Sushil Louis, sushil@cse.unr.edu, http://www.cse.unr.edu/~sushil Games and game trees Multi-agent systems
Artificial Intelligence CS482, CS682, MW 1 2:15, SEM 201, MS 227 Prerequisites: 302, 365 Instructor: Sushil Louis, sushil@cse.unr.edu, http://www.cse.unr.edu/~sushil Games and game trees Multi-agent systems
COMP219: COMP219: Artificial Intelligence Artificial Intelligence Dr. Annabel Latham Lecture 12: Game Playing Overview Games and Search
 COMP19: Artificial Intelligence COMP19: Artificial Intelligence Dr. Annabel Latham Room.05 Ashton Building Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool Lecture 1: Game Playing 1 Overview Last
COMP19: Artificial Intelligence COMP19: Artificial Intelligence Dr. Annabel Latham Room.05 Ashton Building Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool Lecture 1: Game Playing 1 Overview Last
Announcements. Homework 1. Project 1. Due tonight at 11:59pm. Due Friday 2/8 at 4:00pm. Electronic HW1 Written HW1
 Announcements Homework 1 Due tonight at 11:59pm Project 1 Electronic HW1 Written HW1 Due Friday 2/8 at 4:00pm CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search and Game Trees Instructors: Sergey Levine
Announcements Homework 1 Due tonight at 11:59pm Project 1 Electronic HW1 Written HW1 Due Friday 2/8 at 4:00pm CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search and Game Trees Instructors: Sergey Levine
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Game Playing in Practice
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2006 Lecture 23: Games 4/18/2006 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Game Playing in Practice Checkers: Chinook ended 40-year-reign of human world champion Marion Tinsley in 1994.
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2006 Lecture 23: Games 4/18/2006 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Game Playing in Practice Checkers: Chinook ended 40-year-reign of human world champion Marion Tinsley in 1994.
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Announcements
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2011 Lecture 7: Minimax and Alpha-Beta Search 2/9/2011 Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides adapted from Dan Klein 1 Announcements W1 out and due Monday 4:59pm P2
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2011 Lecture 7: Minimax and Alpha-Beta Search 2/9/2011 Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides adapted from Dan Klein 1 Announcements W1 out and due Monday 4:59pm P2
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2007
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2007 Lecture 7: CSP-II and Adversarial Search 2/6/2007 Srini Narayanan ICSI and UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell or
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2007 Lecture 7: CSP-II and Adversarial Search 2/6/2007 Srini Narayanan ICSI and UC Berkeley Many slides over the course adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell or
Adversarial Search. Hal Daumé III. Computer Science University of Maryland CS 421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 9 Feb 2012
 1 Hal Daumé III (me@hal3.name) Adversarial Search Hal Daumé III Computer Science University of Maryland me@hal3.name CS 421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 9 Feb 2012 Many slides courtesy of Dan
1 Hal Daumé III (me@hal3.name) Adversarial Search Hal Daumé III Computer Science University of Maryland me@hal3.name CS 421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 9 Feb 2012 Many slides courtesy of Dan
Game playing. Chapter 6. Chapter 6 1
 Game playing Chapter 6 Chapter 6 1 Outline Games Perfect play minimax decisions α β pruning Resource limits and approximate evaluation Games of chance Games of imperfect information Chapter 6 2 Games vs.
Game playing Chapter 6 Chapter 6 1 Outline Games Perfect play minimax decisions α β pruning Resource limits and approximate evaluation Games of chance Games of imperfect information Chapter 6 2 Games vs.
Game Playing State-of-the-Art CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Fall Deterministic Games. Zero-Sum Games 10/13/17. Adversarial Search
 CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2017 Adversarial Search Mini, pruning, Expecti Dieter Fox Based on slides adapted Luke Zettlemoyer, Dan Klein, Pieter Abbeel, Dan Weld, Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore
CSE 473: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2017 Adversarial Search Mini, pruning, Expecti Dieter Fox Based on slides adapted Luke Zettlemoyer, Dan Klein, Pieter Abbeel, Dan Weld, Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore
Turing Centenary Celebration
 1/18 Turing Celebration Turing s Test for Artificial Intelligence Dr. Kevin Korb Clayton School of Info Tech Building 63, Rm 205 kbkorb@gmail.com 2/18 Can Machines Think? Yes Alan Turing s question (and
1/18 Turing Celebration Turing s Test for Artificial Intelligence Dr. Kevin Korb Clayton School of Info Tech Building 63, Rm 205 kbkorb@gmail.com 2/18 Can Machines Think? Yes Alan Turing s question (and
How AI Won at Go and So What? Garry Kasparov vs. Deep Blue (1997)
 How AI Won at Go and So What? Garry Kasparov vs. Deep Blue (1997) Alan Fern School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Oregon State University Deep Mind s vs. Lee Sedol (2016) Watson vs. Ken
How AI Won at Go and So What? Garry Kasparov vs. Deep Blue (1997) Alan Fern School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Oregon State University Deep Mind s vs. Lee Sedol (2016) Watson vs. Ken
Game playing. Chapter 6. Chapter 6 1
 Game playing Chapter 6 Chapter 6 1 Outline Games Perfect play minimax decisions α β pruning Resource limits and approximate evaluation Games of chance Games of imperfect information Chapter 6 2 Games vs.
Game playing Chapter 6 Chapter 6 1 Outline Games Perfect play minimax decisions α β pruning Resource limits and approximate evaluation Games of chance Games of imperfect information Chapter 6 2 Games vs.
Conversion Masters in IT (MIT) AI as Representation and Search. (Representation and Search Strategies) Lecture 002. Sandro Spina
 Conversion Masters in IT (MIT) AI as Representation and Search (Representation and Search Strategies) Lecture 002 Sandro Spina Physical Symbol System Hypothesis Intelligent Activity is achieved through
Conversion Masters in IT (MIT) AI as Representation and Search (Representation and Search Strategies) Lecture 002 Sandro Spina Physical Symbol System Hypothesis Intelligent Activity is achieved through
COMP219: Artificial Intelligence. Lecture 2: AI Problems and Applications
 COMP219: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 2: AI Problems and Applications 1 Introduction Last time General module information Characterisation of AI and what it is about Today Overview of some common AI
COMP219: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 2: AI Problems and Applications 1 Introduction Last time General module information Characterisation of AI and what it is about Today Overview of some common AI
Game-playing Programs. Game trees
 This article appeared in The Encylopedia of Cognitive Science, 2002 London, Macmillan Reference Ltd. Game-playing Programs Article definition: Game-playing programs rely on fast deep search and knowledge
This article appeared in The Encylopedia of Cognitive Science, 2002 London, Macmillan Reference Ltd. Game-playing Programs Article definition: Game-playing programs rely on fast deep search and knowledge
COMP219: Artificial Intelligence. Lecture 13: Game Playing
 CMP219: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 13: Game Playing 1 verview Last time Search with partial/no observations Belief states Incremental belief state search Determinism vs non-determinism Today We will
CMP219: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 13: Game Playing 1 verview Last time Search with partial/no observations Belief states Incremental belief state search Determinism vs non-determinism Today We will
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence One way to define Artificial Intelligence (AI) is as a branch of science trying to determine and formally describe, permitting a computer implementation the solutions for hard problems.
Artificial Intelligence One way to define Artificial Intelligence (AI) is as a branch of science trying to determine and formally describe, permitting a computer implementation the solutions for hard problems.
Ch.4 AI and Games. Hantao Zhang. The University of Iowa Department of Computer Science. hzhang/c145
 Ch.4 AI and Games Hantao Zhang http://www.cs.uiowa.edu/ hzhang/c145 The University of Iowa Department of Computer Science Artificial Intelligence p.1/29 Chess: Computer vs. Human Deep Blue is a chess-playing
Ch.4 AI and Games Hantao Zhang http://www.cs.uiowa.edu/ hzhang/c145 The University of Iowa Department of Computer Science Artificial Intelligence p.1/29 Chess: Computer vs. Human Deep Blue is a chess-playing
Today. Types of Game. Games and Search 1/18/2010. COMP210: Artificial Intelligence. Lecture 10. Game playing
 COMP10: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 10. Game playing Trevor Bench-Capon Room 15, Ashton Building Today We will look at how search can be applied to playing games Types of Games Perfect play minimax
COMP10: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 10. Game playing Trevor Bench-Capon Room 15, Ashton Building Today We will look at how search can be applied to playing games Types of Games Perfect play minimax
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (CS 370D)
 Princess Nora University Faculty of Computer & Information Systems ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (CS 370D) (CHAPTER-5) ADVERSARIAL SEARCH ADVERSARIAL SEARCH Optimal decisions Min algorithm α-β pruning Imperfect,
Princess Nora University Faculty of Computer & Information Systems ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (CS 370D) (CHAPTER-5) ADVERSARIAL SEARCH ADVERSARIAL SEARCH Optimal decisions Min algorithm α-β pruning Imperfect,
Monte Carlo Tree Search
 Monte Carlo Tree Search 1 By the end, you will know Why we use Monte Carlo Search Trees The pros and cons of MCTS How it is applied to Super Mario Brothers and Alpha Go 2 Outline I. Pre-MCTS Algorithms
Monte Carlo Tree Search 1 By the end, you will know Why we use Monte Carlo Search Trees The pros and cons of MCTS How it is applied to Super Mario Brothers and Alpha Go 2 Outline I. Pre-MCTS Algorithms
Game Playing State of the Art
 Game Playing State of the Art Checkers: Chinook ended 40 year reign of human world champion Marion Tinsley in 1994. Used an endgame database defining perfect play for all positions involving 8 or fewer
Game Playing State of the Art Checkers: Chinook ended 40 year reign of human world champion Marion Tinsley in 1994. Used an endgame database defining perfect play for all positions involving 8 or fewer
A.M. Turing, computer pioneer, worried about intelligence in humans & machines; proposed a test (1950) thinks with electricity
 Progress has been tremendous Lawrence Snyder University of Washington, Seattle The inventors of ENIAC, 1 st computer, said it thinks with electricity Do calculators think? Does performing arithmetic, which
Progress has been tremendous Lawrence Snyder University of Washington, Seattle The inventors of ENIAC, 1 st computer, said it thinks with electricity Do calculators think? Does performing arithmetic, which
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides are based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley.
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Adversarial Search Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides are based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley.
Games vs. search problems. Game playing Chapter 6. Outline. Game tree (2-player, deterministic, turns) Types of games. Minimax
 Game playing Chapter 6 perfect information imperfect information Types of games deterministic chess, checkers, go, othello battleships, blind tictactoe chance backgammon monopoly bridge, poker, scrabble
Game playing Chapter 6 perfect information imperfect information Types of games deterministic chess, checkers, go, othello battleships, blind tictactoe chance backgammon monopoly bridge, poker, scrabble
