Radar Shadow and Superresolution Features for Automatic Recognition of MSTAR targets
|
|
|
- Jemimah Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Radar Shado and Superresolution eatures for utoatic Recognition of STR targets Jingjing Cui, Jon Gudnason, ike Brookes. Iperial College London Key Words: Hidden arkov odel, Target Recognition, High Range Resolution, Synthetic perture Radar, ultiple Signal Classification, eature Extraction, oving and Stationary Target cquisition and Recognition (STR) BSTRCT utoatic target recognition fro high range resolution radar profiles reains an iportant and challenging proble. In this paper, e present a novel feature set for this task that cobines a noise-robust superresolution characterisation of the target scattering centres derived using the USIC algorith ith a representation of the target's radar shado shape. To obtain the shado shape features, three alternative spectral estiation ethods are investigated. Using a Hidden arkov odel to represent aspect dependence, e deonstrate that the inclusion of the shado features results in a significant iproveent in recognition perforance. Using aziuth apertures of 3 and 6 in a -target classification task fro the STR database, e obtain overall classification error rates of.3% and.2% respectively. These results are significantly better than those obtained by other published ethods on the sae database.. INTRODUCTION The autoatic detection and classification of targets fro their radar signatures is an iportant and difficult proble that has attracted considerable research effort. lgoriths for target recognition fro high range resolution (HRR) radar signals generally use as their priary input either a synthetic aperture radar (SR) iage or else a sequence of one or ore one-diensional HRR range profiles. The iage-based approaches generally have higher perforance but are less robust to target otion because of their long data acquisition tie. Soe iage-based algoriths use the pixel values of the iage as their recognition features [, 2, 3] hile others first transfor the iage to another doain [4, 5]. n alternative approach for targets that are large copared ith the radar avelength is to odel the radar return as eanating fro a discrete set of orientation-dependent points knon as scattering centres [6]. In this approach, the SR iage is processed to generate an explicit list of scattering centre positions and associated radar cross sections on hich the recognition features are based [7, 8]. In the sae ay, systes that act on the HRR range profiles can either use the ra [9] or transfored [] profile values as their features or else can process the profiles to estiate the scattering centre locations and cross sections []. Both SR iages and HRR profiles can exhibit large variations for sall changes in target orientation. Target recognition systes ust account for this aspect-dependency by using a rotation invariant transfor [4] or by having ultiple, orientation-dependent, target representations hich ay conveniently be ebedded in a Hidden arkov odel (H) [5,, 2]. In this paper, e present a novel feature set for autoatic target recognition fro a sequence of radar range profiles. Our feature set uses a noise-robust super-resolution technique for identifying scattering centre locations and cobines this inforation ith additional features that characterise the shape of the radar shado. ig. (b) shos a SR iage of a T72 tank taken fro the STR [3, 4] dataset. This iage ay be divided into three regions having significantly different characteristics: (a) the target itself, (b) the target shado and (c) a clutter region surrounding the target. s can be seen in this exaple, the shape of the shado region gives potentially useful inforation about the vertical profile of a target hen it is sited on level ground. This inforation is not available fro the direct target returns hich are insensitive to vertical displaceent. The shado inforation has been used by others to iprove target detection [5] but is not generally used explicitly in target recognition. We shoed in [6] that the shado inforation can be effective in radar target recognition and e present further iproveents in perforance in the present paper HRR Profiles spect ngle [deg] ig.. (a) HRR profiles (b) SR iage of T72 tank SR Iage cross In Section 2 of this paper, e describe our proposed feature set in detail and in Section 3, e describe the Hidden arkov odel that e use to represent the aspect dependency of the radar returns. In Section 4, e evaluate the perforance of our target recognition syste using observation data fro the STR database [4] and copare its perforance ith that of other systes fro the literature that use the sae database. inally, e suarise our results in Section 5.
2 2. RECOGNITION ETURE SET The features that e use for target recognition are derived fro the sequence of coplex-valued HRR profiles, x ( n,, obtained by applying a discrete ourier transfor (DT) to the indoed phase history radar returns. Here n is the profile index and k is the range-bin index covering the region of interest. ig. (a) shos a typical plot of x ( n, and ig. (b) shos the SR iage that results fro indoing x ( n, and taking the DT ith respect to n. Visible in the iage are the target itself, ith signal levels ell above the clutter noise level and also a ell defined shado region ith very lo signal levels. or each value of the profile index n, e obtain to feature vectors: u (n) characterizes the positions and intensities of the scattering centres ithin the target hile (n) characterises the shape of the shado area. Both these feature vectors are derived fro 2 P + consecutive profiles centred on profile n. We therefore define the data atrix x n ( = x( n +, here p { P,..., P}. The procedures to obtain u (n) and (n) are described belo. 2. Target features The derivation of u (n) is illustrated in ig. 2 and the processing steps are described belo here, for clarity, e oit the profile index, n. x( range ask for target USIC in cross range a,k,k aziuth ask y(l, log & dct select lo frequency coponents ig.2. Procedure to calculate target features fro HRR profiles Each scattering centre in range bin k gives rise to a coplex exponential ter in x ( n, and the first step in obtaining u is to identify these ters. We do this by applying the USIC algorith [7] hich uses the data odel: x( = α, e + ε( k here α and ω are the coplex aplitudes and frequencies of the scattering centre ters and ε ( is assued to be hite noise. The reasons for using the USIC algorith are that it is resistant to noise, does not require indoing of x ( n, and is able to estiate ω ith high resolution independently of P. Within range bin k, each of the coponents in () corresponds to a scattering centre hose cross-range displaceent is proportional toω. The axiu nuber of scattering centres,, could be chosen adaptively for each range bin but e have, in the experients belo, fixed it for each range bin according to the nuber of HRR profiles used. fter discarding any scattering centres hose cross-range displaceent lies outside the target ask, e convert the jω p u () continuous displaceents, ω, to discrete values. We create a continuous signal containing an ipulse for each scattering centre hich e then lo-pass filter and saple to give: y( l, = α h( l βω, k ) (2) here h( l) = (.33πl ) sin(.33πl ) is the lo-pass filter response and β =.5λ(2π φ r) is a constant ith λ, φ and r, the avelength, aziuth increent and cross range resolution, respectively. inally, the iage inforation is copressed by taking the 2-diensional discrete cosine transfor (DCT) of log y( l, and e for a 54-eleent feature vector u, retaining only the coefficients in the lo frequency triangle of size -by- and excluding the DC ter. ig. 3(a) shos an exaple of y ( l, corresponding to the central portion of the iage shon in ig. (b) and ig. 3(b) shos the reconstructed logarithic iage using only the coefficients for u Target Iage using USIC cross 2 Reconstruced Target Iage using USIC cross ig. 3 (a) The iage y( l, of the T72 tank (b) The reconstructed logarithic iage using u 2.2 Shado features The shado area of the SR iage consists of deep valleys corresponding to the shado and broad peaks representing the clutter. Unlike the target area of the SR iage, the shado region contains no sharp peaks fro scattering centres and e ish to characterise the shape of its boundary. The procedure for obtaining the shado feature vector,, is shon in ig. 7. olloing a range ask, e perfor spectral estiation in the cross-range direction using one of three ethods described belo. We then identify the shado region using an adaptive threshold and, as ith the target features, copress the inforation using a DCT. x( range ask for shado spectral estiation I(l, threshold b(l, dct select lo frequency coponents ig.7 Procedure to calculate shado features fro HRR profiles using one of the three spectral estiation ethods 2.2. ourier Transfor spectral estiation The first ethod of spectral estiation is to apply a Haing indo to x ( and then to take the DT in the p direction. The shape of the spectru is thus estiated for each range bin k and the iage I( l, is fored in the sae
3 ay as a SR iage. draback of this ethod is that the cross-range resolution is liited by the indoing operation utoregressive spectral estiation better spectral estiate is achieved by deriving the paraeters of a odel of the cross range profile. irst e apply the autocorrelation ethod of autoregressive (R) spectral estiation to x( using the odel: x( = a ( x( p, + u( (3) here a ( are coplex R coefficients and u( is a hite input driving sequence of zero ean and unit variance. We then for the iage I ( l, by converting the R coefficients k ) to the spectru in the p direction: a ( I( l, = a ( e j2πl The R odel is an all-pole odel and the odel order,, is fixed at 25 in the experients belo. The odel order is high because the peaks in the resulting spectru ill odel the clutter around the shado even though the recognition is not done on these peaks but on the shape of the shado oving average spectral estiation We can also estiate the spectru of x( by applying a oving verage () odel: (4) x( = b ( u( p, (5) here b ( are coplex coefficients and u( is the input driving sequence. The odel is an all-zero odel hich characterises the shado. The odel order, in the experients belo, fixed at 2, in order to locate edge of shado. We for the iage I ( l, by converting the coefficients k ) to the spectru in the p direction: b ( I( l, = b ( e j2πl To estiate the coefficients, e first convert the process to a high-order R process [8] and then use standard R estiation procedures to obtain the coefficients. The ethod uses the folloing odel: N x( = u( an ( x( p n, ( N >> ) n= (6) (5) for p = v( = a p ( for < p N + (6) for p > N + v( = u ( b ( v( p, (7) In our ipleentation e used N = Binary Iage oration fter obtaining the iage I ( l, fro the shado ask, e threshold it to give a binary-valued shado iage b ( l, shon in ig. 5 for each of the spectral estiation ethods. The pixel values representing the clutter region in I ( l, have a large spread hereas the shado pixels are concentrated in loer values. This allos us to deterine the threshold fro the histogra by choosing it to be above the highest value of the bins containing the ost pixels. The shado iages in ig. 5 are obtained fro the data shon in ig. using (a) the ourier transfor, (b) R spectral estiation and (c) spectral estiation. The figures sho that the shado is featured proinently as a large black area hile the clutter is shon as ixed points of black and hite. s ith the target features, e copress the shado iage by taking a 2-diensional DCT and retaining 54 lo frequency coefficients to for the shado feature vectors denoted by, and respectively for the three ethods. The reconstructed iages using, and are shon in ig. 6. The shapes of the shados are all ell retained except that the ethod introduces soe horizontal steaks. Shado Iage using T cross Shado Iage using R cross Shado Iage using cross ig. 5 The iage b ( l, using (a) ourier transfor, (b) R spectral estiation, (c) spectral estiation. Reconstruced Shado Iage using T cross Reconstruced Shado Iage using R cross ig. 6 Reconstructed iages fro (a), (b) Reconstruced Shado Iage using cross, (c) The nuber, 2 P +, of HRR profiles used to for the feature vector has a direct effect on the cross-range resolution of and but not on that of. Hoever although R spectral estiation can achieve superresolution, its error criterion concentrates on the high energy features in the clutter region and so does not find the shado edges accurately. In contrast the approach represents the shado region ell even using only a 2 nd order odel. We copare the classification perforances using the three kinds of features in the Section 4.
4 soothed log likelihood soothed log likelihood 3. ZIUTH HIDDEN RKOV ODEL HRR profiles exhibit significant variability ith target orientation. We odel this for each target using an H containing S states hich correspond to different target aspects. Within an observation sequence, consecutive HRR profiles correspond either to the sae or to adjacent states. Thus the only alloable state transitions are fro a state to itself or to the adjacent state in the direction of sensor otion. We initialise the states to correspond to equal aspect increents of S and for each state e train a Gaussian ixture odel (G) [9] using all available training data fro the corresponding range of aspects of a particular target. The transition probability beteen adjacent states is initialised to be S φ / here φ is the aziuth increent beteen successive feature vectors. Using these initial values, e then re-estiate the G paraeters and the H transition probabilities using ebedded Bau-Welch training []. The aziuth interval represented by a state can change during re-estiation as is illustrated in ig. 8(a). This figure shos the log likelihood of test feature vectors as a function of aziuth angle for each of three consecutive odel states. The three odel states ere initially trained ith data fro consecutive 6 aziuth intervals in the region of 6. We see fro ig. 8(a) that the log likelihood does indeed peak at a target orientation of 6 and that there is a second, saller, State Decoposition peak at around S= S= 25 due to target - S=2 syetry. n - enlarged vie of the priary peak is - shon in ig. 8(b) -4 hich shos that -5 each state has retained clearly aspect angle [degree] 35 4 defined boundaries. State Decoposition State is hoever S= S= uch broader than -2 S=2 its initial idth of 6 and no covers -4 about, state -6 covers a relatively narroer angular -8 extent about 2 and - state 2 becoes aspect angle [degree] broader again. ig. 8 State decoposition (a) fro 25 to to 4. EXPERIENTL RESULTS (b) fro 4. STR database The experiental evaluations ake use of the oving and Stationary Target cquisition and Recognition (STR) database collected by the Sandia National Laboratory using an X-band SR sensor in. 3 resolution spotlight ode [4, 3]. The database contains coplex valued SR iage chips of confusable targets and their variants. or each target, the iages cover a full aziuth range at depression angles of 5 and7 for test and training data respectively. The SR iages have a resolution of r =. 3 in both the range (horizontal) and cross range (vertical) directions. or our experients, the SR iage chips ere converted into a sequence of HRR profiles by taking an inverse ourier transfor, reoving the zero padding and finally undoing the Taylor indo in the P direction. The steps of this procedure are suarised in ig. 9. Each iage chip covers an aziuth interval of approxiately 3 [9] ith successive HRR profiles separated by an angular increent of φ =.3. ig.9. Procedure to convert STR iages to HRR profiles. The operations are in cross-range. 4.2 Experiental procedure or our experients e used an H containing S = 6 states each corresponding to an initial aziuth interval of 6. Within each state, feature vector distributions are represented by a diagonal-covariance Gaussian. We used a 9 9 target ask and a 8 9 shado ask. total of iage chips containing 7 depression angle data as used to train a separate H for each of the targets. or testing, e used a total of 5 5 depression angle iages ithout any copensation for the slight isatch in depression angle. We evaluated three alternative feature sets: the target features u, the shado features and the concatenation of the to u +.The first to sets contain 54 eleents hile the last has 8. The feature vectors ere fored using P = 25 corresponding to an aperture of.5.the axiu nuber of scattering centres,, is fixed at for each range bin. We fored a sequence of HRR profiles covering 3 aziuth aperture fro one iage chip and a sequence covering 6 fro to adjacent iage chips. We then deterined the odel ith the highest likelihood. odel training and recognition ere perfored using the HTK recognition softare []. We are interested in knoing hat ethod to use for extracting the shado features. On their on, the shado features do not perfor ell, but in conjunction ith the target features, they can iprove the recognition results significantly. Table shos a closed-set identification results using the target features u, and three proposed shado features, and used both on their on and concatenated ith u to for a 8 eleent feature vector. The table presents the percentage isclassification rates for each
5 individual target, the overall test set isclassification rate (CR) and the standard deviation of the test set isclassification rate (St.Dev) using test sequences hich each cover a 3 aziuth aperture. We can see that if used on their on, the R derived shado features perfor best ith 7.3 % CR. Hoever, hen used ith the target features, the derived shado features produce the best perforance of.3% CR. The reason for this is that the shado ask overlaps the target region and both and anage to include inforation that is already in u. The features on the other hand concentrate on the shado, giving relatively poor perforance on their on but giving the greatest iproveent hen cobined ith the target features, u. We ill use to represent the shado features in the folloing discussions. Table : Recognition error rates ith different shado features (%) Target u u+ u+ u+ BP BRD BTR BTR D T T ZIL3.8.4 ZSU S CR St.Dev We no present the recognition results based on 3 and 6 sequences, respectively. Table 2 shos the recognition error rate for each of the three feature sets for the to cases. In the 6 -sequence observation based recognition, the log likelihood of to adjacent test sequences are added and the recogniser chooses the one ith the highest su. We see that used on their on the u and paraeter sets give CR of.5% and.9% hich is in both cases an iproveent over the one-sequence results. When the to feature sets are cobined to for u + e find that the CR is reduced to.2% ith seven of the ten targets error-free. Table 2: Recognition error rates of to observations (%) 3 aziuth aperture 6 aziuth aperture Target u u+ u u+ BP BRD BTR BTR D T T ZIL3.8 ZSU S CR St.Dev or both the 3 -sequence and 6 -sequence tests, the addition of the features iproves the recognition rate for all targets except one, the BTR6 hich is considerably orsened. This indicates that, for this target at least, the assuption that the feature vector follos a ultivariate Gaussian distribution is a poor one. The error rate of.3% obtained using a 3 aperture can be directly copared ith other published results based on the STR database ith the sae recognition task. In [2], the authors obtained error rates of 4.% using an approach based on the SR iage and in [] an error rate of 7.8% as obtained hen perforing recognition on the HRR profiles directly. The STR database contains variants of the T72 tank and 3 variants of the BP2 vehicle, anifested by different realisations of the fuel tank, antenna, etc []. To evaluate the robustness of our recogniser to these variations, e trained odels on to BP2 variants, four T72 variants as ell as the eight other targets using the u + feature set. We then conducted recognition tests on all targets in the database using to iages. If the recogniser identified an incorrect variant of the correct tank odel, it as counted as an error in the Strict colun of Table 3 but as a correct identification in the Class colun. or targets included in the training set, the CR is.4 % and in ost cases the precise variant of a particular target is identified correctly. or the unseen variants listed in the loer section of the table, the CR as 8.6% ith ore than half of the errors arising fro the T72-s7 and T72-82 targets. The final colun of Table 3 shos the Class error rates reported in [] for the sae task. We see that for all targets except T72-s7 the recognition perforance for our proposed feature set is considerably better. We note hoever that since [] bases its recognition on individual HRR profiles, it ill be less sensitive to target otion than hen the feature set described here is used ith a large value of P. Table 3: Recognition error rates ith unknon targets (%) Target Strict Class Class fro [] BP2-c BP BTR7 4. BRD2 8.6 BTR D7 4.8 T62 9 T72-a T72-a T72-a T ZIL3.3 ZSU S 4.7 BP T72-a T72-a T72-a.5.9 T72-a T72-a T72-s T CONCLUSIONS This paper has presented a novel radar target recognition technique cobining to-diensional target and shado inforation. The ne technique copleents the SR-TR and HRR-TR techniques by using a feature extraction
6 ethod that is robust to noise and that can extract target and shado inforation accurately ith liited aziuth aperture length. Three ethods to obtain the shado features are investigated. The experiental results using STR database indicate that although they perfor relatively poorly on their on, the shado features derived using the ethod perfor exceptionally ell hen cobined ith USICderived target features. Using aziuth apertures of 3 and 6 in a -target classification task, they give overall classification error rates of.3% and.2% respectively. These results are considerably better than other published techniques using the sae dataset. 5. CKNOWLEDGEENT This research as supported by the UK od through ork funded by the Defence Technology Centre for Data and Inforation usion. REERENCES. L.. Novak, coparison of D and 2D algoriths for radar target classification, IEEE International Conference on Systes Engineering, 99, pp L.. Novak, S. D. Halversen, G. Oirka, and. Hiett, Effects of polarization and resolution on SR TR, IEEE Trans. on erospace and Electronic Systes, vol. 33, no., 997, pp J.. O Sullivan,. D. DeVore, V. Kedia, and. I. iller, SR TR perforance using a conditionally Gaussian odel, IEEE Trans. On erospace and Electronic Systes, vol. 37, no.,, pp D. P. Kottke,. Jong-Kae, and K. Bron, Hidden arkov odeling for autoatic target recognition, Proc. Thirty-irst siloar Conference on Signals, Systes and Coputers, vol.. 997, pp P. Runkle, L. H. Nguyen, J. H. cclellan, and L. Carin, ulti-aspect target detection for SR iagery using hidden arkov odels, IEEE Trans. On Geoscience and Reote Sensing, vol. 39, no.,, pp R. Bhalla, H. Ling, J. oore, D. J. ndersh, S. W. Lee, and J. Hughes, 3D scattering centre representation f coplex targets using the shooting and bouncing ray technique: a revie, IEEE ntennas and Propagation agazine, vol. 4, no. 5, 998, pp H. Chiang, R. L., oses, and L. C. Potter, odel-based classification of radar iages, IEEE Trans. on Inforation Theory, vol. 46, no. 5,, pp C. Nilubol, Q. H. Pha, R.. ersereau,. J. T. Sith, and.. Cleents, Hidden arkov odelling for SR autoatic target recognition, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. coustics, Speech, Signal Processing, vol. 2, 998, pp R. Willias, J. Westerka D. Gross,. Paloion, and T. ister, utoatic target recognition of tie critical oving targets using D high range resolution (HRR) radar, IEEE Radar Conference, 999, pp D. E. Nelson, J.. Starzuk, and D. D. Ensley, Iterated avelet transforation and signal discriination for HRR radar target recognition, IEEE Trans. on Systes, an and Cybernetics, Part, vol. 33, no., 3, pp X. Liao, P. Runkle, and L. Carin, Identification of ground targets fro sequential high-range-resolution radar signatures, IEEE Trans. On erospace and Electronic Systes, vol. 38, no. 4, 2, pp B. Pei and Z. Bao, Radar target recognition based on peak location of HRR profile and Hs classifiers, Proc. Radar Conference, 2, pp T. D. Ross and J. C. ossing, The STR Evaluation ethodology, Proc. SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering, vol. 372, 999, pp T. Ross, S. Worrel, V. Velten, J. ossing, and. Bryant, Standard SR TR evaluation experients using the STR public release data set, Proc. SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering, vol. 337, 998, pp P. Lobardo,. Sciotti, and L.. Kaplan, SR prescreening using both target and shado inforation, Proc. IEEE Radar Conference,, pp J. Cui, J. Godnason and.brookes, utoatic Recognition of STR Targets using Radar Shado and superresolution eatures, is accepted by Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. coustics, Speech, Signal Processing, R. Schidt, ultiple eitter location and signal paraeter estiation, IEEE Trans. on ntennas and Propagation, vol., no. 3, 986, pp S. Kay, odern spectral estiation, st ed. Prentice Hall, P. Depster, N.. Laird, and D. B. Rubin, axiu Likelihood fro Incoplete Data via the E lgorith, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, vol. 39, no., 977, pp S. Young, G. Everann, T. Hain, D. Kersha, G. oore, J. Odell, D. Ollason, D. Povey, V. Valtchev, and P. Woodland, The HTK Book, Cabridge University Engineering Dept, 2. [Online] vailable: 2. L.. Novak, utoatic target recognition using enhanced resolution SR data, IEEE Trans. on erospace and Electronic Systes, vol. 35, no., 999, pp BIOGRPHY Jingjing Cui as born in 98. She received her B. S. degree fro the Departent of Counication Engineering in udan University, China, in 2, and in 3 she received her Sc degree fro the Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering in Iperial College London, UK. She is currently doing her PhD degree at the Counication and Signal Processing Group in Iperial College. Her current research interests include echo cancellation and radar target recognition. Her contact address is: Counication and Signal Processing Grou Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Iperial College London, UK, SW7 2BT.
Overlapping Signal Separation in DPX Spectrum Based on EM Algorithm. Chuandang Liu 1, a, Luxi Lu 1, b
 nd International Worshop on Materials Engineering and Coputer Sciences (IWMECS 015) Overlapping Signal Separation in DPX Spectru Based on EM Algorith Chuandang Liu 1, a, Luxi Lu 1, b 1 National Key Laboratory
nd International Worshop on Materials Engineering and Coputer Sciences (IWMECS 015) Overlapping Signal Separation in DPX Spectru Based on EM Algorith Chuandang Liu 1, a, Luxi Lu 1, b 1 National Key Laboratory
Windowing High-Resolution ADC Data Part 2
 Windoing High-Resolution DC Data art Josh Carnes pplications Engineer, ational Seiconductor Corp. bstract nalyzing data fro DCs requires the use of indoing functions for spectral estiation and analysis
Windoing High-Resolution DC Data art Josh Carnes pplications Engineer, ational Seiconductor Corp. bstract nalyzing data fro DCs requires the use of indoing functions for spectral estiation and analysis
DSI3 Sensor to Master Current Threshold Adaptation for Pattern Recognition
 International Journal of Signal Processing Systes Vol., No. Deceber 03 DSI3 Sensor to Master Current Threshold Adaptation for Pattern Recognition David Levy Infineon Austria AG, Autootive Power Train Systes,
International Journal of Signal Processing Systes Vol., No. Deceber 03 DSI3 Sensor to Master Current Threshold Adaptation for Pattern Recognition David Levy Infineon Austria AG, Autootive Power Train Systes,
Kalman Filtering for NLOS Mitigation and Target Tracking in Indoor Wireless Environment
 16 Kalan Filtering for NLOS Mitigation and Target Tracking in Indoor Wireless Environent Chin-Der Wann National Sun Yat-Sen University Taiwan 1. Introduction Kalan filter and its nonlinear extension, extended
16 Kalan Filtering for NLOS Mitigation and Target Tracking in Indoor Wireless Environent Chin-Der Wann National Sun Yat-Sen University Taiwan 1. Introduction Kalan filter and its nonlinear extension, extended
Modeling Beam forming in Circular Antenna Array with Directional Emitters
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN (Print): 2320-9356 Volue 5 Issue 3 ǁ Mar. 2017 ǁ PP.01-05 Modeling Bea foring in Circular Antenna Array
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN (Print): 2320-9356 Volue 5 Issue 3 ǁ Mar. 2017 ǁ PP.01-05 Modeling Bea foring in Circular Antenna Array
Adaptive Harmonic IIR Notch Filter with Varying Notch Bandwidth and Convergence Factor
 Journal of Counication and Coputer (4 484-49 doi:.765/548-779/4.6. D DAVID PUBLISHING Adaptive Haronic IIR Notch Filter with Varying Notch Bandwidth and Convergence Factor Li Tan, Jean Jiang, and Liango
Journal of Counication and Coputer (4 484-49 doi:.765/548-779/4.6. D DAVID PUBLISHING Adaptive Haronic IIR Notch Filter with Varying Notch Bandwidth and Convergence Factor Li Tan, Jean Jiang, and Liango
A Pre-FFT OFDM Adaptive Antenna Array with Eigenvector Combining
 A Pre- OFDM Adaptive Antenna Array ith Eigenvector Cobining Shinsuke Hara y, Montree Budsabathon y, and Yoshitaka Hara y Departent of Electronic, Inforation and Energy Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering,
A Pre- OFDM Adaptive Antenna Array ith Eigenvector Cobining Shinsuke Hara y, Montree Budsabathon y, and Yoshitaka Hara y Departent of Electronic, Inforation and Energy Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering,
Additive Synthesis, Amplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation
 Additive Synthesis, Aplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation Pro Eduardo R Miranda Varèse-Gastproessor eduardo.iranda@btinternet.co Electronic Music Studio TU Berlin Institute o Counications Research
Additive Synthesis, Aplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation Pro Eduardo R Miranda Varèse-Gastproessor eduardo.iranda@btinternet.co Electronic Music Studio TU Berlin Institute o Counications Research
COMBINED FREQUENCY AND SPATIAL DOMAINS POWER DISTRIBUTION FOR MIMO-OFDM TRANSMISSION
 The 8th nnual IEEE International Syposiu on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Counications (PIMRC 07) COMINED FREQUENCY ND SPTIL DOMINS POWER DISTRIUTION FOR MIMO-OFDM TRNSMISSION Wladiir ocquet, Kazunori
The 8th nnual IEEE International Syposiu on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Counications (PIMRC 07) COMINED FREQUENCY ND SPTIL DOMINS POWER DISTRIUTION FOR MIMO-OFDM TRNSMISSION Wladiir ocquet, Kazunori
Iterative Receiver Signal Processing for Joint Mitigation of Transmitter and Receiver Phase Noise in OFDM-Based Cognitive Radio Link
 Iterative Receiver Signal Processing for Joint Mitigation of Transitter and Receiver Phase Noise in OFDM-Based Cognitive Radio Link Ville Syrjälä and Mikko Valkaa Departent of Counications Engineering
Iterative Receiver Signal Processing for Joint Mitigation of Transitter and Receiver Phase Noise in OFDM-Based Cognitive Radio Link Ville Syrjälä and Mikko Valkaa Departent of Counications Engineering
NONLINEAR WAVELET PACKET DENOISING OF IMPULSIVE VIBRATION SIGNALS NIKOLAOS G. NIKOLAOU, IOANNIS A. ANTONIADIS
 NONLINEAR WAVELET PACKET DENOISING OF IMPULSIVE VIBRATION SIGNALS NIKOLAOS G. NIKOLAOU, IOANNIS A. ANTONIADIS Departent of Mechanical Engineering, Machine Design and Control Systes Section National Technical
NONLINEAR WAVELET PACKET DENOISING OF IMPULSIVE VIBRATION SIGNALS NIKOLAOS G. NIKOLAOU, IOANNIS A. ANTONIADIS Departent of Mechanical Engineering, Machine Design and Control Systes Section National Technical
Track-Before-Detect for an Active Towed Array Sonar
 17-20 Noveber 2013, Victor Harbor, Australia Track-Before-Detect for an Active Towed Array Sonar Han X. Vu (1,2), Sauel J. Davey (1,2), Fiona K. Fletcher (1), Sanjeev Arulapala (1,2), Richard Elle (1)
17-20 Noveber 2013, Victor Harbor, Australia Track-Before-Detect for an Active Towed Array Sonar Han X. Vu (1,2), Sauel J. Davey (1,2), Fiona K. Fletcher (1), Sanjeev Arulapala (1,2), Richard Elle (1)
Overlapped frequency-time division multiplexing
 April 29, 16(2): 8 13 www.sciencedirect.co/science/journal/158885 he Journal of China Universities of Posts and elecounications www.buptjournal.cn/xben Overlapped frequency-tie division ultiplexing JIANG
April 29, 16(2): 8 13 www.sciencedirect.co/science/journal/158885 he Journal of China Universities of Posts and elecounications www.buptjournal.cn/xben Overlapped frequency-tie division ultiplexing JIANG
Radar Imaging of Non-Uniformly Rotating Targets via a Novel Approach for Multi-Component AM-FM Signal Parameter Estimation
 Sensors 5, 5, 695-693; doi:.339/s53695 Article OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 44-8 www.dpi.co/journal/sensors Radar Iaging of Non-Uniforly Rotating Targets via a Novel Approach for Multi-Coponent AM-FM Signal
Sensors 5, 5, 695-693; doi:.339/s53695 Article OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 44-8 www.dpi.co/journal/sensors Radar Iaging of Non-Uniforly Rotating Targets via a Novel Approach for Multi-Coponent AM-FM Signal
An orthogonal multi-beam based MIMO scheme. for multi-user wireless systems
 An orthogonal ulti-bea based IO schee for ulti-user wireless systes Dong-chan Oh o and Yong-Hwan Lee School of Electrical Engineering and IC, Seoul ational University Kwana P.O. Box 34, Seoul, 151-600,
An orthogonal ulti-bea based IO schee for ulti-user wireless systes Dong-chan Oh o and Yong-Hwan Lee School of Electrical Engineering and IC, Seoul ational University Kwana P.O. Box 34, Seoul, 151-600,
ELEC2202 Communications Engineering Laboratory Frequency Modulation (FM)
 ELEC Counications Engineering Laboratory ---- Frequency Modulation (FM) 1. Objectives On copletion of this laboratory you will be failiar with: Frequency odulators (FM), Modulation index, Bandwidth, FM
ELEC Counications Engineering Laboratory ---- Frequency Modulation (FM) 1. Objectives On copletion of this laboratory you will be failiar with: Frequency odulators (FM), Modulation index, Bandwidth, FM
APPLICATION OF THE FAN-CHIRP TRANSFORM TO HYBRID SINUSOIDAL+NOISE MODELING OF POLYPHONIC AUDIO
 6th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 8), Lausanne, Switzerland, August 5-9, 8, copyright by EURASIP APPLICATION OF THE FAN-CHIRP TRANSFORM TO HYBRID SINUSOIDAL+NOISE MODELING OF POLYPHONIC
6th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 8), Lausanne, Switzerland, August 5-9, 8, copyright by EURASIP APPLICATION OF THE FAN-CHIRP TRANSFORM TO HYBRID SINUSOIDAL+NOISE MODELING OF POLYPHONIC
EFFECTS OF MASKING ANGLE AND MULTIPATH ON GALILEO PERFORMANCES IN DIFFERENT ENVIRONMENTS
 1 EFFECTS OF MASKING ANGLE AND MULTIPATH ON GALILEO PERFORMANCES IN DIFFERENT ENVIRONMENTS M. Malicorne*, M. Bousquet**, V. Calettes*** SUPAERO, 1 avenue Edouard Belin BP 43, 3155 Toulouse Cedex, France.
1 EFFECTS OF MASKING ANGLE AND MULTIPATH ON GALILEO PERFORMANCES IN DIFFERENT ENVIRONMENTS M. Malicorne*, M. Bousquet**, V. Calettes*** SUPAERO, 1 avenue Edouard Belin BP 43, 3155 Toulouse Cedex, France.
SECURITY AND BER PERFORMANCE TRADE-OFF IN WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS APPLICATIONS
 Latin Aerican Applied Research 39:187-192 (2009) SECURITY AND BER PERFORMANCE TRADE-OFF IN WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS APPLICATIONS L. ARNONE, C. GONZÁLEZ, C. GAYOSO, J. CASTIÑEIRA MOREIRA and M. LIBERATORI
Latin Aerican Applied Research 39:187-192 (2009) SECURITY AND BER PERFORMANCE TRADE-OFF IN WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS APPLICATIONS L. ARNONE, C. GONZÁLEZ, C. GAYOSO, J. CASTIÑEIRA MOREIRA and M. LIBERATORI
Spectral analysis of biosignals. Biosignal processing I, S Autumn 2017
 Spectral analysis o biosignals Biosignal processing I, 573S Autun 07 Introduction Oscillations o biosignals oten have intuitive physiological interpretation breathing rate, heart rate, alpha rhyth, Frequencies
Spectral analysis o biosignals Biosignal processing I, 573S Autun 07 Introduction Oscillations o biosignals oten have intuitive physiological interpretation breathing rate, heart rate, alpha rhyth, Frequencies
ACCURATE DISPLACEMENT MEASUREMENT BASED ON THE FREQUENCY VARIATION MONITORING OF ULTRASONIC SIGNALS
 XVII IMEKO World Congress Metrology in 3rd Millenniu June 22 27, 2003, Dubrovnik, Croatia ACCURATE DISPLACEMENT MEASUREMENT BASED ON THE FREQUENCY VARIATION MONITORING OF ULTRASONIC SIGNALS Ch. Papageorgiou
XVII IMEKO World Congress Metrology in 3rd Millenniu June 22 27, 2003, Dubrovnik, Croatia ACCURATE DISPLACEMENT MEASUREMENT BASED ON THE FREQUENCY VARIATION MONITORING OF ULTRASONIC SIGNALS Ch. Papageorgiou
ROBUST UNDERWATER LOCALISATION OF ULTRA LOW FREQUENCY SOURCES IN OPERATIONAL CONTEXT
 ROBUST UNDERWATER LOCALISATION OF ULTRA LOW FREQUENCY SOURCES IN OPERATIONAL CONTEXT M. Lopatka a, B. Nicolas a, G. Le Touzé a,b, X. Cristol c, B. Chalindar c, J. Mars a, D. Fattaccioli d a GIPSA-Lab /DIS/
ROBUST UNDERWATER LOCALISATION OF ULTRA LOW FREQUENCY SOURCES IN OPERATIONAL CONTEXT M. Lopatka a, B. Nicolas a, G. Le Touzé a,b, X. Cristol c, B. Chalindar c, J. Mars a, D. Fattaccioli d a GIPSA-Lab /DIS/
Cross-correlation tracking for Maximum Length Sequence based acoustic localisation
 Cross-correlation tracking for Maxiu Length Sequence based acoustic localisation Navinda Kottege Research School of Inforation Sciences and Engineering The Australian National University, ACT, Australia
Cross-correlation tracking for Maxiu Length Sequence based acoustic localisation Navinda Kottege Research School of Inforation Sciences and Engineering The Australian National University, ACT, Australia
Statistical Singing Voice Conversion based on Direct Waveform Modification with Global Variance
 INTERSPEECH 15 Statistical Singing Voice Conversion based on Direct Wavefor Modification with Global Variance Kazuhiro Kobayashi, Tooki Toda, Graha Neubig, Sakriani Sakti, Satoshi Nakaura Graduate School
INTERSPEECH 15 Statistical Singing Voice Conversion based on Direct Wavefor Modification with Global Variance Kazuhiro Kobayashi, Tooki Toda, Graha Neubig, Sakriani Sakti, Satoshi Nakaura Graduate School
Efficient Non-linear Changed Mel-filter Bank VAD Algorithm
 Matheatical Models and Methods in Modern Science Efficient on-linear Changed Mel-filter Bank VAD Algorith DAMJA VLAJ, ZDRAVKO KAČIČ, MARKO KOS Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Coputer Science University
Matheatical Models and Methods in Modern Science Efficient on-linear Changed Mel-filter Bank VAD Algorith DAMJA VLAJ, ZDRAVKO KAČIČ, MARKO KOS Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Coputer Science University
A New Localization and Tracking Algorithm for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Internet of Things
 Sensors & Transducers 203 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.co A New Localization and Tracking Algorith for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Internet of Things, 2 Zhang Feng, Xue Hui-Feng, 2 Zhang Yong-Heng,
Sensors & Transducers 203 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.co A New Localization and Tracking Algorith for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Internet of Things, 2 Zhang Feng, Xue Hui-Feng, 2 Zhang Yong-Heng,
This file is part of the following reference: Access to this file is available from:
 This file is part of the following reference: Page, Geoff (27) Mass Transport Evaluation using consolidated VHF Radar and Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler data. Masters (Research) thesis, Jaes Cook University.
This file is part of the following reference: Page, Geoff (27) Mass Transport Evaluation using consolidated VHF Radar and Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler data. Masters (Research) thesis, Jaes Cook University.
Statistical Singing Voice Conversion with Direct Waveform Modification based on the Spectrum Differential
 INTERSPEECH 2014 Statistical Singing Voice Conversion with Direct Wavefor Modification based on the Spectru Differential Kazuhiro Kobayashi, Tooki Toda, Graha Neubig, Sakriani Sakti, Satoshi Nakaura Graduate
INTERSPEECH 2014 Statistical Singing Voice Conversion with Direct Wavefor Modification based on the Spectru Differential Kazuhiro Kobayashi, Tooki Toda, Graha Neubig, Sakriani Sakti, Satoshi Nakaura Graduate
RAKE Receiver. Tommi Heikkilä S Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications, Autumn II.
 S-72333 Postgraduate Course in Radio Counications, Autun 2004 1 RAKE Receiver Toi Heikkilä toiheikkila@teliasoneraco Abstract RAKE receiver is used in CDMA-based (Code Division Multiple Access) systes
S-72333 Postgraduate Course in Radio Counications, Autun 2004 1 RAKE Receiver Toi Heikkilä toiheikkila@teliasoneraco Abstract RAKE receiver is used in CDMA-based (Code Division Multiple Access) systes
ECE 6560 Multirate Signal Processing Analysis & Synthesis Notes
 Multirate Signal Processing Analysis & Synthesis Notes Dr. Bradley J. Bazuin Western Michigan University College of Engineering and Applied Sciences Departent of Electrical and Coputer Engineering 1903
Multirate Signal Processing Analysis & Synthesis Notes Dr. Bradley J. Bazuin Western Michigan University College of Engineering and Applied Sciences Departent of Electrical and Coputer Engineering 1903
Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium Claims, Targets, and Standard Alignment for Math
 Sarter Balanced Assessent Consortiu Clais, s, Stard Alignent for Math The Sarter Balanced Assessent Consortiu (SBAC) has created a hierarchy coprised of clais targets that together can be used to ake stateents
Sarter Balanced Assessent Consortiu Clais, s, Stard Alignent for Math The Sarter Balanced Assessent Consortiu (SBAC) has created a hierarchy coprised of clais targets that together can be used to ake stateents
Notes on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
 Notes on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). Discrete Fourier ransfor As a reinder, the analytic fors of Fourier and inverse Fourier transfors are X f x t t, f dt x t exp j2 ft dt (.) where
Notes on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). Discrete Fourier ransfor As a reinder, the analytic fors of Fourier and inverse Fourier transfors are X f x t t, f dt x t exp j2 ft dt (.) where
Detection of Faults in Power System Using Wavelet Transform and Independent Component Analysis
 Detection of Faults in Power Syste Using Wavelet Transfor and Independent Coponent Analysis 1 Prakash K. Ray, 2 B. K. Panigrahi, 2 P. K. Rout 1 Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, IIIT, Bhubaneswar,
Detection of Faults in Power Syste Using Wavelet Transfor and Independent Coponent Analysis 1 Prakash K. Ray, 2 B. K. Panigrahi, 2 P. K. Rout 1 Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, IIIT, Bhubaneswar,
POWER QUALITY ASSESSMENT USING TWO STAGE NONLINEAR ESTIMATION NUMERICAL ALGORITHM
 POWER QUALITY ASSESSENT USING TWO STAGE NONLINEAR ESTIATION NUERICAL ALGORITH Vladiir Terzia ABB Gerany vadiir.terzia@de.abb.co Vladiir Stanoevic EPS Yugoslavia vla_sta@hotail.co artin axiini ABB Gerany
POWER QUALITY ASSESSENT USING TWO STAGE NONLINEAR ESTIATION NUERICAL ALGORITH Vladiir Terzia ABB Gerany vadiir.terzia@de.abb.co Vladiir Stanoevic EPS Yugoslavia vla_sta@hotail.co artin axiini ABB Gerany
PREDICTING SOUND LEVELS BEHIND BUILDINGS - HOW MANY REFLECTIONS SHOULD I USE? Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK
 PREDICTING SOUND LEVELS BEHIND BUILDINGS - HOW MANY REFLECTIONS SHOULD I USE? W Wei A Cooke J Havie-Clark Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead,
PREDICTING SOUND LEVELS BEHIND BUILDINGS - HOW MANY REFLECTIONS SHOULD I USE? W Wei A Cooke J Havie-Clark Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead,
EQUALIZED ALGORITHM FOR A TRUCK CABIN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM
 EQUALIZED ALGORITHM FOR A TRUCK CABIN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM Guangrong Zou, Maro Antila, Antti Lanila and Jari Kataja Sart Machines, VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland P.O. Box 00, FI-0 Tapere,
EQUALIZED ALGORITHM FOR A TRUCK CABIN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM Guangrong Zou, Maro Antila, Antti Lanila and Jari Kataja Sart Machines, VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland P.O. Box 00, FI-0 Tapere,
OTC Statistics of High- and Low-Frequency Motions of a Moored Tanker. sensitive to lateral loading such as the SAL5 and
 OTC 61 78 Statistics of High- and Low-Frequency Motions of a Moored Tanker by J.A..Pinkster, Maritie Research Inst. Netherlands Copyright 1989, Offshore Technology Conference This paper was presented at
OTC 61 78 Statistics of High- and Low-Frequency Motions of a Moored Tanker by J.A..Pinkster, Maritie Research Inst. Netherlands Copyright 1989, Offshore Technology Conference This paper was presented at
Optical fiber beamformer for processing two independent simultaneous RF beams
 Optical fiber beaforer for processing two independent siultaneous RF beas M. Jaeger, S. Granieri *, and A. Siahakoun Departent of Physics and Optical Engineering, Rose-Hulan Institute of Technology Terre
Optical fiber beaforer for processing two independent siultaneous RF beas M. Jaeger, S. Granieri *, and A. Siahakoun Departent of Physics and Optical Engineering, Rose-Hulan Institute of Technology Terre
Precise Indoor Localization System For a Mobile Robot Using Auto Calibration Algorithm
 Precise Indoor Localization Syste For a Mobile Robot Using Auto Calibration Algorith Sung-Bu Ki, JangMyung Lee, and I.O. Lee : Pusan National University, http://robotics.ee.pusan.ac.r, : Ninety syste Abstract:
Precise Indoor Localization Syste For a Mobile Robot Using Auto Calibration Algorith Sung-Bu Ki, JangMyung Lee, and I.O. Lee : Pusan National University, http://robotics.ee.pusan.ac.r, : Ninety syste Abstract:
A Frequency Domain Approach to Design Constrained Amplitude Spreading Sequences for DS-CDMA Systems for Frequency Selective Fading Channels
 A Frequency Doain Approach to Design Constrained Aplitude Spreading Sequences for DS-CDMA Systes for Frequency Selective Fading Channels B.J.Peiris, K.R.Narayanan and S.L. Miller Dept. of Electrical Engineering
A Frequency Doain Approach to Design Constrained Aplitude Spreading Sequences for DS-CDMA Systes for Frequency Selective Fading Channels B.J.Peiris, K.R.Narayanan and S.L. Miller Dept. of Electrical Engineering
A Mathematical Model for Designing a Multiple MTI
 Int. J. Contep. Math. Sciences, Vol. 5, 200, no. 5, 2537-2545 A Matheatical Model or Designing a Multiple MTI Filter Using MIMO Radar Signals Waleed Khalid College o Engineering, Al-Mustansiryha University,
Int. J. Contep. Math. Sciences, Vol. 5, 200, no. 5, 2537-2545 A Matheatical Model or Designing a Multiple MTI Filter Using MIMO Radar Signals Waleed Khalid College o Engineering, Al-Mustansiryha University,
PARAMETER OPTIMIZATION OF THE ADAPTIVE MVDR QR-BASED BEAMFORMER FOR JAMMING AND MULTIPATH SUPRESSION IN GPS/GLONASS RECEIVERS
 PARAMETER OPTIMIZATION OF THE ADAPTIVE MVDR QR-BASED BEAMFORMER FOR JAMMING AND MULTIPATH SUPRESSION IN GPS/GLONASS RECEIVERS V. Behar 1, Ch. Kabakchiev 2, G. Gaydadjiev 3, G.Kuzanov 4, P. Ganchosov 5
PARAMETER OPTIMIZATION OF THE ADAPTIVE MVDR QR-BASED BEAMFORMER FOR JAMMING AND MULTIPATH SUPRESSION IN GPS/GLONASS RECEIVERS V. Behar 1, Ch. Kabakchiev 2, G. Gaydadjiev 3, G.Kuzanov 4, P. Ganchosov 5
Waveform Design and Receive Processing for Nonrecurrent Nonlinear FMCW Radar
 Wavefor Design and Receive Processing for Nonrecurrent Nonlinear FMCW Radar John Jakabosky and Shannon D. Blunt Radar Systes Lab University of Kansas Lawrence, KS Braha Hied Sensors Directorate Air Force
Wavefor Design and Receive Processing for Nonrecurrent Nonlinear FMCW Radar John Jakabosky and Shannon D. Blunt Radar Systes Lab University of Kansas Lawrence, KS Braha Hied Sensors Directorate Air Force
A NEW APPROACH TO UNGROUNDED FAULT LOCATION IN A THREE-PHASE UNDERGROUND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM USING COMBINED NEURAL NETWORKS & WAVELET ANALYSIS
 A NEW APPROACH TO UNGROUNDED FAULT LOCATION IN A THREE-PHASE UNDERGROUND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM USING COMBINED NEURAL NETWORKS & WAVELET ANALYSIS Jaal Moshtagh University of Bath, UK oshtagh79@yahoo.co Abstract
A NEW APPROACH TO UNGROUNDED FAULT LOCATION IN A THREE-PHASE UNDERGROUND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM USING COMBINED NEURAL NETWORKS & WAVELET ANALYSIS Jaal Moshtagh University of Bath, UK oshtagh79@yahoo.co Abstract
Performance Analysis of an AMC System with an Iterative V-BLAST Decoding Algorithm
 I. J. Counications, Network and Syste Sciences, 008,, 105-06 Published Online May 008 in SciRes (http://www.srpublishing.org/journal/ijcns/). Perforance Analysis of an AMC Syste with an Iterative V-BLAST
I. J. Counications, Network and Syste Sciences, 008,, 105-06 Published Online May 008 in SciRes (http://www.srpublishing.org/journal/ijcns/). Perforance Analysis of an AMC Syste with an Iterative V-BLAST
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, 2
 Subission International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP ) PARAMETRIC AND NON-PARAMETRIC SIGNAL ANALYSIS FOR MAPPING AIR FLOW IN THE EAR-CANALTO TONGUE MOVEMENT: A NEW STRATEGY
Subission International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP ) PARAMETRIC AND NON-PARAMETRIC SIGNAL ANALYSIS FOR MAPPING AIR FLOW IN THE EAR-CANALTO TONGUE MOVEMENT: A NEW STRATEGY
Multitarget Direction Measurement Based on Bistatic Radar
 Sensors & ransducers Vol. 70 Issue 5 May 204 pp. 65-70 Sensors & ransducers 204 by IFSA Publishing S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.co Multitarget Direction Measureent Based on Bistatic Radar Yubao ou School
Sensors & ransducers Vol. 70 Issue 5 May 204 pp. 65-70 Sensors & ransducers 204 by IFSA Publishing S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.co Multitarget Direction Measureent Based on Bistatic Radar Yubao ou School
Power Improvement in 64-Bit Full Adder Using Embedded Technologies Er. Arun Gandhi 1, Dr. Rahul Malhotra 2, Er. Kulbhushan Singla 3
 Power Iproveent in 64-Bit Full Adder Using Ebedded Technologies Er. Arun Gandhi 1, Dr. Rahul Malhotra 2, Er. Kulbhushan Singla 3 1 Departent of ECE, GTBKIET, Chhapianwali Malout, Punjab 2 Director, Principal,
Power Iproveent in 64-Bit Full Adder Using Ebedded Technologies Er. Arun Gandhi 1, Dr. Rahul Malhotra 2, Er. Kulbhushan Singla 3 1 Departent of ECE, GTBKIET, Chhapianwali Malout, Punjab 2 Director, Principal,
Research Article Dynamic Beamforming for Three-Dimensional MIMO Technique in LTE-Advanced Networks
 Antennas and Propagation Volue 213, Article ID 76457, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/76457 Research Article Dynaic Beaforing for Three-Diensional MIMO Technique in LTE-Advanced Networks Yan Li, Xiaodong
Antennas and Propagation Volue 213, Article ID 76457, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/76457 Research Article Dynaic Beaforing for Three-Diensional MIMO Technique in LTE-Advanced Networks Yan Li, Xiaodong
Energy-Efficient Cellular Communications Powered by Smart Grid Technology
 Energy-Efficient Cellular Counications Powered by Sart Grid Technology Itiaz Nasi, Mostafa Zaan Chowdhury, and Md. Syadus Sefat Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Khulna University of Engineering
Energy-Efficient Cellular Counications Powered by Sart Grid Technology Itiaz Nasi, Mostafa Zaan Chowdhury, and Md. Syadus Sefat Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Khulna University of Engineering
Comparison of Fourier Bessel (FB) and EMD-FB Based Noise Removal Techniques for Underwater Acoustic Signals
 Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research Vol. 73, Deceber 214, pp. 756-762 Coparison of Fourier Bessel (FB) and EMD-FB Based Noise Reoval Techniques for Underwater Acoustic Signals V Vijaya Baskar*,
Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research Vol. 73, Deceber 214, pp. 756-762 Coparison of Fourier Bessel (FB) and EMD-FB Based Noise Reoval Techniques for Underwater Acoustic Signals V Vijaya Baskar*,
Parameter Identification of Transfer Functions Using MATLAB
 Paraeter Identification of Transfer Functions Using MATLAB Mato Fruk, Goran Vujisić, Toislav Špoljarić Departent of Electrical Engineering The Polytechnic of Zagreb Konavoska, Zagreb, Croatia ato.fruk@tvz.hr,
Paraeter Identification of Transfer Functions Using MATLAB Mato Fruk, Goran Vujisić, Toislav Špoljarić Departent of Electrical Engineering The Polytechnic of Zagreb Konavoska, Zagreb, Croatia ato.fruk@tvz.hr,
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 10M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 10M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors
A soft decision decoding of product BCH and Reed-Müller codes for error control and peak-factor reduction in OFDM
 A soft decision decoding of product BCH and Reed-Müller codes for error control and pea-factor reduction in OFDM Yves LOUET *, Annic LE GLAUNEC ** and Pierre LERAY ** * PhD Student and ** Professors, Departent
A soft decision decoding of product BCH and Reed-Müller codes for error control and pea-factor reduction in OFDM Yves LOUET *, Annic LE GLAUNEC ** and Pierre LERAY ** * PhD Student and ** Professors, Departent
TESTING OF ADCS BY FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS IN MULTI-TONE MODE
 THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volue 5, Nuber /004, pp.000-000 TESTING OF ADCS BY FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS IN MULTI-TONE MODE Daniel BELEGA
THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volue 5, Nuber /004, pp.000-000 TESTING OF ADCS BY FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS IN MULTI-TONE MODE Daniel BELEGA
Ruohua Zhou, Josh D Reiss ABSTRACT KEYWORDS INTRODUCTION
 Subitted for; Algoriths and Systes, Edited by W. Wang, Published by IGI Global, ISBN-13: 978-1615209194, July, Music Onset Detection Ruohua Zhou, Josh D Reiss Center for Digital Music, Electronic Engineering
Subitted for; Algoriths and Systes, Edited by W. Wang, Published by IGI Global, ISBN-13: 978-1615209194, July, Music Onset Detection Ruohua Zhou, Josh D Reiss Center for Digital Music, Electronic Engineering
International Journal of Advanced Research in Electronics and Communication Engineering (IJARECE) Volume 3, Issue 9, September 2014
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Electronics and Counication Engineering Volue 3, Issue 9, Septeber 2014 High Speed Error Detection and Data Recovery Architecture for Video Testing Applications
International Journal of Advanced Research in Electronics and Counication Engineering Volue 3, Issue 9, Septeber 2014 High Speed Error Detection and Data Recovery Architecture for Video Testing Applications
A Novel NLOS Mitigation Approach for Wireless Positioning System
 2 3rd International Conference on Coputer and Electrical Engineering (ICCEE 2) IPCSIT vol. 53 (22) (22) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI:.7763/IPCSIT.22.V53.No..54 A Novel NLOS Mitigation Approach for Wireless
2 3rd International Conference on Coputer and Electrical Engineering (ICCEE 2) IPCSIT vol. 53 (22) (22) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI:.7763/IPCSIT.22.V53.No..54 A Novel NLOS Mitigation Approach for Wireless
Non-Linear Weighting Function for Non-stationary Signal Denoising
 Non-Linear Weighting Function for Non-stationary Signal Denoising Farès Abda, David Brie, Radu Ranta To cite this version: Farès Abda, David Brie, Radu Ranta. Non-Linear Weighting Function for Non-stationary
Non-Linear Weighting Function for Non-stationary Signal Denoising Farès Abda, David Brie, Radu Ranta To cite this version: Farès Abda, David Brie, Radu Ranta. Non-Linear Weighting Function for Non-stationary
Indoor Multiple-Antenna Channel Characterization from 2 to 8 GHz
 Indoor Multiple-Antenna Channel Characterization fro to 8 GHz Ada S Y Poon and Minnie Ho Counications and Interconnect Lab, Intel Corporation Abstract In ultiple-antenna channels, e optiality of a transission
Indoor Multiple-Antenna Channel Characterization fro to 8 GHz Ada S Y Poon and Minnie Ho Counications and Interconnect Lab, Intel Corporation Abstract In ultiple-antenna channels, e optiality of a transission
Performance Analysis of Atmospheric Field Conjugation Adaptive Arrays
 Perforance Analysis of Atospheric Field Conjugation Adaptive Arrays Aniceto Belonte* a, Joseph M. Kahn b a Technical Univ. of Catalonia, Dept. of Signal Theory and Coun., 08034 Barcelona, Spain; b Stanford
Perforance Analysis of Atospheric Field Conjugation Adaptive Arrays Aniceto Belonte* a, Joseph M. Kahn b a Technical Univ. of Catalonia, Dept. of Signal Theory and Coun., 08034 Barcelona, Spain; b Stanford
Clean Data Training Approach to Active Sonar Classification
 Clean Data Training Approach to Active Sonar Classiication Alexei Kouzoubov (1), Binh Nguyen (1), Shane Wood (1) and Chris Gillard (1) (1) Deence Science and Technology Organisation, Edinburgh, SA, Australia
Clean Data Training Approach to Active Sonar Classiication Alexei Kouzoubov (1), Binh Nguyen (1), Shane Wood (1) and Chris Gillard (1) (1) Deence Science and Technology Organisation, Edinburgh, SA, Australia
Fundamental study for measuring microflow with Michelson interferometer enhanced by external random signal
 Bulletin of the JSME Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systes, and Manufacturing Vol.8, No.4, 2014 Fundaental study for easuring icroflow with Michelson interferoeter enhanced by external rando signal
Bulletin of the JSME Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systes, and Manufacturing Vol.8, No.4, 2014 Fundaental study for easuring icroflow with Michelson interferoeter enhanced by external rando signal
COMPARISON OF TOKEN HOLDING TIME STRATEGIES FOR A STATIC TOKEN PASSING BUS. M.E. Ulug
 COMPARISON OF TOKEN HOLDING TIME STRATEGIES FOR A STATIC TOKEN PASSING BUS M.E. Ulug General Electric Corporate Research and Developent Schenectady, New York 1245 ABSTRACT Waiting ties have been calculated
COMPARISON OF TOKEN HOLDING TIME STRATEGIES FOR A STATIC TOKEN PASSING BUS M.E. Ulug General Electric Corporate Research and Developent Schenectady, New York 1245 ABSTRACT Waiting ties have been calculated
Mitigation of GPS L 2 signal in the H I observation based on NLMS algorithm Zhong Danmei 1, a, Wang zhan 1, a, Cheng zhu 1, a, Huang Da 1, a
 2nd International Conference on Electrical, Coputer Engineering and Electronics (ICECEE 25 Mitigation of GPS L 2 signal in the H I observation based on NLMS algorith Zhong Danei, a, Wang zhan, a, Cheng
2nd International Conference on Electrical, Coputer Engineering and Electronics (ICECEE 25 Mitigation of GPS L 2 signal in the H I observation based on NLMS algorith Zhong Danei, a, Wang zhan, a, Cheng
Robust Acceleration Control of Electrodynamic Shaker Using µ Synthesis
 Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, and the European Control Conference 5 Seville, Spain, Deceber -5, 5 WeIC8. Robust Acceleration Control of Electrodynaic Shaker Using µ Synthesis
Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, and the European Control Conference 5 Seville, Spain, Deceber -5, 5 WeIC8. Robust Acceleration Control of Electrodynaic Shaker Using µ Synthesis
A New Image Denoising Method Based on Wave Atoms and Cycle Spinning
 6 JOURNAL OF SOFTWARE, VOL. 9, NO., JANUARY A New Iage Denoising Method Based on Wave Atos and Cycle Spinning Wei-qiang Zhang College of Matheatics and coputational Science, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen
6 JOURNAL OF SOFTWARE, VOL. 9, NO., JANUARY A New Iage Denoising Method Based on Wave Atos and Cycle Spinning Wei-qiang Zhang College of Matheatics and coputational Science, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen
WIPL-D Pro: What is New in v12.0?
 WIPL-D Pro: What is New in v12.0? Iproveents/new features introduced in v12.0 are: 1. Extended - Extree Liits a. Extreely LOW contrast aterials b. Extended resolution for radiation pattern c. Extreely
WIPL-D Pro: What is New in v12.0? Iproveents/new features introduced in v12.0 are: 1. Extended - Extree Liits a. Extreely LOW contrast aterials b. Extended resolution for radiation pattern c. Extreely
SIG: Signal-Processing
 TH Köln - Technology, Arts, Sciences Prof. Dr. Rainer Bartz SIG: Signal-Processing Copendiu (6) Prof. Dr.-Ing. Rainer Bartz rainer.bartz@th-koeln.de Contact: eail: website: office: rainer.bartz@th-koeln.de
TH Köln - Technology, Arts, Sciences Prof. Dr. Rainer Bartz SIG: Signal-Processing Copendiu (6) Prof. Dr.-Ing. Rainer Bartz rainer.bartz@th-koeln.de Contact: eail: website: office: rainer.bartz@th-koeln.de
Speech Enhancement using Temporal Masking and Fractional Bark Gammatone Filters
 PAGE 420 Speech Enhanceent using Teporal Masking and Fractional Bark Gaatone Filters Teddy Surya Gunawan, Eliathaby Abikairajah School of Electrical Engineering and Telecounications The University of New
PAGE 420 Speech Enhanceent using Teporal Masking and Fractional Bark Gaatone Filters Teddy Surya Gunawan, Eliathaby Abikairajah School of Electrical Engineering and Telecounications The University of New
Keywords Frequency-domain equalization, antenna diversity, multicode DS-CDMA, frequency-selective fading
 Joint Frequency-doain Equalization and Antenna Diversity Cobining for Orthogonal Multicode DS-CDMA Signal Transissions in A Frequency-selective Fading Channel Taeshi ITAGAKI *1 and Fuiyui ADACHI *2 Dept.
Joint Frequency-doain Equalization and Antenna Diversity Cobining for Orthogonal Multicode DS-CDMA Signal Transissions in A Frequency-selective Fading Channel Taeshi ITAGAKI *1 and Fuiyui ADACHI *2 Dept.
Comparison Between PLAXIS Output and Neural Network in the Guard Walls
 Coparison Between PLAXIS Output and Neural Network in the Guard Walls Ali Mahbod 1, Abdolghafar Ghorbani Pour 2, Abdollah Tabaroei 3, Sina Mokhtar 2 1- Departent of Civil Engineering, Shahid Bahonar University,
Coparison Between PLAXIS Output and Neural Network in the Guard Walls Ali Mahbod 1, Abdolghafar Ghorbani Pour 2, Abdollah Tabaroei 3, Sina Mokhtar 2 1- Departent of Civil Engineering, Shahid Bahonar University,
LETTER Adaptive Multi-Stage Parallel Interference Cancellation Receiver for Multi-Rate DS-CDMA System
 IEICE TRANS. COMMUN., VOL.E87 B, NO.8 AUGUST 2004 2401 LETTER Adaptive Multi-Stage Parallel Interference Cancellation Receiver for Multi-Rate DS-CDMA Syste Seung Hee HAN a), Student Meber and Jae Hong
IEICE TRANS. COMMUN., VOL.E87 B, NO.8 AUGUST 2004 2401 LETTER Adaptive Multi-Stage Parallel Interference Cancellation Receiver for Multi-Rate DS-CDMA Syste Seung Hee HAN a), Student Meber and Jae Hong
Hand Gesture Recognition and Its Application in Robot Control
 IJCSI International Journal of Coputer Science Issues, Volue 13, Issue 1, January 016 www.ijcsi.org 10 Hand Gesture Recognition and Its Application in Robot Control Pei-Guo Wu 1 and Qing-Hu Meng 1 Inforation
IJCSI International Journal of Coputer Science Issues, Volue 13, Issue 1, January 016 www.ijcsi.org 10 Hand Gesture Recognition and Its Application in Robot Control Pei-Guo Wu 1 and Qing-Hu Meng 1 Inforation
A Novel TDS-FDMA Scheme for Multi-User Uplink Scenarios
 A Novel TDS-FDMA Schee for Multi-User Uplink Scenarios Linglong Dai, Zhaocheng Wang, Jun Wang, and Zhixing Yang Tsinghua National Laboratory for Inforation Science and Technology, Electronics Engineering
A Novel TDS-FDMA Schee for Multi-User Uplink Scenarios Linglong Dai, Zhaocheng Wang, Jun Wang, and Zhixing Yang Tsinghua National Laboratory for Inforation Science and Technology, Electronics Engineering
Transmit Power and Bit Allocations for OFDM Systems in a Fading Channel
 Transit Power and Bit Allocations for OFD Systes in a Fading Channel Jiho Jang *, Kwang Bok Lee, and Yong-Hwan Lee * Sasung Electronics Co. Ltd., Suwon P.O.Box, Suwon-si, Gyeonggi-do 44-74, Korea School
Transit Power and Bit Allocations for OFD Systes in a Fading Channel Jiho Jang *, Kwang Bok Lee, and Yong-Hwan Lee * Sasung Electronics Co. Ltd., Suwon P.O.Box, Suwon-si, Gyeonggi-do 44-74, Korea School
Relation between C/N Ratio and S/N Ratio
 Relation between C/N Ratio and S/N Ratio In our discussion in the past few lectures, we have coputed the C/N ratio of the received signals at different points of the satellite transission syste. The C/N
Relation between C/N Ratio and S/N Ratio In our discussion in the past few lectures, we have coputed the C/N ratio of the received signals at different points of the satellite transission syste. The C/N
Boris Krnic Nov 15, ECE 1352F. Phase Noise of VCOs
 Boris Krnic Nov 15, 93 187 13 ECE 135F Phase Noise of VCOs. ABSTRACT The ain purpose of this paper is to present siplified first order noise analysis techniques as applied to ring VCOs. The scarcity of
Boris Krnic Nov 15, 93 187 13 ECE 135F Phase Noise of VCOs. ABSTRACT The ain purpose of this paper is to present siplified first order noise analysis techniques as applied to ring VCOs. The scarcity of
Torsion System. Encoder #3 ( 3 ) Third encoder/disk for Model 205a only. Figure 1: ECP Torsion Experiment
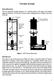 Torsion Syste Introduction This lab experient studies dynaics of a torsional syste with single and ultiple degrees of freedo. The effects of various control configurations are studied in later part of
Torsion Syste Introduction This lab experient studies dynaics of a torsional syste with single and ultiple degrees of freedo. The effects of various control configurations are studied in later part of
Using Adaptive Modulation in a LEO Satellite Communication System
 Proceedings of the 11th WSEAS International Conference on COMMUNICATIONS, Agios Nikolaos, Crete Island, Greece, July 26-28, 27 255 Using Adaptive Modulation in a LEO Satellite Counication Syste L. HADJ
Proceedings of the 11th WSEAS International Conference on COMMUNICATIONS, Agios Nikolaos, Crete Island, Greece, July 26-28, 27 255 Using Adaptive Modulation in a LEO Satellite Counication Syste L. HADJ
Analysis of Time-Frequency Energy for Environmental Vibration Induced by Metro
 6 th International Conference on Advances in periental Structural ngineering th International Workshop on Advanced Sart Materials and Sart Structures Technology August -, 05, University of Illinois, Urbana-Chapaign,
6 th International Conference on Advances in periental Structural ngineering th International Workshop on Advanced Sart Materials and Sart Structures Technology August -, 05, University of Illinois, Urbana-Chapaign,
NINTH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON SOUND AND VIBRATION, ICSV9 PASSIVE CONTROL OF LAUNCH NOISE IN ROCKET PAYLOAD BAYS
 first nae & faily nae: Rick Morgans Page nuber: 1 NINTH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON SOUND AND VIBRATION, ICSV9 PASSIVE CONTROL OF LAUNCH NOISE IN ROCKET PAYLOAD BAYS Rick Morgans, Ben Cazzolato, Anthony
first nae & faily nae: Rick Morgans Page nuber: 1 NINTH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON SOUND AND VIBRATION, ICSV9 PASSIVE CONTROL OF LAUNCH NOISE IN ROCKET PAYLOAD BAYS Rick Morgans, Ben Cazzolato, Anthony
A Hierarchical Likelihood Classifier With Applications to Remote Sensing
 1th WSEAS International Conference on COMMUICATIOS, Heralion, Greece, July 3-5, 8 A Hierarchical Lielihood Classifier With Applications to Reote Sensing E. A. YFATIS Iage Processing Laboratory School of
1th WSEAS International Conference on COMMUICATIOS, Heralion, Greece, July 3-5, 8 A Hierarchical Lielihood Classifier With Applications to Reote Sensing E. A. YFATIS Iage Processing Laboratory School of
Performance of Multiuser MIMO System Employing Block Diagonalization with Antenna Selection at Mobile Stations
 Perforance of Multiuser MIMO Syste Eploying Bloc Diagonalization with Antenna Selection at Mobile Stations Feng Wang, Mare E. Bialowsi School of Inforation Technology and Electrical Engineering The University
Perforance of Multiuser MIMO Syste Eploying Bloc Diagonalization with Antenna Selection at Mobile Stations Feng Wang, Mare E. Bialowsi School of Inforation Technology and Electrical Engineering The University
I GHz. degrees. I pixels. I km. A High-Resolution, Four-Band SAR Testbed with Real-Time Image Formation. de3 db m. < 45 to > 135 < -30
 A High-Resolution, Four-Band SAR Testbed with Real-Tie age Foration Bruce Walker, Grant Sander, Marty Thopson, Bryan Burns, Rick Fellerhoff, and Dale Dub&C Sandia National Laboratories, P.. Box 58 Albuquerque,
A High-Resolution, Four-Band SAR Testbed with Real-Tie age Foration Bruce Walker, Grant Sander, Marty Thopson, Bryan Burns, Rick Fellerhoff, and Dale Dub&C Sandia National Laboratories, P.. Box 58 Albuquerque,
Keywords: Equivalent Instantaneous Inductance, Finite Element, Inrush Current.
 Discriination of Inrush fro Fault Currents in Power Transforers Based on Equivalent Instantaneous Inductance Technique Coupled with Finite Eleent Method Downloaded fro ijeee.iust.ac.ir at 5:47 IRST on
Discriination of Inrush fro Fault Currents in Power Transforers Based on Equivalent Instantaneous Inductance Technique Coupled with Finite Eleent Method Downloaded fro ijeee.iust.ac.ir at 5:47 IRST on
On the field of view of a Galilean telescope
 Transactions of the Optical Society On the field of view of a Galilean telescope To cite this article: H A Hughes and P F Everitt 1920 Trans. Opt. Soc. 22 15 View the article online for updates and enhanceents.
Transactions of the Optical Society On the field of view of a Galilean telescope To cite this article: H A Hughes and P F Everitt 1920 Trans. Opt. Soc. 22 15 View the article online for updates and enhanceents.
New Adaptive Linear Combination Structure for Tracking/Estimating Phasor and Frequency of Power System
 28 Journal of Electrical Engineering & echnology Vol. 5, No., pp. 28~35, 2 New Adaptive Linear Cobination Structure for racking/estiating Phasor and Frequency of Power Syste Choowong-Wattanasakpubal and
28 Journal of Electrical Engineering & echnology Vol. 5, No., pp. 28~35, 2 New Adaptive Linear Cobination Structure for racking/estiating Phasor and Frequency of Power Syste Choowong-Wattanasakpubal and
Design and Implementation of Block Based Transpose Form FIR Filter
 Design and Ipleentation of Bloc Based Transpose For FIR Filter O. Venata rishna 1, Dr. C. Venata Narasihulu 2, Dr.. Satya Prasad 3 1 (ECE, CVR College of Engineering, Hyderabad, India) 2 (ECE, Geethanjali
Design and Ipleentation of Bloc Based Transpose For FIR Filter O. Venata rishna 1, Dr. C. Venata Narasihulu 2, Dr.. Satya Prasad 3 1 (ECE, CVR College of Engineering, Hyderabad, India) 2 (ECE, Geethanjali
Receiver Design for Downlink MIMO MC-CDMA in Cognitive Radio Systems
 1st Annual IEEE International Syposiu on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Counications Receiver Design for Downlink MIMO MC-CDMA in Cognitive Radio Systes M. Raabzadeh 1, and. hoshbin 1 1 Electrical Engineering
1st Annual IEEE International Syposiu on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Counications Receiver Design for Downlink MIMO MC-CDMA in Cognitive Radio Systes M. Raabzadeh 1, and. hoshbin 1 1 Electrical Engineering
Radio Resource Management in a Coordinated Cellular Distributed Antenna System By Using Particle Swarm Optimization
 Radio Resource Manageent in a Coordinated Cellular Distributed Antenna Syste By Using Particle Swar Optiization Oer Haliloglu (1), Cenk Toker (1), Gurhan Bulu (1), Hali Yanikoeroglu (2) (1) Departent of
Radio Resource Manageent in a Coordinated Cellular Distributed Antenna Syste By Using Particle Swar Optiization Oer Haliloglu (1), Cenk Toker (1), Gurhan Bulu (1), Hali Yanikoeroglu (2) (1) Departent of
Phase Noise Modelling and Mitigation Techniques in OFDM Communications Systems
 Phase Noise Modelling and Mitigation Techniques in OFDM Counications Systes Ville Syrjälä, Mikko Valkaa, Nikolay N. Tchaov, and Jukka Rinne Tapere University of Technology Departent of Counications Engineering
Phase Noise Modelling and Mitigation Techniques in OFDM Counications Systes Ville Syrjälä, Mikko Valkaa, Nikolay N. Tchaov, and Jukka Rinne Tapere University of Technology Departent of Counications Engineering
Simplified Analysis and Design of MIMO Ad Hoc Networks
 Siplified Analysis and Design of MIMO Ad Hoc Networks Sunil Srinivasa and Martin Haenggi Departent of Electrical Engineering University of Notre Dae Notre Dae, IN 46556, USA Eail: {ssriniv, haenggi}@nd.edu
Siplified Analysis and Design of MIMO Ad Hoc Networks Sunil Srinivasa and Martin Haenggi Departent of Electrical Engineering University of Notre Dae Notre Dae, IN 46556, USA Eail: {ssriniv, haenggi}@nd.edu
Ignition and monitoring technique for plasma processing of multicell superconducting radio frequency cavities
 Ignition and onitoring technique for plasa processing of ulticell superconducting radio frequency cavities Marc Doleans Oak Ridge ational Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee 3783, USA E ail: doleans@ornl.gov
Ignition and onitoring technique for plasa processing of ulticell superconducting radio frequency cavities Marc Doleans Oak Ridge ational Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee 3783, USA E ail: doleans@ornl.gov
Design of an Arrayed Waveguide Grating with flat spectral response
 Design of an Arrayed Waveguide Grating with flat spectral response Thoas Kaalakis, Thoas Sphicopoulos and Diitris Syvridis (Departent of Inforatics and Telecounications, University of Athens, Panepistiiopolis,
Design of an Arrayed Waveguide Grating with flat spectral response Thoas Kaalakis, Thoas Sphicopoulos and Diitris Syvridis (Departent of Inforatics and Telecounications, University of Athens, Panepistiiopolis,
Intermediate-Node Initiated Reservation (IIR): A New Signaling Scheme for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion
 Interediate-Node Initiated Reservation IIR): A New Signaling Schee for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion Kejie Lu, Jason P. Jue, Tiucin Ozugur, Gaoxi Xiao, and Irich Chlatac The Center
Interediate-Node Initiated Reservation IIR): A New Signaling Schee for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion Kejie Lu, Jason P. Jue, Tiucin Ozugur, Gaoxi Xiao, and Irich Chlatac The Center
This is an author-deposited version published in: Eprints ID: 5737
 Open Archive Toulouse Archive Ouverte (OATAO) OATAO is an open access repository that collects the work of Toulouse researchers and akes it freely available over the web where possible. This is an author-deposited
Open Archive Toulouse Archive Ouverte (OATAO) OATAO is an open access repository that collects the work of Toulouse researchers and akes it freely available over the web where possible. This is an author-deposited
Transmit Beamforming and Iterative Water-Filling Based on SLNR for OFDMA Systems
 Transit Beaforing and Iterative Water-Filling Based on SLNR for OFDMA Systes Kazunori Hayashi, Megui Kaneko, Takeshi Fui, Hideaki Sakai Graduate School of Inforatics, Kyoto University, Yoshida Honachi
Transit Beaforing and Iterative Water-Filling Based on SLNR for OFDMA Systes Kazunori Hayashi, Megui Kaneko, Takeshi Fui, Hideaki Sakai Graduate School of Inforatics, Kyoto University, Yoshida Honachi
Fiber Bragg grating based four-bit optical beamformer
 Fiber Bragg grating based four-bit optical beaforer Sean Durrant a, Sergio Granieri a, Azad Siahakoun a, Bruce Black b a Departent of Physics and Optical Engineering b Departent of Electrical and Coputer
Fiber Bragg grating based four-bit optical beaforer Sean Durrant a, Sergio Granieri a, Azad Siahakoun a, Bruce Black b a Departent of Physics and Optical Engineering b Departent of Electrical and Coputer
Direct F 0 Control of an Electrolarynx based on Statistical Excitation Feature Prediction and its Evaluation through Simulation
 INTERSPEECH 2014 Direct F 0 Control of an Electrolarynx based on Statistical Excitation Prediction and its Evaluation through Siulation Kou Tanaka, Tooki Toda, Graha Neubig, Sakriani Sakti, Satoshi Nakaura
INTERSPEECH 2014 Direct F 0 Control of an Electrolarynx based on Statistical Excitation Prediction and its Evaluation through Siulation Kou Tanaka, Tooki Toda, Graha Neubig, Sakriani Sakti, Satoshi Nakaura
