Analog Lab Experiment Board Ver. 1.0
|
|
|
- Garry O’Connor’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PASSIVE ATTENUATORS Analog Lab Experiment Board Ver. 1.0 QUALITY POLICY To be a Global Provider of Innovative and Affordable Electronic Equipments for Technology Training by enhancing Customer Satisfaction based on Research, Modern manufacturing techniques and continuous improvement in Quality of the products and Services with active participation of employees. An ISO 9001: 2000 company , Electronic Complex, Pardesipura INDORE , India. Tel.: Fax:
2 Web: Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 2
3 Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 3
4 Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 4
5 PASSIVE ATTENUATORS AB50 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.Introduction 4 2. Theory 6 3.Experiments a. Experiment 1 To study the response of Passive T-Attenuator. 12 b. Experiment 2 To study the response of Passive п -Attenuator. 15 c. Experiment 3 To study the response of Passive Bridge T - Attenuator 18 4.Warranty 21 5.List of Service Centers 22 6.List of Accessories with AB Notes 24 Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 5
6 INTRODUCTION AB50 is a compact, ready to use PASSIVE ATTENUATORS experiment board. It incorporates T Attenuator pad, п Attenuator pad and Bridge-T Attenuator pad on a single board and illustrates the functionality of passive attenuator at different attenuation ratio. It can be used as stand alone unit with function generator ST4060 and Oscilloscope. List of boards : Model AB01 AB02 AB03 AB04 AB05 AB06 AB07 AB08 AB09 AB10 AB11 AB12 AB13 AB14 AB15 AB16 AB17 AB18 AB19 AB20 AB21 AB22 AB23 AB25 AB28 AB29 AB30 AB31 AB32 Name Diode characteristics (Si, Zener, LED) Transistor characteristics (CB NPN) Transistor characteristics (CB PNP) Transistor characteristics (CE NPN) Transistor characteristics (CE PNP) Transistor characteristics (CC NPN) Transistor characteristics (CC PNP) FET characteristics Rectifier Circuits Wheatstone Bridge Maxwell s Bridge De Sauty s Bridge Schering Bridge Darlington Pair Common Emitter Amplifier Common Collector Amplifier Common Base Amplifier Cascade Amplifier RC-Coupled Amplifier Direct Coupled Amplifier Class A Amplifier Class B Amplifier (push pull emitter follower) Class C Tuned Amplifier Phase Locked Loop (FM Demodulator & Frequency Divider / Multiplier) Multivibrator ( Mono stable / Astable) F-V and V-F Converter V-I and I-V Converter Zener Voltage Regulator Transistor Series Voltage Regulator Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 6
7 AB33 Transistor Shunt Voltage Regulator AB39 Instrumentation Amplifier AB41 Differential Amplifier (Transistorized) AB42 Operational Amplifier (Inverting / Non-inverting / Differentiator) AB43 Operational Amplifier (Adder/Scalar) AB44 Operational Amplifier (Integrator/ Differentiator) AB45 Schmitt Trigger and Comparator AB51 Active filters (Low Pass and High Pass) AB52 Active Band Pass Filter AB53 Notch Filter AB54 Tschebyscheff Filter AB56 Fiber Optic Analog Link AB64 RC Coupled Amplifier with Feedback AB65 Phase Shift Oscillator AB66 Wien Bridge Oscillators AB67 Colpitt Oscillator AB68 Hartley Oscillator AB80 RLC Series and RLC Parallel Resonance AB81 Kirchoff s Laws (Kirchoff s Current Law & Kirchoff s Voltage Law) AB82 Thevenin s and Maximum power Transfer Theorem AB83 Reciprocity and Superposition Theorem AB84 Tellegen s Theorem AB85 Norton s theorem AB88 Diode Clipper AB89 Diode Clampers AB90 Two port network parameter AB91 Optical Transducer (Photovoltaic cell) AB92 Optical Transducer (Photoconductive cell/ldr) AB93 Optical Transducer (Phototransistor) AB96 Temperature Transducer (RTD & IC335) AB97 Temperature Transducer (Thermocouple) AB101 DSB Modulator and Demodulator AB102 SSB Modulator and Demodulator AB106 FM Modulator and Demodulator and many more Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 7
8 THEORY A Passive Attenuator is a resistive network that is used to introduce a fixed amount of attenuation between source and load, this device creates loss (attenuation) in transmission line. Attenuator reduces or lowers the amplitude or power of the signal without distorting its waveform. Fixed attenuators are often called pads, especially in telephony. Attenuator pads can be designed with many different attributes: matched impedances, unmatched impedances. The amount of power reduction produced by attenuator is measured in decibels while its overall ability depends on the type of attenuator is being used. The concept is that maximum power transfer occurs when the load impedance matches the source impedance. Today, most audio systems operate on the voltage transmission model. Sources have low impedances, and loads are many times this impedance so that total voltage can transfer. Attenuator can model the connection of source and load as a voltage divider, so that majority of the source voltage appears across the load, and only a small fraction is lost in the resistance representing the source impedance. Any application that requires a reduction in power output may require the installation of attenuators. Passive Attenuator pads are used in amplifier, detectors, match circuits, laboratory application and balance transmission lines. Fig.1 shows the network with and without attenuator. Network (a) without attenuator pad (b) with attenuator pad Fig. 1 Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 8
9 In addition to providing attenuation of the signal, the pad usually provide input and output matching, hence R IN must be equal to the source resistance R S and output resistance R OUT must be equal to load resistance R L. If the reference loads current of the network without attenuator is I LO, I LO = E / (R S + R L ) and I L is the reference load current of the attenuation pad (the value of I L is depend on the total resistance of network, which differs according to the resistance arrangement in the network), then the insertion loss (IL) or attenuation due to attenuator pad is, IL = I L / I LO (1) The insertion loss IL is usually quoted in decibels. This will denote by IL db, which by definition is IL db = -20 log [I L / I LO ] (2) The negative sign is to show that attenuation occurs and the insertion loss will be come out as a positive number of decibels. Passive Attenuator has been classified according to the arrangement of resistor in network. Commonly employed attenuator networks are : 1. T attenuator, 2. п attenuator, 3. Bridge-T attenuator. T Attenuator : The name T-attenuator arises due to circuit configured like the letter T of English and is consist of one resistance in each arm. Fig.2 shows the passive T attenuator s circuit diagram. T-attenuator Fig. 2 Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 9
10 Applying the Kirchhoff s voltage law to loop consisting of source and R 1 and R 2. Applying the Kirchhoff s voltage law to loop consisting of R 2, R L and R 3. Thus, Put the value of I L in Eq.1 for insertion loss. Thus, For the value of input resistance, the source is removed and the load left connected. The input resistance is that seen looking to the right into the network. For the output resistance, the load is removed and the source left connected (with source emf. at zero). The output resistance is that seen looking to the left into the network. It causes problem in designing an attenuator to meet specified values of input resistance, output resistance and insertion loss. Above equations can be solved for R 1, R 2 and R 3 but to obtain this resistor s value a complex numerical method is to be employed. Furthermore, not all the combinations of input resistance, output resistance met in given attenuation design, and where the design fails, some of the resistor value come out negative; which shows that the attenuator is physically unrealizable. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 10
11 Although the attenuator design is best achieved by computational methods, but when an attenuator has to provide a specific attenuation between a matched source and load, an analytical solution can be used. If, R IN = R OUT = R O and, R 1 = R 2 = R, Then, п-attenuator : The name п-attenuator is arises due to circuit configured like the Greek letter п. Fig.3 shows the п-attenuator. п-attenuator Fig. 3 The input resistance output resistance and insertion loss can be solved in terms of network resistor. Though, the equation can be easily solved in terms of conduction (reciprocal of resistance). Alternatively, these equations transformed through duality to give, for the п-attenuator. Although the equations are most easily solved in terms of conduction, resistor values will usually be specified. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 11
12 The computations therefore require extra steps of converting source resistance and load resistance into conductance and, once the network conduction is found, converting these back into resistor values. Alternatively, a T-attenuator can be design for given insertion loss and value of R 1, R 2 and R 3 can be converted in to R A, R B and R C by using Y- transformation. For the specific case of equal input and output resistance, these equations can be simplified. Where, R A = R B = R, Then, R IN = R OUT = R O Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 12
13 Bridge T-Attenuator : The Bridge-T attenuator consists of two networks into one attenuator. It is a very useful tool to reduce the level of a signal without changing the impedance of the circuit. Fig.4 shows the Bridge-T diagram. I2 E Bridge-T Attenuator Fig. 4 Taking the condition when load impedance matches the source impedance, and input resistance is equal to output resistance. The value of R 2 and R 3 is equal to the input output load Then, and, where, R 2 = R 3 = R IN = R OUT = R O IL = log -1 [IL db /-20] R 1 = R 3.(N-1) R 4 = R 3 /(N-1) N = log -1 [IL db /20] Thus N can be define as voltage ratio of attenuator. There is no particular advantage of T-Attenuator over п-attenuator or over Bridge-T Attenuator or vice versa, except then when one type is more practical then another i.e. resistance in one network are more physiable then resistance in another network. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 13
14 EXPERIMENT 1 Objective : To study the attenuation response of Passive T-Attenuator. Apparatus required : 1. Analog board of AB Function generator ST Oscilloscope 4. Digital Multimeter 5. 2 mm patch cords. Circuit diagram : Circuit used to study the response of Passive Attenuators is in Fig 5. Fig. 5 Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 14
15 Procedure : Calculate the value of R 2, R 3 and R 4 for 2db attenuation (insertion loss) by equation given below. 1. Adjust the potentiometer R 2, R 3 and R 4 to set the value of resistance according the calculation. 2. Connect function generator ST4060 probes at socket p and ground for T-Attenuator. 3. Set the 1V pp, 1 KHz input sinusoidal signal of function generator and observe the input at oscilloscope CH II. 4. Observe the output waveform between output socket q and ground, on oscilloscope CH I. 5. Measure the amplitude loss on oscilloscope. 6. Increase the input voltage and measure the amplitude loss for each input voltage. 7. Calculate the value of R 2, R 3 and R 4 for 7db attenuation loss by equation given below. 8. Repeat the above step from 1 to Calculate the value of R 2, R 3 and R 4 for 10db attenuation by equation given below. 10. Repeat the above step from 1 to 6. Note : Any specific value of attenuation (insertion loss) can be taken instead of given values. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 15
16 OBSERVATION TABLE S. No. Attenuation IL db (db) IL R 2 R 3 R 4 Input Output (calculated) Output (measured) Calculation : Measure the value of IL for a given value of IL db, IL db = IL = log -1 [IL db /-20] For a condition where input resistance is equal to output resistance If R IN = R OUT = R O = 50Ω and, R 2 = R 3 = R Then, Result : The measured output of T-Attenuator is. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 16
17 EXPERIMENT 2 Objective : To study the attenuation response of Passive Π-Attenuator. Apparatus required : 1. Analog board of AB Function generator ST Oscilloscope 4. Digital Multimeter 5. 2 mm patch cords. Circuit diagram : Circuit used to study the response of Passive Attenuators is in fig 6. Fig. 6 Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 17
18 Procedure : Calculate the value of R 1, R 2 and R 3 for 2db attenuation (insertion loss) by equation given below. 1. Adjust the potentiometer R 1, R 2 and R 3 to set the value of resistance according the calculation. 2. Connect 2mm patch cord between socket b and p and between socket c and q. 3. Connect 2mm patch cord between socket r and ground, to form a п-attenuator. 4. Connect function generator ST4060 probes at socket a and ground, for п-attenuator. 5. Set the 1V pp, 1 KHz input sinusoidal signal of function generator and observe the input at oscilloscope CH II. 6. Observe the output waveform between output socket d and ground, on oscilloscope CH I. 7. Measure the amplitude loss on oscilloscope. 8. Increase the input voltage and measure the amplitude loss for each input voltage. 9. Calculate the value of R 1, R 2 and R 3 for 7db attenuation loss by equation given below. 10. Repeat the above step from 1 to Calculate the value of R 1, R 2 and R 3 for 10db attenuation by equation given below. 12. Repeat the above step from 1 to 8. Note : Any specific value of attenuation (insertion loss) can be taken instead of given values. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 18
19 OBSERVATION TABLE S. No. Attenuation (db) IL R 1 R 2 R 3 Input Output (calculated) Output (measured) Calculation : Measure the value of IL for a given value of IL db, IL db = IL = log -1 [IL db /-20] For a condition where input resistance is equal to output resistance If R IN = R OUT = R O = 50Ω and, R 2 = R 3 = R Then, Result : The measured output of п-attenuator is. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 19
20 EXPERIMENT 3 Objective : To study the attenuation response of Passive Bridge-T Attenuator. Apparatus required : 1. Analog board of AB Function generator ST Oscilloscope 4. Digital Multimeter 5. 2 mm patch cords. Circuit diagram : Circuit used to study the response of Passive Attenuators is in Fig 7. Fig. 7 Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 20
21 Procedure : Calculate the value of R 1, R 2, R 3 and R 4 for 2db attenuation (insertion loss) by equation given below. 1. Adjust the potentiometer R 1, R 2, R 3 and R 4 to set the value of resistance according the calculation. 2. Connect 2mm patch cord between socket b and p and between socket c and q. 3. Connect function generator ST4060 probes at socket a and ground for Bridge-T Attenuator. 4. Set the 1V pp, 1 KHz input sinusoidal signal of function generator and observe the input at oscilloscope CH II 5. Observe the output waveform between output socket d and ground, on oscilloscope CH I. 6. Measure the amplitude loss on oscilloscope. 7. Increase the input voltage and measure the amplitude loss for each input voltage. 8. Calculate the value of R 1, R 2, R 3 and R 4 for 7db attenuation loss by equation given below. 9. Repeat the above step from 1 to Calculate the value of R 1, R 2, R 3 and R 4 for 10db attenuation by equation given below. 11. Repeat the above step from 1 to 7. Note : Any specific value of attenuation (insertion loss) can be taken instead of given values. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 21
22 OBSERVATION TABLE S. No. Attenuation (db) IL R 1 R 3 & R 2 R 4 Input Output (calculated) Output (measured) Calculation : Measure the value of IL for a given value of IL db, IL db = IL = log -1 [IL db /-20] For a condition where input resistance is equal to output resistance If R IN = R OUT = R O = 50Ω For a Bridge-T Attenuator the value of R 2 and R 3 is also equal to input and output resistor, Then, and, R 2 = R 3 = R O R 1 = R 3.(N-1) R 4 = R 3 /(N-1) where N = log -1 [IL db /20] Thus N can be define as voltage ratio of attenuator. Result : The measured output of Bridge-T Attenuator is. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 22
23 WARRANTY 1. We guarantee the instrument against all manufacturing defects during 24 months from the date of sale by us or through our dealers. 2. The guarantee covers manufacturing defects in respect of indigenous components and material limited to the warranty extended to us by the original manufacturer, and defect will be rectified as far as lies within our control. 3. The guarantee will become INVALID. a. If the instrument is not operated as per instruction given in the instruction manual. b. If the agreed payment terms and other conditions of sale are not followed. c. If the customer resells the instrument to another party. d. Provided no attempt have been made to service and modify the instrument. 4. The non-working of the instrument is to be communicated to us immediately giving full details of the complaints and defects noticed specifically mentioning the type and sr. no. of the instrument, date of purchase etc. 5. The repair work will be carried out, provided the instrument is dispatched securely packed and insured with the railways. To and fro charges will be to the account of the customer. DISPATCH PROCEDURE FOR SERVICE Should it become necessary to send back the instrument to factory please observe the following procedure: 1. Before dispatching the instrument please write to us giving fully details of the fault noticed. 2. After receipt of your letter our repairs dept. will advise you whether it is necessary to send the instrument back to us for repairs or the adjustment is possible in your premises. Dispatch the instrument (only on the receipt of our advice) securely packed in original packing duly insured and freight paid along with accessories and a copy of the details noticed to us at our factory address. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 23
24 LIST OF SERVICE CENTERS 1. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 90, Electronic Complex Ph: (0731) Pardesipura, INDORE Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. Ph.: (011) , First Floor, 14, Uday Park, Fax: (011) NEW DELHI Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. New no.2, Old no.10, 4 th street Ph.: (044) , Venkateswara nagar, Adyar Fax: (044) CHENNAI chennai@scientech.bz 4. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 202/19, 4 th main street Ph.: (080) Ganganagar, Fax: (080) BANGALORE bangalore@scientech.bz 5. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. Ph.: (022) ,1st floor, 123-Hariram Mansion, Fax: (022) Dada Saheb Phalke road, stplmum@vsnl.net Dadar (East), MUMBAI Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 988, Sadashiv Peth, Ph.: (020) Gyan Prabodhini Lane, Fax: (020) PUNE pune@scientech.bz 7. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd SPS Apartment, 1 st Floor Ph.: , Ahmed Mamoji Street, kolkata@scientech.bz Behind Jaiswal Hospital, Liluah, HOWRAH W.B. 8. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd Ph.: (040) Flat No. 205, 2 nd Floor, hyd@scientech.bz Lakshminarayana Apartments C wing, Street No. 17, Himaytnagar, HYDERABAD Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 24
25 LIST OF ACCESSORIES 1. 2mm Patch cord (Red)... 2 Nos. 2. 2mm Patch cord (Black)... 2 Nos. 3. 2mm Patch cord (Blue)... 3 Nos. Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 25
26 NOTES Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 26
Analog Lab Experiment Board Ver. 1.0
 PHASE SHIFT OSCILLATOR Analog Lab Experiment Board Ver. 1.0 QUALITY POLICY To be a Global Provider of Innovative and Affordable Electronic Equipments for Technology Training by enhancing Customer Satisfaction
PHASE SHIFT OSCILLATOR Analog Lab Experiment Board Ver. 1.0 QUALITY POLICY To be a Global Provider of Innovative and Affordable Electronic Equipments for Technology Training by enhancing Customer Satisfaction
AB-30 V-I AND I-V CONVERTER
 V-I AND I-V CONVERTER ANALOG LAB EXPERIMENT BOARD Ver. 1.0 An ISO 9001: 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura INDORE-452010, India. Tel.: 91-731-2570301 Fax: 91-731-2555643 Email: info@scientech.bz
V-I AND I-V CONVERTER ANALOG LAB EXPERIMENT BOARD Ver. 1.0 An ISO 9001: 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura INDORE-452010, India. Tel.: 91-731-2570301 Fax: 91-731-2555643 Email: info@scientech.bz
SCHERING BRIDGE AB13. Analog Lab Experiment Board Ver. 1.0
 SCHERING BRIDGE AB13 Analog Lab Experiment Board Ver. 1.0 QUALITY POLICY To be a Global Provider of Innovative and Affordable Electronic Equipments for Technology Training by enhancing Customer Satisfaction
SCHERING BRIDGE AB13 Analog Lab Experiment Board Ver. 1.0 QUALITY POLICY To be a Global Provider of Innovative and Affordable Electronic Equipments for Technology Training by enhancing Customer Satisfaction
AB-45 Operational Amplifier (Schmitt Trigger & Comparators) ANALOG LAB EXPERIMENT BOARD Ver. 1.0
 Operational Amplifier (Schmitt Trigger & Comparators) ANALOG LAB EXPERIMENT BOARD Ver. 1.0 An ISO 9001: 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura INDORE-452010, India. Tel.: 91-731-2570301 Fax:
Operational Amplifier (Schmitt Trigger & Comparators) ANALOG LAB EXPERIMENT BOARD Ver. 1.0 An ISO 9001: 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura INDORE-452010, India. Tel.: 91-731-2570301 Fax:
Operating Manual Ver.1.1
 Colpitt s Oscillator Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731- 2555643 e mail : info@scientech.bz
Colpitt s Oscillator Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731- 2555643 e mail : info@scientech.bz
Operating Manual Ver.1.1
 Phase Shift Oscillator Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731- 2555643 e mail :
Phase Shift Oscillator Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731- 2555643 e mail :
Operating Manual Ver.1.1
 SSB Modulator and Demodulator Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731- 2555643 e
SSB Modulator and Demodulator Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731- 2555643 e
Analog Lab Experiment Board Ver. 1.0
 SILICON, ZENER, LED DIODE CHARACTERISTICS Analog Lab Experiment Board Ver. 1.0 QUALITY POLICY To be a Global Provider of Innovative and Affordable Electronic Equipments for Technology Training by enhancing
SILICON, ZENER, LED DIODE CHARACTERISTICS Analog Lab Experiment Board Ver. 1.0 QUALITY POLICY To be a Global Provider of Innovative and Affordable Electronic Equipments for Technology Training by enhancing
Operating Manual Ver.1.1
 Common Base NPN Transistor Characteristics Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731-
Common Base NPN Transistor Characteristics Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731-
Operating Manual Ver.1.1
 Common Collector Amplifier Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731- 2555643 e mail
Common Collector Amplifier Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731- 2555643 e mail
Operating Manual Ver.1.1
 Multivibrators (Astable and Monostable) Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731-
Multivibrators (Astable and Monostable) Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731-
Operating Manual Ver.1.1
 FET Amplifier Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731- 2555643 e mail : info@scientech.bz
FET Amplifier Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731- 2555643 e mail : info@scientech.bz
Operating Manual Ver.1.1
 SCR Triggering Techniques ST2703 Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731- 2555643
SCR Triggering Techniques ST2703 Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731- 2555643
DIGITAL ELECTRONICS ANALOG ELECTRONICS
 DIGITAL ELECTRONICS 1. N10 4 Bit Binary Universal shift register. 2. N22- Random Access Memory (16*4). 3. N23- Read Only Memory. 4. N4-R-S/D-T Flip flop, characteristic and comparison. 5. Master Slave
DIGITAL ELECTRONICS 1. N10 4 Bit Binary Universal shift register. 2. N22- Random Access Memory (16*4). 3. N23- Read Only Memory. 4. N4-R-S/D-T Flip flop, characteristic and comparison. 5. Master Slave
APPLIED ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS
 SRM UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING ODD Semester-2014-2015 BM1005 APPLIED ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS Course Code: BM1005 Course Title: APPLIED ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS Sem: III SEM B. Tech Second Year
SRM UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING ODD Semester-2014-2015 BM1005 APPLIED ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS Course Code: BM1005 Course Title: APPLIED ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS Sem: III SEM B. Tech Second Year
Operating Manual Ver.1.1
 UJT Characteristics Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731- 2555643 e mail : info@scientech.bz
UJT Characteristics Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100 Fax: 91-731- 2555643 e mail : info@scientech.bz
UNIT 1 MULTI STAGE AMPLIFIES
 UNIT 1 MULTI STAGE AMPLIFIES 1. a) Derive the equation for the overall voltage gain of a multistage amplifier in terms of the individual voltage gains. b) what are the multi-stage amplifiers? 2. Describe
UNIT 1 MULTI STAGE AMPLIFIES 1. a) Derive the equation for the overall voltage gain of a multistage amplifier in terms of the individual voltage gains. b) what are the multi-stage amplifiers? 2. Describe
SCR Triggering Techniques Scientech 2703
 SCR Triggering Techniques Scientech 2703 Learning Material Ver 1.1 An ISO 9001:2008 company Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 94, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura, Indore - 452 010 India, + 91-731 4211100,
SCR Triggering Techniques Scientech 2703 Learning Material Ver 1.1 An ISO 9001:2008 company Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 94, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura, Indore - 452 010 India, + 91-731 4211100,
Operating Manual Ver.1.1
 Fourier Synthesis Trainer ST2603 Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, INDIA Ph: 91-731- 2556638, 2570301 Fax: 91-731- 2555643 E-mail
Fourier Synthesis Trainer ST2603 Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, INDIA Ph: 91-731- 2556638, 2570301 Fax: 91-731- 2555643 E-mail
PRODUCT CATALOG TRAINER KITS FOR ENGINEERING DEGREE COURSES MICROTECH INDUSTRIES
 PRODUCT CATALOG TRAINER KITS FOR ENGINEERING DEGREE COURSES µ MICROTECH INDUSTRIES 14A/ 1G, ULTADANGA ROAD GOPAL BHAVAN KOLKATA 700 004 Phone : (033) 3296 9273, Cell : 98312 63293 E- mail : hkg@cal3.vsnl.net.in
PRODUCT CATALOG TRAINER KITS FOR ENGINEERING DEGREE COURSES µ MICROTECH INDUSTRIES 14A/ 1G, ULTADANGA ROAD GOPAL BHAVAN KOLKATA 700 004 Phone : (033) 3296 9273, Cell : 98312 63293 E- mail : hkg@cal3.vsnl.net.in
DC/AC CIRCUITS: CONVENTIONAL FLOW TEXTBOOKS
 4 PEARSON CUSTOM ELECTRONICS TECHNOLOGY DC/AC CIRCUITS: CONVENTIONAL FLOW TEXTBOOKS AVAILABLE MARCH 2009 Boylestad Introductory Circuit Analysis, 11/e, 0-13-173044-4 Introduction 32 LC4501 Voltage and
4 PEARSON CUSTOM ELECTRONICS TECHNOLOGY DC/AC CIRCUITS: CONVENTIONAL FLOW TEXTBOOKS AVAILABLE MARCH 2009 Boylestad Introductory Circuit Analysis, 11/e, 0-13-173044-4 Introduction 32 LC4501 Voltage and
Lesson Plan. Electronics 1-Total 51 Hours
 Lesson Plan. Electronics 1-Total 5s Unit I: Electrical Engineering materials:(10) Crystal structure & defects; Ceramic materials-structures, composites, processing and uses; Insulating laminates for electronics,
Lesson Plan. Electronics 1-Total 5s Unit I: Electrical Engineering materials:(10) Crystal structure & defects; Ceramic materials-structures, composites, processing and uses; Insulating laminates for electronics,
TEACHING & EXAMINATION SCHEME For the Examination 2015 ELECTRONICS. B.Sc. Part - I
 TEACHING & EXAMINATION SCHEME For the Examination 2015 ELECTRONICS THEORY B.Sc. Part - I Elec. 101 Paper I Circuit Elements and Networks Pd/W Exam. Max. (45mts.) Hours Marks 150 2 3 50 Elec. 102 Paper
TEACHING & EXAMINATION SCHEME For the Examination 2015 ELECTRONICS THEORY B.Sc. Part - I Elec. 101 Paper I Circuit Elements and Networks Pd/W Exam. Max. (45mts.) Hours Marks 150 2 3 50 Elec. 102 Paper
The steeper the phase shift as a function of frequency φ(ω) the more stable the frequency of oscillation
 It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
B.Sc. Syllabus for Electronics under CBCS. Semester-I
 Semester-I Title: Electronic Circuit Analysis Course Code: UELTC101 Credits: 4 Total Marks: 100 Internal Examination: 20 marks End Semester Examination: 80 marks Duration: 3 hours Validity of Syllabus:
Semester-I Title: Electronic Circuit Analysis Course Code: UELTC101 Credits: 4 Total Marks: 100 Internal Examination: 20 marks End Semester Examination: 80 marks Duration: 3 hours Validity of Syllabus:
Gujarat University B. Sc. Electronics Semester I: ELE (Effective from: )
 Unit - I: Components and Instrumentation: Gujarat University B. Sc. Electronics Semester I: ELE - 101 Passive Circuit devices: Resistors, nonlinear resistors, inductors, types of inductors, capacitors,
Unit - I: Components and Instrumentation: Gujarat University B. Sc. Electronics Semester I: ELE - 101 Passive Circuit devices: Resistors, nonlinear resistors, inductors, types of inductors, capacitors,
LINEAR IC APPLICATIONS
 1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
i Intelligent Digitize Emulated Achievement Lab
 Electronics Circuits Equipment Intelligent Digitize Emulated Achievement Lab intelligent digitize emulated achievement lab is a digitized-based training system, which utilizes integrated Hardware Platform,
Electronics Circuits Equipment Intelligent Digitize Emulated Achievement Lab intelligent digitize emulated achievement lab is a digitized-based training system, which utilizes integrated Hardware Platform,
Learning Material Ver 1.1
 Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) ST2701 Learning Material Ver 1.1 An ISO 9001:2008 company Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 94, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura, Indore - 452 010 India, + 91-731
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) ST2701 Learning Material Ver 1.1 An ISO 9001:2008 company Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 94, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura, Indore - 452 010 India, + 91-731
Ohm Technologiees.
 +91-8048706704 Ohm Technologiees https://www.ohmtechnologiees.com/ Our company is engaged in manufacturing, supplying and importing the most sought after range Scientific Electronic Equipment. These products
+91-8048706704 Ohm Technologiees https://www.ohmtechnologiees.com/ Our company is engaged in manufacturing, supplying and importing the most sought after range Scientific Electronic Equipment. These products
Unit/Standard Number. LEA Task # Alignment
 1 Secondary Competency Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding
1 Secondary Competency Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding
Operating Manual Ver 1.1
 Frequency Modulation and Demodulation Trainer ST2203 Operating Manual Ver 1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100
Frequency Modulation and Demodulation Trainer ST2203 Operating Manual Ver 1.1 An ISO 9001 : 2000 company 94-101, Electronic Complex Pardesipura, Indore- 452010, India Tel : 91-731- 2570301/02, 4211100
Associate In Applied Science In Electronics Engineering Technology Expiration Date:
 PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Associate In Applied Science In Electronics Engineering Technology Expiration Date: 1 2330A Current and Voltage 2 2330B Controlling Current
PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Associate In Applied Science In Electronics Engineering Technology Expiration Date: 1 2330A Current and Voltage 2 2330B Controlling Current
Communication Circuit Lab Manual
 German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 2 Tuned Amplifier Eng. Anas Alashqar
German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 2 Tuned Amplifier Eng. Anas Alashqar
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road QUESTION BANK
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK Subject with Code : Electronic Circuit Analysis (16EC407) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK Subject with Code : Electronic Circuit Analysis (16EC407) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & II-Sem
An active filter offers the following advantages over a passive filter:
 ACTIVE FILTERS An electric filter is often a frequency-selective circuit that passes a specified band of frequencies and blocks or attenuates signals of frequencies outside this band. Filters may be classified
ACTIVE FILTERS An electric filter is often a frequency-selective circuit that passes a specified band of frequencies and blocks or attenuates signals of frequencies outside this band. Filters may be classified
DEPT. OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGG SRM INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY LESSON PLAN. Subject Name : Electronic Circuits
 DEPT. OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGG SRM INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY LESSON PLAN Subject Code : EE0208 Subject Name : Electronic Circuits Branch : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS Year : II Section C
DEPT. OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGG SRM INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY LESSON PLAN Subject Code : EE0208 Subject Name : Electronic Circuits Branch : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS Year : II Section C
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT-I - PN DIODEAND ITSAPPLICATIONS 1. What is depletion region in PN junction?
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT-I - PN DIODEAND ITSAPPLICATIONS 1. What is depletion region in PN junction?
Oscillators. An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier.
 Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS. Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi
 EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi 2.1 INTRODUCTION An electronic circuit which is designed to generate a periodic waveform continuously at
EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi 2.1 INTRODUCTION An electronic circuit which is designed to generate a periodic waveform continuously at
Xeltronix.
 +91-8048720001 Xeltronix https://www.indiamart.com/xeltronix/ Reckoned firms engaged in manufacturing and supplying a quality array of Electronic Trainer Kits, we ensure that our products would serve the
+91-8048720001 Xeltronix https://www.indiamart.com/xeltronix/ Reckoned firms engaged in manufacturing and supplying a quality array of Electronic Trainer Kits, we ensure that our products would serve the
UNIT I Introduction to DC & AC circuits
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
State the application of negative feedback and positive feedback (one in each case)
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Subject Code: 073 Model wer Page No: / N Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Subject Code: 073 Model wer Page No: / N Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
 OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
EC202- ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS II Unit- I -FEEEDBACK AMPLIFIER
 EC202- ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS II Unit- I -FEEEDBACK AMPLIFIER 1. What is feedback? What are the types of feedback? 2. Define positive feedback. What are its merits and demerits? 3. Define negative feedback.
EC202- ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS II Unit- I -FEEEDBACK AMPLIFIER 1. What is feedback? What are the types of feedback? 2. Define positive feedback. What are its merits and demerits? 3. Define negative feedback.
Learning Material Ver 1.1
 SCR Triggering Circuits Scientech 2702 Learning Material Ver 1.1 An ISO 9001:2008 company Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 94, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura, Indore - 452 010 India, + 91-731 4211100,
SCR Triggering Circuits Scientech 2702 Learning Material Ver 1.1 An ISO 9001:2008 company Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 94, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura, Indore - 452 010 India, + 91-731 4211100,
UNIT 1. 9 What is the Causes of Free Response in Electrical Circuit. 12 Write the Expression for transient current and voltages of RL circuit.
 SUB: Electric Circuits and Electron Devices Course Code: UBEE309 UNIT 1 PART A 1 State Transient and Transient Time? 2 What is Tansient State? 3 What is Steady State? 4 Define Source Free Response 5 Define
SUB: Electric Circuits and Electron Devices Course Code: UBEE309 UNIT 1 PART A 1 State Transient and Transient Time? 2 What is Tansient State? 3 What is Steady State? 4 Define Source Free Response 5 Define
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET REV. NO. : REV.
 Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET LABORATORY MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO. ISSUE NO. : ISSUE DATE: July 200 REV. NO. : REV.
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET LABORATORY MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO. ISSUE NO. : ISSUE DATE: July 200 REV. NO. : REV.
Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I
 Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I AC Fundamentals & Kirchhoff s Current and Voltage Laws 1. Explain how a sinusoidal signal can be generated and give the significance of each term in the equation? 2. Define
Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I AC Fundamentals & Kirchhoff s Current and Voltage Laws 1. Explain how a sinusoidal signal can be generated and give the significance of each term in the equation? 2. Define
BE Assignment. (1) Explain Active component and Passive component in Detail. (1) Explain practical voltage source and ideal voltage source.
 BE Assignment chapter-1 (1) Explain Active component and Passive component in Detail. (1) Explain practical voltage source and ideal voltage source. (2) Explain practical current source and ideal current
BE Assignment chapter-1 (1) Explain Active component and Passive component in Detail. (1) Explain practical voltage source and ideal voltage source. (2) Explain practical current source and ideal current
Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits
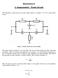 Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits This laboratory session involves circuits which contain a double-t (or TT), a passive RC circuit: Figure 1. Double T passive RC circuit module The upper
Electronics II. 3. measurement : Tuned circuits This laboratory session involves circuits which contain a double-t (or TT), a passive RC circuit: Figure 1. Double T passive RC circuit module The upper
UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI COLLEGE OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHYSICAL SCIENCES FACULTY OF SCIENCE SPH 307 INTRODUCTORY ELECTRONICS
 UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI COLLEGE OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHYSICAL SCIENCES FACULTY OF SCIENCE SPH 307 INTRODUCTORY ELECTRONICS Dr. Kenneth A. Kaduki Department of Physics University of Nairobi Reviewer: Prof. Bernard
UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI COLLEGE OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHYSICAL SCIENCES FACULTY OF SCIENCE SPH 307 INTRODUCTORY ELECTRONICS Dr. Kenneth A. Kaduki Department of Physics University of Nairobi Reviewer: Prof. Bernard
Table of Contents...2. About the Tutorial...6. Audience...6. Prerequisites...6. Copyright & Disclaimer EMI INTRODUCTION Voltmeter...
 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 About the Tutorial...6 Audience...6 Prerequisites...6 Copyright & Disclaimer...6 1. EMI INTRODUCTION... 7 Voltmeter...7 Ammeter...8 Ohmmeter...8 Multimeter...9
1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 About the Tutorial...6 Audience...6 Prerequisites...6 Copyright & Disclaimer...6 1. EMI INTRODUCTION... 7 Voltmeter...7 Ammeter...8 Ohmmeter...8 Multimeter...9
 PREFACE xvii PRACTICAL TRANSISTOR CIRCUIT THEORY 1.1 Iterated Circuits 1.2 Symbols 1.3 Feedback 1.4 The Miller Effect 1.5 Transistors 1.6 The transistor gain-impedance relation 1.7 Ohm's law and dc current-voltage
PREFACE xvii PRACTICAL TRANSISTOR CIRCUIT THEORY 1.1 Iterated Circuits 1.2 Symbols 1.3 Feedback 1.4 The Miller Effect 1.5 Transistors 1.6 The transistor gain-impedance relation 1.7 Ohm's law and dc current-voltage
R & D Electronics DIGITAL IC TRAINER. Model : DE-150. Feature: Object: Specification:
 DIGITAL IC TRAINER Model : DE-150 Object: To Study the Operation of Digital Logic ICs TTL and CMOS. To Study the All Gates, Flip-Flops, Counters etc. To Study the both the basic and advance digital electronics
DIGITAL IC TRAINER Model : DE-150 Object: To Study the Operation of Digital Logic ICs TTL and CMOS. To Study the All Gates, Flip-Flops, Counters etc. To Study the both the basic and advance digital electronics
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) PART - A
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
Lab 4 : Transistor Oscillators
 Objective: Lab 4 : Transistor Oscillators In this lab, you will learn how to design and implement a colpitts oscillator. In part II you will implement a RC phase shift oscillator Hardware Required : Pre
Objective: Lab 4 : Transistor Oscillators In this lab, you will learn how to design and implement a colpitts oscillator. In part II you will implement a RC phase shift oscillator Hardware Required : Pre
PART-A UNIT I Introduction to DC & AC circuits
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207)
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207)
Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter
 SSB Reception Analog Communications Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION On the circuit board, you will set up the SSB transmitter to transmit a 1000 khz SSB signal
SSB Reception Analog Communications Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION On the circuit board, you will set up the SSB transmitter to transmit a 1000 khz SSB signal
Electronic Troubleshooting. Chapter 5 Multistage Amplifiers
 Electronic Troubleshooting Chapter 5 Multistage Amplifiers Overview When more amplification is required than can be supplied by a single stage amp A second stage is added Or more stages are added Aspects
Electronic Troubleshooting Chapter 5 Multistage Amplifiers Overview When more amplification is required than can be supplied by a single stage amp A second stage is added Or more stages are added Aspects
Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months
 PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months 1 2330A Current
PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months 1 2330A Current
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY EN107/1 Department of Electronic and Information Engineering. EN107: OCL Class AB Power Amplifier Objective
 THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY EN107/1 EN107: OCL Class AB Power Amplifier Objective 1. To study the circuit performance of an OCL amplifier. 2. To study the effects of biasing on cross-over distortion
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY EN107/1 EN107: OCL Class AB Power Amplifier Objective 1. To study the circuit performance of an OCL amplifier. 2. To study the effects of biasing on cross-over distortion
Scheme I Sample Question Paper
 Sample Question Paper Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any FIVE of the following. 10 Marks a) Classify configuration of differential amplifier. b) Draw equivalent circuit of an OPAMP c) Suggest and
Sample Question Paper Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any FIVE of the following. 10 Marks a) Classify configuration of differential amplifier. b) Draw equivalent circuit of an OPAMP c) Suggest and
Analog Electronic Circuits Lab-manual
 2014 Analog Electronic Circuits Lab-manual Prof. Dr Tahir Izhar University of Engineering & Technology LAHORE 1/09/2014 Contents Experiment-1:...4 Learning to use the multimeter for checking and indentifying
2014 Analog Electronic Circuits Lab-manual Prof. Dr Tahir Izhar University of Engineering & Technology LAHORE 1/09/2014 Contents Experiment-1:...4 Learning to use the multimeter for checking and indentifying
LIST OF TRAINING MODULES
 LIST OF TRAINING MODULES S.NO. TYPE SECTION-A (CHARACTERISTICS) 1. Diode & Zener Diode Characteristics EE-1 2. Tunnel Diode Characteristics EE-P50 3. L.E.D. Characteristics EE-2 4. Transistor Characteristics
LIST OF TRAINING MODULES S.NO. TYPE SECTION-A (CHARACTERISTICS) 1. Diode & Zener Diode Characteristics EE-1 2. Tunnel Diode Characteristics EE-P50 3. L.E.D. Characteristics EE-2 4. Transistor Characteristics
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUBJECT QUESTION BANK : EC6401 ELECTRONICS CIRCUITS-II SEM / YEAR: IV / II year B.E.
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUBJECT QUESTION BANK : EC6401 ELECTRONICS CIRCUITS-II SEM / YEAR: IV / II year B.E.
Signal Generators and Waveform-Shaping Circuits
 CHAPTER 18 Signal Generators and Waveform-Shaping Circuits Figure 18.1 The basic structure of a sinusoidal oscillator. A positive-feedback loop is formed by an amplifier and a frequency-selective network.
CHAPTER 18 Signal Generators and Waveform-Shaping Circuits Figure 18.1 The basic structure of a sinusoidal oscillator. A positive-feedback loop is formed by an amplifier and a frequency-selective network.
Summer 2015 Examination
 Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS LAB
 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS LAB 1 2 STATE INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS TRAINING AND RESEARCH GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS Rough record and Fair record are needed to record the experiments conducted in the laboratory.
ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS LAB 1 2 STATE INSTITUTE OF TECHNICAL TEACHERS TRAINING AND RESEARCH GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS Rough record and Fair record are needed to record the experiments conducted in the laboratory.
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R059210404 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Supplimentary Examinations, February 2008 ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics)
Code No: R059210404 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Supplimentary Examinations, February 2008 ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics)
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-2012 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
Chapter 8. Chapter 9. Chapter 6. Chapter 10. Chapter 11. Chapter 7
 5.5 Series and Parallel Combinations of 246 Complex Impedances 5.6 Steady-State AC Node-Voltage 247 Analysis 5.7 AC Power Calculations 256 5.8 Using Power Triangles 258 5.9 Power-Factor Correction 261
5.5 Series and Parallel Combinations of 246 Complex Impedances 5.6 Steady-State AC Node-Voltage 247 Analysis 5.7 AC Power Calculations 256 5.8 Using Power Triangles 258 5.9 Power-Factor Correction 261
Small signal Amplifier stages. Figure 5.2 Classification of power amplifiers
 5.1 Introduction When the power requirement to drive the load is in terms of several Watts rather than mili-watts the power amplifiers are used. Power amplifiers form the last stage of multistage amplifiers.
5.1 Introduction When the power requirement to drive the load is in terms of several Watts rather than mili-watts the power amplifiers are used. Power amplifiers form the last stage of multistage amplifiers.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS UNIT-1 SUBJECT : ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE : EC6202 BRANCH: EEE PART -A 1. What is meant by diffusion current in a semi conductor? (APR/MAY 2010, 2011, NOV/DEC
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS UNIT-1 SUBJECT : ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE : EC6202 BRANCH: EEE PART -A 1. What is meant by diffusion current in a semi conductor? (APR/MAY 2010, 2011, NOV/DEC
Electricity and Electronics Constructor Kits
 EEC470 Series The Electricity and Electronics Constructor EEC470 series is a structured practical training programme comprising an unpowered construction deck (EEC470) and a set of educational kits. Each
EEC470 Series The Electricity and Electronics Constructor EEC470 series is a structured practical training programme comprising an unpowered construction deck (EEC470) and a set of educational kits. Each
About the Tutorial. Audience. Prerequisites. Copyright & Disclaimer. Linear Integrated Circuits Applications
 About the Tutorial Linear Integrated Circuits are solid state analog devices that can operate over a continuous range of input signals. Theoretically, they are characterized by an infinite number of operating
About the Tutorial Linear Integrated Circuits are solid state analog devices that can operate over a continuous range of input signals. Theoretically, they are characterized by an infinite number of operating
EC1203: ELECTRONICS CIRCUITS-I UNIT-I TRANSISTOR BIASING PART-A
 SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH., TRICHY 621105 (Approved by AICTE, New Delhi and Affiliated to Anna University Chennai/Trichy) ( ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS &
SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH., TRICHY 621105 (Approved by AICTE, New Delhi and Affiliated to Anna University Chennai/Trichy) ( ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS &
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-2013 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
Devices and Op-Amps p. 1 Introduction to Diodes p. 3 Introduction to Diodes p. 4 Inside the Diode p. 6 Three Diode Models p. 10 Computer Circuit
 Contents p. v Preface p. ix Devices and Op-Amps p. 1 Introduction to Diodes p. 3 Introduction to Diodes p. 4 Inside the Diode p. 6 Three Diode Models p. 10 Computer Circuit Analysis p. 16 MultiSIM Lab
Contents p. v Preface p. ix Devices and Op-Amps p. 1 Introduction to Diodes p. 3 Introduction to Diodes p. 4 Inside the Diode p. 6 Three Diode Models p. 10 Computer Circuit Analysis p. 16 MultiSIM Lab
Function Generator Using Op Amp Ic 741 Theory
 Function Generator Using Op Amp Ic 741 Theory Note: Op-Amps ua741, LM 301, LM311, LM 324 & AD 633 may be used To design an Inverting Amplifier for the given specifications using Op-Amp IC 741. THEORY:
Function Generator Using Op Amp Ic 741 Theory Note: Op-Amps ua741, LM 301, LM311, LM 324 & AD 633 may be used To design an Inverting Amplifier for the given specifications using Op-Amp IC 741. THEORY:
Transistor Digital Circuits
 Recapitulation Transistor Digital Circuits The transistor Operating principle and regions Utilization of the transistor Transfer characteristics, symbols Controlled switch model BJT digital circuits MOSFET
Recapitulation Transistor Digital Circuits The transistor Operating principle and regions Utilization of the transistor Transfer characteristics, symbols Controlled switch model BJT digital circuits MOSFET
UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA EE 206
 UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA EE 206 TRANSISTOR BIASING CIRCUITS Introduction: One of the most critical considerations in the design of transistor amplifier stages is the ability of the circuit to maintain
UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA EE 206 TRANSISTOR BIASING CIRCUITS Introduction: One of the most critical considerations in the design of transistor amplifier stages is the ability of the circuit to maintain
INVITATION FOR QUOTATION. TEQIP-II/2015/UP1G01/Shopping/60
 INVITATION FOR QUOTATION TEQIP-II/2015/UP1G01/Shopping/60 24-Jul-2015 Sub: Invitation for Quotations for supply of Goods Dear Sir, 1. You are invited to submit your most competitive quotation for the following
INVITATION FOR QUOTATION TEQIP-II/2015/UP1G01/Shopping/60 24-Jul-2015 Sub: Invitation for Quotations for supply of Goods Dear Sir, 1. You are invited to submit your most competitive quotation for the following
Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers
 Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers Second Edition ROBERT E. SIMPSON University of New Hampshire Allyn and Bacon, Inc. Boston London Sydney Toronto Contents Preface xiü 1 Direct Current
Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers Second Edition ROBERT E. SIMPSON University of New Hampshire Allyn and Bacon, Inc. Boston London Sydney Toronto Contents Preface xiü 1 Direct Current
Communication Circuit Lab Manual
 German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 3 Crystal Oscillator Eng. Anas Alashqar
German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 3 Crystal Oscillator Eng. Anas Alashqar
B.Tech II SEM Question Bank. Electronics & Electrical Engg UNIT-1
 UNIT-1 1. State & Explain Superposition theorem & Thevinin theorem with example? 2. Calculate the current in the 400Ωm resistor of below figure by Superposition theorem. 3. State & Explain node voltage
UNIT-1 1. State & Explain Superposition theorem & Thevinin theorem with example? 2. Calculate the current in the 400Ωm resistor of below figure by Superposition theorem. 3. State & Explain node voltage
Code: 9A Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks *****
 II B. Tech II Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations, April/May 2012 ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS (Common to EIE, E. Con. E & ECE) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All
II B. Tech II Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations, April/May 2012 ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS (Common to EIE, E. Con. E & ECE) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All
tyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopas dfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzx cvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmq
 qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyui opasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfgh jklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvb nmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwer Instrumentation Device Components Semester 2 nd tyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopas
qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyui opasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfgh jklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvb nmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwer Instrumentation Device Components Semester 2 nd tyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopas
21/10/58. M2-3 Signal Generators. Bill Hewlett and Dave Packard s 1 st product (1939) US patent No HP 200A s schematic
 M2-3 Signal Generators Bill Hewlett and Dave Packard s 1 st product (1939) US patent No.2267782 1 HP 200A s schematic 2 1 The basic structure of a sinusoidal oscillator. A positive feedback loop is formed
M2-3 Signal Generators Bill Hewlett and Dave Packard s 1 st product (1939) US patent No.2267782 1 HP 200A s schematic 2 1 The basic structure of a sinusoidal oscillator. A positive feedback loop is formed
A Simplified Test Set for Op Amp Characterization
 A Simplified Test Set for Op Amp Characterization INTRODUCTION The test set described in this paper allows complete quantitative characterization of all dc operational amplifier parameters quickly and
A Simplified Test Set for Op Amp Characterization INTRODUCTION The test set described in this paper allows complete quantitative characterization of all dc operational amplifier parameters quickly and
Integrated Circuit: Classification:
 Integrated Circuit: It is a miniature, low cost electronic circuit consisting of active and passive components that are irreparably joined together on a single crystal chip of silicon. Classification:
Integrated Circuit: It is a miniature, low cost electronic circuit consisting of active and passive components that are irreparably joined together on a single crystal chip of silicon. Classification:
Sub Code & Name: EC2251- ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS II Unit : I Branch : ECE Year:II
 Unit : I Branch : ECE Year:II Page 01 of 06 UNIT 1 FEEDBACK AMPLIFIERS 9 Block diagram, Loop gain, Gain with feedback, Effects of negative feedback Sensitivity and desensitivity of gain, Cut-off frequencies,
Unit : I Branch : ECE Year:II Page 01 of 06 UNIT 1 FEEDBACK AMPLIFIERS 9 Block diagram, Loop gain, Gain with feedback, Effects of negative feedback Sensitivity and desensitivity of gain, Cut-off frequencies,
LESSON PLAN. SUBJECT: LINEAR IC S AND APPLICATION NO OF HOURS: 52 FACULTY NAME: Mr. Lokesh.L, Hema. B DEPT: ECE. Portions to be covered
 LESSON PLAN SUBJECT: LINEAR IC S AND APPLICATION SUB CODE: 15EC46 NO OF HOURS: 52 FACULTY NAME: Mr. Lokesh.L, Hema. B DEPT: ECE Class# Chapter title/reference literature Portions to be covered MODULE I
LESSON PLAN SUBJECT: LINEAR IC S AND APPLICATION SUB CODE: 15EC46 NO OF HOURS: 52 FACULTY NAME: Mr. Lokesh.L, Hema. B DEPT: ECE Class# Chapter title/reference literature Portions to be covered MODULE I
Electronics Laboratory And Students kits For Self-Study And Distant Learning. By: Charbel T. Fahed
 Electronics Laboratory And Students kits For Self-Study And Distant Learning By: Charbel T. Fahed Table of Contents I. DC and AC fundamentals 1) Color Code 2) Ohm s Law 3) Series Circuits 4) Parallel Circuits
Electronics Laboratory And Students kits For Self-Study And Distant Learning By: Charbel T. Fahed Table of Contents I. DC and AC fundamentals 1) Color Code 2) Ohm s Law 3) Series Circuits 4) Parallel Circuits
LIC & COMMUNICATION LAB MANUAL
 LIC & Communication Lab Manual LIC & COMMUNICATION LAB MANUAL FOR V SEMESTER B.E (E& ( E&C) (For private circulation only) NAME: DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION SRI SIDDHARTHA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
LIC & Communication Lab Manual LIC & COMMUNICATION LAB MANUAL FOR V SEMESTER B.E (E& ( E&C) (For private circulation only) NAME: DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION SRI SIDDHARTHA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
DMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
 DMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC8453 - LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Question Bank (II-ECE) UNIT I BASICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS PART A 1.Mention the
DMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC8453 - LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Question Bank (II-ECE) UNIT I BASICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS PART A 1.Mention the
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks)
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks) 1. What is meant by tuned amplifiers? Tuned amplifiers are amplifiers that are designed to reject a certain
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks) 1. What is meant by tuned amplifiers? Tuned amplifiers are amplifiers that are designed to reject a certain
Figure 1: Closed Loop System
 SIGNAL GENERATORS 3. Introduction Signal sources have a variety of applications including checking stage gain, frequency response, and alignment in receivers and in a wide range of other electronics equipment.
SIGNAL GENERATORS 3. Introduction Signal sources have a variety of applications including checking stage gain, frequency response, and alignment in receivers and in a wide range of other electronics equipment.
EMT212 Analog Electronic II. Chapter 4. Oscillator
 EMT Analog Electronic II Chapter 4 Oscillator Objectives Describe the basic concept of an oscillator Discuss the basic principles of operation of an oscillator Analyze the operation of RC, LC and crystal
EMT Analog Electronic II Chapter 4 Oscillator Objectives Describe the basic concept of an oscillator Discuss the basic principles of operation of an oscillator Analyze the operation of RC, LC and crystal
Operational Amplifiers
 Operational Amplifiers Table of contents 1. Design 1.1. The Differential Amplifier 1.2. Level Shifter 1.3. Power Amplifier 2. Characteristics 3. The Opamp without NFB 4. Linear Amplifiers 4.1. The Non-Inverting
Operational Amplifiers Table of contents 1. Design 1.1. The Differential Amplifier 1.2. Level Shifter 1.3. Power Amplifier 2. Characteristics 3. The Opamp without NFB 4. Linear Amplifiers 4.1. The Non-Inverting
