Jamming-Resistant Collaborative Broadcast In Wireless Networks, Part II: Multihop Networks
|
|
|
- Joel Prosper Ross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Jmming-Resistnt ollbortive Brodcst In Wireless Networks, Prt II: Multihop Networks Ling Xio Ximen University, hin Emil: Huiyu Di N Stte University, Rleigh, N Emil: huiyu di@ncsu.edu Peng Ning N Stte University, Rleigh, N Emil: pning@ncsu.edu Abstrct We propose in [1] collbortive brodcst scheme for wireless networks, which pplies the Uncoordinted Frequency Hopping UFH) technique to counterct jmming nd exploits node coopertion to enhnce brodcst efficiency. In this scheme, some nodes tht lredy obtin the brodcst messge re selected to rely the messge to other nodes. In this pper, we ext the study to the generlized multihop network scenrios, nd provide solutions for importnt relted issues, such s the rely node selection, multiple ccess control, rely chnnel selection nd pcket scheduling. We lso study the sptil nd frequency chnnel) diversity provided by the collbortive brodcst. Simultion results show tht the collbortive brodcst chieves low brodcst dely, with low energy consumption nd smll computtionl overhed in multihop networks. I. INTRODUTION Jmming-resistnt brodcst is importnt for mny sfetycriticl pplictions such s emergency lert brodcst nd nvigtion signl dissemintion, nd is criticl for the distribution of importnt informtion such s the public key nd system control informtion in wireless systems. As mentioned in Prt I [1], nti-jmming communiction without preshredkeys hs been recognized recently [2] [11], leding to series of promising reserch efforts, including Uncoordinted FH UFH) [5] [8] techniques. In UFH [5], messge is divided into multiple short pckets, nd ech pcket is trnsmitted over rndomly selected chnnel, indepent of ech other nd only known to the ser. Such rpid chnnel switching over lrge frequency rnge effectively thwrts the jmming ttempts. On the down side, ech pcket hs to be sent multiple times, due to the low rte of successful reception resulting from the uncoordinted chnnel selection between the ser nd the legitimte receivers. To this, BMA scheme ws proposed to improve the communiction efficiency by combining ersure coding nd one-wy uthentictor bsed on biliner mps [6]. Some dditionl efficient pcket verifiction methods were proposed in [8]. In [7], the USD-FH scheme ws proposed to further improve the efficiency nd robustness, where the The work is prtly supported by NSF No ), the Nturl Science Foundtion of Fujin Province of hin No.2010J01347), SRF for ROS, SEM, nd Tsinghu-Qulcomm reserch center. The work by Di nd Ning is supported by the US Ntionl Science Foundtion under grnts NS nd by the US Army Reserch Office under grnt W911NF mnged by NSU Secure Open Systems Inititive SOSI). The contents of this pper do not necessrily reflect the position or the policies of the U.S. Government. hopping pttern is conveyed through UFH to llow messge trnsmission through coordinted FH. Despite ll these efforts, the UFH-bsed nti-jmming communictions still need to improve the communiction efficiency nd re vulnerble to powerful responsive jmmers [7]. To further enhnce the communiction efficiency, we propose collbortive brodcst scheme to exploit the node coopertion for single-hop wireless networks [1]. As ll nodes in the network expect the sme messge, it is nturl nd convenient to use set of nodes tht lredy receive the messge to help brodcst it. We design two strtegies for rely chnnel selection: Rndom Rely hnnel selection RR) nd Sttic Rely hnnel selection StR). In RR, ech rely node rndomly nd indepently selects one out of chnnels for the trnsmission of ech pcket. For the StR strtegy, the relys tke fixed non-overlpping chnnels through the messge brodcst process for the trnsmission of ll pckets). For exmple, ech rely my select chnnel bsed on its prtil) ID modulo some prime number nd ) so tht no overlpping is incurred. Both strtegies re menble to distributed implementtion nd hve good sclbility, s ech rely node indepently performs the strtegy disregrding the other rely nodes. In this pper, we ext our study to the multihop networks, where nodes tht hve successfully received the messge serve s relys to help forwrd the brodcst messge over multiple chnnels. In this wy, both the source node nd rely nodes s the messge simultneously t multiple chnnels over vrious geogrphicl regions. Thus the receivers hve lrger opportunity to receive the messge ginst jmming, compred to the brodcst without coopertion. In the multihop setting, besides spectrl chnnel) diversity, we cn further explore sptil diversity to fcilitte relible messge brodcst to much wider geogrphic re. Unless the jmmers re powerful enough to simultneously block ll the chnnels cross the whole geogrphic re, which is not prcticl in most multihop rdio networks, there is lwys chnce for the brodcst messge to rech nodes outside the fully jmmed region, which lter rely the messge to more nodes in the network. ompred to [1], we consider more generl jmming model, where ech jmmer, no mtter how powerful she is, cn no longer jm ll nodes s in the single-hop scenrio. While it is sufficient to consider just one powerful jmmer with combined jmming cpbility in the frequency domin in [1],
2 here we further introduce the concept of jmming rdius nd consider multiple jmmers distributed in the re. In ddition, we ddress the networking issues tht re lrgely ignored in the single-hop cse, including multiple ccess control, pcket scheduling nd determintion of trnsmission durtion, nd provide suite of solutions menble to distributed implementtion. The reminder of the pper is orgnized s follows. We formulte the system model in Section II, nd discuss some importnt issues for the collbortive brodcst in the multihop wireless networks in Section III. We present our collbortive brodcst protocols in Section IV, nd evlute their ntijmming performnce in Section V. Finlly, we conclude in Section VI. II. PROBLEM FORMULATION We consider nti-jmming brodcst in multihop rdio network, where the trnsmit power of the source node is not high enough to rech the whole network or it is too costly to do so. Suppose the source node locted t the center of disk re brodcsts messge to N identicl rndomly locted nodes with disk rdius R. All these nodes re ssumed to employ common communiction rnge D. Thus it tkes t lest R/D hops for the messge to rech to the frthest node. We suppose ech node trnsmit or receive) simultneously cross set of c m or c n ) chnnels selected from orthogonl chnnels, where is typiclly lrge number for strong jmming resistnce. In this pper, we ssume c m = c n = 1 for simplicity. Our results cn be esily exted to the multichnnel cses. The brodcst messge is divided into M short pckets, ech of which cn be trnsmitted over one time slot hop) with durtion t p. onsider common pth-loss model [12], where the trnsmitted signl power for ech node including the source) stisfies P T = D/R) γ P MAX, with γ s the pth loss exponent nd P MAX s the power required for the trnsmitted signl to successfully cover the whole disk re with rdius R. For simplicity, we ssume tht the minimum energy for node to trnsmit pcket E t is proportionl to P T, neglecting the energy cost on the signl processing in the bsebnd nd IF bnd, nd tht the minimum energy to receive pcket, E r, is constnt. In our study, we consider the most powerful jmming [5], [6], responsive-sweep, where jmmer conducts both non-responsive nd responsive jmming indepently nd simultneously. The corresponding jmming probbility for single source without rely) is given in [1] by p J = n s s + n J J. 1) The nlysis bsed on the responsive-sweep jmming provides lower bound for the brodcst performnce, nd most conclusions cn be esily dpted for other jmming types. We lso consider smrt jmming for the StR-bsed protocol, where ech jmmer knows the StR rely chnnel selection strtegy nd the fixed rely chnnels in its communiction M Number of pckets consisted in the messge to be sent N Number of nodes to receive the messge Number of chnnels in the system R Rdius of the re of interests D Averge coverge rdius for ech node n Node density = ND 2 /R 2 ) P T Trnsmit power Number of slots tht ech node trnsmits p Probbility tht receiver successfully receives pcket p hnnel ccessing probbility J Number of jmmers p J Probbility for chnnel to be jmmed J Number of chnnels concurrently blocked by jmmer s Number of chnnels concurrently sensed by jmmer n J Number of jmming cycles in slot n s Number of sensing cycles in slot D c Jmming rdius P J Jmming power ρ Normlized jmming power = P J /P T ) TABLE I SUMMARY OF NOTATIONS. region. It is in the interest of the smrt jmmer to first jm the fixed nd known rely chnnels, insted of the remining chnnels tht crry out pcket with less probbility. Note tht this effort is solely limited by the physicl jmming cpbility of the jmmer i.e., n J J ), while the sensing cpbility of the jmmer does not help. If power supply permits, the smrt jmmer then continues to ttck the non-rely chnnels using the responsive-sweep strtegy, to prevent successful reception from the source. lerly this mixed jmming strtegy is even more powerful thn the responsive-sweep jmming for the StR-bsed coopertive brodcst. Let P J denote the jmming power, with corresponding jmming rdius D c, nd ρ = P J /P T = D c /D) γ denote the normlized jmming power compred to legitimte node. The nottion summry is listed in Tble I. III. MULTIHOP BROADAST STRATEGIES We consider conveying messge consisting of M pckets to N nodes through collbortive brodcst in multihop wireless network, for both RR nd StR strtegies. ompred with the single-hop oriented work in [1], relizing collbortive brodcst incurs more chllenges in the multihop setting. In this section, we discuss severl importnt issues concerning multiple ccess control MA), pcket scheduling, trnsmission durtion control, nd power control. Then in the following sections, we will introduce our brodcst protocols nd evlute their performnce. A. MA In the collbortive brodcst, the source node nd rely nodes concurrently s pckets over wireless medi. Without pproprite MA mechnism, this multiple ccess might result in trnsmission confliction, pcket loss nd energy wste, especilly when idel coordintion is not vilble. In this work we consider the slotted Aloh scheme for the ese of distributed implementtion, nd investigte the optiml probbility tht trnsmitter ss pcket to the rdio medi during time slot, for both the RR nd StR rely strtegy.
3 Through our discussion, we ssume lrge greter thn 100 s in typicl frequency hopping system) to provide strong jmming resistnce. In ddition, the lrgest number of one-hop neighboring nodes Υ) is ssumed to be less thn, which is resonble for most typicl wireless d hoc networks. As to the coordintion mong the source nd rely nodes, we consider two scenrios: synchronous nd synchronous. In the former cse, ll trnsmitting nodes in the neighborhood re perfectly synchronized both in time nd in trnsmission content, so no interference is incurred when two more more relys select the sme chnnel. The ltter is more relistic, ssuming tht collision occurs when two relys hop to the sme chnnel due to difference in rrivl time or trnsmitted pckets). First, we consider the RR strtegy, where ech trnsmitter rndomly selects chnnel nd ss pcket on it with the ccess probbility p. Lemm 3.1: If > Υ, the successful pcket reception rte of RR is mximized by p = 1. Proof: Assume tht in the neighborhood of receiver there re m relys, with m Υ, ech trnsmitting with probbility p on rndomly selected chnnel ccording to the RR strtegy. In the synchronous cse, receiver cn successfully receive pcket if t lest one of the m trnsmitters re working on its selected receiving chnnel nd the chnnel is unblocked. The successful pcket reception rte is given by p RR,syn = p RR,syn 1 = mp 1 p 1 ) m ) 1 p J ), 2) which monotoniclly rises with p. As the ccess probbility p [0, 1], p = 1 mximizes p RR,syn. In the synchronous cse, receiver cn successfully receive pcket if exctly one trnsmitter is ccessing the receiving chnnel. Thus successful pcket reception rte in the synchronous cse becomes 1 p 1 ) m 1 1 p J ). 3) Its derivtive with respect to p is p RR,syn p = m 1 p J) 1 p ) m 2 1 p m ). 4) Hence p = min /m, 1) mximizes p RR,syn, s p [0, 1] nd 1. Bsed on the ssumption tht > Υ m, we hve tht p = 1 mximizes p RR,syn. Remrk: By 2) nd 3), both p RR,syn nd p RR,syn monotoniclly increse with m, which indictes tht node coopertion helps reduce the verge brodcst dely. Moreover, since is usully lrge number, the reltive difference between p RR,syn nd p RR,syn is very smll, implying the robustness of RR ginst rely synchroniztion error. Next, we consider the StR strtegy, where ech rely selects fixed non-overlpping chnnel ccording to its node ID while the source node still follows the UFH pproch. As the known rely chnnels provide much lrger trnsmission probbility thn others, it is in the jmmers interest to first block them. Menwhile, smrt receiver cn lso tke dvntge of these fixed rely chnnels unless ll of them re jmmed. Under such strong jmming, receiver cn then switch bck to the whole chnnels. Hence in our scheme, ech receiver first rndomly selects one of these known rely chnnels. If it finds out tht ll the rely chnnels re jmmed, it switches to the mode where it rndomly selects one out of chnnels. Once it comes cross cler rely chnnel, the receiver restricts itself to the rely chnnels gin. The ltter cse hppen s smrt jmmers my just sp enough energy to spoof the receivers wy, insted of continuously jmming the sttic rely chnnels. Lemm 3.2: The successful pcket reception rte of StR is mximized by p = 1. The proof is similr to tht to Lemm 3.1. Note tht the source node cn only rech the first hop nodes, while the trnsmission to ll the other nodes completely relies on the rely nodes. Under the coopertive brodcst, unless ll the chnnels re simultneously jmmed cross the whole re covered by the source node, some nodes in the first hop cn receive the messge with lrge chnce, nd then s it to the other nodes. The bove nlysis cn be esily dpted for the non-first-hop nodes. B. Pcket Scheduling As the source nd rely nodes cooperte to brodcst multiple pckets of the brodcst messge, it is necessry to determine when to strt the trnsmission nd wht to s. We consider two strtegies to decide the beginning of the rely mode: The first one is messge-bsed, where ech node strts relying fter successfully receiving ll the M pckets within the brodcst messge. The second one is pcket-bsed, where ech node relys pcket right fter receiving it, during the next time slots ssigned to s this pcket. In this scheme, the node needs to switch bck nd forth between the relying mode nd receiving mode. The former strtegy is convenient to implement, without requiring idel timing nd synchroniztion. On the other hnd, the ltter strtegy my led to fster brodcst, but it requires perfect timing nd fst switching between the trnsmission mode nd the receiving mode to void the pcket lost. As these requirements re nontrivil to chieve in existing wireless networks, we choose the messge-bsed strtegy for convenience, t the expense of slightly slower brodcst speed. Once strting to rely, ech node ss the M pckets in sequence, nd then periodiclly repets this process before the of the trnsmission which will be further discussed below). It is pprent tht the minimum brodcst dely for receiver to successfully obtin these pckets is M slots, while mostly the dely is much lrger thn M due to lck of coordintion between the trnsmitters nd receivers.. ontrol of Trnsmission Durtion In our collbortive brodcst, ech trnsmitter, either the source node or rely node, stops sing pckets once receiving the Acknowledgements AKs) from ll of its neighboring
4 nodes or reching the mximum trnsmission durtion, whichever comes first. The limit on the trnsmission durtion is set to del with the possible loss of the AK signl due to the deep fding of wireless chnnels or the trnsmission confliction of multiple AK signls. Ech AK signl, including the messge ID, receiver ID nd time stmp, is sent on fixed nd known chnnel by node right fter successfully obtining ll M pckets. In this wy, ech AK signl is sent t time rnging between the M-th slot nd the -th, deping on the dely of the messge to the node from the source or rely node. As we will see, the trnsmission dely for messge to 100-node network is usully s lrge s severl thousnd time slots, during which the 100 AK signls re sent t rndom time. onsequently, the probbility for node to simultneously receive multiple AK signls from its neighbors is smll. Moreover, even if some of the AK signls re lost, the node cn still stop the trnsmission fter the trnsmission limit, nd the system still works well. By integrting the AK mechnism in the trnsmission durtion control, only provides the upper bound of the trnsmission time in cse the AK signls re lost. We set is the verge time used for ll the receivers within the neighboring re to receive the brodcst messge from the trnsmitter. The verge dely is used here, since it is chllenging to predict the exct vlue in prcticl wireless networks. For simplicity, ssume tht trnsmitter periodiclly brodcsts M pckets to n identicl nd indepent nodes within its communiction rnge. It is cler tht the probbility for ll these receivers to obtin the pckets during the first m slots is 1 1 p ) m ) Mn. Hence the verge brodcst dely over this single hop in terms of time slots is αtvg hop, where the coefficient α > 0 nd Tvg hop T hop vg = M m=0 [ p ) m ) Mn]. 5) Assuming uniform node plcement, we hve the verge number of the nodes within the rech of one hop, n = D 2 N/R 2. Hence the trnsmission durtion cn be tken s [ ] = αm p ) m ) D2 NM R 2. 6) m=0 By integrting the AK mechnism in the trnsmission durtion control, the brodcst performnce is not sensitive to the specific vlue of α. Simultion results hve shown tht α = is good choice, with stble brodcst dely nd energy consumption performnce. IV. BROADAST PROTOOL After discussing some key issues in the previous section, we now present two nti-jmming collbortive brodcst protocols for multihop wireless networks, bsed on the RR nd StR strtegies, respectively. It is ssumed tht ech node knows the node IDs of its neighbors, i.e., legitimte nodes within its direct communiction rdius, nd performs distributed lgorithm Algorithm 1 or 2) to receive nd/or trnsmit messge consisting of M pckets. A. RR-bsed Brodcst In the RR-bsed protocol, ech node other thn the source node first enters the receiving mode. In this mode, node indepently nd rndomly selects one out of chnnels nd listens, nd switches to nother rndomly selected chnnel fter one or severl time slots to counterct jmming. This process repets until the node successfully receives ll M pckets. while The node hs not received ll M pckets yet do hid = n integer rndomly selected from [1,] ; Listen to the hid-th chnnel; S AK Messge ID, Node ID, Time Stmp); Eq. 6) ; for i 1 to do if hs not received AKs from ll its neighbors yet then hid = n integer rndomly selected in [1,] ; S pcket on the hid-th chnnel; Stop the trnsmission immeditely Algorithm 1: RR version of the nti-jmming collbortive brodcst protocol Next, the node ss n AK signl to inform its neighbors bout its successful reception of the messge, nd then enters the trnsmission mode. The AK signl contining the messge ID, node ID nd time stmp, is sent on fixed nd known chnnel. The trnsmission mode of different nodes strts t different time e.g., the source node enters this mode from the very beginning while node t the edge of the network my never enter the trnsmission mode). In the trnsmission mode, ech node rndomly selects chnnel out of the chnnels nd ss pcket. In order to del with the possible loss of AK signls due to chnnel fding or jmming, we introduce timeout mechnism, where ech trnsmission stops fter slots, given by Eq. 6), even without receiving enough AK signls. The node repets this process to s ll M pckets in sequence, until it receives ll the AK signls from its neighbors, or time slots elpse, whichever comes first. B. StR-bsed Brodcst In the StR-bsed protocol, ech node relys the messge on fixed chnnel, ssumed distinctly relted to its node ID. Ech node is ssumed to know the rely chnnels tht its neighbors my use. As mentioned in Section III-A, in order to counterct smrt jmming, ech node hs two receiving modes, bsed on whether ny rely chnnel is not blocked: If tht is true, the node is focused on the rely chnnels by rndomly selecting one of the potentil rely chnnels in the neighborhood; otherwise, the node rndomly selects one out of ll the chnnels.
5 F lglerrelyhnnel=true; while The node hs not received ll M pckets yet do if F lglerrelyhnnel=true then hid=n integer rndomly selected from the rely chnnel set in its neighborhood; hid = n integer rndomly selected from [1,]; Listen to the hid-th chnnel; if F lglerrelyhnnel=true then if All recent R p pckets re jmmed then F lglerrelyhnnel=flse; if The hid-th chnnel is unblocked rely chnnel then F lglerrelyhnnel=true; S AK Messge ID, Node ID, Time Stmp); Eq. 6) ; hid = n integer derived from its Node ID ; for i 1 to do if hs not received AKs from ll its neighbors yet then S pcket on the hid-th chnnel; Stop the trnsmission immeditely Algorithm 2: StR version of the nti-jmming collbortive brodcst protocol orrespondingly, the StR protocol uses such sttus flg tht is set to be true t the beginning, nd then updtes it ccording to the R checking results of the recent pckets. When working on the rely chnnels, the receiver chnges the flg to be flse, if filing to receive ll the recent R p pckets, which mens tht ll these rely chnnels re very likely to be jmmed. The prmeter R p is the ctul number of neighboring nodes, or the verge neighboring nodes n if the former is unknown. When coming cross cler rely chnnel, the node sets the flg to be true nd focuses on the rely chnnels gin. Next, like the RR-bsed protocol, the node lso ss n AK signl to its neighbors before entering to the trnsmission mode. Then the node ss the pckets on fixed chnnel corresponding to the prtil node ID modulo. The trnsmission durtion is lso determined by timer of length nd the reception of the AK signls from its neighbors. V. PERFORMANE EVALUATION We evlute the performnce of the proposed collbortive brodcst, where messge consisting of M = 7 pckets is brodcst to N = 100 nodes over = 128 chnnels ginst J jmmers with normlized jmming power ρ = 2, with the RR-bsed strtegy or the StR-bsed strtegy. We clculte the overll brodcst dely, defined s the time durtion from the beginning of brodcst till the time when ll the nodes in the network successfully receive the entire messge, nd the corresponding overll energy consumption, defined s the sum of the trnsmit nd the receive energy consumed by ll the N + 1 legitimte nodes during this process. The energy consumption for node to s nd to receive pcket re set s E t = D γ nd E r = 0.1, respectively. Figure 1 presents the RR performnce in solid curves nd the StR performnce in dshed curves, ginst J = 0 to 20 jmmers described in different colors. We consider both the responsive-sweep jmming nd the smrt jmming specificlly trgeting the StR-bsed protocol in dshed dot curves). It is shown tht both schemes consume smll energy nd brodcst dely, compred to the existing jmming-resistnt FH schemes. For exmple, the verge brodcst delys of StR nd RR re less thn 900 nd 1100 slots, respectively, for the brodcst of 7 pckets to 100 nodes ginst one sweepresponsive jmmer with normlized jmming power 2, when the node density N/R for N = 100 nd D = 1. In this cse, ech node/jmmer cn pproximtely cover the whole network, s ssumed in the BMA [6]. The performnce of our scheme, especilly the StR version, is better thn tht of BMA for single receiving node even without jmming e.g., BMA tkes pproximtely 2000 slots to s messge of 7 pckets to single node [6]). It lso confirms tht the smrt jmming cn ttck StR more efficiently, especilly when the number of jmmers is lrge. But even in this cse, the StR strtegy still outperforms the RR in most cses. It cn lso be seen from Figure 1 tht the brodcst dely nd energy performnce of RR improves with the node density N/R 2, for given N, while the performnce of StR degrdes with it when ttcked by lrge number of strong smrt jmmers. Next, we study the performnce ginst widebnd jmmers tht concurrently ttck multiple chnnels. Assume limittion on the totl energy consumption of jmmer, i.e., widebnd jmmer cn increse the number of simultneously ttcked chnnels t the expense of smller jmming rdius. We consider 3-hop wireless network with n = 20, D = 1 nd N = 100. It is shown in Fig. 2 tht the protocol cn well resist ten jmmers ech concurrently blocking J 40 chnnels with ρ = 2. The StR strtegy cn provide stronger jmming resistnce thn the RR strtegy, even under the smrt jmming focused on the rely chnnels. Moreover, for the RR strtegy, when there re 10 jmmers ech simultneously blocking ll the chnnels with ρ = 2, only 28 out of 100 nodes re jmmed nd the remining 82 nodes cn still successfully receive ll the pckets. ontrst to the intuition, even when ll the chnnels re simultneously jmmed J = ) by the widebnd jmmers, the collbortive brodcst still prtly survives, thnks to the sptil diversity vilble in multihop networks. Finlly, the number of jmmed nodes is mximizes t J = 63, which cn be theoreticlly determined s n s s )/n J. It is shown in Eq. 1) tht responsive-sweep jmmer cn simultneously jm p J = n s s + n J J chnnels. All the nodes in its jmming re re blocked when p J =, or J = n s s )/n J. Afterwrds, the jmming probbility no longer further increses with J, while the number of nodes
6 Overll brodcst dely Slot) Overll brodcst Energy J=0,RR J=1,RR J=10,RR J=20,RR J=0,StR J=1,StR J=10,StR J=20,StR J=0,StR,SJ J=1,StR,SJ J=10,StR,SJ J=20,StR,SJ Network density, N/R x 104 ) Averge brodcst dely J=0,RR J=1,RR J=10,RR J=20,RR J=0,StR J=1,StR J=10,StR J=20,StR J=0,StR,SJ J=1,StR,SJ J=10,StR,SJ J=20,StR,SJ Network density, N/R 2 b) Averge energy consumption Fig. 1. Brodcst performnce vs. node density N/R 2, for the brodcst of M = 7 pckets to N = 100 nodes with chnging network rdius R nd signl coverge rdius D = 1, ginst J responsive-sweep jmmers or smrt jmmers SJs). in its covering re reduces with the shrinking of the jmming rdius. Number of jmmed nodes J=1,RR J=5,RR J=10,RR J=1,StR J=5,StR J=10,StR J=1,StR,SJ J=5,StR,SJ J=10,StR,SJ Number of chnnels concurrently jmmed, J Fig. 2. Averge number of jmmed nodes by J responsive-sweep jmmers ech of which concurrently blocks J jmming chnnels with ρ = 2, in brodcst to N = 100 nodes over = 128 chnnels, with n = 20 nd D = 1. VI. ONLUSION We hve proposed distributed collbortive brodcst protocol tht exploits the uncoordinted frequency hopping technique nd node coopertion to counterct jmming in multihop wireless networks. With coopertion from rely nodes, this scheme provides sptil nd frequency chnnel) diversities to resist jmming nd enhnce communiction efficiency. Unless ll the chnnels cross the whole geogrphic re re simultneously jmmed, the collbortive brodcst cn lwys exploit the white re not being jmmed or white chnnels in the jmmed geogrphic re. Simultion results show tht the collbortive brodcst is robust ginst responsive smrt jmmers specilly trgeting the collbortive relying strtegies. Tke the brodcst in 3-hop network to 100 nodes for exmple, the protocol cn well resist ten responsive-sweep jmmers ech simultneously blocking 40 chnnels with double jmming power ρ = 2). Even when ech jmmer blocks ll = 128 chnnels t the sme time, only 28 nodes re jmmed nd more thn 70% of the nodes cn still receive the brodcst messge. By exploiting the sptil distribution of the multihop wireless networks, this coopertive brodcst scheme cn efficiently improve the communiction efficiency ginst jmming, compred to most existing ntijmming brodcst schemes, including BMA. REFERENES [1] L. Xio, H. Di, nd N. Peng, Jmming-resistnt collbortive brodcst in wireless networks, prt I: Singlehop networks, in Proc. IEEE Globecom 2011, to pper. [2] L. Bird, W. Bhn, M. ollins, M. rlisle, nd S. Butler, Keyless jm resistnce, in Proc. IEEE Informtion Assurnce nd Security Workshop, 2007, pp [3]. Popper, M. Strsser, nd S. pkun, Jmming-resistnt brodcst communiction without shred key, in Proc. USENIX Security Symposium, [4] Y. Liu, P. Ning, H. Di, nd A. Liu, Rndomized differentil DSSS: jmming-resistnt wireless brodcst communiction, in Proc. IEEE Infocom, [5] M. Strsser, S. pkun,. Popper, nd M. glj, Jmming-resistnt key estblishment using uncoordinted frequency hopping, in Proc. IEEE symposium on security nd privcy, [6] M. Strsser,. Popper, nd S. pkun, Efficient uncoordinted FHSS nti-jmming communiction, in Proc. MobiHoc, [7] A. Liu, P. Ning, H. Di, Y. Liu, nd. Wng, USD-FH: Jmmingresistnt wireless communiction using frequency hopping with uncoordinted seed disclosure, in Proc. 7th IEEE Interntionl onference on Mobile Ad-hoc nd Sensor Systems, [8] D. Slter, P. Tgue, R. Poovrn, nd B. Mtt, A coding-theoretic pproch for efficient messge verifiction over insecure chnnels, in Proc. AM onference on Wireless Network Security WiSec 09), [9] T. Jin, G. Noubir, nd B. Thp, Zero pre-shred secret key estblishment in the presence of jmmers, in Proc. AM interntionl symposium on Mobile d hoc networking nd computing, [10] L. Lzos md S. Liu nd M. Krunz, Mitigting control-chnnel jmming ttcks in multi-chnnel d hoc networks, in Proc. AM WiSec, [11] A. Liu, P. Ning, H. Di, Y. Liu, nd. Wng, Defing DSSSbsed brodcst communiction ginst insider jmmers vi delyed seed-disclosure, in Proc. IEEE Annul omputer Security Applictions onference ASA), [12] A. Goldsmith, Wireless ommunictions, chpter 3, mbridge University Press, 2005.
Multi-beam antennas in a broadband wireless access system
 Multi-em ntenns in rodnd wireless ccess system Ulrik Engström, Mrtin Johnsson, nders Derneryd nd jörn Johnnisson ntenn Reserch Center Ericsson Reserch Ericsson SE-4 84 Mölndl Sweden E-mil: ulrik.engstrom@ericsson.com,
Multi-em ntenns in rodnd wireless ccess system Ulrik Engström, Mrtin Johnsson, nders Derneryd nd jörn Johnnisson ntenn Reserch Center Ericsson Reserch Ericsson SE-4 84 Mölndl Sweden E-mil: ulrik.engstrom@ericsson.com,
A Slot-Asynchronous MAC Protocol Design for Blind Rendezvous in Cognitive Radio Networks
 Globecom 04 - Wireless Networking Symposium A Slot-Asynchronous MAC Protocol Design for Blind Rendezvous in Cognitive Rdio Networks Xingy Liu nd Jing Xie Deprtment of Electricl nd Computer Engineering
Globecom 04 - Wireless Networking Symposium A Slot-Asynchronous MAC Protocol Design for Blind Rendezvous in Cognitive Rdio Networks Xingy Liu nd Jing Xie Deprtment of Electricl nd Computer Engineering
METHOD OF LOCATION USING SIGNALS OF UNKNOWN ORIGIN. Inventor: Brian L. Baskin
 METHOD OF LOCATION USING SIGNALS OF UNKNOWN ORIGIN Inventor: Brin L. Bskin 1 ABSTRACT The present invention encompsses method of loction comprising: using plurlity of signl trnsceivers to receive one or
METHOD OF LOCATION USING SIGNALS OF UNKNOWN ORIGIN Inventor: Brin L. Bskin 1 ABSTRACT The present invention encompsses method of loction comprising: using plurlity of signl trnsceivers to receive one or
Y9.ET1.3 Implementation of Secure Energy Management against Cyber/physical Attacks for FREEDM System
 Y9.ET1.3 Implementtion of Secure Energy ngement ginst Cyber/physicl Attcks for FREED System Project Leder: Fculty: Students: Dr. Bruce cillin Dr. o-yuen Chow Jie Dun 1. Project Gols Develop resilient cyber-physicl
Y9.ET1.3 Implementtion of Secure Energy ngement ginst Cyber/physicl Attcks for FREED System Project Leder: Fculty: Students: Dr. Bruce cillin Dr. o-yuen Chow Jie Dun 1. Project Gols Develop resilient cyber-physicl
Interference Cancellation Method without Feedback Amount for Three Users Interference Channel
 Open Access Librry Journl 07, Volume, e57 ISSN Online: -97 ISSN Print: -9705 Interference Cncelltion Method without Feedbc Amount for Three Users Interference Chnnel Xini Tin, otin Zhng, Wenie Ji School
Open Access Librry Journl 07, Volume, e57 ISSN Online: -97 ISSN Print: -9705 Interference Cncelltion Method without Feedbc Amount for Three Users Interference Chnnel Xini Tin, otin Zhng, Wenie Ji School
Algorithms for Memory Hierarchies Lecture 14
 Algorithms for emory Hierrchies Lecture 4 Lecturer: Nodri Sitchinv Scribe: ichel Hmnn Prllelism nd Cche Obliviousness The combintion of prllelism nd cche obliviousness is n ongoing topic of reserch, in
Algorithms for emory Hierrchies Lecture 4 Lecturer: Nodri Sitchinv Scribe: ichel Hmnn Prllelism nd Cche Obliviousness The combintion of prllelism nd cche obliviousness is n ongoing topic of reserch, in
Energy Harvesting Two-Way Channels With Decoding and Processing Costs
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GREEN COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING, VOL., NO., MARCH 07 3 Energy Hrvesting Two-Wy Chnnels With Decoding nd Processing Costs Ahmed Arf, Student Member, IEEE, Abdulrhmn Bknin, Student
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GREEN COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING, VOL., NO., MARCH 07 3 Energy Hrvesting Two-Wy Chnnels With Decoding nd Processing Costs Ahmed Arf, Student Member, IEEE, Abdulrhmn Bknin, Student
MAXIMUM FLOWS IN FUZZY NETWORKS WITH FUNNEL-SHAPED NODES
 MAXIMUM FLOWS IN FUZZY NETWORKS WITH FUNNEL-SHAPED NODES Romn V. Tyshchuk Informtion Systems Deprtment, AMI corportion, Donetsk, Ukrine E-mil: rt_science@hotmil.com 1 INTRODUCTION During the considertion
MAXIMUM FLOWS IN FUZZY NETWORKS WITH FUNNEL-SHAPED NODES Romn V. Tyshchuk Informtion Systems Deprtment, AMI corportion, Donetsk, Ukrine E-mil: rt_science@hotmil.com 1 INTRODUCTION During the considertion
A Cluster-based TDMA System for Inter-Vehicle Communications *
 JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING 30, 213-231 (2014) A Cluster-bsed TDMA System for Inter-Vehicle Communictions * Deprtment of Electricl Engineering Ntionl Sun Yt-Sen University Kohsiung,
JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING 30, 213-231 (2014) A Cluster-bsed TDMA System for Inter-Vehicle Communictions * Deprtment of Electricl Engineering Ntionl Sun Yt-Sen University Kohsiung,
Solutions to exercise 1 in ETS052 Computer Communication
 Solutions to exercise in TS52 Computer Communiction 23 Septemer, 23 If it occupies millisecond = 3 seconds, then second is occupied y 3 = 3 its = kps. kps If it occupies 2 microseconds = 2 6 seconds, then
Solutions to exercise in TS52 Computer Communiction 23 Septemer, 23 If it occupies millisecond = 3 seconds, then second is occupied y 3 = 3 its = kps. kps If it occupies 2 microseconds = 2 6 seconds, then
Synchronous Machine Parameter Measurement
 Synchronous Mchine Prmeter Mesurement 1 Synchronous Mchine Prmeter Mesurement Introduction Wound field synchronous mchines re mostly used for power genertion but lso re well suited for motor pplictions
Synchronous Mchine Prmeter Mesurement 1 Synchronous Mchine Prmeter Mesurement Introduction Wound field synchronous mchines re mostly used for power genertion but lso re well suited for motor pplictions
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE STUDY
 CHAPTER LITERATURE STUDY. Introduction Multipliction involves two bsic opertions: the genertion of the prtil products nd their ccumultion. Therefore, there re two possible wys to speed up the multipliction:
CHAPTER LITERATURE STUDY. Introduction Multipliction involves two bsic opertions: the genertion of the prtil products nd their ccumultion. Therefore, there re two possible wys to speed up the multipliction:
Experiment 3: Non-Ideal Operational Amplifiers
 Experiment 3: Non-Idel Opertionl Amplifiers Fll 2009 Equivlent Circuits The bsic ssumptions for n idel opertionl mplifier re n infinite differentil gin ( d ), n infinite input resistnce (R i ), zero output
Experiment 3: Non-Idel Opertionl Amplifiers Fll 2009 Equivlent Circuits The bsic ssumptions for n idel opertionl mplifier re n infinite differentil gin ( d ), n infinite input resistnce (R i ), zero output
The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points:
 Exercise 4 Bttery Chrging Methods EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you hve completed this exercise, you will be fmilir with the different chrging methods nd chrge-control techniques commonly used when chrging Ni-MI
Exercise 4 Bttery Chrging Methods EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you hve completed this exercise, you will be fmilir with the different chrging methods nd chrge-control techniques commonly used when chrging Ni-MI
Information-Coupled Turbo Codes for LTE Systems
 Informtion-Coupled Turbo Codes for LTE Systems Lei Yng, Yixun Xie, Xiowei Wu, Jinhong Yun, Xingqing Cheng nd Lei Wn rxiv:709.06774v [cs.it] 20 Sep 207 Abstrct We propose new clss of informtion-coupled
Informtion-Coupled Turbo Codes for LTE Systems Lei Yng, Yixun Xie, Xiowei Wu, Jinhong Yun, Xingqing Cheng nd Lei Wn rxiv:709.06774v [cs.it] 20 Sep 207 Abstrct We propose new clss of informtion-coupled
ABB STOTZ-KONTAKT. ABB i-bus EIB Current Module SM/S Intelligent Installation Systems. User Manual SM/S In = 16 A AC Un = 230 V AC
 User Mnul ntelligent nstlltion Systems A B 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 30 ma 30 ma n = AC Un = 230 V AC 30 ma 9 10 11 12 C ABB STOTZ-KONTAKT Appliction Softwre Current Vlue Threshold/1 Contents Pge 1 Device Chrcteristics...
User Mnul ntelligent nstlltion Systems A B 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 30 ma 30 ma n = AC Un = 230 V AC 30 ma 9 10 11 12 C ABB STOTZ-KONTAKT Appliction Softwre Current Vlue Threshold/1 Contents Pge 1 Device Chrcteristics...
Experiment 3: Non-Ideal Operational Amplifiers
 Experiment 3: Non-Idel Opertionl Amplifiers 9/11/06 Equivlent Circuits The bsic ssumptions for n idel opertionl mplifier re n infinite differentil gin ( d ), n infinite input resistnce (R i ), zero output
Experiment 3: Non-Idel Opertionl Amplifiers 9/11/06 Equivlent Circuits The bsic ssumptions for n idel opertionl mplifier re n infinite differentil gin ( d ), n infinite input resistnce (R i ), zero output
Dataflow Language Model. DataFlow Models. Applications of Dataflow. Dataflow Languages. Kahn process networks. A Kahn Process (1)
 The slides contin revisited mterils from: Peter Mrwedel, TU Dortmund Lothr Thiele, ETH Zurich Frnk Vhid, University of liforni, Riverside Dtflow Lnguge Model Drsticlly different wy of looking t computtion:
The slides contin revisited mterils from: Peter Mrwedel, TU Dortmund Lothr Thiele, ETH Zurich Frnk Vhid, University of liforni, Riverside Dtflow Lnguge Model Drsticlly different wy of looking t computtion:
Synchronous Machine Parameter Measurement
 Synchronous Mchine Prmeter Mesurement 1 Synchronous Mchine Prmeter Mesurement Introduction Wound field synchronous mchines re mostly used for power genertion but lso re well suited for motor pplictions
Synchronous Mchine Prmeter Mesurement 1 Synchronous Mchine Prmeter Mesurement Introduction Wound field synchronous mchines re mostly used for power genertion but lso re well suited for motor pplictions
Signaling-Embedded Preamble Design for Flexible Optical Transport Networks
 Signling-Embedded Premble Design for Flexible Opticl Trnsport Networks Linglong Di nd Zhocheng Wng Tsinghu Ntionl Lbortory for Informtion Science nd Technology, Deprtment of Electronic Engineering, Tsinghu
Signling-Embedded Premble Design for Flexible Opticl Trnsport Networks Linglong Di nd Zhocheng Wng Tsinghu Ntionl Lbortory for Informtion Science nd Technology, Deprtment of Electronic Engineering, Tsinghu
4110 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 66, NO. 5, MAY 2017
 40 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 66, NO. 5, MAY 07 Trnsmit Power Control for DD-Underlid Cellulr Networs Bsed on Sttisticl Fetures Peng Sun, Kng G. Shin, Life Fellow, IEEE, Hilin Zhng,
40 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 66, NO. 5, MAY 07 Trnsmit Power Control for DD-Underlid Cellulr Networs Bsed on Sttisticl Fetures Peng Sun, Kng G. Shin, Life Fellow, IEEE, Hilin Zhng,
Adaptive Network Coding for Wireless Access Networks
 Adptive Network Coding for Wireless Access Networks Tun Trn School of Electricl Engineering nd Computer Science Oregon Stte University, Corvllis, Oregon 9733 Emil: trntu@eecs.orst.edu Thinh Nguyen School
Adptive Network Coding for Wireless Access Networks Tun Trn School of Electricl Engineering nd Computer Science Oregon Stte University, Corvllis, Oregon 9733 Emil: trntu@eecs.orst.edu Thinh Nguyen School
A Novel Back EMF Zero Crossing Detection of Brushless DC Motor Based on PWM
 A ovel Bck EMF Zero Crossing Detection of Brushless DC Motor Bsed on PWM Zhu Bo-peng Wei Hi-feng School of Electricl nd Informtion, Jingsu niversity of Science nd Technology, Zhenjing 1003 Chin) Abstrct:
A ovel Bck EMF Zero Crossing Detection of Brushless DC Motor Bsed on PWM Zhu Bo-peng Wei Hi-feng School of Electricl nd Informtion, Jingsu niversity of Science nd Technology, Zhenjing 1003 Chin) Abstrct:
Efficient and Resilient Key Discovery based on Pseudo-Random Key Pre-Deployment
 Efficient nd Resilient Key Discovery sed on Pseudo-Rndom Key Pre-Deployment p. 1 Efficient nd Resilient Key Discovery sed on Pseudo-Rndom Key Pre-Deployment Roerto Di Pietro, Luigi V. Mncini, nd Alessndro
Efficient nd Resilient Key Discovery sed on Pseudo-Rndom Key Pre-Deployment p. 1 Efficient nd Resilient Key Discovery sed on Pseudo-Rndom Key Pre-Deployment Roerto Di Pietro, Luigi V. Mncini, nd Alessndro
Study on SLT calibration method of 2-port waveguide DUT
 Interntionl Conference on Advnced Electronic cience nd Technology (AET 206) tudy on LT clibrtion method of 2-port wveguide DUT Wenqing Luo, Anyong Hu, Ki Liu nd Xi Chen chool of Electronics nd Informtion
Interntionl Conference on Advnced Electronic cience nd Technology (AET 206) tudy on LT clibrtion method of 2-port wveguide DUT Wenqing Luo, Anyong Hu, Ki Liu nd Xi Chen chool of Electronics nd Informtion
Geometric quantities for polar curves
 Roerto s Notes on Integrl Clculus Chpter 5: Bsic pplictions of integrtion Section 10 Geometric quntities for polr curves Wht you need to know lredy: How to use integrls to compute res nd lengths of regions
Roerto s Notes on Integrl Clculus Chpter 5: Bsic pplictions of integrtion Section 10 Geometric quntities for polr curves Wht you need to know lredy: How to use integrls to compute res nd lengths of regions
Example. Check that the Jacobian of the transformation to spherical coordinates is
 lss, given on Feb 3, 2, for Mth 3, Winter 2 Recll tht the fctor which ppers in chnge of vrible formul when integrting is the Jcobin, which is the determinnt of mtrix of first order prtil derivtives. Exmple.
lss, given on Feb 3, 2, for Mth 3, Winter 2 Recll tht the fctor which ppers in chnge of vrible formul when integrting is the Jcobin, which is the determinnt of mtrix of first order prtil derivtives. Exmple.
Kirchhoff s Rules. Kirchhoff s Laws. Kirchhoff s Rules. Kirchhoff s Laws. Practice. Understanding SPH4UW. Kirchhoff s Voltage Rule (KVR):
 SPH4UW Kirchhoff s ules Kirchhoff s oltge ule (K): Sum of voltge drops round loop is zero. Kirchhoff s Lws Kirchhoff s Current ule (KC): Current going in equls current coming out. Kirchhoff s ules etween
SPH4UW Kirchhoff s ules Kirchhoff s oltge ule (K): Sum of voltge drops round loop is zero. Kirchhoff s Lws Kirchhoff s Current ule (KC): Current going in equls current coming out. Kirchhoff s ules etween
Engineer-to-Engineer Note
 Engineer-to-Engineer Note EE-297 Technicl notes on using Anlog Devices DSPs, processors nd development tools Visit our Web resources http://www.nlog.com/ee-notes nd http://www.nlog.com/processors or e-mil
Engineer-to-Engineer Note EE-297 Technicl notes on using Anlog Devices DSPs, processors nd development tools Visit our Web resources http://www.nlog.com/ee-notes nd http://www.nlog.com/processors or e-mil
CSI-SF: Estimating Wireless Channel State Using CSI Sampling & Fusion
 CSI-SF: Estimting Wireless Chnnel Stte Using CSI Smpling & Fusion Riccrdo Crepldi, Jeongkeun Lee, Rul Etkin, Sung-Ju Lee, Robin Krvets University of Illinois t Urbn-Chmpign Hewlett-Pckrd Lbortories Emil:{rcrepl,rhk}@illinoisedu,
CSI-SF: Estimting Wireless Chnnel Stte Using CSI Smpling & Fusion Riccrdo Crepldi, Jeongkeun Lee, Rul Etkin, Sung-Ju Lee, Robin Krvets University of Illinois t Urbn-Chmpign Hewlett-Pckrd Lbortories Emil:{rcrepl,rhk}@illinoisedu,
Lecture 20. Intro to line integrals. Dan Nichols MATH 233, Spring 2018 University of Massachusetts.
 Lecture 2 Intro to line integrls Dn Nichols nichols@mth.umss.edu MATH 233, Spring 218 University of Msschusetts April 12, 218 (2) onservtive vector fields We wnt to determine if F P (x, y), Q(x, y) is
Lecture 2 Intro to line integrls Dn Nichols nichols@mth.umss.edu MATH 233, Spring 218 University of Msschusetts April 12, 218 (2) onservtive vector fields We wnt to determine if F P (x, y), Q(x, y) is
High Speed On-Chip Interconnects: Trade offs in Passive Termination
 High Speed On-Chip Interconnects: Trde offs in Pssive Termintion Rj Prihr University of Rochester, NY, USA prihr@ece.rochester.edu Abstrct In this pper, severl pssive termintion schemes for high speed
High Speed On-Chip Interconnects: Trde offs in Pssive Termintion Rj Prihr University of Rochester, NY, USA prihr@ece.rochester.edu Abstrct In this pper, severl pssive termintion schemes for high speed
Joanna Towler, Roading Engineer, Professional Services, NZTA National Office Dave Bates, Operations Manager, NZTA National Office
 . TECHNICA MEMOANDM To Cc repred By Endorsed By NZTA Network Mngement Consultnts nd Contrctors NZTA egionl Opertions Mngers nd Are Mngers Dve Btes, Opertions Mnger, NZTA Ntionl Office Jonn Towler, oding
. TECHNICA MEMOANDM To Cc repred By Endorsed By NZTA Network Mngement Consultnts nd Contrctors NZTA egionl Opertions Mngers nd Are Mngers Dve Btes, Opertions Mnger, NZTA Ntionl Office Jonn Towler, oding
Mixed CMOS PTL Adders
 Anis do XXVI Congresso d SBC WCOMPA l I Workshop de Computção e Aplicções 14 20 de julho de 2006 Cmpo Grnde, MS Mixed CMOS PTL Adders Déor Mott, Reginldo d N. Tvres Engenhri em Sistems Digitis Universidde
Anis do XXVI Congresso d SBC WCOMPA l I Workshop de Computção e Aplicções 14 20 de julho de 2006 Cmpo Grnde, MS Mixed CMOS PTL Adders Déor Mott, Reginldo d N. Tvres Engenhri em Sistems Digitis Universidde
A VIRTUAL INFRASTRUCTURE FOR MITIGATING TYPICAL CHALLENGES IN SENSOR NETWORKS
 A VIRTUAL INFRASTRUCTURE FOR MITIGATING TYPICAL CHALLENGES IN SENSOR NETWORKS by Hdy S. Abdel Slm B.S. June 1999, Alexndri University, Egypt M.S. June 2004, Alexndri University, Egypt A Disserttion Submitted
A VIRTUAL INFRASTRUCTURE FOR MITIGATING TYPICAL CHALLENGES IN SENSOR NETWORKS by Hdy S. Abdel Slm B.S. June 1999, Alexndri University, Egypt M.S. June 2004, Alexndri University, Egypt A Disserttion Submitted
Redundancy Data Elimination Scheme Based on Stitching Technique in Image Senor Networks
 Sensors & Trnsducers 204 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportl.com Redundncy Dt Elimintion Scheme Bsed on Stitching Technique in Imge Senor Networks hunling Tng hongqing Technology nd Business
Sensors & Trnsducers 204 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportl.com Redundncy Dt Elimintion Scheme Bsed on Stitching Technique in Imge Senor Networks hunling Tng hongqing Technology nd Business
EE Controls Lab #2: Implementing State-Transition Logic on a PLC
 Objective: EE 44 - Controls Lb #2: Implementing Stte-rnsition Logic on PLC ssuming tht speed is not of essence, PLC's cn be used to implement stte trnsition logic. he dvntge of using PLC over using hrdwre
Objective: EE 44 - Controls Lb #2: Implementing Stte-rnsition Logic on PLC ssuming tht speed is not of essence, PLC's cn be used to implement stte trnsition logic. he dvntge of using PLC over using hrdwre
Section 17.2: Line Integrals. 1 Objectives. 2 Assignments. 3 Maple Commands. 1. Compute line integrals in IR 2 and IR Read Section 17.
 Section 7.: Line Integrls Objectives. ompute line integrls in IR nd IR 3. Assignments. Red Section 7.. Problems:,5,9,,3,7,,4 3. hllenge: 6,3,37 4. Red Section 7.3 3 Mple ommnds Mple cn ctully evlute line
Section 7.: Line Integrls Objectives. ompute line integrls in IR nd IR 3. Assignments. Red Section 7.. Problems:,5,9,,3,7,,4 3. hllenge: 6,3,37 4. Red Section 7.3 3 Mple ommnds Mple cn ctully evlute line
LECTURE 9: QUADRATIC RESIDUES AND THE LAW OF QUADRATIC RECIPROCITY
 LECTURE 9: QUADRATIC RESIDUES AND THE LAW OF QUADRATIC RECIPROCITY 1. Bsic roerties of qudrtic residues We now investigte residues with secil roerties of lgebric tye. Definition 1.1. (i) When (, m) 1 nd
LECTURE 9: QUADRATIC RESIDUES AND THE LAW OF QUADRATIC RECIPROCITY 1. Bsic roerties of qudrtic residues We now investigte residues with secil roerties of lgebric tye. Definition 1.1. (i) When (, m) 1 nd
On the Prediction of EPON Traffic Using Polynomial Fitting in Optical Network Units
 On the Prediction of EP Trffic Using Polynomil Fitting in Opticl Networ Units I. Mmounis (1),(3), K. Yinnopoulos (2), G. Ppdimitriou (4), E. Vrvrigos (1),(3) (1) Computer Technology Institute nd Press
On the Prediction of EP Trffic Using Polynomil Fitting in Opticl Networ Units I. Mmounis (1),(3), K. Yinnopoulos (2), G. Ppdimitriou (4), E. Vrvrigos (1),(3) (1) Computer Technology Institute nd Press
A Stochastic Geometry Approach to the Modeling of DSRC for Vehicular Safety Communication
 A Stochstic Geometry Approch to the Modeling of DSRC for Vehiculr Sfety Communiction Zhen Tong, Student Member, IEEE, Hongsheng Lu 2, Mrtin Henggi, Fellow, IEEE, nd Christin Poellbuer 2, Senior Member,
A Stochstic Geometry Approch to the Modeling of DSRC for Vehiculr Sfety Communiction Zhen Tong, Student Member, IEEE, Hongsheng Lu 2, Mrtin Henggi, Fellow, IEEE, nd Christin Poellbuer 2, Senior Member,
MATH 118 PROBLEM SET 6
 MATH 118 PROBLEM SET 6 WASEEM LUTFI, GABRIEL MATSON, AND AMY PIRCHER Section 1 #16: Show tht if is qudrtic residue modulo m, nd b 1 (mod m, then b is lso qudrtic residue Then rove tht the roduct of the
MATH 118 PROBLEM SET 6 WASEEM LUTFI, GABRIEL MATSON, AND AMY PIRCHER Section 1 #16: Show tht if is qudrtic residue modulo m, nd b 1 (mod m, then b is lso qudrtic residue Then rove tht the roduct of the
BP-P2P: Belief Propagation-Based Trust and Reputation Management for P2P Networks
 BP-PP: Belief Propgtion-Bsed Trust nd Reputtion Mngement for PP Networs Ermn Aydy School of Electricl nd Comp. Eng. Georgi Institute of Technology Atlnt, GA 333, USA Emil: eydy@gtech.edu Frmrz Feri School
BP-PP: Belief Propgtion-Bsed Trust nd Reputtion Mngement for PP Networs Ermn Aydy School of Electricl nd Comp. Eng. Georgi Institute of Technology Atlnt, GA 333, USA Emil: eydy@gtech.edu Frmrz Feri School
BP-P2P: Belief Propagation-Based Trust and Reputation Management for P2P Networks
 1 9th Annul IEEE Communictions Society Conference on Sensor, Mesh nd Ad Hoc Communictions nd Networs (SECON) BP-PP: Belief Propgtion-Bsed Trust nd Reputtion Mngement for PP Networs Ermn Aydy School of
1 9th Annul IEEE Communictions Society Conference on Sensor, Mesh nd Ad Hoc Communictions nd Networs (SECON) BP-PP: Belief Propgtion-Bsed Trust nd Reputtion Mngement for PP Networs Ermn Aydy School of
A Development of Earthing-Resistance-Estimation Instrument
 A Development of Erthing-Resistnce-Estimtion Instrument HITOSHI KIJIMA Abstrct: - Whenever erth construction work is done, the implnted number nd depth of electrodes hve to be estimted in order to obtin
A Development of Erthing-Resistnce-Estimtion Instrument HITOSHI KIJIMA Abstrct: - Whenever erth construction work is done, the implnted number nd depth of electrodes hve to be estimted in order to obtin
Math 116 Calculus II
 Mth 6 Clculus II Contents 7 Additionl topics in Integrtion 7. Integrtion by prts..................................... 7.4 Numericl Integrtion.................................... 7 7.5 Improper Integrl......................................
Mth 6 Clculus II Contents 7 Additionl topics in Integrtion 7. Integrtion by prts..................................... 7.4 Numericl Integrtion.................................... 7 7.5 Improper Integrl......................................
Domination and Independence on Square Chessboard
 Engineering nd Technology Journl Vol. 5, Prt, No. 1, 017 A.A. Omrn Deprtment of Mthemtics, College of Eduction for Pure Science, University of bylon, bylon, Irq pure.hmed.omrn@uobby lon.edu.iq Domintion
Engineering nd Technology Journl Vol. 5, Prt, No. 1, 017 A.A. Omrn Deprtment of Mthemtics, College of Eduction for Pure Science, University of bylon, bylon, Irq pure.hmed.omrn@uobby lon.edu.iq Domintion
THE explosive traffic demand is challenging current cellular. MmWave Massive MIMO Based Wireless Backhaul for 5G Ultra-Dense Network
 MmWve Mssive MIMO Bsed Wireless Bchul for 5G Ultr-Dense Networ Zhen Go, Linglong Di, De Mi, Zhocheng Wng, Muhmmd Ali Imrn, nd Muhmmd Zeeshn Shir rxiv:508.03940v3 [cs.it] 27 Nov 205 Abstrct Ultr-dense networ
MmWve Mssive MIMO Bsed Wireless Bchul for 5G Ultr-Dense Networ Zhen Go, Linglong Di, De Mi, Zhocheng Wng, Muhmmd Ali Imrn, nd Muhmmd Zeeshn Shir rxiv:508.03940v3 [cs.it] 27 Nov 205 Abstrct Ultr-dense networ
Spiral Tilings with C-curves
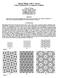 Spirl Tilings with -curves Using ombintorics to Augment Trdition hris K. Plmer 19 North Albny Avenue hicgo, Illinois, 0 chris@shdowfolds.com www.shdowfolds.com Abstrct Spirl tilings used by rtisns through
Spirl Tilings with -curves Using ombintorics to Augment Trdition hris K. Plmer 19 North Albny Avenue hicgo, Illinois, 0 chris@shdowfolds.com www.shdowfolds.com Abstrct Spirl tilings used by rtisns through
CDMA One. International summer students courses: "Plugged In: Modern Networks and Services in Telecommunication"
 INTRAROM S.A. ROMANIAN TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY ROMANIA, Buchrest, 17 Fbric de Glucoz St., Sector 2 Cod 72322, Tel:(+40 1) 2040600 Fx:(+40 1) 2040611 http://www.intrrom.ro Interntionl
INTRAROM S.A. ROMANIAN TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY ROMANIA, Buchrest, 17 Fbric de Glucoz St., Sector 2 Cod 72322, Tel:(+40 1) 2040600 Fx:(+40 1) 2040611 http://www.intrrom.ro Interntionl
Sequential Logic (2) Synchronous vs Asynchronous Sequential Circuit. Clock Signal. Synchronous Sequential Circuits. FSM Overview 9/10/12
 9//2 Sequentil (2) ENGG5 st Semester, 22 Dr. Hden So Deprtment of Electricl nd Electronic Engineering http://www.eee.hku.hk/~engg5 Snchronous vs Asnchronous Sequentil Circuit This Course snchronous Sequentil
9//2 Sequentil (2) ENGG5 st Semester, 22 Dr. Hden So Deprtment of Electricl nd Electronic Engineering http://www.eee.hku.hk/~engg5 Snchronous vs Asnchronous Sequentil Circuit This Course snchronous Sequentil
High-speed Simulation of the GPRS Link Layer
 989 High-speed Simultion of the GPRS Link Lyer J Gozlvez nd J Dunlop Deprtment of Electronic nd Electricl Engineering, University of Strthclyde 204 George St, Glsgow G-lXW, Scotlnd Tel: +44 4 548 206,
989 High-speed Simultion of the GPRS Link Lyer J Gozlvez nd J Dunlop Deprtment of Electronic nd Electricl Engineering, University of Strthclyde 204 George St, Glsgow G-lXW, Scotlnd Tel: +44 4 548 206,
Travel Prediction-based Data Forwarding for Sparse Vehicular Networks. Technical Report
 Trvel Prediction-sed Dt Forwrding for Sprse Vehiculr Networks Technicl Report Deprtment of Computer Science nd Engineering University of Minnesot 4-192 Keller Hll 200 Union Street SE Minnepolis, MN 55455-0159
Trvel Prediction-sed Dt Forwrding for Sprse Vehiculr Networks Technicl Report Deprtment of Computer Science nd Engineering University of Minnesot 4-192 Keller Hll 200 Union Street SE Minnepolis, MN 55455-0159
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE GPS SIGNAL SCINTILLATIONS DURING IONOSPHERIC IRREGULARITIES AND THEIR EFFECTS OVER THE GPS SYSTEM
 CHRCTERISTICS OF THE GPS SIGNL SCINTILLTIONS DURING IONOSPHERIC IRREGULRITIES ND THEIR EFFECTS OVER THE GPS SYSTEM Eurico R. de Paula, I.J.Kantor, L.F.C. de Rezende ERONOMY DIVISION NTIONL INSTITUTE FOR
CHRCTERISTICS OF THE GPS SIGNL SCINTILLTIONS DURING IONOSPHERIC IRREGULRITIES ND THEIR EFFECTS OVER THE GPS SYSTEM Eurico R. de Paula, I.J.Kantor, L.F.C. de Rezende ERONOMY DIVISION NTIONL INSTITUTE FOR
Math Circles Finite Automata Question Sheet 3 (Solutions)
 Mth Circles Finite Automt Question Sheet 3 (Solutions) Nickols Rollick nrollick@uwterloo.c Novemer 2, 28 Note: These solutions my give you the nswers to ll the prolems, ut they usully won t tell you how
Mth Circles Finite Automt Question Sheet 3 (Solutions) Nickols Rollick nrollick@uwterloo.c Novemer 2, 28 Note: These solutions my give you the nswers to ll the prolems, ut they usully won t tell you how
Application Note. Differential Amplifier
 Appliction Note AN367 Differentil Amplifier Author: Dve n Ess Associted Project: Yes Associted Prt Fmily: CY8C9x66, CY8C7x43, CY8C4x3A PSoC Designer ersion: 4. SP3 Abstrct For mny sensing pplictions, desirble
Appliction Note AN367 Differentil Amplifier Author: Dve n Ess Associted Project: Yes Associted Prt Fmily: CY8C9x66, CY8C7x43, CY8C4x3A PSoC Designer ersion: 4. SP3 Abstrct For mny sensing pplictions, desirble
9.4. ; 65. A family of curves has polar equations. ; 66. The astronomer Giovanni Cassini ( ) studied the family of curves with polar equations
 54 CHAPTER 9 PARAMETRIC EQUATINS AND PLAR CRDINATES 49. r, 5. r sin 3, 5 54 Find the points on the given curve where the tngent line is horizontl or verticl. 5. r 3 cos 5. r e 53. r cos 54. r sin 55. Show
54 CHAPTER 9 PARAMETRIC EQUATINS AND PLAR CRDINATES 49. r, 5. r sin 3, 5 54 Find the points on the given curve where the tngent line is horizontl or verticl. 5. r 3 cos 5. r e 53. r cos 54. r sin 55. Show
MONOCHRONICLE STRAIGHT
 UPDATED 09-2010 HYDROCARBON Hydrocrbon is poncho-style cowl in bulky-weight yrn, worked in the round. It ws designed to be s prcticl s it is stylish, with shping tht covers the neck nd shoulders nd the
UPDATED 09-2010 HYDROCARBON Hydrocrbon is poncho-style cowl in bulky-weight yrn, worked in the round. It ws designed to be s prcticl s it is stylish, with shping tht covers the neck nd shoulders nd the
Network Sharing and its Energy Benefits: a Study of European Mobile Network Operators
 Network Shring nd its Energy Benefits: Study of Europen Mobile Network Opertors Mrco Ajmone Mrsn Electronics nd Telecommunictions Dept Politecnico di Torino, nd Institute IMDEA Networks, mrco.jmone@polito.it
Network Shring nd its Energy Benefits: Study of Europen Mobile Network Opertors Mrco Ajmone Mrsn Electronics nd Telecommunictions Dept Politecnico di Torino, nd Institute IMDEA Networks, mrco.jmone@polito.it
Soft-decision Viterbi Decoding with Diversity Combining. T.Sakai, K.Kobayashi, S.Kubota, M.Morikura, S.Kato
 Softdecision Viterbi Decoding with Diversity Combining T.Ski, K.Kobyshi, S.Kubot, M.Morikur, S.Kto NTT Rdio Communiction Systems Lbortories 2356 Tke, Yokosukshi, Kngw, 2383 Jpn ABSTRACT Diversity combining
Softdecision Viterbi Decoding with Diversity Combining T.Ski, K.Kobyshi, S.Kubot, M.Morikur, S.Kto NTT Rdio Communiction Systems Lbortories 2356 Tke, Yokosukshi, Kngw, 2383 Jpn ABSTRACT Diversity combining
DESIGN OF CONTINUOUS LAG COMPENSATORS
 DESIGN OF CONTINUOUS LAG COMPENSATORS J. Pulusová, L. Körösi, M. Dúbrvská Institute of Robotics nd Cybernetics, Slovk University of Technology, Fculty of Electricl Engineering nd Informtion Technology
DESIGN OF CONTINUOUS LAG COMPENSATORS J. Pulusová, L. Körösi, M. Dúbrvská Institute of Robotics nd Cybernetics, Slovk University of Technology, Fculty of Electricl Engineering nd Informtion Technology
Synchronous Generator Line Synchronization
 Synchronous Genertor Line Synchroniztion 1 Synchronous Genertor Line Synchroniztion Introduction One issue in power genertion is synchronous genertor strting. Typiclly, synchronous genertor is connected
Synchronous Genertor Line Synchroniztion 1 Synchronous Genertor Line Synchroniztion Introduction One issue in power genertion is synchronous genertor strting. Typiclly, synchronous genertor is connected
Distributed two-hop proportional fair resource allocation in Long Term Evolution Advanced networks
 WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND MOBILE COMPUTING Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2016; 16:264 278 Published online 12 August 2014 in Wiley Online Librry (wileyonlinelibrry.com)..2517 RESEARCH ARTICLE Distributed
WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND MOBILE COMPUTING Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2016; 16:264 278 Published online 12 August 2014 in Wiley Online Librry (wileyonlinelibrry.com)..2517 RESEARCH ARTICLE Distributed
Module 9. DC Machines. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 9 DC Mchines Version EE IIT, Khrgpur esson 40 osses, Efficiency nd Testing of D.C. Mchines Version EE IIT, Khrgpur Contents 40 osses, efficiency nd testing of D.C. mchines (esson-40) 4 40.1 Gols
Module 9 DC Mchines Version EE IIT, Khrgpur esson 40 osses, Efficiency nd Testing of D.C. Mchines Version EE IIT, Khrgpur Contents 40 osses, efficiency nd testing of D.C. mchines (esson-40) 4 40.1 Gols
Understanding Basic Analog Ideal Op Amps
 Appliction Report SLAA068A - April 2000 Understnding Bsic Anlog Idel Op Amps Ron Mncini Mixed Signl Products ABSTRACT This ppliction report develops the equtions for the idel opertionl mplifier (op mp).
Appliction Report SLAA068A - April 2000 Understnding Bsic Anlog Idel Op Amps Ron Mncini Mixed Signl Products ABSTRACT This ppliction report develops the equtions for the idel opertionl mplifier (op mp).
Section 16.3 Double Integrals over General Regions
 Section 6.3 Double Integrls over Generl egions Not ever region is rectngle In the lst two sections we considered the problem of integrting function of two vribles over rectngle. This sitution however is
Section 6.3 Double Integrls over Generl egions Not ever region is rectngle In the lst two sections we considered the problem of integrting function of two vribles over rectngle. This sitution however is
Lab 8. Speed Control of a D.C. motor. The Motor Drive
 Lb 8. Speed Control of D.C. motor The Motor Drive Motor Speed Control Project 1. Generte PWM wveform 2. Amplify the wveform to drive the motor 3. Mesure motor speed 4. Mesure motor prmeters 5. Control
Lb 8. Speed Control of D.C. motor The Motor Drive Motor Speed Control Project 1. Generte PWM wveform 2. Amplify the wveform to drive the motor 3. Mesure motor speed 4. Mesure motor prmeters 5. Control
Chapter 2 Literature Review
 Chpter 2 Literture Review 2.1 ADDER TOPOLOGIES Mny different dder rchitectures hve een proposed for inry ddition since 1950 s to improve vrious spects of speed, re nd power. Ripple Crry Adder hve the simplest
Chpter 2 Literture Review 2.1 ADDER TOPOLOGIES Mny different dder rchitectures hve een proposed for inry ddition since 1950 s to improve vrious spects of speed, re nd power. Ripple Crry Adder hve the simplest
Lecture 16: Four Quadrant operation of DC Drive (or) TYPE E Four Quadrant chopper Fed Drive: Operation
 Lecture 16: Four Qudrnt opertion of DC Drive (or) TYPE E Four Qudrnt chopper Fed Drive: Opertion The rmture current I is either positive or negtive (flow in to or wy from rmture) the rmture voltge is lso
Lecture 16: Four Qudrnt opertion of DC Drive (or) TYPE E Four Qudrnt chopper Fed Drive: Opertion The rmture current I is either positive or negtive (flow in to or wy from rmture) the rmture voltge is lso
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 Hll Ticket No Question Pper Code: AEC009 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigl, Hyderd - 500 043 MODEL QUESTION PAPER Four Yer B.Tech V Semester End Exmintions, Novemer - 2018 Regultions:
Hll Ticket No Question Pper Code: AEC009 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigl, Hyderd - 500 043 MODEL QUESTION PAPER Four Yer B.Tech V Semester End Exmintions, Novemer - 2018 Regultions:
Exercise 1-1. The Sine Wave EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE. Relationship between a rotating phasor and a sine wave DISCUSSION
 Exercise 1-1 The Sine Wve EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you hve completed this exercise, you will be fmilir with the notion of sine wve nd how it cn be expressed s phsor rotting round the center of circle. You
Exercise 1-1 The Sine Wve EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you hve completed this exercise, you will be fmilir with the notion of sine wve nd how it cn be expressed s phsor rotting round the center of circle. You
Energy-efficient scheduling and hybrid communication architecture for underwater littoral surveillance
 Computer Communictions xxx (26) xxx xxx www.elsevier.com/locte/comcom Energy-efficient scheduling nd hybrid communiction rchitecture for underwter littorl surveillnce Mihel Crdei * Deprtment of Computer
Computer Communictions xxx (26) xxx xxx www.elsevier.com/locte/comcom Energy-efficient scheduling nd hybrid communiction rchitecture for underwter littorl surveillnce Mihel Crdei * Deprtment of Computer
10.4 AREAS AND LENGTHS IN POLAR COORDINATES
 65 CHAPTER PARAMETRIC EQUATINS AND PLAR CRDINATES.4 AREAS AND LENGTHS IN PLAR CRDINATES In this section we develop the formul for the re of region whose oundry is given y polr eqution. We need to use the
65 CHAPTER PARAMETRIC EQUATINS AND PLAR CRDINATES.4 AREAS AND LENGTHS IN PLAR CRDINATES In this section we develop the formul for the re of region whose oundry is given y polr eqution. We need to use the
Temporal Secondary Access Opportunities for WLAN in Radar Bands
 The 4th Interntionl Symposium on Wireless Personl Multimedi Communictions WPMC'), Temporl Secondry Access Opportunities for WLAN in Rdr Bnds Miurel Tercero, Ki Won Sung, nd Jens Znder Wireless@KTH, Royl
The 4th Interntionl Symposium on Wireless Personl Multimedi Communictions WPMC'), Temporl Secondry Access Opportunities for WLAN in Rdr Bnds Miurel Tercero, Ki Won Sung, nd Jens Znder Wireless@KTH, Royl
To provide data transmission in indoor
 Hittite Journl of Science nd Engineering, 2018, 5 (1) 25-29 ISSN NUMBER: 2148-4171 DOI: 10.17350/HJSE19030000074 A New Demodultor For Inverse Pulse Position Modultion Technique Mehmet Sönmez Osmniye Korkut
Hittite Journl of Science nd Engineering, 2018, 5 (1) 25-29 ISSN NUMBER: 2148-4171 DOI: 10.17350/HJSE19030000074 A New Demodultor For Inverse Pulse Position Modultion Technique Mehmet Sönmez Osmniye Korkut
Eliminating Non-Determinism During Test of High-Speed Source Synchronous Differential Buses
 Eliminting Non-Determinism During of High-Speed Source Synchronous Differentil Buses Abstrct The t-speed functionl testing of deep sub-micron devices equipped with high-speed I/O ports nd the synchronous
Eliminting Non-Determinism During of High-Speed Source Synchronous Differentil Buses Abstrct The t-speed functionl testing of deep sub-micron devices equipped with high-speed I/O ports nd the synchronous
April 9, 2000 DIS chapter 10 CHAPTER 3 : INTEGRATED PROCESSOR-LEVEL ARCHITECTURES FOR REAL-TIME DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING
 April 9, 2000 DIS chpter 0 CHAPTE 3 : INTEGATED POCESSO-LEVEL ACHITECTUES FO EAL-TIME DIGITAL SIGNAL POCESSING April 9, 2000 DIS chpter 3.. INTODUCTION The purpose of this chpter is twofold. Firstly, bsic
April 9, 2000 DIS chpter 0 CHAPTE 3 : INTEGATED POCESSO-LEVEL ACHITECTUES FO EAL-TIME DIGITAL SIGNAL POCESSING April 9, 2000 DIS chpter 3.. INTODUCTION The purpose of this chpter is twofold. Firstly, bsic
CHAPTER 3 AMPLIFIER DESIGN TECHNIQUES
 CHAPTER 3 AMPLIFIER DEIGN TECHNIQUE 3.0 Introduction olid-stte microwve mplifiers ply n importnt role in communiction where it hs different pplictions, including low noise, high gin, nd high power mplifiers.
CHAPTER 3 AMPLIFIER DEIGN TECHNIQUE 3.0 Introduction olid-stte microwve mplifiers ply n importnt role in communiction where it hs different pplictions, including low noise, high gin, nd high power mplifiers.
Simultaneous Adversarial Multi-Robot Learning
 Simultneous Adversril Multi-Robot Lerning Michel Bowling nd Mnuel Veloso Computer Science Deprtment Crnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh PA, 15213-3891 Abstrct Multi-robot lerning fces ll of the chllenges
Simultneous Adversril Multi-Robot Lerning Michel Bowling nd Mnuel Veloso Computer Science Deprtment Crnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh PA, 15213-3891 Abstrct Multi-robot lerning fces ll of the chllenges
Secret Key Generation and Agreement in UWB Communication Channels
 Secret Key Genertion nd greement in UW Communiction Chnnels Msoud Ghoreishi Mdiseh, Michel L. McGuire, Stephen S. Neville, Lin Ci, Michel Horie Deprtment of Electricl nd Computer Engineering University
Secret Key Genertion nd greement in UW Communiction Chnnels Msoud Ghoreishi Mdiseh, Michel L. McGuire, Stephen S. Neville, Lin Ci, Michel Horie Deprtment of Electricl nd Computer Engineering University
CS 135: Computer Architecture I. Boolean Algebra. Basic Logic Gates
 Bsic Logic Gtes : Computer Architecture I Boolen Algebr Instructor: Prof. Bhgi Nrhri Dept. of Computer Science Course URL: www.ses.gwu.edu/~bhgiweb/cs35/ Digitl Logic Circuits We sw how we cn build the
Bsic Logic Gtes : Computer Architecture I Boolen Algebr Instructor: Prof. Bhgi Nrhri Dept. of Computer Science Course URL: www.ses.gwu.edu/~bhgiweb/cs35/ Digitl Logic Circuits We sw how we cn build the
A Channel Splitting Technique for Reducing Handoff Delay in Wireless Networks
 Interntionl Journl o Engineering Reserch & Technology (IJERT) A Chnnel Splitting Technique or Reducing Hndo ely in Wireless Networks Jeykumr. J #1, Venktesh. * 2, Vigneswri. G* 3, Nivethith. V *4 # 1 PG
Interntionl Journl o Engineering Reserch & Technology (IJERT) A Chnnel Splitting Technique or Reducing Hndo ely in Wireless Networks Jeykumr. J #1, Venktesh. * 2, Vigneswri. G* 3, Nivethith. V *4 # 1 PG
Information Caching Strategy for Cyber Social Computing Based Wireless Networks
 Received 4 December 26; revised 23 Februry 27; ccepted 2 April 27. Dte of publiction 28 April 27; dte of current version 6 September 27. Digitl Object Identifier.9/TETC.27.2699695 Informtion Cching Strtegy
Received 4 December 26; revised 23 Februry 27; ccepted 2 April 27. Dte of publiction 28 April 27; dte of current version 6 September 27. Digitl Object Identifier.9/TETC.27.2699695 Informtion Cching Strtegy
Analysis of Coding-aware MAC Protocols based on Reverse Direction Protocol for IEEE based Wireless Networks using Network Coding*
 Anlysis of oding-wre MA Protocols sed on Reverse irection Protocol for IEEE 8.-sed Wireless Networks using Network oding* Rul Plcios, Htegereil Kssye Hile, Jesus Alonso-Zrte nd Frizio Grnelli {plciostrujillo,
Anlysis of oding-wre MA Protocols sed on Reverse irection Protocol for IEEE 8.-sed Wireless Networks using Network oding* Rul Plcios, Htegereil Kssye Hile, Jesus Alonso-Zrte nd Frizio Grnelli {plciostrujillo,
A Simple Approach to Control the Time-constant of Microwave Integrators
 5 VOL., NO.3, MA, A Simple Approch to Control the Time-constnt of Microwve Integrtors Dhrmendr K. Updhyy* nd Rkesh K. Singh NSIT, Division of Electronics & Communiction Engineering New Delhi-78, In Tel:
5 VOL., NO.3, MA, A Simple Approch to Control the Time-constnt of Microwve Integrtors Dhrmendr K. Updhyy* nd Rkesh K. Singh NSIT, Division of Electronics & Communiction Engineering New Delhi-78, In Tel:
2016 2Q Wireless Communication Engineering. #10 Spread Spectrum & Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
 16 Q Wireless Communiction Engineering #1 Spred Spectrum & Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA Kei Skguchi skguchi@mobile.ee. July 9, 16 Course Schedule ( Dte ext Contents #7 July 15 4.6 Error correction
16 Q Wireless Communiction Engineering #1 Spred Spectrum & Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA Kei Skguchi skguchi@mobile.ee. July 9, 16 Course Schedule ( Dte ext Contents #7 July 15 4.6 Error correction
Aquauno Select MINUTES. (duration) FREQUENCY LED. OFF 8h AQUAUNO SELECT 5 MIN FREQUENCY. the timer is being programmed;
 Aquuno Select Pg. INSTALLATION. Attch the timer to cold wter tp, following these simple instructions. Do not instll the timer in pit or vlve ox, elow ground level or indoors. Do not use the timer with
Aquuno Select Pg. INSTALLATION. Attch the timer to cold wter tp, following these simple instructions. Do not instll the timer in pit or vlve ox, elow ground level or indoors. Do not use the timer with
Simulation of Transformer Based Z-Source Inverter to Obtain High Voltage Boost Ability
 Interntionl Journl of cience, Engineering nd Technology Reserch (IJETR), olume 4, Issue 1, October 15 imultion of Trnsformer Bsed Z-ource Inverter to Obtin High oltge Boost Ability A.hnmugpriy 1, M.Ishwry
Interntionl Journl of cience, Engineering nd Technology Reserch (IJETR), olume 4, Issue 1, October 15 imultion of Trnsformer Bsed Z-ource Inverter to Obtin High oltge Boost Ability A.hnmugpriy 1, M.Ishwry
Postprint. This is the accepted version of a paper presented at IEEE PES General Meeting.
 http://www.div-portl.org Postprint This is the ccepted version of pper presented t IEEE PES Generl Meeting. Cittion for the originl published pper: Mhmood, F., Hooshyr, H., Vnfretti, L. (217) Sensitivity
http://www.div-portl.org Postprint This is the ccepted version of pper presented t IEEE PES Generl Meeting. Cittion for the originl published pper: Mhmood, F., Hooshyr, H., Vnfretti, L. (217) Sensitivity
(CATALYST GROUP) B"sic Electric"l Engineering
 (CATALYST GROUP) B"sic Electric"l Engineering 1. Kirchhoff s current l"w st"tes th"t (") net current flow "t the junction is positive (b) Hebr"ic sum of the currents meeting "t the junction is zero (c)
(CATALYST GROUP) B"sic Electric"l Engineering 1. Kirchhoff s current l"w st"tes th"t (") net current flow "t the junction is positive (b) Hebr"ic sum of the currents meeting "t the junction is zero (c)
A New Algorithm to Compute Alternate Paths in Reliable OSPF (ROSPF)
 A New Algorithm to Compute Alternte Pths in Relile OSPF (ROSPF) Jin Pu *, Eric Mnning, Gholmli C. Shoj, Annd Srinivsn ** PANDA Group, Computer Science Deprtment University of Victori Victori, BC, Cnd Astrct
A New Algorithm to Compute Alternte Pths in Relile OSPF (ROSPF) Jin Pu *, Eric Mnning, Gholmli C. Shoj, Annd Srinivsn ** PANDA Group, Computer Science Deprtment University of Victori Victori, BC, Cnd Astrct
RT-Link: A Time-Synchronized Link Protocol for Energy Constrained Multi-hop Wireless Networks
 RT-Link: A Time-Synchronized Link Protocol for Energy Constrined Multi-hop Wireless Networks Anthony Rowe, Rhul Mnghrm, Rj Rjkumr Electricl nd Computer Engineering Deprtment, Crnegie Mellon University,
RT-Link: A Time-Synchronized Link Protocol for Energy Constrined Multi-hop Wireless Networks Anthony Rowe, Rhul Mnghrm, Rj Rjkumr Electricl nd Computer Engineering Deprtment, Crnegie Mellon University,
AN IMPROVED METHOD FOR RADIO FREQUENCY DIRECTION FINDING USING WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS
 AN IMPROVED METHOD FOR RADIO FREQUENCY DIRECTION FINDING USING WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS Mickey S. Btson, John C. McEchen, nd Murli Tumml Deprtment of Electricl nd Computer Engineering Nvl Postgrdute School
AN IMPROVED METHOD FOR RADIO FREQUENCY DIRECTION FINDING USING WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS Mickey S. Btson, John C. McEchen, nd Murli Tumml Deprtment of Electricl nd Computer Engineering Nvl Postgrdute School
Network-coded Cooperation for Multi-unicast with Non-Ideal Source-Relay Channels
 This full text pper ws peer reviewed t the direction of IEEE Communictions Society suject mtter experts for puliction in the IEEE ICC 2010 proceedings Network-coded Coopertion for Multi-unicst with Non-Idel
This full text pper ws peer reviewed t the direction of IEEE Communictions Society suject mtter experts for puliction in the IEEE ICC 2010 proceedings Network-coded Coopertion for Multi-unicst with Non-Idel
Improving synchronized transfers in public transit networks using real-time tactics
 Improving synchronized trnsfers in public trnsit networks using rel-time tctics Zhongjun Wu 1,2,3, Grhm Currie 3, Wei Wng 1,2 1 Jingsu Key Lbortory of Urbn ITS, Si Pi Lou 2#, Nnjing, 210096, Chin 2 School
Improving synchronized trnsfers in public trnsit networks using rel-time tctics Zhongjun Wu 1,2,3, Grhm Currie 3, Wei Wng 1,2 1 Jingsu Key Lbortory of Urbn ITS, Si Pi Lou 2#, Nnjing, 210096, Chin 2 School
DYE SOLUBILITY IN SUPERCRITICAL CARBON DIOXIDE FLUID
 THERMAL SCIENCE, Yer 2015, Vol. 19, No. 4, pp. 1311-1315 1311 DYE SOLUBILITY IN SUPERCRITICAL CARBON DIOXIDE FLUID by Jun YAN, Li-Jiu ZHENG *, Bing DU, Yong-Fng QIAN, nd Fng YE Lioning Provincil Key Lbortory
THERMAL SCIENCE, Yer 2015, Vol. 19, No. 4, pp. 1311-1315 1311 DYE SOLUBILITY IN SUPERCRITICAL CARBON DIOXIDE FLUID by Jun YAN, Li-Jiu ZHENG *, Bing DU, Yong-Fng QIAN, nd Fng YE Lioning Provincil Key Lbortory
PB-735 HD DP. Industrial Line. Automatic punch and bind machine for books and calendars
 PB-735 HD DP Automtic punch nd bind mchine for books nd clendrs A further step for the utomtion of double loop binding. A clever nd flexible mchine ble to punch nd bind in line up to 9/16. Using the best
PB-735 HD DP Automtic punch nd bind mchine for books nd clendrs A further step for the utomtion of double loop binding. A clever nd flexible mchine ble to punch nd bind in line up to 9/16. Using the best
Kyushu Institute of Technology
 Title: Integrted Rescue Service Stellite (IRS-St) Primry Point of Contct (POC): Mohmed Ibrhim Co-uthors: Btsuren Amglnbt, Puline Fure, Kevin Chou Orgniztion:, 1-1 Sensui, Tobt, Kitkyushu 804-8550, Jpn
Title: Integrted Rescue Service Stellite (IRS-St) Primry Point of Contct (POC): Mohmed Ibrhim Co-uthors: Btsuren Amglnbt, Puline Fure, Kevin Chou Orgniztion:, 1-1 Sensui, Tobt, Kitkyushu 804-8550, Jpn
Magnetic monopole field exposed by electrons
 Mgnetic monopole field exposed y electrons A. Béché, R. Vn Boxem, G. Vn Tendeloo, nd J. Vereeck EMAT, University of Antwerp, Groenenorgerln 171, 22 Antwerp, Belgium Opticl xis Opticl xis Needle Smple Needle
Mgnetic monopole field exposed y electrons A. Béché, R. Vn Boxem, G. Vn Tendeloo, nd J. Vereeck EMAT, University of Antwerp, Groenenorgerln 171, 22 Antwerp, Belgium Opticl xis Opticl xis Needle Smple Needle
This is a repository copy of Effect of power state on absorption cross section of personal computer components.
 This is repository copy of Effect of power stte on bsorption cross section of personl computer components. White Rose Reserch Online URL for this pper: http://eprints.whiterose.c.uk/10547/ Version: Accepted
This is repository copy of Effect of power stte on bsorption cross section of personl computer components. White Rose Reserch Online URL for this pper: http://eprints.whiterose.c.uk/10547/ Version: Accepted
